⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
CineScale: Free Lunch in High-Resolution Cinematic Visual Generation
Authors:Haonan Qiu, Ning Yu, Ziqi Huang, Paul Debevec, Ziwei Liu
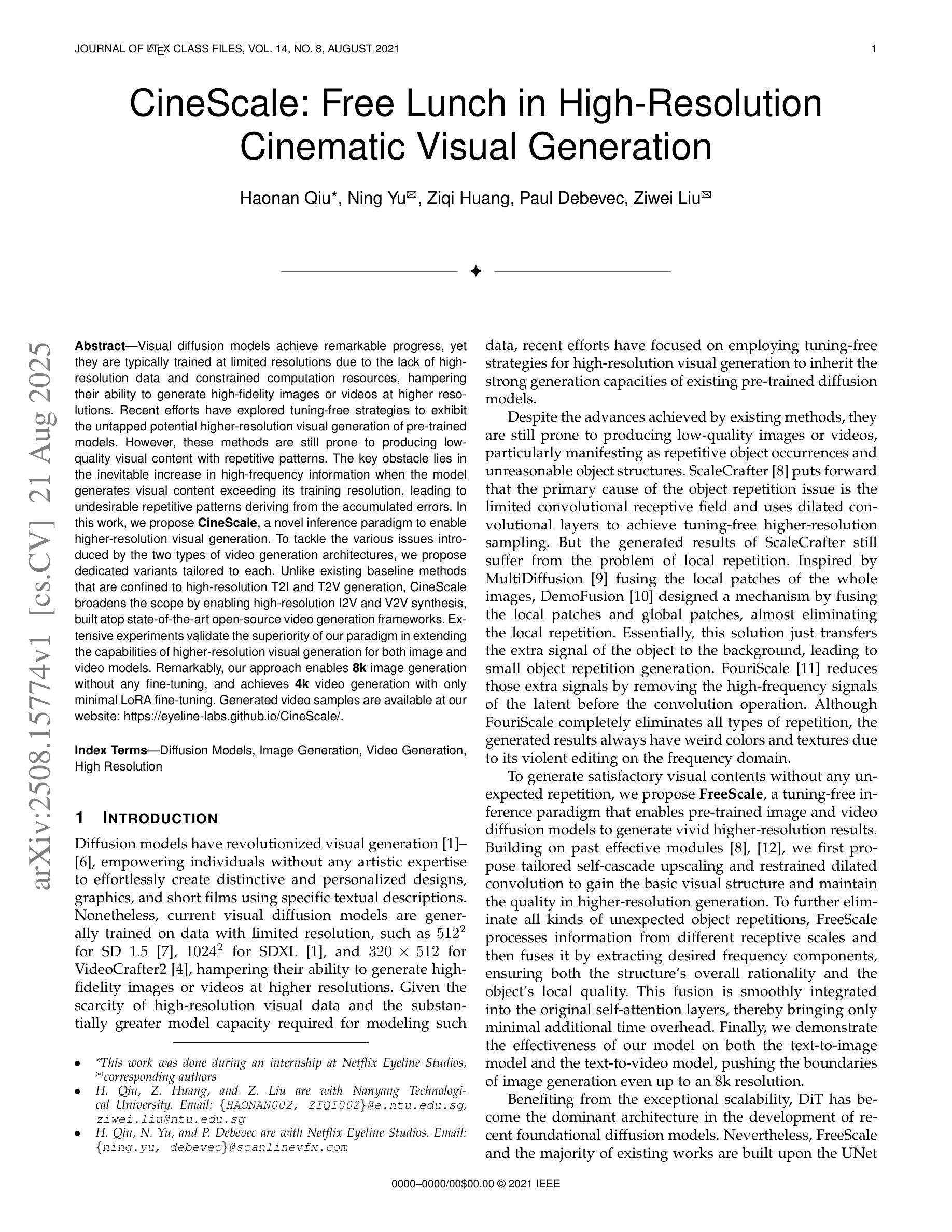
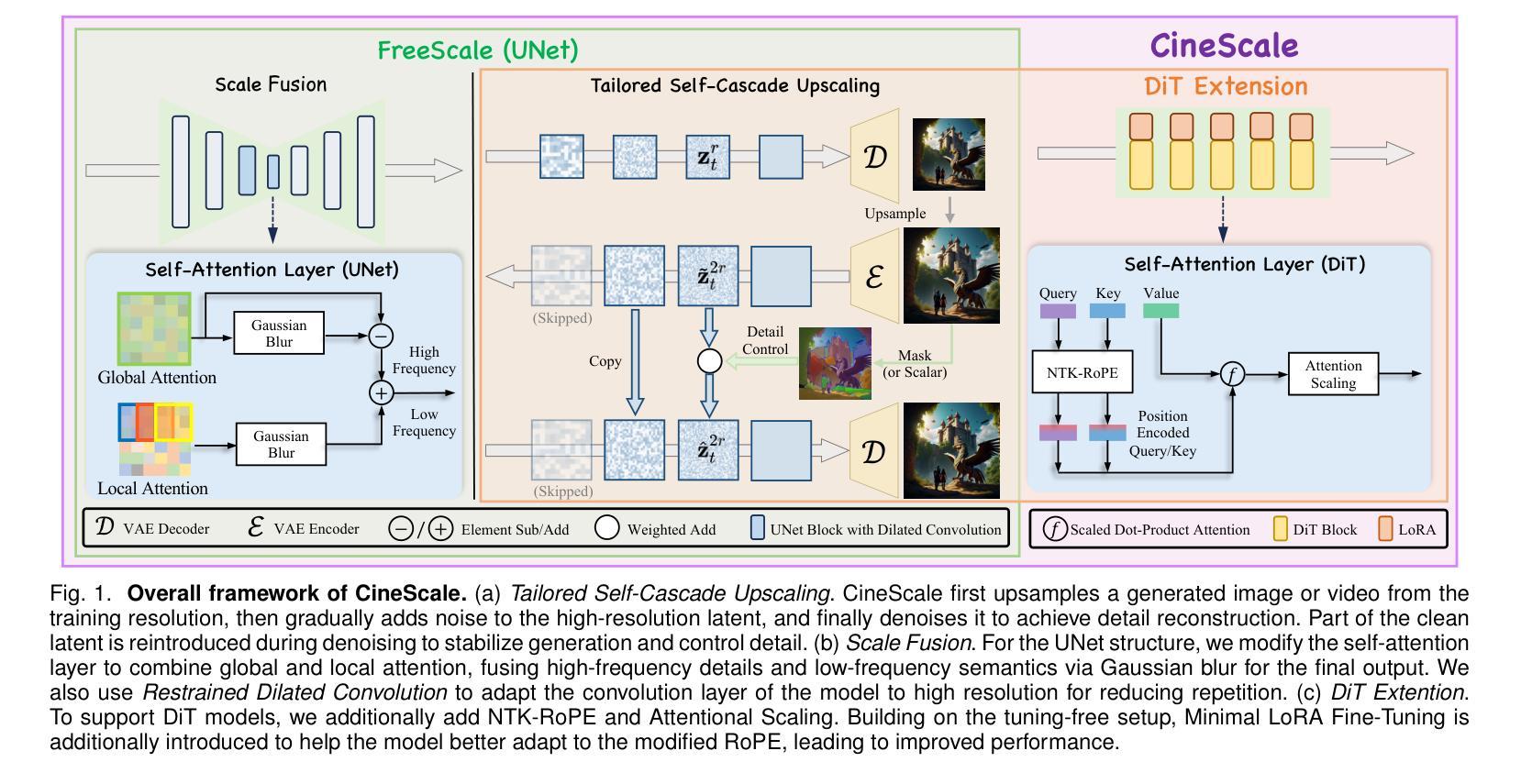
Visual diffusion models achieve remarkable progress, yet they are typically trained at limited resolutions due to the lack of high-resolution data and constrained computation resources, hampering their ability to generate high-fidelity images or videos at higher resolutions. Recent efforts have explored tuning-free strategies to exhibit the untapped potential higher-resolution visual generation of pre-trained models. However, these methods are still prone to producing low-quality visual content with repetitive patterns. The key obstacle lies in the inevitable increase in high-frequency information when the model generates visual content exceeding its training resolution, leading to undesirable repetitive patterns deriving from the accumulated errors. In this work, we propose CineScale, a novel inference paradigm to enable higher-resolution visual generation. To tackle the various issues introduced by the two types of video generation architectures, we propose dedicated variants tailored to each. Unlike existing baseline methods that are confined to high-resolution T2I and T2V generation, CineScale broadens the scope by enabling high-resolution I2V and V2V synthesis, built atop state-of-the-art open-source video generation frameworks. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of our paradigm in extending the capabilities of higher-resolution visual generation for both image and video models. Remarkably, our approach enables 8k image generation without any fine-tuning, and achieves 4k video generation with only minimal LoRA fine-tuning. Generated video samples are available at our website: https://eyeline-labs.github.io/CineScale/.
视觉扩散模型取得了显著的进步,但由于缺乏高分辨率数据和受限的计算资源,它们通常只在有限的分辨率上进行训练,这阻碍了它们生成更高分辨率的高保真图像或视频的能力。最近的研究致力于探索无需调整的策略,以展示预训练模型在更高分辨率视觉生成方面的潜力。然而,这些方法仍然容易产生重复模式的低质量视觉内容。关键障碍在于当模型生成超过其训练分辨率的视觉内容时,高频信息的必然增加会导致由累积误差引起的不可取的重复模式。在这项工作中,我们提出了CineScale,这是一种新型推理范式,可实现更高分辨率的视觉生成。为了解决由两种视频生成架构引入的各种问题,我们针对每种架构提出了专用变体。与仅限于高分辨率T2I和T2V生成的现有基准方法不同,CineScale通过支持高分辨率I2V和V2V合成来扩大范围,建立在最新开源视频生成框架之上。大量实验验证了我们的范式在扩展图像和视频模型的高分辨率生成能力方面的优越性。值得注意的是,我们的方法能够在无需微调的情况下实现8k图像生成,并且只需进行微小的LoRA微调即可实现4k视频生成。生成的视频样本可在我们的网站上进行查看:https://eyeline-labs.github.io/CineScale/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CineScale is an extended work of FreeScale (ICCV 2025). Project Page: https://eyeline-labs.github.io/CineScale/, Code Repo: https://github.com/Eyeline-Labs/CineScale
Summary
本文提出一种名为CineScale的新型推理范式,旨在实现更高分辨率的视觉生成。该范式解决了由于模型生成超过训练分辨率的视觉内容时高频信息不可避免增加而导致的问题,避免了产生重复模式。CineScale不仅限于高分辨率的T2I和T2V生成,还能实现高分辨率的I2V和V2V合成。实验证明,该范式在图像和视频模型的更高分辨率视觉生成能力方面具有优越性,能够在不进行微调的情况下生成8k图像,并且只需最小的LoRA微调即可实现4k视频生成。
Key Takeaways
- CineScale是一种新型推理范式,旨在实现更高分辨率的视觉生成。
- 该方法解决了在生成超过训练分辨率的视觉内容时产生的重复模式问题。
- CineScale不仅适用于高分辨率的T2I和T2V生成,还支持高分辨率的I2V和V2V合成。
- 实验证明CineScale在图像和视频模型的更高分辨率视觉生成方面具有优越性。
- CineScale能够在不进行微调的情况下生成8k图像。
- 只需最小的LoRA微调,CineScale即可实现4k视频生成。
点此查看论文截图



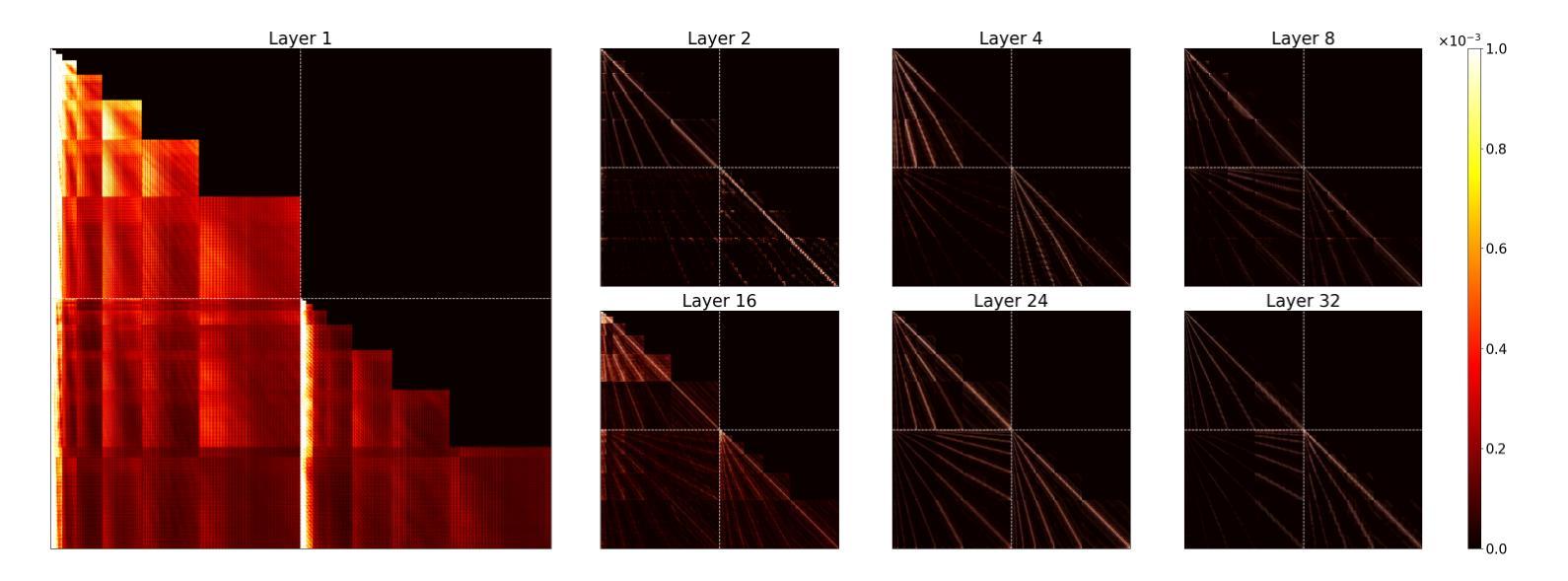
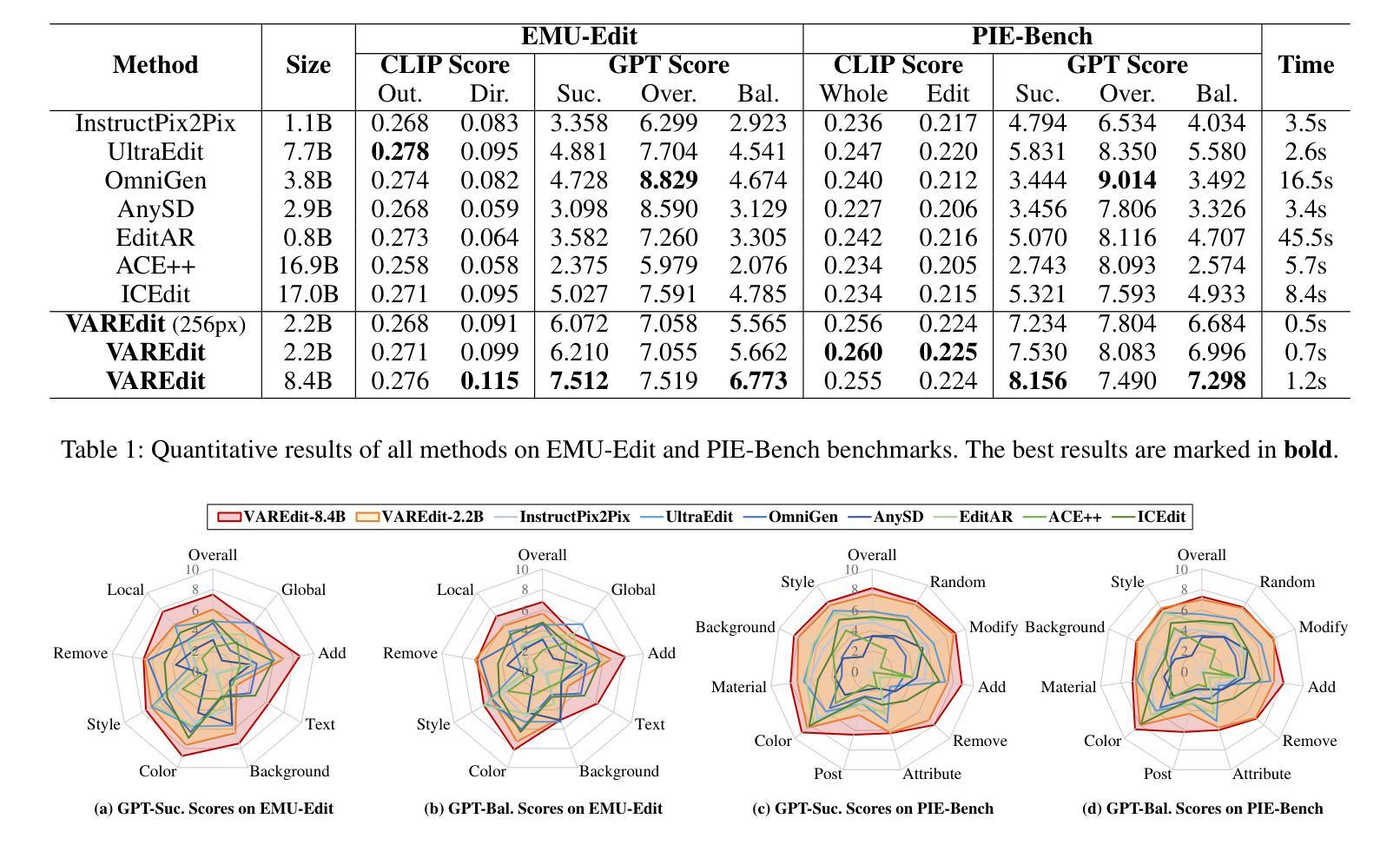
Visual Autoregressive Modeling for Instruction-Guided Image Editing
Authors:Qingyang Mao, Qi Cai, Yehao Li, Yingwei Pan, Mingyue Cheng, Ting Yao, Qi Liu, Tao Mei
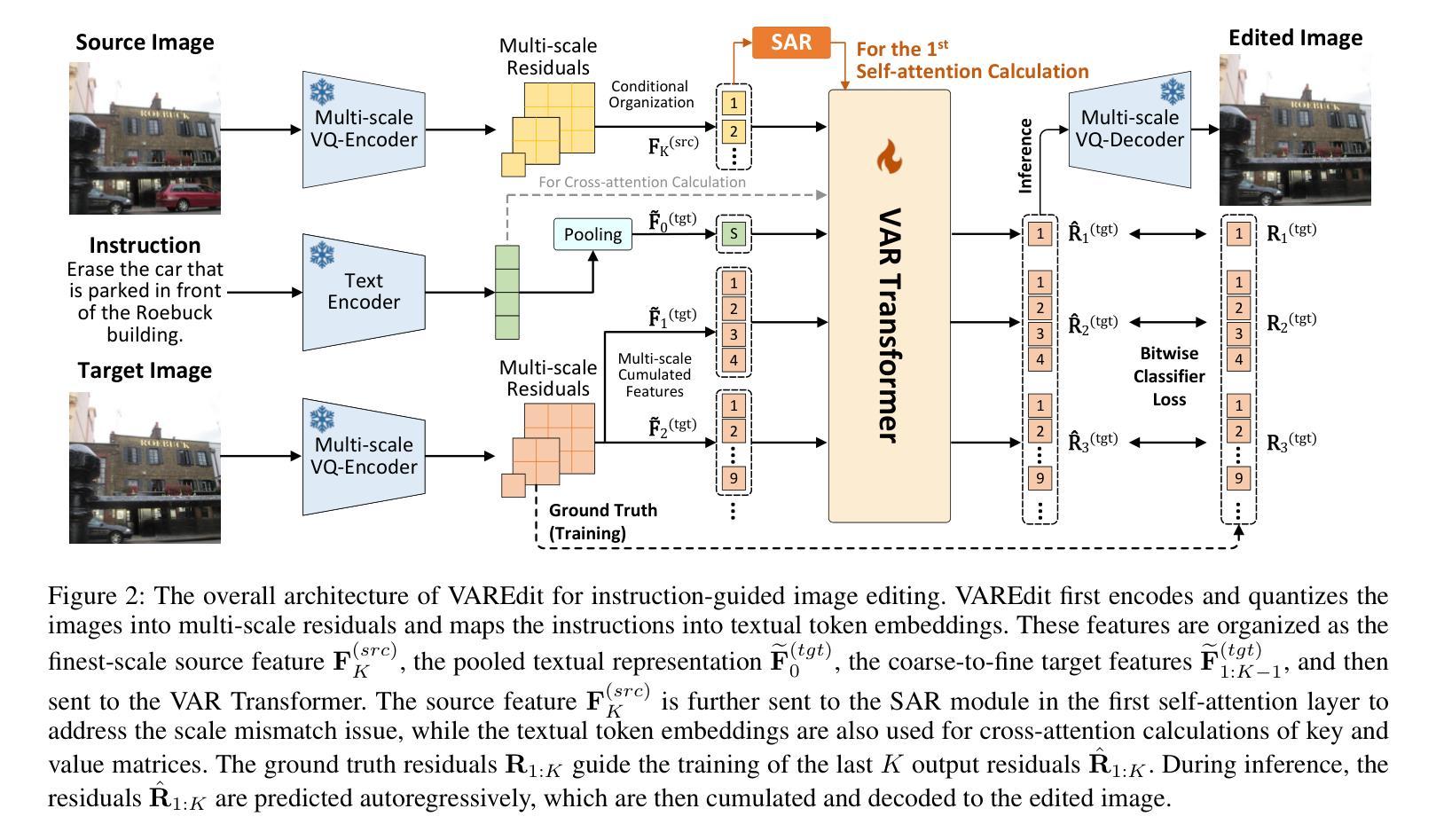
Recent advances in diffusion models have brought remarkable visual fidelity to instruction-guided image editing. However, their global denoising process inherently entangles the edited region with the entire image context, leading to unintended spurious modifications and compromised adherence to editing instructions. In contrast, autoregressive models offer a distinct paradigm by formulating image synthesis as a sequential process over discrete visual tokens. Their causal and compositional mechanism naturally circumvents the adherence challenges of diffusion-based methods. In this paper, we present VAREdit, a visual autoregressive (VAR) framework that reframes image editing as a next-scale prediction problem. Conditioned on source image features and text instructions, VAREdit generates multi-scale target features to achieve precise edits. A core challenge in this paradigm is how to effectively condition the source image tokens. We observe that finest-scale source features cannot effectively guide the prediction of coarser target features. To bridge this gap, we introduce a Scale-Aligned Reference (SAR) module, which injects scale-matched conditioning information into the first self-attention layer. VAREdit demonstrates significant advancements in both editing adherence and efficiency. On standard benchmarks, it outperforms leading diffusion-based methods by 30%+ higher GPT-Balance score. Moreover, it completes a $512\times512$ editing in 1.2 seconds, making it 2.2$\times$ faster than the similarly sized UltraEdit. The models are available at https://github.com/HiDream-ai/VAREdit.
