⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
Long-Context Speech Synthesis with Context-Aware Memory
Authors:Zhipeng Li, Xiaofen Xing, Jingyuan Xing, Hangrui Hu, Heng Lu, Xiangmin Xu
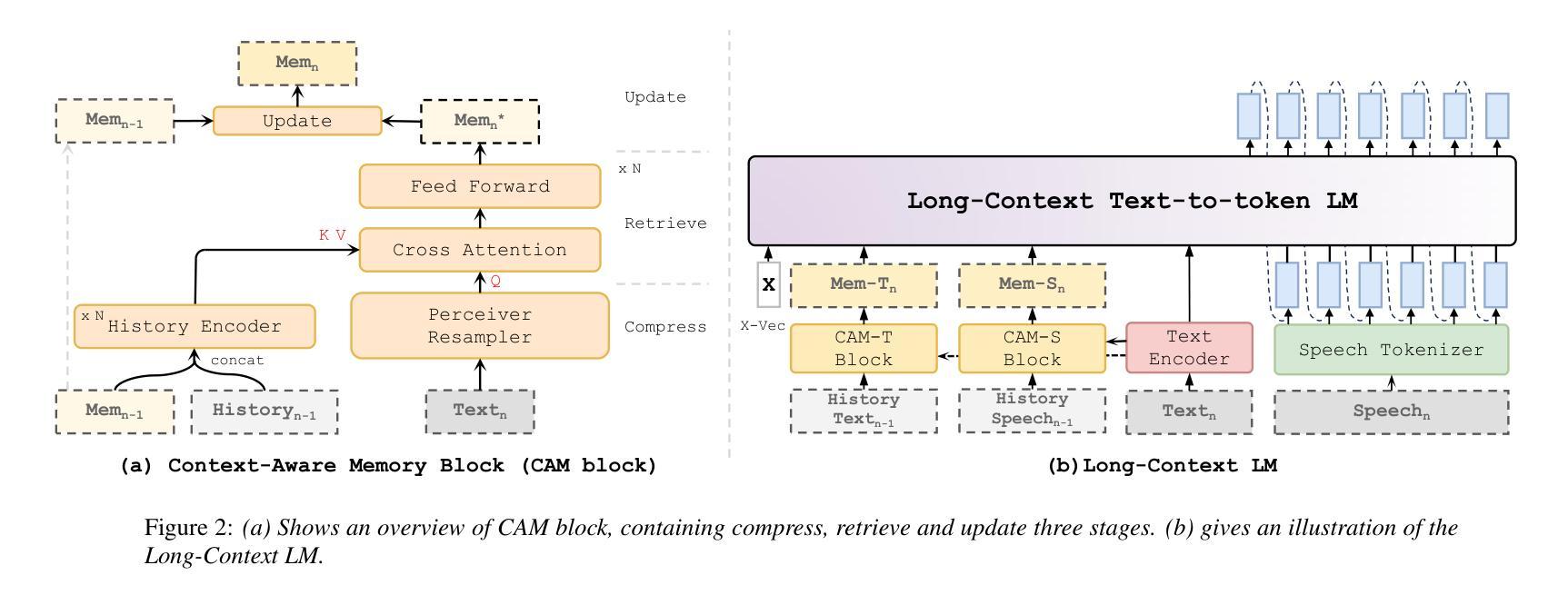
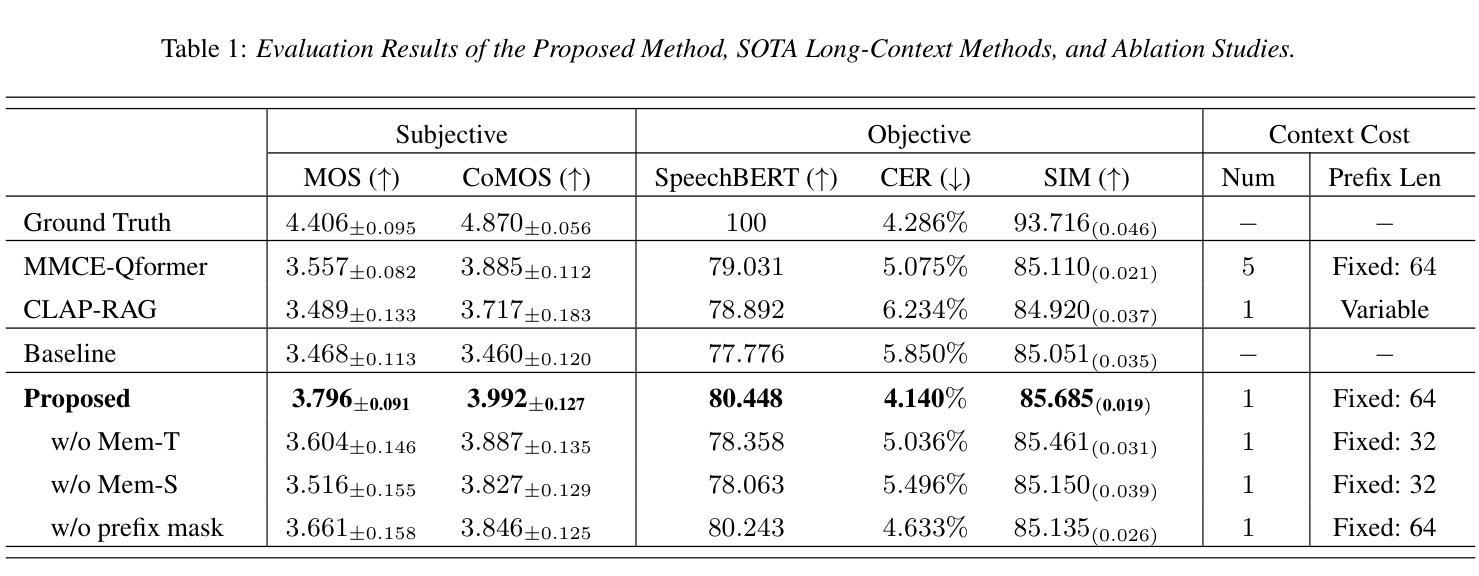
In long-text speech synthesis, current approaches typically convert text to speech at the sentence-level and concatenate the results to form pseudo-paragraph-level speech. These methods overlook the contextual coherence of paragraphs, leading to reduced naturalness and inconsistencies in style and timbre across the long-form speech. To address these issues, we propose a Context-Aware Memory (CAM)-based long-context Text-to-Speech (TTS) model. The CAM block integrates and retrieves both long-term memory and local context details, enabling dynamic memory updates and transfers within long paragraphs to guide sentence-level speech synthesis. Furthermore, the prefix mask enhances the in-context learning ability by enabling bidirectional attention on prefix tokens while maintaining unidirectional generation. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms baseline and state-of-the-art long-context methods in terms of prosody expressiveness, coherence and context inference cost across paragraph-level speech.
