⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
Are Virtual DES Images a Valid Alternative to the Real Ones?
Authors:Ana C. Perre, Luís A. Alexandre, Luís C. Freire
Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) is an imaging modality that provides two types of images, commonly known as low-energy (LE) and dual-energy subtracted (DES) images. In many domains, particularly in medicine, the emergence of image-to-image translation techniques has enabled the artificial generation of images using other images as input. Within CESM, applying such techniques to generate DES images from LE images could be highly beneficial, potentially reducing patient exposure to radiation associated with high-energy image acquisition. In this study, we investigated three models for the artificial generation of DES images (virtual DES): a pre-trained U-Net model, a U-Net trained end-to-end model, and a CycleGAN model. We also performed a series of experiments to assess the impact of using virtual DES images on the classification of CESM examinations into malignant and non-malignant categories. To our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the impact of virtual DES images on CESM lesion classification. The results demonstrate that the best performance was achieved with the pre-trained U-Net model, yielding an F1 score of 85.59% when using the virtual DES images, compared to 90.35% with the real DES images. This discrepancy likely results from the additional diagnostic information in real DES images, which contributes to a higher classification accuracy. Nevertheless, the potential for virtual DES image generation is considerable and future advancements may narrow this performance gap to a level where exclusive reliance on virtual DES images becomes clinically viable.
对比增强光谱乳腺摄影(CESM)是一种成像方式,提供两种类型的图像,通常称为低能量(LE)和双能量减去(DES)图像。在许多领域,特别是在医学领域,图像到图像翻译技术的出现使得可以使用其他图像作为输入来生成图像。在CESM中,将此类技术应用于从LE图像生成DES图像可能高度有益,这有助于减少患者因高能图像采集而暴露于辐射。在这项研究中,我们研究了三种用于生成DES图像(虚拟DES)的模型:预训练的U-Net模型、端到端训练的U-Net模型和CycleGAN模型。我们还进行了一系列实验,以评估使用虚拟DES图像对CESM检查分类为恶性和非恶性类别的影响。据我们所知,这是首次评估虚拟DES图像对CESM病变分类的影响的研究。结果表明,使用预训练的U-Net模型取得了最佳性能,使用虚拟DES图像时的F1分数为85.59%,而使用真实DES图像时的F1分数为90.35%。这种差异可能是由于真实DES图像中额外的诊断信息导致的,有助于提高分类准确性。然而,生成虚拟DES图像具有巨大潜力,未来技术改进可能会缩小性能差距,使得仅依赖虚拟DES图像在临床环境中变得可行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables
Summary:对比增强光谱乳腺成像(CESM)是两种图像成像方式中的一种,包括低能量(LE)和双能量相减(DES)图像。采用图像到图像的翻译技术从LE图像生成DES图像具有诸多好处,可能降低患者受到的高能辐射的风险。研究中对比了三种DES图像生成方法(虚拟DES),发现预训练的U-Net模型表现最佳,使用虚拟DES图像生成的分类结果F1分数为85.59%,而真实DES图像为90.35%。虽然存在一定差距,但虚拟DES图像生成的潜力巨大,未来可能缩小差距至仅依赖虚拟DES图像即可实现临床可行性。
Key Takeaways:
- 对比增强光谱乳腺成像(CESM)包括低能量(LE)和双能量相减(DES)两种图像类型。
- 图像到图像的翻译技术可以用于从LE图像生成DES图像,减少患者受到的高能辐射风险。
- 研究评估了三种生成虚拟DES图像的方法,包括预训练的U-Net模型、端到端训练的U-Net模型和CycleGAN模型。
- 预训练的U-Net模型在生成虚拟DES图像方面表现最佳,但相较于真实DES图像仍存在性能差异。
- 使用虚拟DES图像的F1分数为85.59%,而真实DES图像为90.35%,表明真实DES图像包含更多诊断信息。
- 虽然存在性能差异,但虚拟DES图像生成具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

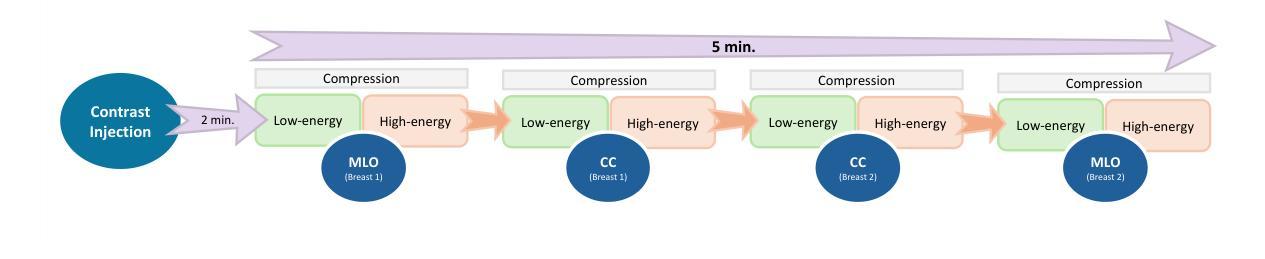
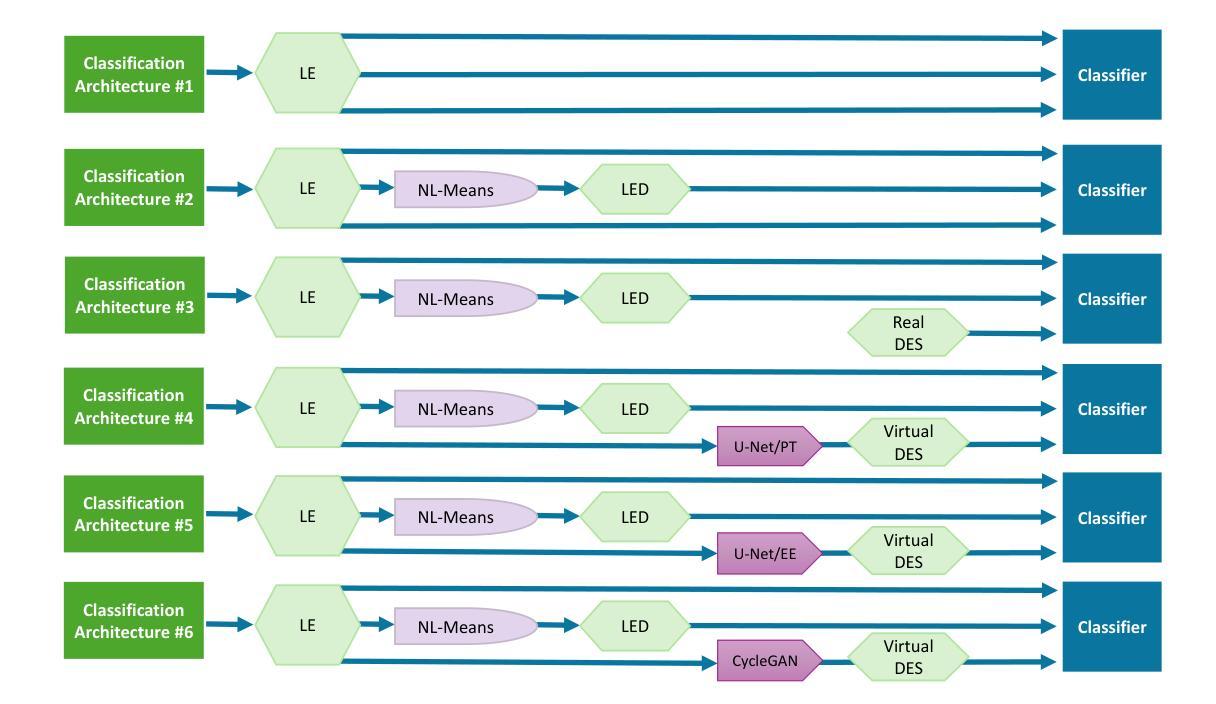
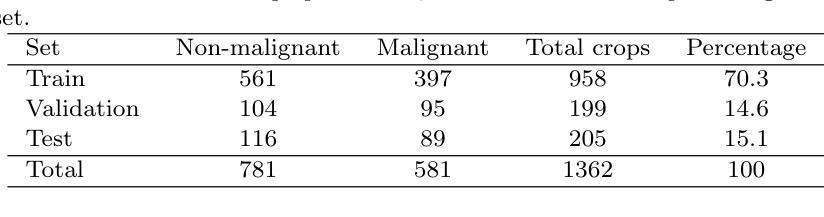
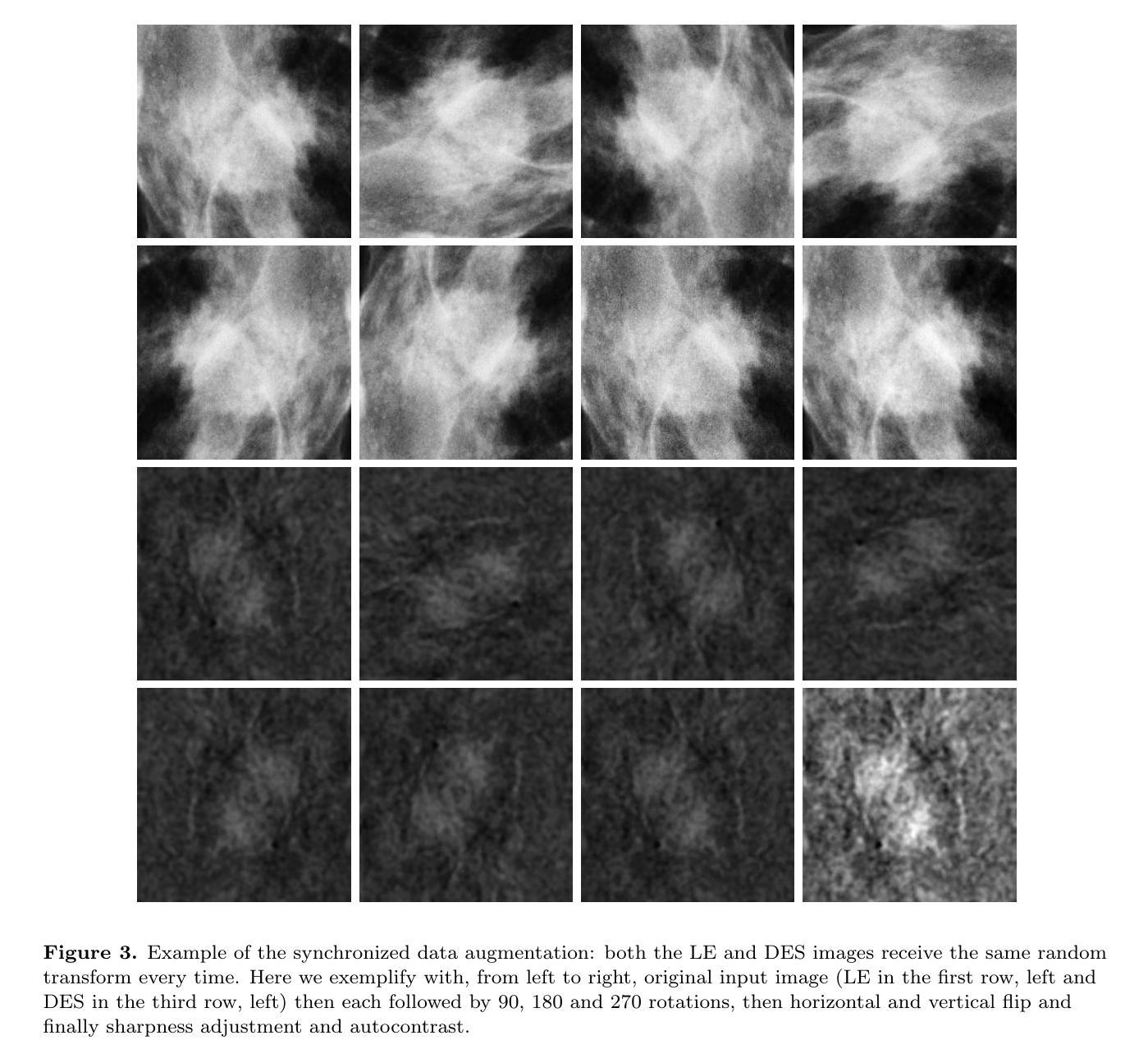