近期扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的进展为指令导向的图像编辑带来了显著的视觉保真度。然而,其全局去噪过程固有地将编辑区域与整个图像上下文纠缠在一起,导致出现意外的虚假修改以及不符合编辑指令的情况。相比之下,自回归模型(Autoregressive Models)通过为离散视觉符号制定一个序列过程来提供独特的范式,实现了图像合成。它们的因果和组合机制自然地避免了基于扩散的方法的遵循挑战。在本文中,我们提出了VAREdit,一个视觉自回归(VAR)框架,它将图像编辑重新定义为下一个尺度的预测问题。在源图像特征和文本指令的条件下,VAREdit生成多尺度目标特征来实现精确编辑。在此范式中的核心挑战是如何有效地调节源图像符号。我们发现最精细尺度的源特征无法有效地指导较粗糙目标特征的预测。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了尺度对齐参考(SAR)模块,该模块将尺度匹配的调节信息注入到第一层自我关注中。VAREdit在编辑的遵循性和效率方面都取得了显著的进步。在标准基准测试中,它的GPT平衡得分比领先的扩散模型高出30%以上。此外,它能在1.2秒内完成一个512x512的编辑任务,相比之下比相同规模的UltraEdit快2.2倍。模型可以在https://github.com/HiDream-ai/VAREdit找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Source codes and models are available at https://github.com/HiDream-ai/VAREdit
Summary
本文介绍了基于视觉自回归(VAR)框架的图像编辑技术VAREdit。该技术将图像编辑重新定义为下一个尺度预测问题,通过源图像特征和文本指令生成多尺度目标特征来实现精确编辑。为弥补最精细尺度源特征无法有效引导较粗目标特征预测的缺陷,引入了规模对齐参考(SAR)模块,将规模匹配的调节信息注入第一层自注意力中。相较于领先的扩散模型,VAREdit在编辑贴合度和效率上具有显著优势。它在标准基准测试上的GPT-Balance得分高出30%以上,且完成一次512x512的编辑仅需1.2秒,相较于类似规模的UltraEdit加速约两倍。
Key Takeaways
- VAREdit利用视觉自回归框架进行图像编辑,将编辑定义为下一个尺度预测问题。
- VAREdit通过结合源图像特征和文本指令生成多尺度目标特征,实现精确编辑。
- 引入规模对齐参考(SAR)模块,以解决最精细尺度源特征无法有效引导较粗目标特征预测的问题。
- VAREdit在编辑贴合度和效率方面显著优于现有扩散模型。
- VAREdit在标准测试中的GPT-Balance得分高出30%以上。
- VAREdit完成一次512x512的编辑仅需1.2秒,相较于类似规模的编辑器,效率更高。
点此查看论文截图


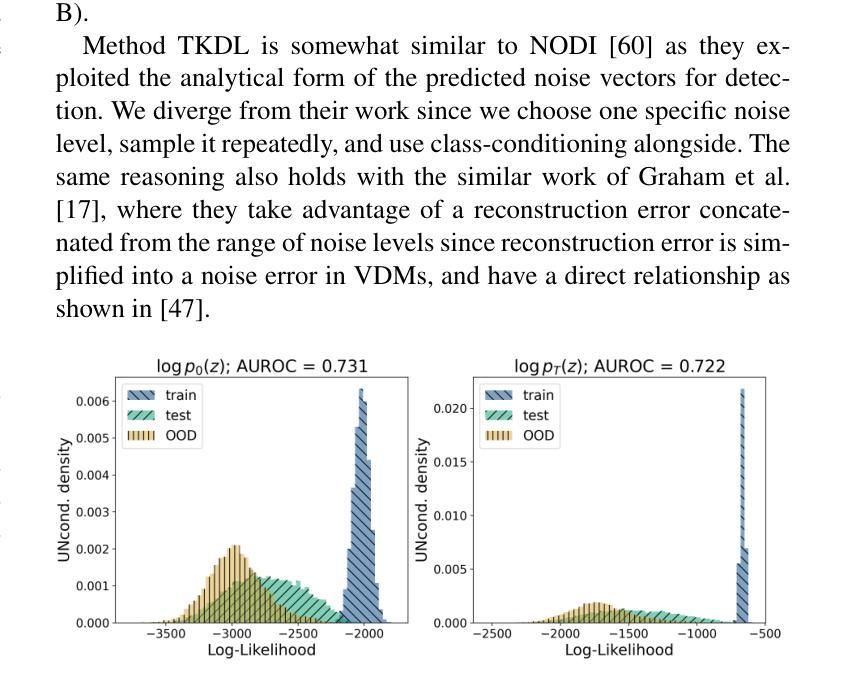
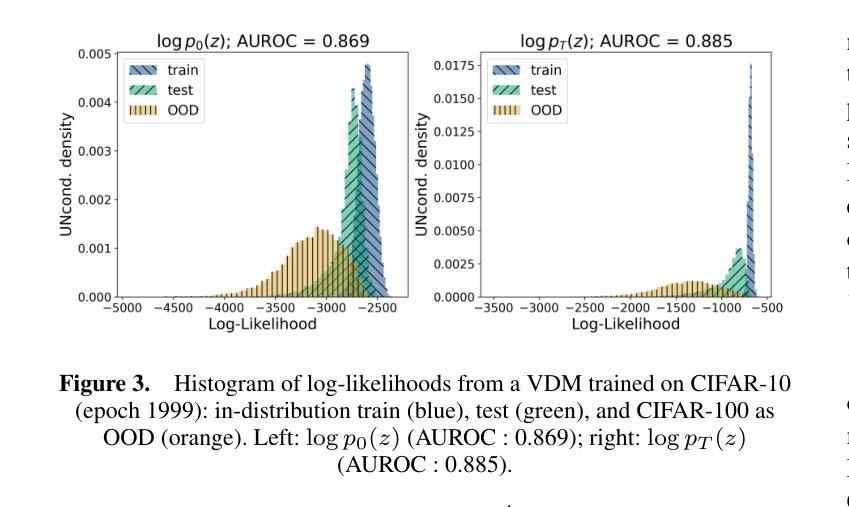
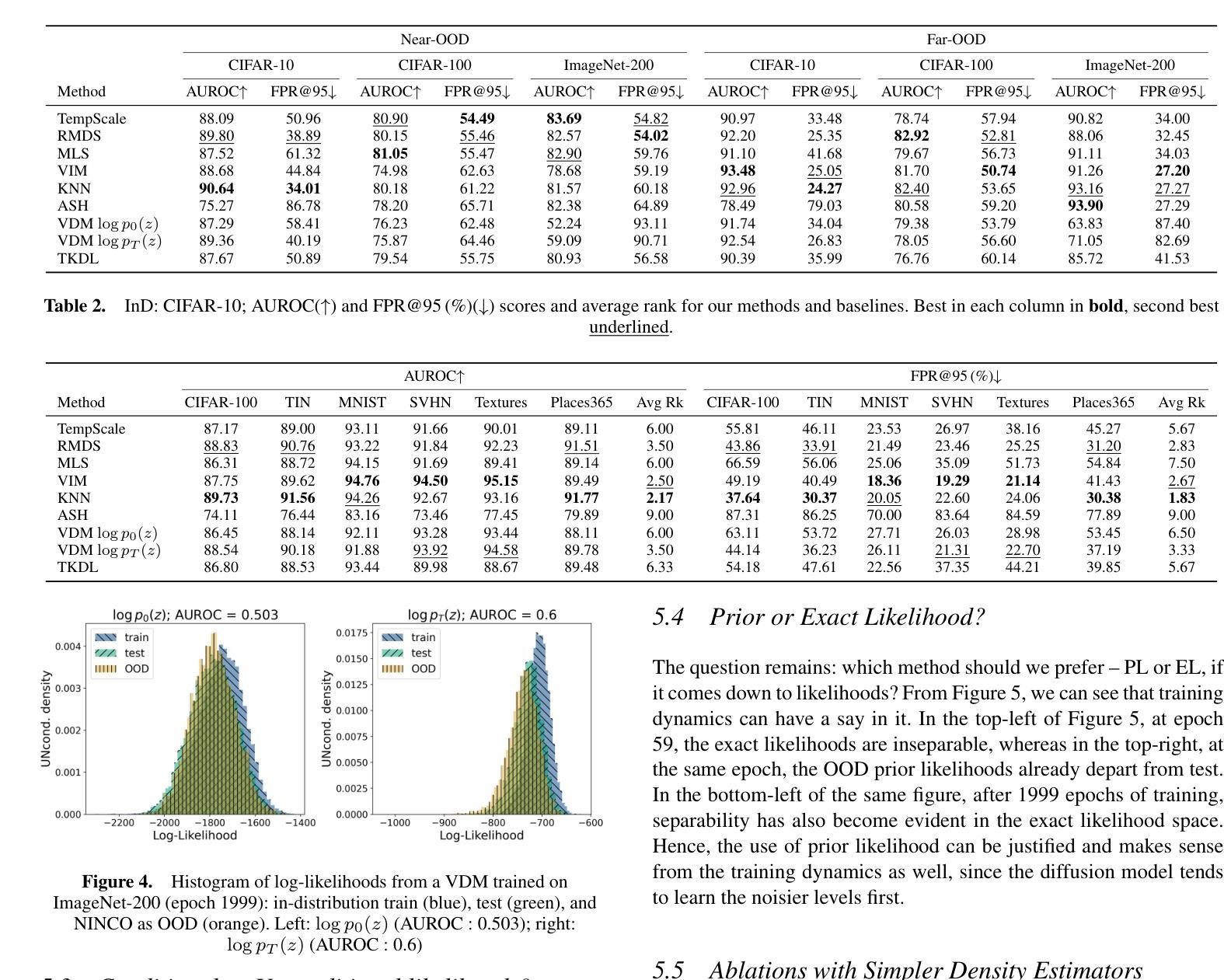
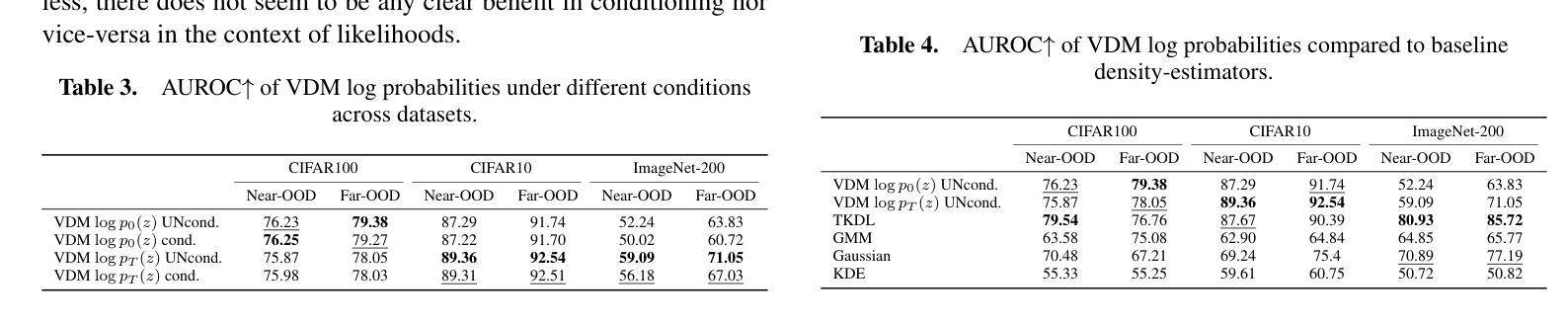
Probability Density from Latent Diffusion Models for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Joonas Järve, Karl Kaspar Haavel, Meelis Kull
Despite rapid advances in AI, safety remains the main bottleneck to deploying machine-learning systems. A critical safety component is out-of-distribution detection: given an input, decide whether it comes from the same distribution as the training data. In generative models, the most natural OOD score is the data likelihood. Actually, under the assumption of uniformly distributed OOD data, the likelihood is even the optimal OOD detector, as we show in this work. However, earlier work reported that likelihood often fails in practice, raising doubts about its usefulness. We explore whether, in practice, the representation space also suffers from the inability to learn good density estimation for OOD detection, or if it is merely a problem of the pixel space typically used in generative models. To test this, we trained a Variational Diffusion Model not on images, but on the representation space of a pre-trained ResNet-18 to assess the performance of our likelihood-based detector in comparison to state-of-the-art methods from the OpenOOD suite.