在长篇文本语音合成中,当前的方法通常是在句子层面将文本转换为语音,并将结果拼接起来形成伪段落级语音。这些方法忽视了段落的上下文连贯性,导致长篇语音的自然度降低,风格和音色不一致。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种基于上下文感知记忆(CAM)的长文本到语音(TTS)模型。CAM模块能够集成并检索长期记忆和局部上下文细节,从而在长段落内实现动态内存更新和传输,以指导句子级语音合成。此外,前缀掩码通过允许前缀标记的双向注意力同时保持单向生成,增强了上下文学习能力。实验结果表明,所提出的方法在语调表现力、连贯性和上下文推理成本方面优于基线方法和先进的长上下文方法,特别是在段落级语音方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech25
Summary:针对长文本语音合成中的语境连贯性问题,提出了一种基于上下文感知记忆(CAM)的长文本语音合成(TTS)模型。该模型通过整合和检索长期记忆和局部上下文细节,实现了动态内存更新和长段落内的传输,从而指导句子级别的语音合成。同时,前缀掩码增强了模型在上下文中的学习能力,通过双向关注前缀令牌来保持单向生成。实验结果表明,该方法在篇章级别的语音合成中,相较于基准方法和先进的长文本方法,具有更强的语调表现力、连贯性和上下文推理成本。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前的长文本语音合成方法忽略了篇章的上下文连贯性,导致生成的语音自然度降低、风格和时间感不一致。
- 提出了基于上下文感知记忆(CAM)的TTS模型,该模型能够整合和检索长期记忆和局部上下文细节。
- CAM模块能够实现动态内存更新和长段落内的信息传输,以指导句子级别的语音合成。
- 前缀掩码增强了模型在上下文中的学习能力,允许双向关注前缀令牌,同时保持单向生成。
- 实验结果表明,该模型在篇章级别的语音合成的语调表现力、连贯性和上下文推理成本方面优于其他方法。
- 该模型解决了长文本语音合成中的语境连贯性问题,提高了语音的自然度和一致性。
点此查看论文截图


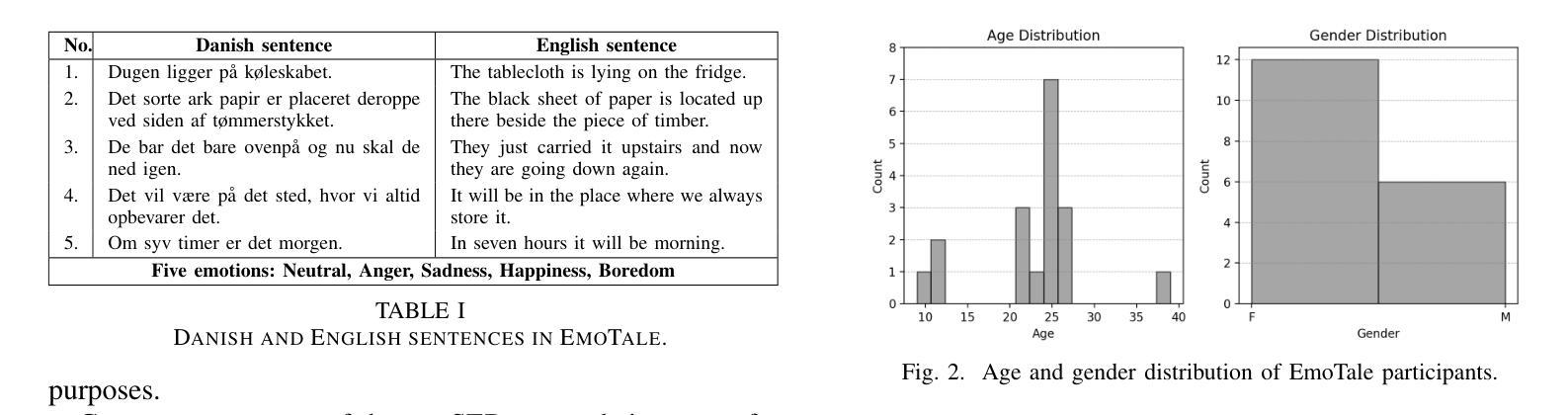
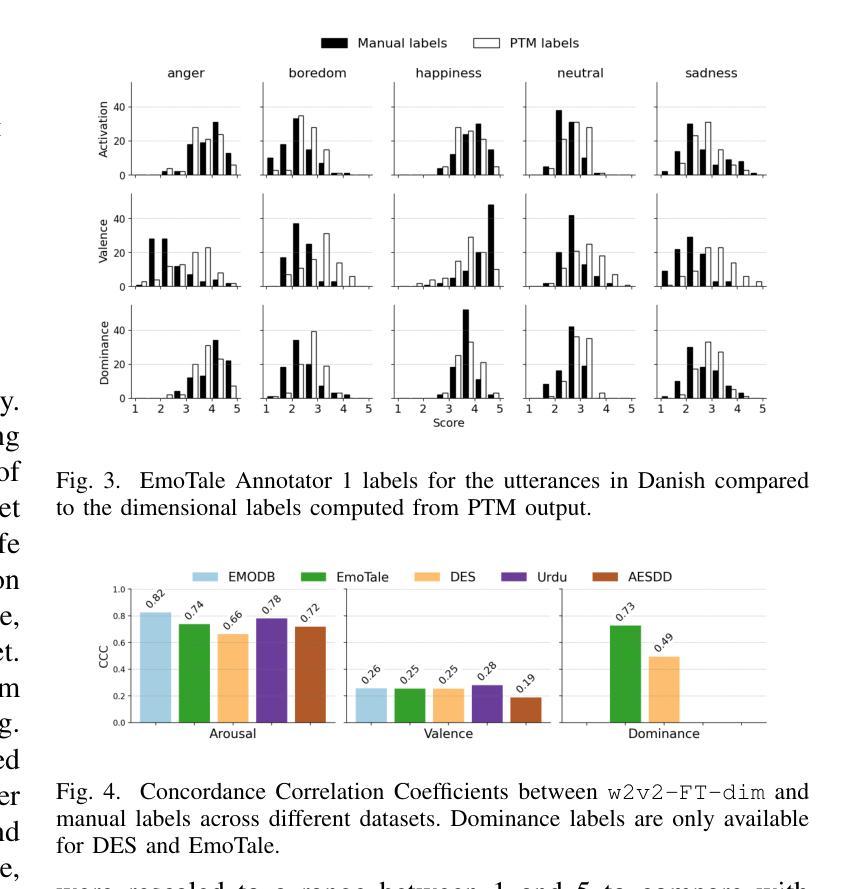
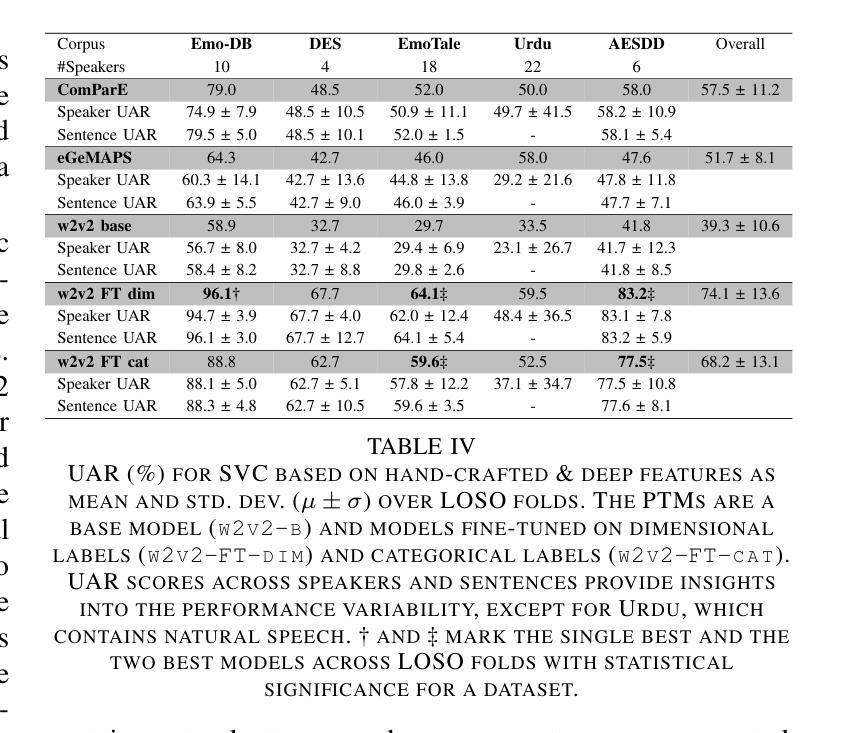
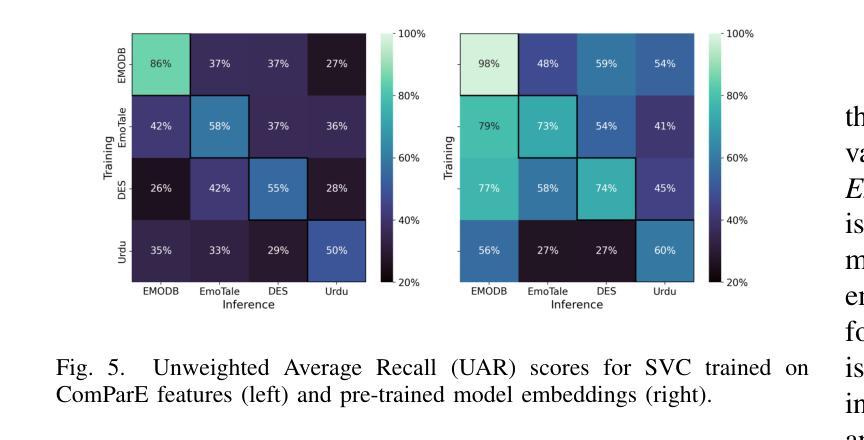
EmoTale: An Enacted Speech-emotion Dataset in Danish
Authors:Maja J. Hjuler, Harald V. Skat-Rørdam, Line H. Clemmensen, Sneha Das
While multiple emotional speech corpora exist for commonly spoken languages, there is a lack of functional datasets for smaller (spoken) languages, such as Danish. To our knowledge, Danish Emotional Speech (DES), published in 1997, is the only other database of Danish emotional speech. We present EmoTale; a corpus comprising Danish and English speech recordings with their associated enacted emotion annotations. We demonstrate the validity of the dataset by investigating and presenting its predictive power using speech emotion recognition (SER) models. We develop SER models for EmoTale and the reference datasets using self-supervised speech model (SSLM) embeddings and the openSMILE feature extractor. We find the embeddings superior to the hand-crafted features. The best model achieves an unweighted average recall (UAR) of 64.1% on the EmoTale corpus using leave-one-speaker-out cross-validation, comparable to the performance on DES.
