⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
Vulnerabilities in AI-generated Image Detection: The Challenge of Adversarial Attacks
Authors:Yunfeng Diao, Naixin Zhai, Changtao Miao, Zitong Yu, Xingxing Wei, Xun Yang, Meng Wang
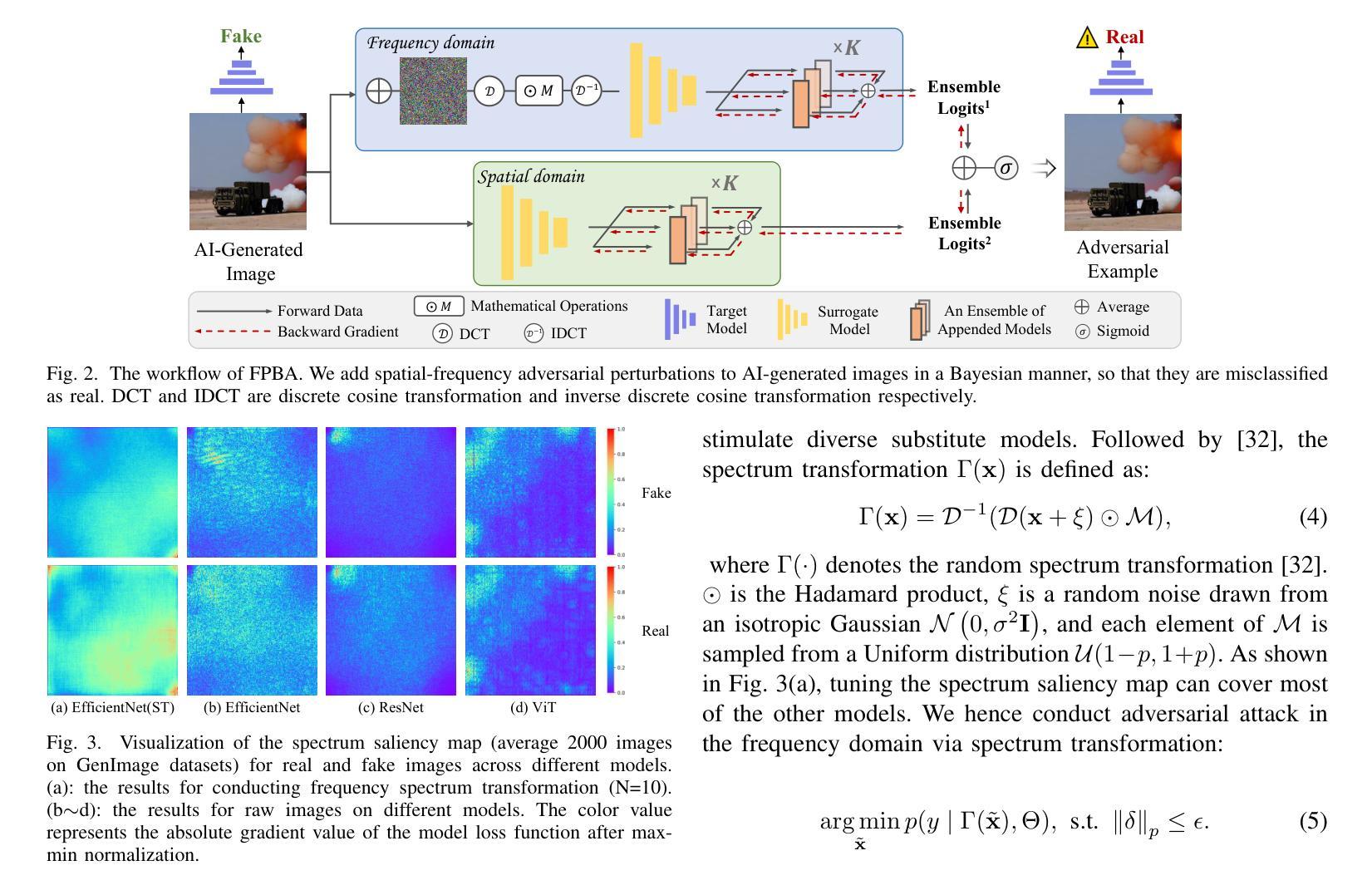
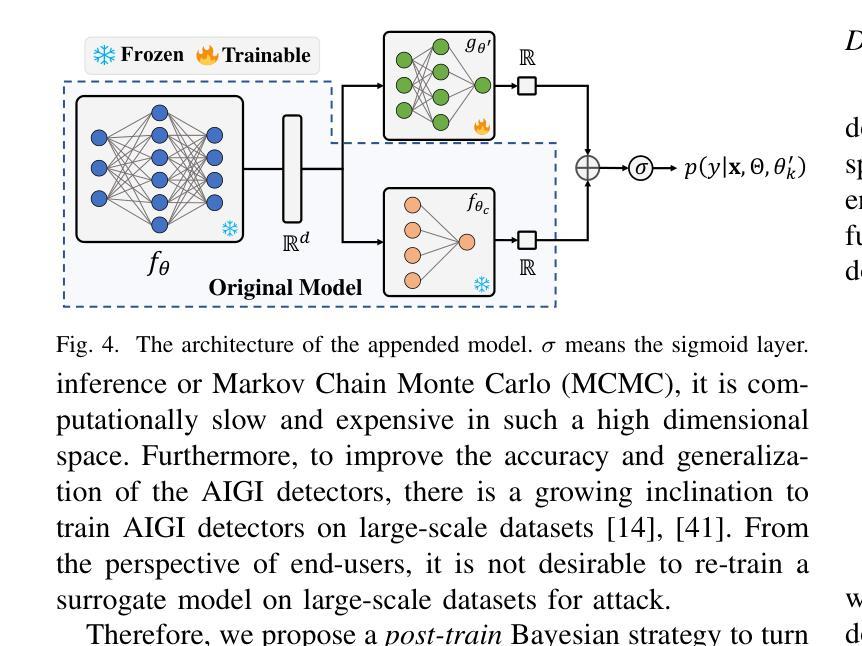
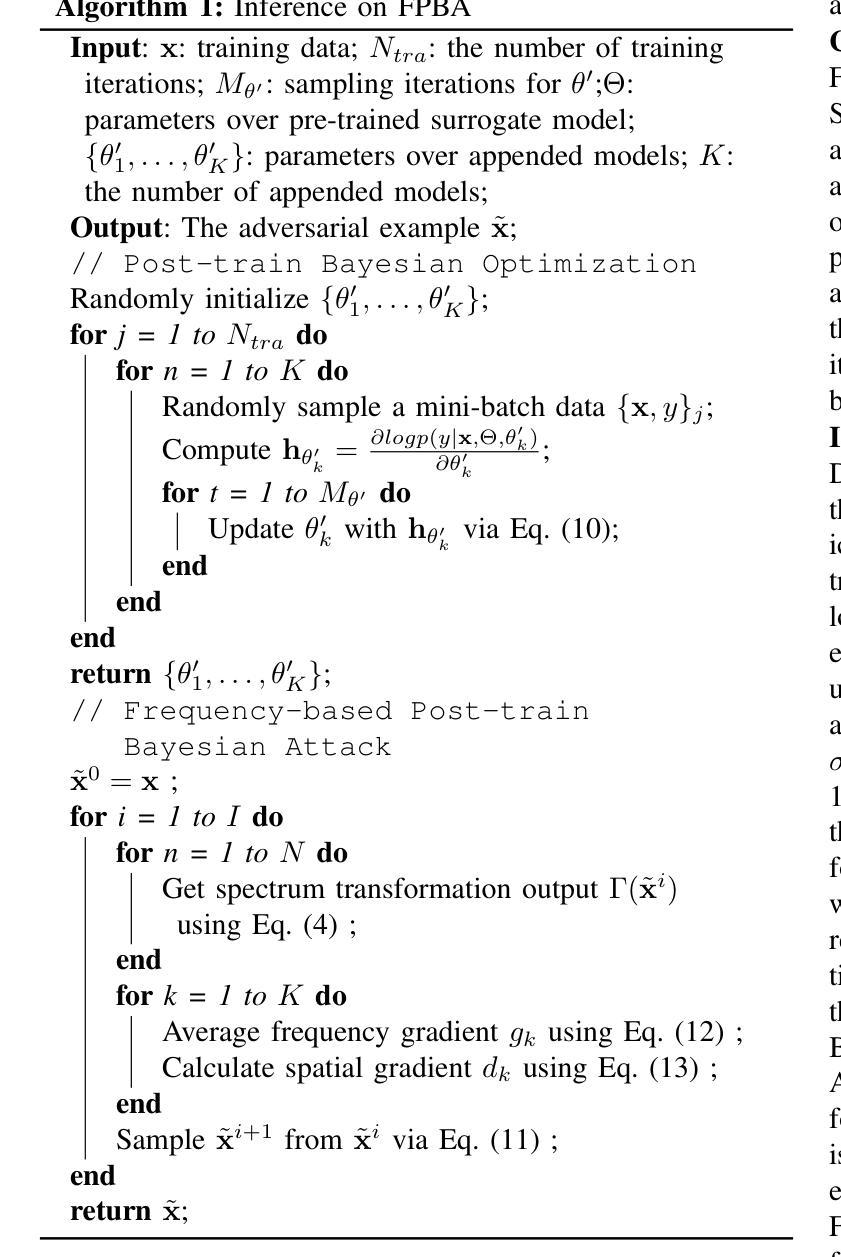
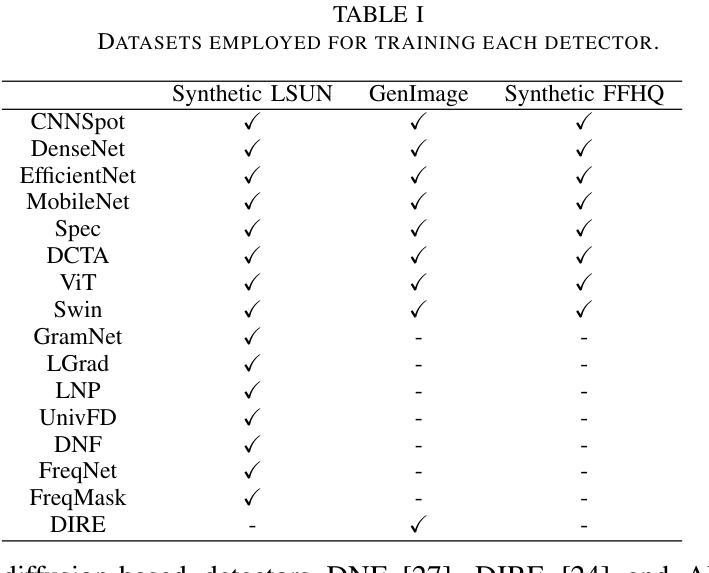
Recent advancements in image synthesis, particularly with the advent of GAN and Diffusion models, have amplified public concerns regarding the dissemination of disinformation. To address such concerns, numerous AI-generated Image (AIGI) Detectors have been proposed and achieved promising performance in identifying fake images. However, there still lacks a systematic understanding of the adversarial robustness of AIGI