⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-23 更新
Pathology-Informed Latent Diffusion Model for Anomaly Detection in Lymph Node Metastasis
Authors:Jiamu Wang, Keunho Byeon, Jinsol Song, Anh Nguyen, Sangjeong Ahn, Sung Hak Lee, Jin Tae Kwak
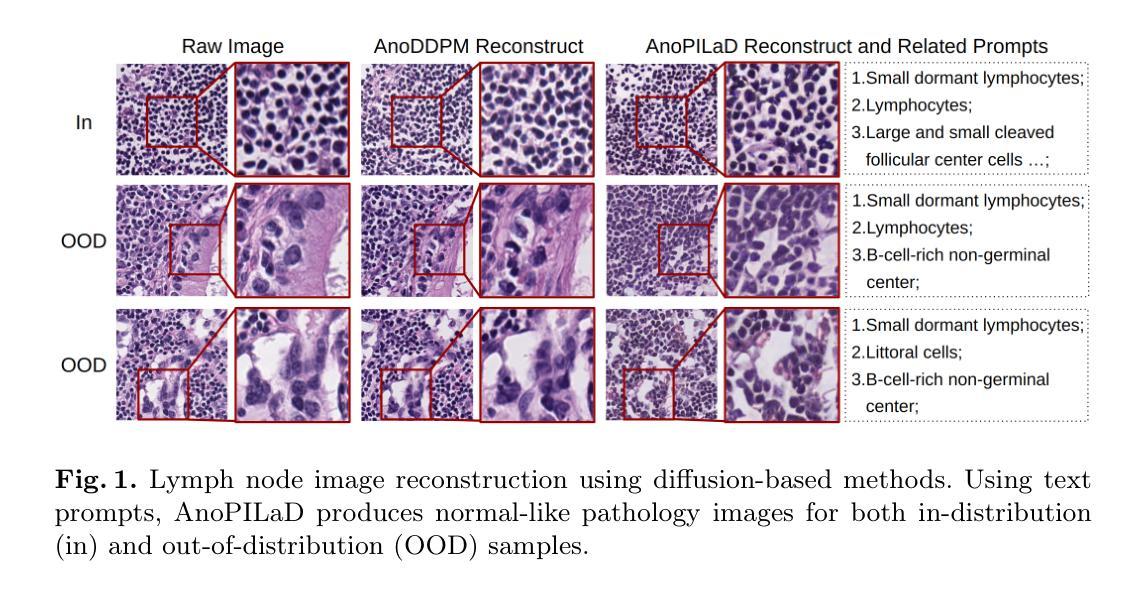
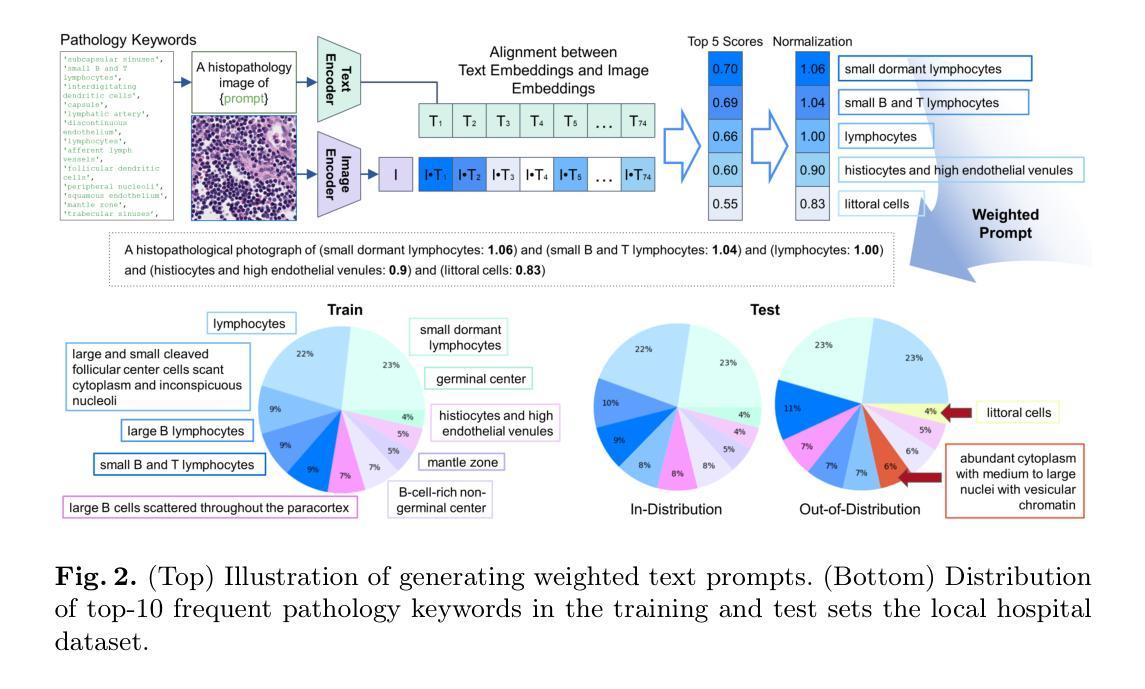
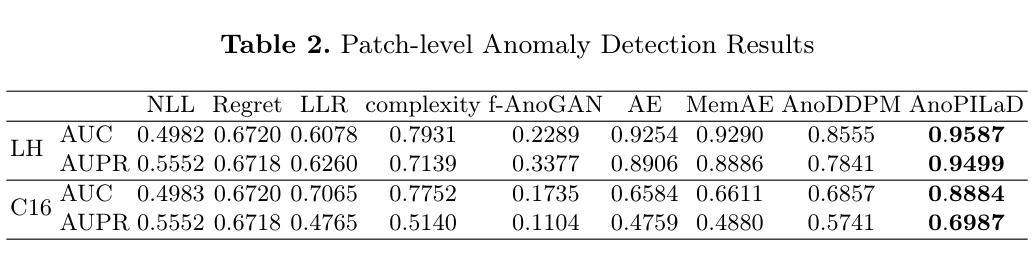
Anomaly detection is an emerging approach in digital pathology for its ability to efficiently and effectively utilize data for disease diagnosis. While supervised learning approaches deliver high accuracy, they rely on extensively annotated datasets, suffering from data scarcity in digital pathology. Unsupervised anomaly detection, however, offers a viable alternative by identifying deviations from normal tissue distributions without requiring exhaustive annotations. Recently, denoising diffusion probabilistic models have gained popularity in unsupervised anomaly detection, achieving promising performance in both natural and medical imaging datasets. Building on this, we incorporate a vision-language model with a diffusion model for unsupervised anomaly detection in digital pathology, utilizing histopathology prompts during reconstruction. Our approach employs a set of pathology-related keywords associated with normal tissues to guide the reconstruction process, facilitating the differentiation between normal and abnormal tissues. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conduct experiments on a gastric lymph node dataset from a local hospital and assess its generalization ability under domain shift using a public breast lymph node dataset. The experimental results highlight the potential of the proposed method for unsupervised anomaly detection across various organs in digital pathology. Code: https://github.com/QuIIL/AnoPILaD.
