⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-22 更新
Local Scale Equivariance with Latent Deep Equilibrium Canonicalizer
Authors:Md Ashiqur Rahman, Chiao-An Yang, Michael N. Cheng, Lim Jun Hao, Jeremiah Jiang, Teck-Yian Lim, Raymond A. Yeh
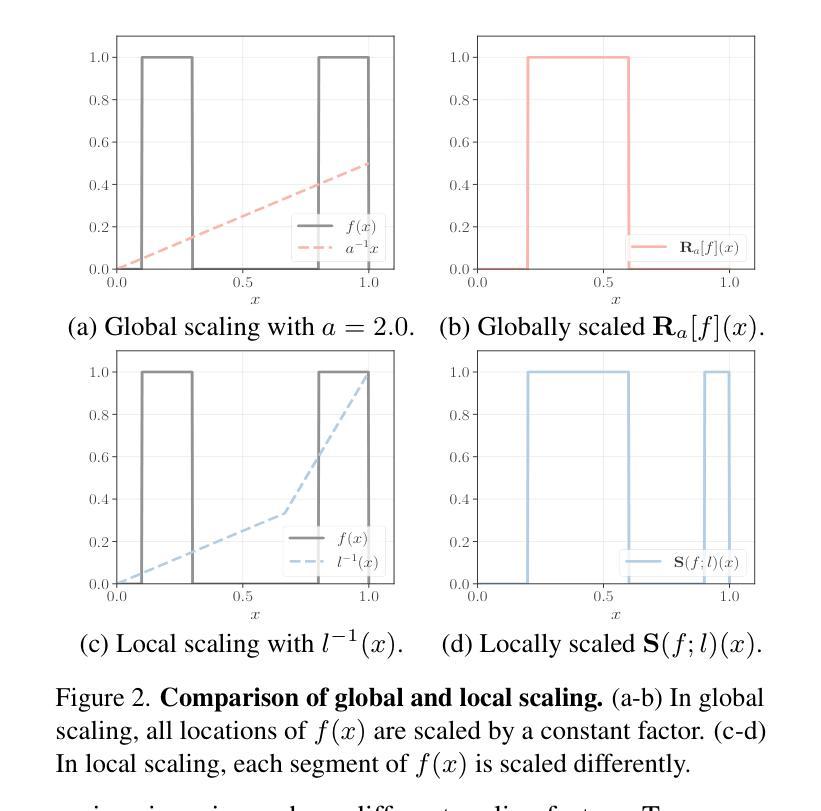
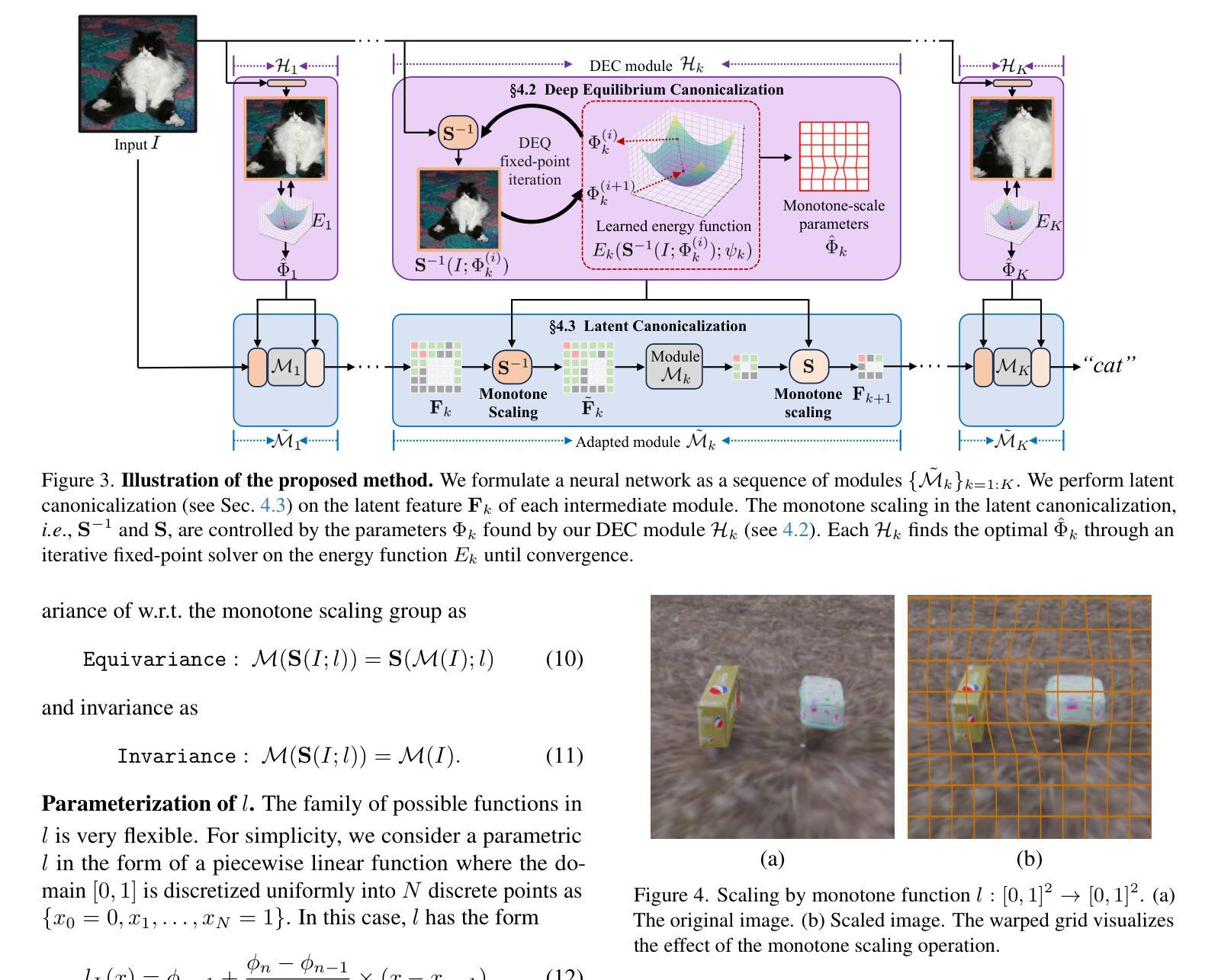
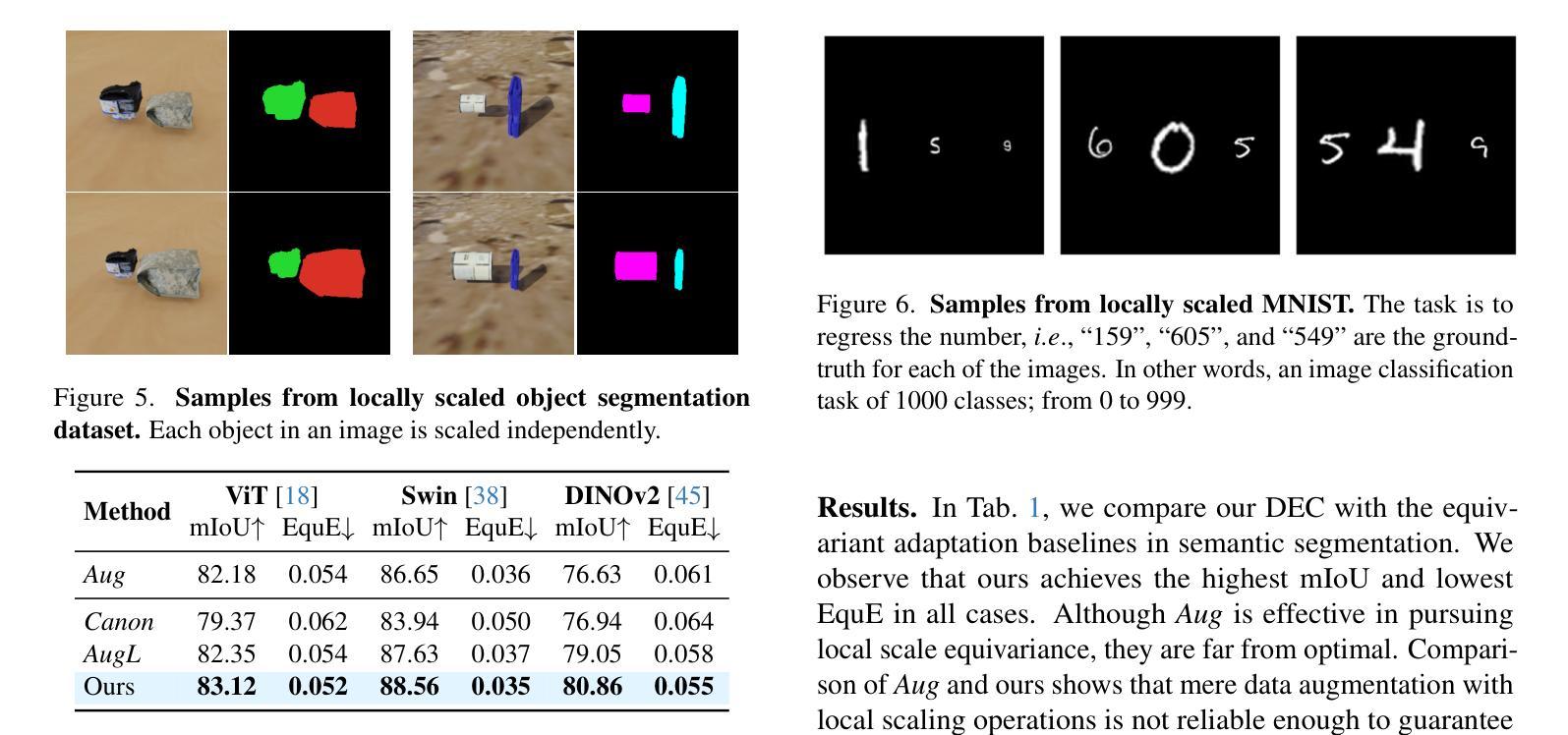
Scale variation is a fundamental challenge in computer vision. Objects of the same class can have different sizes, and their perceived size is further affected by the distance from the camera. These variations are local to the objects, i.e., different object sizes may change differently within the same image. To effectively handle scale variations, we present a deep equilibrium canonicalizer (DEC) to improve the local scale equivariance of a model. DEC can be easily incorporated into existing network architectures and can be adapted to a pre-trained model. Notably, we show that on the competitive ImageNet benchmark, DEC improves both model performance and local scale consistency across four popular pre-trained deep-nets, e.g., ViT, DeiT, Swin, and BEiT. Our code is available at https://github.com/ashiq24/local-scale-equivariance.
