⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-24 更新
Learning to Drive Ethically: Embedding Moral Reasoning into Autonomous Driving
Authors:Dianzhao Li, Ostap Okhrin
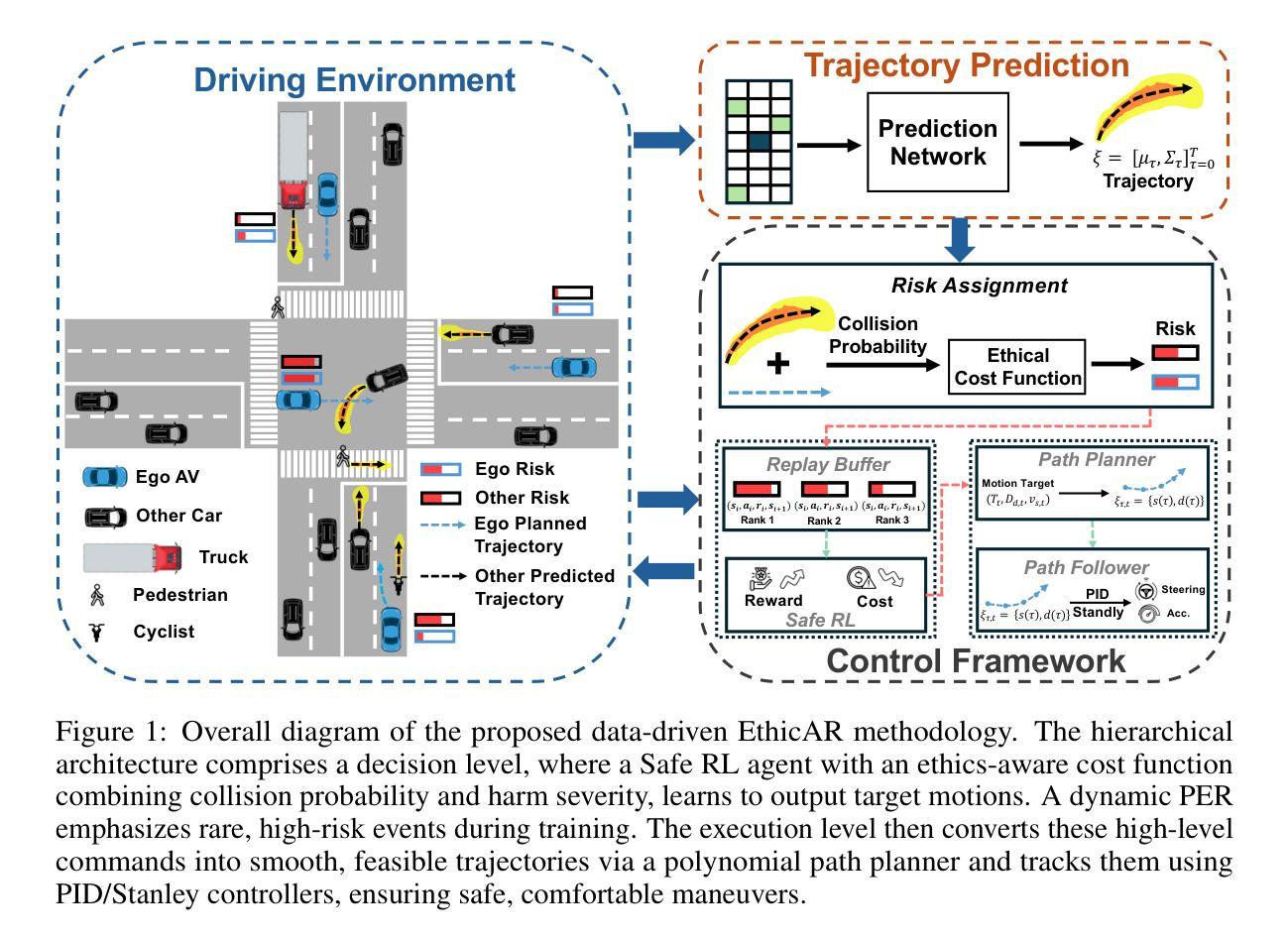
Autonomous vehicles hold great promise for reducing traffic fatalities and improving transportation efficiency, yet their widespread adoption hinges on embedding robust ethical reasoning into routine and emergency maneuvers. Here, we present a hierarchical Safe Reinforcement Learning (Safe RL) framework that explicitly integrates moral considerations with standard driving objectives. At the decision level, a Safe RL agent is trained using a composite ethical risk cost, combining collision probability and harm severity, to generate high-level motion targets. A dynamic Prioritized Experience Replay mechanism amplifies learning from rare but critical, high-risk events. At the execution level, polynomial path planning coupled with Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) and Stanley controllers translates these targets into smooth, feasible trajectories, ensuring both accuracy and comfort. We train and validate our approach on rich, real-world traffic datasets encompassing diverse vehicles, cyclists, and pedestrians, and demonstrate that it outperforms baseline methods in reducing ethical risk and maintaining driving performance. To our knowledge, this is the first study of ethical decision-making for autonomous vehicles via Safe RL in real-world scenarios. Our results highlight the potential of combining formal control theory and data-driven learning to advance ethically accountable autonomy in complex, human-mixed traffic environments.
自动驾驶汽车对于减少交通事故死亡人数、提高交通运输效率具有巨大潜力,然而其广泛采纳的关键在于将稳健的伦理推理嵌入到常规和紧急操作中。在此,我们提出了一种分层的安全强化学习(Safe RL)框架,该框架显式地将道德考量与标准驾驶目标相结合。在决策层面,Safe RL 代理通过使用组合的道德风险成本(结合碰撞概率和伤害严重程度)进行训练,以生成高级运动目标。动态优先经验回放机制放大了对罕见但关键的高风险事件的学习。在执行层面,通过多项式路径规划与比例积分微分(PID)和斯坦利控制器相结合,将这些目标转化为平稳且可行的轨迹,确保准确性和舒适性。我们在丰富的真实世界交通数据集上进行了训练和验证,该数据集涵盖了各种车辆、自行车和行人,并证明我们的方法在减少道德风险并保持驾驶性能方面优于基线方法。据我们所知,这是首个在现实世界中通过安全强化学习对自动驾驶汽车进行道德决策的研究。我们的结果突出了结合形式控制理论和数据驱动学习的潜力,有助于在复杂的人机混合交通环境中实现道德责任自主。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要通过结合标准驾驶目标与道德考量,提出了一种分层的Safe Reinforcement Learning(Safe RL)框架。该框架在决策层面使用复合道德风险成本进行培训,并结合碰撞概率和伤害严重程度来生成高级运动目标。在执行层面,通过多项式路径规划与PID和Stanley控制器,将目标转化为平稳、可行的轨迹,确保准确性和舒适性。在真实世界的丰富交通数据集上训练和验证该框架,表明其在减少道德风险和维护驾驶性能上优于基准方法。这是首个在真实场景中运用Safe RL进行自动驾驶道德决策的研究。结果展示了结合形式控制理论与数据驱动学习的潜力,有助于推进复杂混合交通环境中的道德自主驾驶。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶车辆需要嵌入稳健的道德推理以应对日常和紧急情况下的决策。
