⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
End-to-End Agentic RAG System Training for Traceable Diagnostic Reasoning
Authors:Qiaoyu Zheng, Yuze Sun, Chaoyi Wu, Weike Zhao, Pengcheng Qiu, Yongguo Yu, Kun Sun, Yanfeng Wang, Ya Zhang, Weidi Xie
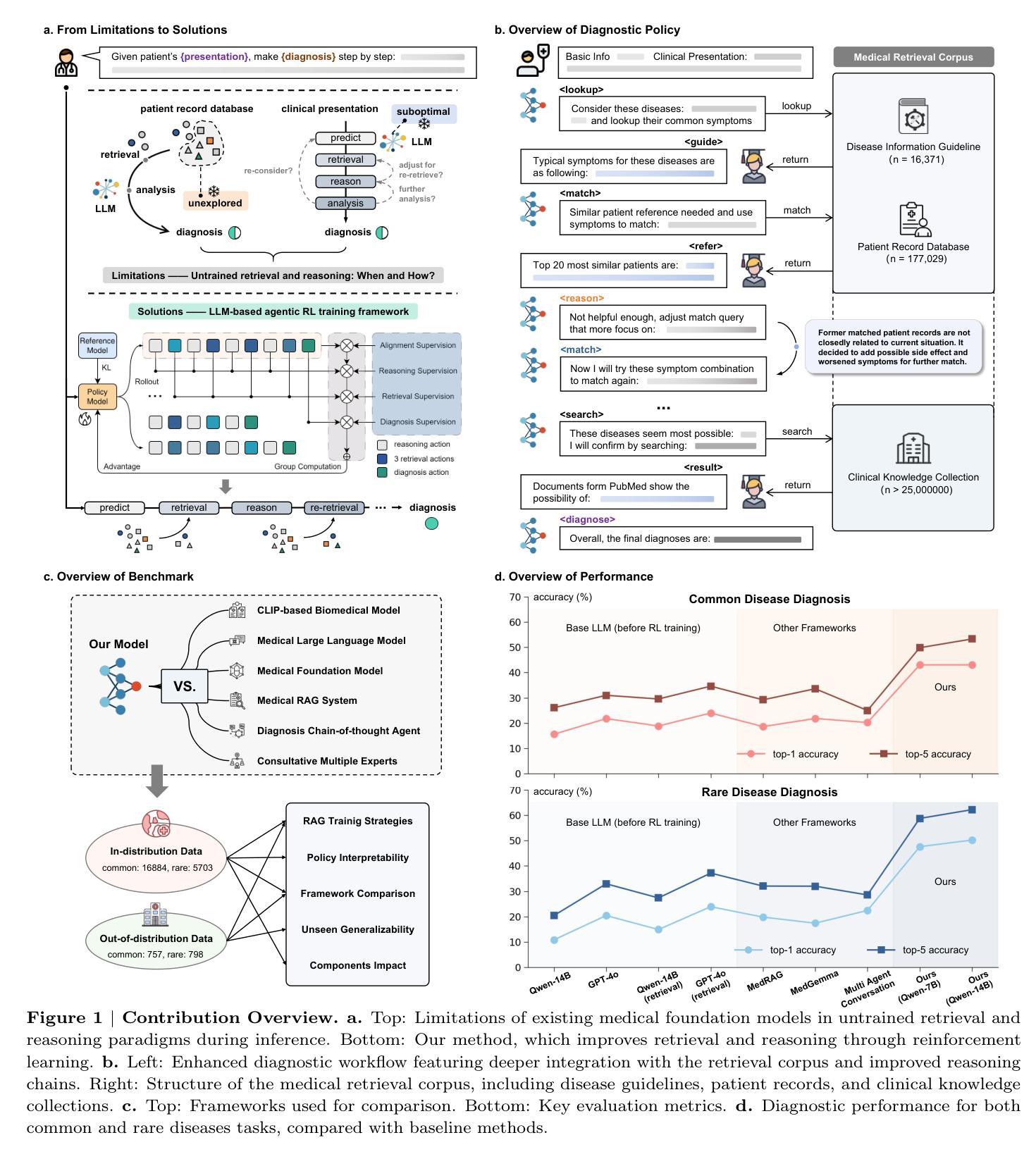
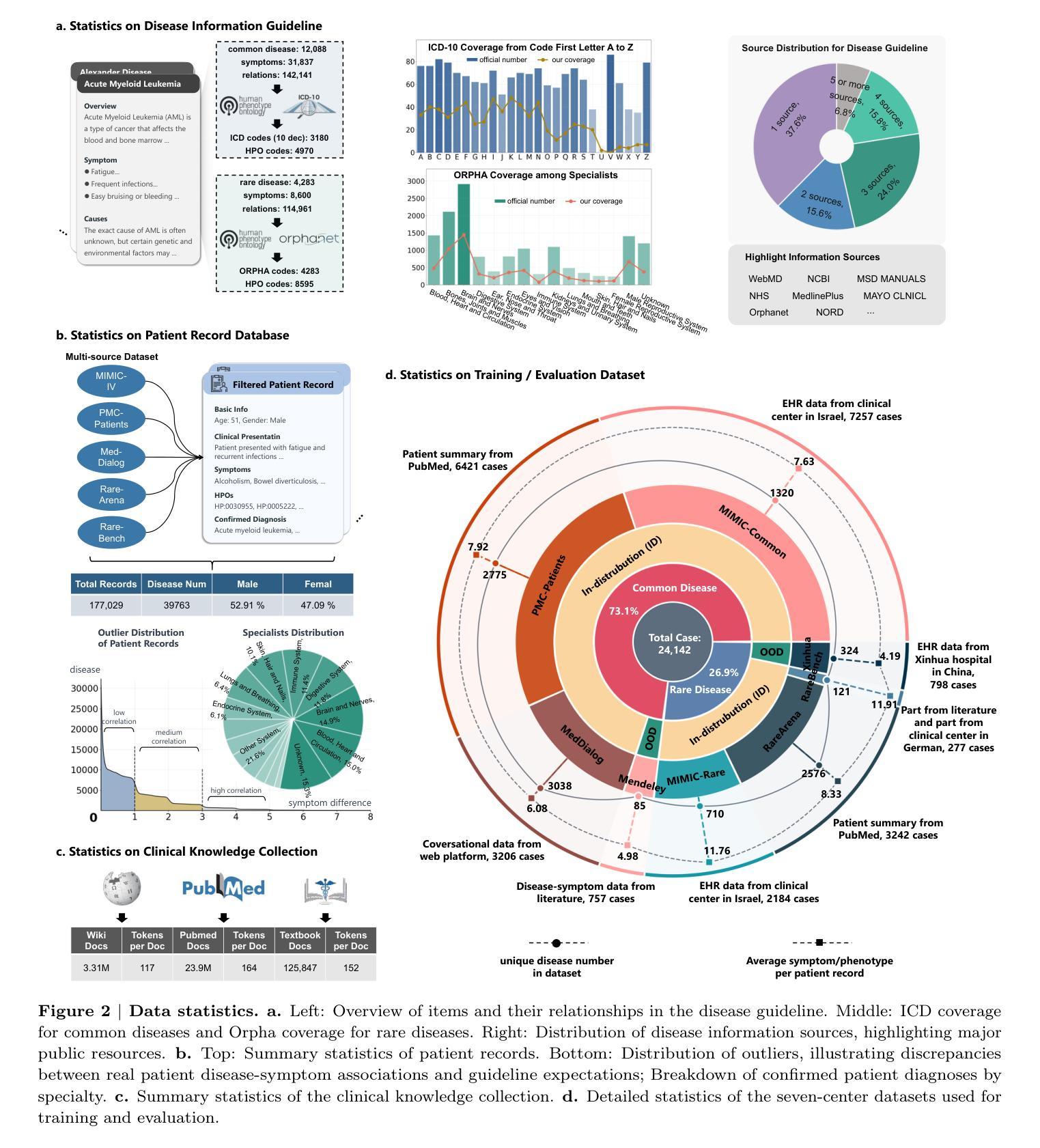
Accurate diagnosis with medical large language models is hindered by knowledge gaps and hallucinations. Retrieval and tool-augmented methods help, but their impact is limited by weak use of external knowledge and poor feedback-reasoning traceability. To address these challenges, We introduce Deep-DxSearch, an agentic RAG system trained end-to-end with reinforcement learning (RL) that enables steer tracebale retrieval-augmented reasoning for medical diagnosis. In Deep-DxSearch, we first construct a large-scale medical retrieval corpus comprising patient records and reliable medical knowledge sources to support retrieval-aware reasoning across diagnostic scenarios. More crutially, we frame the LLM as the core agent and the retrieval corpus as its environment, using tailored rewards on format, retrieval, reasoning structure, and diagnostic accuracy, thereby evolving the agentic RAG policy from large-scale data through RL. Experiments demonstrate that our end-to-end agentic RL training framework consistently outperforms prompt-engineering and training-free RAG approaches across multiple data centers. After training, Deep-DxSearch achieves substantial gains in diagnostic accuracy, surpassing strong diagnostic baselines such as GPT-4o, DeepSeek-R1, and other medical-specific frameworks for both common and rare disease diagnosis under in-distribution and out-of-distribution settings. Moreover, ablation studies on reward design and retrieval corpus components confirm their critical roles, underscoring the uniqueness and effectiveness of our approach compared with traditional implementations. Finally, case studies and interpretability analyses highlight improvements in Deep-DxSearch’s diagnostic policy, providing deeper insight into its performance gains and supporting clinicians in delivering more reliable and precise preliminary diagnoses. See https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/Deep-DxSearch.
使用医疗大型语言模型的准确诊断受到知识差距和幻觉的阻碍。检索和工具增强方法有所帮助,但其影响受限于外部知识利用不足和反馈推理可追溯性较差。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Deep-DxSearch,这是一个以强化学习(RL)进行端到端训练的主动推理图系统(RAG),可实现用于医学诊断的可追溯检索增强推理。在Deep-DxSearch中,我们首先构建了一个大规模医学检索语料库,包含患者记录和可靠医学知识源,以支持跨诊断场景的检索感知推理。更为关键的是,我们将大型语言模型作为核心主体,将检索语料库作为其环境,针对格式、检索、推理结构和诊断准确性设计定制奖励,从而通过强化学习推动主动推理图策略从大规模数据中进化。实验表明,我们的端到端主动强化学习训练框架在多数据中心均表现优异,超过基于提示和免训练RAG方法。经过训练后,Deep-DxSearch在诊断准确性方面取得了实质性提升,在分布内和分布外设置下均超越了强大的诊断基线,如GPT-4o、DeepSeek-R1和其他医学专用框架,无论是常见疾病还是罕见疾病的诊断均如此。此外,对奖励设计和检索语料库组件的消融研究证实了它们的关键作用,强调了我们的方法与传统实施相比的独特性和有效性。最后,案例研究和可解释性分析突出了Deep-DxSearch诊断策略的改进,为深入了解其性能提升提供了依据,并支持临床医生提供更可靠和精确的早期诊断。更多信息请参见https://github.com/MAGIC-AI4Med/DeepDxSearch。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables
Summary
在医疗大语言模型进行准确诊断时,存在知识缺口和虚构问题。虽然检索和工具增强方法有所帮助,但它们对外部知识利用不足,反馈推理可追溯性不佳。为解决这些问题,我们推出Deep-DxSearch,一个经过强化学习训练的自主RAG系统,可实现可追踪检索增强推理,用于医疗诊断。Deep-DxSearch构建大规模医学检索语料库,涵盖患者记录和可靠医学知识源,以支持跨诊断场景的检索感知推理。关键的是,我们以LLM为核心代理,检索语料库为其环境,使用格式、检索、推理结构和诊断准确性的定制奖励,通过大规模数据强化代理策略。实验证明,我们的终端到终端自主RL训练框架在多个数据中心均优于提示工程和免训练RAG方法。Deep-DxSearch在训练后诊断准确性大大提高,超越强大的诊断基线,如GPT-4o、DeepSeek-R1和其他医疗特定框架,适用于常见和罕见疾病的诊断,在内部和外部分布设置下均表现优异。奖励设计和检索语料库组件的消融研究证实了它们的重要性,突显了与传统方法相比的独特性和有效性。最终,案例研究和解释性分析突显了Deep-DxSearch诊断策略的改进,为性能提升提供了深入了解,并支持医生提供更可靠和精确的早期诊断。详情见[网站链接]。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗大语言模型在诊断中面临知识缺口和虚构挑战。
- Deep-DxSearch通过构建大规模医学检索语料库来支持跨诊断场景的检索感知推理。
- LLM作为核心代理,与检索语料库互动,通过强化学习进行训练。
- Deep-DxSearch在多种设置中超越了其他诊断和医学特定框架。
- 消融研究证实了奖励设计和检索语料库组件的重要性。
- Deep-DxSearch改进了诊断策略,提高了诊断准确性。
点此查看论文截图

EcomMMMU: Strategic Utilization of Visuals for Robust Multimodal E-Commerce Models
Authors:Xinyi Ling, Hanwen Du, Zhihui Zhu, Xia Ning
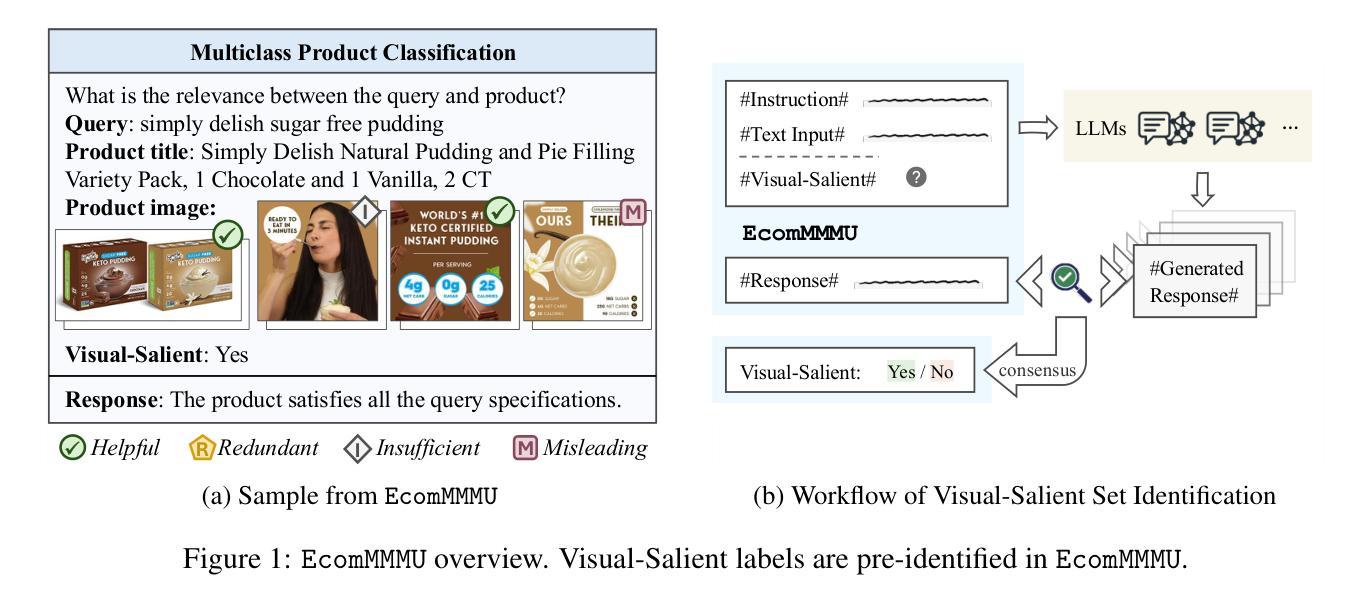
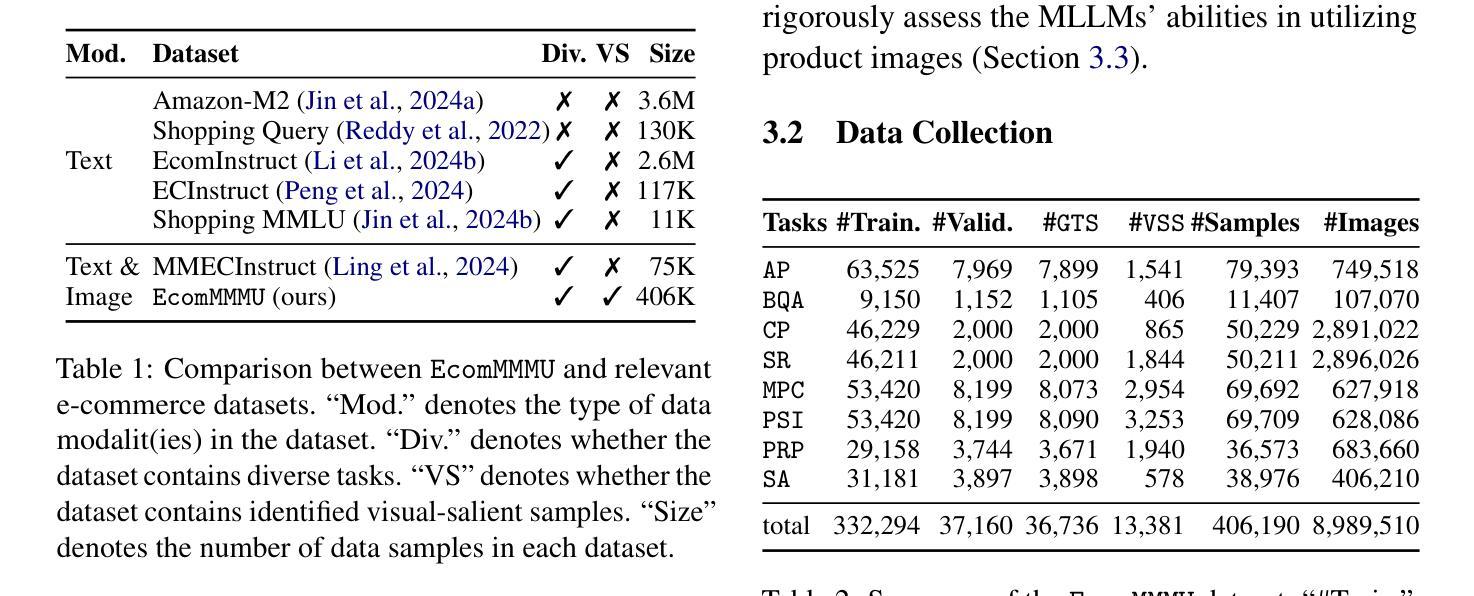
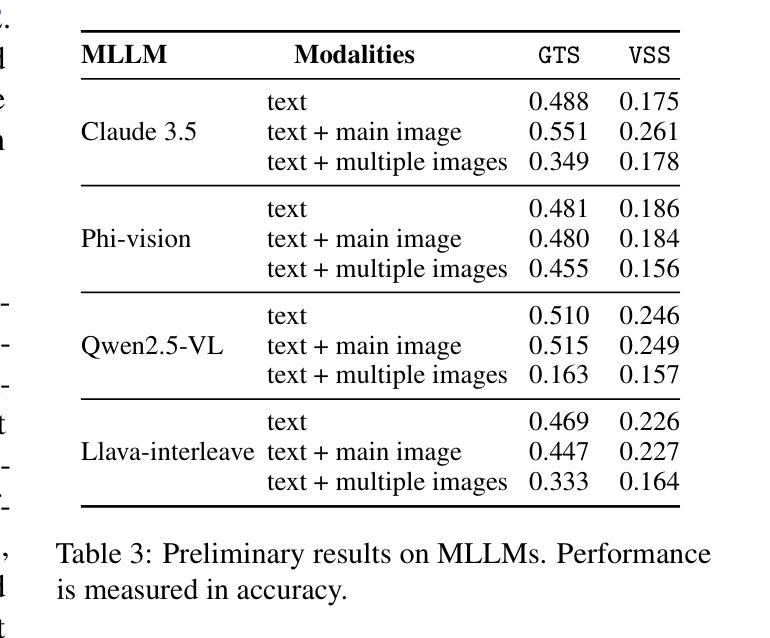
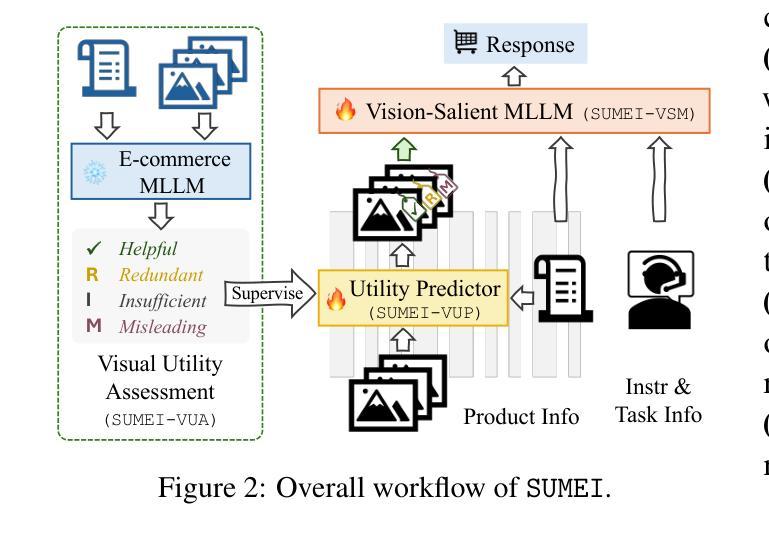
E-commerce platforms are rich in multimodal data, featuring a variety of images that depict product details. However, this raises an important question: do these images always enhance product understanding, or can they sometimes introduce redundancy or degrade performance? Existing datasets are limited in both scale and design, making it difficult to systematically examine this question. To this end, we introduce EcomMMMU, an e-commerce multimodal multitask understanding dataset with 406,190 samples and 8,989,510 images. EcomMMMU is comprised of multi-image visual-language data designed with 8 essential tasks and a specialized VSS subset to benchmark the capability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to effectively utilize visual content. Analysis on EcomMMMU reveals that product images do not consistently improve performance and can, in some cases, degrade it. This indicates that MLLMs may struggle to effectively leverage rich visual content for e-commerce tasks. Building on these insights, we propose SUMEI, a data-driven method that strategically utilizes multiple images via predicting visual utilities before using them for downstream tasks. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of SUMEI. The data and code are available through https://anonymous.4open.science/r/submission25.
