⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
Hessian-based lightweight neural network for brain vessel segmentation on a minimal training dataset
Authors:Alexandra Bernadotte, Elfimov Nikita, Mikhail Shutov, Ivan Menshikov
Accurate segmentation of blood vessels in brain magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is essential for successful surgical procedures, such as aneurysm repair or bypass surgery. Currently, annotation is primarily performed through manual segmentation or classical methods, such as the Frangi filter, which often lack sufficient accuracy. Neural networks have emerged as powerful tools for medical image segmentation, but their development depends on well-annotated training datasets. However, there is a notable lack of publicly available MRA datasets with detailed brain vessel annotations. To address this gap, we propose a novel semi-supervised learning lightweight neural network with Hessian matrices on board for 3D segmentation of complex structures such as tubular structures, which we named HessNet. The solution is a Hessian-based neural network with only 6000 parameters. HessNet can run on the CPU and significantly reduces the resource requirements for training neural networks. The accuracy of vessel segmentation on a minimal training dataset reaches state-of-the-art results. It helps us create a large, semi-manually annotated brain vessel dataset of brain MRA images based on the IXI dataset (annotated 200 images). Annotation was performed by three experts under the supervision of three neurovascular surgeons after applying HessNet. It provides high accuracy of vessel segmentation and allows experts to focus only on the most complex important cases. The dataset is available at https://git.scinalytics.com/terilat/VesselDatasetPartly.
在脑部磁共振血管造影(MRA)中,对血管进行精确分割对于成功的手术程序至关重要,例如动脉瘤修复或搭桥手术。目前,注释主要通过手动分割或经典方法(如Frangi滤波器)进行,但这些方法往往缺乏足够的准确性。神经网络已作为医学图像分割的强大工具出现,但其发展取决于经过良好注释的训练数据集。然而,存在明显的缺乏带有详细脑血管注释的公开MRA数据集。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了一种新型半监督学习轻量级神经网络,该网络在板上配备了Hessian矩阵,用于对管状结构等复杂结构进行3D分割,我们将其命名为HessNet。该解决方案是基于Hessian的神经网络,仅有600related参数。HessNet可在CPU上运行,显着降低了训练神经网络所需的资源要求。在最小训练数据集上的血管分割精度达到了业界领先的结果。它帮助我们基于IXI数据集创建了一个大规模的半手动注释的脑部血管数据集(注释了200张图像)。在神经血管外科医生的监督下,三名专家在应用了HessNet之后进行了注释。它提供了高精度的血管分割,并允许专家专注于最复杂且最重要的病例。数据集可在https://git.scinalytics.com/terilat/VesselDatasetPartly找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文介绍了在脑磁共振血管造影(MRA)中准确分割血管的重要性,并指出目前主要依赖手动分割或经典方法(如Frangi滤波器),但准确性不足。神经网络在医学图像分割中具有潜力,但缺乏详细的MRA数据集。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种基于Hessian矩阵的半监督学习轻量化神经网络(HessNet),用于3D复杂结构(如管状结构)的分割。HessNet仅包含6000个参数,可在CPU上运行,显著降低了训练神经网络所需的资源。在小型训练数据集上的血管分割精度达到了最新水平。利用HessNet,基于IXI数据集创建了一个大型半手动注释的脑MRA图像脑血管数据集,专家可在神经血管外科医生的监督下标注图像,确保高精确度。数据集可在链接获取。
Key Takeaways
- 准确的大脑血管分割对成功进行外科手术(如动脉瘤修复和搭桥手术)至关重要。
- 当前方法(如手动分割和Frangi滤波器)在血管分割方面的准确性不足。
- 神经网络在医学图像分割中具有优势,但需要良好的注释训练数据集。
- 缺乏具有详细大脑血管注释的公开MRA数据集。
- 提出了一种基于Hessian矩阵的半监督学习轻量化神经网络(HessNet),用于复杂结构(如管状结构)的3D分割。
- HessNet可在CPU上运行,显著降低训练神经网络所需的资源。
点此查看论文截图

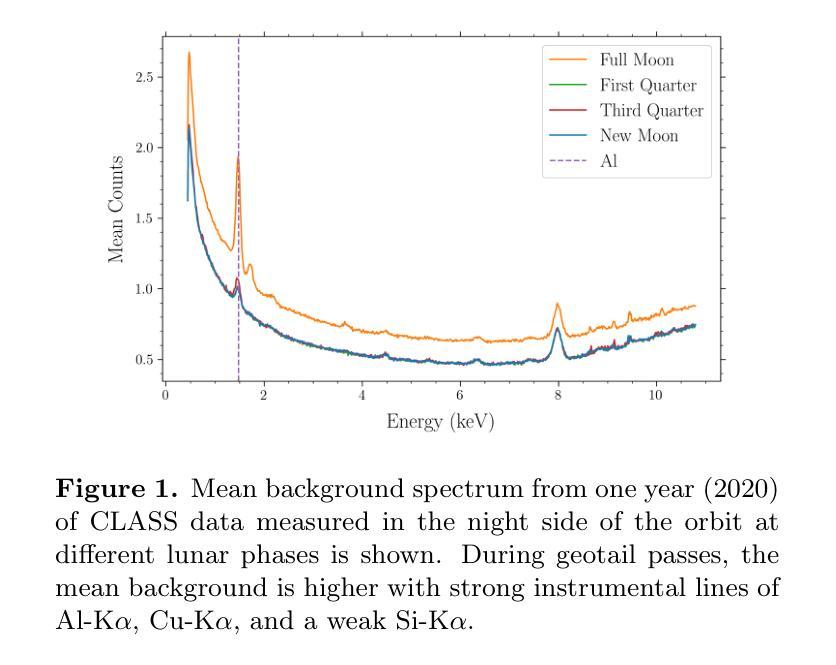
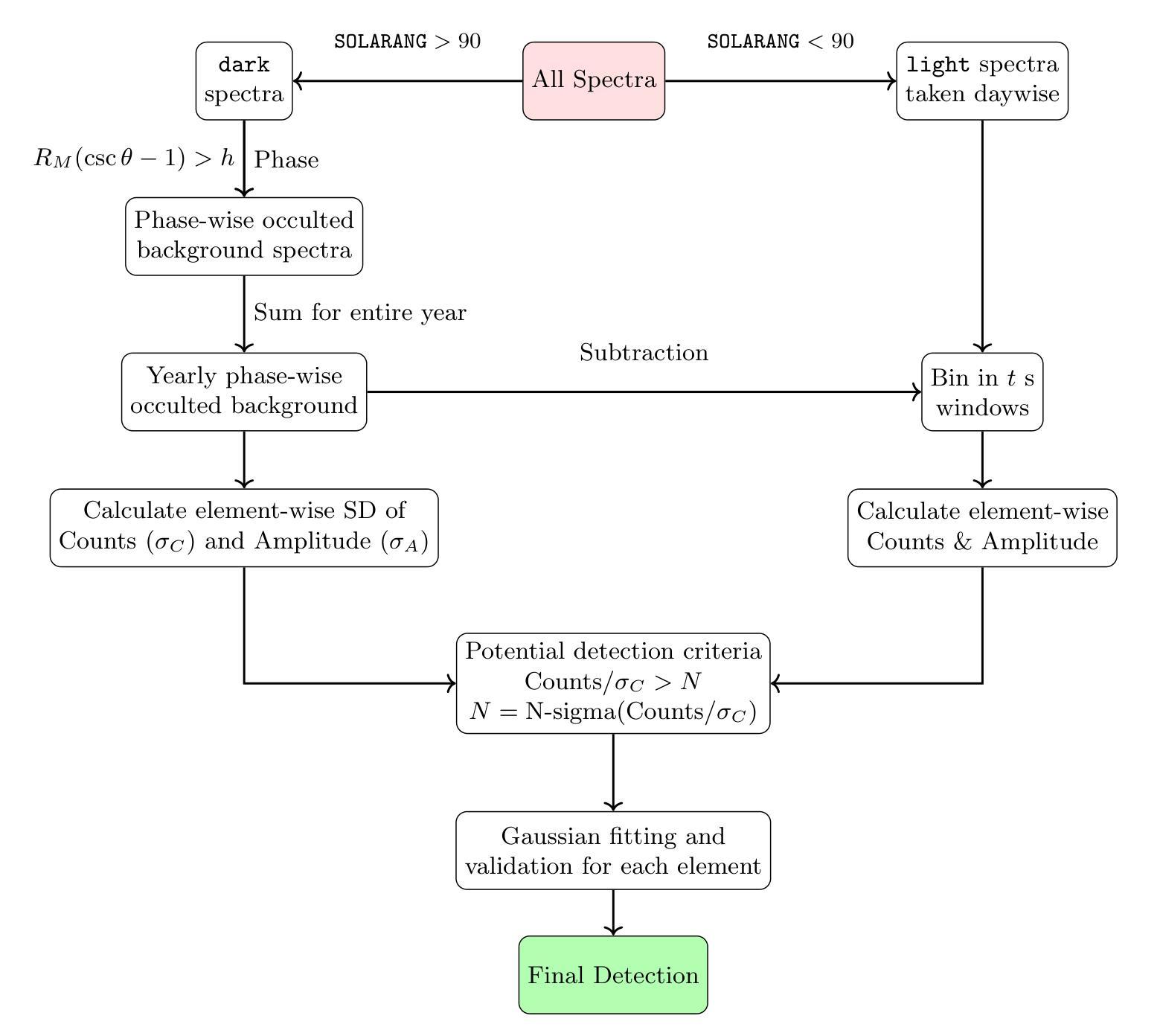
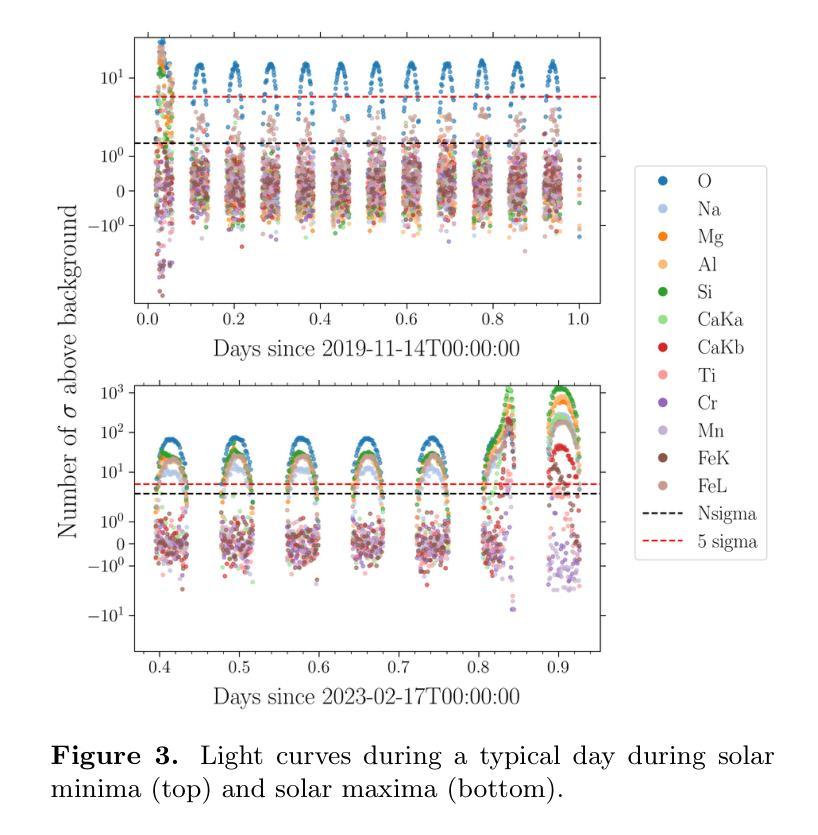
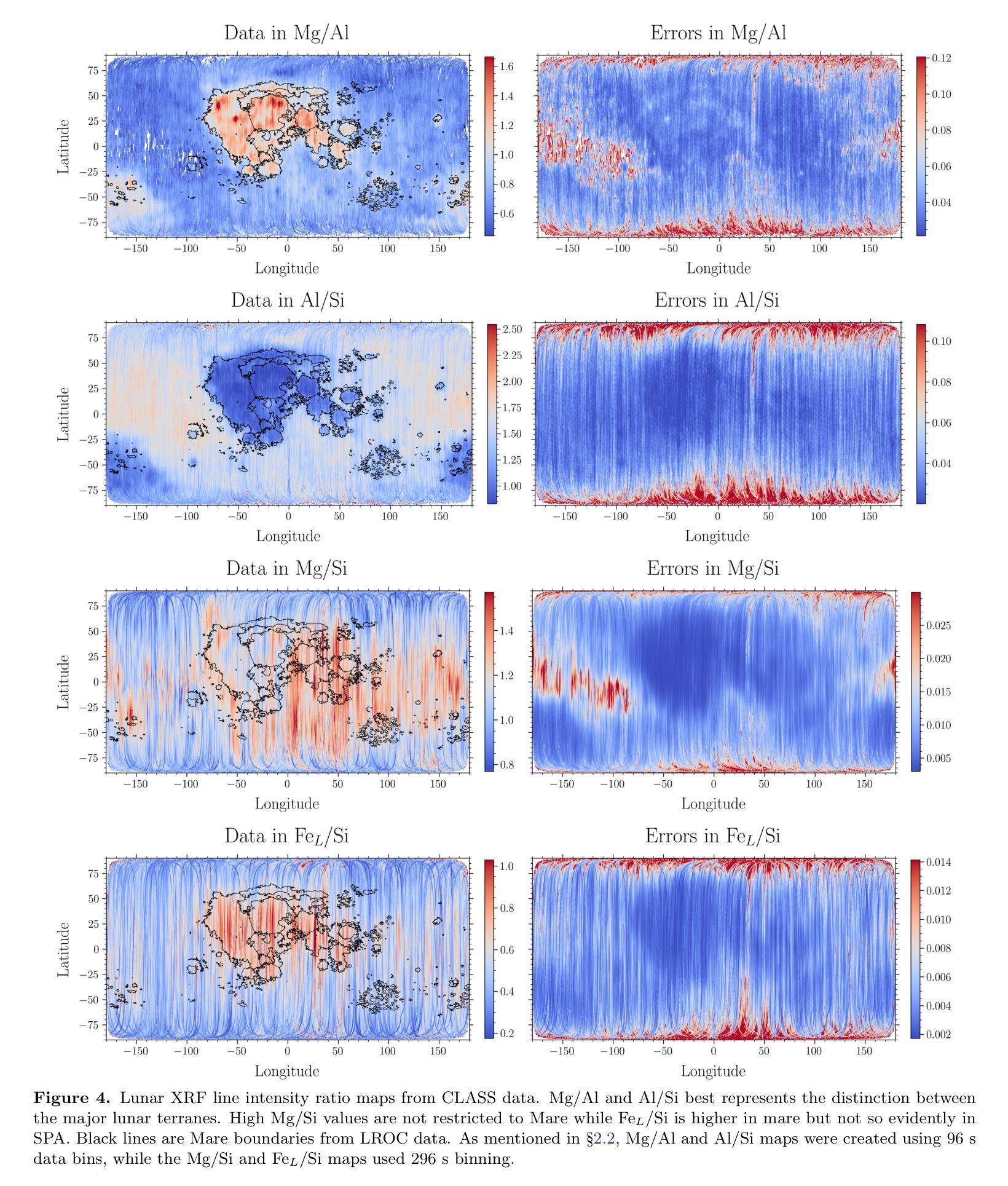
Lunar geochemistry from X-ray line flux ratios using CLASS on Chandrayaan 2
Authors:R. Kumar, Y. Rai, S. Srijan, A. Bansal, Ameya V Singh, A. Kumar, H. Mhatre, M. Goyal, S. Swain, S. Patidar, Aditya P Saikia, A. Ahmad, S. Narendranath, Netra S Pillai, R. Kashyap, V. Bhalerao
Global lunar chemical maps are essential for understanding the origin and evolution of the Moon, its surface characteristics, and its potential for resource extraction. Lunar elemental abundance maps have been derived using X-ray and gamma ray spectroscopy previously but are limited in coverage or have coarse spatial resolution. Here we used X-ray fluorescence line intensity of O, Mg, Al, Si, Ca and Fe derived from five years of data from the Chandrayaan-2 Large Area Soft X-ray Spectrometer (CLASS) to generate global O/Si, Mg/Si, Al/Si, Mg/Al, Ca/Si and Fe/Si line intensity ratio maps at a resolution of 5.3 km/pixel. We have developed an independent data analysis methodology for CLASS, based on open source Python packages. Our analysis shows that the Mg/Al map best represents the geochemical differences between the major terranes, consistent with the findings of the Apollo 15 and 16 X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (XRS) maps. We have also shown a good correlation of the line intensity ratios with the abundance ratios from CLASS using published elemental abundance maps. Further, we apply Gaussian mixture models to the Mg/Si vs Al/Si density maps to map geochemically distinct regions on the Moon that could be of interest for future investigations.
全球月球化学地图对于了解月球的起源和演化、月球表面特征以及其资源提取潜力至关重要。之前已经使用X射线和伽马射线光谱法得到了月球元素丰度地图,但其覆盖范围有限或空间分辨率较低。这里我们使用了来自“嫦娥二号”大型区域软X射线光谱仪(CLASS)五年的数据,从中提取了氧、镁、铝、硅、钙和铁的X射线荧光线强度,生成了全球O/Si、Mg/Si、Al/Si、Mg/Al、Ca/Si和Fe/Si线强度比率地图,分辨率为每像素5.3公里。我们基于开源Python包开发了一种独立的CLASS数据分析方法。分析表明,Mg/Al地图最能反映主要地形的地球化学差异,这与阿波罗15号和16号X射线荧光光谱仪(XRS)地图的发现相一致。我们还展示了线强度比率与CLASS发布的元素丰度地图中的丰度比率之间的良好相关性。此外,我们对Mg/Si与Al/Si密度图应用高斯混合模型,在月球上绘制出地球化学特征明显的区域,这些区域可能对未来的研究感兴趣。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 9 figures. Submitted to the Planetary Science Journal
Summary
全球月球化学地图对于了解月球的起源和演化、表面特征以及资源提取潜力至关重要。以往利用X射线和伽马射线光谱法得到月球元素丰度地图,但覆盖范围有限或空间分辨率较粗。本研究利用来自“月船二号”大型区域软X射线光谱仪(CLASS)五年的数据,生成了全球O/Si、Mg/Si、Al/Si、Mg/Al、Ca/Si和Fe/Si线强度比率地图,空间分辨率为5.3公里/像素。研究采用基于开源Python包独立数据分析方法,发现Mg/Al地图最能反映主要地形的地球化学差异,并与阿波罗15号和16号的X射线荧光光谱仪(XRS)地图的发现相一致。此外,线强度比率与CLASS发布的元素丰度地图之间也呈现出良好的相关性。研究还应用高斯混合模型对Mg/Si与Al/Si密度地图进行分析,以绘制月球上地球化学特征不同的区域,为未来的研究提供兴趣点。
Key Takeaways
- 全球月球化学地图对理解月球特性及资源提取至关重要。
- 利用月船二号CLASS数据生成了高分辨月球元素比例地图。
- 独立数据分析方法基于开源Python包。
- Mg/Al地图反映主要地形地球化学差异,与阿波罗XRS地图一致。
- 线强度比率与元素丰度地图间存在良好相关性。
- 高斯混合模型用于分析Mg/Si与Al/Si密度地图。
点此查看论文截图

