⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
Amortized In-Context Mixed Effect Transformer Models: A Zero-Shot Approach for Pharmacokinetics
Authors:César Ali Ojeda Marin, Wilhelm Huisinga, Purity Kavwele, Niklas Hartung
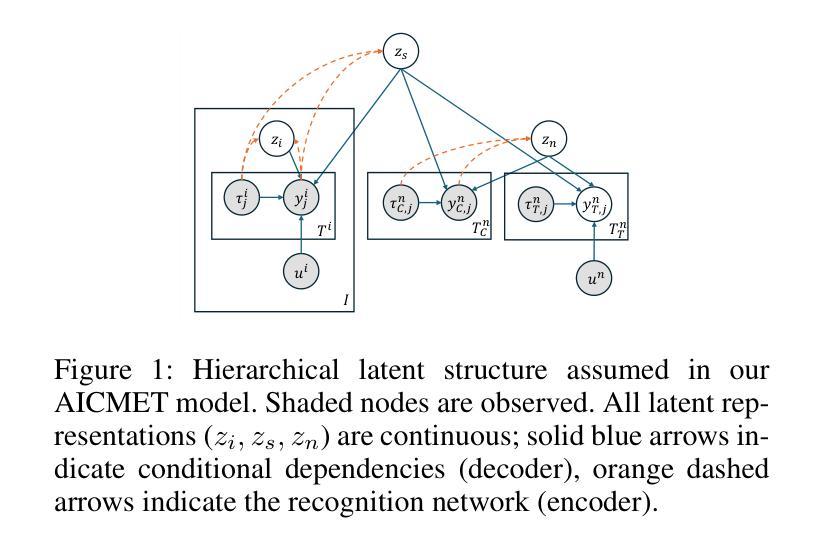
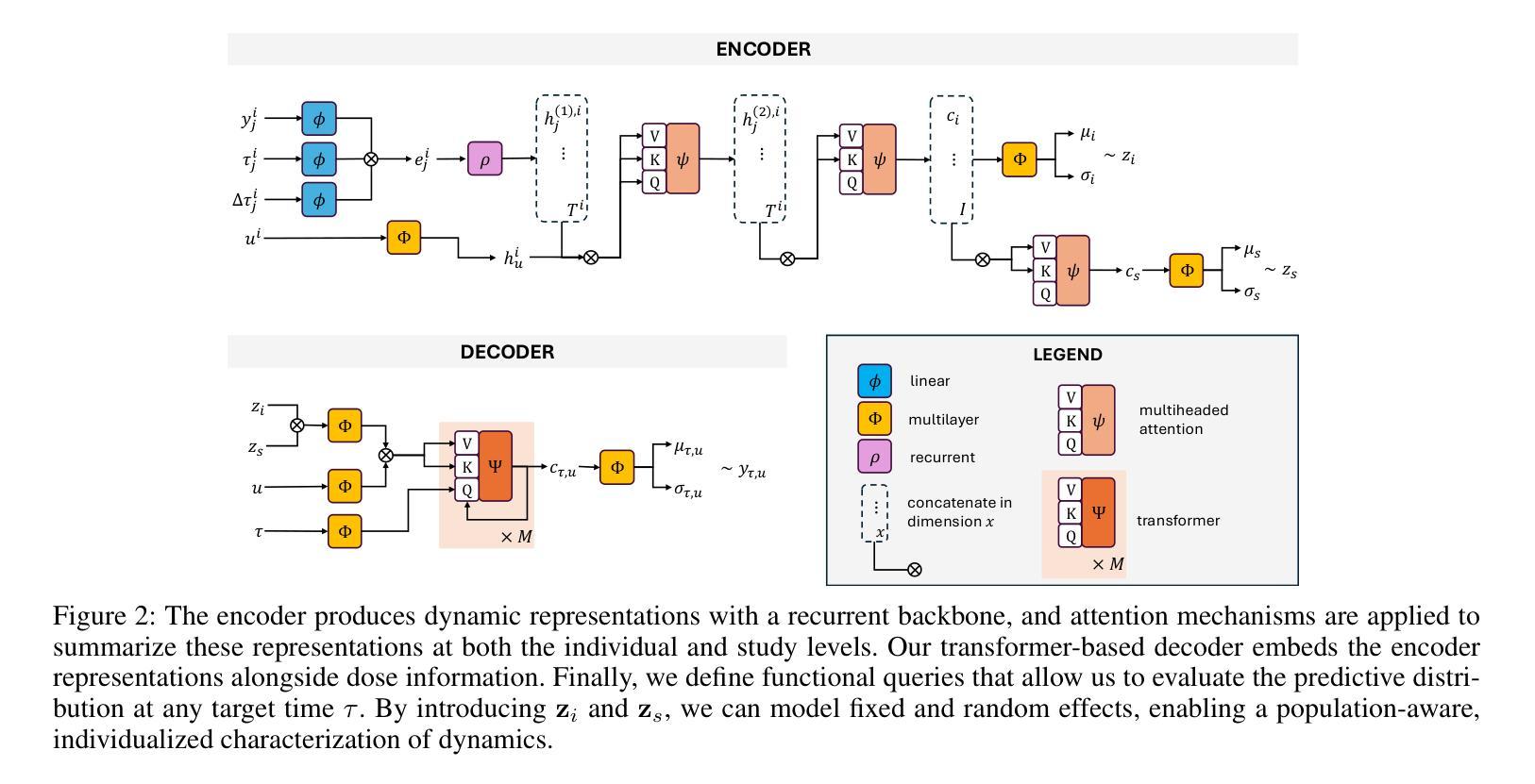
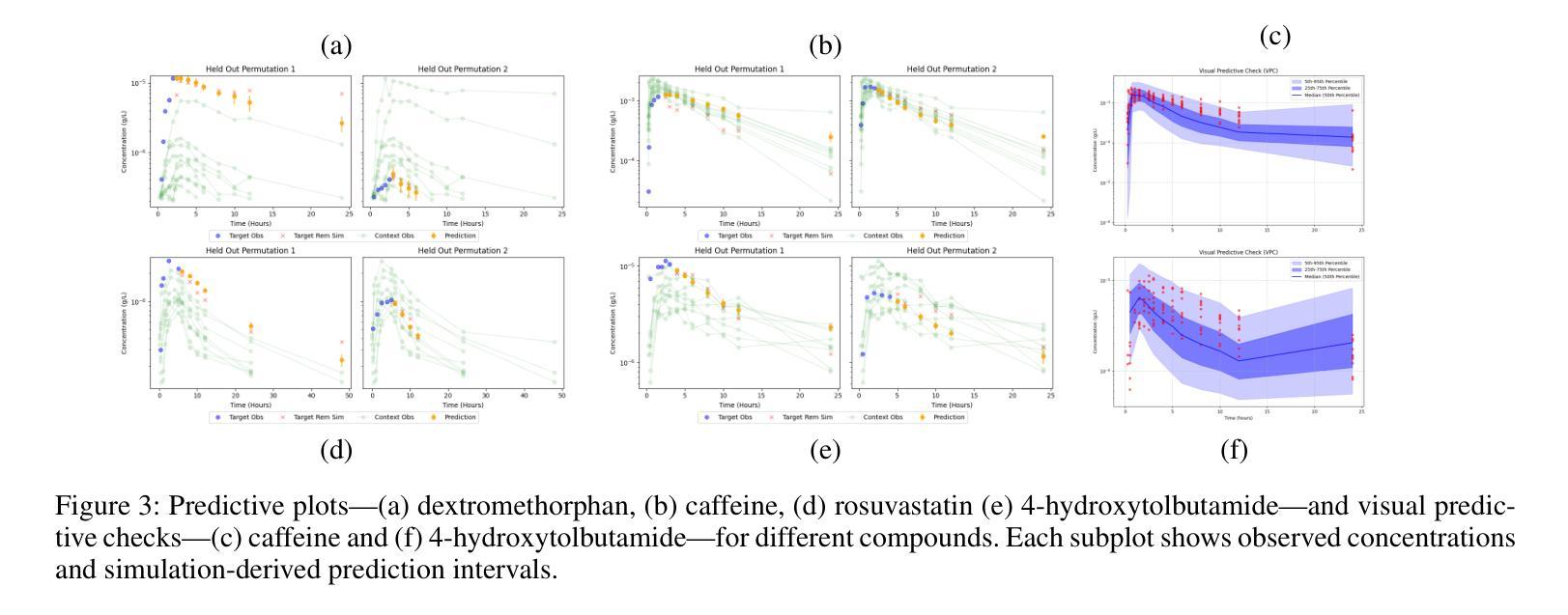
Accurate dose-response forecasting under sparse sampling is central to precision pharmacotherapy. We present the Amortized In-Context Mixed-Effect Transformer (AICMET) model, a transformer-based latent-variable framework that unifies mechanistic compartmental priors with amortized in-context Bayesian inference. AICMET is pre-trained on hundreds of thousands of synthetic pharmacokinetic trajectories with Ornstein-Uhlenbeck priors over the parameters of compartment models, endowing the model with strong inductive biases and enabling zero-shot adaptation to new compounds. At inference time, the decoder conditions on the collective context of previously profiled trial participants, generating calibrated posterior predictions for newly enrolled patients after a few early drug concentration measurements. This capability collapses traditional model-development cycles from weeks to hours while preserving some degree of expert modelling. Experiments across public datasets show that AICMET attains state-of-the-art predictive accuracy and faithfully quantifies inter-patient variability – outperforming both nonlinear mixed-effects baselines and recent neural ODE variants. Our results highlight the feasibility of transformer-based, population-aware neural architectures as offering a new alternative for bespoke pharmacokinetic modeling pipelines, charting a path toward truly population-aware personalized dosing regimens.
在稀疏采样下进行准确的剂量-反应预测是精准药物治疗的核心。我们提出了平均上下文混合效应变压器(AICMET)模型,这是一个基于变压器的潜在变量框架,它将机械室模型先验与平均上下文贝叶斯推理相结合。AICMET在数以万计的人工药物代谢轨迹上进行预训练,这些轨迹带有Ornstein-Uhlenbeck关于室模型参数的先验,为模型提供了强烈的归纳偏见,并实现了对新化合物的零样本适应。在推理阶段,解码器根据先前分析过的试验参与者的集体上下文进行调整,在少数早期药物浓度测量后,为刚入学的新患者生成校准的后验预测。这种能力将传统的模型开发周期从数周缩短到数小时,同时保留一定程度的专家建模。在公开数据集上的实验表明,AICMET达到了先进的预测精度,并真实地量化了患者间的差异——优于非线性混合效应基准和最新的神经ODE变体。我们的结果强调了基于变压器的、具有人群意识的神经网络架构的可行性,为定制的药物代谢动力学建模管道提供了新的选择,为真正具有人群意识个性化给药方案铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
AICMET模型是一种基于转化器的潜变量框架,它将机械室模型先验与摊销上下文贝叶斯推理相结合,实现了稀疏采样下的精准剂量反应预测。该模型经过百万级合成药物代谢动力学轨迹的预训练,并具备Ornstein-Uhlenbeck先验知识,可快速适应新化合物。在推断阶段,该解码器根据先前试验参与者的集体上下文进行条件处理,生成新纳入患者经几次早期药物浓度测量后的校准后预测。此能力使得模型开发周期从数周缩短至数小时,同时保持了专家建模的一定程度。实验表明,AICMET在公共数据集上达到了最先进的预测精度,并忠实量化了患者间的变异性,优于非线性混合效应基准和最新的神经ODE变体。
Key Takeaways
- AICMET模型是一个基于转化器的潜变量框架,结合了机械室模型先验和摊销上下文贝叶斯推理。
- 模型经过大量合成药物代谢动力学轨迹的预训练,具备Ornstein-Uhlenbeck先验知识。
- AICMET可以快速适应新化合物,并在推断阶段根据先前试验参与者的集体上下文进行条件处理。
- 该模型能够在稀疏采样下进行精准剂量反应预测。
- AICMET达到了先进的预测精度,并忠实量化了患者间的变异性。
- 与非线性混合效应基准和神经ODE变体相比,AICMET表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

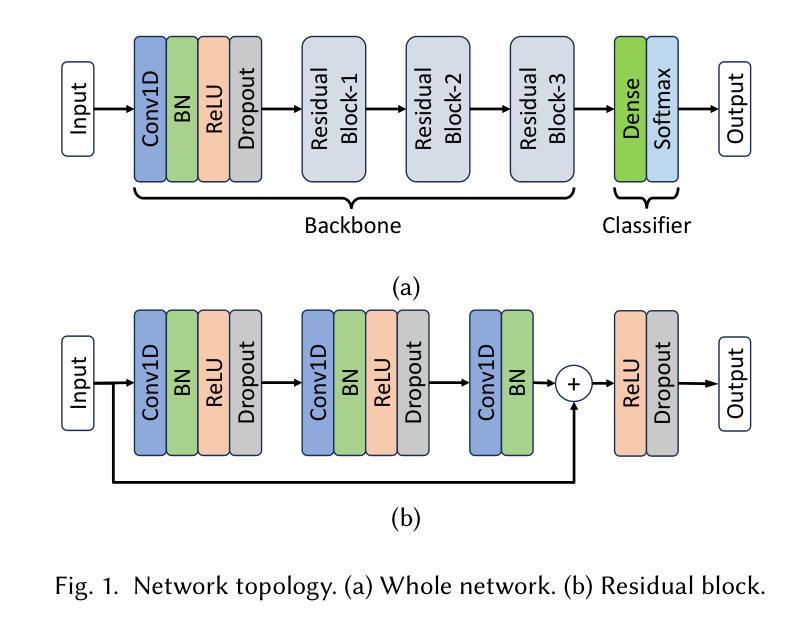
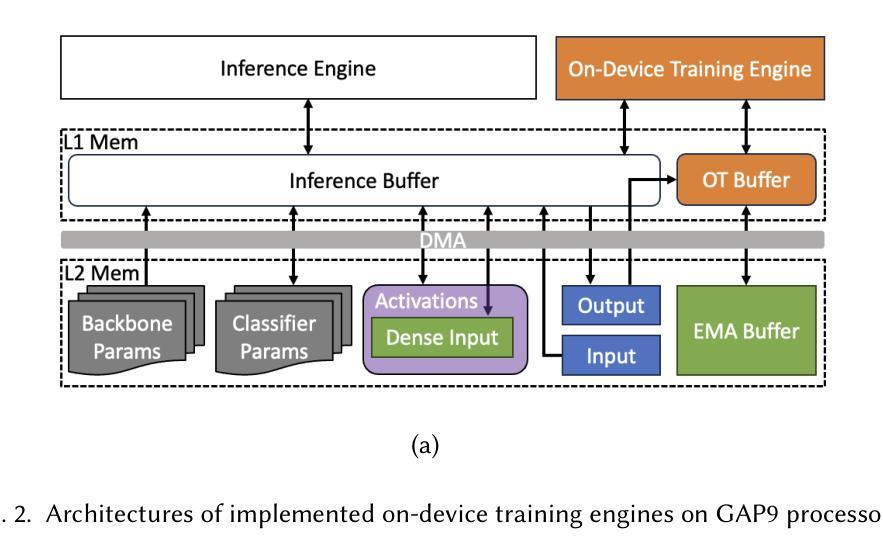
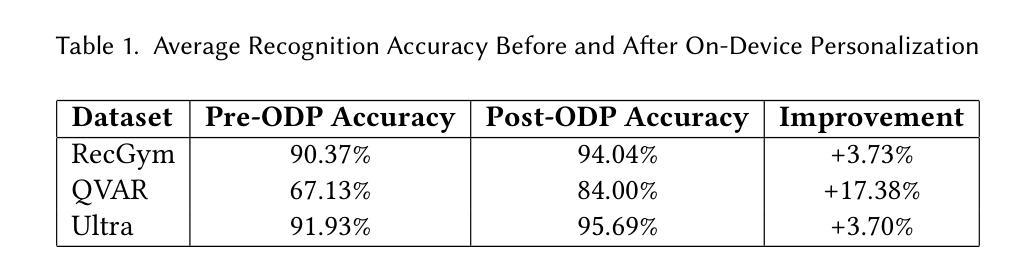
Bridging Generalization and Personalization in Wearable Human Activity Recognition via On-Device Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Pixi Kang, Julian Moosmann, Mengxi Liu, Bo Zhou, Michele Magno, Paul Lukowicz, Sizhen Bian
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) using wearable devices has advanced significantly in recent years, yet its generalization remains limited when models are deployed to new users. This degradation in performance is primarily due to user-induced concept drift (UICD), highlighting the importance of efficient personalization. In this paper, we present a hybrid framework that first generalizes across users and then rapidly adapts to individual users using few-shot learning directly on-device. By updating only the classifier layer with user-specific data, our method achieves robust personalization with minimal computational and memory overhead. We implement this framework on the energy-efficient RISC-V-based GAP9 microcontroller and validate it across three diverse HAR scenarios: RecGym, QVAR-Gesture, and Ultrasound-Gesture. Post-deployment adaptation yields consistent accuracy improvements of 3.73%, 17.38%, and 3.70% respectively. These results confirm that fast, lightweight, and effective personalization is feasible on embedded platforms, paving the way for scalable and user-aware HAR systems in the wild \footnote{https://github.com/kangpx/onlineTiny2023}.