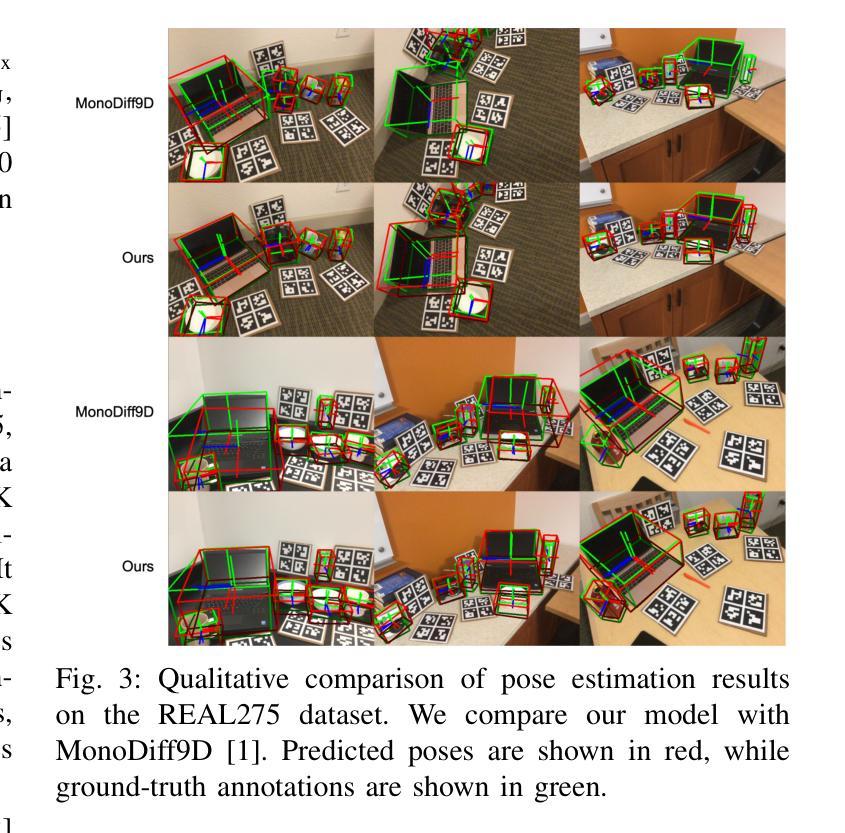
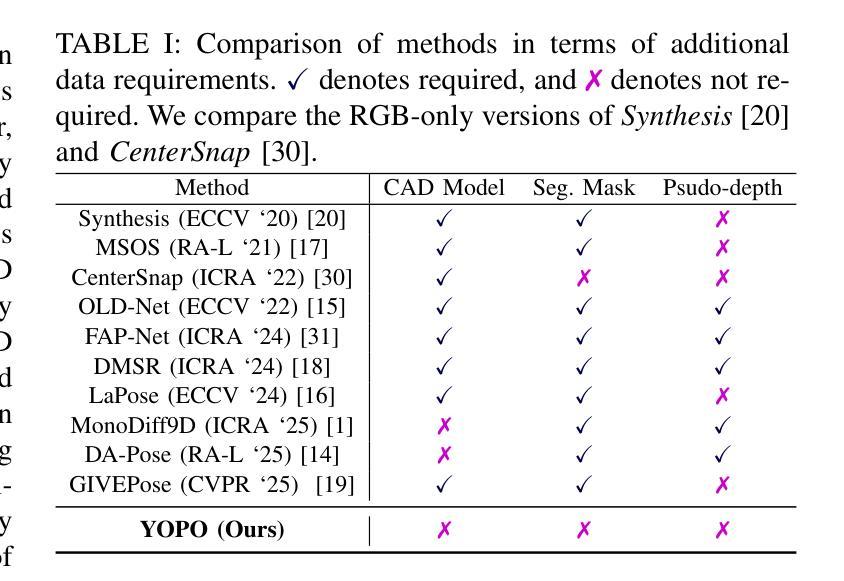
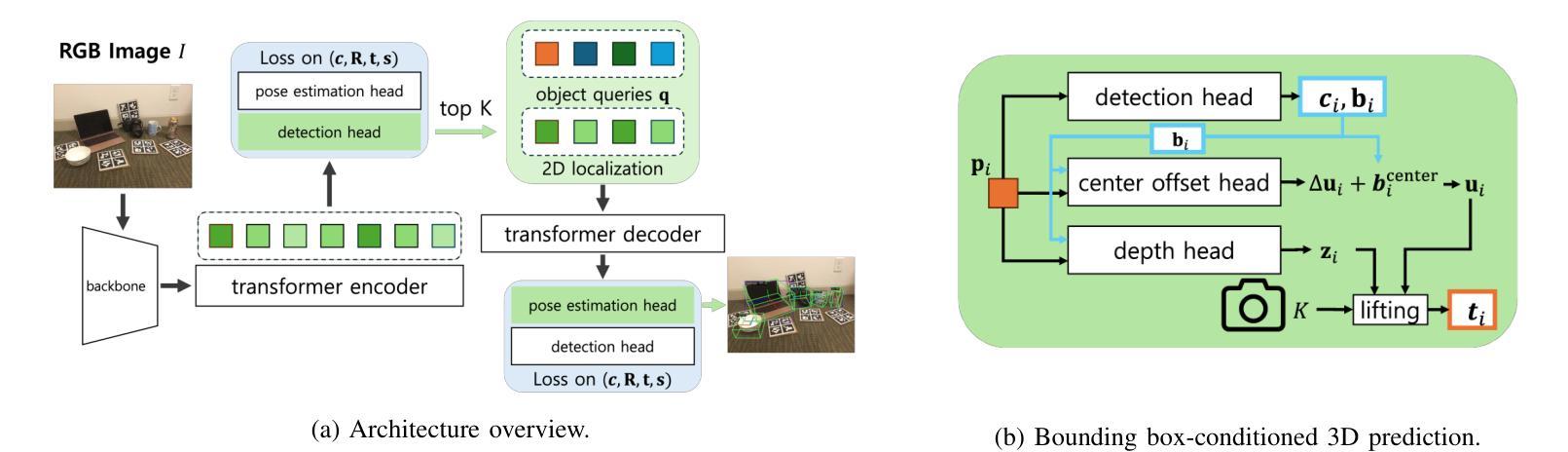
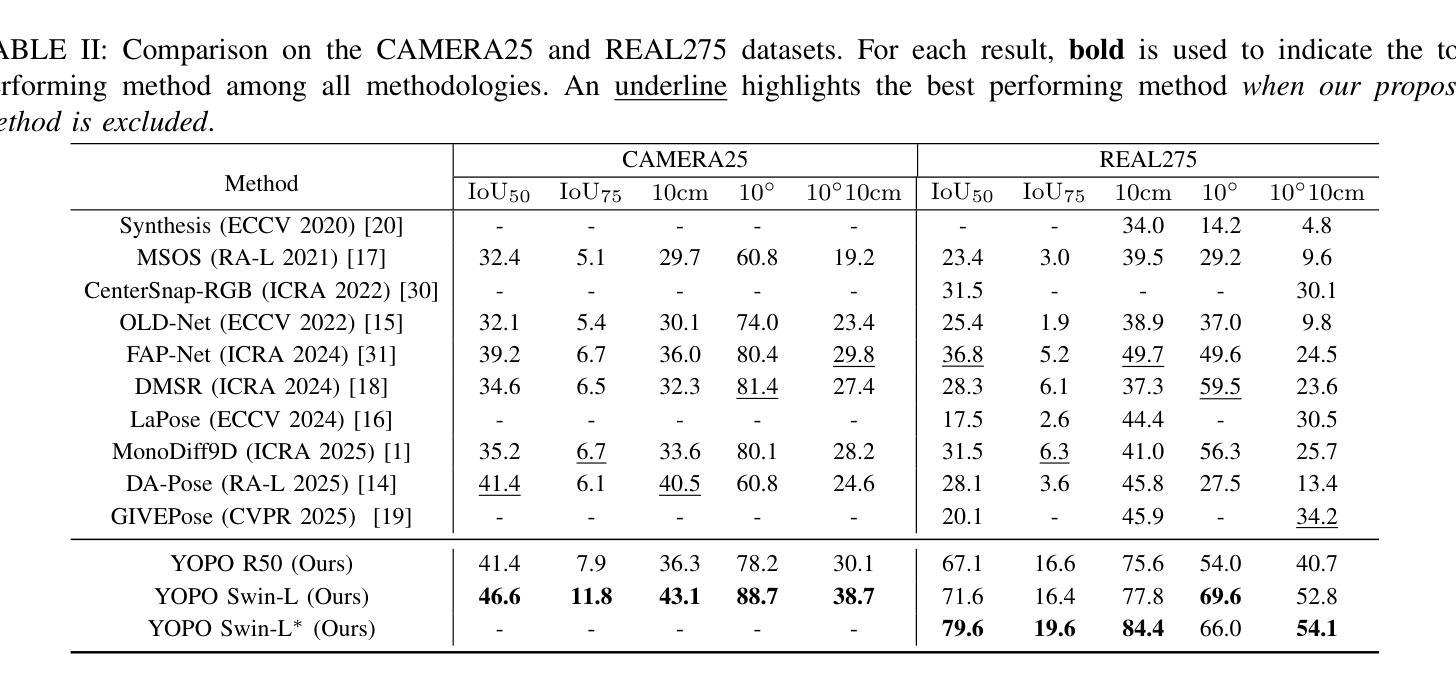
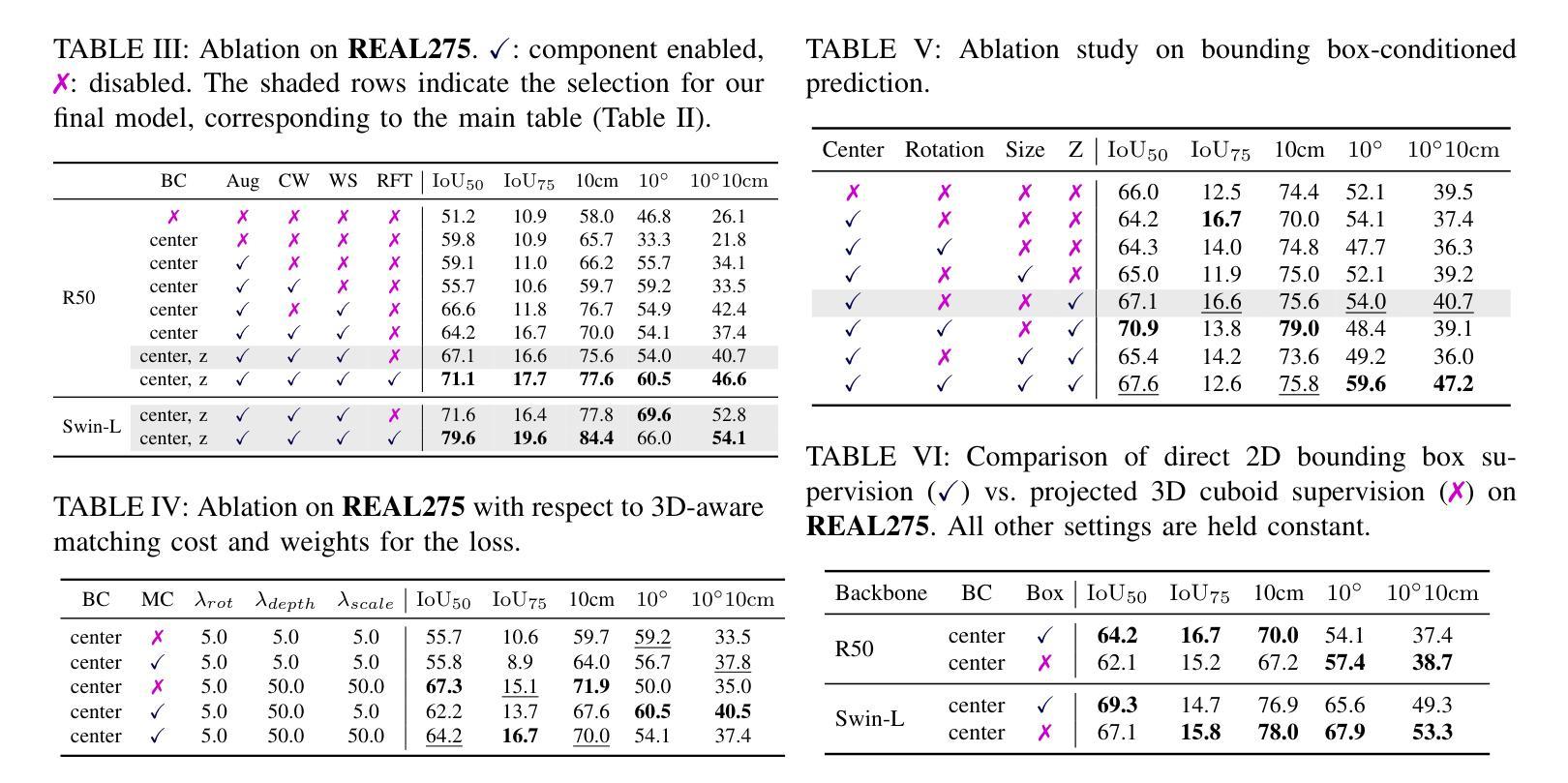
You Only Pose Once: A Minimalist’s Detection Transformer for Monocular RGB Category-level 9D Multi-Object Pose Estimation
Authors:Hakjin Lee, Junghoon Seo, Jaehoon Sim
Accurately recovering the full 9-DoF pose of unseen instances within specific categories from a single RGB image remains a core challenge for robotics and automation. Most existing solutions still rely on pseudo-depth, CAD models, or multi-stage cascades that separate 2D detection from pose estimation. Motivated by the need for a simpler, RGB-only alternative that learns directly at the category level, we revisit a longstanding question: Can object detection and 9-DoF pose estimation be unified with high performance, without any additional data? We show that they can with our method, YOPO, a single-stage, query-based framework that treats category-level 9-DoF estimation as a natural extension of 2D detection. YOPO augments a transformer detector with a lightweight pose head, a bounding-box-conditioned translation module, and a 6D-aware Hungarian matching cost. The model is trained end-to-end only with RGB images and category-level pose labels. Despite its minimalist design, YOPO sets a new state of the art on three benchmarks. On the REAL275 dataset, it achieves 79.6% $\rm{IoU}_{50}$ and 54.1% under the $10^\circ$$10{\rm{cm}}$ metric, surpassing prior RGB-only methods and closing much of the gap to RGB-D systems. The code, models, and additional qualitative results can be found on our project.