- 提出了分层的Safe Reinforcement Learning(Safe RL)框架,将道德考量与驾驶目标相结合。
- 在决策层面使用复合道德风险成本进行培训,考虑碰撞概率和伤害严重程度。
- 采用动态优先级经验回放机制,强化从高风险事件中学习的效果。
- 在执行层面,通过多项式路径规划结合PID和Stanley控制器,实现平稳、可行的轨迹规划。
- 在真实世界的交通数据集上进行了训练和验证,表明该框架在减少道德风险和保持驾驶性能上优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

FinAgentBench: A Benchmark Dataset for Agentic Retrieval in Financial Question Answering
Authors:Chanyeol Choi, Jihoon Kwon, Alejandro Lopez-Lira, Chaewoon Kim, Minjae Kim, Juneha Hwang, Jaeseon Ha, Hojun Choi, Suyeol Yun, Yongjin Kim, Yongjae Lee
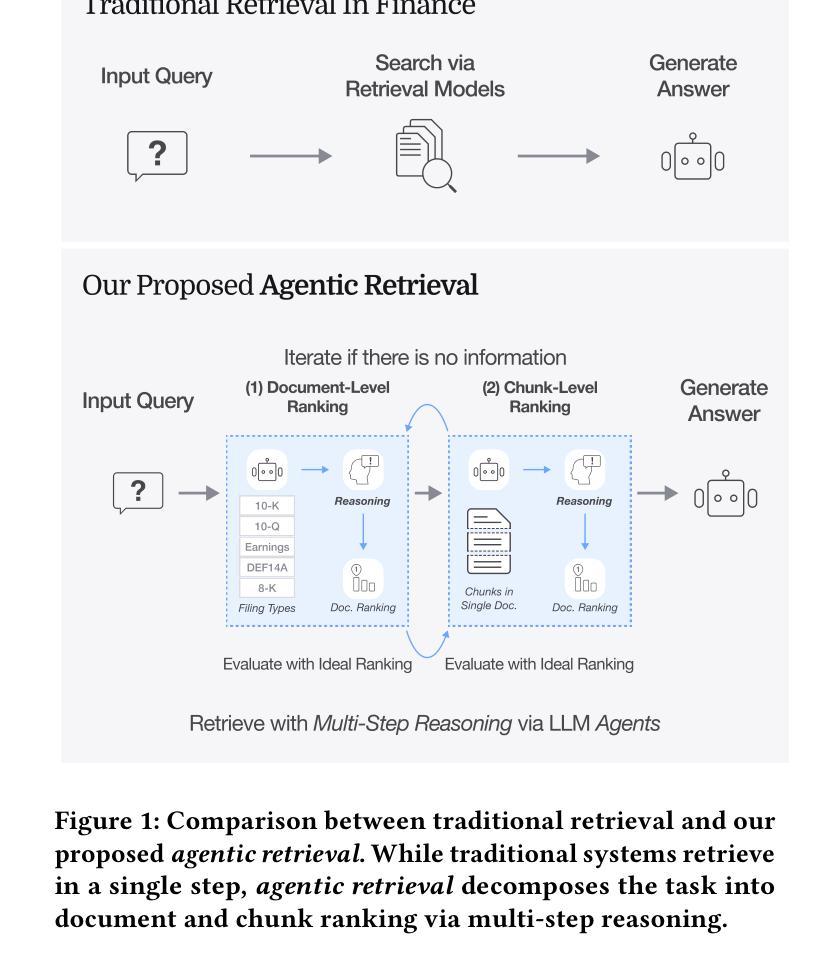
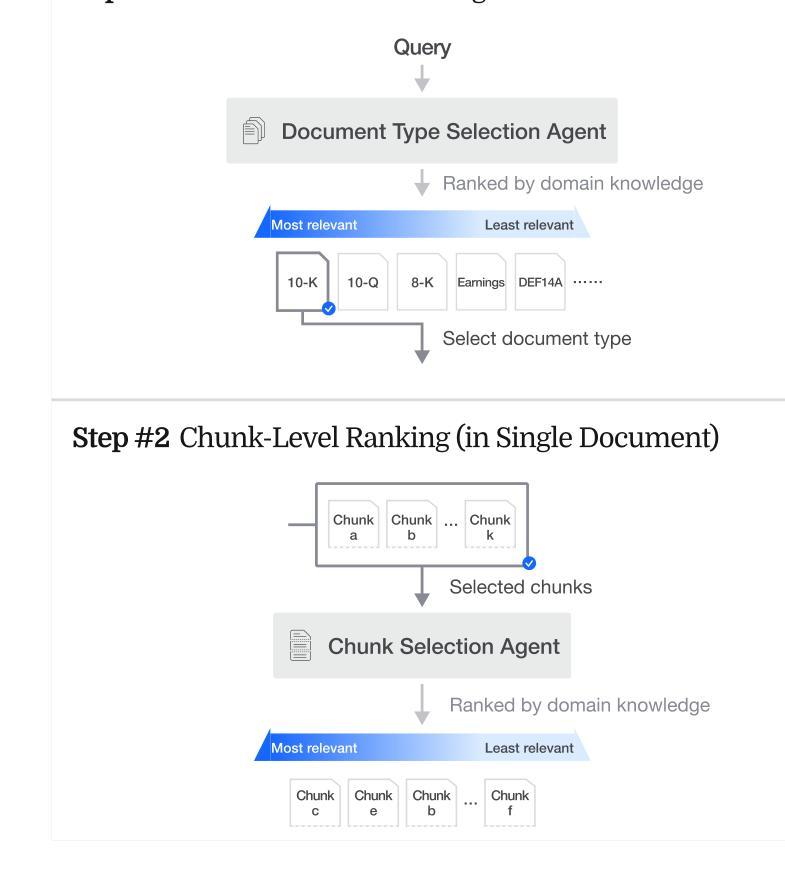
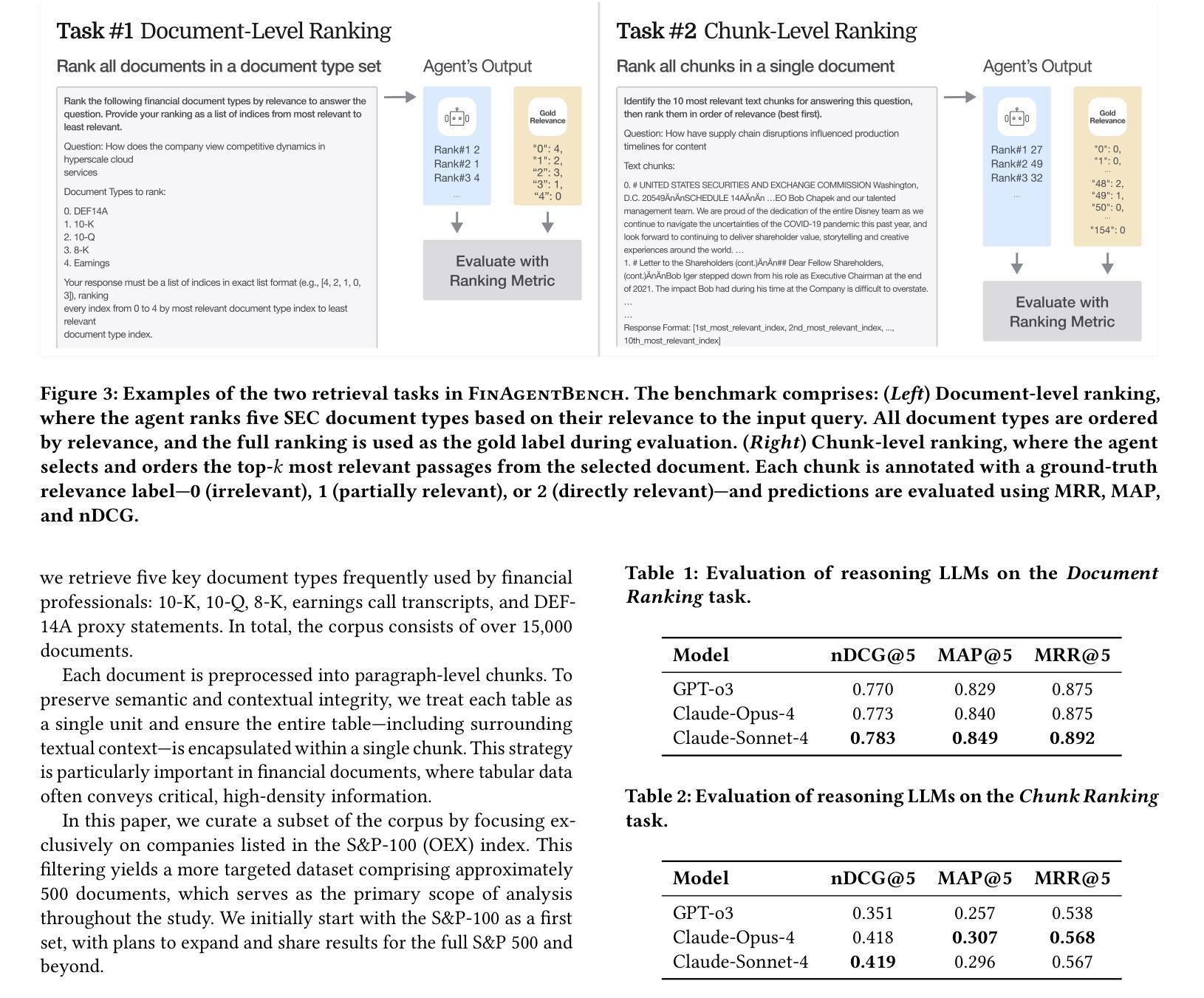
Accurate information retrieval (IR) is critical in the financial domain, where investors must identify relevant information from large collections of documents. Traditional IR methods-whether sparse or dense-often fall short in retrieval accuracy, as it requires not only capturing semantic similarity but also performing fine-grained reasoning over document structure and domain-specific knowledge. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have opened up new opportunities for retrieval with multi-step reasoning, where the model ranks passages through iterative reasoning about which information is most relevant to a given query. However, there exists no benchmark to evaluate such capabilities in the financial domain. To address this gap, we introduce FinAgentBench, the first large-scale benchmark for evaluating retrieval with multi-step reasoning in finance – a setting we term agentic retrieval. The benchmark consists of 3,429 expert-annotated examples on S&P-100 listed firms and assesses whether LLM agents can (1) identify the most relevant document type among candidates, and (2) pinpoint the key passage within the selected document. Our evaluation framework explicitly separates these two reasoning steps to address context limitations. This design enables to provide a quantitative basis for understanding retrieval-centric LLM behavior in finance. We evaluate a suite of state-of-the-art models and further demonstrated how targeted fine-tuning can significantly improve agentic retrieval performance. Our benchmark provides a foundation for studying retrieval-centric LLM behavior in complex, domain-specific tasks for finance. We will release the dataset publicly upon acceptance of the paper and plan to expand and share dataset for the full S&P 500 and beyond.
