⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
Distributed Detection of Adversarial Attacks in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Continuous Action Space
Authors:Kiarash Kazari, Ezzeldin Shereen, György Dán
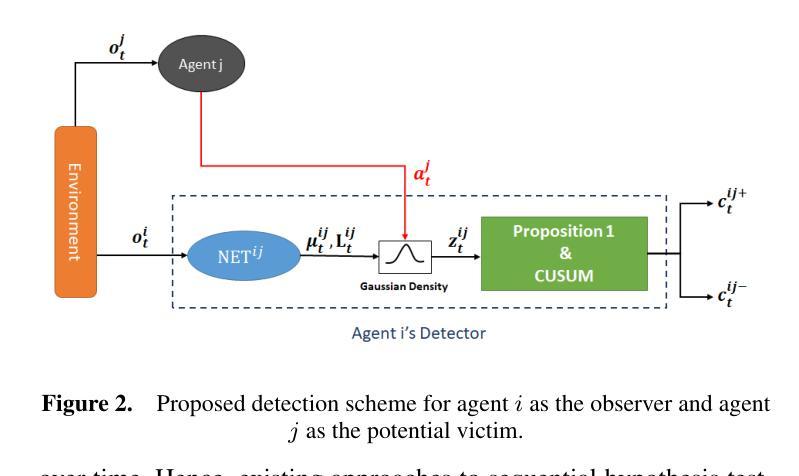
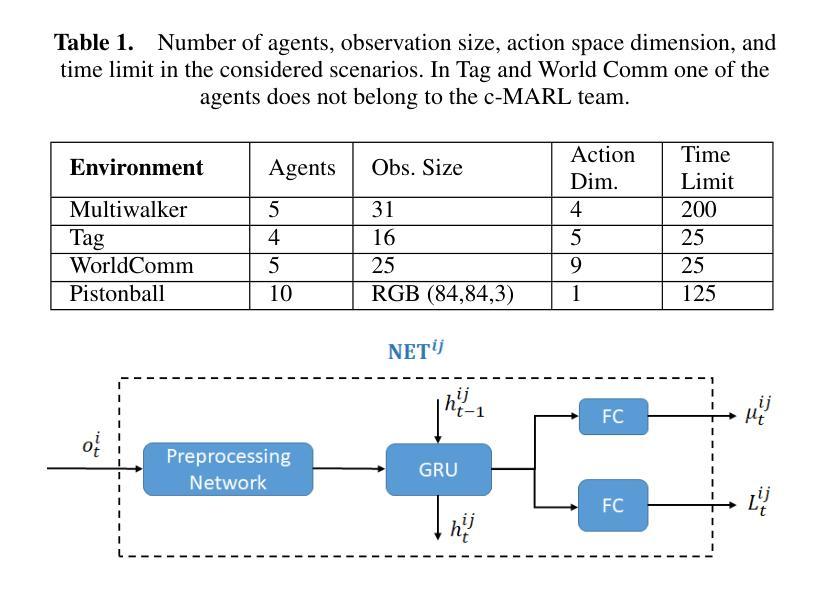
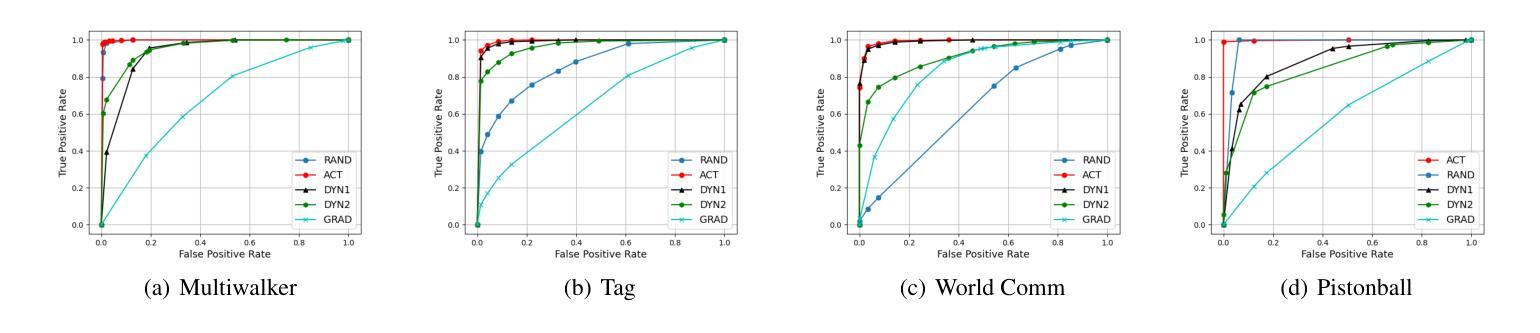
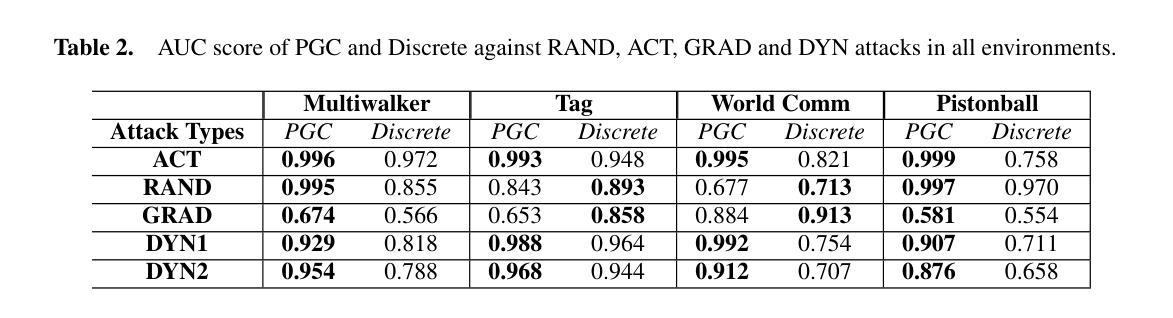
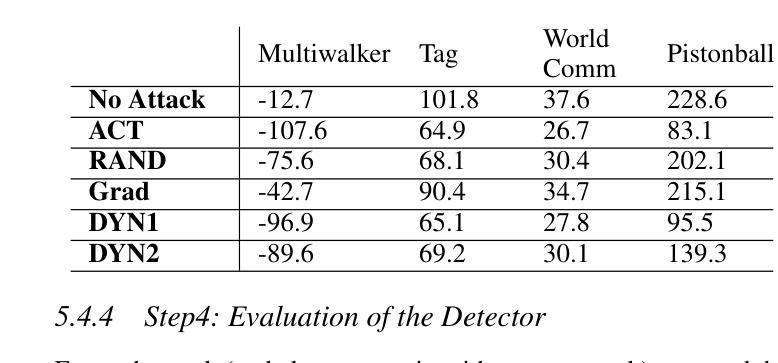
We address the problem of detecting adversarial attacks against cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning with continuous action space. We propose a decentralized detector that relies solely on the local observations of the agents and makes use of a statistical characterization of the normal behavior of observable agents. The proposed detector utilizes deep neural networks to approximate the normal behavior of agents as parametric multivariate Gaussian distributions. Based on the predicted density functions, we define a normality score and provide a characterization of its mean and variance. This characterization allows us to employ a two-sided CUSUM procedure for detecting deviations of the normality score from its mean, serving as a detector of anomalous behavior in real-time. We evaluate our scheme on various multi-agent PettingZoo benchmarks against different state-of-the-art attack methods, and our results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in detecting impactful adversarial attacks. Particularly, it outperforms the discrete counterpart by achieving AUC-ROC scores of over 0.95 against the most impactful attacks in all evaluated environments.
我们解决针对具有连续动作空间的合作多智能体强化学习的对抗攻击检测问题。我们提出了一种分散式检测器,它仅依赖于智能体的局部观察,并利用可观察智能体的正常行为的统计特征。所提出的检测器利用深度神经网络来逼近智能体的正常行为,将其表示为参数化多元高斯分布。基于预测的密度函数,我们定义了一个正常性得分,并给出了其均值和方差的特征描述。这种特征描述使我们能够采用双侧CUSUM程序来检测正常性得分与其均值之间的偏差,从而实时检测异常行为。我们在各种多智能体PettingZoo基准测试上对各种先进的攻击方法进行了评估,结果表明我们的方法在检测有影响力的对抗攻击方面非常有效。尤其值得一提的是,与传统的离散检测方法相比,它在所有评估环境中对最具影响力的攻击取得了超过0..的AUC-ROC得分(95分以上)。特别是在具有挑战性的环境中,它的性能优势更为明显。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at ECAI 2025
Summary
本文解决针对合作型多智能体强化学习的连续动作空间中的对抗攻击检测问题。文章提出了一种基于局部观测的分散式检测器,利用可观测智能体的正常行为的统计特征进行检测。检测器利用深度神经网络近似智能体的正常行为作为参数化的多元高斯分布。基于预测的密度函数,定义了正常行为评分并给出了其均值和方差的特征描述。这种特征描述允许采用双侧CUSUM程序检测正常评分均值上的偏差,实时检测异常行为。评估表明,该方案在多智能体PettingZoo基准测试中能有效检测各种最先进的攻击方法中的影响性对抗攻击,特别是在连续动作空间中,对最具影响力的攻击的AUC-ROC得分超过0.95。
Key Takeaways
- 该文本解决了检测多智能体强化学习连续动作空间中的对抗攻击的问题。
- 提出一种基于局部观测的分散式检测器来识别攻击。
- 检测器通过深度神经网络建模智能体的正常行为为参数化的多元高斯分布。
- 定义了正常行为评分并描述了其均值和方差的特征。
- 采用双侧CUSUM程序实时检测正常评分中的偏差以识别异常行为。
- 在多智能体PettingZoo基准测试中进行了评估,证明该方法对影响性对抗攻击有效。
点此查看论文截图

“Does the cafe entrance look accessible? Where is the door?” Towards Geospatial AI Agents for Visual Inquiries
Authors:Jon E. Froehlich, Jared Hwang, Zeyu Wang, John S. O’Meara, Xia Su, William Huang, Yang Zhang, Alex Fiannaca, Philip Nelson, Shaun Kane
Interactive digital maps have revolutionized how people travel and learn about the world; however, they rely on pre-existing structured data in GIS databases (e.g., road networks, POI indices), limiting their ability to address geo-visual questions related to what the world looks like. We introduce our vision for Geo-Visual Agents–multimodal AI agents capable of understanding and responding to nuanced visual-spatial inquiries about the world by analyzing large-scale repositories of geospatial images, including streetscapes (e.g., Google Street View), place-based photos (e.g., TripAdvisor, Yelp), and aerial imagery (e.g., satellite photos) combined with traditional GIS data sources. We define our vision, describe sensing and interaction approaches, provide three exemplars, and enumerate key challenges and opportunities for future work.
交互式数字地图已经彻底改变了人们旅行和了解世界的方式;然而,它们依赖于GIS数据库中的预先存在的结构化数据(例如,道路网络、POI索引),限制了它们解决与地理视觉相关的世界外观问题。我们介绍了对地理视觉代理的愿景——多模态人工智能代理,能够分析大规模地理空间图像存储库,包括街道景观(例如谷歌街景)、基于地点的照片(例如TripAdvisor、Yelp)和航空图像(例如卫星照片),并结合传统GIS数据源,理解和回答关于世界的微妙视觉空间查询。我们定义了我们的愿景,描述了感知和交互方法,提供了三个示例,并列举了未来工作的关键挑战和机遇。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the ICCV’25 Workshop “Vision Foundation Models and Generative AI for Accessibility: Challenges and Opportunities”
Summary
交互式数字地图已经改变了人们旅行和了解世界的方式,但它们依赖于GIS数据库中的预先结构化数据,限制了解决与地理视觉相关的世界外观问题。我们提出地理视觉代理的愿景——多模态AI代理能够分析大规模地理空间图像存储库,理解并回应关于世界的微妙视觉空间查询,包括街景(如谷歌街景)、基于地点的照片(如猫途鹰、雅虎本地)和空中图像(如卫星照片)与传统的GIS数据源相结合。本文定义了这个愿景,描述了感知和互动方法,给出了三个范例,并列举了未来工作的关键挑战和机遇。
Key Takeaways
- 交互式数字地图已改变旅行和了解世界的方式。
- 地理视觉代理具备理解回应关于世界的微妙视觉空间查询的能力。
- 地理视觉代理依赖于大规模地理空间图像存储库进行分析。
- 引入地理视觉代理能够整合多种数据源,包括街景、基于地点的照片和空中图像等。
- 地理视觉代理具有潜在的多模态交互能力。
- 实现地理视觉代理面临的关键挑战包括技术难题和数据集成问题。
点此查看论文截图

End-to-End Agentic RAG System Training for Traceable Diagnostic Reasoning
Authors:Qiaoyu Zheng, Yuze Sun, Chaoyi Wu, Weike Zhao, Pengcheng Qiu, Yongguo Yu, Kun Sun, Yanfeng Wang, Ya Zhang, Weidi Xie
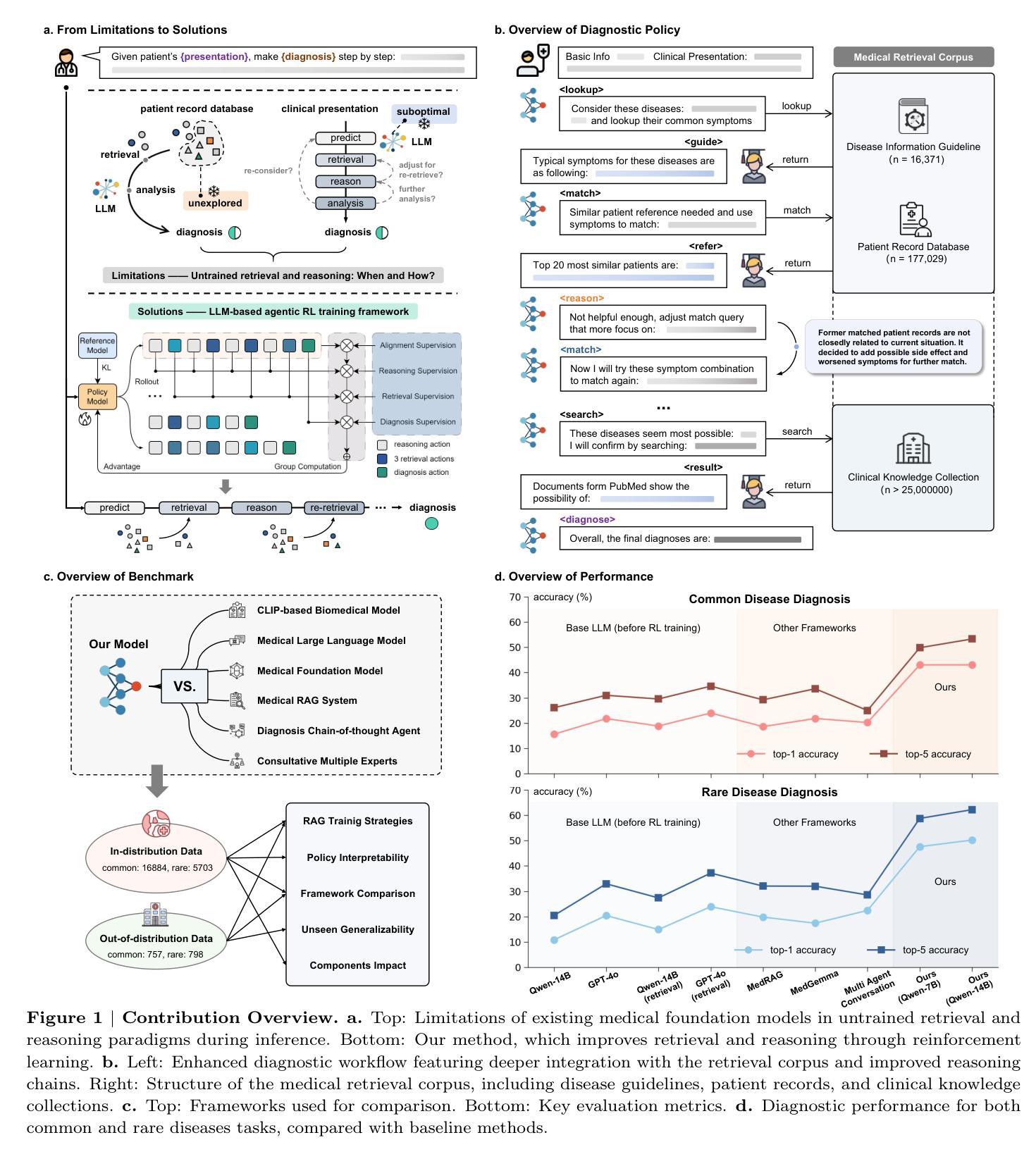
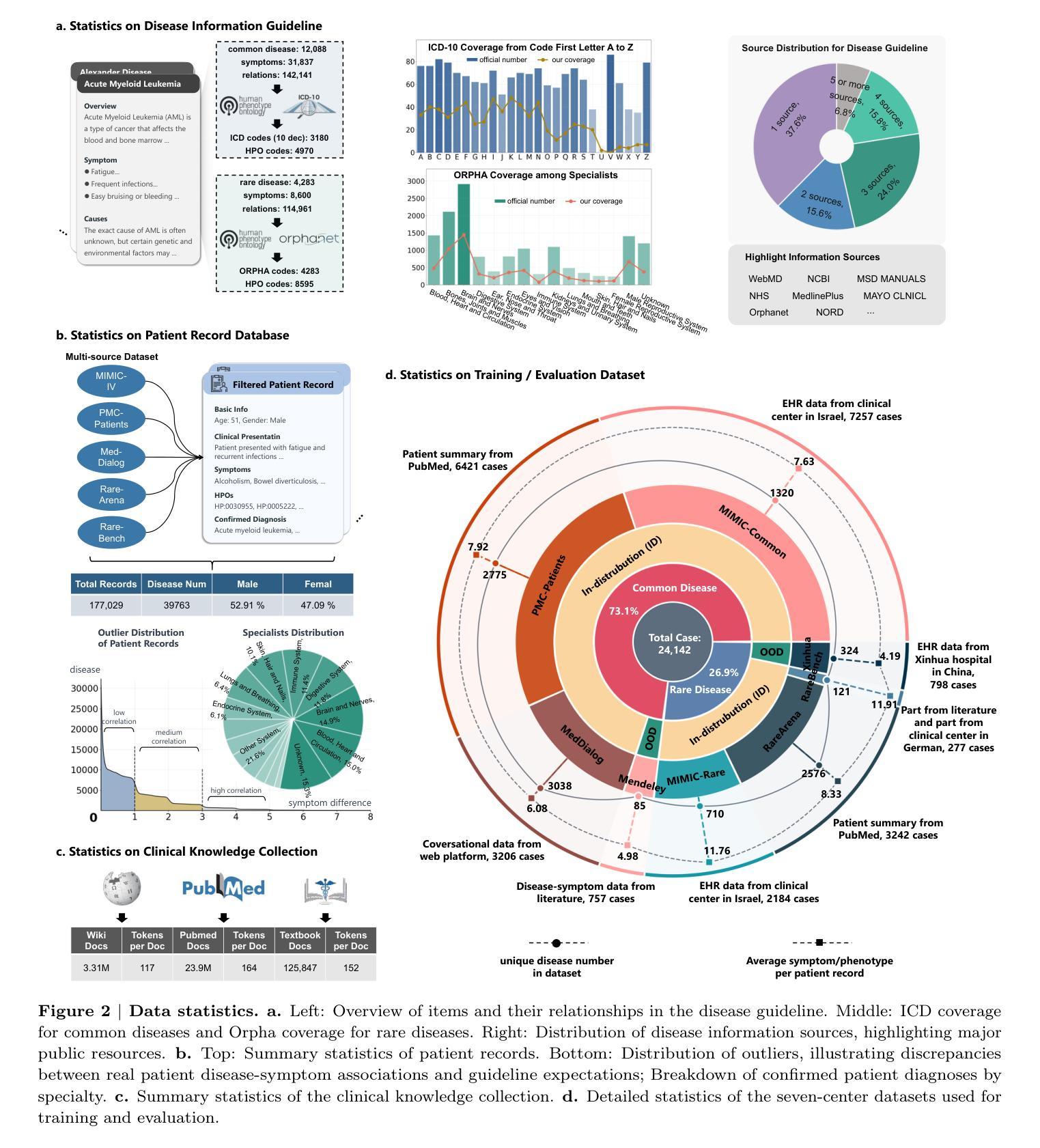
Accurate diagnosis with medical large language models is hindered by knowledge gaps and hallucinations. Retrieval and tool-augmented methods help, but their impact is limited by weak use of external knowledge and poor feedback-reasoning traceability. To address these challenges, We introduce Deep-DxSearch, an agentic RAG system trained end-to-end with reinforcement learning (RL) that enables steer tracebale retrieval-augmented reasoning for medical diagnosis. In Deep-DxSearch, we first construct a large-scale medical retrieval corpus comprising patient records and reliable medical knowledge sources to support retrieval-aware reasoning across diagnostic scenarios. More crutially, we frame the LLM as the core agent and the retrieval corpus as its environment, using tailored rewards on format, retrieval, reasoning structure, and diagnostic accuracy, thereby evolving the agentic RAG policy from large-scale data through RL. Experiments demonstrate that our end-to-end agentic RL training framework consistently outperforms prompt-engineering and training-free RAG approaches across multiple data centers. After training, Deep-DxSearch achieves substantial gains in diagnostic accuracy, surpassing strong diagnostic baselines such as GPT-4o, DeepSeek-R1, and other medical-specific frameworks for both common and rare disease diagnosis under in-distribution and out-of-distribution settings. Moreover, ablation studies on reward design and retrieval corpus components confirm their critical roles, underscoring the uniqueness and effectiveness of our approach compared with traditional implementations. Finally, case studies and interpretability analyses highlight improvements in Deep-DxSearch’s diagnostic policy, providing deeper insight into its performance gains and supporting clinicians in delivering more reliable and precise preliminary diagnoses. See https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/Deep-DxSearch.