detectors. In this paper, we examine the vulnerability of state-of-the-art AIGI detectors against adversarial attack under white-box and black-box settings, which has been rarely investigated so far. To this end, we propose a new method to attack AIGI detectors. First, inspired by the obvious difference between real images and fake images in the frequency domain, we add perturbations under the frequency domain to push the image away from its original frequency distribution. Second, we explore the full posterior distribution of the surrogate model to further narrow this gap between heterogeneous AIGI detectors, e.g. transferring adversarial examples across CNNs and ViTs. This is achieved by introducing a novel post-train Bayesian strategy that turns a single surrogate into a Bayesian one, capable of simulating diverse victim models using one pre-trained surrogate, without the need for re-training. We name our method as Frequency-based Post-train Bayesian Attack, or FPBA. Through FPBA, we show that adversarial attack is truly a real threat to AIGI detectors, because FPBA can deliver successful black-box attacks across models, generators, defense methods, and even evade cross-generator detection, which is a crucial real-world detection scenario. The code will be shared upon acceptance.
近年来,图像合成领域的进步,特别是生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型的出现,加剧了公众对假信息传播问题的担忧。为了解决这些担忧,已经提出了许多人工智能生成图像(AIGI)检测器,并在识别虚假图像方面取得了有前景的表现。然而,目前对AIGI检测器的对抗性稳健性还缺乏系统的理解。本文研究了最先进的AIGI检测器在白盒和黑盒设置下对抗攻击的脆弱性,这一问题迄今为止很少被研究。为此,我们提出了一种攻击AIGI检测器的新方法。首先,受真实图像和虚假图像在频域上明显差异的启发,我们在频域中添加扰动,使图像远离其原始频率分布。其次,我们探索了替代模型的全后验分布,以进一步缩小不同AIGI检测器之间的鸿沟,例如在不同CNN和ViTs之间进行对抗性实例迁移。