尺度变化是计算机视觉中的基本挑战。同一类的物体可以有不同的尺寸,并且它们的感知尺寸还会受到与相机距离的影响。这些变化是局部针对物体的,即同一图像内不同物体的尺寸可能有不同的变化。为了有效地处理尺度变化,我们提出了一种深度平衡规范器(DEC)来改善模型的局部尺度等价性。DEC可以轻松地融入现有的网络架构,并适应预训练模型。值得注意的是,我们在具有竞争力的ImageNet基准测试上展示了DEC在四个流行的预训练深度网络(例如ViT、DeiT、Swin和BeiT)上提高了模型性能和局部尺度一致性。我们的代码位于https://github.com/ashiq24/local-scale-equivariance。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了尺度变化在计算机视觉中的基本挑战。同一类别的物体可能具有不同的尺寸,并且其尺寸感知会受到与相机距离的影响。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种深度均衡规范化器(DEC)以提高模型的局部尺度等变性。DEC可轻松融入现有网络架构并适应预训练模型。在ImageNet基准测试中,DEC提高了模型性能并增强了四种流行预训练深度网络的局部尺度一致性,如ViT、DeiT、Swin和BEiT。
Key Takeaways
- 尺度变化是计算机视觉中的基本挑战,影响物体识别和分类。
- 同一类别的物体可能因为尺度变化导致识别困难。
- 深度均衡规范化器(DEC)可以提高模型的局部尺度等变性,应对尺度变化挑战。
- DEC易于融入现有网络架构,并可适应预训练模型。
- 在ImageNet基准测试中,DEC提高了模型性能。
- DEC增强了四种预训练深度网络的局部尺度一致性。
点此查看论文截图

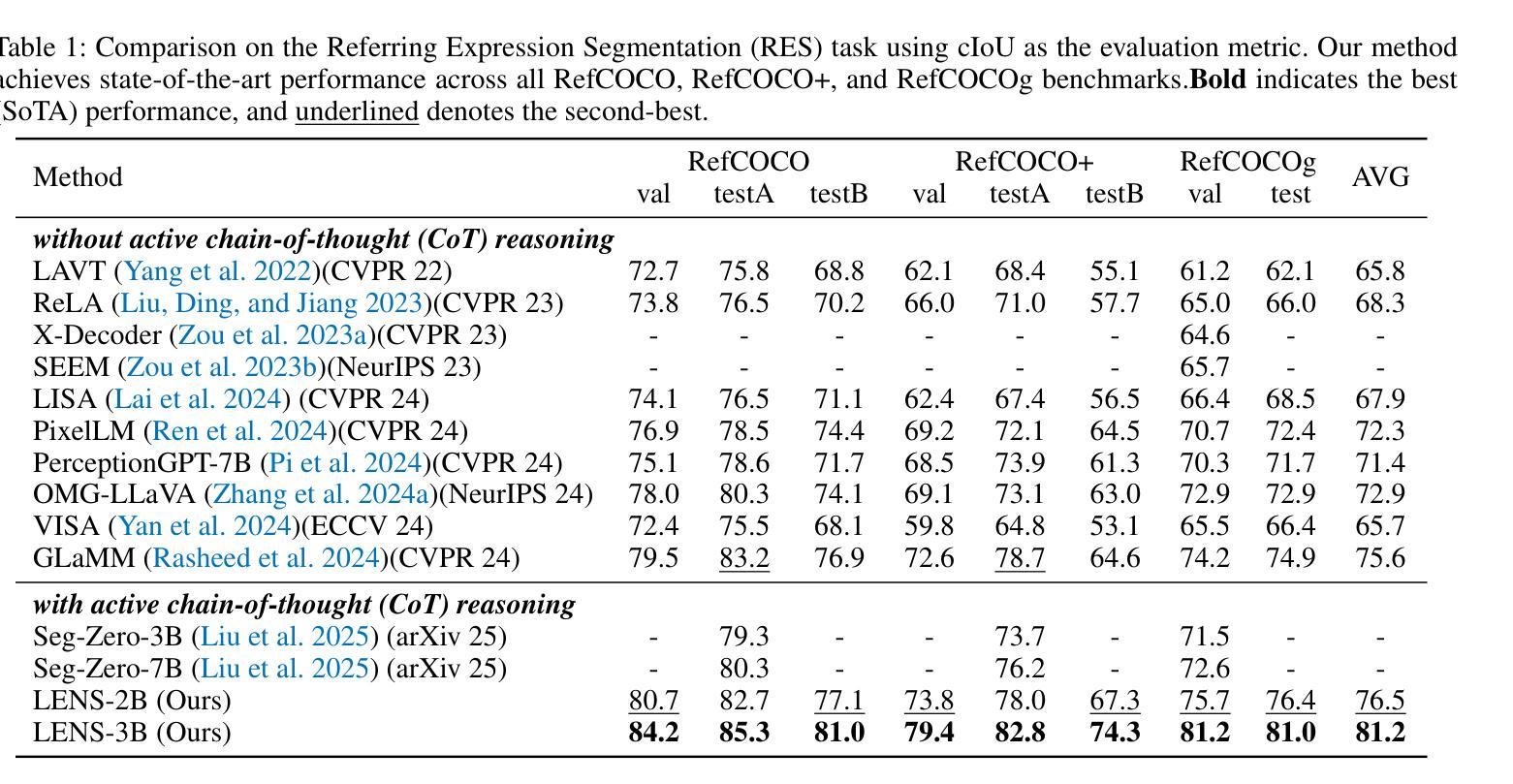