精确诊断与医疗大型语言模型之间存在知识差距和幻觉的障碍。检索和工具增强方法有所帮助,但它们的影响受限于外部知识利用不足和反馈推理追踪能力弱。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了Deep-DxSearch,这是一个通过强化学习(RL)进行端到端训练的主动推理图(RAG)系统,能够实现用于医学诊断的引导追踪增强推理。在Deep-DxSearch中,我们首先构建了一个大规模医学检索语料库,包含患者记录和可靠医学知识来源,以支持跨诊断场景的检索感知推理。更重要的是,我们将大型语言模型作为核心主体,将检索语料库作为其环境,使用针对格式、检索、推理结构和诊断准确度的定制奖励,从而通过强化学习从大规模数据中演化主动推理图策略。实验表明,我们的端到端主动强化学习训练框架在多个数据中心始终优于基于提示和训练免费的RAG方法。经过训练,Deep-DxSearch在诊断准确性方面取得了实质性进展,超越了强大的诊断基线,如GPT-4o、DeepSeek-R1和其他针对常见和罕见疾病诊断的医学特定框架,无论是在内部数据分布还是外部数据分布环境中均表现优异。此外,关于奖励设计和检索语料库组件的消融研究证实了它们的关键作用,强调了我们的方法与传统实施相比的独特性和有效性。最后,案例研究和可解释性分析突出了Deep-DxSearch诊断策略的改进,提供了对其性能提升的更深入见解,并支持临床医生提供更可靠和精确的早期诊断。详见https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/Deep-DxSearch。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables
Summary
大型语言模型在医学诊断中的准确应用受到知识差距和幻觉的制约。虽然检索和工具增强方法有助于改进,但它们受到外部知识利用不足和反馈推理可追溯性差的限制。为应对这些挑战,我们推出Deep-DxSearch,一个以强化学习训练的主体间检索增强推理(RAG)系统,用于医学诊断。Deep-DxSearch构建大规模医学检索语料库,涵盖患者记录和可靠医学知识源,支持跨诊断场景的检索感知推理。将大型语言模型作为核心主体,检索语料库作为其环境,通过针对格式、检索、推理结构和诊断准确性的奖励机制,利用强化学习进行主体间RAG策略的训练与优化。实验表明,我们的终端主体强化学习训练框架在多中心数据中表现出优异的性能,诊断准确率大幅提升,超越了GPT-4o、DeepSeek-R1等强大诊断基线以及传统医学特定框架,适用于常见和罕见疾病的诊断,无论是在内部还是外部分布环境下均表现优异。此外,奖励设计和检索语料库组件的消除研究证实了其关键作用,凸显我们方法的独特性和有效性。最终,案例研究和解释性分析揭示了Deep-DxSearch诊断策略的改进,为性能提升提供了深入见解,支持临床医生提供更可靠和精确的早期诊断。更多信息请参见https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/Deep-DxSearch。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在医学诊断中面临知识差距和幻觉的挑战。
- Deep-DxSearch是一个基于强化学习的主体间检索增强推理系统,用于医学诊断。
- Deep-DxSearch构建了一个大规模的医学检索语料库来支持跨诊断场景的检索感知推理。
- Deep-DxSearch通过针对多个方面的奖励机制,利用强化学习训练核心主体和策略。
- 实验表明Deep-DxSearch在诊断准确率上表现出显著优势,适用于多种环境和疾病类型。
- 奖励设计和检索语料库组件的重要性通过消除研究得到证实。
点此查看论文截图

Understanding Action Effects through Instrumental Empowerment in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Ardian Selmonaj, Miroslav Strupl, Oleg Szehr, Alessandro Antonucci
To reliably deploy Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) systems, it is crucial to understand individual agent behaviors within a team. While prior work typically evaluates overall team performance based on explicit reward signals or learned value functions, it is unclear how to infer agent contributions in the absence of any value feedback. In this work, we investigate whether meaningful insights into agent behaviors can be extracted that are consistent with the underlying value functions, solely by analyzing the policy distribution. Inspired by the phenomenon that intelligent agents tend to pursue convergent instrumental values, which generally increase the likelihood of task success, we introduce Intended Cooperation Values (ICVs), a method based on information-theoretic Shapley values for quantifying each agent’s causal influence on their co-players’ instrumental empowerment. Specifically, ICVs measure an agent’s action effect on its teammates’ policies by assessing their decision uncertainty and preference alignment. The analysis across cooperative and competitive MARL environments reveals the extent to which agents adopt similar or diverse strategies. By comparing action effects between policies and value functions, our method identifies which agent behaviors are beneficial to team success, either by fostering deterministic decisions or by preserving flexibility for future action choices. Our proposed method offers novel insights into cooperation dynamics and enhances explainability in MARL systems.
在部署多智能体强化学习(Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning,简称MARL)系统时,理解团队中单个智能体的行为至关重要。以往的研究通常基于明确的奖励信号或学习到的价值函数来评估团队的整体性能,但在没有任何价值反馈的情况下,如何推断智能体的贡献尚不清楚。在本研究中,我们调查是否仅通过分析政策分布就能提取出与底层价值函数一致的智能体行为的深刻见解。受智能体倾向于追求趋同的工具性价值这一现象的启发,这种价值通常会增加任务成功的可能性,我们提出了基于信息论的Shapley价值的预期合作价值(Intended Cooperation Values,简称ICVs)方法,用于量化每个智能体对其队友工具性赋能的因果影响。具体来说,ICVs通过评估其队友的决策不确定性和偏好一致性来衡量智能体的行为对队友政策的影响。在合作和竞争性的MARL环境中的分析揭示了智能体采用相似或不同策略的程度。通过比较政策和价值函数之间的行为效果,我们的方法确定了哪些智能体行为对团队成功有益,是通过促进确定性决策还是保留未来行动选择的灵活性来实现的。我们提出的方法为合作动力学提供了新的见解,并增强了MARL系统的可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI) 2025
Summary
多智能体强化学习(MARL)系统部署中,理解团队内个体智能行为至关重要。在缺乏价值反馈的情况下,通过分析政策分布来推断智能体行为具有重要意义。本研究受到智能体追求收敛性工具价值的启发,引入意图合作价值(ICVs)方法,基于信息论的沙普利值量化每个智能体对同伴工具赋能的因果影响。ICVs通过评估同伴决策不确定性和偏好一致性来衡量智能体行动对同伴政策的影响。分析合作和竞争性MARL环境揭示了智能体采取相似或不同策略的程度。通过比较政策和价值函数之间的行动效应,我们的方法确定了哪些智能体行为对团队成功有益,要么通过培养确定性决策,要么通过保留未来行动选择的灵活性。该研究为合作动力学提供了新的见解,提高了MARL系统的可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 在多智能体强化学习(MARL)系统部署中,理解个体智能行为对团队至关重要。
- 缺乏价值反馈的情况下,可通过分析政策分布推断智能体行为。
- 智能体追求收敛性工具价值,本研究基于此引入意图合作价值(ICVs)方法。
- ICVs基于信息论的沙普利值量化每个智能体对同伴工具赋能的因果影响。
- ICVs通过分析智能体行动对同伴政策的影响来评估决策不确定性和偏好一致性。
- 分析显示合作和竞争性MARL环境中智能体采取不同策略的程度。
点此查看论文截图

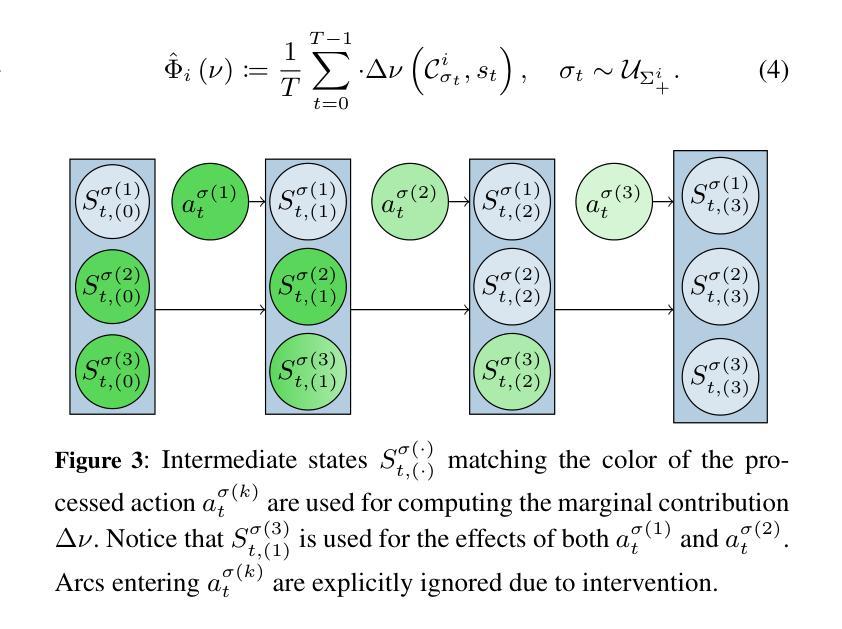
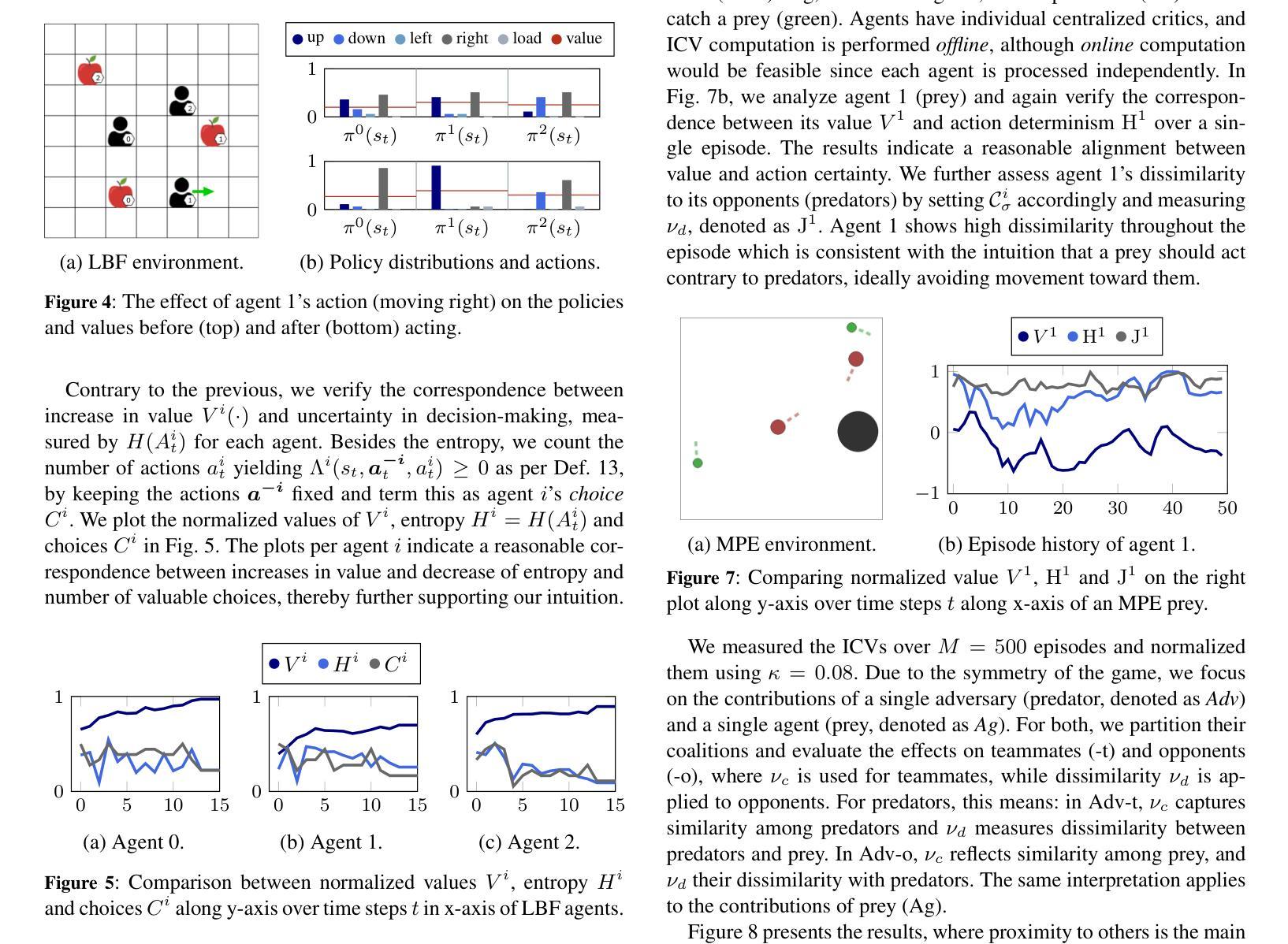

Super-additive Cooperation in Language Model Agents
Authors:Filippo Tonini, Lukas Galke
With the prospect of autonomous artificial intelligence (AI) agents, studying their tendency for cooperative behavior becomes an increasingly relevant topic. This study is inspired by the super-additive cooperation theory, where the combined effects of repeated interactions and inter-group rivalry have been argued to be the cause for cooperative tendencies found in humans. We devised a virtual tournament where language model agents, grouped into teams, face each other in a Prisoner’s Dilemma game. By simulating both internal team dynamics and external competition, we discovered that this blend substantially boosts both overall and initial, one-shot cooperation levels (the tendency to cooperate in one-off interactions). This research provides a novel framework for large language models to strategize and act in complex social scenarios and offers evidence for how intergroup competition can, counter-intuitively, result in more cooperative behavior. These insights are crucial for designing future multi-agent AI systems that can effectively work together and better align with human values. Source code is available at https://github.com/pippot/Superadditive-cooperation-LLMs.