电子商务平台拥有丰富的多模态数据,其中包含了展示产品细节的各种图像。然而,这引发了一个重要问题:这些图像是否总是能增强对产品的理解,还是有时会引入冗余信息或降低性能?现有数据集在规模和设计上都存在局限性,很难系统地研究这个问题。为此,我们推出了EcomMMMU电子商务多模态多任务理解数据集,包含406,190个样本和8,989,510张图像。EcomMMMU由多图像视觉语言数据组成,设计了8个基本任务,并有一个专门的VSS子集,以评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)有效利用视觉内容的能力。对EcomMMMU的分析表明,产品图像并不总能提高性能,有时甚至会降低性能。这表明MLLMs在有效利用丰富的视觉内容方面可能面临困难。基于这些见解,我们提出了SUMEI方法,该方法通过预测视觉效用,有选择地利用多个图像,然后再将其用于下游任务。大量的实验证明了SUMEI的有效性和稳健性。相关数据和代码可通过匿名网址链接获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
电商平台上丰富的多模态数据含有大量商品图片展示信息。但问题在于,这些图片是否总是能增强对商品的理解,或者是否会引入冗余信息、降低性能?现有数据集在规模和设计上的局限性,使得难以系统地研究这一问题。因此,我们推出了EcomMMMU电商多模态多任务理解数据集,包含40万6千多条样本和超过八百万张图片。它涵盖了多图像视觉语言数据设计的八个基本任务和一个专门的VSS子集,旨在评估多模态大型语言模型有效利用视觉内容的能力。对EcomMMMU的分析显示,商品图片并不总是能提高性能,有时甚至会降低性能。这表明大型语言模型可能难以有效地利用丰富的视觉内容完成电商任务。基于此洞察,我们提出SUMEI方法,它通过预测视觉效用,有针对性地使用多张图片来完成下游任务。经过综合实验验证,SUMEI具有有效性和稳健性。相关数据和代码可通过链接https://anonymous.4open.science/r/submission25获取。
关键见解
- 电商平台上商品图片丰富,但图片是否有助于增强对商品的理解尚存疑问。
- 当前数据集在规模和设计上的局限性,使得难以系统地研究这一问题。
- 引入EcomMMMU数据集,包含多模态多任务设计,旨在评估大型语言模型利用视觉内容的能力。
- 分析显示商品图片并不总是能提高性能,有时可能降低性能。
- 大型语言模型在有效利用丰富视觉内容方面可能存在挑战。
- 提出SUMEI方法,通过预测视觉效用有针对性地使用多张图片完成下游任务。
点此查看论文截图

StreamMem: Query-Agnostic KV Cache Memory for Streaming Video Understanding
Authors:Yanlai Yang, Zhuokai Zhao, Satya Narayan Shukla, Aashu Singh, Shlok Kumar Mishra, Lizhu Zhang, Mengye Ren
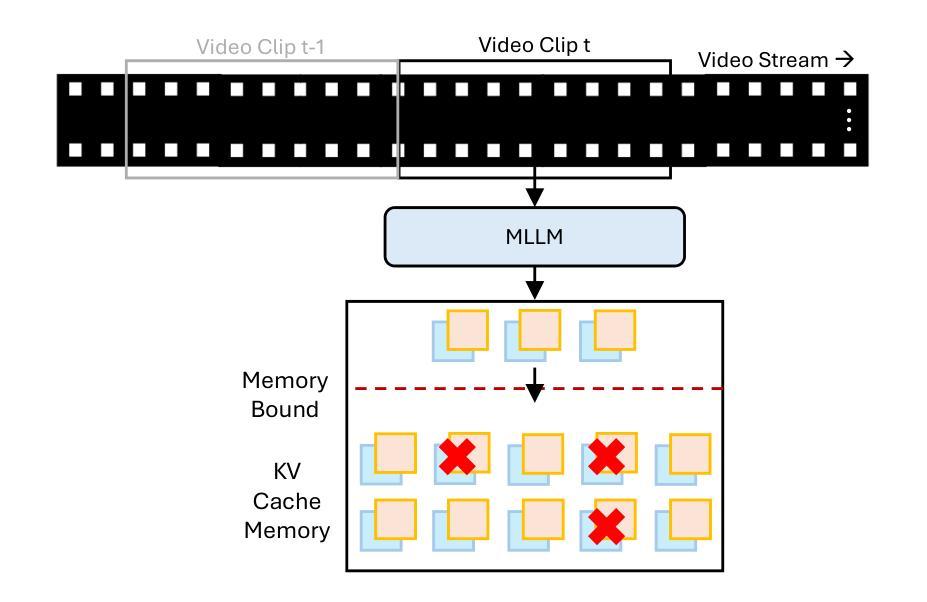
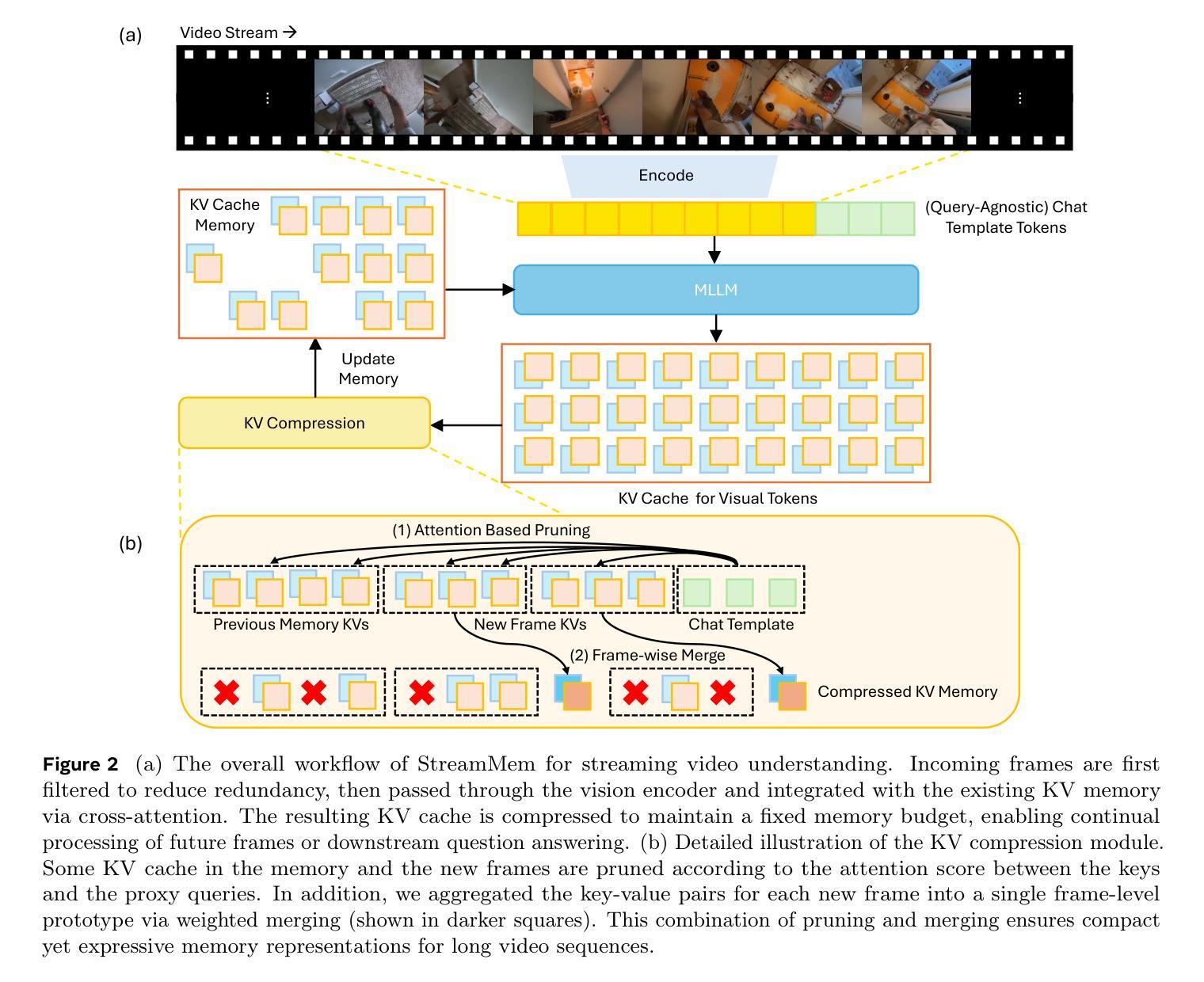
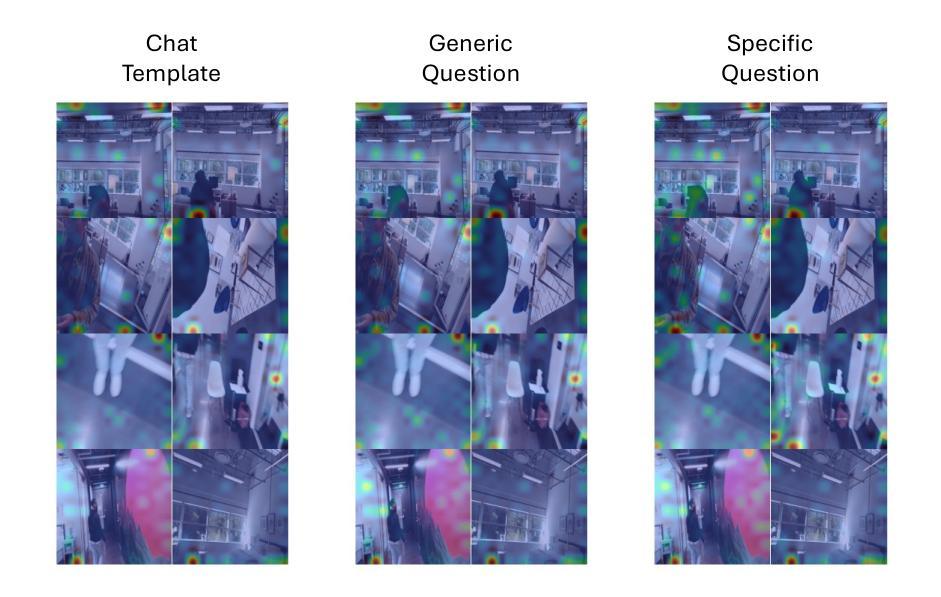
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have made significant progress in visual-language reasoning, but their ability to efficiently handle long videos remains limited. Despite recent advances in long-context MLLMs, storing and attending to the key-value (KV) cache for long visual contexts incurs substantial memory and computational overhead. Existing visual compression methods require either encoding the entire visual context before compression or having access to the questions in advance, which is impractical for long video understanding and multi-turn conversational settings. In this work, we propose StreamMem, a query-agnostic KV cache memory mechanism for streaming video understanding. Specifically, StreamMem encodes new video frames in a streaming manner, compressing the KV cache using attention scores between visual tokens and generic query tokens, while maintaining a fixed-size KV memory to enable efficient question answering (QA) in memory-constrained, long-video scenarios. Evaluation on three long video understanding and two streaming video question answering benchmarks shows that StreamMem achieves state-of-the-art performance in query-agnostic KV cache compression and is competitive with query-aware compression approaches.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言推理方面取得了显著进展,但其高效处理长视频的能力仍然有限。尽管近期在长语境MLLMs方面有所进展,但为长视觉语境存储和关注键值(KV)缓存会产生大量内存和计算开销。现有视觉压缩方法要么需要在压缩之前对整个视觉环境进行编码,要么需要提前了解问题,这对于长视频理解和多回合对话环境来说并不实用。在这项工作中,我们提出了StreamMem,这是一种用于流式视频理解的查询无关键值缓存内存机制。具体来说,StreamMem以流式方式编码新视频帧,使用视觉令牌和通用查询令牌之间的注意力分数压缩键值缓存,同时保持固定大小的键值内存,以在内存受限的长视频场景中实现高效问答(QA)。在三个长视频理解和两个流式视频问答基准测试上的评估表明,StreamMem在查询无关的键值缓存压缩方面达到了最新技术水平,并且在查询感知压缩方法中表现具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 3 figures