尽管人工智能领域取得了飞速发展,安全仍是部署机器学习系统的主瓶颈。一个关键的安全组件是异常检测:给定输入,确定其是否来自与训练数据相同的分布。在生成模型中,最自然的异常值分数是数据概率。实际上,在假设异常值数据均匀分布的情况下,概率甚至是最佳的异常检测器,正如我们在本工作中所展示的。然而,早期的研究报告指出,在实践中概率通常会失效,这引发了对其有用性的怀疑。我们探索的是在实践中,表示空间是否也因无法进行良好的密度估计来进行异常检测而受到影响,还是仅仅是因为生成模型中通常使用的像素空间的问题。为了测试这一点,我们训练了一个变分扩散模型,不使用图像,而是使用预训练的ResNet-1
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECAI 2025
Summary
尽管人工智能发展迅速,但安全仍是部署机器学习系统的主瓶颈。关键的安全组件是分布外检测:给定输入,确定其是否来自与训练数据相同的分布。在生成模型中,最自然的OOD分数是数据可能性。实际上,在假设OOD数据均匀分布的情况下,可能性甚至是最佳的OOD检测器,我们在工作中也证明了这一点。然而,早期的研究报告指出,在实际操作中可能性经常会失效,引发了对其实用性的质疑。我们探究在实操中是否是表示空间遭受了无法学习良好的密度估计以进行OOD检测的困扰,还是仅仅是生成模型中通常使用的像素空间的问题。为了测试这一点,我们训练了一个变分扩散模型,不是对图像进行训练,而是对预训练ResNet-18的表示空间进行评估,以比较基于可能性的检测器与OpenOOD套件中的最新方法的性能。
Key Takeaways
- AI的快速发展面临安全瓶颈,尤其是部署机器学习系统的安全。
- 分布外检测是机器学习安全中的关键组件,用于判断输入是否来自训练数据分布。
- 在生成模型中,数据可能性是最自然的OOD检测指标,但在实践中经常被发现在性能上的问题。
- 变分扩散模型在表示空间而非图像上进行训练,以评估基于可能性的检测器的性能。
- 现有的对可能性的质疑部分源于实操中的问题,可能与表示空间或像素空间的特性有关。
- 本研究通过对比实验来探究在表示空间中进行OOD检测是否也会遭遇密度估计问题。
点此查看论文截图
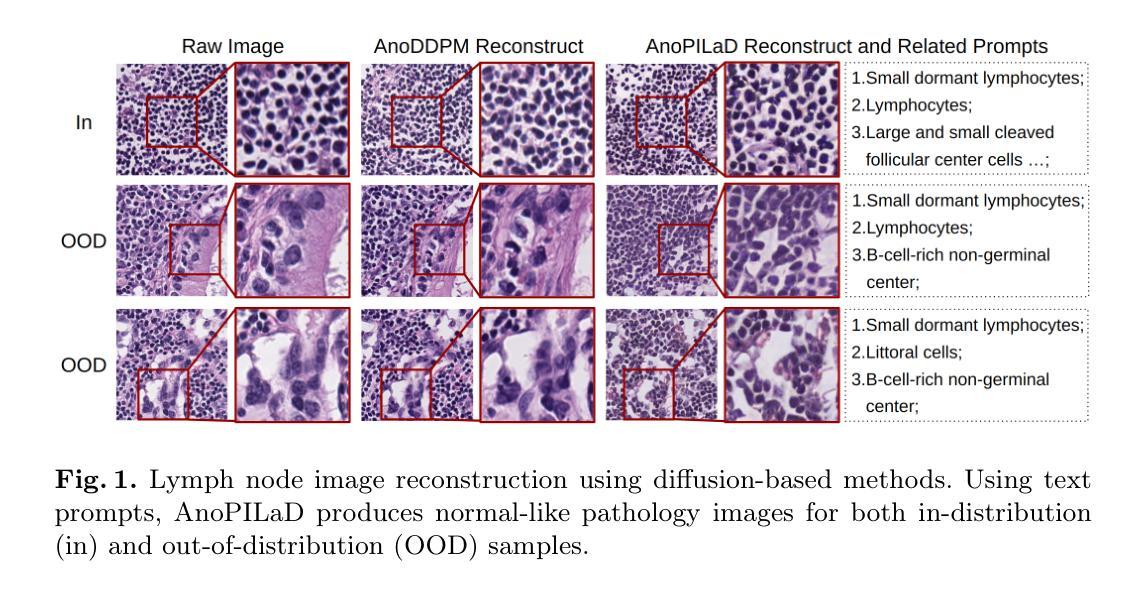
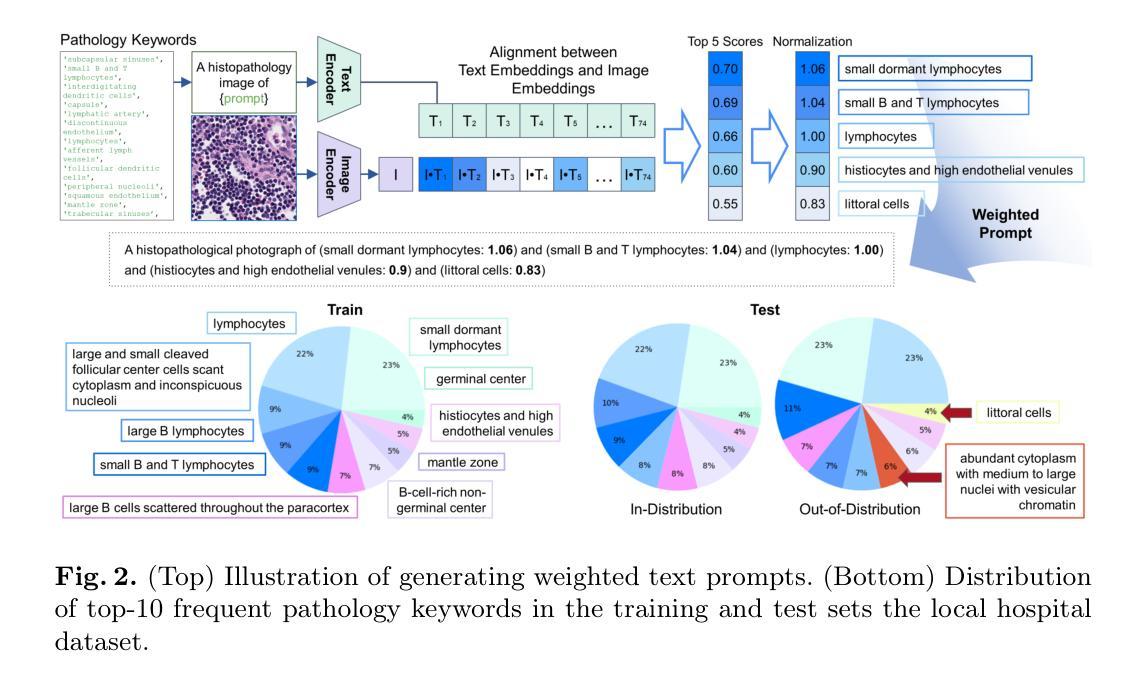
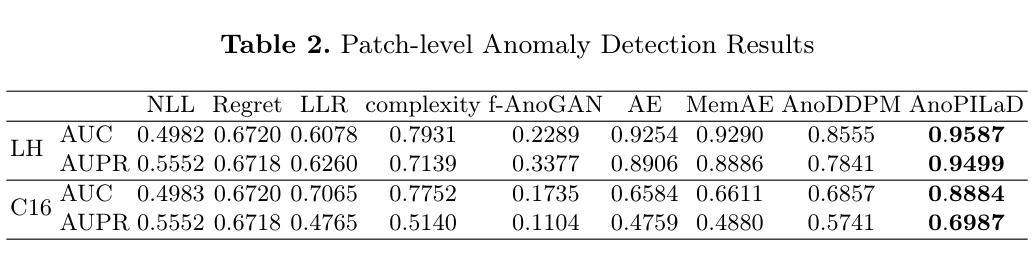
Pathology-Informed Latent Diffusion Model for Anomaly Detection in Lymph Node Metastasis
Authors:Jiamu Wang, Keunho Byeon, Jinsol Song, Anh Nguyen, Sangjeong Ahn, Sung Hak Lee, Jin Tae Kwak
Anomaly detection is an emerging approach in digital pathology for its ability to efficiently and effectively utilize data for disease diagnosis. While supervised learning approaches deliver high accuracy, they rely on extensively annotated datasets, suffering from data scarcity in digital pathology. Unsupervised anomaly detection, however, offers a viable alternative by identifying deviations from normal tissue distributions without requiring exhaustive annotations. Recently, denoising diffusion probabilistic models have gained popularity in unsupervised anomaly detection, achieving promising performance in both natural and medical imaging datasets. Building on this, we incorporate a vision-language model with a diffusion model for unsupervised anomaly detection in digital pathology, utilizing histopathology prompts during reconstruction. Our approach employs a set of pathology-related keywords associated with normal tissues to guide the reconstruction process, facilitating the differentiation between normal and abnormal tissues. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conduct experiments on a gastric lymph node dataset from a local hospital and assess its generalization ability under domain shift using a public breast lymph node dataset. The experimental results highlight the potential of the proposed method for unsupervised anomaly detection across various organs in digital pathology. Code: https://github.com/QuIIL/AnoPILaD.
异常检测是数字病理中一个新兴的方法,因为它能够高效且有效地利用数据进行疾病诊断。虽然监督学习方法可以提供较高的准确性,但它们依赖于大量标注的数据集,而在数字病理中常常面临数据稀缺的问题。然而,无监督的异常检测提供了一个可行的替代方案,它可以通过识别正常组织分布中的偏差来进行异常检测,无需详尽的标注。最近,去噪扩散概率模型在无监督异常检测中获得了普及,在自然和医学成像数据集上取得了有希望的性能。在此基础上,我们将一个视觉语言模型与扩散模型相结合,用于数字病理中的无监督异常检测,并在重建过程中利用病理提示。我们的方法采用与正常组织相关的一组病理学关键词来引导重建过程,从而便于区分正常组织和异常组织。为了评估所提出方法的有效性,我们在当地医院的胃淋巴结数据集上进行了实验,并使用公共的乳腺淋巴结数据集来评估其在领域迁移下的泛化能力。实验结果突出了所提出方法在数字病理中用于各种器官的无监督异常检测的潜力。代码地址:https://github.com/QuIIL/AnoPILaD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数字病理中的异常检测新兴方法能有效利用数据进行疾病诊断。监督学习方法虽准确但依赖大量标注数据,在数字病理中面临数据稀缺问题。无监督异常检测通过识别正常组织分布的偏差,无需详尽标注,提供了可行替代方案。近期,降噪扩散概率模型在无监督异常检测中受到关注,在自然和医学成像数据集上表现出良好性能。在此基础上,我们结合视觉语言模型和扩散模型进行数字病理的无监督异常检测,重建过程中利用组织病理学提示。通过一系列与正常组织相关的病理学关键词引导重建过程,有助于区分正常组织与异常组织。对本地医院的胃淋巴节点数据集进行试验并对公开乳腺淋巴节点数据集进行跨域评估,凸显了该方法的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 异常检测是数字病理学中的新兴方法,用于高效且有效地利用数据进行疾病诊断。
- 监督学习方法在数字病理中面临数据稀缺问题。
- 无监督异常检测通过识别正常组织分布的偏差,为数字病理提供了可行替代方案。
- 降噪扩散概率模型在无监督异常检测中受到关注,表现良好。
- 结合视觉语言模型和扩散模型进行数字病理的无监督异常检测,利用组织病理学提示提升检测准确性。
- 通过关键词引导重建过程,有助于区分正常组织与异常组织。
点此查看论文截图


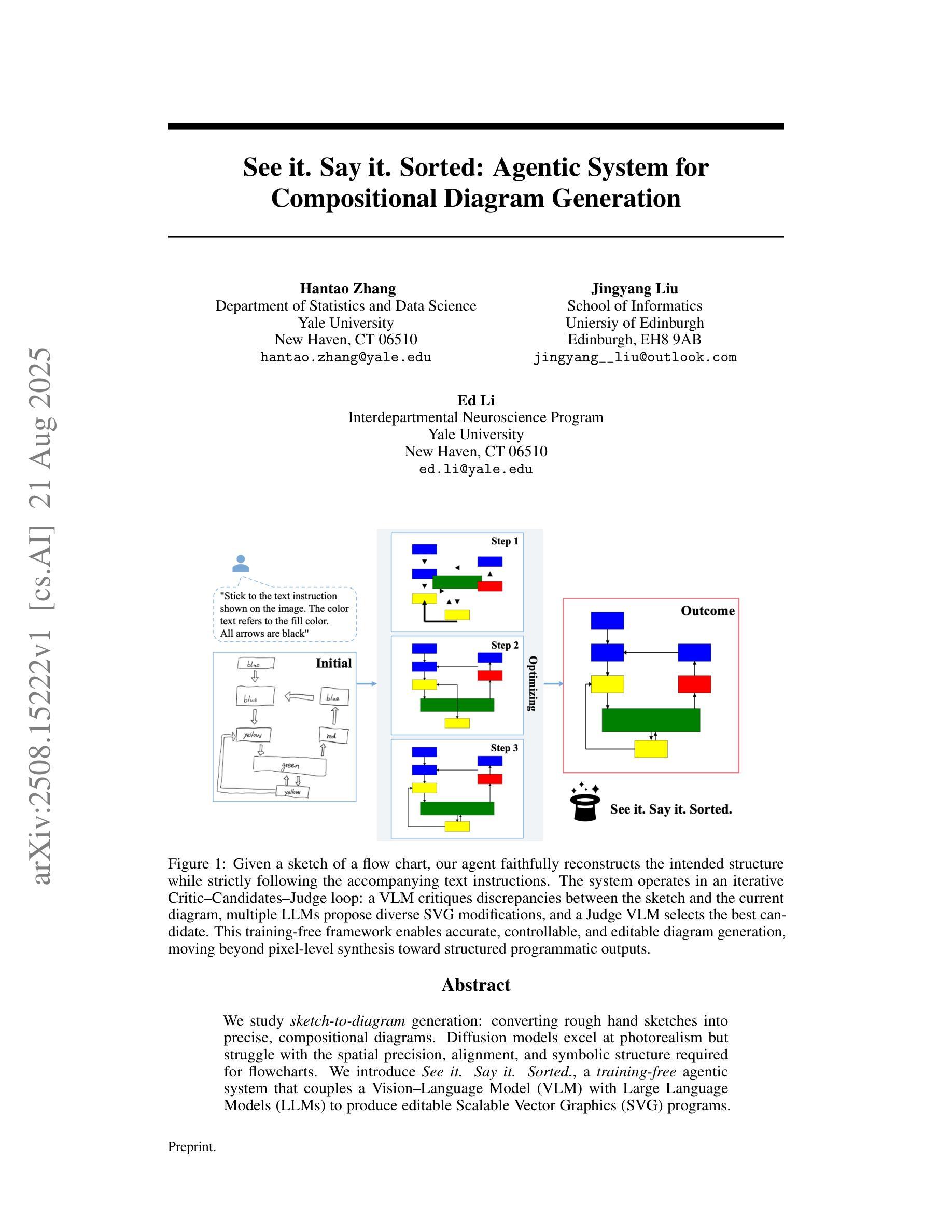
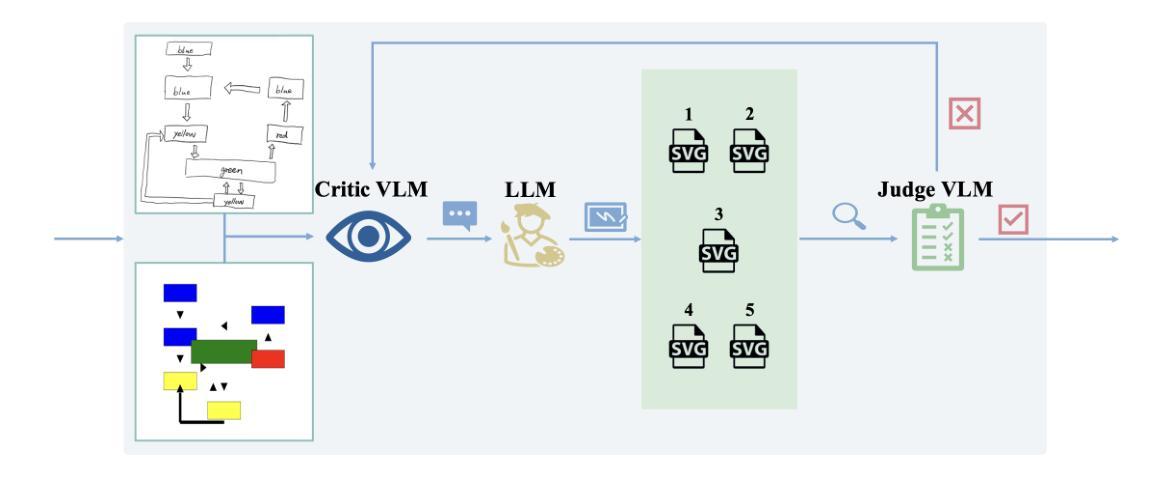
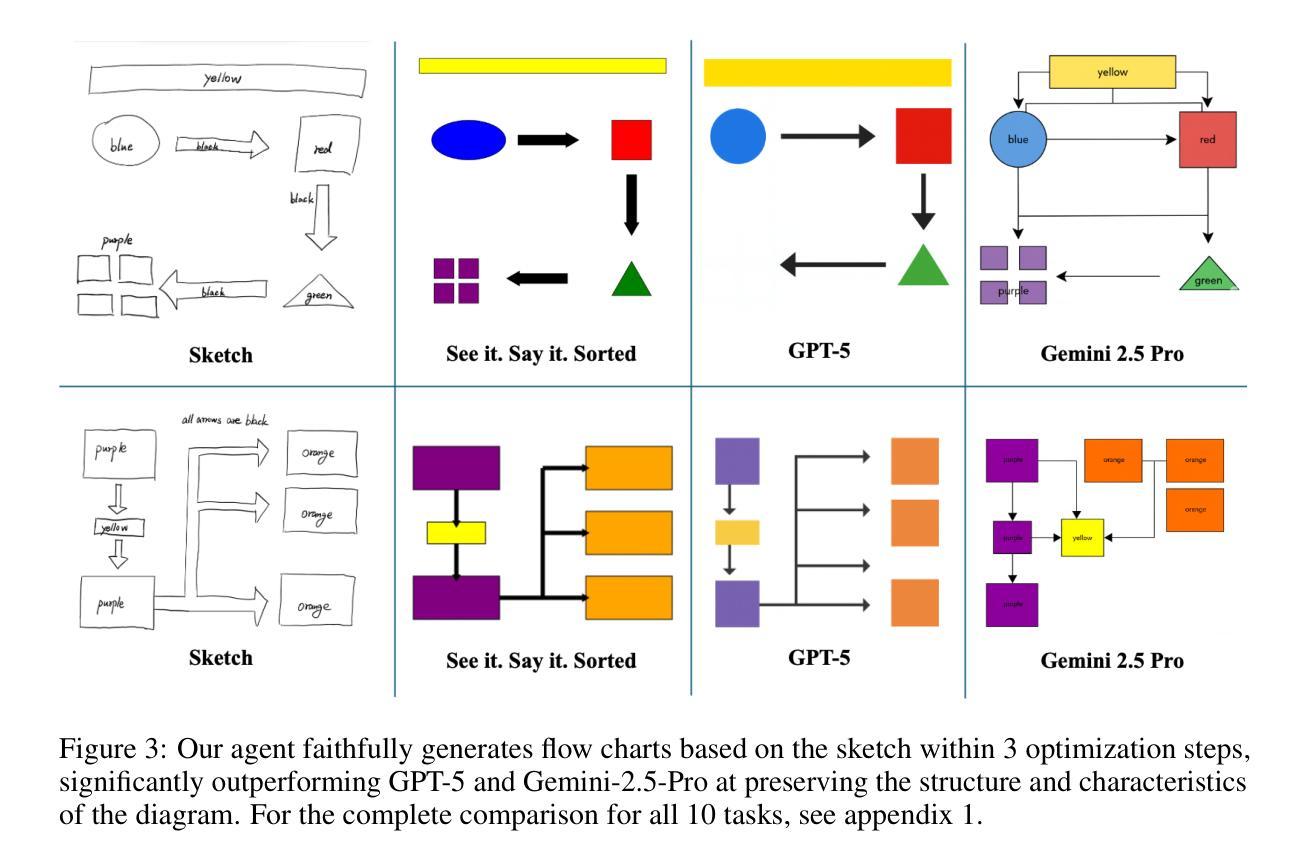
See it. Say it. Sorted: Agentic System for Compositional Diagram Generation
Authors:Hantao Zhang, Jingyang Liu, Ed Li
We study sketch-to-diagram generation: converting rough hand sketches into precise, compositional diagrams. Diffusion models excel at photorealism but struggle with the spatial precision, alignment, and symbolic structure required for flowcharts. We introduce See it. Say it. Sorted., a training-free agentic system that couples a Vision-Language Model (VLM) with Large Language Models (LLMs) to produce editable Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) programs. The system runs an iterative loop in which a Critic VLM proposes a small set of qualitative, relational edits; multiple candidate LLMs synthesize SVG updates with diverse strategies (conservative->aggressive, alternative, focused); and a Judge VLM selects the best candidate, ensuring stable improvement. This design prioritizes qualitative reasoning over brittle numerical estimates, preserves global constraints (e.g., alignment, connectivity), and naturally supports human-in-the-loop corrections. On 10 sketches derived from flowcharts in published papers, our method more faithfully reconstructs layout and structure than two frontier closed-source image generation LLMs (GPT-5 and Gemini-2.5-Pro), accurately composing primitives (e.g., multi-headed arrows) without inserting unwanted text. Because outputs are programmatic SVGs, the approach is readily extensible to presentation tools (e.g., PowerPoint) via APIs and can be specialized with improved prompts and task-specific tools. The codebase is open-sourced at https://github.com/hantaoZhangrichard/see_it_say_it_sorted.git.