随着人工智能(AI)自主代理的前景展现,研究其合作行为的倾向成为一个越来越重要的话题。本研究受到超加性合作理论的启发,该理论认为重复互动的联合效应和团队之间的竞争是导致人类合作倾向的原因。我们设计了一个虚拟锦标赛,语言模型代理被分成团队,在囚徒困境游戏中相互对抗。通过模拟团队内部动态和外部竞争,我们发现这种结合显著提高了整体和初次、单次合作的水平(在一次性互动中合作的倾向)。该研究为大型语言模型在复杂社会场景中的策略制定和行为提供了一个新的框架,并提供了证据,证明团队间的竞争如何出人意料地导致更多的合作行为。这些见解对于设计未来能够协同工作的多智能体AI系统,使其更好地符合人类价值观至关重要。源代码可在https://github.com/pippot/Superadditive-cooperation-LLMs中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF FAIEMA 2025
总结
本研究基于超加性合作理论,探讨语言模型代理在模拟环境中合作的趋势。设计虚拟竞赛环境模拟团队内部和外部竞争对语言模型代理在囚徒困境游戏中的表现。研究结果表明,竞争和合作的结合能显著提高单次和总体合作水平。这为大型语言模型在复杂社会场景中的策略制定和行为提供了新框架,并为未来多智能体AI系统的设计和人类价值观的融合提供了重要启示。代码公开在GitHub上。
关键见解
- 基于超加性合作理论,探讨了语言模型代理的合作行为。
- 设计虚拟竞赛环境模拟语言模型代理的团队动态和外部竞争。
- 发现内部和外部因素的结合提高了单次和总体合作水平。
- 为大型语言模型在复杂社会场景中的策略制定提供了新框架。
- 研究结果证明团队间的竞争可以提高合作行为,这是与直觉相反的现象。
- 此研究对设计未来的多智能体AI系统具有重要意义。这些系统可以更好地与人类协同工作并更好地体现人类价值观。
点此查看论文截图

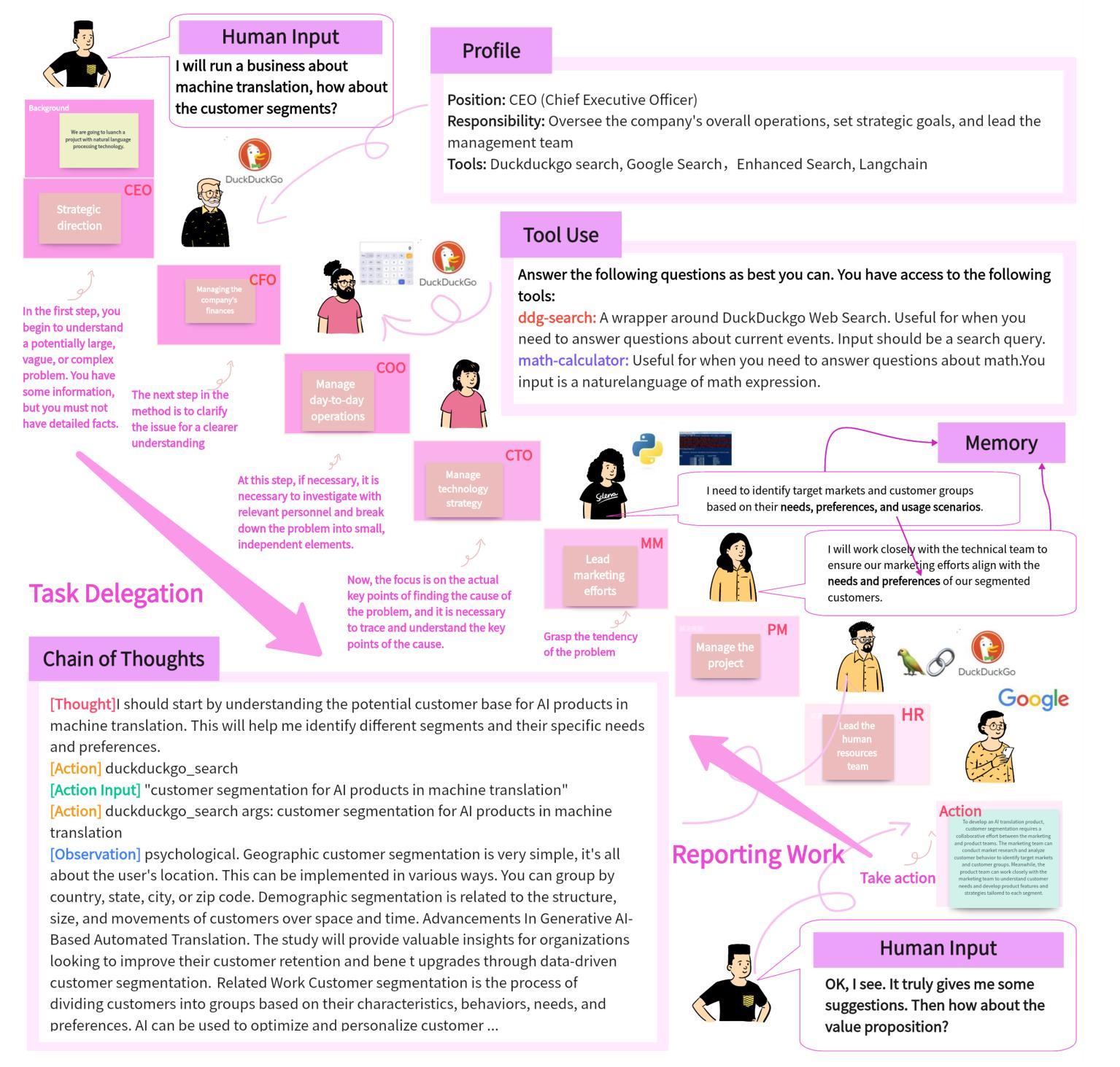
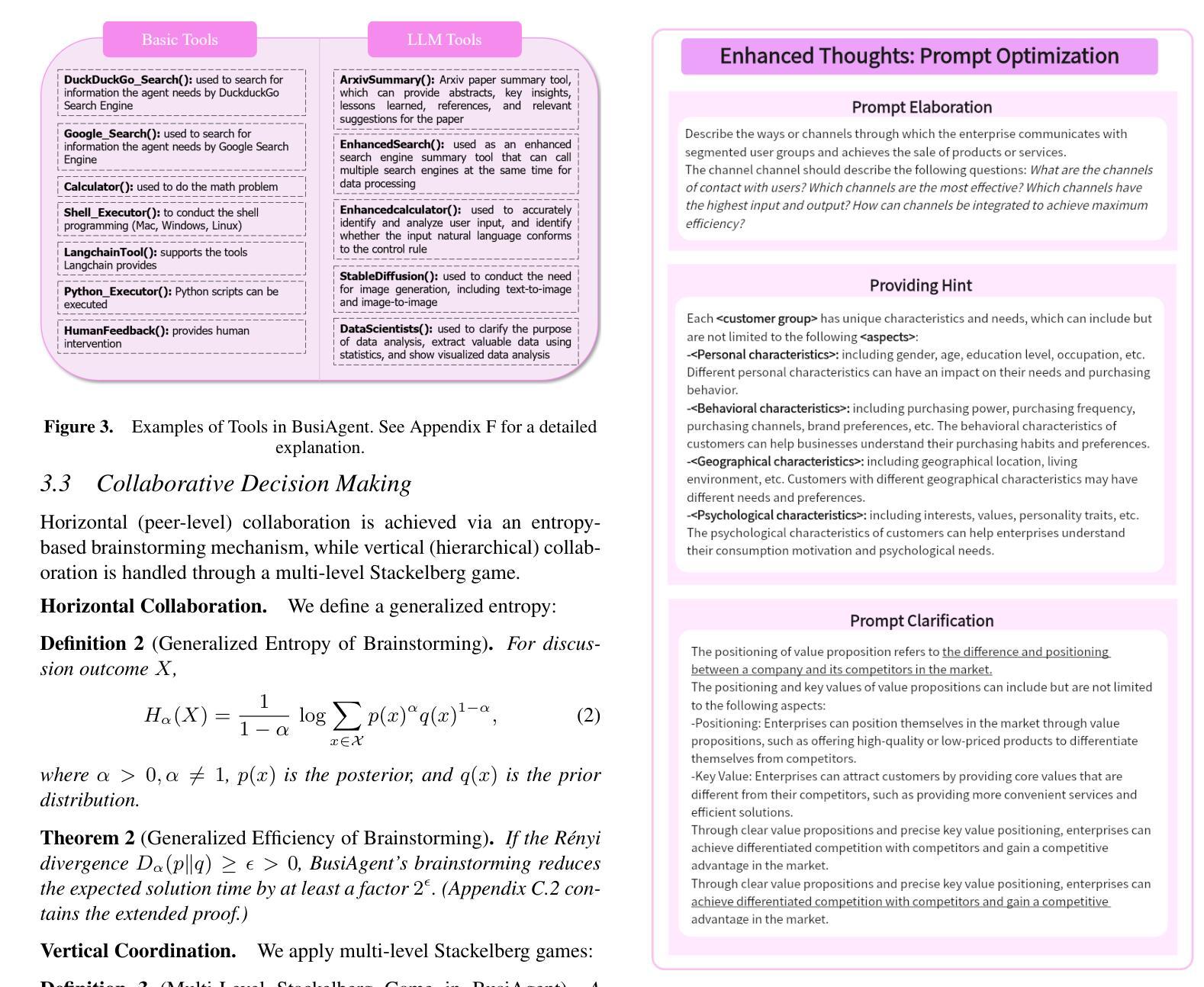
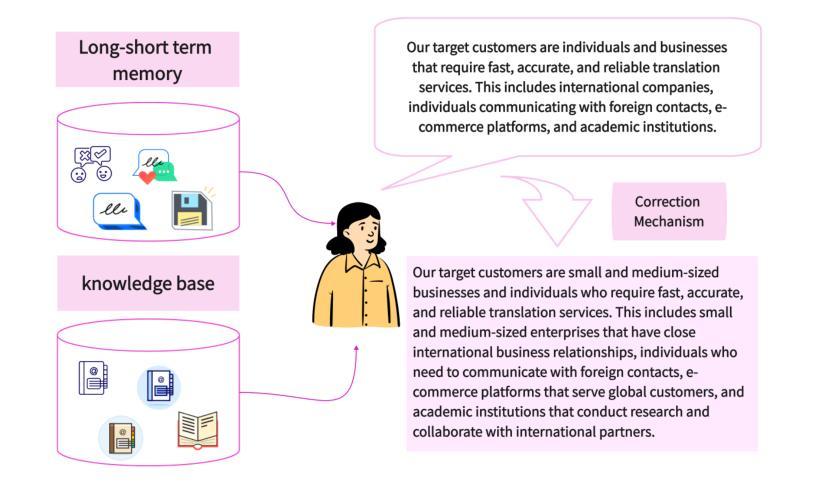
From Bits to Boardrooms: A Cutting-Edge Multi-Agent LLM Framework for Business Excellence
Authors:Zihao Wang, Junming Zhang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promising potential in business applications, particularly in enterprise decision support and strategic planning, yet current approaches often struggle to reconcile intricate operational analyses with overarching strategic goals across diverse market environments, leading to fragmented workflows and reduced collaboration across organizational levels. This paper introduces BusiAgent, a novel multi-agent framework leveraging LLMs for advanced decision-making in complex corporate environments. BusiAgent integrates three core innovations: an extended Continuous Time Markov Decision Process (CTMDP) for dynamic agent modeling, a generalized entropy measure to optimize collaborative efficiency, and a multi-level Stackelberg game to handle hierarchical decision processes. Additionally, contextual Thompson sampling is employed for prompt optimization, supported by a comprehensive quality assurance system to mitigate errors. Extensive empirical evaluations across diverse business scenarios validate BusiAgent’s efficacy, demonstrating its capacity to generate coherent, client-focused solutions that smoothly integrate granular insights with high-level strategy, significantly outperforming established approaches in both solution quality and user satisfaction. By fusing cutting-edge AI technologies with deep business insights, BusiAgent marks a substantial step forward in AI-driven enterprise decision-making, empowering organizations to navigate complex business landscapes more effectively.
大型语言模型(LLM)在商业应用方面显示出巨大的潜力,特别是在企业决策支持和战略规划方面。然而,当前的方法常常难以在多样的市场环境中,将复杂的操作分析与高级战略目标相协调,导致工作流程碎片化,且各级组织间的协作减少。本文介绍了BusiAgent,这是一种新型的多智能体框架,利用LLM在复杂的商业环境中进行高级决策。BusiAgent集成了三项核心创新:采用扩展的连续时间马尔可夫决策过程(CTMDP)进行动态智能体建模,使用广义熵度量优化协作效率,以及采用多层次斯塔克尔伯格博弈处理分层决策过程。此外,还采用上下文汤普森采样进行提示优化,并由全面的质量保证系统提供支持以减轻错误。在多种商业场景下的广泛实证评估验证了BusiAgent的有效性,证明其能够生成连贯、以客户为中心解决方案的能力,能够顺畅地将颗粒状见解与高级策略相结合,在解决方案质量和用户满意度方面都大大优于现有方法。通过将前沿人工智能技术与深刻的商业洞察相结合,BusiAgent在AI驱动的企业决策方面取得了重大进步,使组织能够更有效地应对复杂的商业环境。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ECAI 2025
Summary
大型语言模型在企业决策支持和战略规划方面的应用展现出巨大潜力,但在复杂的商业环境中,现有方法难以将详细的操作分析与高级战略目标相结合,导致工作流程碎片化并降低了组织内的协作效率。本文提出BusiAgent,这是一个利用大型语言模型进行复杂企业环境决策制定的新型多智能体框架。BusiAgent集成了三项核心创新:采用扩展的连续时间马尔可夫决策过程进行动态智能体建模、使用广义熵度量优化协作效率以及利用多层次斯塔克尔伯格博弈处理分层决策过程。此外,还采用情境化汤普森采样法进行提示优化,并由全面的质量保证系统提供支持以减轻错误。在多种商业场景下的广泛实证评估验证了BusiAgent的有效性,表明其在解决方案质量和用户满意度方面均显著优于现有方法,能够生成连贯、以客户为中心且能将详细见解与高级战略顺利结合的解决方案。通过融合尖端人工智能技术与深入的企业洞察,BusiAgent标志着人工智能驱动的企业决策制定取得了重大进步,帮助组织更有效地应对复杂的商业环境挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在业务应用中有巨大潜力,尤其在决策支持和战略规划方面。
- 当前方法难以在复杂环境中整合操作分析与高级战略目标。
- BusiAgent是一个新型的多智能体框架,利用大型语言模型进行企业决策制定。
- BusiAgent集成了三项核心创新技术:连续时间马尔可夫决策过程、广义熵优化和多层次斯塔克尔伯格博弈。
- BusiAgent采用情境化汤普森采样法进行提示优化,具有全面的质量保证系统。
- 在多种商业场景下的评估中,BusiAgent表现出优异的性能,显著提高了解决方案质量和用户满意度。
点此查看论文截图


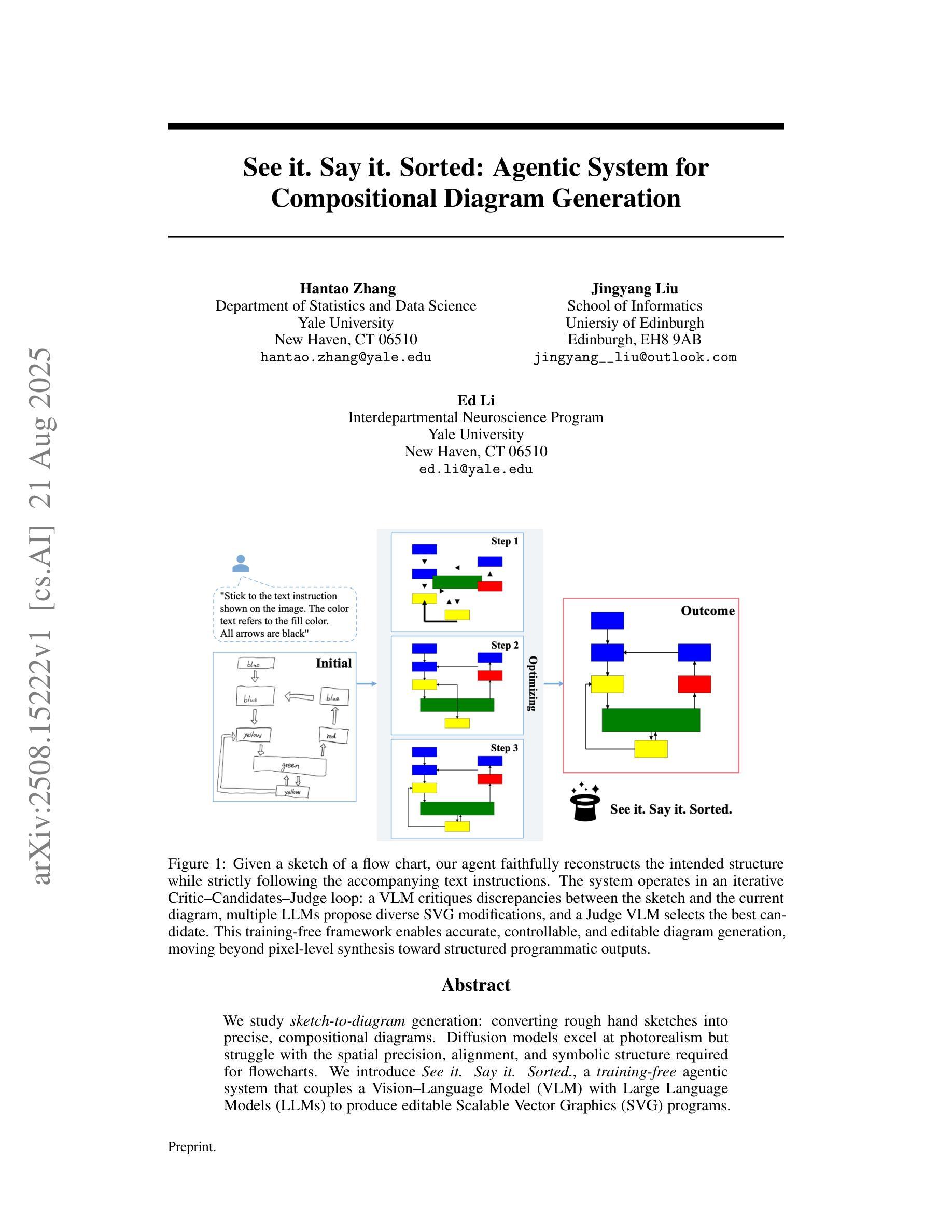
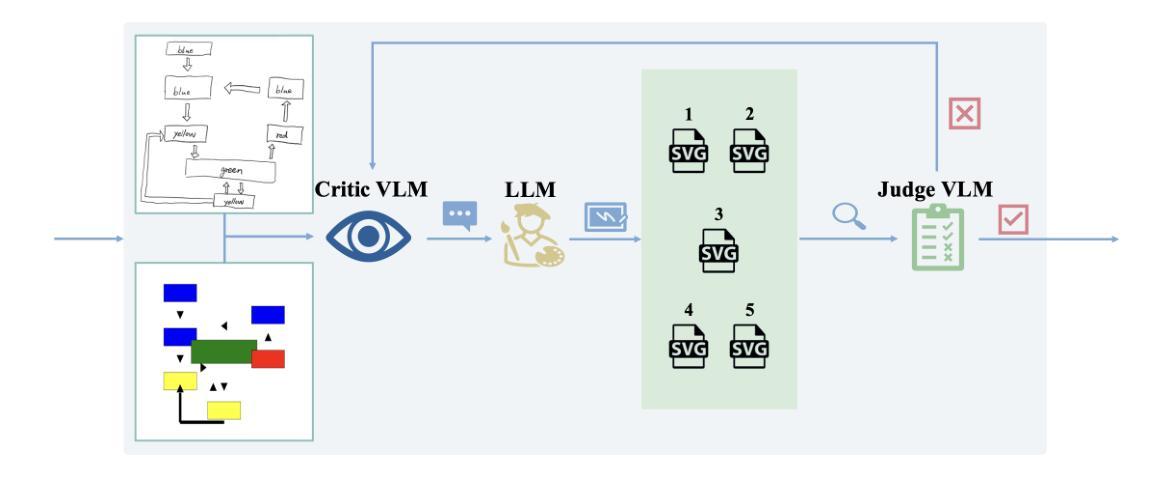
See it. Say it. Sorted: Agentic System for Compositional Diagram Generation
Authors:Hantao Zhang, Jingyang Liu, Ed Li
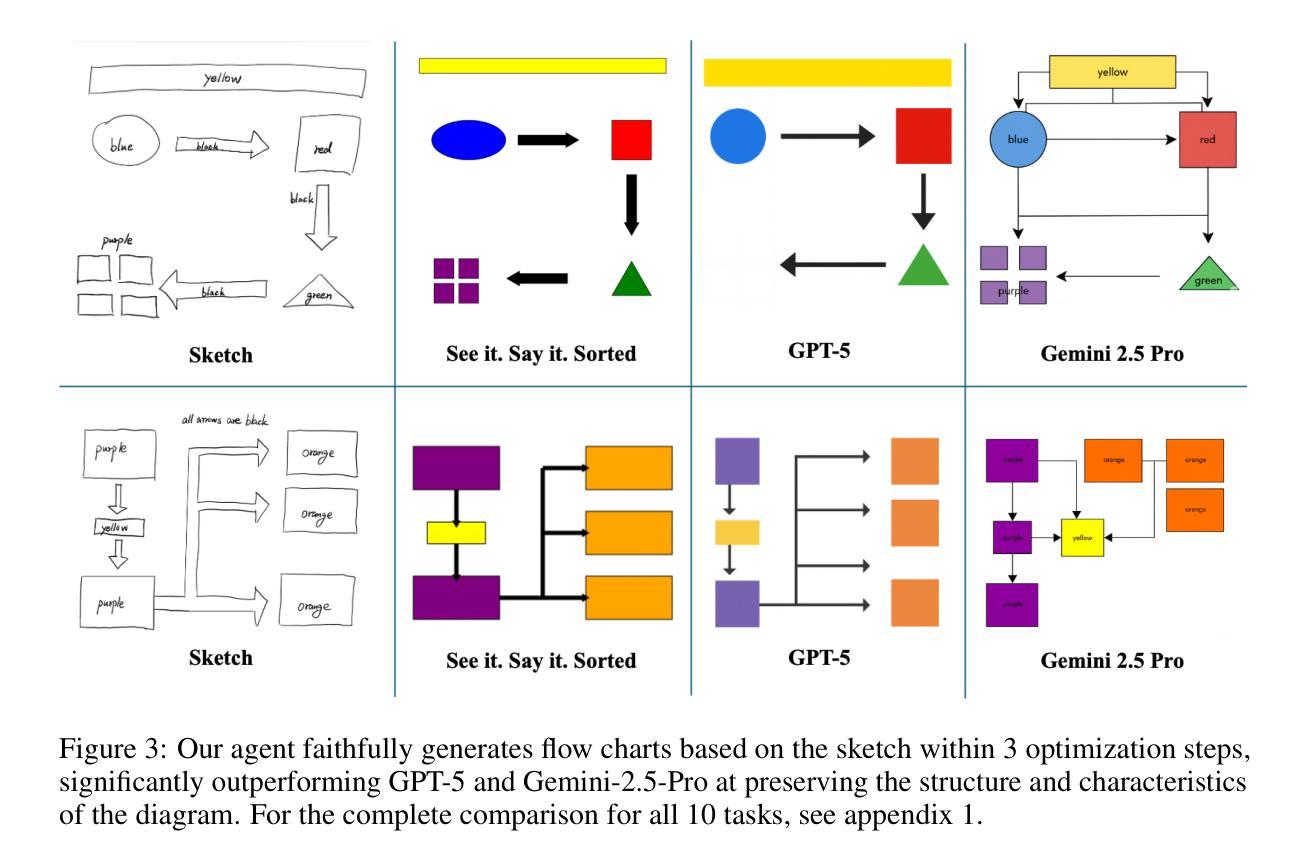
We study sketch-to-diagram generation: converting rough hand sketches into precise, compositional diagrams. Diffusion models excel at photorealism but struggle with the spatial precision, alignment, and symbolic structure required for flowcharts. We introduce See it. Say it. Sorted., a training-free agentic system that couples a Vision-Language Model (VLM) with Large Language Models (LLMs) to produce editable Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) programs. The system runs an iterative loop in which a Critic VLM proposes a small set of qualitative, relational edits; multiple candidate LLMs synthesize SVG updates with diverse strategies (conservative->aggressive, alternative, focused); and a Judge VLM selects the best candidate, ensuring stable improvement. This design prioritizes qualitative reasoning over brittle numerical estimates, preserves global constraints (e.g., alignment, connectivity), and naturally supports human-in-the-loop corrections. On 10 sketches derived from flowcharts in published papers, our method more faithfully reconstructs layout and structure than two frontier closed-source image generation LLMs (GPT-5 and Gemini-2.5-Pro), accurately composing primitives (e.g., multi-headed arrows) without inserting unwanted text. Because outputs are programmatic SVGs, the approach is readily extensible to presentation tools (e.g., PowerPoint) via APIs and can be specialized with improved prompts and task-specific tools. The codebase is open-sourced at https://github.com/hantaoZhangrichard/see_it_say_it_sorted.git.