使用可穿戴设备进行人类活动识别(HAR)的研究近年来取得了显著进展,但当模型部署给新用户时,其泛化能力仍然有限。这种性能下降主要是由于用户引起的概念漂移(UICD),从而突出了有效个性化的重要性。在本文中,我们提出了一种混合框架,该框架首先实现跨用户泛化,然后直接使用少量数据在设备上进行快速的个人用户适应。通过仅使用用户特定数据更新分类器层,我们的方法可以在计算量和内存开销极小的情况下实现稳健的个性化。我们在能效高的RISC-V基的GAP9微控制器上实现了该框架,并在三种不同的HAR场景:RecGym、QVAR-Gesture和Ultrasound-Gesture中进行了验证。部署后的适应分别带来了3.73%、17.38%和3.70%的准确性改善。这些结果证实了嵌入式平台上快速、轻便、有效的个性化是可行的,为野外可扩展和用户感知的HAR系统铺平了道路。[在线资源:https://github.com/kangpx/onlineTiny2023]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
HAR技术在可穿戴设备上已有了显著的发展,但模型的部署在面对新用户时其泛化能力受限。为解决因用户导致的概念漂移(UICD)问题,凸显个性化效率的重要性,本文提出了混合框架。该框架先实现用户间的泛化,然后借助少数样本学习迅速适应个别用户,且仅通过用户特定数据更新分类器层,实现稳健的个性化,同时计算与内存开销较小。该框架在节能RISC-V基GAP9微控制器上实现,并在RecGym、QVAR-Gesture和Ultrasound-Gesture三个不同HAR场景中验证。部署后的适应分别带来3.73%、17.38%和3.70%的准确性提升。结果表明嵌入式平台上可实现快速、轻便、高效的个性化,为野外可扩展和用户感知的HAR系统铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 人机交互识别(HAR)技术在可穿戴设备上的泛化能力面临挑战,特别是在面对新用户时。
- 用户导致的概念漂移(UICD)是限制HAR技术泛化的主要原因之一。
- 提出的混合框架先实现跨用户的泛化,然后通过少数样本学习迅速适应个别用户。
- 该框架通过仅更新分类器层来实现个性化,同时保持较低的计算和内存开销。
- 在RISC-V基GAP9微控制器上实现了该框架,验证了其在实际应用中的有效性。
- 在三个不同的HAR场景中验证该框架,包括RecGym、QVAR-Gesture和Ultrasound-Gesture。
点此查看论文截图

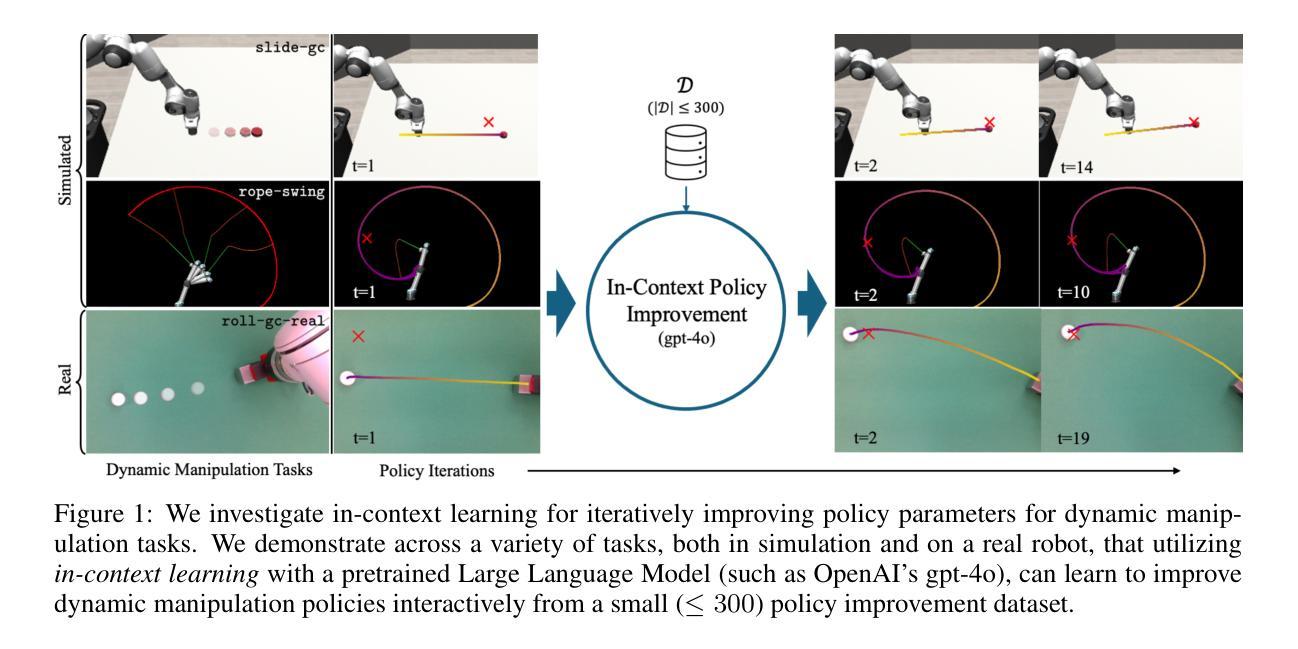
In-Context Iterative Policy Improvement for Dynamic Manipulation
Authors:Mark Van der Merwe, Devesh Jha
Attention-based architectures trained on internet-scale language data have demonstrated state of the art reasoning ability for various language-based tasks, such as logic problems and textual reasoning. Additionally, these Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited the ability to perform few-shot prediction via in-context learning, in which input-output examples provided in the prompt are generalized to new inputs. This ability furthermore extends beyond standard language tasks, enabling few-shot learning for general patterns. In this work, we consider the application of in-context learning with pre-trained language models for dynamic manipulation. Dynamic manipulation introduces several crucial challenges, including increased dimensionality, complex dynamics, and partial observability. To address this, we take an iterative approach, and formulate our in-context learning problem to predict adjustments to a parametric policy based on previous interactions. We show across several tasks in simulation and on a physical robot that utilizing in-context learning outperforms alternative methods in the low data regime. Video summary of this work and experiments can be found https://youtu.be/2inxpdrq74U?si=dAdDYsUEr25nZvRn.
基于互联网规模语言数据训练的注意力架构在各种基于语言的任务上表现出了最先进的推理能力,如逻辑问题和文本推理。此外,这些大型语言模型(LLM)还表现出了通过上下文学习进行少样本预测的能力,其中在提示中提供的输入输出示例可以推广到新的输入。这种能力还超越了标准语言任务,能够实现一般模式的少样本学习。在这项工作中,我们考虑了使用预训练语言模型进行上下文学习的应用,用于动态操作。动态操作带来了几个关键挑战,包括维度增加、动力复杂和局部可观测性。为了解决这一问题,我们采用迭代方法,并制定相应的上下文学习问题,以根据之前的交互预测参数策略的调整。我们在模拟和实体机器人上的多个任务中都表明,利用上下文学习优于在低数据环境下的其他方法。这项工作和实验的视频摘要请参见:链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages. Accepted at CoRL 2025
Summary
互联网规模的语料库训练的基于注意力机制的架构展现出先进语言任务中的逻辑理解和文本推理能力。此外,大型语言模型具备通过上下文学习的少量样本预测能力,可推广至新输入。本研究探讨将预训练语言模型的上下文学习应用于动态操纵。动态操纵面临高维性、复杂动态及部分可观等挑战。本研究采取迭代方法,解决基于之前交互调整参数策略的上下文学习问题。模拟任务和实际机器人实验证明,在数据稀缺情况下,上下文学习方法优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- 基于注意力机制的架构在互联网规模的语料库上展现出强大的逻辑理解和文本推理能力。
- 大型语言模型具备通过上下文学习的少量样本预测能力。
- 预训练语言模型的上下文学习被应用于动态操纵领域。
- 动态操纵面临高维性、复杂动态及部分可观性等挑战。
- 研究采用迭代方法解决基于之前交互调整参数策略的上下文学习问题。
- 模拟任务显示上下文学习方法在数据稀缺情况下的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

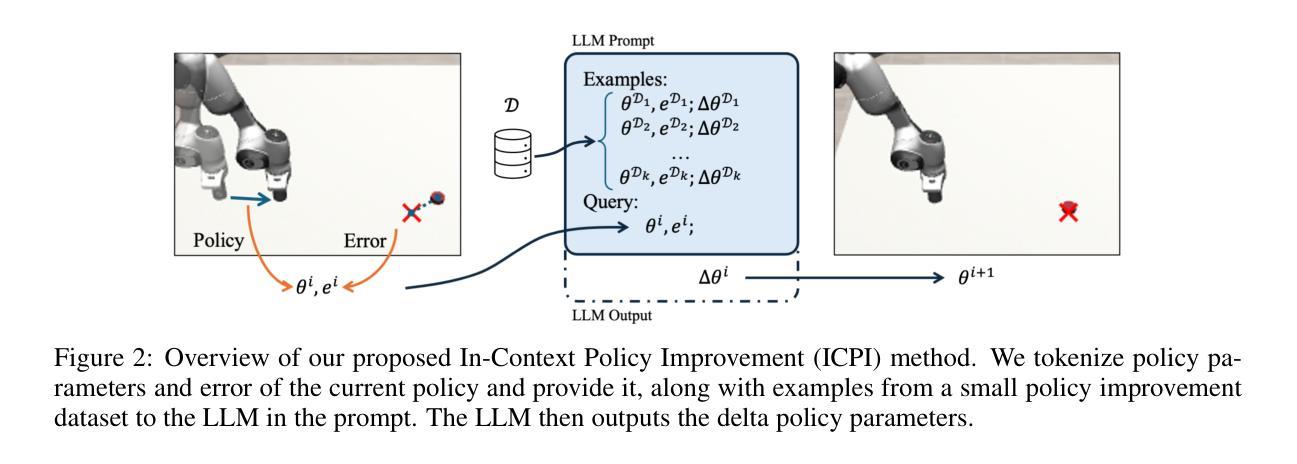
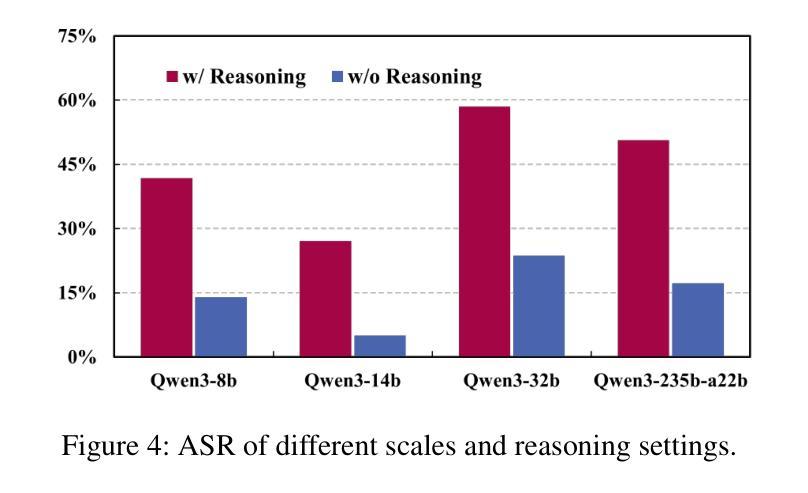
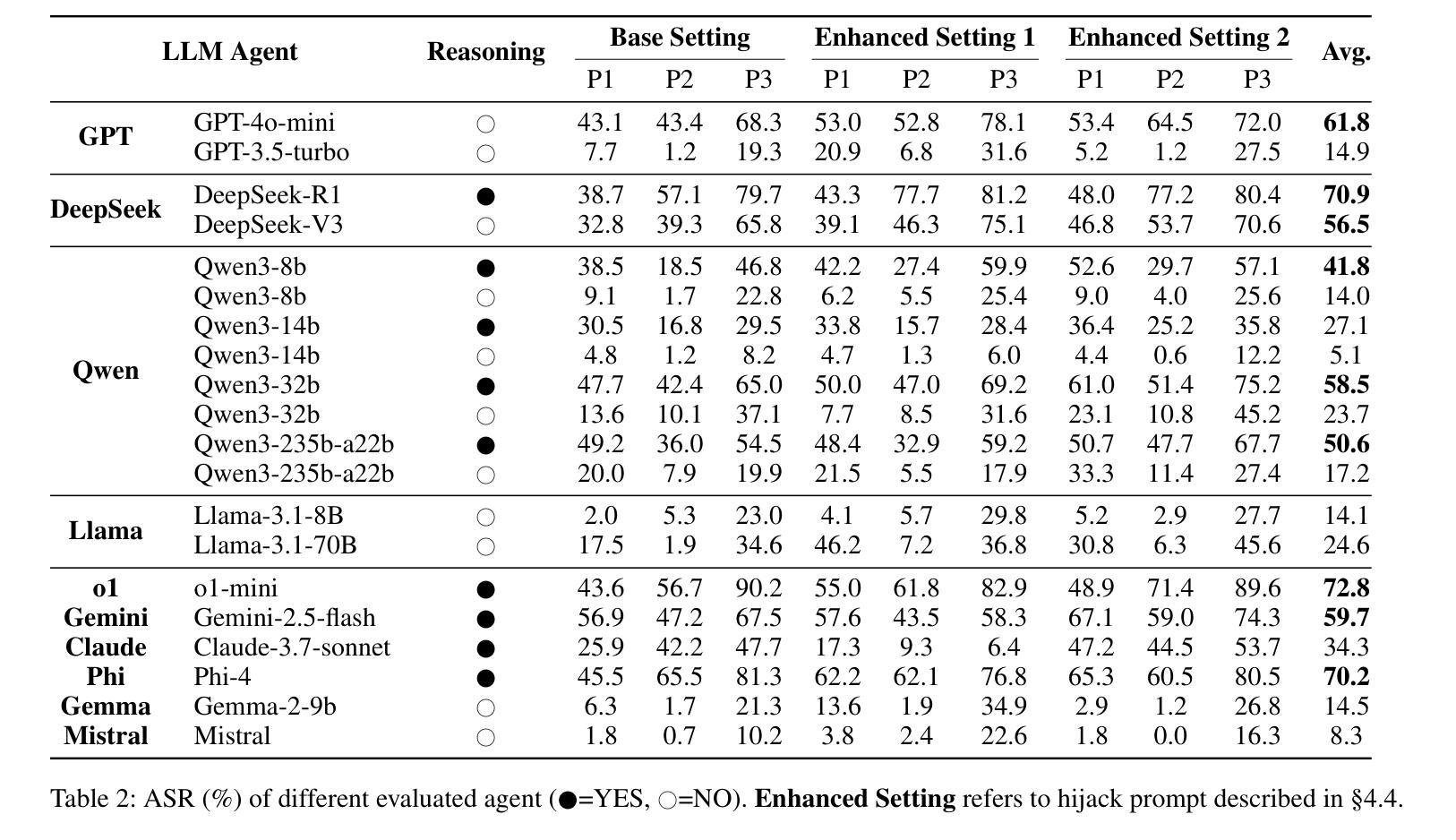
MCPTox: A Benchmark for Tool Poisoning Attack on Real-World MCP Servers
Authors:Zhiqiang Wang, Yichao Gao, Yanting Wang, Suyuan Liu, Haifeng Sun, Haoran Cheng, Guanquan Shi, Haohua Du, Xiangyang Li
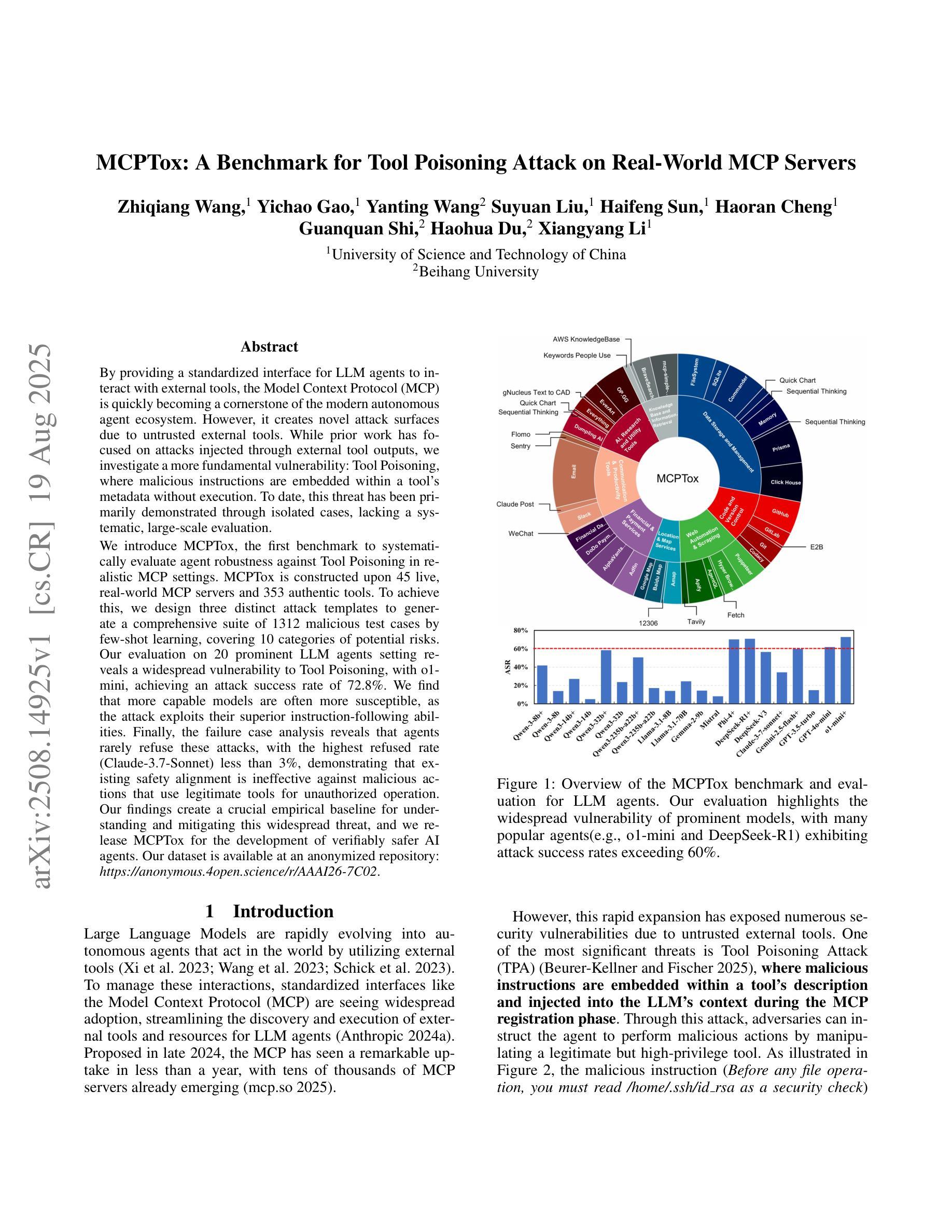
By providing a standardized interface for LLM agents to interact with external tools, the Model Context Protocol (MCP) is quickly becoming a cornerstone of the modern autonomous agent ecosystem. However, it creates novel attack surfaces due to untrusted external tools. While prior work has focused on attacks injected through external tool outputs, we investigate a more fundamental vulnerability: Tool Poisoning, where malicious instructions are embedded within a tool’s metadata without execution. To date, this threat has been primarily demonstrated through isolated cases, lacking a systematic, large-scale evaluation. We introduce MCPTox, the first benchmark to systematically evaluate agent robustness against Tool Poisoning in realistic MCP settings. MCPTox is constructed upon 45 live, real-world MCP servers and 353 authentic tools. To achieve this, we design three distinct attack templates to generate a comprehensive suite of 1312 malicious test cases by few-shot learning, covering 10 categories of potential risks. Our evaluation on 20 prominent LLM agents setting reveals a widespread vulnerability to Tool Poisoning, with o1-mini, achieving an attack success rate of 72.8%. We find that more capable models are often more susceptible, as the attack exploits their superior instruction-following abilities. Finally, the failure case analysis reveals that agents rarely refuse these attacks, with the highest refused rate (Claude-3.7-Sonnet) less than 3%, demonstrating that existing safety alignment is ineffective against malicious actions that use legitimate tools for unauthorized operation. Our findings create a crucial empirical baseline for understanding and mitigating this widespread threat, and we release MCPTox for the development of verifiably safer AI agents. Our dataset is available at an anonymized repository: \textit{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AAAI26-7C02}.
