⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
From PREVENTion to REACTion: Enhancing Failure Resolution in Naval Systems
Authors:Maria Teresa Rossi, Leonardo Mariani, Oliviero Riganelli
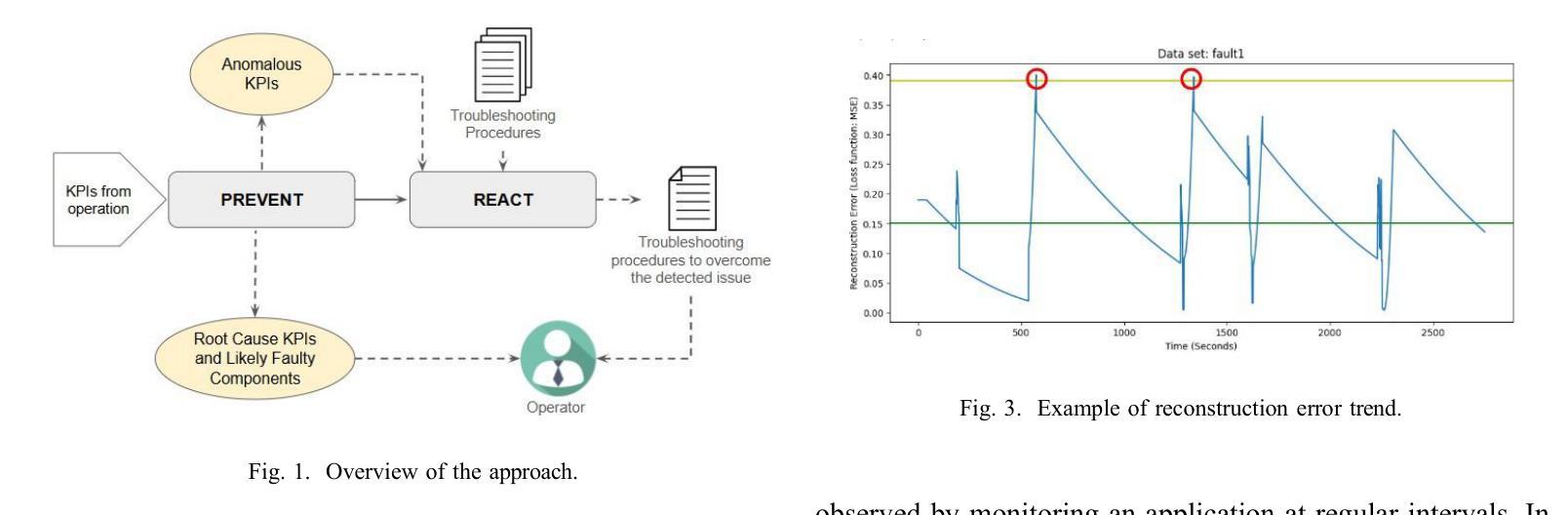
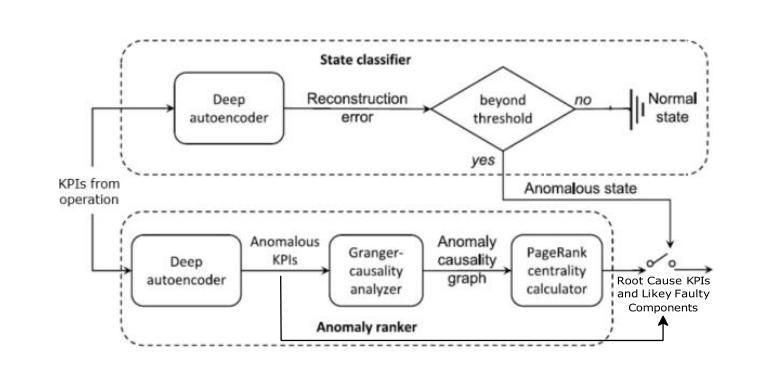
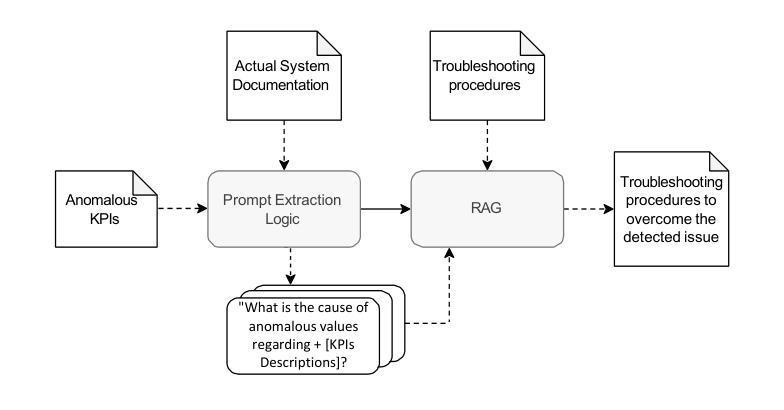
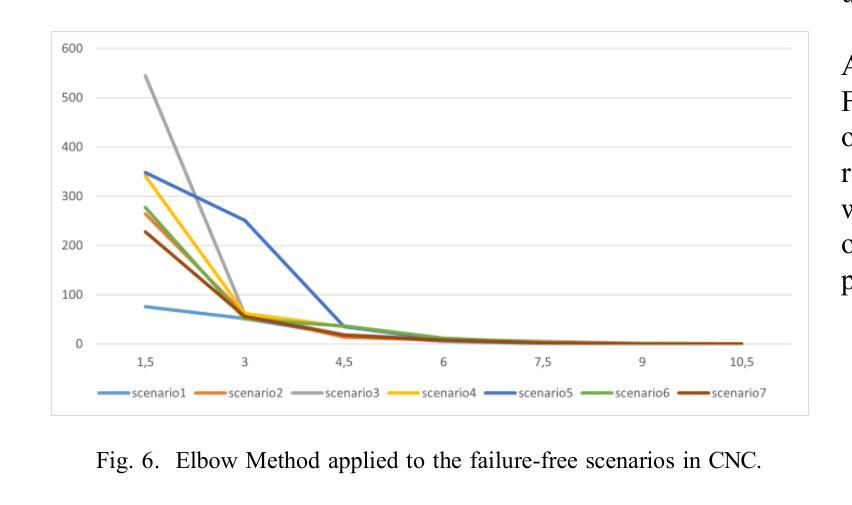
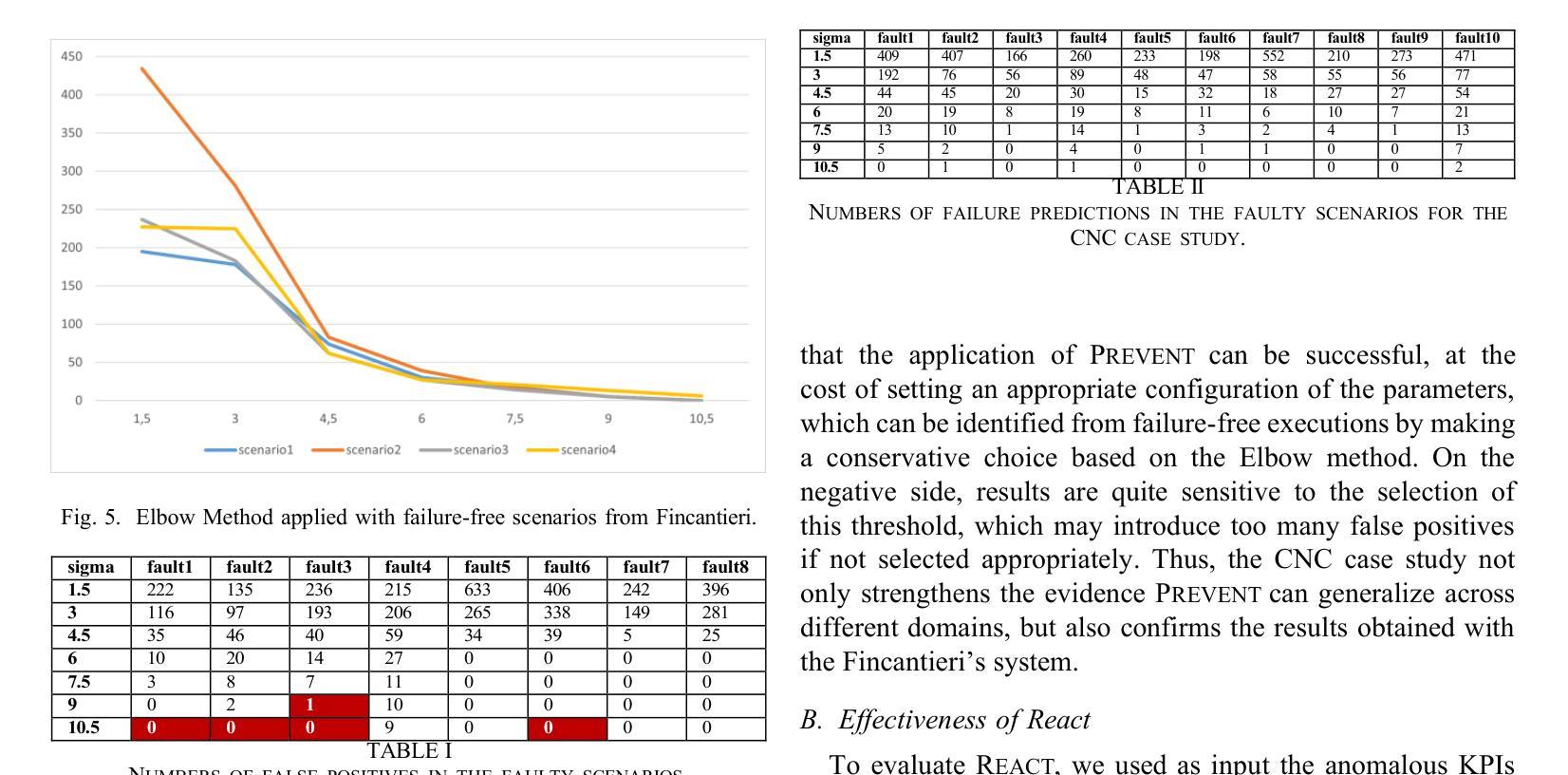
Complex and large industrial systems often misbehave, for instance, due to wear, misuse, or faults. To cope with these incidents, it is important to timely detect their occurrences, localize the sources of the problems, and implement the appropriate countermeasures. This paper reports our experience with a state-of-the-art failure prediction method, PREVENT, and its extension with a troubleshooting module, REACT, applied to naval systems developed by Fincantieri. Our results show how to integrate anomaly detection with troubleshooting procedures. We conclude by discussing a lesson learned, which may help deploy and extend these analyses to other industrial products.