我们研究了从草图到图表生成的研究:将粗略的手绘草图转化为精确、组合式的图表。扩散模型在照片写实方面表现出色,但在流程图所需的空间精度、对齐和符号结构方面存在困难。我们推出了“See it. Say it. Sorted.”系统,这是一个无需训练的主体系统,将视觉语言模型(VLM)与大型语言模型(LLM)相结合,生成可编辑的矢量图形(SVG)程序。该系统运行一个迭代循环,其中批评家VLM提出一小部分定性关系编辑;多个候选LLM使用不同策略(保守到激进、替代、专注)合成SVG更新;法官VLM选择最佳候选者,确保稳定的改进。这种设计优先考虑定性推理而非脆弱的数值估计,保留全局约束(例如对齐、连接),并自然地支持人为循环校正。在对来自已发表论文的10个流程图草图的处理上,我们的方法比前沿的封闭式图像生成LLM(GPT-5和Gemini-2.5 Pro)更忠实地重建布局和结构,能够准确地组合基本元素(例如多头箭头),而不会插入不需要的文本。由于输出是程序化的SVG,因此该方法可以轻松通过API扩展到演示工具(例如PowerPoint),并且可以通过改进提示和任务特定工具进行专门化。该代码库已公开在https://github.com/hantaoZhangrichard/see_it_say_it_sorted.git。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于草图到图表生成的研究,通过无训练的系统See it. Say it. Sorted.,将粗略的手绘草图转化为精确的组成图表。系统采用迭代循环的方式,通过三个组件——Critic VLM提出修改建议,多个候选LLM合成SVG更新内容,Judge VLM选择最佳候选——确保持续改进。该系统注重定性推理,兼顾全局约束和人为校正功能。相较于其他前沿的闭源图像生成LLMs,该系统能更准确地重构流程和结构,准确组合基本元素。输出的程序化SVG格式使其易于扩展到演示工具如PowerPoint等。相关代码已开源。
Key Takeaways
- 研究草图到图表生成技术,将粗略手绘草图转化为精确图表。
- 提出无训练的系统See it. Say it. Sorted.,包含三个组件:Critic VLM、多个候选LLM和Judge VLM。
- 系统注重定性推理,兼顾全局约束和人为校正功能。
- 与其他前沿LLMs相比,该系统能更准确地重构图表布局和结构。
- 输出程序化的SVG格式使得应用场景具有广泛性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图
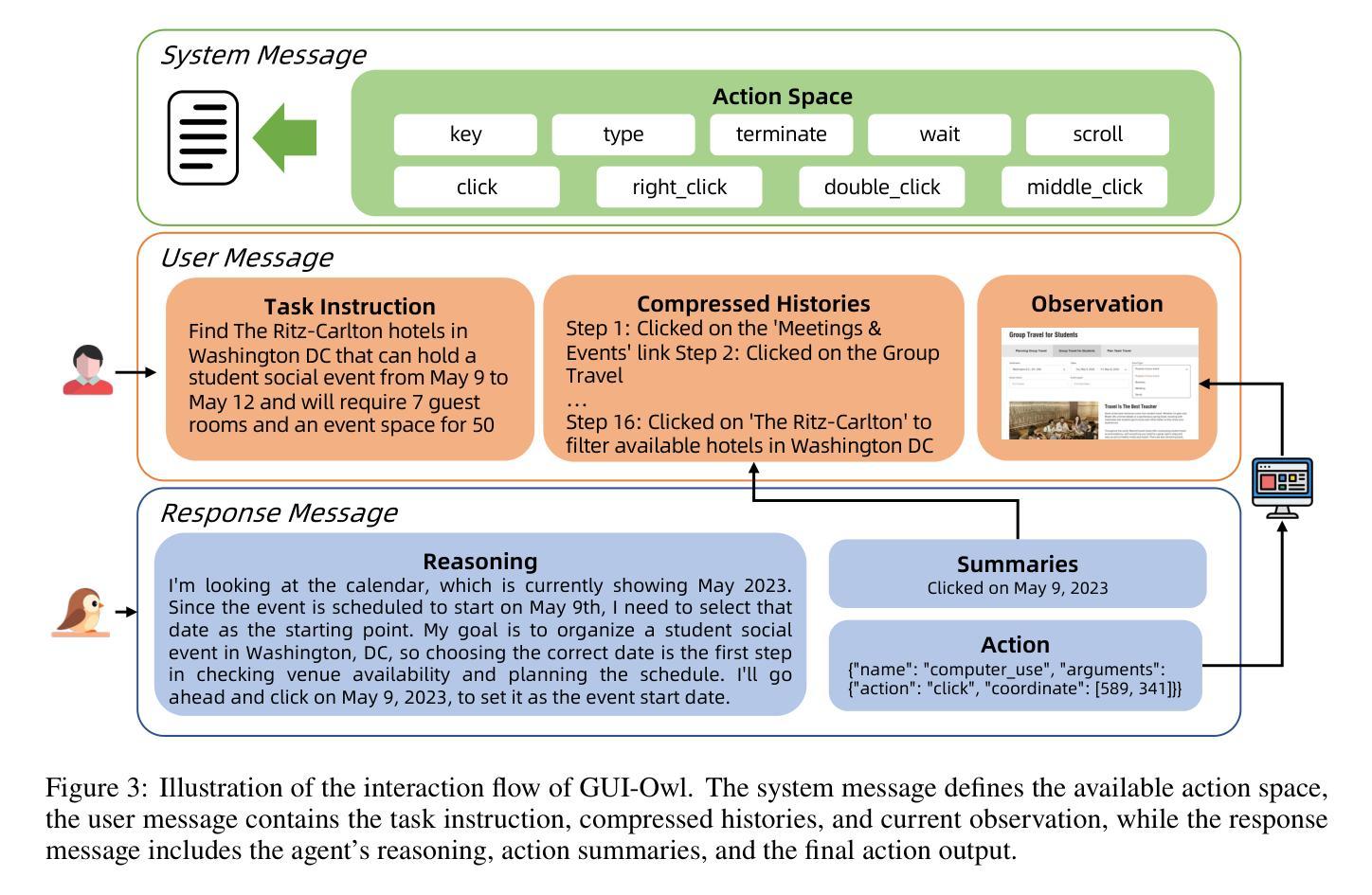
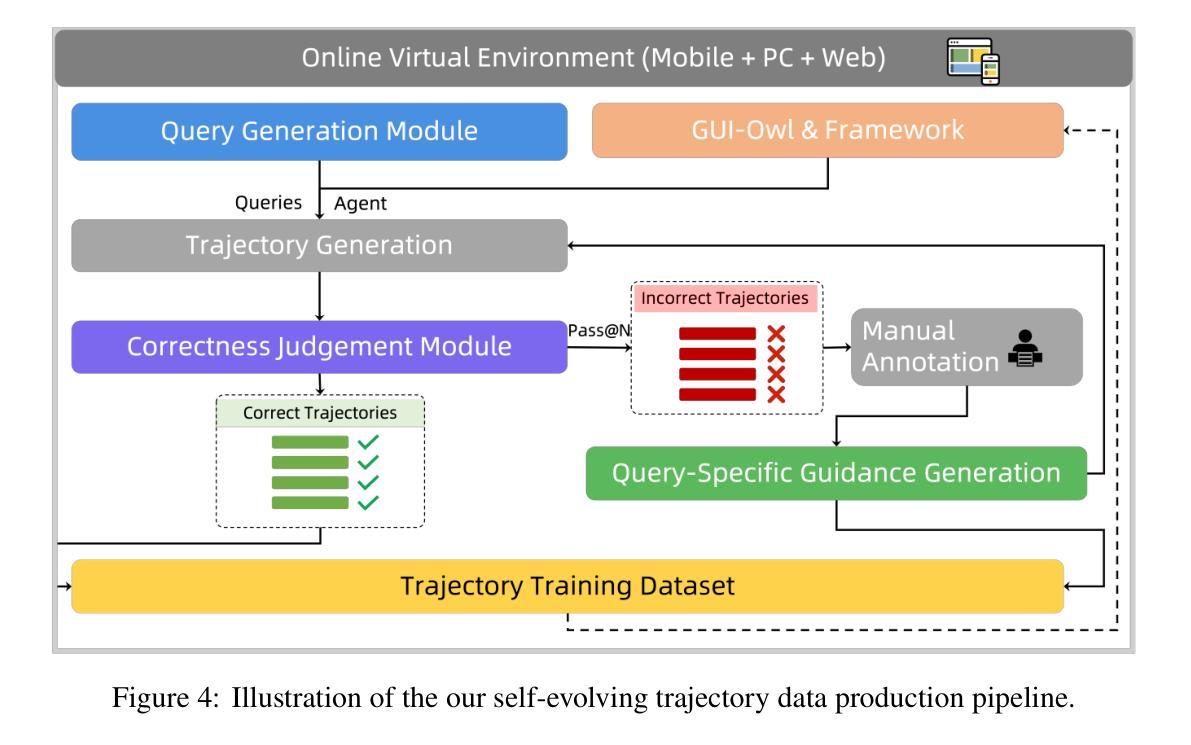
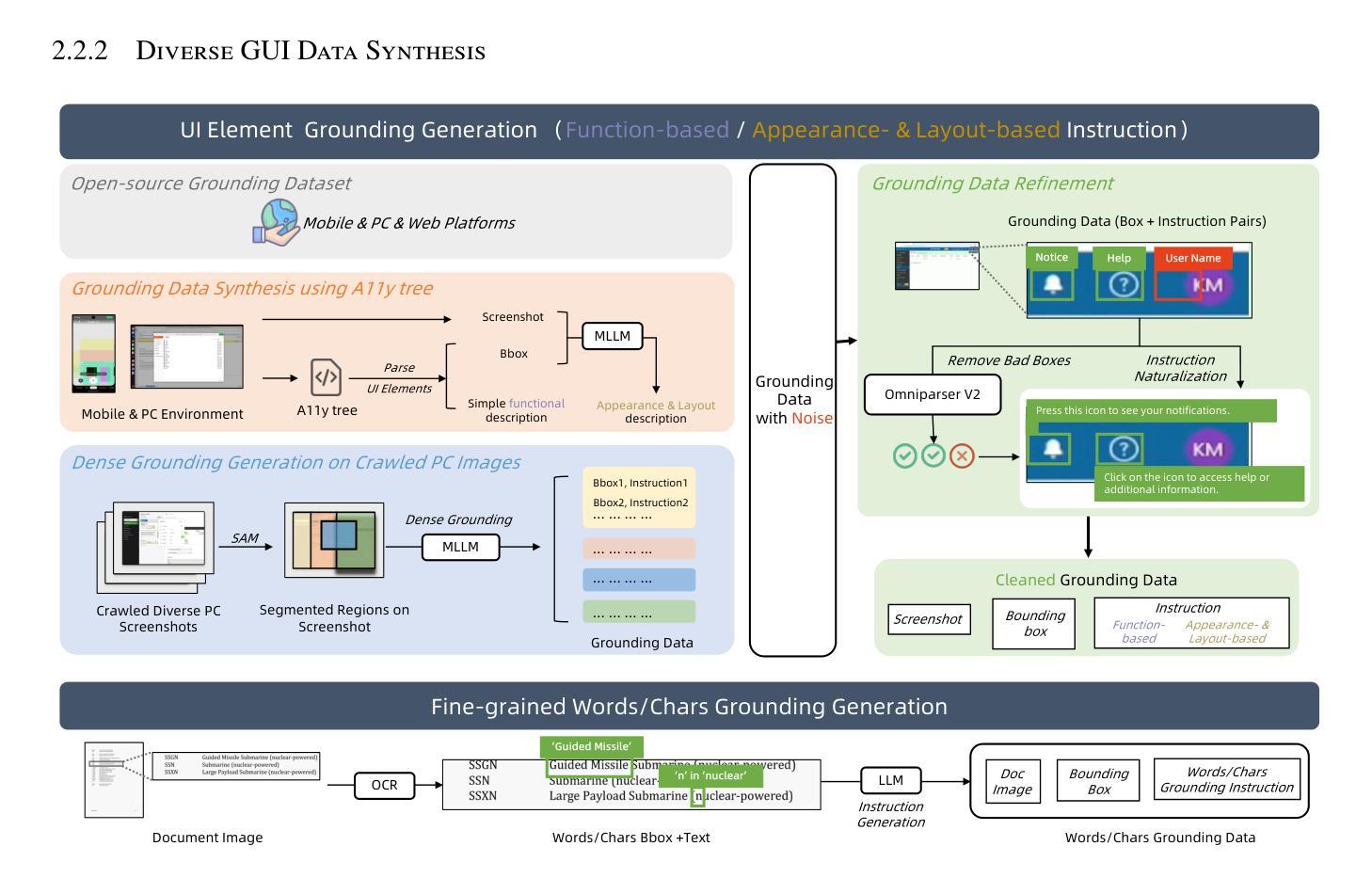
Mobile-Agent-v3: Foundamental Agents for GUI Automation
Authors:Jiabo Ye, Xi Zhang, Haiyang Xu, Haowei Liu, Junyang Wang, Zhaoqing Zhu, Ziwei Zheng, Feiyu Gao, Junjie Cao, Zhengxi Lu, Jitong Liao, Qi Zheng, Fei Huang, Jingren Zhou, Ming Yan
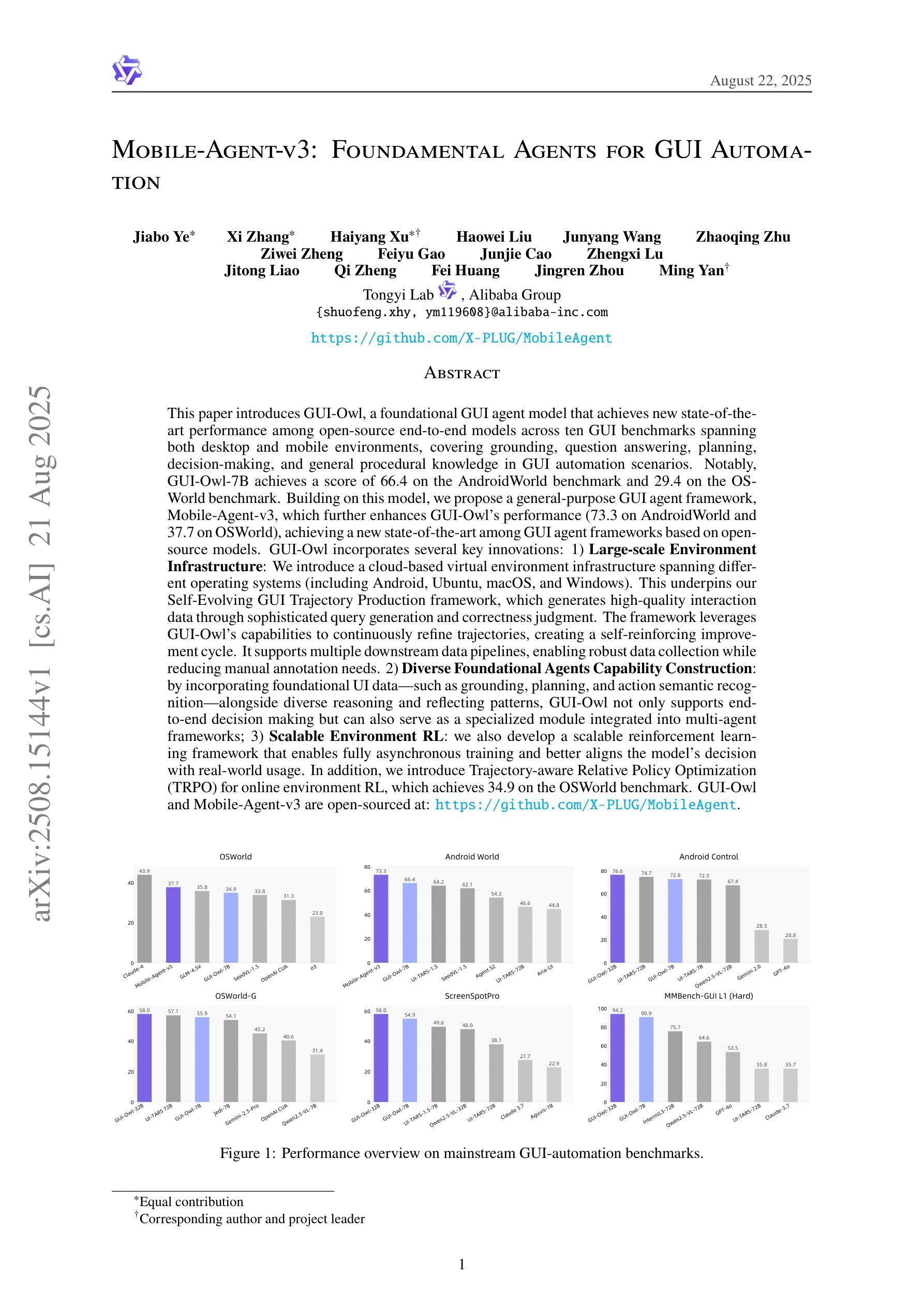
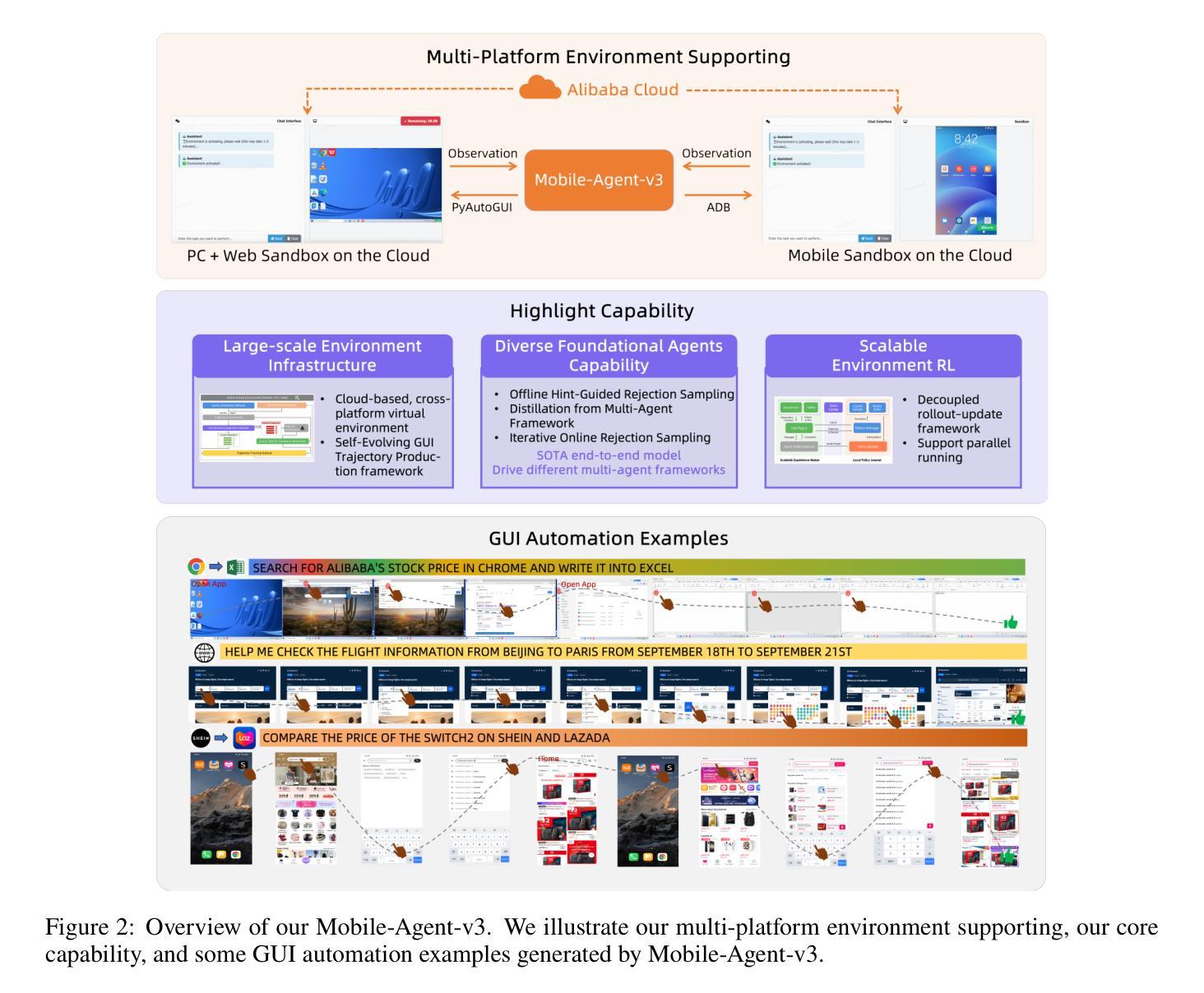
This paper introduces GUI-Owl, a foundational GUI agent model that achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source end-to-end models on ten GUI benchmarks across desktop and mobile environments, covering grounding, question answering, planning, decision-making, and procedural knowledge. GUI-Owl-7B achieves 66.4 on AndroidWorld and 29.4 on OSWorld. Building on this, we propose Mobile-Agent-v3, a general-purpose GUI agent framework that further improves performance to 73.3 on AndroidWorld and 37.7 on OSWorld, setting a new state-of-the-art for open-source GUI agent frameworks. GUI-Owl incorporates three key innovations: (1) Large-scale Environment Infrastructure: a cloud-based virtual environment spanning Android, Ubuntu, macOS, and Windows, enabling our Self-Evolving GUI Trajectory Production framework. This generates high-quality interaction data via automated query generation and correctness validation, leveraging GUI-Owl to refine trajectories iteratively, forming a self-improving loop. It supports diverse data pipelines and reduces manual annotation. (2) Diverse Foundational Agent Capabilities: by integrating UI grounding, planning, action semantics, and reasoning patterns, GUI-Owl supports end-to-end decision-making and can act as a modular component in multi-agent systems. (3) Scalable Environment RL: we develop a scalable reinforcement learning framework with fully asynchronous training for real-world alignment. We also introduce Trajectory-aware Relative Policy Optimization (TRPO) for online RL, achieving 34.9 on OSWorld. GUI-Owl and Mobile-Agent-v3 are open-sourced at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent.