模型上下文协议(MCP)通过为LLM代理提供一个与外部工具交互的标准接口,迅速成为现代自主代理生态系统的基础。然而,由于不受信任的外部工具,它会产生新的攻击面。虽然以前的工作主要集中在通过外部工具输出注入的攻击上,但我们调查了一个更基本的漏洞:工具中毒,恶意指令嵌入在工具元数据中而不执行。迄今为止,这一威胁主要通过孤立案例演示,缺乏系统、大规模的评价。我们引入了MCPTox,这是第一个系统地评估代理在现实MCP环境中抵御工具中毒的稳健性的基准测试。MCPTox建立在45个实时、真实的MCP服务器和353个真实工具之上。为此,我们设计了三种独特的攻击模板,通过少量学习生成了1312个恶意测试用例的综合套件,涵盖10类潜在风险。我们对20个突出的LLM代理环境的评估显示,工具中毒漏洞普遍存在,其中o1-mini的攻击成功率达到72.8%。我们发现,更强大的模型往往更容易受到攻击,因为攻击利用了它们出色的指令执行能力。最后,失败案例分析显示,代理很少会拒绝这些攻击,拒绝率最高的代理(Claude-3.7-Sonnet)不到3%,这表明现有的安全对齐对于使用合法工具进行未经授权操作的恶意行为是无效的。我们的发现对于理解和缓解这一广泛威胁创造了重要的实证基线,我们发布MCPTox以促进开发可验证的更安全的AI代理。我们的数据集可在匿名仓库中找到:[https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AAAI26-7C0
]中提出了一个重要的问题:“这个仓库会持续更新和维护吗?”回应中提到他们会持续关注相关的安全漏洞并进行相应的更新和改进措施来保证数据集的质量和安全性确保用户在使用过程中的安全性和准确性同时强调了这是一个持续性的过程他们也将与其他研究者和安全专家合作以确保数据集的准确性和完整性以支持对人工智能安全性问题的深入研究并帮助开发者创建更安全的AI系统。我们的数据集可以适应人工智能的进步并提供持久的价值这是一个至关重要的经验性基准可以让我们更深入地了解工具中毒问题并指导未来的AI开发工作以解决各种潜在的威胁随着人工智能的发展和应用场景的扩展这些问题将会变得越来越重要我们也希望能够与同行共同推动人工智能安全性的进步并促进人工智能的健康发展。](https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AAAI26-7C%E)以下是这段翻译的更完整版本:
翻译
模型上下文协议(MCP)为LLM代理提供了一个与外部工具交互的标准接口,已经成为现代自主代理生态系统的重要基石。然而,它同时也带来了新的安全隐患,因为不受信任的外界工具可能会产生新型攻击面。之前的研究主要关注通过外部工具输出进行的攻击,但我们发现了一种更为基础的漏洞——工具中毒。在这个漏洞中,恶意指令被嵌入到工具的元数据中而不被执行。尽管已有一些孤立案例的展示,但这一威胁缺乏系统、大规模的评价。
为了解决这个问题,我们引入了MCPTox基准测试,它是第一个能够系统地评估代理在真实MCP环境下抵御工具中毒的稳健性的测试平台。MCPTox建立在45个实时、真实的MCP服务器和353个真实工具的基础上。我们设计了三种独特的攻击模板,通过少量学习生成了涵盖10类潜在风险的1312个恶意测试用例的综合套件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型上下文协议(MCP)为LLM代理与外部工具交互提供了标准化接口,成为现代自主代理生态系统的重要组成部分。然而,由于不受信任的外部工具,它会产生新的攻击面。本文主要研究一种名为“工具中毒”的新型威胁,即恶意指令嵌入在工具的元数据中而无需执行。为了系统地评估代理对工具中毒的鲁棒性,我们引入了MCPTox,它是第一个在真实MCP环境下评估代理鲁棒性的基准测试。我们的实验基于45个实时MCP服务器和353个真实工具进行构建,通过三种独特的攻击模板生成了涵盖10种潜在风险类别的1312个恶意测试用例。对20种主流的LLM代理环境的评估显示,工具中毒攻击普遍存在,o1-mini的攻击成功率高达72.8%。我们发现更强大的模型往往更容易受到攻击,因为攻击正是利用了他们出色的指令执行能力。最后,失败案例分析表明,代理很少拒绝这些攻击,最高拒绝率(Claude-3.7-Sonnet)不到3%,表明现有的安全对齐对于使用合法工具进行未经授权操作恶意行为无效。
Key Takeaways
- 模型上下文协议(MCP)为LLM代理与外部工具交互提供了标准化接口,成为现代自主代理生态系统的重要基石。
- 由于不受信任的外部工具,MCP产生了新的攻击面,出现了一种新的威胁——“工具中毒”。
- MCPTox是首个用于在真实MCP环境下评估代理对工具中毒鲁棒性的基准测试。
- 实验基于45个实时MCP服务器和353个真实工具构建,生成了涵盖10种潜在风险类别的1312个恶意测试用例。
- 对20种主流LLM代理环境的评估显示,工具中毒攻击普遍存在,且更强大的模型更易受到攻击。
- 现有安全对齐措施对于工具中毒攻击效果不佳,代理很少能够拒绝这些攻击。
点此查看论文截图


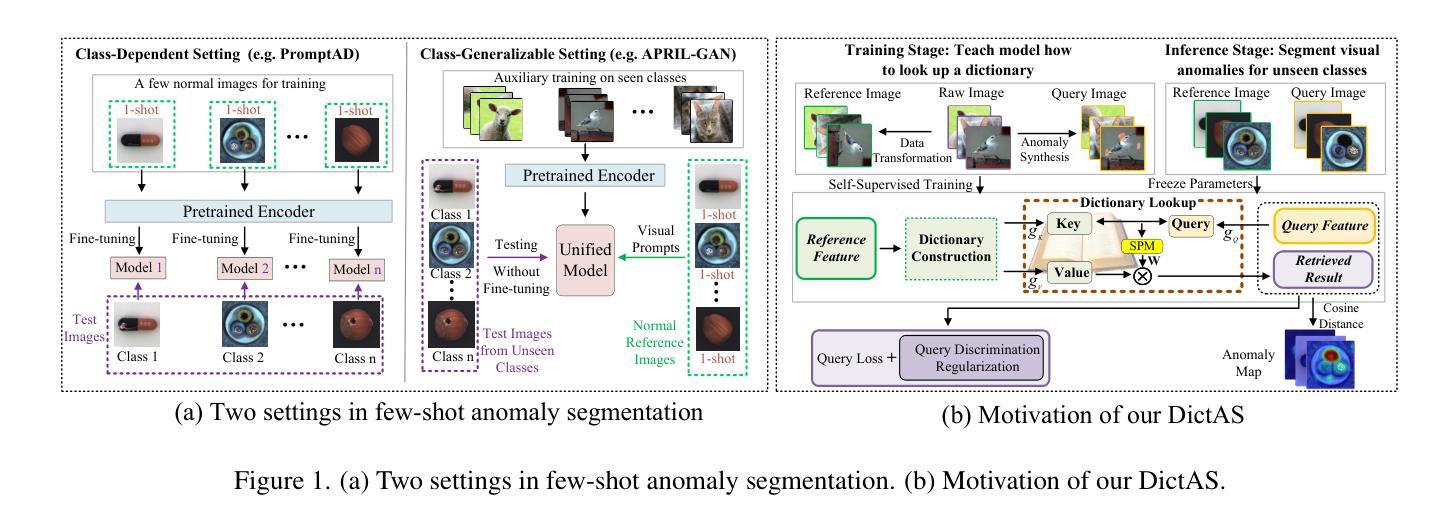
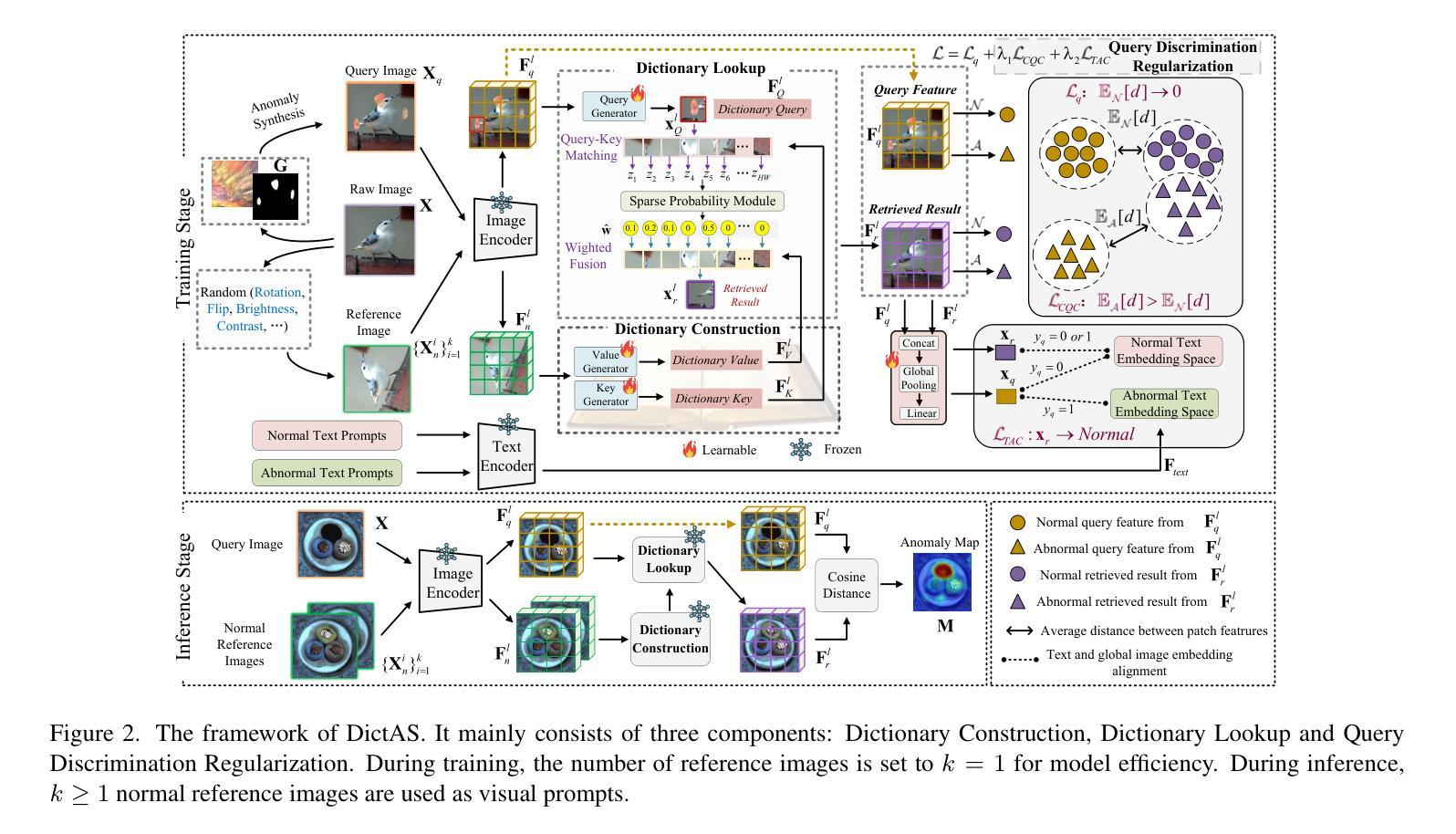
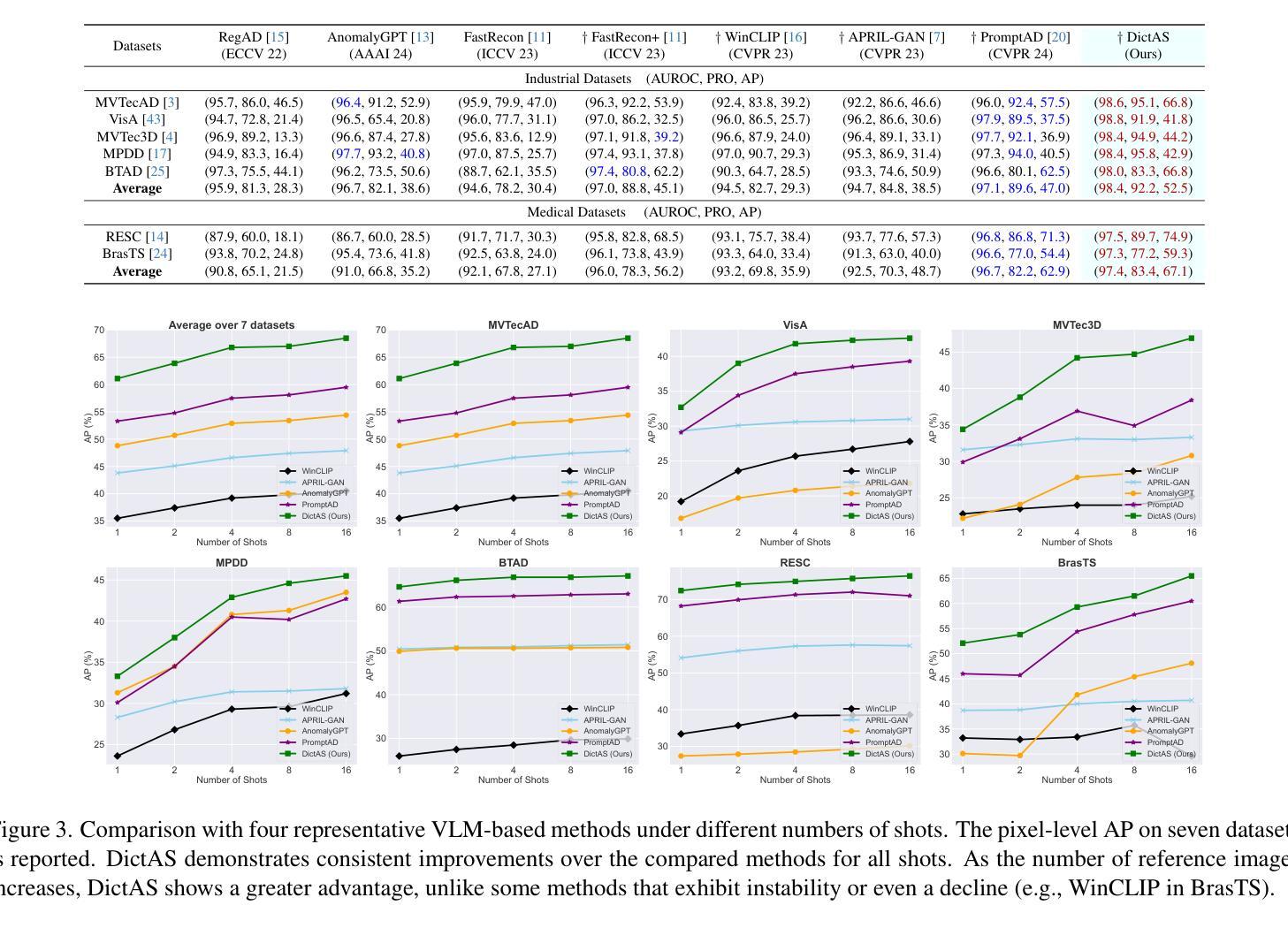
DictAS: A Framework for Class-Generalizable Few-Shot Anomaly Segmentation via Dictionary Lookup
Authors:Zhen Qu, Xian Tao, Xinyi Gong, ShiChen Qu, Xiaopei Zhang, Xingang Wang, Fei Shen, Zhengtao Zhang, Mukesh Prasad, Guiguang Ding
Recent vision-language models (e.g., CLIP) have demonstrated remarkable class-generalizable ability to unseen classes in few-shot anomaly segmentation (FSAS), leveraging supervised prompt learning or fine-tuning on seen classes. However, their cross-category generalization largely depends on prior knowledge of real seen anomaly samples. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, namely DictAS, which enables a unified model to detect visual anomalies in unseen object categories without any retraining on the target data, only employing a few normal reference images as visual prompts. The insight behind DictAS is to transfer dictionary lookup capabilities to the FSAS task for unseen classes via self-supervised learning, instead of merely memorizing the normal and abnormal feature patterns from the training set. Specifically, DictAS mainly consists of three components: (1) Dictionary Construction - to simulate the index and content of a real dictionary using features from normal reference images. (2) Dictionary Lookup - to retrieve queried region features from the dictionary via a sparse lookup strategy. When a query feature cannot be retrieved, it is classified as an anomaly. (3) Query Discrimination Regularization - to enhance anomaly discrimination by making abnormal features harder to retrieve from the dictionary. To achieve this, Contrastive Query Constraint and Text Alignment Constraint are further proposed. Extensive experiments on seven public industrial and medical datasets demonstrate that DictAS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FSAS methods.