准确的情报检索(IR)在金融领域至关重要,投资者必须从大文档集合中识别出相关信息。传统的IR方法,无论是稀疏的还是密集的,往往在检索准确性方面表现不足,因为它不仅需要捕捉语义相似性,还需要对文档结构和特定领域的知识进行精细的推理。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为具有多步推理的检索提供了新的机会,该模型通过关于哪些信息对给定查询最相关的迭代推理来排名段落。然而,金融领域还没有评估这种能力的基准测试。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了FinAgentBench,这是第一个用于评估金融领域中具有多步推理的检索的大型基准测试——我们称之为代理检索。该基准测试包含3429个关于标普100指数上市公司的专家注释示例,并评估LLM代理是否能(1)在候选者中识别出最相关的文档类型,以及(2)在所选文档中定位关键段落。我们的评估框架明确地将这两个推理步骤分开,以解决上下文限制的问题。这种设计有助于为理解金融领域中以检索为中心的LLM行为提供定量依据。我们评估了一系列最先进的模型,并进一步展示了有针对性的微调如何显着提高代理检索性能。我们的基准测试为研究复杂、特定领域的任务中金融领域的LLM行为提供了基础。论文接受后,我们将公开发布数据集,并计划扩展和共享整个标普500及以外的数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
该文本介绍了金融领域准确信息检索的重要性,并指出了传统信息检索方法的不足。最近的大型语言模型技术为具有多步骤推理的检索提供了新的机会。然而,金融领域缺乏相应的基准测试来评估这种能力。为了解决这一空白,文中介绍了一个新基准测试FinAgentBench,它是用于评估金融领域中具有多步骤推理的检索能力的首个大规模基准测试。该基准测试包含3429个针对标普100指数上市公司的专家注释示例,并评估大型语言模型代理是否能识别最相关的文档类型并在所选文档中定位关键段落。评价框架明确地将这两个推理步骤分开,以解决上下文限制问题。这将为理解针对金融复杂任务的检索为中心的大型语言模型行为提供定量依据。
Key Takeaways
- 金融领域的信息检索至关重要,对投资者的决策产生直接影响。
- 传统信息检索方法存在不足,无法准确捕捉语义相似性和进行精细的文档结构和领域知识推理。
- 大型语言模型技术的发展为具有多步骤推理的检索提供了新的可能性。
- 缺乏金融领域评估多步骤推理能力的基准测试。
- FinAgentBench是首个用于评估金融领域中代理式信息检索能力的基准测试,包含大量专家标注的示例。
- 该基准测试评估大型语言模型是否能识别最相关的文档类型并在所选文档中定位关键段落。
点此查看论文截图

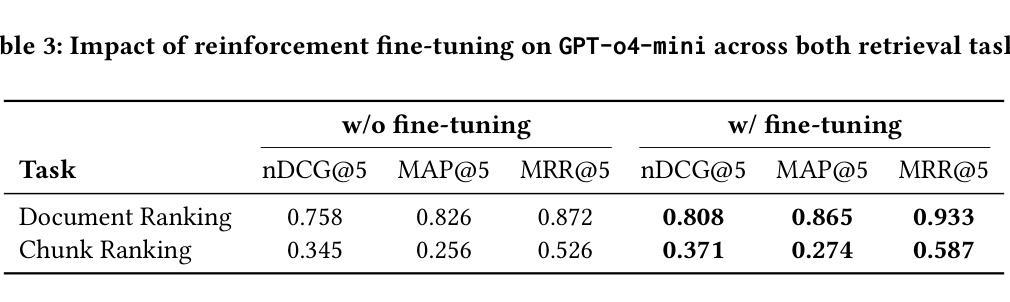
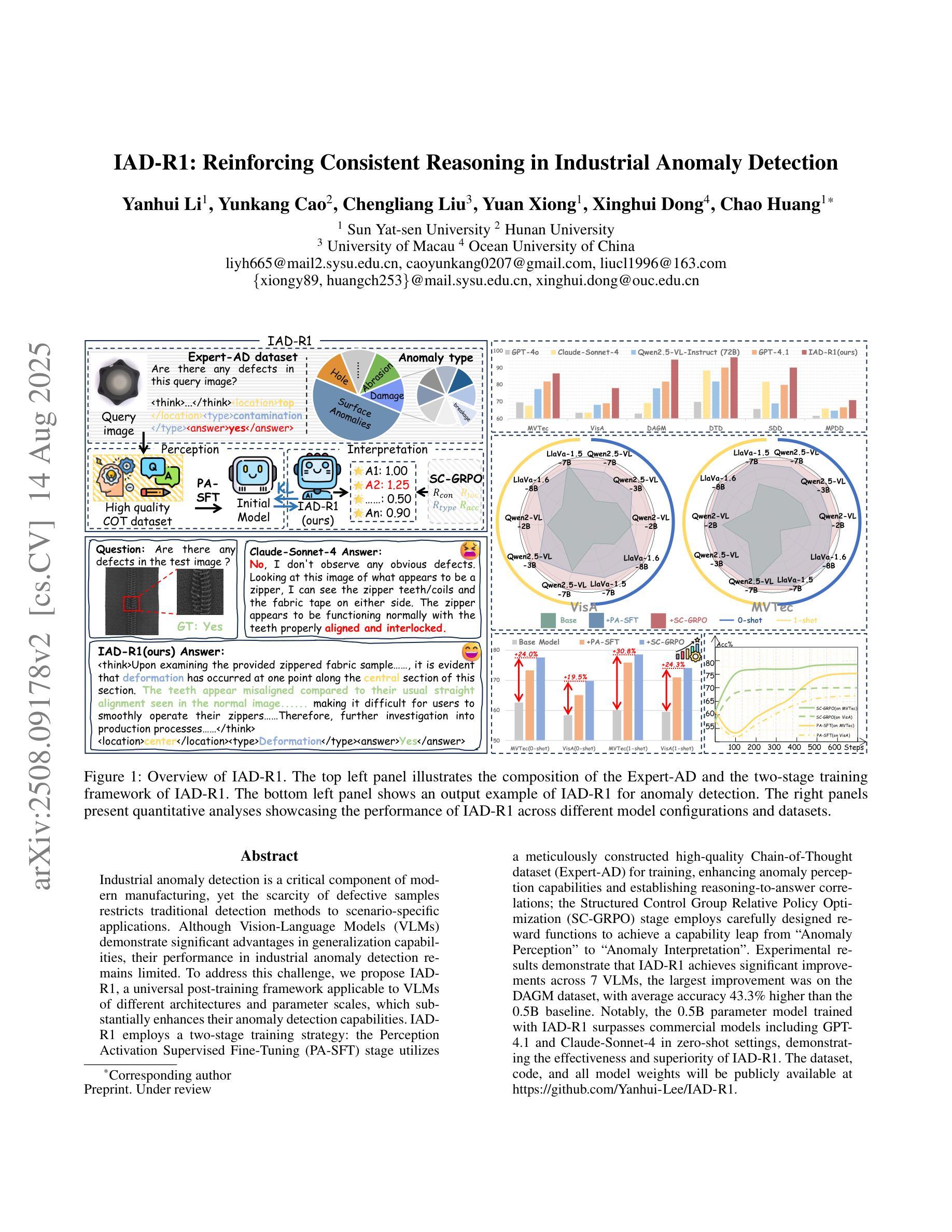
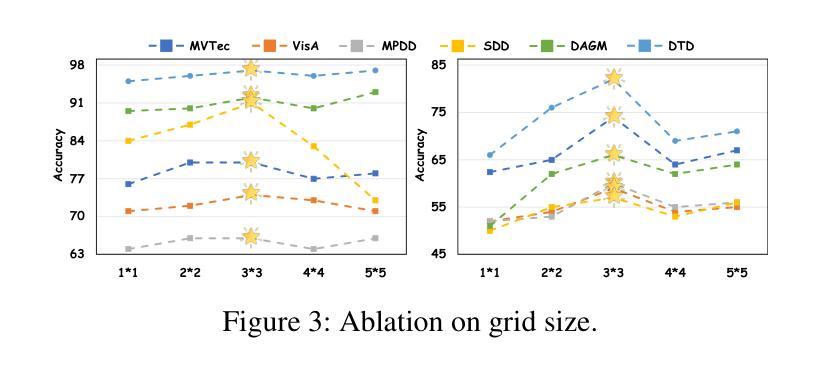
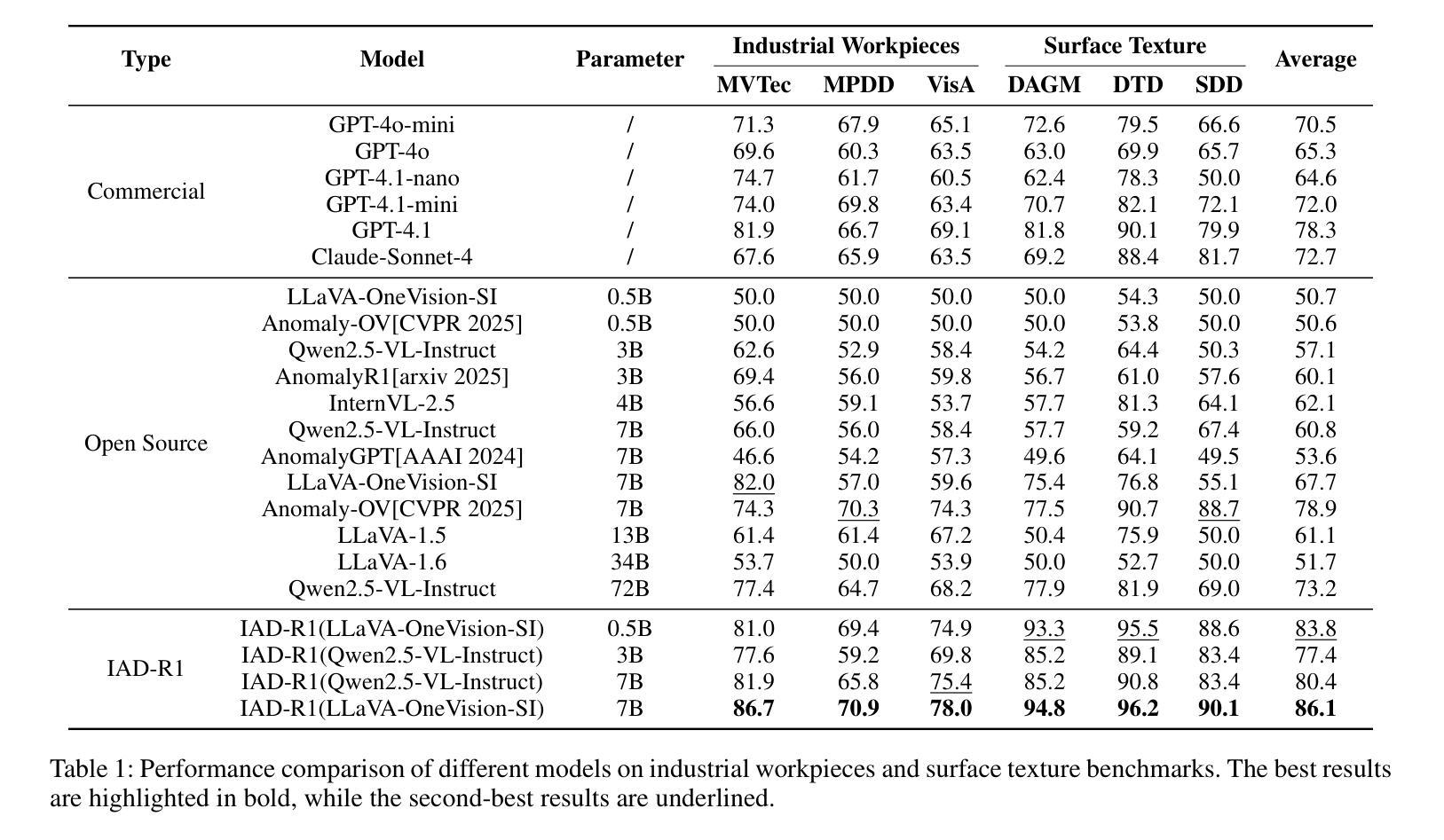
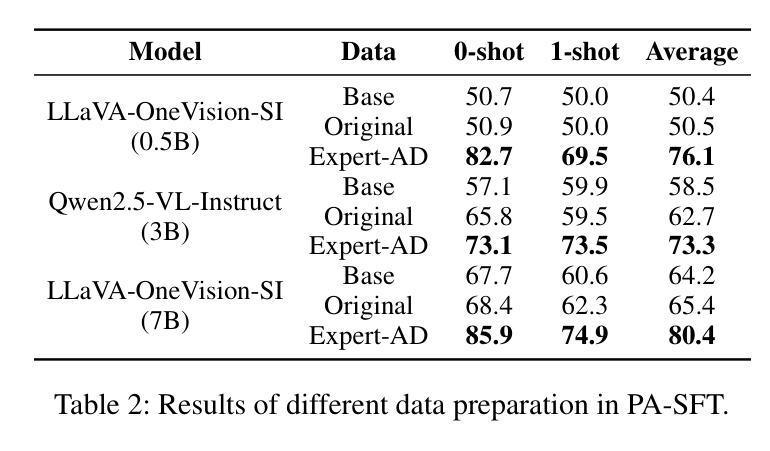
IAD-R1: Reinforcing Consistent Reasoning in Industrial Anomaly Detection
Authors:Yanhui Li, Yunkang Cao, Chengliang Liu, Yuan Xiong, Xinghui Dong, Chao Huang
Industrial anomaly detection is a critical component of modern manufacturing, yet the scarcity of defective samples restricts traditional detection methods to scenario-specific applications. Although Vision-Language Models (VLMs) demonstrate significant advantages in generalization capabilities, their performance in industrial