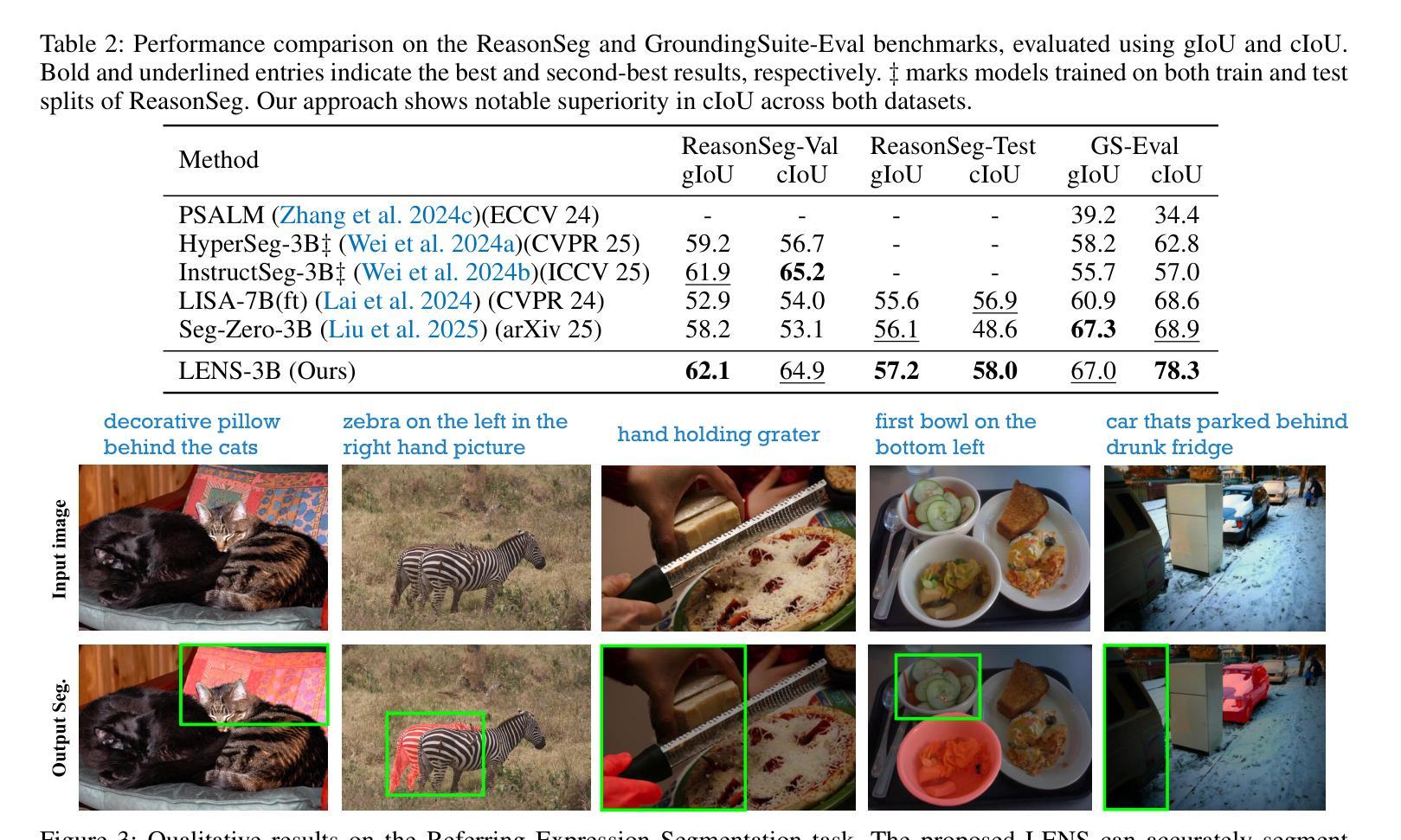
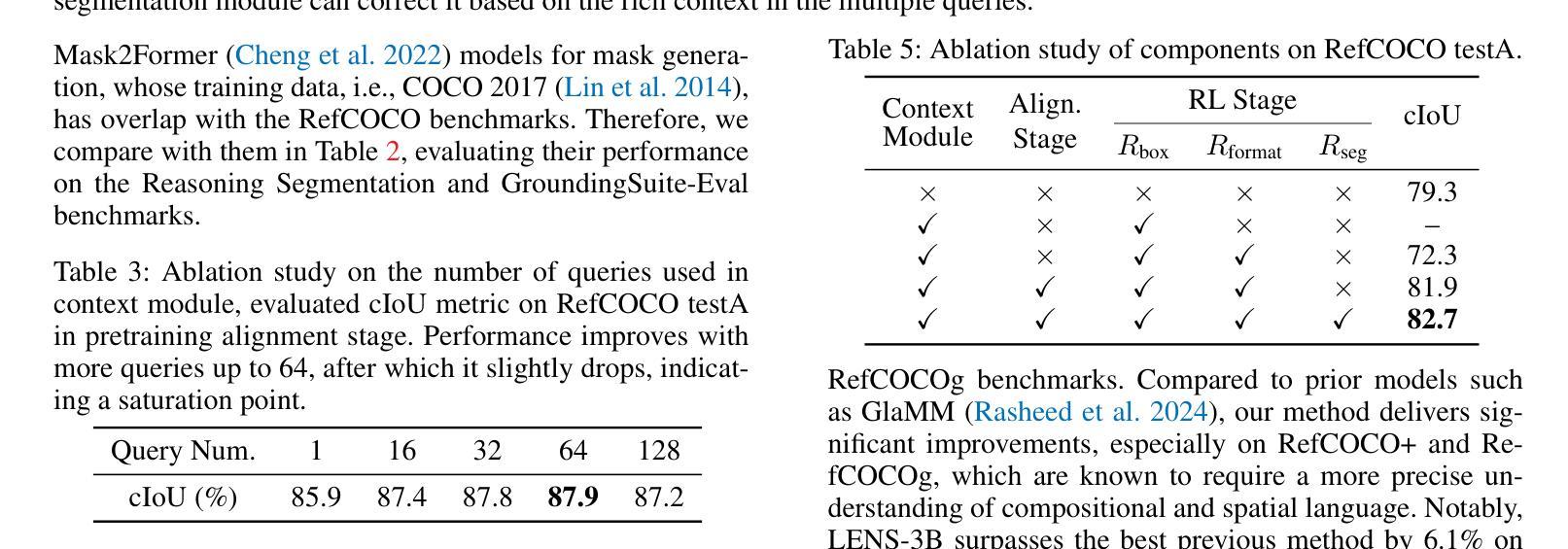
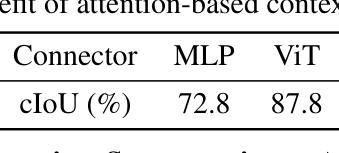
LENS: Learning to Segment Anything with Unified Reinforced Reasoning
Authors:Lianghui Zhu, Bin Ouyang, Yuxuan Zhang, Tianheng Cheng, Rui Hu, Haocheng Shen, Longjin Ran, Xiaoxin Chen, Li Yu, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang
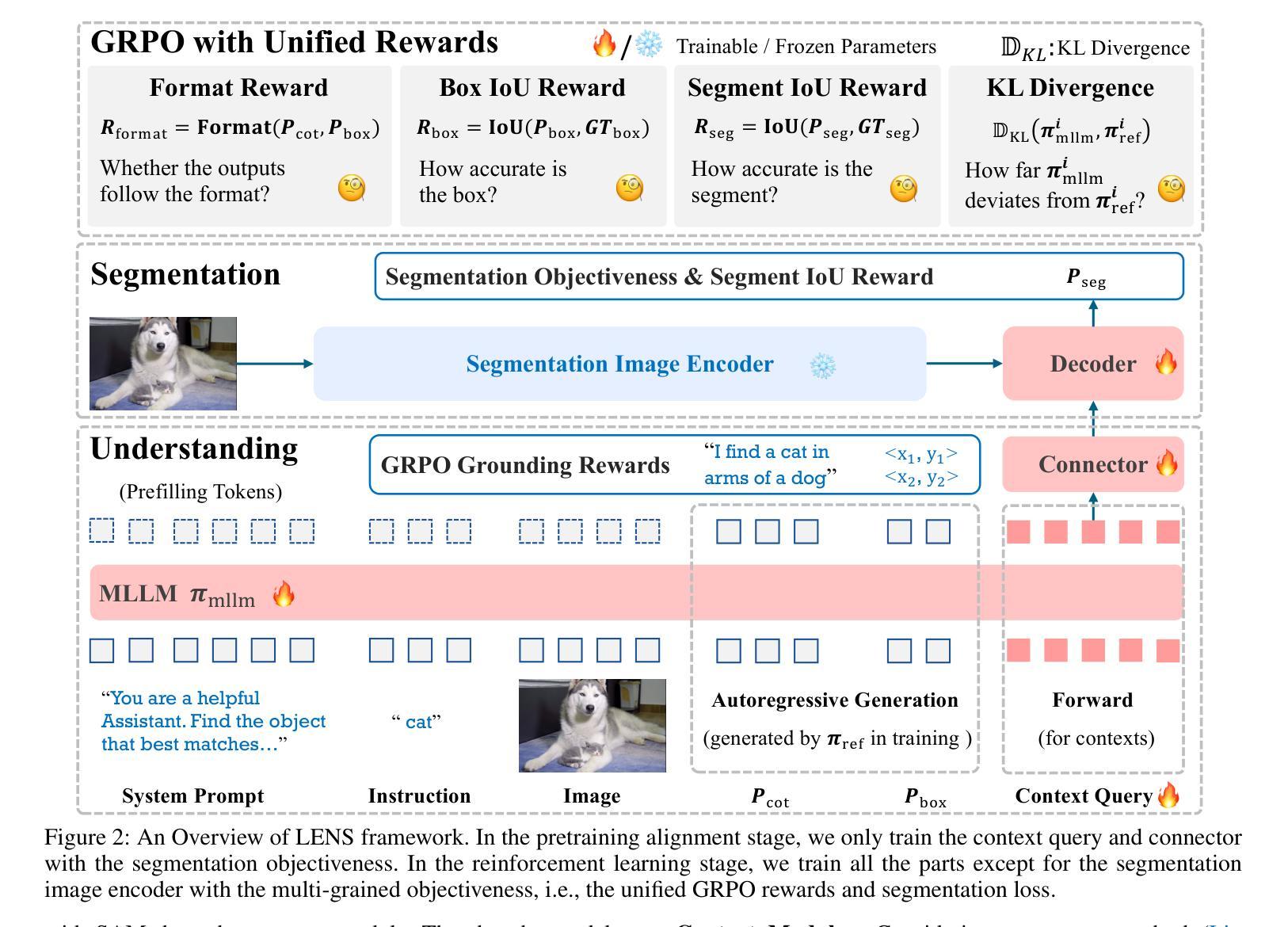
Text-prompted image segmentation enables fine-grained visual understanding and is critical for applications such as human-computer interaction and robotics. However, existing supervised fine-tuning methods typically ignore explicit chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning at test time, which limits their ability to generalize to unseen prompts and domains. To address this issue, we introduce LENS, a scalable reinforcement-learning framework that jointly optimizes the reasoning process and segmentation in an end-to-end manner. We propose unified reinforcement-learning rewards that span sentence-, box-, and segment-level cues, encouraging the model to generate informative CoT rationales while refining mask quality. Using a publicly available 3-billion-parameter vision-language model, i.e., Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct, LENS achieves an average cIoU of 81.2% on the RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg benchmarks, outperforming the strong fine-tuned method, i.e., GLaMM, by up to 5.6%. These results demonstrate that RL-driven CoT reasoning serves as a robust prior for text-prompted segmentation and offers a practical path toward more generalizable Segment Anything models. Code is available at https://github.com/hustvl/LENS.