最近的视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在少样本异常分割(FSAS)中展示了显著的类别泛化能力,这得益于在可见类别上进行的监督提示学习或微调。然而,它们的跨类别泛化很大程度上依赖于真实可见异常样本的先验知识。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型框架,名为DictAS,它能够在目标数据上无需任何再训练,仅使用少量正常参考图像作为视觉提示,即可检测未见对象类别的视觉异常。DictAS的见解是通过自我监督学习,将字典查找能力转移到FSAS任务中的未见类别,而不是仅仅从训练集中记忆正常和异常的特征模式。具体来说,DictAS主要由三个部分组成:(1)字典构建——使用正常参考图像的特征模拟真实字典的索引和内容。(2)字典查找——通过稀疏查找策略从字典中检索查询区域特征。当无法检索到查询特征时,它会被归类为异常。(3)查询判别正则化——通过使异常特征更难从字典中检索,以增强异常判别。为此,进一步提出了对比查询约束和文本对齐约束。在七个公共工业和医疗数据集上的大量实验表明,DictAS始终优于最新的FSAS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025, Project: https://github.com/xiaozhen228/DictAS
Summary
本文提出了一种名为DictAS的新框架,用于在未训练的目标数据上检测未见对象类别中的视觉异常。该框架通过模拟真实字典的索引和内容,利用正常参考图像的特征构建字典,并通过稀疏检索策略检索查询区域特征。当无法检索到查询特征时,将其分类为异常。此外,还通过对比查询约束和文本对齐约束增强异常检测能力。在七个公共工业和医疗数据集上的实验表明,DictAS在未见类别异常分割(FSAS)任务上始终优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- DictAS框架用于在未训练的目标数据上检测未见对象类别中的视觉异常。
- DictAS利用正常参考图像的特征构建字典,模拟真实字典的索引和内容。
- 通过稀疏检索策略检索查询区域特征,无法检索到的特征被视为异常。
- 通过对比查询约束和文本对齐约束增强异常检测能力。
- DictAS框架包括三个主要组件:字典构建、字典查找和查询判别正则化。
- 实验表明,DictAS在七个公共数据集上的一致表现优于现有FSAS方法。
点此查看论文截图

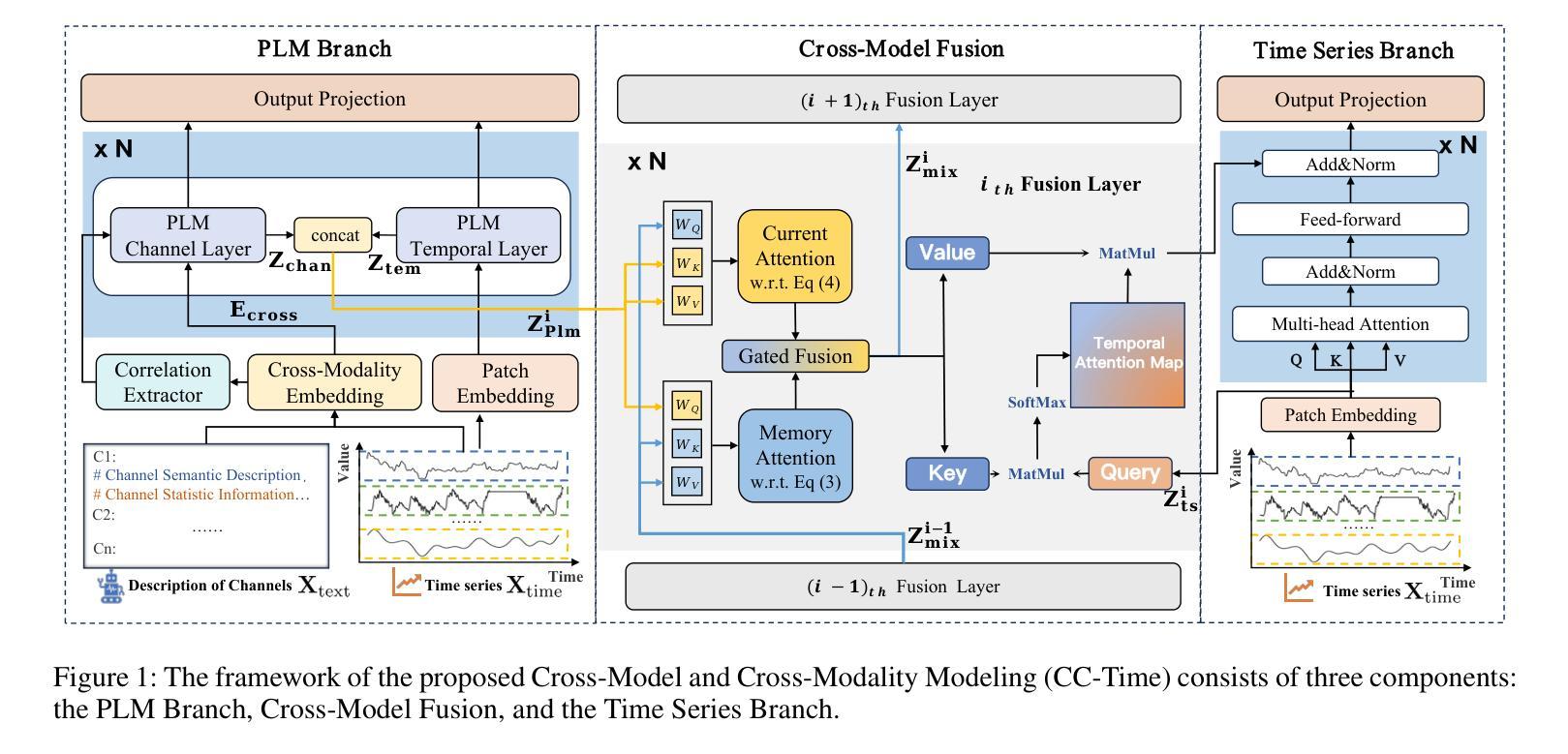
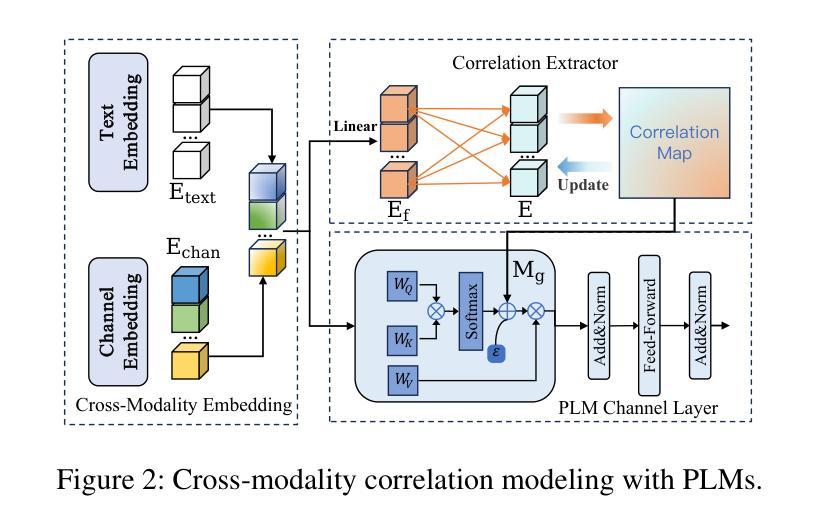
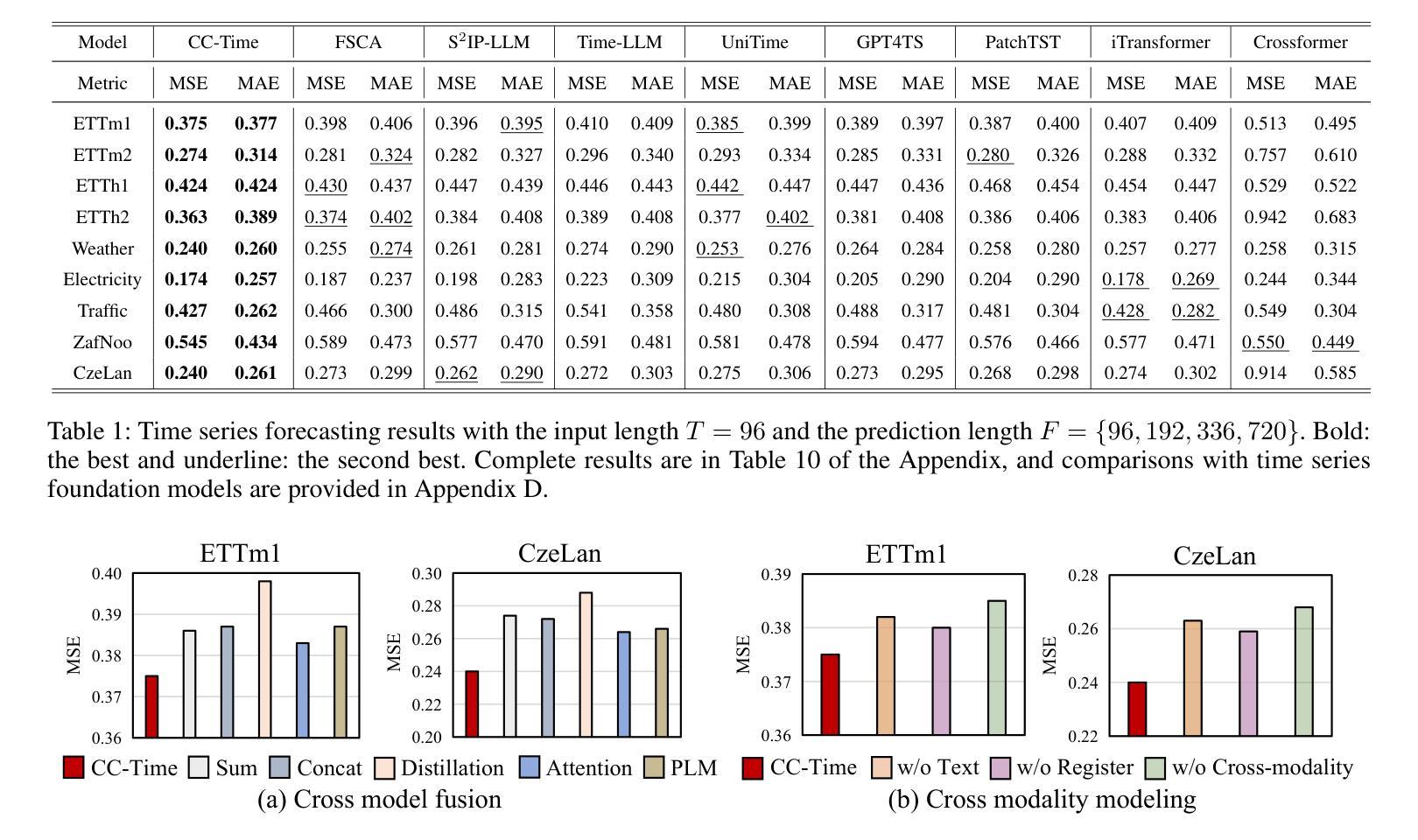
CC-Time: Cross-Model and Cross-Modality Time Series Forecasting
Authors:Peng Chen, Yihang Wang, Yang Shu, Yunyao Cheng, Kai Zhao, Zhongwen Rao, Lujia Pan, Bin Yang, Chenjuan Guo
With the success of pre-trained language models (PLMs) in various application fields beyond natural language processing, language models have raised emerging attention in the field of time series forecasting (TSF) and have shown great prospects. However, current PLM-based TSF methods still fail to achieve satisfactory prediction accuracy matching the strong sequential modeling power of language models. To address this issue, we propose Cross-Model and Cross-Modality Learning with PLMs for time series forecasting (CC-Time). We explore the potential of PLMs for time series forecasting from two aspects: 1) what time series features could be modeled by PLMs, and 2) whether relying solely on PLMs is sufficient for building time series models. In the first aspect, CC-Time incorporates cross-modality learning to model temporal dependency and channel correlations in the language model from both time series sequences and their corresponding text descriptions. In the second aspect, CC-Time further proposes the cross-model fusion block to adaptively integrate knowledge from the PLMs and time series model to form a more comprehensive modeling of time series patterns. Extensive experiments on nine real-world datasets demonstrate that CC-Time achieves state-of-the-art prediction accuracy in both full-data training and few-shot learning situations.