异常检测是数字病理学中新兴的一种方法,因其能够高效且有效地利用数据进行疾病诊断。虽然监督学习方法提供了较高的准确性,但它们依赖于大量标注的数据集,而在数字病理学中存在着数据稀缺的问题。然而,无监督的异常检测提供了一种可行的替代方案,它可以通过识别正常组织分布中的偏差来进行异常检测,无需详尽的标注。最近,去噪扩散概率模型在无监督异常检测中获得了普及,在自然和医学成像数据集上都取得了有希望的性能。在此基础上,我们将视觉语言模型与扩散模型相结合,用于数字病理中的无监督异常检测,并在重建过程中利用病理提示。我们的方法采用与正常组织相关的一组病理学关键词来引导重建过程,有助于区分正常组织和异常组织。为了评估所提出方法的有效性,我们在当地医院的胃淋巴结数据集上进行了实验,并使用公共的乳腺淋巴结数据集来评估其在域变化下的泛化能力。实验结果突出了所提出方法在数字病理学中各种器官的无监督异常检测的潜力。代码:https://github.com/QuIIL/AnoPILaD。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
融合无监督异常检测与病理视觉语言模型的方法,用于数字病理学中的异常检测。通过引入扩散模型并利用组织正常相关的关键词引导重建过程,提高了正常与异常组织的区分能力。实验证明该方法在本地医院胃癌淋巴结数据集上表现良好,并在公开乳房淋巴结数据集上展示了对不同器官的潜在泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 异常检测是数字病理学中的新兴方法,旨在有效利用数据用于疾病诊断。
- 监督学习方法虽准确但依赖大量标注数据,在无标注数据的情况下表现不佳。
- 无监督异常检测通过识别正常组织分布的偏差来识别异常,无需详尽标注。
- 扩散概率模型在异常检测中表现优异,已应用于自然和医学影像数据集。
- 结合视觉语言模型与扩散模型用于数字病理学中的无监督异常检测。
- 利用组织正常的关键词引导重建过程,有助于区分正常与异常组织。
点此查看论文截图


XDR-LVLM: An Explainable Vision-Language Large Model for Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis
Authors:Masato Ito, Kaito Tanaka, Keisuke Matsuda, Aya Nakayama
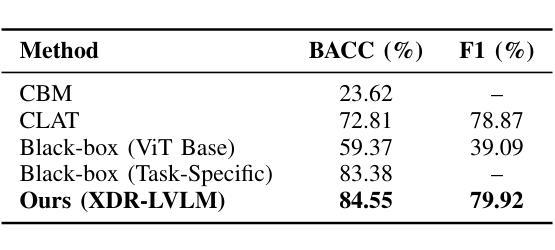
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a major cause of global blindness, necessitating early and accurate diagnosis. While deep learning models have shown promise in DR detection, their black-box nature often hinders clinical adoption due to a lack of transparency and interpretability. To address this, we propose XDR-LVLM (eXplainable Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis with LVLM), a novel framework that leverages Vision-Language Large Models (LVLMs) for high-precision DR diagnosis coupled with natural language-based explanations. XDR-LVLM integrates a specialized Medical Vision Encoder, an LVLM Core, and employs Multi-task Prompt Engineering and Multi-stage Fine-tuning to deeply understand pathological features within fundus images and generate comprehensive diagnostic reports. These reports explicitly include DR severity grading, identification of key pathological concepts (e.g., hemorrhages, exudates, microaneurysms), and detailed explanations linking observed features to the diagnosis. Extensive experiments on the Diabetic Retinopathy (DDR) dataset demonstrate that XDR-LVLM achieves state-of-the-art performance, with a Balanced Accuracy of 84.55% and an F1 Score of 79.92% for disease diagnosis, and superior results for concept detection (77.95% BACC, 66.88% F1). Furthermore, human evaluations confirm the high fluency, accuracy, and clinical utility of the generated explanations, showcasing XDR-LVLM’s ability to bridge the gap between automated diagnosis and clinical needs by providing robust and interpretable insights.
