⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
GOGS: High-Fidelity Geometry and Relighting for Glossy Objects via Gaussian Surfels
Authors:Xingyuan Yang, Min Wei
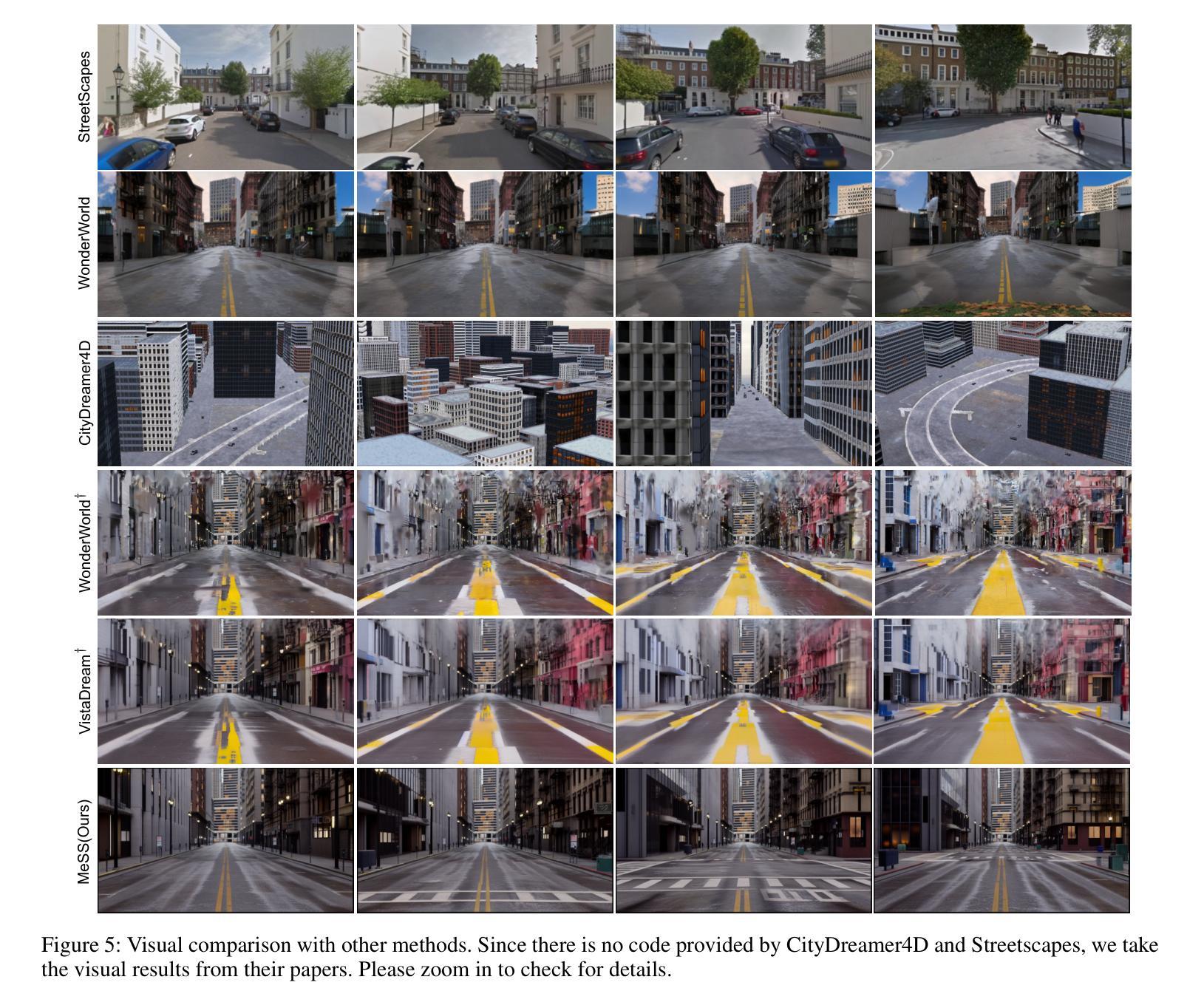
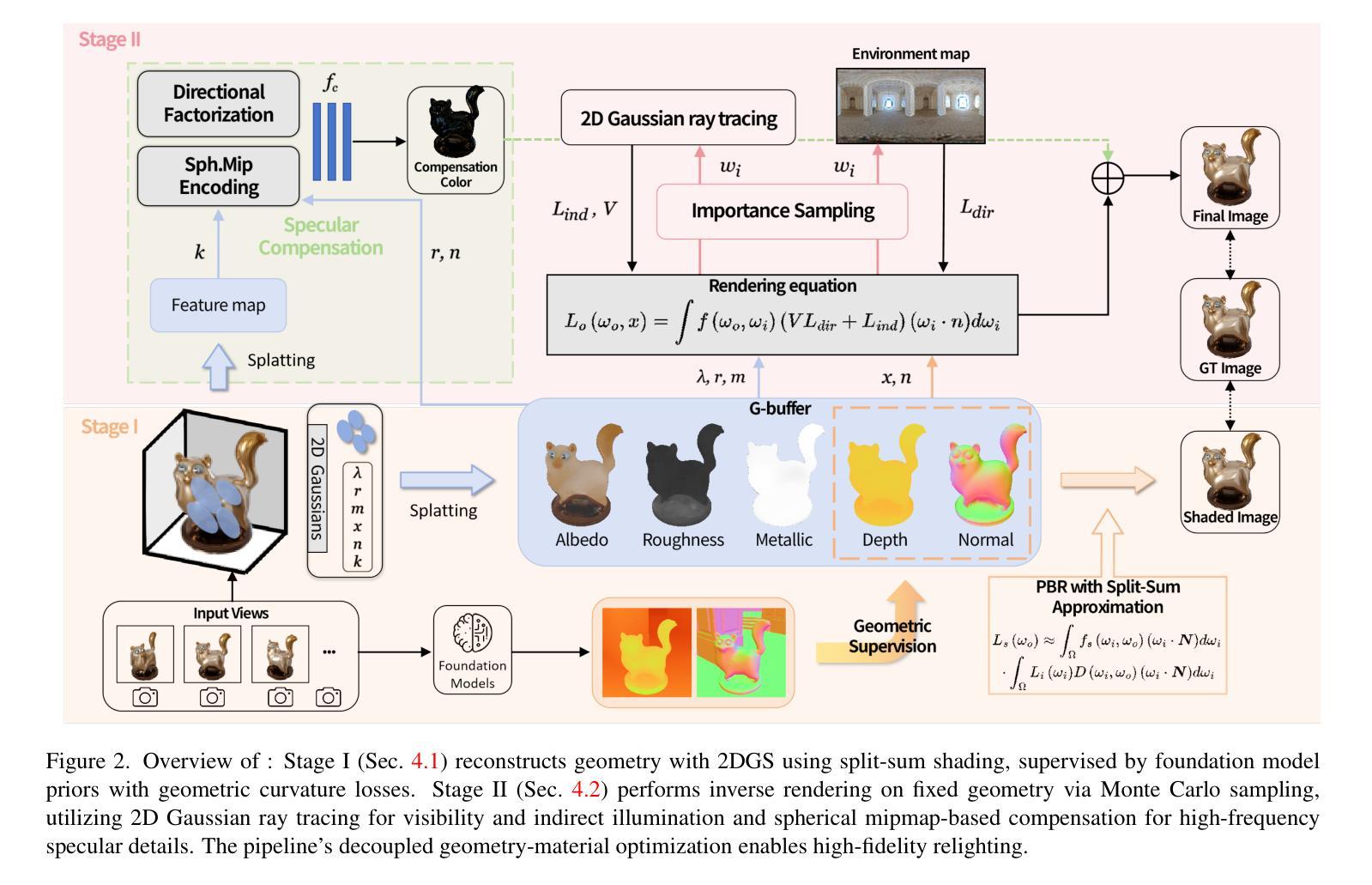
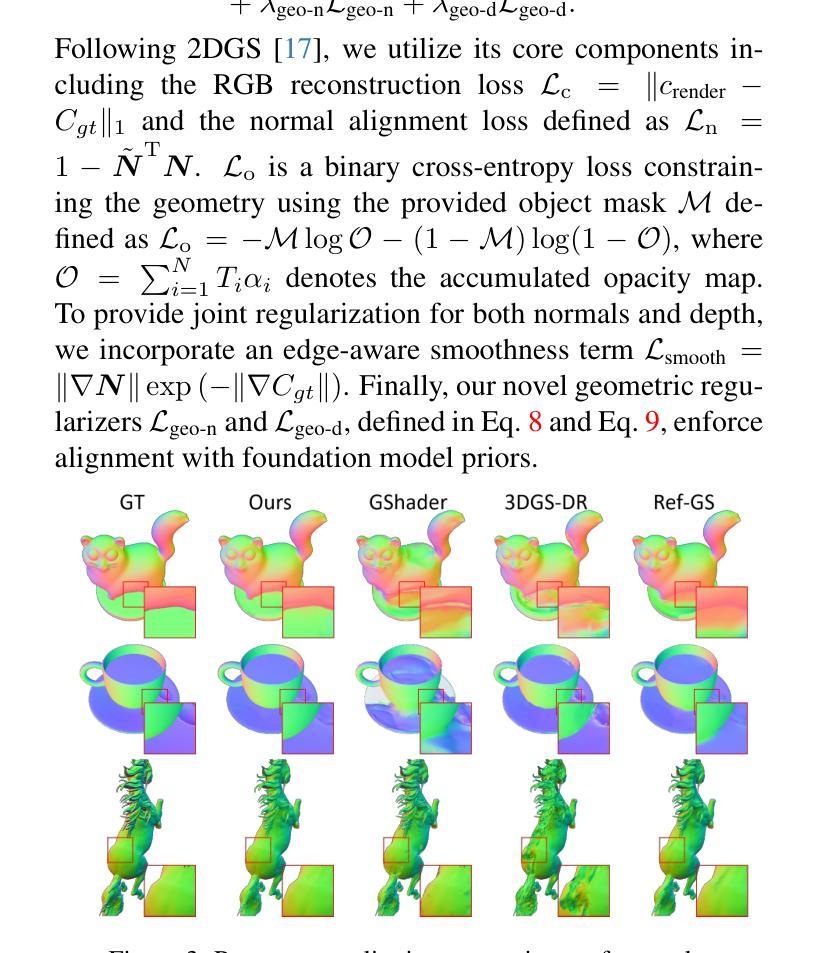
Inverse rendering of glossy objects from RGB imagery remains fundamentally limited by inherent ambiguity. Although NeRF-based methods achieve high-fidelity reconstruction via dense-ray sampling, their computational cost is prohibitive. Recent 3D Gaussian Splatting achieves high reconstruction efficiency but exhibits limitations under specular reflections. Multi-view inconsistencies introduce high-frequency surface noise and structural artifacts, while simplified rendering equations obscure material properties, leading to implausible relighting results. To address these issues, we propose GOGS, a novel two-stage framework based on 2D Gaussian surfels. First, we establish robust surface reconstruction through physics-based rendering with split-sum approximation, enhanced by geometric priors from foundation