虽然多种常用语言的情感语音语料库已经存在,但对于较小的语种(如丹麦语)来说,缺乏功能性的数据集。据我们所知,丹麦情感语音(DES)是丹麦情感语音唯一可用的数据库,发表于1997年。我们推出EmoTale,这是一个包含丹麦语和英语语音记录以及相应的情绪标注数据的语料库。我们通过研究并提出语音情感识别(SER)模型的预测能力来证明数据集的有效性。我们使用自监督语音模型(SSLM)嵌入和开放SMILE特征提取器为EmoTale和参考数据集开发SER模型。我们发现嵌入物的性能优于手工特征。使用留出一位发言人作为验证的交叉验证法,最佳模型在EmoTale语料库上的未加权平均召回率(UAR)达到64.1%,与DES上的性能相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in the proceedings of ASRU 2025
Summary
本研究介绍了针对丹麦语情感语音的语料库EmoTale。该研究填补了丹麦语情感语音功能数据集缺乏的空白,提供了包含丹麦语和英语语音录音及其相关情感注释的语料库。研究通过情感语音识别(SER)模型验证了数据集的有效性,并使用自监督语音模型嵌入和openSMILE特征提取器开发SER模型。研究发现,自监督模型嵌入优于手工特征,最佳模型在EmoTale语料库上的未加权平均召回率(UAR)达到64.1%,与DES性能相当。
Key Takeaways
- EmoTale语料库是包含丹麦语和英语情感语音的数据库,填补了针对小型语言情感语音功能数据集的缺乏。
- 研究通过情感语音识别(SER)模型验证了EmoTale语料库的有效性。
- 使用自监督语音模型嵌入和openSMILE特征提取器开发SER模型。
- 自监督模型嵌入在性能上优于手工特征。
- 最佳模型在EmoTale语料库上的未加权平均召回率(UAR)达到64.1%。
- EmoTale语料库的性能与现有的丹麦情感语音数据库DES相当。
点此查看论文截图

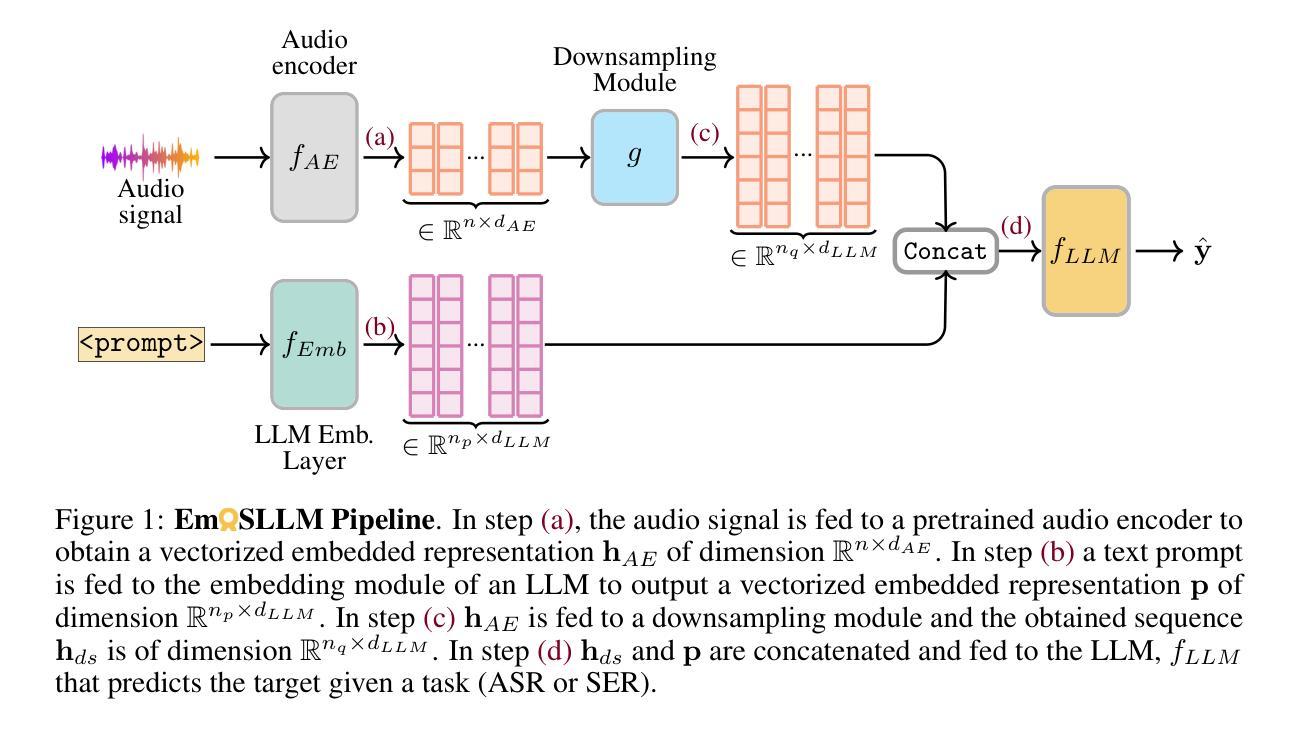
EmoSLLM: Parameter-Efficient Adaptation of LLMs for Speech Emotion Recognition
Authors:Hugo Thimonier, Antony Perzo, Renaud Seguier
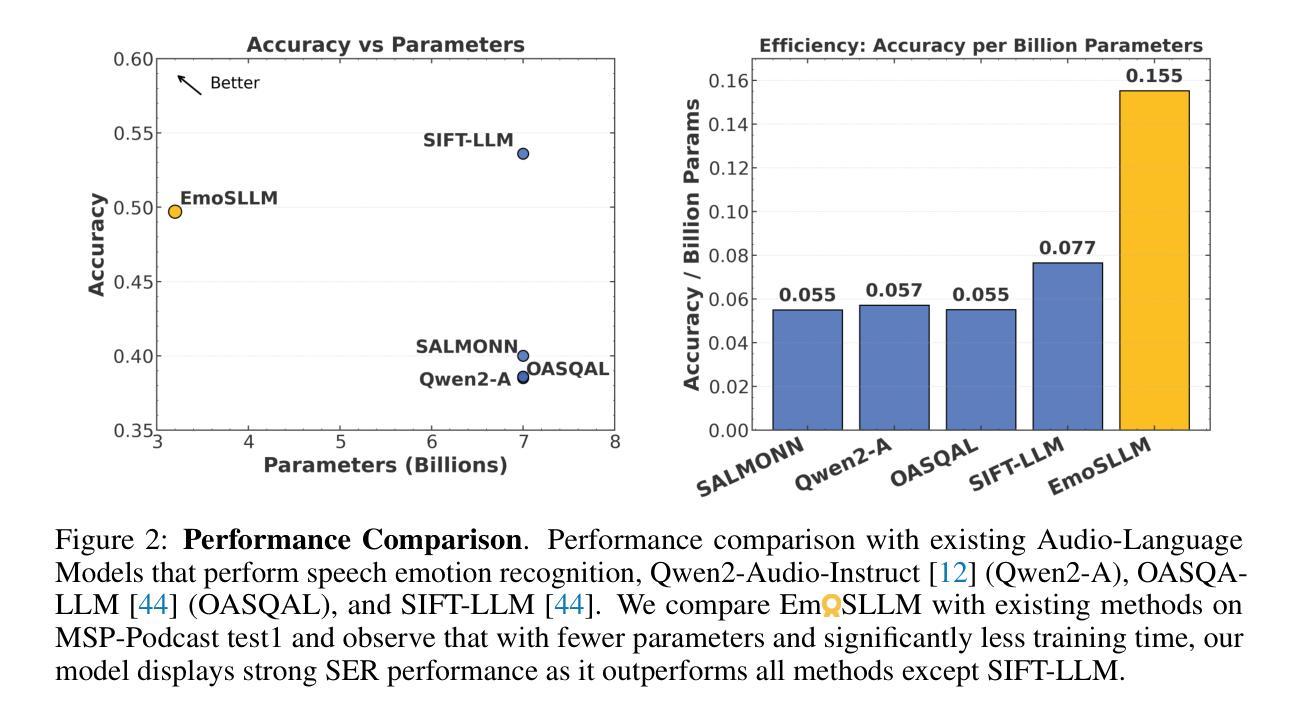
Emotion recognition from speech is a challenging task that requires capturing both linguistic and paralinguistic cues, with critical applications in human-computer interaction and mental health monitoring. Recent works have highlighted the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform tasks outside of the sole natural language area. In particular, recent approaches have investigated coupling LLMs with other data modalities by using pre-trained backbones and different fusion mechanisms. This work proposes a novel approach that fine-tunes an LLM with audio and text representations for emotion prediction. Our method first extracts audio features using an audio feature extractor, which are then mapped into the LLM’s representation space via a learnable interfacing module. The LLM takes as input (1) the transformed audio features, (2) additional features in the form of natural language (e.g., the transcript), and (3) a textual prompt describing the emotion prediction task. To efficiently adapt the LLM to this multimodal task, we employ Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), enabling parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Experimental results on standard emotion recognition benchmarks demonstrate that our model outperforms all but one existing Speech-Text LLMs in the literature, while requiring less than half the parameters of competing approaches. This highlights our approach’s effectiveness in integrating multi-modal inputs for speech-based emotion understanding while maintaining significant computational efficiency.