糖尿病视网膜病变(DR)是全球失明的主要原因之一,因此需要进行早期和准确的诊断。深度学习模型在DR检测方面显示出巨大的潜力,但由于其黑箱性质导致的缺乏透明度和可解释性,常常阻碍其在临床上的采纳。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了XDR-LVLM(利用LVLM进行可解释的糖尿病视网膜病变诊断),这是一个新型框架,利用视觉语言大模型(LVLMs)进行高精度的DR诊断,同时通过自然语言提供解释。XDR-LVLM集成了一个专业的医学视觉编码器、LVLM核心,并采用多任务提示工程和分阶段微调,以深入理解眼底图像中的病理特征,并生成全面的诊断报告。这些报告明确包括DR严重程度分级、关键病理概念(例如出血、渗出、微动脉瘤)的识别,以及将观察到的特征与诊断结果相联系的具体解释。在糖尿病视网膜病变(DDR)数据集上的大量实验表明,XDR-LVLM达到了最先进的性能,平衡准确率为84.55%,疾病诊断的F1分数为79.92%,概念检测的BACC为77.95%,F1分数为66.88%。此外,人类评估证实了生成的解释的高度流畅性、准确性和临床实用性,展示了XDR-LVLM通过提供稳健且可解释的观点来弥合自动化诊断和临床需求之间的差距的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
DR是一种全球主要的失明原因,需要早期和准确的诊断。为解决深度学习模型在DR检测中的不透明和不可解释性,我们提出了XDR-LVLM框架,该框架利用视觉语言大模型(LVLMs)进行高精度DR诊断,同时通过自然语言生成解释。XDR-LVLM集成了医学视觉编码器、LVLM核心,并采用多任务提示工程和分阶段微调技术,深入理解眼底图像的病理特征,生成包含DR严重程度分级、关键病理概念识别(如出血、渗出物、微动脉瘤等)以及诊断详细解释的综合诊断报告。在糖尿病视网膜病变(DDR)数据集上的实验表明,XDR-LVLM取得了最先进的性能,平衡准确率为84.55%,疾病诊断的F1分数为79.92%,概念检测的BACC为77.95%,F1分数为66.88%。此外,人类评估证实了生成的解释的高度流畅性、准确性和临床实用性,展示了XDR-LVLM在提供强大和可解释洞察力方面的能力,缩小了自动化诊断和临床需求之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- DR是全球主要的失明原因之一,需要早期和准确的诊断。
- 深度学习模型在DR检测中具有潜力,但其黑箱性质阻碍了临床采纳。
- XDR-LVLM框架利用视觉语言大模型(LVLMs)进行高精度DR诊断,并结合自然语言解释。
- XDR-LVLM集成了医学视觉编码器、LVLM核心,采用多任务提示工程和分阶段微调技术。
- XDR-LVLM能够生成包含DR严重程度分级、关键病理概念识别以及诊断详细解释的综合诊断报告。
- 在DDR数据集上的实验表明,XDR-LVLM取得了先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

