⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
StreamMem: Query-Agnostic KV Cache Memory for Streaming Video Understanding
Authors:Yanlai Yang, Zhuokai Zhao, Satya Narayan Shukla, Aashu Singh, Shlok Kumar Mishra, Lizhu Zhang, Mengye Ren
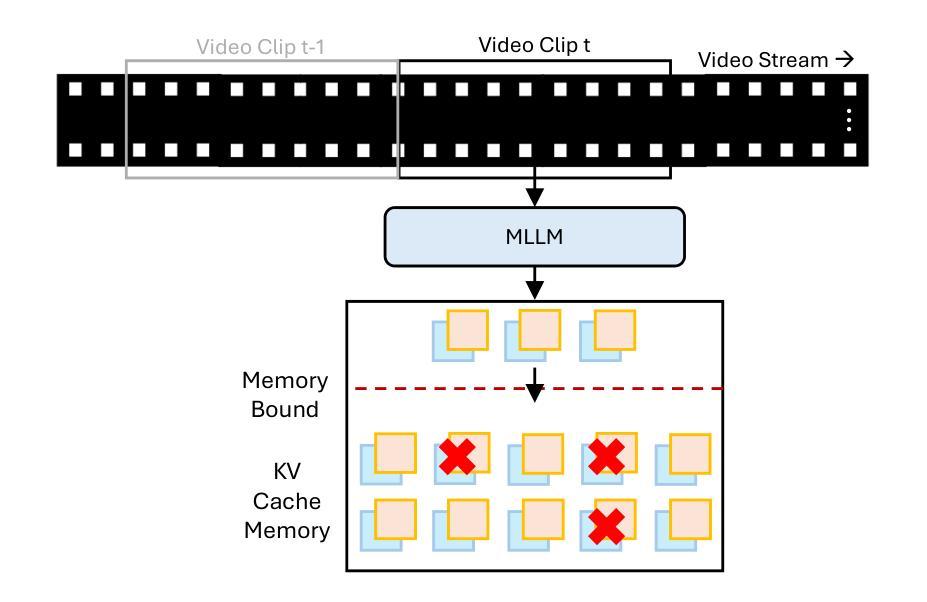
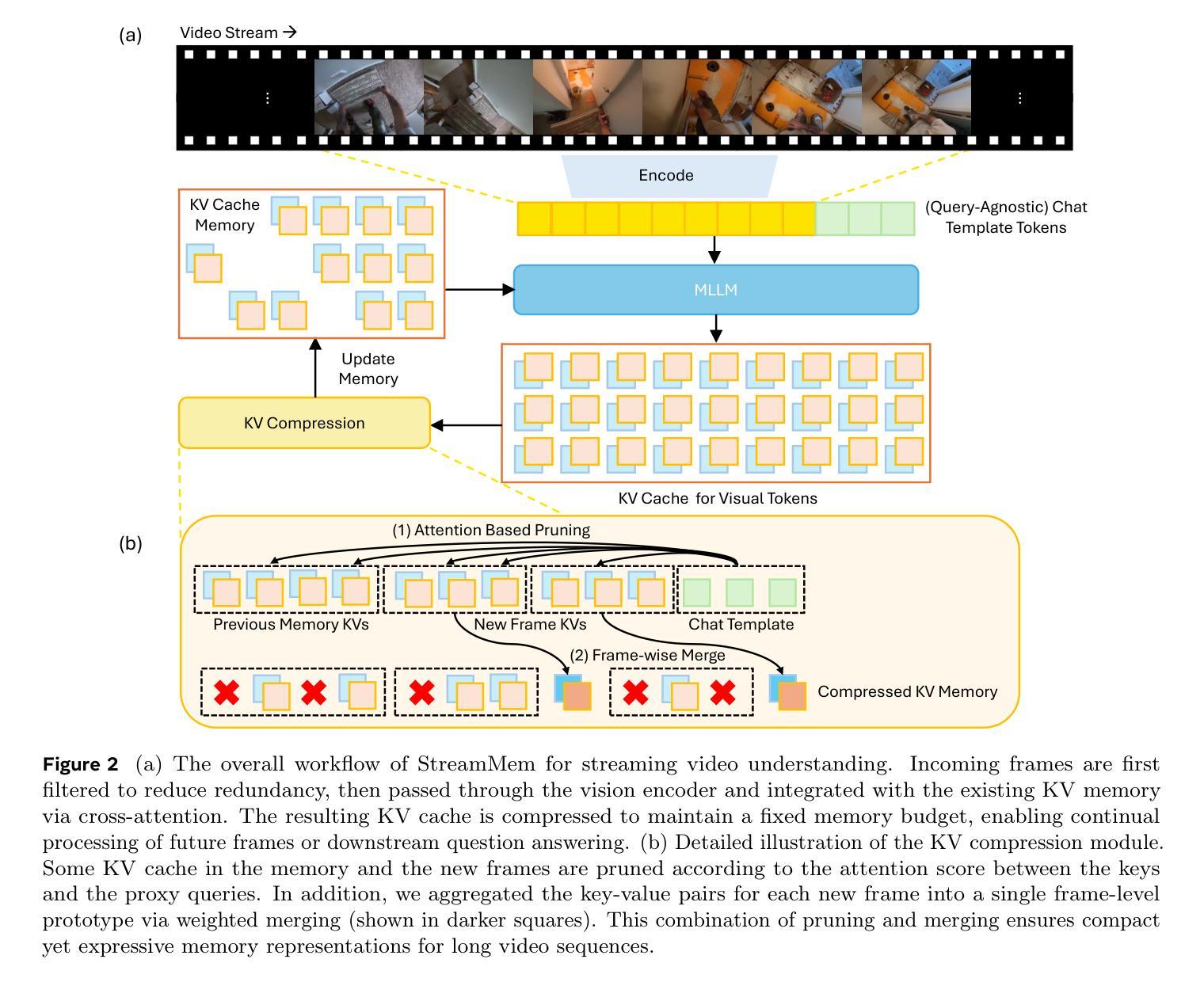
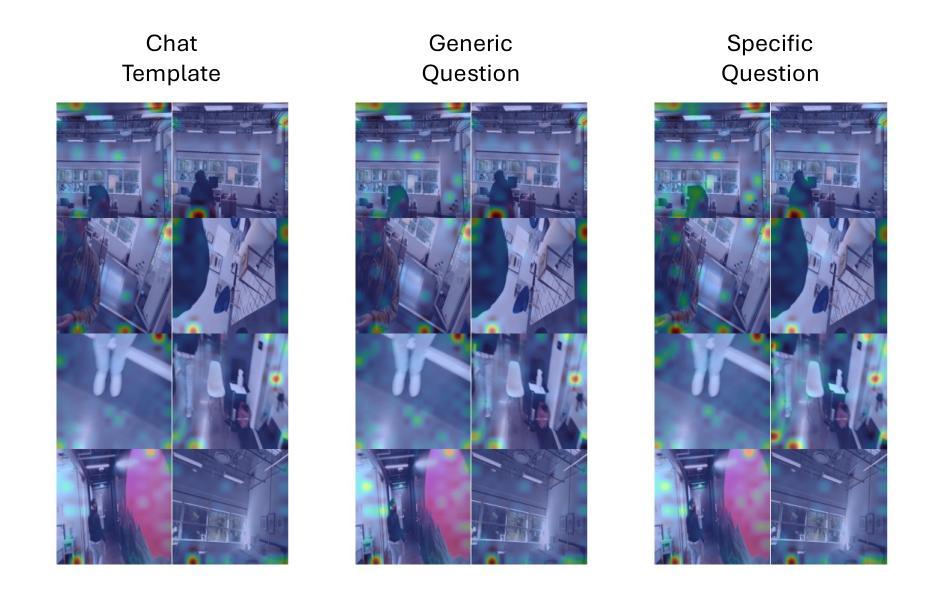
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have made significant progress in visual-language reasoning, but their ability to efficiently handle long videos remains limited. Despite recent advances in long-context MLLMs, storing and attending to the key-value (KV) cache for long visual contexts incurs substantial memory and computational overhead. Existing visual compression methods require either encoding the entire visual context before compression or having access to the questions in advance, which is impractical for long video understanding and multi-turn conversational settings. In this work, we