从语音中进行情感识别是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要捕捉语言和非语言线索,在人机交互和心理健康监测等领域有重要应用。近期的研究工作突出了大型语言模型(LLM)在执行自然语言领域以外任务的能力。特别是近期的方法通过利用预训练的主干网络和不同的融合机制,探索了将LLM与其他数据模式相结合。这项工作提出了一种新型方法,即通过音频和文本表示对LLM进行微调,以进行情感预测。我们的方法首先使用音频特征提取器提取音频特征,然后通过一个可学习的接口模块将这些特征映射到LLM的表示空间。LLM的输入包括(1)转换后的音频特征,(2)以自然语言形式存在的附加特征(例如,文本),以及(3)描述情感预测任务的文本提示。为了有效地将LLM适应于这种多模式任务,我们采用了低秩适应(LoRA)技术,实现了参数高效的微调。在标准情感识别基准测试上的实验结果表明,我们的模型在文献中仅次于一种现有的语音-文本LLM,同时所需的参数少于竞争对手方法的一半。这突显了我们的方法在整合多模式输入进行基于语音的情感理解方面的有效性,同时保持了显著的计算效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行语音情感识别的新方法。该方法结合了音频和文本表示,通过精细调整LLM来进行情感预测。实验结果表明,该方法在标准情感识别基准测试上的表现优于大多数现有的语音文本LLM,同时计算效率更高。
Key Takeaways
- 情感识别是一项挑战任务,需要捕捉语言和非语言线索,在人机交互和心理健康监测等领域有重要应用。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)具备执行自然语言领域外任务的能力。
- 本文提出了一种结合LLM和其他数据模态的新方法,通过预训练的主干网络和不同的融合机制进行情感预测。
- 该方法使用音频特征提取器提取音频特征,然后通过可学习的接口模块将这些特征映射到LLM的表示空间。
- LLM接受转换后的音频特征、以自然语言形式存在的附加特征(如转录)以及描述情感预测任务的文本提示作为输入。
- 为了有效地适应多模态任务,采用了低秩适应(LoRA)方法,实现了参数高效的精细调整。
点此查看论文截图

DiffIER: Optimizing Diffusion Models with Iterative Error Reduction
Authors:Ao Chen, Lihe Ding, Tianfan Xue
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating high-quality samples and enhancing performance across diverse domains through Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG). However, the quality of generated samples is highly sensitive to the selection of the guidance weight. In this work, we identify a critical ``training-inference gap’’ and we argue that it is the presence of this gap that undermines the performance of conditional generation and renders outputs highly sensitive to the guidance weight. We quantify this gap by measuring the accumulated error during the inference stage and establish a correlation between the selection of guidance weight and minimizing this gap. Furthermore, to mitigate this gap, we propose DiffIER, an optimization-based method for high-quality generation. We demonstrate that the accumulated error can be effectively reduced by an iterative error minimization at each step during inference. By introducing this novel plug-and-play optimization framework, we enable the optimization of errors at every single inference step and enhance generation quality. Empirical results demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms baseline approaches in conditional generation tasks. Furthermore, the method achieves consistent success in text-to-image generation, image super-resolution, and text-to-speech generation, underscoring its versatility and potential for broad applications in future research.
扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)在生成高质量样本以及提高不同领域的性能上展现了显著的能力。然而,生成样本的质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。在这项工作中,我们识别出了一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,我们认为正是这个差距影响了条件生成的性能,并导致输出对引导权重的高度敏感。我们通过测量推理阶段的累积误差来量化这个差距,并建立引导权重的选择与最小化这个差距之间的关联。此外,为了缓解这一差距,我们提出了DiffIER,这是一种基于优化的高质量生成方法。我们证明通过推理过程中每一步的迭代误差最小化,可以有效减少累积误差。通过引入这种新颖即插即用的优化框架,我们能够在每一个单独的推理步骤中优化误差,提高生成质量。经验结果表明,我们所提出的方法在条件生成任务中优于基准方法。此外,该方法在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成方面取得了持续的成功,突显了其通用性和在未来研究中广泛应用的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在生成高质量样本和提升不同领域性能方面的显著能力,特别是通过无分类器引导(CFG)实现。然而,生成的样本质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。本文识别出一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,并指出这一差距影响了条件生成性能,使输出对引导权重高度敏感。为了量化这一差距并减少其对生成质量的影响,本文提出了DiffIER,一种基于优化的高质量生成方法。通过迭代误差最小化,在推理阶段的每一步优化误差,提高了生成质量。实证结果表明,该方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法,并在文本到图像生成、图像超分辨率和文本到语音生成等任务中取得了持续的成功。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过无分类器引导(CFG)生成高质量样本并提升不同领域性能。
- 生成的样本质量对引导权重的选择非常敏感。
- 存在一个关键的“训练-推理差距”,影响条件生成性能。
- 本文通过测量推理阶段的累积误差来量化这一差距。
- 提出了DiffIER方法,通过迭代误差最小化减少累积误差,提高生成质量。
- DiffIER方法在条件生成任务上优于基准方法。
点此查看论文截图





FNH-TTS: A Fast, Natural, and Human-Like Speech Synthesis System with advanced prosodic modeling based on Mixture of Experts
Authors:Qingliang Meng, Yuqing Deng, Wei Liang, Limei Yu, Huizhi Liang, Tian Li
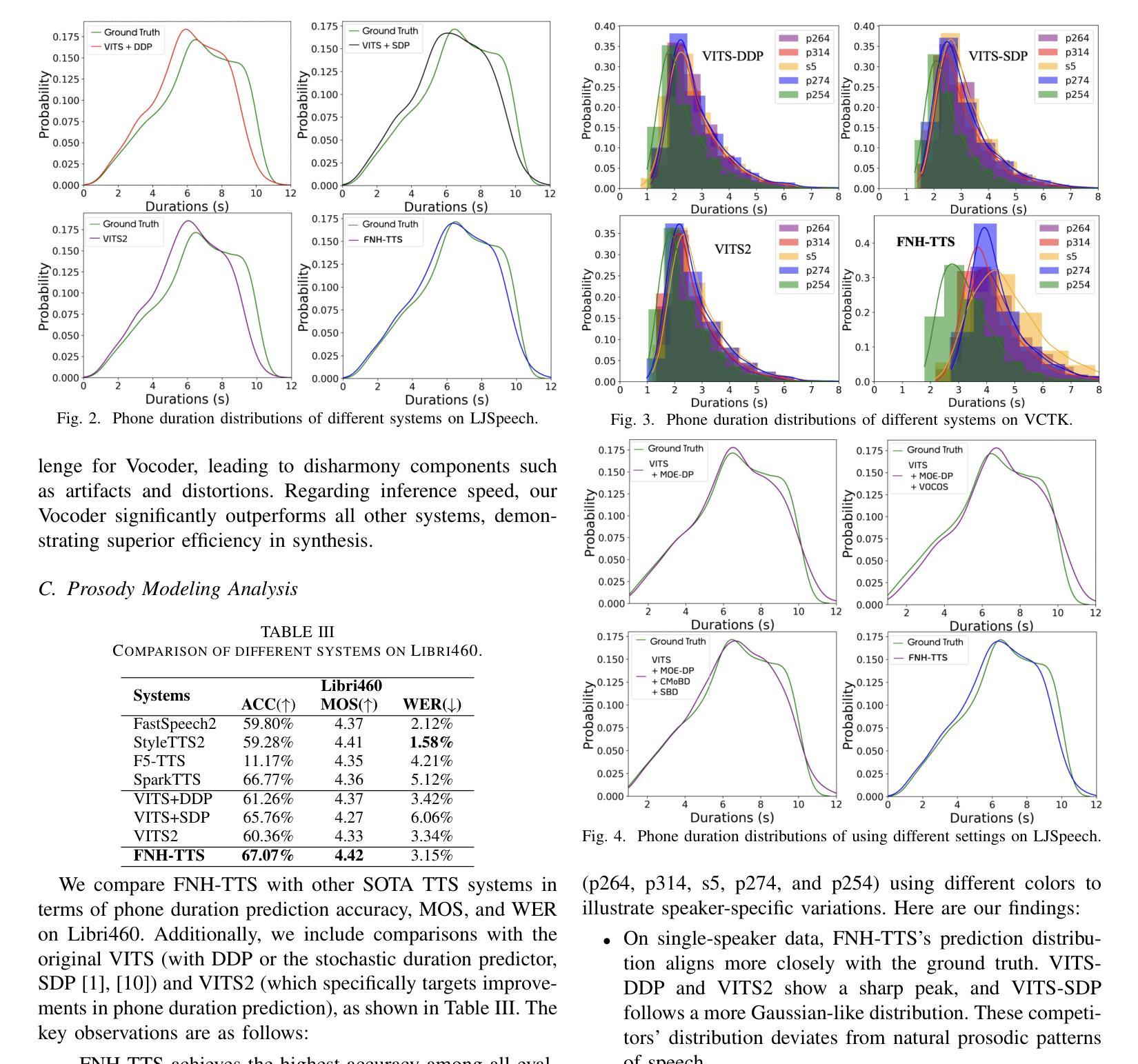
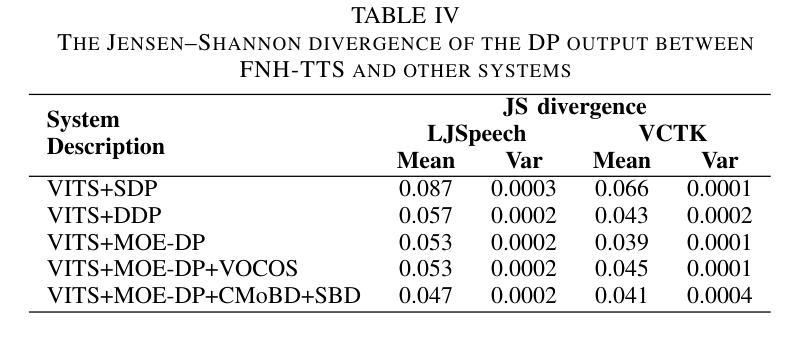
Achieving natural and human-like speech synthesis with low inference costs remains a major challenge in speech synthesis research. This study focuses on human prosodic patterns and synthesized spectrum harmony, addressing the challenges of prosody modeling and artifact issues in non-autoregressive models. To enhance prosody modeling and synthesis quality, we introduce a new Duration Predictor based on the Mixture of Experts alongside a new Vocoder with two advanced multi-scale discriminators. We integrated the these new modules into the VITS system, forming our FNH-TTS system. Our experiments on LJSpeech, VCTK, and LibriTTS demonstrate the system’s superiority in synthesis quality, phoneme duration prediction, Vocoder results, and synthesis speed. Our prosody visualization results show that FNH-TTS produces duration predictions that more closely align with natural human beings than other systems.