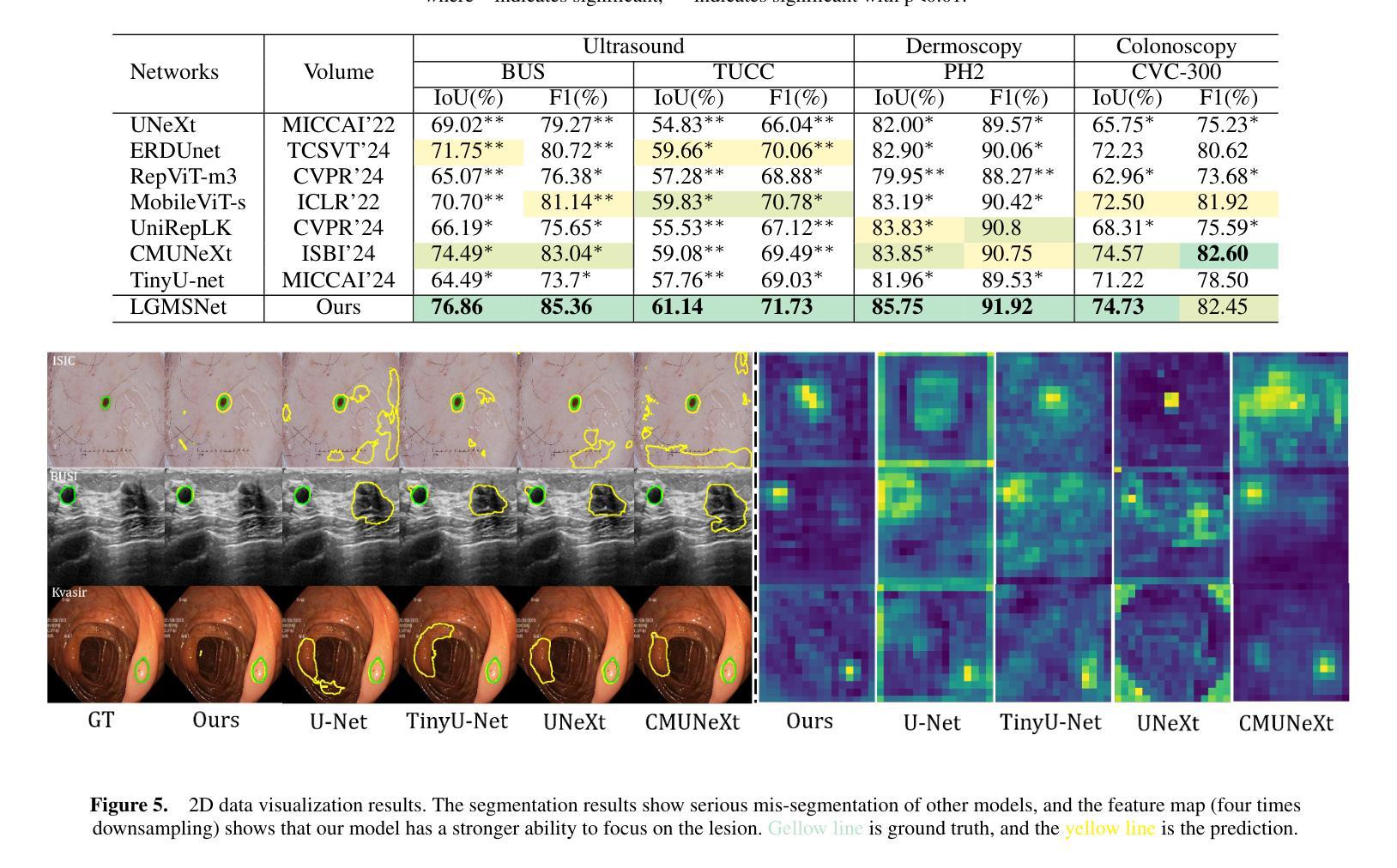
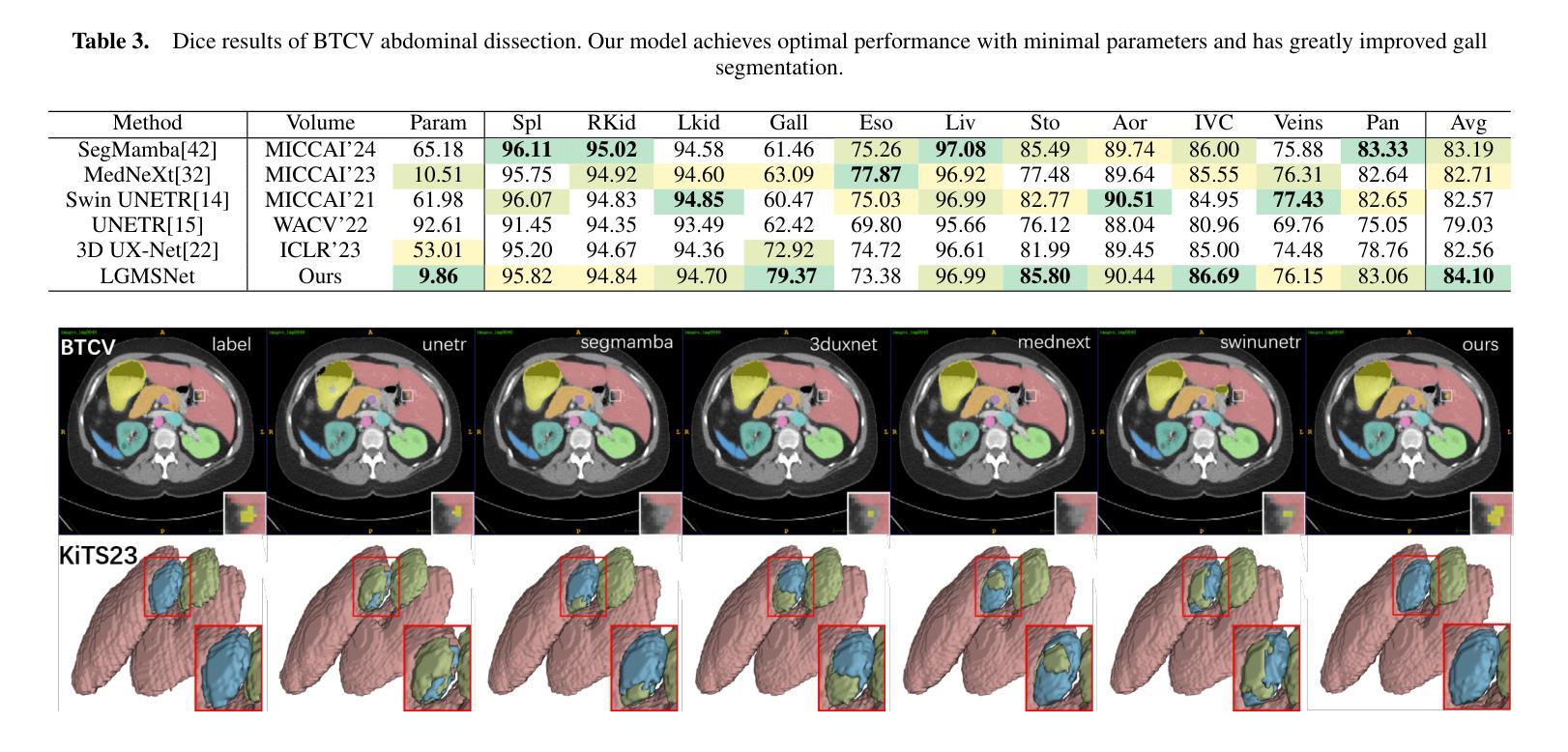
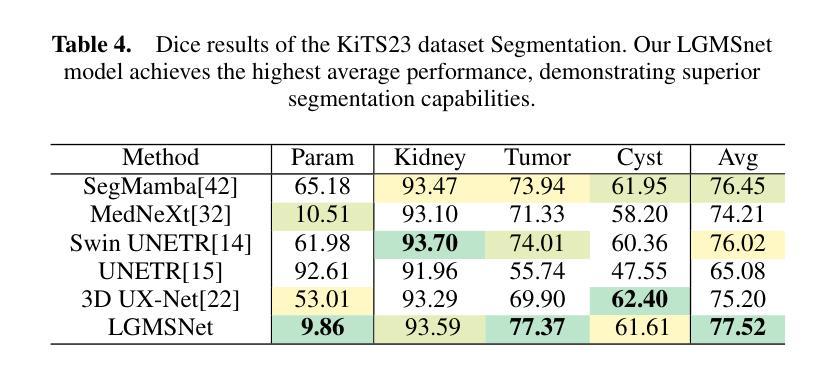
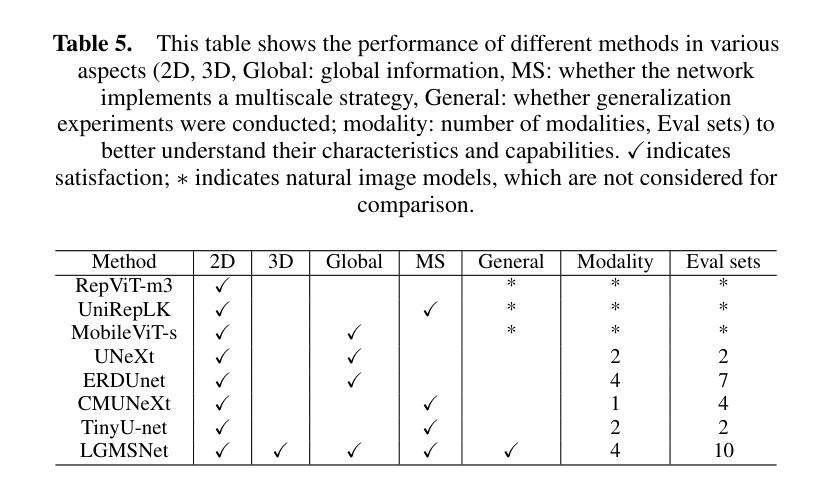
LGMSNet: Thinning a medical image segmentation model via dual-level multiscale fusion
Authors:Chengqi Dong, Fenghe Tang, Rongge Mao, Xinpei Gao, S. Kevin Zhou
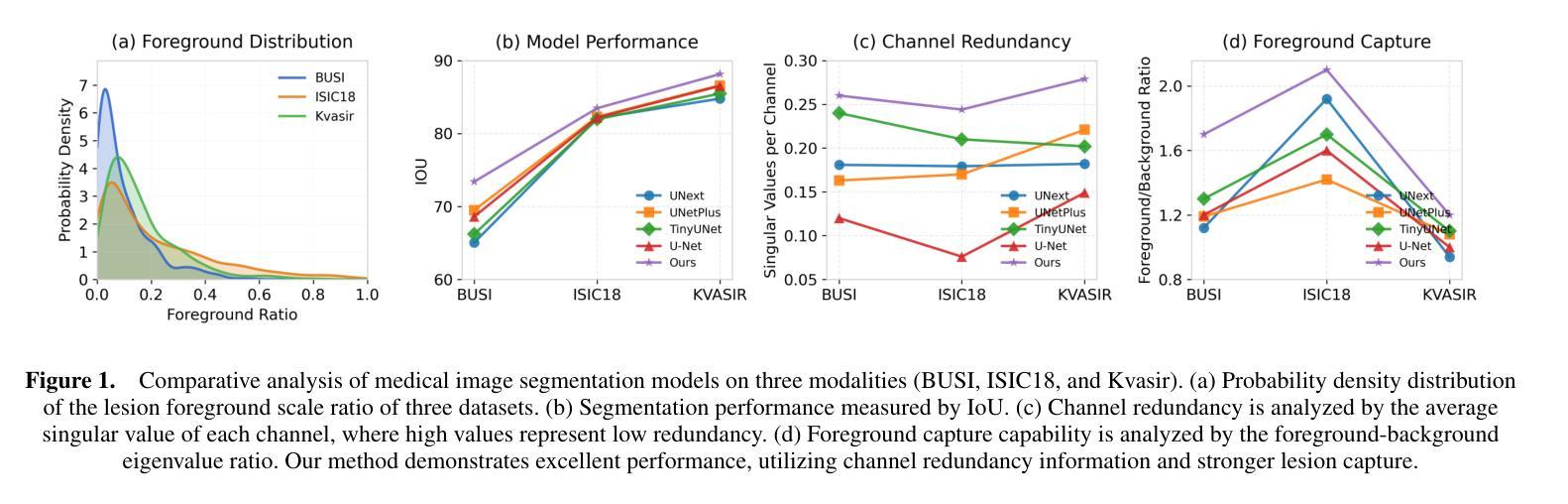
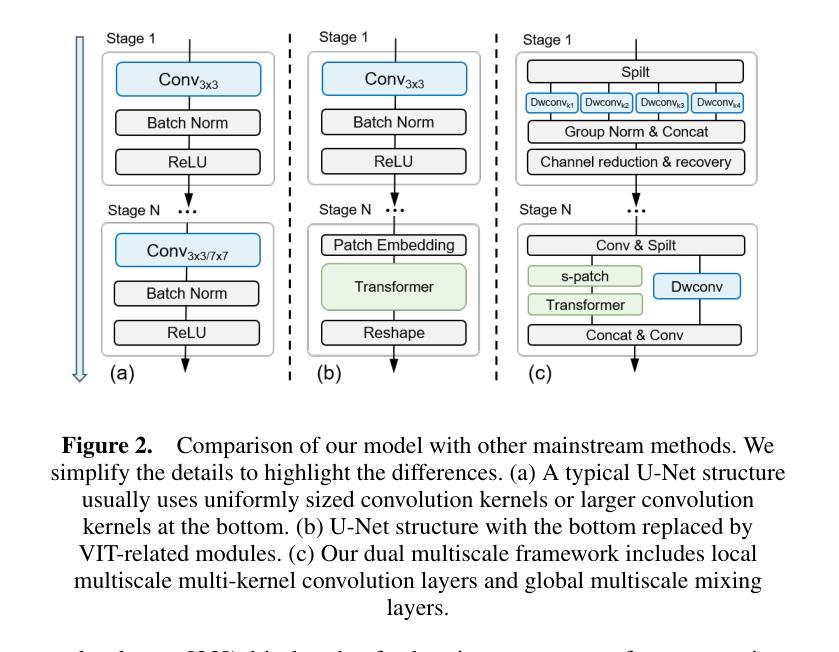
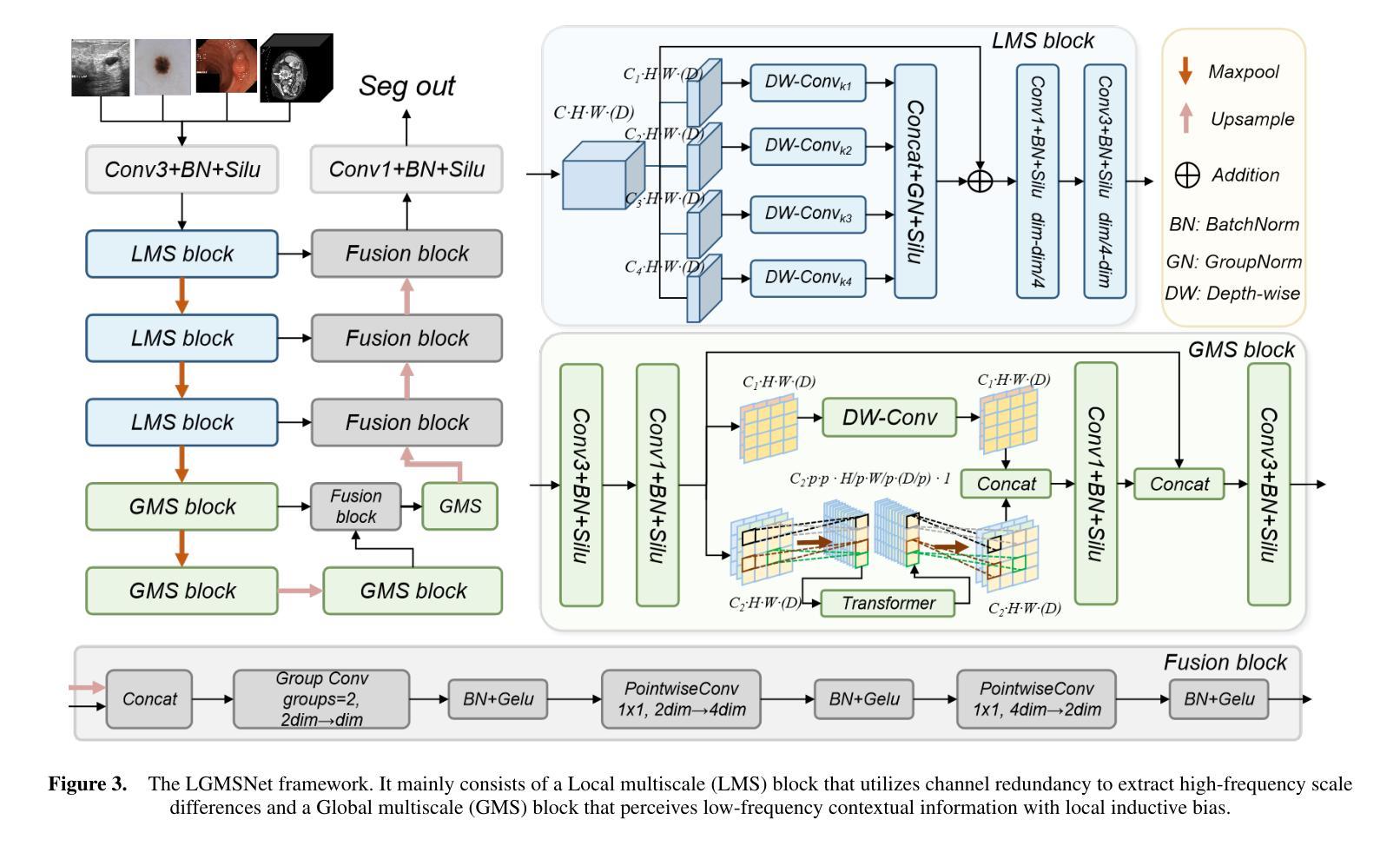
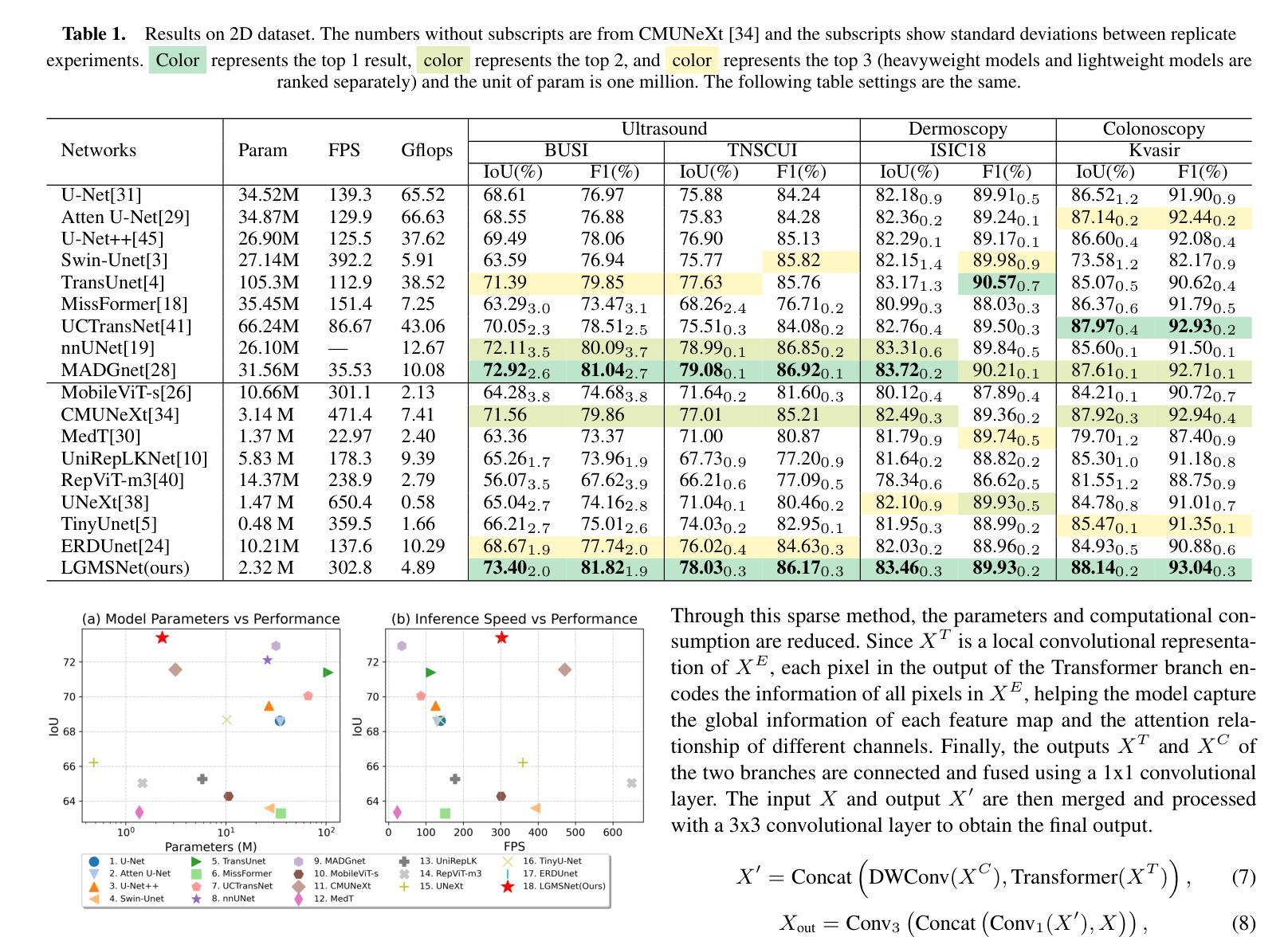
Medical image segmentation plays a pivotal role in disease diagnosis and treatment planning, particularly in resource-constrained clinical settings where lightweight and generalizable models are urgently needed. However, existing lightweight models often compromise performance for efficiency and rarely adopt computationally expensive attention mechanisms, severely restricting their global contextual perception capabilities. Additionally, current architectures neglect the channel redundancy issue under the same convolutional kernels in medical imaging, which hinders effective feature extraction. To address these challenges, we propose LGMSNet, a novel lightweight framework based on local and global dual multiscale that achieves state-of-the-art performance with minimal computational overhead. LGMSNet employs heterogeneous intra-layer kernels to extract local high-frequency information while mitigating channel redundancy. In addition, the model integrates sparse transformer-convolutional hybrid branches to capture low-frequency global information. Extensive experiments across six public datasets demonstrate LGMSNet’s superiority over existing state-of-the-art methods. In particular, LGMSNet maintains exceptional performance in zero-shot generalization tests on four unseen datasets, underscoring its potential for real-world deployment in resource-limited medical scenarios. The whole project code is in https://github.com/cq-dong/LGMSNet.
医学图像分割在疾病诊断和治疗计划制定中发挥着至关重要的作用,特别是在资源受限的临床环境中,急需轻便且通用的模型。然而,现有的轻便模型往往为了在效率上做出妥协而牺牲了性能,并且很少采用计算昂贵的注意力机制,这严重限制了它们的全局上下文感知能力。此外,当前架构忽略了医学影像中同一卷积核下的通道冗余问题,这阻碍了有效的特征提取。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了LGMSNet,这是一种基于局部和全局双重多尺度的新型轻便框架,以最小的计算开销实现了最先进的性能。LGMSNet采用异质内层核来提取局部高频信息,同时减轻通道冗余。此外,该模型结合了稀疏的transformer卷积混合分支来捕获低频全局信息。在六个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,LGMSNet在现有最先进的方法中表现出卓越的性能。特别是在四个未见数据集上的零样本泛化测试中,LGMSNet保持了出色的性能,突显其在资源受限的医学场景中进行实际部署的潜力。整个项目代码位于https://github.com/cq-dong/LGMSNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECAI 2025
Summary
医学图像分割在疾病诊断和治疗计划中具有至关重要的作用,特别是在资源受限的临床环境中。现有轻量化模型通常需要在性能和效率之间做出妥协,并且很少采用计算量较大的注意力机制,这严重限制了其全局上下文感知能力。为解决这些问题,提出了LGMSNet,一种基于局部和全局双多尺度的轻量化框架,以最小的计算开销实现了最先进的性能。LGMSNet采用异质内核来提取局部高频信息并减轻通道冗余问题,同时结合稀疏transformer-卷积混合分支捕获低频全局信息。在六个公共数据集上的广泛实验表明,LGMSNet在未见数据集上的零样本泛化测试中表现出卓越的性能,突显其在资源受限医学场景中的实际应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在疾病诊断和治疗计划中起重要作用,特别是在资源受限环境中。
- 现有轻量化模型需要在性能和效率之间进行权衡,且缺乏全局上下文感知能力。
- LGMSNet是一种基于局部和全局双多尺度的轻量化框架,旨在解决上述问题。
- LGMSNet采用异质内核提取局部高频信息并减轻通道冗余。
- 模型结合稀疏transformer-卷积混合分支捕获低频全局信息。
- 在多个公共数据集上的实验表明LGMSNet具有卓越性能,特别是在未见数据集的零样本泛化测试中。
点此查看论文截图

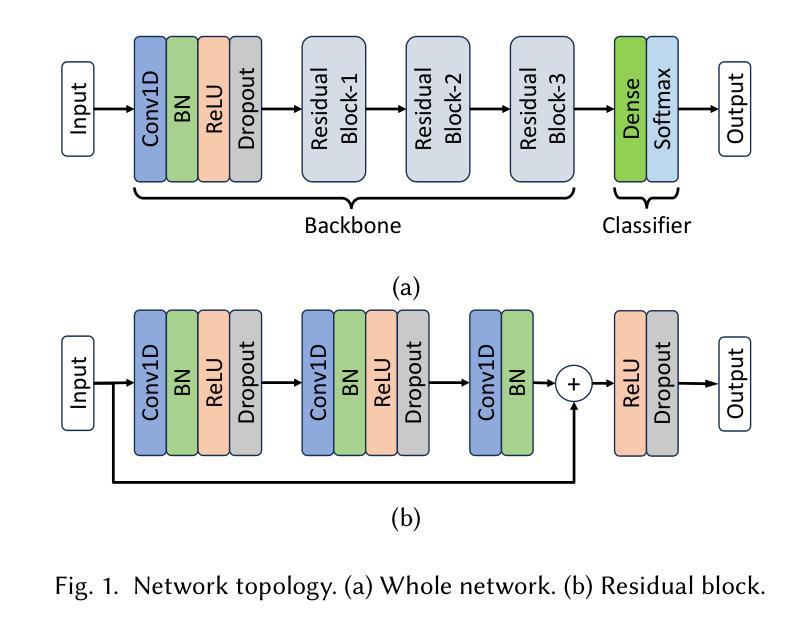
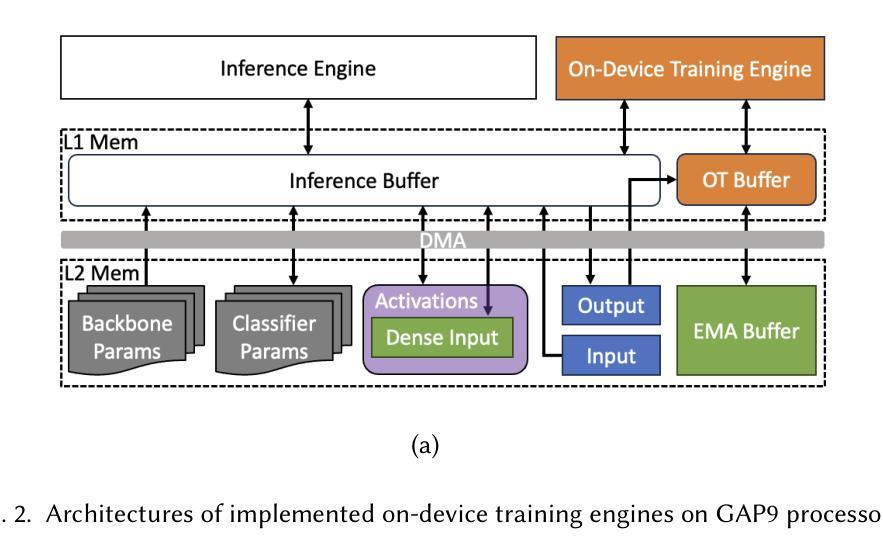
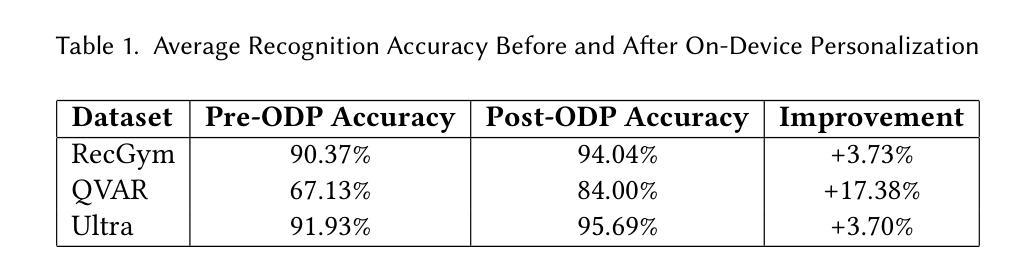
Bridging Generalization and Personalization in Wearable Human Activity Recognition via On-Device Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Pixi Kang, Julian Moosmann, Mengxi Liu, Bo Zhou, Michele Magno, Paul Lukowicz, Sizhen Bian
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) using wearable devices has advanced significantly in recent years, yet its generalization remains limited when models are deployed to new users. This degradation in performance is primarily due to user-induced concept drift (UICD), highlighting the importance of efficient personalization. In this paper, we present a hybrid framework that first generalizes across users and then rapidly adapts to individual users using few-shot learning directly on-device. By updating only the classifier layer with user-specific data, our method achieves robust personalization with minimal computational and memory overhead. We implement this framework on the energy-efficient RISC-V-based GAP9 microcontroller and validate it across three diverse HAR scenarios: RecGym, QVAR-Gesture, and Ultrasound-Gesture. Post-deployment adaptation yields consistent accuracy improvements of 3.73%, 17.38%, and 3.70% respectively. These results confirm that fast, lightweight, and effective personalization is feasible on embedded platforms, paving the way for scalable and user-aware HAR systems in the wild \footnote{https://github.com/kangpx/onlineTiny2023}.
使用可穿戴设备进行人类活动识别(HAR)近年来取得了显著进展,但当模型部署给新用户时,其通用性仍然有限。这种性能下降主要是由于用户引起的概念漂移(UICD)所导致的,这强调了有效个性化方法的重要性。在本文中,我们提出了一种混合框架,该框架首先实现跨用户通用化,然后使用少量样本学习直接在设备上快速适应个别用户。通过仅使用用户特定数据更新分类器层,我们的方法可以在计算量和内存开销极小的情况下实现稳健的个性化。我们在能效高的RISC-V基GAP9微控制器上实现了该框架,并在三种不同的HAR场景中进行了验证:RecGym、QVAR手势和超声手势。部署后的适应分别产生了稳定的准确性提高3.73%、提高高达个人本身的初次测准确度之前上均能进步三点的这种基本替代不同化学贵格的演练与实际稍有损失不一样占十分重要的研究成果认可这表明嵌入式平台上快速、轻便、有效的个性化方法是可行的,为野外可扩展和用户感知的HAR系统铺平了道路。如需更多信息,请访问我们的GitHub页面:[https://github.com/kangpx/onlineTiny2023]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种混合框架,该框架首先实现跨用户泛化,然后通过少量样本学习快速适应个体用户。通过仅更新分类器层以包含用户特定数据,该方法实现了具有最小计算和内存开销的稳健个性化。在RISC-V架构的GAP9微控制器上实现了该框架,并在三种不同的HAR场景中进行了验证,显示出有效性和可靠性。该方法在部署后快速适应不同场景的能力使HAR系统的泛化能力得到提高。因此,实现在嵌入式平台上的快速、轻量级且有效的个性化是可行的。具体验证方法可以参考该论文的GitHub页面^链接为额外注释,已跳过其内容。该工作为未来在真实世界环境下构建可扩展和用户感知的HAR系统铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的关键要点:
- 提出了一种混合框架,能够跨用户泛化并快速适应个体用户。
- 通过仅更新分类器层实现稳健个性化,减少计算和内存开销。
点此查看论文截图