DictAS: A Framework for Class-Generalizable Few-Shot Anomaly Segmentation via Dictionary Lookup
Authors:Zhen Qu, Xian Tao, Xinyi Gong, ShiChen Qu, Xiaopei Zhang, Xingang Wang, Fei Shen, Zhengtao Zhang, Mukesh Prasad, Guiguang Ding
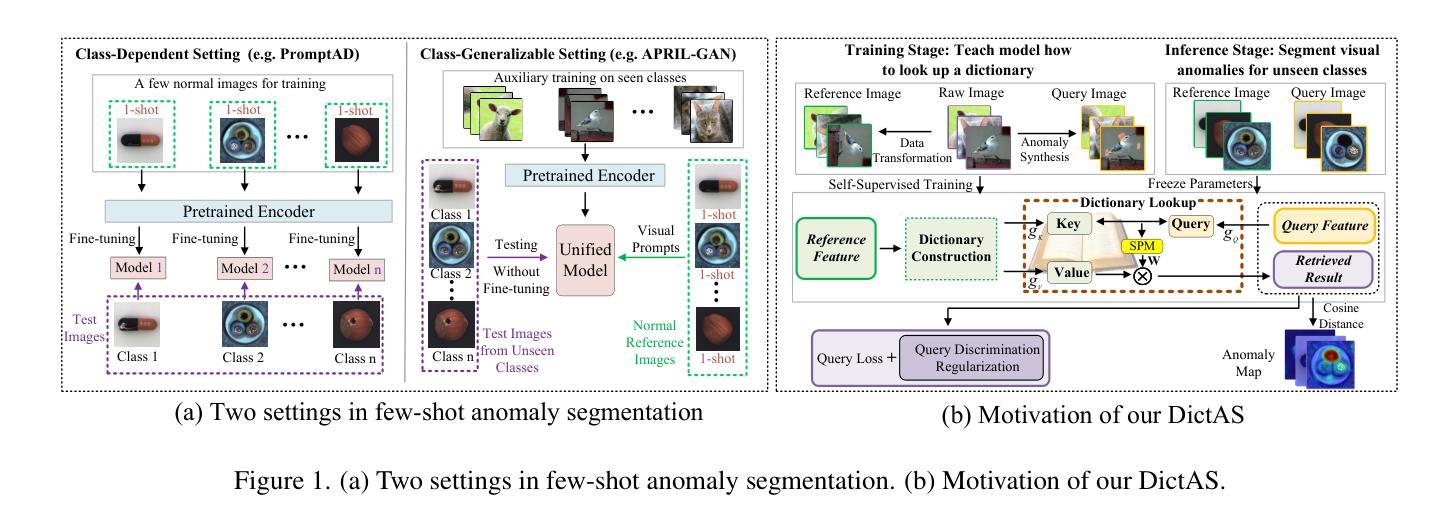
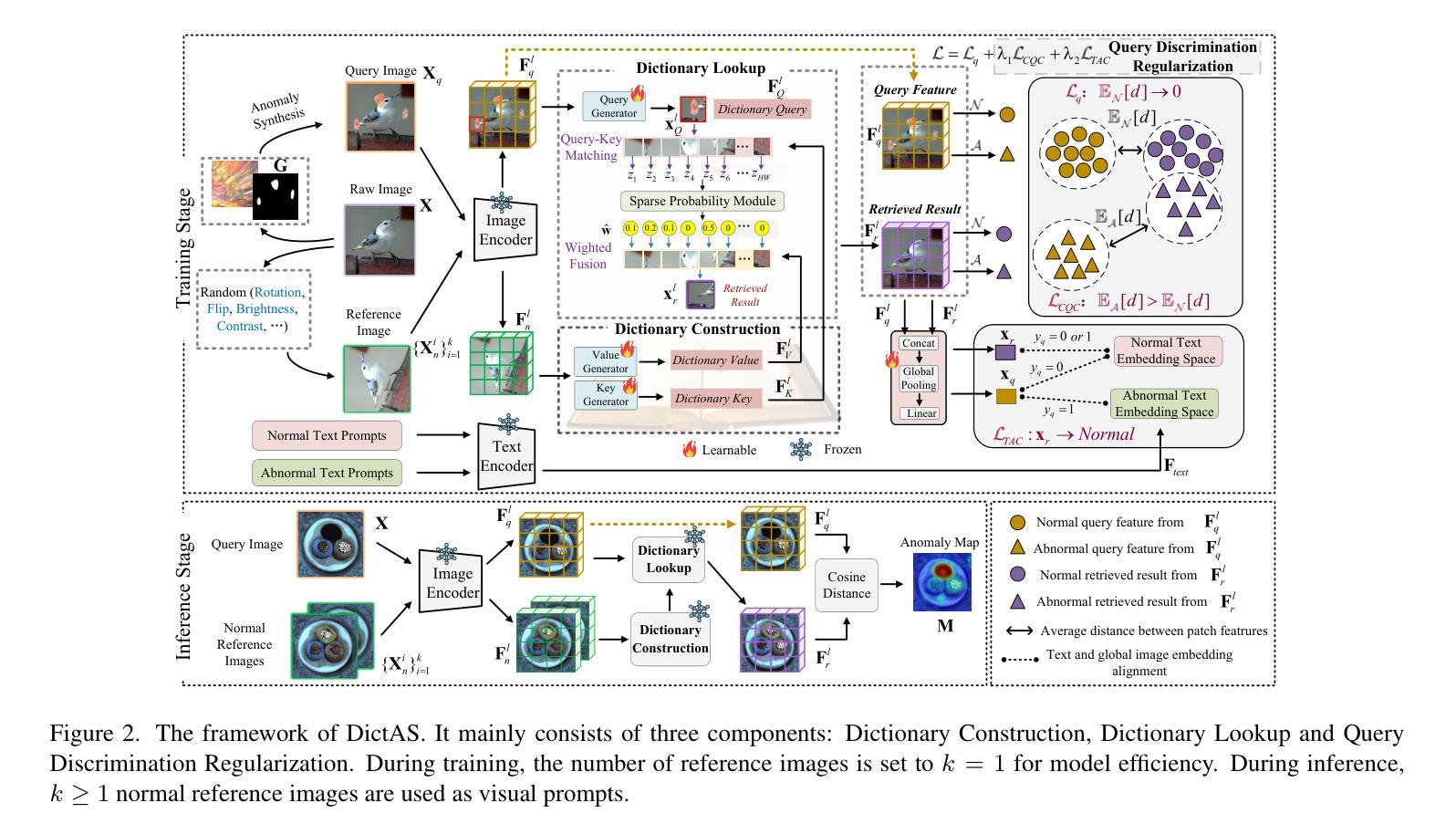
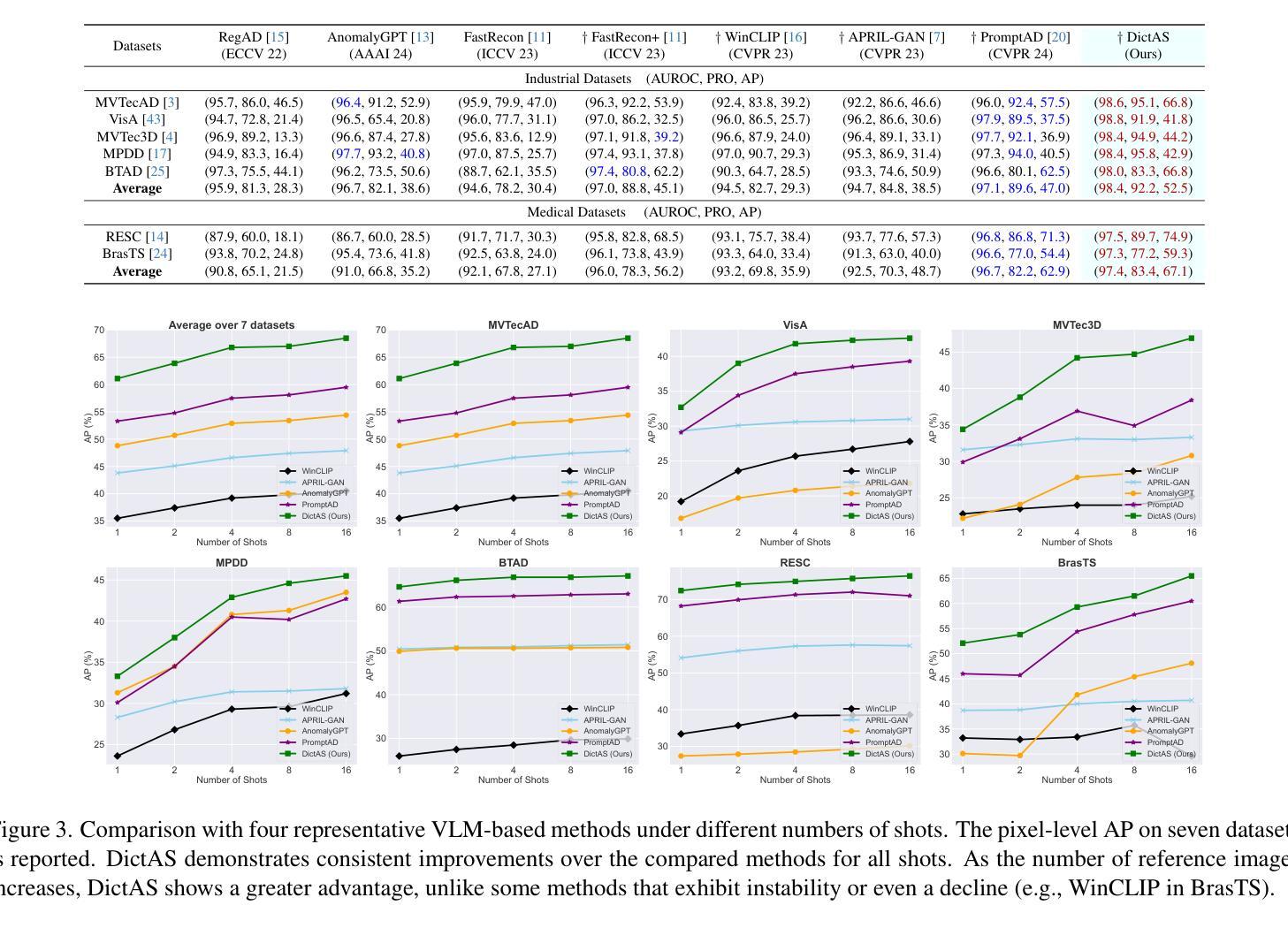
Recent vision-language models (e.g., CLIP) have demonstrated remarkable class-generalizable ability to unseen classes in few-shot anomaly segmentation (FSAS), leveraging supervised prompt learning or fine-tuning on seen classes. However, their cross-category generalization largely depends on prior knowledge of real seen anomaly samples. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, namely DictAS, which enables a unified model to detect visual anomalies in unseen object categories without any retraining on the target data, only employing a few normal reference images as visual prompts. The insight behind DictAS is to transfer dictionary lookup capabilities to the FSAS task for unseen classes via self-supervised learning, instead of merely memorizing the normal and abnormal feature patterns from the training set. Specifically, DictAS mainly consists of three components: (1) Dictionary