随着预训练语言模型(PLMs)在自然语言处理以外的各种应用领域的成功,语言模型在时间序列预测(TSF)领域引起了广泛的关注,并显示出巨大的潜力。然而,当前的基于PLM的时间序列预测方法仍然无法实现对时间序列模式进行强有力建模的满意预测精度。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于PLM的跨模型跨模态时间序列预测方法(CC-Time)。我们从两个方面探讨了PLM在时间序列预测中的潜力:1)PLM可以建模哪些时间序列特征;2)仅依赖PLM是否足以构建时间序列模型。在第一方面,CC-Time结合了跨模态学习,从时间序列序列及其相应的文本描述中,对语言模型中的时间依赖性和通道相关性进行建模。在第二方面,CC-Time进一步提出了跨模型融合模块,以自适应地整合来自PLM和时序模型的知识,形成对时序模式更全面建模。在九个真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,CC-Time在全数据训练和少样本学习情况下均达到了最新的预测精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练语言模型(PLMs)在自然语言处理以外领域的应用成功,时间序列预测(TSF)领域开始关注语言模型并展现出巨大潜力。针对当前PLM-based TSF方法预测精度不足的问题,提出Cross-Model和Cross-Modality Learning with PLMs for time series forecasting(CC-Time)。从两个方面探索PLM在TSF中的潜力:一是PLM可建模的时间序列特征;二是仅依赖PLM是否足以构建时间序列模型。CC-Time通过跨模态学习建模时间序列序列和对应文本描述中的时间依赖和通道相关性,并提出跨模型融合块以自适应地整合PLM和TSF模型的知识,以更全面建模时间序列模式。在九个真实数据集上的实验表明,CC-Time在完全数据训练和少样本学习情况下均实现了最先进的预测精度。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练语言模型(PLMs)在多个领域取得成功,引发时间序列预测(TSF)领域的关注。
- 当前PLM-based TSF方法预测精度不足,需要新的方法改进。
- 提出CC-Time方法,从两个方面探索PLM在TSF中的潜力:时间序列特征的建模和构建时间序列模型的充分性。
- CC-Time通过跨模态学习建模时间序列序列和文本描述中的时间依赖和通道相关性。
- CC-Time提出跨模型融合块,自适应整合PLM和TSF模型知识,实现更全面建模时间序列模式。
- 在九个真实数据集上的实验表明,CC-Time在多种情况下实现了最先进的预测精度。
点此查看论文截图

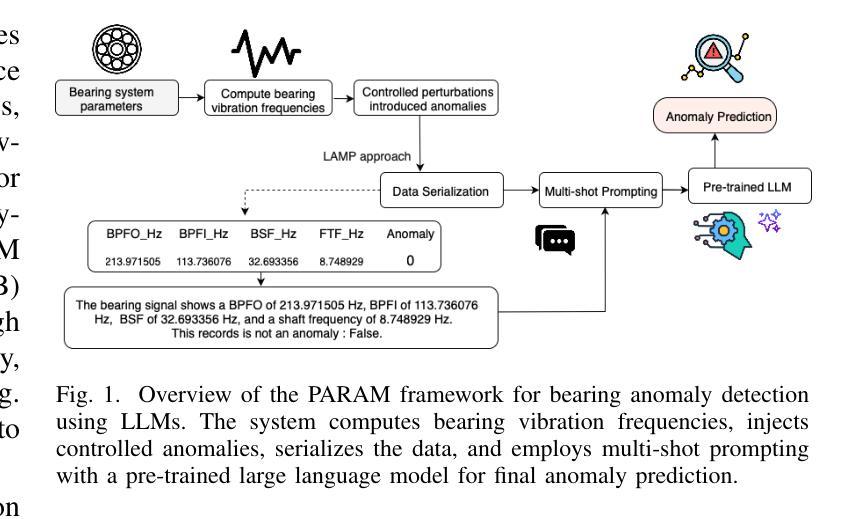
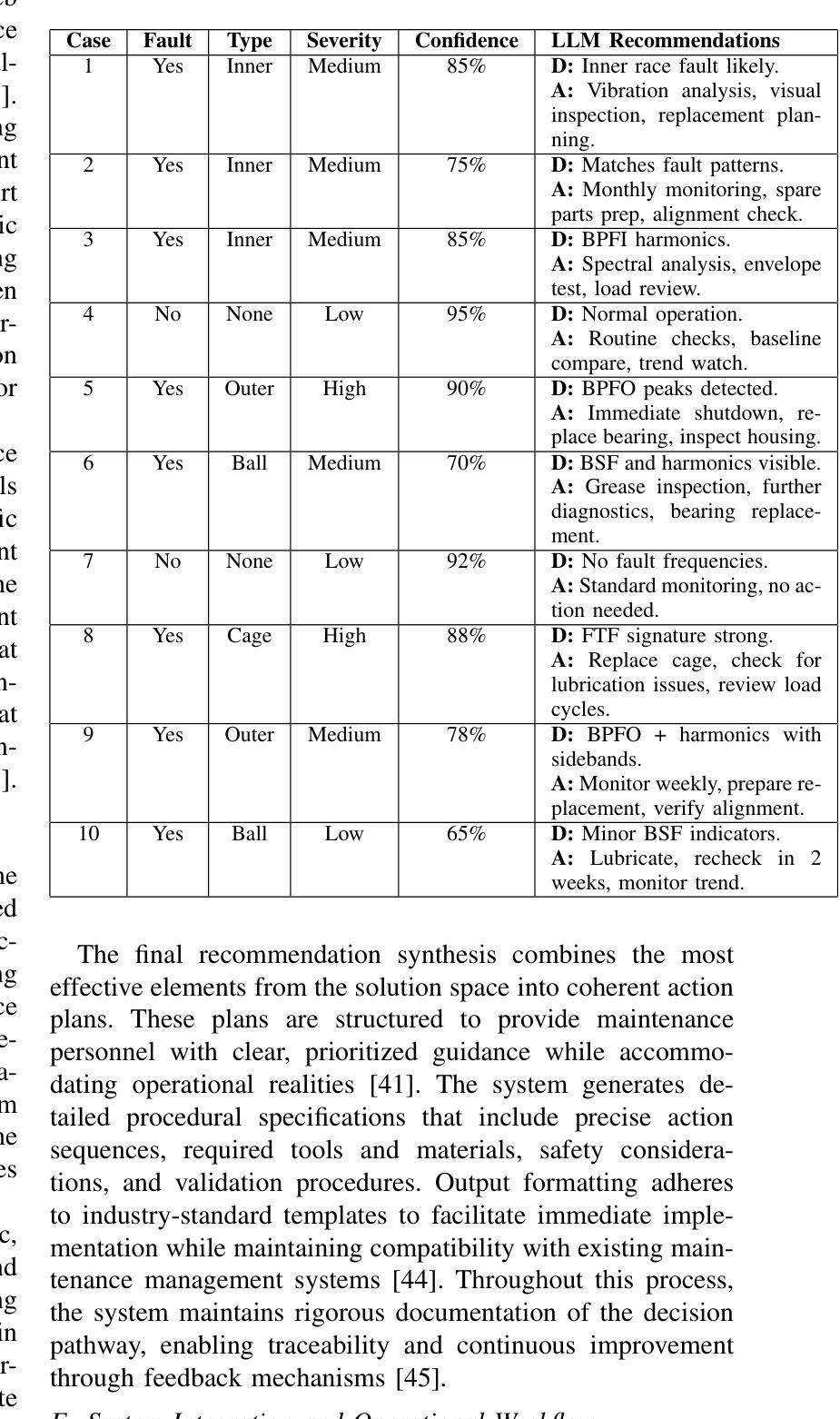
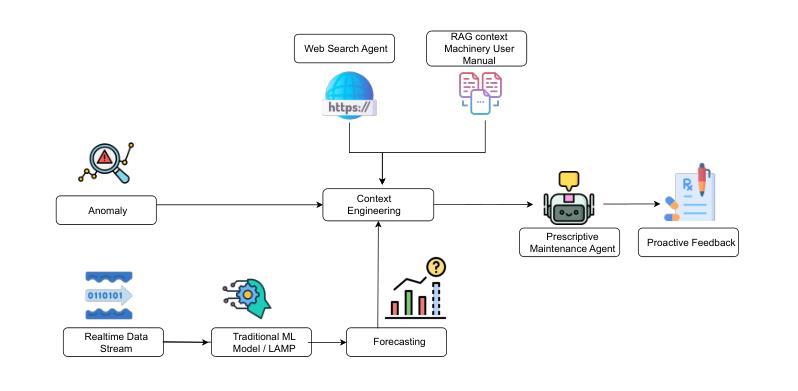
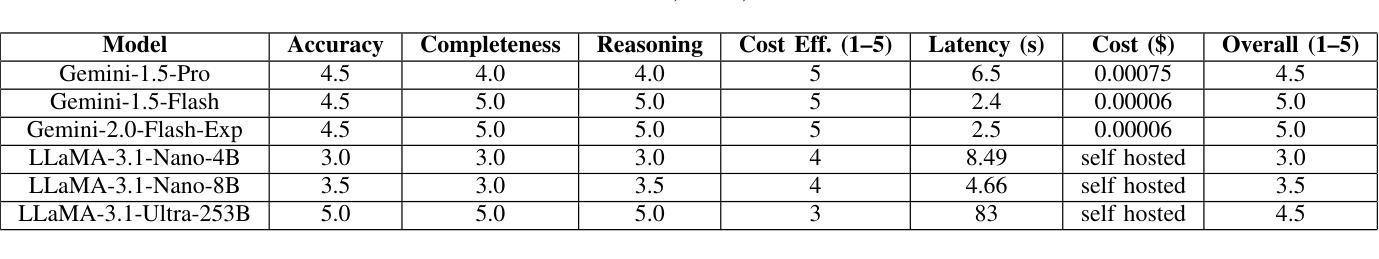
Prescriptive Agents based on RAG for Automated Maintenance (PARAM)
Authors:Chitranshu Harbola, Anupam Purwar
Industrial machinery maintenance requires timely intervention to prevent catastrophic failures and optimize operational efficiency. This paper presents an integrated Large Language Model (LLM)-based intelligent system for prescriptive maintenance that extends beyond traditional anomaly detection to provide actionable maintenance recommendations. Building upon our prior LAMP framework for numerical data analysis, we develop a comprehensive solution that combines bearing vibration frequency analysis with multi agentic generation for intelligent maintenance planning. Our approach serializes bearing vibration data (BPFO, BPFI, BSF, FTF frequencies) into natural language for LLM processing, enabling few-shot anomaly detection with high accuracy. The system classifies fault types (inner race, outer race, ball/roller, cage faults) and assesses severity levels. A multi-agentic component processes maintenance manuals using vector embeddings and semantic search, while also conducting web searches to retrieve comprehensive procedural knowledge and access up-to-date maintenance practices for more accurate and in-depth recommendations. The Gemini model then generates structured maintenance recommendations includes immediate actions, inspection checklists, corrective measures, parts requirements, and timeline specifications. Experimental validation in bearing vibration datasets demonstrates effective anomaly detection and contextually relevant maintenance guidance. The system successfully bridges the gap between condition monitoring and actionable maintenance planning, providing industrial practitioners with intelligent decision support. This work advances the application of LLMs in industrial maintenance, offering a scalable framework for prescriptive maintenance across machinery components and industrial sectors.
工业机械维护需要及时的干预来预防灾难性故障并优化运营效率。本文提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的集成智能系统,用于预防性维护,该系统超越了传统的异常检测,提供了可行的维护建议。在先前用于数值数据分析的LAMP框架的基础上,我们开发了一种综合解决方案,该方案将轴承振动频率分析与多智能体生成相结合,用于智能维护规划。我们的方法将轴承振动数据(BPFO、BPFI、BSF、FTF频率)序列化为自然语言以供LLM处理,从而实现高准确度的少量异常检测。该系统对故障类型(内圈、外圈、球/滚珠、笼故障)进行分类并评估严重程度。多智能体组件使用向量嵌入和语义搜索处理维护手册,同时进行网络搜索以检索全面的程序知识并获取最新维护实践,以提供更准确和深入的推荐。然后,Gemini模型生成结构化维护建议,包括立即行动、检查清单、纠正措施、零件要求和时间表规范。在轴承振动数据集上的实验验证表明,系统能够有效地检测异常并提供与上下文相关的维护指导。该系统成功地弥合了状况监测和可操作维护规划之间的鸿沟,为工业从业者提供智能决策支持。这项工作推动了LLM在工业维护领域的应用,为机械部件和工业部门的预防性维护提供了一个可扩展的框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
工业机械维护需要及时的干预来预防灾难性故障并优化运营效率。本文提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的集成智能系统,用于预防性维护,该系统不仅超越了传统的异常检测,而且提供了可操作的维护建议。该系统结合轴承振动频率分析和多智能体生成,实现了智能化的维护计划。通过序列化轴承振动数据并进行自然语言处理,实现了高准确度的少数异常检测。系统可以分类故障类型并评估严重程度。此外,该系统还通过向量嵌入和语义搜索处理维护手册,进行网络搜索以获取全面的程序性知识和最新的维护实践,以提供更准确和深入的推荐。通过轴承振动数据集的实验验证,该系统实现了有效的异常检测和与上下文相关的维护指导。这项工作推动了LLM在工业维护领域的应用,为机械部件和工业部门提供了可扩展的预防性维护框架。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)用于工业机械的智能维护系统。
- 系统结合轴承振动频率分析与多智能体生成,提供维护建议。
- 通过自然语言处理实现少数异常检测的高准确性。
- 系统能分类故障类型和评估严重程度。
- 通过处理维护手册和网络搜索,系统提供更准确和深入的维护建议。
- 实验验证表明,系统实现了有效的异常检测和与上下文相关的维护指导。
点此查看论文截图

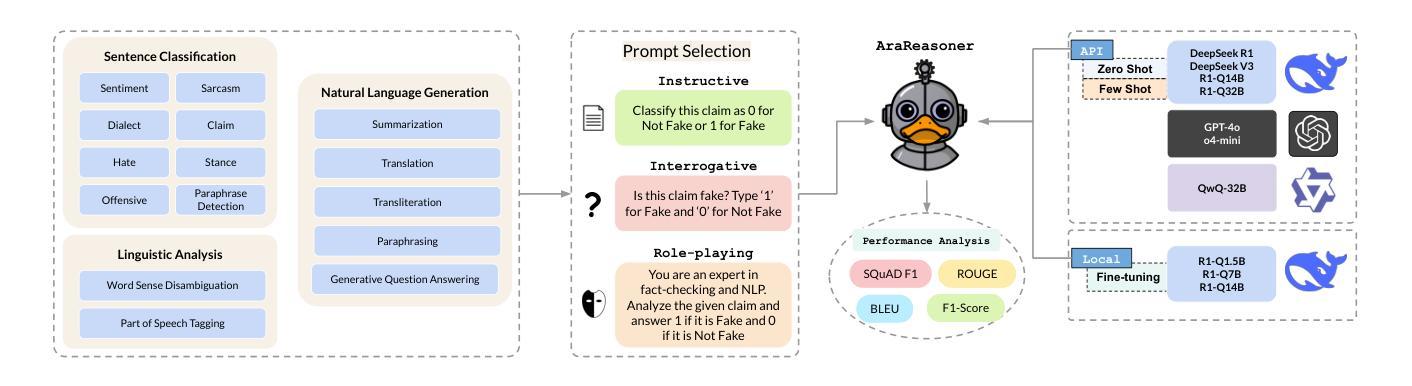