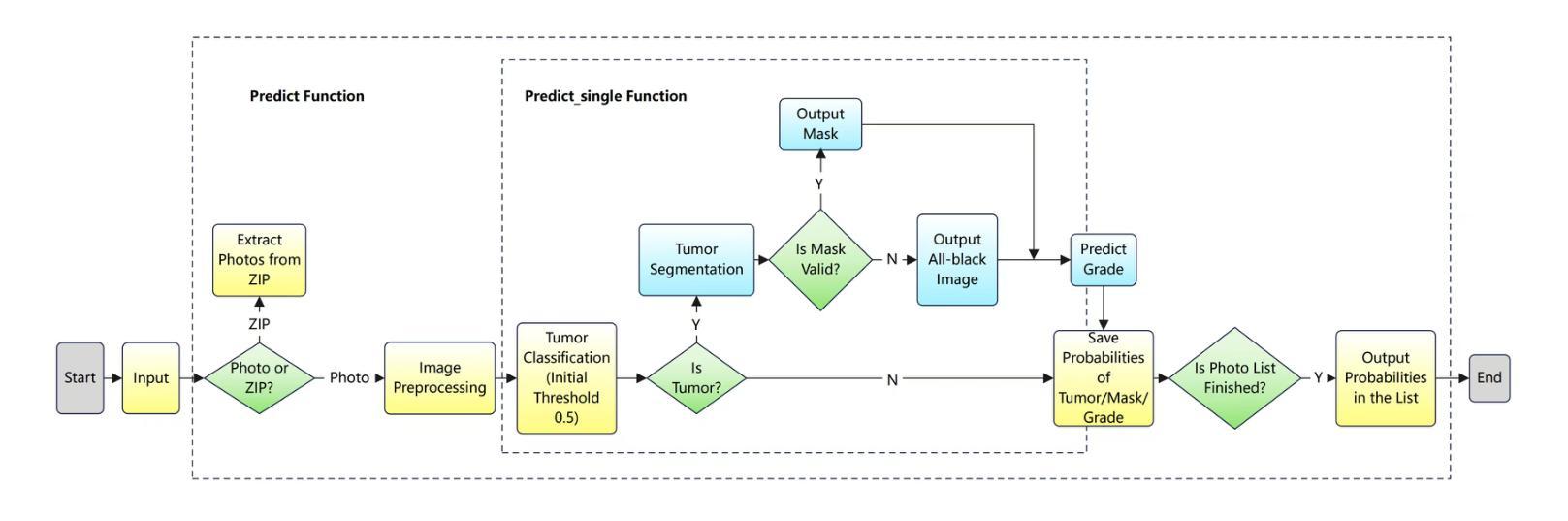
Bladder Cancer Diagnosis with Deep Learning: A Multi-Task Framework and Online Platform
Authors:Jinliang Yu, Mingduo Xie, Yue Wang, Tianfan Fu, Xianglai Xu, Jiajun Wang
Clinical cystoscopy, the current standard for bladder cancer diagnosis, suffers from significant reliance on physician expertise, leading to variability and subjectivity in diagnostic outcomes. There is an urgent need for objective, accurate, and efficient computational approaches to improve bladder cancer diagnostics. Leveraging recent advancements in deep learning, this study proposes an integrated multi-task deep learning framework specifically designed for bladder cancer diagnosis from cystoscopic images. Our framework includes a robust classification model using EfficientNet-B0 enhanced with Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM), an advanced segmentation model based on ResNet34-UNet++ architecture with self-attention mechanisms and attention gating, and molecular subtyping using ConvNeXt-Tiny to classify molecular markers such as HER-2 and Ki-67. Additionally, we introduce a Gradio-based online diagnostic platform integrating all developed models, providing intuitive features including multi-format image uploads, bilingual interfaces, and dynamic threshold adjustments. Extensive experimentation demonstrates the effectiveness of our methods, achieving outstanding accuracy (93.28%), F1-score (82.05%), and AUC (96.41%) for classification tasks, and exceptional segmentation performance indicated by a Dice coefficient of 0.9091. The online platform significantly improved the accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of clinical bladder cancer diagnostics, enabling practical and user-friendly deployment. The code is publicly available. Our multi-task framework and integrated online tool collectively advance the field of intelligent bladder cancer diagnosis by improving clinical reliability, supporting early tumor detection, and enabling real-time diagnostic feedback. These contributions mark a significant step toward AI-assisted decision-making in urology.
临床膀胱镜检查是目前膀胱癌诊断的标准,但其对医生专业知识的依赖性强,导致诊断结果存在变异性和主观性。因此,急需客观、准确、高效的计算方法来改进膀胱癌的诊断。本研究利用深度学习领域的最新进展,提出了一个专为膀胱癌诊断设计的多任务深度学习框架。该框架包括一个使用EfficientNet-B0并结合卷积块注意力模块(CBAM)的稳健分类模型,一个基于ResNet34-UNet++架构并使用自注意机制和注意力门的高级分割模型,以及使用ConvNeXt-Tiny进行分子亚型的分类,如HER-2和Ki-67等分子标记。此外,我们还引入了一个基于Gradio的在线诊断平台,该平台集成了所有已开发的模型,提供了多格式图像上传、双语界面和动态阈值调整等直观功能。广泛的实验证明了我们的方法的有效性,在分类任务中取得了出色的准确率(93.28%)、F1分数(82.05%)和AUC(96.41%),分割性能也十分突出,Dice系数为0.9091。在线平台显著提高了膀胱癌诊断的准确性、效率和可及性,实现了实用且用户友好的部署。相关代码已公开可用。我们的多任务框架和集成在线工具共同推动了智能膀胱癌诊断领域的发展,提高了临床可靠性,支持早期肿瘤检测,并能够实现实时诊断反馈。这些贡献标志着在泌尿科领域实现人工智能辅助决策的重大进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文本介绍了针对膀胱癌诊断的智能多任务深度学习框架以及基于该框架的在线诊断平台。该框架利用深度学习技术,通过集成分类模型、分割模型和分子分型技术,实现了膀胱癌诊断的客观化、精确性和高效性。此外,开发了一种基于Gradio的在线诊断平台,提高了诊断的准确性、效率和可及性。研究表明,该方法具有良好的性能表现,并公开了相关代码。
Key Takeaways
- 临床膀胱癌诊断现状存在依赖医生经验和主观判断的问题,需要客观、准确和高效的计算方法来改进。
- 研究提出了一种基于深度学习的多任务深度学习框架,用于膀胱癌诊断。包括用于分类的EfficientNet-B0与CBAM结合模型、用于分割的ResNet34-UNet++架构以及用于分子分型的ConvNeXt-Tiny模型。
- 开发了基于Gradio的在线诊断平台,集成了所有开发的模型,并提供了多格式图像上传、双语界面和动态阈值调整等直观功能。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在分类任务上表现出较高的准确性、F1分数和AUC值,在分割任务上也取得了优异的Dice系数。
- 在线平台显著提高了膀胱癌诊断的准确性、效率和可及性,实现了实用且用户友好的部署。
- 代码已公开,为智能膀胱癌诊断领域的研究和应用提供了有价值的资源。
点此查看论文截图

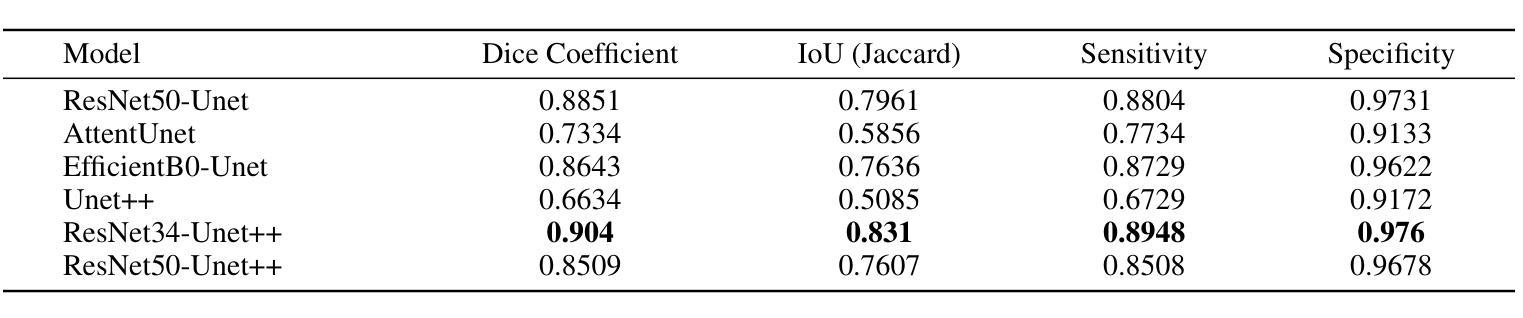
TPA: Temporal Prompt Alignment for Fetal Congenital Heart Defect Classification
Authors:Darya Taratynova, Alya Almsouti, Beknur Kalmakhanbet, Numan Saeed, Mohammad Yaqub
Congenital heart defect (CHD) detection in ultrasound videos is hindered by image noise and probe positioning variability. While automated methods can reduce operator dependence, current machine learning approaches often neglect temporal information, limit themselves to binary classification, and do not account for prediction calibration. We propose Temporal Prompt Alignment (TPA), a method leveraging foundation image-text model and prompt-aware contrastive learning to classify fetal CHD on cardiac ultrasound videos. TPA extracts features from each frame of video subclips using an image encoder, aggregates them with a trainable temporal extractor to capture heart motion, and aligns the video representation with class-specific text prompts via a margin-hinge contrastive loss. To enhance calibration for clinical reliability, we introduce a Conditional Variational Autoencoder Style Modulation (CVAESM) module, which learns a latent style vector to modulate embeddings and quantifies classification uncertainty. Evaluated on a private dataset for CHD detection and on a large public dataset, EchoNet-Dynamic, for systolic dysfunction, TPA achieves state-of-the-art macro F1 scores of 85.40% for CHD diagnosis, while also reducing expected calibration error by 5.38% and adaptive ECE by 6.8%. On EchoNet-Dynamic’s three-class task, it boosts macro F1 by 4.73% (from 53.89% to 58.62%). Temporal Prompt Alignment (TPA) is a framework for fetal congenital heart defect (CHD) classification in ultrasound videos that integrates temporal modeling, prompt-aware contrastive learning, and uncertainty quantification.
先天性心脏缺陷(CHD)的超声视频检测受到图像噪声和探头定位可变性的阻碍。虽然自动化方法可以减少对操作员的依赖,但当前的机器学习方法常常忽略了时间信息,仅限于二元分类,并且没有考虑到预测校准。我们提出了Temporal Prompt Alignment(TPA)方法,该方法利用基础图像文本模型和提示感知对比学习来对胎儿CHD进行心脏超声视频分类。TPA通过图像编码器从视频的每个帧中提取特征,并使用可训练的时间提取器来捕捉心脏运动,并通过边距铰链对比损失将视频表示与特定类别的文本提示对齐。为了提高临床可靠性的校准,我们引入了条件变分自动编码器风格调制(CVAESM)模块,该模块学习潜在的风格向量来调制嵌入并量化分类的不确定性。在用于CHD检测的私有数据集和用于收缩功能障碍的大型公共数据集EchoNet-Dynamic上进行了评估,TPA达到了最先进的宏观F1分数,CHD诊断的F1分数为85.40%,同时降低了期望校准误差5.38%和自适应ECE 6.8%。在EchoNet-Dynamic的三类任务中,它提高了宏观F1分数4.73%(从53.89%到58.62%)。Temporal Prompt Alignment(TPA)是一个用于超声视频中胎儿先天性心脏缺陷(CHD)分类的框架,它集成了时间建模、提示感知对比学习和不确定性量化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于图像-文本模型和提示感知对比学习的先天性心脏缺陷(CHD)分类方法,称为Temporal Prompt Alignment(TPA)。该方法能够从超声视频中提取特征,捕捉心脏运动,并与类别特定的文本提示对齐。为增强分类的临床可靠性,引入条件变分自编码器风格调制模块来学习潜在的风格向量以调整嵌入并量化分类的不确定性。评估结果表明,TPA在私人数据集上的CHD检测以及公共数据集EchoNet-Dynamic上的收缩功能障碍均达到了先进水平,并在多类任务上实现了宏观F1分数的显著提升。总体来说,Temporal Prompt Alignment是一个结合了时间建模、提示感知对比学习和不确定性量化的框架,用于胎儿先天性心脏缺陷的分类。
Key Takeaways
- 先天性心脏缺陷(CHD)在超声视频检测中面临图像噪声和探头定位可变性的挑战。
- 当前机器学习方法忽略了时间信息,仅限于二元分类,并且未考虑预测校准。
- 提出一种名为Temporal Prompt Alignment(TPA)的方法,利用图像-文本模型和提示感知对比学习对先天性心脏缺陷进行分类。
- TPA使用图像编码器从视频子剪辑的每一帧中提取特征,并用可训练的时间提取器捕捉心脏运动。
- 通过引入条件变分自编码器风格调制模块(CVAESM),增强分类的临床可靠性并量化分类的不确定性。
点此查看论文截图

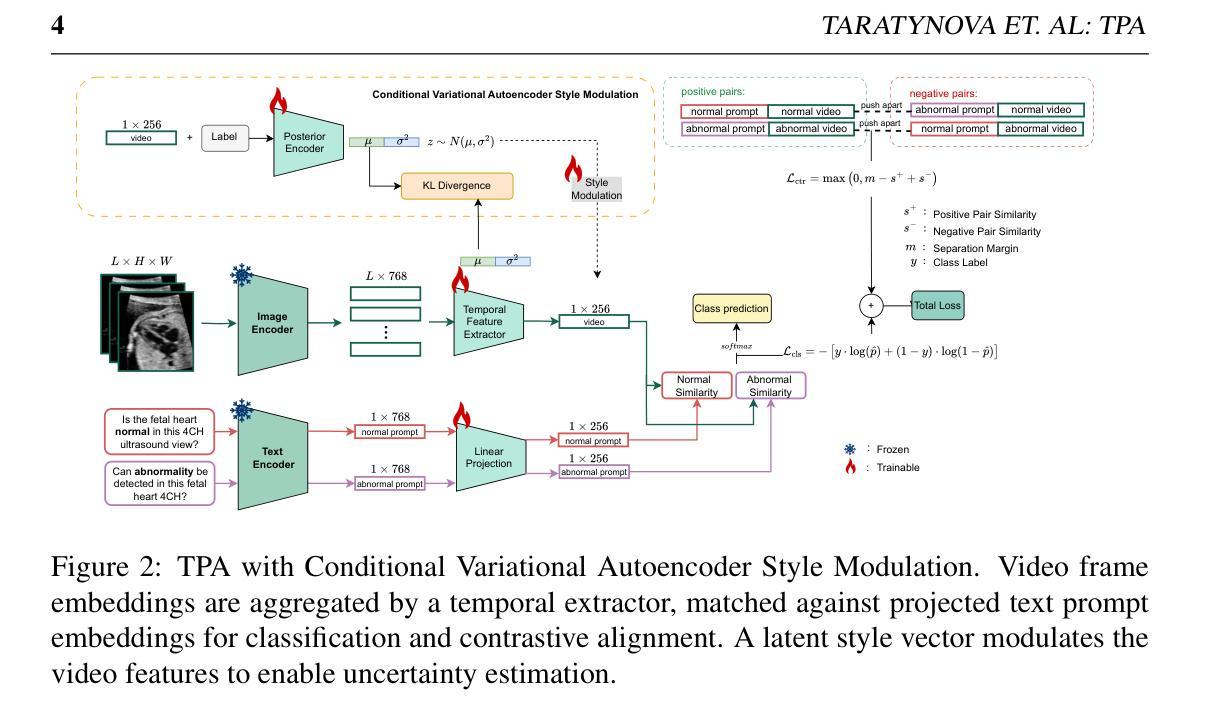
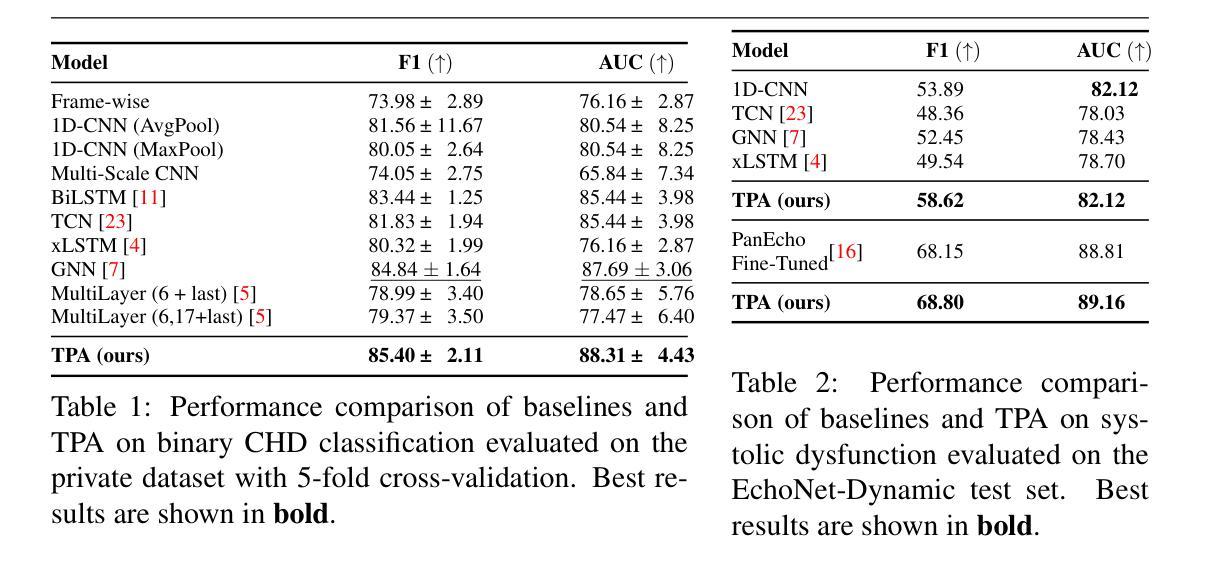
Conditional Cube Attack on Round-Reduced ASCON
Authors:Zheng Li, Xiaoyang Dong, Xiaoyun Wang
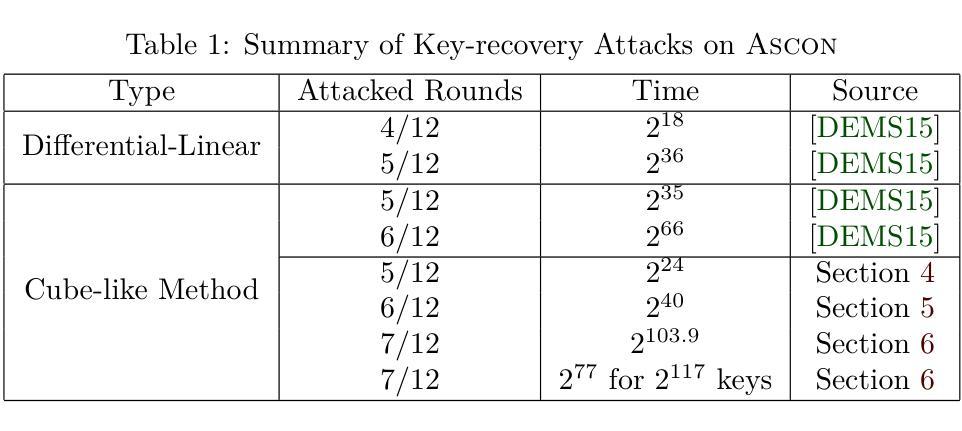
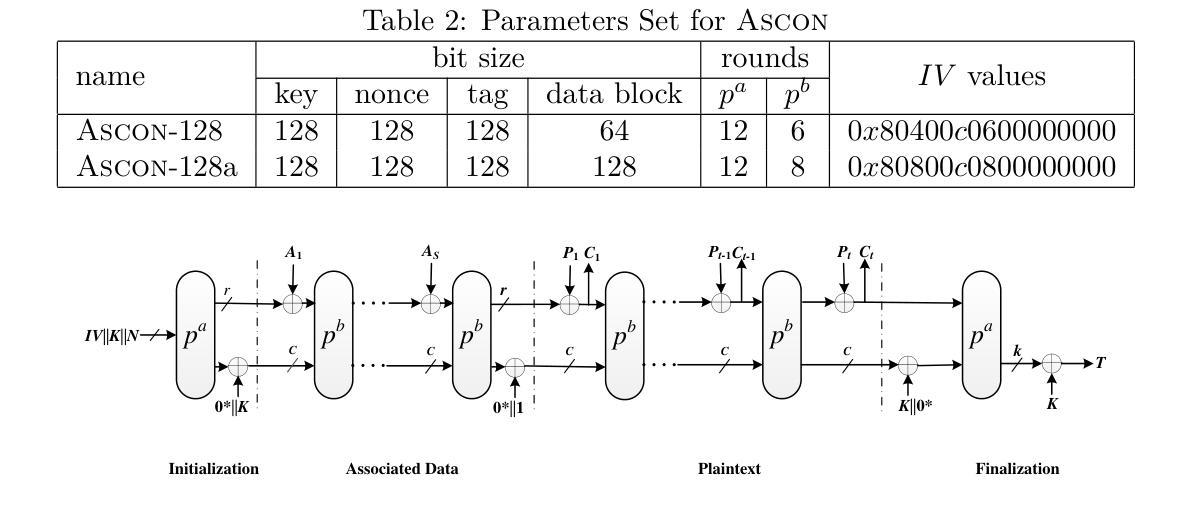
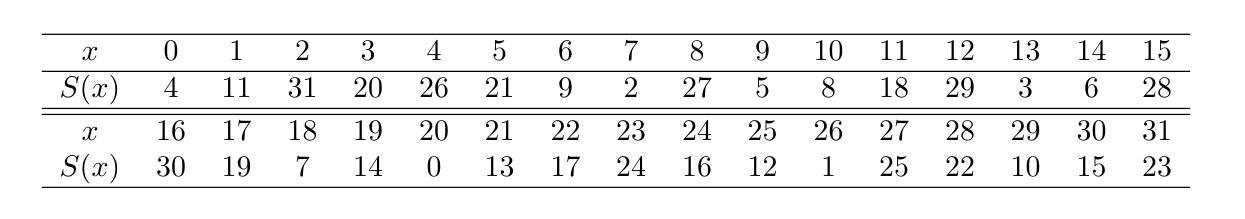
This paper evaluates the secure level of authenticated encryption \textsc{Ascon} against cube-like method. \textsc{Ascon} submitted by Dobraunig \emph{etal.} is one of 16 survivors of the 3rd round CAESAR competition. The cube-like method is first used by Dinur \emph{etal.} to analyze Keccak keyed modes. At CT-RSA 2015, Dobraunig \emph{etal.} applied this method to 5/6-round reduced \textsc{Ascon}, whose structure is similar to Keccak keyed modes. However, for \textsc{Ascon} the non-linear layer is more complex and state is much smaller, which make it hard for the attackers to select enough cube variables that do not multiply with each other after the first round. This seems to be the reason why the best previous key-recovery attack is on 6-round \textsc{Ascon}, while for Keccak keyed modes (Keccak-MAC and Keyak) the attacked round is no less than 7-round. In this paper, we generalize the conditional cube attack proposed by Huang \emph{etal.}, and find new cubes depending on some key bit conditions for 5/6-round reduced \textsc{Ascon}, and translate the previous theoretic 6-round attack with $2^{66}$ time complexity to a practical one with $2^{40}$ time complexity. Moreover, we propose the first 7-round key-recovery attack on \textsc{Ascon}. By introducing \emph{the cube-like key-subset technique}, we divide the full key space into many subsets according to different key conditions. For each key subset, we launch the cube tester to determine if the key falls into it. Finally, we recover the full key space by testing all the key subsets. The total time complexity is about $2^{103.9}$. In addition, for a weak-key subset, whose size is $2^{117}$, the attack is more efficient and costs only $2^{77}$ time complexity. Those attacks do not threaten the full round (12 rounds) \textsc{Ascon}.
本文评估了认证加密算法\Asco对抗立方体攻击的安全级别。由Dobraunig等人提交的\Asco是第三轮CAESAR竞赛中幸存的16个算法之一。立方体攻击方法最初由Dinur等人用于分析Keccak密钥模式。在CT-RSA 2015年会议上,Dobraunig等人将此方法应用于经过减少的5/6轮\Asco,其结构与Keccak密钥模式相似。然而,对于\Asco来说,其非线性层更加复杂且状态更小,这使得攻击者难以选择足够的立方体变量,这些变量在第一轮之后不会相互相乘。这似乎就是为什么之前的最佳密钥恢复攻击针对的是经过减少的6轮\Asco的原因,而对于Keccak密钥模式(Keccak-MAC和Keyak),攻击轮次不少于第7轮。在本文中,我们推广了Huang等人提出的条件立方体攻击,并针对经过减少的5/6轮\Asco找到了依赖于某些密钥位条件的新的立方体,并将之前的理论上的针对经过减少的6轮攻击的$2^{66}$的时间复杂度转化为具有实际可行性的$2^{40}$的时间复杂度。此外,我们首次提出了针对\Asco的针对经过减少的7轮的密钥恢复攻击。通过引入立方体类似密钥子集技术,我们根据不同的密钥条件将完整的密钥空间划分为多个子集。对于每个密钥子集,我们启动立方体测试器来确定密钥是否属于它。最后,我们通过测试所有密钥子集来恢复完整的密钥空间。总的时间复杂度大约是$2^{103.9}$。此外,对于大小为$2^{117}$的弱密钥子集,攻击更为有效且仅耗时$2^{77}$的时间复杂度。这些攻击不会威胁到经过完整设计(总共进行三轮加解)的完整的原始版的Ascon算法的安全性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文评估了身份验证加密方法Ascón的安全性,采用立方体攻击方法进行研究。文章对Ascón进行了条件立方体攻击,提出了新的立方体结构,并将理论上的六轮攻击转化为实际攻击,降低了时间复杂度。同时,文章还提出了针对Ascón的首个七轮密钥恢复攻击,通过引入立方体密钥子集技术,将整个密钥空间划分为多个子集进行测试,最终恢复出完整的密钥空间。但攻击并不威胁到完整的Ascón安全性。
Key Takeaways:
- Ascón通过了立方体攻击方法的评估。
- 条件立方体攻击应用于Ascón的新立方体结构提出。
- 将理论上的六轮攻击转化为实际攻击,时间复杂度降低。
- 首次提出了针对Ascón的七轮密钥恢复攻击。
- 通过立方体密钥子集技术将整个密钥空间划分为多个子集进行测试。
- 最终成功恢复出完整的密钥空间,总时间复杂度约为$2^{103.9}$。
点此查看论文截图

