⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
Quantization Meets dLLMs: A Systematic Study of Post-training Quantization for Diffusion LLMs
Authors:Haokun Lin, Haobo Xu, Yichen Wu, Ziyu Guo, Renrui Zhang, Zhichao Lu, Ying Wei, Qingfu Zhang, Zhenan Sun
Recent advances in diffusion large language models (dLLMs) have introduced a promising alternative to autoregressive (AR) LLMs for natural language generation tasks, leveraging full attention and denoising-based decoding strategies. However, the deployment of these models on edge devices remains challenging due to their massive parameter scale and high resource demands. While post-training quantization (PTQ) has emerged as a widely adopted technique for compressing AR LLMs, its applicability to dLLMs remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present the first systematic study on quantizing diffusion-based language models. We begin by identifying the presence of activation outliers, characterized by abnormally large activation values that dominate the dynamic range. These outliers pose a key challenge to low-bit quantization, as they make it difficult to preserve precision for the majority of values. More importantly, we implement state-of-the-art PTQ methods and conduct a comprehensive evaluation across multiple task types and model variants. Our analysis is structured along four key dimensions: bit-width, quantization method, task category, and model type. Through this multi-perspective evaluation, we offer practical insights into the quantization behavior of dLLMs under different configurations. We hope our findings provide a foundation for future research in efficient dLLM deployment. All codes and experimental setups will be released to support the community.
近期扩散大型语言模型(dLLMs)的进展为自然语言生成任务提供了一种有前途的自回归(AR)LLMs的替代方案,利用全关注力和基于去噪的解码策略。然而,由于这些模型的参数规模庞大且资源需求高,因此在边缘设备上部署它们仍然具有挑战性。虽然后训练量化(PTQ)已经成为压缩AR LLMs的广泛采用的技术,但其对dLLMs的适用性仍很大程度上未被探索。在这项工作中,我们对基于扩散的语言模型的量化进行了首次系统研究。我们首先确定了激活异常值的存在,这些异常值具有异常大的激活值并主导动态范围。这些异常值对低比特量化构成了关键挑战,因为它们很难保持大多数值的精度。更重要的是,我们实现了最先进的PTQ方法,并对多种任务类型和模型变体进行了全面评估。我们的分析沿着四个关键维度展开:位宽、量化方法、任务类别和模型类型。通过多角度评估,我们提供了关于不同配置下dLLM量化行为的实用见解。我们希望我们的研究结果能为未来在有效部署dLLM方面的相关研究奠定基础。所有代码和实验设置都将发布,以支持研究社区。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report, Work in Progress
Summary
最近扩散大型语言模型(dLLMs)的进展为自然语言生成任务提供了有前途的自回归(AR)LLMs替代方案,利用全注意力机制和基于去噪的解码策略。然而,在边缘设备上部署这些模型仍具有挑战性,因为其参数规模庞大且资源需求高。尽管已有关于压缩自回归LLMs的模型后量化(PTQ)技术被广泛采用,但其对dLLMs的应用仍然缺乏研究。本文首次系统地研究了扩散型语言模型的量化问题。首先识别了激活异常值的存在,这些异常值表现为主导动态范围的异常大的激活值。这些异常值对低比特量化构成了关键挑战,因为它们很难保持大多数值的精度。更重要的是,我们实施了最先进的PTQ方法,并对多种任务类型和模型变体进行了全面评估。我们的分析从四个关键维度展开:位宽、量化方法、任务类别和模型类型。通过多角度评估,我们提供了在不同配置下dLLM量化的实用见解。我们希望我们的研究结果能为未来高效dLLM部署的研究提供基础。
Key Takeaways
- dLLMs作为一种自然语言生成任务的替代方案受到广泛关注,但其在边缘设备上的部署仍然具有挑战性。
- 激活异常值在dLLMs中的存在是一个关键问题,对低比特量化构成挑战。
- 对不同位宽、量化方法、任务类别和模型类型的dLLMs进行了全面的量化评估。
- 本文首次系统地研究了扩散型语言模型的量化问题,并提供实用见解。
- 通过多角度评估,为高效dLLM部署的未来研究提供了基础。
- 公开所有代码和实验设置以支持研究社区。
点此查看论文截图

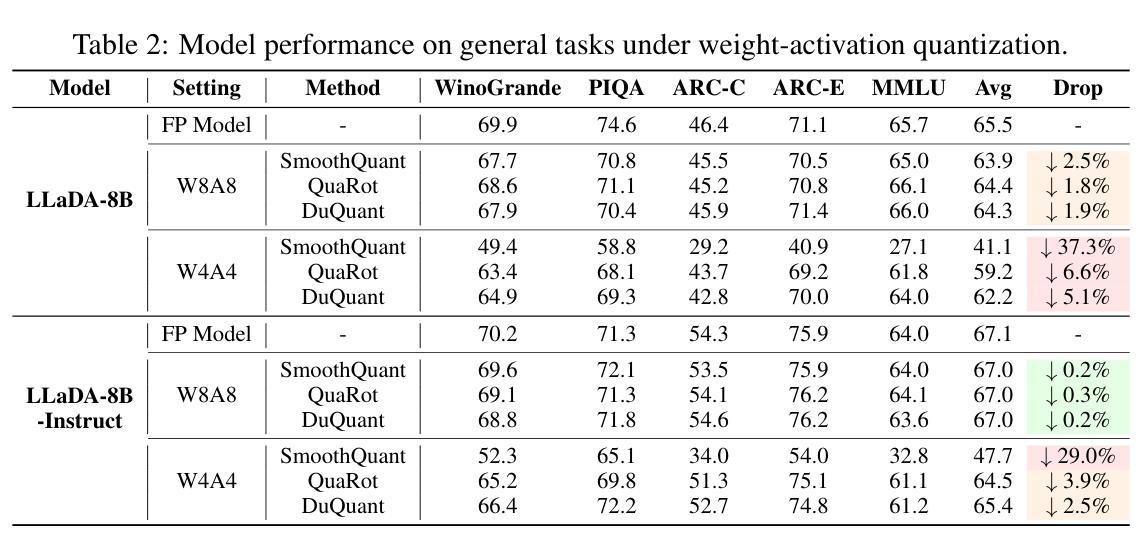
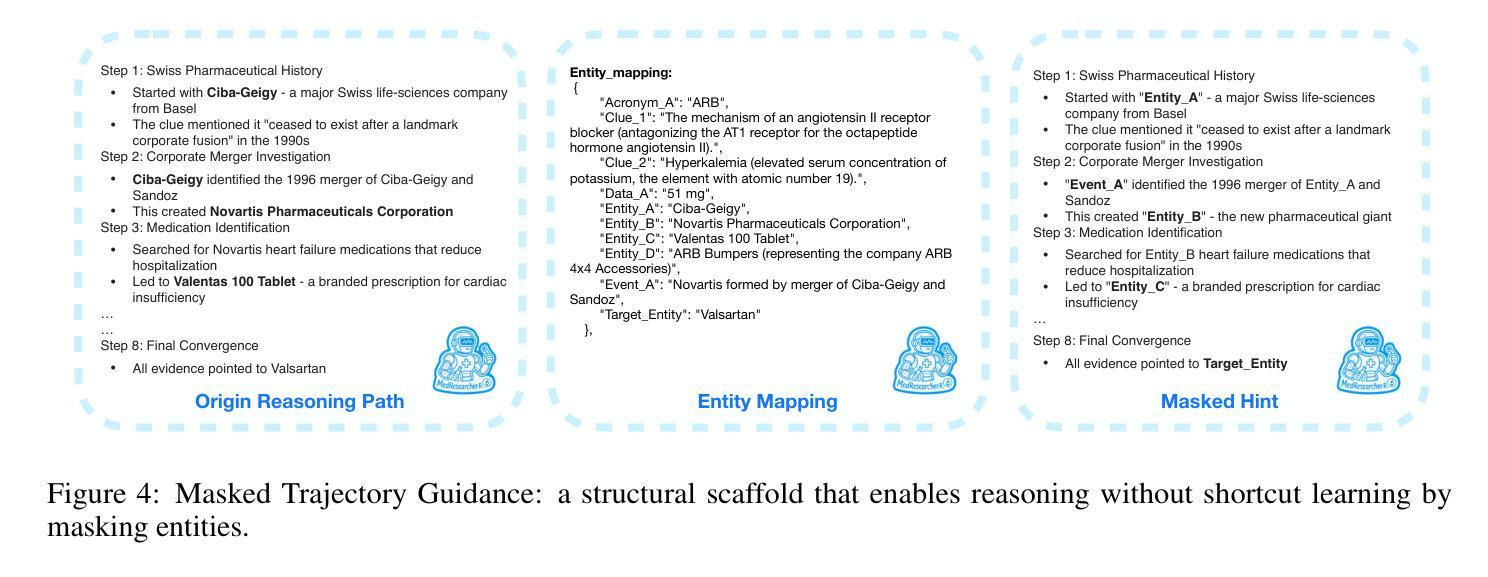
MedReseacher-R1: Expert-Level Medical Deep Researcher via A Knowledge-Informed Trajectory Synthesis Framework
Authors:Ailing Yu, Lan Yao, Jingnan Liu, Zhe Chen, Jiajun Yin, Yuan Wang, Xinhao Liao, Zhiling Ye, Ji Li, Yun Yue, Hansong Xiao, Hualei Zhou, Chunxiao Guo, Peng Wei, Jinjie Gu
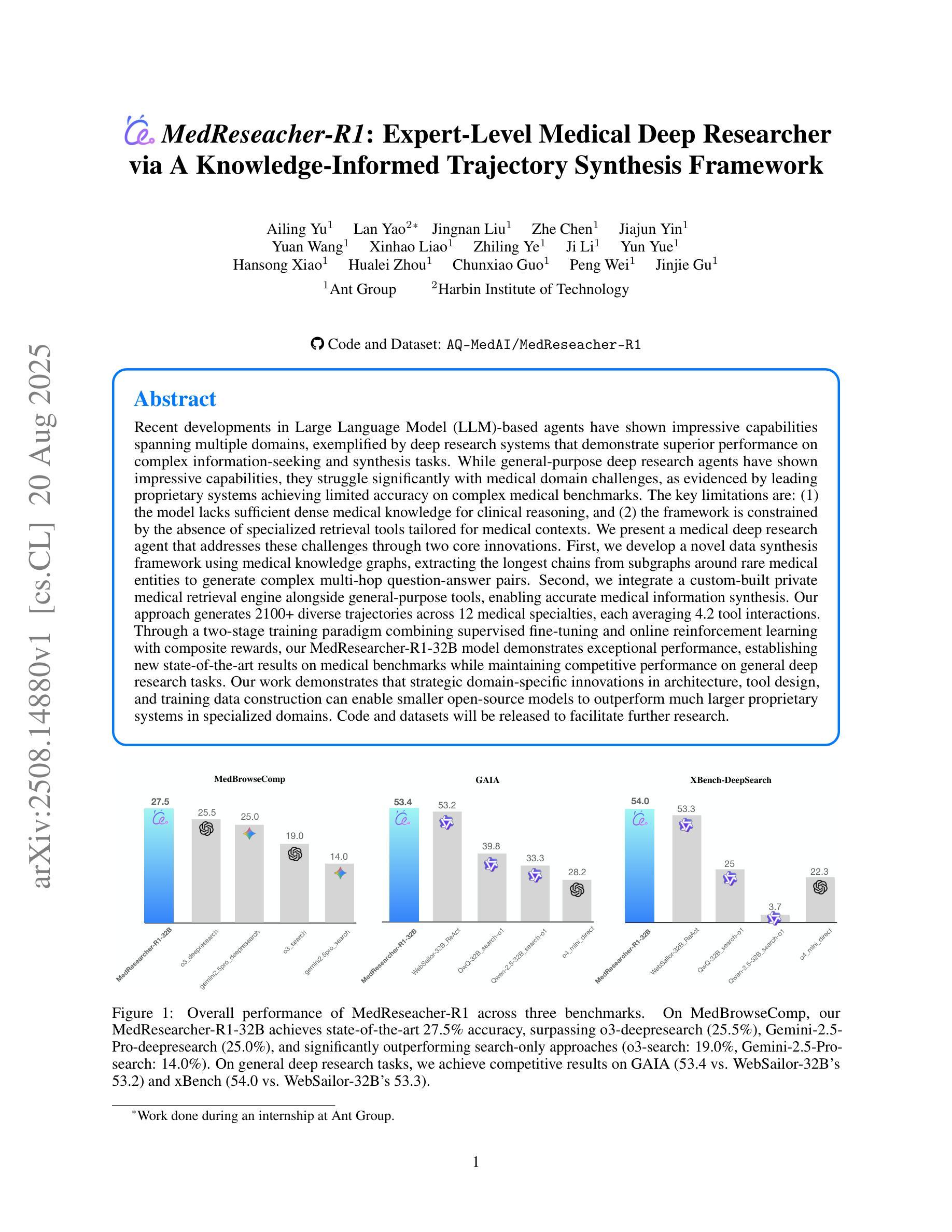
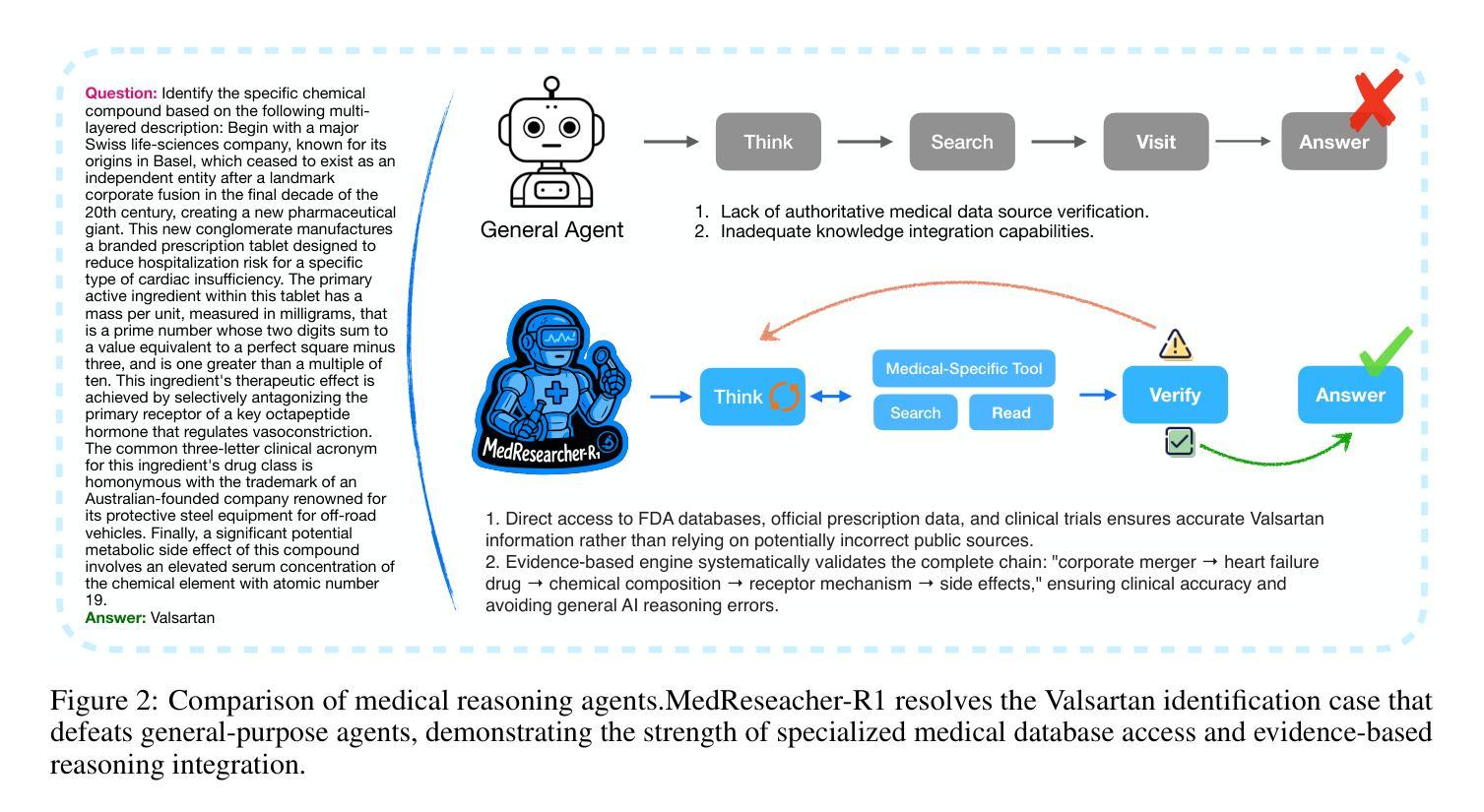
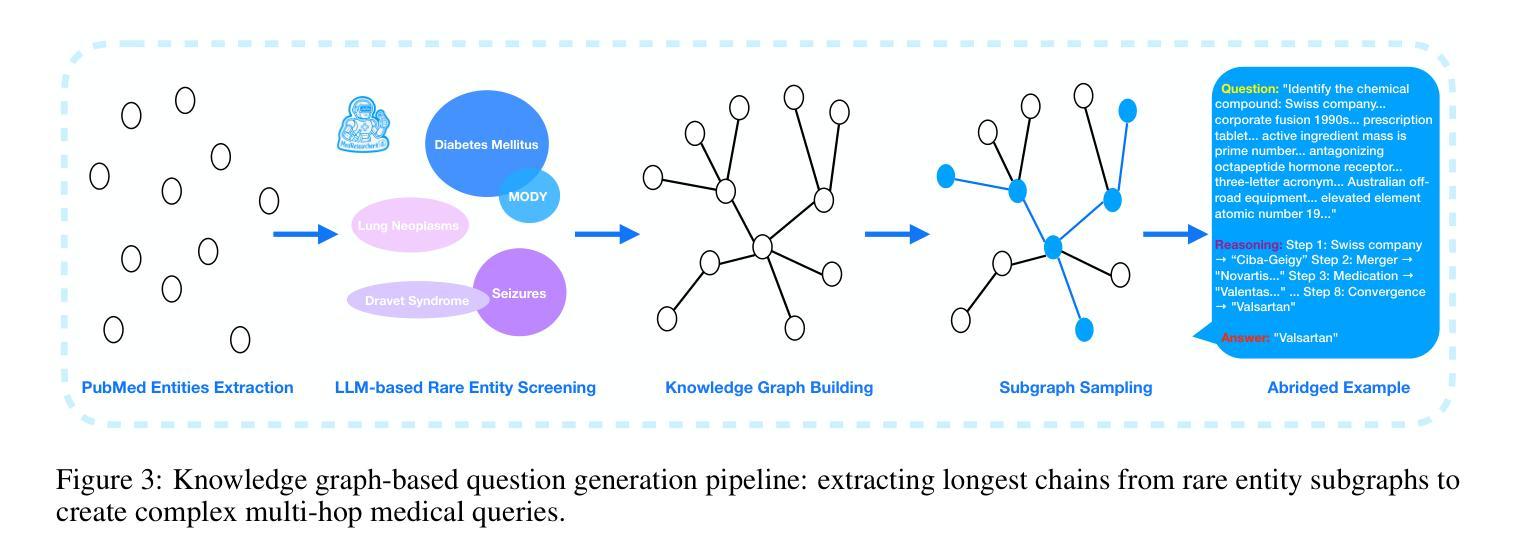
Recent developments in Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have shown impressive capabilities spanning multiple domains, exemplified by deep research systems that demonstrate superior performance on complex information-seeking and synthesis tasks. While general-purpose deep research agents have shown impressive capabilities, they struggle significantly with medical domain challenges, as evidenced by leading proprietary systems achieving limited accuracy on complex medical benchmarks. The key limitations are: (1) the model lacks sufficient dense medical knowledge for clinical reasoning, and (2) the framework is constrained by the absence of specialized retrieval tools tailored for medical contexts.We present a medical deep research agent that addresses these challenges through two core innovations. First, we develop a novel data synthesis framework using medical knowledge graphs, extracting the longest chains from subgraphs around rare medical entities to generate complex multi-hop question-answer pairs. Second, we integrate a custom-built private medical retrieval engine alongside general-purpose tools, enabling accurate medical information synthesis. Our approach generates 2100+ diverse trajectories across 12 medical specialties, each averaging 4.2 tool interactions.Through a two-stage training paradigm combining supervised fine-tuning and online reinforcement learning with composite rewards, our MedResearcher-R1-32B model demonstrates exceptional performance, establishing new state-of-the-art results on medical benchmarks while maintaining competitive performance on general deep research tasks. Our work demonstrates that strategic domain-specific innovations in architecture, tool design, and training data construction can enable smaller open-source models to outperform much larger proprietary systems in specialized domains.
近期基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理人在多个领域表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,体现在深度研究系统在复杂的信息检索和综合任务中展现出卓越的性能。尽管通用深度研究代理人在许多领域表现出强大的能力,但在医学领域的挑战面前,它们遇到了很大的困难,领先的专有系统虽然在医学基准测试上取得了一定的准确性,但仍有很大的局限性。主要限制因素有:(1)模型缺乏用于临床推理的充足密集医学知识;(2)框架受到缺乏针对医学上下文量身定制的专用检索工具的制约。我们提出了一种医学深度研究代理人,通过两个核心创新来解决这些挑战。首先,我们利用医学知识图谱开发了一种新型数据合成框架,从围绕罕见医学实体的子图中提取最长的链来生成复杂的多跳问答对。其次,我们将自定义的私人医学检索引擎与通用工具相结合,实现准确医学信息的综合。我们的方法在12个医学专业领域生成了2100多个不同的轨迹,每个轨迹平均交互4.2个工具。通过结合监督微调的两阶段训练模式和在线强化学习以及复合奖励,我们的MedResearcher-R1-32B模型在医学基准测试上表现出卓越的性能,同时在一般深度研究任务上保持竞争力。我们的工作表明,在架构、工具设计和训练数据构建方面采用有针对性的领域特定创新,可以使较小的开源模型在专用领域超越更大的专有系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures
摘要
最新发展的大型语言模型(LLM)代理系统在多个领域展现出强大的能力,例如在深度研究系统中,其在复杂信息检索和合成任务上的表现尤为出色。尽管通用深度研究代理具有强大的能力,但它们在医学领域面临巨大挑战,领先的专有系统在这方面实现的准确率有限。主要局限在于模型缺乏用于临床推理的密集医学知识,以及框架受限于缺乏针对医学环境的专门检索工具。我们提出了一种医学深度研究代理,通过两个核心创新来解决这些挑战。首先,我们开发了一种新的数据合成框架,使用医学知识图谱生成复杂的多跳问答对。其次,我们集成了定制的私人医学检索引擎和通用工具,以实现准确的信息合成。我们的方法生成了超过两千一百个跨越十二种医学专业的不同轨迹,每个轨迹平均使用工具交互四次以上。通过结合监督微调与在线强化学习复合奖励的两阶段训练模式,我们的MedResearcher-R1-32B模型在医学基准测试中实现了卓越的性能表现,同时在一般深度研究任务上保持了竞争力。我们的工作表明,在架构、工具设计和训练数据构建方面有针对性的领域特定创新可以使较小的开源模型在专门领域中超越更大的专有系统。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在多个领域展现强大能力,特别是在深度研究系统中。
- 通用深度研究代理在医学领域面临挑战,因为医学知识的复杂性和特定语境的需求。
- 医学深度研究代理的核心挑战包括缺乏临床推理的密集医学知识和缺乏专门用于医学环境的检索工具。
- 介绍了一种新的医学深度研究代理,通过数据合成框架和定制检索引擎的结合来解决这些挑战。
- 该方法生成了跨越多个医学专业的多样化轨迹,并实现了在医学基准测试上的卓越性能。
- 采用两阶段训练模式结合监督微调和在线强化学习,提高了模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图
Universal and Transferable Adversarial Attack on Large Language Models Using Exponentiated Gradient Descent
Authors:Sajib Biswas, Mao Nishino, Samuel Jacob Chacko, Xiuwen Liu
As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in critical applications, ensuring their robustness and safety alignment remains a major challenge. Despite the overall success of alignment techniques such as reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) on typical prompts, LLMs remain vulnerable to jailbreak attacks enabled by crafted adversarial triggers appended to user prompts. Most existing jailbreak methods either rely on inefficient searches over discrete token spaces or direct optimization of continuous embeddings. While continuous embeddings can be given directly to selected open-source models as input, doing so is not feasible for proprietary models. On the other hand, projecting these embeddings back into valid discrete tokens introduces additional complexity and often reduces attack effectiveness. We propose an intrinsic optimization method which directly optimizes relaxed one-hot encodings of the adversarial suffix tokens using exponentiated gradient descent coupled with Bregman projection, ensuring that the optimized one-hot encoding of each token always remains within the probability simplex. We provide theoretical proof of convergence for our proposed method and implement an efficient algorithm that effectively jailbreaks several widely used LLMs. Our method achieves higher success rates and faster convergence compared to three state-of-the-art baselines, evaluated on five open-source LLMs and four adversarial behavior datasets curated for evaluating jailbreak methods. In addition to individual prompt attacks, we also generate universal adversarial suffixes effective across multiple prompts and demonstrate transferability of optimized suffixes to different LLMs.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在关键应用中的部署越来越多,确保其鲁棒性和安全对齐仍然是一个主要挑战。尽管强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)等对齐技术在典型提示上的总体成功,LLM仍容易受到通过用户提示附加的精心制作的对抗触发而启动的越狱攻击。大多数现有的越狱方法要么依赖于离散标记空间上的低效搜索,要么直接优化连续嵌入。虽然可以将连续嵌入直接作为选定开源模型的输入,但对于专有模型来说,这样做并不可行。另一方面,将这些嵌入投影回有效的离散标记又引入了额外的复杂性,并且通常会降低攻击效果。我们提出了一种内在的优化方法,该方法直接使用指数梯度下降法结合Bregman投影优化对抗性后缀标记的松弛独热编码,确保每个标记的优化独热编码始终保持在概率单纯形内。我们为所提出的方法提供了收敛性的理论证明,并实现了一种有效的算法,该算法可以有效地突破几个广泛使用的LLM。我们的方法与三个最先进的基线相比,成功率更高,收敛更快,并在五个开源LLM和四个专为评估越狱方法策划的对抗性行为数据集上进行了评估。除了单个提示攻击外,我们还生成了跨多个提示有效的通用对抗性后缀,并证明了优化后缀在不同LLM之间的可转移性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在关键应用中的部署日益增多,但其稳健性和安全对齐性仍是重大挑战。尽管强化学习从人类反馈(RLHF)等对齐技术在典型提示上取得了成功,但LLM仍容易受到监狱突破攻击,这些攻击通过添加精心制作的对抗触发器来触发。现有方法大多在离散令牌空间进行低效搜索或直接优化连续嵌入。虽然连续嵌入可以直接作为选定开源模型的输入,但对于专有模型却不可行。本文提出了一种内在的优化方法,直接使用指数梯度下降法优化对抗后缀令牌的松弛独热编码,并通过Bregman投影确保每个令牌的优化独热编码始终保持在概率简单形内。该方法实现了较高的成功率和更快的收敛速度,相较于三种最先进的基线方法,并在五个开源LLM和四个用于评估监狱突破方法的数据集上进行了有效评估。此外,我们还对个别提示攻击进行了通用对抗后缀的生成,并证明了优化后缀在不同LLM之间的可转移性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在关键应用中的部署面临稳健性和安全对齐的挑战。
- LLM容易受到通过添加对抗触发器进行的监狱突破攻击。
- 现有方法大多在离散令牌空间进行低效搜索或直接优化连续嵌入,存在局限性。
- 提出的内在优化方法直接使用指数梯度下降法优化对抗后缀令牌的松弛独热编码。
- 该方法通过Bregman投影确保优化后的独热编码始终保持在概率简单形内。
- 方法实现了较高的成功率和更快的收敛速度,优于其他基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