Construction - to simulate the index and content of a real dictionary using features from normal reference images. (2) Dictionary Lookup - to retrieve queried region features from the dictionary via a sparse lookup strategy. When a query feature cannot be retrieved, it is classified as an anomaly. (3) Query Discrimination Regularization - to enhance anomaly discrimination by making abnormal features harder to retrieve from the dictionary. To achieve this, Contrastive Query Constraint and Text Alignment Constraint are further proposed. Extensive experiments on seven public industrial and medical datasets demonstrate that DictAS consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FSAS methods.
最近,视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在少数异常分割(FSAS)中展示了对于未见类别的显著类泛化能力,这利用了可见类别的监督提示学习或微调。然而,它们的跨类别泛化在很大程度上依赖于真实可见异常样本的先验知识。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型框架,名为DictAS,它能够在未见对象类别中检测视觉异常,而无需对目标数据进行任何重新训练,仅使用少量正常参考图像作为视觉提示。DictAS的见解是通过自我监督学习将字典查找能力转移到未见类别的FSAS任务上,而不是仅仅从训练集中记忆正常和异常的特征模式。具体来说,DictAS主要由三个部分组成:(1)字典构建——使用正常参考图像的特征模拟真实字典的索引和内容。(2)字典查找——通过稀疏查找策略从字典中检索查询区域特征。当无法检索查询特征时,它会被归类为异常。(3)查询判别正则化——通过使异常特征更难从字典中检索来提高异常判别能力。为此,进一步提出了对比查询约束和文本对齐约束。在七个公共工业和医疗数据集上的大量实验表明,DictAS始终优于最新的FSAS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV 2025, Project: https://github.com/xiaozhen228/DictAS