准确地从单一RGB图像中恢复特定类别中未见实例的完整9自由度姿态,仍然是机器人和自动化领域的核心挑战。现有的大多数解决方案仍然依赖于伪深度、CAD模型或分阶段级联,将2D检测与姿态估计分开。受需要更简单、仅使用RGB的替代方案驱动,该方案直接在类别层面学习,我们重新考虑了一个长期存在的问题:是否可以将对象检测和9自由度姿态估计统一起来,实现高性能,而无需任何额外数据?我们的方法YOPO表明可以做到这一点。YOPO是一种基于查询的单阶段框架,它将类别层面的9自由度估计视为2D检测的自然延伸。YOPO通过轻量级的姿态头、受边界框约束的翻译模块和6D感知匈牙利匹配成本来增强变压器检测器。该模型仅通过RGB图像和类别级别的姿态标签进行端到端的训练。尽管其设计简约,但YOPO在三个基准测试上创下了最新纪录。在REAL275数据集上,它达到了79.6%的IoU50,在10°10cm指标下达到54.1%,超过了先前的仅RGB方法和缩小了与RGB-D系统的差距。我们的项目可以找到代码、模型和额外的定性结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://mikigom.github.io/YOPO-project-page
Summary
本文提出了一种新的RGB图像中的物体类别级别的9自由度姿态估计方法,名为YOPO。该方法将物体检测与姿态估计统一在一个单阶段查询框架中,通过增加一个轻量级的姿态头、一个基于边界框的翻译模块和一个6D感知匈牙利匹配成本来实现。仅使用RGB图像和类别级别的姿态标签进行端到端的训练,YOPO在三个基准测试中均达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- RGB图像中的物体类别级别姿态估计是一个核心挑战。
- 当前解决方案依赖于伪深度、CAD模型或多阶段级联方法,这些方法将二维检测和姿态估计分开。
- 研究动机在于需要更简单、仅使用RGB的方法,该方法可以直接在类别级别学习。
- YOPO是一个基于查询的单阶段框架,将类别级别的9自由度姿态估计视为二维检测的自然延伸。
- YOPO通过使用轻量级姿态头、边界框条件翻译模块和6D感知匈牙利匹配成本进行工作。
- YOPO仅使用RGB图像和类别级别的姿态标签进行端到端训练。
点此查看论文截图


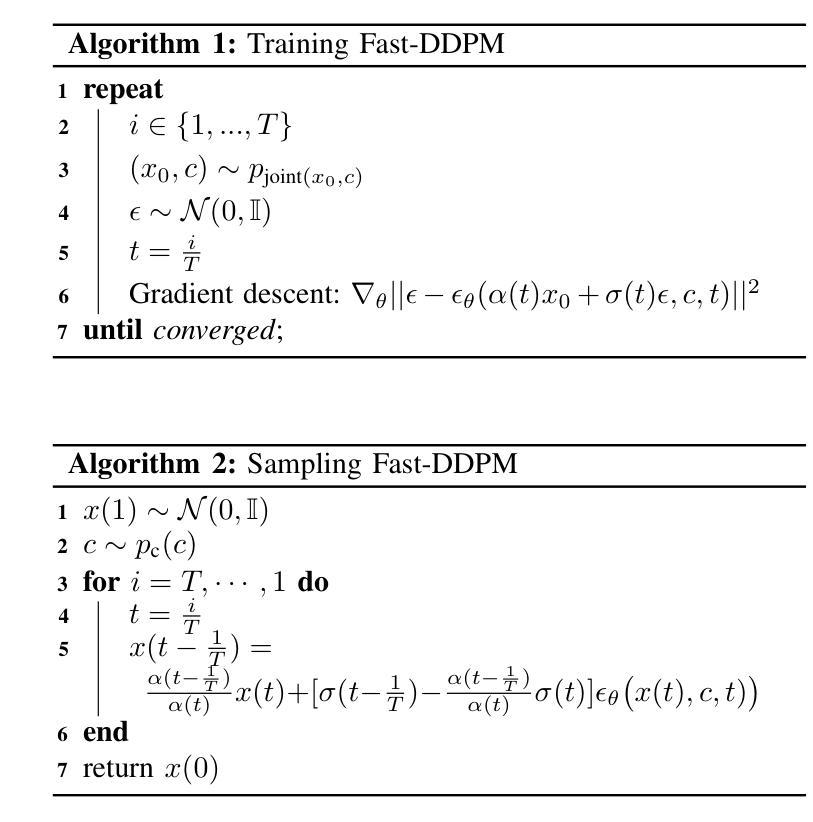
Fast-DDPM: Fast Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Medical Image-to-Image Generation
Authors:Hongxu Jiang, Muhammad Imran, Teng Zhang, Yuyin Zhou, Muxuan Liang, Kuang Gong, Wei Shao
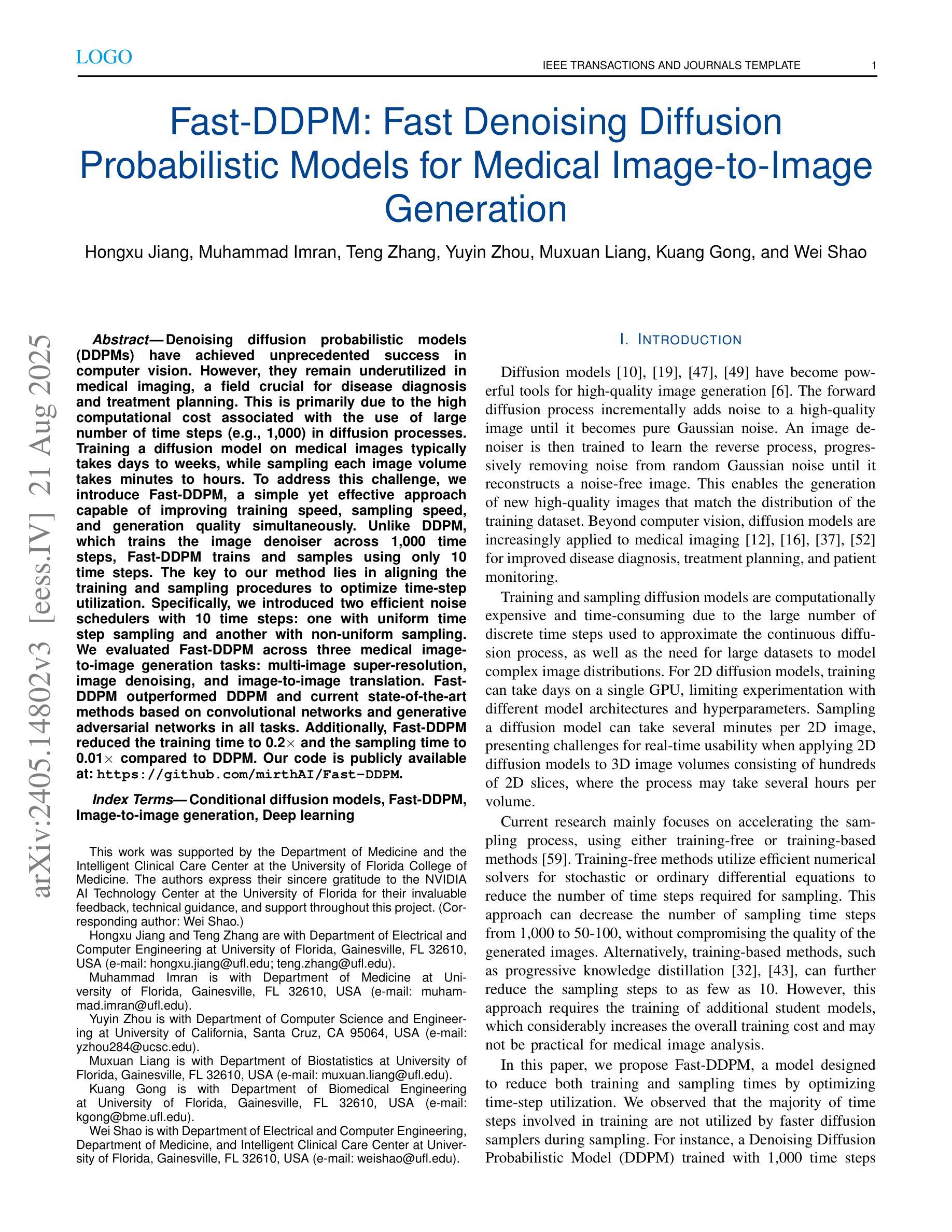
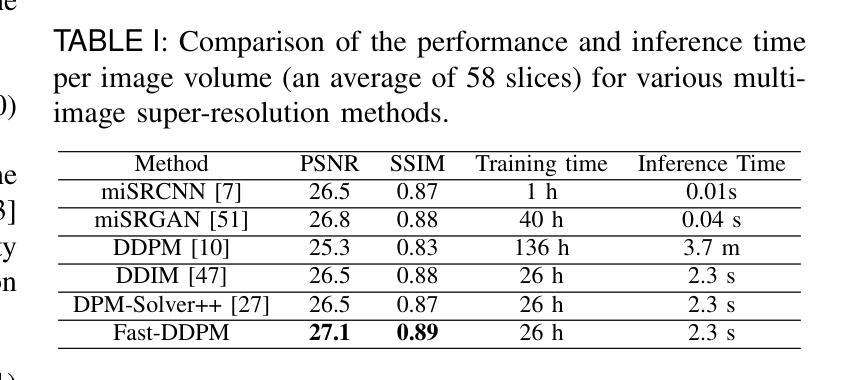
Denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) have achieved unprecedented success in computer vision. However, they remain underutilized in medical imaging, a field crucial for disease diagnosis and treatment planning. This is primarily due to the high computational cost associated with (1) the use of large number of time steps (e.g., 1,000) in diffusion processes and (2) the increased dimensionality of medical images, which are often 3D or 4D. Training a diffusion model on medical images typically takes days to weeks, while sampling each image volume takes minutes to hours. To address this challenge, we introduce Fast-DDPM, a simple yet effective approach capable of improving training speed, sampling speed, and generation quality simultaneously. Unlike DDPM, which trains the image denoiser across 1,000 time steps, Fast-DDPM trains and samples using only 10 time steps. The key to our method lies in aligning the training and sampling procedures to optimize time-step utilization. Specifically, we introduced two efficient noise schedulers with 10 time steps: one with uniform time step sampling and another with non-uniform sampling. We evaluated Fast-DDPM across three medical image-to-image generation tasks: multi-image super-resolution, image denoising, and image-to-image translation. Fast-DDPM outperformed DDPM and current state-of-the-art methods based on convolutional networks and generative adversarial networks in all tasks. Additionally, Fast-DDPM reduced the training time to 0.2x and the sampling time to 0.01x compared to DDPM. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM.