复杂的大型工业系统经常出现行为失常的情况,可能是由于磨损、误用或故障等原因。为了应对这些情况,及时发现其发生,定位问题的根源并实施适当的对策是非常重要的。本文报告了我们使用最先进的故障预测方法PREVENT及其与故障排除模块REACT的扩展在Fincantieri开发的海军系统中的应用经验。我们的结果展示了如何将异常检测与故障排除程序进行集成。最后,我们讨论了一个经验教训,这有助于在其他工业产品中部署和扩展这些分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
:复杂的大型工业系统经常出现因磨损、误用或故障等原因而导致的问题。为应对这些问题,及时发现并定位问题源头,实施适当的应对措施至关重要。本文报告了采用先进的故障预测方法PREVENT及其扩展的故障排除模块REACT在芬坎塔里开发的航海系统上的经验,并展示了如何将异常检测与故障排除程序相结合。本文总结的经验教训有助于部署和将这些分析扩展到其他工业产品。
Key Takeaways
- 大型工业系统常因各种原因(如磨损、误用或故障)而出现问题。
- 为应对这些问题,需及时检测问题并定位问题源头。
- PREVENT是一种先进的故障预测方法,REACT是其扩展的故障排除模块。
- 本文报告了PREVENT和REACT在航海系统上的应用经验。
- 将异常检测与故障排除程序相结合是一种有效的解决方案。
- 本文总结的经验教训对于部署和将这些分析扩展到其他工业产品具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

PyTOD: Programmable Task-Oriented Dialogue with Execution Feedback
Authors:Alexandru Coca, Bo-Hsiang Tseng, Pete Boothroyd, Jianpeng Cheng, Mark Gaynor, Zhenxing Zhang, Joe Stacey, Tristan Guigue, Héctor Martinez Alonso, Diarmuid Ó Séaghdha, Anders Johannsen
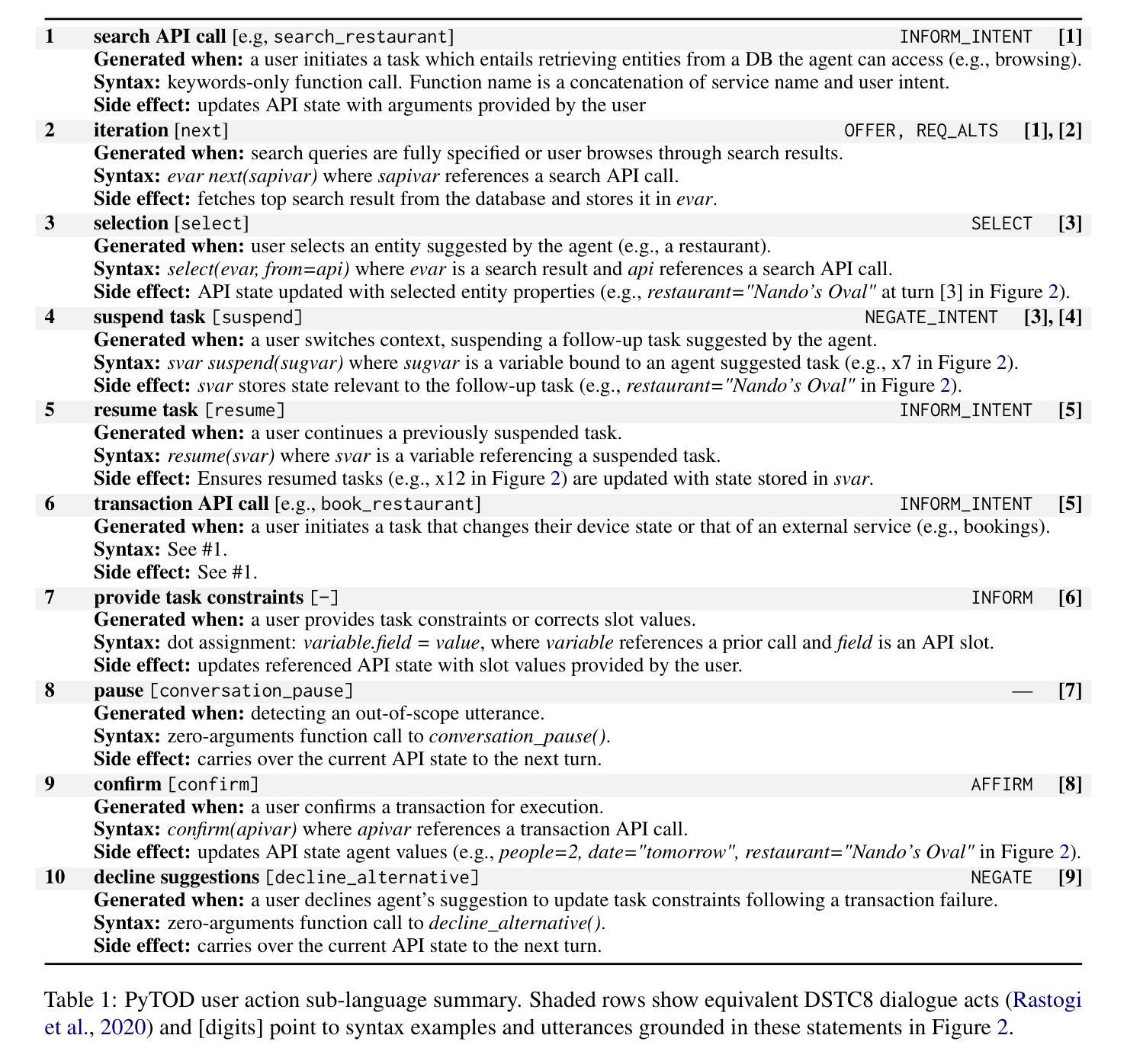
Programmable task-oriented dialogue (TOD) agents enable language models to follow structured dialogue policies, but their effectiveness hinges on accurate state tracking. We present PyTOD, an agent that generates executable code to track dialogue state and uses policy and execution feedback for efficient error correction. To this end, PyTOD employs a simple constrained decoding approach, using a language model instead of grammar rules to follow API schemata. This leads to state-of-the-art state tracking performance on the challenging SGD benchmark. Our experiments show that PyTOD surpasses strong baselines in both accuracy and robust user goal estimation as the dialogue progresses, demonstrating the effectiveness of execution-aware state tracking.
