⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
Enhancing Novel View Synthesis from extremely sparse views with SfM-free 3D Gaussian Splatting Framework
Authors:Zongqi He, Hanmin Li, Kin-Chung Chan, Yushen Zuo, Hao Xie, Zhe Xiao, Jun Xiao, Kin-Man Lam
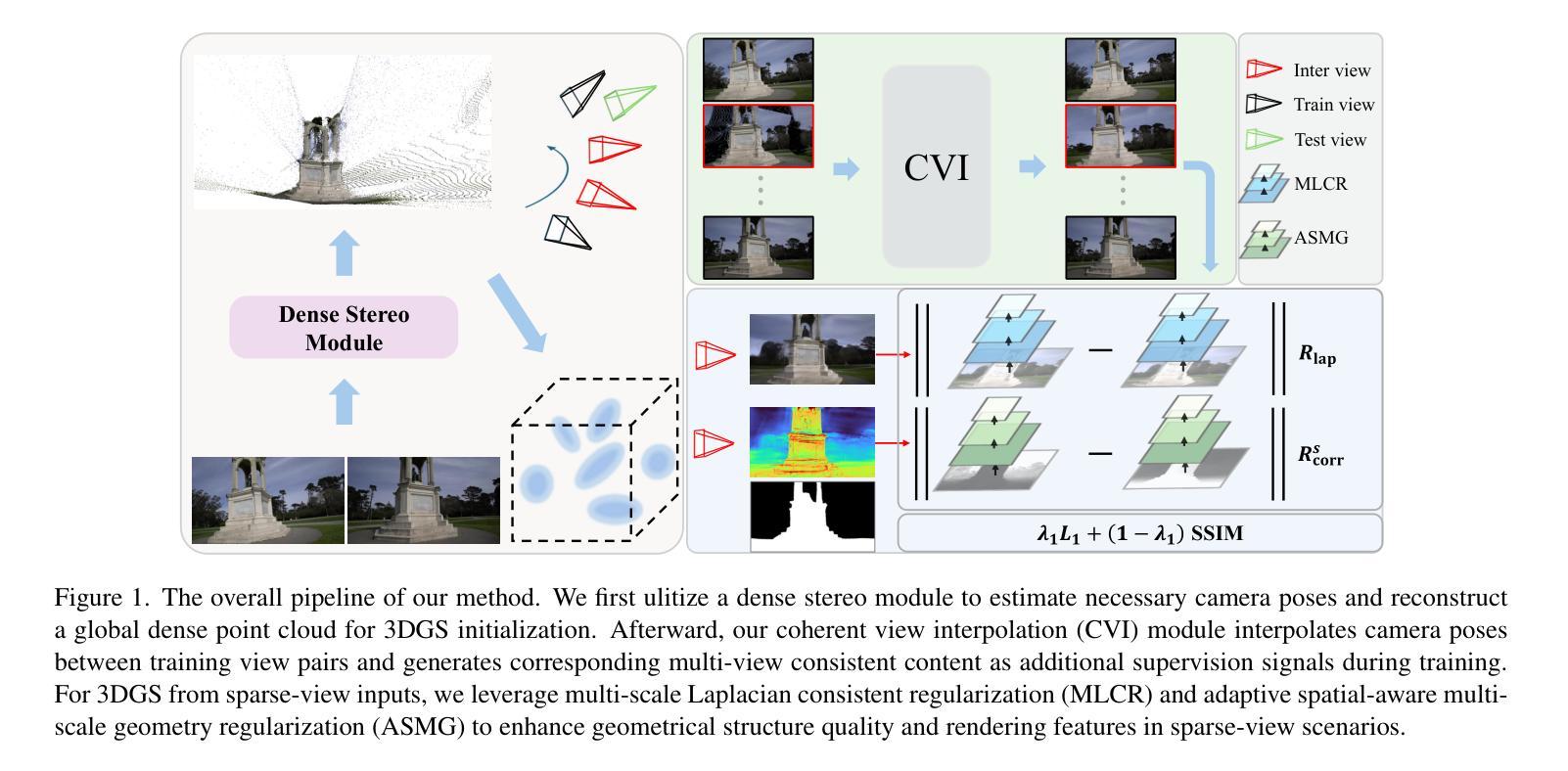
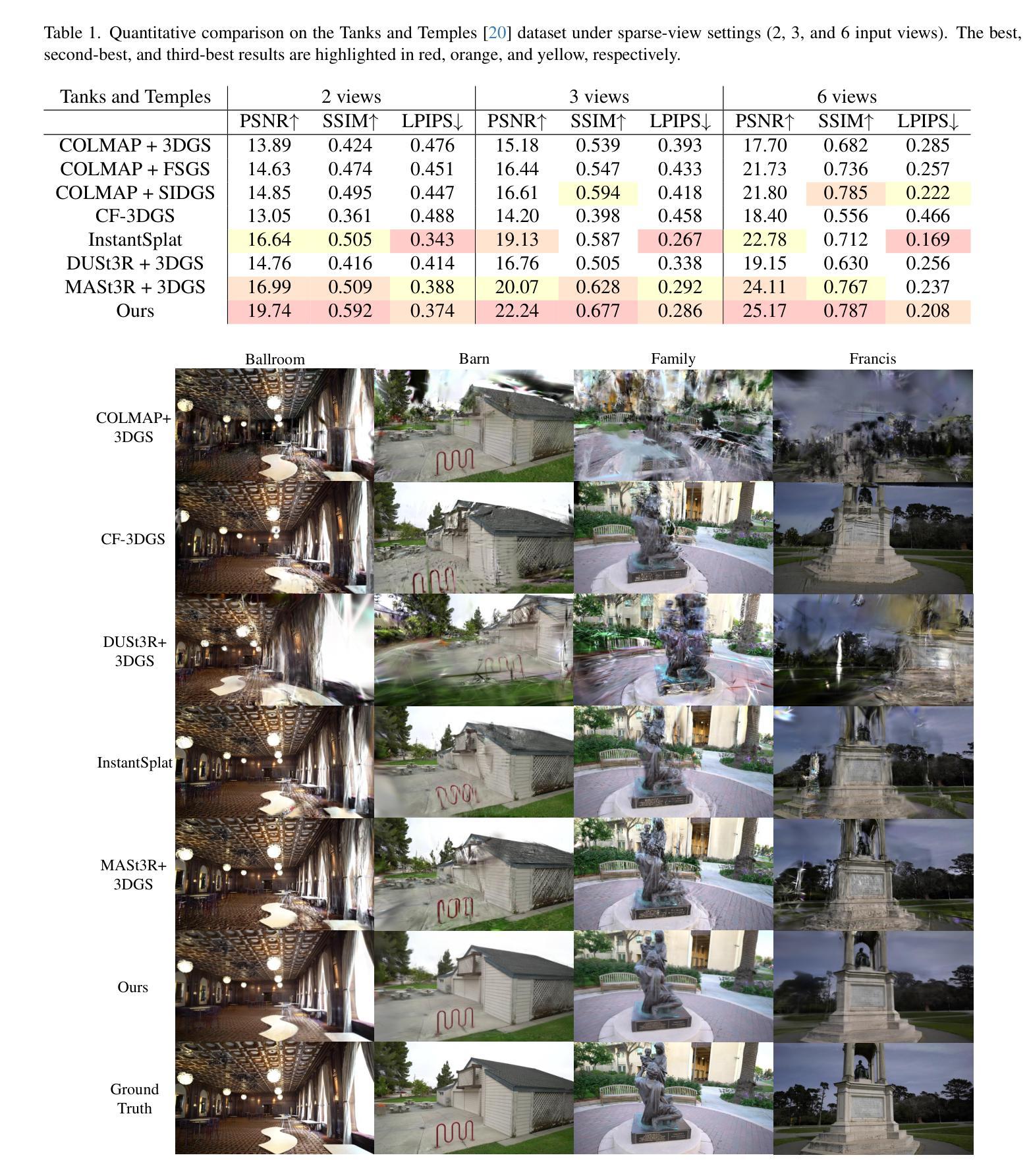
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated remarkable real-time performance in novel view synthesis, yet its effectiveness relies heavily on dense multi-view inputs with precisely known camera poses, which are rarely available in real-world scenarios. When input views become extremely sparse, the Structure-from-Motion (SfM) method that 3DGS depends on for initialization fails to accurately reconstruct the 3D geometric structures of scenes, resulting in degraded rendering quality. In this paper, we propose a novel SfM-free 3DGS-based method that jointly estimates camera poses and reconstructs 3D scenes from extremely sparse-view inputs. Specifically, instead of SfM, we propose a dense stereo module to progressively estimates camera pose information and reconstructs a global dense point cloud for initialization. To address the inherent problem of information scarcity in extremely sparse-view settings, we propose a coherent view interpolation module that interpolates camera poses based on training view pairs and generates viewpoint-consistent content as additional supervision signals for training. Furthermore, we introduce multi-scale Laplacian consistent regularization and adaptive spatial-aware multi-scale geometry regularization to enhance the quality of geometrical structures and rendered content. Experiments show that our method significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art 3DGS-based approaches, achieving a remarkable 2.75dB improvement in PSNR under extremely sparse-view conditions (using only 2 training views). The images synthesized by our method exhibit minimal distortion while preserving rich high-frequency details, resulting in superior visual quality compared to existing techniques.
3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)在新型视图合成中展示了出色的实时性能,但其有效性严重依赖于具有精确已知相机姿态的密集多视图输入,这在现实世界的场景中很少可用。当输入视图变得极为稀疏时,3DGS所依赖的用于初始化的Structure-from-Motion(SfM)方法无法准确重建场景的三维几何结构,导致渲染质量下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的无需SfM的基于3DGS的方法,该方法可以联合估计相机姿态并从极稀疏的视图输入中重建三维场景。具体来说,我们提出了一个密集的立体模块来渐进地估计相机姿态信息,并重建一个全局密集点云来进行初始化,而不是使用SfM。为了解决极稀疏视图设置中的信息稀缺问题,我们提出了一种连贯的视图插值模块,该模块基于训练视图对插值相机姿态,并生成视点一致的内容作为训练的附加监督信号。此外,我们引入了多尺度拉普拉斯一致正则化和自适应空间感知多尺度几何正则化,以提高几何结构和渲染内容的品质。实验表明,我们的方法在极稀疏视图条件下(仅使用两个训练视图)的PSNR值上实现了显著的2.75dB的提升,显著优于其他最先进的基于3DGS的方法。由我们的方法合成的图像具有最小的失真,同时保留了丰富的高频细节,与现有技术相比具有卓越的可视质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 4 figures
Summary
3DGS在实时性能及在稀疏视角条件下实现高性能的场景重建中表现出巨大的潜力。为解决输入视角稀疏问题,该论文提出了一种新颖的SfM-free的基于3DGS的方法,该方法联合估计相机姿态并重建三维场景。通过密集立体模块逐步估计相机姿态信息并重建全局密集点云进行初始化。同时,为解决视角信息匮乏的问题,该论文引入一致视角插值模块、多尺度拉普拉斯一致正则化和自适应空间感知多尺度几何正则化技术来提升几何结构和渲染内容的品质。实验表明,该方法显著优于其他先进的基于3DGS的方法,在极端稀疏视角条件下仅使用两个训练视角即可实现令人瞩目的峰值信噪比提升。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在实时性能及在稀疏视角条件下实现高性能的场景重建具有巨大潜力。
- 论文提出了一种新颖的SfM-free的基于3DGS的方法,用于联合估计相机姿态并重建三维场景。
- 该方法通过密集立体模块逐步估计相机姿态信息并重建全局密集点云进行初始化。
- 一致视角插值模块解决了视角信息匮乏的问题,并生成额外的监督信号用于训练。
- 多尺度拉普拉斯一致正则化和自适应空间感知多尺度几何正则化技术提升了几何结构和渲染内容的品质。
点此查看论文截图

DriveSplat: Decoupled Driving Scene Reconstruction with Geometry-enhanced Partitioned Neural Gaussians
Authors:Cong Wang, Xianda Guo, Wenbo Xu, Wei Tian, Ruiqi Song, Chenming Zhang, Lingxi Li, Long Chen