本文介绍了GUI-Owl,这是一种基础GUI代理模型,在桌面和移动环境的十个GUI基准测试中,它在开源端到端模型中实现了最先进的性能,涵盖了接地、问答、规划、决策和程序知识。GUI-Owl-7B在AndroidWorld上得分为66.4,在OSWorld上得分为29.4。在此基础上,我们提出了Mobile-Agent-v3,这是一个通用的GUI代理框架,进一步提高了性能,在AndroidWorld上达到73.3,在OSWorld上达到37.7,为开源GUI代理框架创造了新的最先进的水平。GUI-Owl有三个关键创新点:(1)大规模环境基础设施:一个跨越Android、Ubuntu、macOS和Windows的基于云的虚拟环境,使我们的自我进化GUI轨迹生产框架成为可能。它通过自动化查询生成和正确性验证生成高质量交互数据,利用GUI-Owl迭代优化轨迹,形成一个自我改进循环。它支持多样化的数据管道,减少手动注释。(2)多样化的基础代理功能:通过集成UI接地、规划、动作语义和推理模式,GUI-Owl支持端到端的决策制定,并可以作为多代理系统中的模块化组件。 (3)可扩展的环境强化学习:我们开发了一个可扩展的强化学习框架,具有完全异步训练以实现现实世界对齐。我们还引入了轨迹感知相对策略优化(TRPO)进行在线强化学习,在OSWorld上实现34.9得分。GUI-Owl和Mobile-Agent-v3在https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GUI-Owl是一款基础GUI代理模型,在桌面和移动环境的十个GUI基准测试上实现了卓越的性能。通过引入大型环境基础设施、多样化的基础代理能力和可扩展的环境强化学习,GUI-Owl不断提升自我进化轨迹生产框架的质量。其开源版本为研究者提供了一个强大的工具。Mobile-Agent-v3在此基础上进一步提高性能,展示了其出色的GUI代理框架优势。这些模型为创建更加智能、自主的交互系统开辟了新的可能。
Key Takeaways
- GUI-Owl模型在桌面和移动环境的GUI基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
- GUI-Owl具备大型环境基础设施,支持多样化数据管道和减少手动标注。
- 通过结合UI接地、规划、动作语义和推理模式,GUI-Owl支持端到端的决策制定。
- Mobile-Agent-v3作为通用GUI代理框架,提高了性能并设定了新的开源GUI代理框架标准。
- GUI-Owl采用自我进化轨迹生产框架,形成自我改进循环,提升交互数据质量。
- 强化学习框架具备可扩展性和完全异步训练特性,适用于真实世界场景。
点此查看论文截图
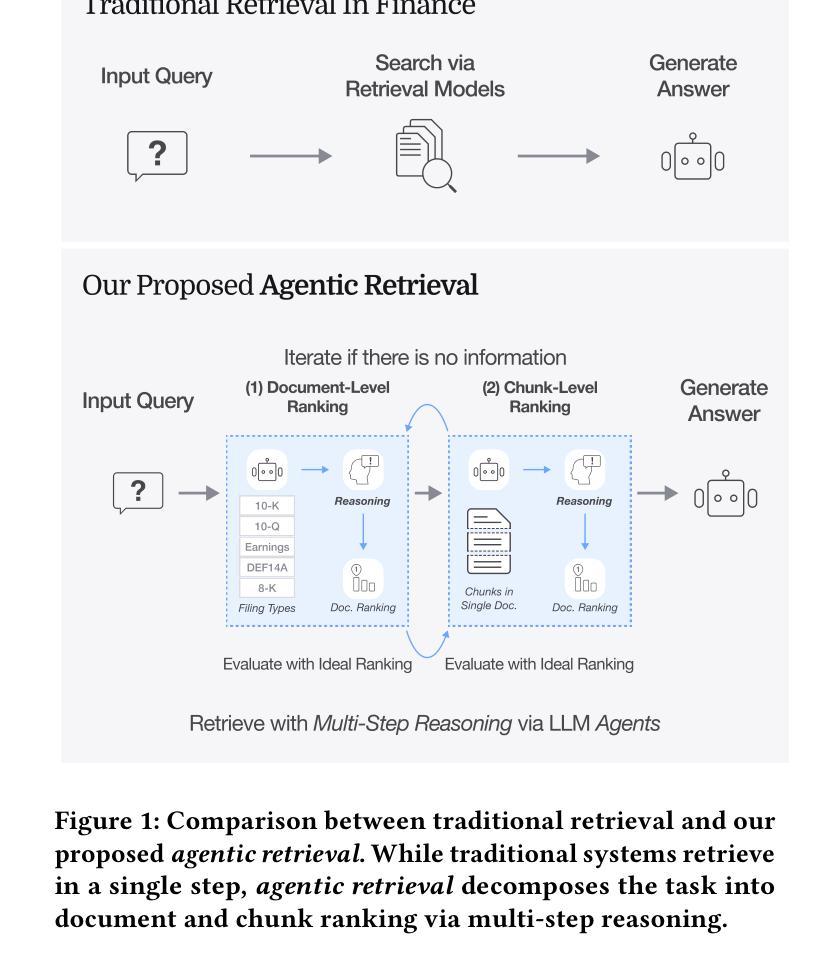
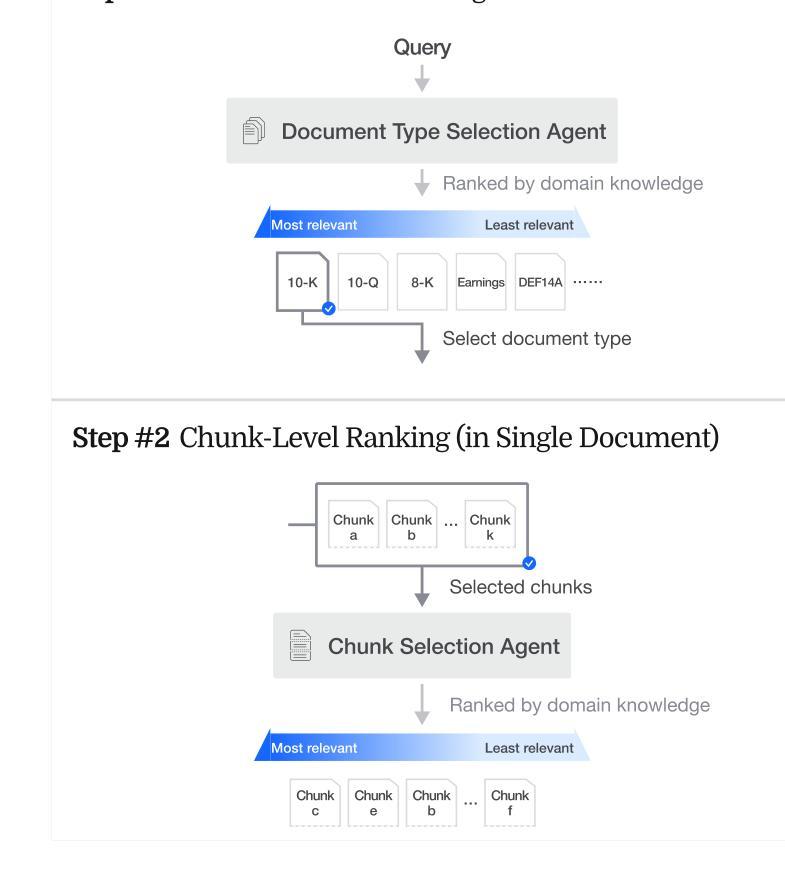
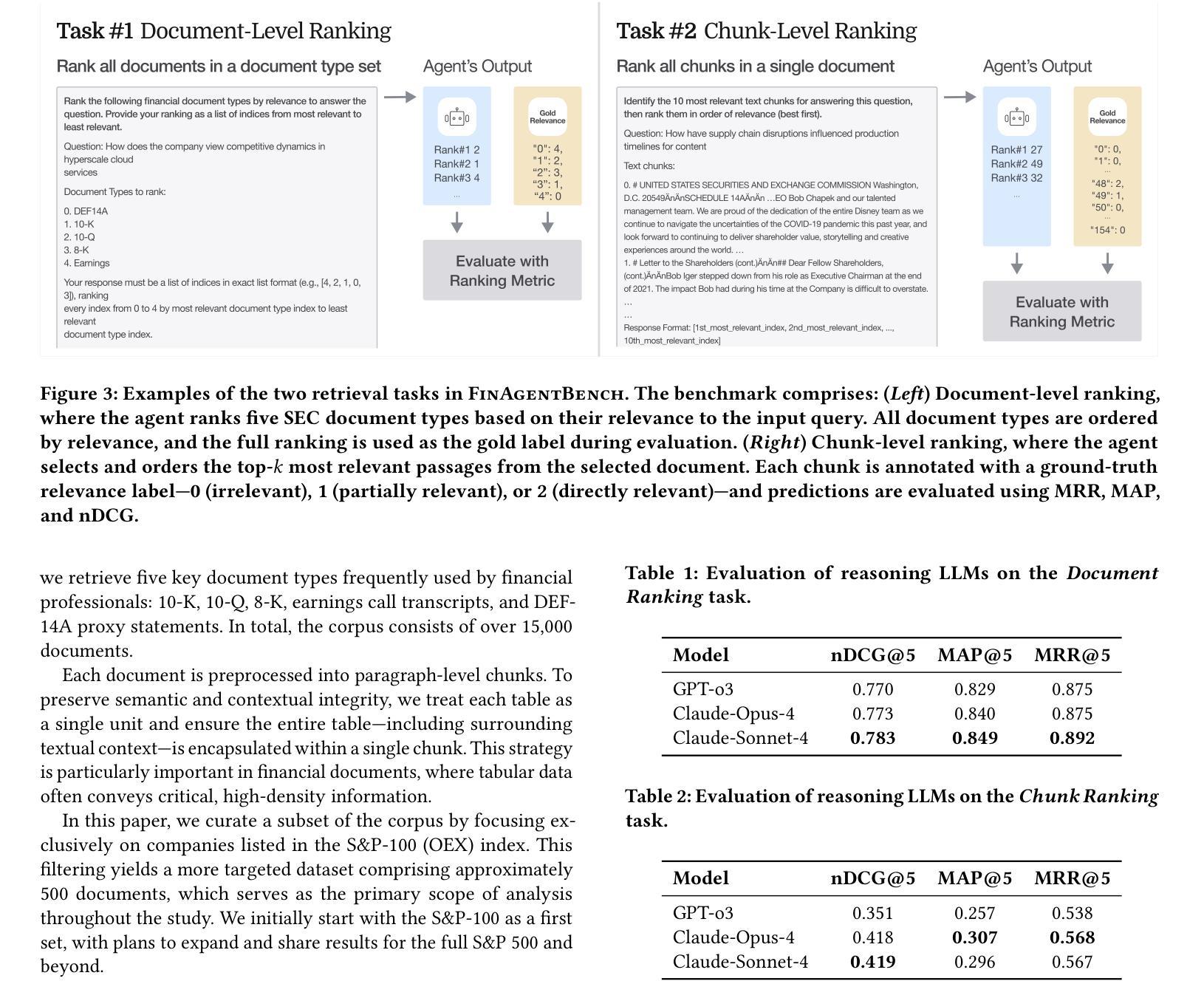
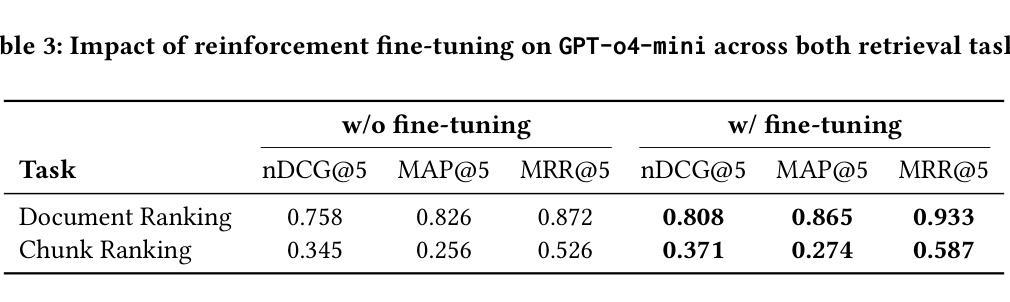
FinAgentBench: A Benchmark Dataset for Agentic Retrieval in Financial Question Answering
Authors:Chanyeol Choi, Jihoon Kwon, Alejandro Lopez-Lira, Chaewoon Kim, Minjae Kim, Juneha Hwang, Jaeseon Ha, Hojun Choi, Suyeol Yun, Yongjin Kim, Yongjae Lee
Accurate information retrieval (IR) is critical in the financial domain, where investors must identify relevant information from large collections of documents. Traditional IR methods-whether sparse or dense-often fall short in retrieval accuracy, as it requires not only capturing semantic similarity but also performing fine-grained reasoning over document structure and domain-specific knowledge. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have opened up new opportunities for retrieval with multi-step reasoning, where the model ranks passages through iterative reasoning about which information is most relevant to a given query. However, there exists no benchmark to evaluate such capabilities in the financial domain. To address this gap, we introduce FinAgentBench, the first large-scale benchmark for evaluating retrieval with multi-step reasoning in finance – a setting we term agentic retrieval. The benchmark consists of 3,429 expert-annotated examples on S&P-100 listed firms and assesses whether LLM agents can (1) identify the most relevant document type among candidates, and (2) pinpoint the key passage within the selected document. Our evaluation framework explicitly separates these two reasoning steps to address context limitations. This design enables to provide a quantitative basis for understanding retrieval-centric LLM behavior in finance. We evaluate a suite of state-of-the-art models and further demonstrated how targeted fine-tuning can significantly improve agentic retrieval performance. Our benchmark provides a foundation for studying retrieval-centric LLM behavior in complex, domain-specific tasks for finance. We will release the dataset publicly upon acceptance of the paper and plan to expand and share dataset for the full S&P 500 and beyond.
准确的情报检索(IR)在金融领域至关重要,投资者必须在大量的文档集合中找到相关信息。传统的IR方法,无论稀疏还是密集,往往在检索准确性方面存在不足,因为它不仅需要捕捉语义相似性,还需要对文档结构和特定领域的知识进行精细的推理。自然语言处理领域的大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为具有多步推理的检索提供了新的机会,该模型通过迭代推理对与给定查询最相关的信息进行排名。然而,金融领域尚未有基准测试来评估这种能力。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了FinAgentBench,这是第一个用于评估金融领域中具有多步推理的检索的大型基准测试——我们称之为代理检索。该基准测试包含3429个关于标普100上市公司的专家注释示例,并评估LLM代理是否能(1)在候选者中识别出最相关的文档类型,(2)在所选文档中定位关键段落。我们的评估框架明确地将这两个推理步骤分开,以解决上下文限制问题。这种设计能够提供定量依据,以了解金融领域中以检索为中心的LLM的行为。我们评估了一系列最先进的模型,并进一步展示了有针对性的微调如何显着提高代理检索性能。我们的基准测试为研究金融领域的复杂特定任务的以检索为中心的LLM行为提供了基础。论文接受后,我们将公开发布数据集,并计划对标普500指数及以后的数据集进行扩展和共享。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
金融领域的信息检索(IR)至关重要,投资者需从大量文档中找到相关信息。传统IR方法常因未能捕捉语义相似性及进行精细的文档结构和领域特定知识推理而导致检索精度不足。大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为具有多步推理的检索提供了新的机会,该模型通过迭代推理对与给定查询最相关的信息进行排名。然而,金融领域缺乏评估这种能力的基准测试。为解决此空白,我们推出了FinAgentBench,这是第一个用于评估金融领域中具有多步推理的检索能力的大规模基准测试——我们称之为agentic检索。该基准测试包含3429个关于标普100家上市公司的专家注释示例,评估LLM代理是否能(1)在候选文档中识别出最相关的文档类型,(2)在所选文档中定位关键段落。我们的评估框架明确地将这两个推理步骤分开,以解决上下文局限性。这种设计有助于为理解金融领域中以检索为中心的LLM行为提供定量依据。我们评估了一系列最新模型,并展示了如何有针对性地微调以显著改善agentic检索性能。我们的基准测试为研究金融领域的复杂、特定任务中的检索中心LLM行为奠定了基础。我们将在论文被接受后公开发布数据集,并计划扩展到整个标普500指数及更广泛领域。
Key Takeaways
- 金融领域的信息检索(IR)至关重要,需要准确捕捉语义相似性、文档结构和领域知识。