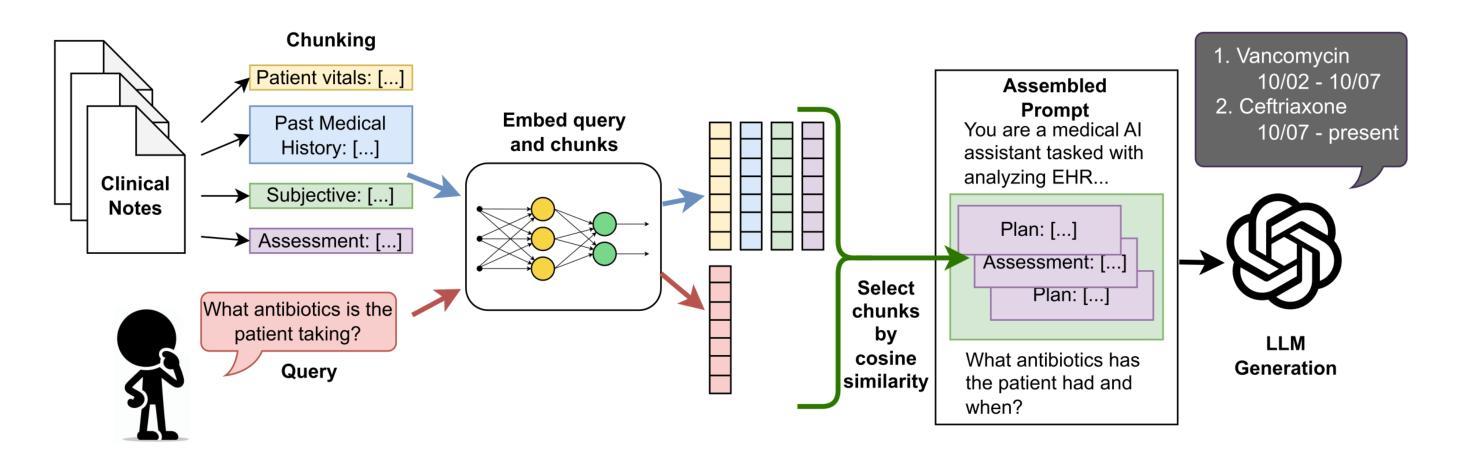
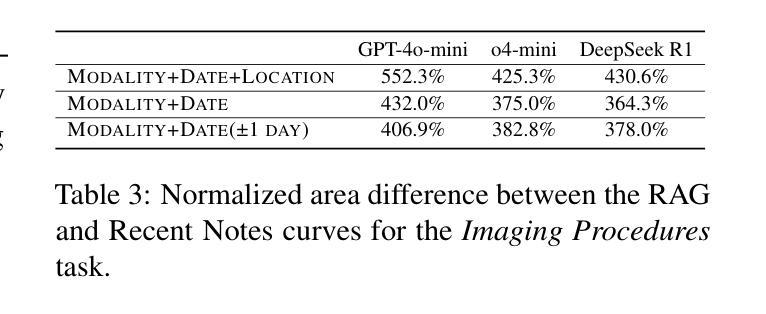
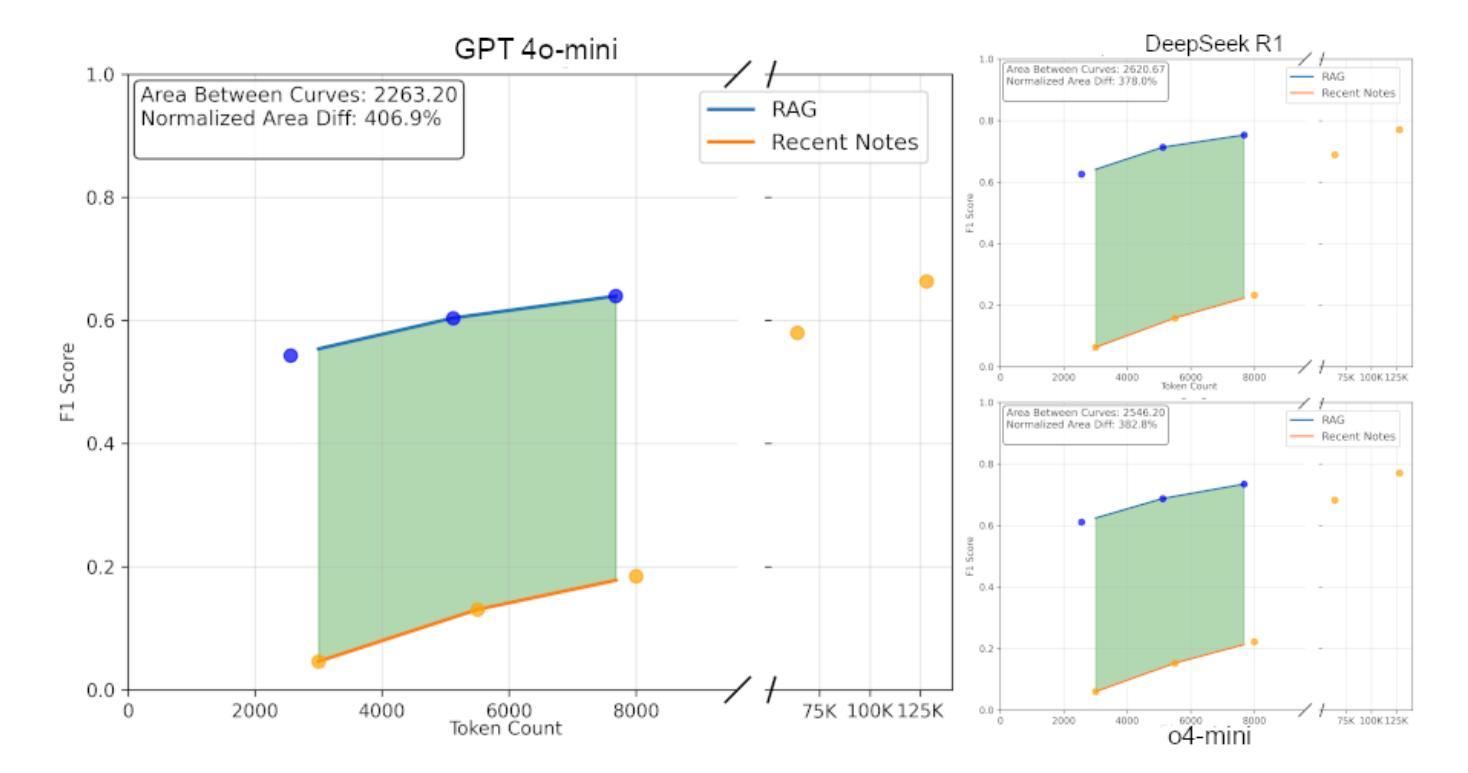
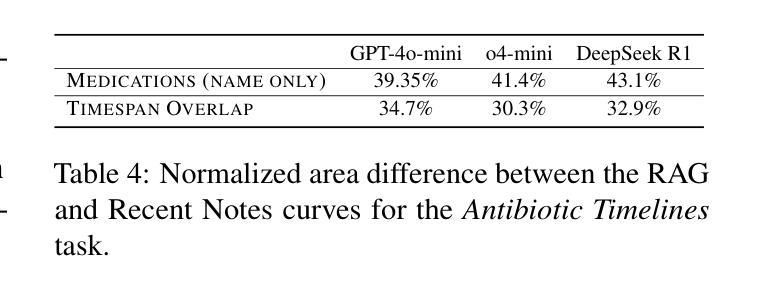
Evaluating Retrieval-Augmented Generation vs. Long-Context Input for Clinical Reasoning over EHRs
Authors:Skatje Myers, Dmitriy Dligach, Timothy A. Miller, Samantha Barr, Yanjun Gao, Matthew Churpek, Anoop Mayampurath, Majid Afshar
Electronic health records (EHRs) are long, noisy, and often redundant, posing a major challenge for the clinicians who must navigate them. Large language models (LLMs) offer a promising solution for extracting and reasoning over this unstructured text, but the length of clinical notes often exceeds even state-of-the-art models’ extended context windows. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) offers an alternative by retrieving task-relevant passages from across the entire EHR, potentially reducing the amount of required input tokens. In this work, we propose three clinical tasks designed to be replicable across health systems with minimal effort: 1) extracting imaging procedures, 2) generating timelines of antibiotic use, and 3) identifying key diagnoses. Using EHRs from actual hospitalized patients, we test three state-of-the-art LLMs with varying amounts of provided context, using either targeted text retrieval or the most recent clinical notes. We find that RAG closely matches or exceeds the performance of using recent notes, and approaches the performance of using the models’ full context while requiring drastically fewer input tokens. Our results suggest that RAG remains a competitive and efficient approach even as newer models become capable of handling increasingly longer amounts of text.
电子健康记录(EHRs)内容冗长、繁杂,对于需要查阅这些记录的医护人员来说是一个巨大的挑战。大型语言模型(LLM)为解决这一难题提供了一个可行的解决方案,可从非结构化文本中提取并进行分析。然而,临床笔记的长度甚至超过了现有最先进模型的上下文窗口长度。通过从整个电子健康记录中检索与任务相关的段落,检索增强生成(RAG)提供了一种替代方案,可能会减少所需输入标记的数量。在这项研究中,我们提出了三个可在健康系统中进行复制的临床任务,这些任务所需努力极小:1)提取成像程序;2)生成抗生素使用的时间线;3)识别关键诊断。我们使用实际住院患者的电子健康记录进行测试,测试了三个最先进的大型语言模型,这些模型提供的上下文各不相同,我们使用了有针对性的文本检索或最新的临床笔记。我们发现,检索增强生成法的效果接近或超过了使用最新笔记的效果,并接近使用模型全语境时的表现,同时所需的输入令牌大大减少。我们的结果表明,即使在新的模型能够处理越来越长的文本量时,检索增强生成法仍然是一个有竞争力的有效方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
电子病历(EHRs)长且复杂,常含有大量冗余信息,对医生来说是一大挑战。大型语言模型(LLM)为解决此问题提供了可能方案,但临床笔记的长度常超出模型的语境处理范围。本研究提出通过检索增强生成(RAG)方法,从整个电子病历中检索任务相关段落,可能减少所需输入标记的数量。本研究设计了三项可在不同医疗系统中复制的任务:提取成像程序、生成抗生素使用的时间线以及识别关键诊断。我们测试了三种最新LLM模型处理实际住院患者电子病历的能力,使用目标文本检索或最新临床笔记作为上下文。研究发现,RAG的性能接近或超过使用最新笔记的效果,且使用输入标记的数量大大减少。结果提示,即使在新模型处理文本长度增加的情况下,RAG仍然是一种有竞争力的有效方法。
Key Takeaways
- 电子病历(EHRs)存在信息冗长、复杂的问题,对医生造成挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在解决EHRs问题上具有潜力,但面临处理长文本的挑战。
- 检索增强生成(RAG)方法通过从整个EHR中检索任务相关段落,减少了所需的输入标记数量。
- 本研究设计了三项临床任务用于测试LLM模型性能:提取成像程序、生成抗生素使用的时间线以及识别关键诊断。
- RAG性能接近使用最新临床笔记的效果,同时减少输入标记数量。
- RAG方法即使在处理更长的文本时仍然有效且具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

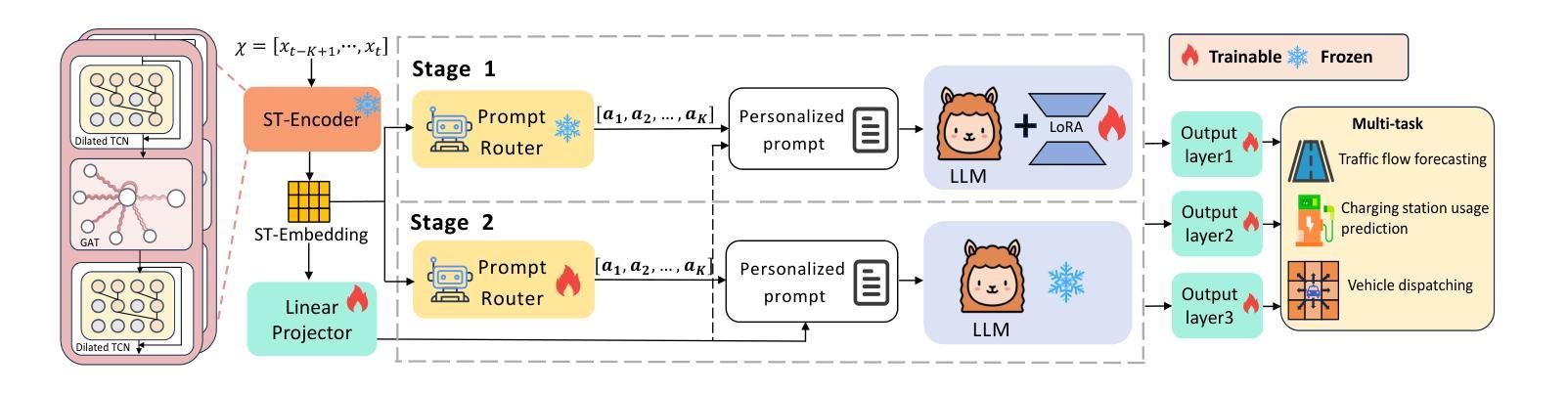
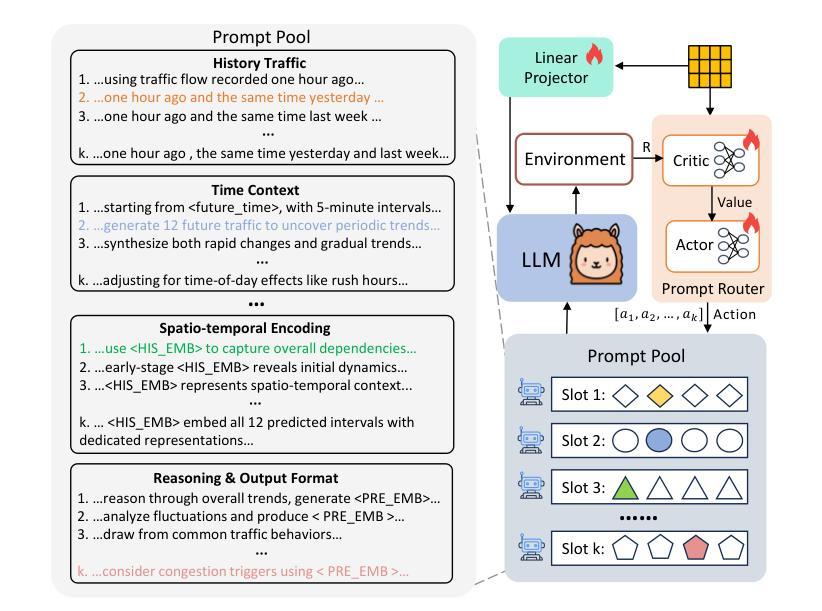
TransLLM: A Unified Multi-Task Foundation Framework for Urban Transportation via Learnable Prompting
Authors:Jiaming Leng, Yunying Bi, Chuan Qin, Bing Yin, Yanyong Zhang, Chao Wang
Urban transportation systems encounter diverse challenges across multiple tasks, such as traffic forecasting, electric vehicle (EV) charging demand prediction, and taxi dispatch. Existing approaches suffer from two key limitations: small-scale deep learning models are task-specific and data-hungry, limiting their generalizability across diverse scenarios, while large language models (LLMs), despite offering flexibility through natural language interfaces, struggle with structured spatiotemporal data and numerical reasoning in transportation domains. To address these limitations, we propose TransLLM, a unified foundation framework that integrates spatiotemporal modeling with large language models through learnable prompt composition. Our approach features a lightweight spatiotemporal encoder that captures complex dependencies via dilated temporal convolutions and dual-adjacency graph attention networks, seamlessly interfacing with LLMs through structured embeddings. A novel instance-level prompt routing mechanism, trained via reinforcement learning, dynamically personalizes prompts based on input characteristics, moving beyond fixed task-specific templates. The framework operates by encoding spatiotemporal patterns into contextual representations, dynamically composing personalized prompts to guide LLM reasoning, and projecting the resulting representations through specialized output layers to generate task-specific predictions. Experiments across seven datasets and three tasks demonstrate the exceptional effectiveness of TransLLM in both supervised and zero-shot settings. Compared to ten baseline models, it delivers competitive performance on both regression and planning problems, showing strong generalization and cross-task adaptability. Our code is available at https://github.com/BiYunying/TransLLM.
城市交通系统面临多种任务中的多样化挑战,如交通预测、电动汽车(EV)充电需求预测和出租车调度等。现有方法存在两个主要局限性:小规模深度学习模型是特定任务的,并且依赖大量数据,限制了它们在多种场景中的通用性;而大型语言模型(LLM),尽管通过自然语言接口提供了灵活性,但在交通领域的结构化时空数据和数值推理方面却遇到了困难。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了TransLLM,这是一个统一的基础框架,通过可学习的提示组合,将时空建模与大型语言模型结合起来。我们的方法采用轻量级的时空编码器,通过扩张的临时卷积和双重邻接图注意力网络来捕捉复杂的依赖关系,与LLM无缝接口通过结构化嵌入。一种新的基于实例级别的提示路由机制,通过强化学习进行训练,根据输入特征动态个性化提示,超越了固定的任务特定模板。该框架通过将时空模式编码为上下文表示,动态组合个性化提示来指导LLM推理,并通过专用输出层投影表示来生成特定任务的预测。在七个数据集和三个任务上的实验表明,TransLLM在监督学习和零样本设置中的出色有效性。与十个基准模型相比,它在回归和规划问题上均表现出竞争力,显示出强大的泛化和跨任务适应性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/BiYunying/TransLLM中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文针对城市交通系统中的多样挑战,如交通预测、电动汽车充电需求预测和出租车调度等问题,提出了TransLLM框架。该框架结合了时空建模与大型语言模型,通过可学习的提示组成来实现统一的任务处理。TransLLM框架具有轻量级的时空编码器,能够捕捉复杂的时空依赖关系,并与LLM无缝接口。实验表明,TransLLM在监督学习和零样本设置下均表现出优异的性能,与基准模型相比具有强大的泛化和跨任务适应性。
Key Takeaways
- TransLLM是一个统一的基础框架,用于处理城市交通系统中的多样挑战,如交通预测、电动汽车充电需求预测和出租车调度。
- 该框架结合了时空建模与大型语言模型(LLMs),以应对不同任务。
- TransLLM具有轻量级的时空编码器,能够捕捉复杂的时空依赖关系。
- 通过可学习的提示组成,TransLLM可以动态地个性化提示,而无需固定的任务特定模板。
- TransLLM框架在监督学习和零样本设置下均表现出优异的性能。
- 与多种基准模型相比,TransLLM具有强大的泛化能力,能在不同的交通任务中表现出良好的性能。
- TransLLM框架的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图
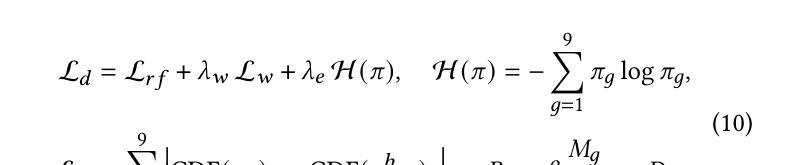
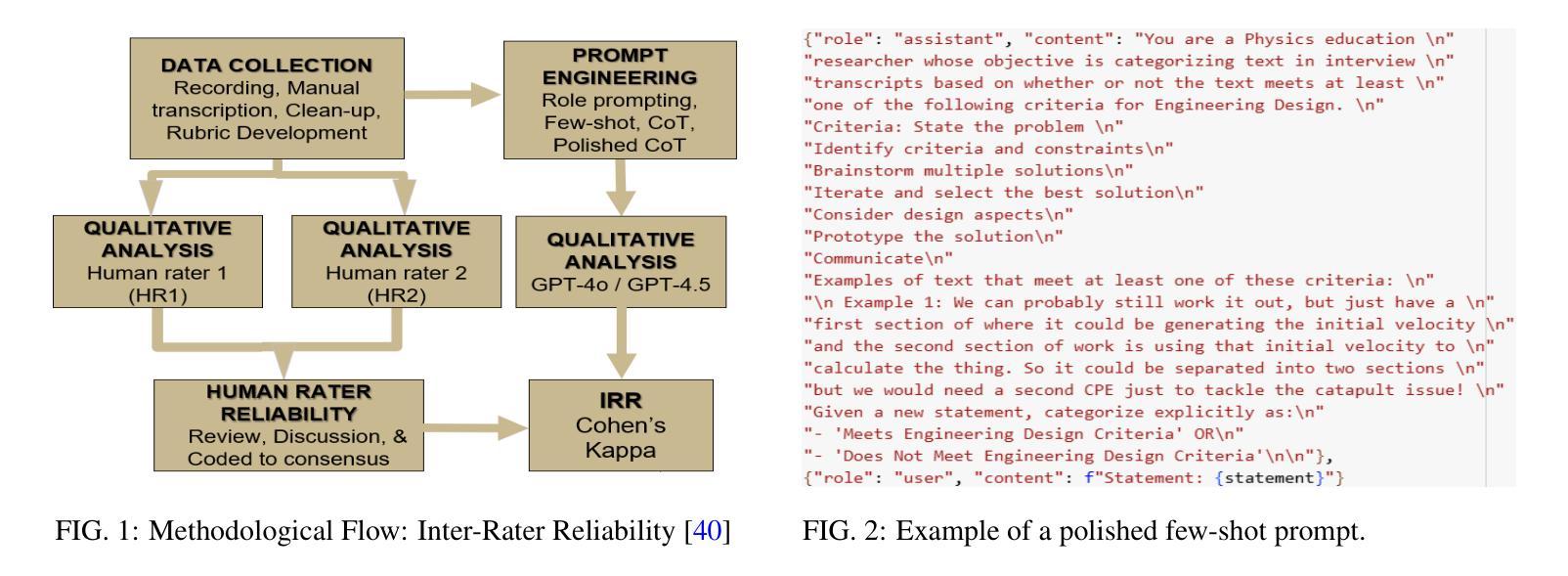
Investigation of the Inter-Rater Reliability between Large Language Models and Human Raters in Qualitative Analysis
Authors:Nikhil Sanjay Borse, Ravishankar Chatta Subramaniam, N. Sanjay Rebello
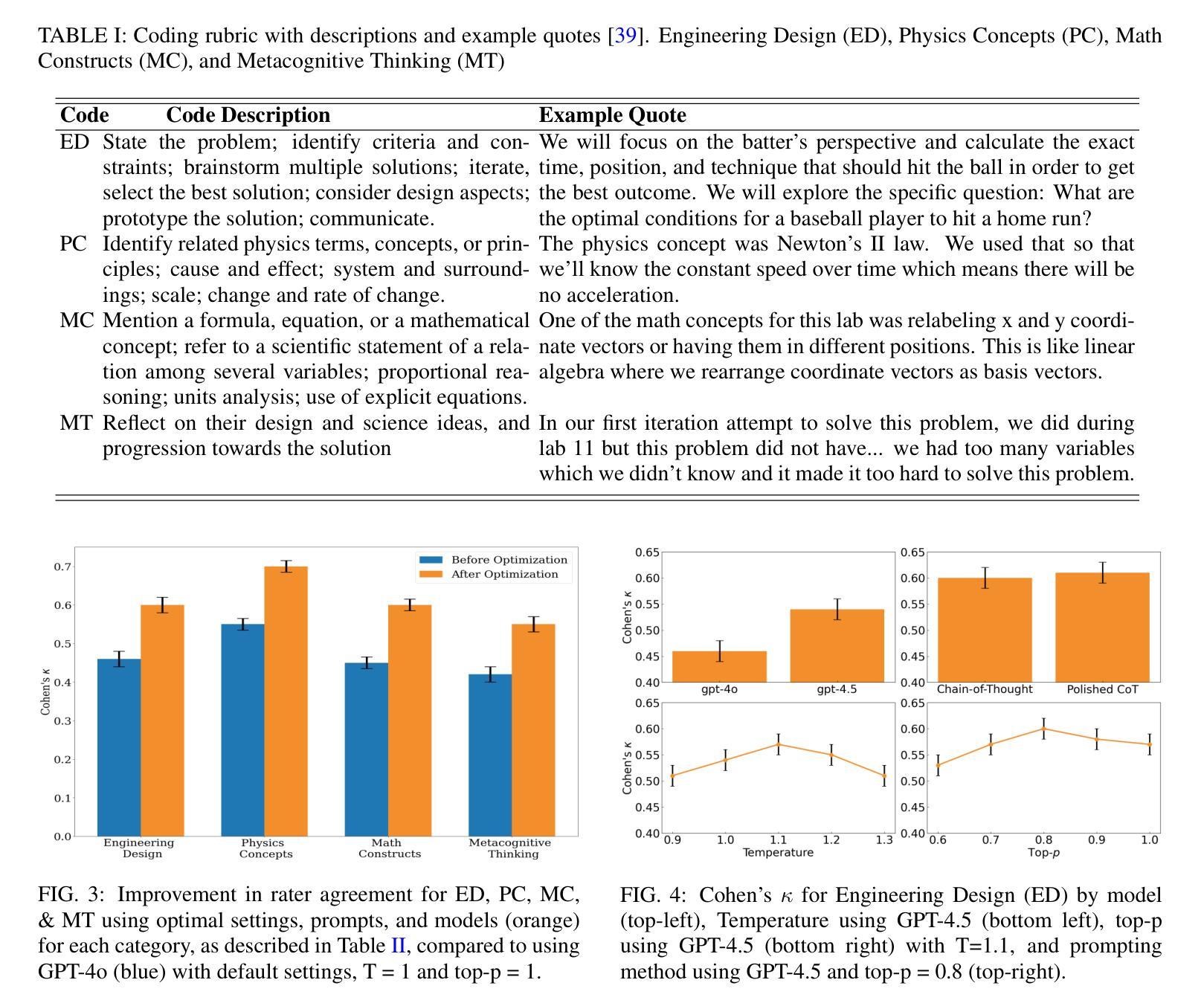
Qualitative analysis is typically limited to small datasets because it is time-intensive. Moreover, a second human rater is required to ensure reliable findings. Artificial intelligence tools may replace human raters if we demonstrate high reliability compared to human ratings. We investigated the inter-rater reliability of state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs), ChatGPT-4o and ChatGPT-4.5-preview, in rating audio transcripts coded manually. We explored prompts and hyperparameters to optimize model performance. The participants were 14 undergraduate student groups from a university in the midwestern United States who discussed problem-solving strategies for a project. We prompted an LLM to replicate manual coding, and calculated Cohen’s Kappa for inter-rater reliability. After optimizing model hyperparameters and prompts, the results showed substantial agreement (${\kappa}>0.6$) for three themes and moderate agreement on one. Our findings demonstrate the potential of GPT-4o and GPT-4.5 for efficient, scalable qualitative analysis in physics education and identify their limitations in rating domain-general constructs.
定性分析通常仅限于小数据集,因为它非常耗时。此外,需要第二位人类评分者以确保结果可靠。如果我们证明与人工评分相比具有高度的可靠性,人工智能工具可能会取代人类评分者。我们调查了最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)ChatGPT-4o和ChatGPT-4.5预览版在手动编码音频转录时的评分员间可靠性。我们探索了提示和超参数以优化模型性能。参与者为来自美国中西部一所大学的14个本科生小组,他们讨论了一个项目的解决问题策略。我们提示LLM复制手动编码,并计算了Cohen的Kappa值以衡量评分员间可靠性。在优化模型超参数和提示后,结果显示三个主题上有显著的共识(κ> 0.6),一个主题上中度共识。我们的研究结果表明GPT-4o和GPT-4.5在物理教育中的高效、可扩展的定性分析方面的潜力,并指出了他们在评价领域通用结构方面的局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 4 figures, Physics Education Research Conference 2025
摘要
在手动编码音频转录时使用最新大型语言模型(LLM),探讨了LLM之间的评估可靠性。发现通过对模型进行提示和超参数优化后,能够得出显著的协议,但仍存在一些限制。这为物理教育中的定性分析提供了高效、可扩展的潜在工具。
关键见解
- 定性分析受限于小数据集,因为它耗时且需要第二个人类评估者以确保结果的可靠性。
- 人工智能工具可以取代人类评估者,前提是证明其与人类评估具有高度的可靠性。
- 对最新的大型语言模型(LLM)进行了评估者间可靠性的研究,涉及ChatGPT-4o和ChatGPT-4.5预览版。
- 在对音频转录进行手动编码时,探讨了如何优化模型的提示和超参数以提高性能。
- 实验对象包括来自美国中西部某大学的十四组本科生,他们讨论了一个关于解决项目问题的策略。
- 在模型提示和超参数优化后,对三个主题的评估显示出显著的一致性(κ> 0.6),而对一个主题的评估显示出中等一致性。
点此查看论文截图