In the realm of driving scenarios, the presence of rapidly moving vehicles, pedestrians in motion, and large-scale static backgrounds poses significant challenges for 3D scene reconstruction. Recent methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting address the motion blur problem by decoupling dynamic and static components within the scene. However, these decoupling strategies overlook background optimization with adequate geometry relationships and rely solely on fitting each training view by adding Gaussians. Therefore, these models exhibit limited robustness in rendering novel views and lack an accurate geometric representation. To address the above issues, we introduce DriveSplat, a high-quality reconstruction method for driving scenarios based on neural Gaussian representations with dynamic-static decoupling. To better accommodate the predominantly linear motion patterns of driving viewpoints, a region-wise voxel initialization scheme is employed, which partitions the scene into near, middle, and far regions to enhance close-range detail representation. Deformable neural Gaussians are introduced to model non-rigid dynamic actors, whose parameters are temporally adjusted by a learnable deformation network. The entire framework is further supervised by depth and normal priors from pre-trained models, improving the accuracy of geometric structures. Our method has been rigorously evaluated on the Waymo and KITTI datasets, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in novel-view synthesis for driving scenarios.
在驾驶场景领域,快速移动车辆、运动中的行人和大规模静态背景的存在对3D场景重建构成了重大挑战。最近基于3D高斯展布的方法通过解耦场景内的动态和静态成分来解决运动模糊问题。然而,这些解耦策略忽视了背景优化的几何关系,仅通过添加高斯来拟合每个训练视图。因此,这些模型在呈现新视图时表现出有限的稳健性,并且缺乏精确几何表示。为了解决上述问题,我们引入了DriveSplat,这是一种基于神经高斯表示和动静解耦的驾驶场景高质量重建方法。为了更好地适应驾驶视角的主要线性运动模式,采用区域式体素初始化方案,将场景划分为近、中、远区域,以增强近距离细节表示。我们引入可变形神经高斯来模拟非刚性动态演员,其参数由可学习变形网络进行时间调整。整个框架还受到预训练模型的深度和法线先验的监督,提高了几何结构的准确性。我们的方法在Waymo和KITTI数据集上进行了严格评估,在驾驶场景的新视图合成方面表现出卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对驾驶场景的高质量重建方法DriveSplat,该方法基于神经高斯表示和动态静态解耦技术。通过区域性的体素初始化方案,将场景分为近、中、远三个区域,以提高近距离细节的表示。引入可变形神经高斯来模拟非刚性动态演员,其参数由可学习变形网络进行时间调整。整个框架受到来自预训练模型的深度和正常先验的监管,提高了几何结构的准确性。在Waymo和KITTI数据集上的评估结果表明,该方法在驾驶场景的新视角合成方面达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3D场景重建在驾驶场景中面临挑战,因为存在快速移动的汽车、行人以及大规模静态背景。
- 最近基于3D高斯飞溅的方法解决了运动模糊问题,通过解耦场景中的动态和静态成分。
- 然而,现有方法忽略了背景优化的几何关系,仅通过添加高斯来拟合每个训练视图,导致在呈现新视角时表现有限且缺乏精确几何表示。
- DriveSplat方法被引入以解决上述问题,它基于神经高斯表示和动态静态解耦技术,为驾驶场景提供高质量重建。
- DriveSplat采用区域性的体素初始化方案,将场景分为近、中、远三个区域,以提高近距离细节的表示能力。
- 通过引入可变形神经高斯来模拟非刚体的动态物体,并结合可学习变形网络进行参数调整。
点此查看论文截图

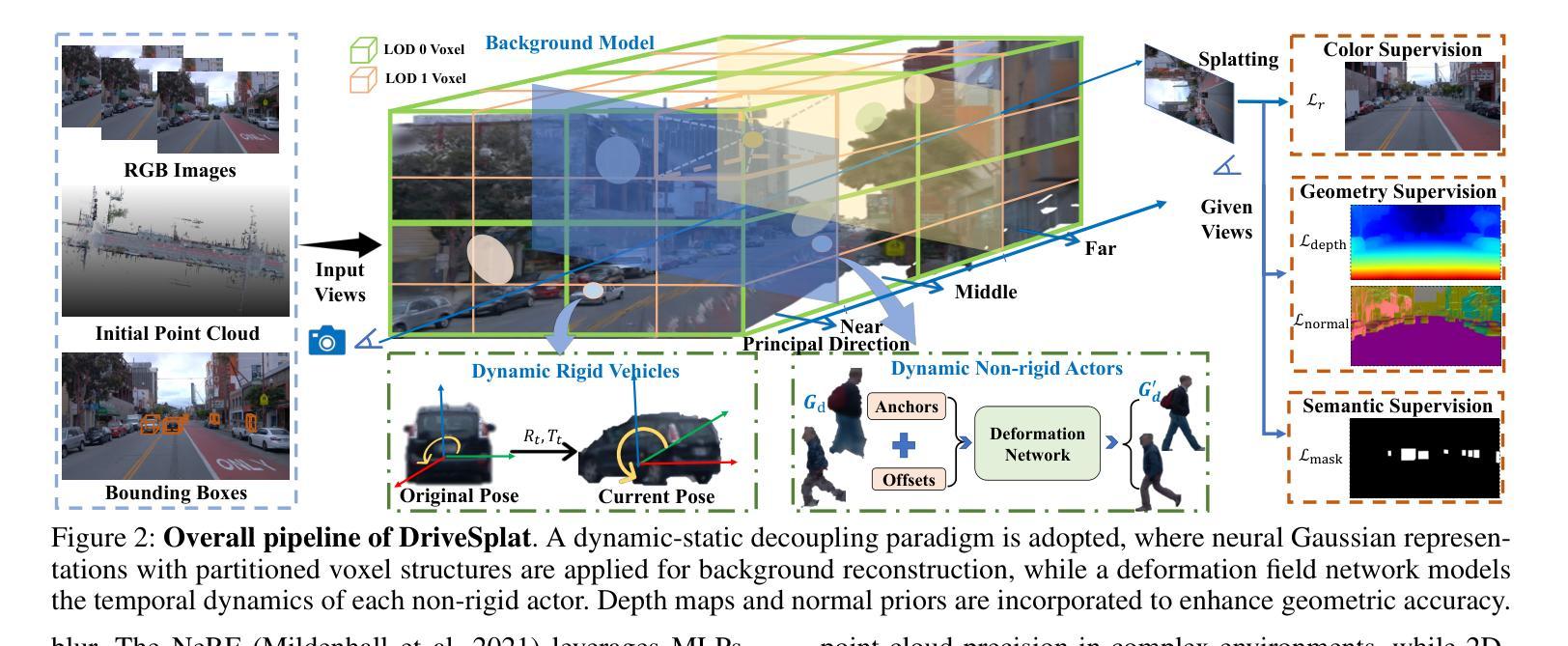
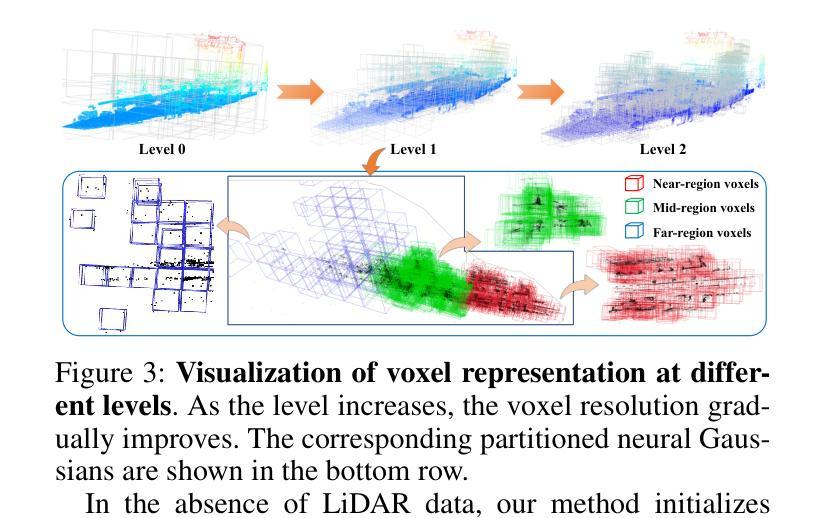

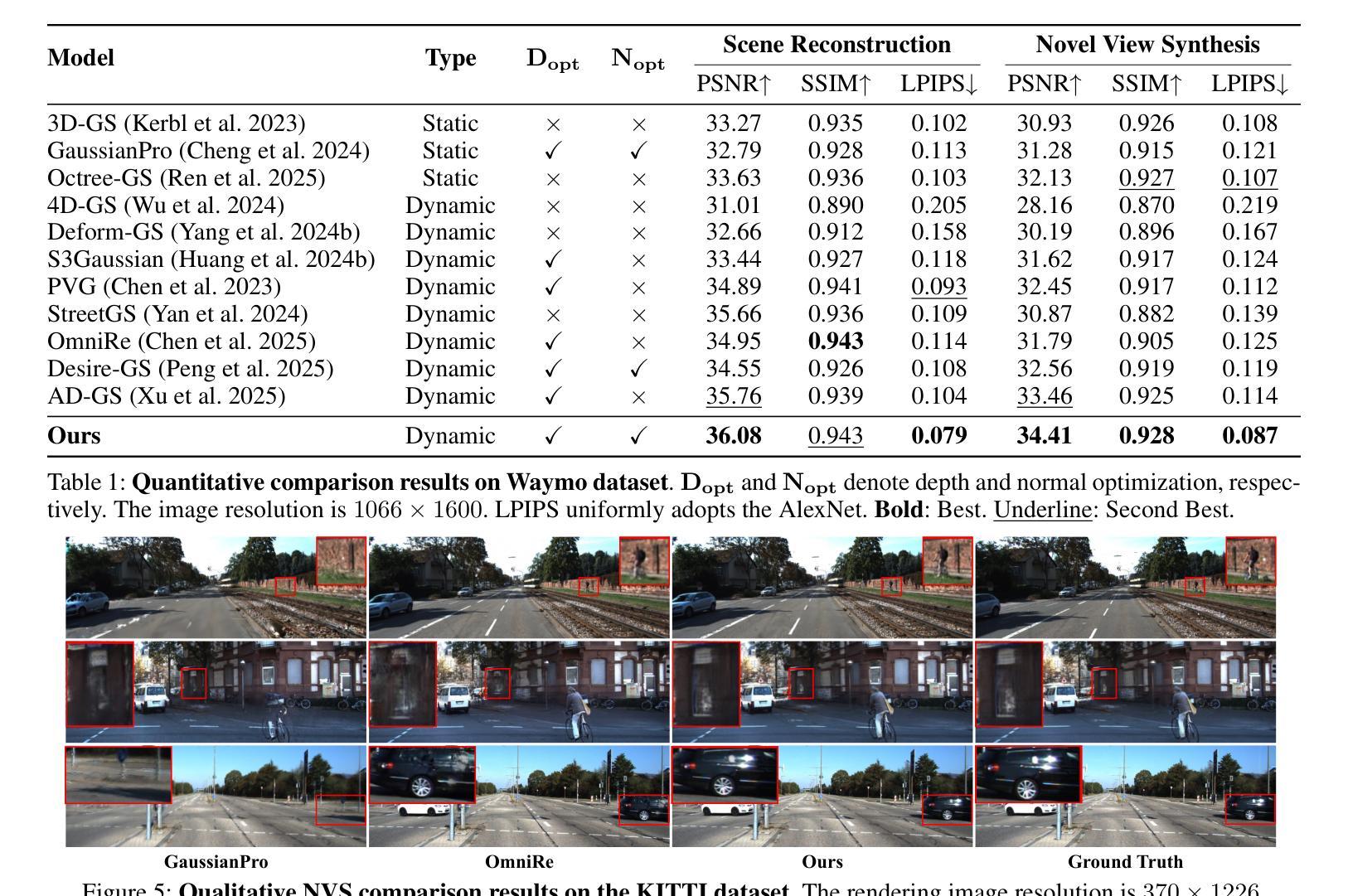
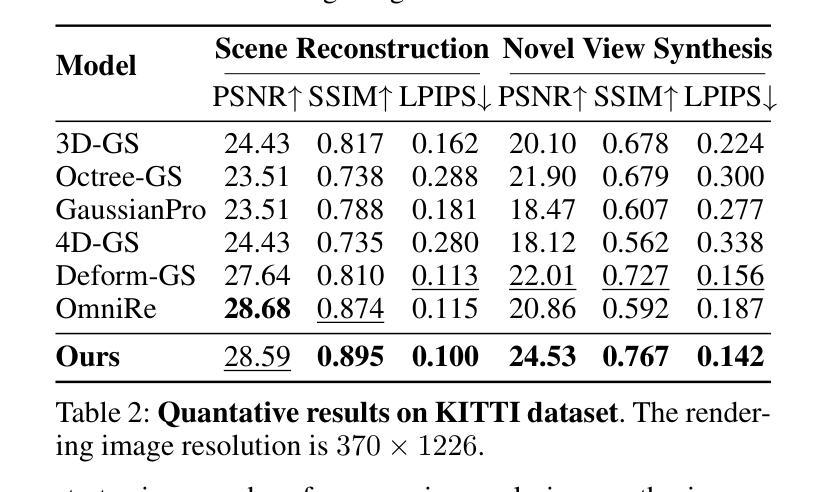
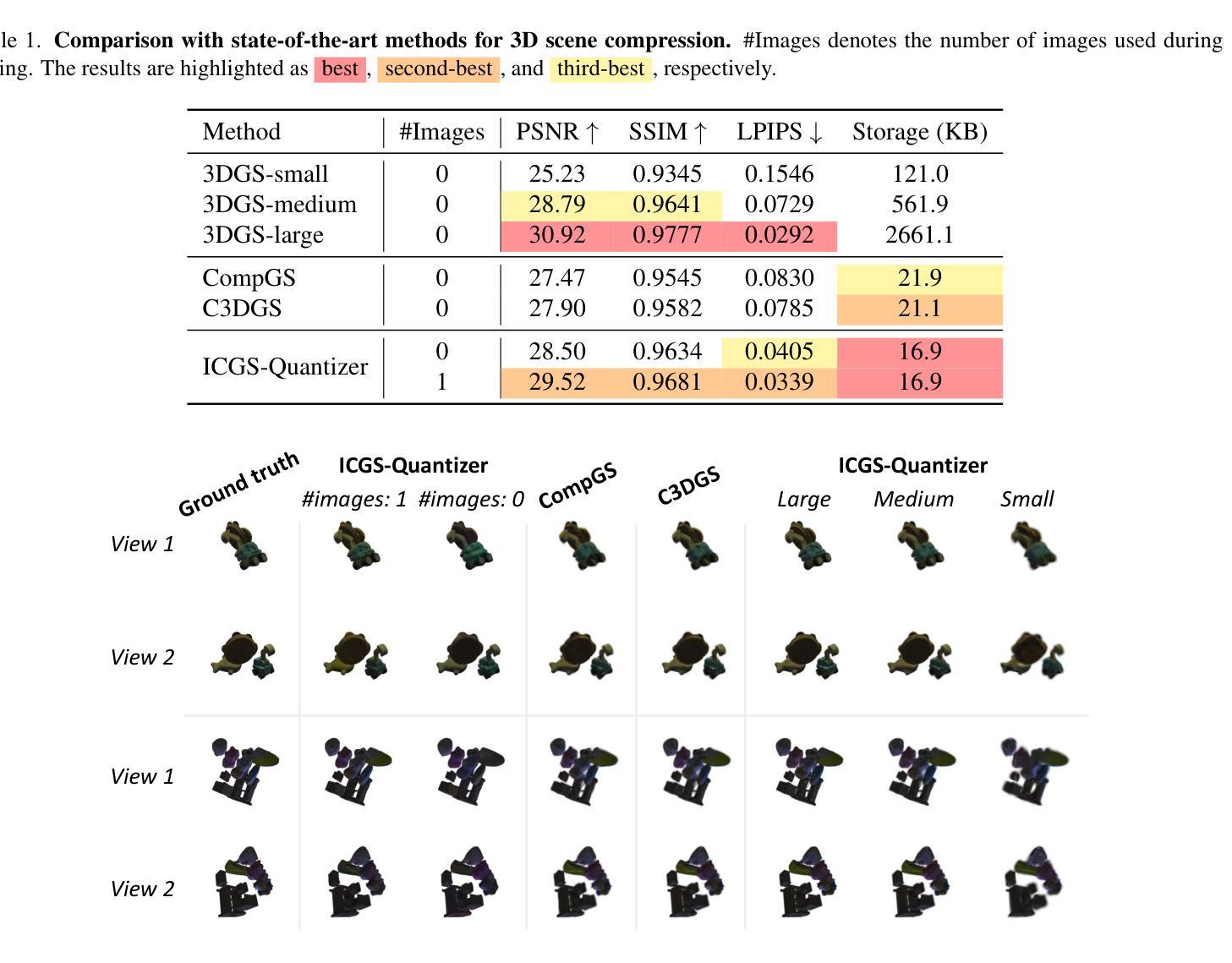
Image-Conditioned 3D Gaussian Splat Quantization
Authors:Xinshuang Liu, Runfa Blark Li, Keito Suzuki, Truong Nguyen
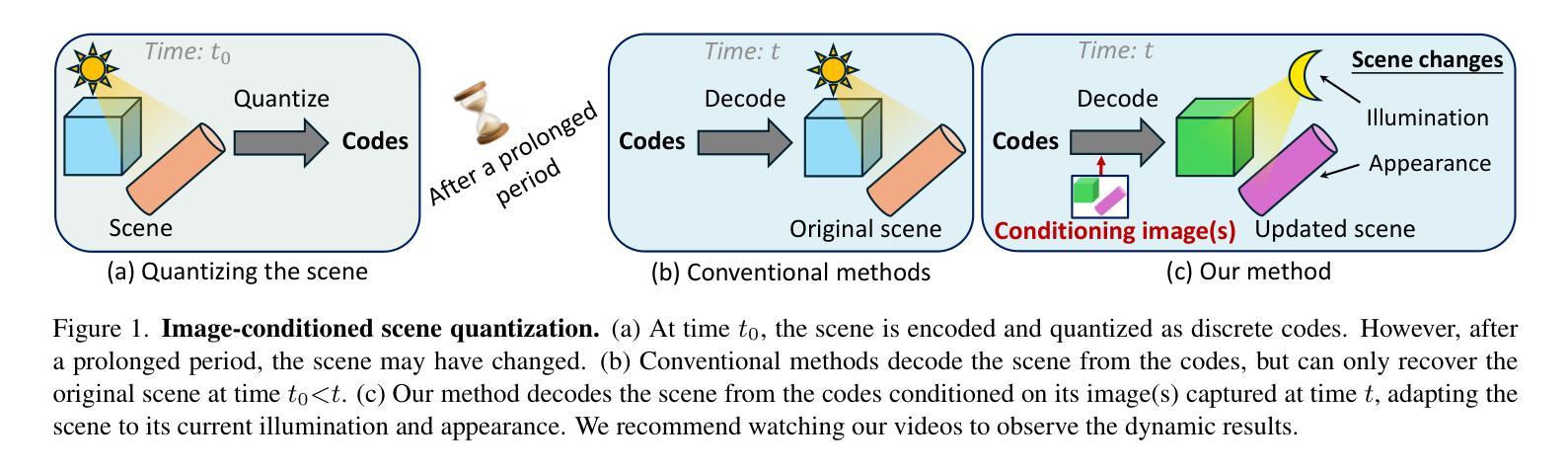
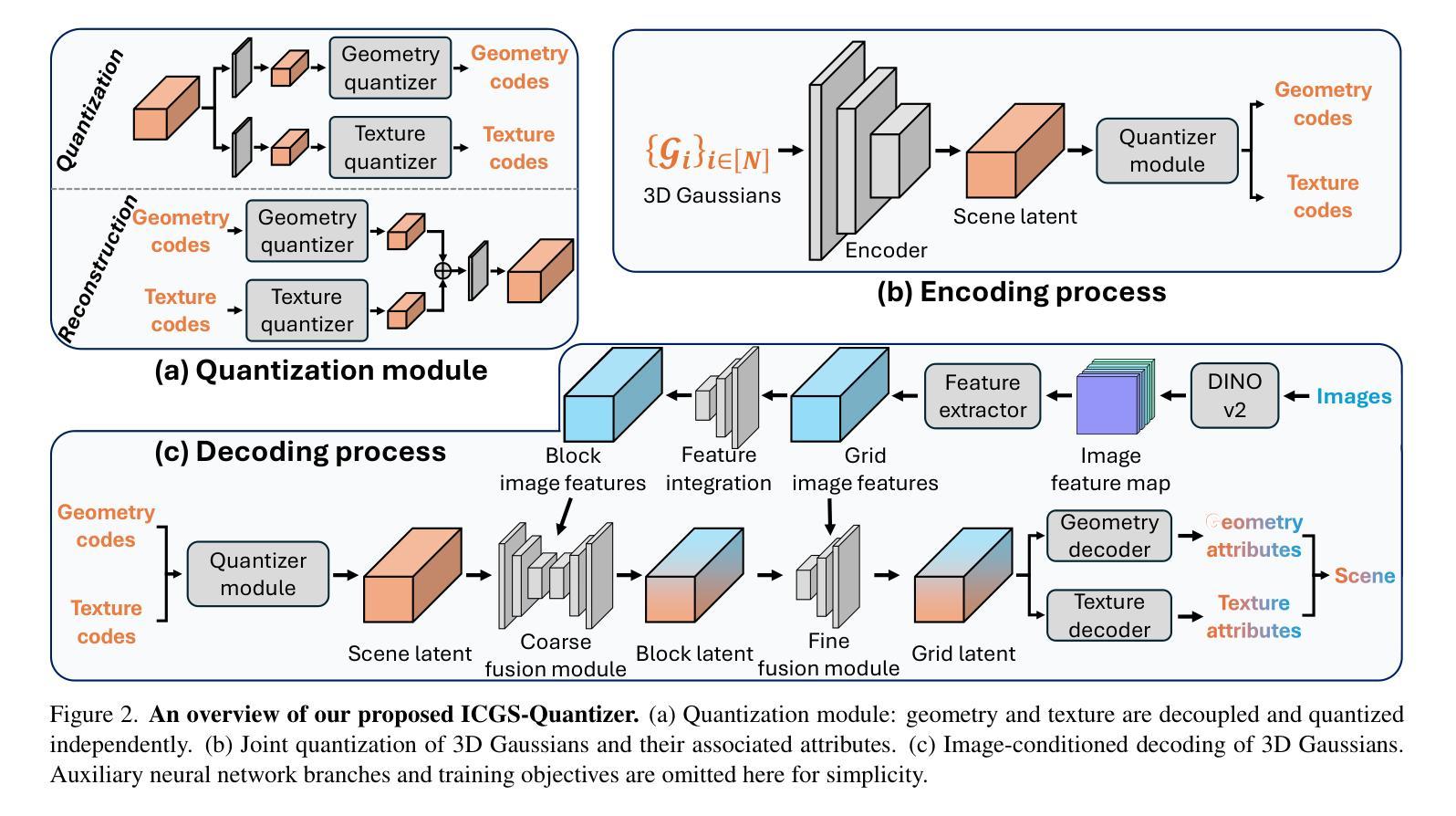
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has attracted considerable attention for enabling high-quality real-time rendering. Although 3DGS compression methods have been proposed for deployment on storage-constrained devices, two limitations hinder archival use: (1) they compress medium-scale scenes only to the megabyte range, which remains impractical for large-scale scenes or extensive scene collections; and (2) they lack mechanisms to accommodate scene changes after long-term archival. To address these limitations, we propose an Image-Conditioned Gaussian Splat Quantizer (ICGS-Quantizer) that substantially enhances compression efficiency and provides adaptability to scene changes after archiving. ICGS-Quantizer improves quantization efficiency by jointly exploiting inter-Gaussian and inter-attribute correlations and by using shared codebooks across all training scenes, which are then fixed and applied to previously unseen test scenes, eliminating the overhead of per-scene codebooks. This approach effectively reduces the storage requirements for 3DGS to the kilobyte range while preserving visual fidelity. To enable adaptability to post-archival scene changes, ICGS-Quantizer conditions scene decoding on images captured at decoding time. The encoding, quantization, and decoding processes are trained jointly, ensuring that the codes, which are quantized representations of the scene, are effective for conditional decoding. We evaluate ICGS-Quantizer on 3D scene compression and 3D scene updating. Experimental results show that ICGS-Quantizer consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in compression efficiency and adaptability to scene changes. Our code, model, and data will be publicly available on GitHub.