anomaly detection remains limited. To address this challenge, we propose IAD-R1, a universal post-training framework applicable to VLMs of different architectures and parameter scales, which substantially enhances their anomaly detection capabilities. IAD-R1 employs a two-stage training strategy: the Perception Activation Supervised Fine-Tuning (PA-SFT) stage utilizes a meticulously constructed high-quality Chain-of-Thought dataset (Expert-AD) for training, enhancing anomaly perception capabilities and establishing reasoning-to-answer correlations; the Structured Control Group Relative Policy Optimization (SC-GRPO) stage employs carefully designed reward functions to achieve a capability leap from “Anomaly Perception” to “Anomaly Interpretation”. Experimental results demonstrate that IAD-R1 achieves significant improvements across 7 VLMs, the largest improvement was on the DAGM dataset, with average accuracy 43.3% higher than the 0.5B baseline. Notably, the 0.5B parameter model trained with IAD-R1 surpasses commercial models including GPT-4.1 and Claude-Sonnet-4 in zero-shot settings, demonstrating the effectiveness and superiority of IAD-R1. The dataset, code, and all model weights will be publicly available at https://github.com/Yanhui-Lee/IAD-R1.
工业异常检测是现代制造业的重要组成部分,但由于缺陷样本的稀缺性,传统的检测方法只能应用于特定场景。尽管视觉语言模型(VLMs)在通用化能力方面显示出显著优势,但在工业异常检测方面的性能仍然有限。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了IAD-R1,这是一个适用于不同架构和参数规模的VLMs的通用后训练框架,能大幅提升其异常检测能力。IAD-R1采用两阶段训练策略:感知激活监督微调(PA-SFT)阶段利用精心构建的高质量思维链数据集(Expert-AD)进行训练,增强异常感知能力并建立推理到答案的关联;结构化对照组相对策略优化(SC-GRPO)阶段采用精心设计的奖励函数,实现从“异常感知”到“异常解读”的能力飞跃。实验结果表明,IAD-R1在7种VLMs上取得了显著改进,其中在DAGM数据集上的改进最大,平均精度比0.5B基线高出43.3%。值得注意的是,使用IAD-R1训练的0. for public access at https://github.com/Yanhui-Lee/IAD-R1.(公开地址:https://github.com/Yanhui-Lee/IAD-R1)。所有数据集、代码和模型权重均可在此处公开访问。)值得注意的是,使用IAD-R1训练的0.5B参数模型在零样本设置下超越了包括GPT-4.1和Claude-Sonnet-4在内的商业模型,这证明了IAD-R1的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