- 传统IR方法在某些情况下表现不足,需要新的方法提高检索精度。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)可以通过多步推理提高检索能力,通过迭代推理排名相关信息。
- 金融领域缺乏评估LLM进行多步推理检索的基准测试。
- 推出FinAgentBench基准测试,评估LLM在识别最相关文档类型和定位关键段落方面的能力。
- 评估框架明确区分两个推理步骤,解决上下文局限性问题。
点此查看论文截图

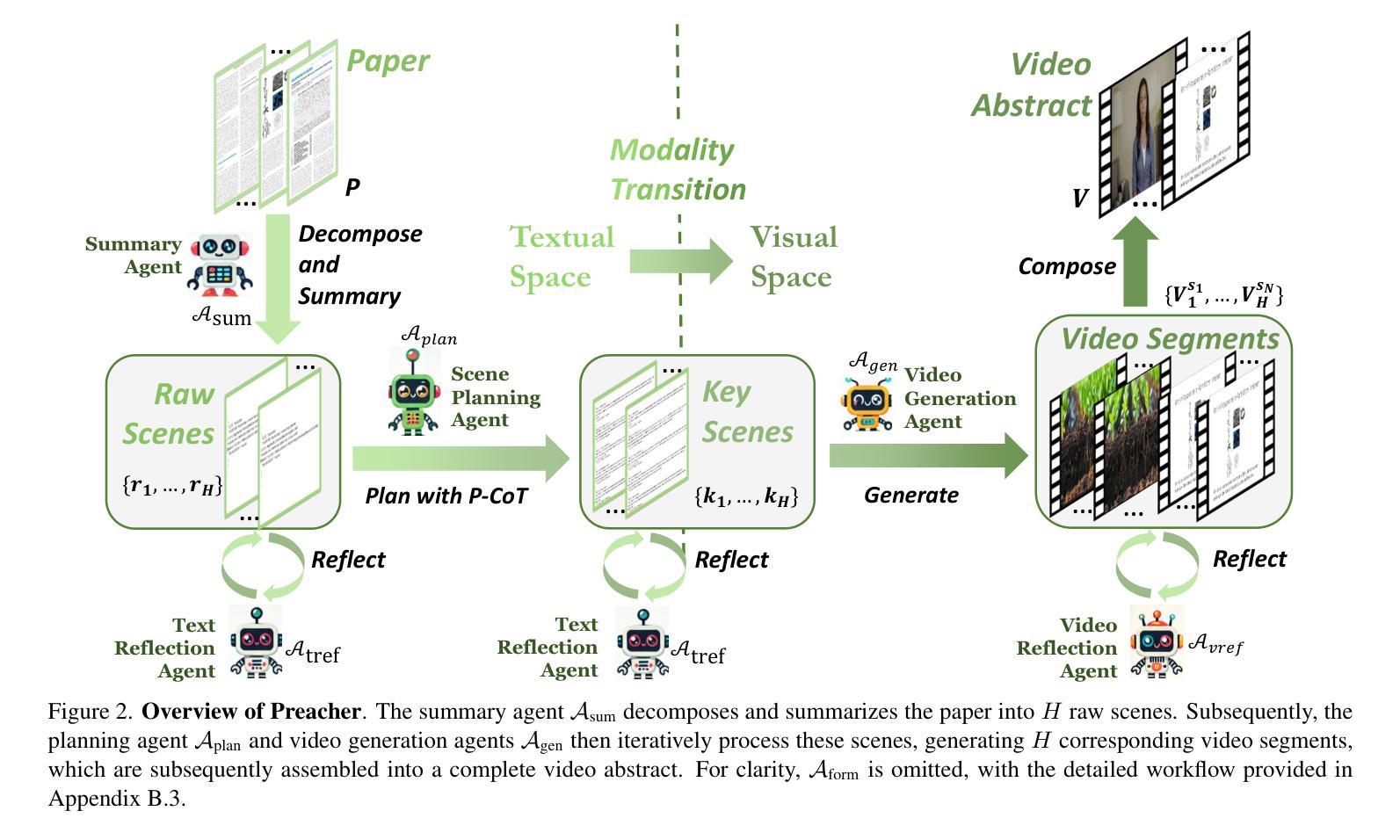
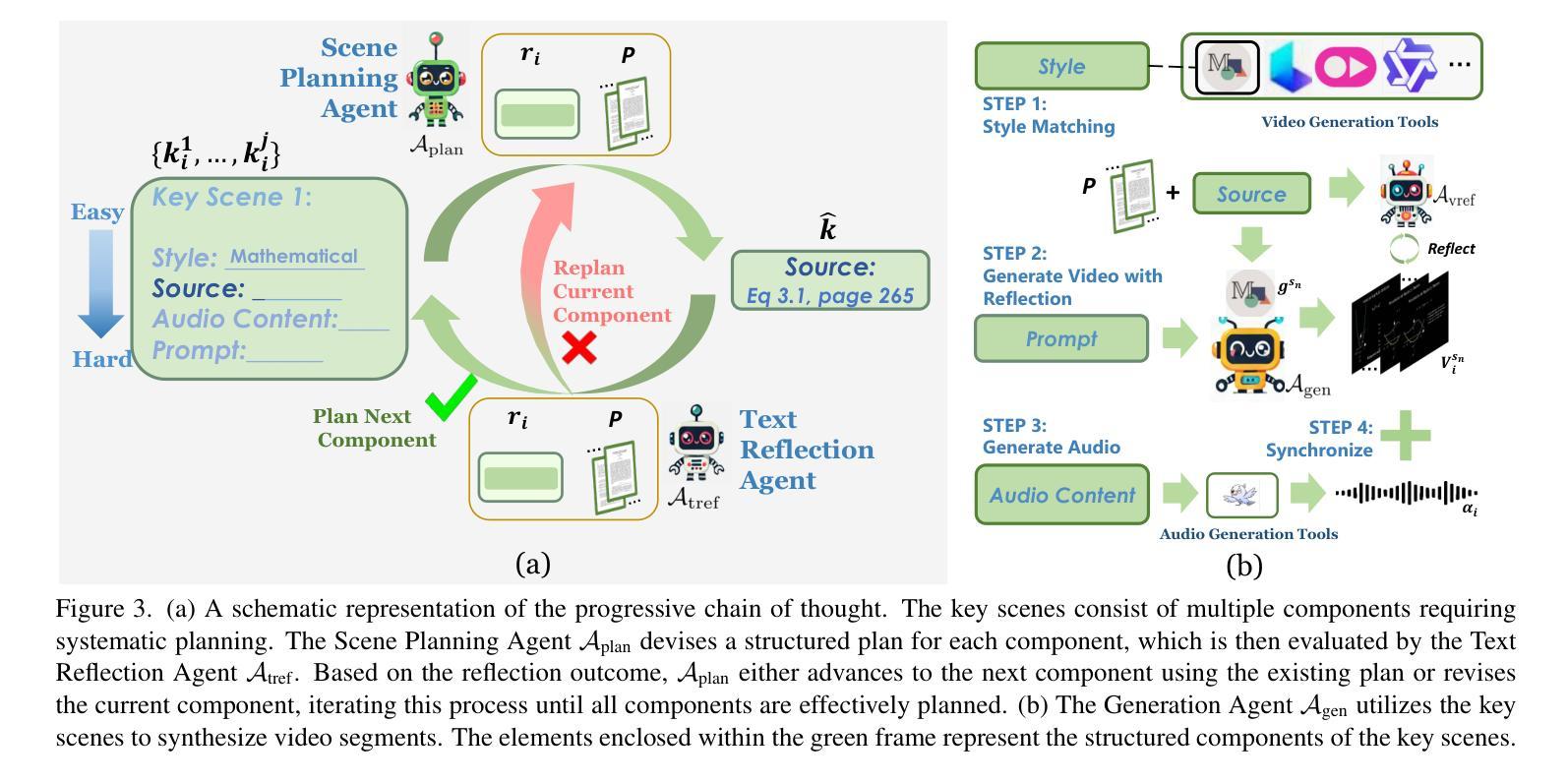
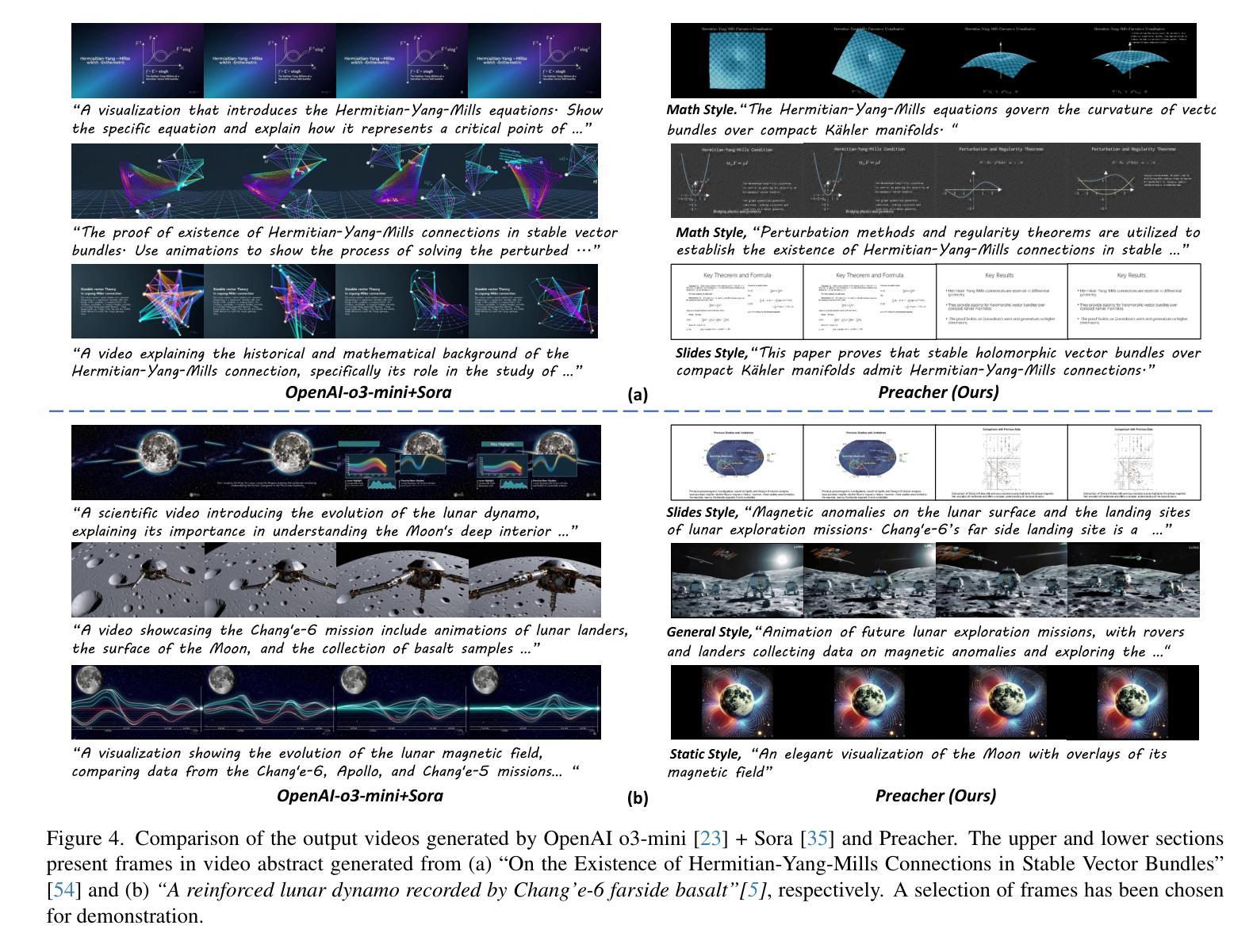
Preacher: Paper-to-Video Agentic System
Authors:Jingwei Liu, Ling Yang, Hao Luo, Fan Wang, Hongyan Li, Mengdi Wang
The paper-to-video task converts a research paper into a structured video abstract, distilling key concepts, methods, and conclusions into an accessible, well-organized format. While state-of-the-art video generation models demonstrate potential, they are constrained by limited context windows, rigid video duration constraints, limited stylistic diversity, and an inability to represent domain-specific knowledge. To address these limitations, we introduce Preacher, the first paper-to-video agentic system. Preacher employs a topdown approach to decompose, summarize, and reformulate the paper, followed by bottom-up video generation, synthesizing diverse video segments into a coherent abstract. To align cross-modal representations, we define key scenes and introduce a Progressive Chain of Thought (P-CoT) for granular, iterative planning. Preacher successfully generates high-quality video abstracts across five research fields, demonstrating expertise beyond current video generation models. Code will be released at: https://github.com/GenVerse/Paper2Video
这篇论文将研究论文转化为结构化的视频摘要,提炼关键概念、方法和结论,使其易于理解并以良好的组织方式呈现。尽管最先进的视频生成模型显示出潜力,但它们受限于有限的上下文窗口、严格的视频持续时间限制、有限的风格多样性和无法表示特定领域知识。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了Preacher,这是第一个论文到视频的智能系统。Preacher采用自上而下的方法分解、总结和重构论文,然后进行自下而上的视频生成,将多样化的视频片段合成一个连贯的摘要。为了对齐跨模态表示,我们定义了关键场景并引入了渐进思维链(P-CoT)进行精细的迭代规划。Preacher成功地在五个研究领域生成了高质量的视频摘要,展示了超越当前视频生成模型的专长。代码将在https://github.com/GenVerse/Paper2Video上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Include some mistakes
Summary
文本中的研究论文探讨了将论文转换为视频摘要的技术,详细介绍了如何抽取关键概念、方法和结论并将其制作成有条理的视频。为突破当前视频生成模型的局限,例如有限的语境窗口、视频时长限制和缺乏特定的知识表示等,论文提出了一种新的解决方案。介绍了名为Preacher的系统,它是一个纸媒转换视频的代理人系统。该系统通过自上而下方式处理文献分解和摘要编写过程,然后进行自下而上的视频生成过程,并融合多种视频片段生成连贯的摘要。通过定义关键场景并引入渐进链式思维方法(P-CoT),该系统能够完成精细、迭代规划过程,实现跨模态表示的匹配。Preacher成功生成了五个研究领域的视频摘要,展现了超越现有视频生成模型的专业能力。更多信息可通过访问相关代码库获取:https://github.com/GenVerse/Paper2Video。
Key Takeaways
- 研究论文转化为视频摘要技术介绍。
- 当前视频生成模型的局限性包括有限的语境窗口、视频时长限制和缺乏特定知识表示等。
- Preacher系统是一种新的纸媒转换视频的代理人系统,采用自上而下和自下而上的处理方式。
点此查看论文截图

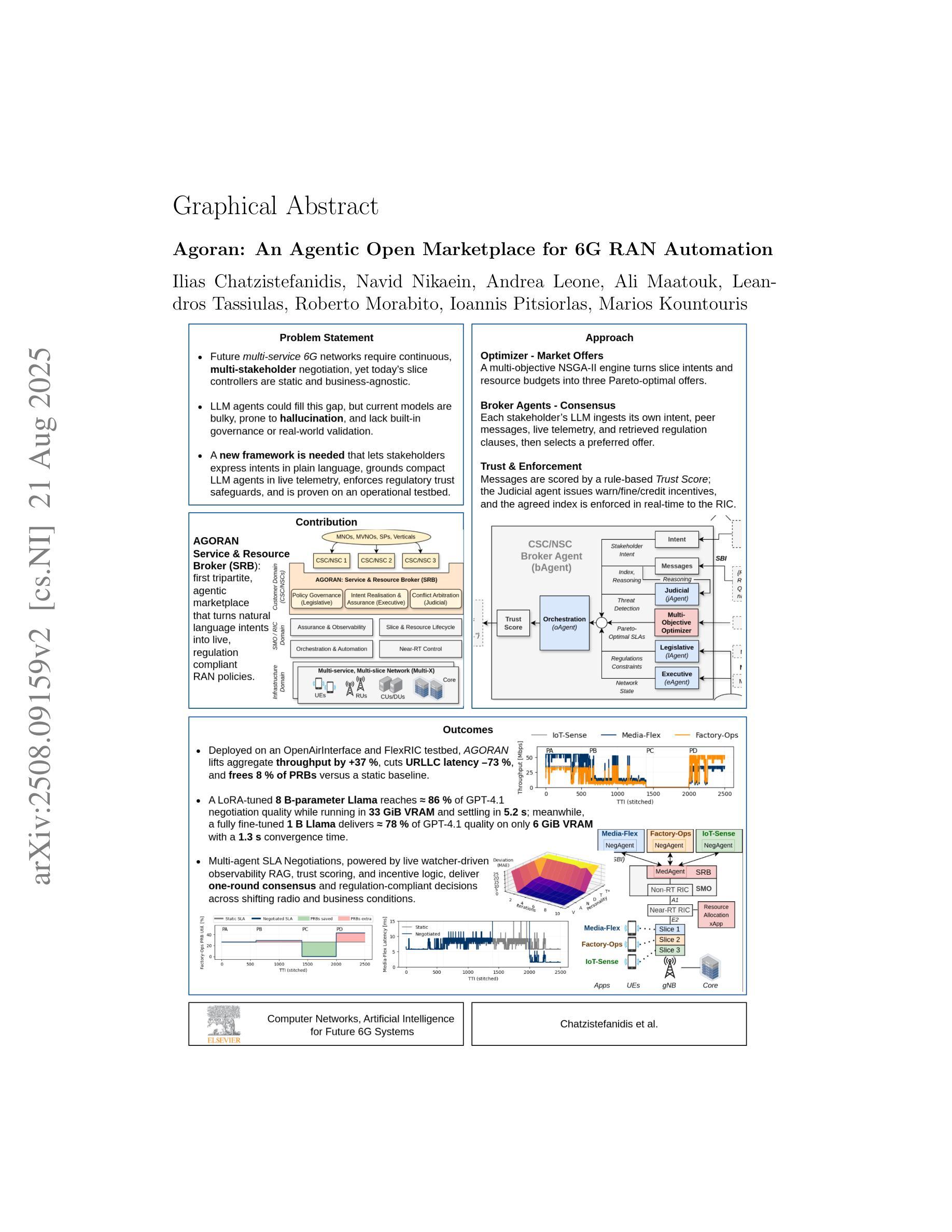
Agoran: An Agentic Open Marketplace for 6G RAN Automation
Authors:Ilias Chatzistefanidis, Navid Nikaein, Andrea Leone, Ali Maatouk, Leandros Tassiulas, Roberto Morabito, Ioannis Pitsiorlas, Marios Kountouris
Next-generation mobile networks must reconcile the often-conflicting goals of multiple service owners. However, today’s network slice controllers remain rigid, policy-bound, and unaware of the business context. We introduce Agoran Service and Resource Broker (SRB), an agentic marketplace that brings stakeholders directly into the operational loop. Inspired by the ancient Greek agora, Agoran distributes authority across three autonomous AI branches: a Legislative branch that answers compliance queries using retrieval-augmented Large Language Models (LLMs); an Executive branch that maintains real-time situational awareness through a watcher-updated vector database; and a Judicial branch that evaluates each agent message with a rule-based Trust Score, while arbitrating LLMs detect malicious behavior and apply real-time incentives to restore trust. Stakeholder-side Negotiation Agents and the SRB-side Mediator Agent negotiate feasible, Pareto-optimal offers produced by a multi-objective optimizer, reaching a consensus intent in a single round, which is then deployed to Open and AI RAN controllers. Deployed on a private 5G testbed and evaluated with realistic traces of vehicle mobility, Agoran achieved significant gains: (i) a 37% increase in throughput of eMBB slices, (ii) a 73% reduction in latency of URLLC slices, and concurrently (iii) an end-to-end 8.3% saving in PRB usage compared to a static baseline. An 1B-parameter Llama model, fine-tuned for five minutes on 100 GPT-4 dialogues, recovers approximately 80% of GPT-4.1’s decision quality, while operating within 6 GiB of memory and converging in only 1.3 seconds. These results establish Agoran as a concrete, standards-aligned path toward ultra-flexible, stakeholder-centric 6G networks. A live demo is presented https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h7vEyMu2f5w\&ab_channel=BubbleRAN.