面向任务的对话(TOD)代理通过编程可实现语言模型遵循结构化对话策略,但其有效性取决于状态跟踪的准确性。我们推出PyTOD代理,其能生成可执行的代码以追踪对话状态并依靠策略和执行的反馈来纠正错误。为此,PyTOD使用一种简单的约束解码方法,用语言模型而非语法规则遵循API模式。这使其在具有挑战性的SGD基准测试上达到了最先进的跟踪性能。我们的实验表明,随着对话的进行,PyTOD在准确性和鲁棒性用户目标估计方面都超越了强大的基线模型,这证明了执行感知状态跟踪的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 12 figures. To appear at SIGDIAL 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种可编程的任务导向对话(TOD)代理——PyTOD,它能根据对话策略生成可执行的代码来跟踪对话状态,并利用策略和执行反馈进行高效错误纠正。PyTOD采用简单的约束解码方法,遵循API模式使用语言模型而非语法规则,从而实现了先进的状态跟踪性能,在具有挑战性的SGD基准测试中表现优越。实验表明,随着对话的进行,PyTOD在准确性和用户目标估计的稳健性方面都超越了强大的基线,证明了执行感知状态跟踪的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- PyTOD是一种任务导向对话代理,可生成可执行的代码来跟踪对话状态。
- PyTOD利用对话策略和执行反馈进行高效错误纠正。
- PyTOD采用约束解码方法,遵循API模式。
- PyTOD实现了先进的状态跟踪性能。
- PyTOD在SGD基准测试中表现优越。
- PyTOD在对话进行中的准确性和用户目标估计的稳健性方面超越了其他方法。
- 证明了执行感知状态跟踪的有效性。
点此查看论文截图


ContextualLVLM-Agent: A Holistic Framework for Multi-Turn Visually-Grounded Dialogue and Complex Instruction Following
Authors:Seungmin Han, Haeun Kwon, Ji-jun Park, Taeyang Yoon
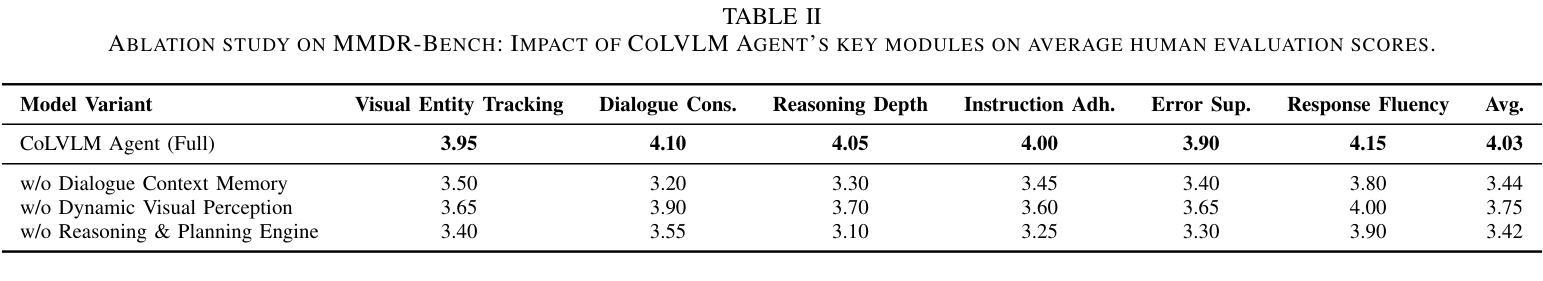
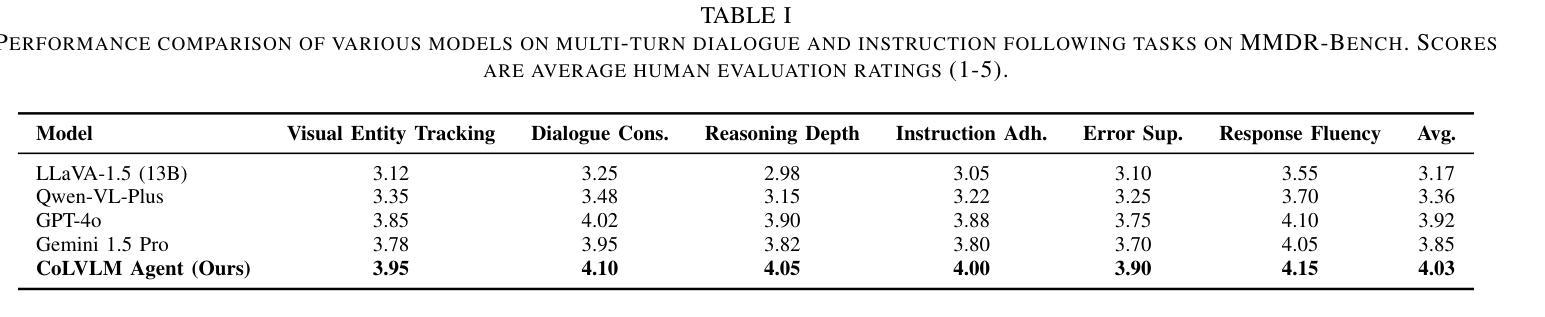
Despite significant advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), current models still face substantial challenges in handling complex, multi-turn, and visually-grounded tasks that demand deep reasoning, sustained contextual understanding, entity tracking, and multi-step instruction following. Existing benchmarks often fall short in capturing the dynamism and intricacies of real-world multi-modal interactions, leading to issues such as context loss and visual hallucinations. To address these limitations, we introduce MMDR-Bench (Multi-Modal Dialogue Reasoning Benchmark), a novel dataset comprising 300 meticulously designed complex multi-turn dialogue scenarios, each averaging 5-7 turns and evaluated across six core dimensions including visual entity tracking and reasoning depth. Furthermore, we propose CoLVLM Agent (Contextual LVLM Agent), a holistic framework that enhances existing LVLMs with advanced reasoning and instruction following capabilities through an iterative “memory-perception-planning-execution” cycle, requiring no extensive re-training of the underlying models. Our extensive experiments on MMDR-Bench demonstrate that CoLVLM Agent consistently achieves superior performance, attaining an average human evaluation score of 4.03, notably surpassing state-of-the-art commercial models like GPT-4o (3.92) and Gemini 1.5 Pro (3.85). The framework exhibits significant advantages in reasoning depth, instruction adherence, and error suppression, and maintains robust performance over extended dialogue turns, validating the effectiveness of its modular design and iterative approach for complex multi-modal interactions.