propose StreamMem, a query-agnostic KV cache memory mechanism for streaming video understanding. Specifically, StreamMem encodes new video frames in a streaming manner, compressing the KV cache using attention scores between visual tokens and generic query tokens, while maintaining a fixed-size KV memory to enable efficient question answering (QA) in memory-constrained, long-video scenarios. Evaluation on three long video understanding and two streaming video question answering benchmarks shows that StreamMem achieves state-of-the-art performance in query-agnostic KV cache compression and is competitive with query-aware compression approaches.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言推理方面取得了显著进展,但它们高效处理长视频的能力仍然有限。尽管长上下文MLLMs的最新进展显著,但为长视觉上下文存储和关注键值(KV)缓存会产生巨大的内存和计算开销。现有的视觉压缩方法要么需要在压缩之前对整个视觉上下文进行编码,要么需要提前了解问题,这对于长视频理解和多轮对话环境来说并不实用。在本研究中,我们提出了StreamMem,这是一种用于流式视频理解的查询无关键值缓存记忆机制。具体来说,StreamMem以流式方式编码新的视频帧,使用视觉令牌和通用查询令牌之间的注意力分数压缩键值缓存,同时保持固定大小的键值内存,以在内存受限的长视频场景中实现高效的问题回答(QA)。在三个长视频理解和两个流式视频问答基准测试上的评估表明,StreamMem在查询无关键值缓存压缩方面达到了最新技术水平,并且在查询感知压缩方法中具有很强的竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对长视频理解的查询无关KV缓存压缩方法StreamMem。它能够以流式方式编码视频帧,利用视觉令牌和通用查询令牌之间的注意力分数进行KV缓存压缩,同时保持固定大小的KV内存,从而在内存受限的长视频场景中实现高效问答。评估结果表明,StreamMem在查询无关的KV缓存压缩方面达到了先进水平,并与查询感知压缩方法具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型在处理长视频时存在效率限制。
- 现有视觉压缩方法需要预先编码整个视觉上下文或提前获取问题,不适用于长视频理解和多回合对话场景。
- StreamMem是一种针对流式视频理解的查询无关KV缓存记忆机制。
- StreamMem以流式方式编码新的视频帧,利用视觉令牌和通用查询令牌之间的注意力分数进行KV缓存压缩。
- StreamMem保持固定大小的KV内存,实现在内存受限的长视频场景中的高效问答。
- StreamMem在查询无关的KV缓存压缩方面达到了先进水平。
点此查看论文截图

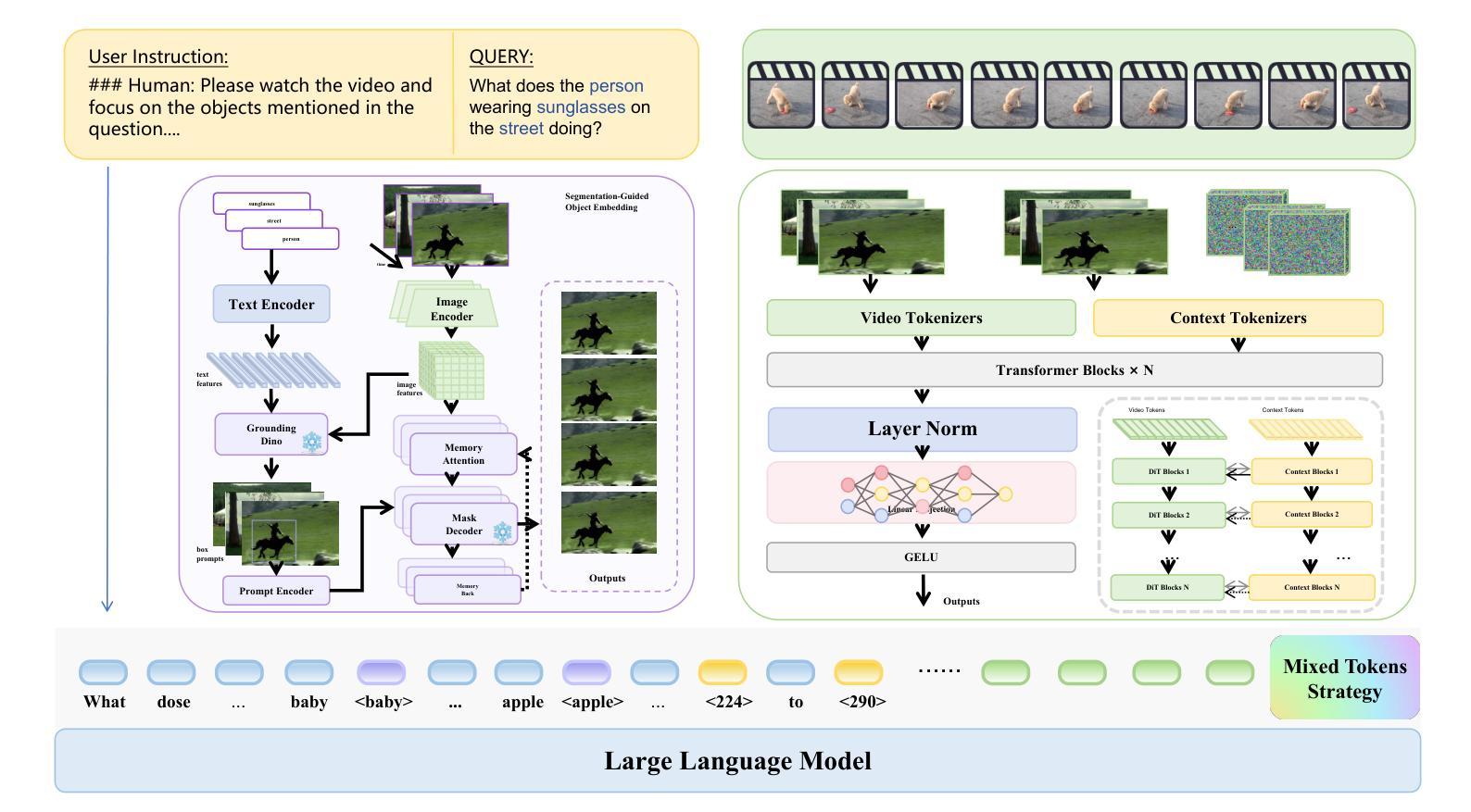
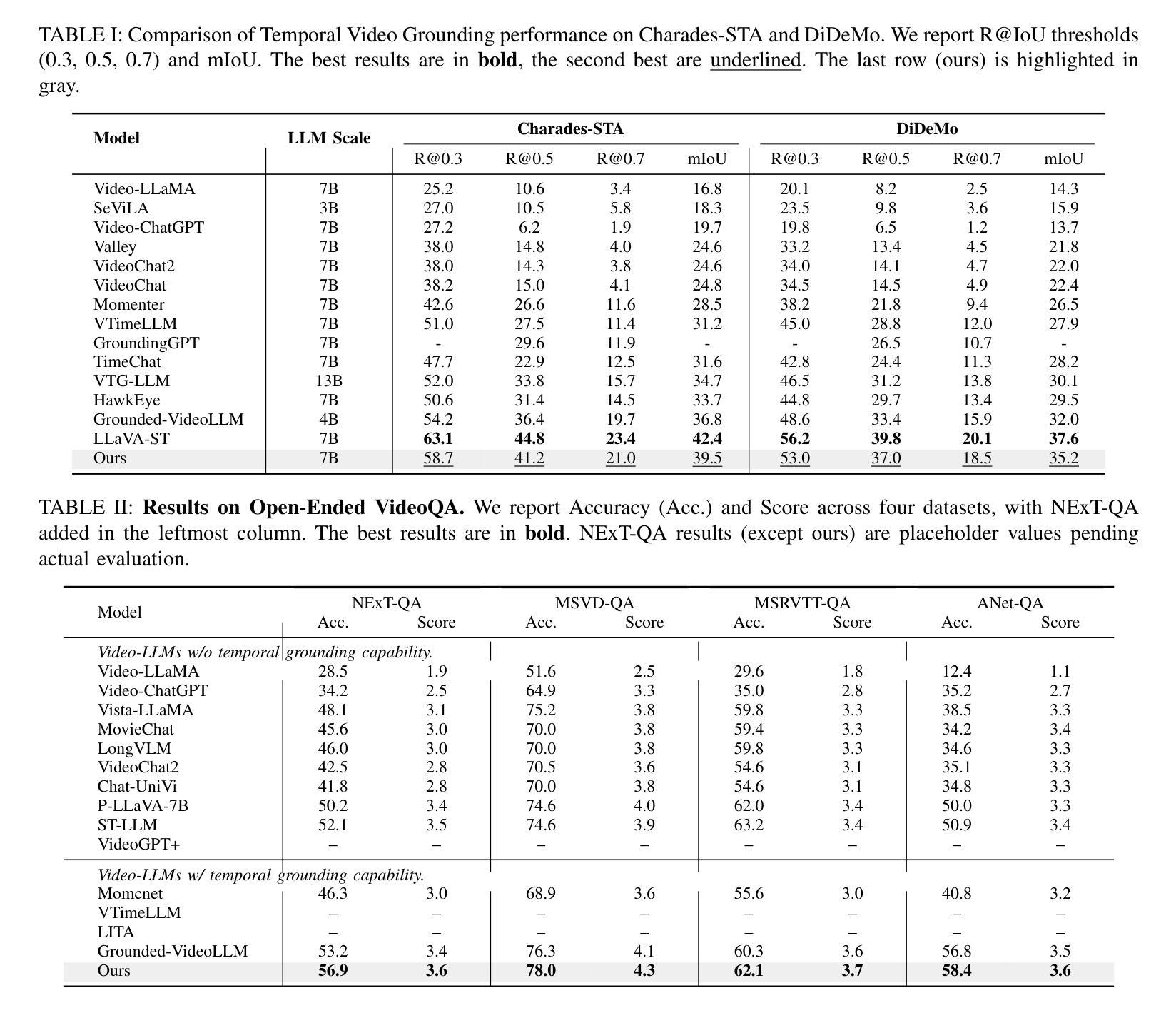
When and What: Diffusion-Grounded VideoLLM with Entity Aware Segmentation for Long Video Understanding
Authors:Pengcheng Fang, Yuxia Chen, Rui Guo
Understanding videos requires more than answering open ended questions, it demands the ability to pinpoint when events occur and how entities interact across