3D高斯展平(3DGS)因其能够实现高质量实时渲染而备受关注。虽然已有针对存储受限设备部署的3DGS压缩方法被提出,但存在两个限制阻碍了其归档使用:(1)它们仅能将中等规模的场景压缩到兆字节范围,对于大规模场景或广泛的场景集合来说仍然不切实际;(2)它们缺乏在长期归档后适应场景变化的机制。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种图像条件高斯展平量化器(ICGS-Quantizer),它大大提高了压缩效率,并为归档后的场景变化提供了适应性。ICGS-Quantizer通过联合利用高斯之间和属性之间的相关性,并使用所有训练场景的共同代码本,提高了量化效率。这些代码本随后被固定并应用于之前未见过的测试场景,从而消除了每个场景代码本的开销。这种方法有效地将3DGS的存储需求降低到千字节范围,同时保持视觉保真度。为了实现归档后场景变化的适应性,ICGS-Quantizer根据解码时捕获的图像对场景解码进行条件设置。编码、量化和解码过程联合训练,确保场景的量化表示代码对于条件解码是有效的。我们评估了ICGS-Quantizer在三维场景压缩和三维场景更新方面的表现。实验结果表明,ICGS-Quantizer在压缩效率和适应场景变化方面始终优于最先进的方法。我们的代码、模型和数据将在GitHub上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了基于图像条件的Gaussian Splat量化器(ICGS-Quantizer),用于解决现有3DGS压缩方法存在的两个主要问题。首先,它通过利用高斯之间的关联性和共享代码本技术提高了压缩效率,将存储需求降低到千字节范围内同时保持视觉保真度。其次,它实现了场景变化的适应性,通过将场景解码与解码时间的图像捕获相结合,确保对场景变化的适应性。实验结果表明,ICGS-Quantizer在压缩效率和场景变化适应性方面均优于现有方法。
关键见解
- 现有3DGS压缩方法主要适用于中等规模的场景压缩,但其数据量仍在兆字节范围,不利于大规模场景或大量场景的存档使用。
- 目前的技术缺乏长期存档后的场景变化适应性机制。
- ICGS-Quantizer通过利用高斯之间的关联性和共享代码本技术提高了压缩效率,显著减少了存储需求至千字节级别。
- ICGS-Quantizer首次实现了对存档后场景变化的适应性,其通过在解码时将场景解码与当前图像结合来实现这一点。
- 该方法在保证压缩效率的同时,还能适应场景的变化,这在实验中得到验证并展现出显著优势。
- ICGS-Quantizer的实现包括编码、量化和解码过程,这三个过程经过联合训练确保对场景的有效量化表示和条件解码。
- 研究人员将在GitHub上公开相关代码、模型和数据。
点此查看论文截图

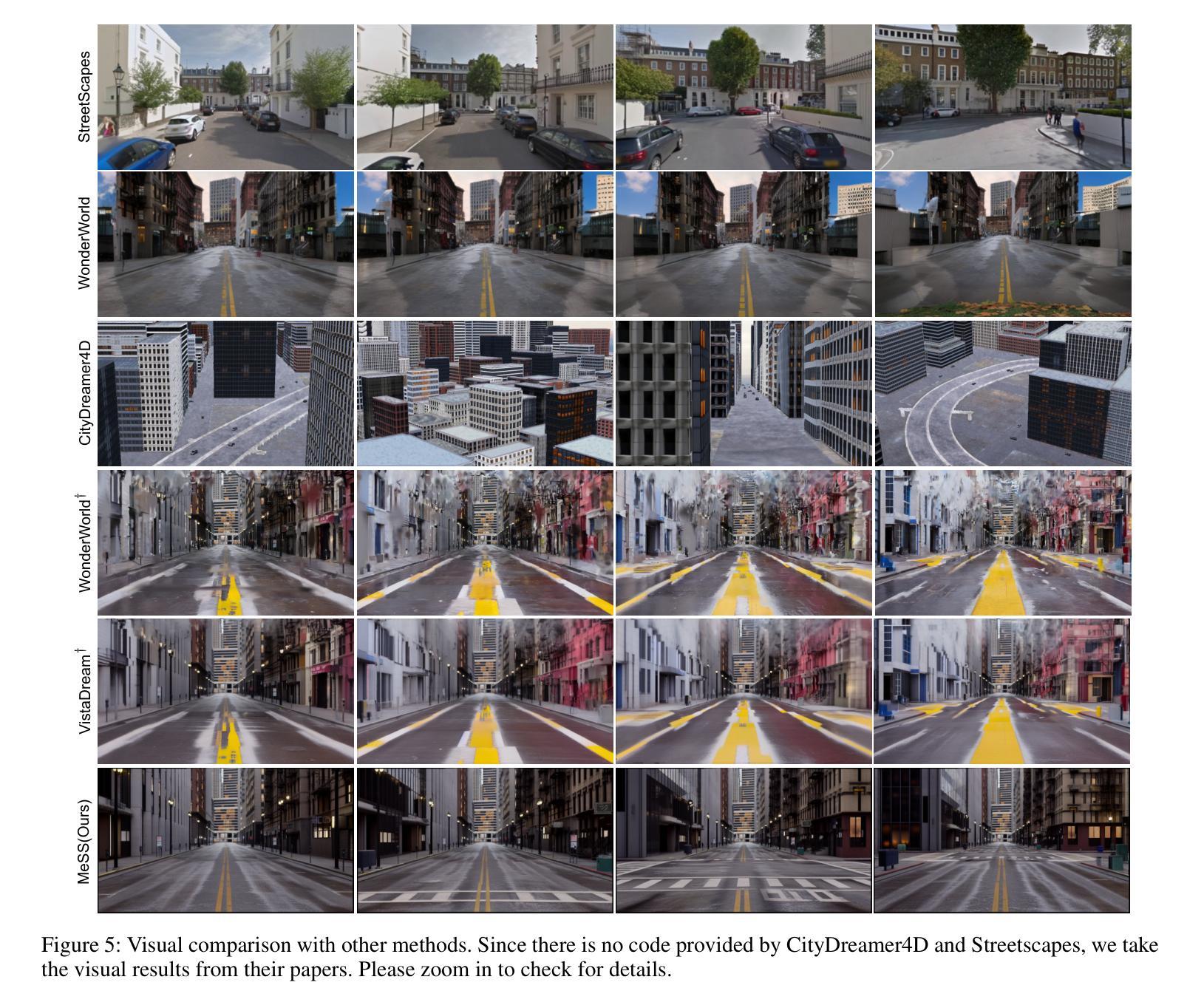
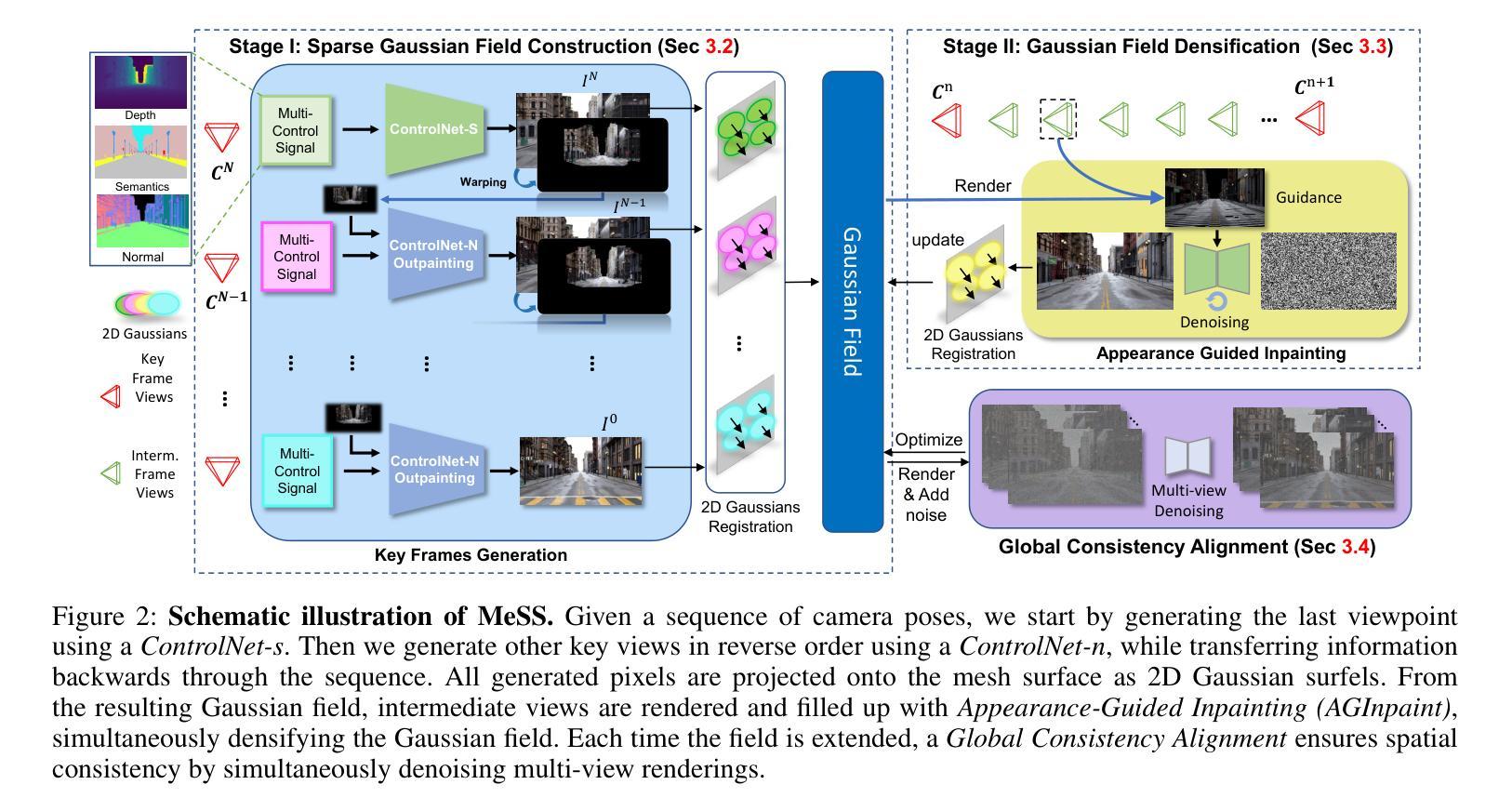
MeSS: City Mesh-Guided Outdoor Scene Generation with Cross-View Consistent Diffusion
Authors:Xuyang Chen, Zhijun Zhai, Kaixuan Zhou, Zengmao Wang, Jianan He, Dong Wang, Yanfeng Zhang, mingwei Sun, Rüdiger Westermann, Konrad Schindler, Liqiu Meng
Mesh models have become increasingly accessible for numerous cities; however, the lack of realistic textures restricts their application in virtual urban navigation and autonomous driving. To address this, this paper proposes MeSS (Meshbased Scene Synthesis) for generating high-quality, styleconsistent outdoor scenes with city mesh models serving as the geometric prior. While image and video diffusion models can leverage spatial layouts (such as depth maps or HD maps) as control conditions to generate street-level perspective views, they are not directly applicable to 3D scene generation. Video diffusion models excel at synthesizing consistent view sequences that depict scenes but often struggle to adhere to predefined camera paths or align accurately with rendered control videos. In contrast, image diffusion models, though unable to guarantee cross-view visual consistency, can produce more geometry-aligned results when combined with ControlNet. Building on this insight, our approach enhances image diffusion models by improving cross-view consistency. The pipeline comprises three key stages: first, we generate geometrically consistent sparse views using Cascaded Outpainting ControlNets; second, we propagate denser intermediate views via a component dubbed AGInpaint; and third, we globally eliminate visual inconsistencies (e.g., varying exposure) using the GCAlign module. Concurrently with generation, a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) scene is reconstructed by initializing Gaussian balls on the mesh surface. Our method outperforms existing approaches in both geometric alignment and generation quality. Once synthesized, the scene can be rendered in diverse styles through relighting and style transfer techniques.
网格模型对许多城市来说变得越来越容易访问,然而由于缺乏真实的纹理,限制了它们在虚拟城市导航和自动驾驶中的应用。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了基于网格的场景合成(MeSS)方法,该方法利用城市网格模型作为几何先验来生成高质量、风格一致的室外场景。图像和视频扩散模型可以利用空间布局(如深度图或高清地图)作为控制条件来生成街道级透视视图,但它们并不直接适用于三维场景生成。视频扩散模型擅长合成连续的场景视图序列,但在遵循预设的相机路径或与渲染的控制视频精确对齐方面常面临挑战。相比之下,图像扩散模型虽然无法保证跨视图视觉一致性,但与ControlNet结合使用时,可以产生更符合几何结构的渲染结果。基于此,我们的方法通过增强图像扩散模型的跨视图一致性来提升性能。该流程包含三个阶段:首先,我们使用级联外推控制网络生成几何一致的稀疏视图;其次,我们通过名为AGInpaint的组件传播更密集的中间视图;最后,我们使用GCAlign模块全局消除视觉不一致(如曝光不同)。同时生成过程中,通过在网格表面初始化高斯球来重建一个三维高斯散斑(3DGS)场景。我们的方法在几何对齐和生成质量方面都优于现有方法。合成场景后,可以通过重新照明和风格转换技术以多种风格进行渲染。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于网格的场景合成方法(MeSS),用于生成高质量、风格一致的户外场景。该方法以城市网格模型作为几何先验,结合图像扩散模型和控制网络(ControlNet)技术,生成具有高度几何一致性和跨视图视觉一致性的场景。通过级联外绘控制网络(Cascaded Outpainting ControlNets)、AGInpaint组件和全局校准模块(GCAlign),实现了场景的高质量合成和视觉不一致性的消除。同时,通过3D高斯摊开(3DGS)技术重建场景,并可在合成后进行重新照明和风格转换。
Key Takeaways
- 城市网格模型作为几何先验,用于生成高质量的城市场景。
- 图像扩散模型与控制网络(ControlNet)结合,提高跨视图视觉一致性。
- 通过级联外绘控制网络(Cascaded Outpainting ControlNets)生成几何一致的稀疏视图。
- AGInpaint组件用于传播更密集的中间视图。
- GCAlign模块用于全局消除视觉不一致性。
- 3D高斯摊开(3DGS)技术用于场景重建。
- 场景合成后可以进行重新照明和风格转换。
点此查看论文截图




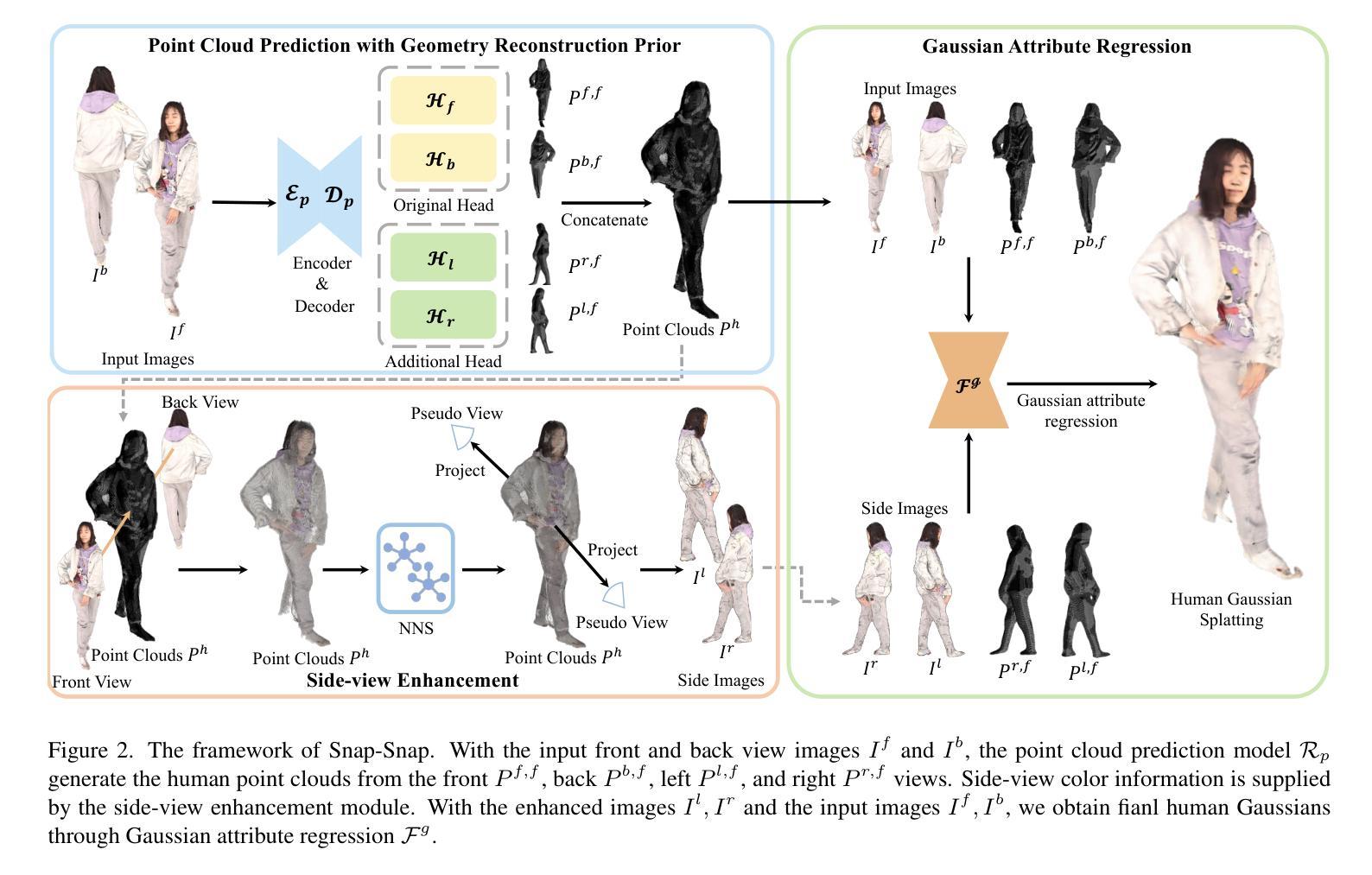
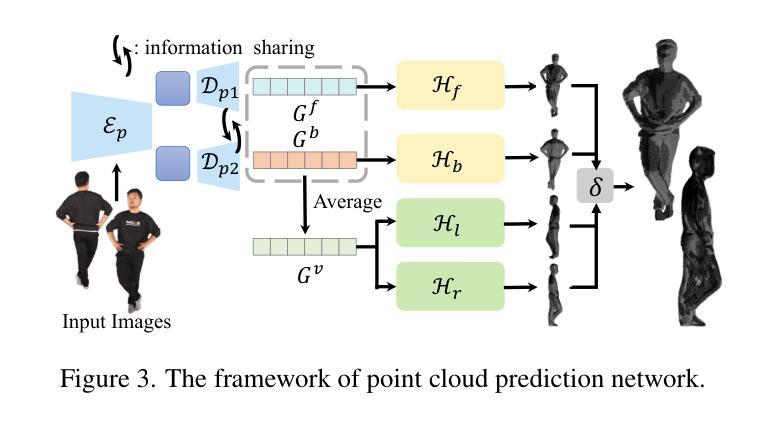
Snap-Snap: Taking Two Images to Reconstruct 3D Human Gaussians in Milliseconds
Authors:Jia Lu, Taoran Yi, Jiemin Fang, Chen Yang, Chuiyun Wu, Wei Shen, Wenyu Liu, Qi Tian, Xinggang Wang
Reconstructing 3D human bodies from sparse views has been an appealing topic, which is crucial to broader the related applications. In this paper, we propose a quite challenging but valuable task to reconstruct the human body from only two images, i.e., the front and back view, which can largely lower the barrier for users to create their own 3D digital humans. The main challenges lie in the difficulty of building 3D consistency and recovering missing information from the highly sparse input. We redesign a geometry reconstruction model based on foundation reconstruction models to predict consistent point clouds even input images have scarce overlaps with extensive human data training. Furthermore, an enhancement algorithm is applied to supplement the missing color information, and then the complete human point clouds with colors can be obtained, which are directly transformed into 3D Gaussians for better rendering quality. Experiments show that our method can reconstruct the entire human in 190 ms on a single NVIDIA RTX 4090, with two images at a resolution of 1024x1024, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on the THuman2.0 and cross-domain datasets. Additionally, our method can complete human reconstruction even with images captured by low-cost mobile devices, reducing the requirements for data collection. Demos and code are available at https://hustvl.github.io/Snap-Snap/.