在语音合成研究中,实现低成本、自然、拟人化的语音合成仍然是一个重大挑战。本研究关注人类语调模式和合成频谱和谐性,解决语调建模和非自回归模型中的伪影问题的挑战。为了增强语调建模和合成质量,我们引入了一种基于专家混合的新持续时间预测器,以及一种具有两个先进多尺度鉴别器的新Vocoder。我们将这些新模块集成到VITS系统中,形成了我们的FNH-TTS系统。我们在LJSpeech、VCTK和LibriTTS上的实验证明了该系统在合成质量、音素持续时间预测、Vocoder结果和合成速度方面的优越性。我们的语调可视化结果表明,FNH-TTS产生的持续时间预测与其他系统相比更接近于自然人类。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究关注人类语调模式和合成频谱和谐性,旨在解决非自回归模型中的语调建模和人工制品问题。通过引入基于专家混合的新持续时间预测器和具有两个先进多尺度鉴别器的全新编码器,提高了语调建模和合成质量。集成这些新模块到VITS系统,形成了我们的FNH-TTS系统。实验表明,该系统在合成质量、音素持续时间预测、编码器结果和合成速度方面均优于其他系统,产生的持续时间预测更符合自然人类的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注自然和人类化的语音合成,应对语调建模和人工制品的挑战。
- 引入基于专家混合的持续时间预测器,改善语调建模和合成质量。
- 提出新型编码器,配备两个先进的多尺度鉴别器,提升合成效果。
- 新系统FNH-TTS集成了上述模块,显著提高合成质量、音素持续时间预测和合成速度。
- 在LJSpeech、VCTK和LibriTTS上的实验验证了FNH-TTS系统的优越性。
- FNH-TTS产生的持续时间预测更接近自然人类的表现。
点此查看论文截图




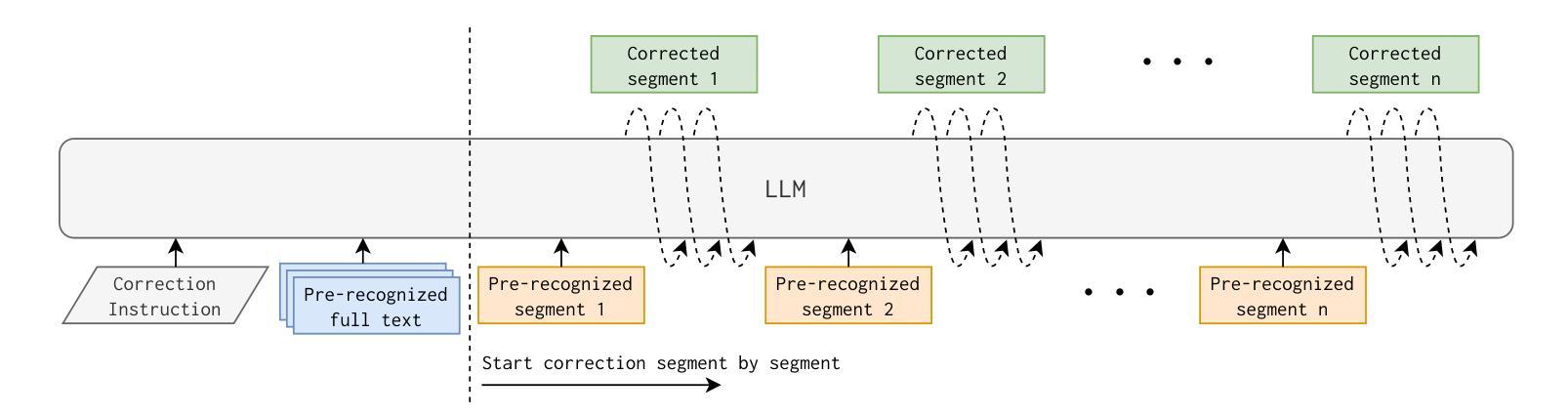
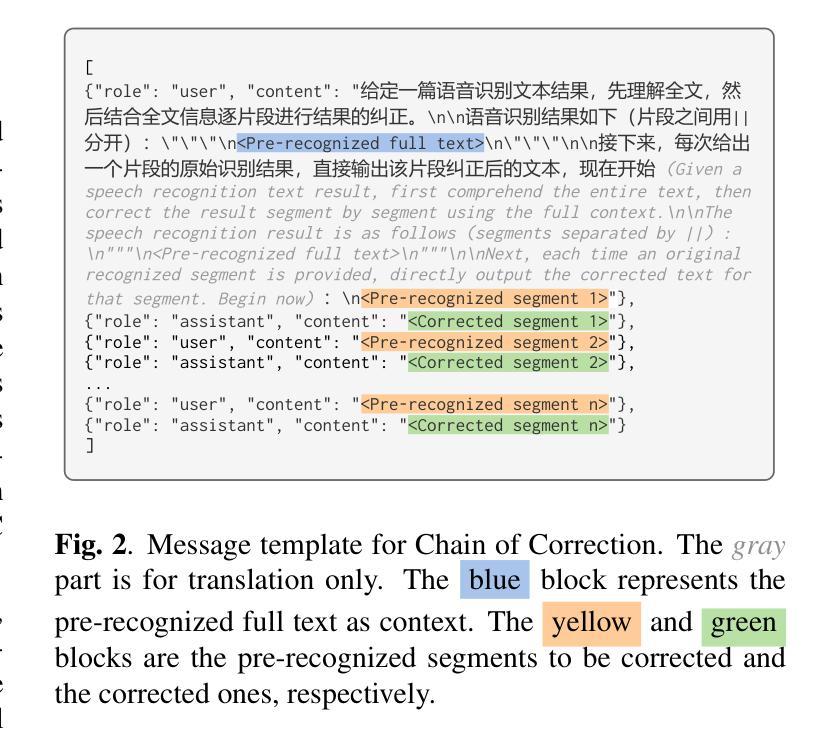
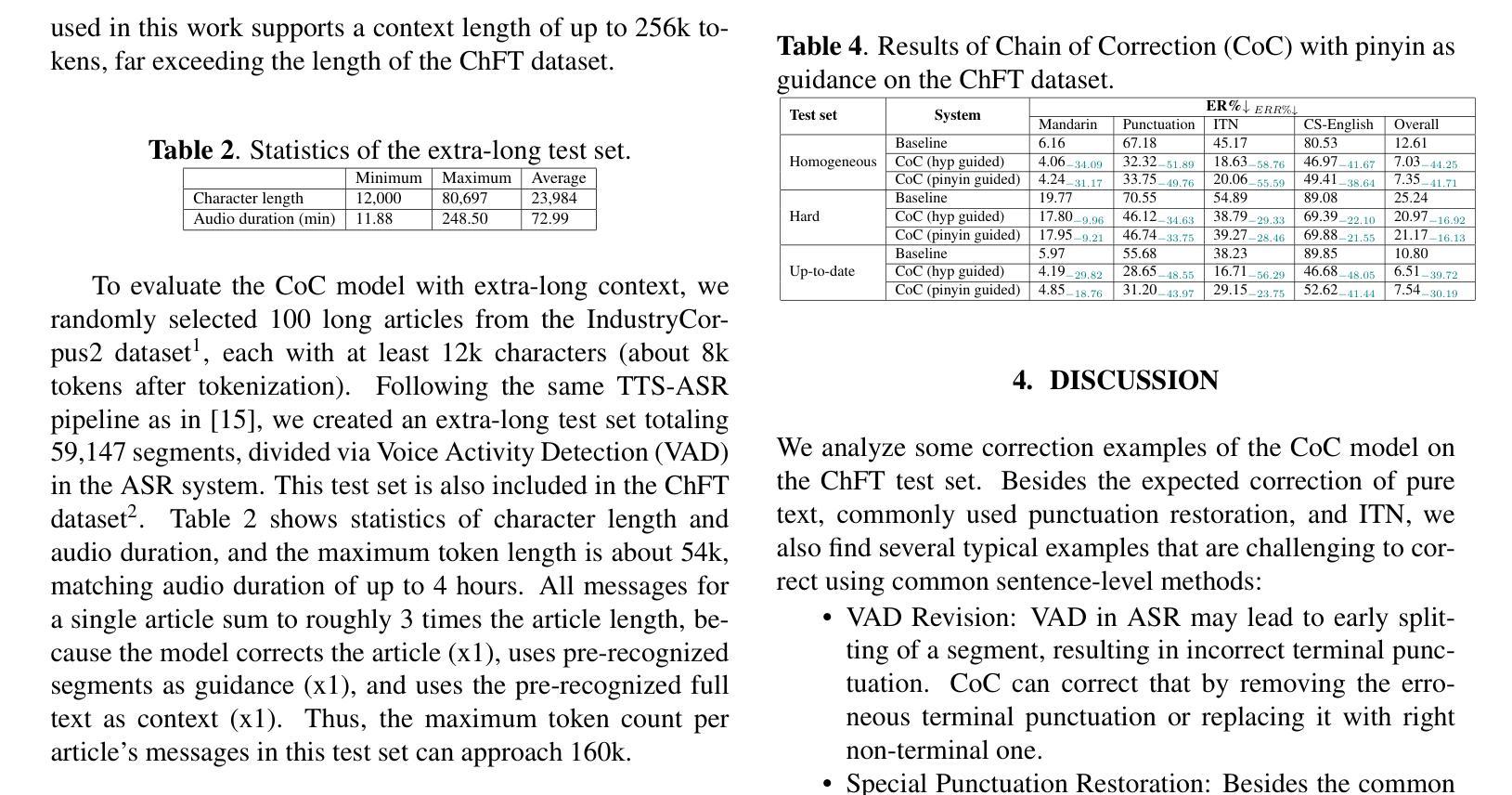
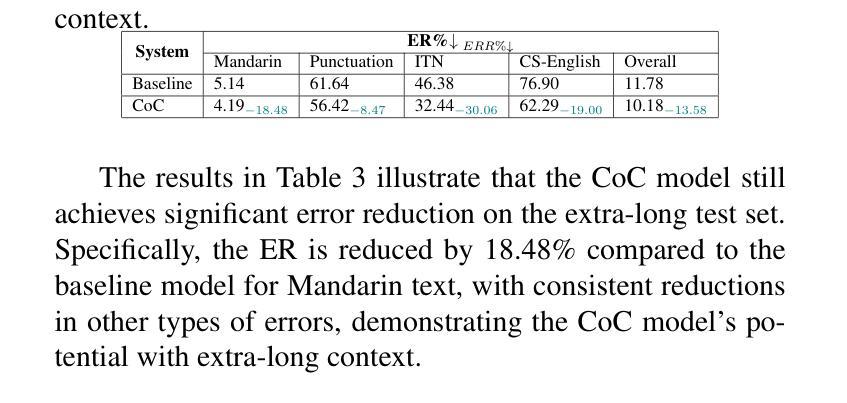
Chain of Correction for Full-text Speech Recognition with Large Language Models
Authors:Zhiyuan Tang, Dong Wang, Zhikai Zhou, Yong Liu, Shen Huang, Shidong Shang