下一代移动网络必须协调多个服务所有者经常冲突的目标。然而,当前的网络切片控制器仍然僵化、受政策限制,且不了解业务上下文。我们引入了Agoran服务资源经纪人(SRB),这是一个代理市场,它直接将利益相关者纳入运营循环。Agoran以古希腊的市集为灵感,将权力分散到三个自主的人工智能分支机构:立法部门使用增强检索的大型语言模型(LLM)回答合规查询;行政部门通过观察者更新的向量数据库维持实时情况了解;司法部门评估每个代理消息,采用基于规则的信任评分,同时仲裁LLM检测恶意行为并应用实时激励来恢复信任。利益相关方谈判代理人和SRB调解人代理谈判由多目标优化器产生的可行且帕累托最优报价,在单轮谈判中达成共识意图,然后部署到开放和AI RAN控制器。在私有5G测试床上部署,并用实际的车辆移动轨迹进行评估,Agoran取得了显著成效:(i)eMBB切片的吞吐量提高了37%,(ii)URLLC切片的延迟减少了73%,同时(iii)与静态基线相比,在PRB使用上实现了端到端8.3%的节省。一个1000亿参数的Llama模型,在100个GPT-4对话上进行五分钟微调,能够恢复大约80%的GPT-4.1决策质量,同时在6GiB内存内运行,并在仅1.3秒内收敛。这些结果证明了Agoran作为实现超灵活、以利益相关者为中心的6G网络的切实、符合标准的道路。现场演示请参见:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h7vEyMu2f5w&ab_channel=BubbleRAN。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-print submitted to Computer Networks AI-for-6G
Summary
下一代移动网络需要协调多个服务所有者经常相互冲突的目标。针对当前网络切片控制器的僵化、受政策限制且不了解业务上下文的问题,提出了Agoran服务和资源经纪人(SRB)作为中介市场,将利益相关者直接纳入操作循环。Agoran通过立法分支、行政分支和司法分支三个自主人工智能分支分配权力,实现了灵活的网络管理。通过部署在私有5G测试床上,用真实的车辆移动轨迹进行评估,Agoran取得了显著成效。此外,其LLama模型在GPT-4的基础上微调后表现出良好的决策质量。这些成果标志着Agoran成为一条实现超灵活、以利益相关者为中心的6G网络的切实可行路径。
Key Takeaways
- 下一代移动网络需要解决多个服务所有者之间的冲突目标。
- 当前网络切片控制器存在僵化、受政策限制且不了解业务上下文的问题。
- Agoran作为一个中介市场,将利益相关者纳入操作循环中。
- Agoran通过立法、行政和司法三个自主人工智能分支分配权力,实现灵活的网络管理。
- Agoran在私有5G测试床上的评估结果显示出显著成效,包括eMBB切片吞吐量增加37%、URLLC切片延迟减少73%,并实现了PRB使用端到端节省8.3%。
- Agoran使用的LLama模型在GPT-4的基础上表现出良好的决策质量。
- Agoran有望成为实现超灵活、以利益相关者为中心的6G网络的切实路径。
点此查看论文截图
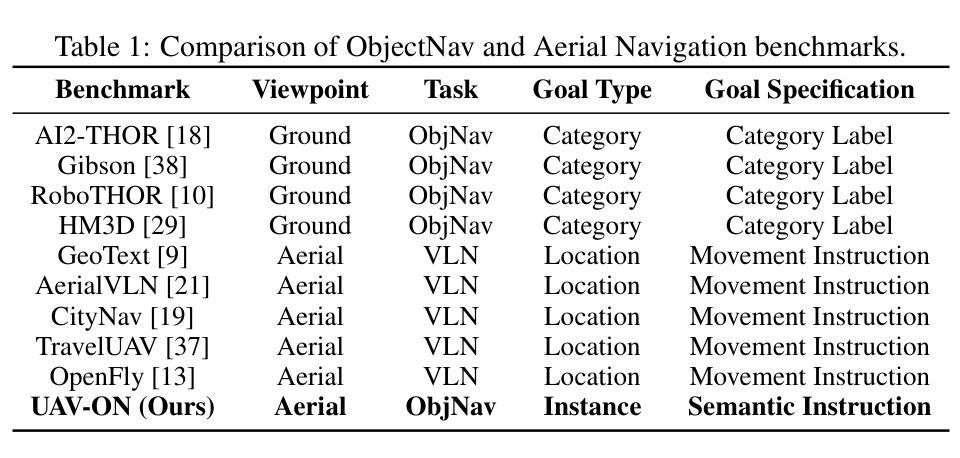
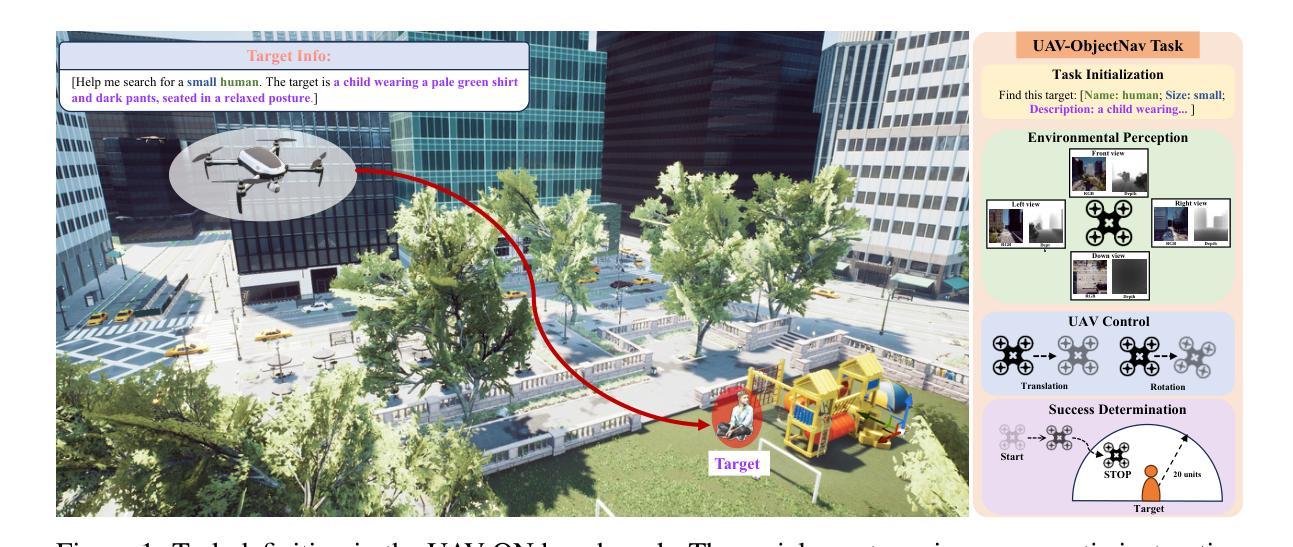
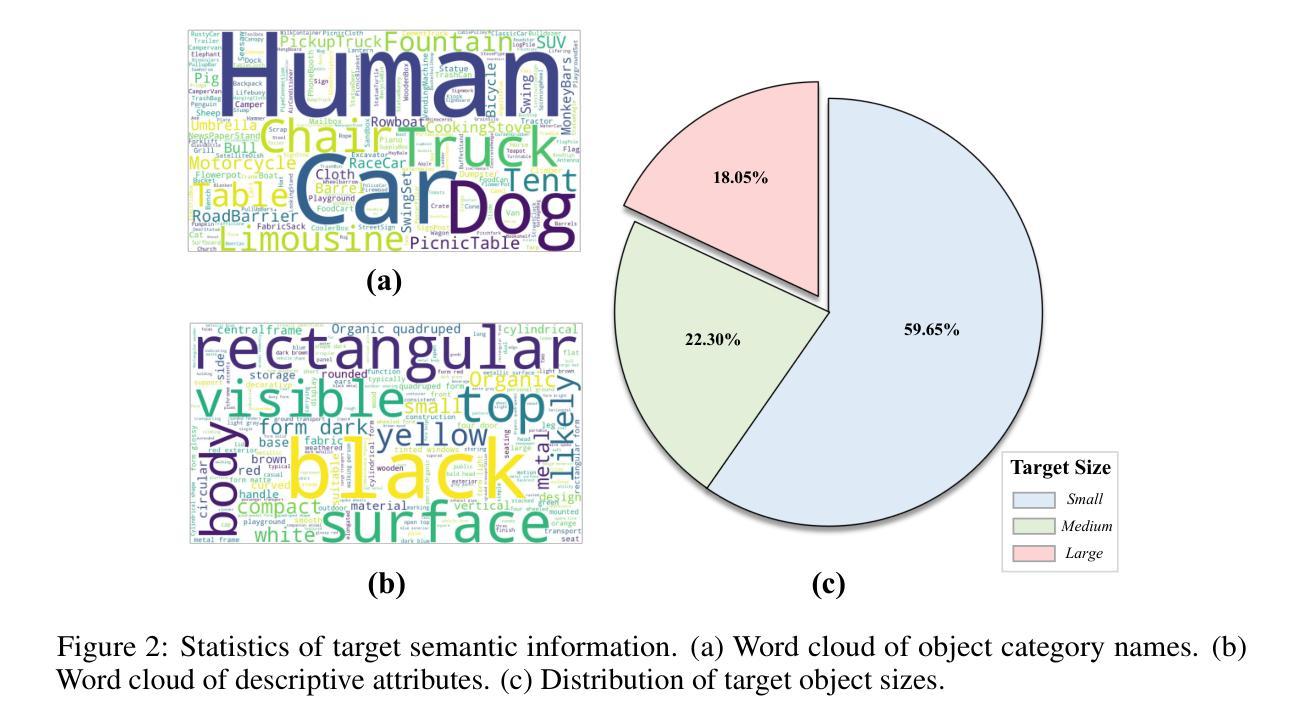
UAV-ON: A Benchmark for Open-World Object Goal Navigation with Aerial Agents
Authors:Jianqiang Xiao, Yuexuan Sun, Yixin Shao, Boxi Gan, Rongqiang Liu, Yanjing Wu, Weili Gua, Xiang Deng
Aerial navigation is a fundamental yet underexplored capability in embodied intelligence, enabling agents to operate in large-scale, unstructured environments where traditional navigation paradigms fall short. However, most existing research follows the Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) paradigm, which heavily depends on sequential linguistic instructions, limiting its scalability and autonomy. To address this gap, we introduce UAV-ON, a benchmark for large-scale Object Goal Navigation (ObjectNav) by aerial agents in open-world environments, where agents operate based on high-level semantic goals without relying on detailed instructional guidance as in VLN. UAV-ON comprises 14 high-fidelity Unreal Engine environments with diverse semantic regions and complex spatial layouts, covering urban, natural, and mixed-use settings. It defines 1270 annotated target objects, each characterized by an instance-level instruction that encodes category, physical footprint, and visual descriptors, allowing grounded reasoning. These instructions serve as semantic goals, introducing realistic ambiguity and complex reasoning challenges for aerial agents. To evaluate the benchmark, we implement several baseline methods, including Aerial ObjectNav Agent (AOA), a modular policy that integrates instruction semantics with egocentric observations for long-horizon, goal-directed exploration. Empirical results show that all baselines struggle in this setting, highlighting the compounded challenges of aerial navigation and semantic goal grounding. UAV-ON aims to advance research on scalable UAV autonomy driven by semantic goal descriptions in complex real-world environments.
无人机导航是智能体(embodied intelligence)中的一项基本但尚未被充分探索的能力,使得智能体能够在大规模、非结构化环境中进行运行,而这些环境中传统的导航模式并不适用。然而,现有的大多数研究都遵循视觉与语言导航(VLN)模式,该模式严重依赖于连续的语言指令,限制了其可扩展性和自主性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了UAV-ON基准测试,这是无人机在大规模开放世界环境中进行目标物体导航(ObjectNav)的基准测试。在这个基准测试中,智能体基于高级语义目标进行操作,不再依赖于像VLN那样详细的指导性指令。UAV-ON包含使用高质量的游戏引擎——Unreal Engine模拟制作的14个高度逼真的环境,其中包含多样化的语义区域和复杂的空间布局,涵盖城市、自然和混合用途场景。它定义了有标注的1270个目标对象,每个对象都可以通过实例级别的指令进行特征化描述,这些指令包含了类别、物理足迹和视觉描述符,允许基于实际情境进行推理。这些指令作为语义目标存在,为无人机引入了现实存在的模糊性和复杂的推理挑战。为了评估这个基准测试,我们实施了几种基线方法,包括空中目标导航代理(AOA),这是一种模块化策略,它将指令语义与自我中心观察相结合,以实现长期、目标导向的探索。实验结果表明,所有基线方法在这个环境下都面临挑战,凸显了无人机导航和语义目标定位的挑战性。UAV-ON的目标是推进基于复杂现实环境中的语义目标描述的可扩展无人机自主性研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM MM Dataset Track 2025
Summary
在体智能中,空中导航是一项基础且尚未充分研究的能力,使代理能够在大规模、非结构化环境中运作,而传统的导航范式在这方面表现不足。针对此研究领域的不足,我们推出无人机目标导航基准测试(UAV-ON),该测试模拟大规模空中代理物体目标导航(ObjectNav)在开放世界环境中的场景。UAV-ON包含具有多样语义区域和复杂空间布局的高保真Unreal Engine环境,涵盖城市、自然和混合用途场景。它定义了标注的目标物体,每个物体都有实例级别的指令,包括类别、物理足迹和视觉描述符,允许基于指令进行推理。为了评估基准测试,我们实施了包括空中目标导航代理(AOA)在内的几种基线方法。结果表明,所有基线方法在这个环境中都面临挑战,突显了空中导航和语义目标接地技术的复杂性。UAV-ON旨在推动复杂现实环境中基于语义目标描述的无人机自主性研究的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 空中导航在体智能中是一个关键且尚未完全研究的领域。传统的导航方式在大规模非结构化环境中难以满足需求。为了填补这一空缺,引入了无人机目标导航基准测试(UAV-ON)。
- UAV-ON包含多样化的高保真环境模拟,涵盖城市、自然和混合用途场景。提供了丰富的语义区域和复杂空间布局的挑战。
- 每个目标物体都有详细的实例级别指令,包括类别、物理属性和视觉描述等,这为空中导航提供了语义目标导向的推理基础。这增加了真实世界的复杂性并引入了语义模糊性挑战。
点此查看论文截图

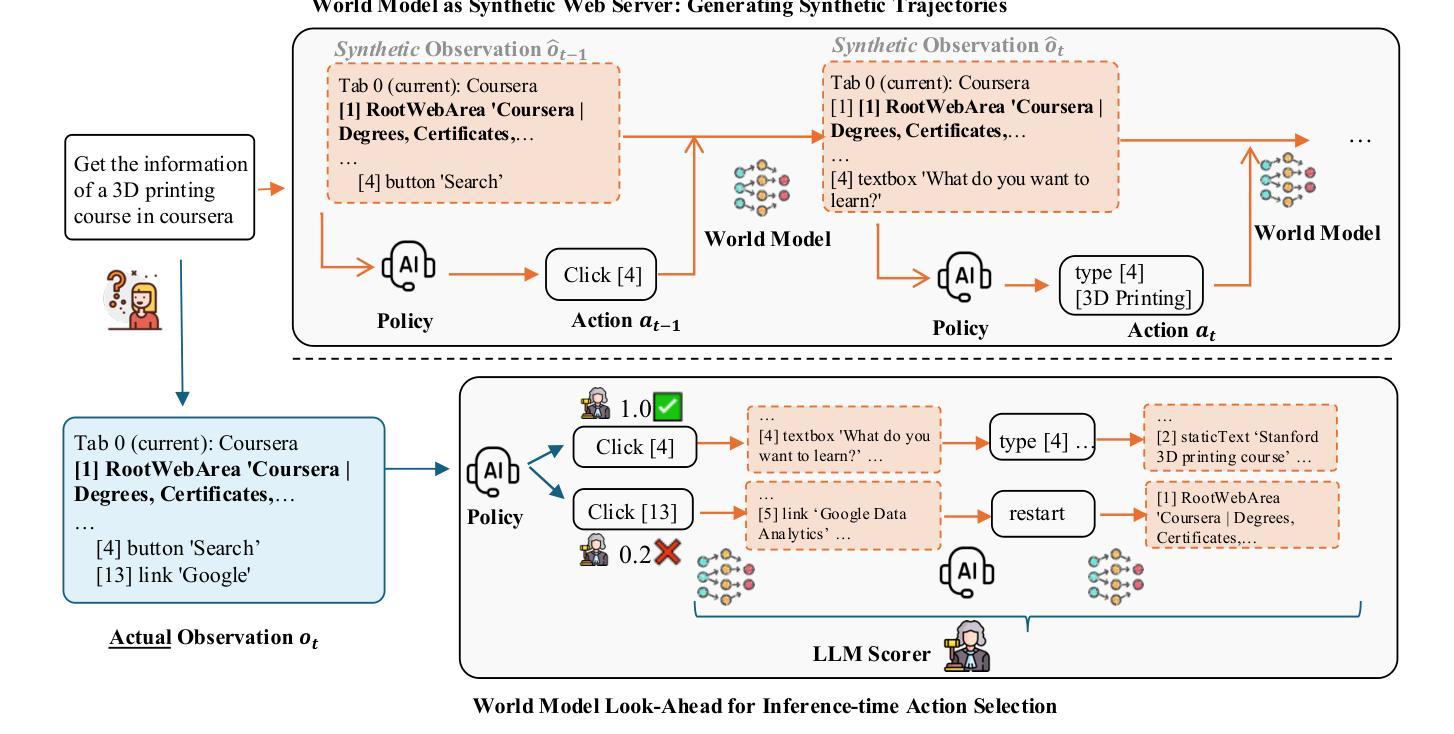
WebEvolver: Enhancing Web Agent Self-Improvement with Coevolving World Model
Authors:Tianqing Fang, Hongming Zhang, Zhisong Zhang, Kaixin Ma, Wenhao Yu, Haitao Mi, Dong Yu
Agent self-improvement, where the backbone Large Language Model (LLM) of the agent are trained on trajectories sampled autonomously based on their own policies, has emerged as a promising approach for enhancing performance. Recent advancements, particularly in web environments, face a critical limitation: their performance will reach a stagnation point during autonomous learning cycles, hindering further improvement. We argue that this stems from limited exploration of the web environment and insufficient exploitation of pre-trained web knowledge in LLMs. To improve the performance of self-improvement, we propose a novel framework that introduces a co-evolving World Model LLM. This world model predicts the next observation based on the current observation and action within the web environment. Leveraging LLMs’ pretrained knowledge of abundant web content, the World Model serves dual roles: (1) as a virtual web server generating self-instructed training data to continuously refine the agent’s policy, and (2) as an imagination engine during inference, enabling look-ahead simulation to guide action selection for the agent LLM. Experiments in real-world web environments (Mind2Web-Live, WebVoyager, and GAIA-web) show a 10% performance gain over existing self-evolving agents, demonstrating the efficacy and generalizability of our approach, without using any distillation from more powerful close-sourced models. Our work establishes the necessity of integrating world models into autonomous agent frameworks to unlock sustained adaptability. Code is available at https://github.com/Tencent/SelfEvolvingAgent