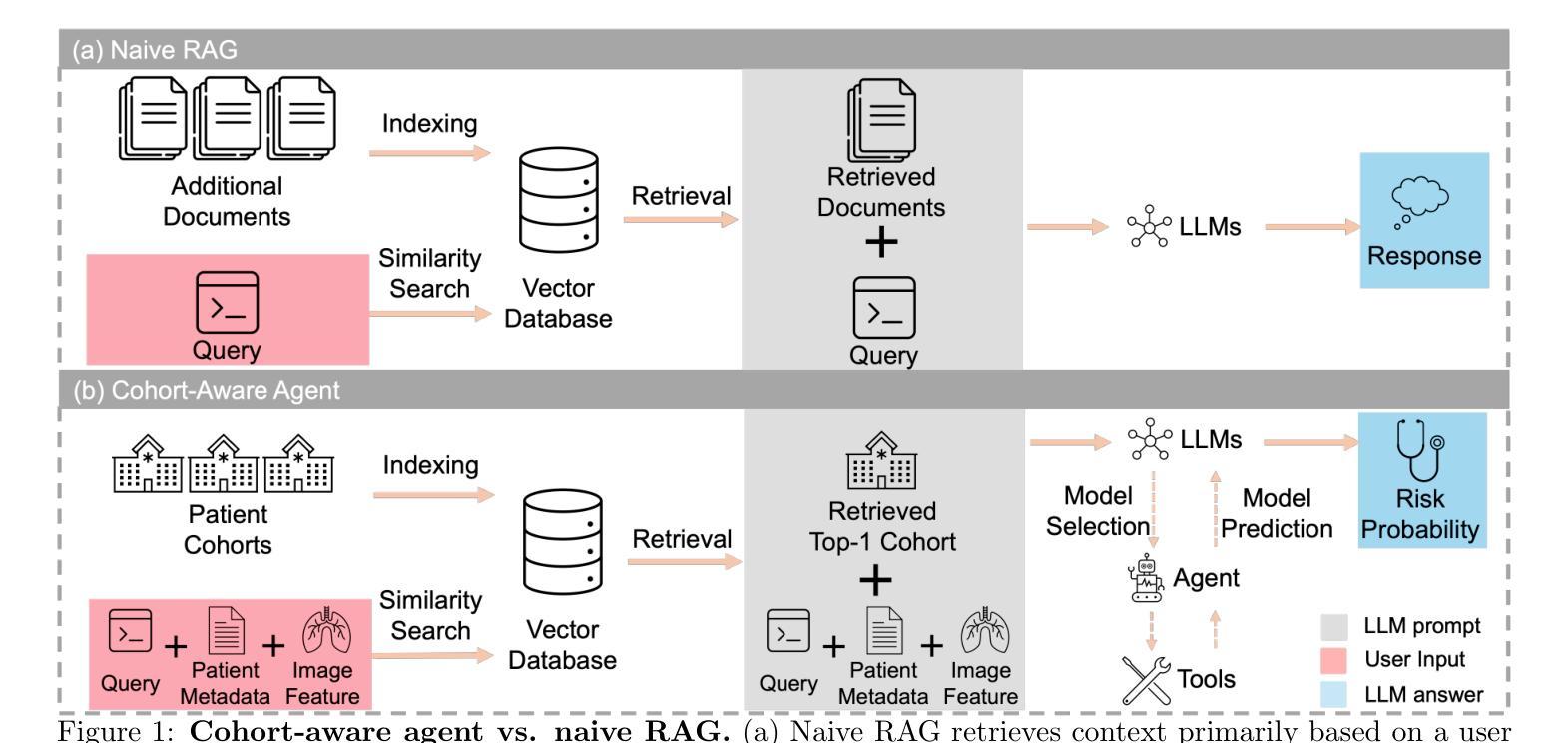
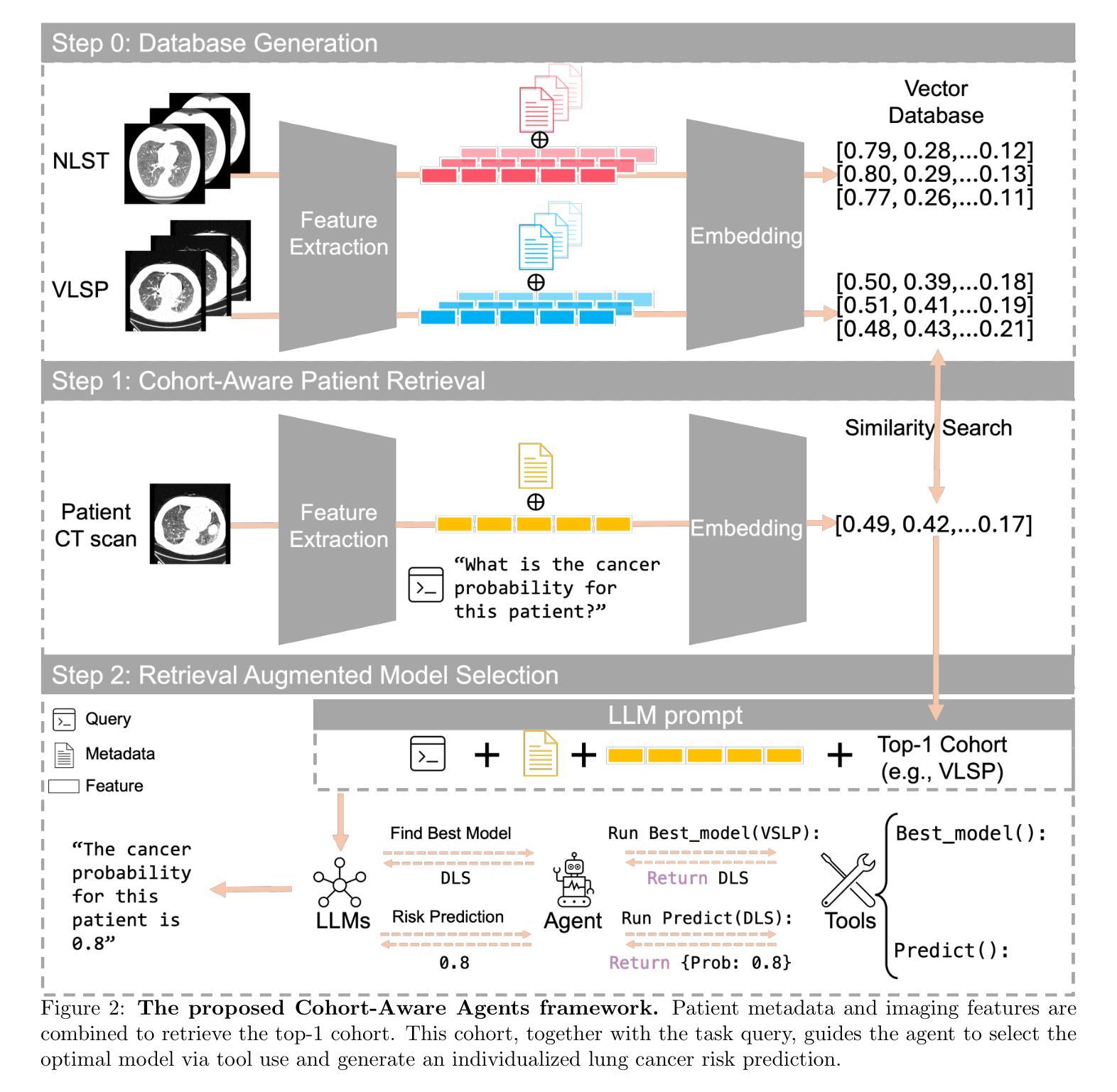
Cohort-Aware Agents for Individualized Lung Cancer Risk Prediction Using a Retrieval-Augmented Model Selection Framework
Authors:Chongyu Qu, Allen J. Luna, Thomas Z. Li, Junchao Zhu, Junlin Guo, Juming Xiong, Kim L. Sandler, Bennett A. Landman, Yuankai Huo
Accurate lung cancer risk prediction remains challenging due to substantial variability across patient populations and clinical settings – no single model performs best for all cohorts. To address this, we propose a personalized lung cancer risk prediction agent that dynamically selects the most appropriate model for each patient by combining cohort-specific knowledge with modern retrieval and reasoning techniques. Given a patient’s CT scan and structured metadata – including demographic, clinical, and nodule-level features – the agent first performs cohort retrieval using FAISS-based similarity search across nine diverse real-world cohorts to identify the most relevant patient population from a multi-institutional database. Second, a Large Language Model (LLM) is prompted with the retrieved cohort and its associated performance metrics to recommend the optimal prediction algorithm from a pool of eight representative models, including classical linear risk models (e.g., Mayo, Brock), temporally-aware models (e.g., TDVIT, DLSTM), and multi-modal computer vision-based approaches (e.g., Liao, Sybil, DLS, DLI). This two-stage agent pipeline – retrieval via FAISS and reasoning via LLM – enables dynamic, cohort-aware risk prediction personalized to each patient’s profile. Building on this architecture, the agent supports flexible and cohort-driven model selection across diverse clinical populations, offering a practical path toward individualized risk assessment in real-world lung cancer screening.
精确预测肺癌风险仍然是一个挑战,因为不同患者群体和临床环境之间存在很大的差异——没有任何单一模型适用于所有群体。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种个性化的肺癌风险预测代理,该代理通过结合特定人群的知识与现代检索和推理技术,动态为每位患者选择最合适的模型。给定患者的CT扫描和结构化元数据(包括人口统计、临床和结节级特征),代理首先使用基于FAISS的相似性搜索在九个多样化的真实世界群体中进行人群检索,以识别与多机构数据库中最相关的人群。其次,使用大型语言模型(LLM)根据检索到的群体及其相关性能指标,从八个代表性模型中推荐最佳的预测算法,包括经典线性风险模型(例如Mayo、Brock)、时间感知模型(例如TDVIT、DLSTM)和多模态计算机视觉方法(例如Liao、Sybil、DLS、DLI)。这种两阶段的代理管道——通过FAISS进行检索,通过LLM进行推理——实现了针对每个患者资料的动态、人群感知风险预测。基于这一架构,代理支持在多样化的临床人群中实现灵活和基于人群模型的选择,为真实世界肺癌筛查中的个性化风险评估提供了实际路径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种个性化肺癌风险预测模型,它通过结合患者人群特定的知识以及现代检索和推理技术,针对每个患者动态选择最合适的预测模型。模型首先通过基于FAISS的相似性搜索在多个真实世界的患者人群中检索最相关的患者群体,然后使用大型语言模型(LLM)推荐最佳的预测算法。这种两阶段模型管道实现了针对每个患者个人资料的动态、人群感知的风险预测。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌风险预测具有挑战性,因为不同患者人群和临床环境之间存在很大的变异性。
- 提出了一种个性化肺癌风险预测模型,能结合特定人群知识和现代检索及推理技术为患者动态选择最合适的预测模型。
- 该模型首先使用基于FAISS的相似性搜索在多个真实世界的人群中检索最相关的患者群体。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)推荐最佳预测算法,从八个代表性模型中选取。
- 模型包括经典线性风险模型、时间感知模型和基于多模态计算机视觉的方法。
- 该模型管道通过动态、人群感知的风险预测实现了个性化的风险评估。
点此查看论文截图


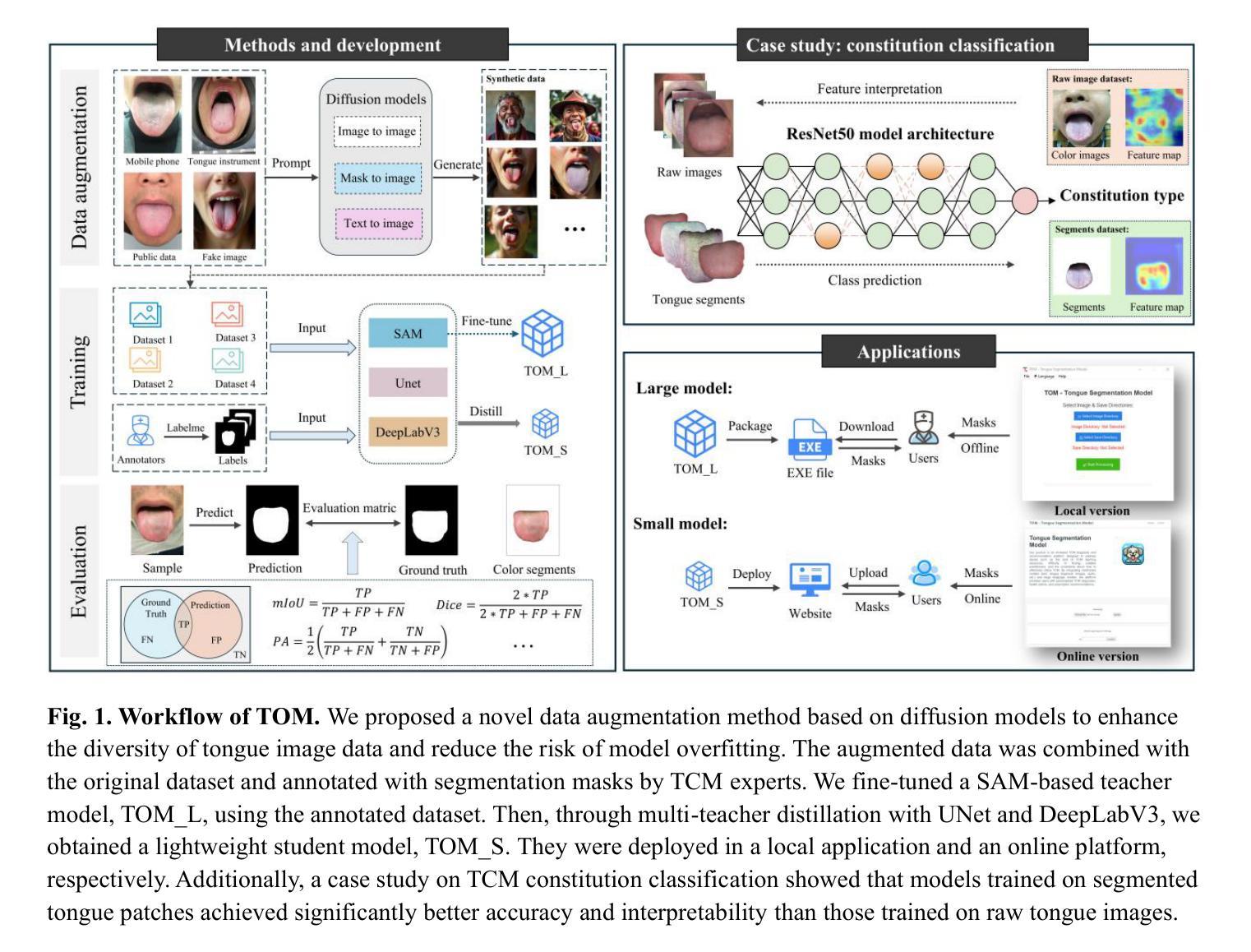
TOM: An Open-Source Tongue Segmentation Method with Multi-Teacher Distillation and Task-Specific Data Augmentation
Authors:Jiacheng Xie, Ziyang Zhang, Biplab Poudel, Congyu Guo, Yang Yu, Guanghui An, Xiaoting Tang, Lening Zhao, Chunhui Xu, Dong Xu
Tongue imaging serves as a valuable diagnostic tool, particularly in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). The quality of tongue surface segmentation significantly affects the accuracy of tongue image classification and subsequent diagnosis in intelligent tongue diagnosis systems. However, existing research on tongue image segmentation faces notable limitations, and there is a lack of robust and user-friendly segmentation tools. This paper proposes a tongue image segmentation model (TOM) based on multi-teacher knowledge distillation. By incorporating a novel diffusion-based data augmentation method, we enhanced the generalization ability of the segmentation model while reducing its parameter size. Notably, after reducing the parameter count by 96.6% compared to the teacher models, the student model still achieves an impressive segmentation performance of 95.22% mIoU. Furthermore, we packaged and deployed the trained model as both an online and offline segmentation tool (available at https://itongue.cn/), allowing TCM practitioners and researchers to use it without any programming experience. We also present a case study on TCM constitution classification using segmented tongue patches. Experimental results demonstrate that training with tongue patches yields higher classification performance and better interpretability than original tongue images. To our knowledge, this is the first open-source and freely available tongue image segmentation tool.
舌成像作为一种诊断工具,在中医中具有重要价值。舌表面分割的质量显著影响智能舌诊断系统中舌图像分类和随后诊断的准确性。然而,现有的舌图像分割研究面临显著局限性,缺乏稳健且用户友好的分割工具。本文提出了一种基于多教师知识蒸馏的舌图像分割模型(TOM)。通过引入一种新型基于扩散的数据增强方法,我们提高了分割模型的泛化能力,同时减小了其参数规模。值得注意的是,与教师模型相比,我们将参数数量减少了96.6%,学生模型仍实现了95.22%的mIoU分割性能。此外,我们将训练好的模型打包部署为一个在线和离线的分割工具(可在[https://itongue.cn/访问),使中医从业者和研究人员无需编程经验即可使用。我们还展示了一项关于使用分割舌片进行中医体质分类的案例研究。实验结果表明,使用舌片进行训练可以获得比使用原始舌图像更高的分类性能和更好的可解释性。据我们所知,这是第一个开源且免费使用的舌图像分割工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tongue segmentation, data augmentation, synthetic data for AI training, prompt engineering, Segment Anything Model, knowledge distillation, tongue classification
Summary
舌象成像在中医诊断中具有重要价值。本文提出了一种基于多教师知识蒸馏的舌图像分割模型(TOM),通过引入扩散式数据增强方法,提高了分割模型的泛化能力并减小了参数规模。该模型不仅在线和线下均可作为分割工具使用,而且实现了较高的分割性能。此外,研究还展示了使用分割舌斑进行中医体质分类的案例研究,结果表明使用舌斑进行训练可以提高分类性能和解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 舌象成像在中医诊断中具重要价值。
- 现有舌图像分割技术存在局限性和缺乏稳健、用户友好的分割工具。
- 本文提出了一种基于多教师知识蒸馏的舌图像分割模型(TOM)。
- 引入扩散式数据增强方法,提高模型的泛化能力并减小参数规模。
- 模型实现较高的分割性能,达到95.22%的mIoU。
- 该模型被打包并部署为在线和线下分割工具,网址为https://itongue.cn/。
点此查看论文截图