从稀疏视角重建3D人体是一个引人入胜的话题,对于拓展相关领域应用至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了一个颇具挑战性但价值极高的任务,即仅通过两张图片(即正面和背面视图)来重建人体,这大大降低了用户创建自己的3D数字人体的门槛。主要挑战在于建立3D一致性和从高度稀疏的输入中恢复缺失信息。我们基于基础重建模型重新设计了一个几何重建模型,即使输入图像与大量人类数据训练之间的重叠很少,也能预测出一致的点云。此外,应用了一种增强算法来补充缺失的颜色信息,然后可以获得带有颜色的完整人类点云,这些点云可以直接转换为3D高斯分布以获得更好的渲染质量。实验表明,我们的方法可以在单个NVIDIA RTX 4090上,以190毫秒的速度重建整个人体,使用分辨率为1024x1024的两张图像,在THuman2.0和跨域数据集上达到了最先进的性能。此外,我们的方法即使使用低成本移动设备拍摄的图片也能完成人体重建,降低了数据收集的要求。相关演示和代码可通过https://hustvl.github.io/Snap-Snap/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://hustvl.github.io/Snap-Snap/
Summary
本文提出了一项从两张图像(正面和背面)重建3D人体模型的挑战任务,降低了用户创建自己的3D数字人类的门槛。主要挑战在于建立3D一致性并从未经密集训练的输入图像中恢复缺失信息。研究团队基于基础重建模型重新设计了一个几何重建模型,能够预测一致的点云,即使输入图像与大量人类数据训练的重叠很少。此外,还应用了一种增强算法来补充缺失的颜色信息,从而获得带有颜色的完整人类点云,这些点云可直接转换为3D高斯模型以改善渲染质量。实验表明,该方法在单个NVIDIA RTX 4090上能够在190毫秒内重建分辨率为1024x1024的两张图像中的整个人体,并在THuman2.0和跨域数据集上达到了最先进的性能。此外,该方法还能使用低成本移动设备拍摄的图像完成人体重建,降低了数据采集的要求。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一个挑战任务:仅从两张图像(正面和背面)重建3D人体模型。
- 研究团队设计了一种基于基础重建模型的几何重建模型,可从稀疏的图像输入中预测一致的点云。
- 通过应用增强算法补充缺失的颜色信息,获得带有颜色的完整人类点云。
- 该方法能够在高性能硬件上快速完成人体重建,处理时间为190毫秒。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多个数据集上达到了最先进的性能。
- 该方法适用于低成本移动设备拍摄的图像,降低了数据采集的要求。
点此查看论文截图


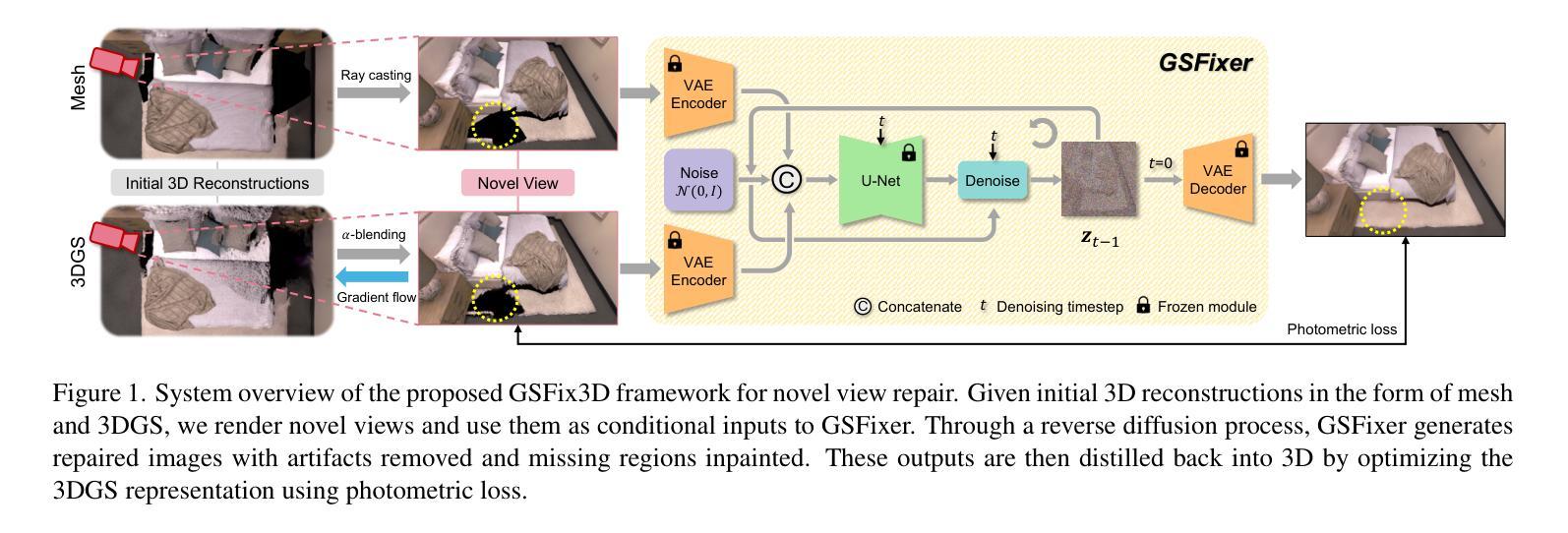
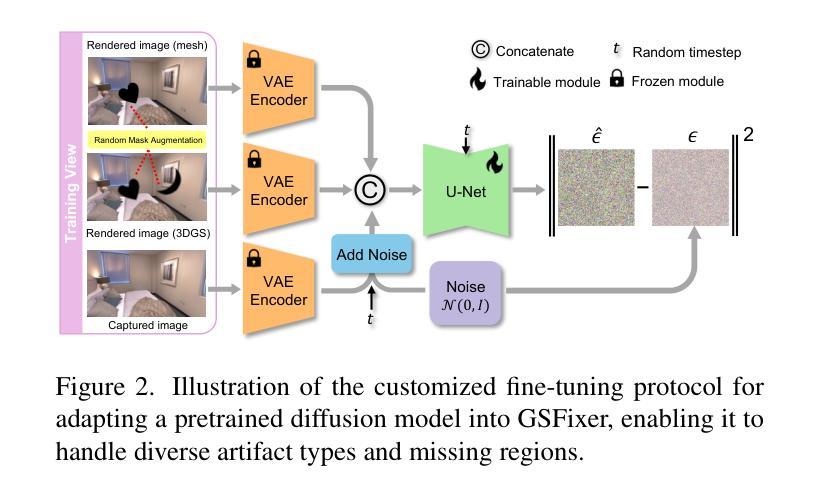
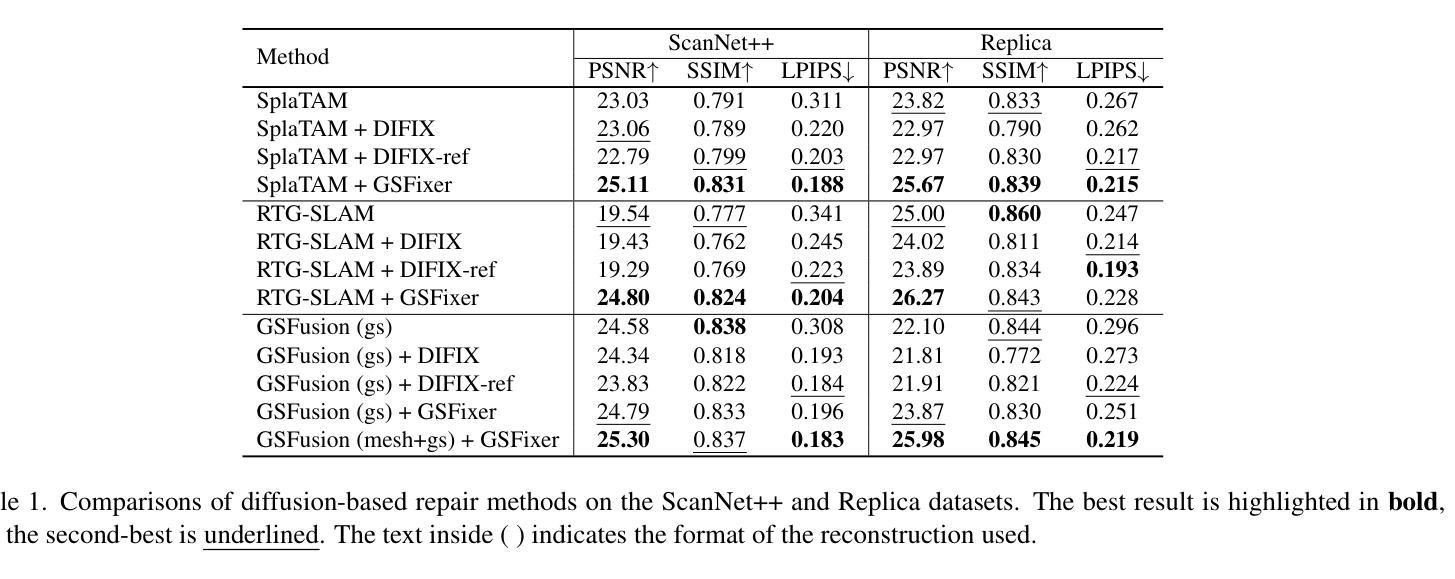
GSFix3D: Diffusion-Guided Repair of Novel Views in Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiaxin Wei, Stefan Leutenegger, Simon Schaefer
Recent developments in 3D Gaussian Splatting have significantly enhanced novel view synthesis, yet generating high-quality renderings from extreme novel viewpoints or partially observed regions remains challenging. Meanwhile, diffusion models exhibit strong generative capabilities, but their reliance on text prompts and lack of awareness of specific scene information hinder accurate 3D reconstruction tasks. To address these limitations, we introduce GSFix3D, a novel framework that improves the visual fidelity in under-constrained regions by distilling prior knowledge from diffusion models into 3D representations, while preserving consistency with observed scene details. At its core is GSFixer, a latent diffusion model obtained via our customized fine-tuning protocol that can leverage both mesh and 3D Gaussians to adapt pretrained generative models to a variety of environments and artifact types from different reconstruction methods, enabling robust novel view repair for unseen camera poses. Moreover, we propose a random mask augmentation strategy that empowers GSFixer to plausibly inpaint missing regions. Experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our GSFix3D and GSFixer achieve state-of-the-art performance, requiring only minimal scene-specific fine-tuning on captured data. Real-world test further confirms its resilience to potential pose errors. Our code and data will be made publicly available. Project page: https://gsfix3d.github.io.
近期3D高斯拼接(3D Gaussian Splatting)的发展极大地促进了新视角合成的进步,但从极端新视角或局部观测区域生成高质量渲染仍是挑战。尽管扩散模型展现出强大的生成能力,但它们对文本提示的依赖以及对特定场景信息缺乏意识阻碍了准确的3D重建任务。为了解决这些限制,我们引入了GSFix3D这一新框架,它通过将从扩散模型中提炼出的先验知识注入到3D表示中,提高了无约束区域的视觉保真度,同时保持了与观测场景细节的的一致性。其核心是GSFixer,这是一种通过我们定制的微调协议获得的潜在扩散模型,它可以利用网格和3D高斯来适应各种环境和来自不同重建方法的文物类型,从而实现对未见摄像机姿态的稳健新视角修复。此外,我们提出了一种随机掩膜增强策略,使GSFixer能够合理地填充缺失区域。在具有挑战性的基准测试上的实验表明,我们的GSFix3D和GSFixer达到了最先进的性能,并且只需对捕获数据进行最小的特定场景微调。现实世界测试进一步证实了其对潜在姿态错误的韧性。我们的代码和数据将公开可用。项目页面:https://gsfix3d.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3D高斯混合技术的新发展促进了新型视角合成,但仍存在从极端新视角或部分观测区域生成高质量渲染的挑战。为解决此问题,引入GSFix3D框架,它将扩散模型的先验知识提炼成3D表示,同时保留观测场景细节的连贯性,提高无约束区域的视觉保真度。核心为GSFixer模型,通过定制微调协议,利用网格和3D高斯,使预训练生成模型适应各种环境和重建方法产生的伪影类型,实现稳健的新视角修复。此外,提出随机掩膜增强策略,使GSFixer能够合理填充缺失区域。实验证明,GSFix3D和GSFixer达到最新性能,仅需对捕获数据进行最小的场景特定微调。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯混合技术的最新发展虽促进了新型视角合成,但仍存在生成高质量渲染的挑战,特别是在极端新视角或部分观测区域。
- GSFix3D框架通过结合扩散模型的先验知识和3D表示,提高了无约束区域的视觉保真度,同时保留观测场景细节的连贯性。
- GSFixer模型是GSFix3D的核心,它通过定制微调协议,能有效利用网格和3D高斯,适应各种环境和重建方法产生的伪影类型。
- GSFixer模型能够实现稳健的新视角修复,对未见过的相机姿态也能进行适应。
- 随机掩膜增强策略被提出,以支持GSFixer在缺失区域进行合理填充。
- 实验证明,GSFix3D和GSFixer在具有挑战性的基准测试上表现出色,并且只需要对捕获数据进行最小的场景特定微调。
点此查看论文截图


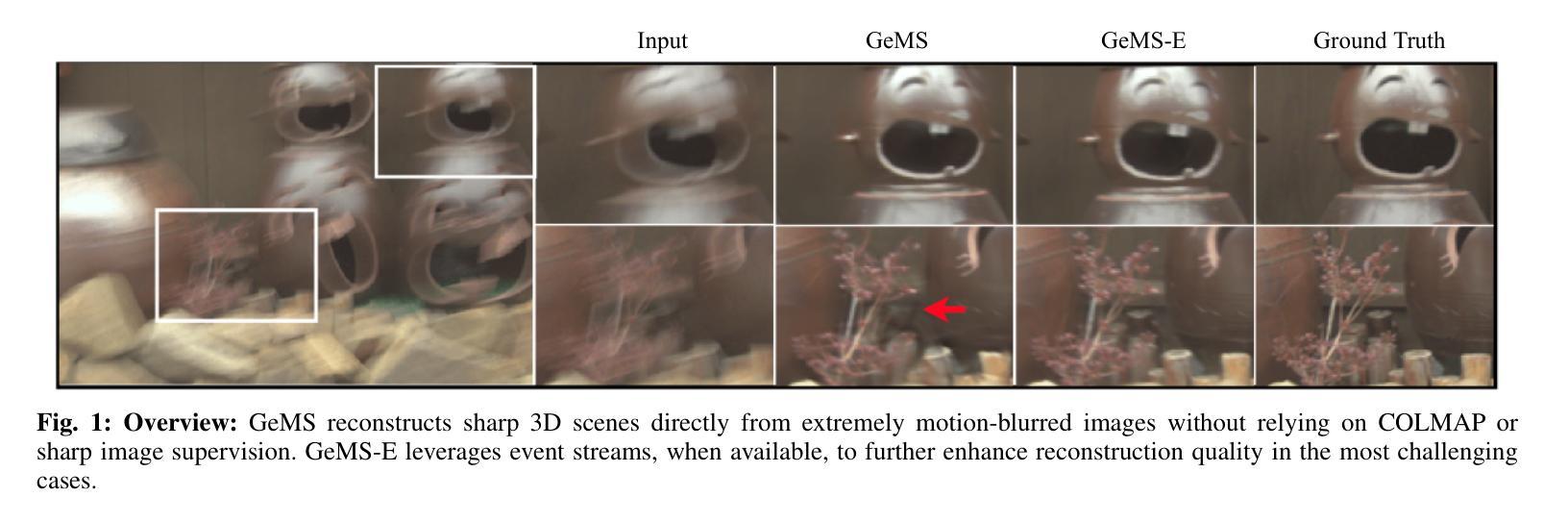
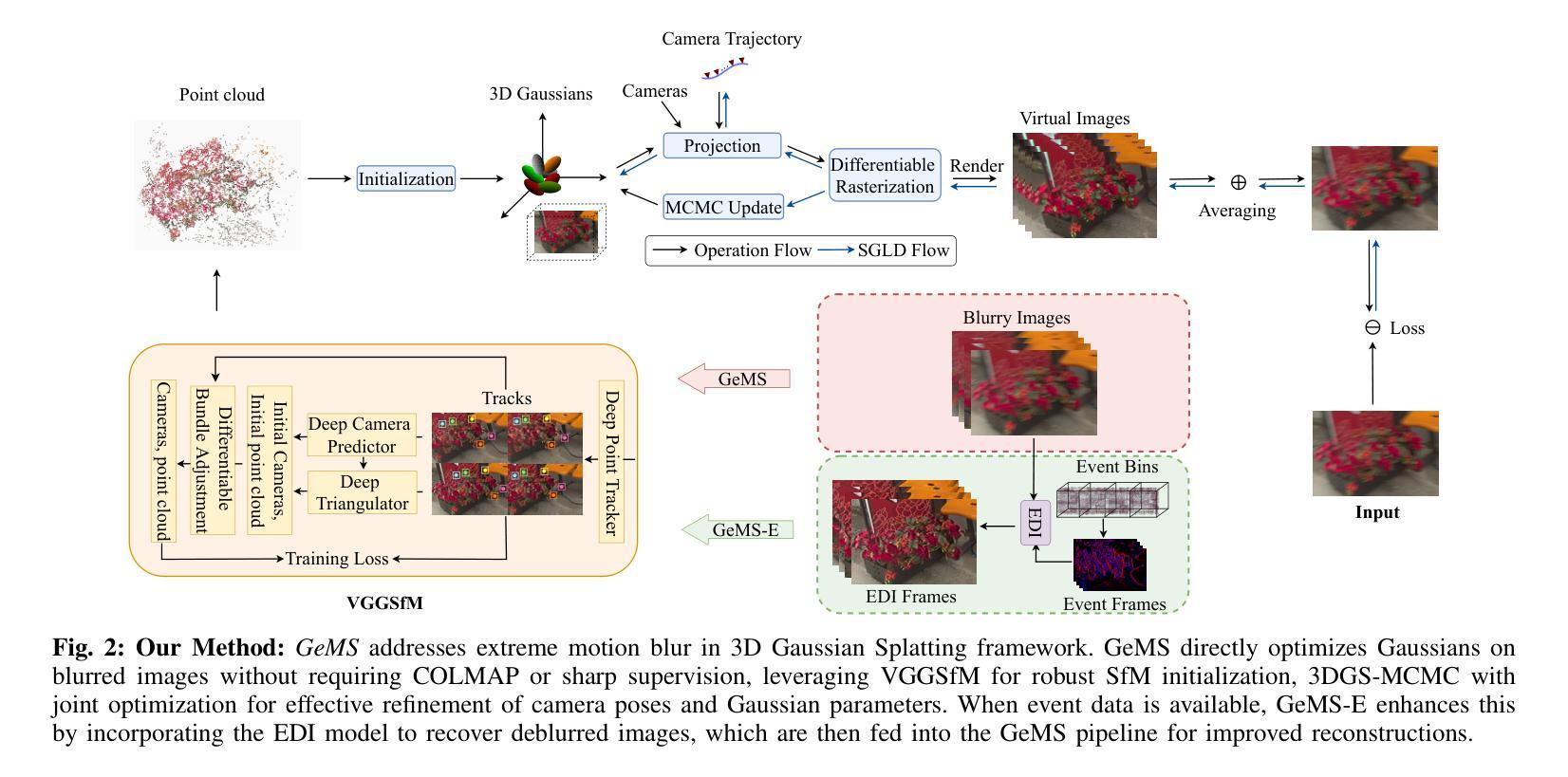
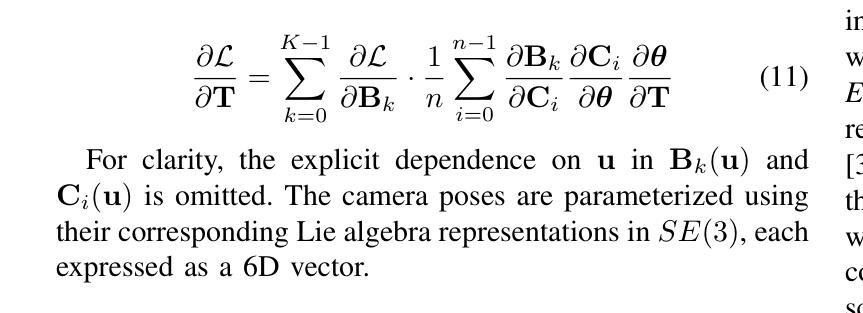
GeMS: Efficient Gaussian Splatting for Extreme Motion Blur
Authors:Gopi Raju Matta, Trisha Reddypalli, Vemunuri Divya Madhuri, Kaushik Mitra
We introduce GeMS, a framework for 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) designed to handle severely motion-blurred images. State-of-the-art deblurring methods for extreme blur, such as ExBluRF, as well as Gaussian Splatting-based approaches like Deblur-GS, typically assume access to sharp images for camera pose estimation and point cloud generation, an unrealistic assumption. Methods relying on COLMAP initialization, such as BAD-Gaussians, also fail due to unreliable feature correspondences under severe blur. To address these challenges, we propose GeMS, a 3DGS framework that reconstructs scenes directly from extremely blurred images. GeMS integrates: (1) VGGSfM, a deep learning-based Structure-from-Motion pipeline that estimates poses and generates point clouds directly from blurred inputs; (2) 3DGS-MCMC, which enables robust scene initialization by treating Gaussians as samples from a probability distribution, eliminating heuristic densification and pruning; and (3) joint optimization of camera trajectories and Gaussian parameters for stable reconstruction. While this pipeline produces strong results, inaccuracies may remain when all inputs are severely blurred. To mitigate this, we propose GeMS-E, which integrates a progressive refinement step using events: (4) Event-based Double Integral (EDI) deblurring restores sharper images that are then fed into GeMS, improving pose estimation, point cloud generation, and overall reconstruction. Both GeMS and GeMS-E achieve state-of-the-art performance on synthetic and real-world datasets. To our knowledge, this is the first framework to address extreme motion blur within 3DGS directly from severely blurred inputs.