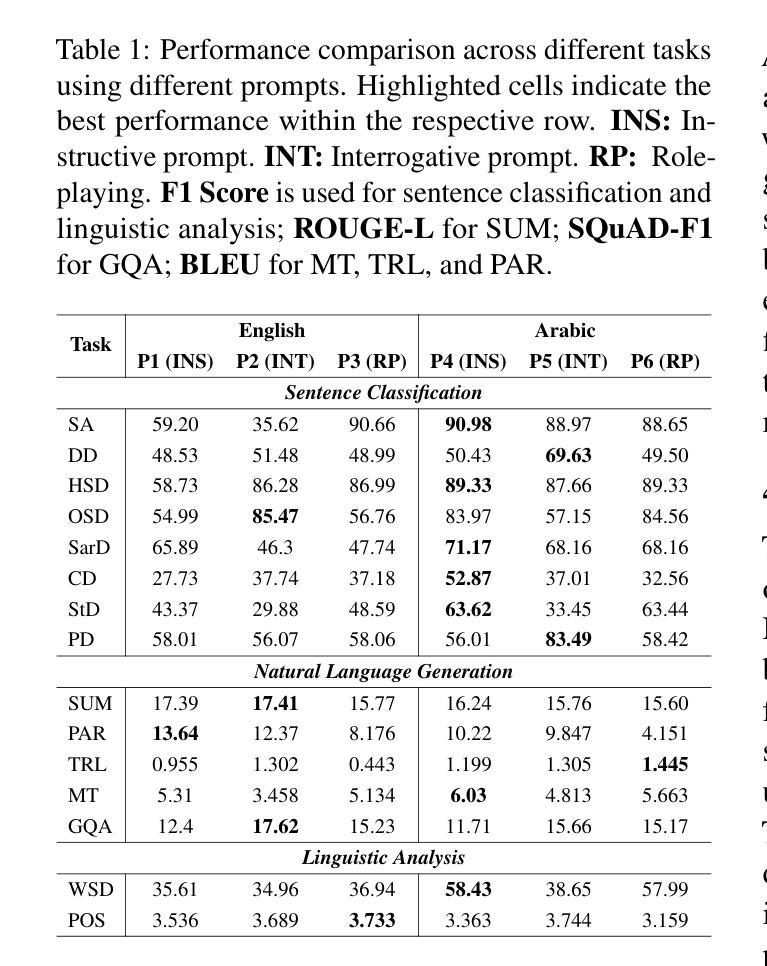
AraReasoner: Evaluating Reasoning-Based LLMs for Arabic NLP
Authors:Ahmed Hasanaath, Aisha Alansari, Ahmed Ashraf, Chafik Salmane, Hamzah Luqman, Saad Ezzini
Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable progress in reasoning abilities and general natural language processing (NLP) tasks, yet their performance on Arabic data, characterized by rich morphology, diverse dialects, and complex script, remains underexplored. This paper presents a comprehensive benchmarking study of multiple reasoning-focused LLMs, with a special emphasis on the newly introduced DeepSeek models, across a suite of fifteen Arabic NLP tasks. We experiment with various strategies, including zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuning. This allows us to systematically evaluate performance on datasets covering a range of applications to examine their capacity for linguistic reasoning under different levels of complexity. Our experiments reveal several key findings. First, carefully selecting just three in-context examples delivers an average uplift of over 13 F1 points on classification tasks-boosting sentiment analysis from 35.3% to 87.5% and paraphrase detection from 56.1% to 87.0%. Second, reasoning-focused DeepSeek architectures outperform a strong GPT o4-mini baseline by an average of 12 F1 points on complex inference tasks in the zero-shot setting. Third, LoRA-based fine-tuning yields up to an additional 8 points in F1 and BLEU compared to equivalent increases in model scale. The code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AraReasoner41299
大型语言模型(LLM)在推理能力和自然语言处理(NLP)的一般任务上取得了显著的进步,然而,它们在处理阿拉伯数据方面的表现,这些阿拉伯数据以丰富的形态、多样的方言和复杂的脚本为特征,仍被研究得不够透彻。本文全面评估了多个注重推理的LLM模型,特别强调新推出的DeepSeek模型,涵盖十五项阿拉伯语NLP任务。我们尝试了多种策略,包括零样本、少样本和微调。这使我们能够系统地评估数据集上的性能,涵盖各种应用程序,以检查它们在不同复杂程度下的语言推理能力。我们的实验揭示了几个关键发现。首先,只需精心选择三个上下文实例,就可以在分类任务上平均提高超过13个F1点——情感分析从35.3%提高到87.5%,而改述检测从56.1%提高到87.0%。其次,注重推理的DeepSeek架构在零样本设置下的复杂推理任务上平均比强大的GPT o4-mini基线高出12个F1点。第三,基于LoRA的微调与模型规模的等效增长相比,额外提高了高达8个F1点和BLEU值。代码可用https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AraReasoner41299查询。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在具有丰富形态、多样方言和复杂脚本的阿拉伯语数据上性能尚待探索。本文通过一系列阿拉伯NLP任务全面评估多个注重推理的LLMs,尤其是新推出的DeepSeek模型。研究发现,精选三个实例的few-shot方式能提高分类任务的平均F1分数超过13点;DeepSeek架构在零样本设置下比GPT o4-mini基线平均高出12 F1点;基于LoRA的微调技术相比模型规模的增加可提高最多8点的F1和BLEU分数。相关代码已公开分享。
Key Takeaways
- 在阿拉伯语NLP任务中,大型语言模型(LLMs)的性能仍有待充分探索。
- 通过一系列实验评估了多种推理型LLMs,尤其是新出现的DeepSeek模型。
- 精选三个实例的few-shot方式显著提高分类任务性能。
- DeepSeek架构在零样本设置下表现出优越性能。
- LoRA微调技术能有效提升模型性能。
- 实验结果详细说明了不同策略对阿拉伯语NLP任务性能的影响。
点此查看论文截图

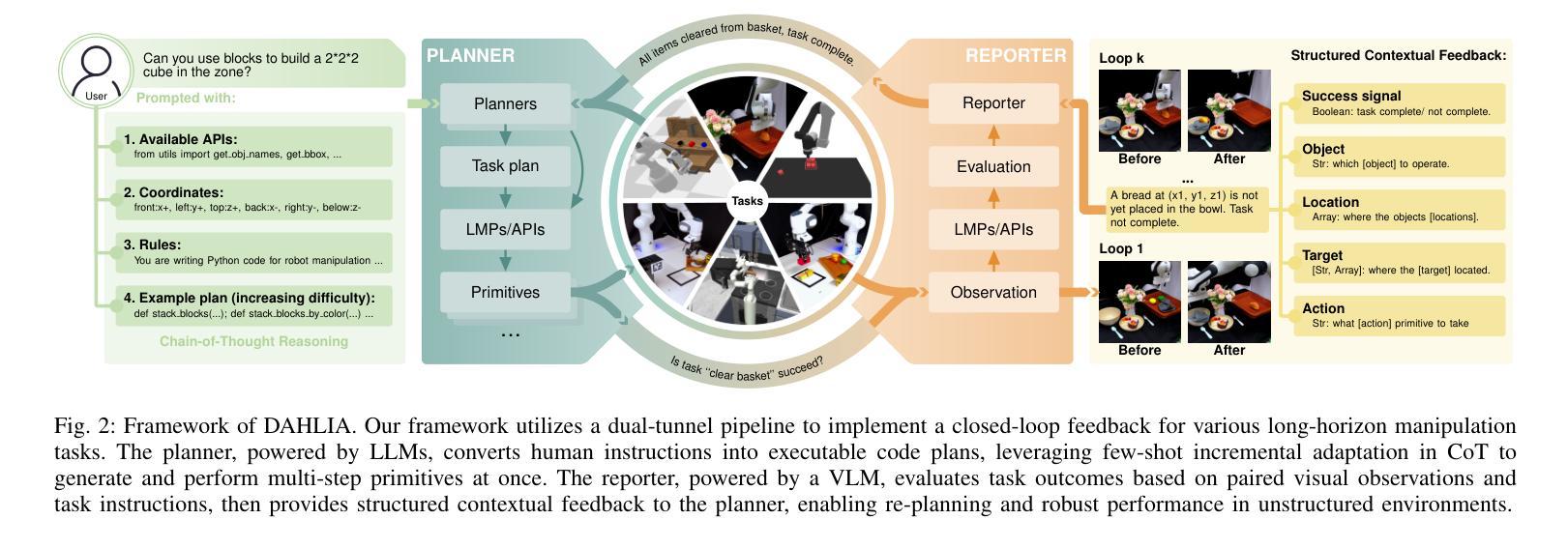
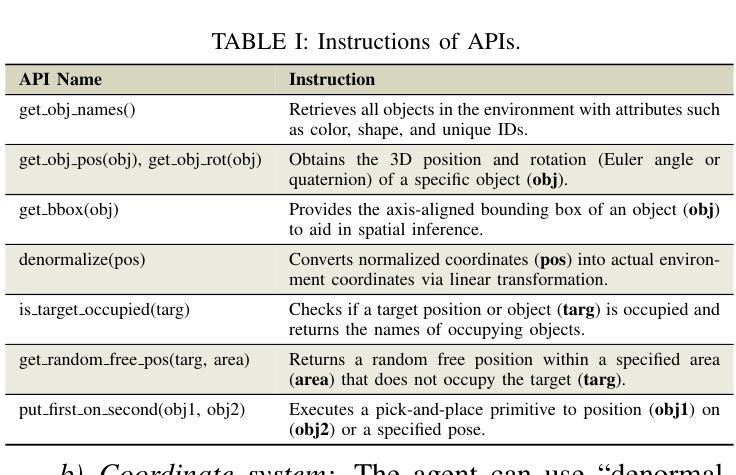
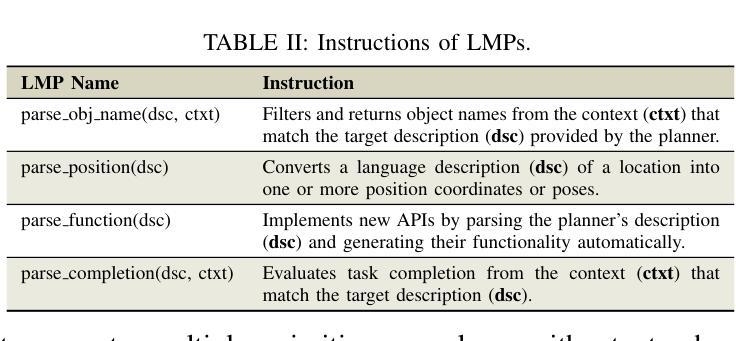
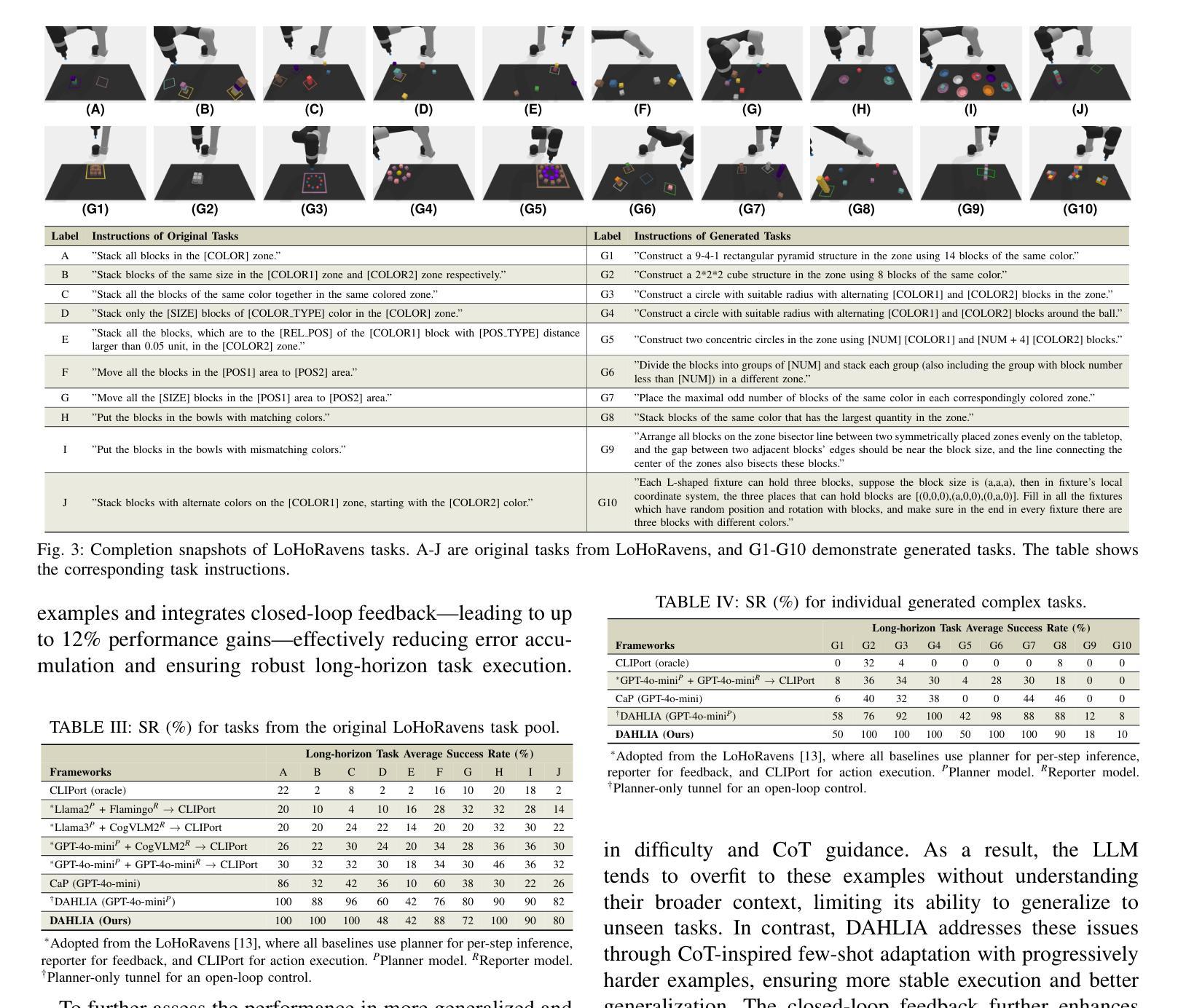
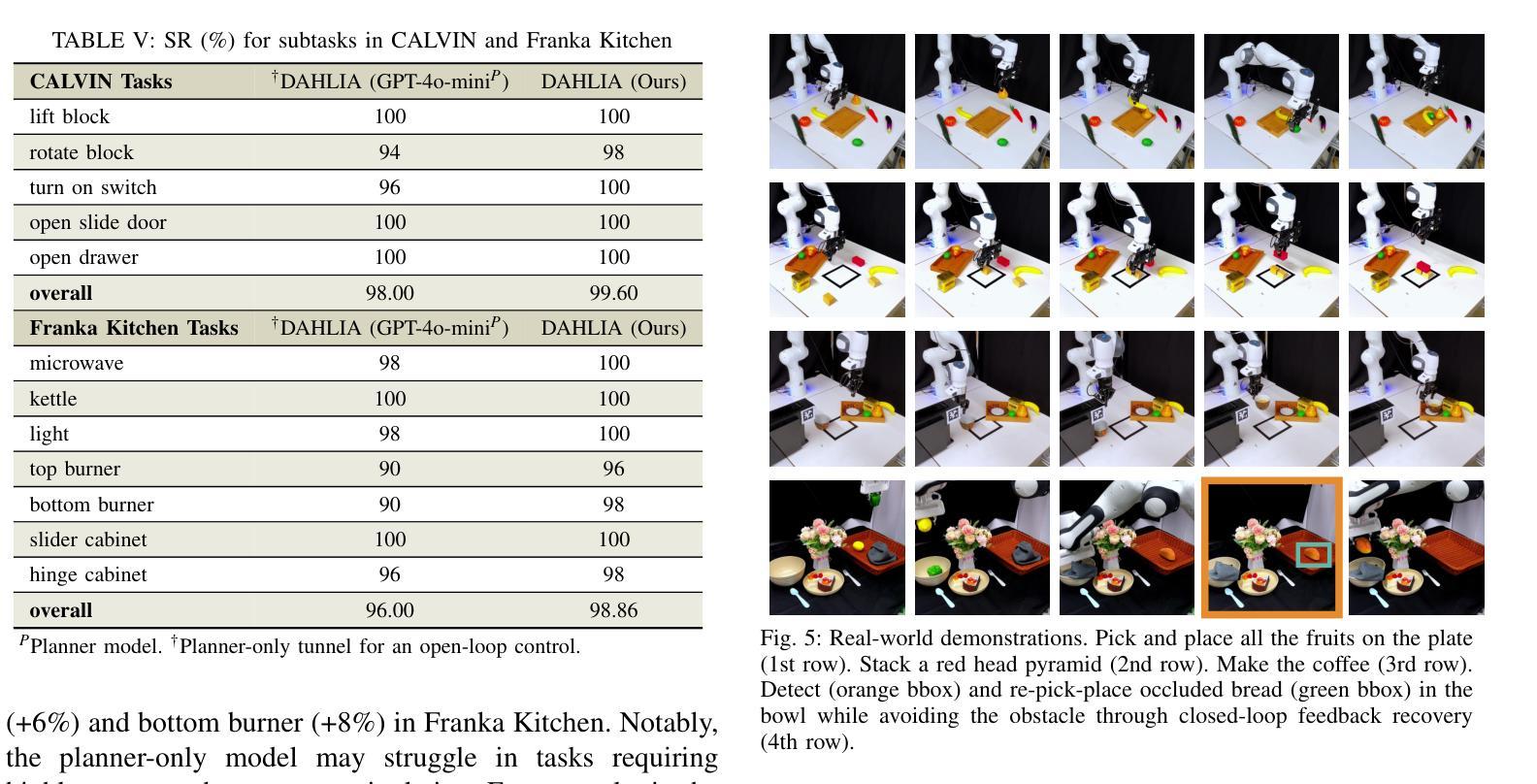
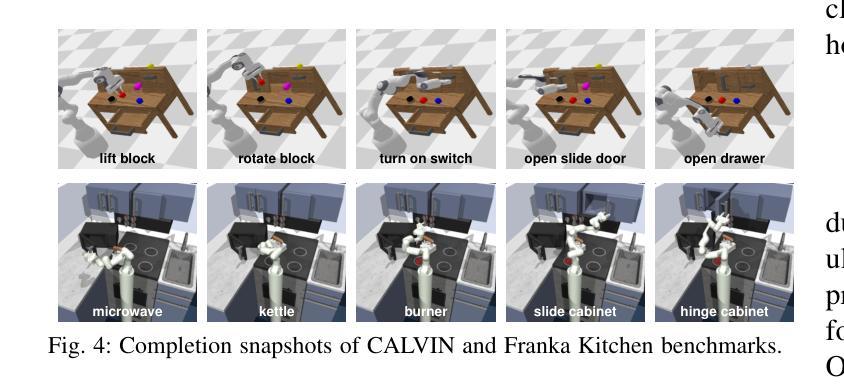
Embodied Long Horizon Manipulation with Closed-loop Code Generation and Incremental Few-shot Adaptation
Authors:Yuan Meng, Xiangtong Yao, Haihui Ye, Yirui Zhou, Shengqiang Zhang, Zhenguo Sun, Xukun Li, Zhenshan Bing, Alois Knoll
Embodied long-horizon manipulation requires robotic systems to process multimodal inputs-such as vision and natural language-and translate them into executable actions. However, existing learning-based approaches often depend on large, task-specific datasets and struggle to generalize to unseen scenarios. Recent methods have explored using large language models (LLMs) as high-level planners that decompose tasks into subtasks using natural language and guide pretrained low-level controllers. Yet, these approaches assume perfect execution from low-level policies, which is unrealistic in real-world environments with noise or suboptimal behaviors. To overcome this, we fully discard the pretrained low-level policy and instead use the LLM to directly generate executable code plans within a closed-loop framework. Our planner employs chain-of-thought (CoT)-guided few-shot learning with incrementally structured examples to produce robust and generalizable task plans. Complementing this, a reporter evaluates outcomes using RGB-D and delivers structured feedback, enabling recovery from misalignment and replanning under partial observability. This design eliminates per-step inference, reduces computational overhead, and limits error accumulation that was observed in previous methods. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on 30+ diverse seen and unseen long-horizon tasks across LoHoRavens, CALVIN, Franka Kitchen, and cluttered real-world settings.