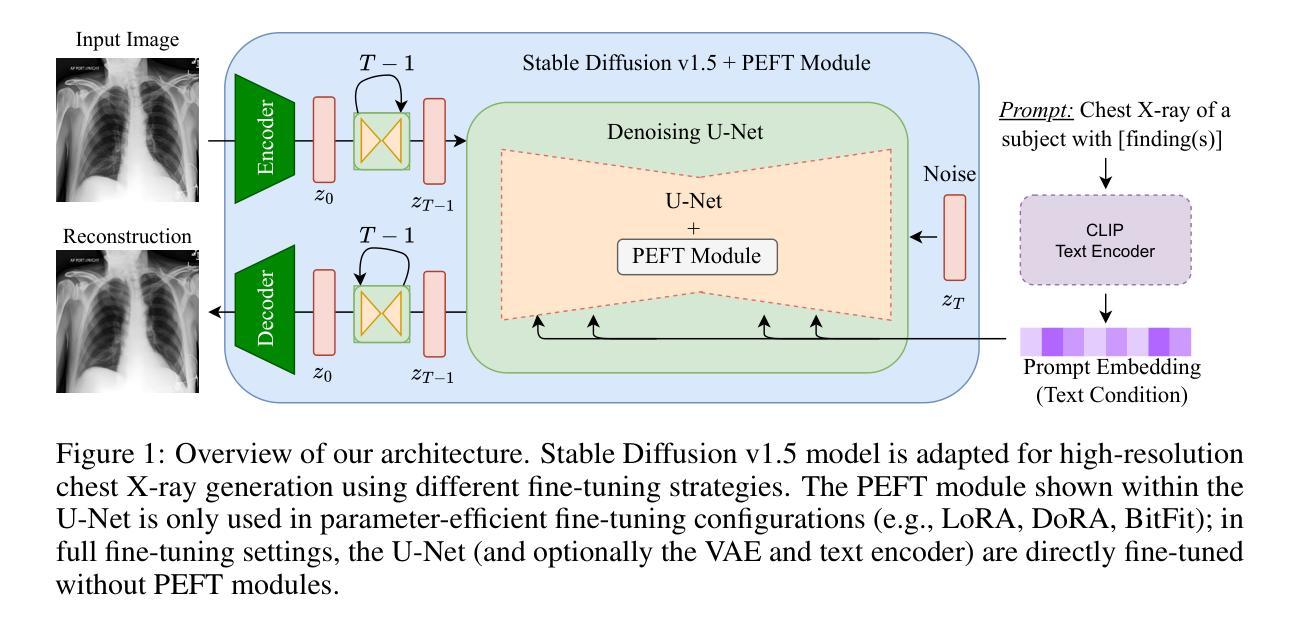
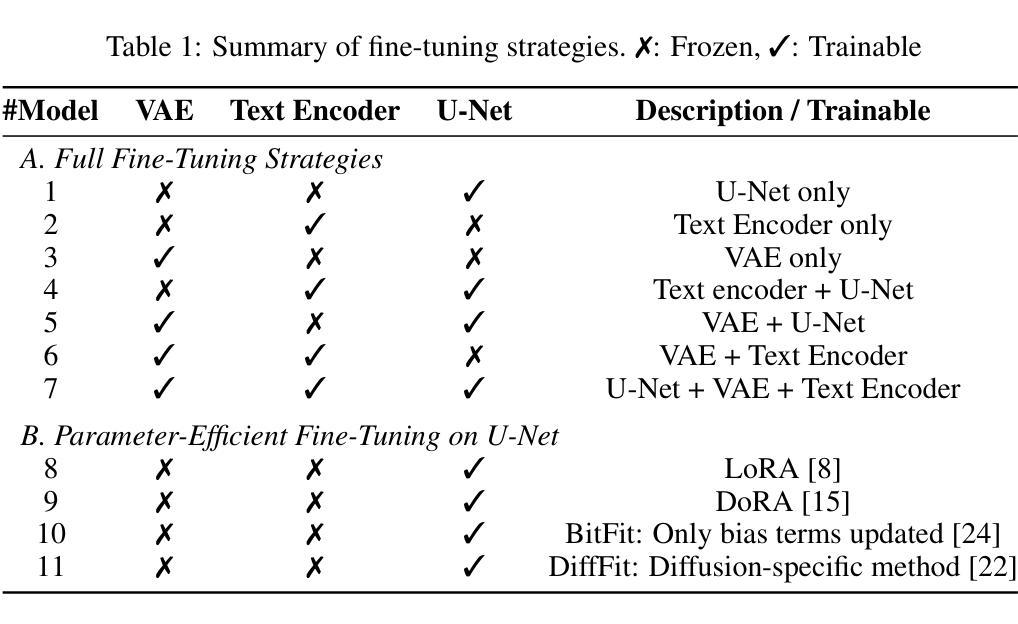
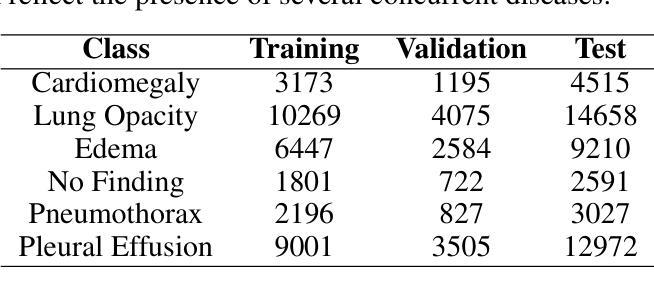
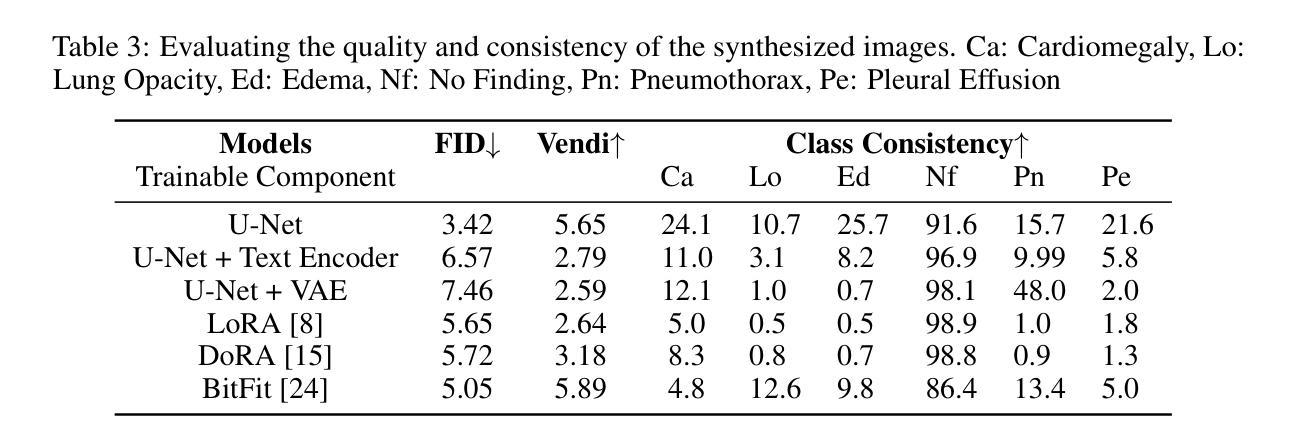
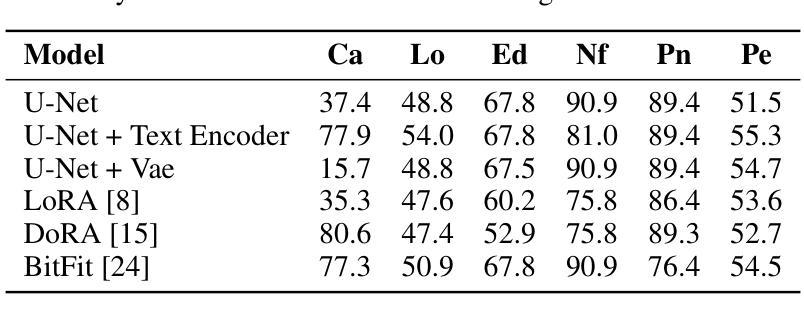
Pixels Under Pressure: Exploring Fine-Tuning Paradigms for Foundation Models in High-Resolution Medical Imaging
Authors:Zahra TehraniNasab, Amar Kumar, Tal Arbel
Advancements in diffusion-based foundation models have improved text-to-image generation, yet most efforts have been limited to low-resolution settings. As high-resolution image synthesis becomes increasingly essential for various applications, particularly in medical imaging domains, fine-tuning emerges as a crucial mechanism for adapting these powerful pre-trained models to task-specific requirements and data distributions. In this work, we present a systematic study, examining the impact of various fine-tuning techniques on image generation quality when scaling to high resolution 512x512 pixels. We benchmark a diverse set of fine-tuning methods, including full fine-tuning strategies and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). We dissect how different fine-tuning methods influence key quality metrics, including Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID), Vendi score, and prompt-image alignment. We also evaluate the utility of generated images in a downstream classification task under data-scarce conditions, demonstrating that specific fine-tuning strategies improve both generation fidelity and downstream performance when synthetic images are used for classifier training and evaluation on real images. Our code is accessible through the project website - https://tehraninasab.github.io/PixelUPressure/.
基于扩散的基础模型的进步已经提高了文本到图像生成的能力,但大多数努力都局限于低分辨率环境。随着高分辨率图像合成在各个领域,特别是在医学影像领域变得越来越重要,微调作为一种适应这些强大预训练模型以满足特定任务和数据分布需求的机制显得至关重要。在这项工作中,我们进行了系统研究,探讨了各种微调技术对图像生成质量的影响,特别是在扩展到高分辨率(512x512像素)时。我们对一系列微调方法进行了基准测试,包括全微调策略和参数高效微调(PEFT)。我们分析了不同的微调方法如何影响关键的质量指标,包括Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)、Vendi分数和提示图像对齐。我们还评估了在数据稀缺条件下生成图像在下游分类任务中的实用性,证明了特定的微调策略在提高生成保真度和下游性能方面的作用,尤其是在使用合成图像进行分类器训练和评估真实图像时。我们的代码可通过项目网站访问:网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了不同精细调整技术对高分辨率(512x512像素)图像生成质量的影响。文章探讨了多种精细调整方法,包括全精细调整策略和参数高效精细调整(PEFT)。研究结果表明,不同的精细调整方法会影响关键质量指标,如Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)、Vendi分数和提示图像对齐等。此外,在数据稀缺的条件下,对生成图像在下游分类任务中的实用性进行了评估,证明了特定的精细调整策略在提高生成图像保真度和下游性能方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散基础模型在文本到图像生成方面的进展已有所提升,但大多数努力仅限于低分辨率设置。
- 高分辨率图像合成在各种应用,特别是在医学影像领域变得越来越重要。
- 精细调整是适应这些强大预训练模型以符合特定任务和数据处理分布的关键机制。
- 研究对多种精细调整方法进行了系统研究,包括全精细调整和参数高效精细调整(PEFT)。
- 不同精细调整方法会影响图像生成的关键质量指标,如Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)、Vendi分数和提示图像对齐。
- 在数据稀缺的条件下,生成图像在下游分类任务中的实用性得到了评估。
- 特定的精细调整策略在提高生成图像的保真度和下游性能方面都表现出了有效性。
点此查看论文截图

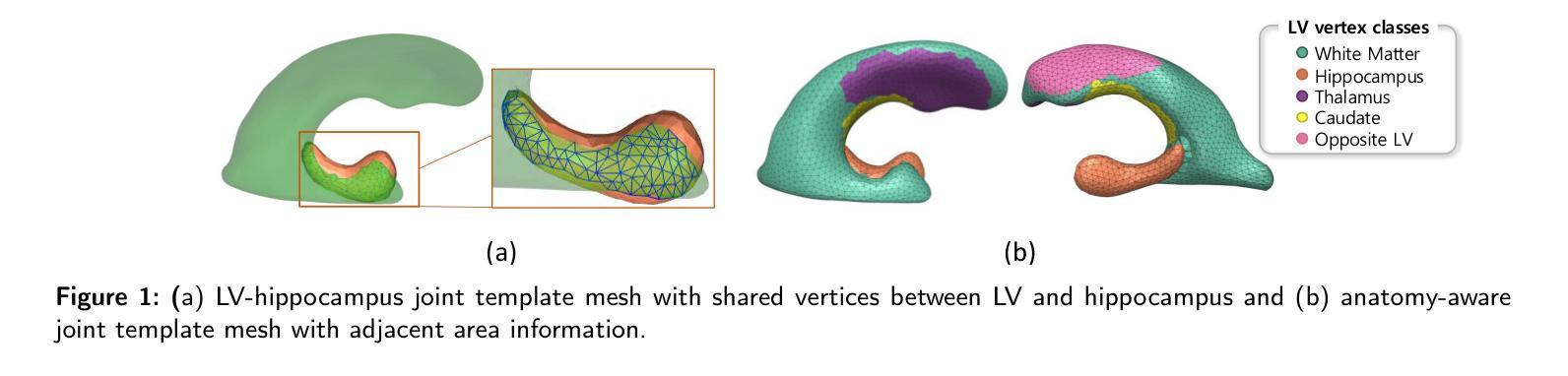
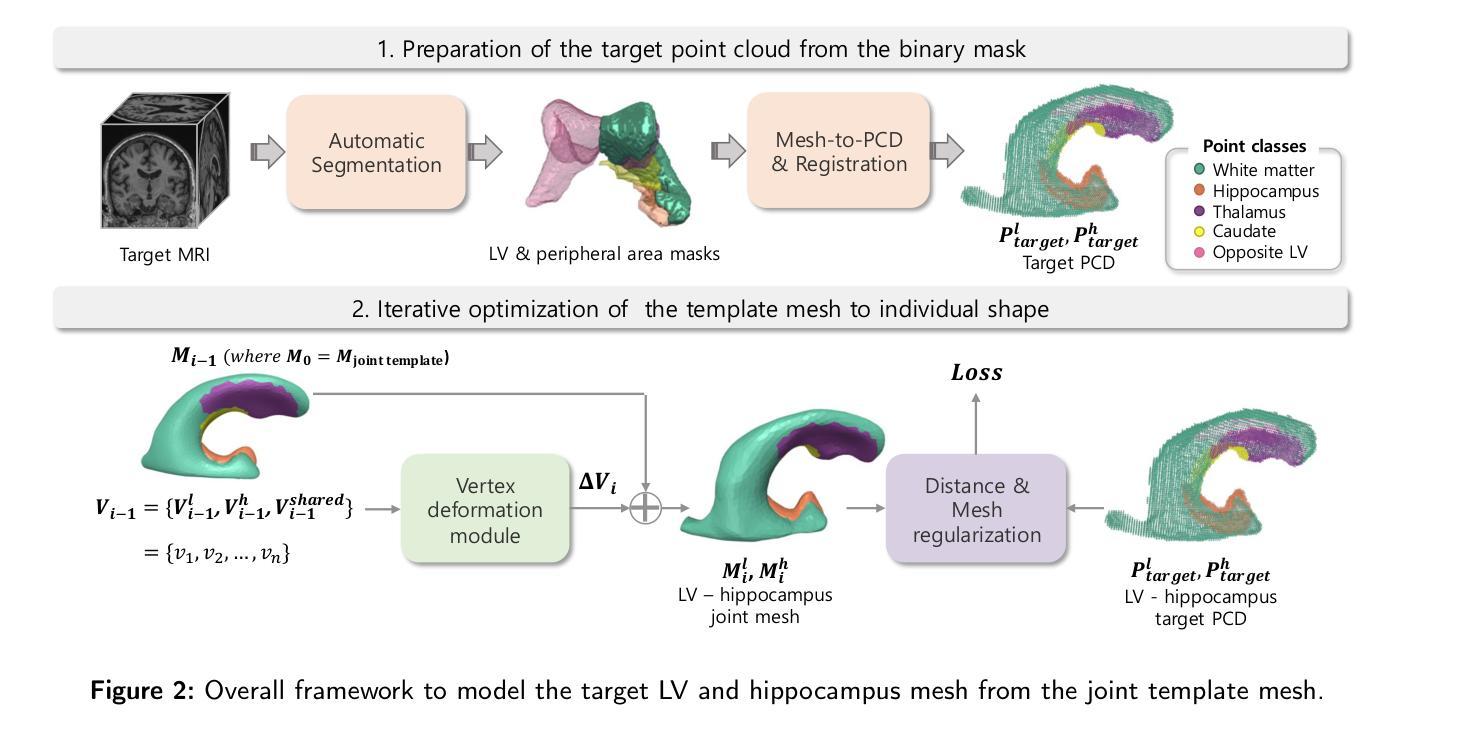
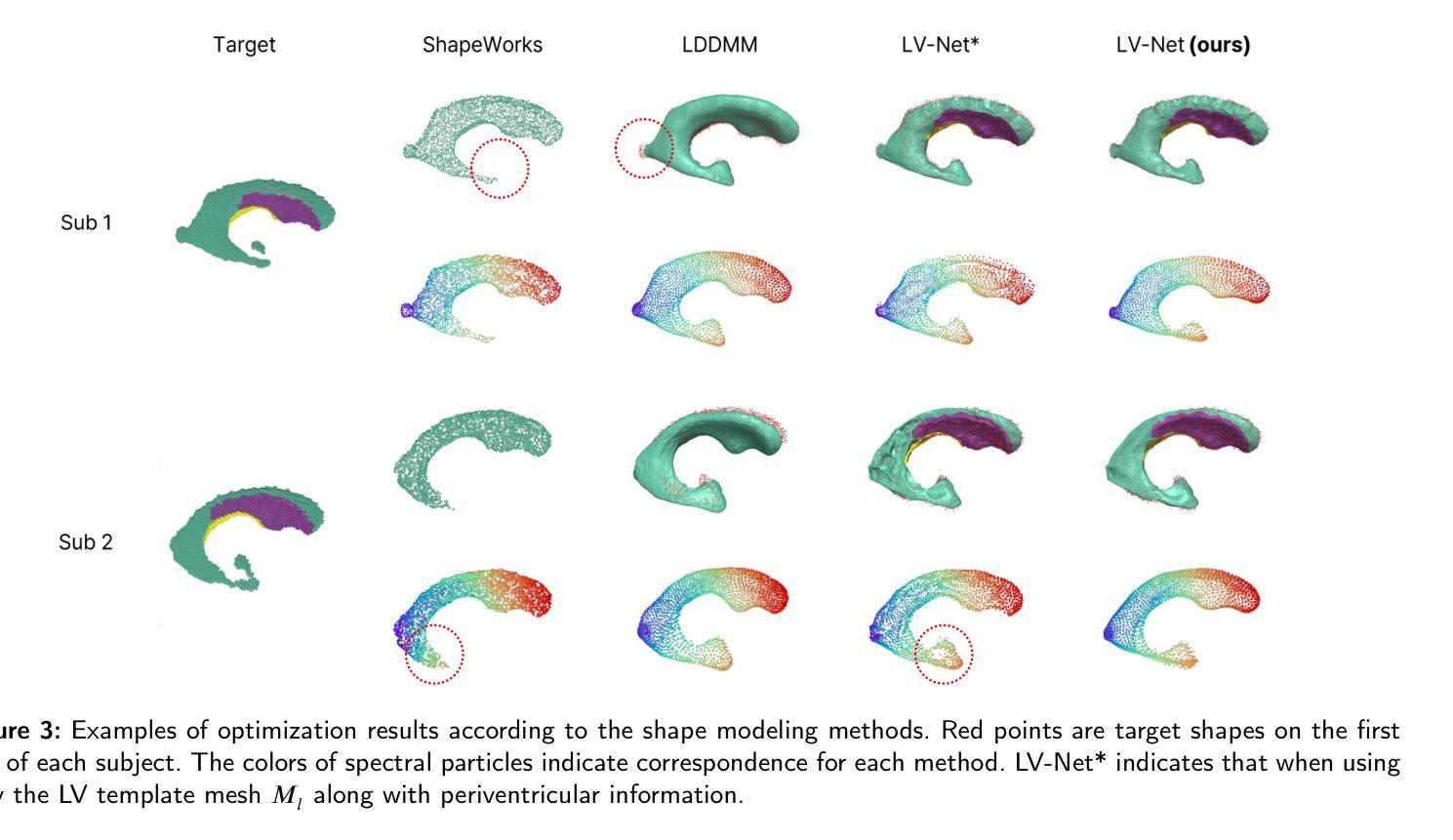
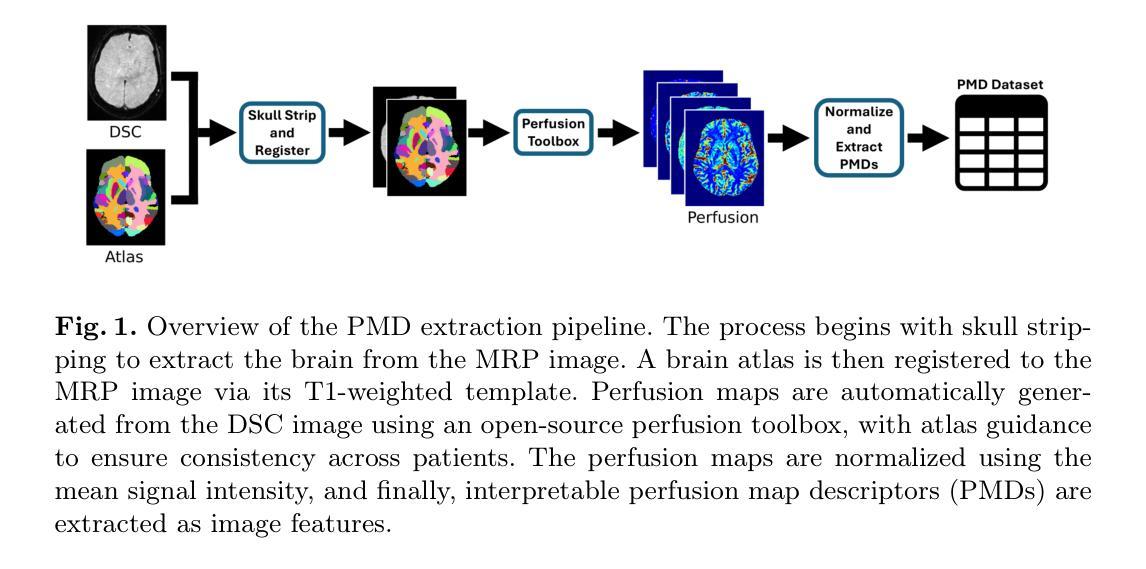
LV-Net: Anatomy-aware lateral ventricle shape modeling with a case study on Alzheimer’s disease
Authors:Wonjung Park, Suhyun Ahn, Jinah Park
Lateral ventricle (LV) shape analysis holds promise as a biomarker for neurological diseases; however, challenges remain due to substantial shape variability across individuals and segmentation difficulties arising from limited MRI resolution. We introduce LV-Net, a novel framework for producing individualized 3D LV meshes from brain MRI by deforming an anatomy-aware joint LV-hippocampus template mesh. By incorporating anatomical relationships embedded within the joint template, LV-Net reduces boundary segmentation artifacts and improves reconstruction robustness. In addition, by classifying the vertices of the template mesh based on their anatomical adjacency, our method enhances point correspondence across subjects, leading to more accurate LV shape statistics. We demonstrate that LV-Net achieves superior reconstruction accuracy, even in the presence of segmentation imperfections, and delivers more reliable shape descriptors across diverse datasets. Finally, we apply LV-Net to Alzheimer’s disease analysis, identifying LV subregions that show significantly associations with the disease relative to cognitively normal controls. The codes for LV shape modeling are available at https://github.com/PWonjung/LV_Shape_Modeling.
侧脑室(LV)形态分析作为神经疾病的生物标志物具有广阔前景,但由于个体间形态差异较大以及MRI分辨率有限导致的分割困难,仍存在挑战。我们引入了LV-Net,这是一个新型框架,通过变形一个了解结构的联合LV-海马模板网格,从脑部MRI生成个性化的3D LV网格。通过融入联合模板内的结构关系,LV-Net减少了边界分割伪影,提高了重建的稳健性。此外,通过基于其结构邻接对模板网格的顶点进行分类,我们的方法增强了不同受试者间的点对应关系,从而得到更准确的LV形态统计。我们证明,即使在存在分割缺陷的情况下,LV-Net也能实现较高的重建精度,并在各种数据集中提供更可靠的形状描述符。最后,我们将LV-Net应用于阿尔茨海默病分析,识别出与认知正常对照相比,与疾病显著相关的LV子区域。LV形态建模的代码可在https://github.com/PWonjung/LV_Shape_Modeling找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于医学图像的研究,LV(侧脑室)形状分析作为神经性疾病的生物标志物具有潜力,但仍然存在挑战,如个体间形状差异大以及MRI分辨率限制导致的分割困难。本文引入LV-Net框架,通过变形解剖联合LV-海马模板网格,从脑部MRI生成个性化3D LV网格。LV-Net利用联合模板中的解剖关系,减少了边界分割伪影,提高了重建的稳健性。此外,该方法通过对模板网格的顶点按其解剖部位进行分类,增强了跨主体的点对应关系,从而获得更准确的LV形状统计信息。实验表明,LV-Net即使在存在分割缺陷的情况下也能实现较高的重建精度,并且在不同的数据集中提供更可靠的形状描述。最后,LV-Net在阿尔茨海默病分析中的应用,识别出与正常认知对照组相比,与疾病密切相关的LV子区域。
Key Takeaways
- LV(侧脑室)形状分析作为神经性疾病的生物标志物具有潜力,但仍面临个体间形状差异及MRI分辨率限制的挑战。
- LV-Net框架能够生成个性化的3D LV网格,通过变形解剖联合LV-海马模板网格实现。
- LV-Net利用解剖关系减少边界分割伪影,提高重建稳健性。
- 通过分类模板网格的顶点,LV-Net增强跨主体点对应关系,获得更准确LV形状统计。
- LV-Net实现高重建精度,即使在存在分割缺陷的情况下。
- LV-Net提供可靠形状描述,适用于不同数据集。
- LV-Net成功应用于阿尔茨海默病分析,识别出与疾病相关的LV子区域。
点此查看论文截图