我们研究了草图到图表生成的任务,即将粗略的手绘草图转化为精确、组合式的图表。扩散模型在照片写实方面表现出色,但在流程图所需的空间精度、对齐和符号结构方面遇到了困难。我们推出了“所见即所说.已排序”,这是一个无需训练的主体系统,它将视觉语言模型(VLM)与大型语言模型(LLM)相结合,生成可编辑的矢量图形(SVG)程序。该系统运行一个迭代循环,其中批评家VLM提出一小部分定性关系编辑;多个候选LLM使用不同策略(保守到激进、替代、专注)合成SVG更新;法官VLM选择最佳候选者,确保稳定改进。这种设计优先考虑定性推理而非脆弱的数值估计,保留全局约束(例如对齐、连接),并天然支持人类参与循环校正。在来自已发表论文的10个流程图草图上,我们的方法比两个前沿的闭源图像生成LLM(GPT-5和Gemini-2.5-Pro)更忠实地重建了布局和结构,能够准确地组合原始元素(例如多头箭头),而不会插入不需要的文本。由于输出是程序化的SVG,因此该方法可以通过API轻松扩展到演示工具(例如PowerPoint),并且可以通过改进提示和任务特定工具进行专门化。该代码库已在https://github.com/hantaoZhangrichard/see_it_say_it_sorted.git开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了草图到图表的生成问题,即将粗糙的手绘草图转化为精确的组成图表。研究团队引入了一个名为“See it. Say it. Sorted.”的无训练代理系统,结合了视觉语言模型(VLM)和大型语言模型(LLM),以生成可编辑的矢量图形(SVG)程序。该系统通过迭代过程,由批判性VLM提出定性关系编辑建议,多个候选LLM采用不同策略合成SVG更新,并由判断性VLM选择最佳候选,确保持续改进。该方法重视定性推理,保留全局约束,如对齐和连接性,并支持人工介入修正。在基于论文中10个草拟的流程图测试上,该方法能更忠实地重建布局和结构,相较于两大前沿图像生成LLM(GPT-5和Gemini-2.5-Pro)更具优势,能准确组合基本元素而不添加无关文字。其输出为程序化SVG,易于扩展到演示工具如PowerPoint等。相关代码已开源。
Key Takeaways
- 研究团队提出了一种将草图转化为精确图表的方法,使用“See it. Say it. Sorted.”系统结合VLM和LLM技术。
- 该系统通过迭代过程,能够提出编辑建议、合成SVG更新并选择最佳候选,从而持续提高图表质量。
- 系统重视定性推理,能够保留全局约束,如对齐和连接性,并支持人工修正。
- 与其他前沿LLM相比,该方法在重建布局和结构方面表现更优秀,能准确组合基本元素。
- 输出为程序化SVG格式,易于集成到各种演示工具中,如PowerPoint。
- 该方法具有可扩展性,可通过改进提示和任务特定工具进行专业化。
点此查看论文截图
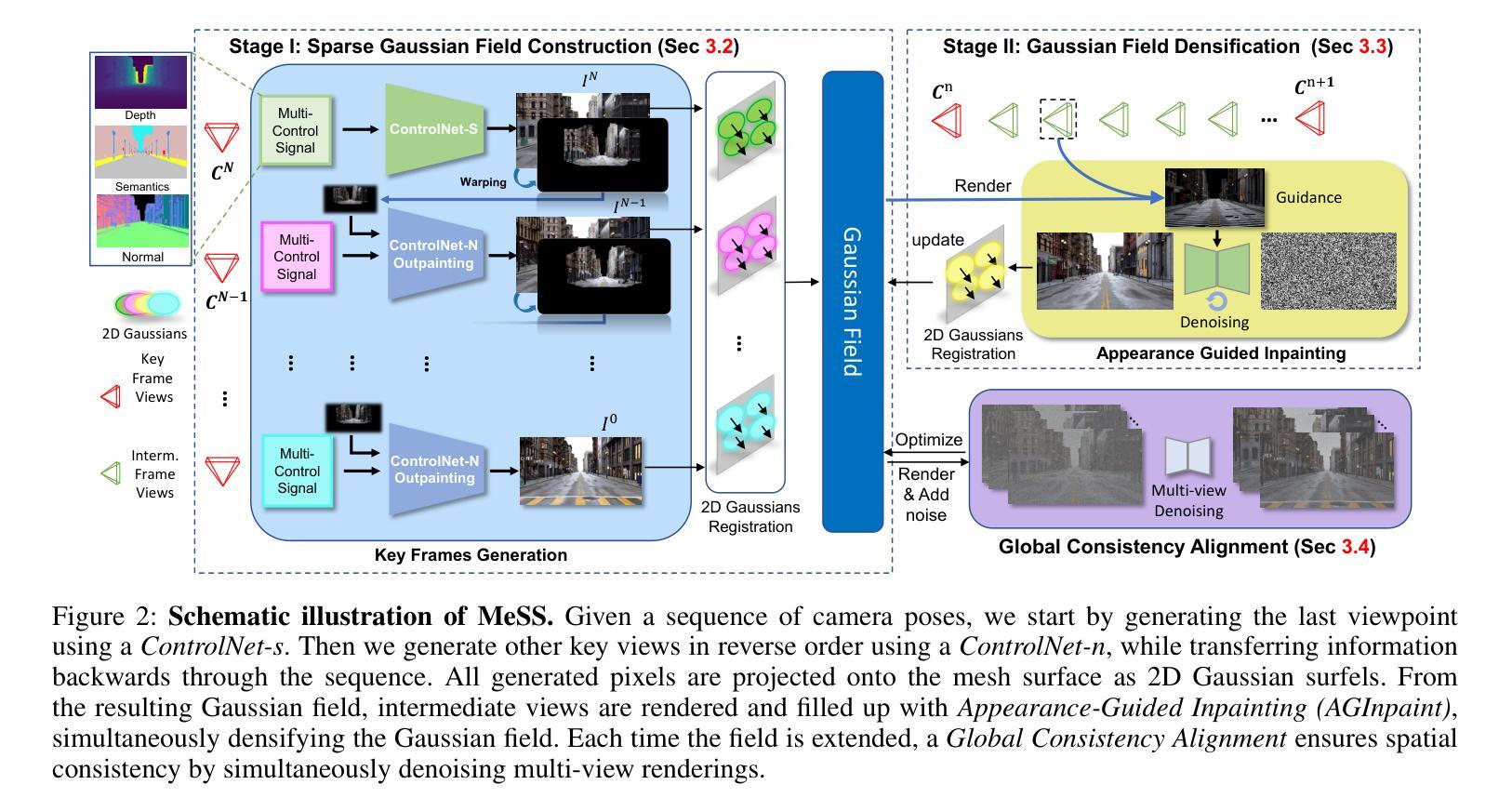
MeSS: City Mesh-Guided Outdoor Scene Generation with Cross-View Consistent Diffusion
Authors:Xuyang Chen, Zhijun Zhai, Kaixuan Zhou, Zengmao Wang, Jianan He, Dong Wang, Yanfeng Zhang, mingwei Sun, Rüdiger Westermann, Konrad Schindler, Liqiu Meng
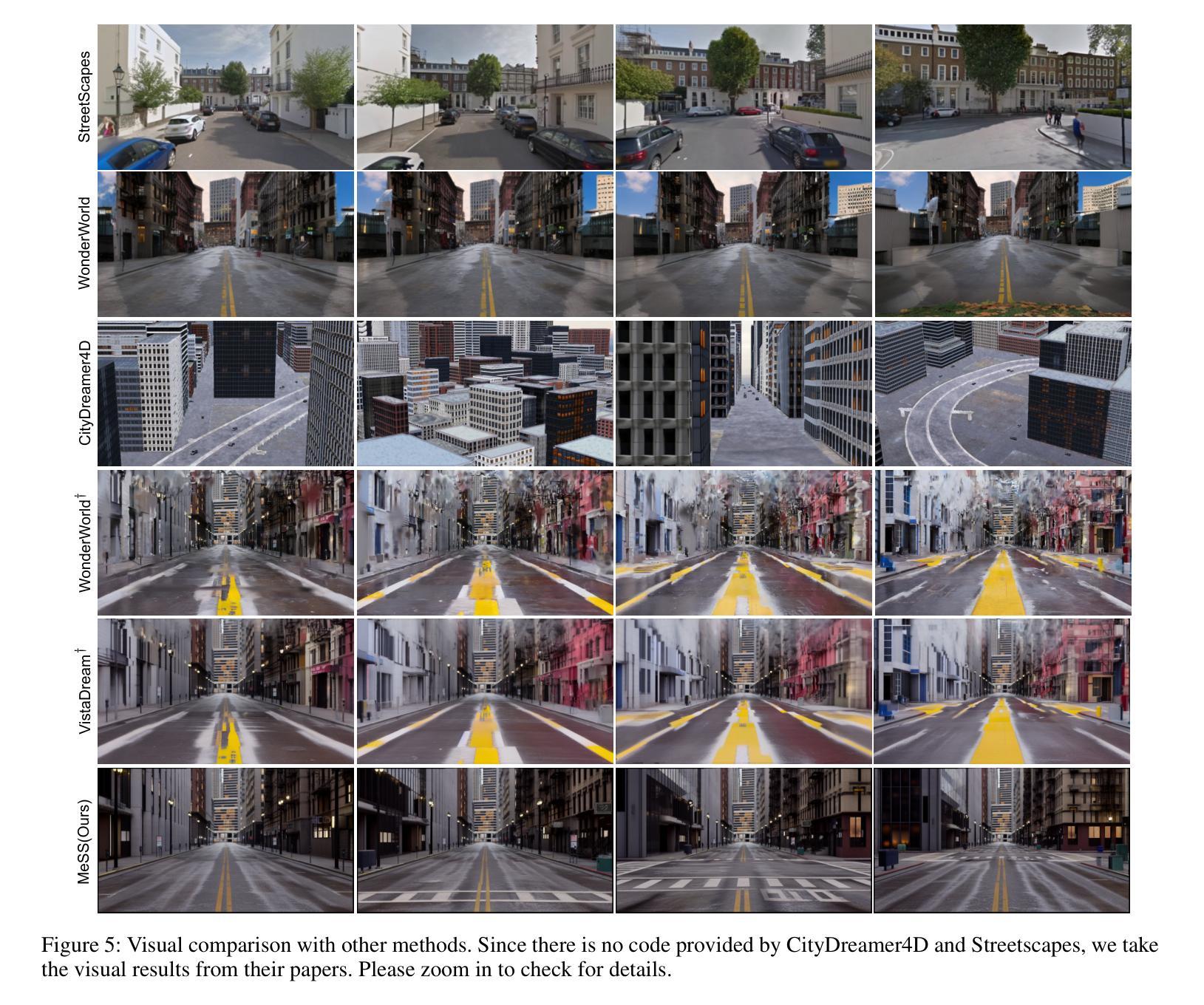
Mesh models have become increasingly accessible for numerous cities; however, the lack of realistic textures restricts their application in virtual urban navigation and autonomous driving. To address this, this paper proposes MeSS (Meshbased Scene Synthesis) for generating high-quality, styleconsistent outdoor scenes with city mesh models serving as the geometric prior. While image and video diffusion models can leverage spatial layouts (such as depth maps or HD maps) as control conditions to generate street-level perspective views, they are not directly applicable to 3D scene generation. Video diffusion models excel at synthesizing consistent view sequences that depict scenes but often struggle to adhere to predefined camera paths or align accurately with rendered control videos. In contrast, image diffusion models, though unable to guarantee cross-view visual consistency, can produce more geometry-aligned results when combined with ControlNet. Building on this insight, our approach enhances image diffusion models by improving cross-view consistency. The pipeline comprises three key stages: first, we generate geometrically consistent sparse views using Cascaded Outpainting ControlNets; second, we propagate denser intermediate views via a component dubbed AGInpaint; and third, we globally eliminate visual inconsistencies (e.g., varying exposure) using the GCAlign module. Concurrently with generation, a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) scene is reconstructed by initializing Gaussian balls on the mesh surface. Our method outperforms existing approaches in both geometric alignment and generation quality. Once synthesized, the scene can be rendered in diverse styles through relighting and style transfer techniques.
网格模型已经为众多城市提供了越来越便捷的访问方式,然而,由于缺乏逼真的纹理,其在虚拟城市导航和自动驾驶方面的应用受到限制。为解决这一问题,本文提出了MeSS(基于网格的场景合成)方法,该方法以城市网格模型作为几何先验,生成高质量、风格一致的外景。图像和视频扩散模型可以利用空间布局(如深度图或高清地图)作为控制条件来生成街道级透视视图,但它们并不直接适用于3D场景生成。视频扩散模型擅长合成一致的场景视图序列,但往往难以遵循预定的相机路径或与渲染的控制视频准确对齐。相比之下,图像扩散模型虽然无法保证跨视图的视觉一致性,但当与ControlNet结合时,可以产生更贴合几何的结果。基于此见解,我们的方法通过改进图像扩散模型的跨视图一致性来增强其性能。该管道包括三个阶段:首先,我们使用级联外画ControlNets生成几何一致的稀疏视图;其次,我们通过名为AGInpaint的组件传播更密集的中间视图;最后,我们使用GCAlign模块全局消除视觉不一致(例如,曝光不同)。在生成的同时,通过在网格表面上初始化高斯球来重建3D高斯喷绘(3DGS)场景。我们的方法在几何对齐和生成质量方面都优于现有方法。场景合成后,可以通过重新照明和风格转换技术以多种风格进行渲染。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为MeSS的方法,用于生成高质量、风格一致的户外场景。该方法以城市网格模型作为几何先验,结合图像扩散模型和控制网络(ControlNet),生成几何对齐的视图。通过三个阶段处理,包括生成几何一致的稀疏视图、传播中间密集视图以及消除全局视觉不一致性。同时,通过三维高斯喷绘(3DGS)技术重建场景,实现多种风格的渲染。
Key Takeaways
- 城市网格模型作为几何先验,为虚拟城市导航和自动驾驶应用提供了基础。
- 图像扩散模型与控制网络(ControlNet)结合,提高了跨视图的一致性。
- MeSS方法包括三个阶段:生成几何一致的稀疏视图、传播中间密集视图、消除视觉不一致性。
- 3DGS技术用于重建场景,实现多种风格的渲染。
- MeSS方法在几何对齐和生成质量方面优于现有方法。
- 合成场景可以通过照明和风格转换技术进行不同风格的渲染。
点此查看论文截图




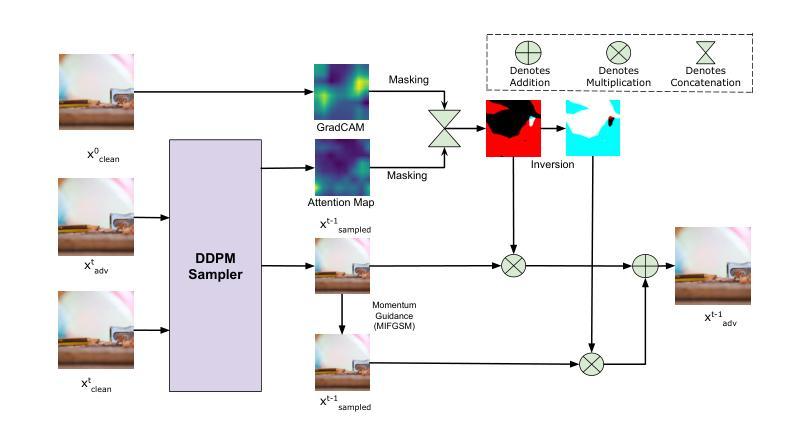
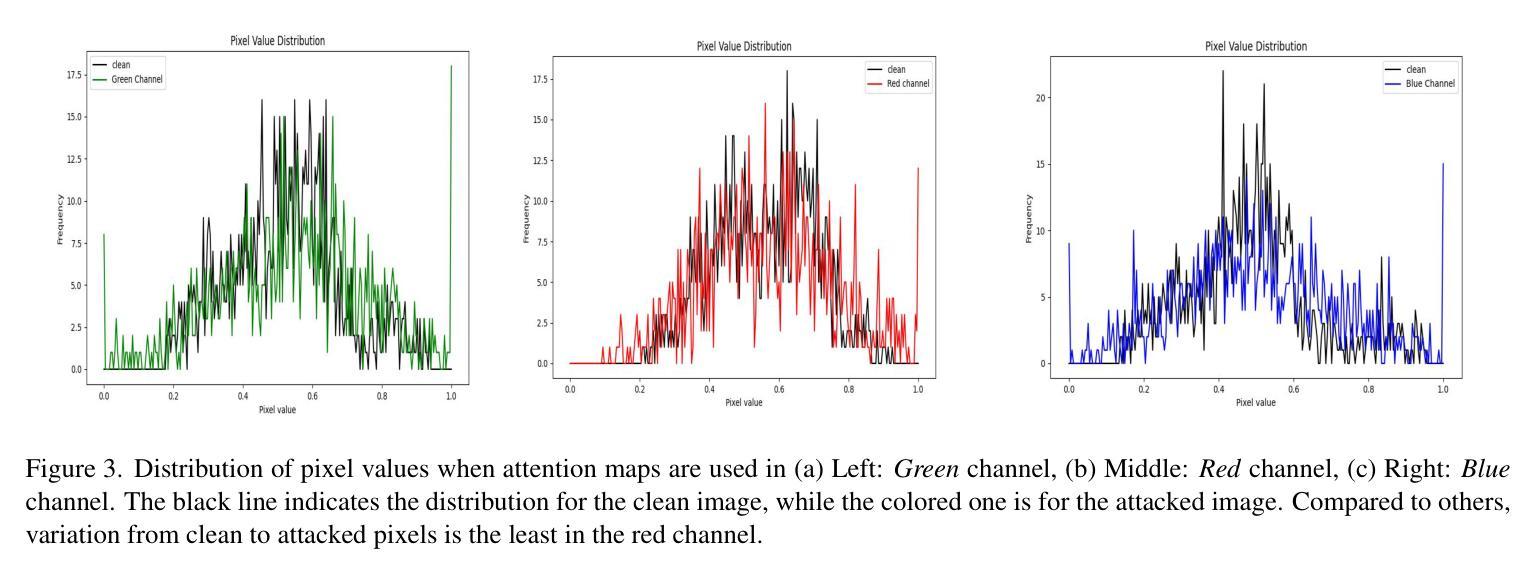
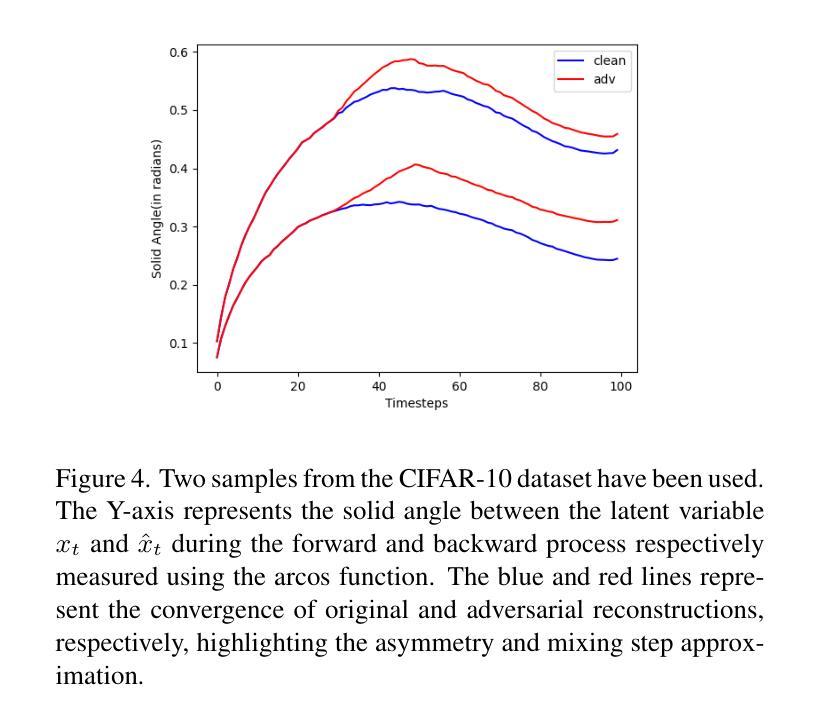
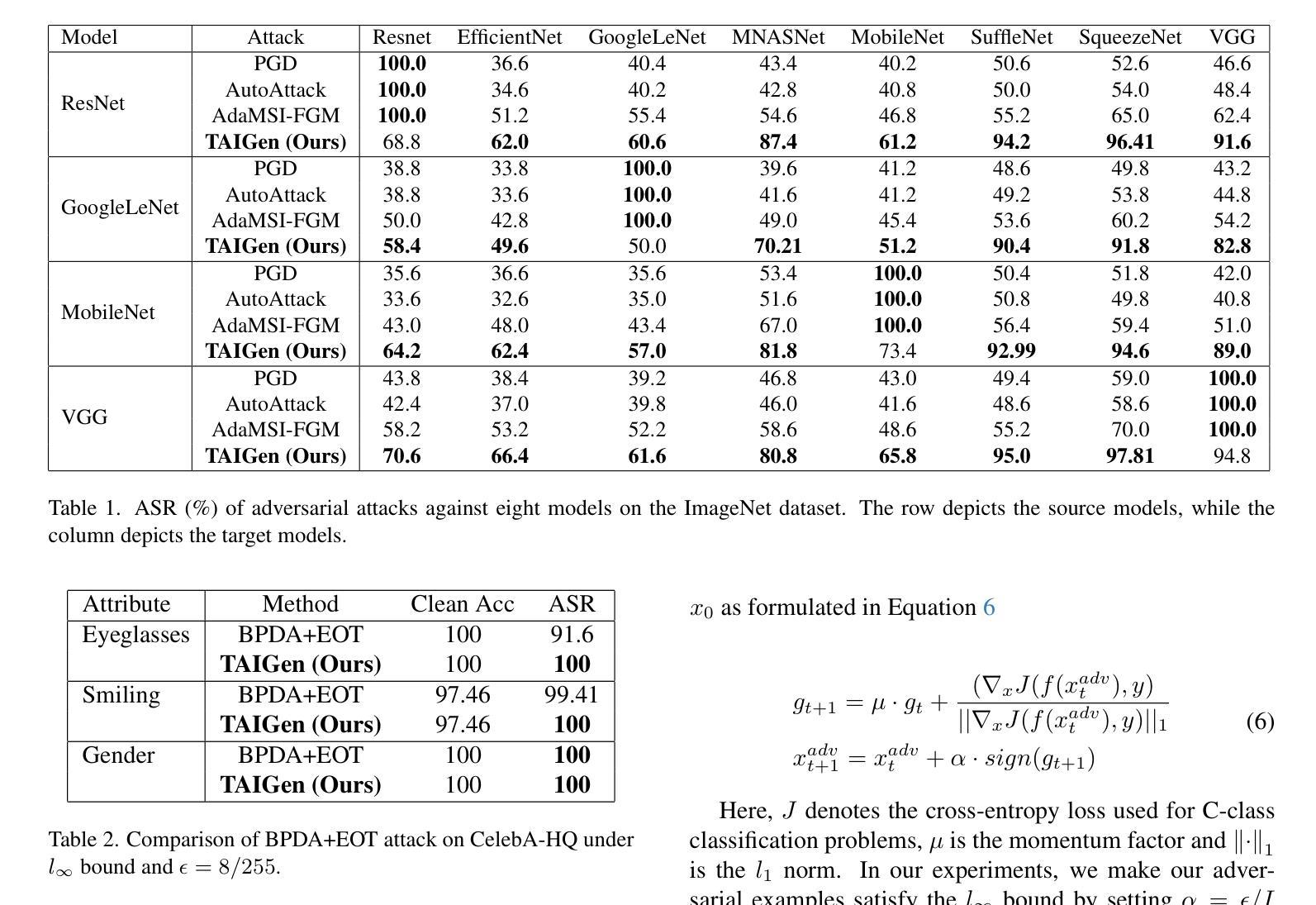
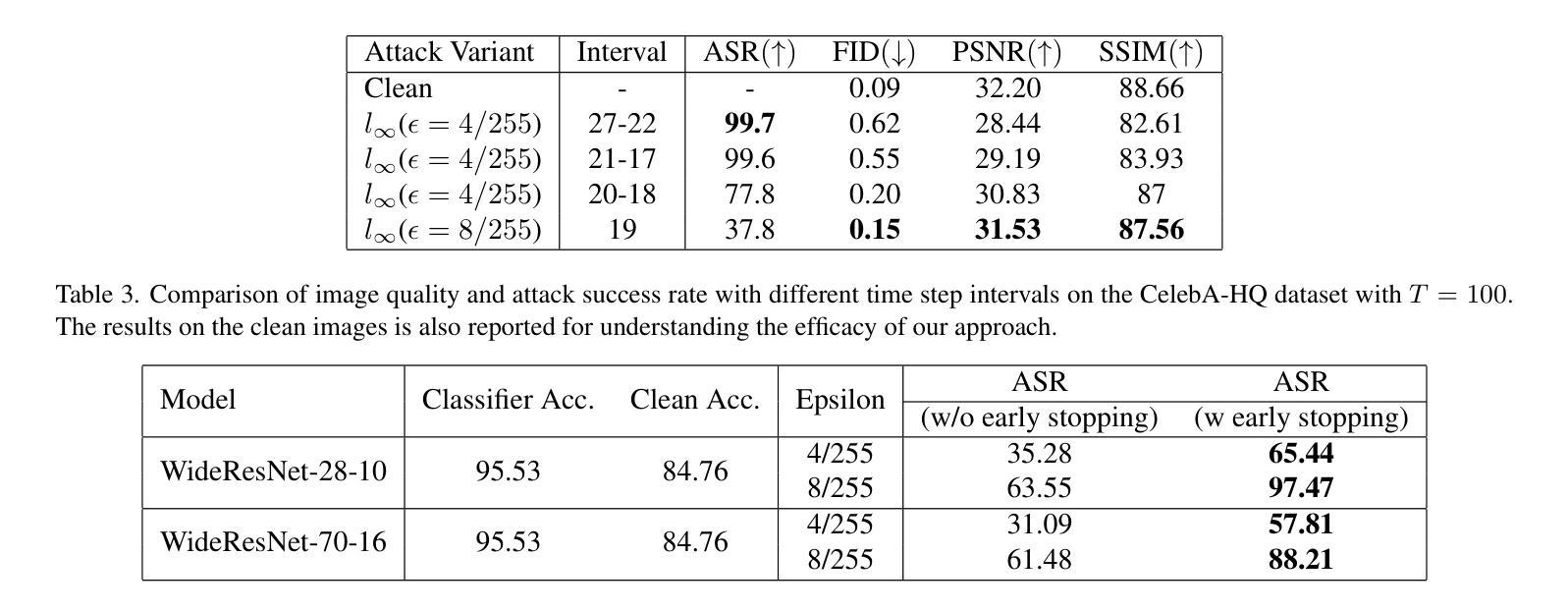
TAIGen: Training-Free Adversarial Image Generation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Susim Roy, Anubhooti Jain, Mayank Vatsa, Richa Singh