Summary
MLLM在处理长视频方面存在效率限制,特别是在存储和关注长视觉上下文的关键值缓存时会产生大量的内存和计算开销。现有视觉压缩方法需要提前对整个视觉上下文进行编码或提前获取问题,这对于长视频理解和多轮对话场景来说不切实际。本研究提出了一种名为StreamMem的查询无关的关键值缓存记忆机制,以流式处理视频理解。它通过关注视觉令牌和通用查询令牌之间的注意力分数来压缩关键值缓存,同时保持固定大小的关键值内存,以在内存受限的长视频场景中实现高效的问题回答。在三个长视频理解和两个流式视频问答基准测试上的评估表明,StreamMem在查询无关的关键值缓存压缩方面达到了最新技术水平,并且在查询感知压缩方法中具有很强的竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- MLLM在处理长视频时存在效率限制,特别是在处理视觉上下文的关键值缓存时面临内存和计算开销的挑战。
- 现有视觉压缩方法在处理长视频理解和多轮对话场景时存在困难,需要提前对视觉上下文进行编码或提前获取问题。
- StreamMem是一种查询无关的关键值缓存记忆机制,以流式处理视频理解,能够压缩关键值缓存并维持固定大小的关键值内存。
- StreamMem通过关注视觉令牌和通用查询令牌之间的注意力分数来实现高效的视频理解。
- StreamMem在多个基准测试上表现优异,实现了最新的技术性能,在查询感知压缩方法中具有很强的竞争力。
- StreamMem适用于内存受限的长视频场景中的高效问题回答。
点此查看论文截图

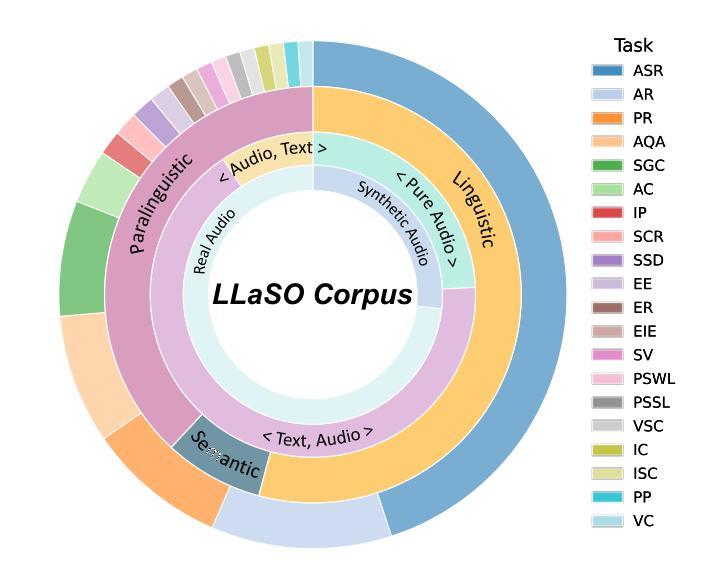
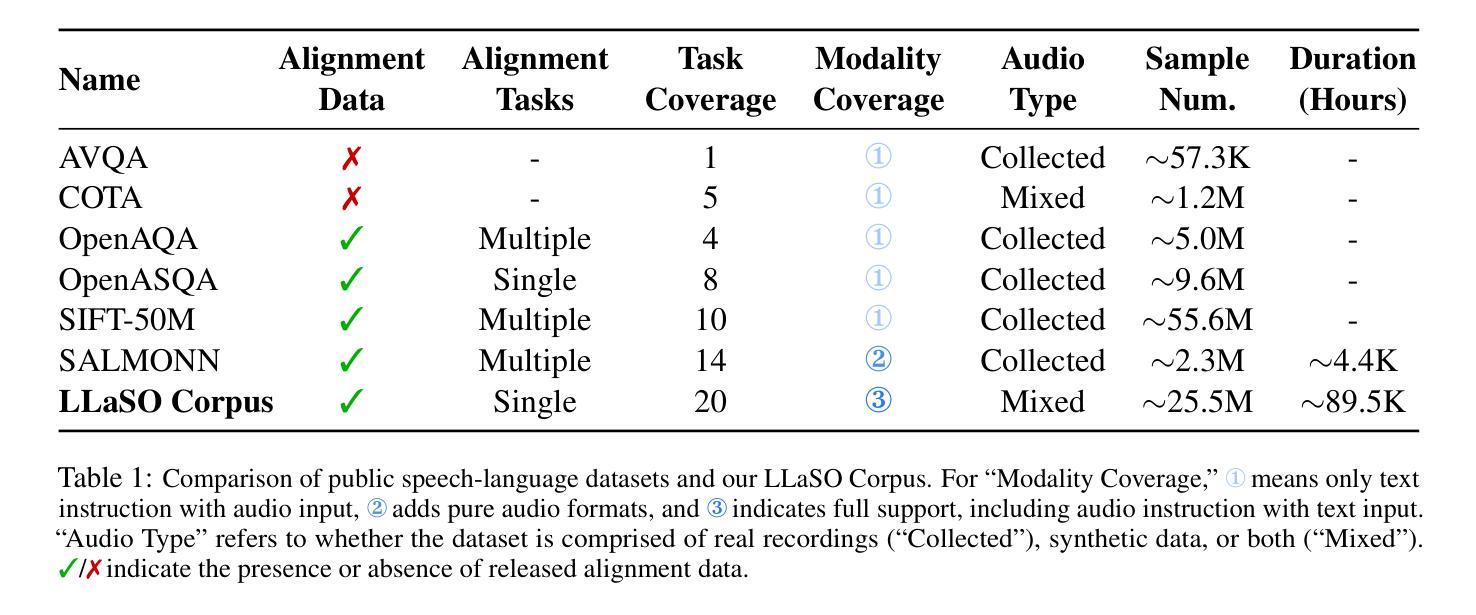
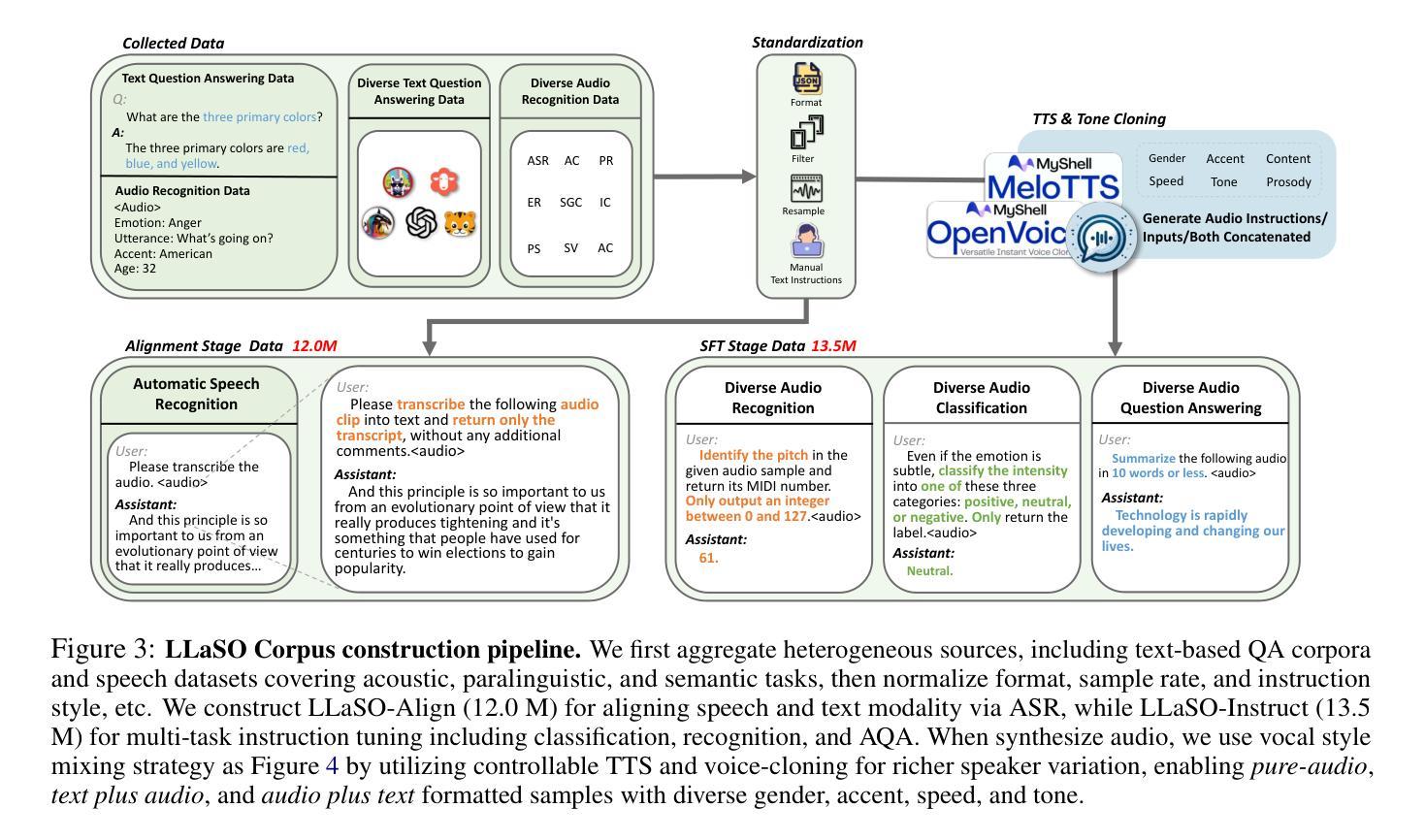
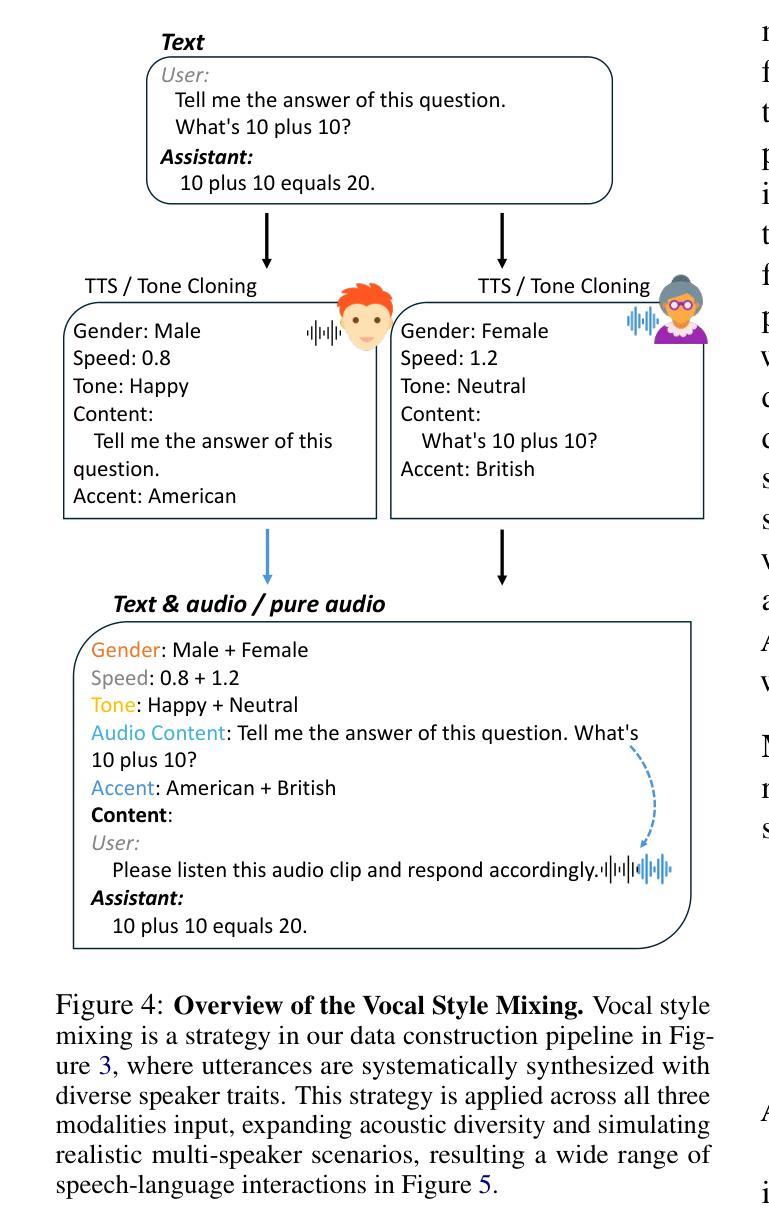
LLaSO: A Foundational Framework for Reproducible Research in Large Language and Speech Model
Authors:Yirong Sun, Yizhong Geng, Peidong Wei, Yanjun Chen, Jinghan Yang, Rongfei Chen, Wei Zhang, Xiaoyu Shen
The development of Large Speech-Language Models (LSLMs) has been slowed by fragmented architectures and a lack of transparency, hindering the systematic comparison and reproducibility of research. Unlike in the vision-language domain, the LSLM field suffers from the common practice of releasing model weights without their corresponding training data and configurations. To address these critical gaps, we introduce LLaSO, the first fully open, end-to-end framework for large-scale speech-language modeling. LLaSO provides the community with three essential resources: (1) LLaSO-Align, a 12M-instance speech-text alignment corpus; (2) LLaSO-Instruct, a 13.5M-instance multi-task instruction-tuning dataset; and (3) LLaSO-Eval, a reproducible benchmark for standardized evaluation. To validate our framework, we build and release LLaSO-Base, a 3.8B-parameter reference model trained exclusively on our public data. It achieves a normalized score of 0.72, establishing a strong, reproducible baseline that surpasses comparable models. Our analysis reveals that while broader training coverage enhances performance, significant generalization gaps persist on unseen tasks, particularly in pure audio scenarios. By releasing the complete stack of data, benchmarks, and models, LLaSO establishes a foundational open standard to unify research efforts and accelerate community-driven progress in LSLMs. We release the code, dataset, pretrained models, and results in https://github.com/EIT-NLP/LLaSO.