time. While recent Video LLMs have achieved remarkable progress in holistic reasoning, they remain coarse in temporal perception: timestamps are encoded only implicitly, frame level features are weak in capturing continuity, and language vision alignment often drifts from the entities of interest. In this paper, we present Grounded VideoDiT, a Video LLM designed to overcome these limitations by introducing three key innovations. First, a Diffusion Temporal Latent (DTL) encoder enhances boundary sensitivity and maintains temporal consistency. Second, object grounded representations explicitly bind query entities to localized visual evidence, strengthening alignment. Third, a mixed token scheme with discrete temporal tokens provides explicit timestamp modeling, enabling fine grained temporal reasoning. Together, these designs equip Grounded VideoDiT with robust grounding capabilities, as validated by state of the art results on Charades STA, NExT GQA, and multiple VideoQA benchmarks.
理解视频不仅需要回答开放式问题,还要求能够精确指出事件发生的时机以及实体如何在时间中进行互动。尽管最近的视频大型语言模型(LLM)在整体推理方面取得了显著的进步,但在时间感知方面仍然较为粗糙:时间戳仅被隐式编码,帧级特征在捕捉连续性方面较弱,语言与视觉的对齐常常偏离感兴趣的实体。在本文中,我们介绍了Grounded VideoDiT,这是一款旨在通过三项关键创新克服这些局限的视频LLM。首先,扩散时间潜在(DTL)编码器增强了边界敏感性并保持时间一致性。其次,对象基础表示法显式地将查询实体绑定到局部视觉证据,加强了对齐。第三,采用带有离散时间标记的混合令牌方案提供了显式的时间戳建模,实现了精细的时间推理。这些设计共同使Grounded VideoDiT具备强大的接地能力,通过Charades STA、NExT GQA和多个视频QA基准测试的结果验证了其先进性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该文探讨了视频理解领域的新挑战,指出当前视频LLM在时空感知方面的局限性。为此,提出了一种名为Grounded VideoDiT的新型视频LLM模型。该模型通过引入三项关键技术突破应对这些挑战:采用扩散时间潜在(DTL)编码器提高边界敏感性和维持时间一致性;对象接地表示法显式绑定查询实体与局部视觉证据,加强对齐;采用带有离散时间标记的混合令牌方案,提供显式时间戳建模,实现精细的时间推理。这些设计使Grounded VideoDiT具备强大的接地能力,并通过Charades STA、NExT GQA等多个VideoQA基准测试验证了其有效性。
要点掌握
- 视频理解需要更精细的时空感知能力,当前视频LLM存在局限性。
- Grounded VideoDiT模型通过三项关键技术突破应对这些挑战。
- 采用扩散时间潜在(DTL)编码器提高边界敏感性和维持时间一致性。
- 对象接地表示法加强查询实体与视觉证据的对齐。
- 离散时间标记的混合令牌方案提供显式时间戳建模,实现精细的时间推理。
- Grounded VideoDiT模型在多个VideoQA基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图