Summary
基于视觉语言模型的异常分割方法通常依赖于对真实异常样本的先验知识。本文提出了一种名为DictAS的新框架,无需对目标数据进行任何重新训练,仅使用少数正常参考图像作为视觉提示,即可检测未见对象类别中的视觉异常。DictAS的主要思路是通过自监督学习,将字典查找能力转移到未见类别的少数镜头异常分割任务上,而不是仅仅通过记忆训练集中的正常和异常特征模式来实现这一点。该框架包含字典构建、字典查找和查询辨别正则化三个主要组成部分。该方法的性能在一系列公共工业医疗数据集上得到了验证,并表现出优于现有少数镜头异常分割方法的一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 少数镜头异常分割任务中的视觉语言模型通常依赖真实异常样本的先验知识。
- 提出了一种新的框架DictAS,能够在未见对象类别中检测视觉异常,无需对目标数据进行重新训练。
- DictAS利用正常参考图像作为视觉提示,通过自监督学习实现字典查找能力。
- DictAS主要包含字典构建、字典查找和查询辨别正则化三个组件。
- 对比查询约束和文本对齐约束进一步增强异常识别能力。
- 在多个公共工业医疗数据集上的实验验证了DictAS的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Vulnerabilities in AI-generated Image Detection: The Challenge of Adversarial Attacks
Authors:Yunfeng Diao, Naixin Zhai, Changtao Miao, Zitong Yu, Xingxing Wei, Xun Yang, Meng Wang
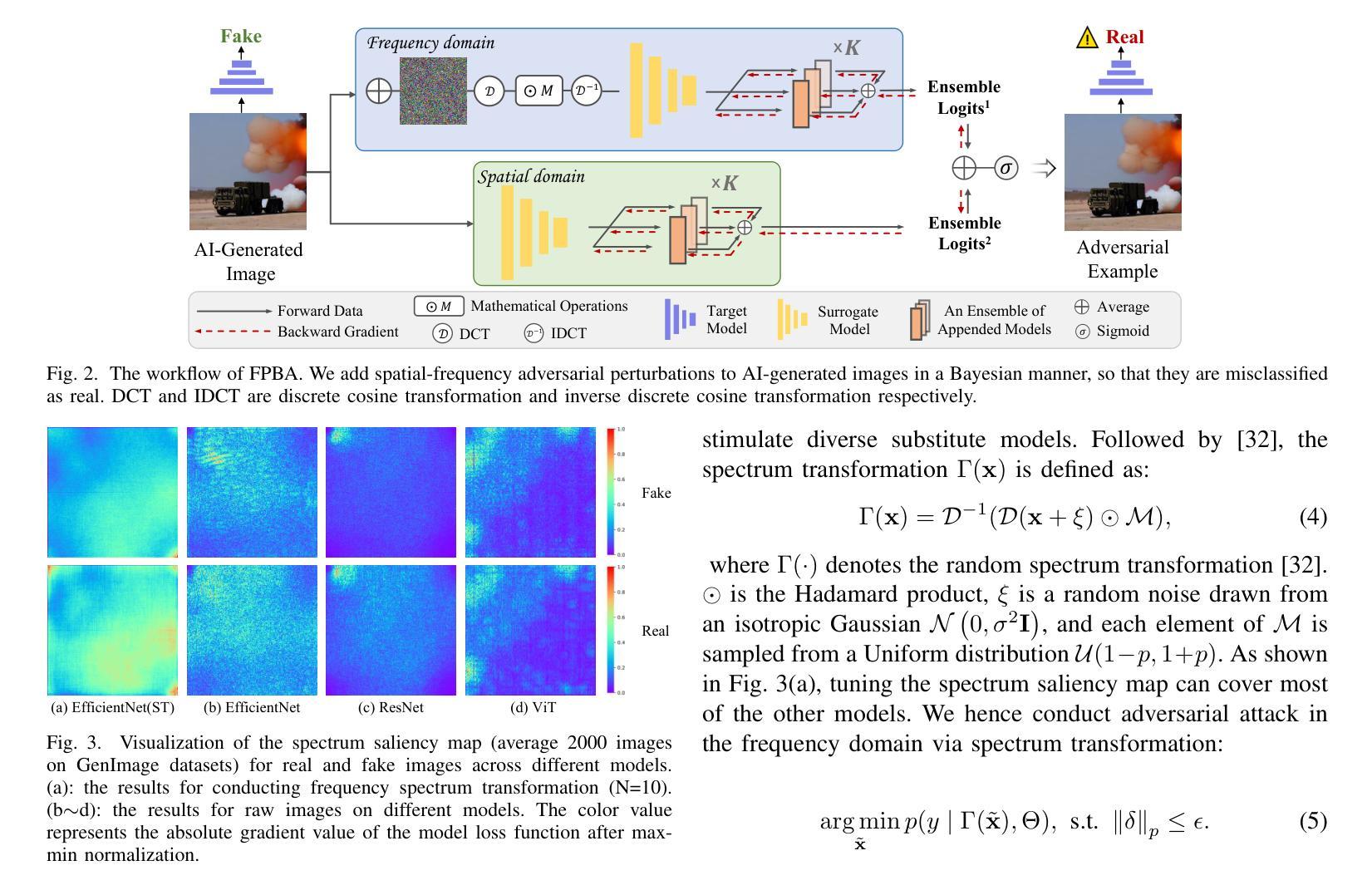
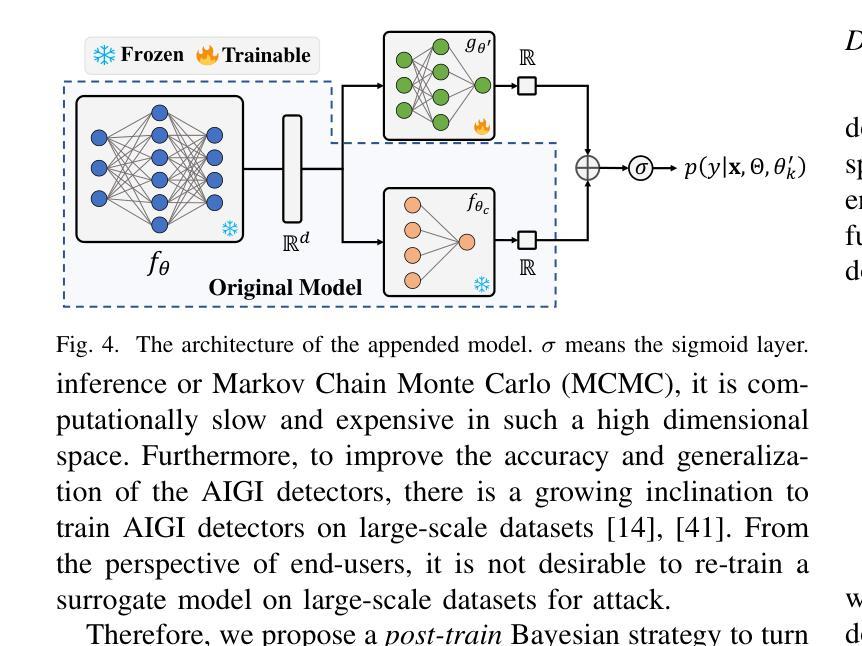
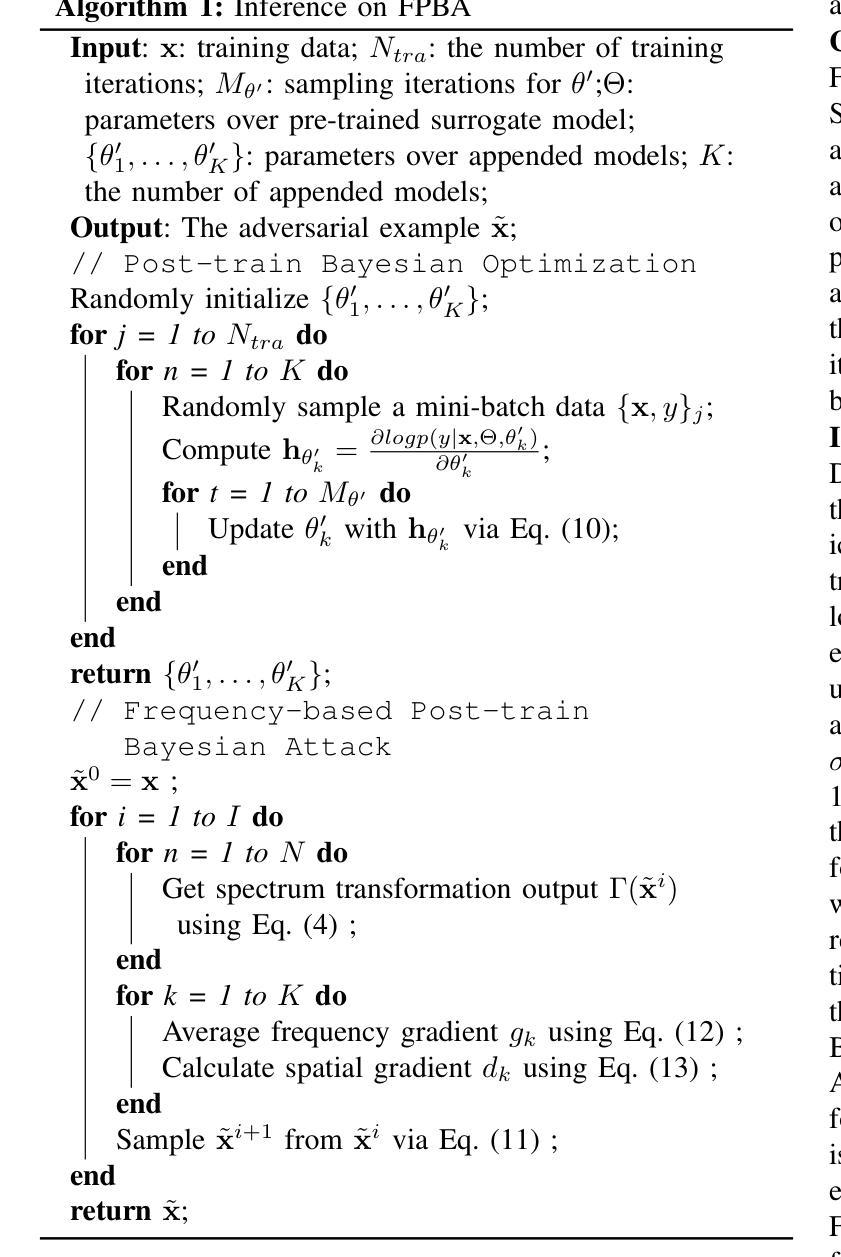
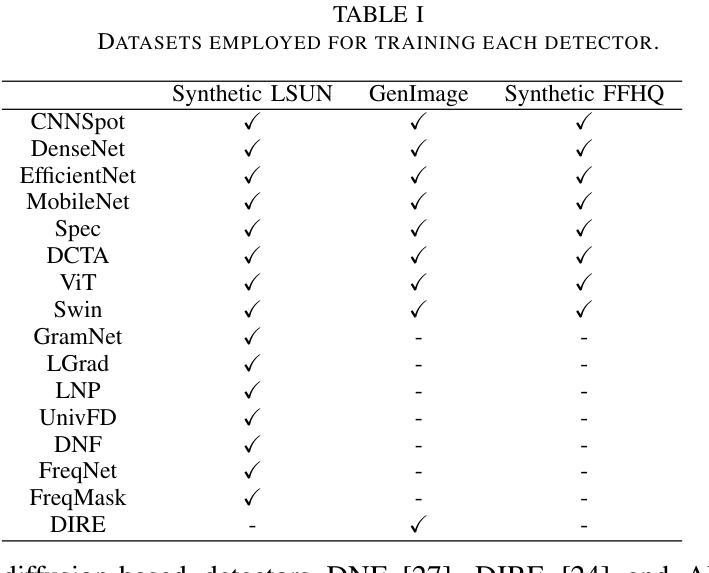
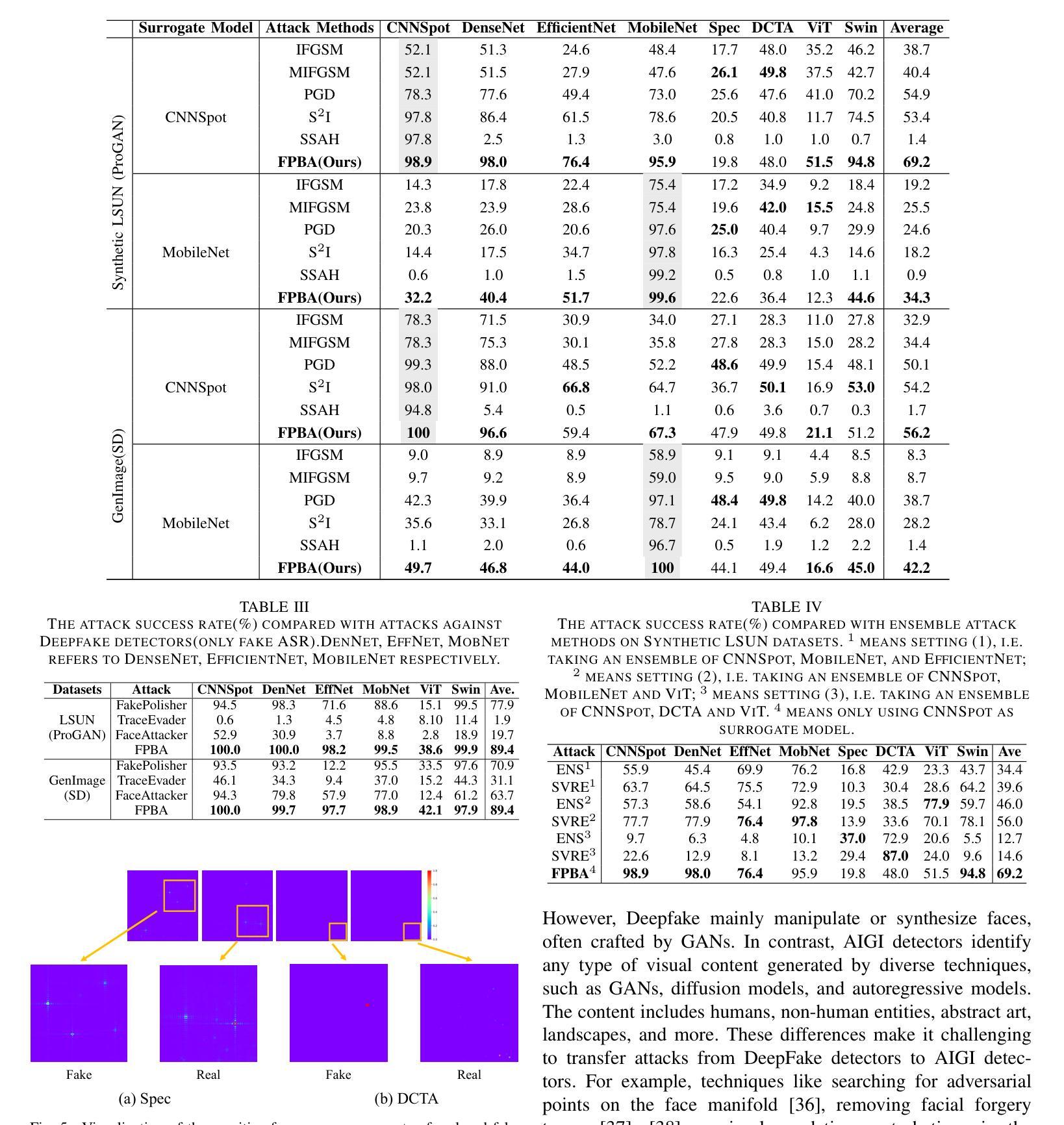
Recent advancements in image synthesis, particularly with the advent of GAN and Diffusion models, have amplified public concerns regarding the dissemination of disinformation. To address such concerns, numerous AI-generated Image (AIGI) Detectors have been proposed and achieved promising performance