大规模语言模型(LSLM)的发展受到了架构分散和透明度不足的阻碍,这妨碍了研究的系统比较和可重复性。与视觉语言领域不同,LSLM领域普遍存在发布模型权重而没有相应训练数据和配置的做法。为了解决这些关键差距,我们推出了LLaSO,这是第一个完全开放的大规模语言建模端到端框架。LLaSO为社区提供了三种重要资源:(1)LLaSO-Align,一个包含1200万实例的语音文本对齐语料库;(2)LLaSO-Instruct,一个包含1350万实例的多任务指令微调数据集;(3)LLaSO-Eval,一个可复现的标准化评估基准。为了验证我们的框架,我们构建并发布了LLaSO-Base,这是一个仅在我们公开数据上训练的38亿参数参考模型,其归一化得分为0.72,建立了强大且可复现的基线,超越了同类模型。我们的分析表明,虽然更广泛的训练覆盖有助于提高性能,但在未见任务上仍然存在重大的泛化差距,特别是在纯音频场景中。通过发布数据、基准测试和模型的完整堆栈,LLaSO建立了一个统一的开放标准,以整合研究努力并加速LSLM的社区驱动进展。我们在https://github.com/EIT-NLP/LLaSO发布代码、数据集、预训练模型和结果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大语音语言模型(LSLM)的发展受到了架构碎片化及缺乏透明度的影响,阻碍了研究的系统比较和可重复性。针对这一问题,我们推出LLaSO,首个完全开放的大规模语音语言建模端到端框架。LLaSO为社区提供三大资源:LLaSO-Align语音文本对齐语料库、LLaSO-Instruct多任务指令调整数据集及LLaSO-Eval可重复基准测试平台,用于标准化评估。基于该框架,我们构建了仅使用公开数据训练的LLaSO-Base基准模型,参数规模达3.8B,归一化得分为0.72,在可比较模型中表现优异且可复制性强。研究分析表明,尽管更广泛的训练覆盖有助于提升性能,但在未见任务上仍存在重大泛化差距,特别是在纯音频场景中。我们发布整套数据、基准测试及模型,LLaSO确立了一个统一研究努力、加速LSLM社区驱动发展的开放标准。相关代码、数据集、预训练模型及结果已发布在https://github.com/EIT-NLP/LLaSO。
关键见解
- LSLM领域发展受到架构碎片化和透明度缺乏的阻碍,影响研究的比较和可重复性。
- 推出LLaSO框架,为LSLM研究提供全面开放的资源,包括语料库、数据集和评估平台。
- 基于LLaSO框架建立LLaSO-Base模型,在标准化测试中表现优异。
- 研究发现更广泛的训练覆盖有助于提升性能,但未见任务上的泛化能力仍有差距。
- LLaSO的建立为LSLM研究提供了统一的开放标准,有助于整合研究力量,加速发展。
- LLaSO框架及相关资源已完全公开,方便研究人员使用。
点此查看论文截图


Improving LLMs for Machine Translation Using Synthetic Preference Data
Authors:Dario Vajda, Domen Vreš, Marko Robnik-Šikonja
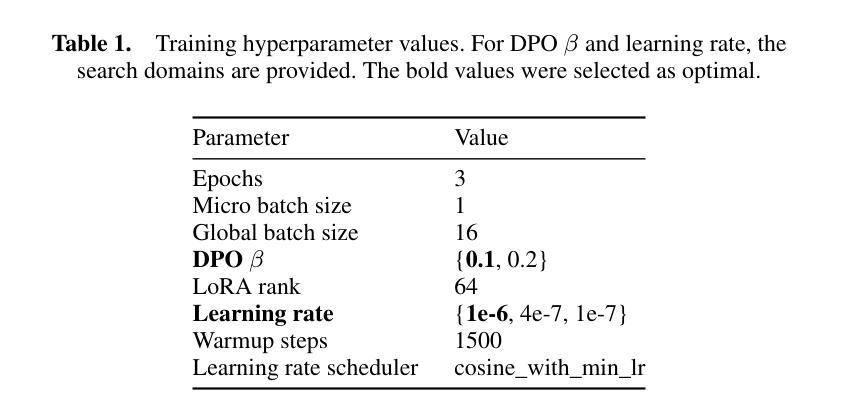
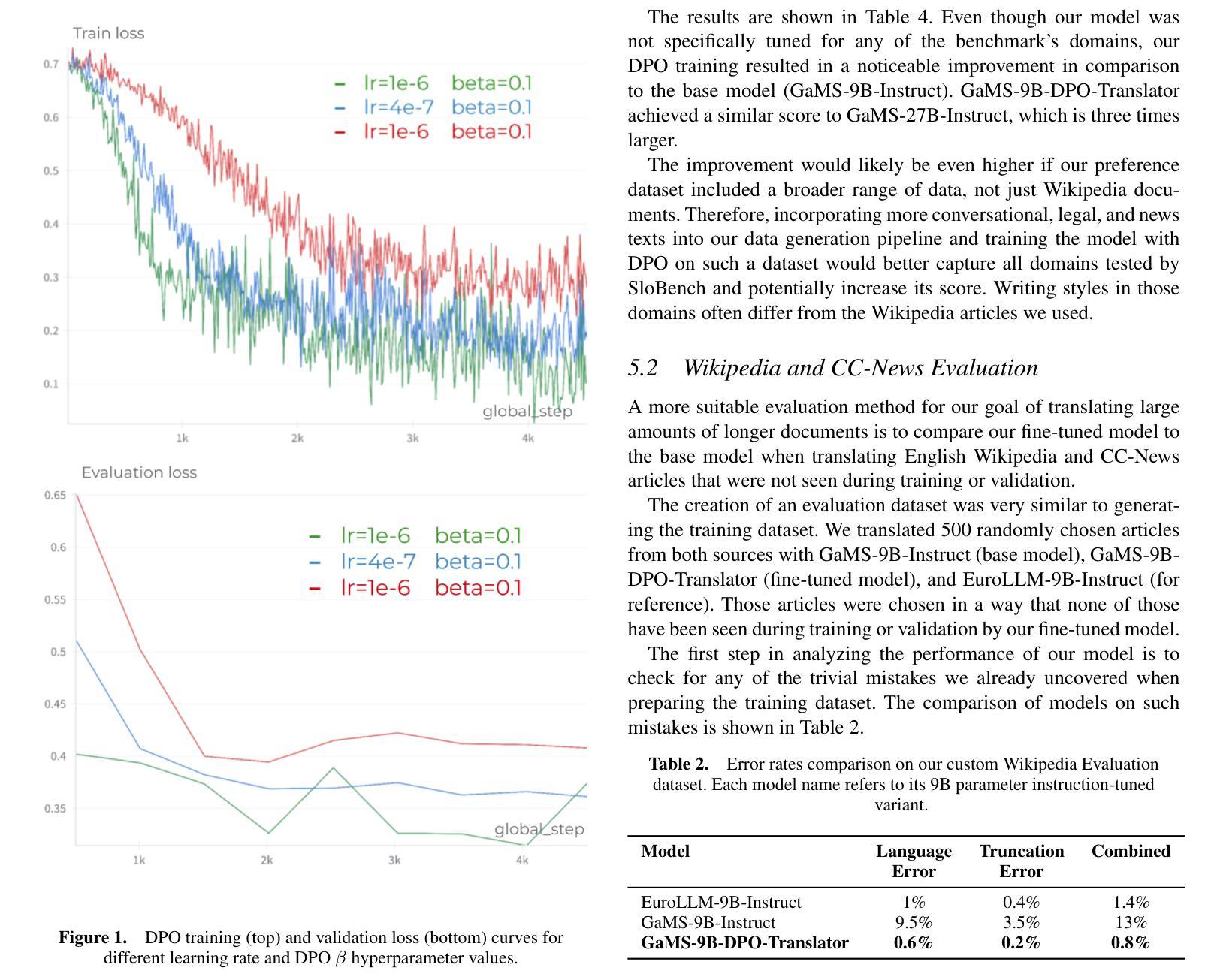
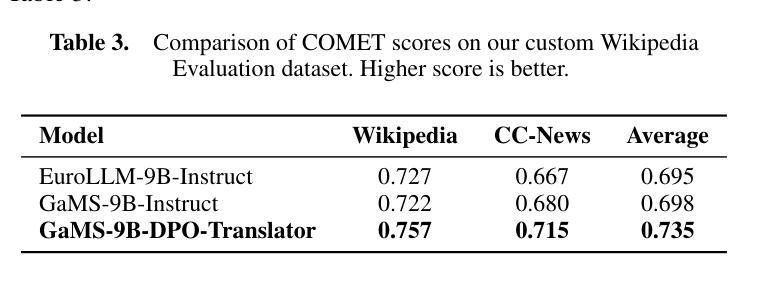
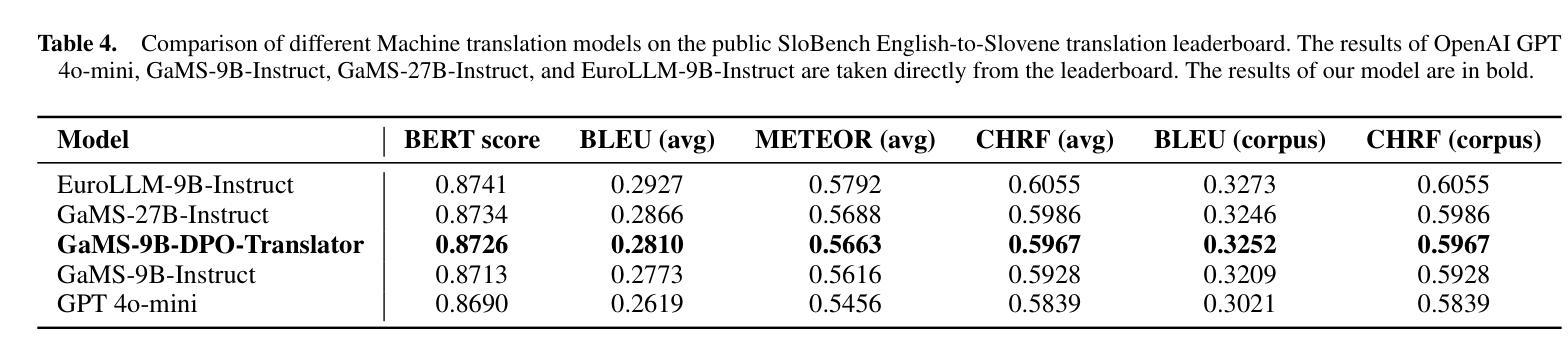
Large language models have emerged as effective machine translation systems. In this paper, we explore how a general instruction-tuned large language model can be improved for machine translation using relatively few easily produced data resources. Using Slovene as a use case, we improve the GaMS-9B-Instruct model using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) training on a programmatically curated and enhanced subset of a public dataset. As DPO requires pairs of quality-ranked instances, we generated its training dataset by translating English Wikipedia articles using two LLMs, GaMS-9B-Instruct and EuroLLM-9B-Instruct. We ranked the resulting translations based on heuristics coupled with automatic evaluation metrics such as COMET. The evaluation shows that our fine-tuned model outperforms both models involved in the dataset generation. In comparison to the baseline models, the fine-tuned model achieved a COMET score gain of around 0.04 and 0.02, respectively, on translating Wikipedia articles. It also more consistently avoids language and formatting errors.
大型语言模型已经作为有效的机器翻译系统出现。在本文中,我们探讨了如何通过利用相对容易获取的数据资源,对通用指令调整的大型语言模型进行改进,以提高其机器翻译的性能。以斯洛文尼亚语为使用案例,我们通过对公共数据集的编程策划和增强子集进行直接偏好优化(DPO)训练,改进了GaMS-9B-Instruct模型。由于DPO需要成对的质量排名实例,我们通过使用两个大型语言模型GaMS-9B-Instruct和EuroLLM-9B-Instruct翻译英文维基百科文章来生成其训练数据集。我们根据与自动评估指标(如COMET)结合的启发式方法,对所得翻译进行排名。评估结果表明,我们微调的模型在翻译维基百科文章方面的表现优于参与数据集生成的这两个模型。与基线模型相比,微调模型在维基百科文章翻译上的COMET得分分别提高了约0.04和0.02。此外,它还能更一致地避免语言和格式错误。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper with individual presentation at LUHME workshop at ECAI 2025
Summary
大型语言模型已成为有效的机器翻译系统。本文探索了如何使用少量易获取的数据资源改进通用指令调整的大型语言模型。以斯洛文尼亚语为例,我们改进了GaMS-9B-Instruct模型,采用Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)训练法对公开数据集的一个程序化精选增强子集进行训练。由于DPO需要质量排序的实例对,我们通过使用两个大型语言模型GaMS-9B-Instruct和EuroLLM-9B-Instruct翻译英文维基百科文章来生成其训练数据集。我们根据启发式方法和自动评估指标(如COMET)对翻译结果进行了排名。评估表明,我们的精细调整模型优于参与数据集生成的模型。与基线模型相比,精细调整模型在翻译维基百科文章时的COMET得分分别提高了约0.04和0.02。它还更一致地避免了语言和格式错误。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在机器翻译领域表现卓越。
- 使用斯洛文尼亚语作为案例,对通用指令调整的大型语言模型进行了改进。
- 采用Direct Preference Optimization(DPO)训练法优化模型性能。
- 训练数据集是通过两个大型语言模型翻译英文维基百科文章并使用质量评估排名生成的。
- 精细调整模型的性能优于参与数据集生成的模型。
- 与基线模型相比,精细调整模型在COMET得分上有所提高。
点此查看论文截图

NVIDIA Nemotron Nano 2: An Accurate and Efficient Hybrid Mamba-Transformer Reasoning Model
Authors: NVIDIA, :, Aarti Basant, Abhijit Khairnar, Abhijit Paithankar, Abhinav Khattar, Adithya Renduchintala, Aditya Malte, Akhiad Bercovich, Akshay Hazare, Alejandra Rico, Aleksander Ficek, Alex Kondratenko, Alex Shaposhnikov, Alexander Bukharin, Ali Taghibakhshi, Amelia Barton, Ameya Sunil Mahabaleshwarkar, Amy Shen, Andrew Tao, Ann Guan, Anna Shors, Anubhav Mandarwal, Arham Mehta, Arun Venkatesan, Ashton Sharabiani, Ashwath Aithal, Ashwin Poojary, Ayush Dattagupta, Balaram Buddharaju, Banghua Zhu, Barnaby Simkin, Bilal Kartal, Bita Darvish Rouhani, Bobby Chen, Boris Ginsburg, Brandon Norick, Brian Yu, Bryan Catanzaro, Charles Wang, Charlie Truong, Chetan Mungekar, Chintan Patel, Chris Alexiuk, Christian Munley, Christopher Parisien, Dan Su, Daniel Afrimi, Daniel Korzekwa, Daniel Rohrer, Daria Gitman, David Mosallanezhad, Deepak Narayanan, Dima Rekesh, Dina Yared, Dmytro Pykhtar, Dong Ahn, Duncan Riach, Eileen Long, Elliott Ning, Eric Chung, Erick Galinkin, Evelina Bakhturina, Gargi Prasad, Gerald Shen, Haifeng Qian, Haim Elisha, Harsh Sharma, Hayley Ross, Helen Ngo, Herman Sahota, Hexin Wang, Hoo Chang Shin, Hua Huang, Iain Cunningham, Igor Gitman, Ivan Moshkov, Jaehun Jung, Jan Kautz, Jane Polak Scowcroft, Jared Casper, Jian Zhang, Jiaqi Zeng, Jimmy Zhang, Jinze Xue, Jocelyn Huang, Joey Conway, John Kamalu, Jonathan Cohen, Joseph Jennings, Julien Veron Vialard, Junkeun Yi, Jupinder Parmar, Kari Briski, Katherine Cheung, Katherine Luna, Keith Wyss, Keshav Santhanam, Kezhi Kong, Krzysztof Pawelec, Kumar Anik, Kunlun Li, Kushan Ahmadian, Lawrence McAfee, Laya Sleiman, Leon Derczynski, Luis Vega, Maer Rodrigues de Melo, Makesh Narsimhan Sreedhar, Marcin Chochowski, Mark Cai, Markus Kliegl, Marta Stepniewska-Dziubinska, Matvei Novikov, Mehrzad Samadi, Meredith Price, Meriem Boubdir, Michael Boone, Michael Evans, Michal Bien, Michal Zawalski, Miguel Martinez, Mike Chrzanowski, Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Namit Dhameja, Nave Assaf, Negar Habibi, Nidhi Bhatia, Nikki Pope, Nima Tajbakhsh, Nirmal Kumar Juluru, Oleg Rybakov, Oleksii Hrinchuk, Oleksii Kuchaiev, Oluwatobi Olabiyi, Pablo Ribalta, Padmavathy Subramanian, Parth Chadha, Pavlo Molchanov, Peter Dykas, Peter Jin, Piotr Bialecki, Piotr Januszewski, Pradeep Thalasta, Prashant Gaikwad, Prasoon Varshney, Pritam Gundecha, Przemek Tredak, Rabeeh Karimi Mahabadi, Rajen Patel, Ran El-Yaniv, Ranjit Rajan, Ria Cheruvu, Rima Shahbazyan, Ritika Borkar, Ritu Gala, Roger Waleffe, Ruoxi Zhang, Russell J. Hewett, Ryan Prenger, Sahil Jain, Samuel Kriman, Sanjeev Satheesh, Saori Kaji, Sarah Yurick, Saurav Muralidharan, Sean Narenthiran, Seonmyeong Bak, Sepehr Sameni, Seungju Han, Shanmugam Ramasamy, Shaona Ghosh, Sharath Turuvekere Sreenivas, Shelby Thomas, Shizhe Diao, Shreya Gopal, Shrimai Prabhumoye, Shubham Toshniwal, Shuoyang Ding, Siddharth Singh, Siddhartha Jain, Somshubra Majumdar, Soumye Singhal, Stefania Alborghetti, Syeda Nahida Akter, Terry Kong, Tim Moon, Tomasz Hliwiak, Tomer Asida, Tony Wang, Tugrul Konuk, Twinkle Vashishth, Tyler Poon, Udi Karpas, Vahid Noroozi, Venkat Srinivasan, Vijay Korthikanti, Vikram Fugro, Vineeth Kalluru, Vitaly Kurin, Vitaly Lavrukhin, Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Wei Du, Wonmin Byeon, Ximing Lu, Xin Dong, Yashaswi Karnati, Yejin Choi, Yian Zhang, Ying Lin, Yonggan Fu, Yoshi Suhara, Zhen Dong, Zhiyu Li, Zhongbo Zhu, Zijia Chen
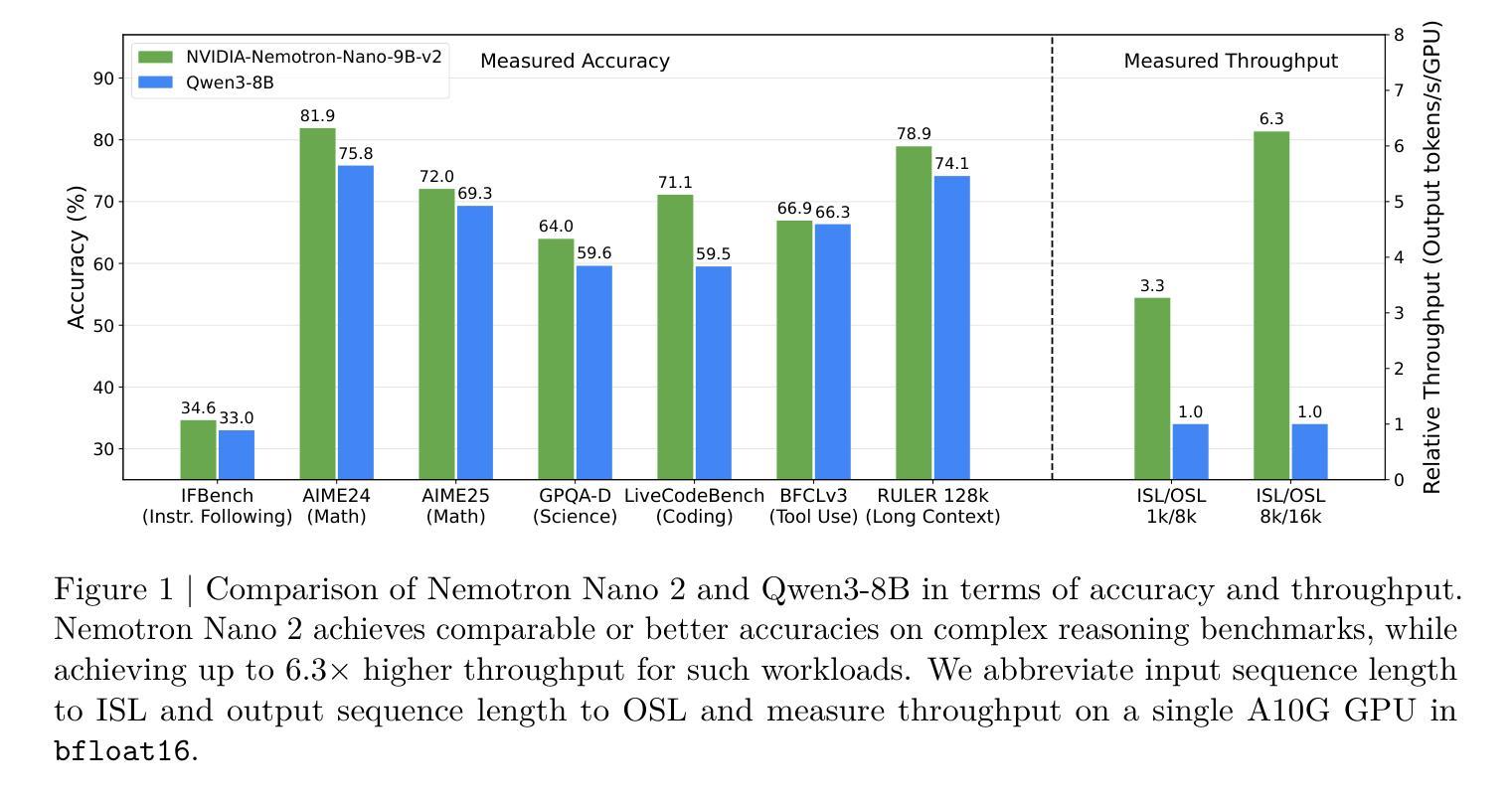
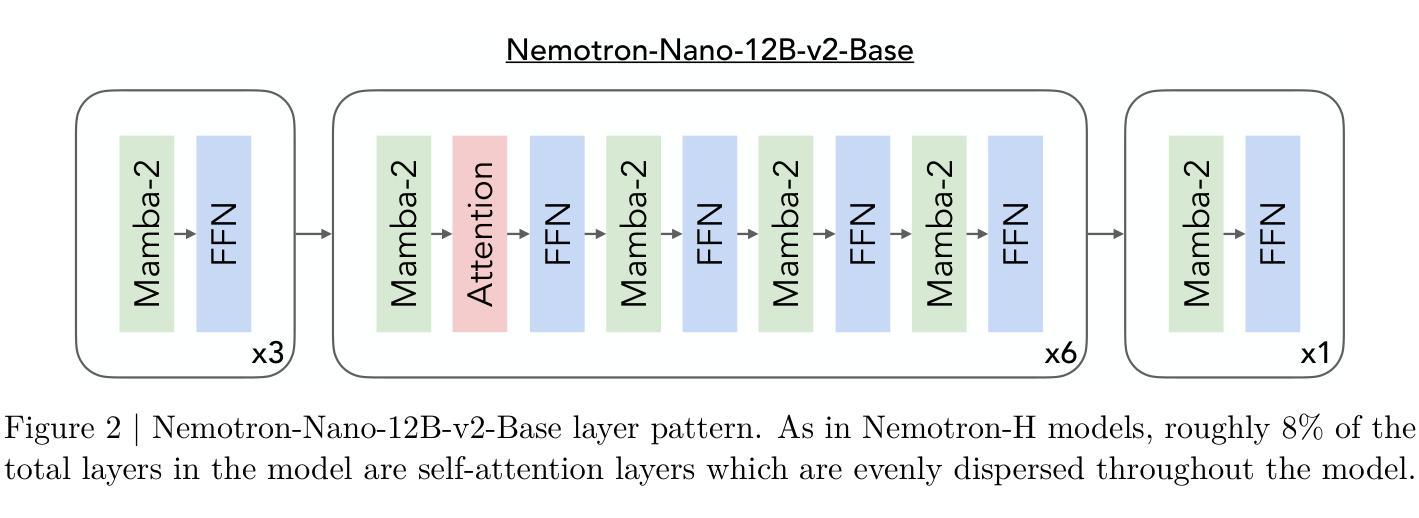
We introduce Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, a hybrid Mamba-Transformer language model designed to increase throughput for reasoning workloads while achieving state-of-the-art accuracy compared to similarly-sized models. Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 builds on the Nemotron-H architecture, in which the majority of the self-attention layers in the common Transformer architecture are replaced with Mamba-2 layers, to achieve improved inference speed when generating the long thinking traces needed for reasoning. We create Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 by first pre-training a 12-billion-parameter model (Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base) on 20 trillion tokens using an FP8 training recipe. After aligning Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base, we employ the Minitron strategy to compress and distill the model with the goal of enabling inference on up to 128k tokens on a single NVIDIA A10G GPU (22GiB of memory, bfloat16 precision). Compared to existing similarly-sized models (e.g., Qwen3-8B), we show that Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2 achieves on-par or better accuracy on reasoning benchmarks while achieving up to 6x higher inference throughput in reasoning settings like 8k input and 16k output tokens. We are releasing Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2, Nemotron-Nano12B-v2-Base, and Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2-Base checkpoints along with the majority of our pre- and post-training datasets on Hugging Face.