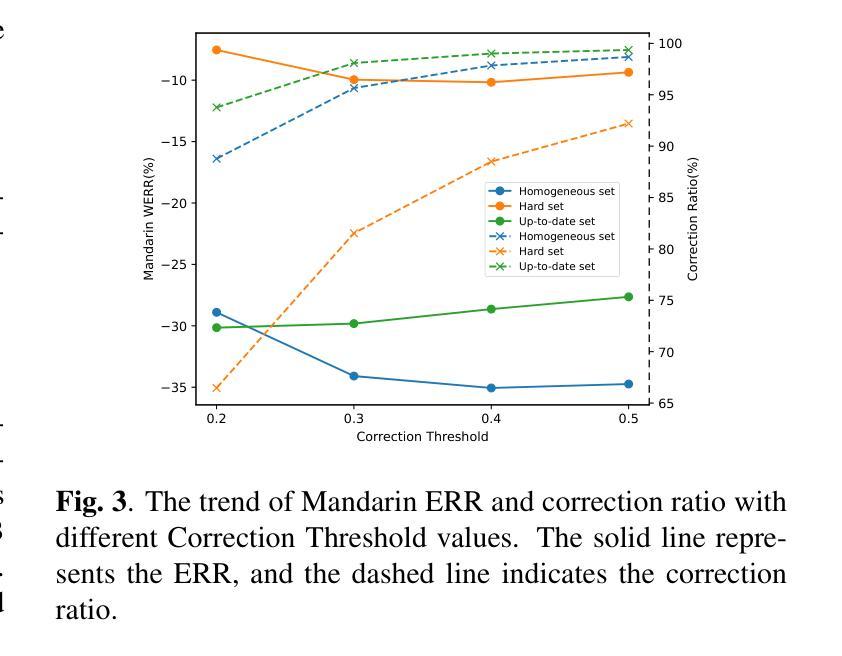
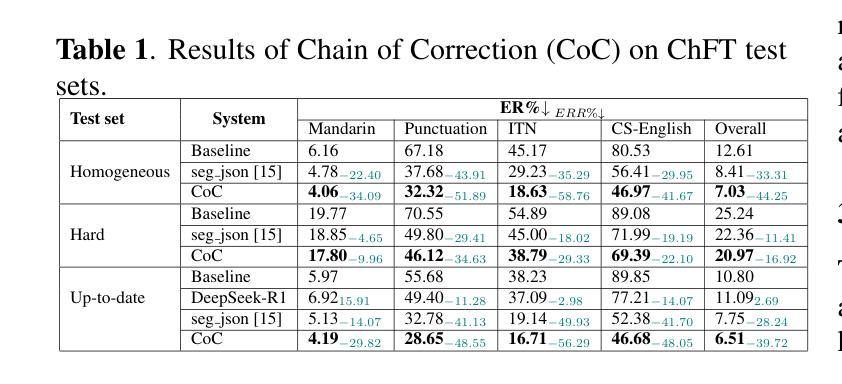
Full-text error correction with Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is attracting increased attention for its ability to address a wide range of error types, such as punctuation restoration and inverse text normalization, across long context. However, challenges remain regarding stability, controllability, completeness, and fluency. To mitigate these issues, this paper proposes the Chain of Correction (CoC), which uses a multi-turn chat format to correct errors segment by segment, guided by pre-recognized text and full-text context for better semantic understanding. Utilizing the open-sourced ChFT dataset, we fine-tune a pre-trained LLM to evaluate CoC’s performance. Experiments show that CoC significantly outperforms baseline and benchmark systems in correcting full-text ASR outputs. We also analyze correction thresholds to balance under-correction and over-rephrasing, extrapolate CoC on extra-long ASR outputs, and explore using other types of information to guide error correction.