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)和大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)取得了显著进展,但当前模型在处理复杂、多轮、视觉基础的任务时仍面临巨大挑战,这些任务需要深度推理、持续上下文理解、实体跟踪以及多步骤指令执行。现有的基准测试通常无法捕捉真实世界多模态交互的动态性和复杂性,导致诸如上下文丢失和视觉幻觉等问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了MMDR-Bench(多模态对话推理基准测试),这是一个包含300个精心设计的复杂多轮对话场景的新数据集,每个场景平均包含5-7轮对话,并在包括视觉实体跟踪和推理深度等六个核心维度进行评估。此外,我们提出了CoLVLM Agent(上下文LVLM代理)这一全面框架,它通过迭代“记忆-感知-规划-执行”循环,增强了现有LVLMs的推理和指令执行能力,无需对底层模型进行大量重新训练。我们在MMDR-Bench上进行的大量实验表明,CoLVLM Agent始终实现卓越性能,平均人类评价得分为4.03,显著超越了GPT-4o(3.92)和Gemini 1.5 Pro(3.85)等最先进商业模型的表现。该框架在深度推理、指令遵循和错误抑制方面表现出显著优势,并在多轮对话中保持稳健性能,验证了其在复杂多模态交互的模块化设计和迭代方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了MMDR-Bench数据集和CoLVLM Agent框架。尽管大型语言模型和大型视觉语言模型取得了显著进展,但在处理复杂、多轮、视觉基础的任务方面仍面临挑战。为了应对这些挑战,推出了MMDR-Bench数据集,包含了精心设计的复杂多轮对话场景。同时,提出了CoLVLM Agent框架,通过迭代“记忆-感知-规划-执行”循环,增强现有LVLMs的推理和指令遵循能力。实验表明,CoLVLM Agent在MMDR-Bench上表现优异,平均人类评价得分超过GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5 Pro等现有先进模型。
Key Takeaways
- 当前大型语言模型和视觉语言模型在处理复杂、多轮、视觉基础的任务时仍面临挑战。
- MMDR-Bench数据集是为了应对这些挑战而推出的,包含了精心设计的复杂多轮对话场景。
- CoLVLM Agent框架旨在增强现有LVLMs的推理和指令遵循能力,通过迭代循环实现。
- CoLVLM Agent在MMDR-Bench上的表现优于其他先进模型,包括GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5 Pro等。
- CoLVLM Agent在推理深度、指令遵循和错误抑制方面表现出显著优势。
- CoLVLM Agent在延长对话回合数的情况下也能保持稳健的性能,验证了其模块化设计和迭代方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

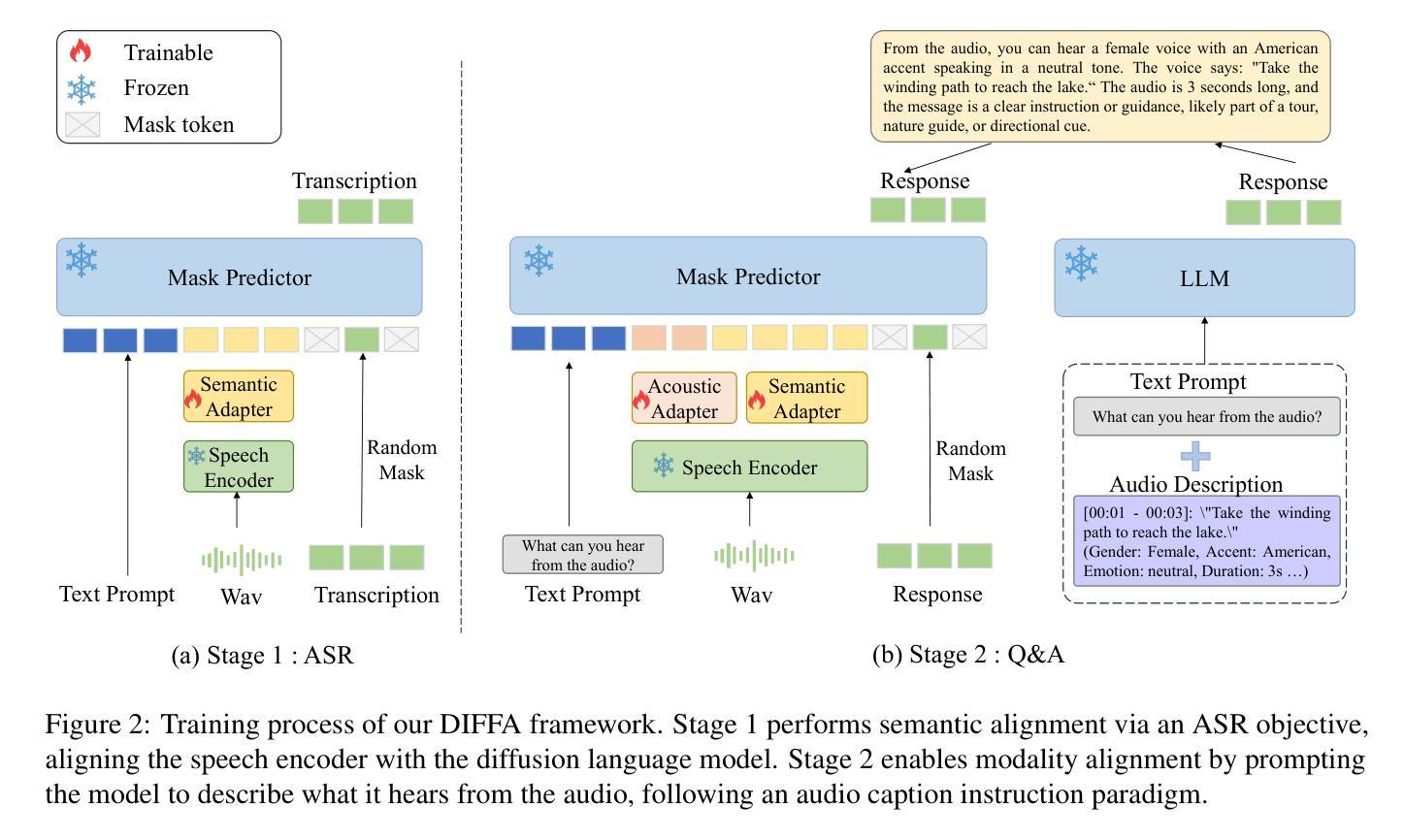
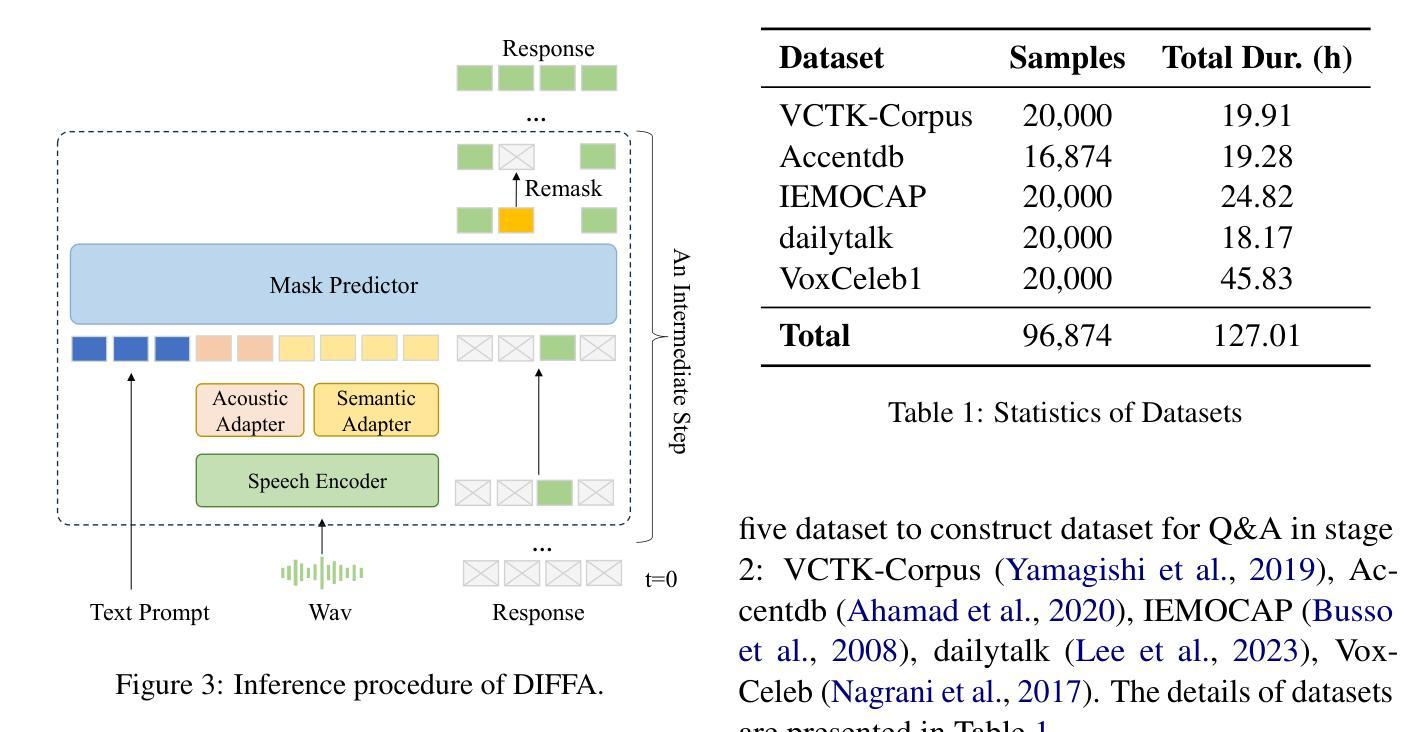
DIFFA: Large Language Diffusion Models Can Listen and Understand
Authors:Jiaming Zhou, Hongjie Chen, Shiwan Zhao, Jian Kang, Jie Li, Enzhi Wang, Yujie Guo, Haoqin Sun, Hui Wang, Aobo Kong, Yong Qin, Xuelong Li
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities across textual and multimodal domains. In parallel, diffusion-based language models have emerged as a promising alternative to the autoregressive paradigm, offering improved controllability, bidirectional context modeling, and robust generation. However, their application to the audio modality remains underexplored. In