文本提示的图像分割技术为实现精细粒度的视觉理解提供了可能,对于人机交互和机器人技术等应用至关重要。然而,现有的监督微调方法通常在测试时忽略了明确的思维链(CoT)推理,这限制了它们对未见过的提示和领域的泛化能力。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了LENS,这是一个可扩展的强化学习框架,以端到端的方式联合优化推理过程和分割。我们提出了统一的强化学习奖励,涵盖句子、框和分段级别的线索,鼓励模型在细化掩膜质量的同时生成信息丰富的CoT推理。我们使用公开的30亿参数视觉语言模型(即Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct),在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg基准测试上实现了平均cIoU为81.2%,超越了强大的微调方法(即GLaMM)高达5.6%。这些结果表明,RL驱动的CoT推理为文本提示的分割提供了一个稳健的先验,并为实现更具泛化能力的“分割任何事物”模型提供了实际途径。相关代码可在https://github.com/hustvl/LENS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is released at https://github.com/hustvl/LENS
Summary
本文介绍了LENS框架,该框架采用强化学习优化推理过程和图像分割,通过统一奖励机制整合句子、框和分割级别的线索,鼓励模型生成有说服力的理由同时改进掩模质量。在RefCOCO等基准测试中,使用公开可用的视觉语言模型Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct时,LENS的平均cIoU为81.2%,超越强精细方法GLaMM高达5.6%。表明强化学习驱动的链式推理对于文本提示分割具有稳健性,并为更通用的分割模型提供了实用路径。
Key Takeaways
- LENS框架首次将强化学习应用于文本提示的图像分割任务,优化推理过程和分割。
- LENS框架通过统一奖励机制整合不同级别的线索,提升模型性能。
- Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct视觉语言模型在基准测试中表现优异,与GLaMM相比有显著优势。
- LENS框架在RefCOCO等基准测试的平均cIoU达到81.2%,显示出其强大的性能。
- 强化学习驱动的链式推理为文本提示分割任务提供了稳健的先验知识。
- LENS框架的代码已公开,为相关研究提供便利。
点此查看论文截图

ViT-FIQA: Assessing Face Image Quality using Vision Transformers
Authors:Andrea Atzori, Fadi Boutros, Naser Damer