利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行自动语音识别(ASR)的全文错误校正正日益受到关注,因为它能够解决广泛的错误类型,例如标点恢复和文本逆向归一化等,贯穿整个语境。然而,在稳定性、可控性、完整性和流畅性方面仍存在挑战。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了纠错链(CoC),它采用多轮聊天格式分段纠错,由预先识别的文本和全文上下文引导,以更好地语义理解。我们利用开源的ChFT数据集对预训练的LLM进行微调,以评估CoC的性能。实验表明,在纠正全自动语音识别输出文本方面,CoC显著优于基准和基准系统。我们还分析了校正阈值以平衡欠校正和过度改述,将CoC外推到超长ASR输出,并探索使用其他类型的信息来引导错误校正。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注基于大型语言模型(LLM)的全文错误校正技术在自动语音识别(ASR)领域的应用。针对ASR结果中广泛存在的多种错误类型,如标点恢复和逆向文本归一化等,提出使用纠错链(CoC)进行分段纠错。结合预识别文本和全文上下文,以提高语义理解,并通过多轮聊天格式进行纠错。通过微调预训练LLM并在ChFT数据集上进行实验评估,显示纠错链在纠正全文ASR输出方面显著优于基准和基准系统。同时探讨了修正阈值的平衡、对超长ASR输出的外推应用以及使用其他信息引导错误校正的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)用于全文错误校正,能处理多种ASR错误类型。
- 提出了纠错链(CoC)方法,通过多轮聊天格式分段纠错。
- 结合预识别文本和全文上下文提高语义理解。
- 通过对预训练LLM的微调及在ChFT数据集上的实验评估,显示CoC在纠正全文ASR输出方面性能优异。
- 研究了修正阈值的平衡,以避免过度修正和重述。
- 探讨了纠错链在超长ASR输出上的应用。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Long-duration Talking Video Synthesis with Linear Diffusion Transformer under Multimodal Guidance
Authors:Haojie Zhang, Zhihao Liang, Ruibo Fu, Bingyan Liu, Zhengqi Wen, Xuefei Liu, Jianhua Tao, Yaling Liang
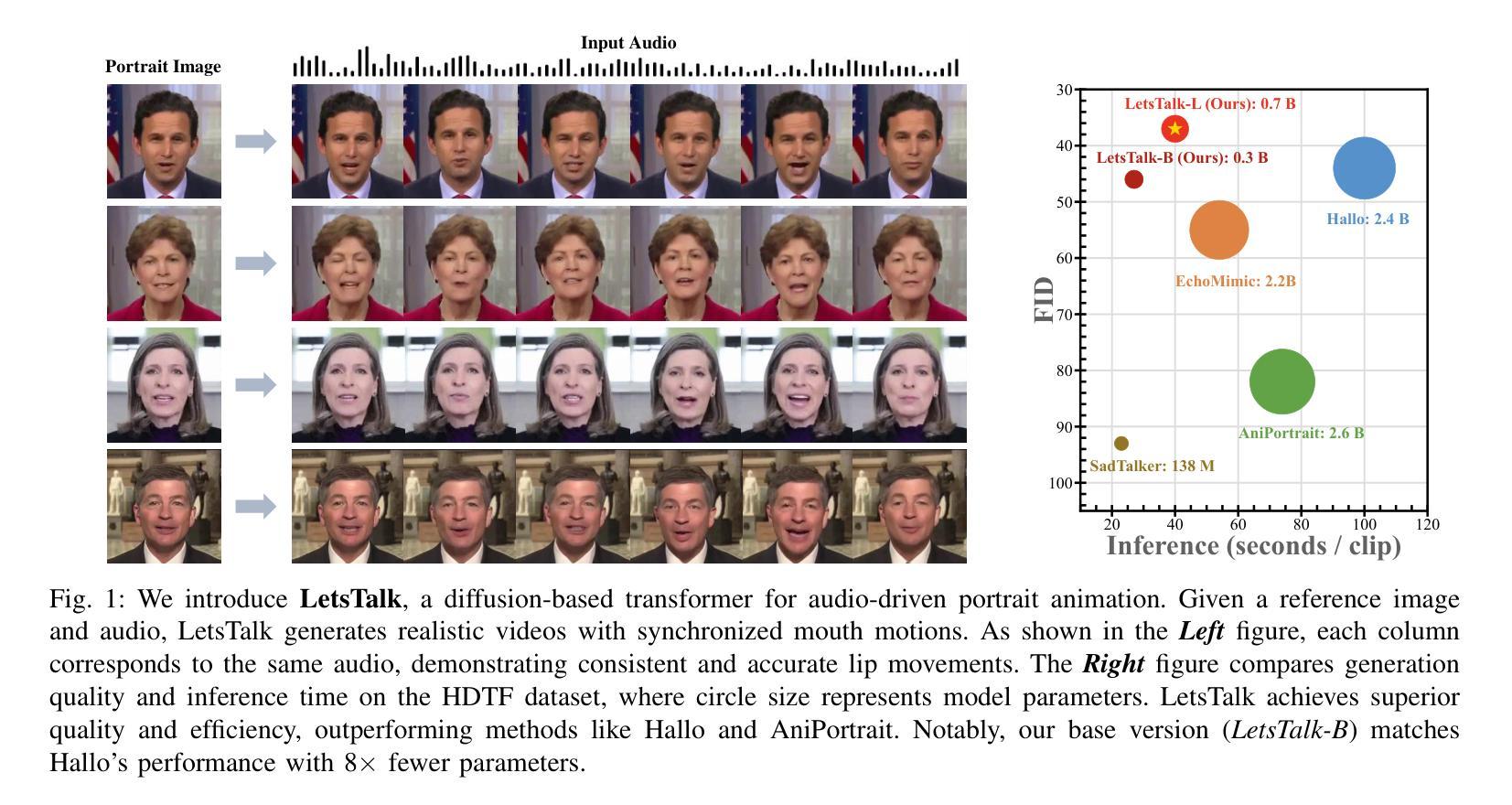
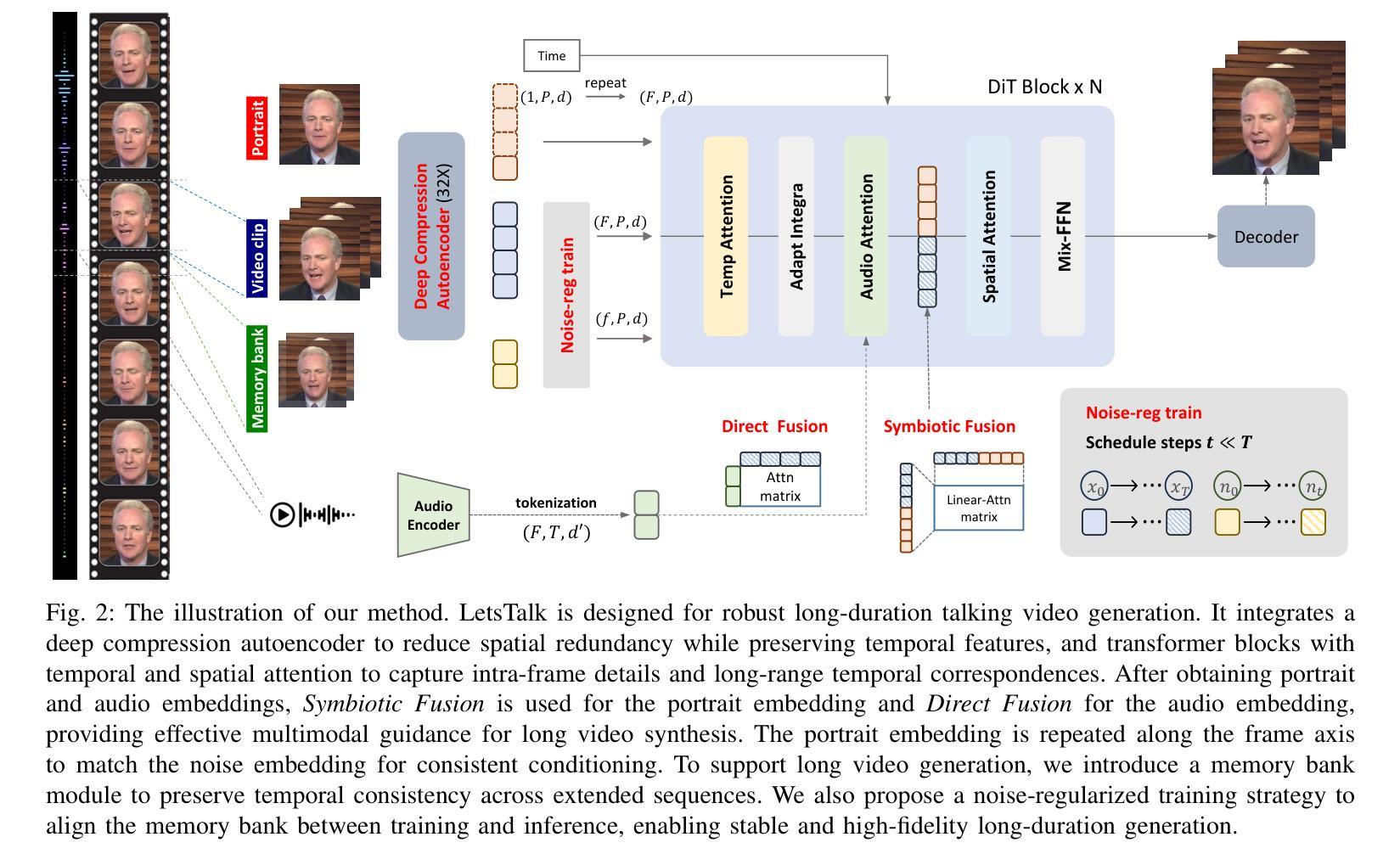
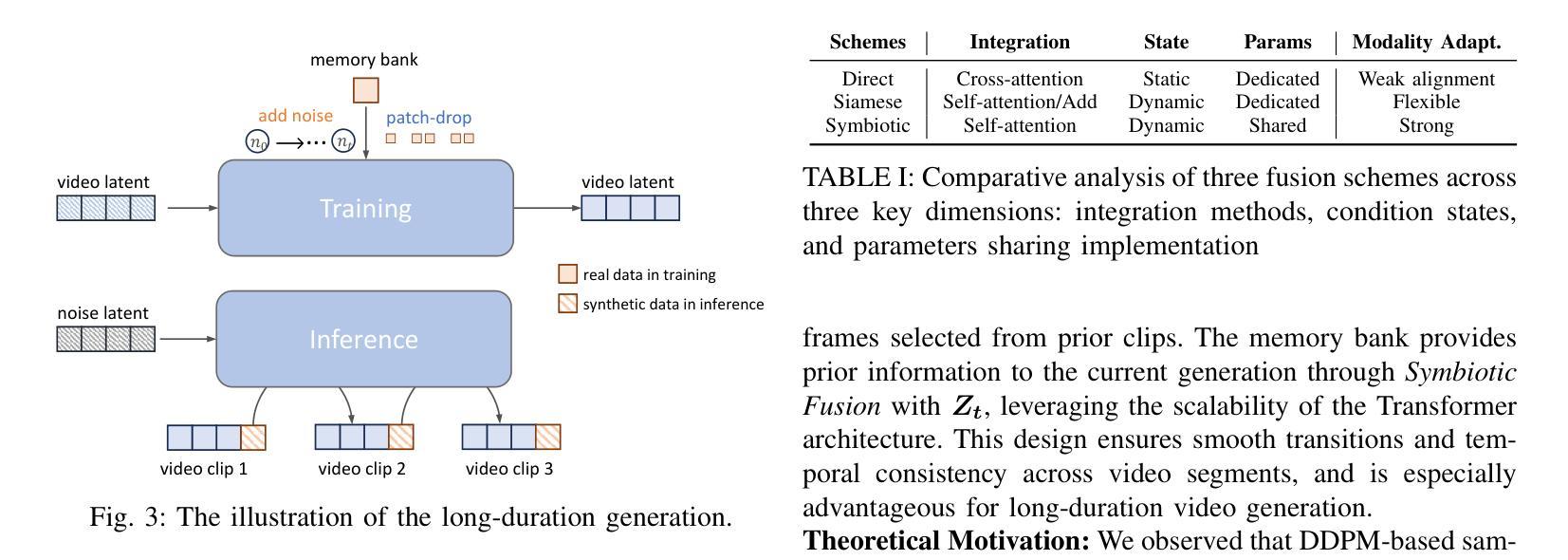
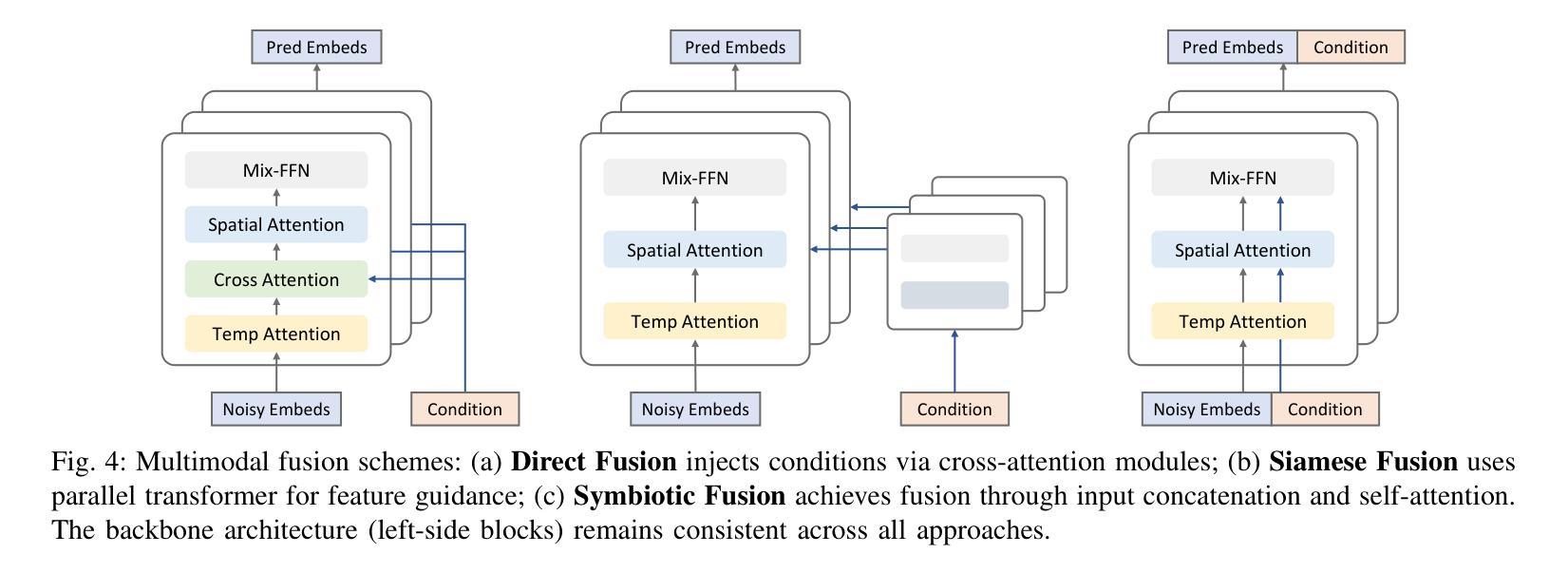
Long-duration talking video synthesis faces persistent challenges in simultaneously achieving high video quality, portrait and temporal consistency, and computational efficiency. As video length increases, issues such as visual degradation, loss of identity consistency, temporal incoherence, and error accumulation become increasingly prominent, severely impacting the realism and reliability of generated results. To address these issues, we present LetsTalk, a diffusion transformer framework that incorporates multimodal guidance and a novel memory bank mechanism, explicitly maintaining contextual continuity and enabling robust, high-quality, and efficient long-duration talking video generation. Specifically, LetsTalk