去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs)在计算机视觉领域取得了前所未有的成功。然而,它们在医学成像这一对疾病诊断和治疗计划至关重要的领域却应用不足。这主要是因为与(1)扩散过程中使用的大量时间步数(例如,1000步)和(2)医学图像增加的维度(通常是3D或4D)相关的计算成本高昂。在医学图像上训练扩散模型通常需要几天到几周的时间,而对每个图像体积进行采样则需要几分钟到几小时。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了Fast-DDPM,这是一种简单而有效的方法,可以同时提高训练速度、采样速度和生成质量。与DDPM不同,它在整个过程中训练图像去噪器跨越了1000个时间步长,而Fast-DDPM在训练和采样过程中仅使用了短短的十步。我们方法的要点在于调整训练和采样过程以优化时间步长使用效率。具体来说,我们引入了两个带有十步的有效噪声调度器:一个采用均匀时间步长采样,另一个采用非均匀采样。我们在三项医学图像到图像生成任务上评估了Fast-DDPM:多图像超分辨率、图像去噪和图像到图像的转换。Fast-DDPM在所有任务中都优于DDPM和基于卷积网络和生成对抗网络的当前最新方法。此外,Fast-DDPM将训练时间缩短至DDPM的0.2倍,采样时间缩短至DDPM的0.01倍。我们的代码公开在:https://github.com/mirthAI/Fast-DDPM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
快速DDPM模型在医学图像生成领域提升了DDPM(去噪扩散概率模型)的速度和质量。该模型通过优化时间步长利用,在医学图像去噪、超分辨率和图像到图像翻译等任务上表现出超越DDPM和其他当前最先进方法的性能。它减少了训练时间和采样时间。
Key Takeaways
- Fast-DDPM模型针对医学成像领域的DDPM进行了优化,提高了模型的速度和生成质量。
- Fast-DDPM通过在训练和采样过程中优化时间步长的利用,实现了性能提升。
- 该模型引入了两种高效的噪声调度策略,包括均匀和非均匀时间步长采样。
- Fast-DDPM在医学图像去噪、超分辨率和图像到图像翻译等任务上表现出超越DDPM和其他当前最先进方法的性能。
- Fast-DDPM将训练时间缩短至DDPM的0.2倍,采样时间缩短至DDPM的0.01倍。
- Fast-DDPM模型具有公开可用的代码,可供进一步研究和使用。
点此查看论文截图
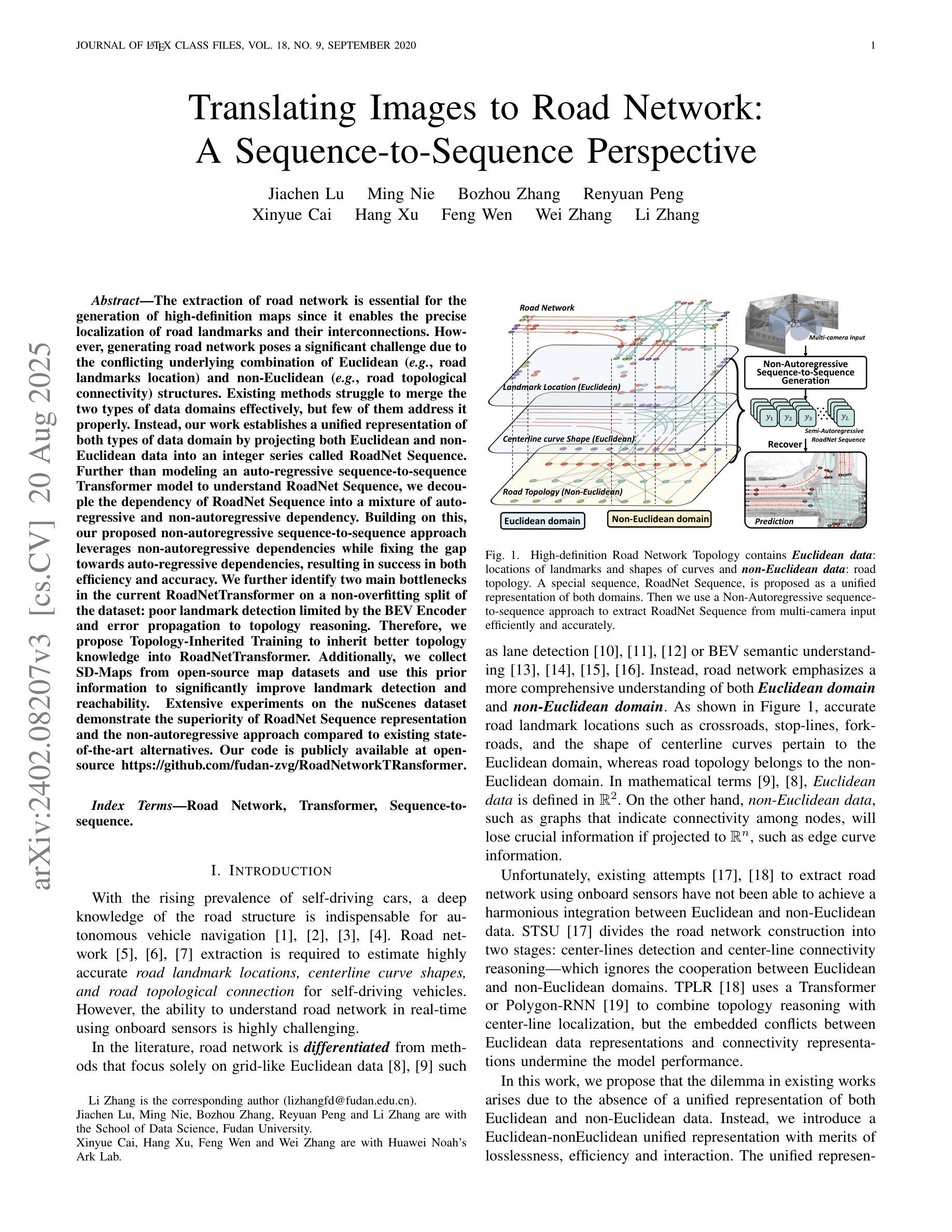
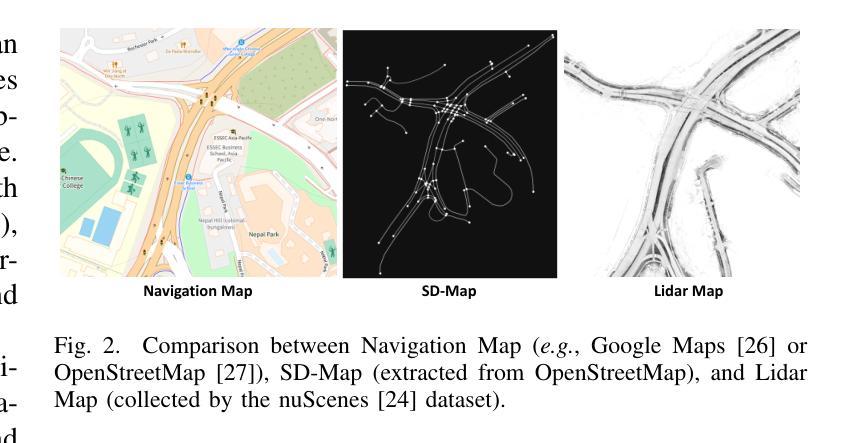
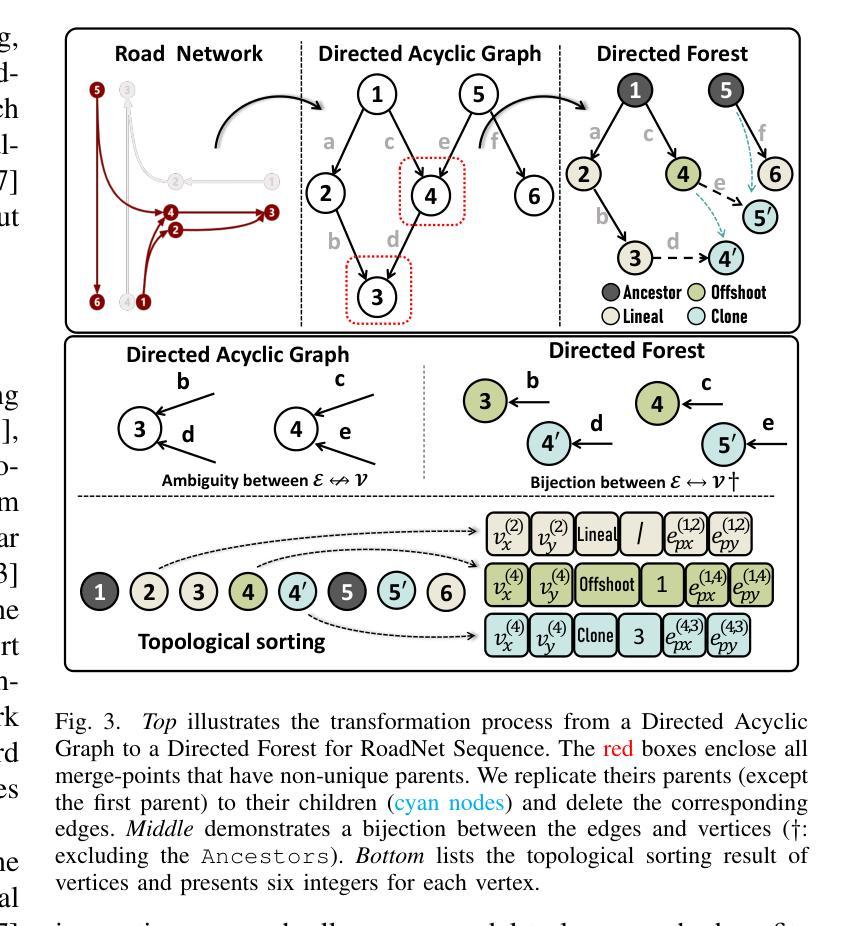
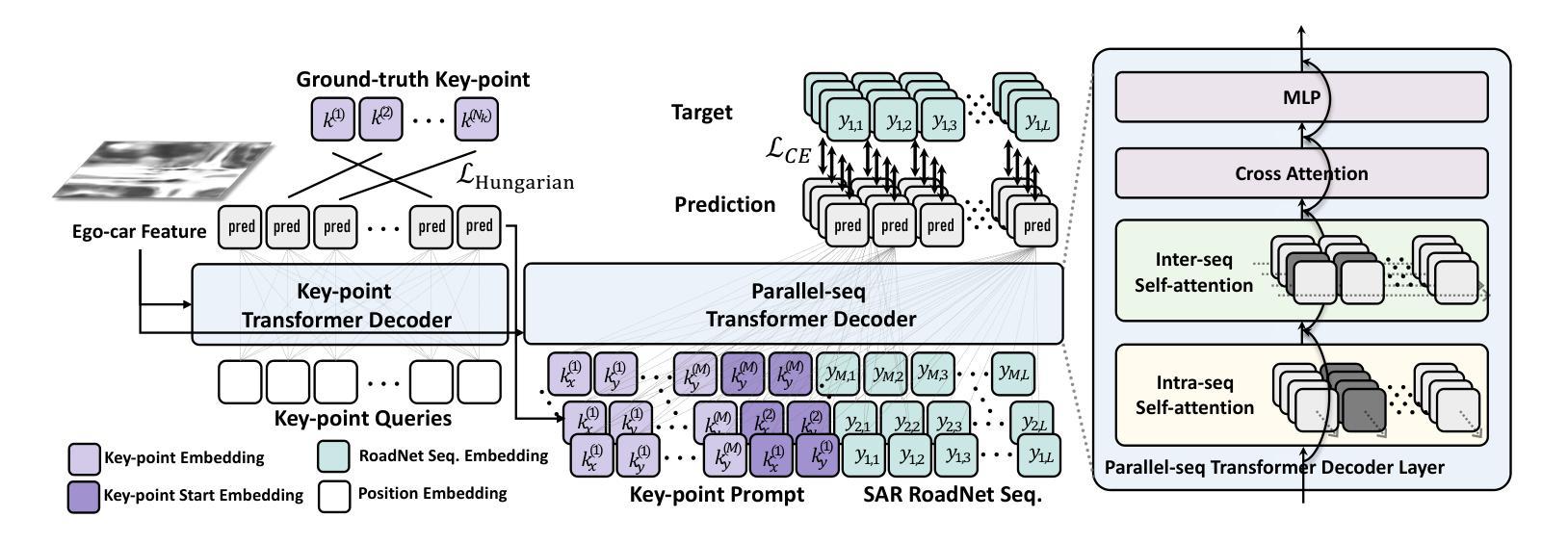
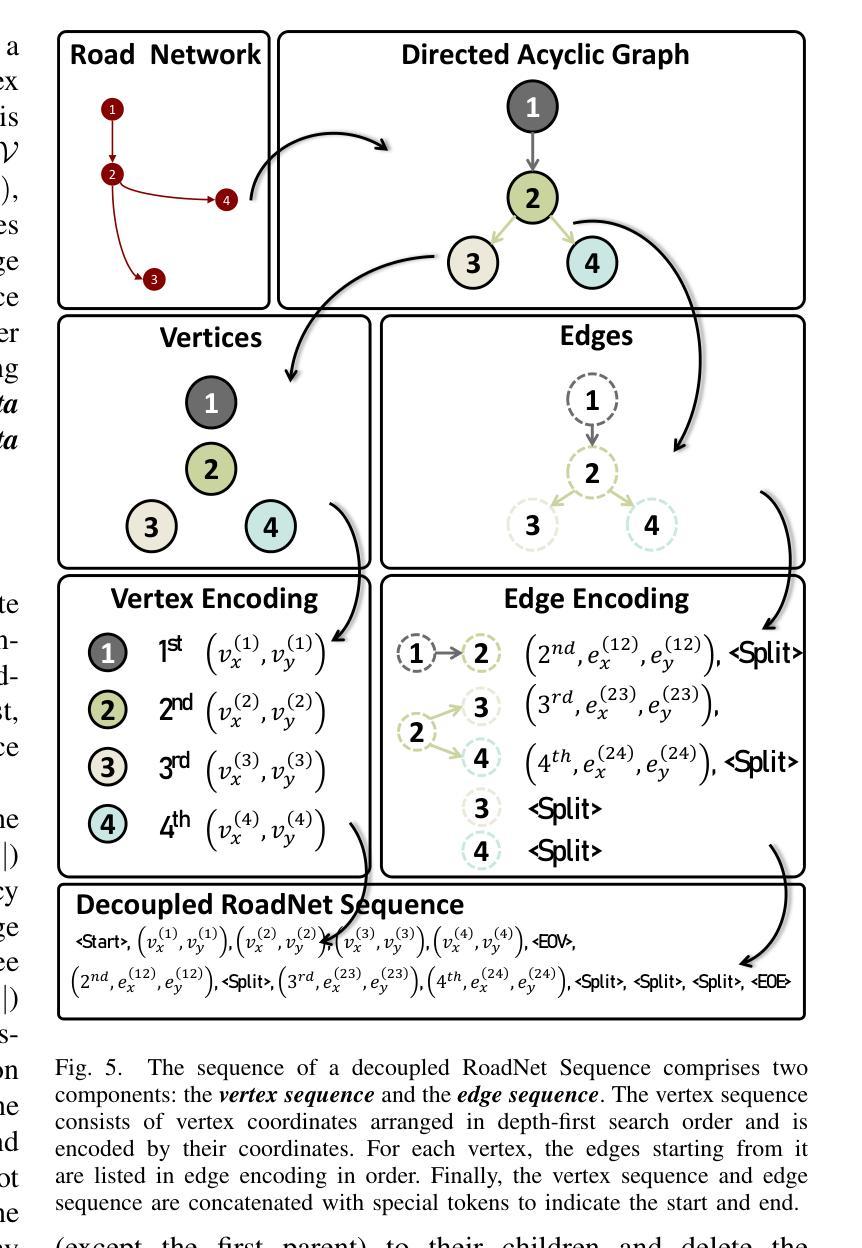
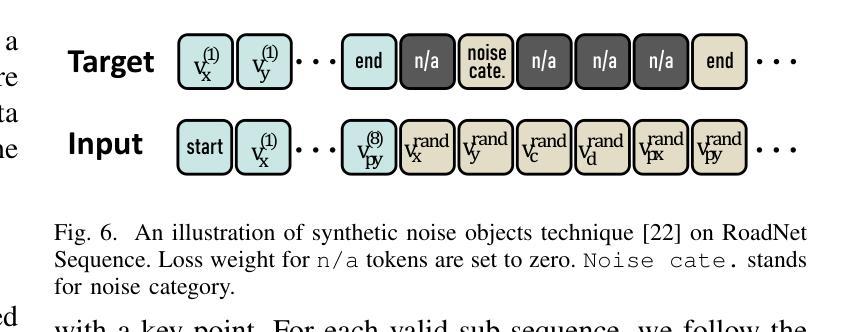
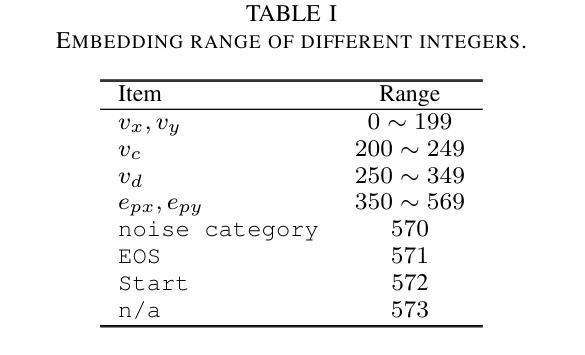
Translating Images to Road Network: A Sequence-to-Sequence Perspective
Authors:Jiachen Lu, Ming Nie, Bozhou Zhang, Reyuan Peng, Xinyue Cai, Hang Xu, Feng Wen, Wei Zhang, Li Zhang