代理自我改进作为一种增强性能的有前途的方法已经崭露头角,其中代理的后端大型语言模型(LLM)是在根据自主政策采样的轨迹上进行训练的。最近的进展,特别是在网络环境中,面临一个关键的局限性:它们在自主学习周期中的性能会达到停滞点,阻碍了进一步的改进。我们认为这源于网络环境的有限探索和对LLM中预训练网络知识的不充分利用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2025 Main Conference
Summary
基于自主策略的轨迹采样,Agent自我改进方法已经崭露头角,特别是在网络环境中。然而,其性能在自主学习周期中会达到停滞点。本文提出一种新型协同进化世界模型LLM框架,利用LLM的预训练网络知识,预测下一个观察结果,作为虚拟服务器生成自我指导的训练数据,并用于持续优化agent的策略。实验表明,该框架在真实网络环境中的性能比现有自进化agent提高了10%,证明了其有效性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- Agent自我改进方法基于自主策略的轨迹采样,旨在提高性能。
- 网络环境中的自主学习方法存在性能停滞问题。
- 新型协同进化世界模型LLM框架被提出,以解决性能停滞问题。
- 该框架利用LLM的预训练网络知识,预测下一个观察结果。
- 世界模型作为虚拟服务器生成自我指导的训练数据,以优化agent策略。
- 实验证明该框架在真实网络环境中性能优越,比现有自进化agent提高10%。
点此查看论文截图

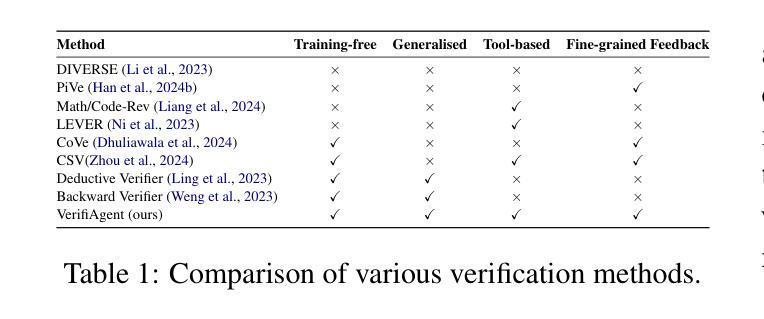
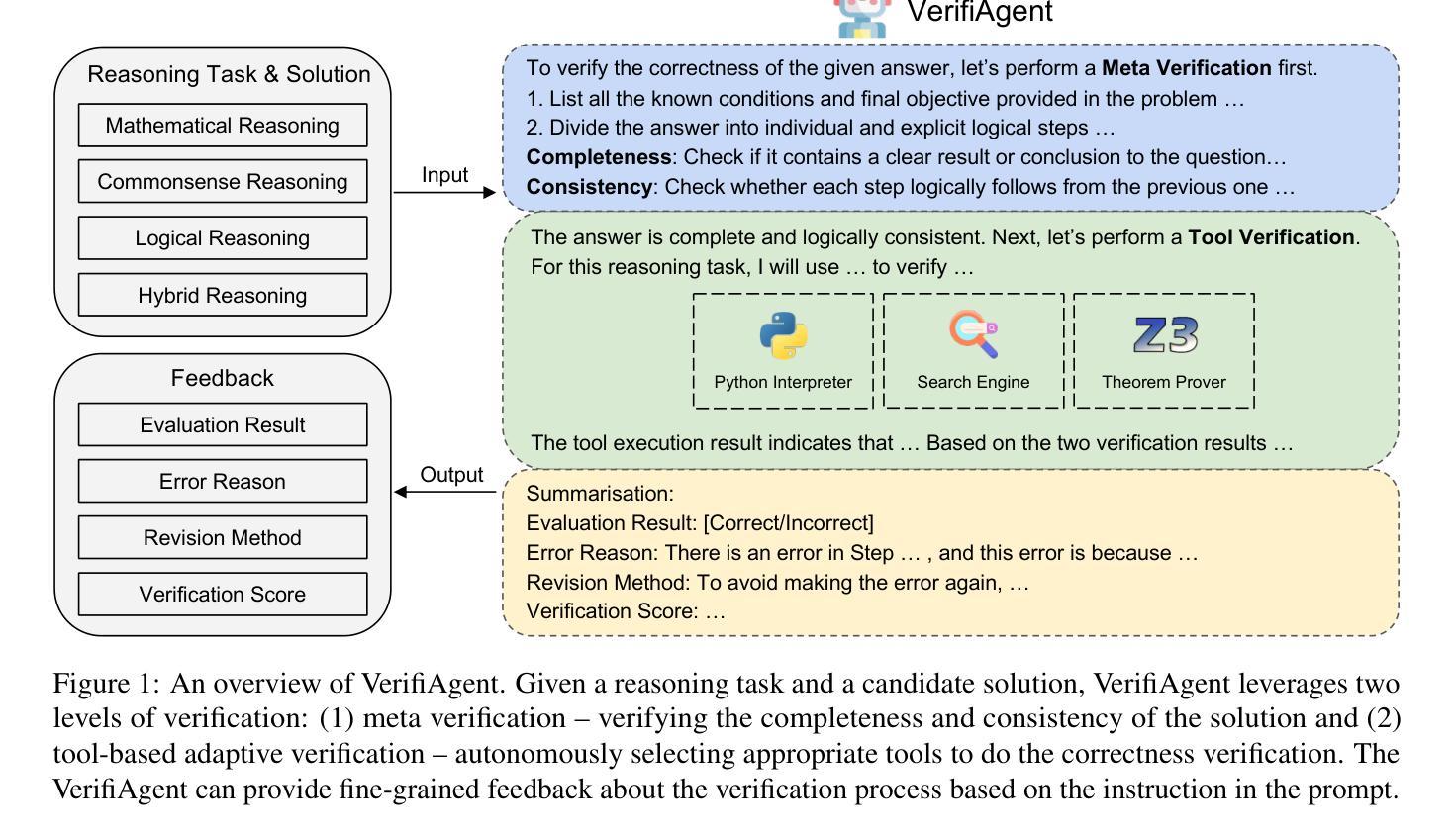
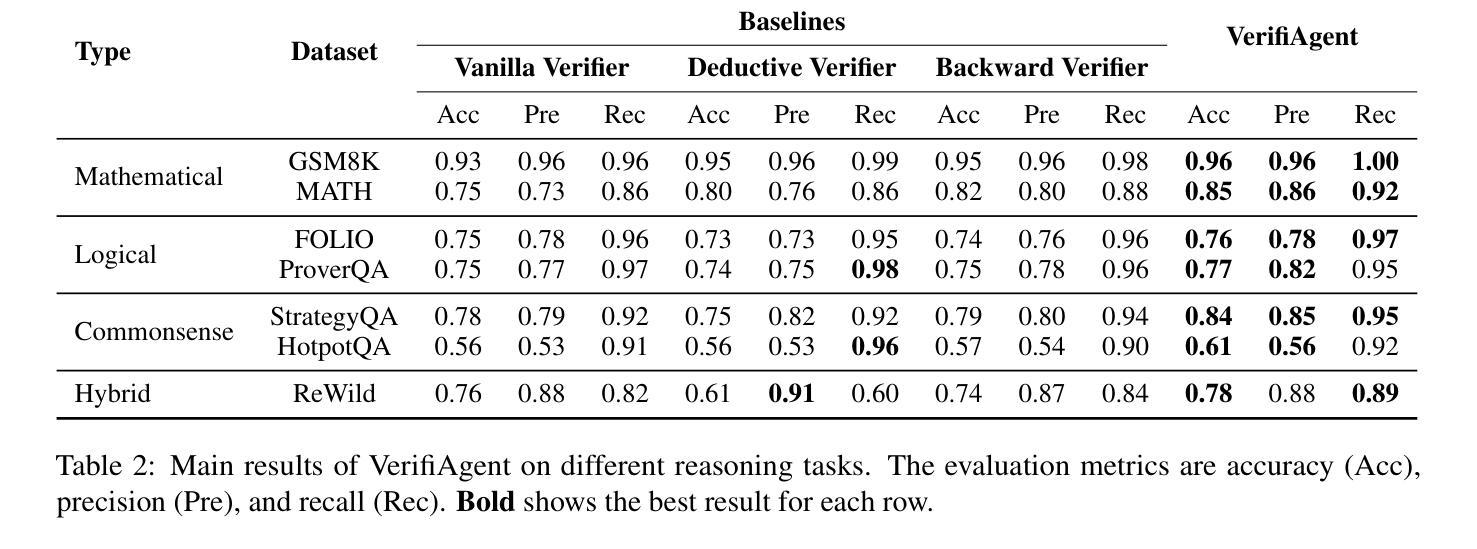
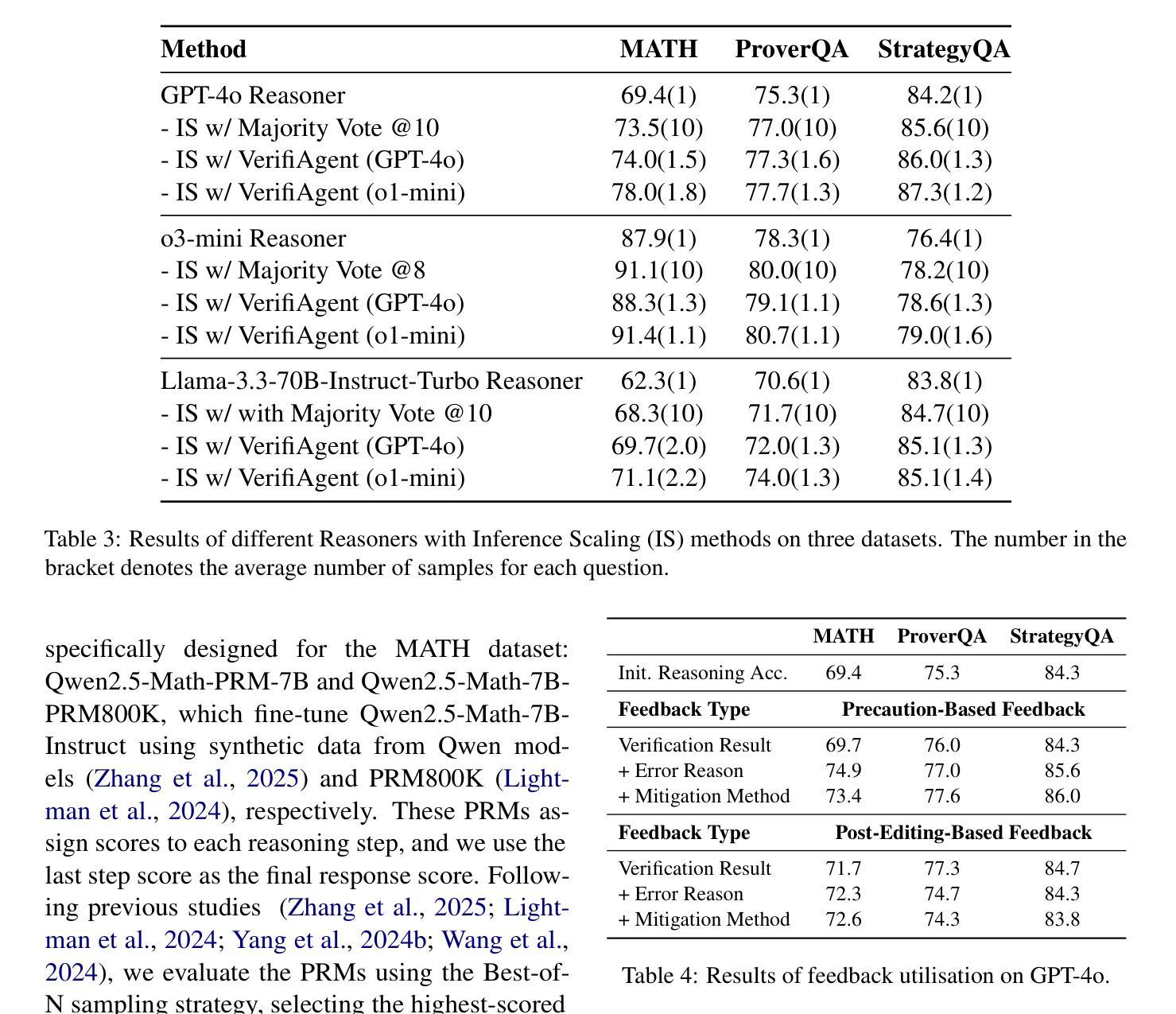
VerifiAgent: a Unified Verification Agent in Language Model Reasoning
Authors:Jiuzhou Han, Wray Buntine, Ehsan Shareghi
Large language models demonstrate remarkable reasoning capabilities but often produce unreliable or incorrect responses. Existing verification methods are typically model-specific or domain-restricted, requiring significant computational resources and lacking scalability across diverse reasoning tasks. To address these limitations, we propose VerifiAgent, a unified verification agent that integrates two levels of verification: meta-verification, which assesses completeness and consistency in model responses, and tool-based adaptive verification, where VerifiAgent autonomously selects appropriate verification tools based on the reasoning type, including mathematical, logical, or commonsense reasoning. This adaptive approach ensures both efficiency and robustness across different verification scenarios. Experimental results show that VerifiAgent outperforms baseline verification methods (e.g., deductive verifier, backward verifier) among all reasoning tasks. Additionally, it can further enhance reasoning accuracy by leveraging feedback from verification results. VerifiAgent can also be effectively applied to inference scaling, achieving better results with fewer generated samples and costs compared to existing process reward models in the mathematical reasoning domain. Code is available at https://github.com/Jiuzhouh/VerifiAgent
大型语言模型展现出惊人的推理能力,但常常产生不可靠或错误的回应。现有的验证方法通常是模型特定或领域限制的,需要大量的计算资源,并且在不同的推理任务中缺乏可扩展性。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了VerifiAgent,这是一个统一的验证代理,它整合了两个层次的验证:元验证,评估模型响应的完整性和一致性;以及基于工具的自适应验证,VerifiAgent根据推理类型(包括数学、逻辑或常识推理)自主选择合适的验证工具。这种自适应方法确保了不同验证场景下的效率和稳健性。实验结果表明,VerifiAgent在所有推理任务中的性能优于基准验证方法(例如演绎验证器、向后验证器)。此外,它还可以通过利用验证结果的反馈来提高推理准确性。VerifiAgent还可以有效地应用于推理缩放,与数学推理领域中的现有流程奖励模型相比,使用更少的生成样本和成本实现更好的结果。代码可在https://github.com/Jiuzhouh/VerifiAgent获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2025
摘要
大规模语言模型具备出色的推理能力,但常产生不可靠或错误的回应。现有验证方法通常模型特定或局限于特定领域,需要大量计算资源,且在跨不同推理任务时缺乏可扩展性。为解决这些问题,我们提出VerifiAgent统一验证代理,它整合了两种层次的验证:元验证,评估模型回应的完整性和一致性;以及基于工具的自适应验证,VerifiAgent根据推理类型(如数学、逻辑或常识推理)自主选择合适的验证工具。这种自适应方法确保了不同验证场景下的效率和稳健性。实验结果显示,VerifiAgent在所有推理任务中的表现优于基准验证方法(如演绎验证器、反向验证器等)。此外,它还能通过利用验证结果反馈进一步提高推理准确性。VerifiAgent还可有效应用于推理扩展,与现有数学推理领域的流程奖励模型相比,使用更少的生成样本和成本实现更好的结果。
关键见解
- VerifiAgent是一个统一验证代理,用于验证大规模语言模型的响应。
- 它结合了元验证和工具基于自适应验证两种层次的验证方法。
- 元验证评估模型回应的完整性和一致性。
- 基于工具的自适应验证能根据推理类型自主选择验证工具。
- VerifiAgent在多种推理任务中表现优于其他基准验证方法。
- VerifiAgent可以利用验证结果反馈提高推理准确性。
- VerifiAgent可应用于推理扩展,并在数学推理领域实现了更好的结果和成本效益。
点此查看论文截图

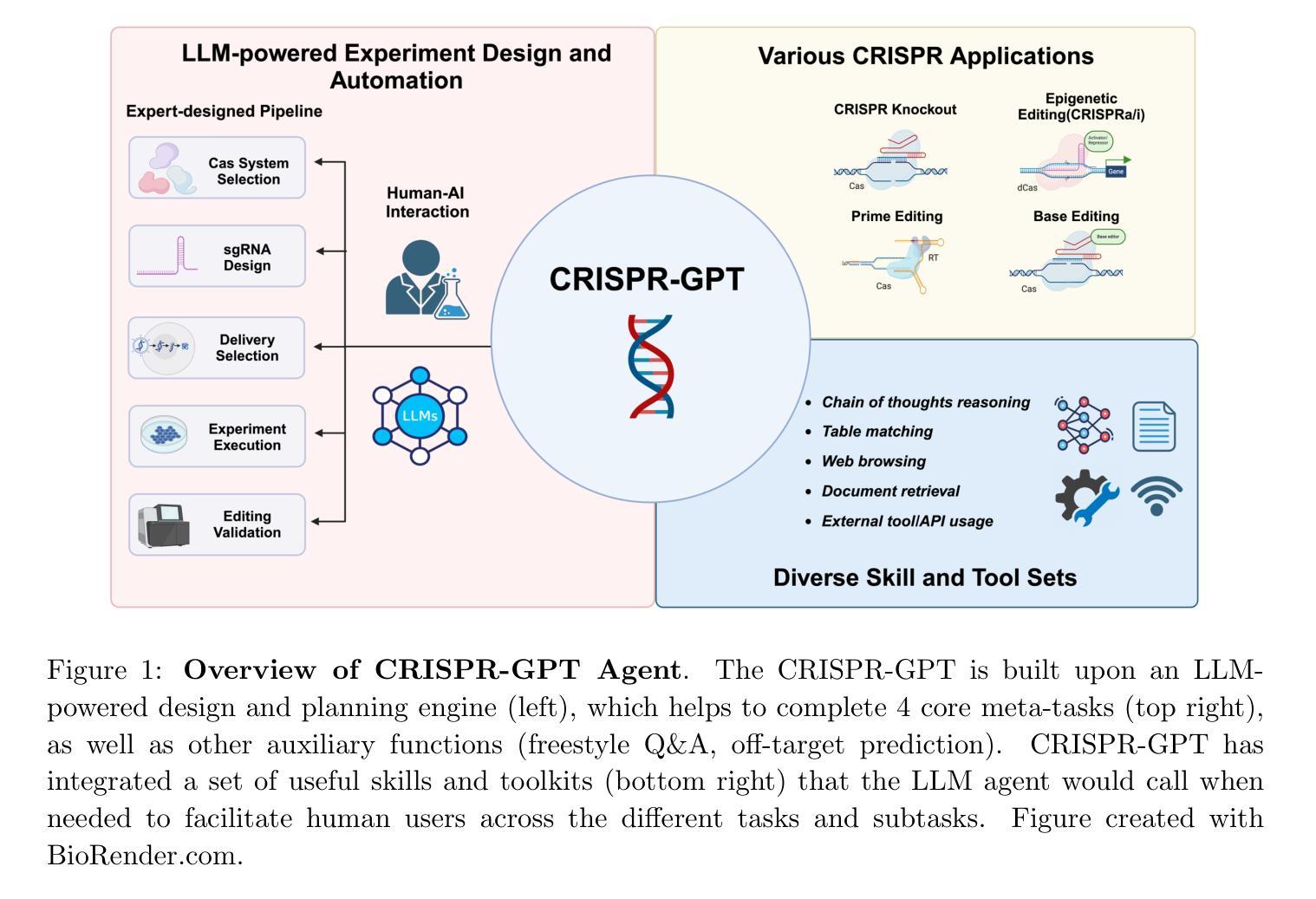
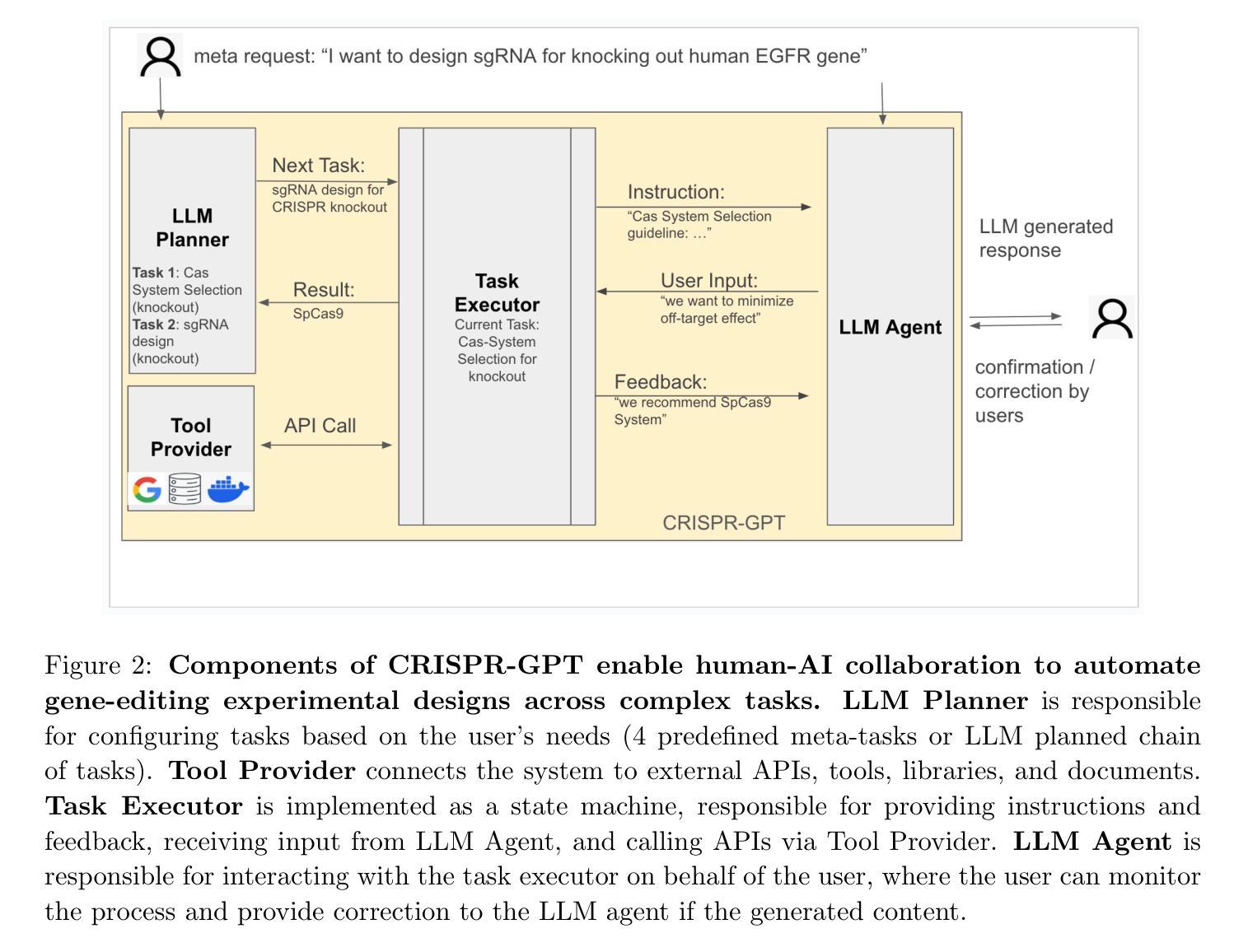
CRISPR-GPT for Agentic Automation of Gene-editing Experiments
Authors:Yuanhao Qu, Kaixuan Huang, Ming Yin, Kanghong Zhan, Dyllan Liu, Di Yin, Henry C. Cousins, William A. Johnson, Xiaotong Wang, Mihir Shah, Russ B. Altman, Denny Zhou, Mengdi Wang, Le Cong
The introduction of genome engineering technology has transformed biomedical research, making it possible to make precise changes to genetic information. However, creating an efficient gene-editing system requires a deep understanding of CRISPR technology, and the complex experimental systems under investigation. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in various tasks, they often lack specific knowledge and struggle to accurately solve biological design problems. In this work, we introduce CRISPR-GPT, an LLM agent augmented with domain knowledge and external tools to automate and enhance the design process of CRISPR-based gene-editing experiments. CRISPR-GPT leverages the reasoning ability of LLMs to facilitate the process of selecting CRISPR systems, designing guide RNAs, recommending cellular delivery methods, drafting protocols, and designing validation experiments to confirm editing outcomes. We showcase the potential of CRISPR-GPT for assisting non-expert researchers with gene-editing experiments from scratch and validate the agent’s effectiveness in a real-world use case. Furthermore, we explore the ethical and regulatory considerations associated with automated gene-editing design, highlighting the need for responsible and transparent use of these tools. Our work aims to bridge the gap between beginner biological researchers and CRISPR genome engineering techniques, and demonstrate the potential of LLM agents in facilitating complex biological discovery tasks. The published version of this draft is available at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01463-z.
基因组工程技术的引入已经改变了生物医学研究,使得对遗传信息进行精确改变成为可能。然而,创建一个高效的基因编辑系统需要深入了解CRISPR技术以及复杂的实验系统。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中表现出潜力,但它们通常缺乏特定知识,在解决生物设计问题时难以做到精确。在这项工作中,我们介绍了CRISPR-GPT,这是一个结合了领域知识和外部工具的LLM代理,旨在自动化并增强CRISPR基因编辑实验的设计过程。CRISPR-GPT利用LLM的推理能力,促进选择CRISPR系统、设计引导RNA、推荐细胞传递方法、起草协议以及设计验证实验来确认编辑结果的过程。我们展示了CRISPR-GPT在非专家研究人员中进行基因编辑实验方面的潜力,并通过实际使用案例验证了该代理的有效性。此外,我们探讨了与自动化基因编辑设计相关的伦理和监管问题,强调这些工具需要负责任和透明地使用。我们的工作旨在缩小初级生物研究人员与CRISPR基因组工程技术之间的差距,并展示LLM代理在促进复杂生物学发现任务中的潜力。本文的发布版本可通过https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01463-z获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Nature Biomedical Engineering
Summary
基因编辑技术引入生物医学研究,为精准改变遗传信息提供了可能。本研究提出CRISPR-GPT,这是一种结合领域知识和外部工具的大型语言模型代理,旨在自动化并优化CRISPR基因编辑实验设计过程。CRISPR-GPT能够利用大型语言模型的推理能力协助选择CRISPR系统、设计导向RNA、推荐细胞传递方法、起草协议以及设计验证实验以确认编辑结果。此模型展现出在真实案例中协助非专业研究人员进行基因编辑实验的潜力,并探讨了自动化基因编辑设计的伦理和法规考量。本研究旨在缩小初学者与CRISPR基因组工程技术之间的差距,并展示大型语言模型代理在促进复杂生物学发现任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 基因编辑技术已深刻改变生物医学研究,CRISPR技术是其中的核心部分。
- CRISPR-GPT是一个结合了领域知识和外部工具的大型语言模型代理,旨在优化CRISPR基因编辑实验的设计过程。
- CRISPR-GPT能协助选择CRISPR系统、设计导向RNA、推荐细胞传递方法、起草协议以及设计验证实验。
- CRISPR-GPT在非专业研究人员中的实际应用得到展示,验证了其在真实案例中的有效性。
- 此研究探讨了自动化基因编辑设计的伦理和法规考量。
- CRISPR-GPT旨在缩小初学者与复杂的基因组工程技术之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图