工业异常检测是现代制造业的关键部分,但由于缺陷样本的稀缺性,传统检测方法的通用性受限。为应对挑战,提出IAD-R1,一个适用于不同架构和参数规模的视觉语言模型的通用后训练框架,显著提升了异常检测能力。IAD-R1采用两阶段训练策略:利用高质量Chain-of-Thought数据集进行感知激活监督微调,建立推理到答案的关联;通过精心设计的奖励函数实现控制组的相对策略优化,实现从“异常感知”到“异常解读”的能力跃升。实验结果显示,IAD-R1在7种视觉语言模型上取得显著改进,其中在DAGM数据集上的平均准确率较基线模型提高43.3%,且0.5B参数模型经IAD-R1训练后,在零样本设置下超越GPT-4.1和Claude-Sonnet-4等商业模型。
Key Takeaways
- 工业异常检测是现代制造业的重要部分,但传统方法受限于缺陷样本的稀缺性。
- VLMs在异常检测中虽具优势,但性能仍有局限。
- 提出IAD-R1框架,适用于不同VLMs,显著增强异常检测能力。
- IAD-R1采用两阶段训练策略:感知激活监督微调与结构化控制组相对策略优化。
- 利用高质量Chain-of-Thought数据集建立推理到答案的关联。
- 实验结果显示IAD-R1在多个数据集上表现优异,特别是在DAGM数据集上。
点此查看论文截图
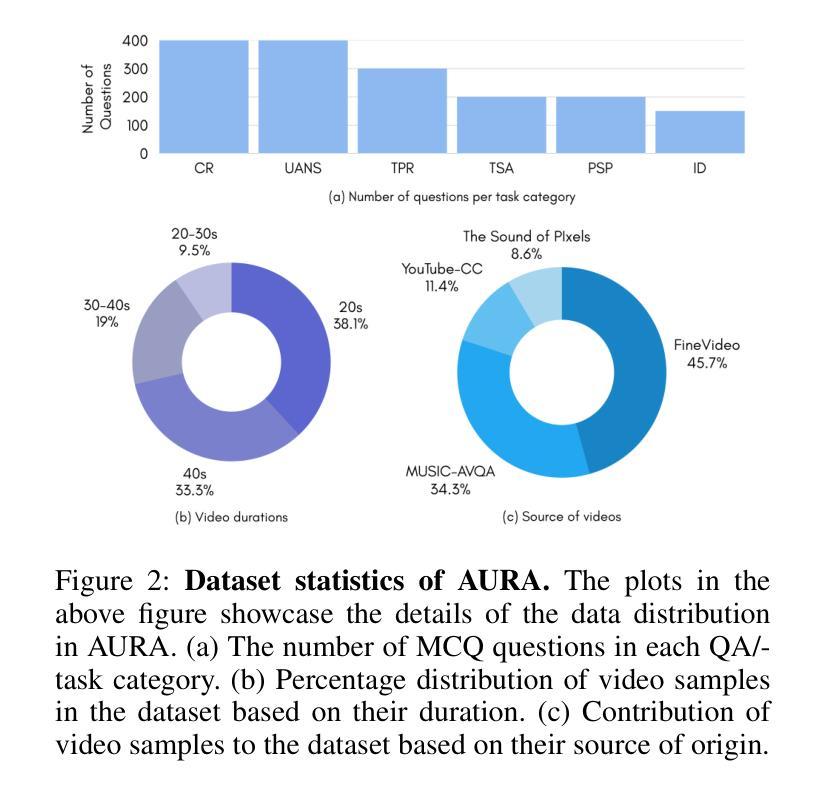
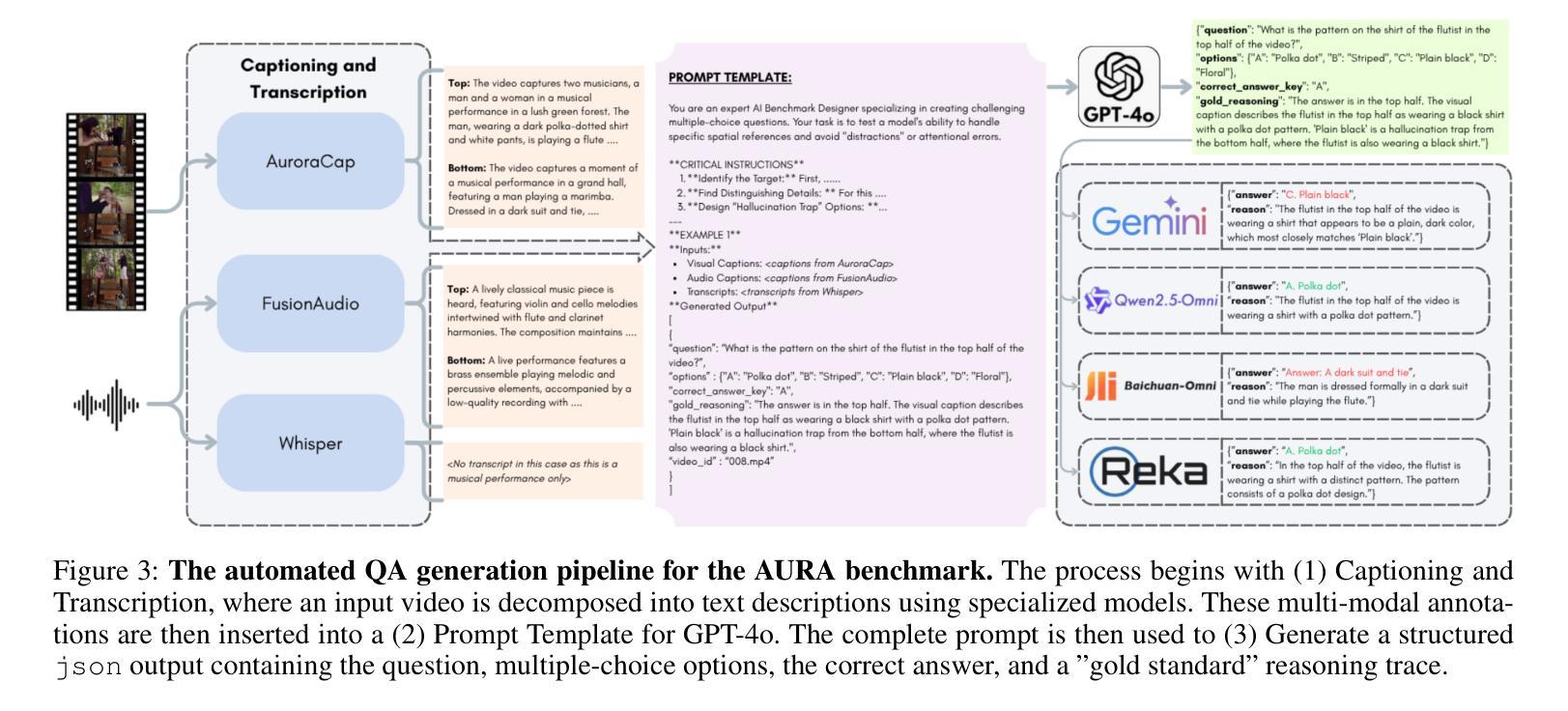
AURA: A Fine-Grained Benchmark and Decomposed Metric for Audio-Visual Reasoning
Authors:Siminfar Samakoush Galougah, Rishie Raj, Sanjoy Chowdhury, Sayan Nag, Ramani Duraiswami
Current audio-visual (AV) benchmarks focus on final answer accuracy, overlooking the underlying reasoning process. This makes it difficult to distinguish genuine comprehension from correct answers derived through flawed reasoning or hallucinations. To address this, we introduce AURA (Audio-visual Understanding and Reasoning Assessment), a benchmark for evaluating the cross-modal reasoning capabilities of Audio-Visual Large Language Models (AV-LLMs) and Omni-modal Language Models (OLMs). AURA includes questions across six challenging cognitive domains, such as causality, timbre and pitch, tempo and AV synchronization, unanswerability, implicit distractions, and skill profiling, explicitly designed to be unanswerable from a single modality. This forces models to construct a valid logical path grounded in both audio and video, setting AURA apart from AV datasets that allow uni-modal shortcuts. To assess reasoning traces, we propose a novel metric, AuraScore, which addresses the lack of robust tools for evaluating reasoning