in identifying fake images. However, there still lacks a systematic understanding of the adversarial robustness of AIGI detectors. In this paper, we examine the vulnerability of state-of-the-art AIGI detectors against adversarial attack under white-box and black-box settings, which has been rarely investigated so far. To this end, we propose a new method to attack AIGI detectors. First, inspired by the obvious difference between real images and fake images in the frequency domain, we add perturbations under the frequency domain to push the image away from its original frequency distribution. Second, we explore the full posterior distribution of the surrogate model to further narrow this gap between heterogeneous AIGI detectors, e.g. transferring adversarial examples across CNNs and ViTs. This is achieved by introducing a novel post-train Bayesian strategy that turns a single surrogate into a Bayesian one, capable of simulating diverse victim models using one pre-trained surrogate, without the need for re-training. We name our method as Frequency-based Post-train Bayesian Attack, or FPBA. Through FPBA, we show that adversarial attack is truly a real threat to AIGI detectors, because FPBA can deliver successful black-box attacks across models, generators, defense methods, and even evade cross-generator detection, which is a crucial real-world detection scenario. The code will be shared upon acceptance.
近期图像合成领域的进展,特别是生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型的出现,加剧了公众对虚假信息传播问题的担忧。为了解决这些担忧,已经提出了许多人工智能生成图像(AIGI)检测器,并在识别虚假图像方面取得了令人鼓舞的性能。然而,目前对于AIGI检测器的对抗性稳健性还缺乏系统的理解。本文研究了最先进的AIGI检测器在白盒和黑盒设置下对抗攻击时的脆弱性,这一研究内容迄今为止很少被探索。为此,我们提出了一种新的方法来攻击AIGI检测器。首先,受真实图像和虚假图像在频域内明显差异的启发,我们在频域内添加扰动,使图像偏离其原始频率分布。其次,我们探索了替代模型的后验分布,以进一步缩小不同AIGI检测器之间的差距,例如将对抗性示例从CNN转移到ViTs。这是通过引入一种新的后训练贝叶斯策略实现的,它将单一的替代模型转变为贝叶斯模型,能够使用预先训练的替代模型模拟多种受害者模型,而无需重新训练。我们将我们的方法命名为基于频率的后训练贝叶斯攻击(FPBA)。通过FPBA,我们证明了对抗性攻击确实对AIGI检测器构成了真正的威胁,因为FPBA可以在不同模型、生成器、防御方法之间实现成功的黑盒攻击,甚至可以逃避跨生成器检测,这是现实世界中的关键检测场景。代码将在接受后共享。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
先进的图像合成技术引发公众对假信息传播问题的担忧,针对此,AI生成的图像检测器(AIGI)已被提出并展现出良好的性能。然而,关于其对抗鲁棒性的系统理解尚缺乏。本研究探讨了最先进的AIGI探测器在面对白盒和黑盒环境下的对抗攻击时的脆弱性。为此,我们提出了一种新的攻击AIGI检测器的方法——FPBA(基于频率的后训练贝叶斯攻击)。该方法通过模拟真实图像和假图像在频域上的差异,并利用后训练贝叶斯策略来模拟不同的受害者模型。研究结果表明,对抗性攻击对AIGI检测器的威胁真实存在,FPBA可以在不同的模型、生成器、防御方法和跨生成器检测场景中实现成功的黑盒攻击。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的图像合成技术引发公众对假图像传播的担忧,AI生成的图像检测器(AIGI)已展现出良好的性能。
- 目前缺乏对AIGI探测器对抗鲁棒性的系统理解。
- 本研究探讨了AIGI探测器在白盒和黑盒环境下的对抗攻击的脆弱性。
- 提出了一种新的攻击方法——FPBA(基于频率的后训练贝叶斯攻击)。
- FPBA利用真实和假图像在频域的差异,通过添加扰动使图像远离其原始频域分布。
- 后训练贝叶斯策略用于模拟不同的受害者模型,实现跨模型的攻击。
点此查看论文截图