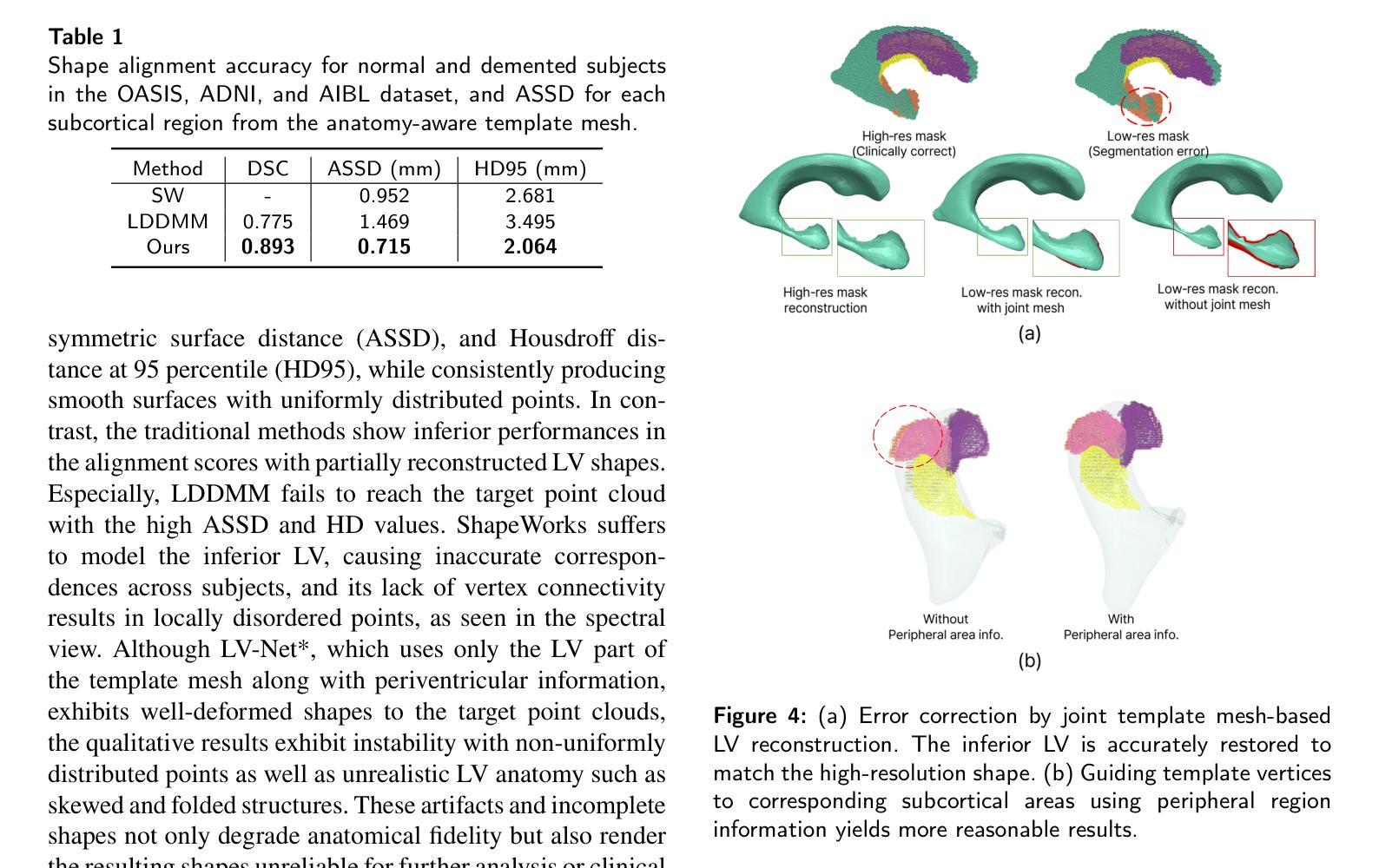
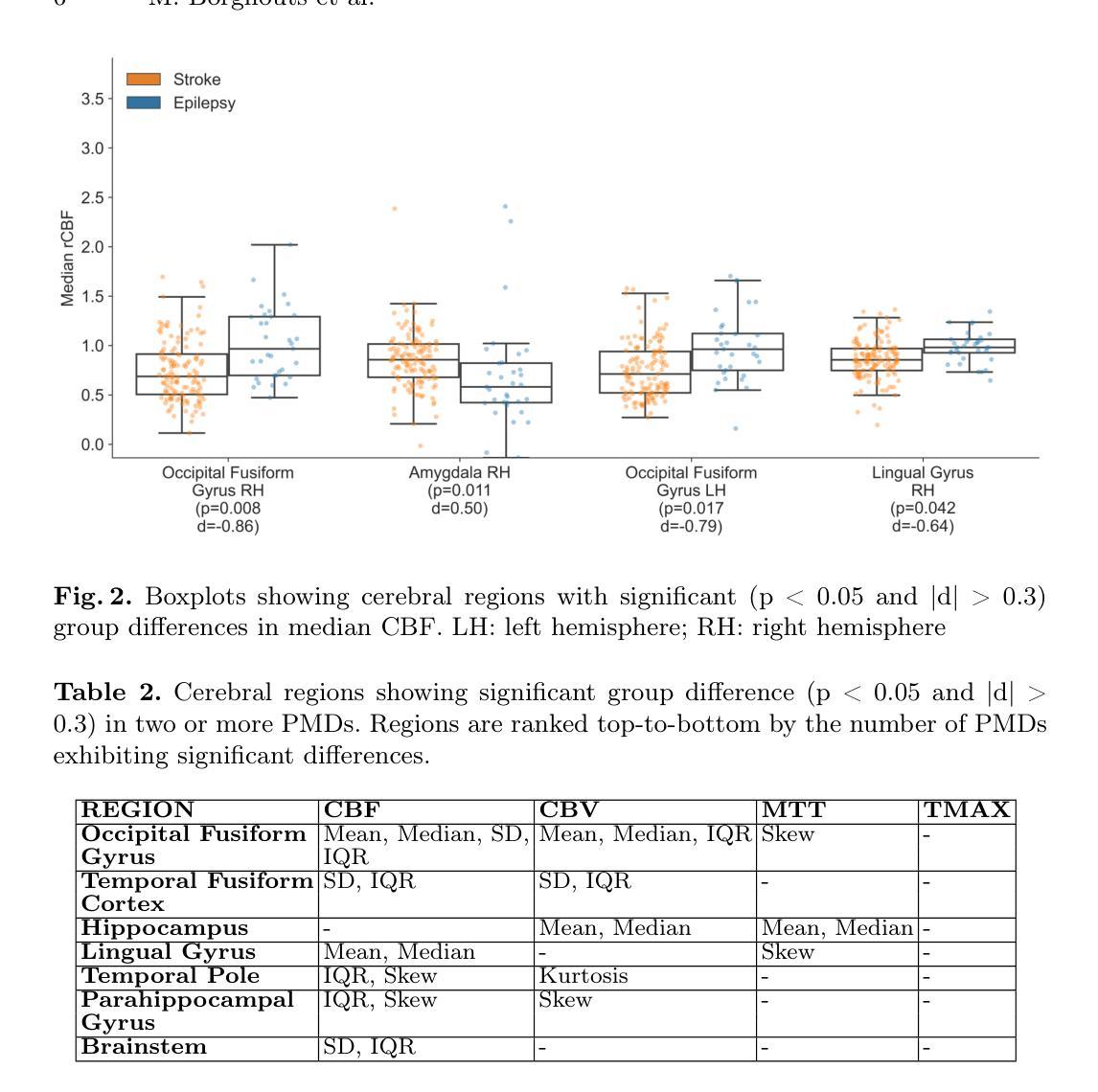
Discriminating Distal Ischemic Stroke from Seizure-Induced Stroke Mimics Using Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MRI
Authors:Marijn Borghouts, Richard McKinley, Manuel Köstner, Josien Pluim, Roland Wiest, Ruisheng Su
Distinguishing acute ischemic strokes (AIS) from stroke mimics (SMs), particularly in cases involving medium and small vessel occlusions, remains a significant diagnostic challenge. While computed tomography (CT) based protocols are commonly used in emergency settings, their sensitivity for detecting distal occlusions is limited. This study explores the potential of magnetic resonance perfusion (MRP) imaging as a tool for differentiating distal AIS from epileptic seizures, a prevalent SM. Using a retrospective dataset of 162 patients (129 AIS, 33 seizures), we extracted region-wise perfusion map descriptors (PMDs) from dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) images. Statistical analyses identified several brain regions, located mainly in the temporal and occipital lobe, exhibiting significant group differences in certain PMDs. Hemispheric asymmetry analyses further highlighted these regions as discriminative. A logistic regression model trained on PMDs achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.90, and an area under the precision recall curve (AUPRC) of 0.74, with a specificity of 92% and a sensitivity of 73%, suggesting strong performance in distinguishing distal AIS from seizures. These findings support further exploration of MRP-based PMDs as interpretable features for distinguishing true strokes from various mimics. The code is openly available at our GitHub https://github.com/Marijn311/PMD_extraction_and_analysis{github.com/Marijn311/PMD\_extraction\_and\_analysis
在急性缺血性中风(AIS)与中风模仿者(SMs)之间进行区分,特别是在涉及中、小血管闭塞的情况下,仍然是一个重要的诊断挑战。虽然基于计算机断层扫描(CT)的协议在紧急情况下常用,但其在检测远端闭塞方面的敏感性有限。本研究探讨了磁共振灌注(MRP)成像在区分远端AIS与常见SM癫痫发作方面的潜力。通过回顾分析包含129例AIS和33例癫痫发作的162例患者数据集,我们从动态易感性对比图像中提取区域灌注映射描述符(PMDs)。统计分析发现主要位于颞叶和枕叶的某些大脑区域在某些PMDs上存在显著的群体差异。半球不对称分析进一步强调了这些区域的鉴别作用。使用PMD训练的逻辑回归模型在受试者工作特征曲线(AUROC)下的面积达到0.90,在精确度召回曲线(AUPRC)下的面积达到0.74,特异度为92%,灵敏度为73%,在区分远端AIS与癫痫发作方面表现出良好的性能。这些发现支持进一步探索基于MRP的PMD作为区分真实中风与各种模仿者的可解释特征。代码公开在我们的GitHub上可用:github.com/Marijn311/PMD_extraction_and_analysis。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to SWITCH2025
Summary
本研究探讨了磁共振灌注(MRP)成像在区分远端急性缺血性脑卒中(AIS)与常见的卒中模仿(SM)——癫痫发作为例的潜力。通过对动态磁敏感对比(DSC)图像的区域灌注图描述符(PMDs)的分析,研究在位于颞叶和枕叶等主要区域的特定PMDs表现出显著的组间差异。一个基于PMDs的逻辑回归模型在区分远端AIS与癫痫发作方面表现出良好的性能,其ROC曲线下的面积为0.90,精确度召回曲线下的面积为0.74,特异度为92%,敏感度为73%。这为进一步探索基于MRP的PMDs作为区分真实卒中与各种模仿的可解释特征提供了支持。
Key Takeaways
- 急性缺血性脑卒中(AIS)与卒中模仿(SM)之间的诊断仍然具有挑战性,特别是在涉及中小血管闭塞的情况下。
- 计算机断层扫描(CT)在检测远端闭塞方面的灵敏度有限。
- 本研究使用磁共振灌注(MRP)成像来区分远端AIS和常见的SM——癫痫发作。
- 通过动态磁敏感对比(DSC)图像分析,发现某些大脑区域的灌注图描述符(PMDs)存在显著的组间差异。
- 这些差异在颞叶和枕叶等主要区域尤为明显。
- 基于PMDs的逻辑回归模型在区分远端AIS与癫痫发作方面表现出良好的性能,ROC曲线下的面积为0.90。
点此查看论文截图

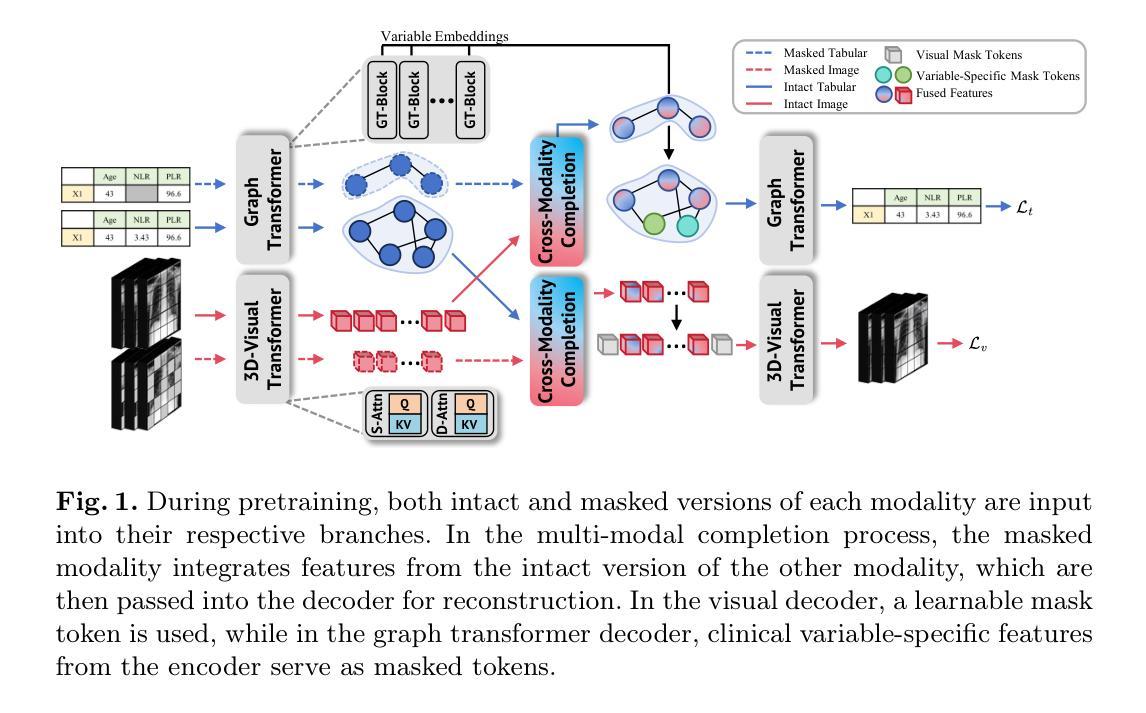
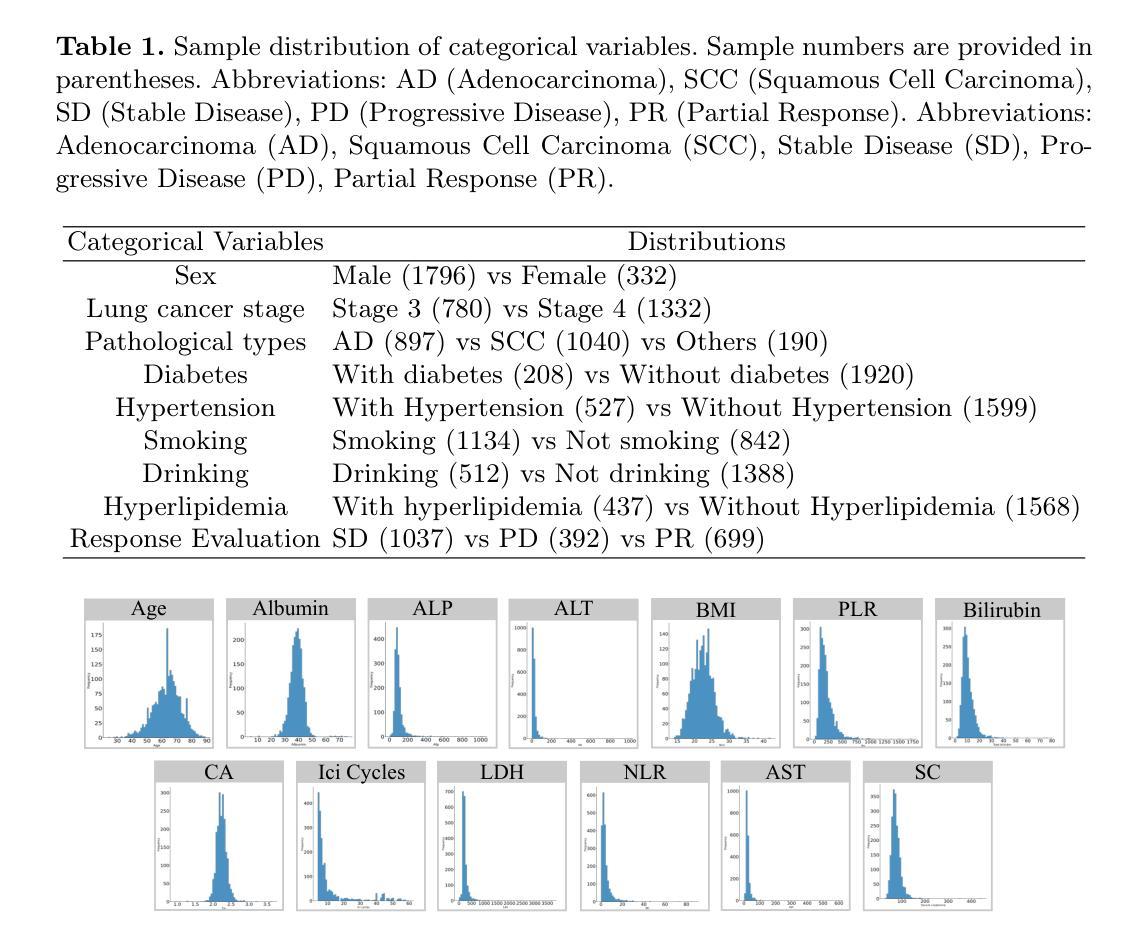
Cross-Modality Masked Learning for Survival Prediction in ICI Treated NSCLC Patients
Authors:Qilong Xing, Zikai Song, Bingxin Gong, Lian Yang, Junqing Yu, Wei Yang
Accurate prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients undergoing immunotherapy is essential for personalized treatment planning, enabling informed patient decisions, and improving both treatment outcomes and quality of life. However, the lack of large, relevant datasets and effective multi-modal feature fusion strategies pose significant challenges in this domain. To address these challenges, we present a large-scale dataset and introduce a novel framework for multi-modal feature fusion aimed at enhancing the accuracy of survival prediction. The dataset comprises 3D CT images and corresponding clinical records from NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), along with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) data. We further propose a cross-modality masked learning approach for medical feature fusion, consisting of two distinct branches, each tailored to its respective modality: a Slice-Depth Transformer for extracting 3D features from CT images and a graph-based Transformer for learning node features and relationships among clinical variables in tabular data. The fusion process is guided by a masked modality learning strategy, wherein the model utilizes the intact modality to reconstruct missing components. This mechanism improves the integration of modality-specific features, fostering more effective inter-modality relationships and feature interactions. Our approach demonstrates superior performance in multi-modal integration for NSCLC survival prediction, surpassing existing methods and setting a new benchmark for prognostic models in this context.
对接受免疫治疗的非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者进行准确的预后评估对于个性化治疗计划的制定、患者决策的知情以及改善治疗结果和生活质量至关重要。然而,缺乏相关的大型数据集和有效的多模式特征融合策略,给这一领域带来了重大挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一个大规模的数据集,并介绍了一个旨在提高生存预测准确性的多模式特征融合的新框架。数据集包含接受免疫检查点抑制剂(ICI)治疗的NSCLC患者的3D CT图像和相应的临床记录,以及无进展生存(PFS)和总生存(OS)数据。我们还提出了一种用于医学特征融合的跨模态掩膜学习方法,包括两个针对其各自模态的分支:一个切片深度转换器,用于从CT图像中提取3D特征;一个基于图的转换器,用于学习节点特征和表格数据中的临床变量之间的关系。融合过程由掩膜模态学习策略引导,该策略使模型利用完整模态来重建缺失组件。这种机制改善了模态特定特征的集成,促进了更有效的跨模态关系和特征交互。我们的方法在NSCLC生存预测的多模式集成中展示了卓越的性能,超越了现有方法,为这一背景下的预后模型设定了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
摘要
肺癌精准预后预测在个性化治疗、患者决策以及治疗成果与质量提升等方面都具有重要作用。面对相关数据集缺失以及多模态特征融合策略的局限性等挑战,我们提出了一个大型数据集与新型多模态特征融合框架来提高生存预测的准确性。数据集涵盖了接受免疫检查点抑制剂治疗的非小细胞肺癌患者的3D CT图像、相关临床记录以及无进展生存和总生存数据。我们进一步提出了跨模态掩膜学习方法进行医学特征融合,包括针对两种不同模态的专门分支:用于从CT图像中提取3D特征的Slice-Depth Transformer,以及用于学习临床变量节点特征和关系的图基Transformer。融合过程由掩膜模态学习策略引导,该策略使模型利用完整模态来重建缺失部分,提高了模态特定特征的集成,促进了跨模态的有效关系和特征交互。我们的方法在NSCLC生存预测的多模态融合中表现出卓越性能,超越了现有方法,为这一领域的预后模型设定了新的基准。
关键见解
- 非小细胞肺癌的精准预后预测对个性化治疗与患者决策至关重要。
- 缺乏大型相关数据集和多模态特征融合策略是当前的挑战。
- 提出了一种大型数据集,包含接受免疫检查点抑制剂治疗的NSCLC患者的3D图像和临床记录。
- 介绍了一种新型多模态特征融合框架,旨在提高生存预测的准确性。
- 提出了跨模态掩膜学习方法进行医学特征融合,包括Slice-Depth Transformer和图基Transformer。
- 融合过程采用掩膜模态学习策略,提高了模态特征的集成。
点此查看论文截图

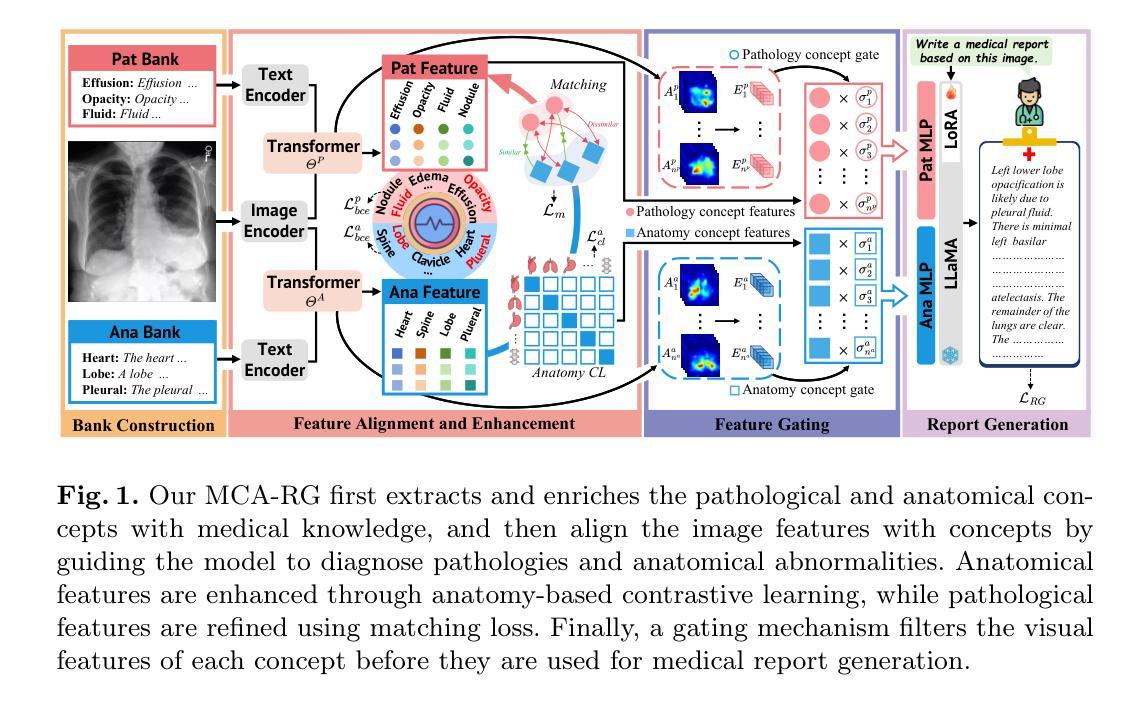
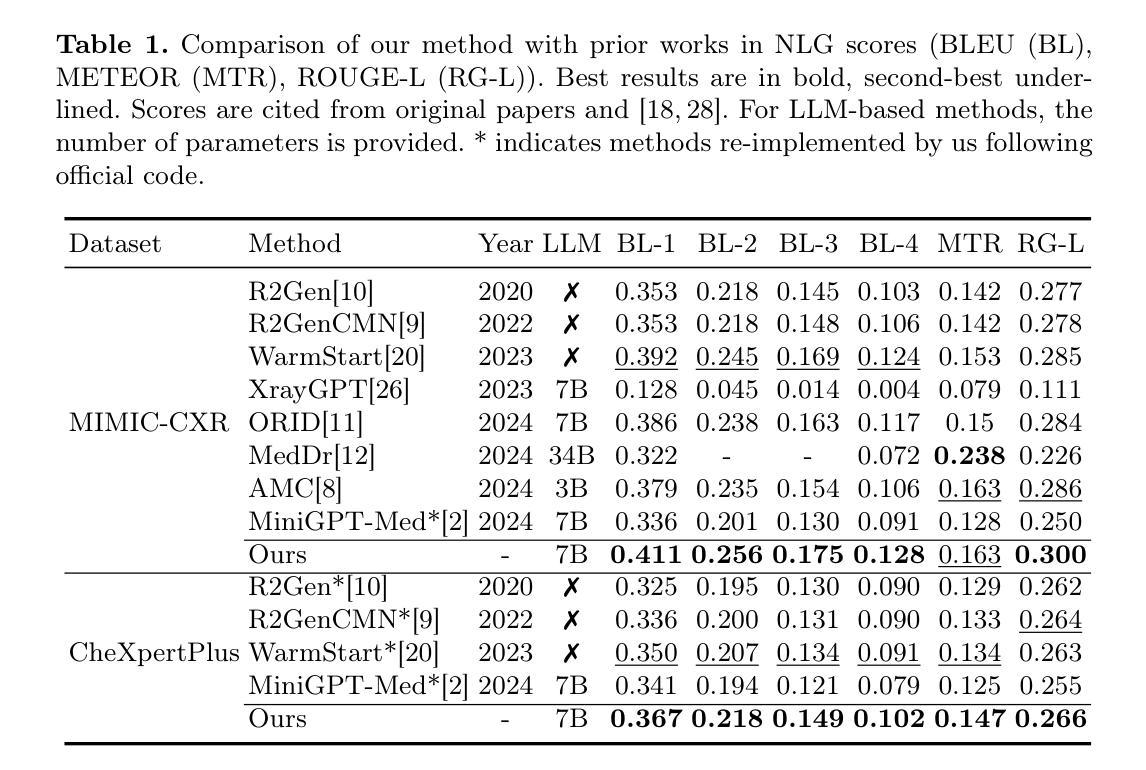
MCA-RG: Enhancing LLMs with Medical Concept Alignment for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Qilong Xing, Zikai Song, Youjia Zhang, Na Feng, Junqing Yu, Wei Yang
Despite significant advancements in adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) for radiology report generation (RRG), clinical adoption remains challenging due to difficulties in accurately mapping pathological and anatomical features to their corresponding text descriptions. Additionally, semantic agnostic feature extraction further hampers the generation of accurate diagnostic reports. To address these challenges, we introduce Medical Concept Aligned Radiology Report Generation (MCA-RG), a knowledge-driven framework that explicitly aligns visual features with distinct medical concepts to enhance the report generation process. MCA-RG utilizes two curated concept banks: a pathology bank containing lesion-related knowledge, and an anatomy bank with anatomical descriptions. The visual features are aligned with these medical concepts and undergo tailored enhancement. We further propose an anatomy-based contrastive learning procedure to improve the generalization of anatomical features, coupled with a matching loss for pathological features to prioritize clinically relevant regions. Additionally, a feature gating mechanism is employed to filter out low-quality concept features. Finally, the visual features are corresponding to individual medical concepts, and are leveraged to guide the report generation process. Experiments on two public benchmarks (MIMIC-CXR and CheXpert Plus) demonstrate that MCA-RG achieves superior performance, highlighting its effectiveness in radiology report generation.
尽管在将大型语言模型(LLM)适应于放射学报告生成(RRG)方面取得了重大进展,但由于将病理和解剖特征准确映射到相应的文本描述中的困难,其在临床上的应用仍然具有挑战性。此外,语义无关的特征提取进一步阻碍了准确诊断报告的生成。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了医学概念对齐放射学报告生成(MCA-RG),这是一个知识驱动框架,通过明确地将视觉特征与独特的医学概念对齐,以增强报告生成过程。MCA-RG利用两个精选的概念库:一个包含病变相关知识的病理库和一个包含解剖描述的解剖库。视觉特征与这些医学概念对齐,并进行有针对性的增强。我们进一步提出了一种基于解剖学的对比学习程序,以提高解剖特征的泛化能力,并结合病理特征的匹配损失来优先处理临床相关区域。此外,还采用了特征门控机制来过滤掉低质量的概念特征。最后,将视觉特征与单个医学概念相对应,并用于指导报告生成过程。在两个公共基准测试(MIMIC-CXR和CheXpert Plus)上的实验表明,MCA-RG取得了卓越的性能,突显其在放射学报告生成中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025
Summary
医学图像报告生成领域虽然已有大型语言模型的应用尝试,但由于病理和解剖特征与文本描述之间的映射困难以及语义无关的特征提取问题,临床采纳仍面临挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出医学概念对齐的放射学报告生成框架(MCA-RG),通过明确对齐视觉特征与特定的医学概念来强化报告生成过程。该框架利用两个精选的概念库:包含病变相关知识的病理学库和包含解剖学描述的解剖学库。实验结果表明,MCA-RG在公开数据集上表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在放射学报告生成中的应用面临病理和解剖特征与文本映射困难的问题。
- MCA-RG是一个知识驱动框架,旨在解决上述问题,通过明确对齐视觉特征与医学概念来强化报告生成。
- 框架包含两个概念库:病理学库和解剖学库,用于对齐视觉特征。
- 解剖学对比学习程序和匹配损失用于改善特征泛化能力和关注临床重要区域。
- 特征门控机制用于过滤低质量概念特征。
- 实验结果证明MCA-RG在放射学报告生成中的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