introduces a memory bank combined with a noise-regularized training strategy to mitigate error accumulation and sampling artifacts during long video generation. To further enhance efficiency and spatiotemporal consistency, LetsTalk employs a deep compression autoencoder and a spatiotemporal-aware transformer with linear attention for effective multimodal fusion. Furthermore, we systematically analyze three multimodal fusion schemes, adopting deep (Symbiotic Fusion) for portrait features to ensure visual consistency, and shallow (Direct Fusion) for audio to synchronize animation with speech while preserving motion diversity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LetsTalk achieves state-of-the-art generation quality, producing temporally coherent and realistic talking videos with enhanced diversity and liveliness, while maintaining remarkable efficiency with 8 fewer parameters than previous approaches.
长期对话视频合成面临着持续挑战,尤其是在同时实现高质量视频、肖像和时序一致性以及计算效率方面。随着视频长度的增加,视觉失真、身份一致性丧失、时序不一致和误差累积等问题变得越来越突出,严重影响到生成结果的真实性和可靠性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了LetsTalk,这是一个融合了多模态指导和新式存储库机制的扩散变压器框架,可以明确地保持上下文连续性,并实现稳健、高质量和高效的长期对话视频生成。具体来说,LetsTalk引入了结合噪声正则化训练策略的存储库,以减轻长视频生成过程中的误差累积和采样伪影。为了进一步提高效率和时空一致性,LetsTalk采用深度压缩自编码器和具有线性注意力的时空感知变压器,以实现有效的多模态融合。此外,我们系统地分析了三种多模态融合方案,采用深度(共生融合)用于肖像特征以确保视觉一致性,以及浅层(直接融合)用于音频,以同步动画和语音同时保持动作多样性。大量实验表明,LetsTalk达到了最先进的生成质量,产生了时序一致和逼真的对话视频,具有增强的多样性和生动性,同时保持了卓越的效率,比以前的方法少了8个参数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本摘要介绍了长期对话视频合成面临的挑战以及应对方案。为了解决高质量视频生成过程中的视觉失真、身份一致性丧失、时间不一致和误差累积等问题,提出了一种名为LetsTalk的扩散变换框架。该框架结合了多模式指导和新型记忆库机制,显式维护上下文连续性,实现稳健、高效、高质量的长时对话视频生成。实验证明,LetsTalk达到了最先进的生成质量,生成的对话视频具有时间连贯性和逼真度,同时保持了出色的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 长期对话视频合成面临诸多挑战,如高视频质量、肖像和时间一致性以及计算效率的平衡。
- 提出的LetsTalk框架结合了多模式指导和新型记忆库机制,以改善视频生成的质量。
- 记忆库和噪声正则化训练策略有助于减少长视频生成过程中的误差累积和采样伪影。
- 框架采用深度压缩自编码器和时空感知变压器来提高效率和时空一致性。
- 三种多模式融合方案的系统分析显示,深度融合适用于肖像特征以确保视觉一致性,而浅层融合适用于音频以同步动画和语音同时保持动作多样性。
- 实验表明,LetsTalk达到了最先进的生成质量,能生成连贯且逼真的对话视频,并维持了高效率。
点此查看论文截图