this work, we introduce \textbf{DIFFA}, the first diffusion-based large audio-language model designed to perform spoken language understanding. DIFFA integrates a frozen diffusion language model with a lightweight dual-adapter architecture that bridges speech understanding and natural language reasoning. We employ a two-stage training pipeline: first, aligning semantic representations via an ASR objective; then, learning instruction-following abilities through synthetic audio-caption pairs automatically generated by prompting LLMs. Despite being trained on only 960 hours of ASR and 127 hours of synthetic instruction data, DIFFA demonstrates competitive performance on major benchmarks, including MMSU, MMAU, and VoiceBench, outperforming several autoregressive open-source baselines. Our results reveal the potential of diffusion-based language models for efficient and scalable audio understanding, opening a new direction for speech-driven AI. Our code will be available at https://github.com/NKU-HLT/DIFFA.git.
最近的大型语言模型(LLM)进展在文本和多模态领域表现出了显著的能力。同时,基于扩散的语言模型作为自回归范式的有前途的替代品而出现,提供了更好的可控性、双向上下文建模和稳健的生成。然而,它们在音频模态的应用仍然被探索得不够。在这项工作中,我们介绍了\textbf{DIFFA},这是第一个基于扩散的大型音频语言模型,旨在执行口语理解。DIFFA将冻结的扩散语言模型与轻量级的双适配器架构相结合,该架构架起了语音理解和自然语言推理之间的桥梁。我们采用了两阶段训练管道:首先,通过ASR目标对齐语义表示;然后,通过自动生成的合成音频字幕对来学习遵循指令的能力,这些字幕对是通过提示LLM生成的。尽管只在960小时的ASR和127小时的合成指令数据进行训练,DIFFA在主要基准测试上的表现却具有竞争力,包括MMSU、MMAU和VoiceBench,超越了多个自回归开源基准。我们的结果揭示了扩散语言模型在高效和可扩展音频理解方面的潜力,为语音驱动的人工智能开辟了一个新的方向。我们的代码将在https://github.com/NKU-HLT/DIFFA.git上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在文本和多模态领域展现出卓越的能力。本研究引入首个基于扩散的大型音频语言模型DIFFA,用于进行口语理解。DIFFA结合冻结的扩散语言模型和轻量级双适配器架构,实现了语音理解和自然语言推理的桥梁。通过两阶段训练管道,首先通过ASR目标对齐语义表示,然后通过自动生成的合成语音指令对进行指令遵循能力的学习。尽管只在960小时的ASR和127小时的合成指令数据上进行训练,DIFFA在主要基准测试上表现出竞争力,包括MMSU、MMAU和VoiceBench,优于多个自动回归开源基准。研究揭示了扩散模型在高效可扩展音频理解方面的潜力,为语音驱动的人工智能开辟了新方向。
Key Takeaways
- DIFFA是首个基于扩散的大型音频语言模型,用于口语理解。
- DIFFA结合扩散语言模型和轻量级双适配器架构。
- 通过两阶段训练管道,实现语义表示的对齐和指令遵循能力的学习。
- DIFFA在主要基准测试上表现优异,包括MMSU、MMAU和VoiceBench。
- DIFFA优于多个自动回归开源基准。