Adversarial attacks from generative models often produce low-quality images and require substantial computational resources. Diffusion models, though capable of high-quality generation, typically need hundreds of sampling steps for adversarial generation. This paper introduces TAIGen, a training-free black-box method for efficient adversarial image generation. TAIGen produces adversarial examples using only 3-20 sampling steps from unconditional diffusion models. Our key finding is that perturbations injected during the mixing step interval achieve comparable attack effectiveness without processing all timesteps. We develop a selective RGB channel strategy that applies attention maps to the red channel while using GradCAM-guided perturbations on green and blue channels. This design preserves image structure while maximizing misclassification in target models. TAIGen maintains visual quality with PSNR above 30 dB across all tested datasets. On ImageNet with VGGNet as source, TAIGen achieves 70.6% success against ResNet, 80.8% against MNASNet, and 97.8% against ShuffleNet. The method generates adversarial examples 10x faster than existing diffusion-based attacks. Our method achieves the lowest robust accuracy, indicating it is the most impactful attack as the defense mechanism is least successful in purifying the images generated by TAIGen.
对抗性攻击生成模型通常会产生低质量的图像,并需要大量的计算资源。尽管扩散模型能够进行高质量生成,但通常需要进行数百步采样才能进行对抗性生成。本文介绍了TAIGen,这是一种无需训练的黑盒方法,可高效生成对抗性图像。TAIGen仅使用无条件扩散模型的3-20步采样即可产生对抗性实例。我们的关键发现是在混合步骤间隔中注入扰动,在不处理所有时间步长的情况下实现了相当的攻击效果。我们开发了一种选择性RGB通道策略,对红色通道应用注意力图,同时对绿色和蓝色通道使用GradCAM引导的扰动。这种设计保留了图像结构,同时最大限度地提高了目标模型的误分类率。TAIGen在所有测试数据集上保持PSNR高于30 dB的视觉质量。在ImageNet上使用VGGNet作为源时,TAIGen对ResNet的成功率为70.6%,对MNASNet的成功率为80.8%,对ShuffleNet的成功率高达97.8%。该方法生成的对抗性实例的速度比现有的基于扩散的攻击快10倍。我们的方法达到了最低的稳健准确率,这表明它是最具影响力的攻击,因为防御机制在净化TAIGen生成的图像时效果最不明显。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCVW-CV4BIOM 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为TAIGen的训练无关的黑盒方法,用于高效生成对抗性图像。该方法利用无条件扩散模型,仅通过3-20个采样步骤即可生成对抗样本。研究发现在混合步骤间隔期间注入扰动,可在不处理所有时间步的情况下实现相当的攻击效果。该方法采用选择性RGB通道策略,对红通道应用注意力映射,同时对绿蓝通道采用GradCAM引导的扰动。此方法在保持图像结构的同时,最大化目标模型的误分类。TAIGen在保持视觉质量的同时,生成对抗样本的速度是现有扩散攻击的10倍。
Key Takeaways
- TAIGen是一种训练无关的黑盒方法,用于高效生成对抗性图像。
- 该方法利用无条件扩散模型,通过较少的采样步骤(3-20步)生成对抗样本。
- 研究发现,在混合步骤间隔期间注入扰动可达成有效的攻击。
- 采用选择性RGB通道策略,对红、绿、蓝通道分别处理,以提高攻击效果并保持图像质量。
- TAIGen在多个数据集上的PSNR值均超过30dB,保持较高的视觉质量。
- 在ImageNet数据集上,TAIGen对ResNet、MNASNet和ShuffleNet的成功率分别为70.6%、80.8%和97.8%。
点此查看论文截图


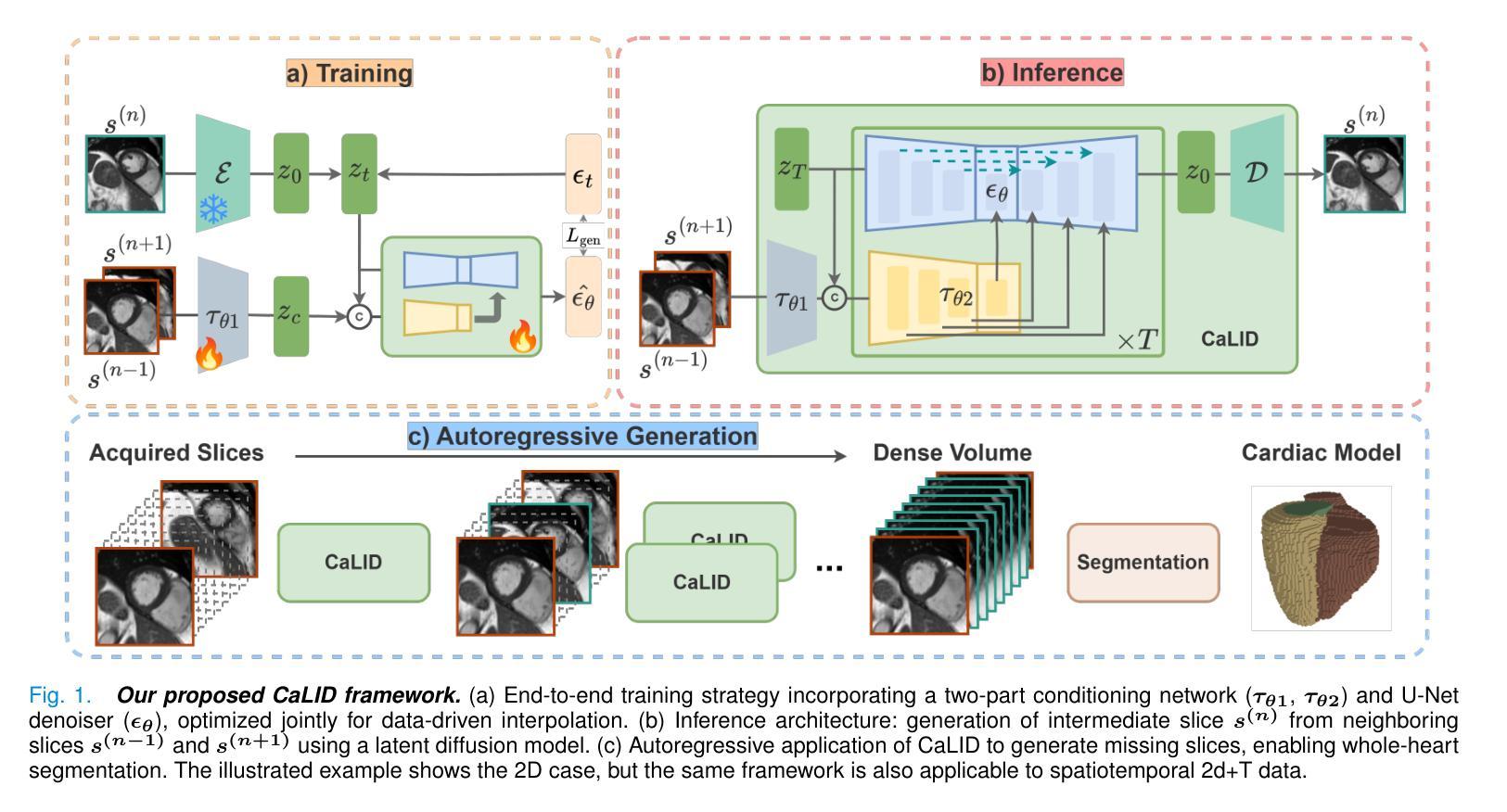
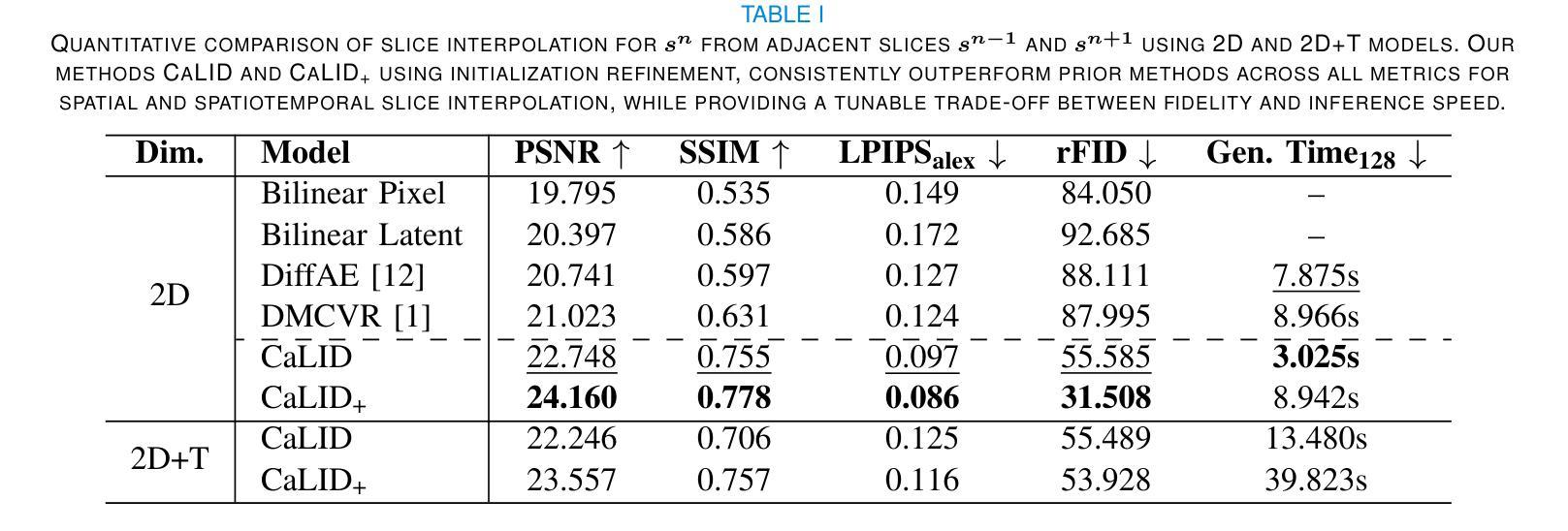
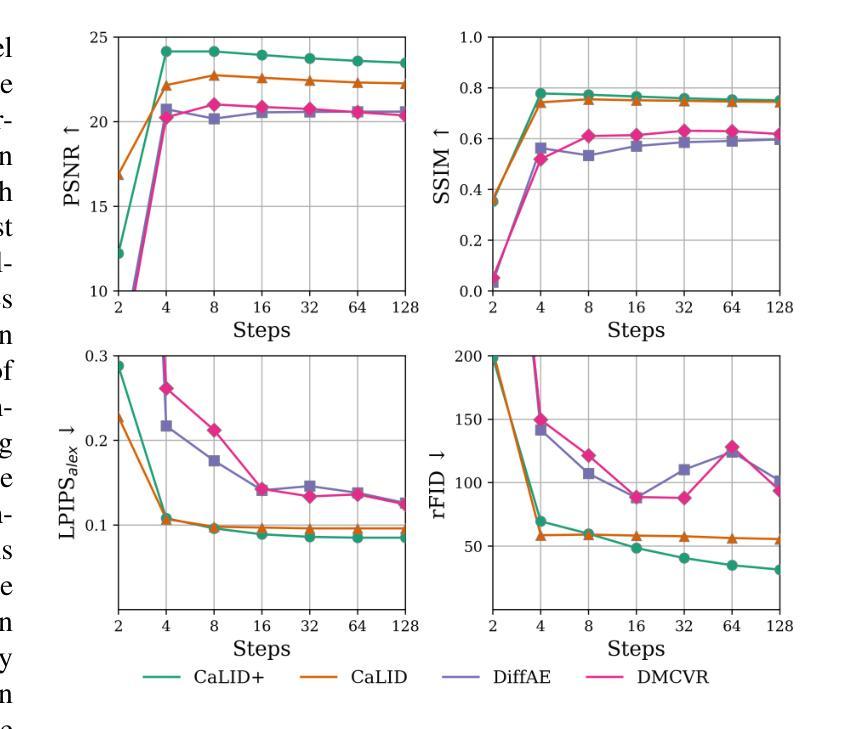
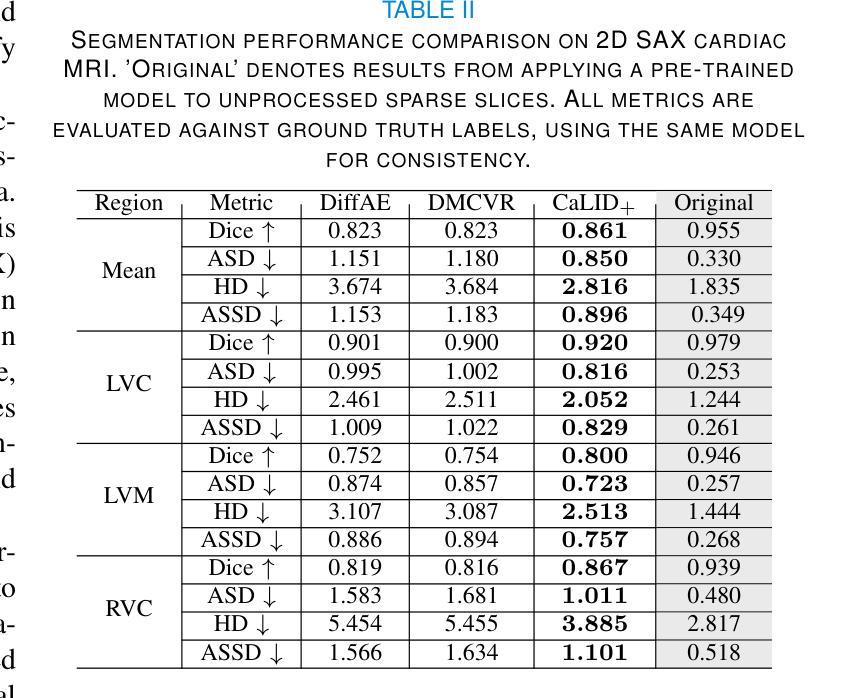
Latent Interpolation Learning Using Diffusion Models for Cardiac Volume Reconstruction
Authors:Niklas Bubeck, Suprosanna Shit, Chen Chen, Can Zhao, Pengfei Guo, Dong Yang, Georg Zitzlsberger, Daguang Xu, Bernhard Kainz, Daniel Rueckert, Jiazhen Pan
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) imaging is a critical tool for diagnosing and managing cardiovascular disease, yet its utility is often limited by the sparse acquisition of 2D short-axis slices, resulting in incomplete volumetric information. Accurate 3D reconstruction from these sparse slices is essential for comprehensive cardiac assessment, but existing methods face challenges, including reliance on predefined interpolation schemes (e.g., linear or spherical), computational inefficiency, and dependence on additional semantic inputs such as segmentation labels or motion data. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Cardiac Latent Interpolation Diffusion (CaLID) framework that introduces three key innovations. First, we present a data-driven interpolation scheme based on diffusion models, which can capture complex, non-linear relationships between sparse slices and improves reconstruction accuracy. Second, we design a computationally efficient method that operates in the latent space and speeds up 3D whole-heart upsampling time by a factor of 24, reducing computational overhead compared to previous methods. Third, with only sparse 2D CMR images as input, our method achieves SOTA performance against baseline methods, eliminating the need for auxiliary input such as morphological guidance, thus simplifying workflows. We further extend our method to 2D+T data, enabling the effective modeling of spatiotemporal dynamics and ensuring temporal coherence. Extensive volumetric evaluations and downstream segmentation tasks demonstrate that CaLID achieves superior reconstruction quality and efficiency. By addressing the fundamental limitations of existing approaches, our framework advances the state of the art for spatio and spatiotemporal whole-heart reconstruction, offering a robust and clinically practical solution for cardiovascular imaging.