models. Second, we perform material decomposition by leveraging Monte Carlo importance sampling of the full rendering equation, modeling indirect illumination via differentiable 2D Gaussian ray tracing and refining high-frequency specular details through spherical mipmap-based directional encoding that captures anisotropic highlights. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in geometry reconstruction, material separation, and photorealistic relighting under novel illuminations, outperforming existing inverse rendering approaches.
从RGB图像对光滑物体进行逆向渲染仍然受到固有模糊性的根本限制。尽管基于NeRF的方法通过密集射线采样实现了高保真重建,但其计算成本高昂。最近的3D高斯拼贴技术实现了高效的重建,但在镜面反射下表现出局限性。多视图不一致性引入了高频表面噪声和结构伪影,而简化的渲染方程掩盖了材料属性,导致不合理的重新照明结果。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了GOGS,这是一种基于二维高斯surfels的新型两阶段框架。首先,我们通过基于物理的渲染和分割求和近似法建立稳健的表面重建,并通过基础模型的几何先验知识增强其功能。其次,我们利用全渲染方程的蒙特卡罗重要性采样进行材料分解,通过可微分的二维高斯光线追踪对间接照明进行建模,并通过基于球形mipmap的方向编码来完善高频镜面细节,捕捉各向异性的高光。大量实验表明,我们在几何重建、材料分离和新型照明下的逼真重新照明方面的性能达到了最新水平,超越了现有的逆向渲染方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 13 figures
Summary