我们介绍了Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2,这是一种混合Mamba-Transformer语言模型,旨在提高推理工作负载的吞吐量,同时与类似规模的模型相比实现最先进的准确性。Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2建立在Nemotron-H架构的基础上,将Transformer架构中大部分的自注意力层替换为Mamba-2层,以实现在生成推理所需的长思考轨迹时的更快推理速度。我们通过首先在20万亿个令牌上使用FP8训练配方预训练一个12亿参数模型(Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base)来创建Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2。在对Nemotron-Nano-12B-v2-Base进行对齐后,我们采用Minitron策略来压缩和蒸馏模型,旨在能够在单个NVIDIA A10G GPU(具有22GiB内存,bfloat16精度)上进行最多达128k令牌的推理。与现有的类似规模模型(例如Qwen3-8B)相比,我们在推理基准测试中显示,Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2实现了相当或更好的准确性,同时在如8k输入和16k输出令牌的推理设置中实现了高达6倍的推理吞吐量。我们将Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2、Nemotron-Nano12B-v2-Base以及Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2的检查点连同我们大部分预训练和后续训练数据集一起在Hugging Face上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2的诞生背景和优势。这是一款基于Mamba-Transformer架构的语言模型,通过用Mamba-2层替代Transformer架构中的大部分自注意力层,旨在提升处理推理任务时的效率与准确度。其训练数据采用大规模数据集训练并使用了FP8训练配方,能够在单个NVIDIA A10G GPU上实现高达128k标记的推理能力。相较于其他类似规模的模型,它在推理任务上表现卓越,提高了推理速度。文章最后将模型和预训练数据集发布在Hugging Face上供大众使用。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于文本的关键见解:
- Nemotron-Nano-9B-v2是一个基于Mamba-Transformer架构的语言模型,用于提高推理工作负载的吞吐量并保持与类似规模模型相比的最佳准确性。
- 该模型基于Nemotron-H架构构建,该架构通过替换Transformer架构中的大部分自注意力层为Mamba-2层,以实现生成长思考轨迹所需的推理过程中的改进推断速度。
- 模型通过大规模数据集进行预训练,并采用FP8训练配方来提升性能。
- 该模型能够在单个NVIDIA A10G GPU上处理高达128k的标记推理任务,目标是为了实现在内存使用率和处理速度之间的优化平衡。
- 模型表现出优于同类模型的推理速度性能表现。相对于同样规模的模型(如Qwen3-8B),在如输入为8k标记和输出为16k标记的推理任务上可以达到更高的推理速度(高达6倍)。
- 作者已经将该模型和主要的预训练和后续训练数据集在Hugging Face上发布,以供大众访问和使用。这将促进未来模型的研究和发展。
点此查看论文截图

TabulaX: Leveraging Large Language Models for Multi-Class Table Transformations
Authors:Arash Dargahi Nobari, Davood Rafiei
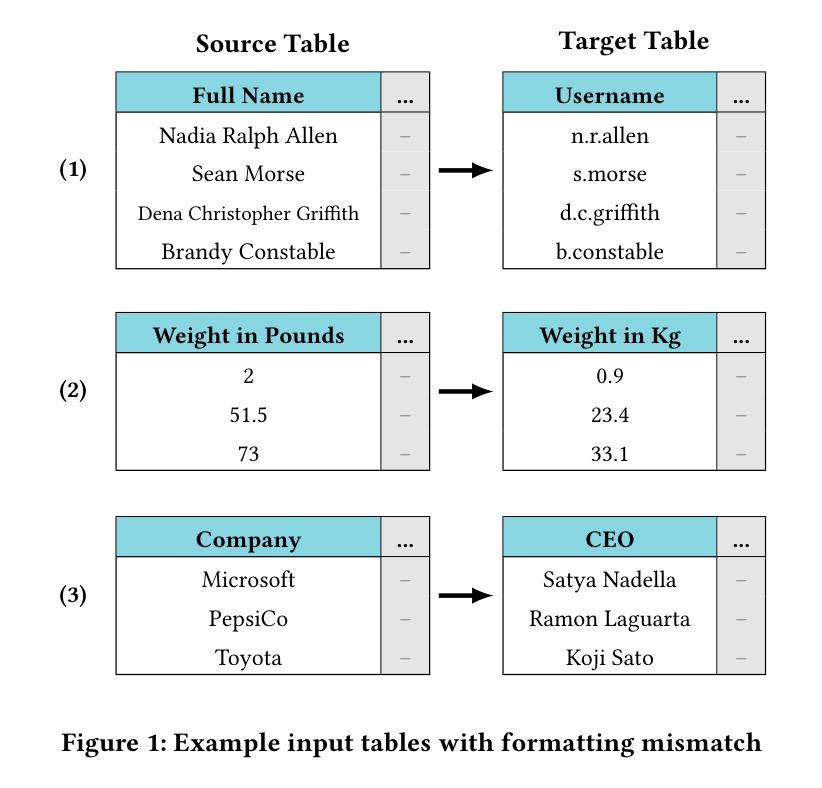
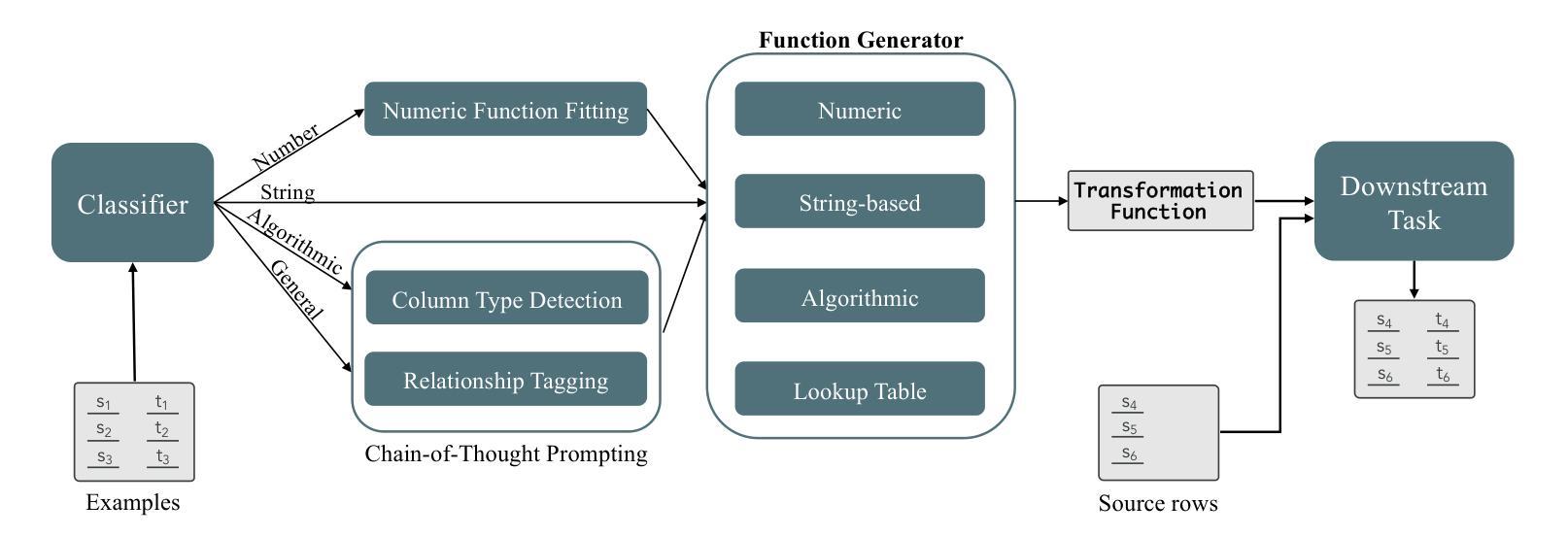
The integration of tabular data from diverse sources is often hindered by inconsistencies in formatting and representation, posing significant challenges for data analysts and personal digital assistants. Existing methods for automating tabular data transformations are limited in scope, often focusing on specific types of transformations or lacking interpretability. In this paper, we introduce TabulaX, a novel framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for multi-class column-level tabular transformations. TabulaX first classifies input columns into four transformation types (string-based, numerical, algorithmic, and general) and then applies tailored methods to generate human-interpretable transformation functions, such as numeric formulas or programming code. This approach enhances transparency and allows users to understand and modify the mappings. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets from various domains, we demonstrate that TabulaX outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in terms of accuracy, supports a broader class of transformations, and generates interpretable transformations that can be efficiently applied.
从不同来源整合表格数据常常因格式和表示的不一致性而受阻,对数据分析师和个人数字助理构成重大挑战。现有的自动化表格数据转换方法范围有限,通常只专注于特定类型的转换或缺乏可解释性。在本文中,我们介绍了TabulaX,一个利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行多类列级表格转换的新型框架。TabulaX首先将对输入列进行四种转换类型(基于字符串、数值、算法和通用)的分类,然后应用定制的方法生成人类可解释转换函数,如数值公式或程序代码。这种方法提高了透明度,使用户能够理解和修改映射关系。通过在不同领域真实数据集上的大量实验,我们证明了TabulaX在准确性方面优于现有最先进的方法,支持更广泛的转换类型,并生成可解释的转换,可高效应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据从不同来源的表格集成常常受到格式和表示不一致性的阻碍,给数据分析人员和个人数字助理带来重大挑战。现有的自动化表格数据转换方法范围有限,通常只关注特定类型的转换或缺乏可解释性。本文介绍了一个新型框架TabulaX,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行多类列级表格转换。TabulaX首先根据输入的列将其分为四类(基于字符串的、数字的、算法的和一般的),然后采用相应的方法生成人类可解释性的转换函数,如数值公式或程序代码。此方法增强了透明度并允许用户理解和修改映射关系。在现实世界的多个领域数据集上进行的大量实验表明,TabulaX在准确性方面优于现有最先进的方案,支持更广泛的转换类型,并能生成可解释的转换,可有效地应用。
Key Takeaways
- 表格数据集成面临格式和表示不一致的挑战。
- 现有自动化表格数据转换方法具有局限性。
- TabulaX利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行多类列级表格转换。
- TabulaX将输入列分为四类:基于字符串的、数字的、算法的和一般的。
- TabulaX生成人类可解释性的转换函数,如数值公式或程序代码。
- TabulaX在准确性方面优于现有方案,并支持更广泛的转换类型。
点此查看论文截图

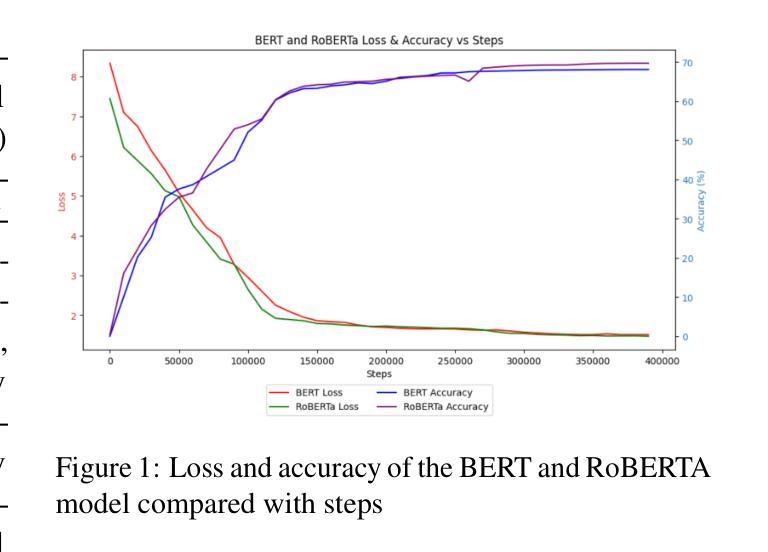
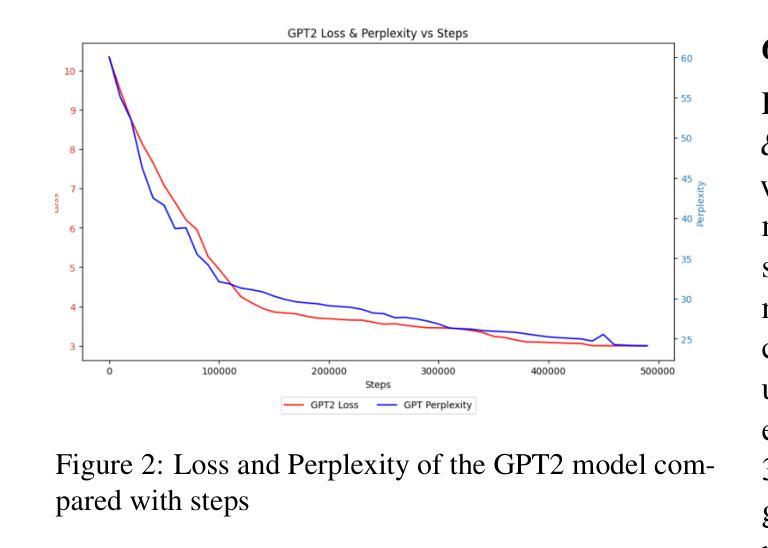
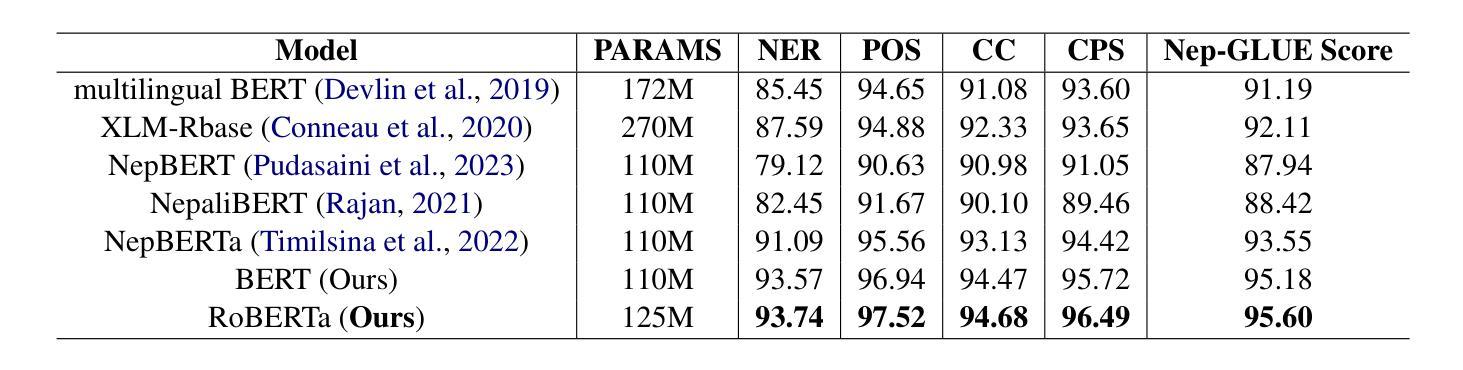
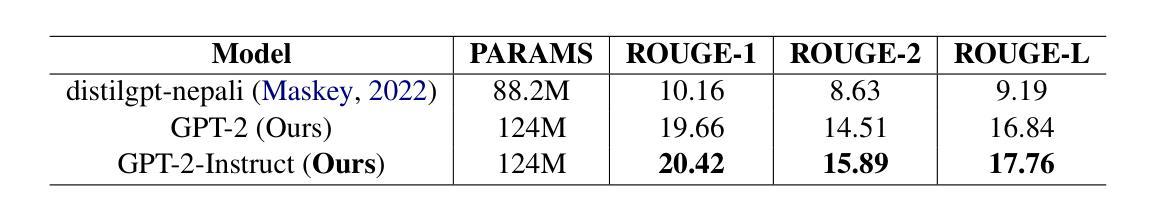
Development of Pre-Trained Transformer-based Models for the Nepali Language
Authors:Prajwal Thapa, Jinu Nyachhyon, Mridul Sharma, Bal Krishna Bal
Transformer-based pre-trained language models have dominated the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) for quite some time now. However, the Nepali language, spoken by approximately 32 million people worldwide, remains significantly underrepresented in this domain. This underrepresentation is primarily attributed to the scarcity of monolingual data corpora and limited available resources for the Nepali language. While existing efforts have predominantly concentrated on basic encoder-based models, there is a notable gap in the exploration of decoder-based architectures. To address this gap, we have collected 27.5 GB of Nepali text data, approximately 2.4x larger than any previously available Nepali language corpus. Leveraging this data, we pre-trained three different models i.e., BERT, RoBERTa, and GPT-2, exclusively for the Nepali Language. Furthermore, we performed instruction tuning and explored its potential for monolingual Nepali data, providing a foundation for future research. Our models outperformed the existing best model by 2 points on Nep-gLUE benchmark, scoring 95.60 and also outperformed existing models on text generation tasks, demonstrating improvements in both understanding and generating Nepali text.