The extraction of road network is essential for the generation of high-definition maps since it enables the precise localization of road landmarks and their interconnections. However, generating road network poses a significant challenge due to the conflicting underlying combination of Euclidean (e.g., road landmarks location) and non-Euclidean (e.g., road topological connectivity) structures. Existing methods struggle to merge the two types of data domains effectively, but few of them address it properly. Instead, our work establishes a unified representation of both types of data domain by projecting both Euclidean and non-Euclidean data into an integer series called RoadNet Sequence. Further than modeling an auto-regressive sequence-to-sequence Transformer model to understand RoadNet Sequence, we decouple the dependency of RoadNet Sequence into a mixture of auto-regressive and non-autoregressive dependency. Building on this, our proposed non-autoregressive sequence-to-sequence approach leverages non-autoregressive dependencies while fixing the gap towards auto-regressive dependencies, resulting in success in both efficiency and accuracy. We further identify two main bottlenecks in the current RoadNetTransformer on a non-overfitting split of the dataset: poor landmark detection limited by the BEV Encoder and error propagation to topology reasoning. Therefore, we propose Topology-Inherited Training to inherit better topology knowledge into RoadNetTransformer. Additionally, we collect SD-Maps from open-source map datasets and use this prior information to significantly improve landmark detection and reachability. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate the superiority of RoadNet Sequence representation and the non-autoregressive approach compared to existing state-of-the-art alternatives.