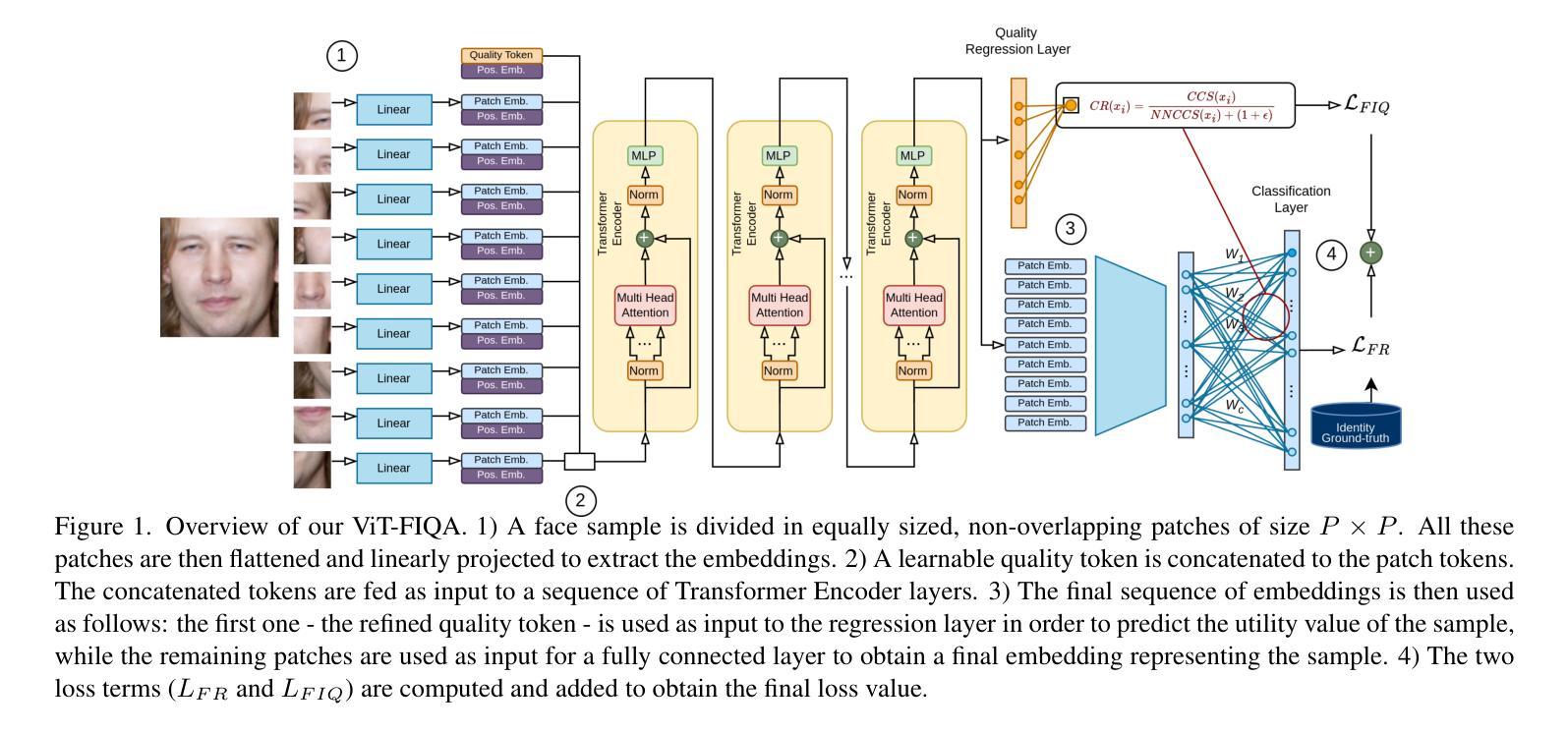
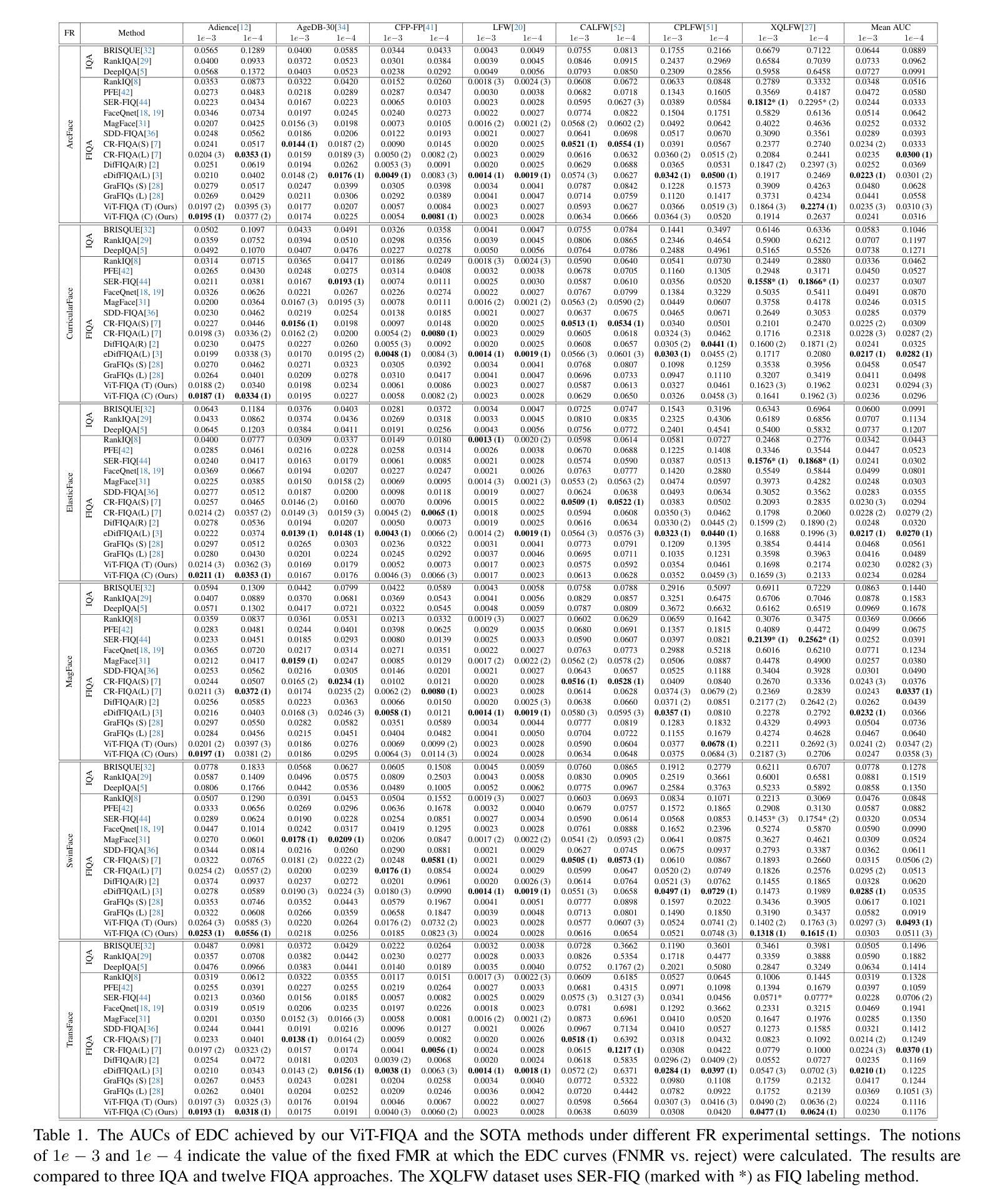
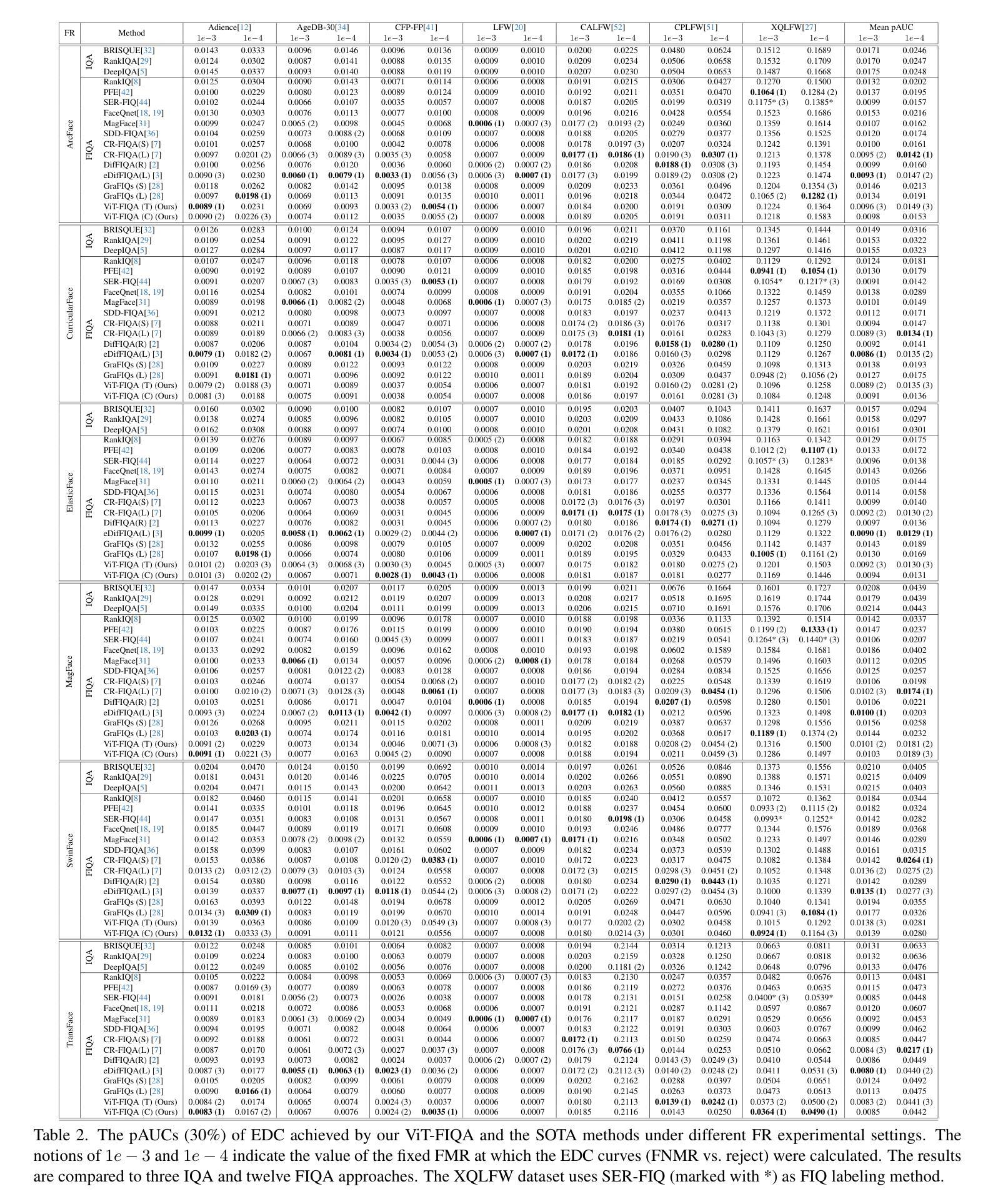
Face Image Quality Assessment (FIQA) aims to predict the utility of a face image for face recognition (FR) systems. State-of-the-art FIQA methods mainly rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs), leaving the potential of Vision Transformer (ViT) architectures underexplored. This work proposes ViT-FIQA, a novel approach that extends standard ViT backbones, originally optimized for FR, through a learnable quality token designed to predict a scalar utility score for any given face image. The learnable quality token is concatenated with the standard image patch tokens, and the whole sequence is processed via global self-attention by the ViT encoders to aggregate contextual information across all patches. At the output of the backbone, ViT-FIQA branches into two heads: (1) the patch tokens are passed through a fully connected layer to learn discriminative face representations via a margin-penalty softmax loss, and (2) the quality token is fed into a regression head to learn to predict the face sample’s utility. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks and several FR models, including both CNN- and ViT-based architectures, demonstrate that ViT-FIQA consistently achieves top-tier performance. These results underscore the effectiveness of transformer-based architectures in modeling face image utility and highlight the potential of ViTs as a scalable foundation for future FIQA research https://cutt.ly/irHlzXUC.
人脸识别图像质量评估(FIQA)旨在预测人脸图像对人脸识别(FR)系统的实用性。最先进的FIQA方法主要依赖于卷积神经网络(CNN),而忽略了对视觉转换器(ViT)架构的潜在探索。这项工作提出了ViT-FIQA,这是一种新方法,它通过扩展标准ViT骨干网,结合一个可学习的质量令牌,能够预测任何给定人脸图像的质量分数,从而达到优化的效果。这个可学习的质量令牌被拼接到标准的图像补丁令牌中,然后通过全局自注意力处理的ViT编码器来处理整个序列信息聚合在所有补丁中。在骨干网输出端,ViT-FIQA分为两个分支:(1)补丁令牌通过全连接层学习判别性面部表示,通过边界损失进行softmax损失;(2)质量令牌被送入回归头学习预测面部样本的效用。在具有挑战性的基准测试和对包括CNN和ViT架构在内的人脸识别模型的广泛实验中,证明了ViT-FIQA始终达到了顶尖的性能水平。这些结果证明了基于转换器的架构在建模人脸图像效用方面的有效性,并突出了ViT作为未来FIQA研究可扩展基础的潜力。https://cutt.ly/irHlzXUC。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops 2025 (ICCVW 2025)
Summary
本文提出了ViT-FIQA,这是一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构的新方法,用于面部图像质量评估(FIQA)。它通过设计可学习的质量令牌来扩展标准的ViT骨干网,该令牌可以预测给定面部图像标量效用分数。在面部识别(FR)系统的背景下,ViT-FIQA展示了其卓越性能,为未来的FIQA研究提供了可扩展的基础。
Key Takeaways
- ViT-FIQA是基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构进行面部图像质量评估(FIQA)的新方法。
- 方法通过设计可学习的质量令牌来扩展标准的ViT骨干网。
- 质量令牌用于预测给定面部图像的效用分数。
- ViT-FIQA通过全局自注意力机制聚合所有补丁的上下文信息。
- 方法包括两个分支:一个用于学习面部表示,另一个用于预测面部样本的效用。
- 在具有挑战性的基准测试和各种面部识别模型上,ViT-FIQA均取得了顶尖性能。
点此查看论文截图