基于Transformer的预训练语言模型在自然语言处理(NLP)领域已经占据主导地位很长时间了。然而,世界上约有3200万人使用的尼泊尔语在这个领域仍然显著缺乏代表性。这种代表性不足主要归因于单语数据语料库的稀缺以及尼泊尔语可用资源的有限。虽然现有的努力主要集中在基本的编码器模型上,但在解码器架构的探索方面仍存在明显的差距。为了弥补这一差距,我们收集了27.5GB的尼泊尔文本数据,大约是之前任何可用的尼泊尔语语料库的2.4倍。利用这些数据,我们针对尼泊尔语预训练了三种不同的模型,即BERT、RoBERTa和GPT-2。此外,我们对指令进行了调整,并探索了其在单语尼泊尔语数据中的潜力,为未来研究奠定了基础。我们的模型在Nep-gLUE基准测试上的得分比现有最佳模型高出2分,得分为95.60,并且在文本生成任务上也超越了现有模型,这表明我们在理解和生成尼泊尔语文本方面都有所改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于Transformer的预训练语言模型在自然语言处理领域占据主导地位已久,但尼泊尔语在该领域受到严重忽视。这主要归因于缺乏单语数据语料库和可用的尼泊尔语资源有限。为了解决这个问题,我们收集了迄今为止最大的尼泊尔语文本数据集,并利用该数据集对BERT、RoBERTa和GPT-2等三种模型进行了训练。在指导微调下,该模型在尼泊尔语言理解和文本生成任务上都超越了现有的模型表现。在Nep-gLUE基准测试中,得分高出目前最佳模型两分,达到了95.6的高分。该模型的训练和研发为后续相关研究奠定了坚实基础。
Key Takeaways:
- Transformer-based预训练语言模型在自然语言处理领域占主导地位,但尼泊尔语的相关研究十分匮乏。
- 缺乏单语数据语料库和可用的尼泊尔语资源是尼泊尔语在自然语言处理领域受忽视的主要原因。
- 研究人员收集了迄今为止最大的尼泊尔语文本数据集,用于训练模型。
- 利用该数据集训练的模型包括BERT、RoBERTa和GPT-2等三种模型。
- 通过指导微调,这些模型在理解和生成尼泊尔语文本方面表现优异。
- 在Nep-gLUE基准测试中,这些模型的得分高于现有最佳模型两分,达到95.6的高分。
点此查看论文截图

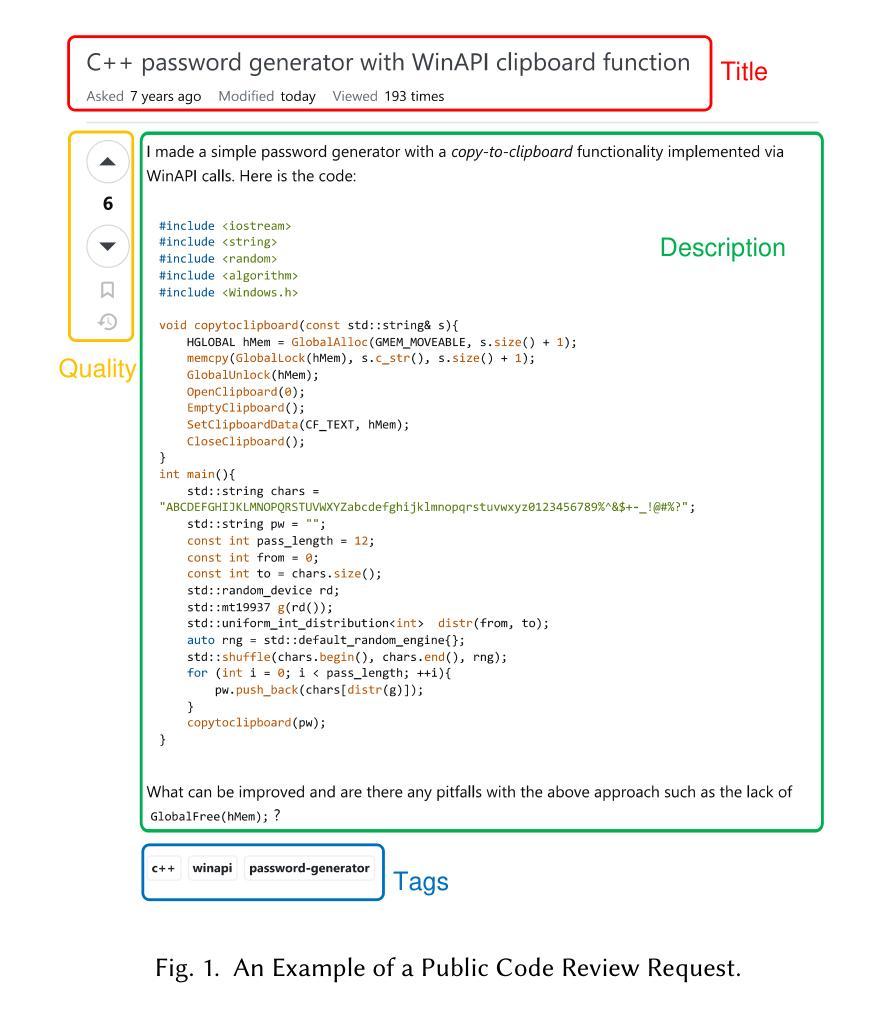
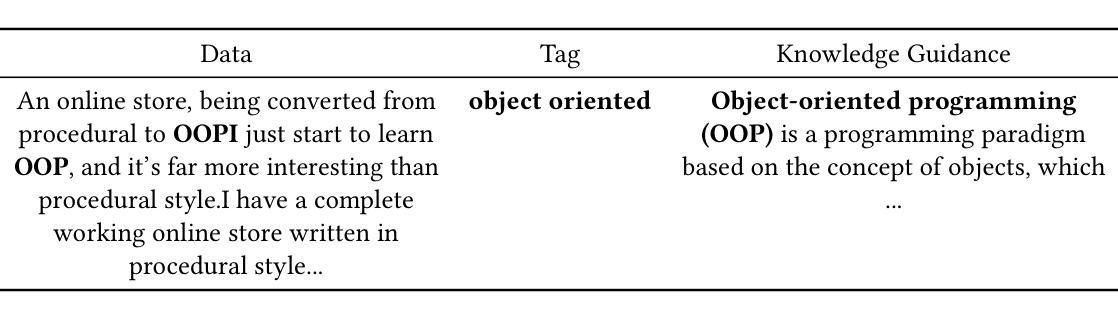
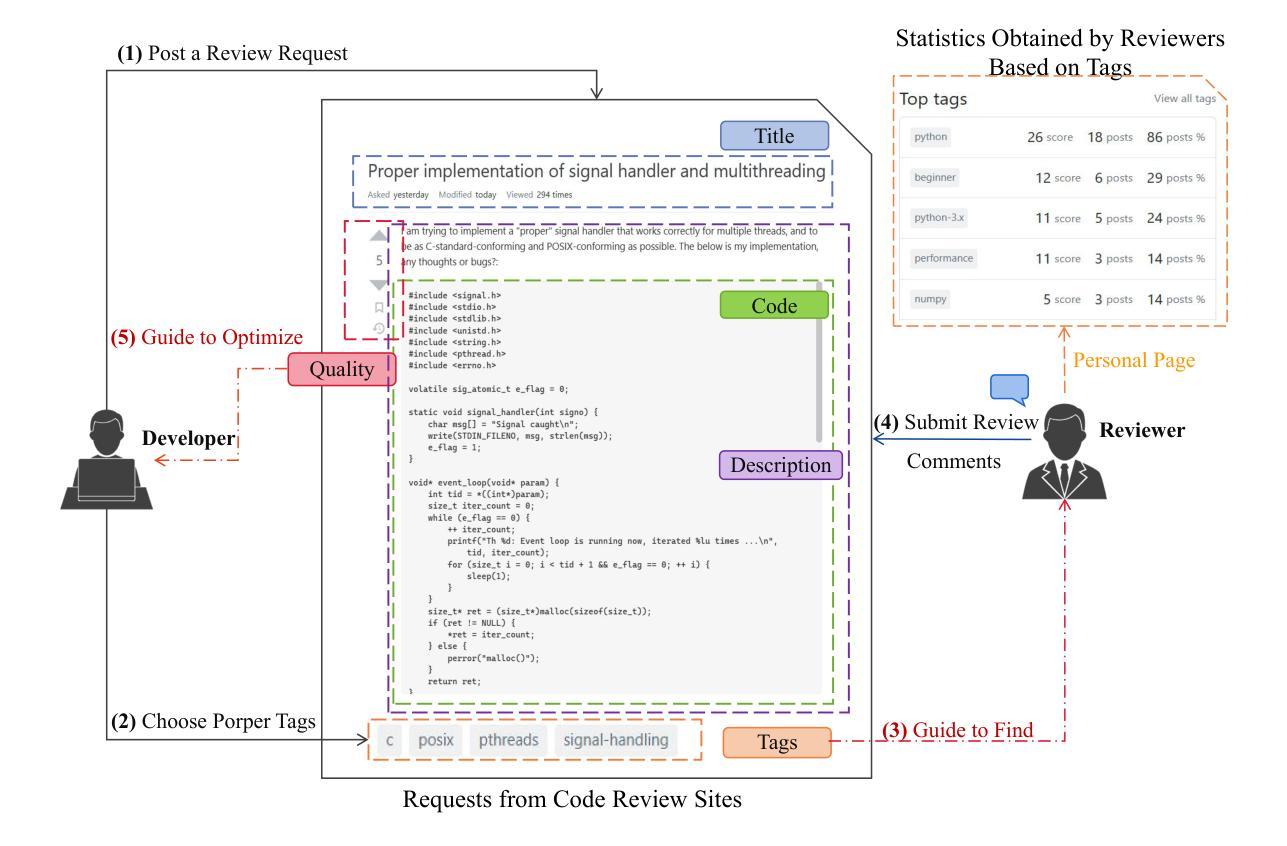
Knowledge-Guided Prompt Learning for Request Quality Assurance in Public Code Review
Authors:Lin Li, Xinchun Yu, Xinyu Chen, Peng Liang
Public Code Review (PCR) is developed in the Software Question Answering (SQA) community, assisting developers in exploring high-quality and efficient review services. Current methods on PCR mainly focus on the reviewer’s perspective, including finding a capable reviewer, predicting comment quality, and recommending/generating review comments. However, it is not well studied that how to satisfy the review necessity requests posted by developers which can increase their visibility, which in turn acts as a prerequisite for better review responses. To this end, we propose K nowledge-guided P rompt learning for P ublic Code Review (KP-PCR) to achieve developer-based code review request quality assurance (i.e., predicting request necessity and recommending tags subtask). Specifically, we reformulate the two subtasks via 1) text prompt tuning which converts both of them into a Masked Language Model (MLM) by constructing prompt templates using hard prompt; and 2) knowledge and code prefix tuning which introduces knowledge guidance from fine-tuned large language models by soft prompt, and uses program dependence graph to characterize code snippets. Finally, both of the request necessity prediction and tag recommendation subtasks output predicted results through an answer engineering module. In addition, we further analysis the time complexity of our KP-PCR that has lightweight prefix based the operation of introducing knowledge guidance. Experimental results on the PCR dataset for the period 2011-2023 demonstrate that our KP-PCR outperforms baselines by 2.3%-8.4% in the request necessity prediction and by 1.4%-6.9% in the tag recommendation. The code implementation is released at https://github.com/WUT-IDEA/KP-PCR.