Evaluating Multilingual and Code-Switched Alignment in LLMs via Synthetic Natural Language Inference
Authors:Samir Abdaljalil, Erchin Serpedin, Khalid Qaraqe, Hasan Kurban
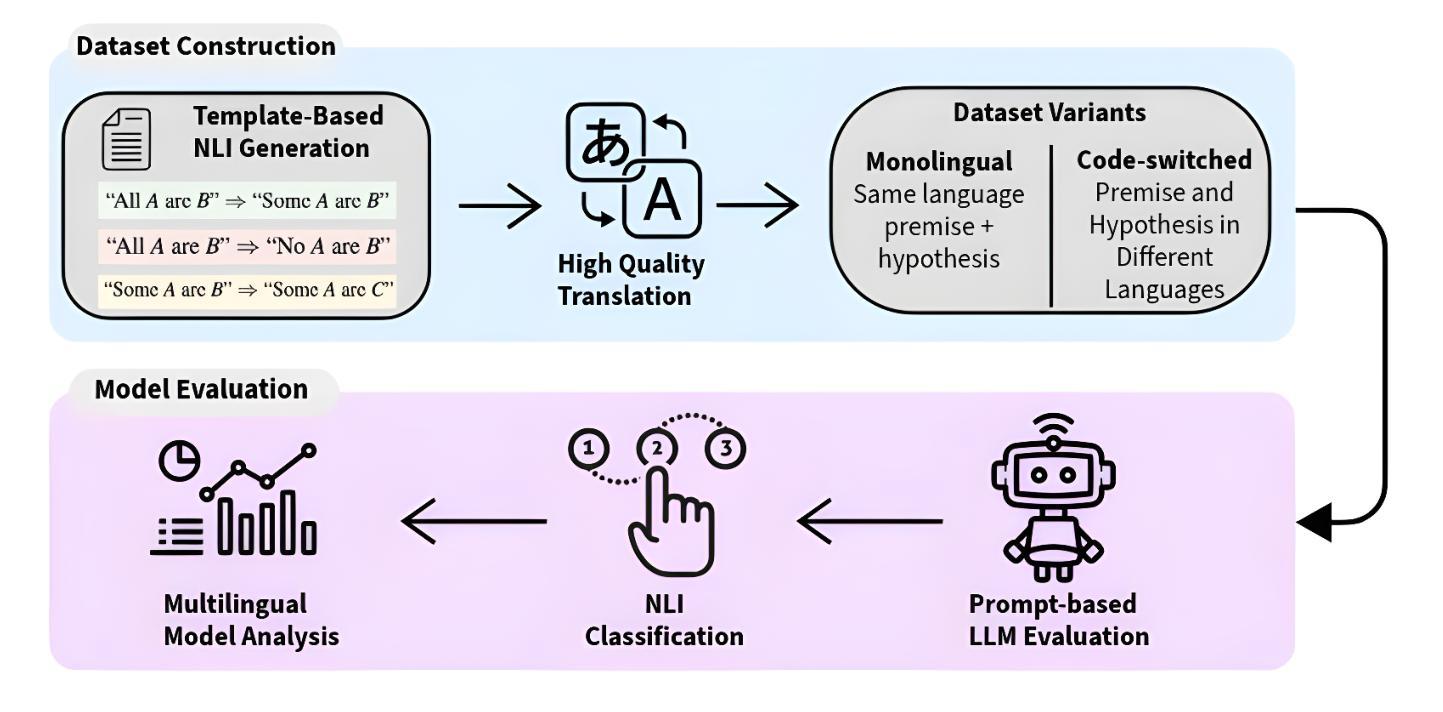
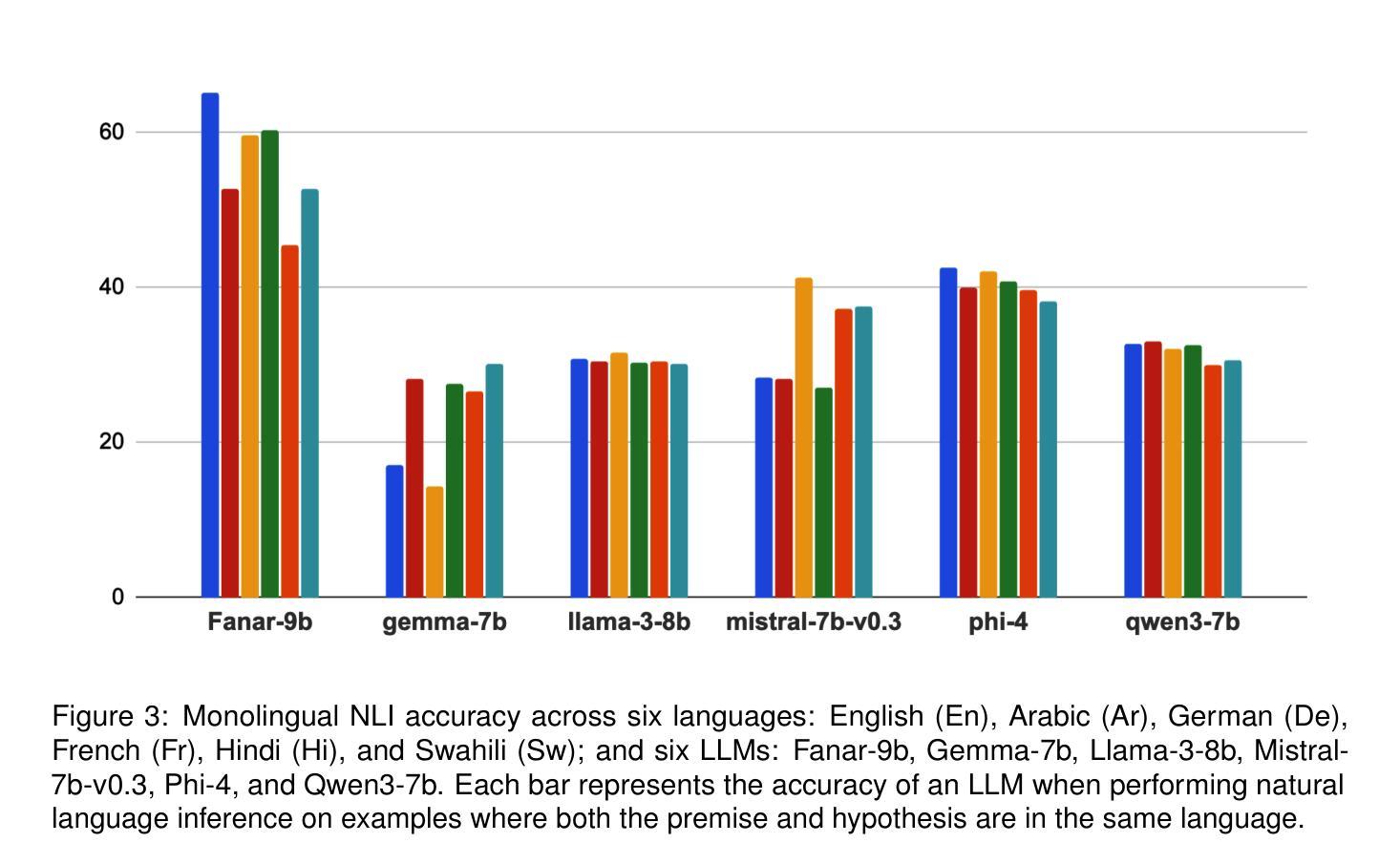
Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied in multilingual contexts, yet their capacity for consistent, logically grounded alignment across languages remains underexplored. We present a controlled evaluation framework for multilingual natural language inference (NLI) that generates synthetic, logic-based premise-hypothesis pairs and translates them into a typologically diverse set of languages. This design enables precise control over semantic relations and allows testing in both monolingual and mixed-language (code-switched) conditions. Surprisingly, code-switching does not degrade, and can even improve, performance, suggesting that translation-induced lexical variation may serve as a regularization signal. We validate semantic preservation through embedding-based similarity analyses and cross-lingual alignment visualizations, confirming the fidelity of translated pairs. Our findings expose both the potential and the brittleness of current LLM cross-lingual reasoning, and identify code-switching as a promising lever for improving multilingual robustness. Code available at: https://github.com/KurbanIntelligenceLab/nli-stress-testing
大型语言模型(LLM)在多语言环境中的应用越来越广泛,然而,它们在跨语言的一致性和逻辑基础对齐方面的能力仍然未被充分探索。我们提出了一种针对多语言自然语言推理(NLI)的控制评估框架,该框架生成基于逻辑的前提假设对,并将其翻译成类型多样的语言集。这种设计能够精确控制语义关系,并允许在单语和混合语言(代码切换)条件下进行测试。令人惊讶的是,代码切换并不会降低性能,甚至可能有所提高,这表明翻译引起的词汇变化可能作为一种正则化信号。我们通过基于嵌入的相似度分析和跨语言对齐可视化来验证语义保留,证实了翻译对的保真度。我们的研究既暴露了当前LLM跨语言推理的潜力和脆弱性,也识别出代码切换是提高多语言稳健性的一个有前途的杠杆。相关代码可在:https://github.com/KurbanIntelligenceLab/nli-stress-testing获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在多语言环境中的应用日益广泛,但其跨语言的逻辑一致性对齐能力尚未得到充分探索。本研究提出了一种控制评估框架,用于多语言自然语言推理(NLI),生成基于逻辑的合成前提假设对,并将其翻译成多种类型语言。这种设计能够精确控制语义关系,并允许在单语和混合语言(代码切换)条件下进行测试。令人惊讶的是,代码切换并不会降低性能,甚至可能提高性能,这表明翻译引起的词汇变化可能作为一种常规信号。通过基于嵌入的相似性分析和跨语言对齐可视化验证语义的保留,确认了翻译对的保真性。本研究结果揭示了当前LLM跨语言推理的潜力和脆弱性,并将代码切换作为提高多语言稳健性的有力手段。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在多语言环境中的应用逐渐普及,但其在逻辑一致性方面的跨语言对齐能力尚未充分研究。
- 提出了一种控制评估框架用于多语言自然语言推理,包括生成合成逻辑前提假设对并将其翻译成多种语言。
- 代码切换(即使用多种语言进行交流)对大型语言模型的性能有积极影响,并不会降低模型性能。
- 翻译引起的词汇变化可能作为一种常规信号,有助于提高模型的性能。
- 通过嵌入相似性分析和跨语言对齐可视化验证了语义在翻译过程中的保留。
- 研究结果揭示了当前大型语言模型跨语言推理的潜力和脆弱性。
点此查看论文截图

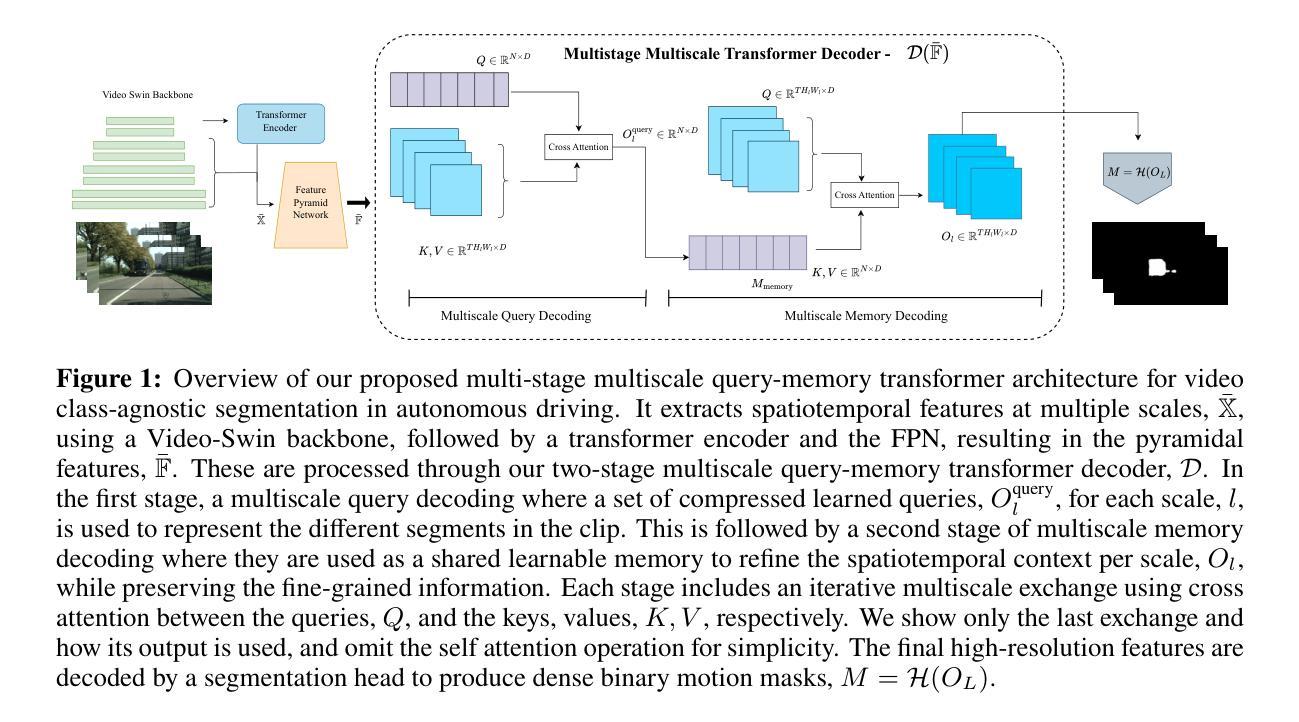
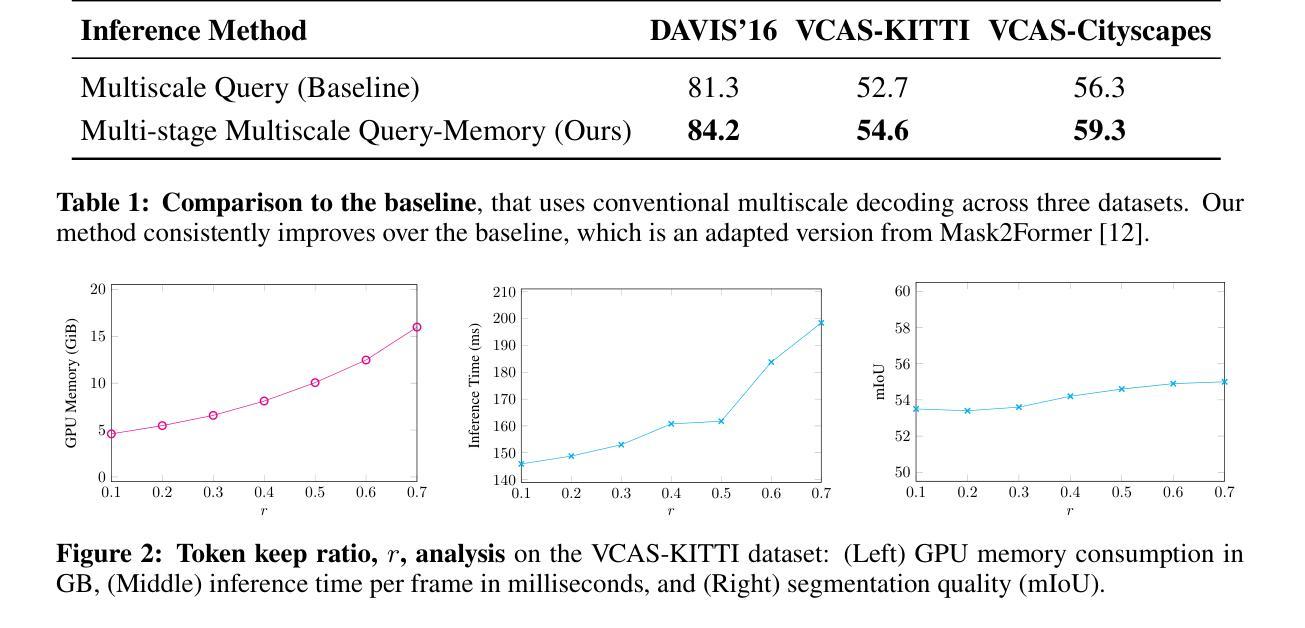
Multiscale Video Transformers for Class Agnostic Segmentation in Autonomous Driving
Authors:Leila Cheshmi, Mennatullah Siam
Ensuring safety in autonomous driving is a complex challenge requiring handling unknown objects and unforeseen driving scenarios. We develop multiscale video transformers capable of detecting unknown objects using only motion cues. Video semantic and panoptic segmentation often relies on known classes seen during training, overlooking novel categories. Recent visual grounding with large language models is computationally expensive, especially for pixel-level output. We propose an efficient video transformer trained end-to-end for class-agnostic segmentation without optical flow. Our method uses multi-stage multiscale query-memory decoding and a scale-specific random drop-token to ensure efficiency and accuracy, maintaining detailed spatiotemporal features with a shared, learnable memory module. Unlike conventional decoders that compress features, our memory-centric design preserves high-resolution information at multiple scales. We evaluate on DAVIS’16, KITTI, and Cityscapes. Our method consistently outperforms multiscale baselines while being efficient in GPU memory and run-time, demonstrating a promising direction for real-time, robust dense prediction in safety-critical robotics.
确保自动驾驶的安全性是一项复杂的挑战,需要处理未知物体和未曾预见的驾驶场景。我们开发了多尺度视频转换器,仅使用运动线索即可检测未知物体。视频语义和全景分割通常依赖于训练期间看到的已知类别,从而忽略了新类别。最近与大型语言模型一起进行的视觉定位计算成本高昂,尤其是对于像素级输出。我们提出了一种高效视频转换器,针对类别不可知分割进行端到端训练,无需光学流。我们的方法使用多阶段多尺度查询内存解码和特定规模的随机丢弃令牌,以确保效率和准确性,利用共享的可学习内存模块,保留详细的时空特征。与传统的压缩特征的解码器不同,我们以内存为中心的设计在多个尺度上保留了高分辨率信息。我们在DAVIS’16、KITTI和Cityscapes上进行了评估。我们的方法在GPU内存和运行时方面始终优于多尺度基线,显示出在实时、稳健的密集预测方面很有前途,对于安全关键的机器人技术具有重要意义。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 2 figures, 1 table
Summary
针对自动驾驶中的安全挑战,研究团队提出一种多尺度视频转换器,利用运动线索检测未知物体。该研究开发了一种高效视频转换器,采用分阶段多尺度查询-内存解码和尺度特定随机丢弃令牌技术,用于类别不可知的分割,无需光学流动。该方法在细节时空特征方面表现出色,通过一个共享的可学习内存模块进行维护。该研究在DAVIS’16、KITTI和Cityscapes等数据集上进行了评估,显示出在多尺度基准测试中的优越性,同时提高了GPU内存和运行时间的效率,为安全关键的机器人实时、稳健的密集预测提供了有前途的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对自动驾驶中的安全挑战,提出了一种多尺度视频转换器来检测未知物体。
- 利用运动线索进行类别不可知的分割,无需光学流动。
- 提出一种高效视频转换器,采用分阶段多尺度查询-内存解码技术。
- 采用尺度特定随机丢弃令牌技术,以提高效率和准确性。
- 通过共享的可学习内存模块来维护细节时空特征。
- 在多个数据集上进行了评估,显示出在多尺度基准测试中的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