基于RGB图像的光泽物体逆向渲染仍存在根本上的局限。NeRF方法虽能通过密集射线采样实现高保真重建,但计算成本高昂。3D高斯拼贴法虽能高效重建,但在镜面反射下存在局限。多视角不一致会导致高频表面噪声和结构伪影,而简化的渲染方程会掩盖材质属性,导致照明结果不可信。为解决这些问题,我们提出了基于二维高斯surfels的新型两阶段框架GOGS。首先,我们通过物理渲染和分割求和近似法建立稳健的表面重建,并由基础模型的几何先验增强。其次,我们利用全渲染方程的蒙特卡罗重要性采样进行材质分解,通过可微分的二维高斯光线追踪对间接照明进行建模,并通过基于球形mipmap的方向编码捕捉各向异性的高光点,以细化高频的镜面细节。广泛的实验表明,我们的方法在几何重建、材质分离和光影真实感的重新照明方面表现出卓越的性能,超越了现有的逆向渲染方法。
Key Takeaways
- 逆向渲染光泽物体存在根本限制,现有方法如NeRF计算成本高。
- 3D高斯拼贴法在镜面反射下存在局限。
- 多视角不一致会导致表面噪声和结构伪影。
- 简化的渲染方程可能掩盖材质属性,影响照明结果的真实性。
- GOGS框架基于二维高斯surfels,分为表面重建和材质分解两个阶段。
- 表面重建通过物理渲染和分割求和近似法建立,增强几何先验。
点此查看论文截图

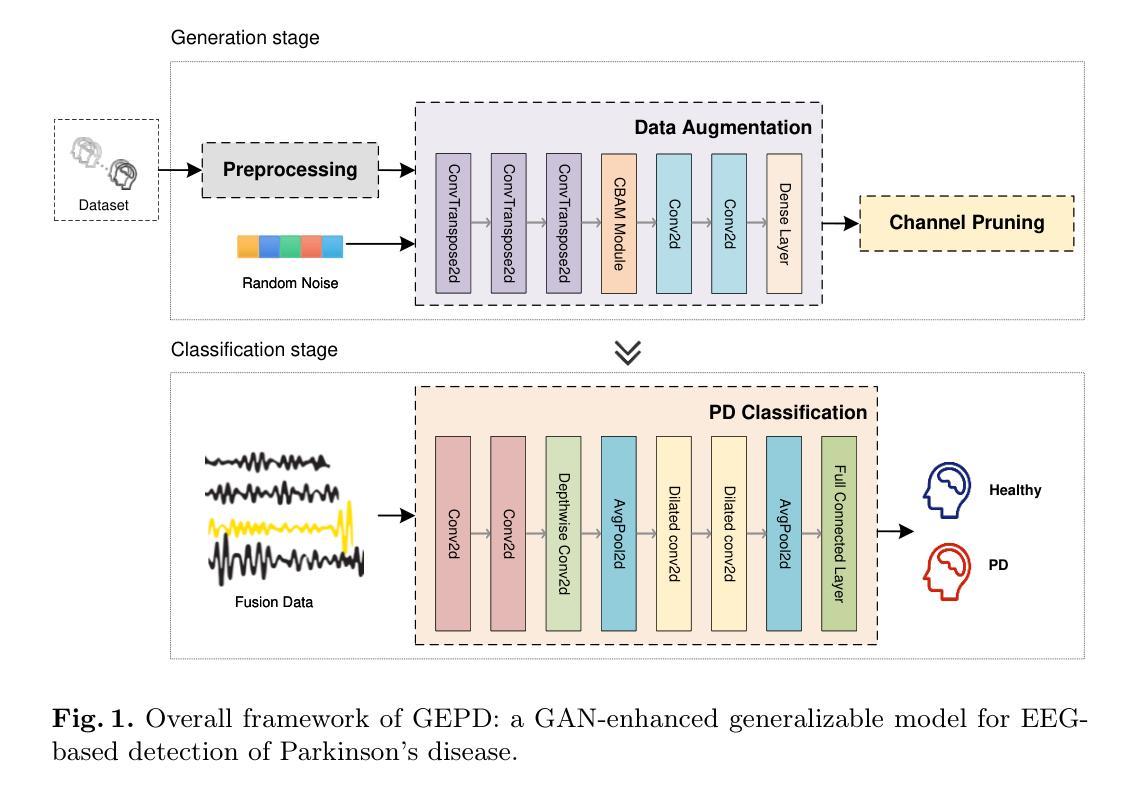
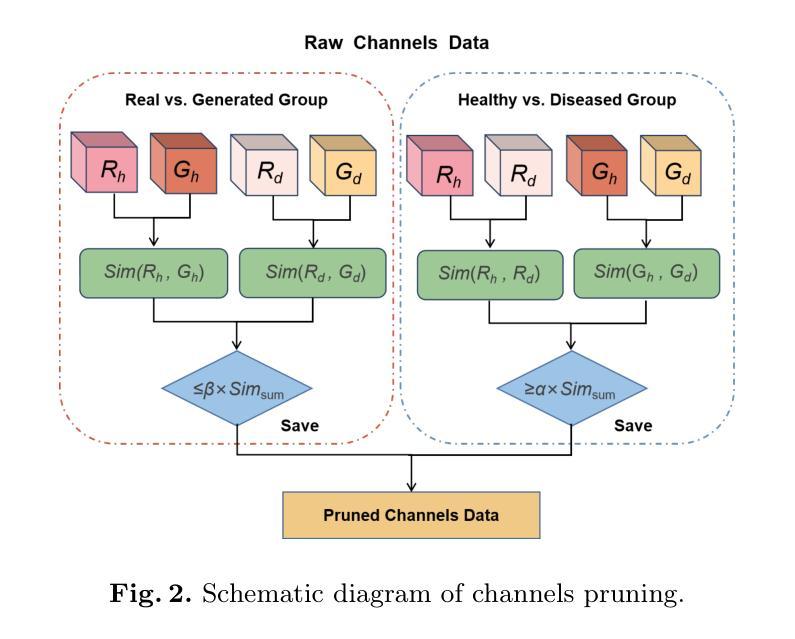
GEPD:GAN-Enhanced Generalizable Model for EEG-Based Detection of Parkinson’s Disease
Authors:Qian Zhang, Ruilin Zhang, Biaokai Zhu, Xun Han, Jun Xiao, Yifan Liu, Zhe Wang
Electroencephalography has been established as an effective method for detecting Parkinson’s disease, typically diagnosed early.Current Parkinson’s disease detection methods have shown significant success within individual datasets, however, the variability in detection methods across different EEG datasets and the small size of each dataset pose