道路网络的提取对于生成高精度地图至关重要,因为它能够精确地定位道路地标及其相互连接。然而,生成道路网络是一个巨大的挑战,因为欧几里得(例如道路地标的位置)和非欧几里得(例如道路拓扑连接)结构的底层组合存在冲突。现有方法很难有效地合并这两种类型的数据域,而且很少有方法能够恰当地处理这个问题。相反,我们的工作通过建立一种统一表示两种数据域的方法,通过将欧几里得和非欧几里得数据投影到一个称为RoadNet序列的整数序列中,来解决这个问题。我们不仅建立了一个自回归序列到序列的Transformer模型来理解RoadNet序列,而且将RoadNet序列的依赖性解耦为自回归和非自回归依赖性的混合。在此基础上,我们提出的非自回归序列到序列的方法利用了非自回归依赖性,同时解决了自回归依赖性的差距,从而在效率和准确性方面都取得了成功。我们进一步识别了当前RoadNetTransformer在非数据集过拟合拆分中的两个主要瓶颈:受限于BEV编码器的地标检测不佳,以及拓扑推理中的错误传播。因此,我们提出了拓扑继承训练,以将更好的拓扑知识融入到RoadNetTransformer中。此外,我们从开源地图数据集中收集了SD-Maps,并利用这些先验信息显著提高了地标检测可达性。在nuScenes数据集上的大量实验表明,与现有的最先进方法相比,RoadNet序列表示和非自回归方法具有优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF V1 is the ICCV 2023 conference version, and V2 is the extended version
摘要
文中提出一种融合欧几里得和非欧几里得数据结构的方法,用于生成道路网络。通过统一表示这两种数据域,将道路网络提取转化为高清晰度地图生成的关键步骤。文章建立了一种名为RoadNet Sequence的整数序列表示,并采用自回归序列到序列的Transformer模型进行理解。在此基础上,提出了一种非自回归序列到序列的方法,既利用非自回归依赖关系又解决自回归依赖的缺陷,提高了效率和准确性。文章还指出了当前RoadNetTransformer的两个主要瓶颈,并提出了Topology-Inherited Training方法来解决。此外,通过收集SD-Maps开放源码地图数据集并使用先验信息,显著提高了地标检测和可达性。在nuScenes数据集上的实验证明了RoadNet Sequence表示和非自回归方法的优越性。
关键见解
- 道路网络提取对于高清晰度地图生成至关重要,它实现了道路地标及其连接的精确定位。
- 现有方法难以有效融合欧几里得和非欧几里得数据结构,而本文通过建立统一表示解决了这一问题。
- 提出了一种名为RoadNet Sequence的整数序列表示法,用于表示这两种数据域的统一表示。
- 采用自回归和非自回归结合的序列到序列Transformer模型理解RoadNet Sequence。
- 识别了当前RoadNetTransformer的两个主要瓶颈:BEV Encoder对地标检测的限制以及拓扑推理中的误差传播。
- 提出了Topology-Inherited Training方法,以更好地将拓扑知识融入RoadNetTransformer。
点此查看论文截图