公共代码审查(PCR)是在软件问答(SQA)社区中开发的,旨在帮助开发者探索高质量和高效的审查服务。当前PCR的主要方法主要集中在审查者的角度,包括寻找能力强的审查者、预测评论质量和推荐/生成审查评论。然而,如何满足开发者提出的审查需求请求并未得到很好的研究,而这些请求的增加可以提高其可见度,从而更好地获得审查回应。为此,我们提出知识引导提示学习公共代码审查(KP-PCR),以实现基于开发者的代码审查请求质量保证(即预测请求必要性和推荐标签子任务)。具体来说,我们通过1)文本提示调整,将这两个子任务转换为掩码语言模型(MLM),通过构建硬提示的提示模板来实现;2)知识和代码前缀调整,引入经过微调的大型语言模型的知识指导,使用软提示和程序依赖图来表征代码片段。最后,请求必要性预测和标签推荐子任务都通过答案工程模块输出预测结果。此外,我们进一步分析了我们的KP-PCR的时间复杂度,它具有基于引入知识指导的前缀的轻量级操作。在2011-2023年的PCR数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的KP-PCR在请求必要性预测方面优于基线2.3%-8.4%,在标签推荐方面优于基线1.4%-6.9%。代码实现已发布在https://github.com/WUT-IDEA/KP-PCR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 5 images, 12 tables, Manuscript revision submitted to a journal (2025)
Summary
本文介绍了公共代码审查(PCR)在软件问答(SQA)社区的发展情况,并指出当前PCR方法主要关注评审者的角度。为满足开发者提出的审查需求请求,提高可见性并获取更好的审查回应,提出了知识引导提示学习公共代码审查(KP-PCR)方法。KP-PCR通过文本提示调整和知识与代码前缀调整两个步骤,将请求必要性预测和标签推荐子任务转化为掩码语言模型(MLM)的任务。此外,文章还分析了KP-PCR的时间复杂度,并通过实验验证了其在请求必要性预测和标签推荐方面的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 公共代码审查(PCR)在软件问答(SQA)社区中得到发展,主要关注评审者的角度,包括寻找能力强的评审者、预测评论质量和生成推荐评论。
- KP-PCR方法旨在满足开发者的审查需求请求,提高其在PCR中的可见性,从而获取更好的审查回应。
- KP-PCR通过文本提示调整和知识与代码前缀调整两个步骤,将请求必要性预测和标签推荐子任务转化为掩码语言模型(MLM)的任务。
- KP-PCR引入知识指导,使用程序依赖图来表征代码片段,并通过轻量级的前缀操作实现。
- 实验结果表明,KP-PCR在请求必要性预测和标签推荐方面优于基线方法。
- KP-PCR的代码实现已发布在https://github.com/WUT-IDEA/KP-PCR。
点此查看论文截图

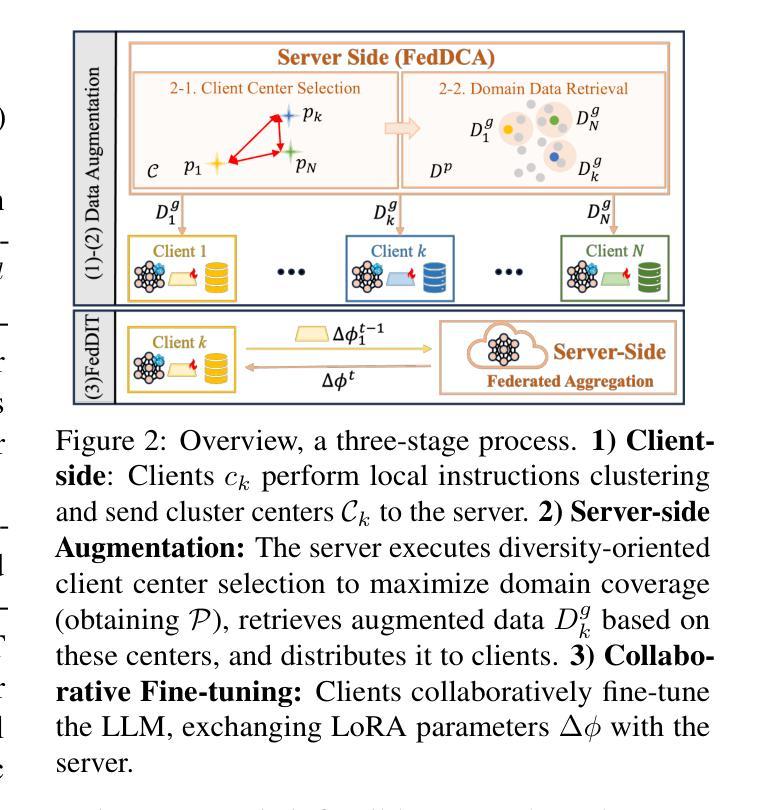
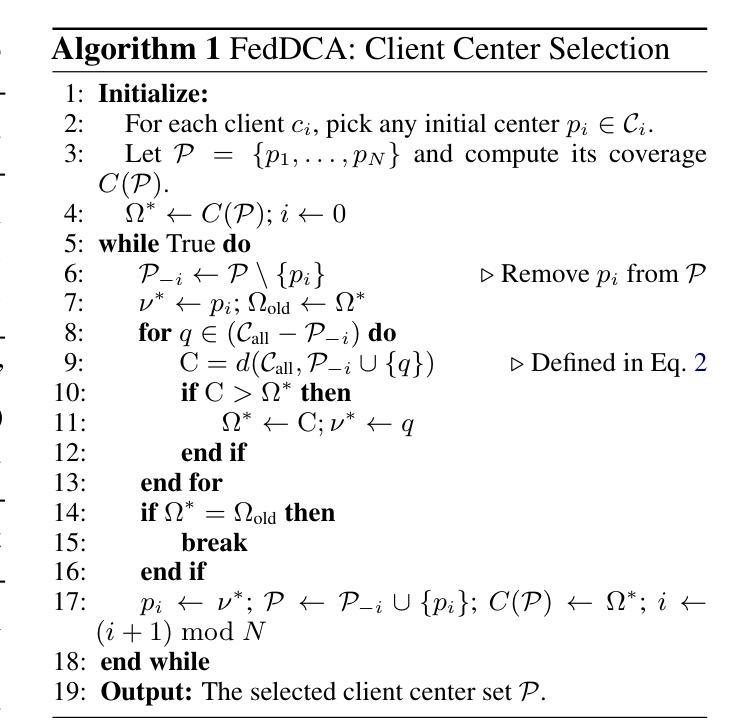
Optimizing Cross-Client Domain Coverage for Federated Instruction Tuning of Large Language Models
Authors:Zezhou Wang, Yaxin Du, Xingjun Ma, Yugang Jiang, Zhuzhong Qian, Siheng Chen
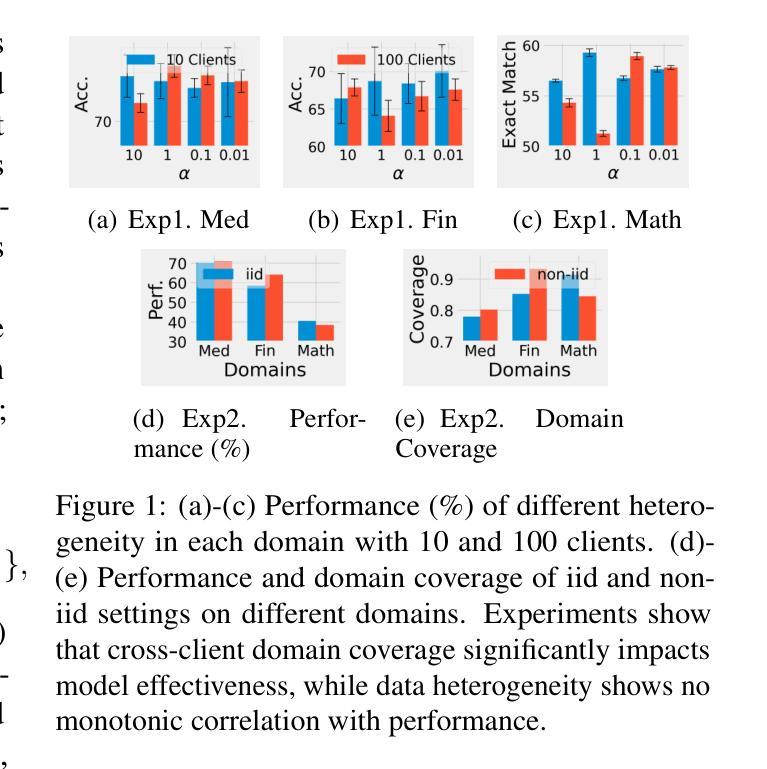
Federated domain-specific instruction tuning (FedDIT) for large language models (LLMs) aims to enhance performance in specialized domains using distributed private and limited data, yet identifying key performance drivers and optimal augmentation strategies remains challenging. We empirically establish that cross-client domain coverage, rather than data heterogeneity, is the pivotal factor. We then introduce FedDCA, an algorithm that explicitly maximizes this coverage through diversity-oriented client center selection and retrieval-based augmentation, constructing diverse, non-redundant cross-client instruction sets. Extensive experiments across multiple domains demonstrate FedDCA’s superiority over eleven baselines, achieving performance gains of up to 29.19% and domain coverage improvements of 4.82%-21.36%. FedDCA maintains its effectiveness in diverse and challenging scenarios, including data selection, held-out settings where task-specific public data is scarce and various data heterogeneity, with manageable privacy risks. This work clarifies critical FedDIT dynamics and presents FedDCA as an effective, privacy-preserving, and scalable solution for advancing domain-specific LLM tuning.
针对大型语言模型(LLM)的联邦特定领域指令调整(FedDIT)旨在利用分布式私有和有限数据提高在特定领域的性能,然而,确定关键性能驱动因素和最佳增强策略仍然具有挑战性。我们通过实证研究证实,跨客户端领域覆盖(而非数据异质性)是关键要素。随后,我们引入了FedDCA算法,该算法通过面向多样性的客户端中心选择和检索增强法,显式地最大化这种覆盖,构建多样化、非冗余的跨客户端指令集。跨多个领域的广泛实验表明,FedDCA在超过11个基准测试中具有优势,性能提升幅度高达29.19%,领域覆盖改善幅度在4.82%~21.36%之间。FedDCA在多样化的挑战场景中保持了其有效性,包括数据选择、任务特定公开数据稀缺的保留设置以及各种数据异质性,同时可控隐私风险。这项工作明确了关键的FedDIT动态,并展示了FedDCA作为一种有效、保护隐私和可扩展的解决方案,可推动特定领域的LLM调优。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2025
摘要
针对大型语言模型(LLM)的联邦特定域指令调整(FedDIT)旨在利用分布式私有和有限数据提高在特定领域的性能,但确定关键性能驱动因素和最佳增强策略仍具有挑战性。我们实证地证明了跨客户端的域覆盖是关键因素,而不是数据异质性。接着引入了FedDCA算法,它通过面向多样性的客户端中心选择和检索增强方法,显式地最大化这种覆盖,构建多样且非冗余的跨客户端指令集。在多领域的广泛实验证明,FedDCA优于十一种基线方法,实现了高达29.19%的性能提升和4.82%-21.36%的域覆盖改善。FedDCA在数据选择、任务特定公开数据稀缺的保留设置以及多种数据异质性等多样和复杂场景中保持其有效性,同时管理隐私风险。本研究明确了关键的FedDIT动态,并提出FedDCA是一种有效、隐私保护、可扩展的解决方案,可推动特定领域的LLM调优。
关键见解
- 联邦特定域指令调整(FedDIT)旨在提高大型语言模型(LLM)在特定领域的性能。
- 跨客户端的域覆盖是提升LLM性能的关键因素。
- FedDCA算法通过多样性导向的客户端中心选择和检索增强方法,最大化跨客户端的域覆盖。
- FedDCA在多个领域实验中表现出优越性能,相较于基线方法有高达29.19%的性能提升。
- FedDCA在数据选择、任务特定公开数据稀缺以及数据异质性等复杂场景中表现稳健。
- FedDCA能有效管理隐私风险。
- 此研究明确了关键的FedDIT动态,并提出FedDCA作为一种有效、可扩展到特定领域的LLM调优解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

Judging the Judges: Evaluating Alignment and Vulnerabilities in LLMs-as-Judges
Authors:Aman Singh Thakur, Kartik Choudhary, Venkat Srinik Ramayapally, Sankaran Vaidyanathan, Dieuwke Hupkes
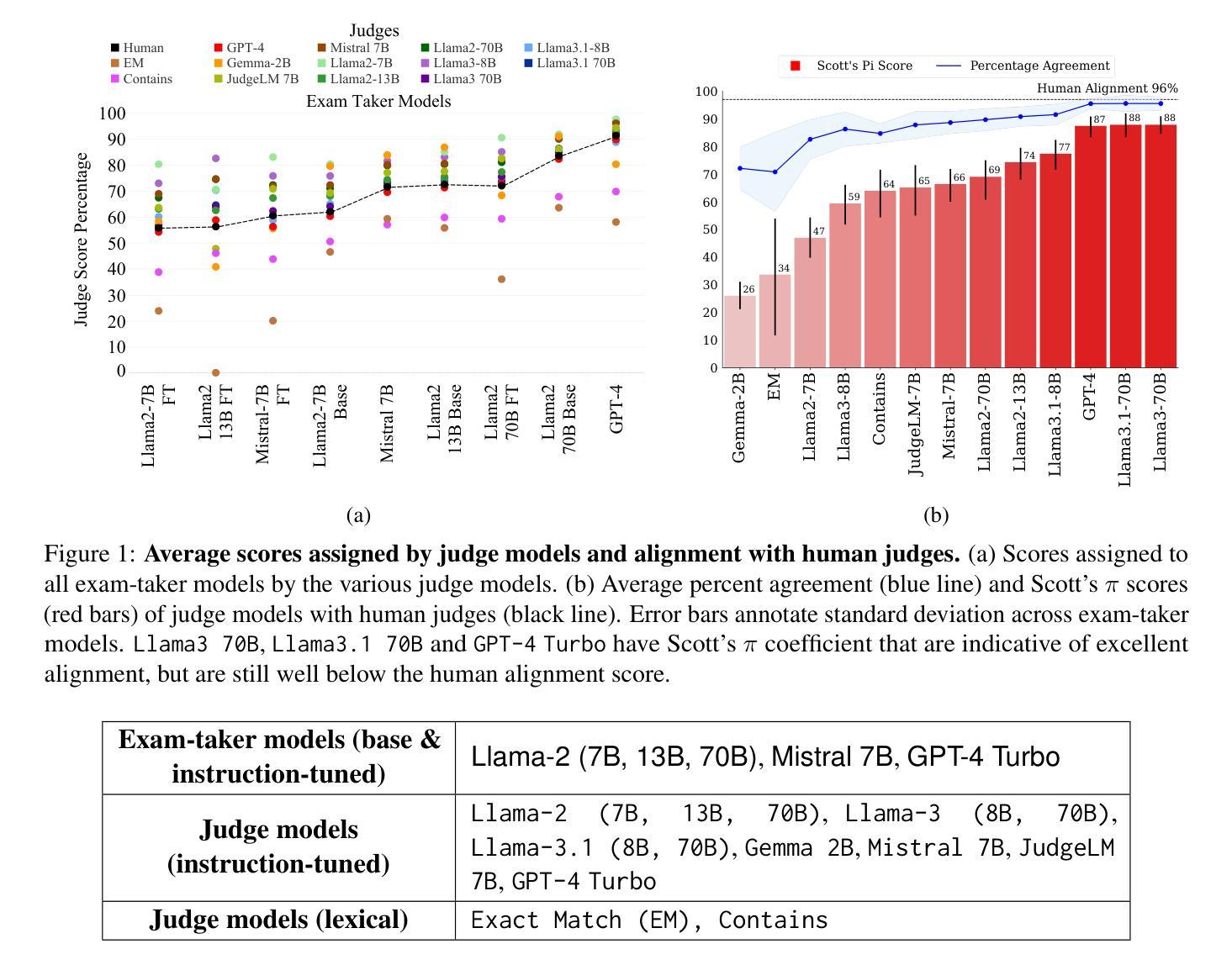
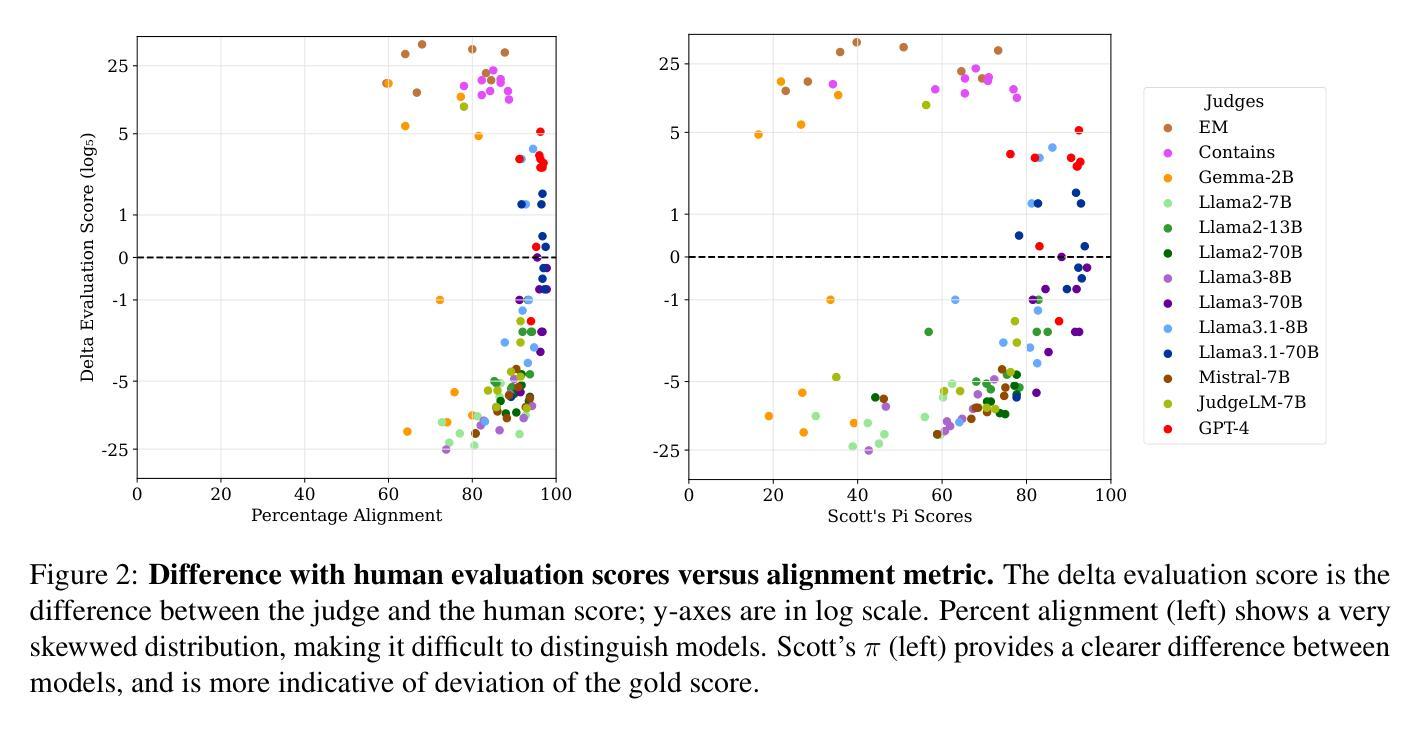
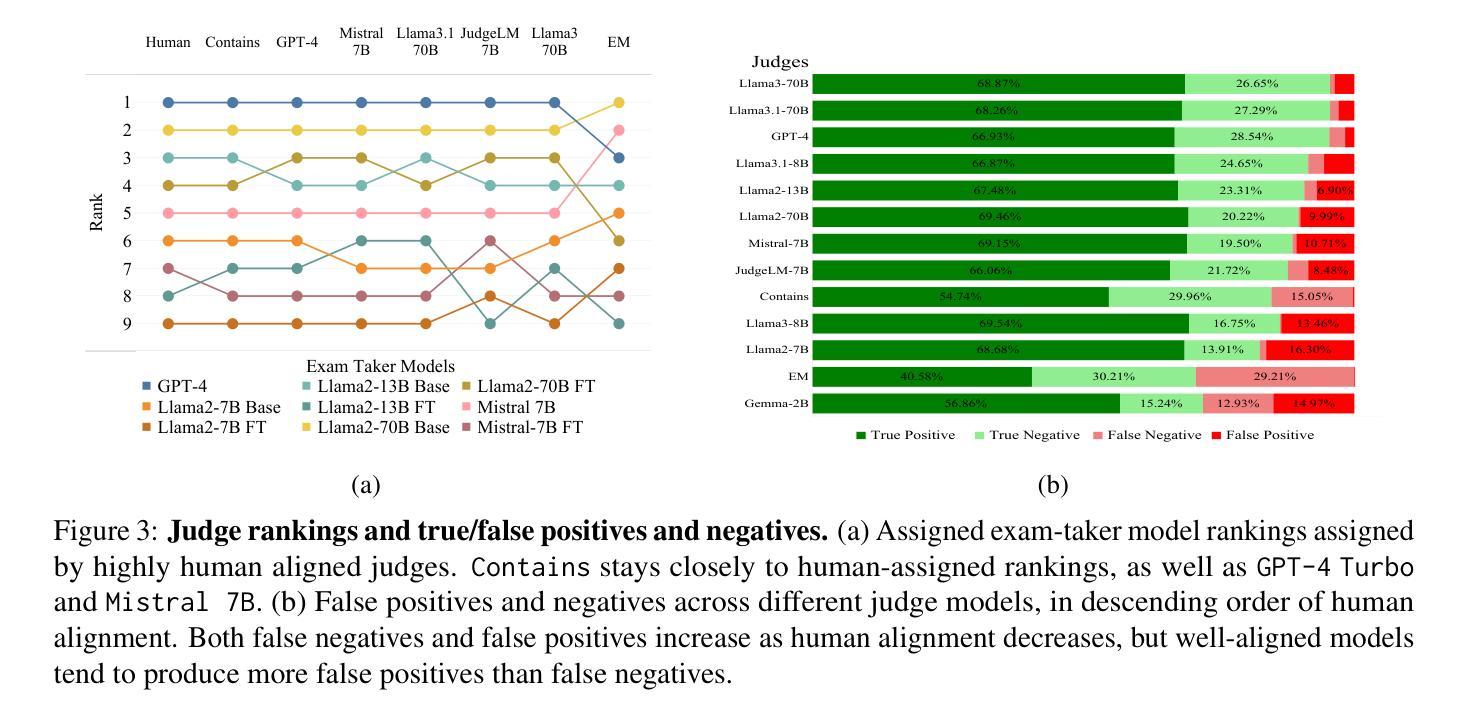
Offering a promising solution to the scalability challenges associated with human evaluation, the LLM-as-a-judge paradigm is rapidly gaining traction as an approach to evaluating large language models (LLMs). However, there are still many open questions about the strengths and weaknesses of this paradigm, and what potential biases it may hold. In this paper, we present a comprehensive study of the performance of various LLMs acting as judges, focusing on a clean scenario in which inter-human agreement is high. Investigating thirteen judge models of different model sizes and families, judging answers of nine different ‘examtaker models’ - both base and instruction-tuned - we find that only the best (and largest) models achieve reasonable alignment with humans. However, they are still quite far behind inter-human agreement and their assigned scores may still differ with up to 5 points from human-assigned scores. In terms of their ranking of the nine exam-taker models, instead, also smaller models and even the lexical metric contains may provide a reasonable signal. Through error analysis and other studies, we identify vulnerabilities in judge models, such as their sensitivity to prompt complexity and length, and a tendency toward leniency. The fact that even the best judges differ from humans in this comparatively simple setup suggest that caution may be wise when using judges in more complex setups. Lastly, our research rediscovers the importance of using alignment metrics beyond simple percent alignment, showing that judges with high percent agreement can still assign vastly different scores.