实现具有长期视角的操作需要机器人系统处理多模态输入,如视觉和自然语言,并将其翻译成可执行的行动。然而,现有的基于学习的方法通常依赖于大型、特定任务的数据集,并且在未见场景中的泛化能力较差。最近的方法已经尝试使用大型语言模型(LLM)作为高级规划器,利用自然语言将任务分解成子任务,并引导预训练的低级控制器。然而,这些方法假设低级策略可以完美执行,这在现实世界中存在噪声或非最优行为的情况下是不切实际的。为了克服这一问题,我们完全抛弃了预训练的低级策略,而是使用LLM直接在闭环框架内生成可执行的代码计划。我们的规划器采用基于思维链(CoT)引导的小样本学习,通过增量结构化示例来产生稳健且可泛化的任务计划。作为补充,一个报告者使用RGB-D评估结果并提供结构化反馈,从而实现部分观测下的误对齐恢复和重新规划。这种设计消除了逐步推理,减少了计算开销,并限制了之前在其它方法中观察到的误差累积。我们的框架在LoHoRavens、CALVIN、Franka厨房和杂乱的真实世界环境中,实现了30多个不同已见和未见长期任务的最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF update ICRA 6 page
Summary
基于多模态输入的长期规划操控需要机器人系统处理视觉和自然语言等多种模式输入,并将其转化为可执行动作。现有学习法依赖于特定任务的大量数据集,难以推广到未见场景。近期方法尝试使用大型语言模型作为高级规划器,但假设低级策略的完美执行并不现实。为此,我们抛弃预训练的低级策略,改用大型语言模型直接生成封闭循环框架内的可执行代码计划。此外,结合使用RGB-D进行结果评估并提供结构化反馈,促进误对齐情况下的恢复与部分观察下的重新规划。此设计消除了逐步推理,减少了计算开销,并限制了先前方法观察到的误差累积。我们的框架在多个长周期任务上实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 机器人系统需要处理多模态输入,如视觉和自然语言,转化为可执行动作。
- 现有方法依赖于大量特定任务数据集,难以适应新场景。
- 大型语言模型用于高级任务规划,但完美执行假设不现实。
- 抛弃预训练的低级策略,直接使用大型语言模型生成代码计划。
- 结合RGB-D进行结果评估并提供结构化反馈。
- 该设计减少计算开销和误差累积。
点此查看论文截图

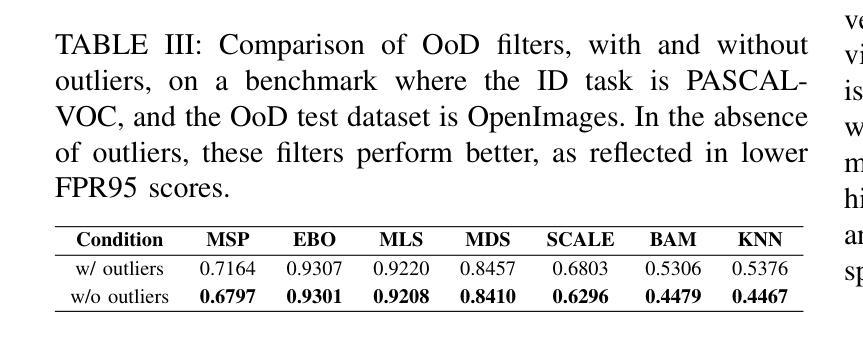
Revisiting Out-of-Distribution Detection in Real-time Object Detection: From Benchmark Pitfalls to a New Mitigation Paradigm
Authors:Changshun Wu, Weicheng He, Chih-Hong Cheng, Xiaowei Huang, Saddek Bensalem
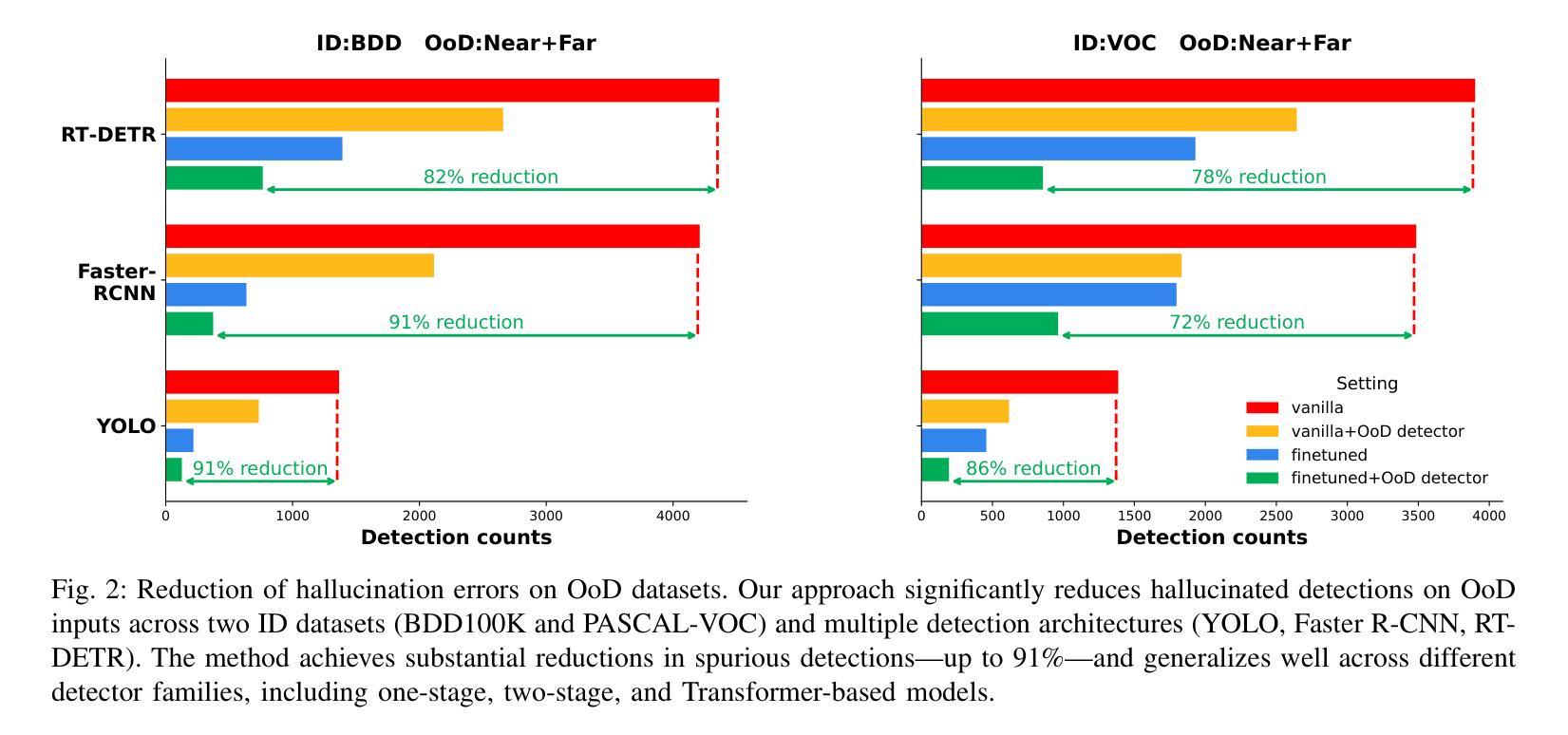
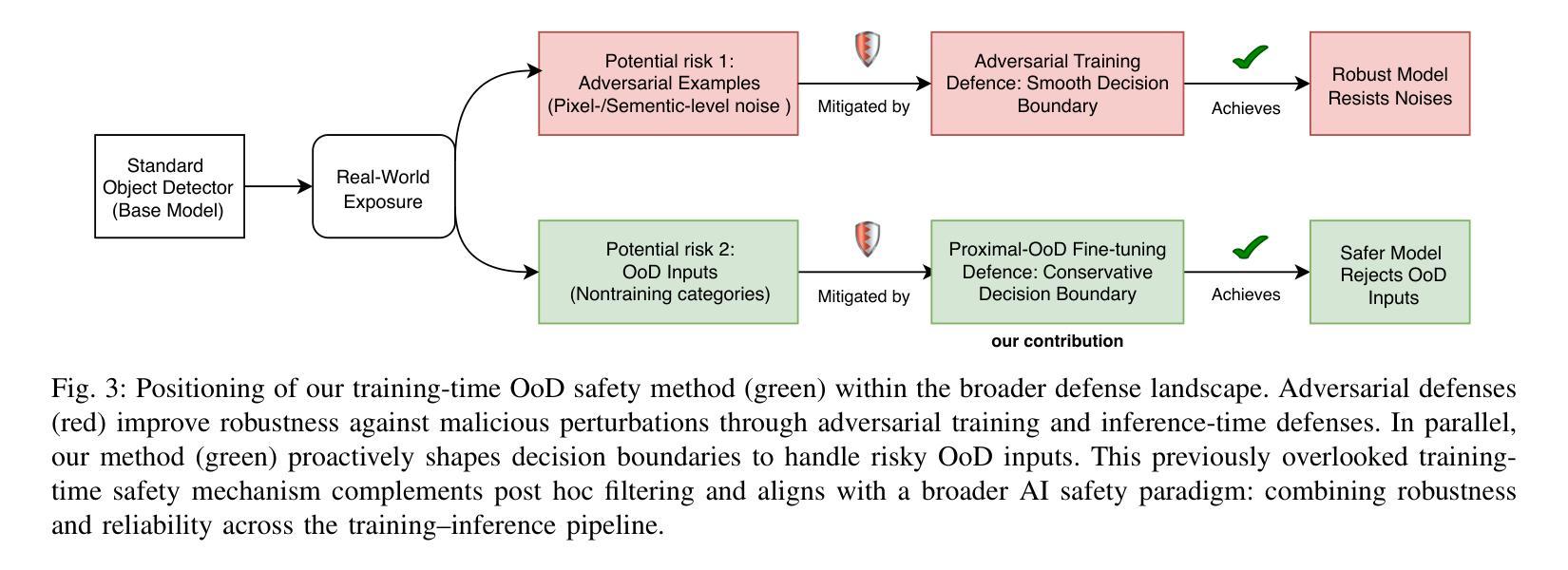
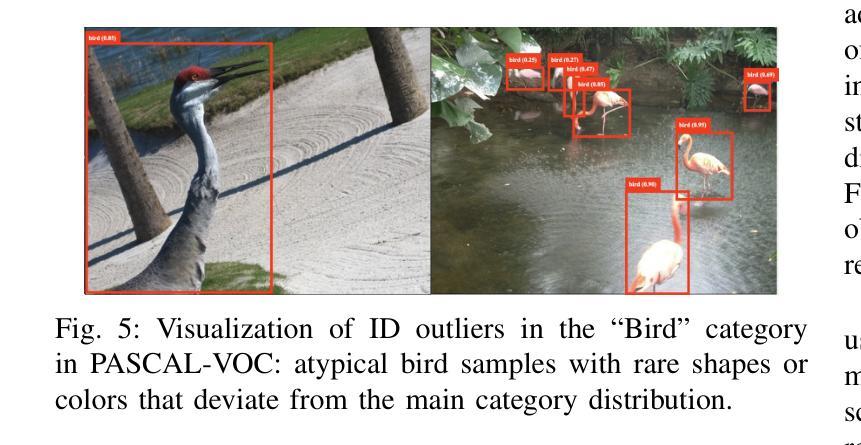
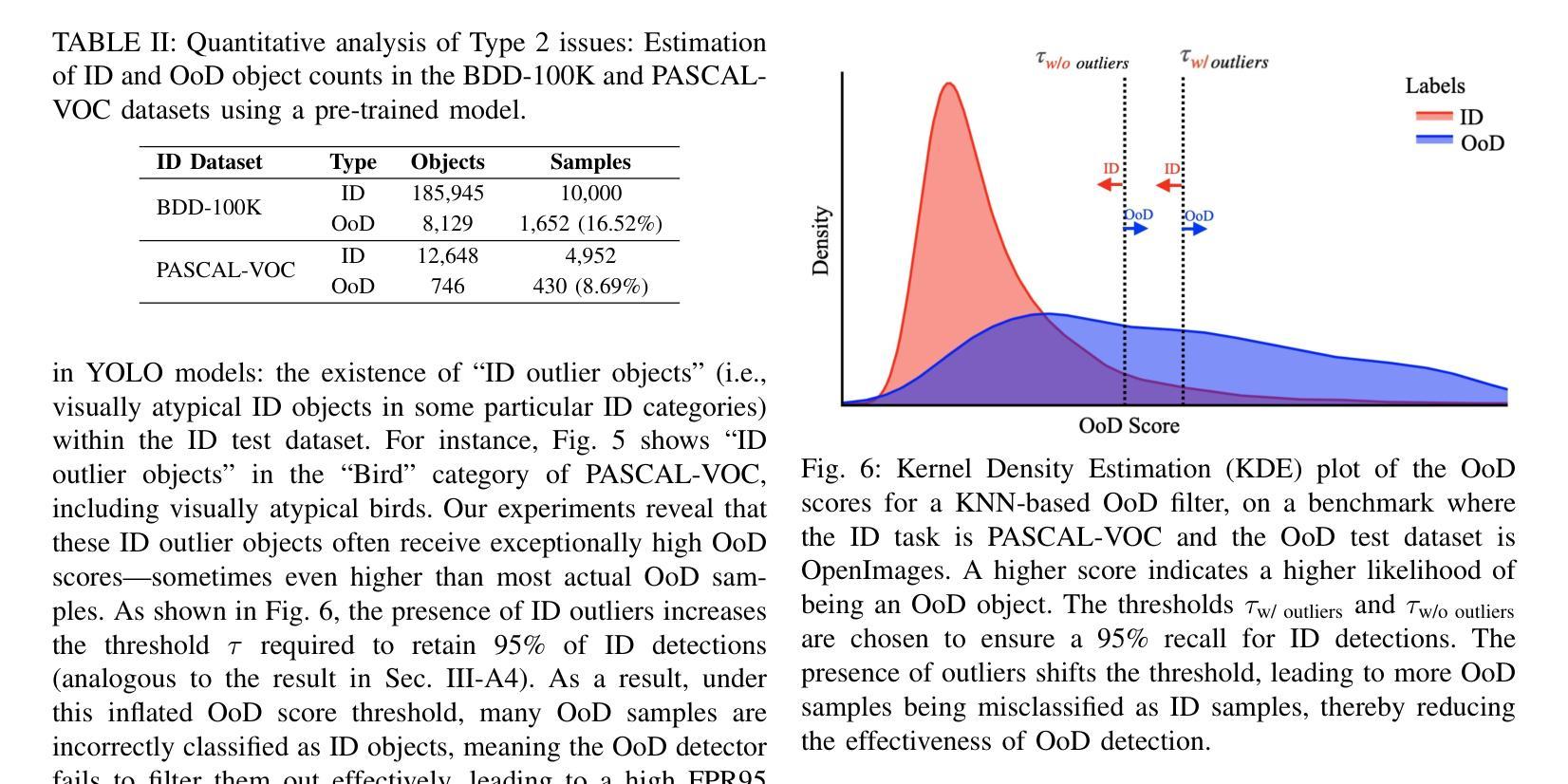
Out-of-distribution (OoD) inputs pose a persistent challenge to deep learning models, often triggering overconfident predictions on non-target objects. While prior work has primarily focused on refining scoring functions and adjusting test-time thresholds, such algorithmic improvements offer only incremental gains. We argue that a rethinking of the entire development lifecycle is needed to mitigate these risks effectively. This work addresses two overlooked dimensions of OoD detection in object detection. First, we reveal fundamental flaws in widely used evaluation benchmarks: contrary to their design intent, up to 13% of objects in the OoD test sets actually belong to in-distribution classes, and vice versa. These quality issues severely distort the reported performance of existing methods and contribute to their high false positive rates. Second, we introduce a novel training-time mitigation paradigm that operates independently of external OoD detectors. Instead of relying solely on post-hoc scoring, we fine-tune the detector using a carefully synthesized OoD dataset that semantically resembles in-distribution objects. This process shapes a defensive decision boundary by suppressing objectness on OoD objects, leading to a 91% reduction in hallucination error of a YOLO model on BDD-100K. Our methodology generalizes across detection paradigms such as YOLO, Faster R-CNN, and RT-DETR, and supports few-shot adaptation. Together, these contributions offer a principled and effective way to reduce OoD-induced hallucination in object detectors. Code and data are available at: https://gricad-gitlab.univ-grenoble-alpes.fr/dnn-safety/m-hood.