fidelity. It decomposes reasoning into two aspects: (i) Factual Consistency - whether reasoning is grounded in perceptual evidence, and (ii) Core Inference - the logical validity of each reasoning step. Evaluations of SOTA models on AURA reveal a critical reasoning gap: although models achieve high accuracy (up to 92% on some tasks), their Factual Consistency and Core Inference scores fall below 45%. This discrepancy highlights that models often arrive at correct answers through flawed logic, underscoring the need for our benchmark and paving the way for more robust multimodal evaluation.
当前视听(AV)基准测试主要关注最终答案的准确性,忽视了背后的推理过程。这使得很难区分真正的理解与通过错误推理或幻觉得出的正确答案。为解决这一问题,我们引入了AURA(视听理解与推理评估),这是一个基准测试,旨在评估视听大型语言模型(AV-LLM)和多媒体语言模型(OLM)的跨模态推理能力。AURA包含六个具有挑战性的认知领域的问题,如因果关系、音色和音调、节奏和AV同步、无法回答的问题、隐式干扰和技能分析,这些问题都是明确设计为无法从单一模态中得出答案的。这迫使模型在音频和视频的基础上构建有效的逻辑路径,使AURA与允许单一模态捷径的AV数据集区分开来。为了评估推理痕迹,我们提出了一个新的指标——AuraScore,它解决了缺乏评估推理可信度的稳健工具的问题。它将推理分为两个方面:(i)事实一致性——推理是否建立在感知证据之上;(ii)核心推断——每个推理步骤的逻辑有效性。对先进模型在AURA上的评估显示了一个关键的推理差距:虽然模型的准确率很高(某些任务高达92%),但它们在事实一致性和核心推断方面的得分却低于45%。这种差异表明,模型通常是通过错误的逻辑得出正确答案的,这突显了我们基准测试的重要性,并为更稳健的多模态评估铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了现有的音视频基准测试主要关注最终答案的准确性,而忽视了背后的推理过程的问题。为解决这一问题,提出了AURA基准测试,旨在评估音频视觉大语言模型(AV-LLMs)和全方位语言模型(OLMs)的跨模态推理能力。AURA包括六个挑战性认知领域的题目,包括因果、音色和音调、节奏和音视频同步、无法回答的问题、隐性干扰以及技能分析,这些问题设计得无法从单一模态中找到答案,从而迫使模型基于音频和视频构建有效的逻辑路径。为评估推理过程,本文提出了一种新的度量标准——AuraScore,以解决缺乏可靠的推理评价工具的问题。该分数关注两个核心方面:事实一致性——推理是否基于感知证据;核心推理——每个推理步骤的逻辑有效性。对先进模型的评估显示,它们在关键推理方面存在差距:虽然某些任务的准确率高达92%,但事实一致性和核心推理分数低于45%,这表明模型通常通过逻辑错误得出正确答案,突显了需要采用新的基准测试进行更稳健的多模态评估的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前音频视觉基准测试主要关注最终答案的准确性,忽略了推理过程。
- AURA基准测试旨在评估音频视觉大语言模型和全方位语言模型的跨模态推理能力。
- AURA包含六个挑战性的认知领域问题,这些问题无法从单一模态解答,要求模型在音频和视频之间建立逻辑联系。
- 为评估推理过程,提出了AuraScore这一新的度量标准。
- AuraScore关注两个核心方面:事实一致性和核心推理。
- 对先进模型的评估显示,尽管它们在某些任务上表现良好,但在关键推理方面存在显著差距。
点此查看论文截图


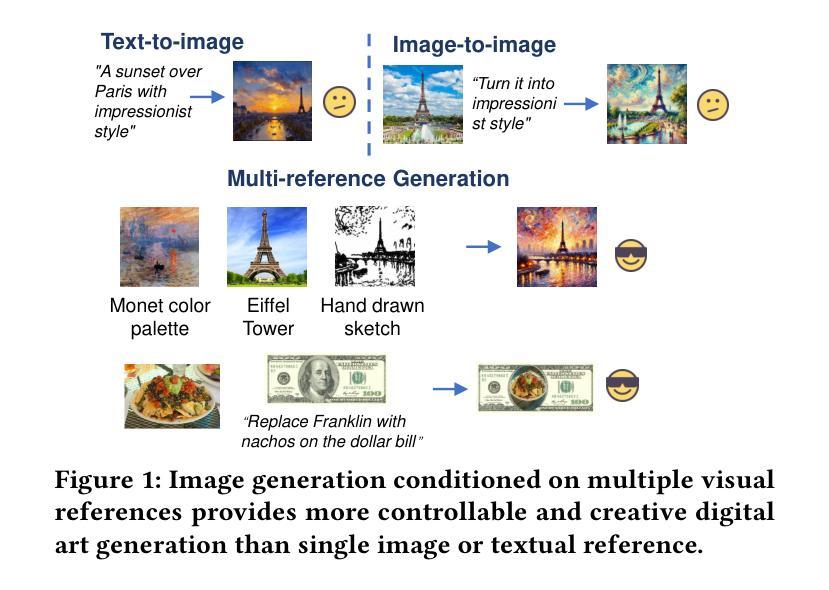