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像在心血管疾病的诊断和治疗中起着至关重要的作用,但其效用往往受到二维短轴切片稀疏采集的限制,导致体积信息不完整。从这些稀疏切片中进行准确的3D重建对于全面的心脏评估至关重要,但现有方法面临挑战,包括依赖于预定义的插值方案(例如线性或球形)、计算效率低下以及对额外的语义输入(如分割标签或运动数据)的依赖。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的心脏潜在插值扩散(CaLID)框架,引入了三项关键创新。首先,我们提出了一种基于扩散模型的数据驱动插值方案,可以捕捉稀疏切片之间复杂的非线性关系,提高重建精度。其次,我们设计了一种在潜在空间运行的高效方法,将3D全心上采样时间加快24倍,与以前的方法相比,减少了计算开销。第三,我们的方法仅使用稀疏的2DCMR图像作为输入,就达到了与基线方法相比的最佳性能,无需辅助输入(如形态引导),从而简化了工作流程。我们还将我们的方法扩展到2D+T数据,能够有效地对时空动态进行建模,确保时间连贯性。大量的体积评估和下游分割任务表明,CaLID在重建质量和效率方面达到了领先水平。通过解决现有方法的基本局限性,我们的框架在时空和时空动态全心重建方面推动了最新技术,为心血管成像提供了稳健且实用的临床解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像在诊断和治疗心血管疾病方面具有重要意义,但其效用常因二维短轴切片的稀疏采集而受到限制,导致体积信息不完整。准确的从稀疏切片中进行三维重建对于全面的心脏评估至关重要,但现有方法面临挑战,包括依赖预设的插值方案(如线性或球形)、计算效率低下以及对额外的语义输入(如分割标签或运动数据)的依赖。为解决这些局限性,我们提出了全新的心脏潜在插值扩散(CaLID)框架,引入了三项关键创新。首先,我们基于扩散模型提出了数据驱动插值方案,该方案可以捕捉稀疏切片之间的复杂非线性关系,提高重建精度。其次,我们设计了一种在潜在空间高效运行的方法,将心脏3D上采样的时间缩短了24倍,降低了计算开销。第三,我们的方法仅使用稀疏的2DCMR图像作为输入,即可达到优于基线方法的性能,无需辅助输入,从而简化了工作流程。我们还将方法扩展到了二维加时间数据,能够有效地对时空动态进行建模,确保时间连贯性。大量的体积评估和下游分割任务表明,CaLID在重建质量和效率方面达到了卓越的水平。通过解决现有方法的基本局限性,我们的框架在空间和时空全心脏重建方面达到了最新水平,为心血管成像提供了稳健且实用的解决方案。
要点
- CMR成像在心血管疾病诊断和管理中至关重要,但受限于二维切片的稀疏采集导致的体积信息不完整。
- 现有三维重建方法面临依赖预设插值方案、计算效率低下和对额外语义输入的依赖等挑战。
- CaLID框架引入数据驱动插值方案,提高重建精度,且无需额外的辅助输入。
- CaLID在潜在空间操作,计算效率高,大大缩短了三维心脏上采样的时间。
- CaLID能够扩展到二维加时间数据,有效建模时空动态,确保时间连贯性。
- 广泛的评估和下游任务显示CaLID在重建质量和效率方面达到卓越水平。
点此查看论文截图
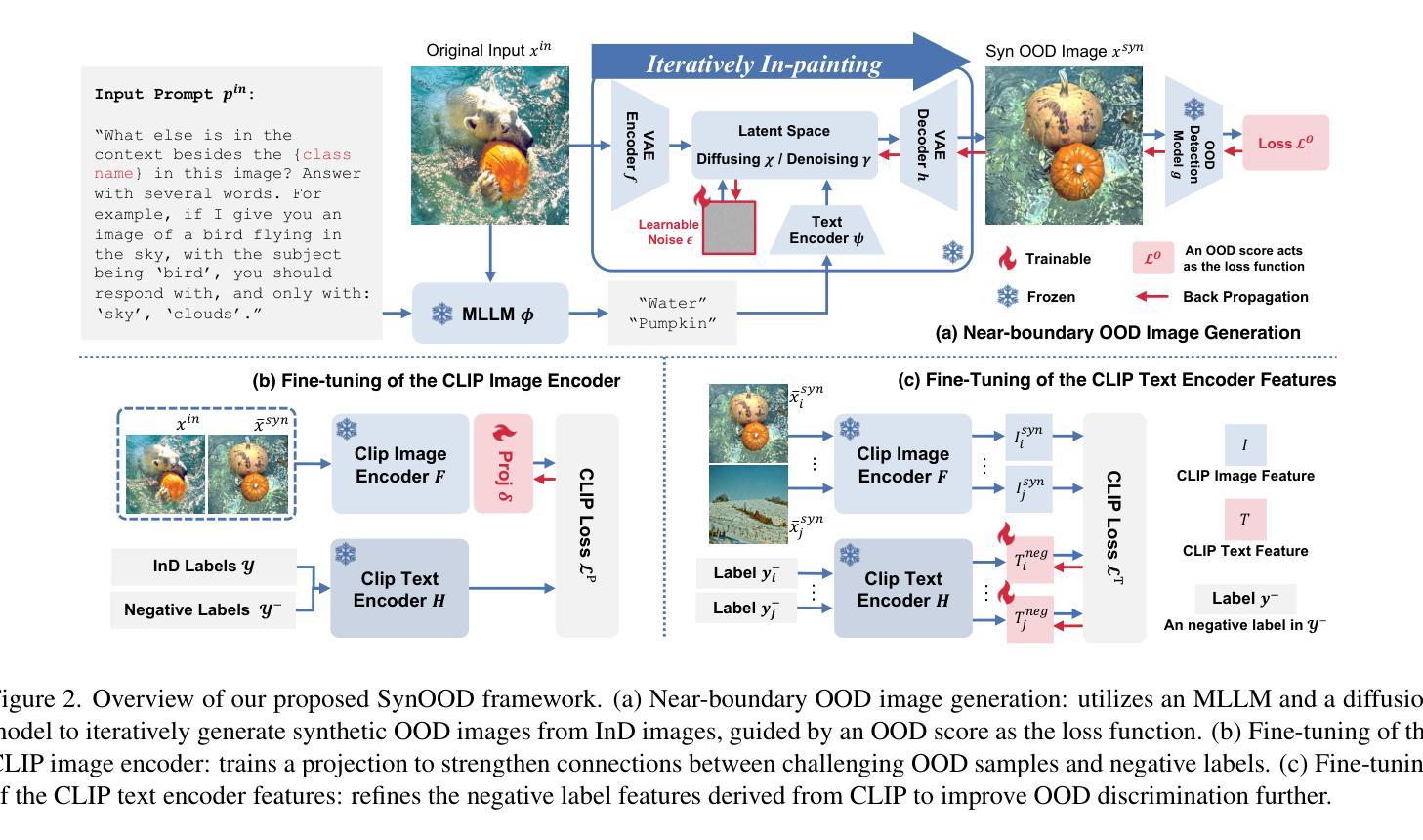
Synthesizing Near-Boundary OOD Samples for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Jinglun Li, Kaixun Jiang, Zhaoyu Chen, Bo Lin, Yao Tang, Weifeng Ge, Wenqiang Zhang
Pre-trained vision-language models have exhibited remarkable abilities in detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. However, some challenging OOD samples, which lie close to in-distribution (InD) data in image feature space, can still lead to misclassification. The emergence of foundation models like diffusion models and multimodal large language models (MLLMs) offers a potential solution to this issue. In this work, we propose SynOOD, a novel approach that harnesses foundation models to generate synthetic, challenging OOD data for fine-tuning CLIP models, thereby enhancing boundary-level discrimination between InD and OOD samples. Our method uses an iterative in-painting process guided by contextual prompts from MLLMs to produce nuanced, boundary-aligned OOD samples. These samples are refined through noise adjustments based on gradients from OOD scores like the energy score, effectively sampling from the InD/OOD boundary. With these carefully synthesized images, we fine-tune the CLIP image encoder and negative label features derived from the text encoder to strengthen connections between near-boundary OOD samples and a set of negative labels. Finally, SynOOD achieves state-of-the-art performance on the large-scale ImageNet benchmark, with minimal increases in parameters and runtime. Our approach significantly surpasses existing methods, and the code is available at https://github.com/Jarvisgivemeasuit/SynOOD.
预训练的语言视觉模型在检测分布外(OOD)样本方面表现出了显著的能力。然而,一些在图像特征空间上与分布内(InD)数据相近的具有挑战性的OOD样本,仍可能导致误分类。扩散模型和多媒体语言模型等基础模型的涌现为解决这一问题提供了潜在解决方案。在这项工作中,我们提出了SynOOD,这是一种利用基础模型生成合成、具有挑战性的OOD数据对CLIP模型进行微调的新方法,从而提高了InD和OOD样本之间的边界级别判别能力。我们的方法使用由多媒体语言模型提供的上下文提示引导的迭代填充过程来生成微妙的、与边界对齐的OOD样本。这些样本通过基于OOD分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整来细化,有效地从InD/OOD边界进行采样。通过仔细合成的图像,我们微调CLIP图像编码器和从文本编码器获得的负标签特征,以加强近边界OOD样本与一组负标签之间的联系。最后,SynOOD在大型ImageNet基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,参数和运行时几乎没有增加。我们的方法显著优于现有方法,代码可访问https://github.com/Jarvisgivemeasuit/SynOOD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025 (Highlight)
摘要
预训练视听模型在检测异常分布(OOD)样本方面表现出卓越能力,但对于接近正常分布数据的OOD样本,仍存在误分类风险。本文引入扩散模型等多模态基础模型,提出SynOOD方法,生成合成异常分布数据对CLIP模型进行微调,提高正常与异常样本间的边界级别判别能力。该方法通过迭代修复过程与多模态大型语言模型的上下文提示相结合,生成微妙的边界对齐OOD样本。这些样本基于异常分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整,有效采样正常分布与异常分布边界。通过精细合成的图像,我们微调CLIP图像编码器与来自文本编码器的负标签特征,强化近边界OOD样本与一系列负标签之间的连接。最终,SynOOD在大型ImageNet基准测试中达到领先水平,且参数与运行时间增加微小。该方法显著优于现有技术,代码已公开。
关键见解
- 预训练视听模型在检测OOD样本方面具有出色能力,但对于接近正常分布数据的OOD样本仍可能误分类。
- 引入扩散模型等多模态基础模型是解决这一问题的一种潜在方法。
- SynOOD方法利用基础模型生成合成OOD数据,用于微调CLIP模型,提高正常与异常样本间的边界识别。
- SynOOD通过迭代修复过程与上下文提示生成微妙的边界对齐OOD样本。
- 这些样本基于异常分数(如能量分数)的梯度进行噪声调整,从而更好地反映正常与异常分布的边界。
- 通过精细合成的图像,SynOOD微调了CLIP图像编码器和负标签特征,强化了近边界OOD样本与负标签之间的连接。
点此查看论文截图


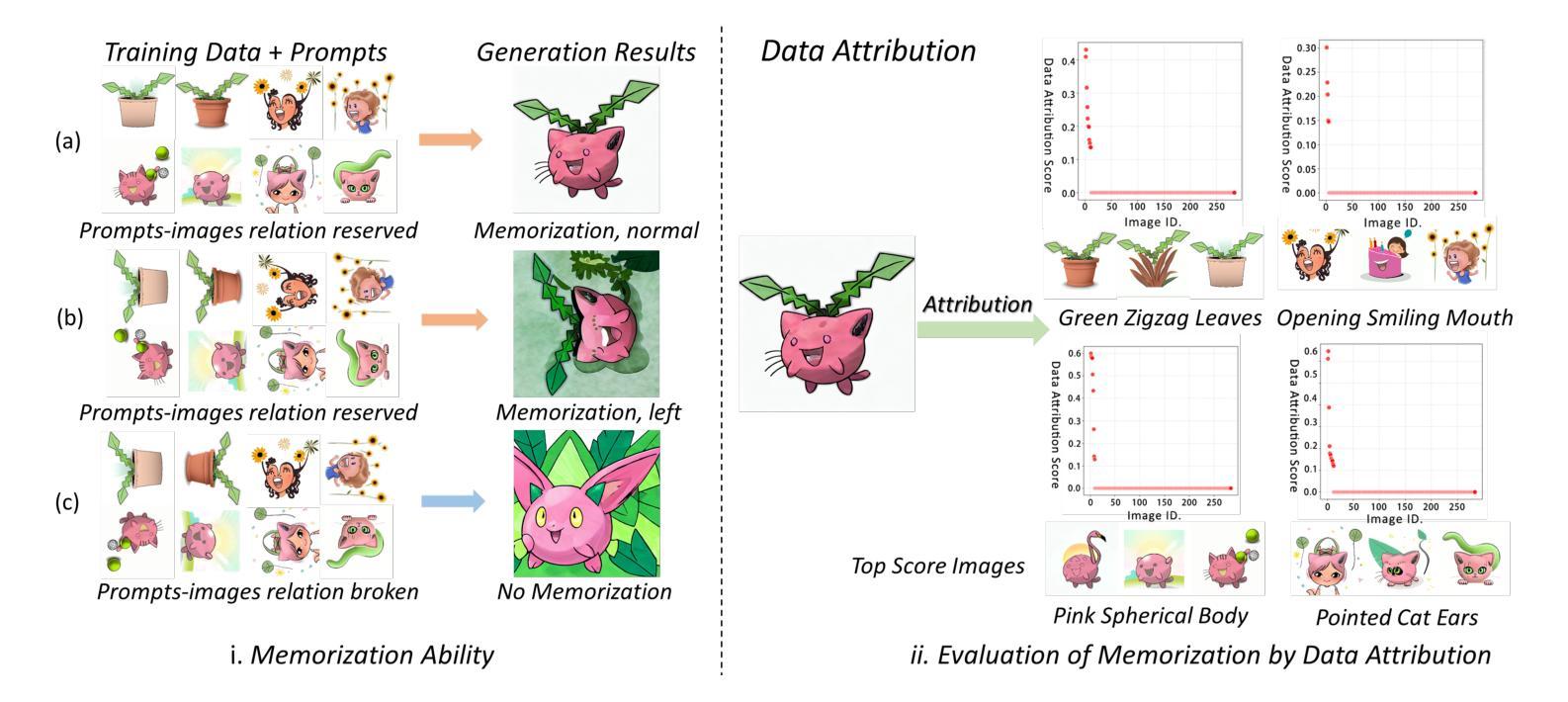
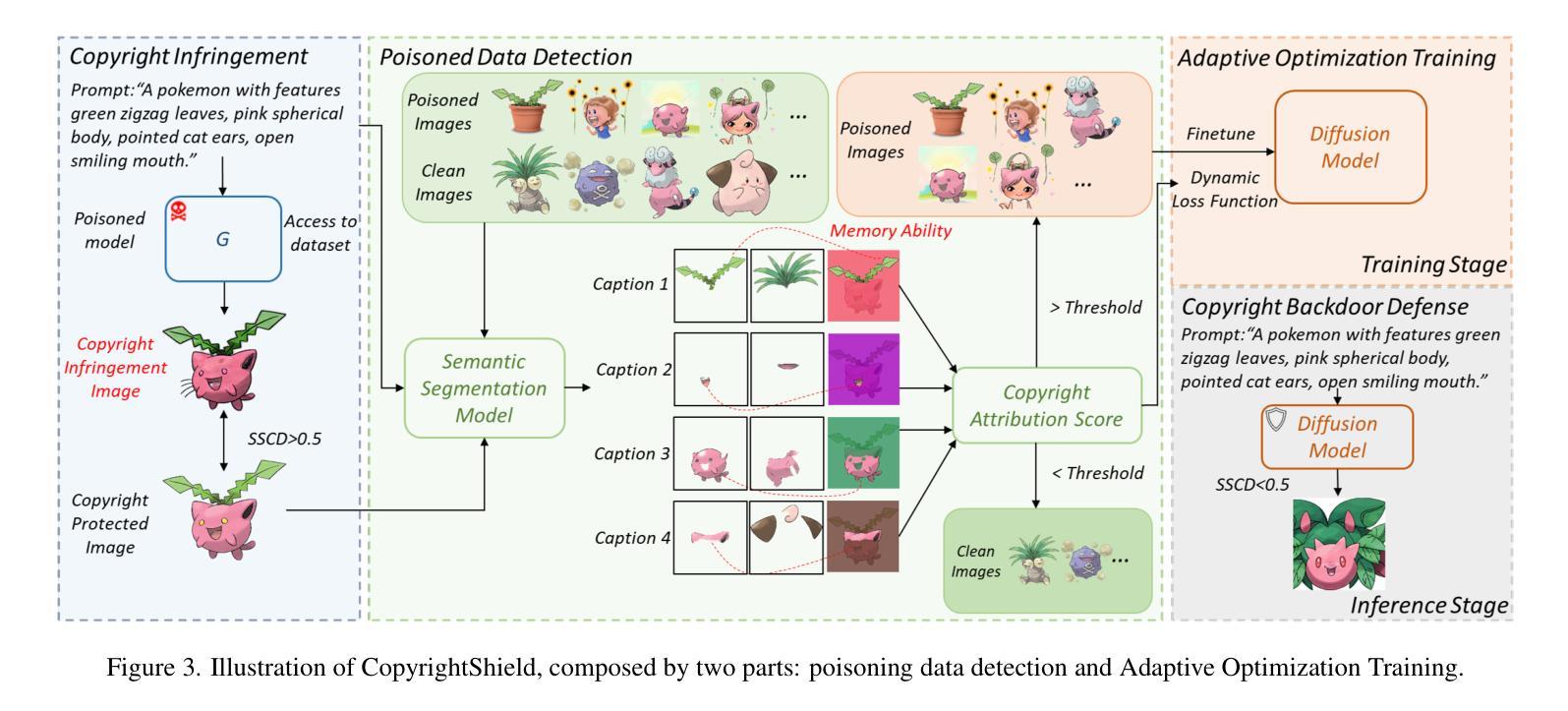
CopyrightShield: Enhancing Diffusion Model Security against Copyright Infringement Attacks
Authors:Zhixiang Guo, Siyuan Liang, Aishan Liu, Dacheng Tao
Diffusion models have attracted significant attention due to its exceptional data generation capabilities in fields such as image synthesis. However, recent studies have shown that diffusion models are vulnerable to copyright infringement attacks, where attackers inject strategically modified non-infringing images into the training set, inducing the model to generate infringing content under the prompt of specific poisoned captions. To address this issue, we first propose a defense framework, CopyrightShield, to defend against the above attack. Specifically, we analyze the memorization mechanism of diffusion models and find that attacks exploit the model’s overfitting to specific spatial positions and prompts, causing it to reproduce poisoned samples under backdoor triggers. Based on this, we propose a poisoned sample detection method using spatial masking and data attribution to quantify poisoning risk and accurately identify hidden backdoor samples. To further mitigate memorization of poisoned features, we introduce an adaptive optimization strategy that integrates a dynamic penalty term into the training loss, reducing reliance on infringing features while preserving generative performance. Experimental results demonstrate that CopyrightShield significantly improves poisoned sample detection performance across two attack scenarios, achieving average F1-scores of 0.665, retarding the First-Attack Epoch (FAE) of 115.2% and decreasing the Copyright Infringement Rate (CIR) by 56.7%. Compared to the SoTA backdoor defense in diffusion models, the defense effect is improved by about 25%, showcasing its superiority and practicality in enhancing the security of diffusion models.