这是通过引入一种新的后训练贝叶斯策略实现的,它将单一的替代模型转变为贝叶斯模型,能够利用一个预训练的替代模型模拟多种受害者模型,无需重新训练。我们将我们的方法命名为基于频率的后训练贝叶斯攻击,或FPBA。通过FPBA,我们证明对抗性攻击确实对AIGI检测器构成威胁,因为FPBA可以在不同的模型、生成器、防御方法之间进行成功的黑盒攻击,甚至可以躲避跨生成器检测,这在现实世界的检测场景中至关重要。论文被接受后,代码将予以分享。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了先进的图像合成技术(如GAN和Diffusion模型)所带来的虚假信息问题。针对此问题,已提出许多AI生成的图像(AIGI)检测器,其性能良好。然而,本文强调了当前研究中缺乏对抗性攻击下AIGI检测器的系统理解。本文提出一种针对先进AIGI检测器的新攻击方法,称为基于频率的后训练贝叶斯攻击(FPBA)。该方法通过频率域的扰动和模拟多种受害者模型的贝叶斯策略,实现了跨模型、生成器、防御方法的成功黑箱攻击,并能逃避跨生成器检测。
Key Takeaways
- GAN和Diffusion模型等先进图像合成技术引发公众对虚假信息传播的担忧。
- AIGI检测器在识别虚假图像方面表现出良好性能,但缺乏对其对抗性稳健性的系统理解。
- 本文提出一种名为FPBA的新方法,旨在攻击先进的AIGI检测器,并在白盒和黑盒设置下测试其脆弱性。
- FPBA通过频率域的扰动来推动图像远离其原始频率分布,并利用贝叶斯策略模拟多种受害者模型。
- FPBA实现了跨模型、生成器、防御方法的成功黑箱攻击,并能逃避跨生成器检测。
- FPBA方法强调对抗性攻击对AIGI检测器的真正威胁。
- 代码将在接受后共享。
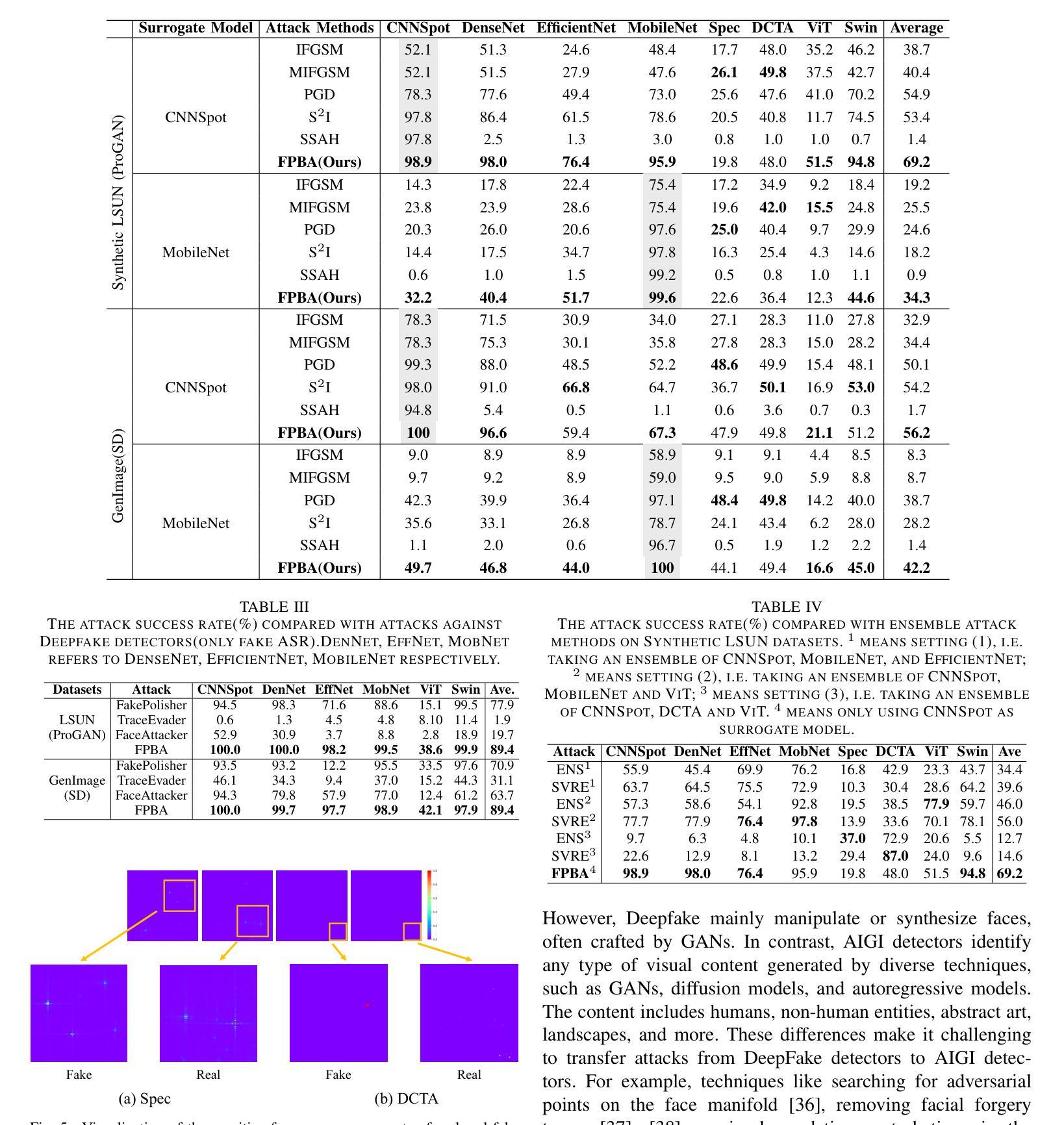
点此查看论文截图