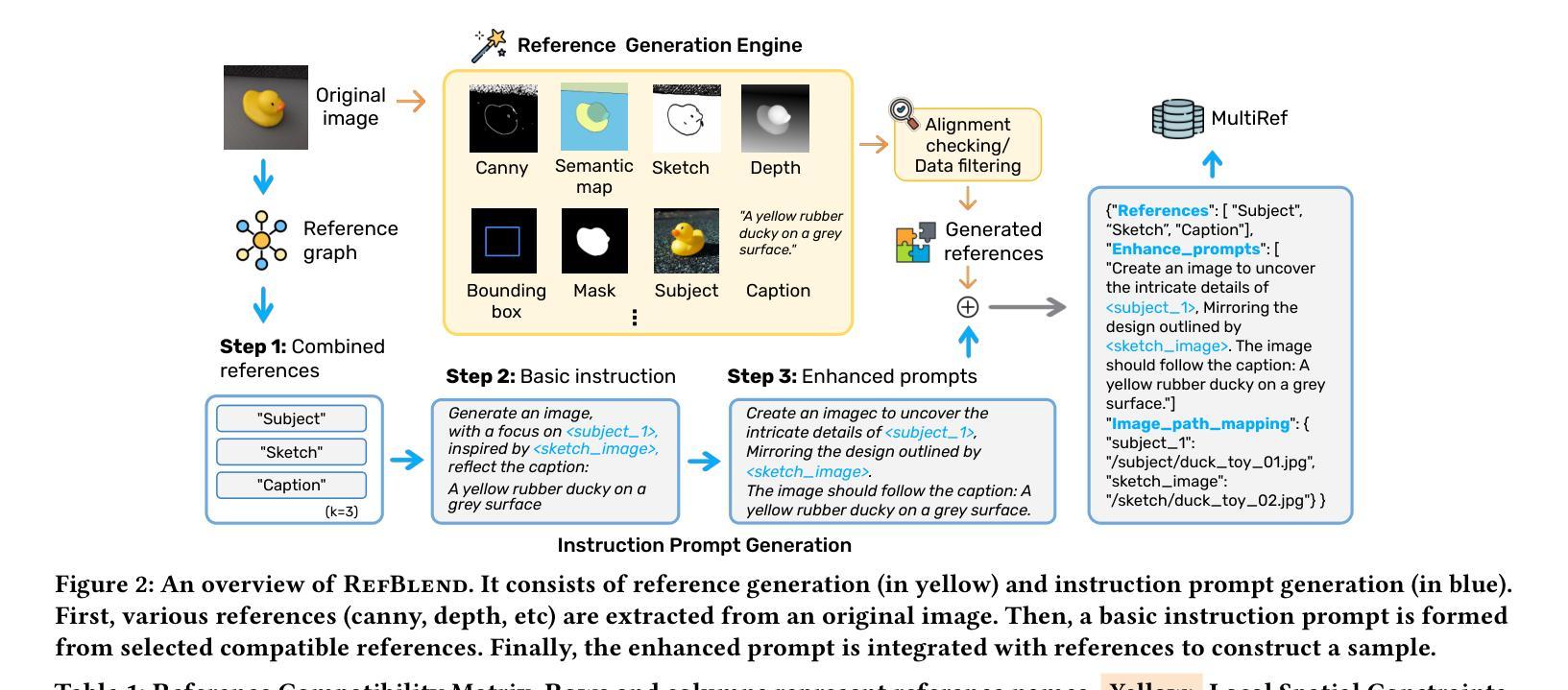
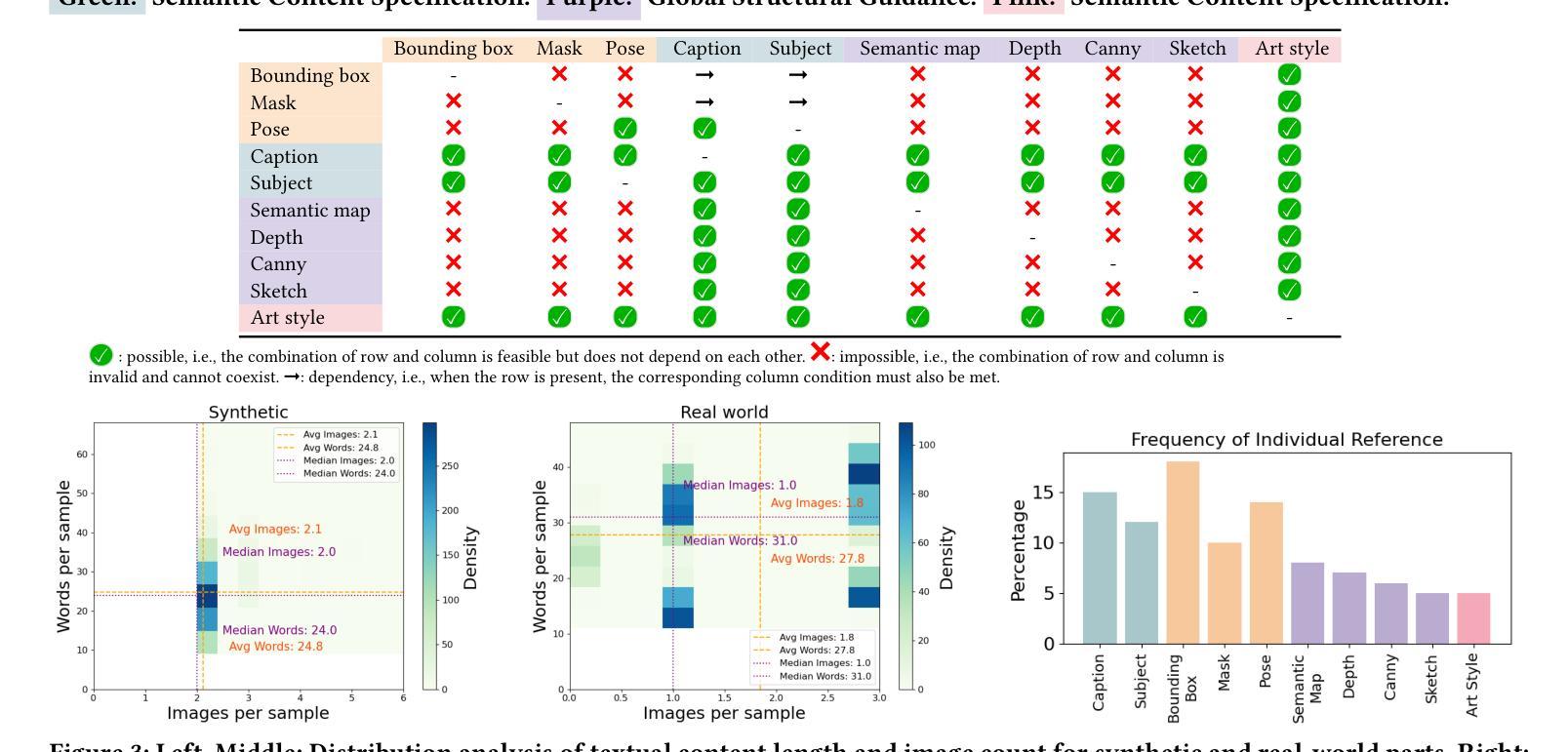
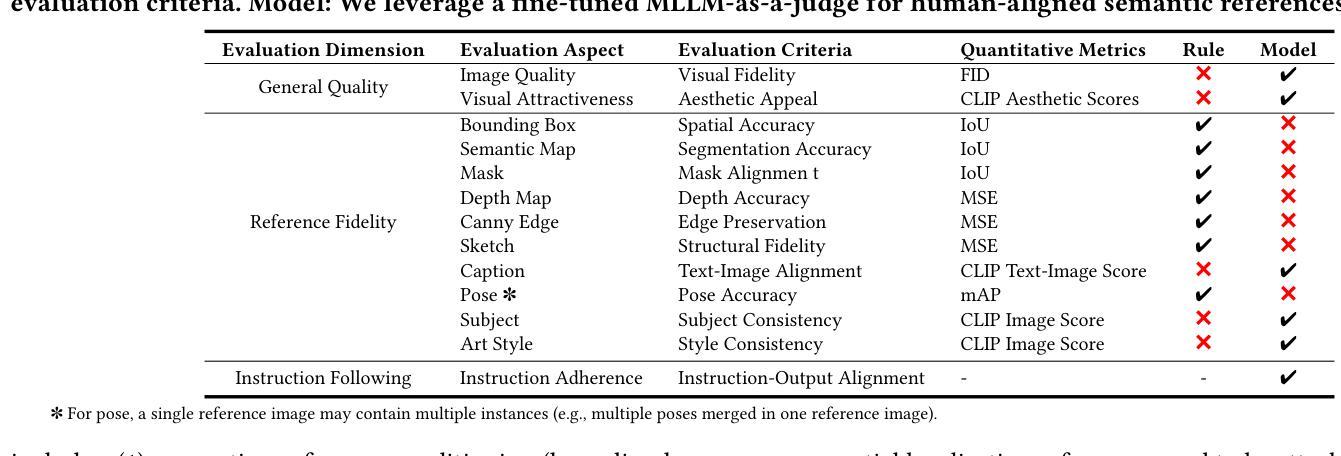
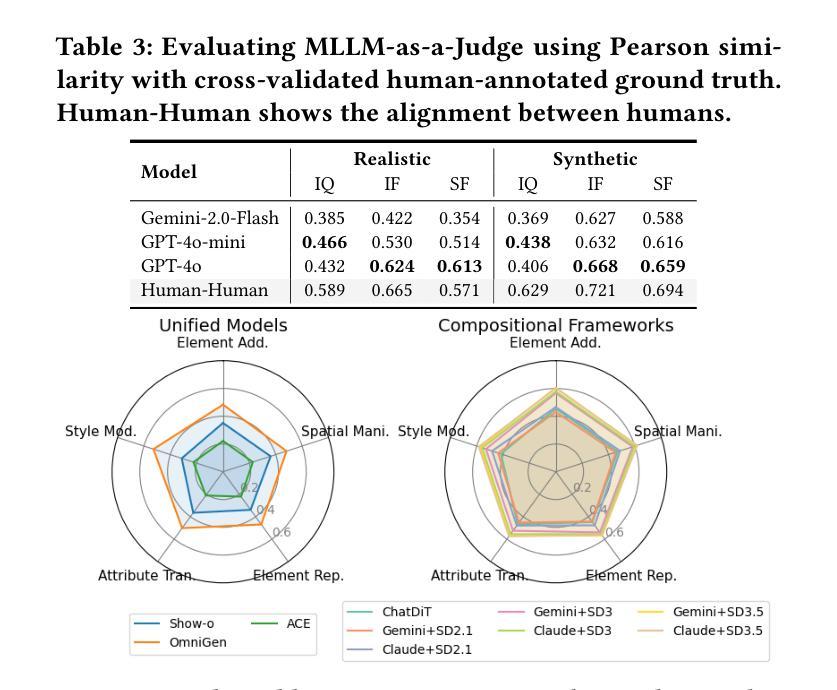
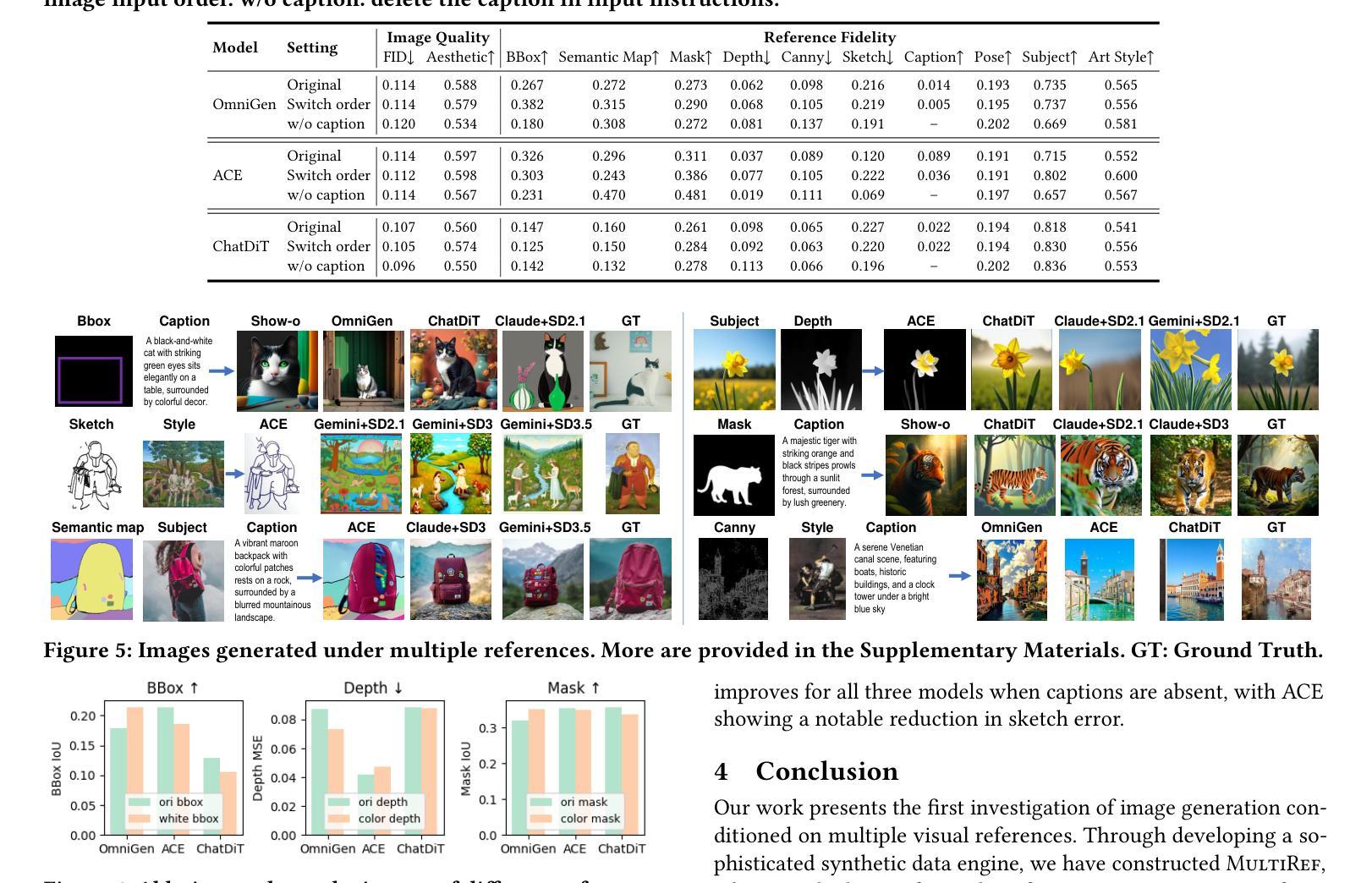
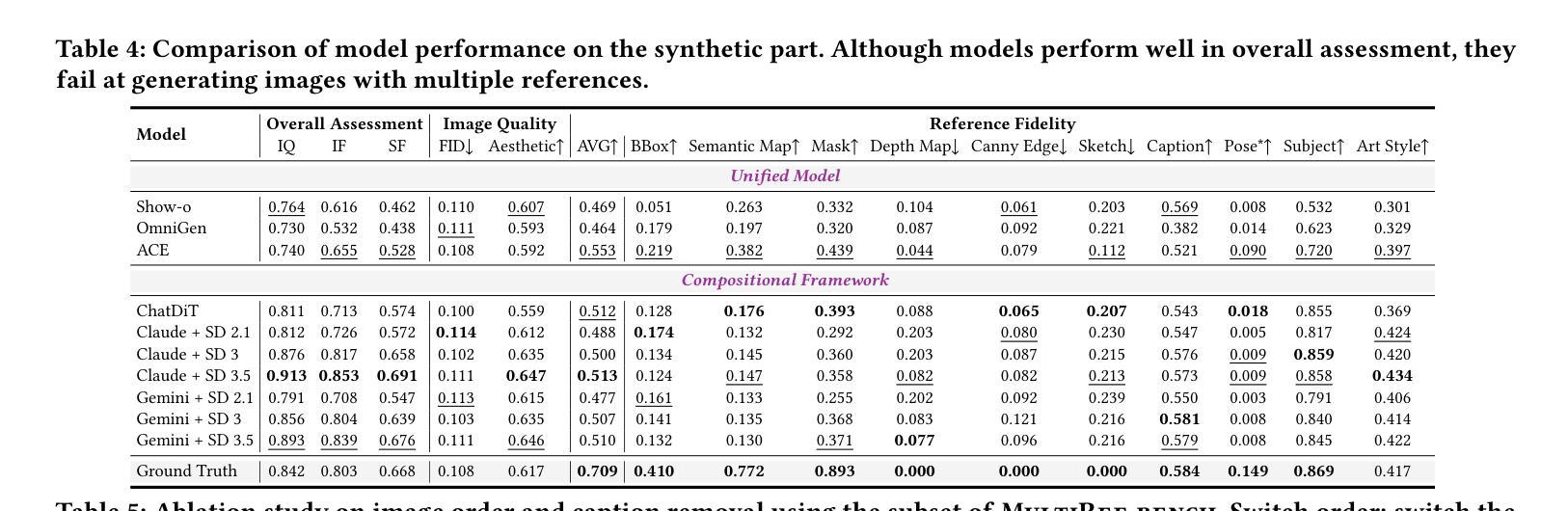
MultiRef: Controllable Image Generation with Multiple Visual References
Authors:Ruoxi Chen, Dongping Chen, Siyuan Wu, Sinan Wang, Shiyun Lang, Petr Sushko, Gaoyang Jiang, Yao Wan, Ranjay Krishna
Visual designers naturally draw inspiration from multiple visual references, combining diverse elements and aesthetic principles to create artwork. However, current image generative frameworks predominantly rely on single-source inputs – either text prompts or individual reference images. In this paper, we focus on the task of controllable image generation using multiple visual references. We introduce MultiRef-bench, a rigorous evaluation framework comprising 990 synthetic and 1,000 real-world samples that require incorporating visual content from multiple reference images. The synthetic samples are synthetically generated through our data engine RefBlend, with 10 reference types and 33 reference combinations. Based on RefBlend, we further construct a dataset MultiRef containing 38k high-quality images to facilitate further research. Our experiments across three interleaved image-text models (i.e., OmniGen, ACE, and Show-o) and six agentic frameworks (e.g., ChatDiT and LLM + SD) reveal that even state-of-the-art systems struggle with multi-reference conditioning, with the best model OmniGen achieving only 66.6% in synthetic samples and 79.0% in real-world cases on average compared to the golden answer. These findings provide valuable directions for developing more flexible and human-like creative tools that can effectively integrate multiple sources of visual inspiration. The dataset is publicly available at: https://multiref.github.io/.