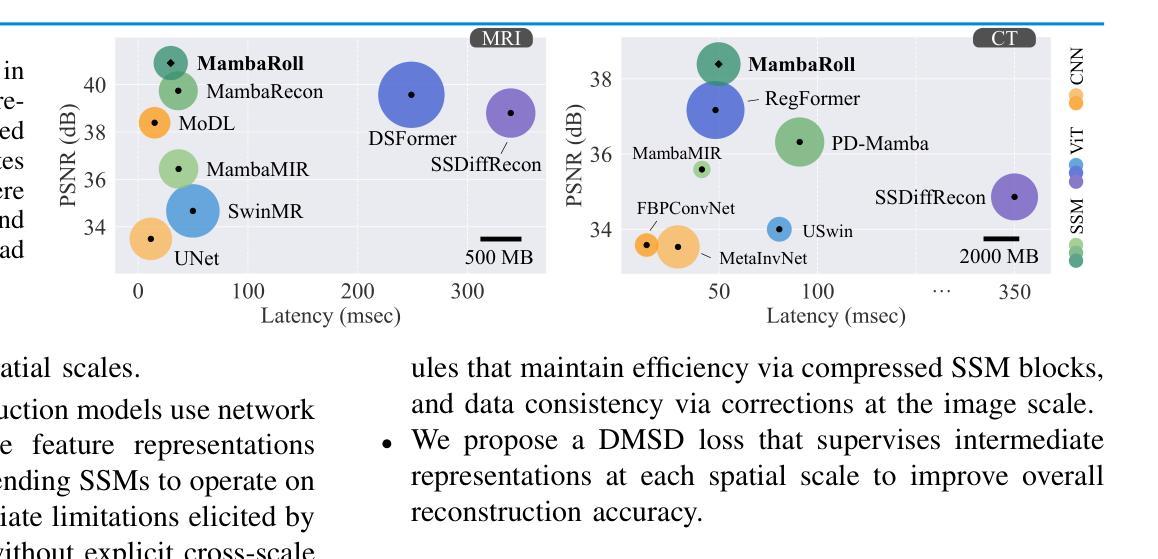
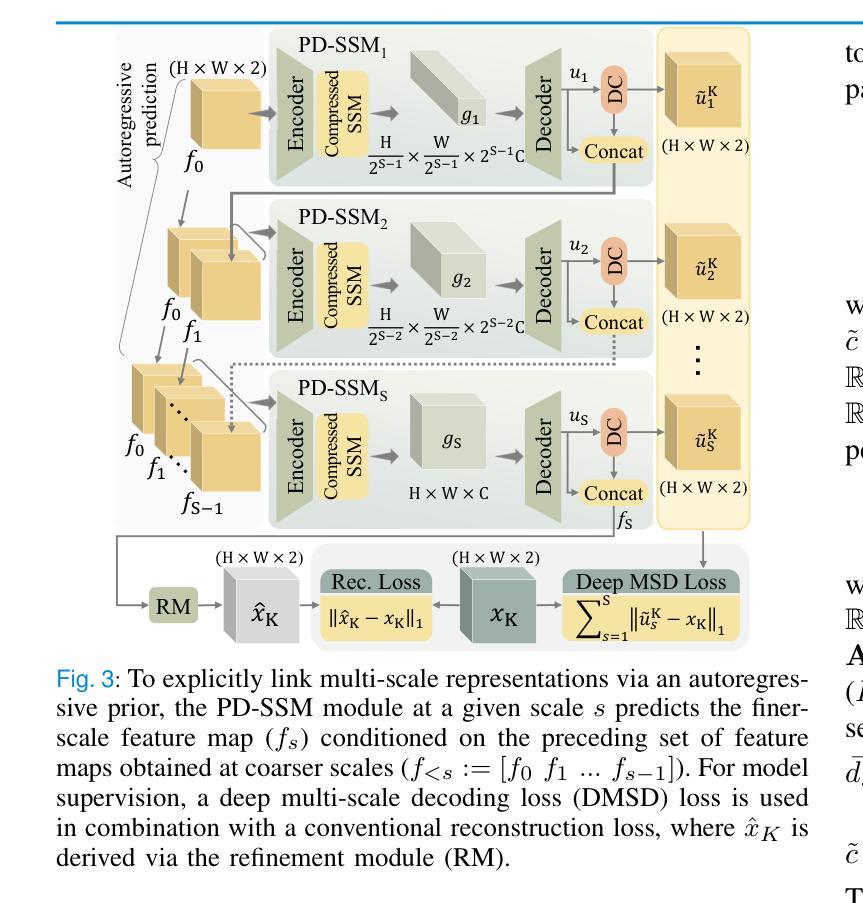
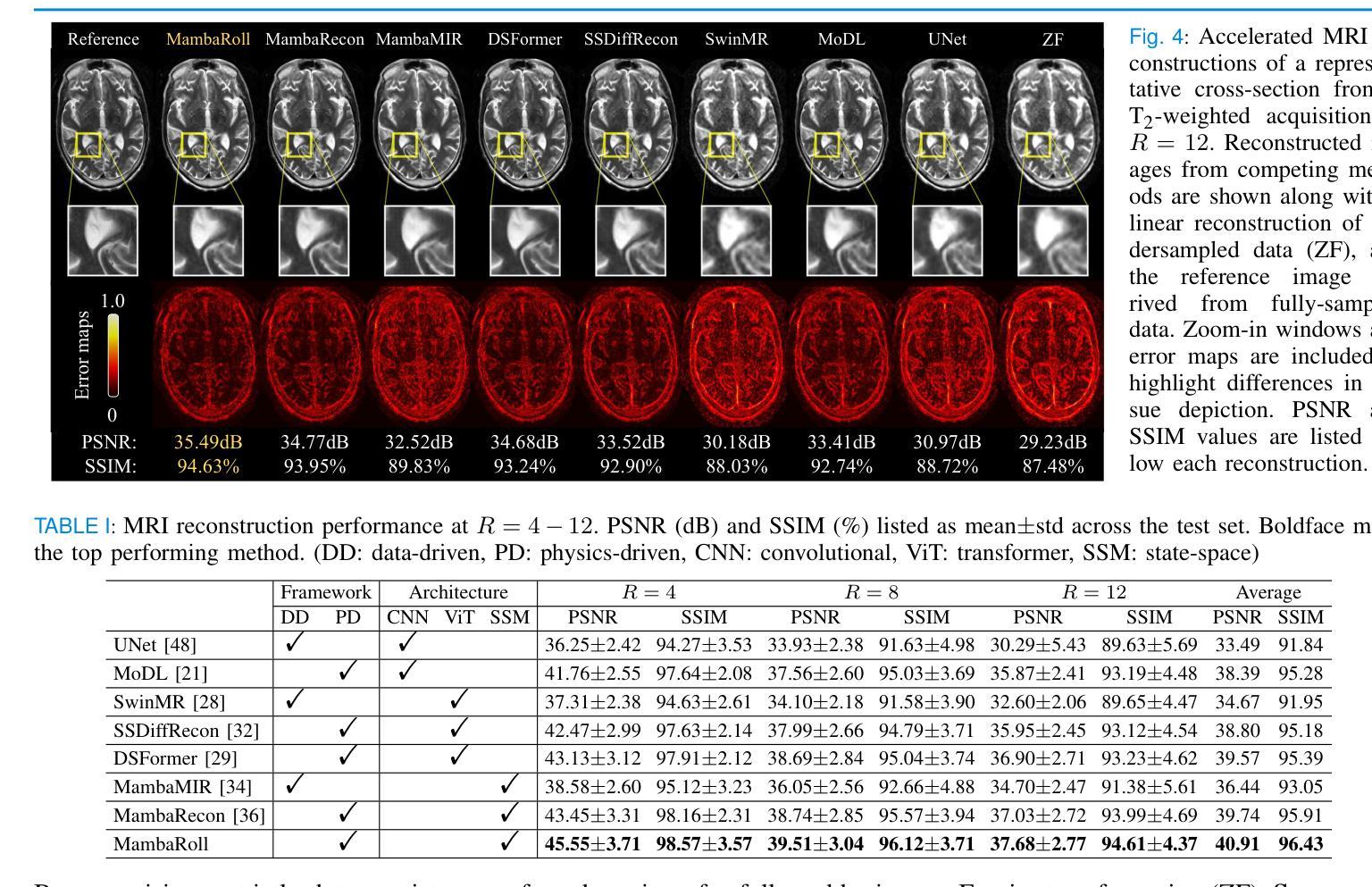
Physics-Driven Autoregressive State Space Models for Medical Image Reconstruction
Authors:Bilal Kabas, Fuat Arslan, Valiyeh A. Nezhad, Saban Ozturk, Emine U. Saritas, Tolga Çukur
Medical image reconstruction from undersampled acquisitions is an ill-posed inverse problem requiring accurate recovery of anatomical structures from incomplete measurements. Physics-driven (PD) network models have gained prominence for this task by integrating data-consistency mechanisms with learned priors, enabling improved performance over purely data-driven approaches. However, reconstruction quality still hinges on the network’s ability to disentangle artifacts from true anatomical signals-both of which exhibit complex, multi-scale contextual structure. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) capture local correlations but often struggle with non-local dependencies. While transformers aim to alleviate this limitation, practical implementations involve design compromises to reduce computational cost by balancing local and non-local sensitivity, occasionally resulting in performance comparable to CNNs. To address these challenges, we propose MambaRoll, a novel physics-driven autoregressive state space model (SSM) for high-fidelity and efficient image reconstruction. MambaRoll employs an unrolled architecture where each cascade autoregressively predicts finer-scale feature maps conditioned on coarser-scale representations, enabling consistent multi-scale context propagation. Each stage is built on a hierarchy of scale-specific PD-SSM modules that capture spatial dependencies while enforcing data consistency through residual correction. To further improve scale-aware learning, we introduce a Deep Multi-Scale Decoding (DMSD) loss, which provides supervision at intermediate spatial scales in alignment with the autoregressive design. Demonstrations on accelerated MRI and sparse-view CT reconstructions show that MambaRoll consistently outperforms state-of-the-art CNN-, transformer-, and SSM-based methods.
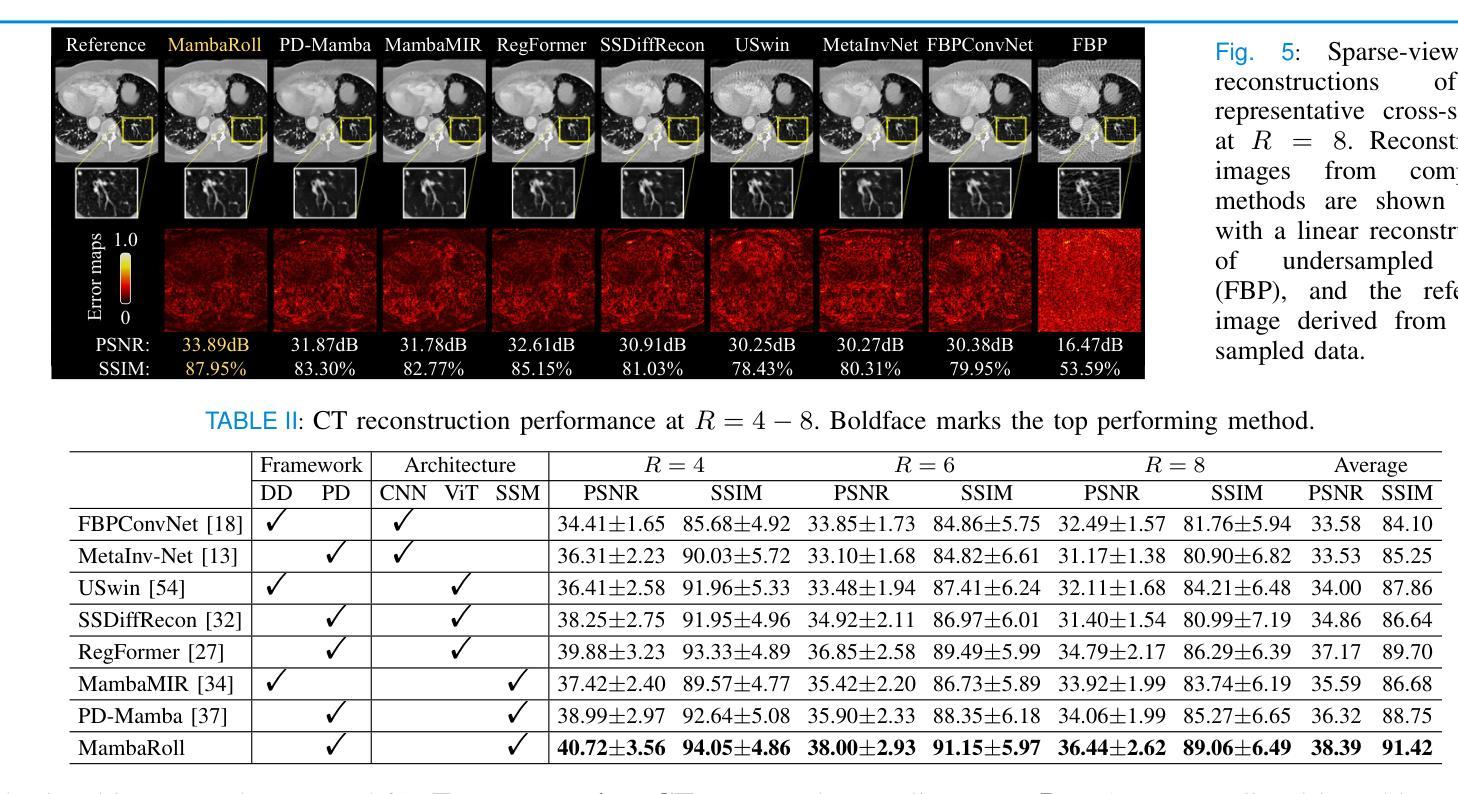
从欠采样采集中进行医学图像重建是一个不适定的逆问题,需要从不完全的测量中准确恢复解剖结构。物理驱动(PD)网络模型通过整合数据一致性和学习先验机制而在此任务中崭露头角,相比纯粹的数据驱动方法实现了性能提升。然而,重建质量仍然取决于网络区分伪影和真实解剖信号的能力,这两者都表现出复杂的多尺度上下文结构。卷积神经网络(CNN)能够捕捉局部相关性,但经常对非局部依赖性处理得吃力。虽然变压器旨在缓解这一局限性,但实际应用中的实现需要在减少计算成本的同时平衡局部和非局部敏感性,偶尔会导致性能与CNN相当。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了MambaRoll,这是一种用于高保真和高效图像重建的新型物理驱动自回归状态空间模型(SSM)。MambaRoll采用展开架构,其中每个级联自回归预测基于较粗糙尺度表示的较细尺度特征图,从而实现一致的多尺度上下文传播。每个阶段都建立在层次化的尺度特定PD-SSM模块上,这些模块能够捕获空间依赖性,同时通过残差修正来强制数据一致性。为了进一步提高尺度感知学习,我们引入了深度多尺度解码(DMSD)损失,该损失在自回归设计的中间空间尺度上提供监督。在加速MRI和稀疏视图CT重建的演示中,MambaRoll始终优于最先进的CNN、变压器和SSM方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 10 figures
摘要
本文提出一种名为MambaRoll的新型物理驱动自回归状态空间模型(SSM),用于高保真和高效的医学图像重建。该模型采用解卷架构,每个阶段自回归地预测更精细尺度的特征图,这些预测基于较粗糙尺度的表示,从而实现一致的多尺度上下文传播。每个阶段都建立在层次化的尺度特定PD-SSM模块上,这些模块在捕获空间依赖性的同时,通过残差校正强制执行数据一致性。为进一步提高尺度感知学习,引入深度多尺度解码(DMSD)损失,在自回归设计对齐的中间空间尺度上提供监督。在加速MRI和稀疏视图CT重建的演示中,MambaRoll一致地优于基于CNN、transformer和SSM的方法。
关键见解
- 医学图像重建是从不完全测量中准确恢复解剖结构的一个不适定逆问题。
- 物理驱动(PD)网络模型通过整合数据一致性与学习先验,在医学图像重建任务中表现优异。
- 现有方法(如卷积神经网络和变压器)在解决非局部依赖性和多尺度上下文结构方面存在挑战。
- MambaRoll模型采用自回归状态空间模型(SSM)架构,旨在实现高保真和高效的图像重建。
- MambaRoll在每个阶段使用层次化的尺度特定PD-SSM模块,捕获空间依赖性并强制执行数据一致性。
- 引入深度多尺度解码(DMSD)损失,以改进尺度感知学习并符合自回归设计。
点此查看论文截图
Kinetic-Diffusion-Rotation Algorithm for Dose Estimation in Electron Beam Therapy
Authors:Klaas Willems, Vince Maes, Zhirui Tang, Giovanni Samaey
Monte Carlo methods are state-of-the-art when it comes to dosimetric computations in radiotherapy. However, the execution time of these methods suffers in high-collisional regimes. We address this problem by introducing a kinetic-diffusion particle tracing scheme. This algorithm, first proposed in the context of neutral transport in fusion energy, relies on explicit simulation of the kinetic motion in low-collisional regimes and dynamically switches to motion based on a random walk in high-collisional regimes. The random walk motion maintains the first two moments (mean and variance) of the kinetic motion. We derive an analytic formula for the mean kinetic motion and discuss the addition of a multiple scattering distribution to the algorithm. In contrast to neutral transport, the radiation transfer setting does not readily admit to an analytical expression for the variance of the kinetic motion, and we therefore resort to the use of a lookup table. We test the algorithm for dosimetric computations in radiation therapy on a 2D CT scan of a lung patient. Using a simple particle model, our Python implementation of the algorithm is nearly 33 times faster than an equivalent kinetic simulation at the cost of a small modeling error.
蒙特卡洛方法在放射治疗剂量计算方面属于最先进技术。然而,这些方法的执行时间在碰撞率较高的情况下会受到很大影响。我们通过引入一种动力学扩散粒子追踪方案来解决这个问题。该算法最初在核聚变能量中的中性粒子传输背景下提出,依赖于在低碰撞率环境中显式模拟动力学运动,并在高碰撞率环境中动态切换到基于随机游走的运动。随机游走运动保持了动力学运动的前两个矩(均值和方差)。我们为平均动力学运动推导了一个分析公式,并讨论了向算法中添加多重散射分布的问题。与中性粒子传输不同,辐射传输设置不便于接受动力学运动的方差的分析表达式,因此我们使用查找表。我们在肺部患者的2D CT扫描上测试了该算法在放射治疗剂量计算中的应用。使用简单的粒子模型,我们的算法Python实现比等效动力学模拟速度快近33倍,只需付出较小的建模误差代价。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对放疗中的剂量计算,提出一种基于动力学扩散粒子追踪方案的蒙特卡罗方法改进算法。该算法在低碰撞体制下显式模拟动力学运动,并在高碰撞体制下采用基于随机游走的运动。通过推导平均动力学运动的解析公式,并加入多重散射分布,在辐射传输环境中实现了快速且相对准确的剂量计算。
Key Takeaways
- 蒙特卡罗方法在放疗剂量计算中处于前沿地位,但在高碰撞体制下执行时间较长。
- 提出一种基于动力学扩散粒子追踪方案的算法,解决这一问题。
- 该算法在低碰撞体制下显式模拟动力学运动,并在高碰撞体制下采用随机游走运动。
- 算法通过推导平均动力学运动的解析公式,并加入多重散射分布,提高计算准确性。
- 辐射传输环境不支持对动力学运动的方差进行解析表达式计算,因此采用查找表。
- 在二维肺部CT扫描上测试该算法进行放疗剂量计算。
点此查看论文截图