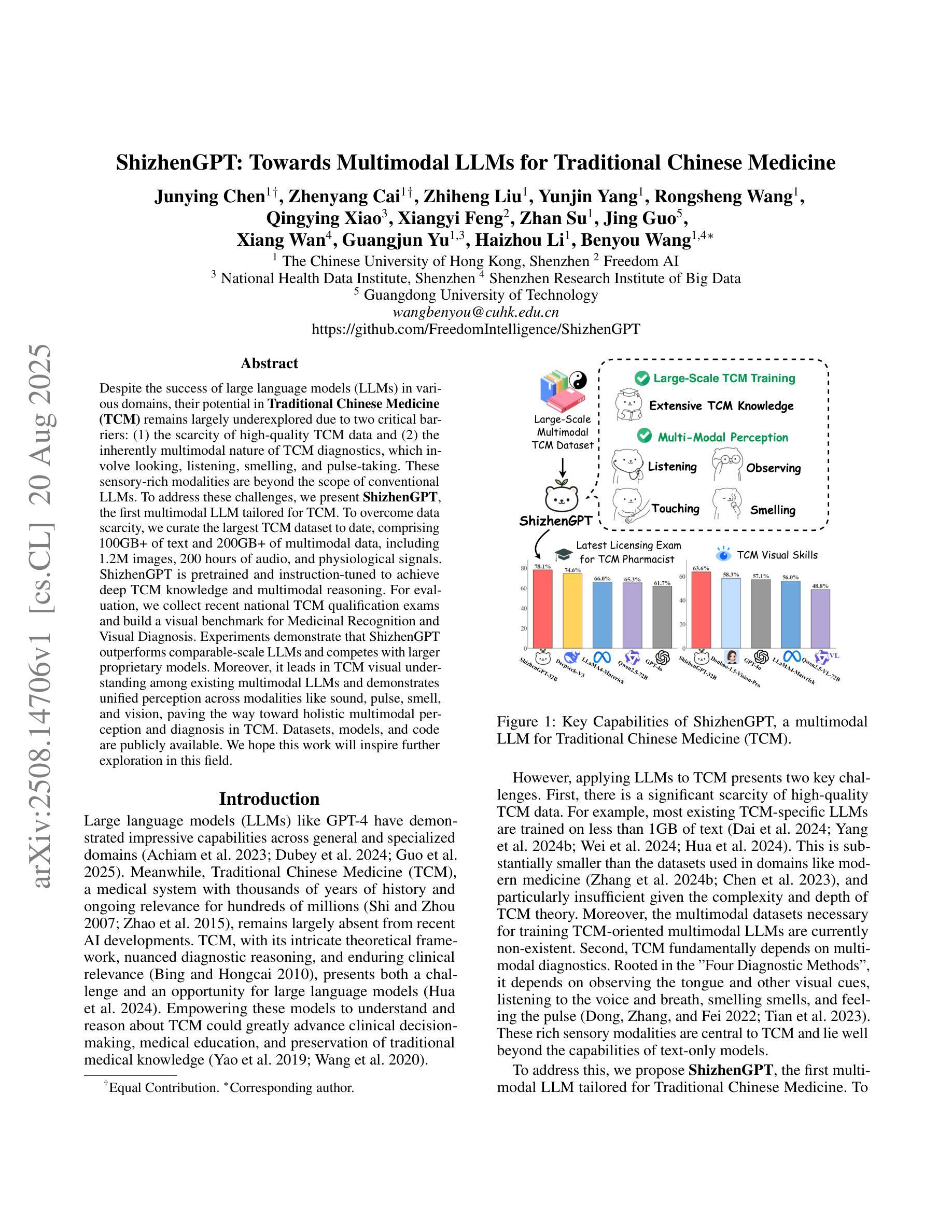
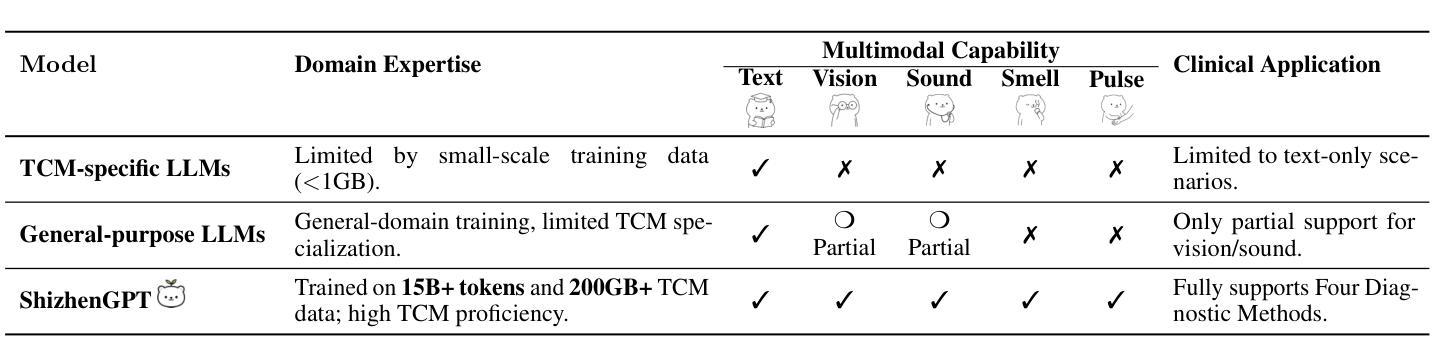
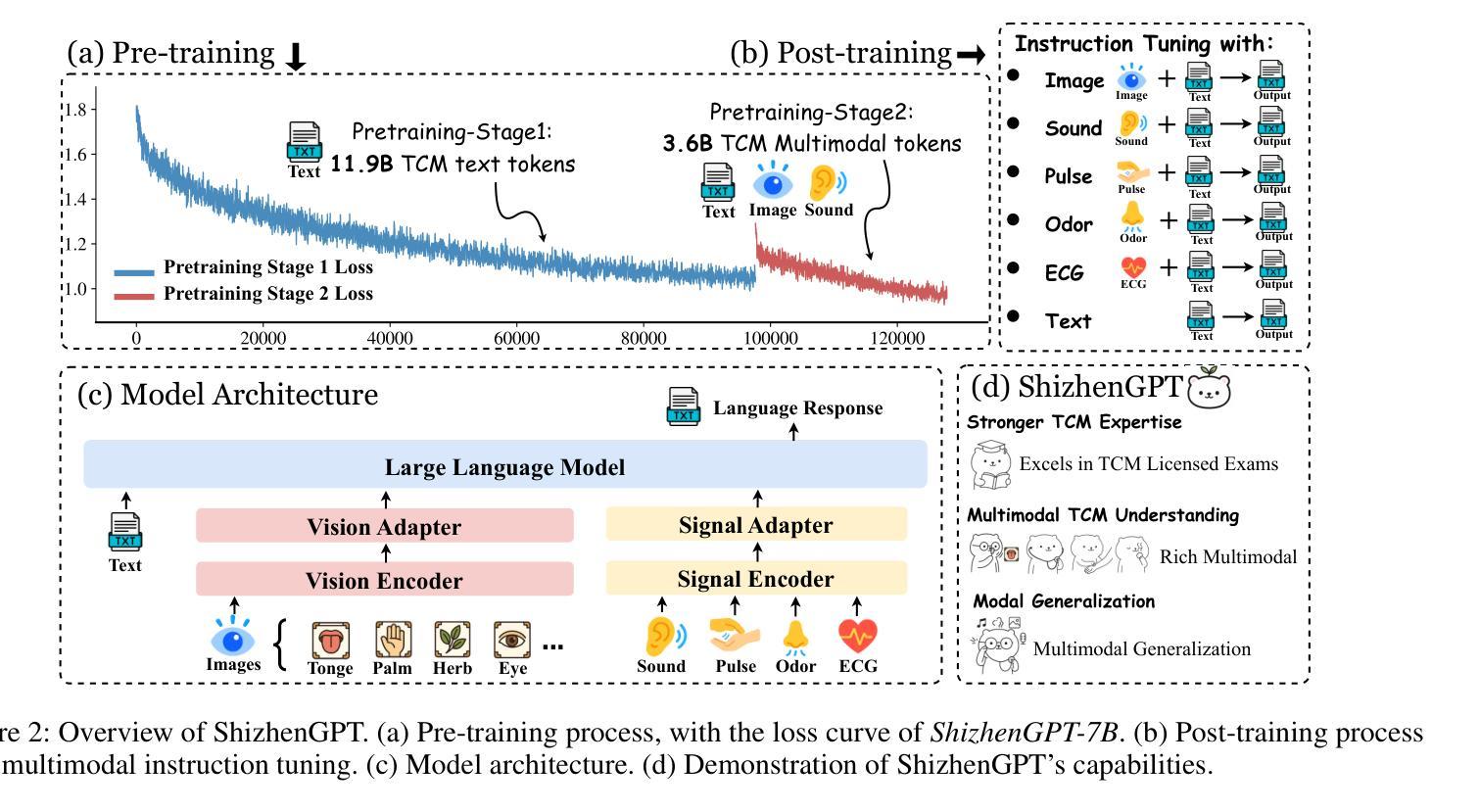
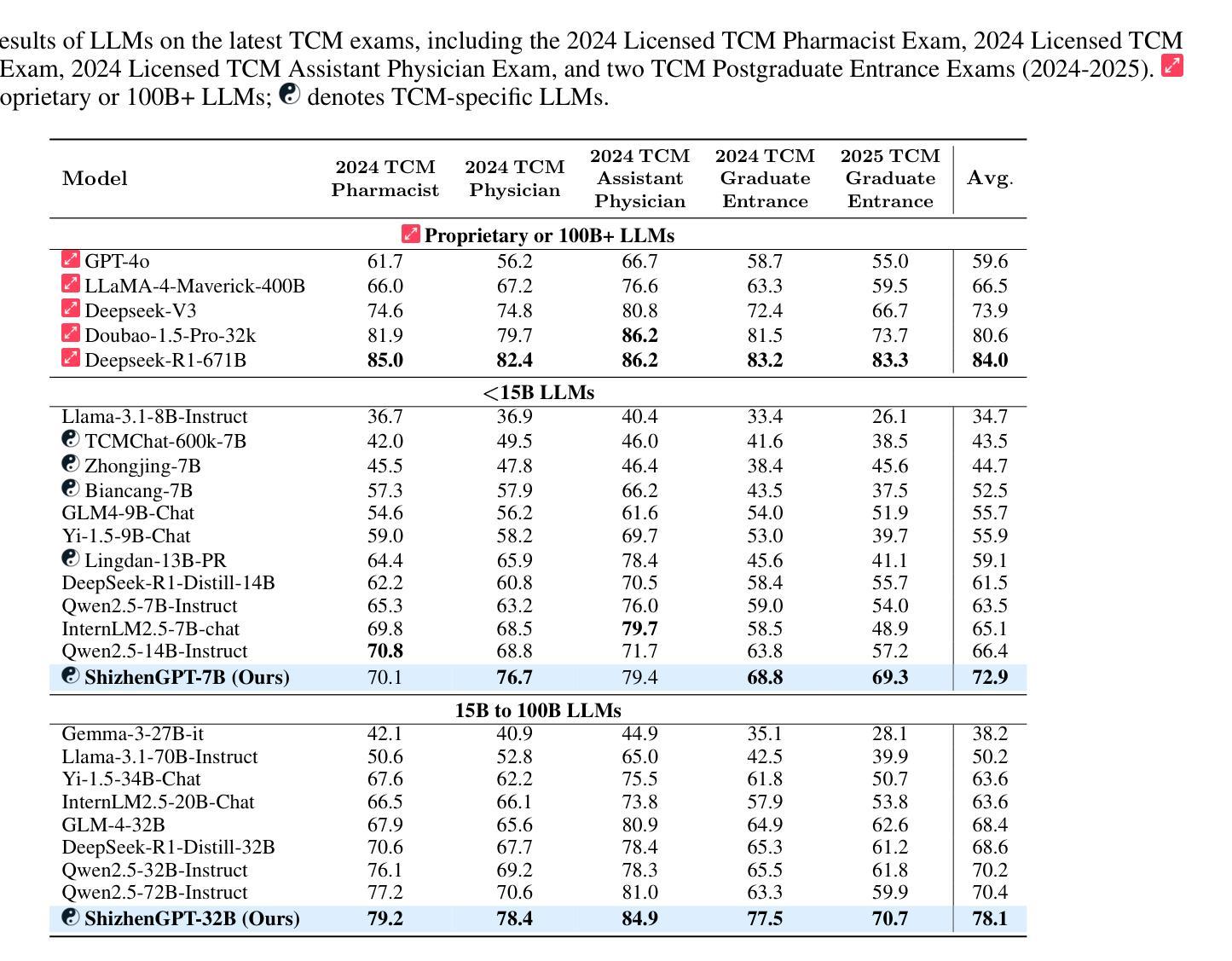
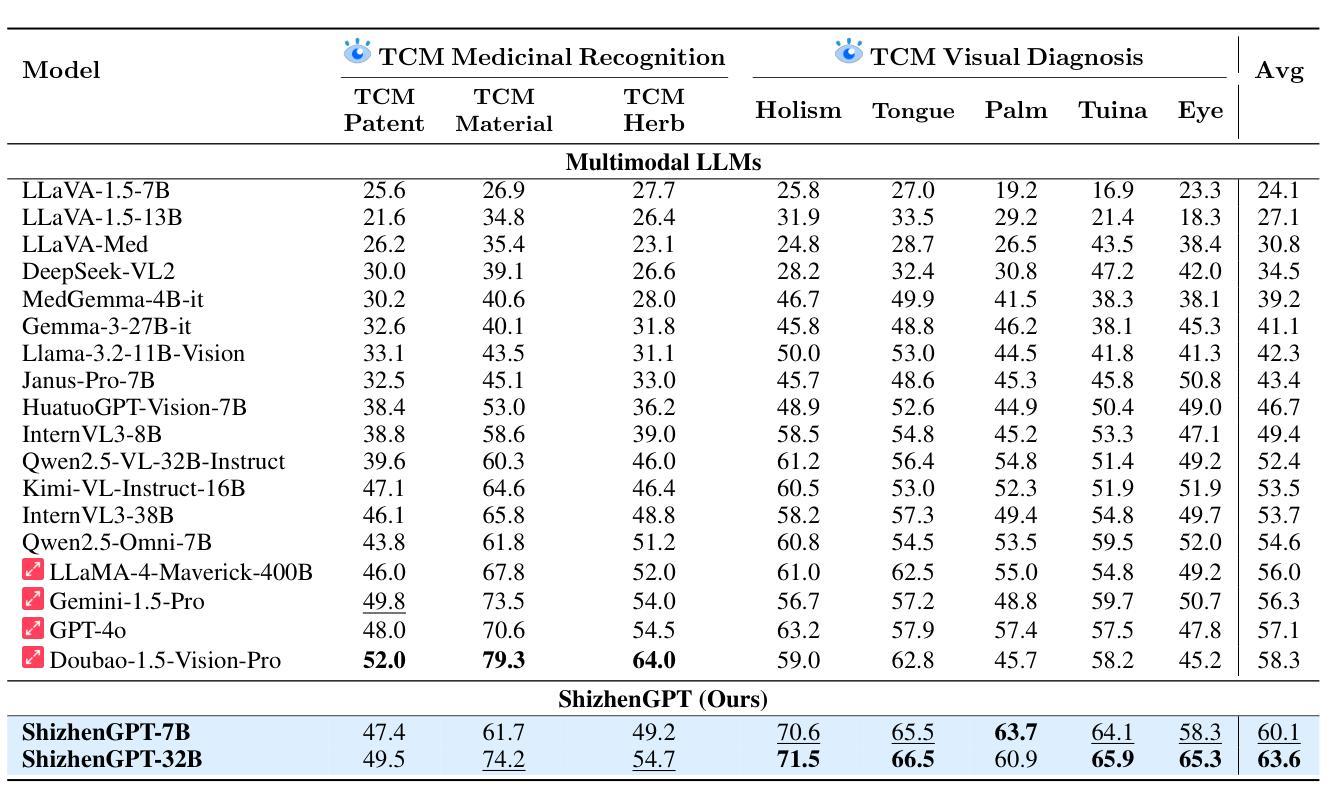
ShizhenGPT: Towards Multimodal LLMs for Traditional Chinese Medicine
Authors:Junying Chen, Zhenyang Cai, Zhiheng Liu, Yunjin Yang, Rongsheng Wang, Qingying Xiao, Xiangyi Feng, Zhan Su, Jing Guo, Xiang Wan, Guangjun Yu, Haizhou Li, Benyou Wang
Despite the success of large language models (LLMs) in various domains, their potential in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) remains largely underexplored due to two critical barriers: (1) the scarcity of high-quality TCM data and (2) the inherently multimodal nature of TCM diagnostics, which involve looking, listening, smelling, and pulse-taking. These sensory-rich modalities are beyond the scope of conventional LLMs. To address these challenges, we present ShizhenGPT, the first multimodal LLM tailored for TCM. To overcome data scarcity, we curate the largest TCM dataset to date, comprising 100GB+ of text and 200GB+ of multimodal data, including 1.2M images, 200 hours of audio, and physiological signals. ShizhenGPT is pretrained and instruction-tuned to achieve deep TCM knowledge and multimodal reasoning. For evaluation, we collect recent national TCM qualification exams and build a visual benchmark for Medicinal Recognition and Visual Diagnosis. Experiments demonstrate that ShizhenGPT outperforms comparable-scale LLMs and competes with larger proprietary models. Moreover, it leads in TCM visual understanding among existing multimodal LLMs and demonstrates unified perception across modalities like sound, pulse, smell, and vision, paving the way toward holistic multimodal perception and diagnosis in TCM. Datasets, models, and code are publicly available. We hope this work will inspire further exploration in this field.
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在各个领域取得了成功,但由于两个关键障碍,它们在传统中医(TCM)领域的应用潜力仍被大大忽视:一是高质量中医数据的稀缺性;二是中医诊断的固有跨模态性质,涉及观察、聆听、闻诊和脉诊。这些感官丰富的模态超出了传统LLM的范围。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了适用于中医的多模态LLM——石阵GPT。为了克服数据稀缺的问题,我们整理了迄今为止最大的中医数据集,包含超过100GB的文本数据和超过200GB的多模态数据,包括120万张图像、200小时的音频和生理信号。石阵GPT经过预训练和执行指令微调,以实现深入的中医知识和多模态推理。为了评估其性能,我们收集了最近的中医资格考试,并建立了药物识别和视觉诊断的视觉基准测试。实验表明,石阵GPT在同类规模的LLM中表现突出,并与更大的专有模型相竞争。此外,它在现有的多模态LLM中领先中医视觉理解,并展示了跨声音、脉搏、气味和视觉等模态的统一感知,为中医的整体多模态感知和诊断铺平了道路。数据集、模型和代码均公开可用。我们希望这项工作将激发该领域的进一步探索。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对传统中医领域推出的首个多模态大型语言模型——石阵GPT。该模型旨在克服中医领域两大挑战:高质量数据的稀缺性和中医诊断的感官丰富性。通过构建迄今为止最大的中医数据集,包括超过100GB的文本数据和超过200GB的多模态数据(包括图像、音频和生理信号),ShizhenGPT实现了深度中医知识和多模态推理。实验表明,它在中医视觉理解方面领先现有的多模态大型语言模型,并展示了跨声音、脉象、气味和视觉等模态的统一感知能力,为中医领域的全息多模态感知和诊断铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 石阵GPT是首个针对传统中医领域的多模态大型语言模型。
- 中医领域面临两大挑战:高质量数据的稀缺性和中医诊断的感官丰富性。
- 石阵GPT通过构建迄今为止最大的中医数据集来克服这些挑战,包括文本和多模态数据。
- ShizhenGPT实现了深度中医知识和多模态推理。
- 实验表明,石阵GPT在中医视觉理解方面领先现有的多模态大型语言模型。
- 石阵GPT展示了跨声音、脉象、气味和视觉等模态的统一感知能力。
点此查看论文截图

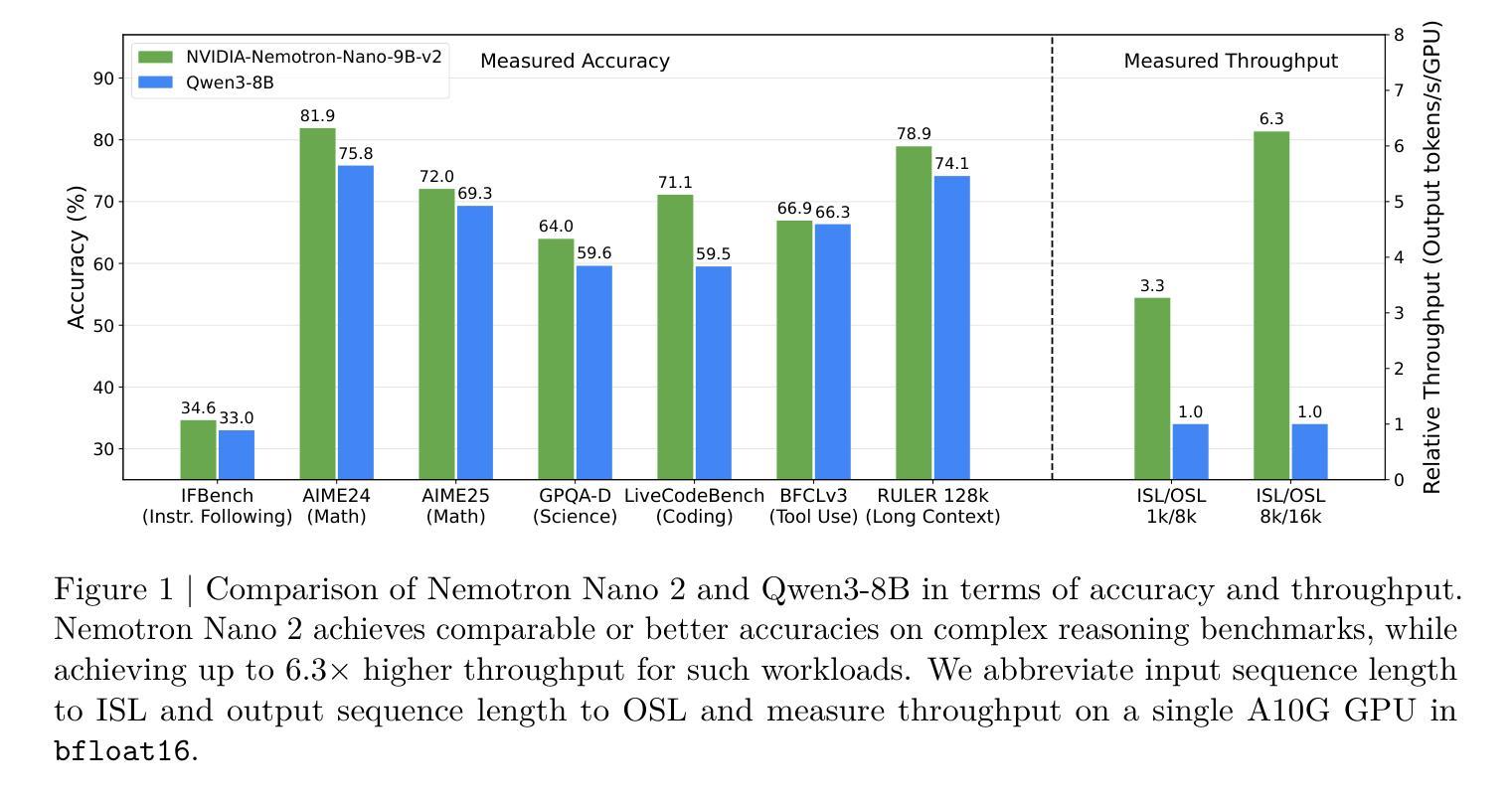
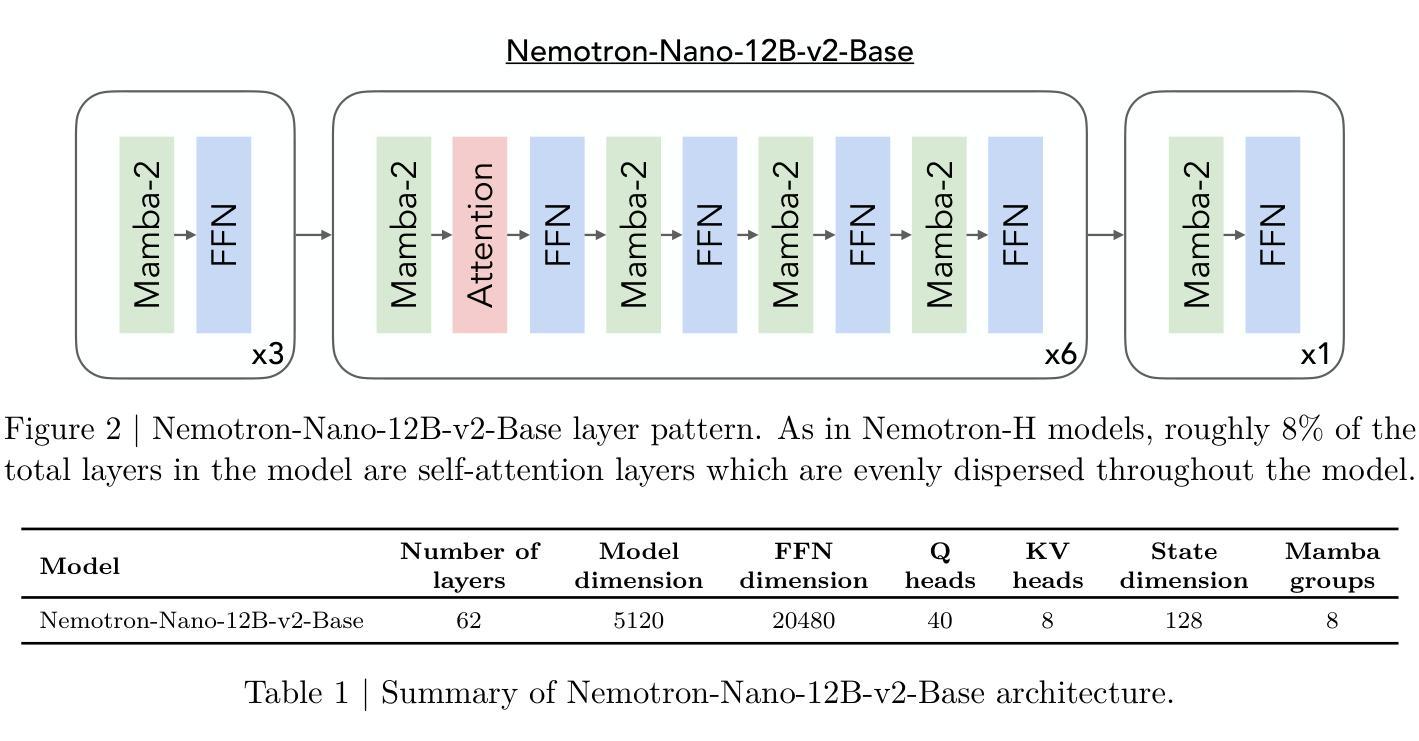
NVIDIA Nemotron Nano 2: An Accurate and Efficient Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Reasoning Model
Authors: NVIDIA, :, Aarti Basant, Abhijit Khairnar, Abhijit Paithankar, Abhinav Khattar, Adi Renduchintala, Adithya Renduchintala, Aditya Malte, Akhiad Bercovich, Akshay Hazare, Alejandra Rico, Aleksander Ficek, Alex Kondratenko, Alex Shaposhnikov, Ali Taghibakhshi, Amelia Barton, Ameya Sunil Mahabaleshwarkar, Amy Shen, Andrew Tao, Ann Guan, Anna Shors, Anubhav Mandarwal, Arham Mehta, Arun Venkatesan, Ashton Sharabiani, Ashwath Aithal, Ashwin Poojary, Ayush Dattagupta, Balaram Buddharaju, Banghua Zhu, Barnaby Simkin, Bilal Kartal, Bita Darvish Rouhani, Bobby Chen, Boris Ginsburg, Brandon Norick, Brian Yu, Bryan Catanzaro, Charles Wang, Charlie Truong, Chetan Mungekar, Chintan Patel, Chris Alexiuk, Christian Munley, Christopher Parisien, Dan Su, Daniel Afrimi, Daniel Korzekwa, Daniel Rohrer, Daria Gitman, David Mosallanezhad, Deepak Narayanan, Dima Rekesh, Dina Yared, Dmytro Pykhtar, Dong Ahn, Duncan Riach, Eileen Long, Elliott Ning, Eric Chung, Erick Galinkin, Evelina Bakhturina, Gargi Prasad, Gerald Shen, Haim Elisha, Harsh Sharma, Hayley Ross, Helen Ngo, Herman Sahota, Hexin Wang, Hoo Chang Shin, Hua Huang, Iain Cunningham, Igor Gitman, Ivan Moshkov, Jaehun Jung, Jan Kautz, Jane Polak Scowcroft, Jared Casper, Jimmy Zhang, Jinze Xue, Jocelyn Huang, Joey Conway, John Kamalu, Jonathan Cohen, Joseph Jennings, Julien Veron Vialard, Junkeun Yi, Jupinder Parmar, Kari Briski, Katherine Cheung, Katherine Luna, Keith Wyss, Keshav Santhanam, Kezhi Kong, Krzysztof Pawelec, Kumar Anik, Kunlun Li, Kushan Ahmadian, Lawrence McAfee, Laya Sleiman, Leon Derczynski, Luis Vega, Maer Rodrigues de Melo, Makesh Narsimhan Sreedhar, Marcin Chochowski, Mark Cai, Markus Kliegl, Marta Stepniewska-Dziubinska, Matvei Novikov, Mehrzad Samadi, Meredith Price, Meriem Boubdir, Michael Boone, Michael Evans, Michal Bien, Michal Zawalski, Miguel Martinez, Mike Chrzanowski, Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Namit Dhameja, Nave Assaf, Negar Habibi, Nidhi Bhatia, Nikki Pope, Nima Tajbakhsh, Nirmal Kumar Juluru, Oleg Rybakov, Oleksii Hrinchuk, Oleksii Kuchaiev, Oluwatobi Olabiyi, Pablo Ribalta, Padmavathy Subramanian, Parth Chadha, Pavlo Molchanov, Peter Dykas, Peter Jin, Piotr Bialecki, Piotr Januszewski, Pradeep Thalasta, Prashant Gaikwad, Prasoon Varshney, Pritam Gundecha, Przemek Tredak, Rabeeh Karimi Mahabadi, Rajen Patel, Ran El-Yaniv, Ranjit Rajan, Ria Cheruvu, Rima Shahbazyan, Ritika Borkar, Ritu Gala, Roger Waleffe, Ruoxi Zhang, Russell J. Hewett, Ryan Prenger, Sahil Jain, Samuel Kriman, Sanjeev Satheesh, Saori Kaji, Sarah Yurick, Saurav Muralidharan, Sean Narenthiran, Seonmyeong Bak, Sepehr Sameni, Seungju Han, Shanmugam Ramasamy, Shaona Ghosh, Sharath Turuvekere Sreenivas, Shelby Thomas, Shizhe Diao, Shreya Gopal, Shrimai Prabhumoye, Shubham Toshniwal, Shuoyang Ding, Siddharth Singh, Siddhartha Jain, Somshubra Majumdar, Stefania Alborghetti, Syeda Nahida Akter, Terry Kong, Tim Moon, Tomasz Hliwiak, Tomer Asida, Tony Wang, Twinkle Vashishth, Tyler Poon, Udi Karpas, Vahid Noroozi, Venkat Srinivasan, Vijay Korthikanti, Vikram Fugro, Vineeth Kalluru, Vitaly Kurin, Vitaly Lavrukhin, Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Wei Du, Wonmin Byeon, Ximing Lu, Xin Dong, Yashaswi Karnati, Yejin Choi, Yian Zhang, Ying Lin, Yonggan Fu, Yoshi Suhara, Zhen Dong, Zhiyu Li, Zhongbo Zhu, Zijia Chen
We introduce Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, a hybrid Mamba-Transformer language model designed to increase throughput for reasoning workloads while achieving state-of-the-art accuracy compared to similarly-sized models. Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 builds on the Nemotron-H architecture, in which the majority of the self-attention layers in the common Transformer architecture are replaced with Mamba-2 layers, to achieve improved inference speed when generating the long thinking traces needed for reasoning. We create Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 by first pre-training a 12-billion-parameter model (Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base) on 20 trillion tokens using an FP8 training recipe. After aligning Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base, we employ the Minitron strategy to compress and distill the model with the goal of enabling inference on up to 128k tokens on a single NVIDIA A10G GPU (22GiB of memory, bfloat16 precision). Compared to existing similarly-sized models (e.g., Qwen3-8B), we show that Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 achieves on-par or better accuracy on reasoning benchmarks while achieving up to 6x higher inference throughput in reasoning settings like 8k input and 16k output tokens. We are releasing Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, Nemotron-Nano12B-v2-Base, and Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2-Base checkpoints along with the majority of our pre- and post-training datasets on Hugging Face.
我们介绍了Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2,这是一种混合Mamba-Transformer语言模型,旨在提高推理工作负载的吞吐量,同时与同类模型相比实现最先进的准确性。Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2建立在Nemotron-H架构的基础上,将Transformer架构中大部分的自注意力层替换为Mamba-2层,以实现在生成推理所需的长思考轨迹时提高推理速度。我们通过首先使用FP8训练配方在20万亿个令牌上预训练一个12亿参数模型(Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base)来创建Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2。在对Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base进行对齐后,我们采用Minitron策略来压缩和蒸馏模型,旨在能够在单个NVIDIA A10G GPU(具有22GiB内存,bfloat16精度)上进行高达128k令牌的推理。与现有的类似规模模型(例如Qwen3-8B)相比,我们在推理基准测试上展示了Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2的同等或更好的准确性,同时在诸如8k输入和16k输出令牌的推理设置中实现了高达6倍的推理吞吐量。我们将Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2、Nemotron-Nano12B-v2-Base和Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2-Base检查点以及我们大部分预训练和后训练数据集在Hugging Face上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Mamba-Transformer架构的Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2混合语言模型旨在提高推理工作负载的吞吐量,同时在同类模型中实现最先进的准确性。它通过引入Mamba-2层替代Transformer架构中的大部分自注意力层,以加快生成长期推理轨迹时的推理速度。经过在20万亿个令牌上预训练的12亿参数模型(Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base),并采用Minitron策略进行压缩和蒸馏,实现了在单个NVIDIA A10G GPU上高达128k令牌的推理能力。相较于其他类似规模的模型,Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2在推理基准测试上实现了相当或更好的准确性,同时在8k输入和16k输出令牌等推理场景中实现了高达6倍的推理吞吐量。该模型及相关数据集已在Hugging Face上发布。
Key Takeaways
- Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2是一个基于Mamba-Transformer架构的混合语言模型,旨在提高推理的吞吐量和准确性。
- 该模型通过引入Mamba-2层替代Transformer架构中的自注意力层,以加快推理速度。
- Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2经过在大量数据上的预训练,然后采用Minitron策略进行压缩和蒸馏。
- 模型可以在单个NVIDIA A10G GPU上处理高达128k令牌的推理任务。
- 与类似规模的模型相比,Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2在推理基准测试上表现出色。
- 该模型在特定推理场景下实现了高达6倍的推理吞吐量提升。
点此查看论文截图