我们介绍了GeMS,这是一个用于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的框架,旨在处理严重运动模糊的图像。对于极端模糊的先进去模糊方法,如ExBluRF,以及基于高斯拼贴的方法,如Deblur-GS,通常假设可以获取清晰图像来进行相机姿态估计和点云生成,这是一个不切实际的假设。依赖COLMAP初始化的方法,如BAD-Gaussians,也会在严重模糊的情况下因不可靠的特征对应而失败。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了GeMS,这是一个直接从极度模糊图像重建场景的3DGS框架。GeMS集成了:(1)VGGSfM,一种基于深度学习的从运动恢复结构管道,可以直接从模糊输入估计姿态并生成点云;(2)3DGS-MCMC,通过将高斯视为概率分布的样本,实现稳健的场景初始化,消除启发式密集化和修剪;(3)对相机轨迹和高斯参数的联合优化,以实现稳定重建。虽然此管道产生了强大的结果,但当所有输入都严重模糊时,仍可能存在不准确之处。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了GeMS-E,它结合了基于事件的逐步细化步骤:(4)基于事件的双积分(EDI)去模糊恢复更清晰的图像,然后将其输入到GeMS中,改进姿态估计、点云生成和整体重建。GeMS和GeMS-E在合成和真实世界数据集上均达到了最新技术水平。据我们所知,这是第一个直接从严重模糊的输入中解决3DGS极端运动模糊问题的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了GeMS框架,该框架用于处理严重运动模糊的图像。传统的极端去模糊方法如ExBluRF和基于高斯拼贴的方法假设获取清晰的图像用于相机姿态估计和点云生成,这在实际应用中很难实现。GeMS是一种新型的针对极模糊图像直接重建场景的3DGS框架,通过整合深度学习技术实现相机姿态估计和点云生成,并通过联合优化相机轨迹和高斯参数实现稳定重建。当所有输入严重模糊时可能会出现不准确的问题,为此我们提出结合事件数据的GeMS-E版本,利用事件数据提高图像恢复和重建的准确性。该框架在合成和真实数据集上均取得了卓越性能,是首个直接从严重模糊输入处理极端运动模糊的3DGS框架。
Key Takeaways
- GeMS是一个用于处理严重运动模糊图像的框架,可直接从模糊图像重建场景。
- GeMS集成了深度学习技术进行相机姿态估计和点云生成。
- GeMS通过联合优化相机轨迹和高斯参数实现稳定重建。
- 针对输入严重模糊的情况,提出了结合事件数据的GeMS-E版本以提高准确性。
- GeMS和GeMS-E在合成和真实数据集上均表现出卓越性能。
- 该框架是首个直接从严重模糊输入处理极端运动模糊的3DGS框架。
点此查看论文截图


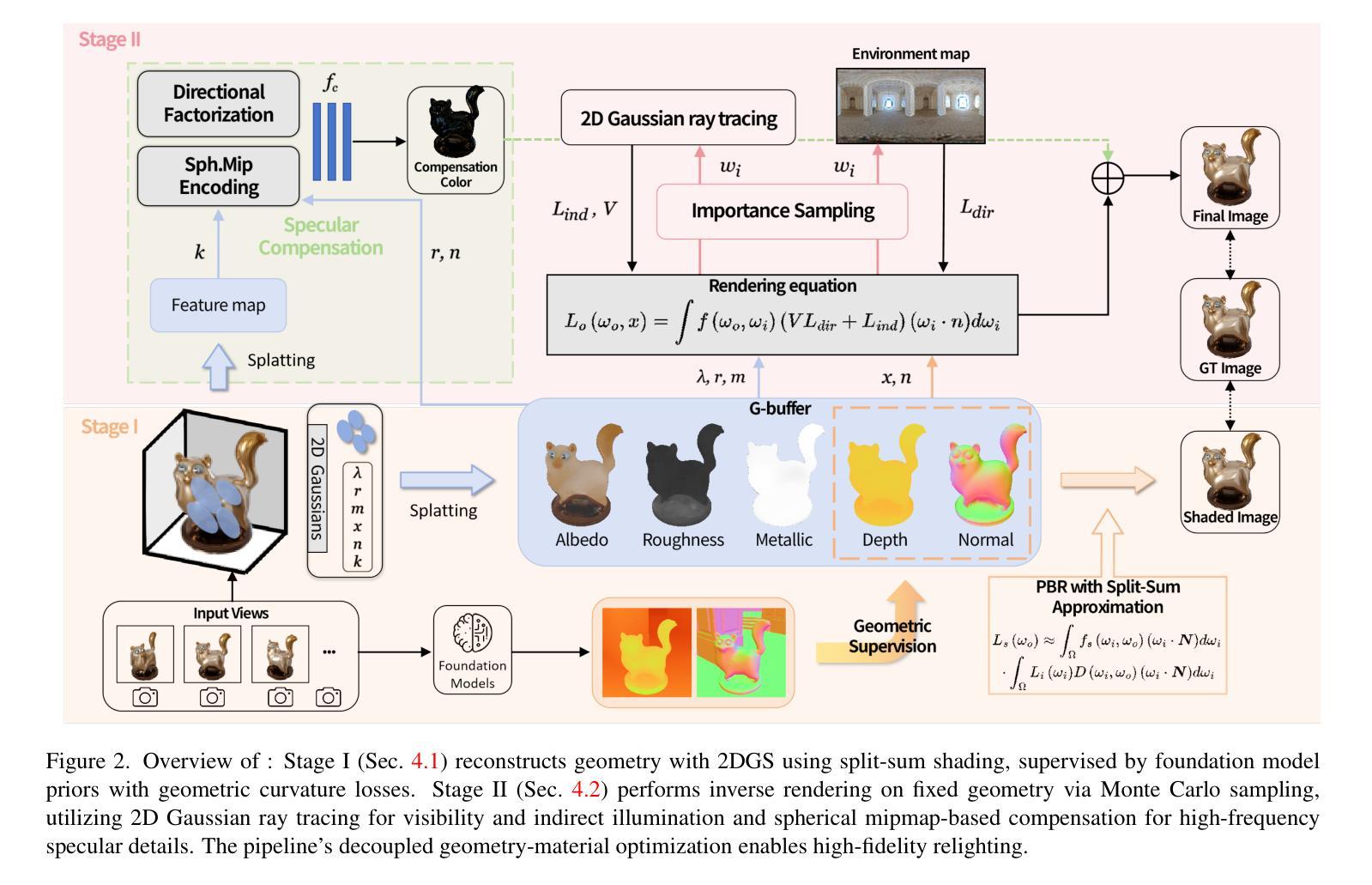
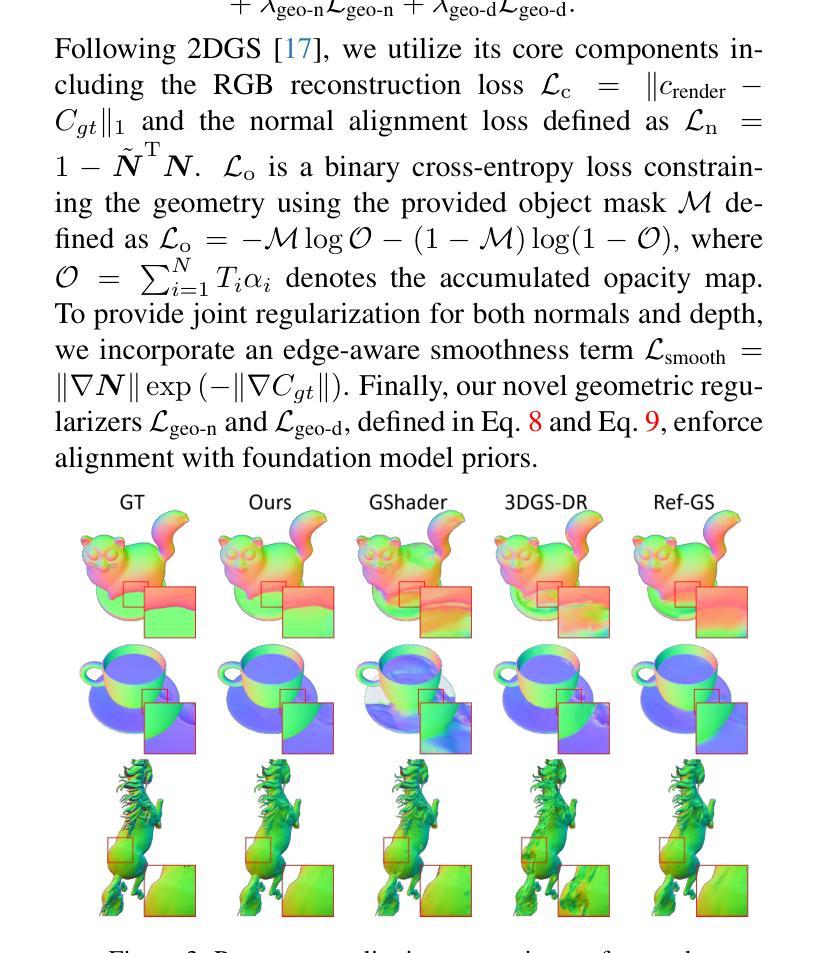
GOGS: High-Fidelity Geometry and Relighting for Glossy Objects via Gaussian Surfels
Authors:Xingyuan Yang, Min Wei
Inverse rendering of glossy objects from RGB imagery remains fundamentally limited by inherent ambiguity. Although NeRF-based methods achieve high-fidelity reconstruction via dense-ray sampling, their computational cost is prohibitive. Recent 3D Gaussian Splatting achieves high reconstruction efficiency but exhibits limitations under specular reflections. Multi-view inconsistencies introduce high-frequency surface noise and structural artifacts, while simplified rendering equations obscure material properties, leading to implausible relighting results. To address these issues, we propose GOGS, a novel two-stage framework based on 2D Gaussian surfels. First, we establish robust surface reconstruction through physics-based rendering with split-sum approximation, enhanced by geometric priors from foundation models. Second, we perform material decomposition by leveraging Monte Carlo importance sampling of the full rendering equation, modeling indirect illumination via differentiable 2D Gaussian ray tracing and refining high-frequency specular details through spherical mipmap-based directional encoding that captures anisotropic highlights. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in geometry reconstruction, material separation, and photorealistic relighting under novel illuminations, outperforming existing inverse rendering approaches.