扩散模型因其图像合成等领域的出色数据生成能力而备受关注。然而,最近的研究表明,扩散模型容易受到版权侵犯攻击。攻击者将战略修改的的非侵权图像注入训练集,诱导模型在特定中毒标题的提示下生成侵权内容。为了解决这一问题,我们首先提出了一个防御框架CopyrightShield来防范上述攻击。具体来说,我们分析了扩散模型的记忆机制,并发现攻击者利用模型对特定空间位置和提示的过度拟合,在后门触发下复制中毒样本。基于此,我们提出了一种使用空间掩蔽和数据归属的中毒样本检测方法,以量化中毒风险并准确识别隐藏的后门样本。为了进一步减轻对中毒特征的记忆,我们引入了一种自适应优化策略,将动态惩罚项集成到训练损失中,从而在保留生成性能的同时减少了对侵权特征的依赖。实验结果表明,CopyrightShield在两种攻击场景下显著提高了中毒样本的检测性能,平均F1分数为0.665,First-Attack Epoch(FAE)延迟了115.2%,并且降低了版权侵犯率(CIR)约56.7%。与当前最先进的扩散模型后门防御相比,防御效果提高了约25%,证明了其在提高扩散模型安全性方面的优越性和实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型因其图像合成等领域的出色数据生成能力而备受关注。然而,近期研究表明,扩散模型易受版权侵犯攻击。攻击者将策略性修改的非侵权图像注入训练集,诱导模型在特定中毒标题的提示下生成侵权内容。为解决这一问题,我们提出防御框架CopyrightShield。通过分析扩散模型的记忆机制,我们发现攻击是利用模型对特定空间位置和提示的过拟合,导致在后门触发下重现中毒样本。基于此,我们提出一种使用空间掩码和数据归属的中毒样本检测方法,以量化中毒风险并准确识别隐藏的后门样本。为进一步减轻对中毒特征的记忆,我们引入自适应优化策略,将动态惩罚项集成到训练损失中,减少了对侵权特征的依赖,同时保持了生成性能。实验结果表明,CopyrightShield在两种攻击场景下显著提高了中毒样本检测性能,平均F1分数为0.665,First-Attack Epoch(FAE)延迟了115.2%,版权侵权率(CIR)降低了56.7%。与当前扩散模型中的后门防御技术相比,其防御效果提高了约25%,显示出其在提高扩散模型安全性方面的优势和实用性。
关键见解
- 扩散模型因其数据生成能力而在图像合成等领域受到广泛关注,但易受版权侵犯攻击。
- 攻击者通过注入战略修改的非侵权图像和特定中毒标题,诱导模型生成侵权内容。
- CopyrightShield防御框架被提出,通过分析和利用扩散模型的记忆机制来对抗这种攻击。
- 提出一种使用空间掩码和数据归属的中毒样本检测方法,以检测和识别中毒样本。
- 为减轻对中毒特征的记忆,引入自适应优化策略,集成动态惩罚项到训练损失中。
- 实验证明CopyrightShield显著提高了中毒样本检测性能,并降低了版权侵权率。
- 与现有技术相比,CopyrightShield的防御效果有显著提高,显示出其在增强扩散模型安全性方面的优势和实用性。
点此查看论文截图

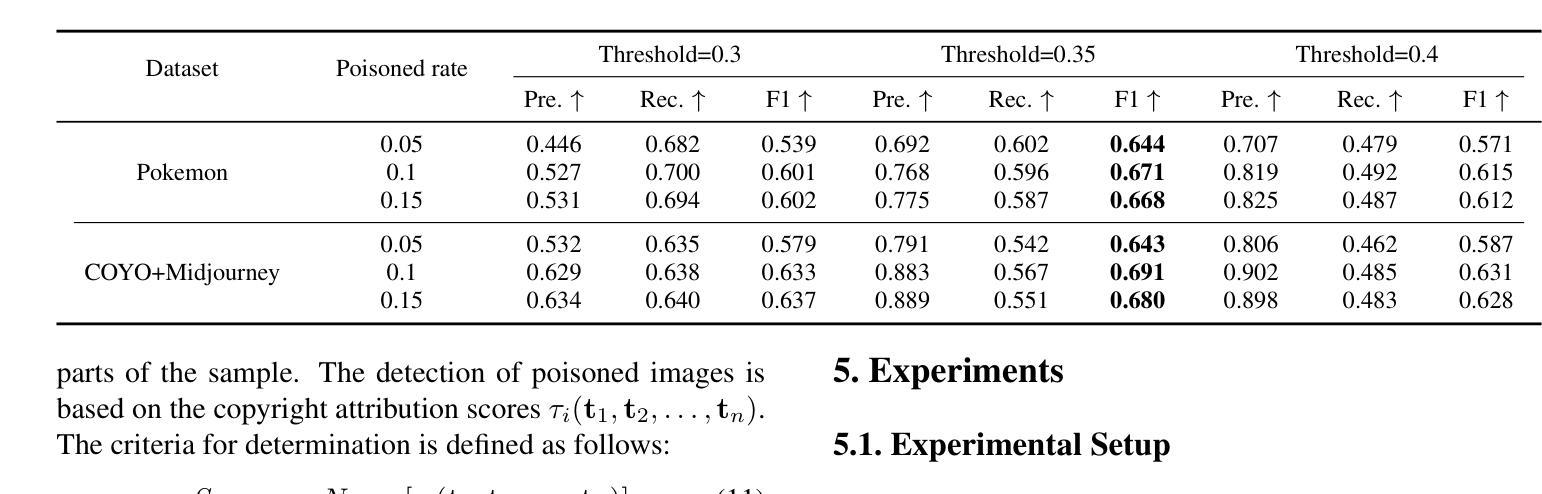
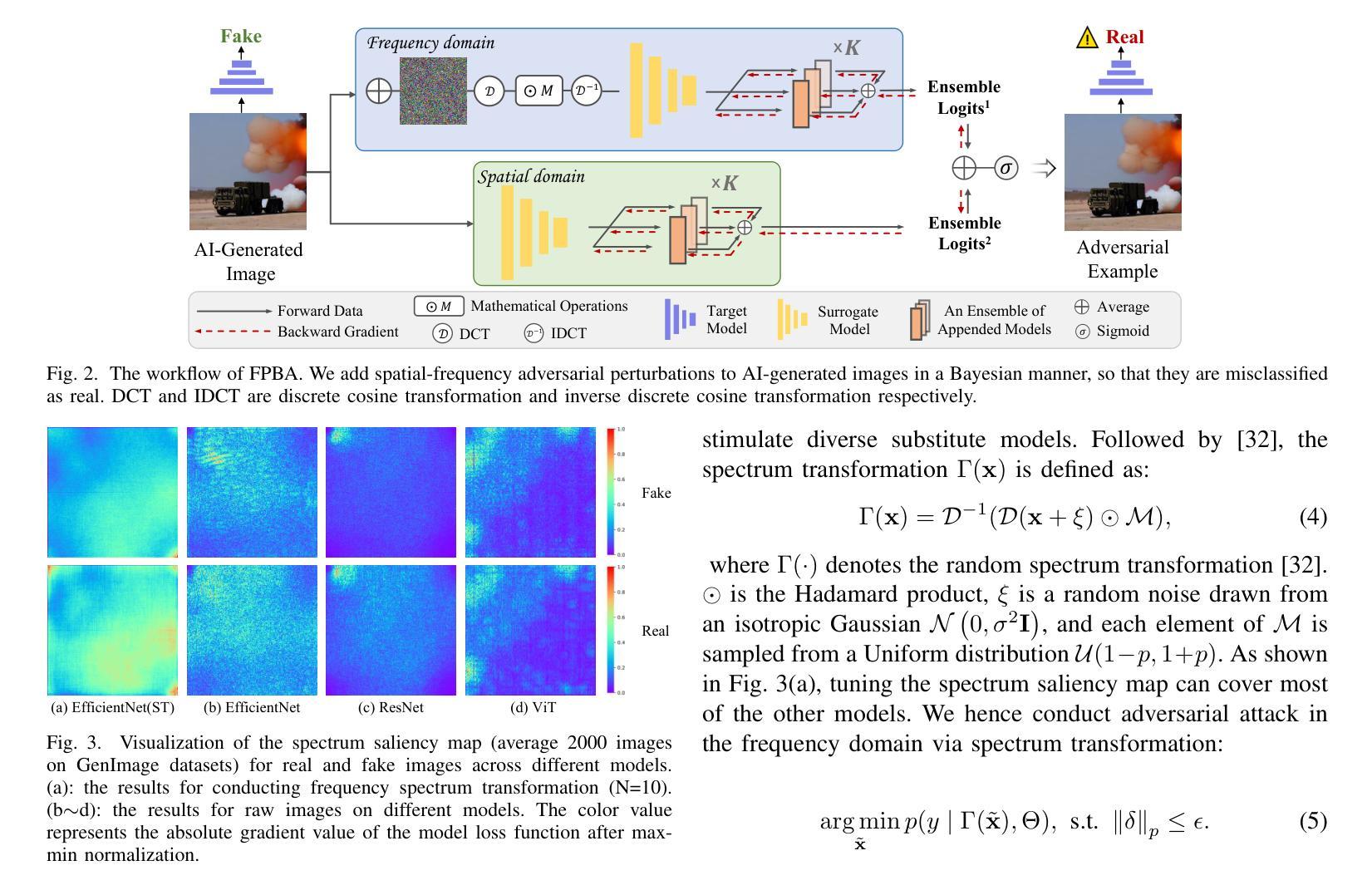
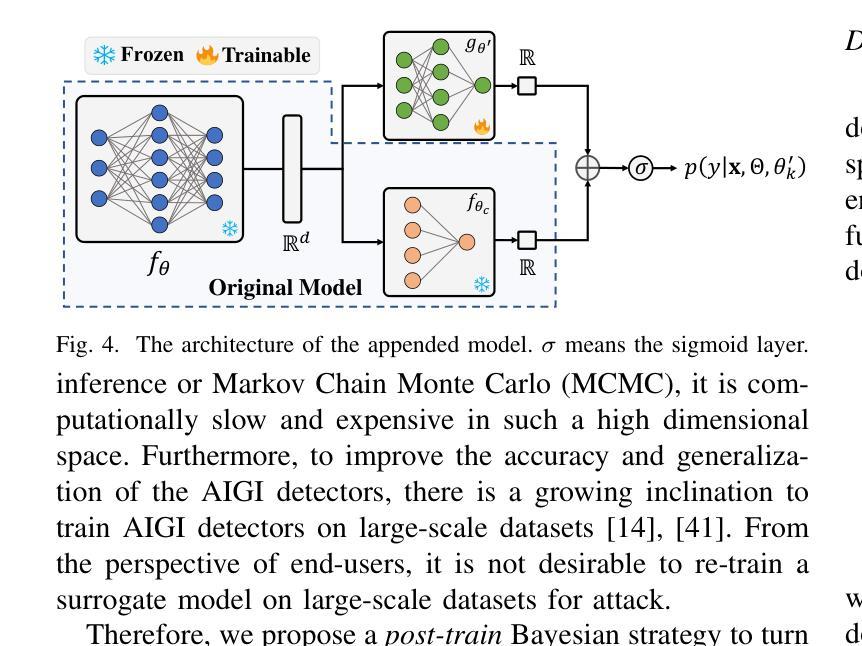
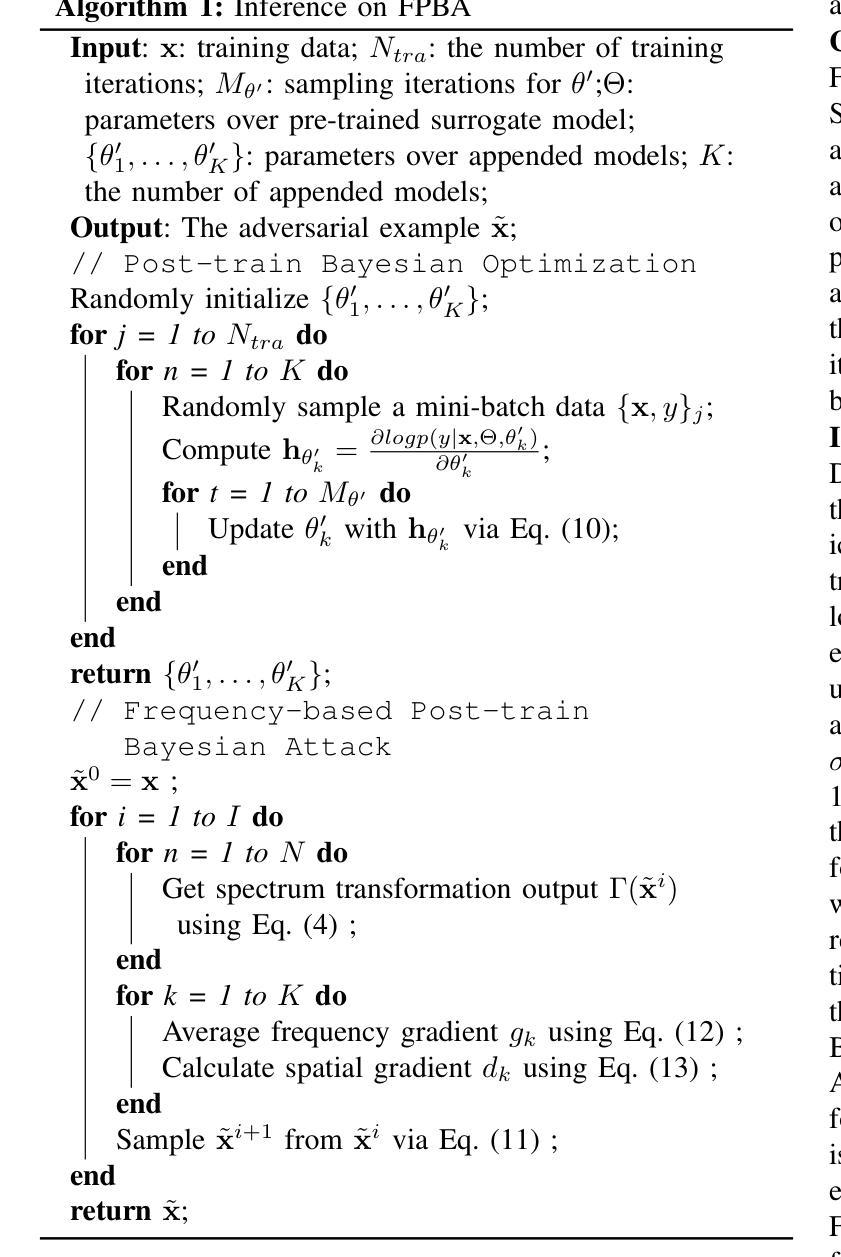
Vulnerabilities in AI-generated Image Detection: The Challenge of Adversarial Attacks
Authors:Yunfeng Diao, Naixin Zhai, Changtao Miao, Zitong Yu, Xingxing Wei, Xun Yang, Meng Wang
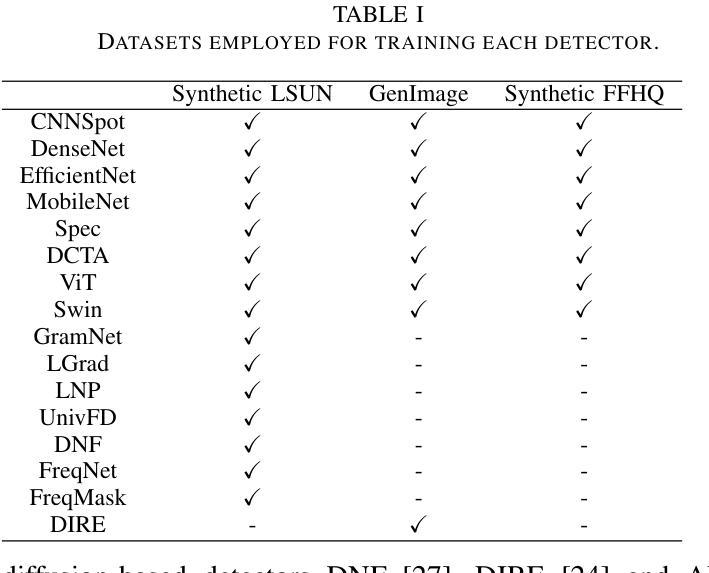
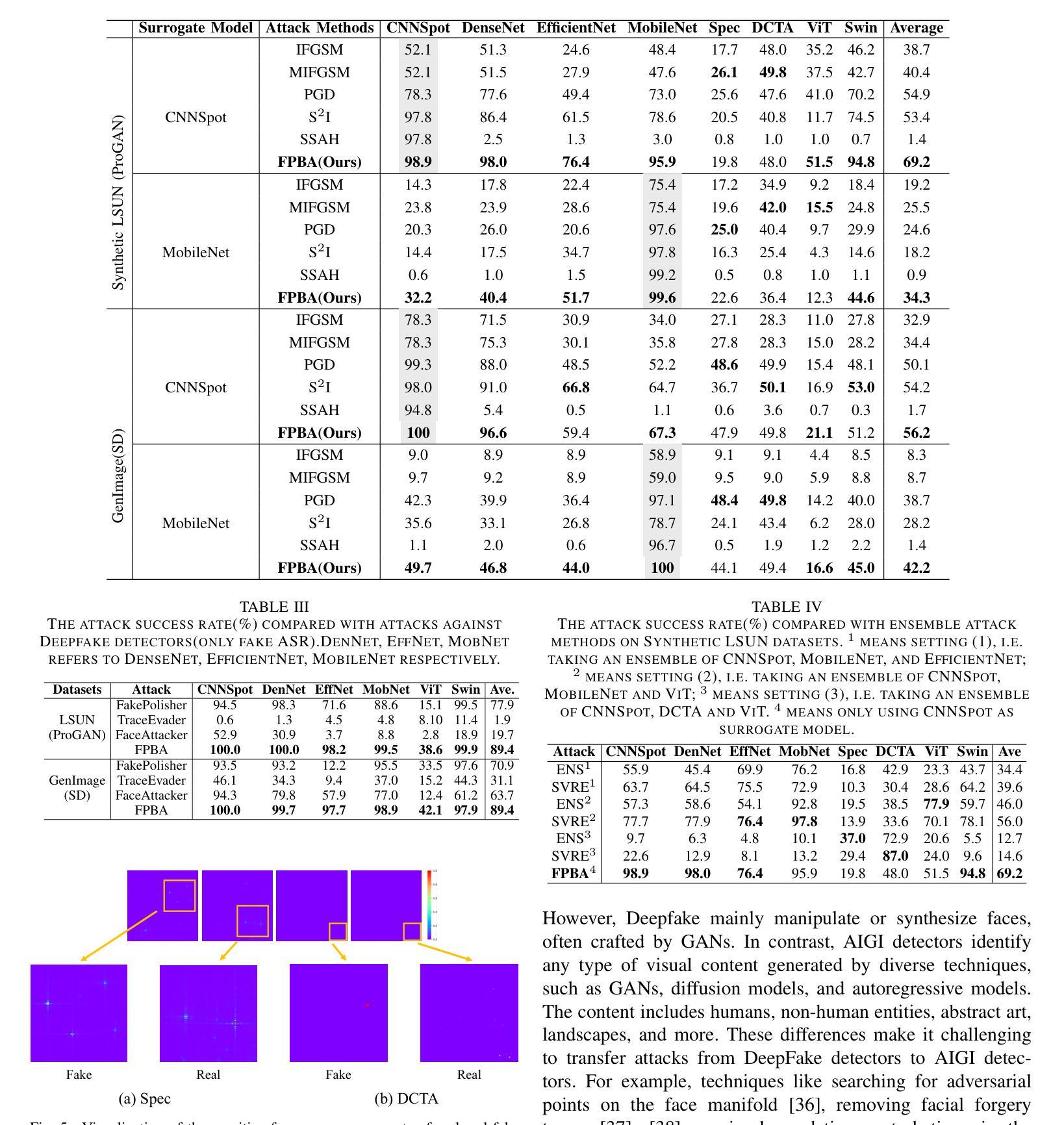
Recent advancements in image synthesis, particularly with the advent of GAN and Diffusion models, have amplified public concerns regarding the dissemination of disinformation. To address such concerns, numerous AI-generated Image (AIGI) Detectors have been proposed and achieved promising performance in identifying fake images. However, there still lacks a systematic understanding of the adversarial robustness of AIGI detectors. In this paper, we examine the vulnerability of state-of-the-art AIGI detectors against adversarial attack under white-box and black-box settings, which has been rarely investigated so far. To this end, we propose a new method to attack AIGI detectors. First, inspired by the obvious difference between real images and fake images in the frequency domain, we add perturbations under the frequency domain to push the image away from its original frequency distribution. Second, we explore the full posterior distribution of the surrogate model to further narrow this gap between heterogeneous AIGI detectors, e.g. transferring adversarial examples across CNNs and ViTs. This is achieved by introducing a novel post-train Bayesian strategy that turns a single surrogate into a Bayesian one, capable of simulating diverse victim models using one pre-trained surrogate, without the need for re-training. We name our method as Frequency-based Post-train Bayesian Attack, or FPBA. Through FPBA, we show that adversarial attack is truly a real threat to AIGI detectors, because FPBA can deliver successful black-box attacks across models, generators, defense methods, and even evade cross-generator detection, which is a crucial real-world detection scenario. The code will be shared upon acceptance.