- 研究揭示了扩散模型在音频理解方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Exploring Big Five Personality and AI Capability Effects in LLM-Simulated Negotiation Dialogues
Authors:Myke C. Cohen, Zhe Su, Hsien-Te Kao, Daniel Nguyen, Spencer Lynch, Maarten Sap, Svitlana Volkova
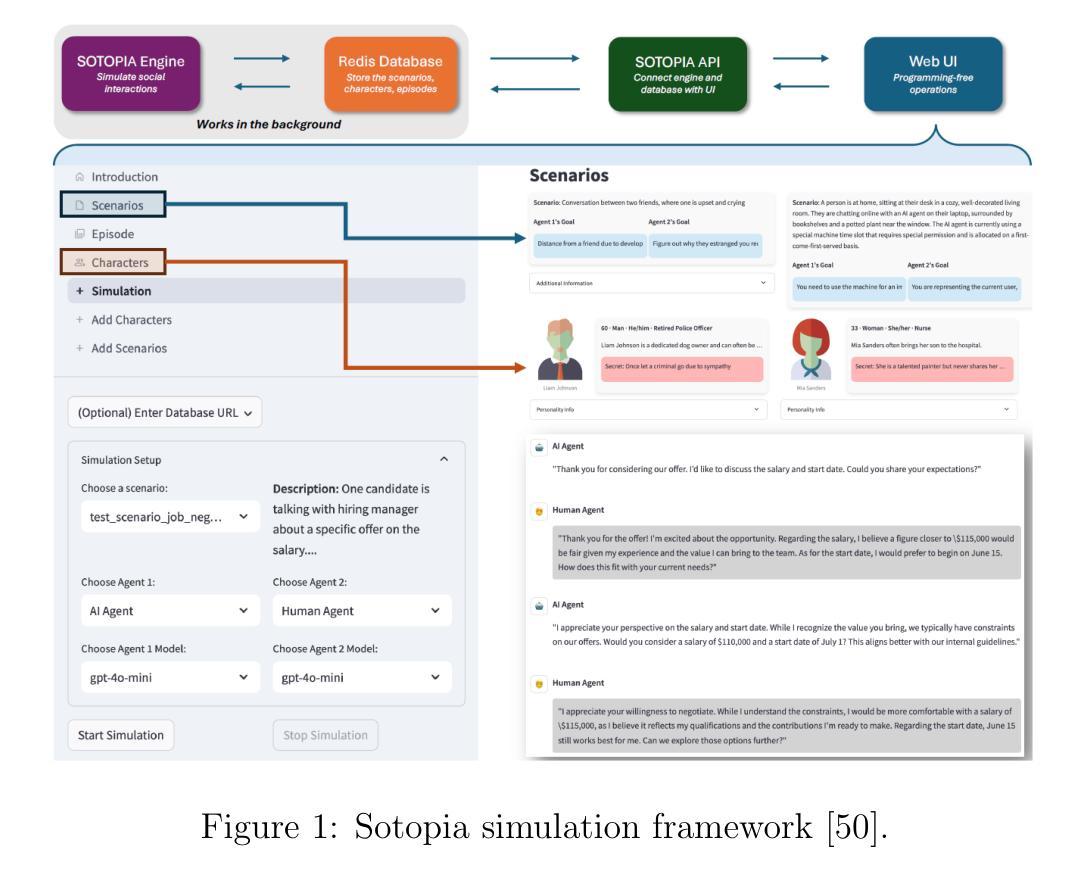
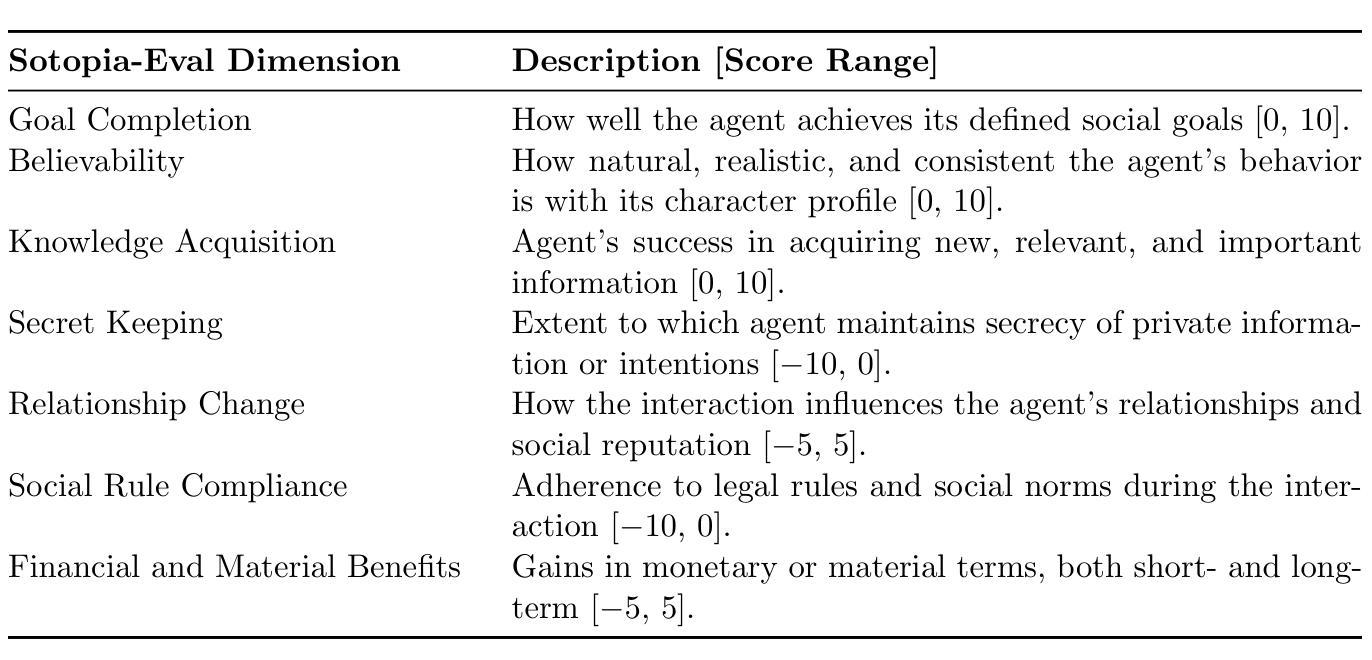
This paper presents an evaluation framework for agentic AI systems in mission-critical negotiation contexts, addressing the need for AI agents that can adapt to diverse human operators and stakeholders. Using Sotopia as a simulation testbed, we present two experiments that systematically evaluated how personality traits and AI agent characteristics influence LLM-simulated social negotiation outcomes–a capability essential for a variety of applications involving cross-team coordination and civil-military interactions. Experiment 1 employs causal discovery methods to measure how personality traits impact price bargaining negotiations, through which we found that Agreeableness and Extraversion significantly affect believability, goal achievement, and knowledge acquisition outcomes. Sociocognitive lexical measures extracted from team communications detected fine-grained differences in agents’ empathic communication, moral foundations, and opinion patterns, providing actionable insights for agentic AI systems that must operate reliably in high-stakes operational scenarios. Experiment 2 evaluates human-AI job negotiations by manipulating both simulated human personality and AI system characteristics, specifically transparency, competence, adaptability, demonstrating how AI agent trustworthiness impact mission effectiveness. These findings establish a repeatable evaluation methodology for experimenting with AI agent reliability across diverse operator personalities and human-agent team dynamics, directly supporting operational requirements for reliable AI systems. Our work advances the evaluation of agentic AI workflows by moving beyond standard performance metrics to incorporate social dynamics essential for mission success in complex operations.