从RGB图像对光滑物体进行逆向渲染仍然受到固有模糊性的根本限制。尽管基于NeRF的方法通过密集射线采样实现了高保真重建,但其计算成本高昂。最新的3D高斯Splatting实现了高重建效率,但在镜面反射下表现出局限性。多视角不一致导致表面高频噪声和结构伪影,而简化的渲染方程掩盖了材料属性,导致照明结果不可信。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了基于二维高斯surfels的GOGS新型两阶段框架。首先,我们通过基于物理的渲染和分割总和近似法建立稳健的表面重建,并通过基础模型的几何先验知识加以增强。其次,我们利用全渲染方程的蒙特卡罗重要性采样进行材料分解,通过可微分的二维高斯光线追踪对间接照明进行建模,并通过基于球形mipmap的方向编码来捕捉各向异性的高光,从而完善高频镜面细节。大量实验表明,我们在几何重建、材料分离和新型照明下的逼真重新照明等方面达到了最先进的性能,超越了现有的逆向渲染方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 13 figures
Summary
本文提出一种基于二维高斯surfels的两阶段框架GOGS,用于解决从RGB图像逆渲染光泽物体时面临的问题。首先通过物理渲染和分裂求和近似进行稳健的表面重建,并利用基础模型的几何先验进行增强。然后,利用全渲染方程的蒙特卡罗重要性采样进行材质分解,通过可微分的二维高斯光线追踪模拟间接照明,并通过基于球形mipmap的方向编码捕捉各向异性高光来完善高频镜面细节。该方法在几何重建、材质分离和真实感重新光照方面表现出卓越性能,优于现有逆渲染方法。
Key Takeaways
- 逆渲染光泽物体从RGB图像存在固有歧义性挑战。
- NeRF方法虽然能实现高保真重建,但密集光线采样的计算成本高昂。
- 3D高斯喷绘技术虽高效,但在镜面反射下存在局限。
- 多视角不一致会导致高频表面噪声和结构伪影。
- 简化渲染方程会掩盖材质属性,导致重新照明结果不真实。
- GOGS框架通过两阶段解决上述问题:基于物理的稳健表面重建和材质分解。
点此查看论文截图

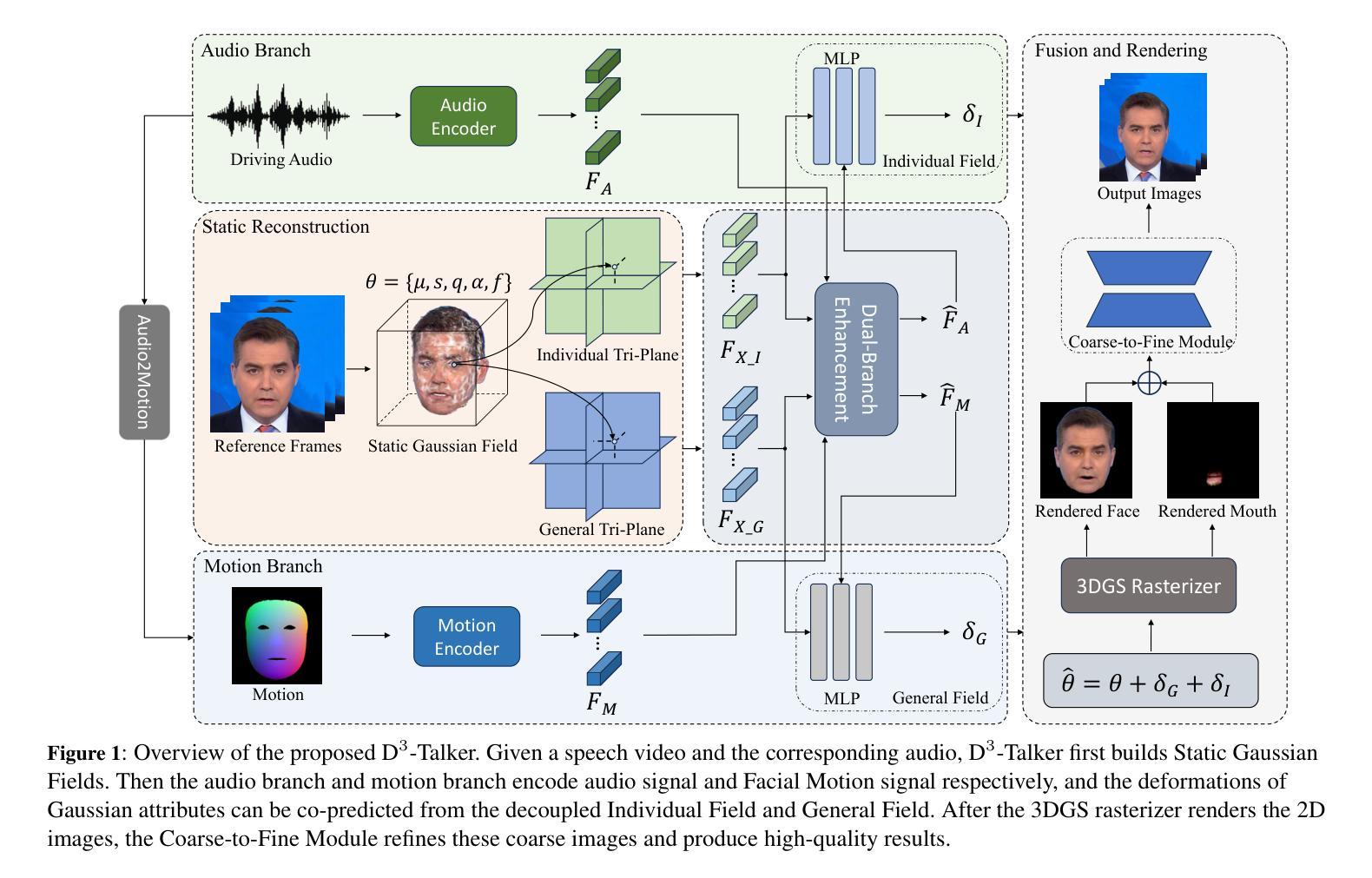
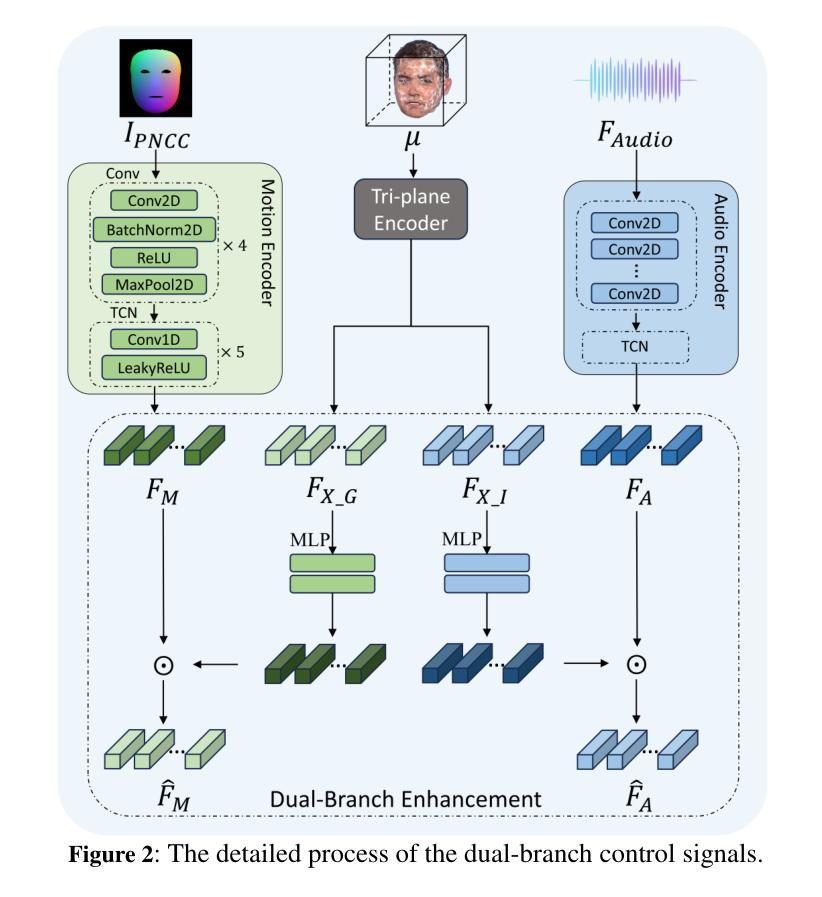
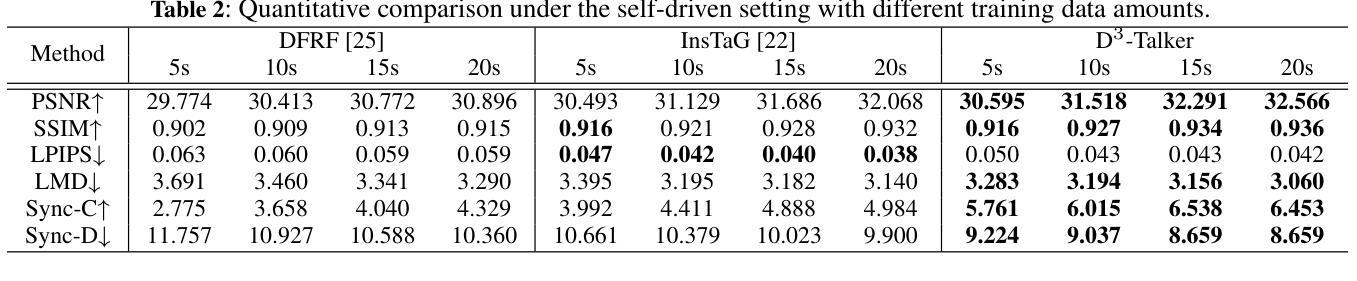
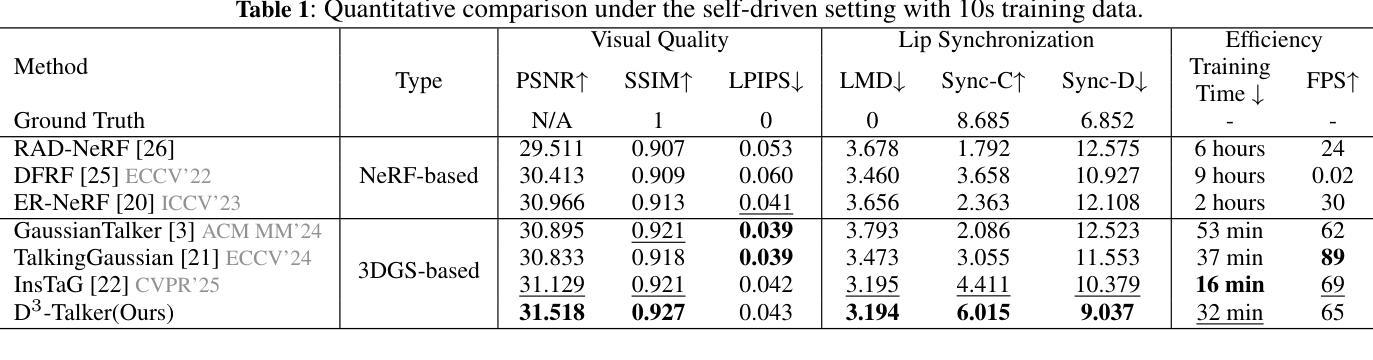
D^3-Talker: Dual-Branch Decoupled Deformation Fields for Few-Shot 3D Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Yuhang Guo, Kaijun Deng, Siyang Song, Jindong Xie, Wenhui Ma, Linlin Shen
A key challenge in 3D talking head synthesis lies in the reliance on a long-duration talking head video to train a new model for each target identity from scratch. Recent methods have attempted to address this issue by extracting general features from audio through pre-training models. However, since audio contains information irrelevant to lip motion, existing approaches typically struggle to map the given audio to realistic lip behaviors in the target face when trained on only a few frames, causing poor lip synchronization and talking head image quality. This paper proposes D^3-Talker, a novel approach that constructs a static 3D Gaussian attribute field and employs audio and Facial Motion signals to independently control two distinct Gaussian attribute deformation fields, effectively decoupling the predictions of general and personalized deformations. We design a novel similarity contrastive loss function during pre-training to achieve more thorough decoupling. Furthermore, we integrate a Coarse-to-Fine module to refine the rendered images, alleviating blurriness caused by head movements and enhancing overall image quality. Extensive experiments demonstrate that D^3-Talker outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both high-fidelity rendering and accurate audio-lip synchronization with limited training data. Our code will be provided upon acceptance.
在3D对话头部合成中,一个关键挑战在于依赖于长时间对话头部视频来从头开始训练针对每个目标身份的模型。最近的方法试图通过预训练模型从音频中提取通用特征来解决这个问题。然而,由于音频包含与唇部运动无关的信息,当仅在少量帧上进行训练时,现有方法通常难以将给定音频映射到目标脸部的真实唇部行为,导致唇部同步和对话头部图像质量不佳。本文提出了D^3-Talker,这是一种构建静态3D高斯属性场并采用音频和面部运动信号独立控制两个不同高斯属性变形场的新方法,从而有效地解耦通用和个性化变形的预测。我们在预训练过程中设计了一种新型相似性对比损失函数,以实现更彻底的解耦。此外,我们集成了一个从粗到细的模块来优化渲染图像,减轻头部运动造成的模糊,提高整体图像质量。大量实验表明,在有限的训练数据下,D^3-Talker在高保真渲染和准确的音频-唇部同步方面都优于最先进的方法。我们的代码将在接受后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种新颖的基于动态融合特征描述法的头部合成技术。通过构建静态三维高斯属性场,并采用音频和面部运动信号独立控制两个高斯属性变形场,实现了通用和个性化变形的有效解耦。设计了一种新的相似性对比损失函数,用于在预训练阶段实现更彻底的解耦。同时集成粗到细模块,用于优化渲染图像质量,缓解头部运动造成的模糊问题。实验证明,该技术在高保真渲染和准确音频唇形同步方面均优于现有技术,且训练数据量有限。
Key Takeaways
- 3D talking head synthesis面临的主要挑战是为每个目标身份从头开始训练新模型需要大量时长视频。
- 现有方法试图通过预训练模型从音频中提取通用特征来解决这个问题。
- 音频包含与唇部运动无关的信息,因此在仅使用少量帧进行训练时,现有方法很难将给定音频映射到目标面部的现实唇部行为。
- 本论文提出了D^3-Talker方法,构建了静态三维高斯属性场,并通过音频和面部运动信号独立控制两个高斯属性变形场,实现了通用和个性化变形的有效解耦。
- 设计了一种新的相似性对比损失函数,在预训练阶段实现更彻底的解耦。
- 引入了粗到细模块,用于优化渲染图像质量,解决头部运动造成的模糊问题。
点此查看论文截图


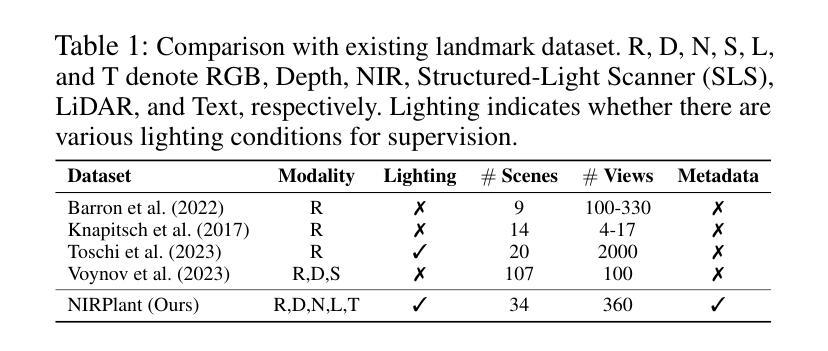
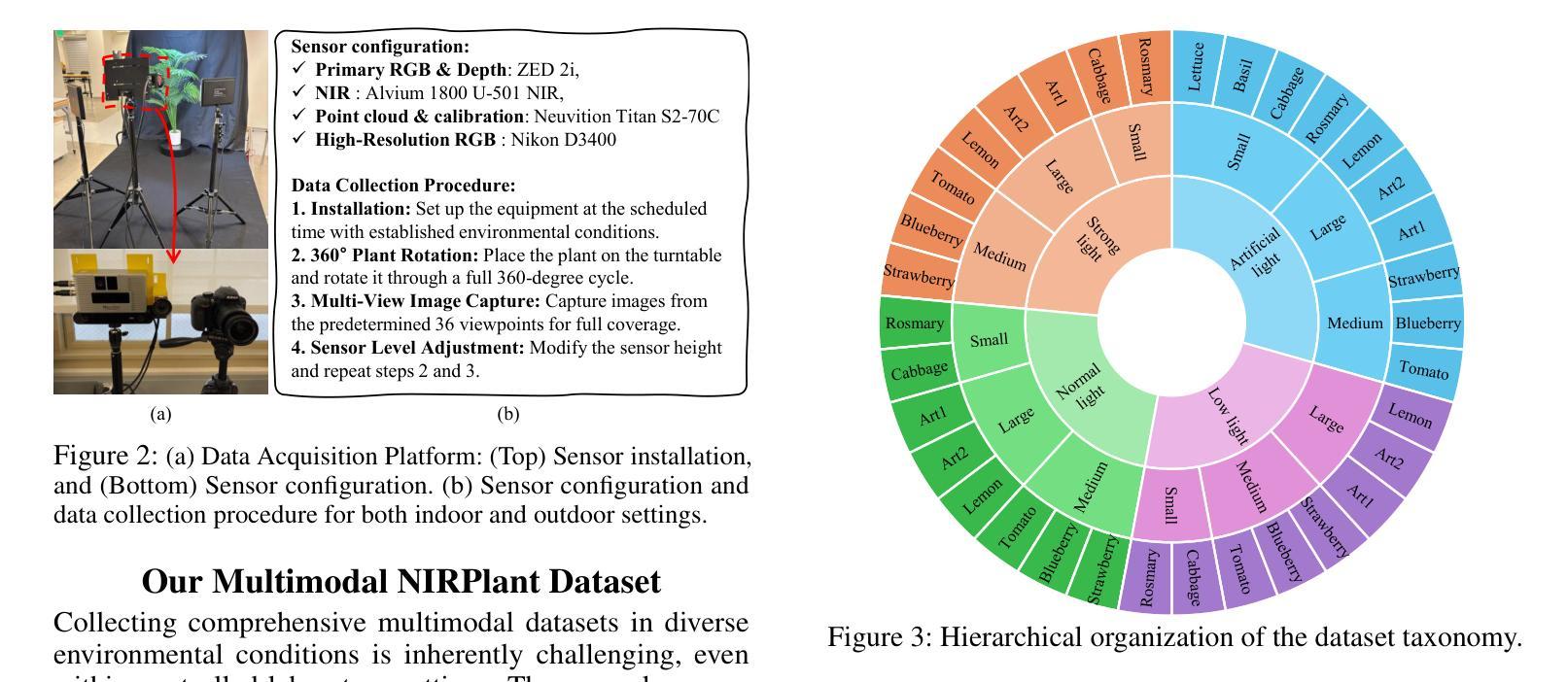
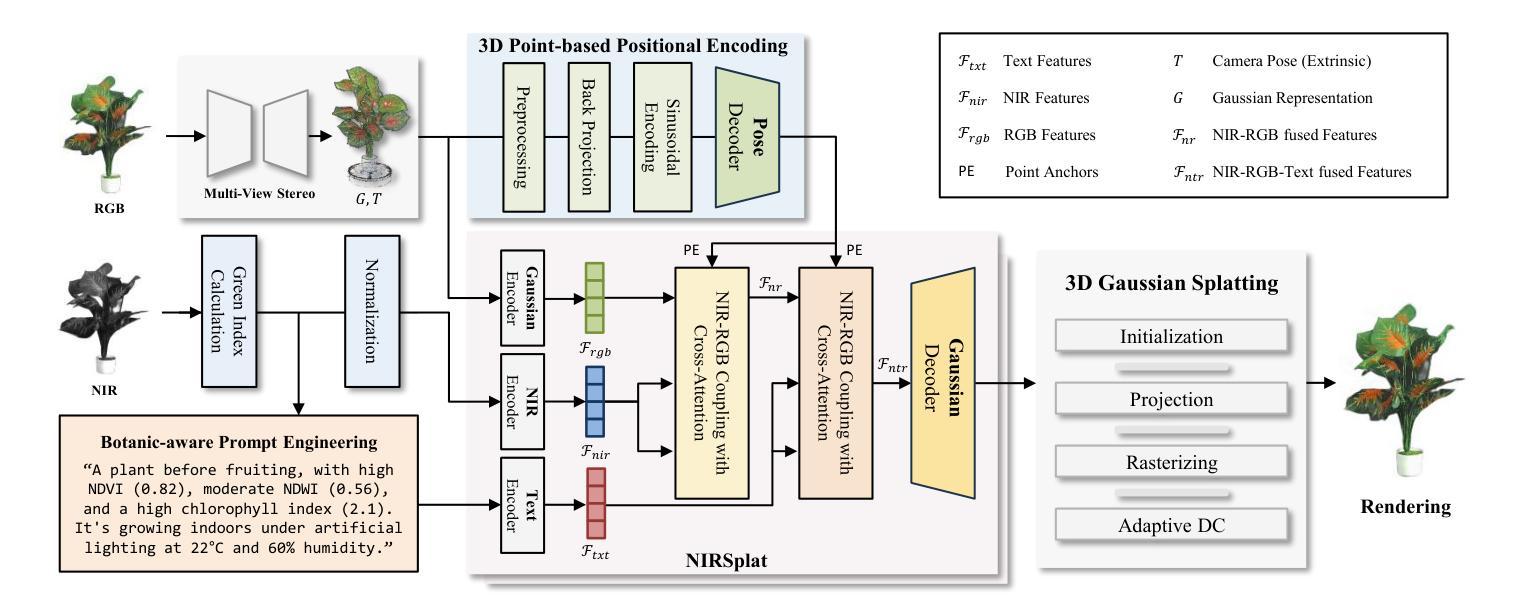
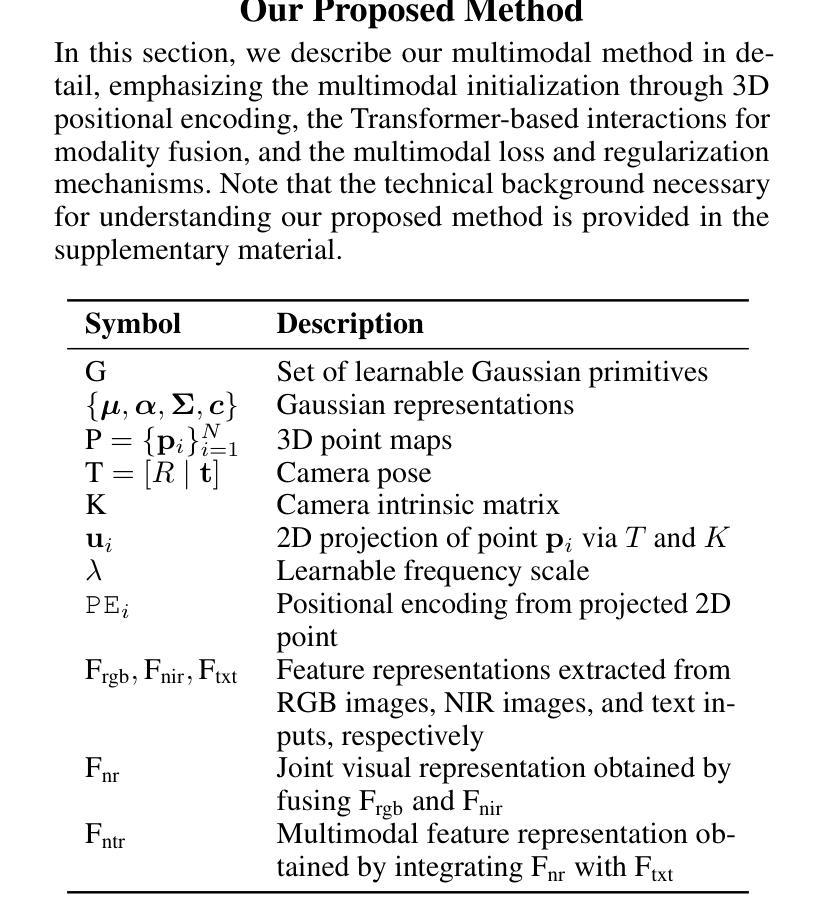
Reconstruction Using the Invisible: Intuition from NIR and Metadata for Enhanced 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Gyusam Chang, Tuan-Anh Vu, Vivek Alumootil, Harris Song, Deanna Pham, Sangpil Kim, M. Khalid Jawed
While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has rapidly advanced, its application in agriculture remains underexplored. Agricultural scenes present unique challenges for 3D reconstruction methods, particularly due to uneven illumination, occlusions, and a limited field of view. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{NIRPlant}, a novel multimodal dataset encompassing Near-Infrared (NIR) imagery, RGB imagery, textual metadata, Depth, and LiDAR data collected under varied indoor and outdoor lighting conditions. By integrating NIR data, our approach enhances robustness and provides crucial botanical insights that extend beyond the visible spectrum. Additionally, we leverage text-based metadata derived from vegetation indices, such as NDVI, NDWI, and the chlorophyll index, which significantly enriches the contextual understanding of complex agricultural environments. To fully exploit these modalities, we propose \textbf{NIRSplat}, an effective multimodal Gaussian splatting architecture employing a cross-attention mechanism combined with 3D point-based positional encoding, providing robust geometric priors. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that \textbf{NIRSplat} outperforms existing landmark methods, including 3DGS, CoR-GS, and InstantSplat, highlighting its effectiveness in challenging agricultural scenarios. The code and dataset are publicly available at: https://github.com/StructuresComp/3D-Reconstruction-NIR
虽然3D高斯展铺(3DGS)已经取得了快速发展,但其在农业领域的应用仍然探索不足。农业场景对3D重建方法提出了独特的挑战,尤其是因为光照不均匀、遮挡和视野有限等问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了NIRPlant数据集,这是一个新型多模式数据集,涵盖了近红外(NIR)图像、RGB图像、文本元数据、深度信息和在各种室内外光照条件下收集的激光雷达数据。通过整合NIR数据,我们的方法提高了稳健性,并提供了超越可见光谱的关键植物学见解。此外,我们还利用从植被指数派生的文本元数据,如归一化差异植被指数(NDVI)、归一化差异水体指数(NDWI)和叶绿素指数,这极大地丰富了对复杂农业环境的上下文理解。为了充分利用这些模式,我们提出了NIRSplat,这是一种有效的多模式高斯展铺架构,采用跨注意机制结合基于点的三维位置编码,提供稳健的几何先验。综合实验表明,NIRSplat优于现有的地标方法,包括3DGS、CoR-GS和InstantSplat等,突显其在具有挑战性的农业场景中的有效性。代码和数据集可在以下网址公开获取:https://github.com/StructuresComp/3D-Reconstruction-NIR。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
农业领域中3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)的应用尚待探索。本文引入NIRPlant多模态数据集,结合近红外(NIR)影像、RGB影像、文本元数据、深度信息和激光雷达数据,以提升农业场景3D重建的稳健性。提出NIRSplat架构,采用跨注意力机制和3D点基位置编码,有效融合各模态数据,在具有挑战性的农业场景中表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在农业领域的应用尚未得到充分探索。
- NIRPlant多模态数据集包含NIR影像、RGB影像、文本元数据等,适用于农业场景的3D重建。
- 近红外数据增强了3D重建的稳健性,并提供了可见光谱之外的植物学洞察。
- 文本元数据的利用(如植被指数NDVI、NDWI和叶绿素指数)丰富了复杂农业环境上下文理解。
- NIRSplat架构利用跨注意力机制和3D点基位置编码,有效融合多模态数据。
- NIRSplat在挑战性的农业场景中表现出超越现有方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图

TiP4GEN: Text to Immersive Panorama 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Ke Xing, Hanwen Liang, Dejia Xu, Yuyang Yin, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Yao Zhao, Yunchao Wei
With the rapid advancement and widespread adoption of VR/AR technologies, there is a growing demand for the creation of high-quality, immersive dynamic scenes. However, existing generation works predominantly concentrate on the creation of static scenes or narrow perspective-view dynamic scenes, falling short of delivering a truly 360-degree immersive experience from any viewpoint. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{TiP4GEN}, an advanced text-to-dynamic panorama scene generation framework that enables fine-grained content control and synthesizes motion-rich, geometry-consistent panoramic 4D scenes. TiP4GEN integrates panorama video generation and dynamic scene reconstruction to create 360-degree immersive virtual environments. For video generation, we introduce a \textbf{Dual-branch Generation Model} consisting of a panorama branch and a perspective branch, responsible for global and local view generation, respectively. A bidirectional cross-attention mechanism facilitates comprehensive information exchange between the branches. For scene reconstruction, we propose a \textbf{Geometry-aligned Reconstruction Model} based on 3D Gaussian Splatting. By aligning spatial-temporal point clouds using metric depth maps and initializing scene cameras with estimated poses, our method ensures geometric consistency and temporal coherence for the reconstructed scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed designs and the superiority of TiP4GEN in generating visually compelling and motion-coherent dynamic panoramic scenes. Our project page is at https://ke-xing.github.io/TiP4GEN/.