Let’s Use ChatGPT To Write Our Paper! Benchmarking LLMs To Write the Introduction of a Research Paper
Authors:Krishna Garg, Firoz Shaikh, Sambaran Bandyopadhyay, Cornelia Caragea
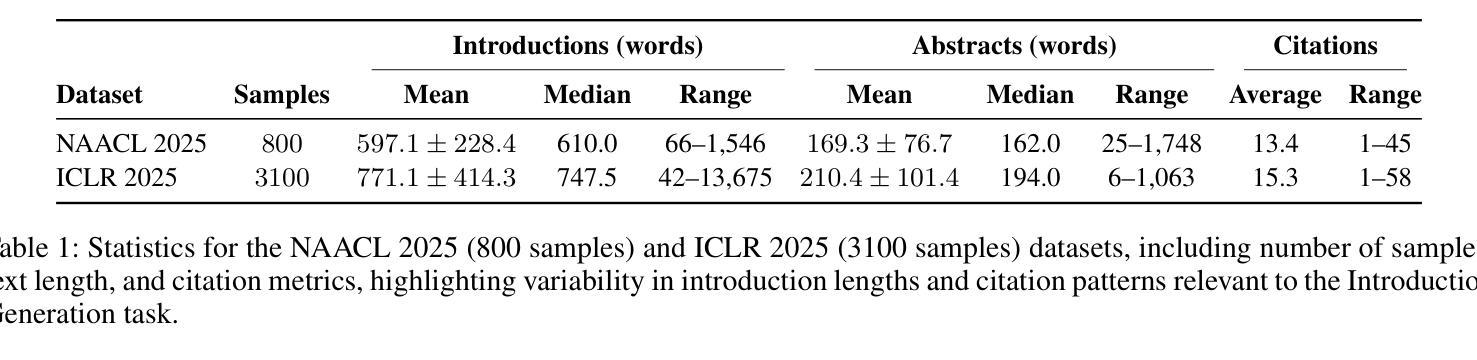
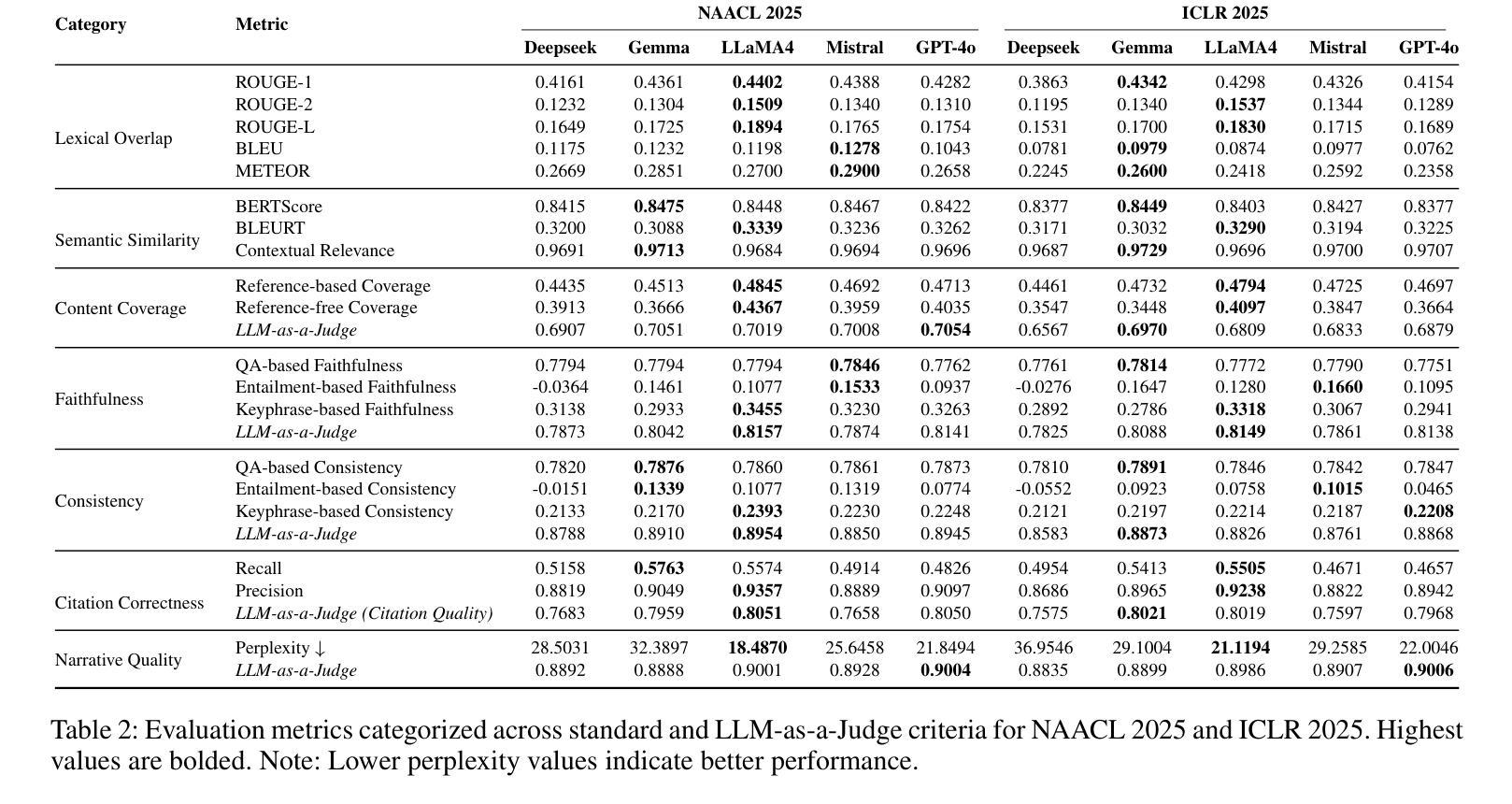
As researchers increasingly adopt LLMs as writing assistants, generating high-quality research paper introductions remains both challenging and essential. We introduce Scientific Introduction Generation (SciIG), a task that evaluates LLMs’ ability to produce coherent introductions from titles, abstracts, and related works. Curating new datasets from NAACL 2025 and ICLR 2025 papers, we assess five state-of-the-art models, including both open-source (DeepSeek-v3, Gemma-3-12B, LLaMA 4-Maverick, MistralAI Small 3.1) and closed-source GPT-4o systems, across multiple dimensions: lexical overlap, semantic similarity, content coverage, faithfulness, consistency, citation correctness, and narrative quality. Our comprehensive framework combines automated metrics with LLM-as-a-judge evaluations. Results demonstrate LLaMA-4 Maverick’s superior performance on most metrics, particularly in semantic similarity and faithfulness. Moreover, three-shot prompting consistently outperforms fewer-shot approaches. These findings provide practical insights into developing effective research writing assistants and set realistic expectations for LLM-assisted academic writing. To foster reproducibility and future research, we will publicly release all code and datasets.
随着越来越多的研究者采用大型语言模型作为写作助手,生成高质量的研究论文引言仍然是一项既具挑战性又必不可少的工作。我们介绍了科学引言生成(SciIG)任务,该任务旨在评估大型语言模型从标题、摘要和相关工作中生成连贯引言的能力。我们使用来自NAACL 2025和ICLR 2025论文的新数据集,评估了五个最新模型,包括开源模型(DeepSeek-v3、Gemma-3-12B、LLaMA 4-Maverick、MistralAI Small 3.1)和闭源GPT-4o系统,涉及多个维度:词汇重叠、语义相似性、内容覆盖、忠实性、一致性、引用正确性和叙述质量。我们的综合框架结合了自动度量指标与大型语言模型作为法官的评价。结果表明,LLaMA-4 Maverick在大多数指标上表现优越,特别是在语义相似性和忠实性方面。此外,三提示法始终如一地优于少提示法。这些发现为开发有效的研究写作助手提供了实际见解,并为大型语言模型辅助学术写作设定了现实期望。为了促进可重复性和未来研究,我们将公开发布所有代码和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 15 figures
Summary
基于文本内容,摘要可以概括为:“研究人员采用大型语言模型作为写作助手,生成高质量的研究论文引言仍然充满挑战且至关重要。本研究介绍了科学引言生成(SciIG)任务,评估大型语言模型从标题、摘要和相关工作中生成连贯引言的能力。研究使用新的数据集评估了五个先进模型的表现,包括开源模型(DeepSeek-v3等)和闭源GPT-4o系统,涵盖多个维度。研究结果表明LLaMA-4 Maverick模型在多数指标上表现优越,特别是语义相似性和忠实度方面。此外,本研究还发现三提示法优于少提示法。这些发现对于开发有效的研究写作助手提供了实际见解,并为大型语言模型辅助学术写作设定了合理的期望。”
Key Takeaways
以下是关于该文本的主要见解列表:
- 大型语言模型被越来越多的研究人员用作写作助手。生成高质量研究论文引言是一个重要的挑战。
- 研究介绍了科学引言生成(SciIG)任务,以评估大型语言模型生成连贯引言的能力。
- 研究使用新的数据集评估了五个模型的表现,包括开源和闭源模型。评估涵盖多个维度,如词汇重叠、语义相似性、内容覆盖等。
- LLaMA-4 Maverick模型在多数评估指标上表现最佳,特别是在语义相似性和忠实度方面。
点此查看论文截图

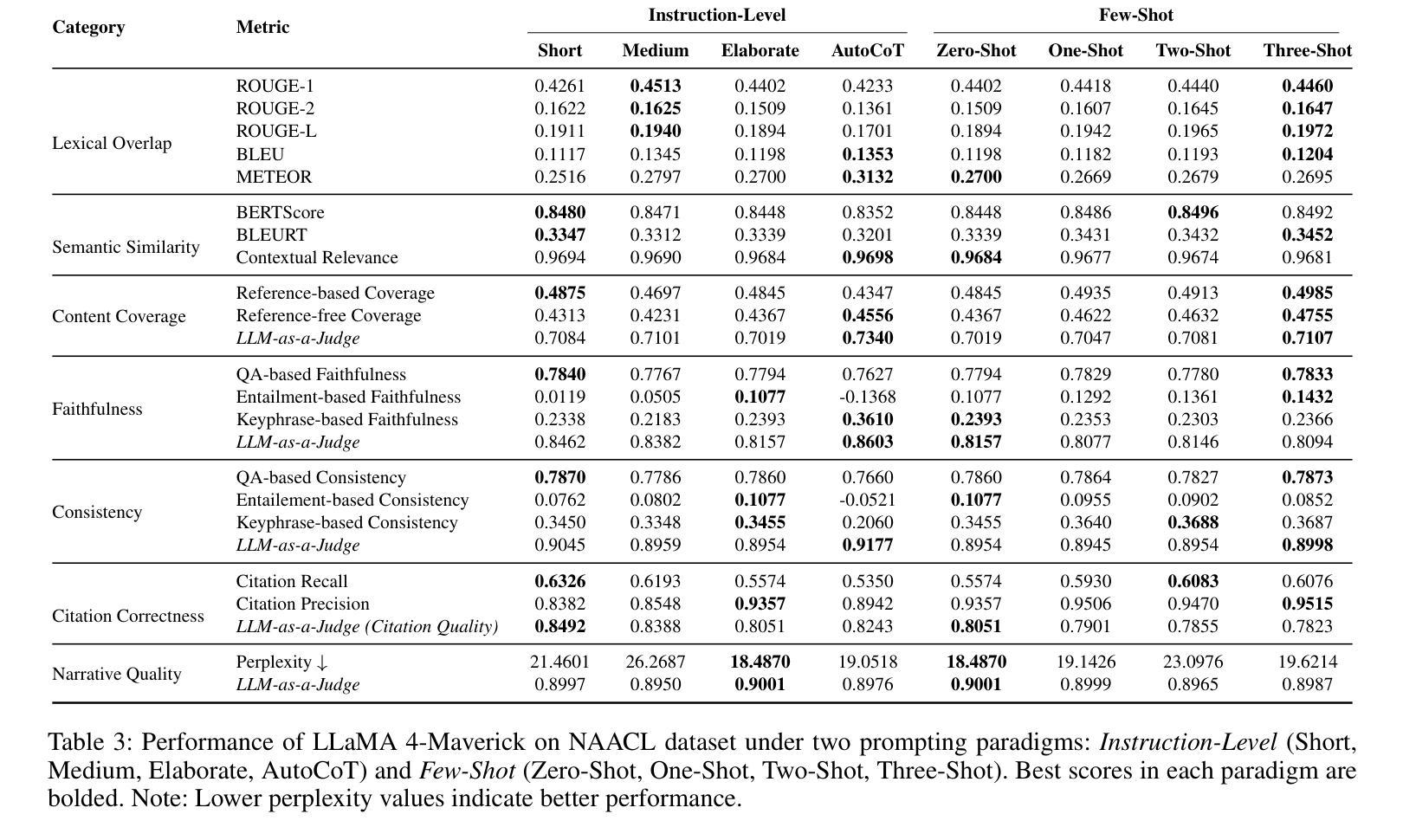
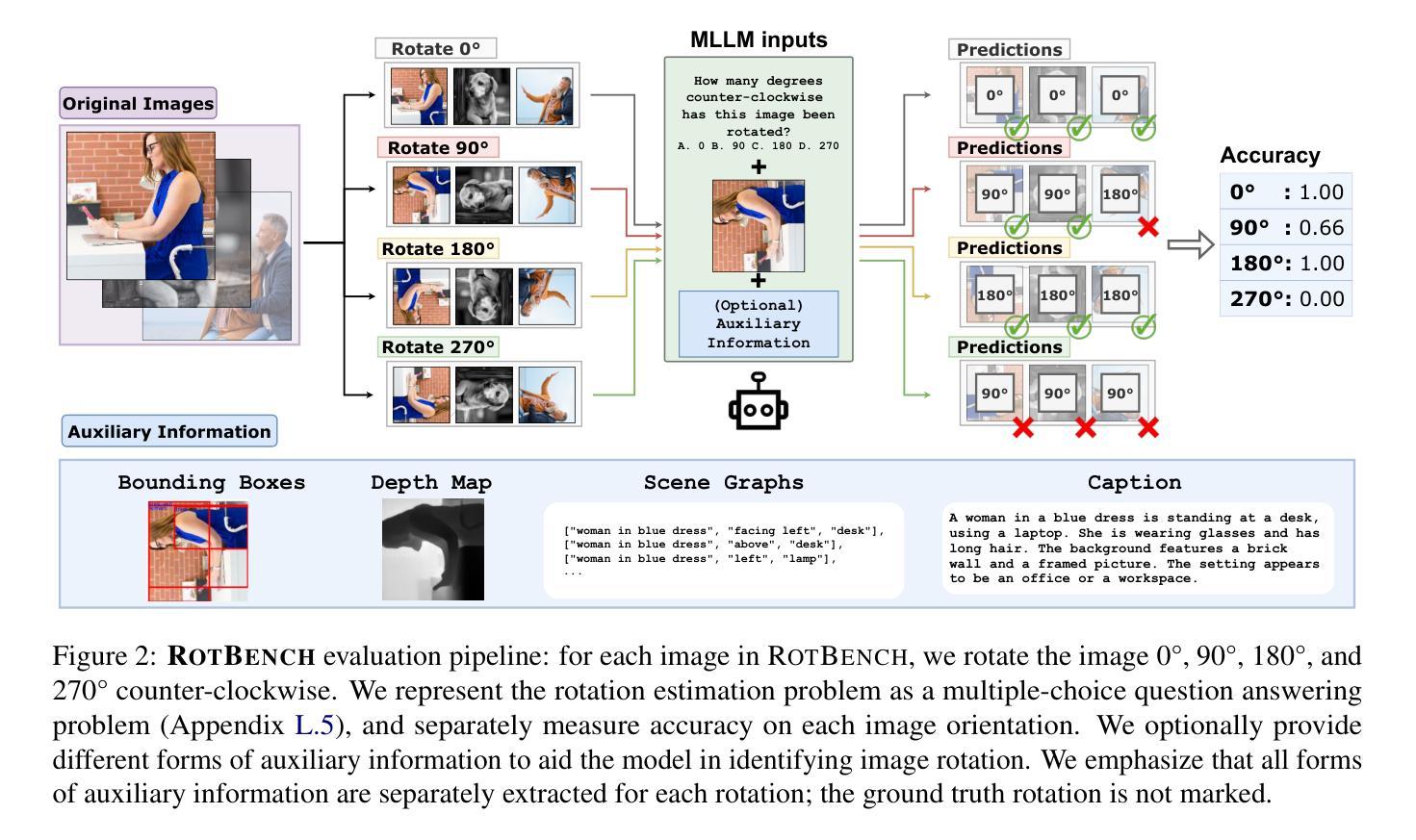
RotBench: Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models on Identifying Image Rotation
Authors:Tianyi Niu, Jaemin Cho, Elias Stengel-Eskin, Mohit Bansal
We investigate to what extent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) can accurately identify the orientation of input images rotated 0{\deg}, 90{\deg}, 180{\deg}, and 270{\deg}. This task demands robust visual reasoning capabilities to detect rotational cues and contextualize spatial relationships within images, regardless of their orientation. To evaluate MLLMs on these abilities, we introduce RotBench – a 350-image manually-filtered benchmark comprising lifestyle, portrait, and landscape images. Despite the relatively simple nature of this task, we show that several state-of-the-art open and proprietary MLLMs, including GPT-5, o3, and Gemini-2.5-Pro, do not reliably identify rotation in input images. Providing models with auxiliary information – including captions, depth maps, and more – or using chain-of-thought prompting offers only small and inconsistent improvements. Our results indicate that most models are able to reliably identify right-side-up (0{\deg}) images, while certain models are able to identify upside-down (180{\deg}) images. None can reliably distinguish between 90{\deg} and 270{\deg}. Simultaneously showing the image rotated in different orientations leads to moderate performance gains for reasoning models, while a modified setup using voting improves the performance of weaker models. We further show that fine-tuning does not improve models’ ability to distinguish 90{\deg} and 270{\deg} rotations, despite substantially improving the identification of 180{\deg} images. Together, these results reveal a significant gap between MLLMs’ spatial reasoning capabilities and human perception in identifying rotation.
我们调查了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)能够在多大程度上准确识别输入图像旋转0°、90°、180°和270°的方向。这项任务需要强大的视觉推理能力来检测旋转线索并理解图像内的空间关系,无论其方向如何。为了评估MLLMs的这些能力,我们引入了RotBench——一个包含生活方式、肖像和风景图像的350张手动过滤的基准测试集。尽管这项任务相对简单,但我们发现包括GPT-5、o3和Gemini-2.5-Pro在内的若干最先进的开源和专有MLLMs并不能可靠地识别输入图像中的旋转。为模型提供辅助信息,如字幕、深度图等,或使用思维链提示只能带来微小且不一致的改进。我们的结果表明,大多数模型能够可靠地识别正面朝上(0°)的图像,而某些模型能够识别倒置(180°)的图像。没有任何模型能够可靠地区分90°和270°的图像。同时展示以不同方向旋转的图像会导致推理模型的性能适度提升,而使用投票的修改设置则会提高较弱模型的性能。我们进一步表明,微调并不会提高模型区分90°和270°旋转的能力,尽管它大大提高了对180°图像的识别能力。总的来说,这些结果揭示了MLLMs的空间推理能力与人类感知在识别旋转方面的重大差距。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages. Code and data: https://github.com/tianyiniu/RotBench
摘要
本研究调查了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在准确识别输入图像旋转角度方面的能力,涉及的旋转角度包括0°、90°、180°和270°。这一任务要求模型具备稳健的视觉推理能力,以检测旋转线索并在图像中上下文化空间关系,无论其方向如何。为了评估MLLMs的这些能力,我们引入了RotBench——一个包含350张手动筛选的图像基准测试集,其中包括生活方式、肖像和风景图像。尽管任务相对简单,但我们发现一些先进的开源和专有MLLMs,包括GPT-5、o3和Gemini-2.5-Pro,无法可靠地识别输入图像的旋转角度。为模型提供辅助信息(包括字幕、深度图等)或使用链式思维提示只能带来微小且不一致的改进。我们的结果表明,大多数模型能够可靠地识别正面朝上(0°)的图像,而某些模型能够识别倒置(180°)的图像。没有任何模型能够可靠地区分90°和270°的图像。同时展示以不同方向旋转的图像会导致推理模型的性能适度提升,而使用投票的改进设置则提高了较弱模型的性能。此外,我们还发现微调并不能提高模型区分90°和270°旋转的能力,尽管它在识别180°图像方面有了显著改进。总体而言,这些结果揭示了MLLMs的空间推理能力和人类感知在识别旋转方面的巨大差距。
关键见解
- 研究了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在识别图像旋转角度方面的能力。
- 引入了RotBench基准测试集,用于评估MLLMs的视觉推理能力。
- 发现大多数MLLMs无法可靠地区分90°和270°旋转的图像。
- 辅助信息和链式思维提示只能带来有限的性能改进。
- 同时展示不同旋转角度的图像可以提高模型的性能。
- 投票的改进设置有助于提高较弱模型的性能。
- 微调无法显著提高模型区分90°和270°旋转的能力,但可显著改善对180°图像的识别。
点此查看论文截图