challenges for training a generalizable model for cross-dataset scenarios. To address these issues, this paper proposes a GAN-enhanced generalizable model, named GEPD, specifically for EEG-based cross-dataset classification of Parkinson’s disease.First, we design a generative network that creates fusion EEG data by controlling the distribution similarity between generated data and real data.In addition, an EEG signal quality assessment model is designed to ensure the quality of generated data great.Second, we design a classification network that utilizes a combination of multiple convolutional neural networks to effectively capture the time-frequency characteristics of EEG signals, while maintaining a generalizable structure and ensuring easy convergence.This work is dedicated to utilizing intelligent methods to study pathological manifestations, aiming to facilitate the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases.The evaluation results demonstrate that our model performs comparably to state-of-the-art models in cross-dataset settings, achieving an accuracy of 84.3% and an F1-score of 84.0%, showcasing the generalizability of the proposed model.
脑电图学已被确立为检测帕金森病的有效方法,通常早期进行诊断。当前帕金森病检测方法在单个数据集中取得了显著的成功,然而,不同脑电图数据集之间检测方法的差异以及每个数据集的小规模,为跨数据集场景的通用模型训练带来了挑战。针对这些问题,本文提出了一种增强型通用模型,名为GEPD,专门用于基于脑电图的帕金森病跨数据集分类。首先,我们设计了一个生成网络,通过控制生成数据与实际数据之间的分布相似性来创建融合脑电图数据。此外,还设计了脑电图信号质量评估模型,以确保生成数据的质量。其次,我们设计了一个分类网络,它结合了多个卷积神经网络,以有效地捕捉脑电图信号的时间-频率特征,同时保持通用结构并确保易于收敛。这项工作致力于利用智能方法研究病理表现,旨在促进神经疾病的诊断和监测。评估结果表明,我们的模型在跨数据集设置中的表现与最新模型相当,准确率达到了84.3%,F1分数为84.0%,展示了所提出模型的可推广性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by International Conference on Intelligent Computing(ICIC 2025)
Summary:
帕金森病是常见的神经系统疾病,通常早期发现并通过脑电图诊断。目前对帕金森病检测方法在不同脑电图数据集之间有很大的差异性和局限性,本研究提出了一种基于生成对抗网络的通用模型GEPD来解决这个问题。通过生成融合脑电图数据并设计信号质量评估模型,确保生成数据的质量。同时,利用多个卷积神经网络组合的分类网络捕捉脑电图信号的时间-频率特征,具有良好的泛化性和收敛性。评价结果显示,该模型在跨数据集环境下表现优异,准确率和F1分数分别达到了84.3%和84.0%。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前帕金森病检测方法面临跨数据集检测方法和数据集规模限制的挑战。
- 本研究提出了基于生成对抗网络的通用模型GEPD,用于解决帕金森病的跨数据集检测问题。
- 设计了生成网络生成融合脑电图数据并控制生成数据与真实数据的分布相似性。
- 设计了脑电图信号质量评估模型以确保生成数据的质量。
- 采用多个卷积神经网络组合的分类网络有效捕捉脑电图信号的时间-频率特征,保持模型的泛化性和收敛性。
- 在跨数据集环境下,GEPD模型表现出较高的性能,准确率和F1分数均达到了较高水平。
点此查看论文截图