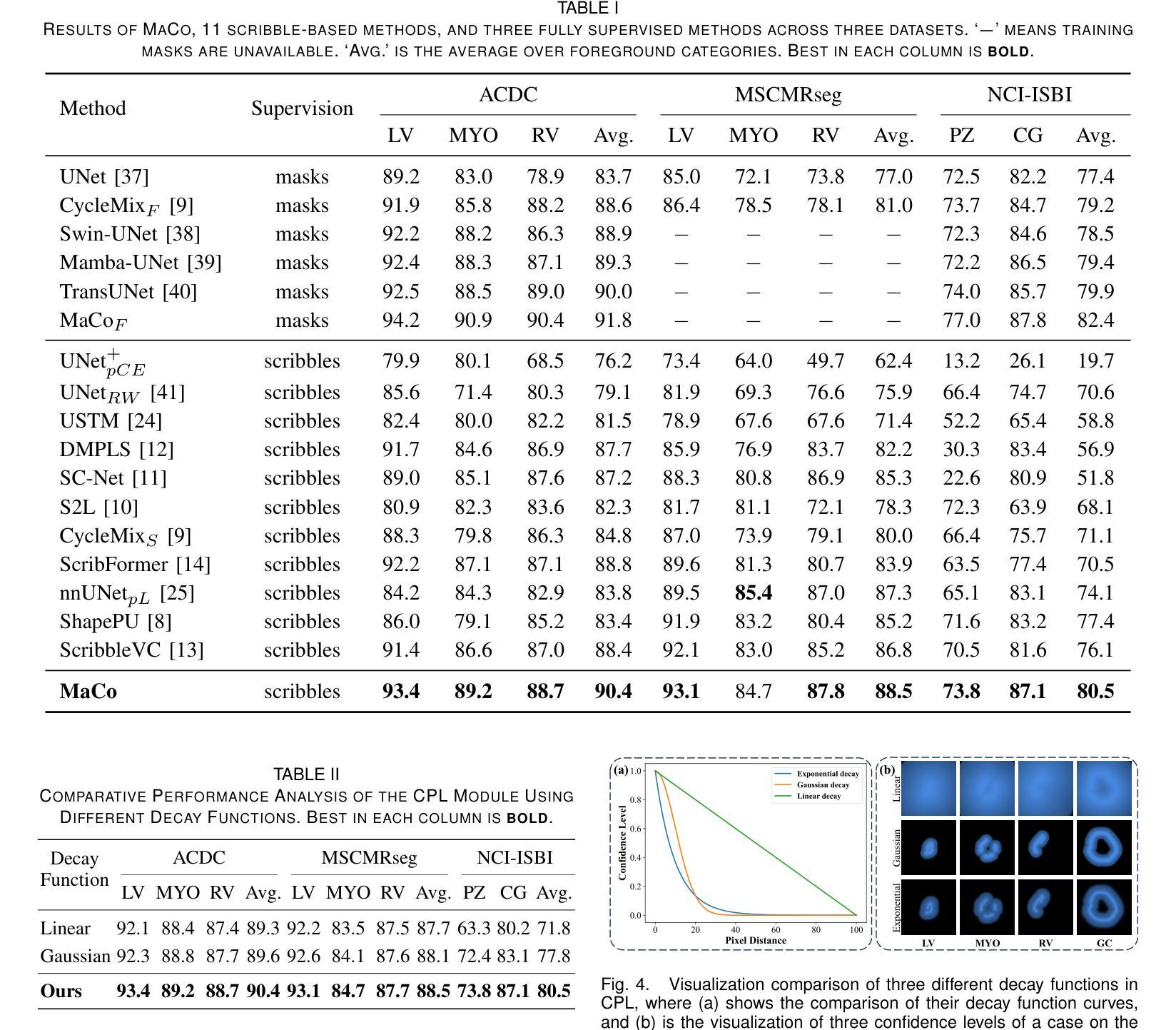
From Few to More: Scribble-based Medical Image Segmentation via Masked Context Modeling and Continuous Pseudo Labels
Authors:Zhisong Wang, Yiwen Ye, Ziyang Chen, Minglei Shu, Yanning Zhang, Yong Xia
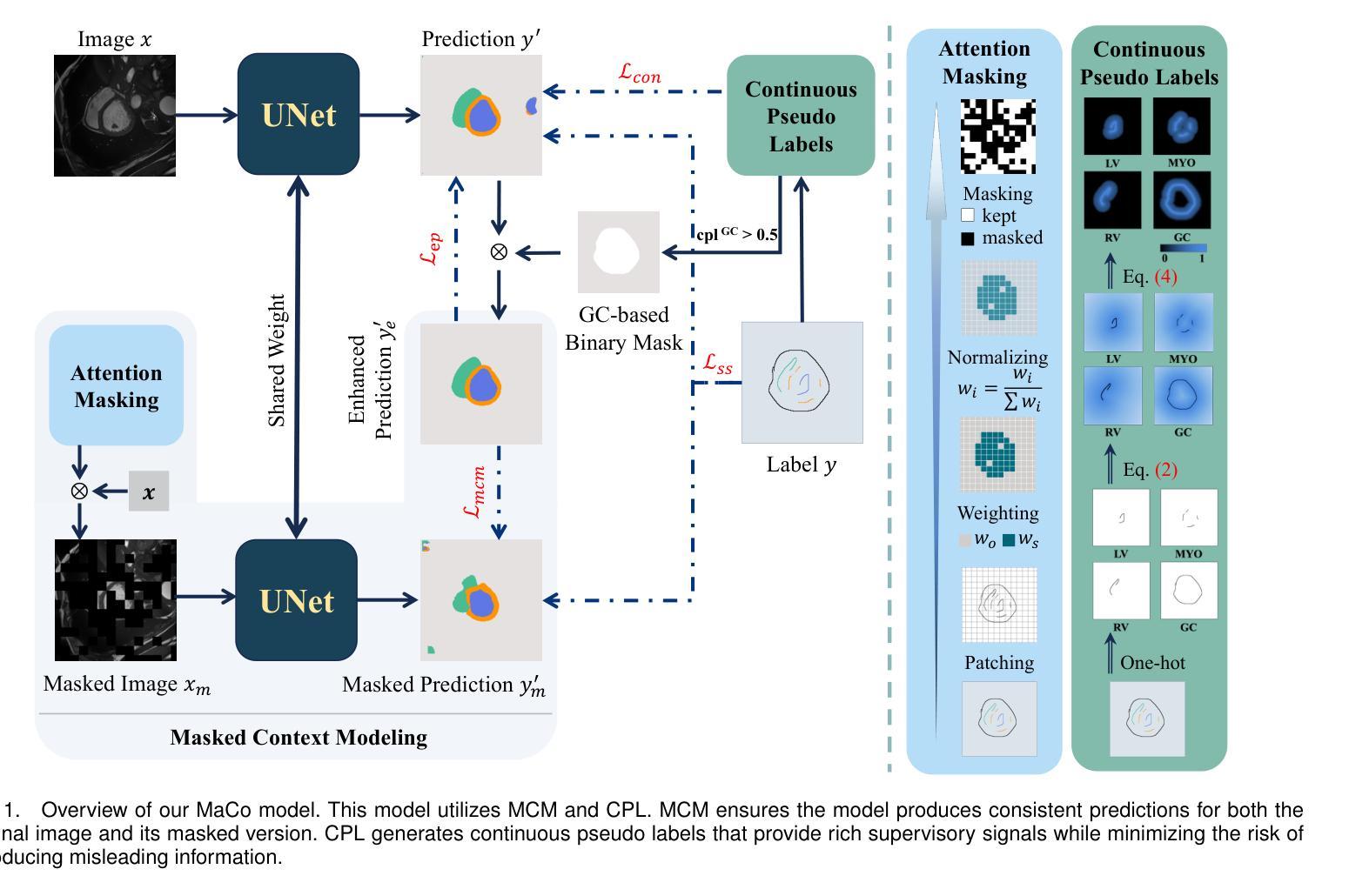
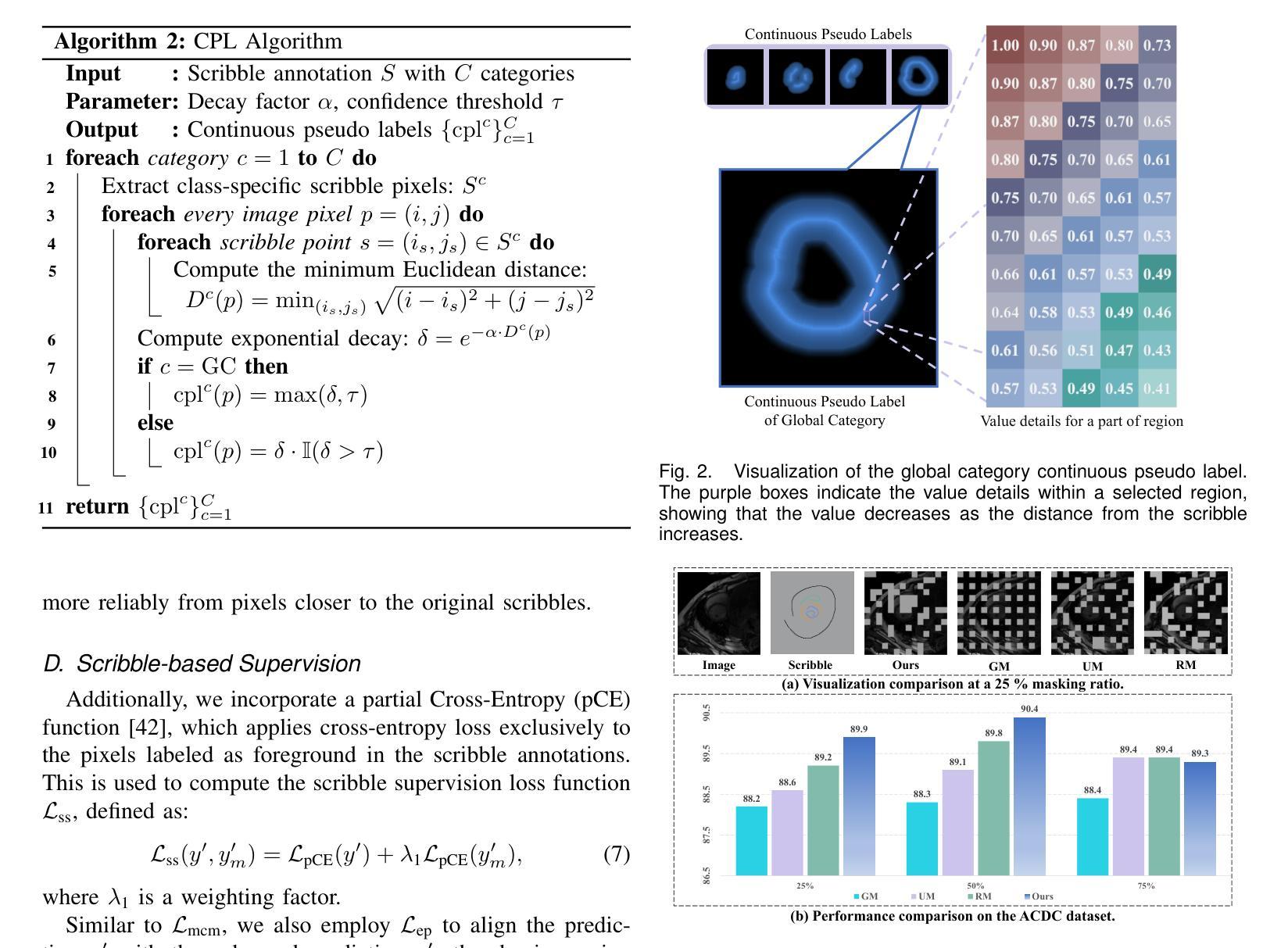
Scribble-based weakly supervised segmentation methods have shown promising results in medical image segmentation, significantly reducing annotation costs. However, existing approaches often rely on auxiliary tasks to enforce semantic consistency and use hard pseudo labels for supervision, overlooking the unique challenges faced by models trained with sparse annotations. These models must predict pixel-wise segmentation maps from limited data, making it crucial to handle varying levels of annotation richness effectively. In this paper, we propose MaCo, a weakly supervised model designed for medical image segmentation, based on the principle of “from few to more.” MaCo leverages Masked Context Modeling (MCM) and Continuous Pseudo Labels (CPL). MCM employs an attention-based masking strategy to perturb the input image, ensuring that the model’s predictions align with those of the original image. CPL converts scribble annotations into continuous pixel-wise labels by applying an exponential decay function to distance maps, producing confidence maps that represent the likelihood of each pixel belonging to a specific category, rather than relying on hard pseudo labels. We evaluate MaCo on three public datasets, comparing it with other weakly supervised methods. Our results show that MaCo outperforms competing methods across all datasets, establishing a new record in weakly supervised medical image segmentation.
基于涂画弱监督的分割方法在汽车图像分割方面展现出了良好的结果,显著降低了标注成本。然而,现有方法通常依赖辅助任务来强制执行语义一致性,并使用硬伪标签进行监督,从而忽略了用稀疏注释训练的模型所面临的独特挑战。这些模型必须从有限数据中预测像素级的分割图,因此有效处理不同级别的注释丰富度至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了MaCo,这是一种为医学图像分割设计的弱监督模型,基于“从少到多”的原则。MaCo利用掩模上下文建模(MCM)和连续伪标签(CPL)。MCM采用基于注意力的掩模策略来扰动输入图像,确保模型的预测与原始图像的预测一致。CPL通过应用指数衰减函数将涂画注释转换为连续的像素级标签,生成置信图,表示每个像素属于特定类别的可能性,而不是依赖硬伪标签。我们在三个公共数据集上评估了MaCo,并将其与其他弱监督方法进行了比较。结果表明,MaCo在所有数据集上的表现均优于其他方法,在弱监督医学图像分割方面创造了新的纪录。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 10 figures, 10 tables, JBHI
Summary
本文提出了一种基于弱监督的医学图像分割模型MaCo,采用“从少到多”的设计原则。模型结合Masked Context Modeling(MCM)和Continuous Pseudo Labels(CPL)技术,有效处理稀疏标注数据,预测像素级分割图。实验证明,MaCo在三个公开数据集上的表现均超越其他弱监督方法,创下了新的纪录。
Key Takeaways
- Scribble-based弱监督分割方法在医学图像分割中展现出降低标注成本的优势。
- 现有方法常借助辅助任务来加强语义一致性,但忽视了稀疏标注数据带来的挑战。
- MaCo模型利用Masked Context Modeling(MCM)和Continuous Pseudo Labels(CPL)技术应对挑战。
- MCM通过注意力机制干扰输入图像,确保模型预测与原始图像一致。
- CPL将涂鸦标注转化为连续的像素级标签,通过指数衰减函数生成置信图。
- MaCo模型在三个公开数据集上的表现优于其他弱监督方法。
点此查看论文截图


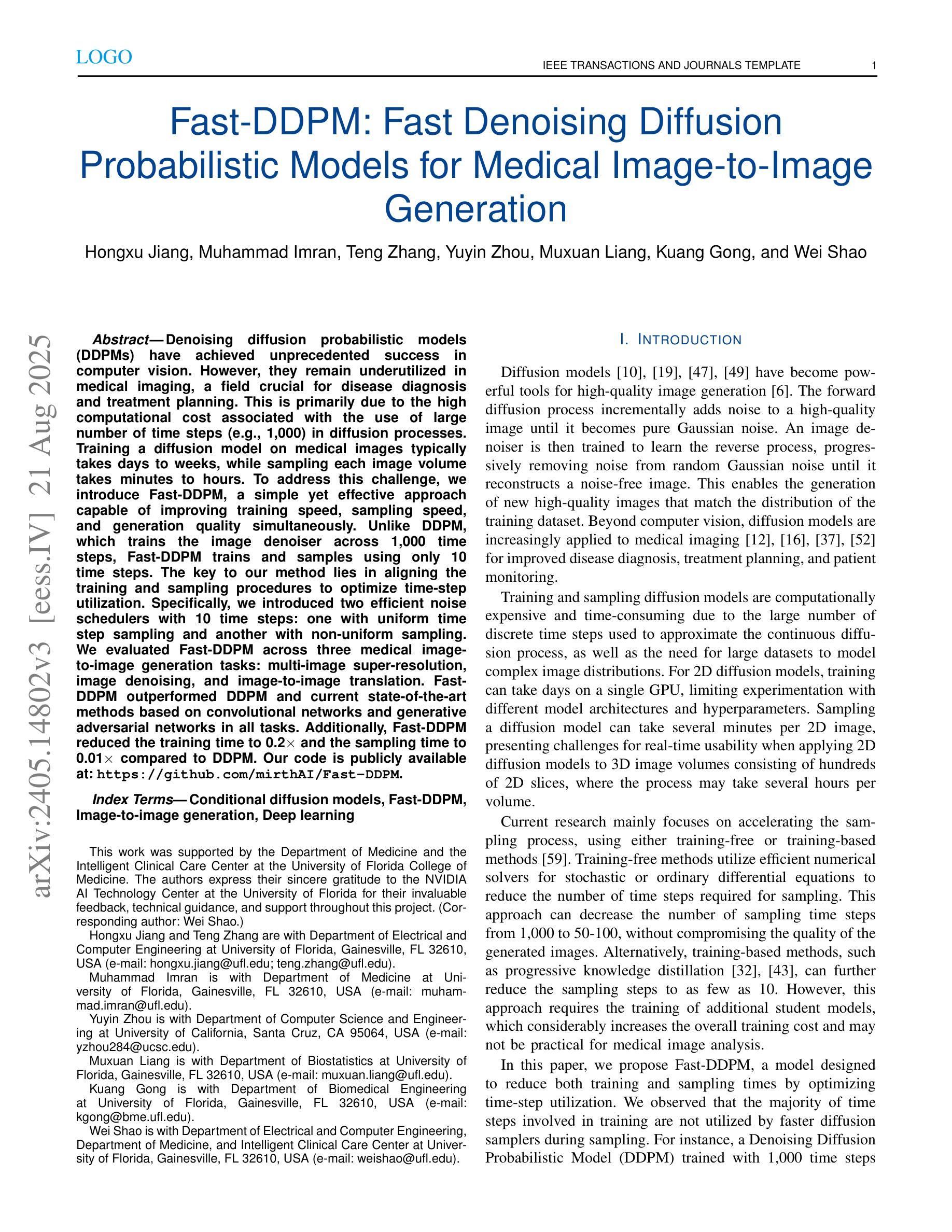
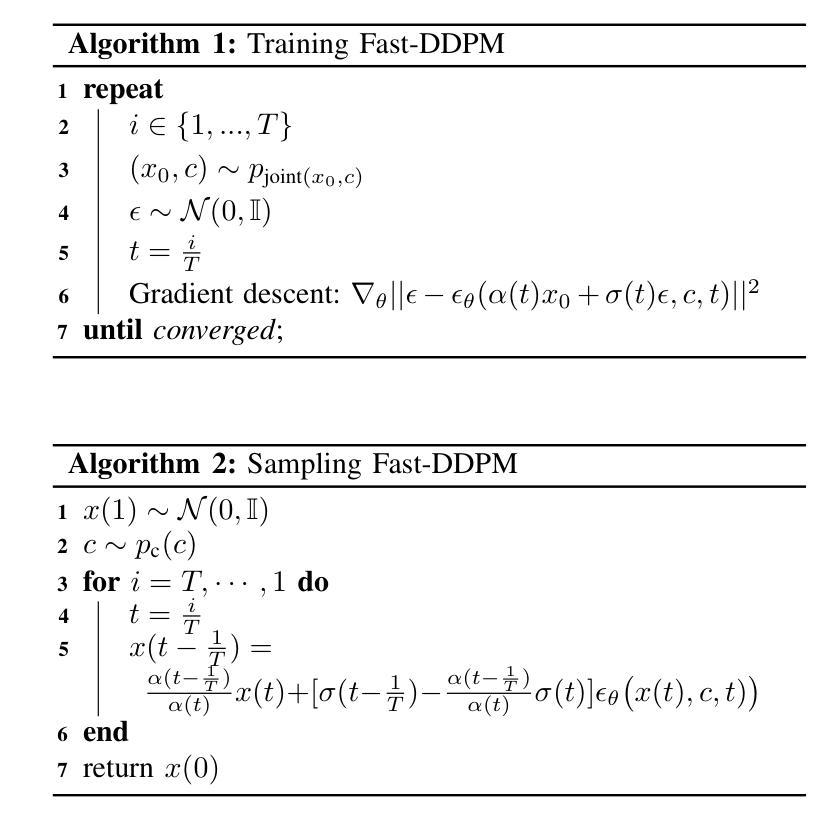
Fast-DDPM: Fast Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Medical Image-to-Image Generation
Authors:Hongxu Jiang, Muhammad Imran, Teng Zhang, Yuyin Zhou, Muxuan Liang, Kuang Gong, Wei Shao
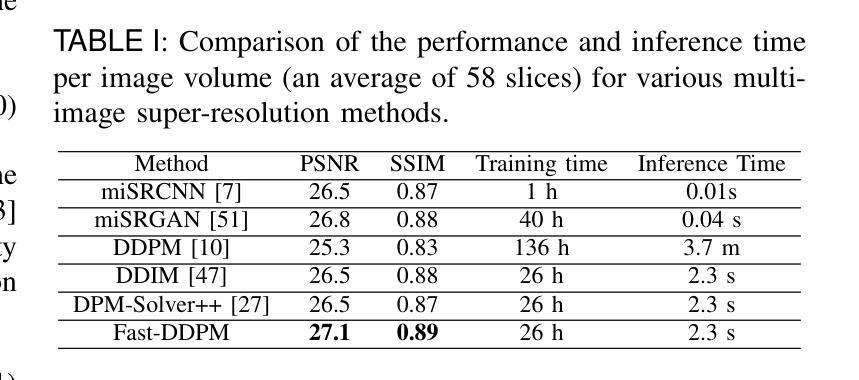
Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) have achieved unprecedented success in computer vision. However, they remain underutilized in medical imaging, a field crucial for disease diagnosis and treatment planning. This is primarily due to the high computational cost associated with (1) the use of large number of time steps (e.g., 1,000) in diffusion processes and (2) the increased dimensionality of medical images, which are often 3D or 4D. Training a diffusion model on medical images typically takes days to weeks, while sampling each image volume takes minutes to hours. To address this challenge, we introduce Fast-DDPM, a simple yet effective approach capable of improving training speed, sampling speed, and generation quality simultaneously. Unlike DDPM, which trains the image denoiser across 1,000 time steps, Fast-DDPM trains and samples using only 10 time steps. The key to our method lies in aligning the training and sampling procedures to optimize time-step utilization. Specifically, we introduced two efficient noise schedulers with 10 time steps: one with uniform time step sampling and another with non-uniform sampling. We evaluated Fast-DDPM across three medical image-to-image generation tasks: multi-image super-resolution, image denoising, and image-to-image translation. Fast-DDPM outperformed DDPM and current state-of-the-art methods based on convolutional networks and generative adversarial networks in all tasks. Additionally, Fast-DDPM reduced the training time to 0.2x and the sampling time to 0.01x compared to DDPM. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM.
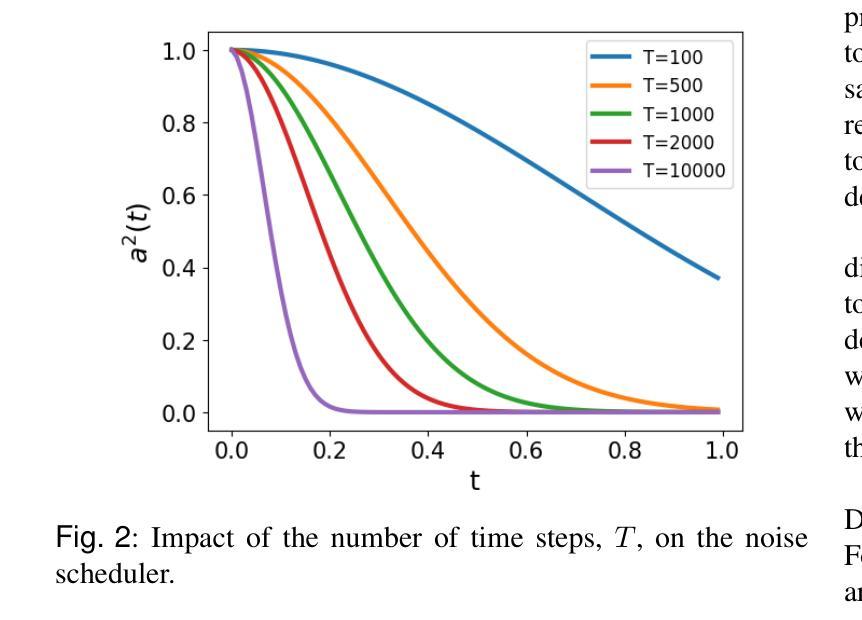
去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)在计算机视觉领域取得了前所未有的成功。然而,它们在医学成像领域的应用仍然被低估,而医学成像对于疾病诊断和治疗计划至关重要。这主要是因为与(1)扩散过程中使用的大量时间步数(例如,1000步)和(2)医学图像增加的维度(通常为3D或4D)相关的计算成本高昂。在医学图像上训练扩散模型通常需要几天到几周的时间,而对每个图像体积进行采样则需要几分钟到几小时。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了Fast-DDPM,这是一种简单而有效的方法,可以同时提高训练速度、采样速度和生成质量。与DDPM不同,它在整个训练过程中跨一千个时间步训练图像去噪器,而Fast-DDPM仅使用十个时间步进行训练和采样。我们的方法的关键在于对齐训练和采样过程以优化时间步长的利用。具体来说,我们引入了两种具有十个时间步的高效噪声调度器:一种具有均匀时间步长采样,另一种具有非均匀采样。我们在三项医学图像到图像生成任务中评估了Fast-DDPM:多图像超分辨率、图像去噪和图像到图像转换。Fast-DDPM在所有任务中都优于DDPM和基于卷积网络和生成对抗网络的最先进方法。此外,Fast-DDPM将训练时间缩短至DDPM的0.2倍,采样时间缩短至DDPM的0.01倍。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
快速DDPM模型优化了训练与采样过程,能在医疗图像领域以较少的步骤实现高质量的图像生成。相较于DDPM模型使用的一千步扩散过程,快速DDPM仅使用十个步骤即可完成训练和采样过程。模型包含两个噪声调度器以提高效率,包括均匀和非均匀采样步骤。实验结果显示,在多种医疗图像生成任务中,快速DDPM模型均优于DDPM模型和当前其他先进的卷积网络模型与生成对抗网络模型,并且在训练与采样时间上显著缩短了原有模型所需的时间。其代码已公开分享于网址:https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM。
关键要点
- 快速DDPM模型适用于医疗图像领域,通过优化训练和采样过程提高了效率。
- 与DDPM模型相比,快速DDPM通过使用更少的步骤实现了训练和采样过程的提速。通过两个高效的噪声调度器(均匀与非均匀采样步骤)提高了时间步长的利用率。
- 在多种医疗图像生成任务中,快速DDPM模型表现出超越其他先进模型的优势,如多图像超分辨率、图像去噪和图像转换任务等。
- 与其他模型相比,快速DDPM模型显著缩短了训练时间和采样时间。这对于实际应用中的快速响应和高效处理至关重要。
- 该模型的公开代码可供研究者和开发者使用,进一步推动了其在医疗图像处理领域的应用和发展。
- 快速DDPM模型的引入为医疗图像处理领域带来了新的视角和解决方案,有望推动该领域的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图