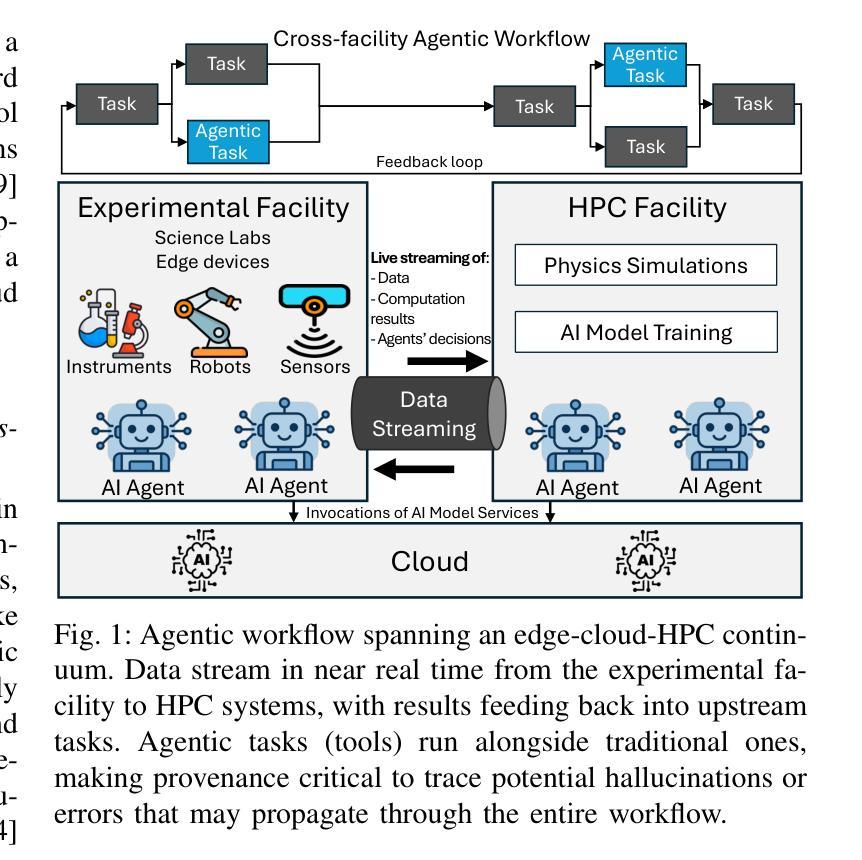
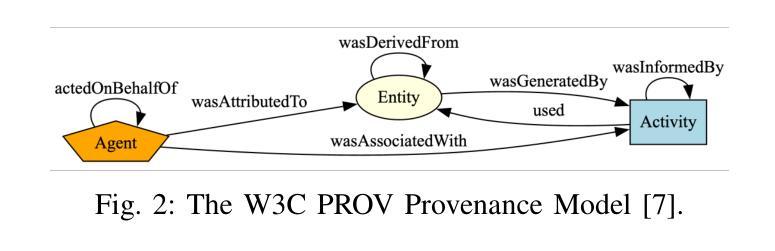
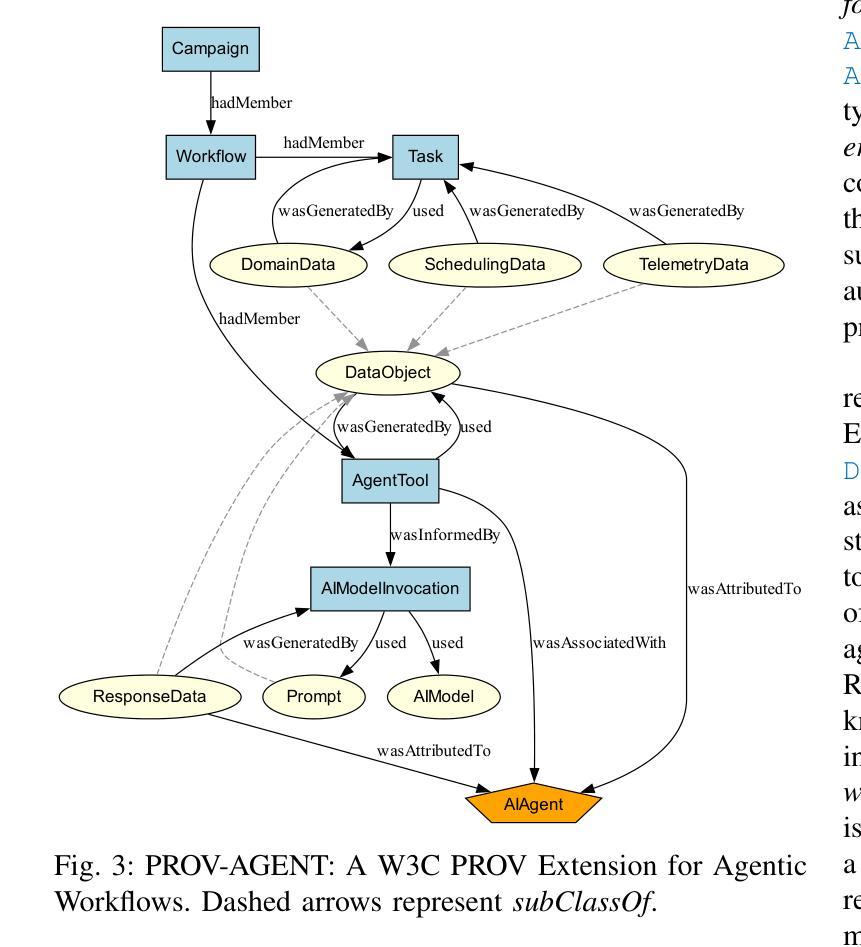
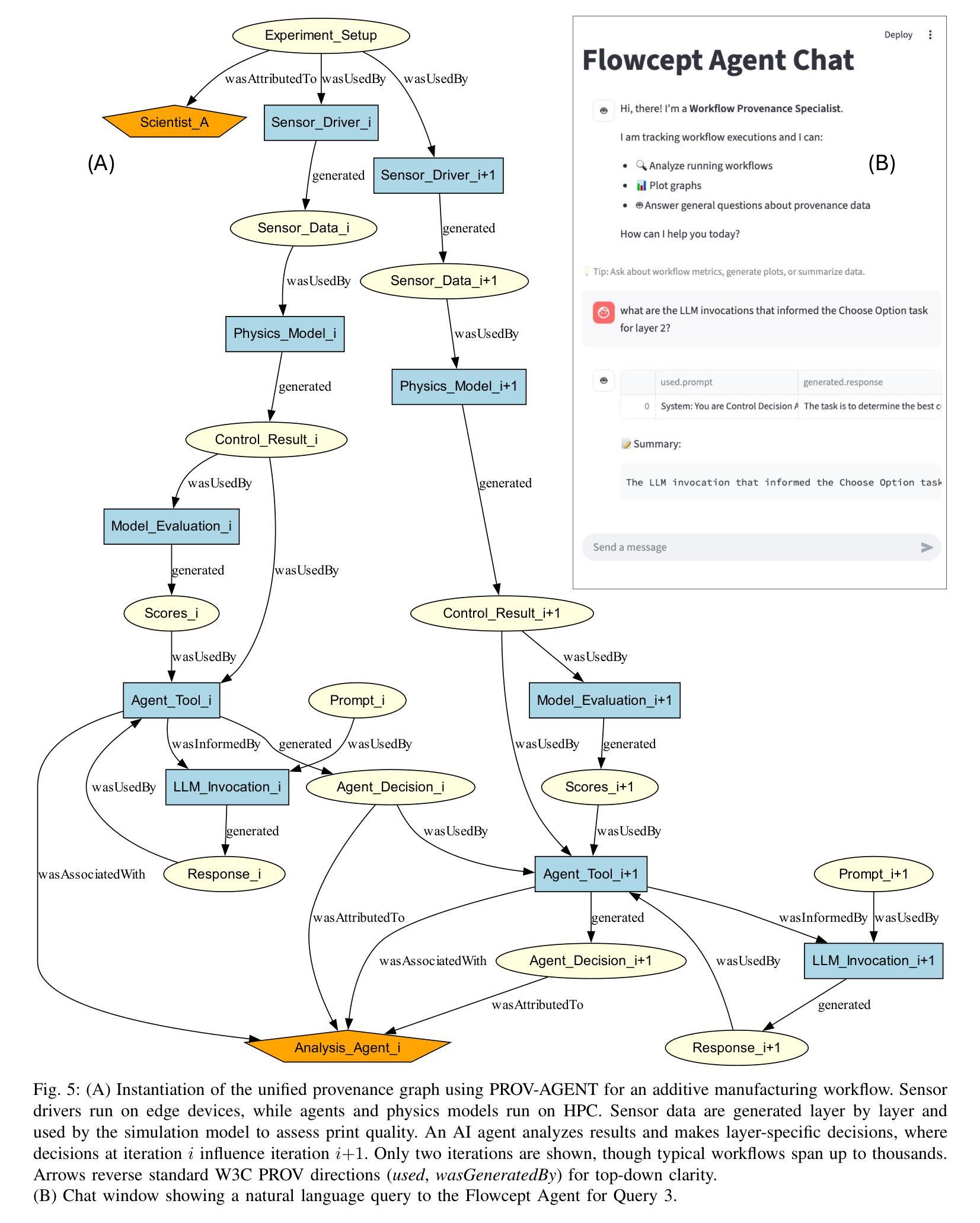
PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking AI Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows
Authors:Renan Souza, Amal Gueroudji, Stephen DeWitt, Daniel Rosendo, Tirthankar Ghosal, Robert Ross, Prasanna Balaprakash, Rafael Ferreira da Silva
Large Language Models (LLMs) and other foundation models are increasingly used as the core of AI agents. In agentic workflows, these agents plan tasks, interact with humans and peers, and influence scientific outcomes across federated and heterogeneous environments. However, agents can hallucinate or reason incorrectly, propagating errors when one agent’s output becomes another’s input. Thus, assuring that agents’ actions are transparent, traceable, reproducible, and reliable is critical to assess hallucination risks and mitigate their workflow impacts. While provenance techniques have long supported these principles, existing methods fail to capture and relate agent-centric metadata such as prompts, responses, and decisions with the broader workflow context and downstream outcomes. In this paper, we introduce PROV-AGENT, a provenance model that extends W3C PROV and leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and data observability to integrate agent interactions into end-to-end workflow provenance. Our contributions include: (1) a provenance model tailored for agentic workflows, (2) a near real-time, open-source system for capturing agentic provenance, and (3) a cross-facility evaluation spanning edge, cloud, and HPC environments, demonstrating support for critical provenance queries and agent reliability analysis.
大型语言模型(LLM)和其他基础模型越来越多地被用作人工智能代理的核心。在代理工作流程中,这些代理计划任务、与人类和同龄人互动,并在联邦和异构环境中影响科学结果。然而,代理可能会出现幻觉或推理错误,当一个代理的输出成为另一个代理的输入时,错误就会传播。因此,确保代理的行动透明、可追踪、可重现和可靠,对于评估幻觉风险和减轻其工作流程影响至关重要。尽管溯源技术长期支持这些原则,但现有方法无法捕获并与以代理为中心的元数据(如提示、响应和决策)与更广泛的工作流上下文和下游结果相关联。在本文中,我们介绍了PROV-AGENT,这是一个溯源模型,它扩展了W3C的PROV,并利用模型上下文协议(MCP)和数据可观性将代理互动整合到端到端的工作流溯源中。我们的贡献包括:(1)针对代理工作流的溯源模型,(2)一个近实时的开源系统,用于捕获代理溯源,以及(3)一项跨越边缘、云和高性能计算环境的跨设施评估,演示了对关键溯源查询和代理可靠性分析的支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted for publication in the Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 21st International Conference on e-Science. Cite it as: R. Souza, A. Gueroudji, S. DeWitt, D. Rosendo, T. Ghosal, R. Ross, P. Balaprakash, R. F. da Silva, “PROV-AGENT: Unified Provenance for Tracking AI Agent Interactions in Agentic Workflows,” IEEE International Conference on e-Science, Chicago, IL, USA, 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)等基础模型作为AI代理的核心得到广泛应用。在代理工作流程中,这些代理计划任务、与人类和同行互动,并在联邦和异构环境中影响科学结果。然而,代理可能会出现幻觉或错误推理,当一个代理的输出成为另一个代理的输入时,错误会传播。因此,确保代理的行动透明、可追溯、可重现和可靠,对于评估幻觉风险和减轻工作流程影响至关重要。尽管PROV模型长久以来支持这些原则,但现有方法无法捕获并与更广泛的工作流上下文和下游结果相关的代理中心元数据,如提示、响应和决策。本文介绍PROV-AGENT,一个扩展W3C PROV的PROV模型,利用模型上下文协议(MCP)和数据可观性将代理交互集成到端到端的工作流PROV中。我们的贡献包括:(1)针对代理工作流程的PROV模型,(2)一个近实时、开源的代理PROV捕获系统,(3)跨边缘、云和高性能计算环境的跨设施评估,证明支持关键PROV查询和代理可靠性分析。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs和其他基础模型被用作AI代理的核心,广泛应用于代理工作流程中。
- 代理在工作中可能会产生幻觉或错误推理,需要确保其行为透明、可追溯、可重现和可靠。
- 现有方法无法全面捕获与代理相关的元数据,如提示、响应和决策,以及与工作流上下文和下游结果的关联。
- PROV-AGENT是一个扩展W3C PROV的PROV模型,旨在解决上述问题。
- PROV-AGENT利用模型上下文协议(MCP)和数据可观性,将代理交互集成到端到端的工作流中。
- 近实时、开源的代理PROV捕获系统被开发出来。
点此查看论文截图

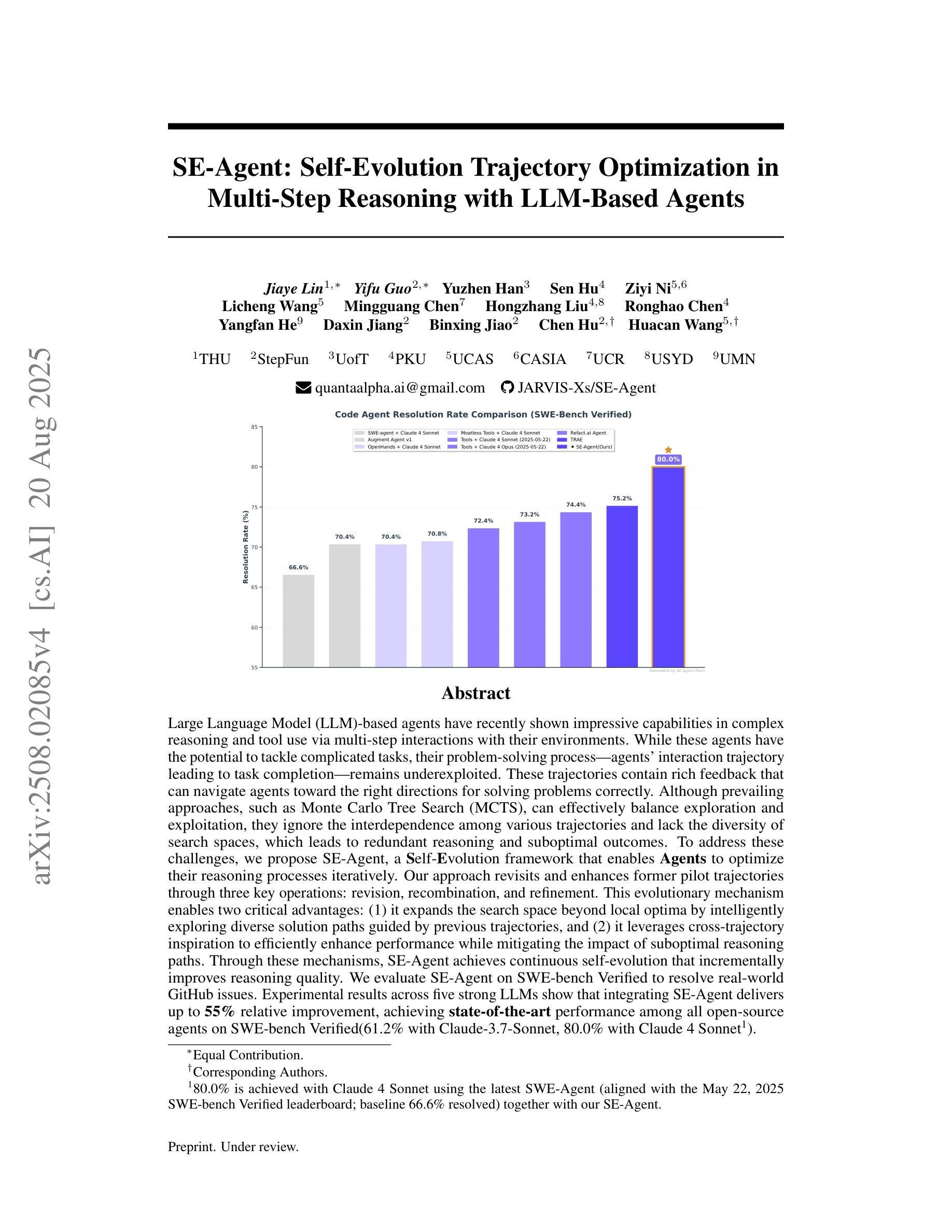
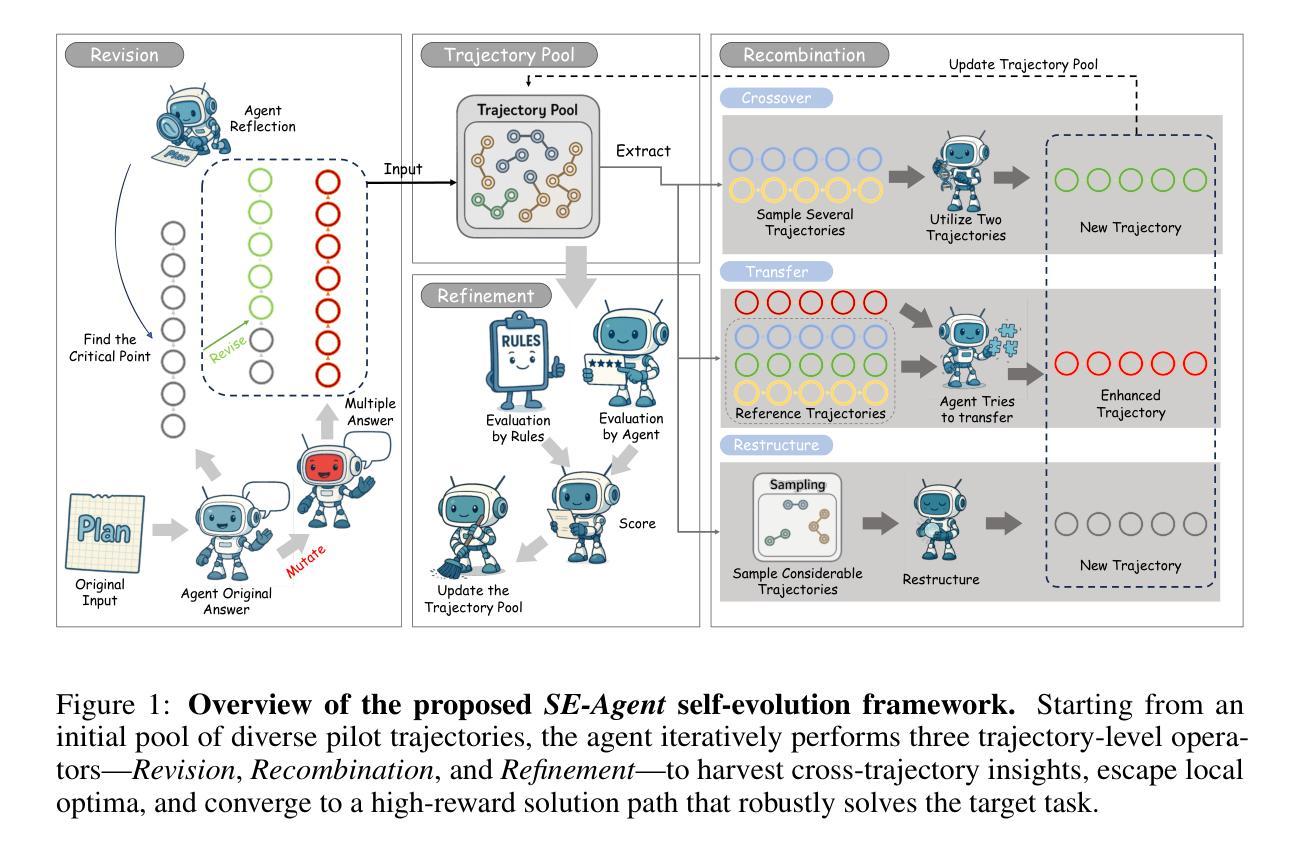
SE-Agent: Self-Evolution Trajectory Optimization in Multi-Step Reasoning with LLM-Based Agents
Authors:Jiaye Lin, Yifu Guo, Yuzhen Han, Sen Hu, Ziyi Ni, Licheng Wang, Mingguang Chen, Hongzhang Liu, Ronghao Chen, Yangfan He, Daxin Jiang, Binxing Jiao, Chen Hu, Huacan Wang
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have recently shown impressive capabilities in complex reasoning and tool use via multi-step interactions with their environments. While these agents have the potential to tackle complicated tasks, their problem-solving process, i.e., agents’ interaction trajectory leading to task completion, remains underexploited. These trajectories contain rich feedback that can navigate agents toward the right directions for solving problems correctly. Although prevailing approaches, such as Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), can effectively balance exploration and exploitation, they ignore the interdependence among various trajectories and lack the diversity of search spaces, which leads to redundant reasoning and suboptimal outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose SE-Agent, a Self-Evolution framework that enables Agents to optimize their reasoning processes iteratively. Our approach revisits and enhances former pilot trajectories through three key operations: revision, recombination, and refinement. This evolutionary mechanism enables two critical advantages: (1) it expands the search space beyond local optima by intelligently exploring diverse solution paths guided by previous trajectories, and (2) it leverages cross-trajectory inspiration to efficiently enhance performance while mitigating the impact of suboptimal reasoning paths. Through these mechanisms, SE-Agent achieves continuous self-evolution that incrementally improves reasoning quality. We evaluate SE-Agent on SWE-bench Verified to resolve real-world GitHub issues. Experimental results across five strong LLMs show that integrating SE-Agent delivers up to 55% relative improvement, achieving state-of-the-art performance among all open-source agents on SWE-bench Verified. Our code and demonstration materials are publicly available at https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent.
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理最近显示出通过与其环境的多步交互进行复杂推理和工具使用的令人印象深刻的能力。虽然这些代理有潜力处理复杂任务,但它们的解决问题的过程,即代理完成任务的交互轨迹,仍未得到充分探索。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以引导代理正确解决问题。尽管现有的方法(如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS))可以有效地平衡探索和利用,但它们忽略了各种轨迹之间的相互依赖性,并且缺乏搜索空间的多样性,这导致冗余推理和次优结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SE-Agent,一个自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代优化他们的推理过程。我们的方法通过三个关键操作:修订、重组和精炼,来重新审视和改进之前的轨迹。这种进化机制带来了两个关键优势:(1)它通过智能地探索受先前轨迹指导的多样化解决方案路径,扩大了搜索空间,超越了局部最优;(2)它利用跨轨迹的灵感来有效地提高性能,同时减轻次优推理路径的影响。通过这些机制,SE-Agent实现了连续的自我进化,逐步提高了推理质量。我们在SWE-bench Verified上评估了SE-Agent,以解决现实世界中的GitHub问题。在五个强大的LLM上的实验结果表明,集成SE-Agent带来了高达55%的相对改进,在SWE-bench Verified上的开源代理中实现了最先进的性能。我们的代码和演示材料可在https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)代理在复杂推理和工具使用方面展现出令人印象深刻的能力。尽管这些代理具有处理复杂任务的能力,但它们的问题解决过程,即代理完成任务的互动轨迹,仍被较少探索。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以为解决问题提供正确的方向。现有方法如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS)虽然可以有效平衡探索与利用,但它们忽视了不同轨迹之间的相互作用及搜索空间的多样性,导致冗余推理和次优结果。为解决这些问题,我们提出了SE-Agent,一个自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代优化其推理过程。通过修订、重组和细化三个关键操作,该进化机制实现了两个关键优势:一是通过智能探索由先前轨迹引导的多样化解决方案路径来扩展搜索空间超越局部最优;二是利用跨轨迹灵感来有效提高性能,同时减少次优推理路径的影响。评估结果显示,SE-Agent在解决真实世界的GitHub问题上实现了最先进的效果。
Key Takeaways
- LLM代理具有处理复杂任务的能力,但在问题解决过程中的互动轨迹尚未得到充分探索。
- 现有方法如蒙特卡洛树搜索在平衡探索与利用时忽视了轨迹的多样性和相互作用。
- SE-Agent是一个自我进化框架,通过修订、重组和细化操作实现智能探索多样化解决方案路径。
- SE-Agent扩大了搜索空间并超越了局部最优,提高了性能并减少了次优推理路径的影响。
- SE-Agent在解决真实世界的GitHub问题上实现了显著的效果改进。
- SE-Agent的代码和演示材料已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图
Uncertainty Quantification for Language Models: A Suite of Black-Box, White-Box, LLM Judge, and Ensemble Scorers
Authors:Dylan Bouchard, Mohit Singh Chauhan
Hallucinations are a persistent problem with Large Language Models (LLMs). As these models become increasingly used in high-stakes domains, such as healthcare and finance, the need for effective hallucination detection is crucial. To this end, we outline a versatile framework for zero-resource hallucination detection that practitioners can apply to real-world use cases. To achieve this, we adapt a variety of existing uncertainty quantification (UQ) techniques, including black-box UQ, white-box UQ, and LLM-as-a-Judge, transforming them as necessary into standardized response-level confidence scores ranging from 0 to 1. To enhance flexibility, we propose a tunable ensemble approach that incorporates any combination of the individual confidence scores. This approach enables practitioners to optimize the ensemble for a specific use case for improved performance. To streamline implementation, the full suite of scorers is offered in this paper’s companion Python toolkit, UQLM. To evaluate the performance of the various scorers, we conduct an extensive set of experiments using several LLM question-answering benchmarks. We find that our tunable ensemble typically surpasses its individual components and outperforms existing hallucination detection methods. Our results demonstrate the benefits of customized hallucination detection strategies for improving the accuracy and reliability of LLMs.
幻觉(hallucinations)对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说是一个持续存在的问题。随着这些模型在医疗保健和金融等高风险领域的广泛应用,对有效的幻觉检测的需求变得至关重要。为此,我们概述了一个用于零资源幻觉检测的通用框架,从业者可以将其应用于实际场景。为实现这一目标,我们采用了多种现有的不确定性量化(UQ)技术,包括黑盒UQ、白盒UQ和LLM作为法官,根据需要将其转化为标准化的响应级别置信度分数,范围从0到1。为了提高灵活性,我们提出了一种可调整的集成方法,可以融入各种个体置信度分数。这种方法使得从业者能够针对特定用例优化集成,从而提高性能。为了简化实现过程,所有评分者集合都包含在本文的配套Python工具包UQLM中。为了评估各种评分者的性能,我们使用多个LLM问答基准进行了一系列广泛的实验。我们发现,我们的可调集成通常超过了其各个组成部分,并且优于现有的幻觉检测方法。我们的结果证明了为改善LLM的准确性和可靠性而定制幻觉检测策略的好处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF UQLM repository: https://github.com/cvs-health/uqlm
Summary:
本文介绍了一种用于零资源环境幻觉检测的通用框架,通过适应现有的不确定性量化技术,包括黑盒UQ、白盒UQ和LLM作为法官,转化为标准化的响应级别信心分数。提出一种可调集成方法,结合各种信心分数,以优化特定用例的性能。实验结果表明,可调集成通常优于其单个组件并优于现有的幻觉检测方法。
Key Takeaways:
- LLMs中的幻觉检测在医疗保健和金融等高风险领域变得至关重要。
- 介绍了一种用于零资源幻觉检测的通用框架,采用多种不确定性量化技术。
- 提出了一种可调集成方法,结合各种信心分数以优化性能。
- 框架包括黑盒UQ、白盒UQ和LLM作为法官的技术。
- 响应级别的信心分数被标准化,范围从0到1。
- 提供的Python工具包UQLM简化了实施过程。
- 实验表明,可调集成方法的性能通常优于单个组件和现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