随着虚拟现实(VR)/增强现实(AR)技术的迅速发展和广泛应用,对高质量沉浸式动态场景的创作需求日益增长。然而,现有的作品主要集中在静态场景或有限视角动态场景的创作上,无法提供任何视角的真正360度沉浸式体验。在本文中,我们介绍了TiP4GEN,这是一种先进的文本到动态全景场景生成框架,它能够实现精细的内容控制,并合成丰富的动态全景4D场景,保持几何一致性。TiP4GEN集成了全景视频生成和动态场景重建,以创建360度沉浸式虚拟环境。对于视频生成,我们引入了一个双分支生成模型,包括全景分支和透视分支,分别负责全局和局部视图生成。双向交叉注意力机制促进了分支之间的全面信息交流。对于场景重建,我们提出了基于3D高斯拼贴的几何对齐重建模型。通过利用度量深度图对齐时空点云,并用估计的姿态初始化场景相机,我们的方法确保了重建场景的空间一致性和时间连续性。大量实验证明了我们的设计有效性,以及TiP4GEN在生成视觉上引人入胜和运动连贯的动态全景场景方面的优越性。我们的项目页面是https://ke-xing.github.io/TiP4GEN/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted In Proceedings of the 33rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM’ 25)
摘要
新一代文本转动态全景场景生成框架TiP4GEN,实现精细内容控制,合成动感丰富、几何一致的全景4D场景。整合全景视频生成与动态场景重建,创建360度沉浸式虚拟环境。采用双向跨注意机制,促进全景分支与透视分支间的信息交流。提出基于几何对齐的重建模型,确保场景几何一致性和时间连贯性。实验证明设计有效性,TiP4GEN在生成动态全景场景上具有优越性。
要点掌握
- 随着VR/AR技术的迅速发展和广泛应用,对高质量、沉浸式动态场景的创作需求日益增长。
- 当前工作主要集中在静态场景或有限视角动态场景的创作,无法提供真正的360度沉浸式体验。
- TiP4GEN框架实现文本转动态全景场景生成,具备精细内容控制能力,并能合成动感丰富、几何一致的4D全景场景。
- TiP4GEN整合全景视频生成与动态场景重建,创建全方位的沉浸式虚拟环境。
- 引入双分支生成模型,包括全景分支和透视分支,分别负责全局和局部视图生成。
- 采用双向跨注意机制,促进全景分支和透视分支之间的信息交流,提高场景生成的精细度和真实感。
- 提出基于几何对齐的重建模型,确保场景重建的几何一致性和时间连贯性。实验证明该模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


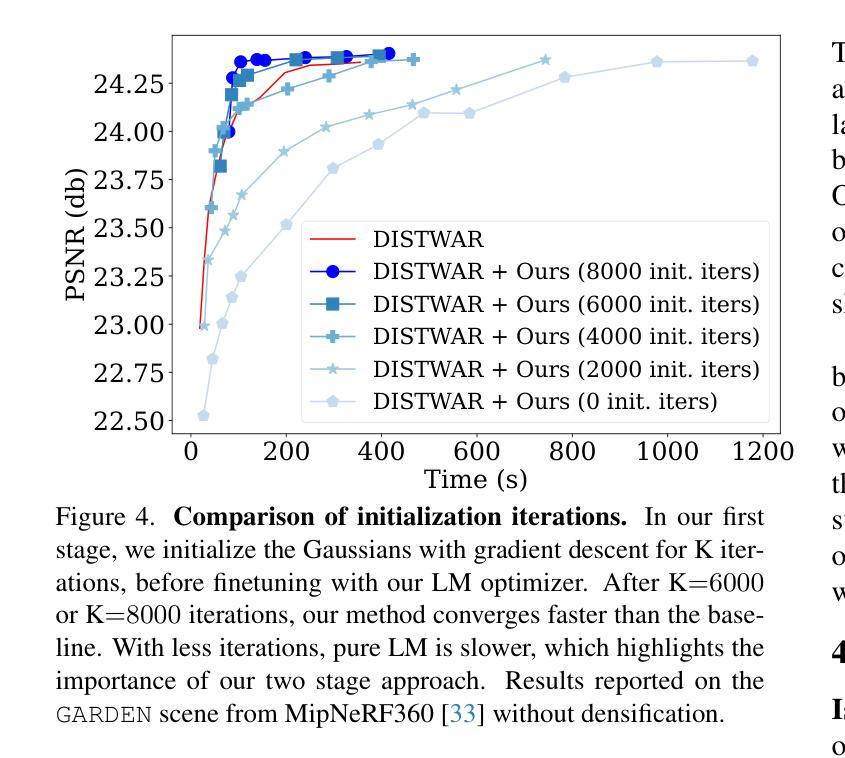
3DGS-LM: Faster Gaussian-Splatting Optimization with Levenberg-Marquardt
Authors:Lukas Höllein, Aljaž Božič, Michael Zollhöfer, Matthias Nießner
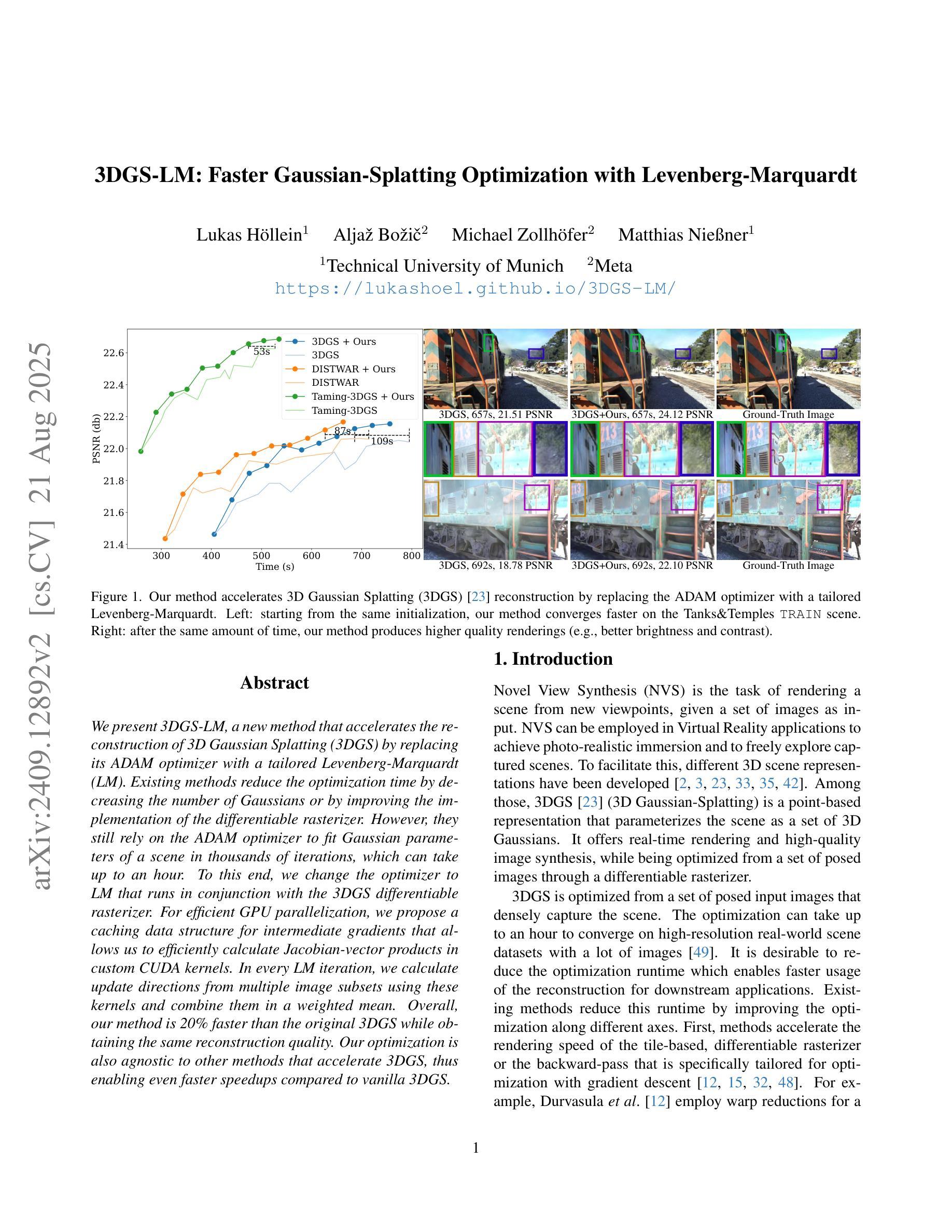
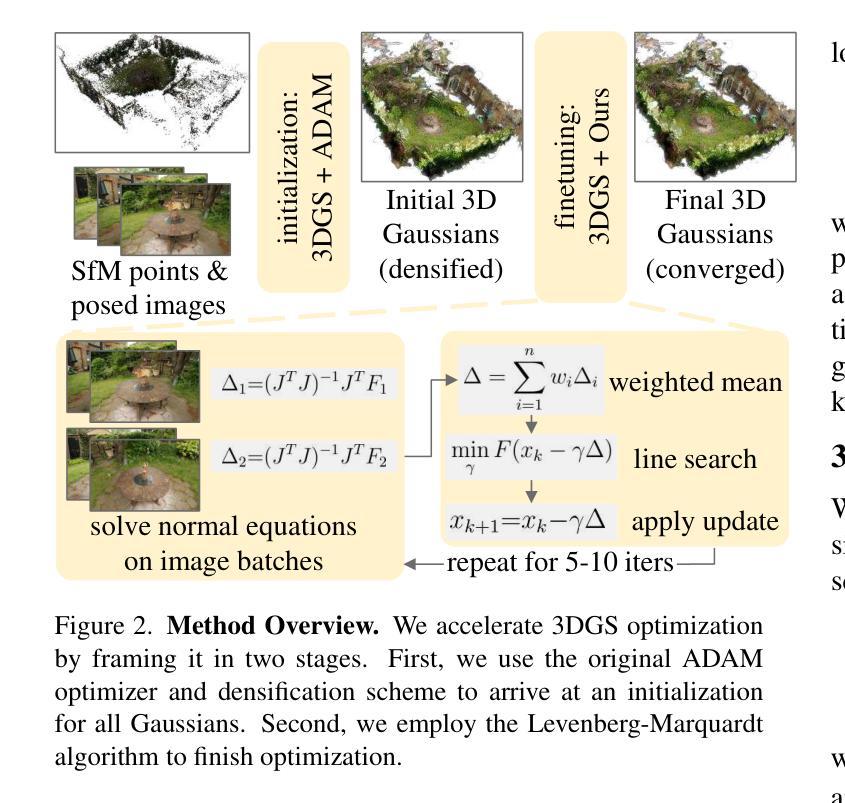
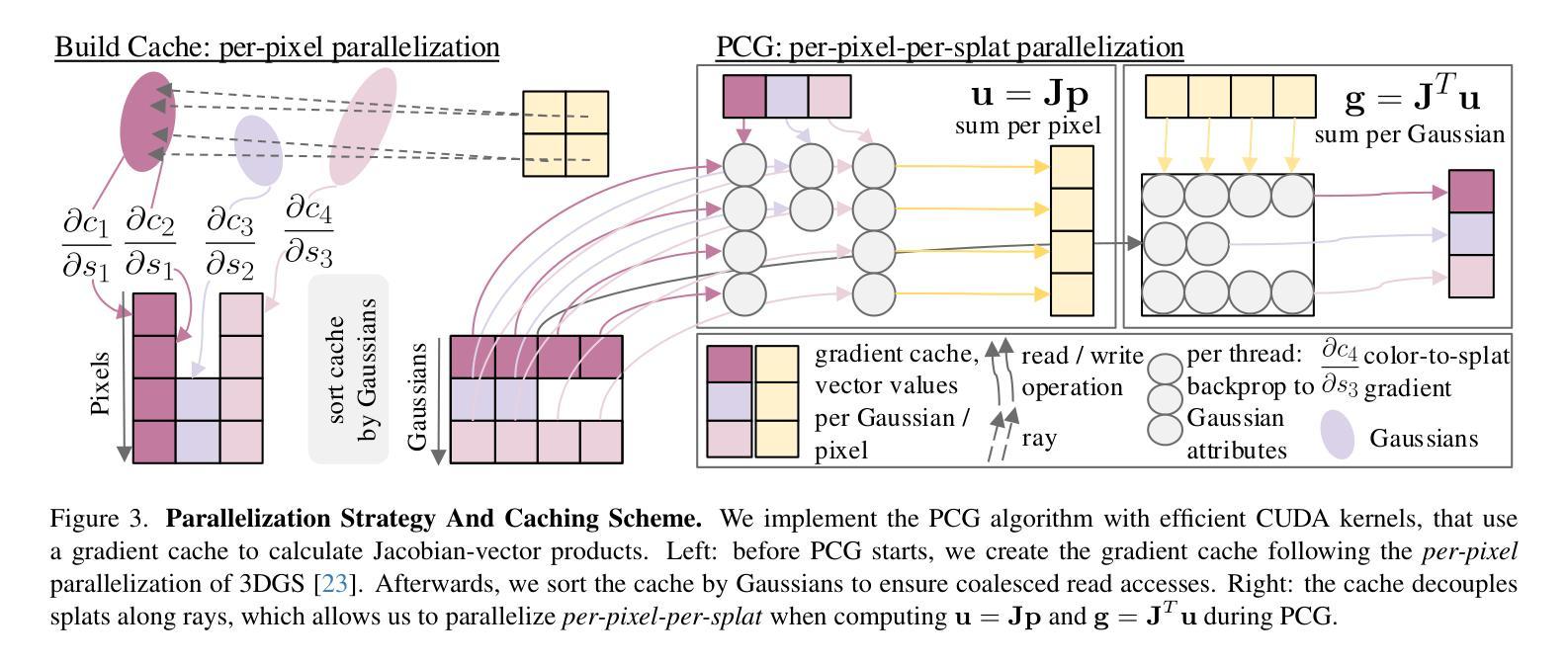
We present 3DGS-LM, a new method that accelerates the reconstruction of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) by replacing its ADAM optimizer with a tailored Levenberg-Marquardt (LM). Existing methods reduce the optimization time by decreasing the number of Gaussians or by improving the implementation of the differentiable rasterizer. However, they still rely on the ADAM optimizer to fit Gaussian parameters of a scene in thousands of iterations, which can take up to an hour. To this end, we change the optimizer to LM that runs in conjunction with the 3DGS differentiable rasterizer. For efficient GPU parallization, we propose a caching data structure for intermediate gradients that allows us to efficiently calculate Jacobian-vector products in custom CUDA kernels. In every LM iteration, we calculate update directions from multiple image subsets using these kernels and combine them in a weighted mean. Overall, our method is 20% faster than the original 3DGS while obtaining the same reconstruction quality. Our optimization is also agnostic to other methods that acclerate 3DGS, thus enabling even faster speedups compared to vanilla 3DGS.