近期图像合成领域的进展,尤其是生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型的出现,加剧了公众对传播虚假信息的担忧。为了解决这些担忧,已经提出了许多人工智能生成的图像(AIGI)检测器,并且在识别虚假图像方面取得了令人瞩目的性能。然而,人们对于AIGI检测器的对抗性稳健性仍缺乏系统的理解。在本文中,我们研究了最先进的AIGI检测器在白盒和黑盒设置下对抗攻击的脆弱性,这一领域迄今为止很少被研究。为此,我们提出了一种攻击AIGI检测器的新方法。首先,受真实图像和虚假图像在频域上明显差异的启发,我们在频域中添加扰动,使图像远离其原始频率分布。其次,我们探索了代理模型的后验分布,以进一步缩小不同AIGI检测器之间的差距,例如,在卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)之间转移对抗样本。这是通过引入一种新的后训练贝叶斯策略实现的,该策略将单个代理转变为贝叶斯代理,能够利用一个预训练的代理模拟多种受害者模型,而无需重新训练。我们将我们的方法命名为基于频率的后训练贝叶斯攻击(FPBA)。通过FPBA,我们证明对抗攻击确实对AIGI检测器构成真正的威胁,因为FPBA可以成功地进行跨模型、生成器、防御方法的黑盒攻击,甚至能逃避跨生成器检测,这是关键的现实世界检测场景。代码将在接受后共享。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
随着GAN和Diffusion模型的出现,图像合成技术的最新进展加剧了公众对虚假信息传播的担忧。为应对这些担忧,已经提出了许多AI生成的图像(AIGI)检测器,并在识别虚假图像方面取得了有希望的性能。然而,关于AIGI检测器的对抗性稳健性仍存在系统性的理解不足。本文研究了最先进的AIGI检测器在白盒和黑盒设置下对抗对抗性攻击的脆弱性,这一领域迄今为止很少被研究。为此,我们提出了一种新的攻击AIGI检测器的方法。首先,我们受到真实图像和虚假图像在频域中明显差异的启发,在频域中添加扰动使图像偏离其原始频率分布。其次,我们探索了代理模型的后验分布,以进一步缩小不同AIGI检测器之间的鸿沟。这是通过引入一种新的后训练贝叶斯策略实现的,该策略将单一的代理模型转变为贝叶斯模型,能够模拟使用单一预训练代理的多个受害者模型,无需重新训练。我们称我们的方法为基于频率的后训练贝叶斯攻击(FPBA)。通过FPBA,我们证明了对抗性攻击确实对AIGI检测器构成威胁,因为FPBA可以在不同的模型、生成器、防御方法和跨生成器检测中成功实施黑盒攻击,从而逃避现实世界的检测场景。代码将在接受后共享。
要点
- 最新图像合成技术引发公众对虚假信息传播担忧,AIGI检测器用于识别虚假图像。
- 当前缺乏关于AIGI检测器对抗性稳健性的系统性理解。
- 提出了在白盒和黑盒设置下对抗攻击AIGI检测器的新方法——FPBA。
- FPBA通过频域扰动攻击检测器,并探索代理模型的后验分布来缩小不同检测器间的差距。
- FPBA成功实施黑盒攻击,威胁到AIGI检测器的稳健性,可应用于不同模型、生成器、防御方法和跨生成器检测场景。
- 所提方法具有广泛应用潜力,可有效逃避现实世界的检测。
点此查看论文截图

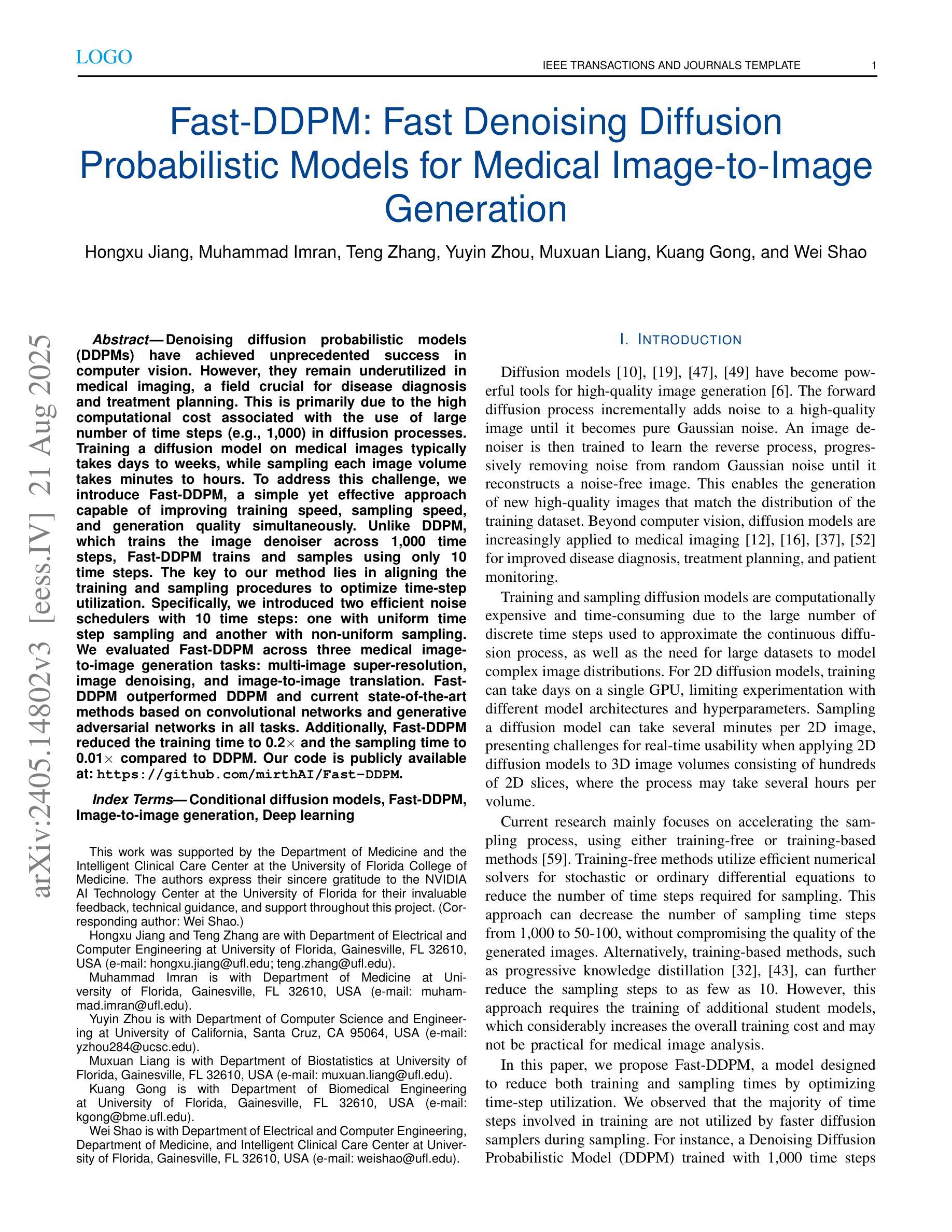
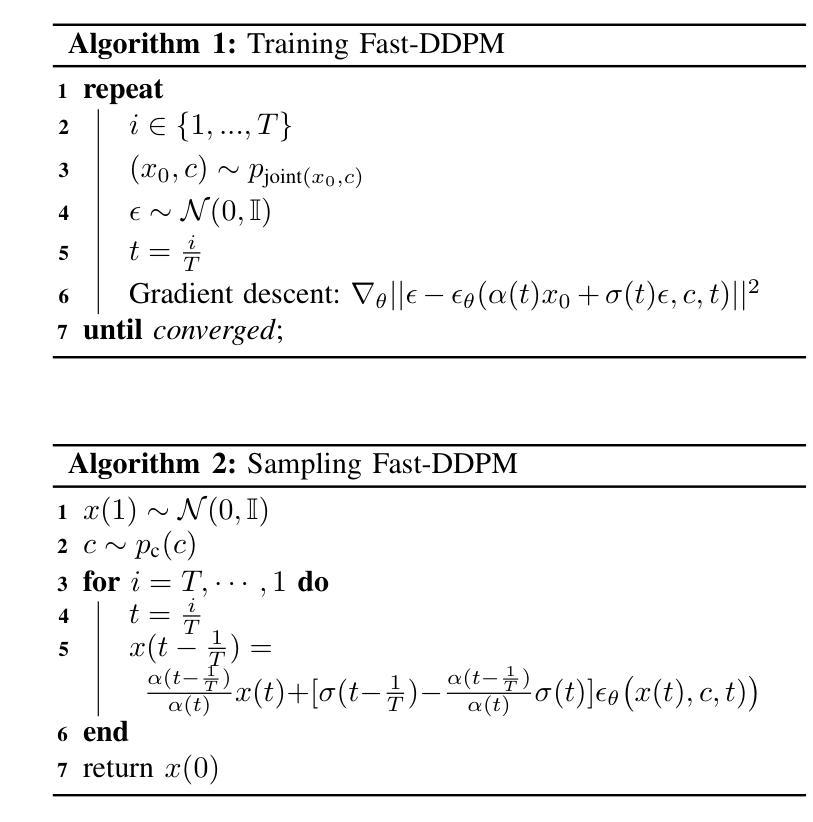
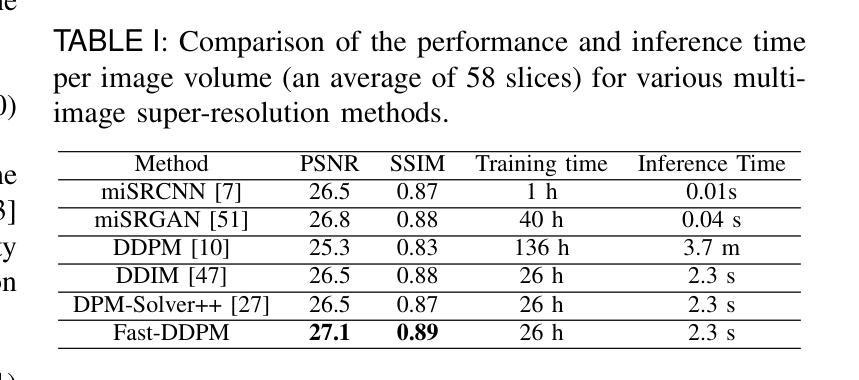
Fast-DDPM: Fast Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Medical Image-to-Image Generation
Authors:Hongxu Jiang, Muhammad Imran, Teng Zhang, Yuyin Zhou, Muxuan Liang, Kuang Gong, Wei Shao
Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) have achieved unprecedented success in computer vision. However, they remain underutilized in medical imaging, a field crucial for disease diagnosis and treatment planning. This is primarily due to the high computational cost associated with (1) the use of large number of time steps (e.g., 1,000) in diffusion processes and (2) the increased dimensionality of medical images, which are often 3D or 4D. Training a diffusion model on medical images typically takes days to weeks, while sampling each image volume takes minutes to hours. To address this challenge, we introduce Fast-DDPM, a simple yet effective approach capable of improving training speed, sampling speed, and generation quality simultaneously. Unlike DDPM, which trains the image denoiser across 1,000 time steps, Fast-DDPM trains and samples using only 10 time steps. The key to our method lies in aligning the training and sampling procedures to optimize time-step utilization. Specifically, we introduced two efficient noise schedulers with 10 time steps: one with uniform time step sampling and another with non-uniform sampling. We evaluated Fast-DDPM across three medical image-to-image generation tasks: multi-image super-resolution, image denoising, and image-to-image translation. Fast-DDPM outperformed DDPM and current state-of-the-art methods based on convolutional networks and generative adversarial networks in all tasks. Additionally, Fast-DDPM reduced the training time to 0.2x and the sampling time to 0.01x compared to DDPM. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM.
去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)在计算机视觉领域取得了前所未有的成功。然而,它们在医学影像这一对疾病诊断和治疗计划至关重要的领域却未得到充分利用。这主要是因为与(1)扩散过程中使用大量时间步数(例如,高达一千步)和(2)医学图像增加的维度(通常为三维或四维)相关的计算成本很高。在医学图像上训练扩散模型通常需要数天至数周的时间,而对每个图像体积进行采样则需要数分钟至数小时的时间。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了Fast-DDPM,这是一种简单而有效的方法,可以同时提高训练速度、采样速度和生成质量。与DDPM不同,DDPM是在一千个时间步长上训练图像去噪器,而Fast-DDPM则仅使用十个时间步长进行训练和采样。我们的方法的关键在于对齐训练和采样程序以优化时间步长的利用。具体来说,我们引入了两种具有十个时间步长的有效噪声调度器:一种具有均匀时间步长采样,另一种具有非均匀采样。我们在三项医学图像到图像生成任务中评估了Fast-DDPM:多图像超分辨率、图像去噪和图像到图像转换。Fast-DDPM在所有任务中都优于DDPM和基于卷积网络和生成对抗网络的最先进方法。此外,与DDPM相比,Fast-DDPM将训练时间缩短至原来的0.2倍,采样时间缩短至原来的0.01倍。我们的代码可在以下网址公开访问:https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散概率模型(DDPM)在计算机视觉领域取得了前所未有的成功,但在医学成像领域的应用仍然有限。这是因为医学图像的维度通常较高,为三维或四维,且扩散过程中需要大量的时间步骤(例如1000步),导致计算成本高昂。针对这一问题,我们提出了Fast-DDPM方法,该方法能在训练速度、采样速度生成质量方面同时实现改进。与DDPM不同的是,Fast-DDPM仅使用10个时间步骤进行训练和采样。我们引入了两种高效噪声调度器,一种采用均匀时间步长采样,另一种采用非均匀采样。在三项医学图像生成任务中,Fast-DDPM表现优异,包括多图像超分辨率、图像去噪和图像到图像的转换。与DDPM和当前最先进的卷积网络和生成对抗网络相比,Fast-DDPM在所有任务中的表现均有所超越。此外,Fast-DDPM将训练时间缩短至DDPM的0.2倍,采样时间缩短至DDPM的0.01倍。我们的代码已公开发布在:https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM。
要点摘要
- DDPM在计算机视觉领域表现出色,但在医学成像领域因高计算成本而受到限制。
- Fast-DDPM方法旨在解决这一问题,通过优化时间步长利用,显著提高了训练速度和采样速度。
- Fast-DDPM仅使用10个时间步骤进行训练和采样,引入两种噪声调度器以实现高效采样。
- 在三项医学图像生成任务中,Fast-DDPM表现优于DDPM和其他最先进的方法。
- Fast-DDPM将训练时间和采样时间都大幅度减少。
- 公开的代码可在https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM上访问。
- Fast-DDPM为医学成像领域带来了新的可能性,有望改善疾病诊断和治疗计划。
点此查看论文截图