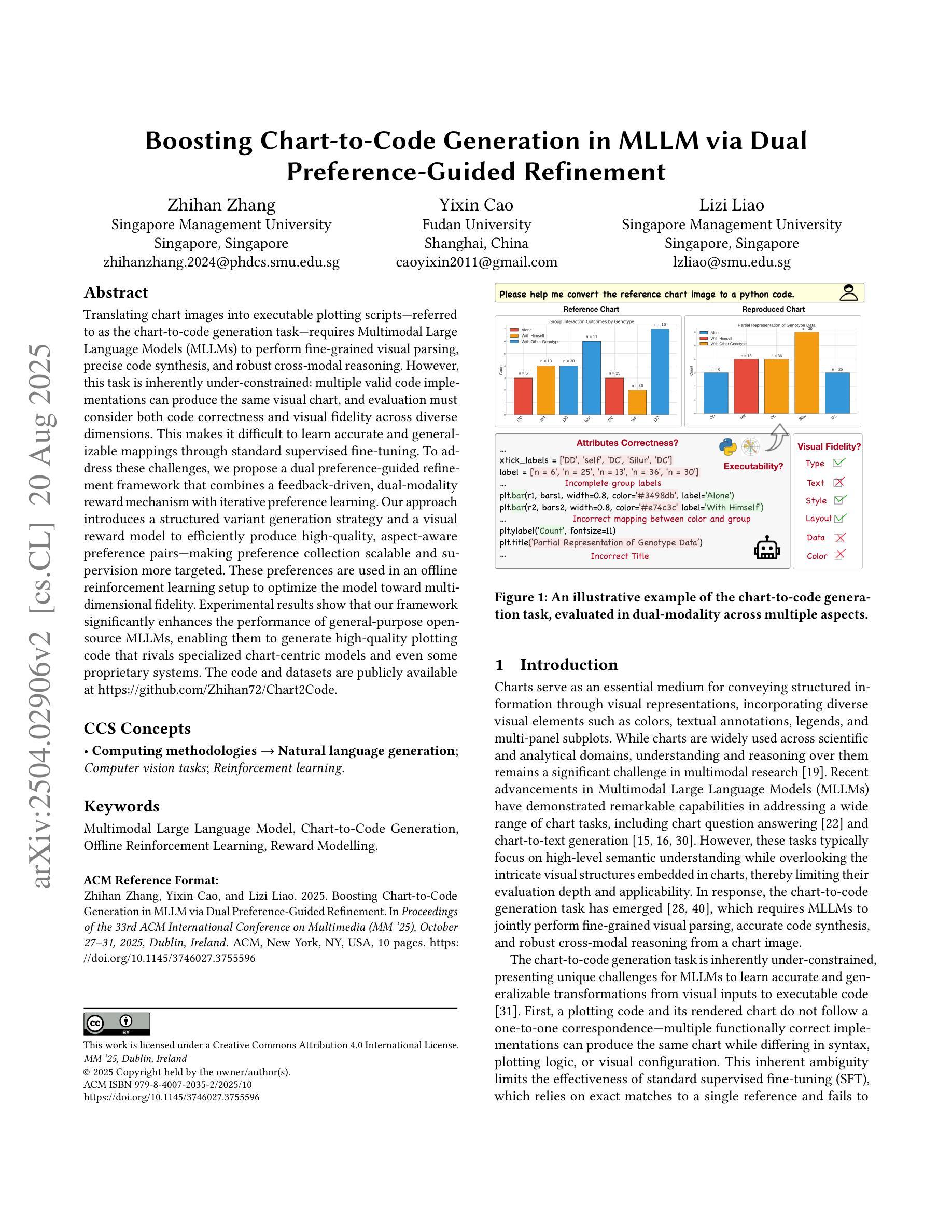
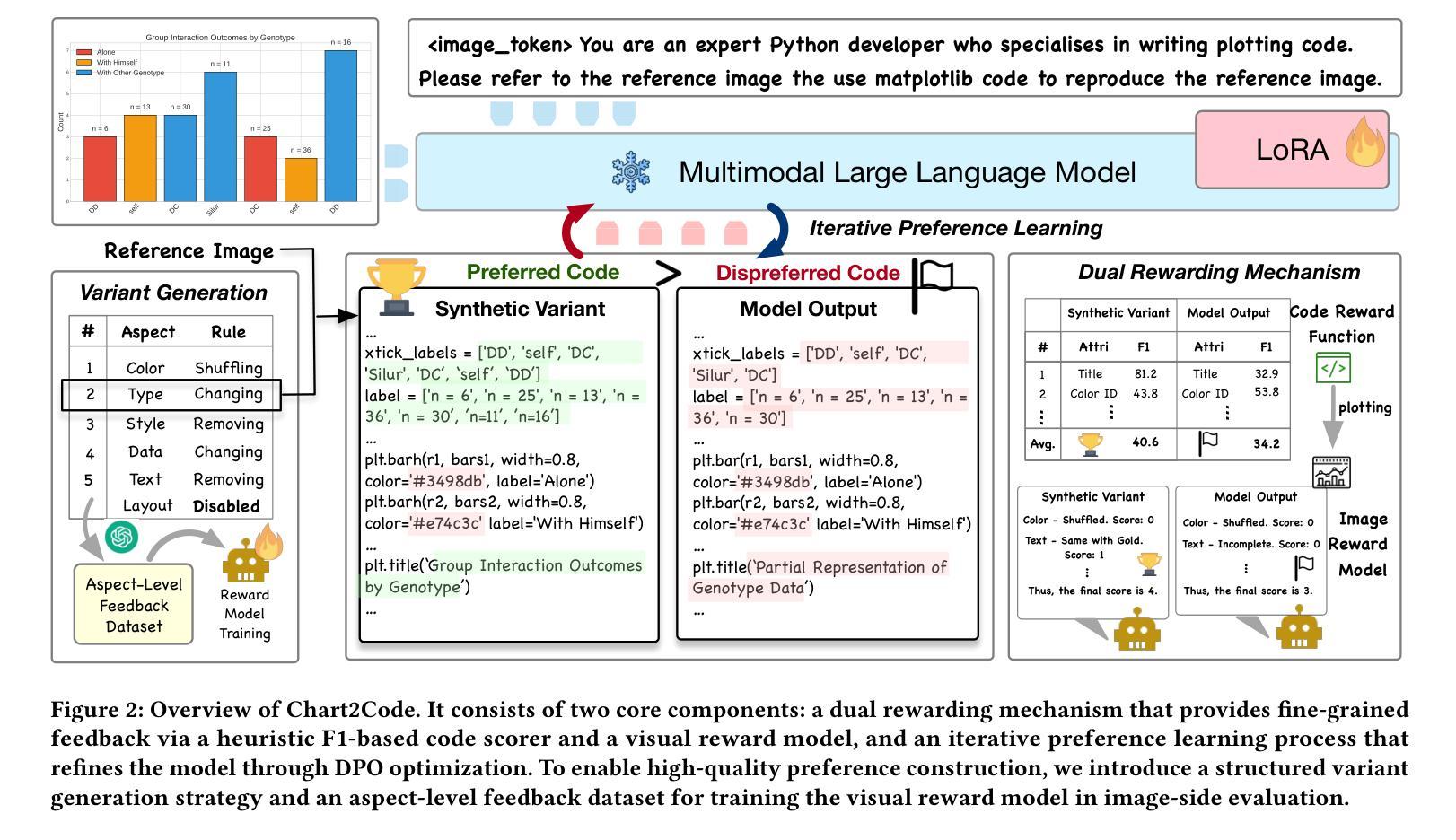
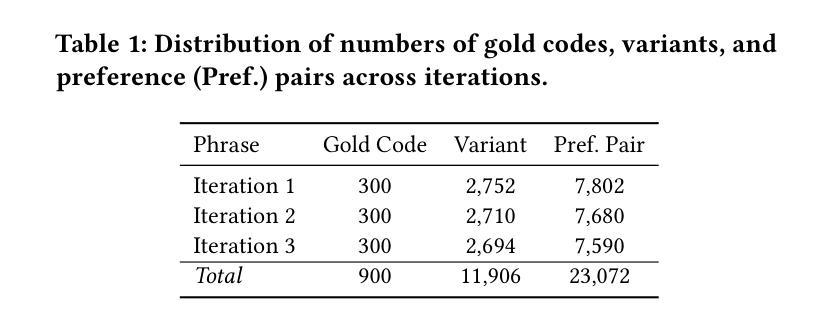
Boosting Chart-to-Code Generation in MLLM via Dual Preference-Guided Refinement
Authors:Zhihan Zhang, Yixin Cao, Lizi Liao
Translating chart images into executable plotting scripts-referred to as the chart-to-code generation task-requires Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform fine-grained visual parsing, precise code synthesis, and robust cross-modal reasoning. However, this task is inherently under-constrained: multiple valid code implementations can produce the same visual chart, and evaluation must consider both code correctness and visual fidelity across diverse dimensions. This makes it difficult to learn accurate and generalizable mappings through standard supervised fine-tuning. To address these challenges, we propose a dual preference-guided refinement framework that combines a feedback-driven, dual-modality reward mechanism with iterative preference learning. Our approach introduces a structured variant generation strategy and a visual reward model to efficiently produce high-quality, aspect-aware preference pairs-making preference collection scalable and supervision more targeted. These preferences are used in an offline reinforcement learning setup to optimize the model toward multi-dimensional fidelity. Experimental results show that our framework significantly enhances the performance of general-purpose open-source MLLMs, enabling them to generate high-quality plotting code that rivals specialized chart-centric models and even some proprietary systems. The code and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/Zhihan72/Chart2Code.
将图表图像翻译成可执行的绘图脚本,即所谓的图表到代码生成任务,需要多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)进行精细的视觉解析、精确的代码合成和稳健的跨模态推理。然而,这个任务本质上是欠约束的:多个有效的代码实现可以产生相同的视觉图表,评估必须考虑代码正确性和跨多个维度的视觉保真度。这使得通过标准监督微调学习准确和通用的映射变得困难。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种双偏好引导优化框架,该框架结合了反馈驱动的双模态奖励机制和迭代偏好学习。我们的方法引入了结构化变体生成策略和视觉奖励模型,以有效地产生高质量、方面感知的偏好对,使偏好收集可扩展,监督更具针对性。这些偏好被用于线下强化学习设置,以优化模型的多维保真度。实验结果表明,我们的框架显著提高了通用开源MLLM的性能,使它们能够生成高质量的绘图代码,与专注于图表的模型甚至某些专有系统相竞争。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/Zhihan72/Chart2Code公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
本文介绍了使用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)执行图表图像到绘图代码的转换任务。文章提出了一个双向偏好引导优化框架,通过反馈驱动的双模态奖励机制和迭代偏好学习来解决这一任务的内在挑战。该框架能高效生成高质量、面向方面的偏好对,使偏好收集更具可扩展性,监督更加有针对性。实验结果表明,该框架显著提高了通用开源MLLMs的性能,能够生成高质量的绘图代码,与专注于图表的模型甚至某些专有系统相媲美。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)被用于将图表图像转换为可执行绘图代码。
- 图表到代码的生成任务需要精细的视觉解析、精确的代码合成和跨模态推理。
- 此任务具有内在的不确定性,因为多个有效的代码实现可以生成相同的图表。
- 评估必须同时考虑代码的正确性和视觉保真度。
- 提出了一种双向偏好引导优化框架,结合反馈驱动的双模态奖励机制和迭代偏好学习来解决挑战。
- 框架通过结构化变体生成策略和视觉奖励模型来高效产生高质量、面向方面的偏好对。
点此查看论文截图
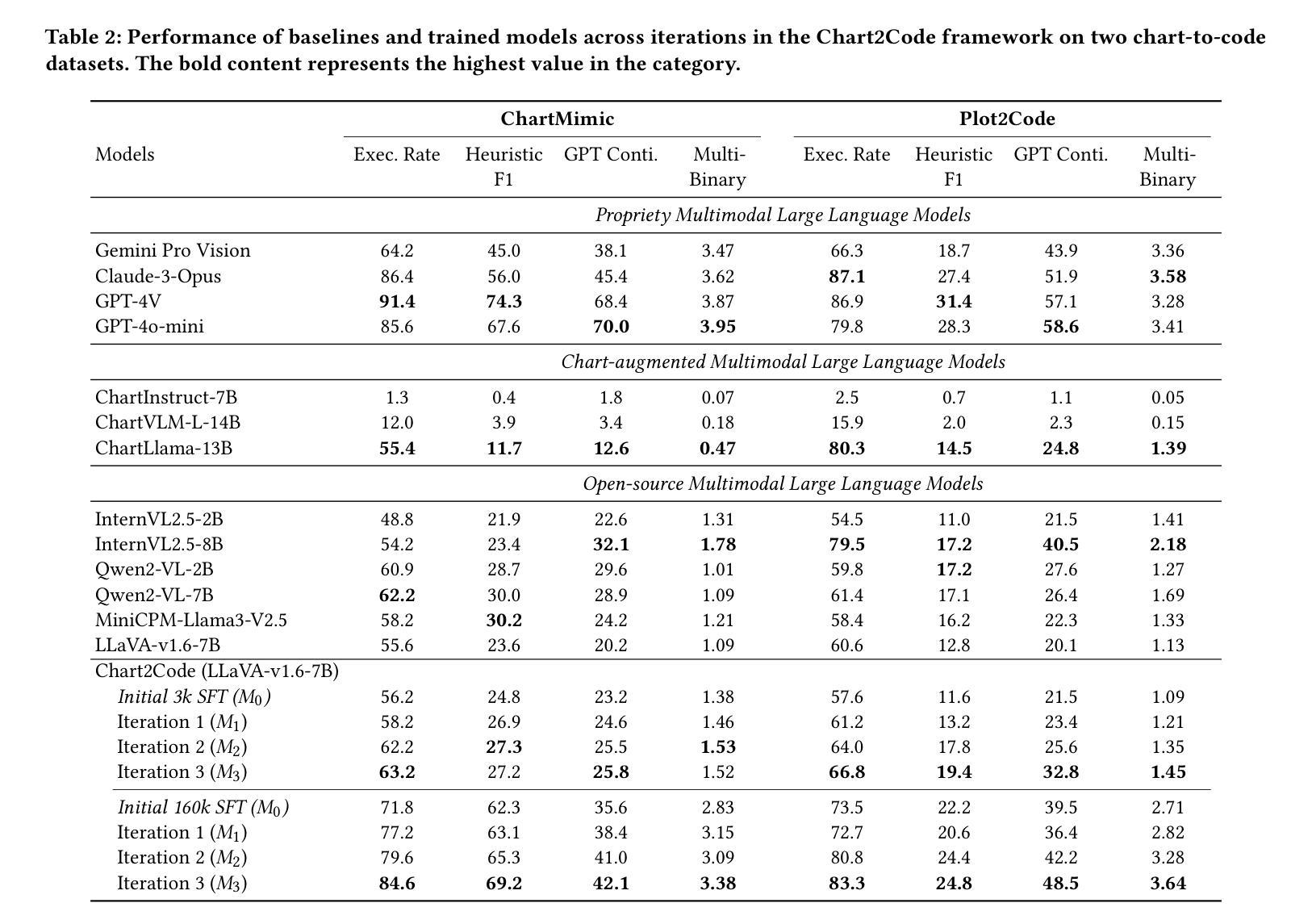
JudgeLRM: Large Reasoning Models as a Judge
Authors:Nuo Chen, Zhiyuan Hu, Qingyun Zou, Jiaying Wu, Qian Wang, Bryan Hooi, Bingsheng He
The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) as evaluators offers a scalable alternative to human annotation, yet existing Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) for judges approaches often fall short in domains requiring complex reasoning. In this work, we investigate whether LLM judges truly benefit from enhanced reasoning capabilities. Through a detailed analysis of reasoning requirements across evaluation tasks, we reveal a negative correlation between SFT performance gains and the proportion of reasoning-demanding samples - highlighting the limitations of SFT in such scenarios. To address this, we introduce JudgeLRM, a family of judgment-oriented LLMs trained using reinforcement learning (RL) with judge-wise, outcome-driven rewards. JudgeLRM models consistently outperform both SFT-tuned and state-of-the-art reasoning models. Notably, JudgeLRM-3B surpasses GPT-4, and JudgeLRM-7B outperforms DeepSeek-R1 by 2.79% in F1 score, particularly excelling in judge tasks requiring deep reasoning.
大型语言模型(LLM)作为评估器的兴起为人类标注提供了一种可扩展的替代方案,然而,现有的监督微调(SFT)在需要复杂推理的领域往往表现不足。在这项工作中,我们调查了LLM评估器是否真的受益于增强的推理能力。通过对评估任务中推理需求的详细分析,我们发现监督微调性能提升与需要推理的样本比例之间存在负相关,这突出了监督微调在这些场景中的局限性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了JudgeLRM,这是一个以判断为导向的LLM家族,采用强化学习(RL)训练,以评估者为导向、以结果驱动的奖励机制。JudgeLRM模型在性能上持续超越了监督微调模型和最新的推理模型。值得注意的是,JudgeLRM-3B超越了GPT-4,而JudgeLRM-7B在F1分数上超越了DeepSeek-R1达2.79%,特别是在需要深度推理的评估任务中表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)作为评估者提供了可规模化替代人工注释的方法,但在需要复杂推理的领域,现有的监督微调(SFT)方法往往效果不佳。本研究探讨了LLM评估者是否真正受益于增强的推理能力。通过对评估任务中推理需求的深入分析,我们发现SFT性能提升与需要推理的样本比例之间存在负相关,突显了SFT在这些场景中的局限性。为解决这一问题,我们引入了JudgeLRM系列判断导向型LLM,采用强化学习(RL)训练,以评估者为中心、结果驱动的奖励机制。JudgeLRM模型在性能上持续超越SFT调优模型和现有先进推理模型。特别地,JudgeLRM-3B超越了GPT-4,而JudgeLRM-7B在F1分数上超越了DeepSeek-R1达2.79%,在需要深度推理的评估任务中表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- LLM作为评估者提供了可规模化替代人工注释的方法。
- 在需要复杂推理的领域,监督微调(SFT)方法存在局限性。
- SFT性能提升与需要推理的样本比例之间存在负相关。
- JudgeLRM系列模型采用强化学习训练,以评估者为中心、结果驱动的奖励机制。
- JudgeLRM模型在性能上超越了SFT调优模型和现有先进推理模型。
- JudgeLRM-3B在性能上超越了GPT-4。
点此查看论文截图

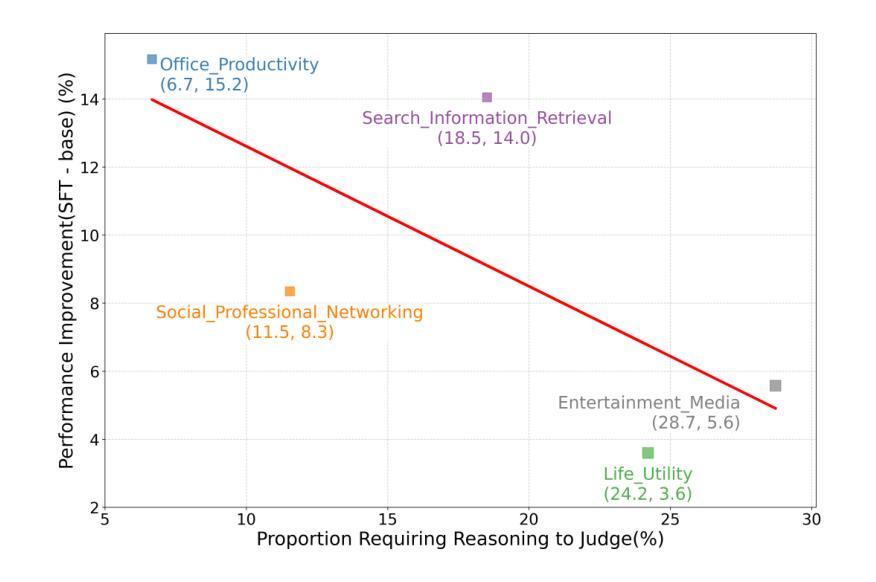

On Fusing ChatGPT and Ensemble Learning in Discon-tinuous Named Entity Recognition in Health Corpora
Authors:Tzu-Chieh Chen, Wen-Yang Lin
Named Entity Recognition has traditionally been a key task in natural language processing, aiming to identify and extract important terms from unstructured text data. However, a notable challenge for contemporary deep-learning NER models has been identifying discontinuous entities, which are often fragmented within the text. To date, methods to address Discontinuous Named Entity Recognition have not been explored using ensemble learning to the best of our knowledge. Furthermore, the rise of large language models, such as ChatGPT in recent years, has shown significant effectiveness across many NLP tasks. Most existing approaches, however, have primarily utilized ChatGPT as a problem-solving tool rather than exploring its potential as an integrative element within ensemble learning algorithms. In this study, we investigated the integration of ChatGPT as an arbitrator within an ensemble method, aiming to enhance performance on DNER tasks. Our method combines five state-of-the-art NER models with ChatGPT using custom prompt engineering to assess the robustness and generalization capabilities of the ensemble algorithm. We conducted experiments on three benchmark medical datasets, comparing our method against the five SOTA models, individual applications of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, and a voting ensemble method. The results indicate that our proposed fusion of ChatGPT with the ensemble learning algorithm outperforms the SOTA results in the CADEC, ShARe13, and ShARe14 datasets, showcasing its potential to enhance NLP applications in the healthcare domain.
命名实体识别(NER)一直是自然语言处理中的关键任务,旨在从非结构化文本数据中识别和提取重要术语。然而,对于当代深度学习的NER模型来说,识别不连续的实体是一个显著的挑战,这些实体通常在文本中是碎片化的。据我们所知,迄今为止,尚未有方法尝试使用集成学习来解决不连续命名实体识别问题。此外,近年来大型语言模型(如ChatGPT)的崛起在多个自然语言处理任务中都显示出显著的有效性。然而,大多数现有方法主要将ChatGPT用作问题解决工具,而没有探索其在集成学习算法中作为整合元素的可能性。本研究调查了ChatGPT作为仲裁者在集成方法中的集成,旨在提高其在DNER任务上的性能。我们的方法结合了五个最先进的NER模型与ChatGPT,使用自定义提示工程来评估集成算法的稳健性和泛化能力。我们在三个基准医疗数据集上进行了实验,将我们的方法与五个最先进模型、GPT-3.5和GPT-4的个别应用以及投票集成方法进行了比较。结果表明,我们提出的将ChatGPT与集成学习算法相结合的方法在CADEC、ShARe13和ShARe14数据集上的表现超过了最先进的结果,展示了其在增强医疗保健领域NLP应用的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages; a short version named “Beyond GPT-NER: ChatGPT as Ensemble Arbitrator for Discontinuous Named Entity Recognition in Health Corpora” has been accpeted for presentation at MedInfo2025
Summary:本研究探索了将ChatGPT作为集成学习算法中的仲裁者,以提高在断断续命名实体识别(DNER)任务上的性能。该研究结合了五种最先进的NER模型与ChatGPT,通过自定义提示工程来评估集成算法的鲁棒性和泛化能力。实验表明,该融合方法在三个医疗基准数据集上优于单独模型及集成学习方法,展示其在医疗保健领域自然语言处理应用的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- NER是自然语言处理中的关键任务,旨在从非结构化文本数据中识别和提取重要术语。
- 断断续续命名实体识别(DNER)是当代深度学习NER模型面临的一个挑战,尤其是在识别被文本中断的实体时。
- 集成学习在解决DNER问题方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。
- ChatGPT等大型语言模型在许多NLP任务上显示出显著的有效性。
- 本研究结合五种最先进NER模型与ChatGPT,利用自定义提示工程来提高集成算法的性能。
- 实验表明,融合ChatGPT的集成学习算法在三个医疗基准数据集上的性能优于单独模型和投票集成方法。
点此查看论文截图