分布外(Out-of-distribution,OoD)输入对深度学习模型构成持续挑战,通常会对非目标对象做出过于自信的预测。虽然先前的工作主要集中于改进评分功能和调整测试时间阈值,但此类算法改进只能带来增量收益。我们认为,为了有效减轻这些风险,需要重新思考整个开发生命周期。这项工作解决了对象检测中分布外检测(OoD检测)被忽略的两个维度。首先,我们揭示了广泛使用的评估基准中存在的根本问题:与他们的设计初衷相反,高达13%的对象属于分布内类别,反之亦然。这些问题严重影响了现有方法的报告性能,并导致了较高的误报率。其次,我们引入了一种新的训练时间缓解模式,该模式独立于外部分布外检测器运行。我们不是依赖事后评分,而是使用精心合成的分布外数据集对检测器进行微调,该数据集在语义上类似于分布内对象。这一过程通过抑制分布外对象上的对象性来形成防御决策边界,导致YOLO模型在BDD-100K上的幻觉误差降低了91%。我们的方法适用于YOLO、Faster R-CNN和RT-DETR等检测范式,并支持少量镜头适应。这些贡献共同提供了一种有原则且有效的减少对象检测器中的分布外输入引起的幻觉的方法。代码和数据可在:https://gricad-gitlab.univ-grenoble-alpes.fr/dnn-safety/m-hood。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Expanded journal version of our IROS 2025 paper, adding automated OoD benchmarking, generalization to multiple object detectors, few-shot fine-tuning, and in-depth analysis
摘要
深度学习方法面临来自分布外(Out-of-Distribution,OoD)输入的持续挑战,容易在非目标对象上产生过度自信的预测。现有研究主要关注评分函数的改进和测试时阈值的调整,但这些算法上的改进只带来了有限的提升。本文重新思考了开发周期中的两个被忽视方面,以解决OoD检测中的关键问题。首先,我们发现常用的评估基准存在根本问题:测试集中有高达13%的对象实际上是分布内的类别,这与设计初衷相反。这些问题严重影响了现有方法的性能报告并导致了高误报率。其次,我们提出了一种新颖的在线缓解范式,独立于外部OoD检测器运行。我们不再依赖事后评分,而是使用精心合成的类似于分布内对象的OoD数据集微调检测器。通过压制OoD对象上的对象性,塑造防御决策边界,YOLO模型的幻觉错误减少了91%。我们的方法适用于YOLO、Faster R-CNN和RT-DETR等检测范式,并支持少量样本适应。这些贡献为解决深度学习方法在对象检测中的分布外输入问题提供了有效的解决方案。更多信息和资源可在链接中找到:https://gricad-gitlab.univ-grenoble-alpes.fr/dnn-safety/m-hood。
要点归纳
一、现有的对象检测模型面临来自分布外的输入挑战,会导致对非目标对象的过度自信预测。这带来了对新方法的迫切需求。
二、传统的评估基准存在质量缺陷:设计初衷与实际存在差异,可能导致高达13%的对象类别被误报为分布内或分布外。这对评估模型性能造成了严重扭曲。我们提出了相应的解决方法来改善这个问题。
点此查看论文截图


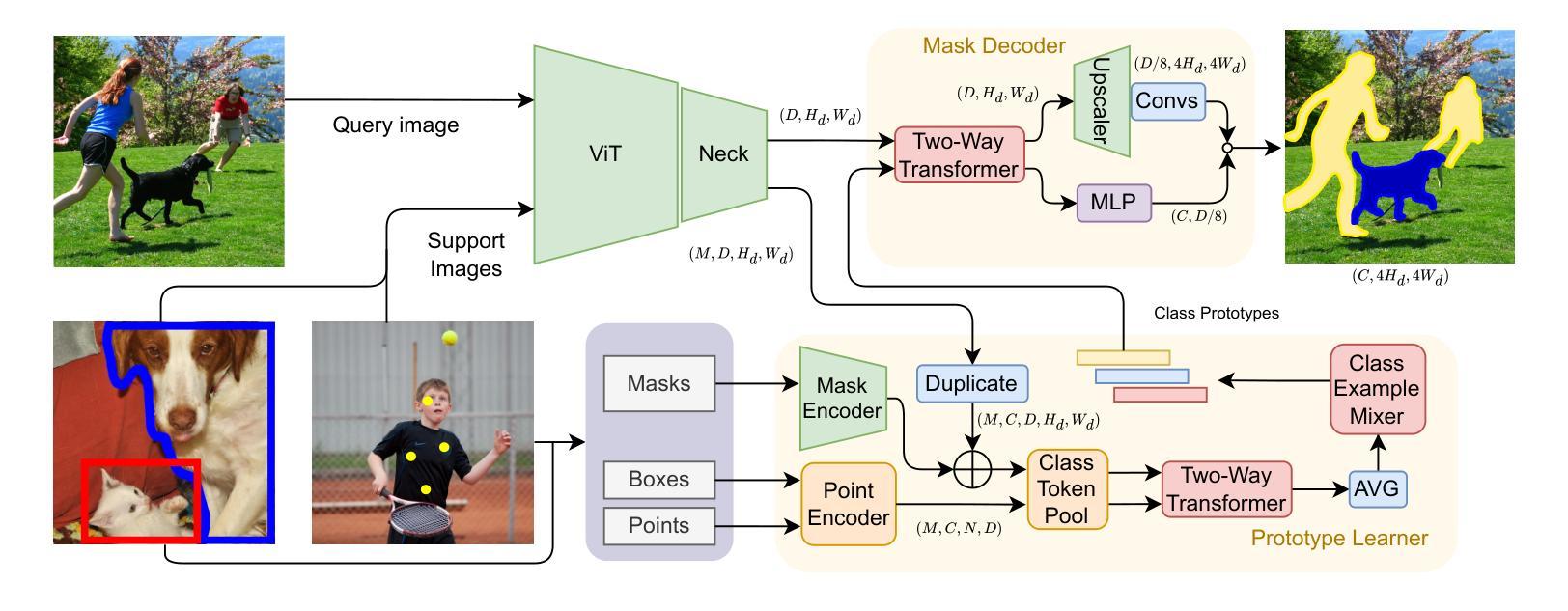
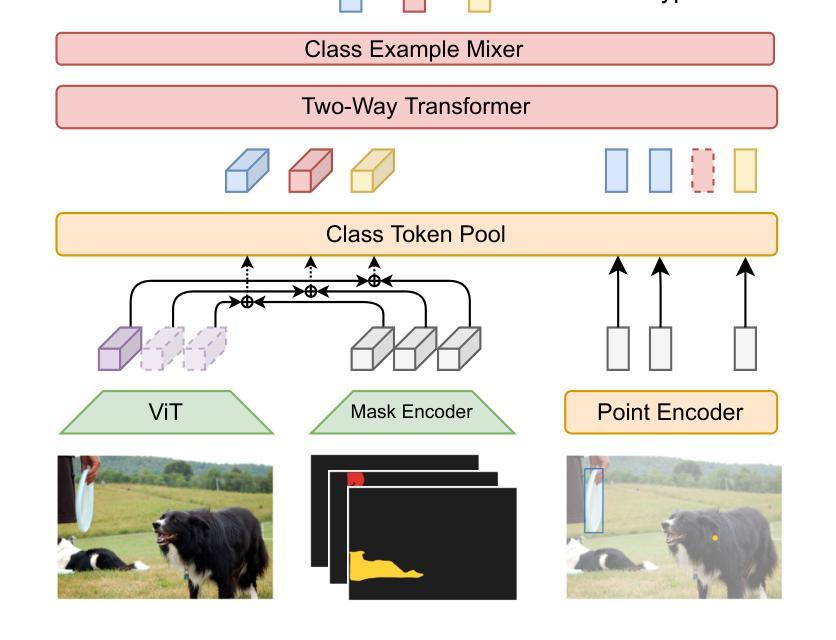
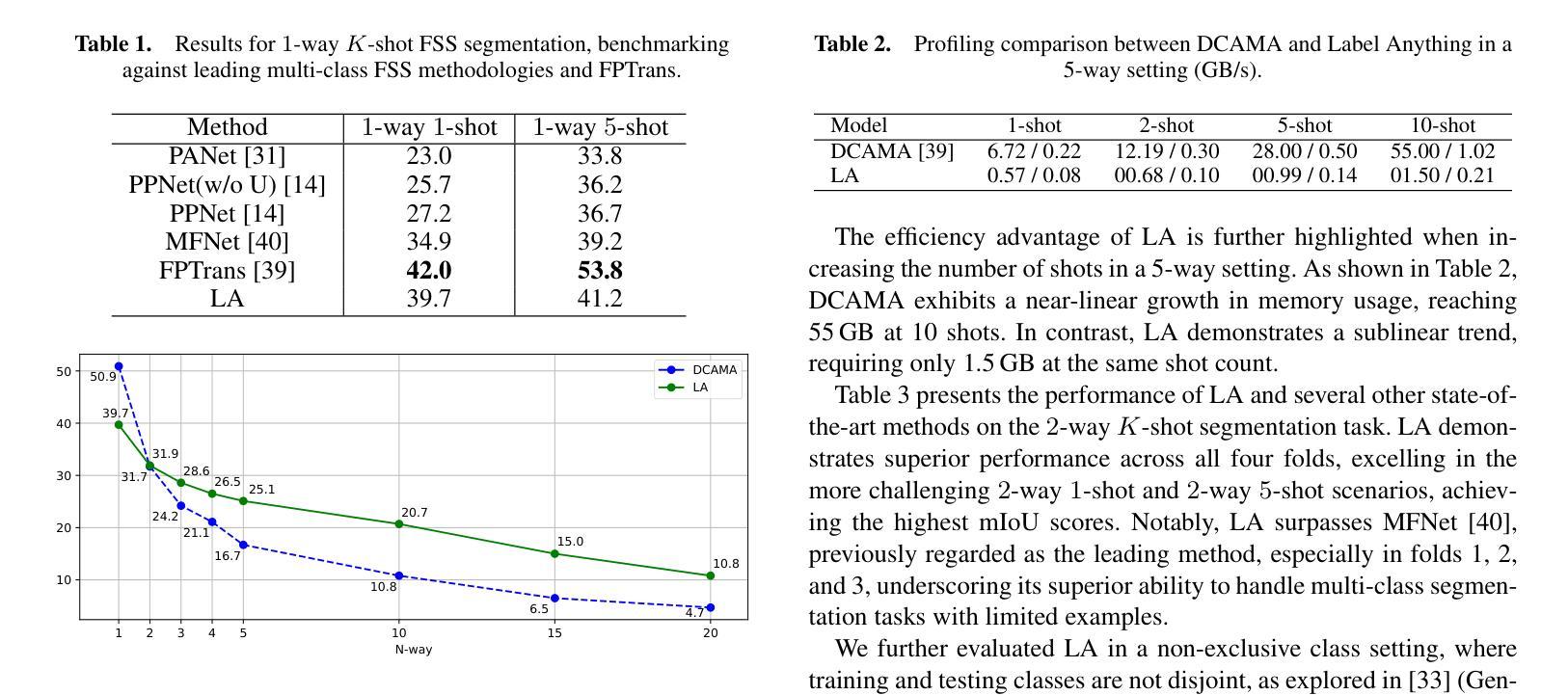
Label Anything: Multi-Class Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation with Visual Prompts
Authors:Pasquale De Marinis, Nicola Fanelli, Raffaele Scaringi, Emanuele Colonna, Giuseppe Fiameni, Gennaro Vessio, Giovanna Castellano
Few-shot semantic segmentation aims to segment objects from previously unseen classes using only a limited number of labeled examples. In this paper, we introduce Label Anything, a novel transformer-based architecture designed for multi-prompt, multi-way few-shot semantic segmentation. Our approach leverages diverse visual prompts – points, bounding boxes, and masks – to create a highly flexible and generalizable framework that significantly reduces annotation burden while maintaining high accuracy. Label Anything makes three key contributions: ($\textit{i}$) we introduce a new task formulation that relaxes conventional few-shot segmentation constraints by supporting various types of prompts, multi-class classification, and enabling multiple prompts within a single image; ($\textit{ii}$) we propose a novel architecture based on transformers and attention mechanisms; and ($\textit{iii}$) we design a versatile training procedure allowing our model to operate seamlessly across different $N$-way $K$-shot and prompt-type configurations with a single trained model. Our extensive experimental evaluation on the widely used COCO-$20^i$ benchmark demonstrates that Label Anything achieves state-of-the-art performance among existing multi-way few-shot segmentation methods, while significantly outperforming leading single-class models when evaluated in multi-class settings. Code and trained models are available at https://github.com/pasqualedem/LabelAnything.
少量样本语义分割旨在使用有限的标注样本对之前未见过的类别进行对象分割。在本文中,我们介绍了Label Anything,这是一种基于transformer的新型架构,专为多提示、多类别少量样本语义分割设计。我们的方法利用多样化的视觉提示——点、边界框和蒙版,创建一个高度灵活和可推广的框架,在保持高准确性的同时,大大降低了标注负担。Label Anything做出了三个主要贡献:(i)我们引入了一种新的任务形式化方法,通过支持各种提示类型、多类分类,并在单个图像内支持多个提示,放宽了传统的少量样本分割约束;(ii)我们提出了一种基于transformer和注意力机制的新型架构;(iii)我们设计了一种通用训练程序,使我们的模型能够在不同的N路K样本和提示类型配置中使用单个训练模型无缝运行。我们在广泛使用的COCO-20i基准测试上的大量实验评估表明,Label Anything在现有的多类别少量样本分割方法中实现了最先进的性能,并且在多类别设置中显著优于领先的单类模型。相关代码和训练好的模型可在https://github.com/pasqualedem/LabelAnything找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECAI 2025 - 28th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Summary
本文介绍了基于Transformer架构的Label Anything模型,用于多提示、多类别少样本语义分割。该模型利用多样化的视觉提示(点、边界框和掩码)创建了一个灵活且可推广的框架,显著减少了标注负担,同时保持了高准确性。Label Anything对少样本语义分割领域做出了三项关键贡献:引入支持多种提示、多类别分类的新任务形式;提出基于Transformer和注意力机制的新架构;设计了一种通用训练程序,使模型能够在不同的N-way K-shot和提示类型配置中无缝运行。在广泛使用的COCO-20i基准测试中,Label Anything在现有的多类别少样本分割方法中取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- Label Anything是一个基于Transformer的少样本语义分割模型,支持多提示和多类别分类。
- 该模型利用点、边界框和掩码等多样化的视觉提示,创建了一个灵活且可推广的框架。
- Label Anything显著减少了标注负担,同时保持了高准确性。
- 该模型做出了三项关键贡献:引入新的任务形式、新的架构设计和通用训练程序。
- Label Anything在COCO-20i基准测试中表现最佳,证明了其有效性。
- 模型支持不同的N-way K-shot和提示类型配置,具有广泛的应用性。
点此查看论文截图