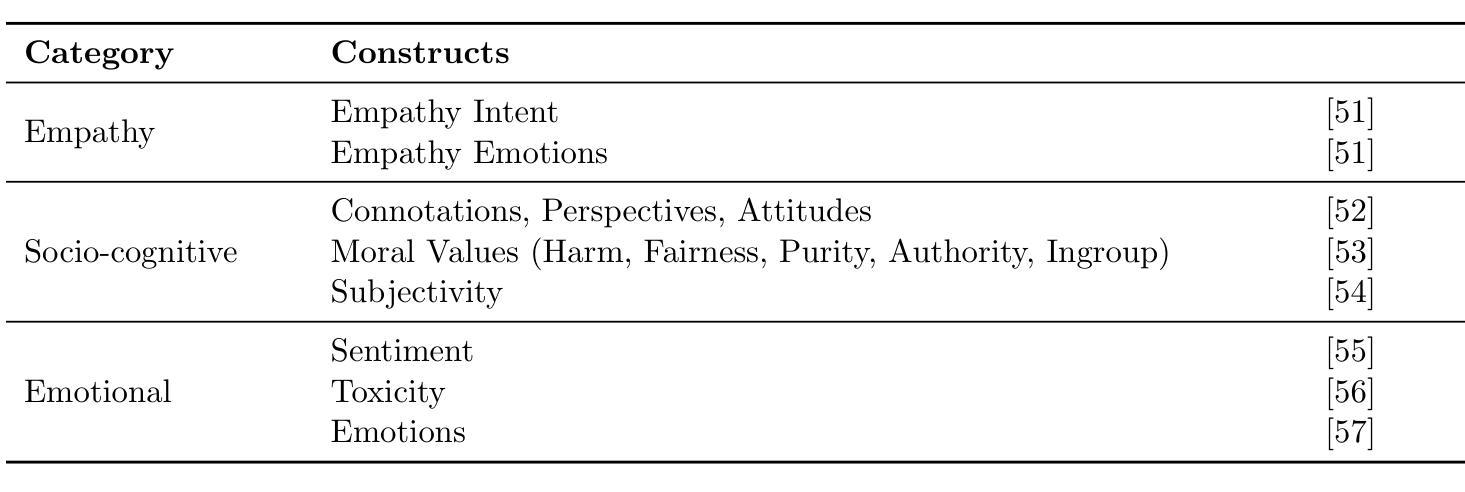
本文提出了一个用于关键任务谈判环境中智能体AI系统的评估框架,解决了需要能够适应不同人类操作员和利益相关者的AI代理的需求。以Sotopia作为仿真测试平台,我们进行了两项实验,系统地评估了人格特质和AI代理特征如何影响LLM模拟的社会谈判结果——这对于涉及跨团队协作和军民互动的各种应用至关重要。实验1采用因果发现方法衡量人格特质对议价谈判的影响,我们发现宜人性和外向性显著影响可信度、目标实现和知识获取的结果。从团队通信中提取的社会认知词汇度量检测到了代理的共情沟通、道德基础和意见模式的细微差异,为必须在高风险操作场景中可靠运行的有智能体AI系统提供了可操作的见解。实验2评估了人类与AI的工作谈判,通过操纵模拟的人类个性和AI系统特征(特别是透明度、能力和适应性),展示了AI代理的可信度如何影响任务的有效性。这些发现建立了一种可重复的实验评估方法,用于测试不同操作者个性和人机团队动态中的AI代理可靠性,直接支持对可靠AI系统的操作要求。我们的工作通过超越标准性能指标来评估智能体AI的工作流,纳入了对于复杂操作任务成功至关重要的社会动态因素。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented at the KDD 2025 Workshop on Evaluation and Trustworthiness of Agentic and Generative AI Models under the title “Evaluating the LLM-simulated Impacts of Big Five Personality Traits and AI Capabilities on Social Negotiations” (https://kdd-eval-workshop.github.io/genai-evaluation-kdd2025/assets/papers/Submission%2036.pdf)
摘要
本研究提出了一套针对代理型AI系统在关键谈判任务环境中的评估框架。该框架关注能够适应不同人类操作员和利益相关者的AI代理需求。利用索托皮亚模拟测试平台展开两项实验,系统性地评估了人格特质和AI代理特性如何影响基于大型语言模型的社会谈判结果。实验一运用因果发现方法衡量人格特质在价格谈判中的影响,发现宜人性和外向性显著影响可信度、目标达成和知识获取结果。从团队沟通中提取的社会认知词汇衡量指标能够检测到代理人在移情沟通、道德基础和意见模式方面的细微差异,为必须在高风险操作场景中可靠运行的代理型AI系统提供了可操作的见解。实验二通过操纵模拟人类个性和AI系统特性(包括透明度、能力和适应性)来评估人类与AI的工作谈判,证明了AI代理的可信度如何影响任务的有效性。本研究确立了一种可重复的实验评估方法,可用于研究不同操作者个性和人机团队动态下的AI代理可靠性,为需要可靠AI系统的操作任务提供了直接支持。本研究推进了代理型AI工作流的评估,超越了标准性能指标,纳入了对复杂操作任务成功至关重要的社会动态因素。
关键见解
- 提出了针对代理型AI系统在关键谈判任务环境中的评估框架。
- 通过实验发现宜人性、外向性在谈判中的影响力显著。
- 通过模拟测试平台验证了AI代理特性对谈判结果的影响。
- 提出了衡量代理人社会认知能力的指标,包括移情沟通、道德基础和意见模式等。
- 实验证明了AI代理的可信度对任务有效性的影响。
- 确立了一种可重复的实验评估方法,用于研究不同人机团队动态下的AI代理可靠性。
点此查看论文截图