针对与人类评估相关的可扩展性挑战,LLM作为法官的范式为解决该问题提供了前景广阔的解决方案,并作为评估大型语言模型(LLM)的一种方法迅速获得了支持。然而,关于该范式的优缺点及其可能存在的潜在偏见,仍有许多悬而未决的问题。在本文中,我们对作为法官的各种LLM的性能进行了全面的研究,重点关注人类之间共识度较高的清洁场景。我们调查了13个不同规模和家族的法官模型,评估了9个不同参加考试模型的答案(包括基础模型和指令调优模型),我们发现只有最好的(也是最大的)模型才能实现与人类的合理对齐。然而,它们仍然远远落后于人类之间的共识,其分配的分数可能与人类分配的分数相差高达5分。而在对九个考试模型的排名方面,较小的模型甚至词汇度量也可能提供合理的信号。通过错误分析和其他研究,我们发现了法官模型的漏洞,如它们对提示的复杂性和长度的敏感性,以及倾向于宽容的趋势。即使在相对简单的设置中,即使最好的法官也与人类存在差异,因此在更复杂的设置中使用法官时可能需要谨慎。最后,我们的研究重新发现了使用超越简单百分比对齐的对齐指标的重要性,表明即使百分比协议很高的法官仍然可以分配截然不同的分数。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://aclanthology.org/2025.gem-1.33/
Summary
LLM作为评估者的模式在解决语言模型评估的可扩展性挑战方面展现出巨大潜力。本文全面研究了不同大小的LLM模型作为评委的表现,发现只有最优秀的模型才能达到与人类之间的合理对齐。然而,这些模型仍然与人类评估存在差距,且存在对提示复杂性和长度的敏感性和宽松倾向等漏洞。因此,在更复杂的设置中使用这些模型时需要谨慎。此外,研究还发现简单的对齐百分比不能完全反映模型的真实性能。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-as-a-judge模式解决了人类评估可扩展性的挑战。
- 只有最优秀的LLM模型才能实现与人类的合理对齐。
- 优秀的LLM模型仍与人类评估存在差距,需谨慎使用于复杂环境。
- LLM作为评委存在对提示复杂性和长度的敏感性和宽松倾向等漏洞。
- 简单的对齐百分比不能完全反映模型的真实性能。
- 研究重新发现了使用超越简单百分比对齐的对齐指标的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

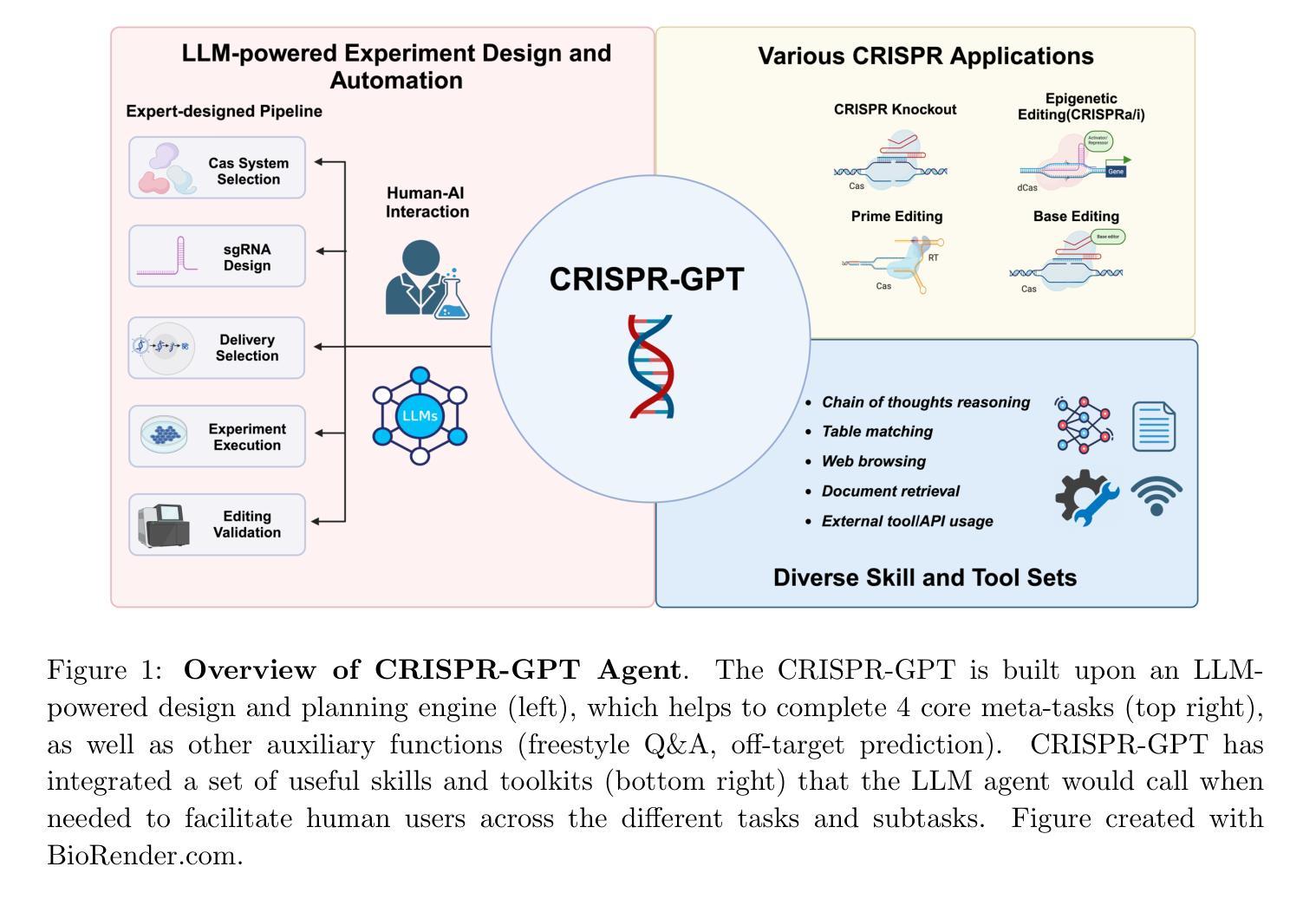
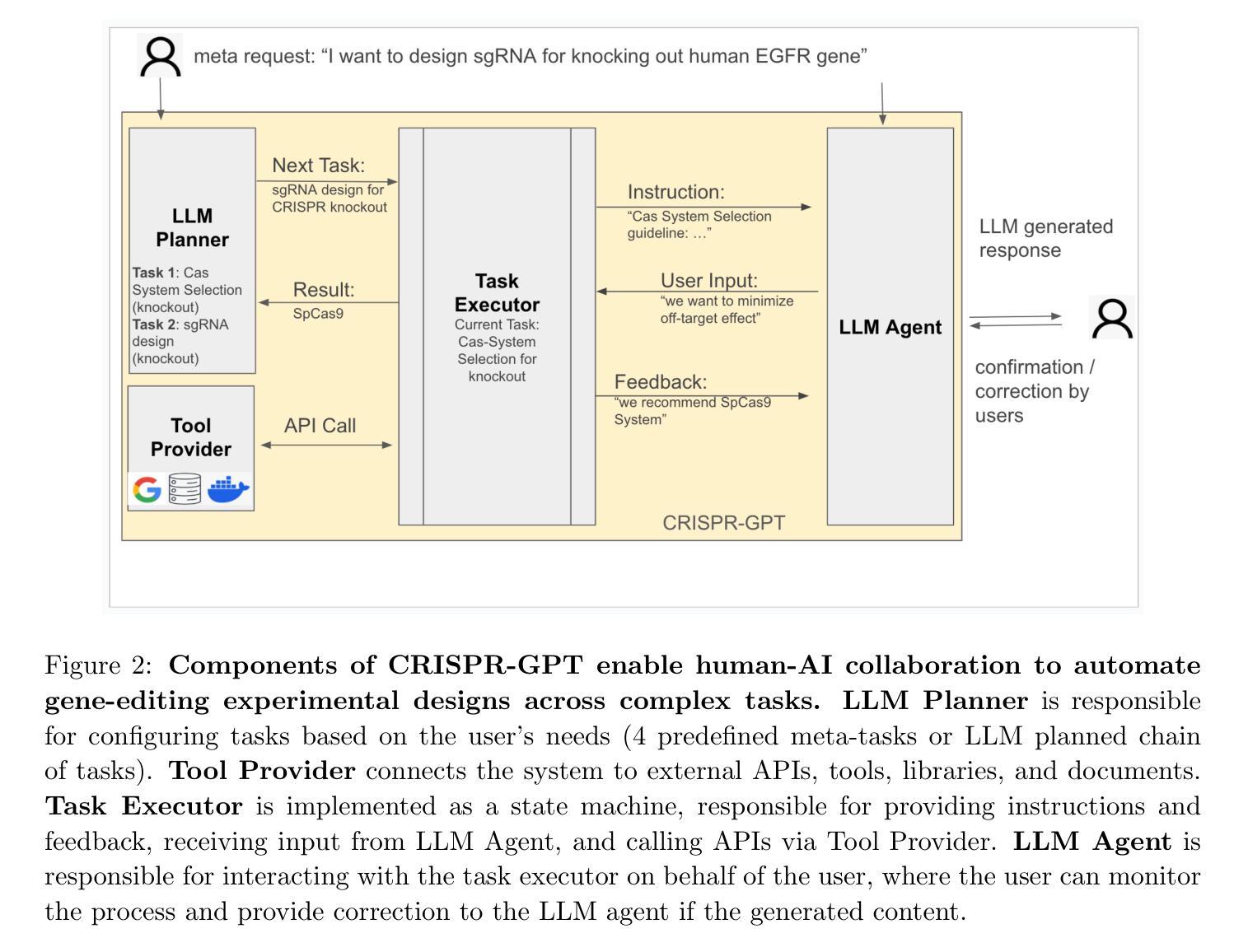
CRISPR-GPT for Agentic Automation of Gene-editing Experiments
Authors:Yuanhao Qu, Kaixuan Huang, Ming Yin, Kanghong Zhan, Dyllan Liu, Di Yin, Henry C. Cousins, William A. Johnson, Xiaotong Wang, Mihir Shah, Russ B. Altman, Denny Zhou, Mengdi Wang, Le Cong
The introduction of genome engineering technology has transformed biomedical research, making it possible to make precise changes to genetic information. However, creating an efficient gene-editing system requires a deep understanding of CRISPR technology, and the complex experimental systems under investigation. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in various tasks, they often lack specific knowledge and struggle to accurately solve biological design problems. In this work, we introduce CRISPR-GPT, an LLM agent augmented with domain knowledge and external tools to automate and enhance the design process of CRISPR-based gene-editing experiments. CRISPR-GPT leverages the reasoning ability of LLMs to facilitate the process of selecting CRISPR systems, designing guide RNAs, recommending cellular delivery methods, drafting protocols, and designing validation experiments to confirm editing outcomes. We showcase the potential of CRISPR-GPT for assisting non-expert researchers with gene-editing experiments from scratch and validate the agent’s effectiveness in a real-world use case. Furthermore, we explore the ethical and regulatory considerations associated with automated gene-editing design, highlighting the need for responsible and transparent use of these tools. Our work aims to bridge the gap between beginner biological researchers and CRISPR genome engineering techniques, and demonstrate the potential of LLM agents in facilitating complex biological discovery tasks. The published version of this draft is available at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01463-z.
基因组工程技术的引入已经彻底改变了生物医学研究,使得对遗传信息进行精确修改成为可能。然而,要创建一个高效的基因编辑系统,需要深入了解CRISPR技术以及复杂的实验系统。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在各种任务中显示出潜力,但它们通常缺乏特定知识,难以准确解决生物设计问题。在我们的工作中,我们介绍了CRISPR-GPT,这是一个通过领域知识和外部工具增强功能的大型语言模型代理,可以自动化和增强CRISPR基因编辑实验的设计过程。CRISPR-GPT利用LLM的推理能力来促进选择CRISPR系统、设计引导RNA、推荐细胞传递方法、起草协议以及设计验证实验以确认编辑结果的过程。我们展示了CRISPR-GPT在协助非专业研究人员进行基因编辑实验方面的潜力,并通过实际使用案例验证了该代理的有效性。此外,我们还探讨了与自动化基因编辑设计相关的伦理和监管问题,强调这些工具需要负责任和透明地使用。我们的工作旨在缩小初级生物研究人员与CRISPR基因组工程技术之间的差距,并展示大型语言模型代理在促进复杂生物学发现任务中的潜力。该论文的发布版本可通过https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01463-z访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Nature Biomedical Engineering
Summary:CRISPR基因编辑技术革命性地改变了生物医学研究。为了提高基因编辑的效率,本文引入CRISPR-GPT,这是一种利用大型语言模型(LLM)技术和外部工具辅助CRISPR基因编辑实验设计的系统。CRISPR-GPT可帮助非专业研究人员完成从实验设计到验证的全过程,并探讨了自动化基因编辑设计的伦理和监管问题。本文旨在缩小初学者与CRISPR基因工程技术的差距,展示LLM在促进复杂生物学发现任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- CRISPR基因编辑技术的引入为生物医学研究带来了巨大的变革。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)技术可提高基因编辑效率,但仍缺乏特定领域的解决方案。
- CRISPR-GPT结合了CRISPR技术和LLM的优势,辅助完成基因编辑实验的全过程。
- CRISPR-GPT具备选择CRISPR系统、设计引导RNA、推荐细胞传递方法、起草协议和设计验证实验的能力。
- CRISPR-GPT有助于非专业研究人员进行基因编辑实验,验证了其在真实世界中的有效性。
- 自动化基因编辑设计需要考虑伦理和监管问题,需要负责任和透明地使用这些工具。
点此查看论文截图