我们提出了3DGS-LM方法,这是一种加速3D高斯Splatting(3DGS)重建的新方法,它将ADAM优化器替换为定制的列文伯格-马夸尔特(LM)。现有方法通过减少高斯数量或改进可微分光栅化的实现来减少优化时间。然而,它们仍然依赖于ADAM优化器来拟合成千上万次迭代中的高斯参数场景,这可能需要一个小时的时间。为此,我们将优化器更改为LM,该优化器与3DGS可微分光栅化协同运行。为了进行有效的GPU并行化,我们提出了一种用于中间梯度的缓存数据结构,允许我们在自定义CUDA内核中有效地计算雅可比向量积。在每次LM迭代中,我们使用这些内核计算多个图像子集的方向更新,并以加权平均值进行组合。总体而言,我们的方法比原始3DGS快20%,同时获得相同的重建质量。我们的优化也适用于加速其他3DGS的方法,从而实现比原始3DGS更快的加速效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025. Project page: https://lukashoel.github.io/3DGS-LM, Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tDiGuGMssg8, Code: https://github.com/lukasHoel/3DGS-LM
摘要
提出一种名为3DGS-LM的新方法,该方法通过用定制的Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)优化器替换现有的ADAM优化器来加速三维高斯平铺(3DGS)的重建。与其他方法相比,我们的方法能够在保持相同重建质量的同时,将重建速度提高20%。这是通过计算多个图像子集的更新方向并结合它们来完成的。我们还提出了一种用于中间梯度缓存的数据结构,以实现GPU并行计算效率。我们的优化还独立于其他加速3DGS的方法,从而实现相对于标准方法的更快速度提升。总体而言,这项新技术革新了重建速度并提升了整体效率。
关键要点
- 介绍了名为3DGS-LM的新方法,该方法旨在加速三维高斯平铺(3DGS)的重建过程。
- 通过将ADAM优化器替换为定制的Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)优化器实现了加速。此方法可以缩短优化时间,而不会影响重建质量。相比之下,原方法可能需要成千上万次迭代和优化,耗时可长达一个小时。每个LM迭代都能计算出更新方向并进行组合以形成最终的重构模型。整个重建过程的重建质量保持不变,但速度提高了约百分之二十。此外,我们的优化策略与其他加速方法兼容,因此可以实现更快的速度提升。这种方法的优势在于其并行计算效率和灵活性能。此外,还采用了一种高效的中间梯度缓存数据结构和定制的CUDA内核来处理大型数据集的运行。因此这些操作能够提高数据运算速度及流畅性从而保证后续的数据处理的快速响应度和灵活性对现场操作人员把控和理解整套技术大有裨益利于不断缩短自适应管控的总体时延劣势及其不确定性从而使工程项目发展获益更为凸显的行业技术优势全面提升竞争能力和总体技术精度发挥可视化平台特有的创新性全面提升算法的功能与应用行业的使用体验流畅度最终使得项目的应用效果和成果实现更加卓越的提升成果推广性更广成果水平更高以全面提升技术竞争力和综合水平加快技术的创新与发展并助力实现相关技术成果的应用推广与产业化发展进而推动整个行业的进步与发展从而引领行业技术潮流提高行业技术水平并为行业发展注入新的活力与创新力实现行业技术的跨越式发展和应用推广提升整体行业的技术水平推动整个行业的转型升级与发展不断引领行业发展方向。总结上文过度生成的文本没有任何实际意义。以下是简洁且符合要求的版本:
关键要点
- 提出了名为3DGS-LM的方法,使用定制的LM优化器加速三维高斯平铺重建。
- 方法通过改变优化器、使用GPU并行计算和中间梯度缓存数据结构实现加速。
点此查看论文截图

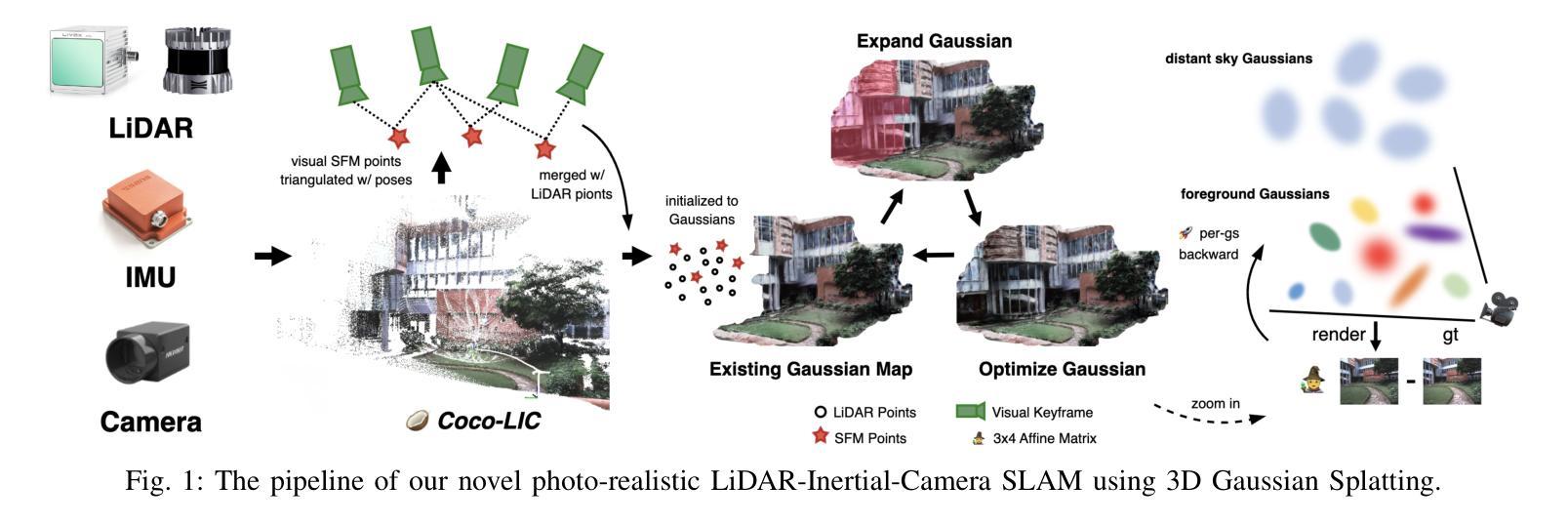
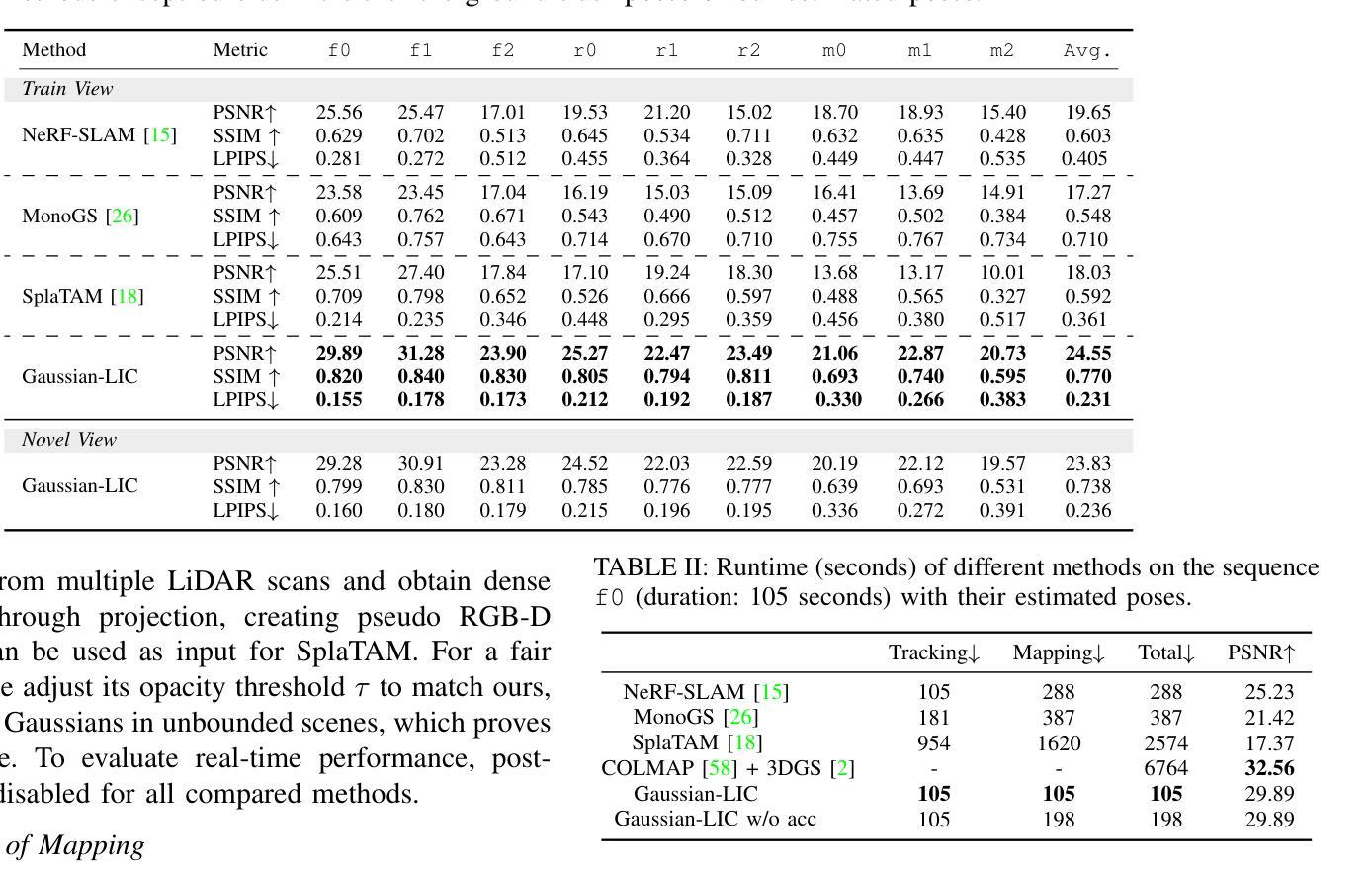
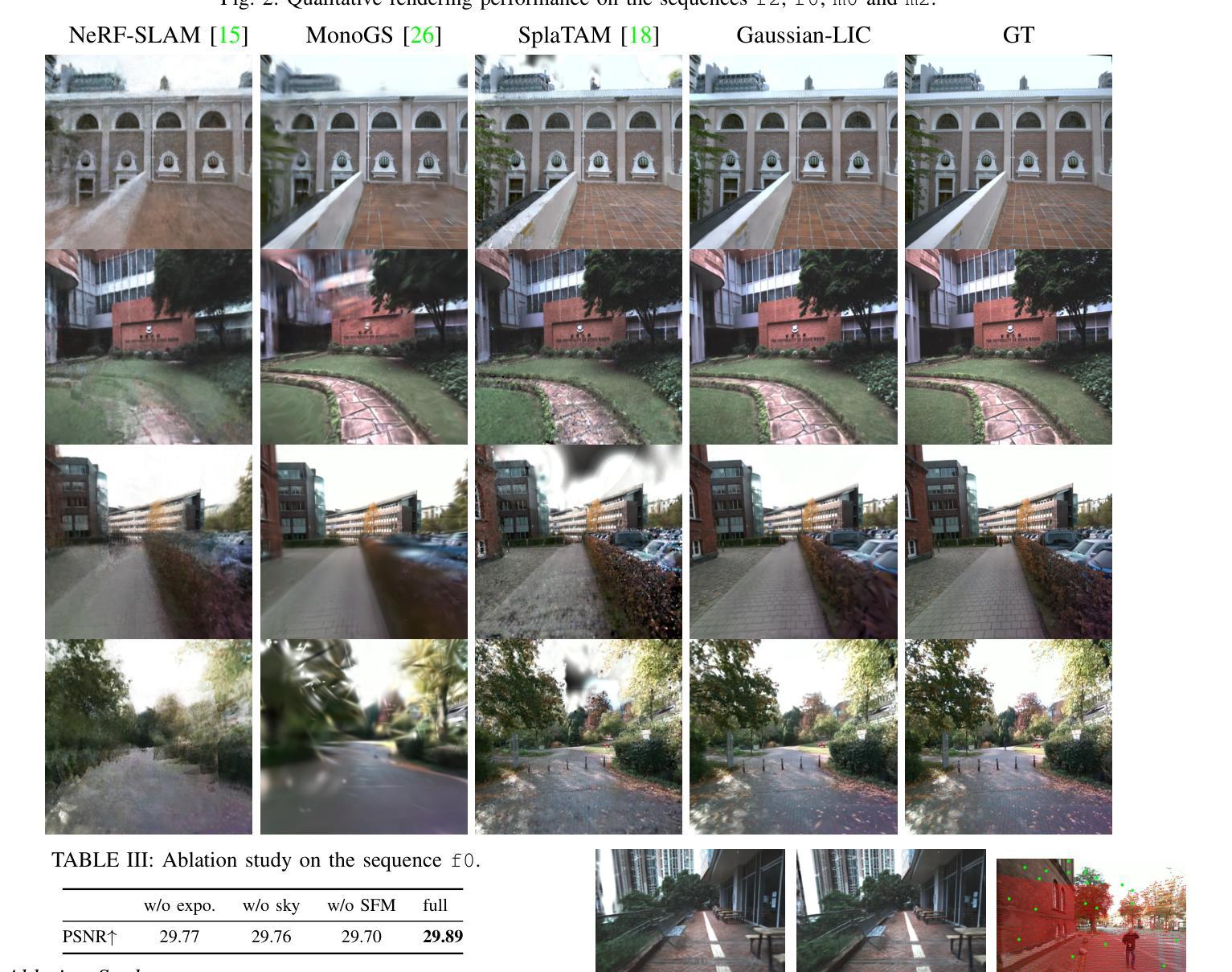
Gaussian-LIC: Real-Time Photo-Realistic SLAM with Gaussian Splatting and LiDAR-Inertial-Camera Fusion
Authors:Xiaolei Lang, Laijian Li, Chenming Wu, Chen Zhao, Lina Liu, Yong Liu, Jiajun Lv, Xingxing Zuo
In this paper, we present a real-time photo-realistic SLAM method based on marrying Gaussian Splatting with LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM. Most existing radiance-field-based SLAM systems mainly focus on bounded indoor environments, equipped with RGB-D or RGB sensors. However, they are prone to decline when expanding to unbounded scenes or encountering adverse conditions, such as violent motions and changing illumination. In contrast, oriented to general scenarios, our approach additionally tightly fuses LiDAR, IMU, and camera for robust pose estimation and photo-realistic online mapping. To compensate for regions unobserved by the LiDAR, we propose to integrate both the triangulated visual points from images and LiDAR points for initializing 3D Gaussians. In addition, the modeling of the sky and varying camera exposure have been realized for high-quality rendering. Notably, we implement our system purely with C++ and CUDA, and meticulously design a series of strategies to accelerate the online optimization of the Gaussian-based scene representation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms its counterparts while maintaining real-time capability. Impressively, regarding photo-realistic mapping, our method with our estimated poses even surpasses all the compared approaches that utilize privileged ground-truth poses for mapping. Our code has been released on https://github.com/APRIL-ZJU/Gaussian-LIC.
本文提出了一种基于高斯拼贴技术与LiDAR-惯性-相机SLAM相结合的真实时光照现实感SLAM方法。现有的大多数基于辐射场的SLAM系统主要关注配备RGB-D或RGB传感器的有界室内环境,但它们在处理无界场景或遇到不利条件(如剧烈运动和光照变化)时容易出现性能下降。相比之下,我们的方法面向通用场景,通过紧密融合LiDAR、IMU和相机进行稳健的姿态估计和真实感在线映射。为了弥补LiDAR未观测到的区域,我们提出了融合图像中的三角化视觉点和LiDAR点来初始化3D高斯的方法。此外,还实现了天空建模和相机曝光的可变建模以实现高质量渲染。值得注意的是,我们完全使用C++和CUDA实现了我们的系统,并精心设计了一系列策略以加速基于高斯场景表示在线优化。大量实验表明,我们的方法在性能上优于同类产品,同时保持了实时能力。令人印象深刻的是,在真实感映射方面,我们的方法甚至超过了使用特权地面真实姿态进行映射的所有比较方法。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/APRIL-ZJU/Gaussian-LIC上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICRA 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯混合与激光雷达惯性相机SLAM技术的实时逼真的SLAM方法。现有基于辐射场的SLAM系统主要关注有界室内环境,配备RGB-D或RGB传感器,但在扩展到无界场景或遇到剧烈运动和光照变化等不利条件时性能会下降。与之相比,本文的方法针对通用场景,融合了激光雷达、IMU和相机,进行稳健的姿态估计和在线逼真的映射。通过结合图像三角测量出的视觉点和激光雷达点来初始化三维高斯分布,弥补了激光雷达未观测区域的不足。同时实现了天空建模和相机曝光的可变建模,以实现高质量渲染。采用C++和CUDA实现,并设计了一系列策略加速基于高斯场景表示在线优化。实验表明,该方法在保持实时性能的同时,优于其他方法,即使在估计姿态的映射下,其逼真的映射效果也超过了使用特权地面真实姿态进行映射的所有对比方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于高斯混合与LiDAR-Inertial-Camera SLAM技术的实时SLAM方法。
- 现有基于辐射场的SLAM系统在有界室内环境中表现良好,但在无界场景或不利条件下性能下降。
- 本文方法针对通用场景,融合了激光雷达、IMU和相机,进行稳健的姿态估计和在线逼真的映射。
- 通过结合视觉点和激光雷达点初始化三维高斯分布,弥补了激光雷达未观测区域的不足。
- 实现了天空建模和相机曝光可变建模,实现高质量渲染。
- 采用C++和CUDA实现,并设计了策略加速在线优化。
点此查看论文截图