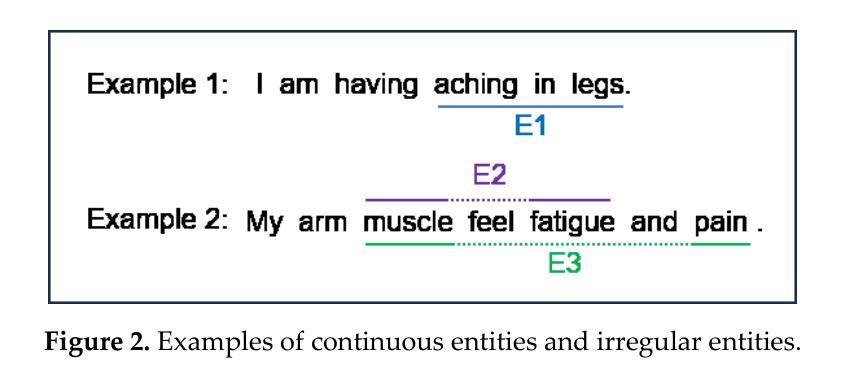
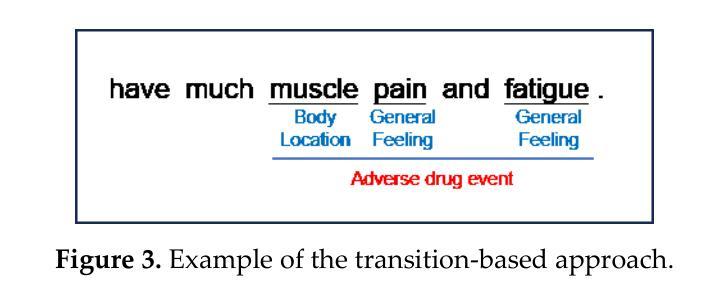
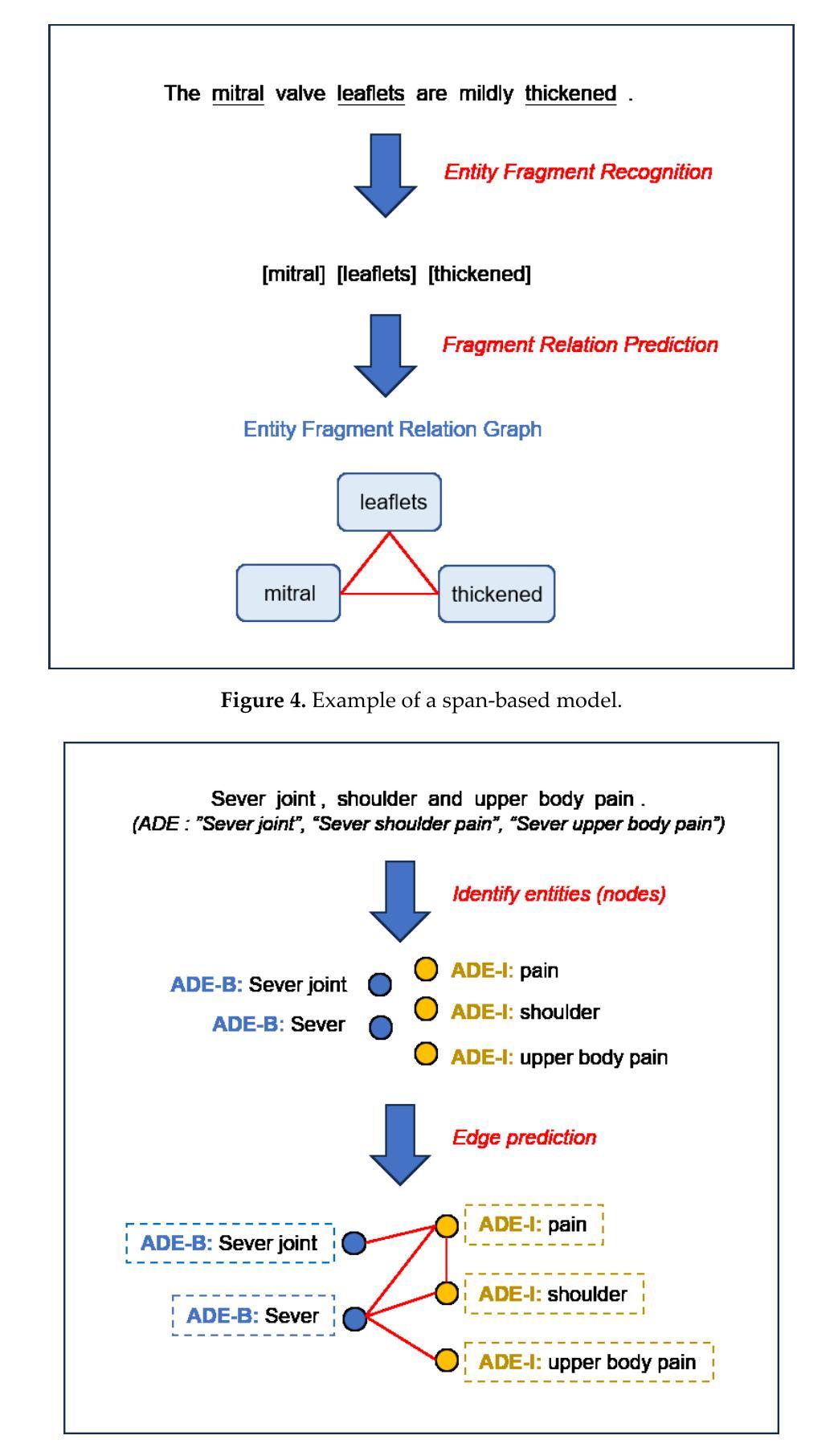
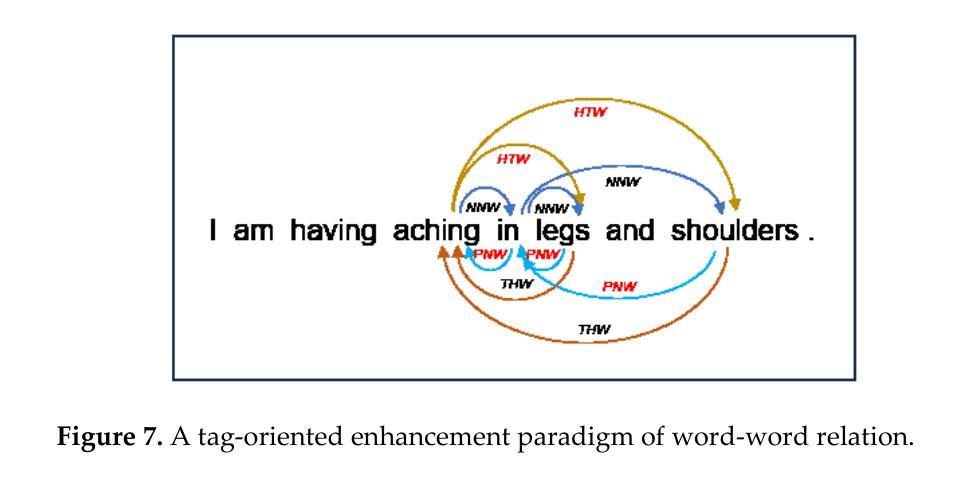
Mastering Collaborative Multi-modal Data Selection: A Focus on Informativeness, Uniqueness, and Representativeness
Authors:Qifan Yu, Zhebei Shen, Zhongqi Yue, Yang Wu, Bosheng Qin, Wenqiao Zhang, Yunfei Li, Juncheng Li, Siliang Tang, Yueting Zhuang
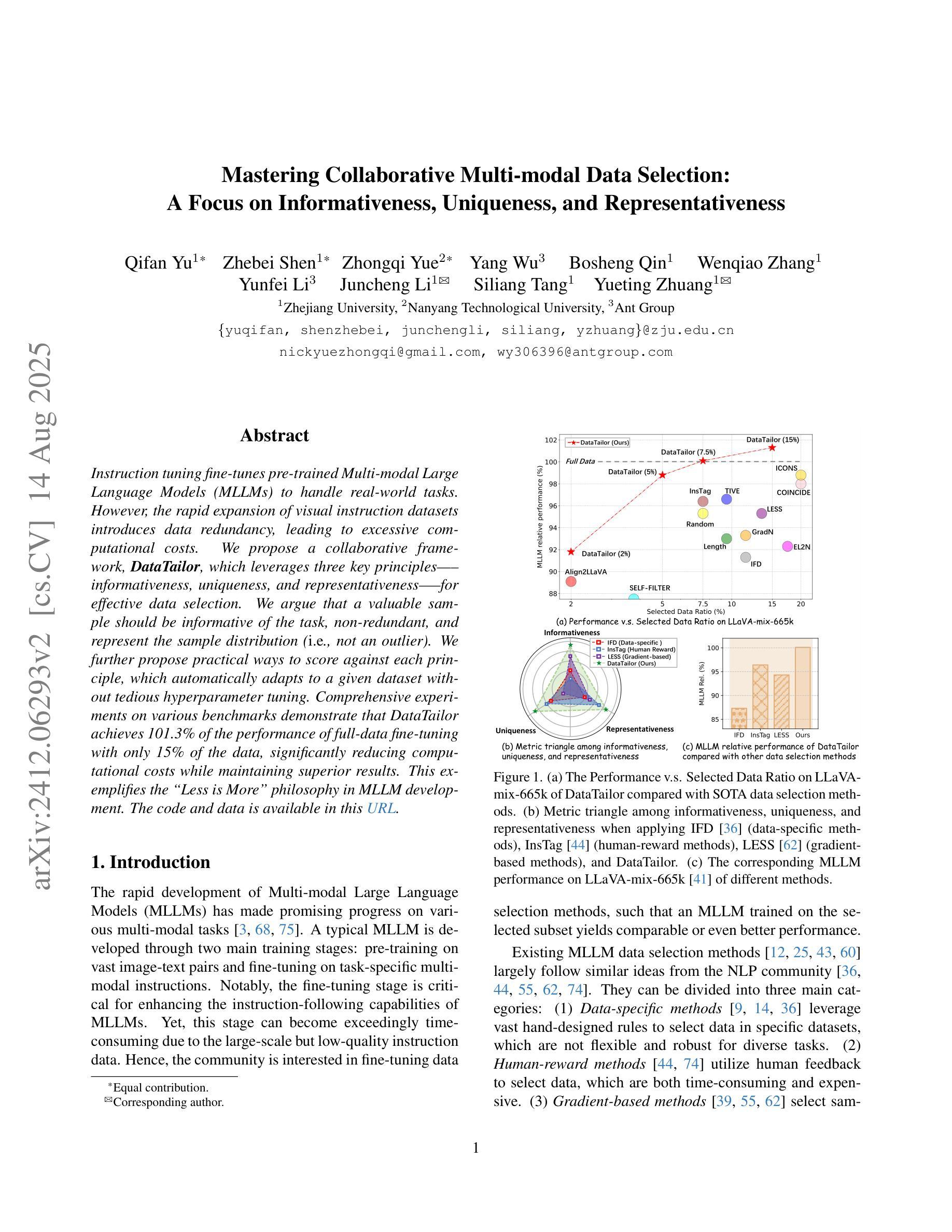
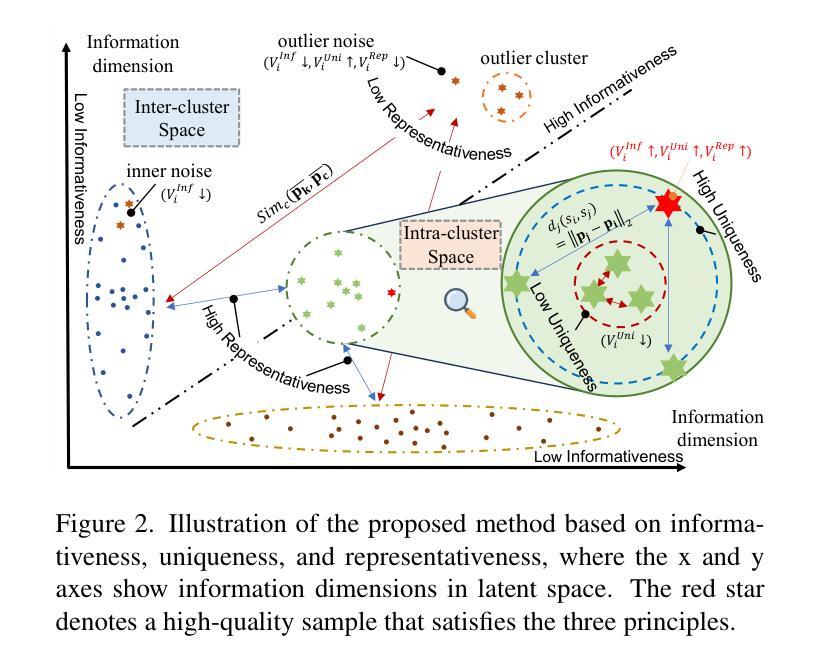
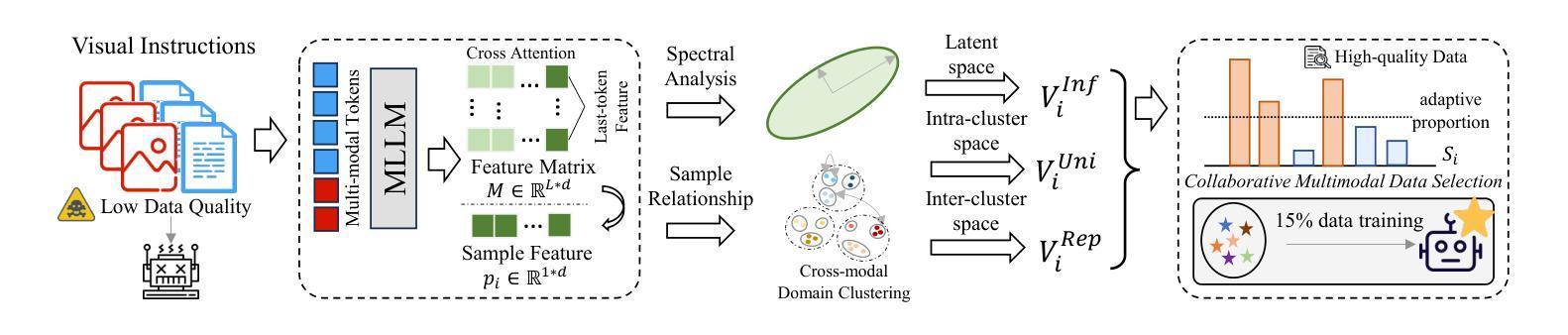
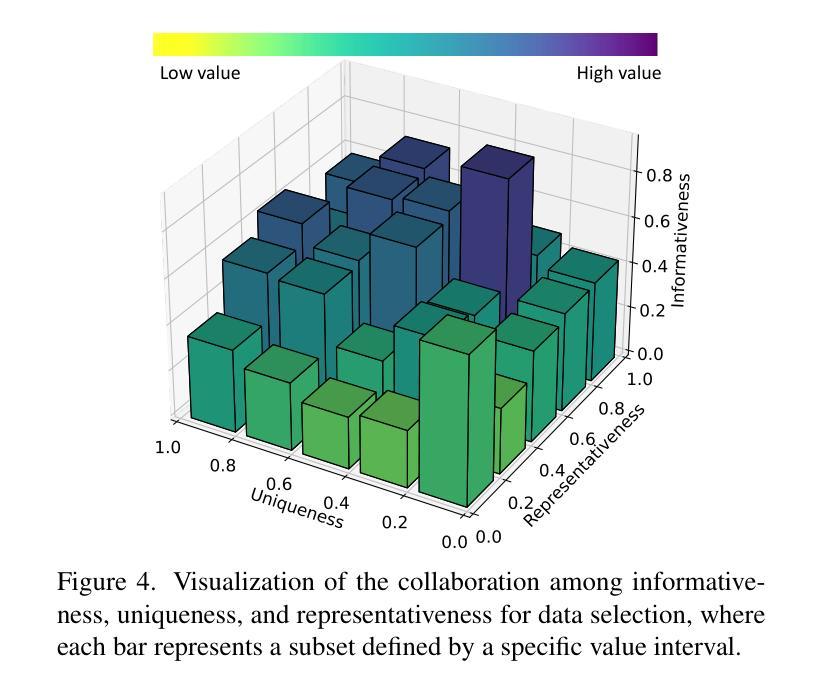
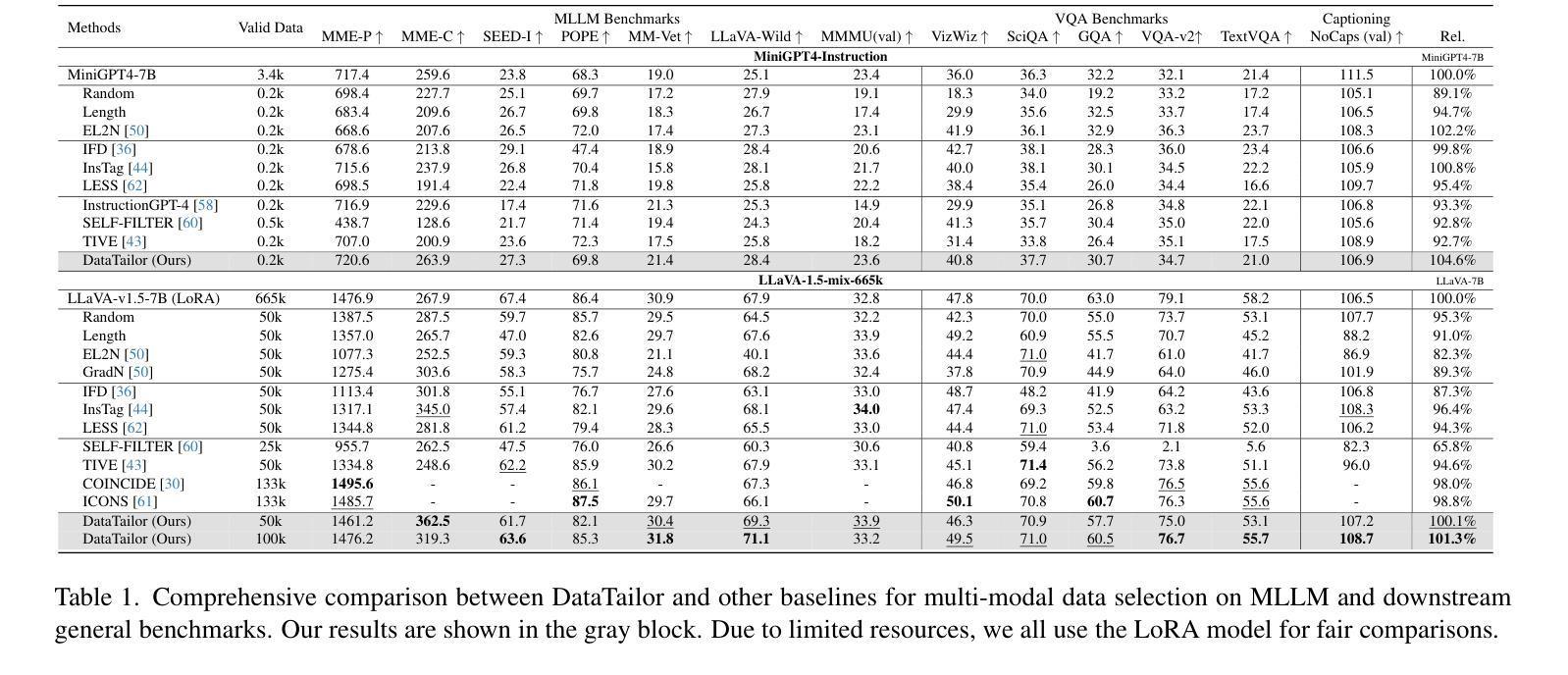
Instruction tuning fine-tunes pre-trained Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to handle real-world tasks. However, the rapid expansion of visual instruction datasets introduces data redundancy, leading to excessive computational costs. We propose a collaborative framework, DataTailor, which leverages three key principles–informativeness, uniqueness, and representativeness–for effective data selection. We argue that a valuable sample should be informative of the task, non-redundant, and represent the sample distribution (i.e., not an outlier). We further propose practical ways to score against each principle, which automatically adapts to a given dataset without tedious hyperparameter tuning. Comprehensive experiments on various benchmarks demonstrate that DataTailor achieves 101.3% of the performance of full-data fine-tuning with only 15% of the data, significantly reducing computational costs while maintaining superior results. This exemplifies the “Less is More” philosophy in MLLM development. The code and data is available in this \href{https://github.com/Yuqifan1117/DataTailor}{URL}.
指令微调对预训练的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行微调以处理现实世界任务。然而,视觉指令数据集的快速扩张导致了数据冗余,从而增加了计算成本。我们提出了一个协作框架DataTailor,它利用三个关键原则——信息性、唯一性和代表性——进行有效的数据选择。我们认为有价值的样本应该具有任务的信息性、非冗余性,并代表样本分布(即不是异常值)。我们进一步提出了针对每条原则进行评分的实际方法,这些方法可以自动适应给定的数据集,而无需繁琐的超参数调整。在各种基准测试上的综合实验表明,DataTailor仅使用15%的数据就实现了全数据微调性能的101.3%,在降低计算成本的同时保持了卓越的结果。这体现了MLLM发展中的“少即是多”理念。代码和数据可以在以下网址中找到:[URL](https://github.com/Yuqifan1117/DataTailor)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Highlight
Summary
数据冗余使得大型多模态语言模型的指令调优面临计算成本过高的挑战。本研究提出了一个协作框架DataTailor,利用信息性、独特性和代表性三个关键原则进行高效数据选择。DataTailor能在降低计算成本的同时维持模型性能,实现“少即是多”的理念。相关代码和数据已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 数据冗余导致大型多模态语言模型(MLLMs)的计算成本激增。这成为了对现实任务进行预训练模型微调的主要挑战之一。
- 本研究提出的DataTailor框架基于三个原则:信息性、独特性和代表性来选择数据样本,以优化模型性能并降低计算成本。这三个原则确保所选样本包含有关任务的信息量,并且非冗余且具有代表性。
- DataTailor自动适应给定数据集,无需繁琐的超参数调整。这一特性简化了数据处理过程并提高了效率。
点此查看论文截图
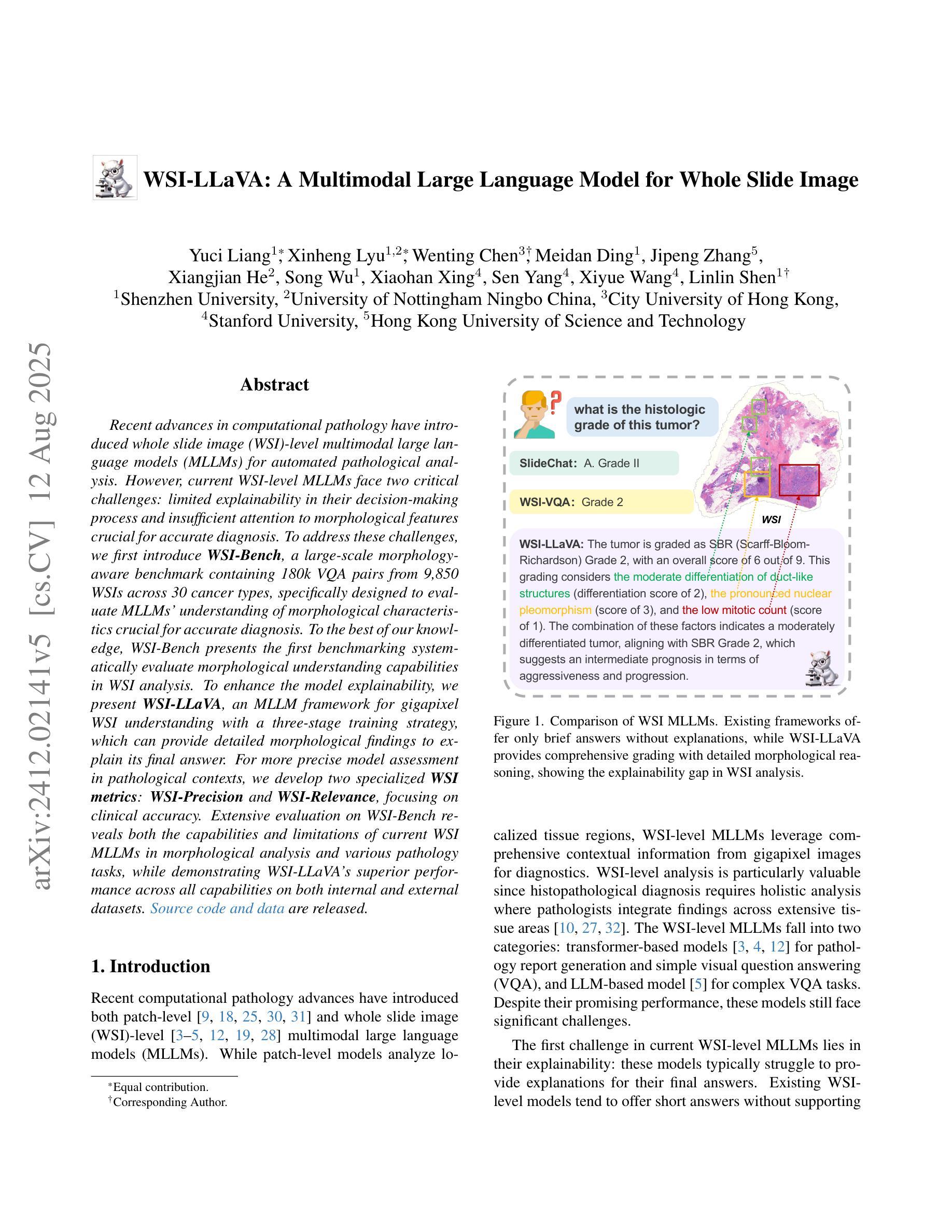
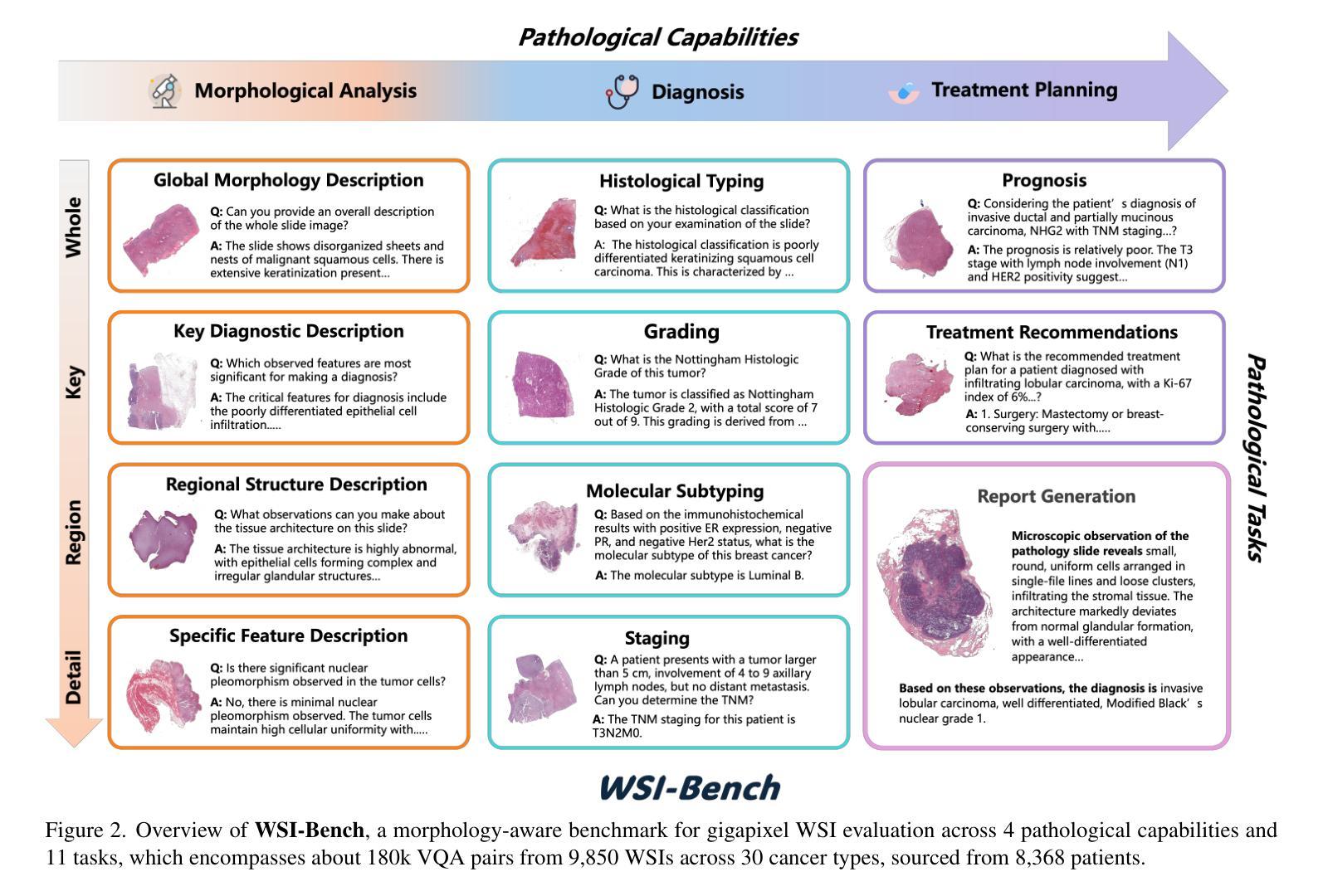
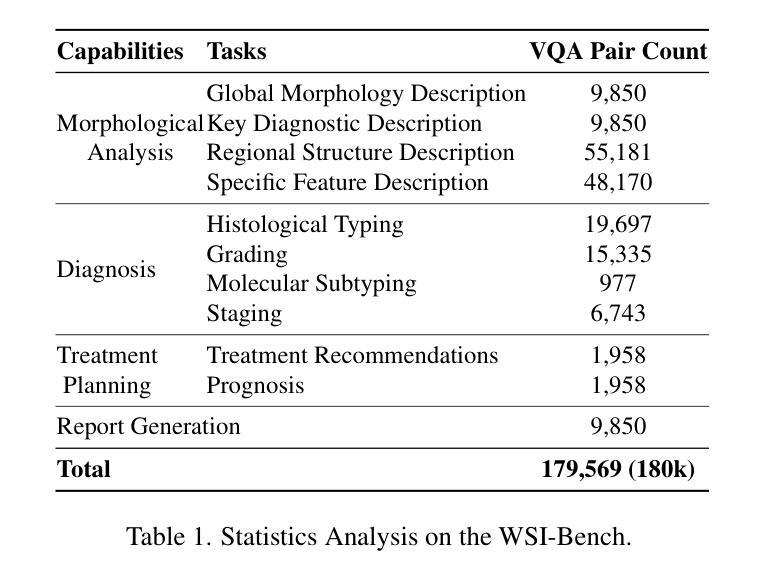
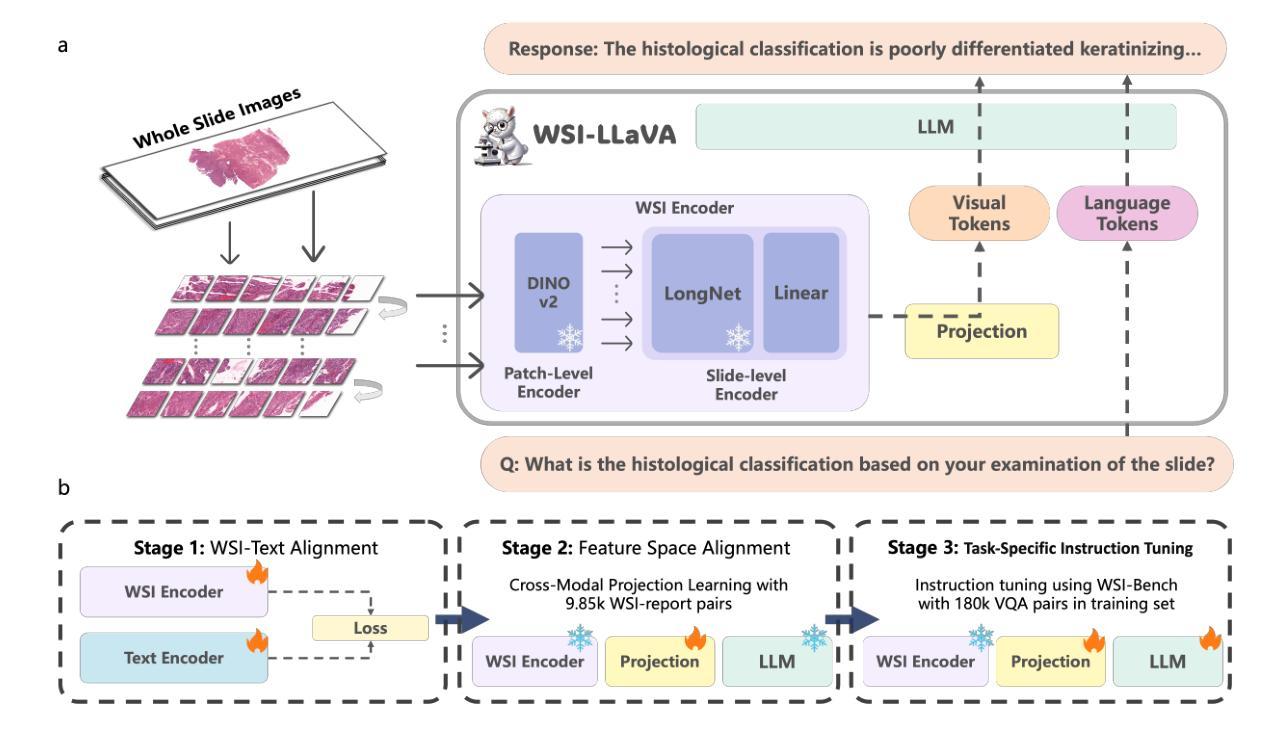
WSI-LLaVA: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Whole Slide Image
Authors:Yuci Liang, Xinheng Lyu, Wenting Chen, Meidan Ding, Jipeng Zhang, Xiangjian He, Song Wu, Xiaohan Xing, Sen Yang, Xiyue Wang, Linlin Shen
Recent advancements in computational pathology have produced patch-level Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), but these models are limited by their inability to analyze whole slide images (WSIs) comprehensively and their tendency to bypass crucial morphological features that pathologists rely on for diagnosis. To address these challenges, we first introduce WSI-Bench, a large-scale morphology-aware benchmark containing 180k VQA pairs from 9,850 WSIs across 30 cancer types, designed to evaluate MLLMs’ understanding of morphological characteristics crucial for accurate diagnosis. Building upon this benchmark, we present WSI-LLaVA, a novel framework for gigapixel WSI understanding that employs a three-stage training approach: WSI-text alignment, feature space alignment, and task-specific instruction tuning. To better assess model performance in pathological contexts, we develop two specialized WSI metrics: WSI-Precision and WSI-Relevance. Experimental results demonstrate that WSI-LLaVA outperforms existing models across all capability dimensions, with a significant improvement in morphological analysis, establishing a clear correlation between morphological understanding and diagnostic accuracy.
计算病理学领域的最新进展已经产生了补丁级别的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),但这些模型受到无法全面分析全幻灯片图像(WSIs)的局限,并且倾向于绕过病理学家依赖的用于诊断的关键形态特征。为了解决这些挑战,我们首先引入了WSI-Bench,这是一个大规模的形态感知基准测试,包含来自9850张幻灯片图像的18万对问答(VQA),涵盖30种癌症类型,旨在评估MLLMs对形态特征的准确理解,这对于准确诊断至关重要。基于此基准测试,我们提出了WSI-LLaVA,这是一个用于千兆像素WSI理解的全新框架,采用三阶段训练方法:WSI文本对齐、特征空间对齐和任务特定指令调整。为了更好地评估模型在病理背景下的性能,我们开发了两个专门的WSI指标:WSI精确度和WSI相关性。实验结果表明,WSI-LLaVA在所有能力维度上都优于现有模型,在形态分析方面取得了显著改进,建立了形态理解与诊断准确性之间的明确相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025, 38 pages, 22 figures, 35 tables
Summary
近期计算病理学领域的进展推动了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在斑块层面的应用,但其在全切片图像(WSIs)分析方面的综合能力和对关键形态特征的识别上仍有不足。为应对这些挑战,本文引入了WSI-Bench基准测试集,并基于该基准测试集提出WSI-LLaVA框架,用于理解吉像素(gigapixel)级别的WSI。该框架采用三阶段训练方法,包括WSI文本对齐、特征空间对齐和任务特定指令调整。同时,开发了两个针对WSI的专业评估指标:WSI精度和WSI相关性。实验结果表明,WSI-LLaVA在各方面性能均优于现有模型,形态分析显著改善,并建立了形态理解与诊断准确性之间的明确关联。
Key Takeaways
- 计算病理学领域发展出多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),但其在全切片图像分析方面存在局限性。
- 引入WSI-Bench基准测试集,包含来自9850个WSIs的18万问答对,旨在评估MLLMs对关键形态特征的理解能力。
- 提出WSI-LLaVA框架,采用三阶段训练方法进行全切片图像理解。包括WSI文本对齐、特征空间对齐和任务特定指令调整。
- 开发两个针对全切片图像的评估指标:WSI精度和WSI相关性。
- 实验结果显示,WSI-LLaVA框架在形态分析方面表现出显著改进。
点此查看论文截图