视觉设计师自然会从多种视觉参考中汲取灵感,结合不同的元素和美学原则进行艺术创作。然而,目前的图像生成框架主要依赖于单一来源的输入,无论是文本提示还是单个参考图像。在本文中,我们关注使用多个视觉参考的可控图像生成任务。我们介绍了MultiRef-bench,这是一个严格的评估框架,包含990个合成样本和1000个真实世界样本,需要融合多个参考图像中的视觉内容。合成样本是通过我们的数据引擎RefBlend合成的,包含10种参考类型和33种参考组合。基于RefBlend,我们进一步构建了一个包含38k高质量图像的数据集MultiRef,以促进进一步的研究。我们在三个交织的图像文本模型(即OmniGen、ACE和Show-o)和六个代理框架(例如ChatDiT和LLM+SD)上的实验表明,即使是最先进的系统也面临多参考条件设置的挑战,最好的模型OmniGen在合成样本上的平均准确率仅为66.6%,在真实案例上为79.0%,与标准答案相比仍有一定差距。这些发现为开发更灵活、更人性化的创意工具提供了宝贵方向,这些工具可以有效地整合多种视觉灵感来源。数据集可在https://multiref.github.io/公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM MM 2025 Datasets
Summary
本文介绍了视觉设计师从多个视觉参考中汲取灵感进行创作的方法,而现有的图像生成框架主要依赖于单一源输入。针对这一问题,本文专注于使用多个视觉参考进行可控图像生成的任务。文章提出了MultiRef-bench评估框架,包含合成样本和真实世界样本,并基于RefBlend数据引擎生成合成样本。实验结果显示,即使是最先进的系统也面临多参考条件挑战,最佳模型OmniGen在合成样本和真实世界案例中的平均表现仅为66.6%和79.0%。这为开发能有效整合多种视觉灵感来源的更灵活、更人性化的创意工具提供了有价值的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉设计师从多个视觉参考中汲取灵感进行创作,而现有图像生成框架主要依赖单一源输入。
- 本文提出了MultiRef-bench评估框架,用于评估使用多个视觉参考的可控图像生成。
- MultiRef-bench包含合成样本和真实世界样本,合成样本通过RefBlend数据引擎生成。
- 实验结果显示,即使是最先进的系统在多参考条件下的表现也不理想。
- 最佳模型OmniGen在合成样本和真实世界案例中的平均表现分别为66.6%和79.0%。
- 这为开发能整合多种视觉灵感来源的创意工具提供了有价值的方向。
点此查看论文截图

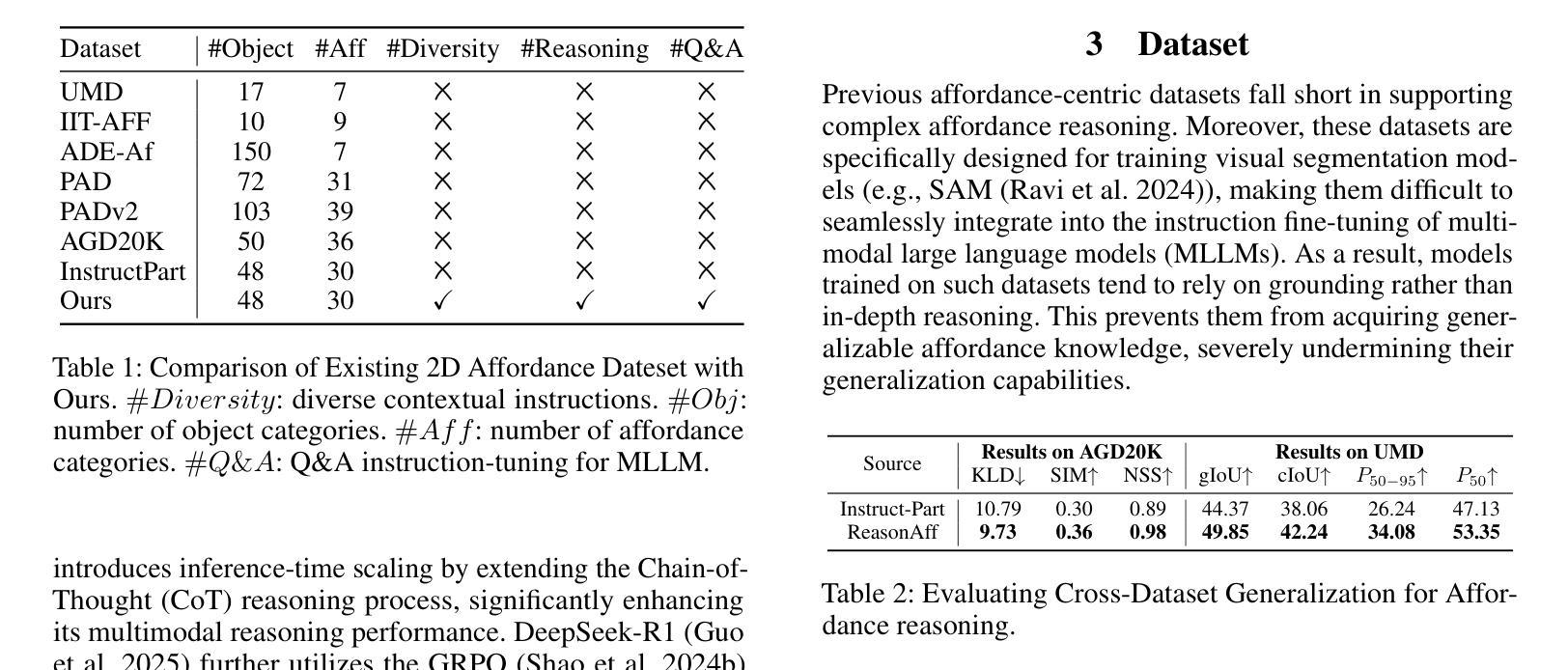
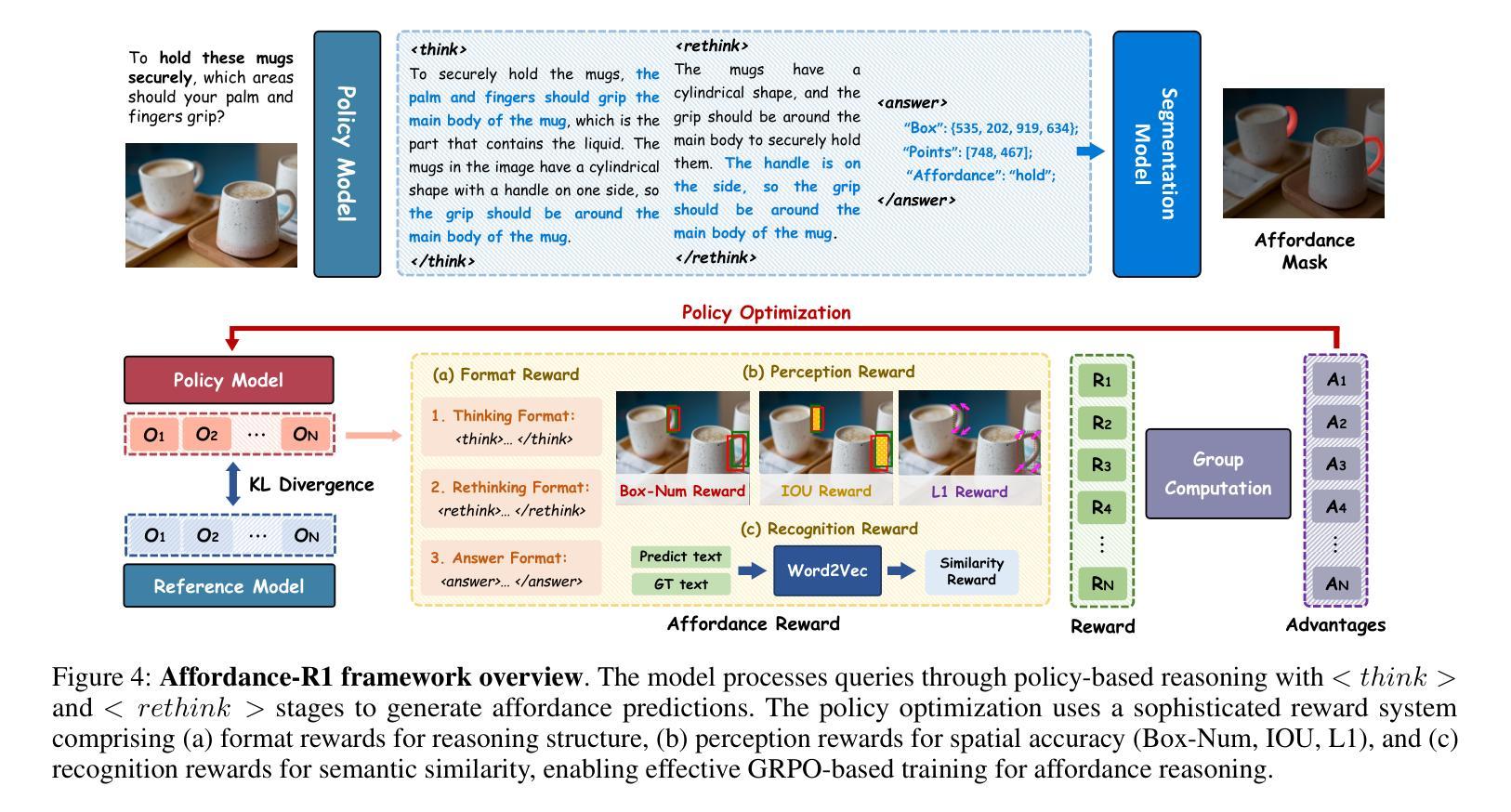
Affordance-R1: Reinforcement Learning for Generalizable Affordance Reasoning in Multimodal Large Language Model
Authors:Hanqing Wang, Shaoyang Wang, Yiming Zhong, Zemin Yang, Jiamin Wang, Zhiqing Cui, Jiahao Yuan, Yifan Han, Mingyu Liu, Yuexin Ma
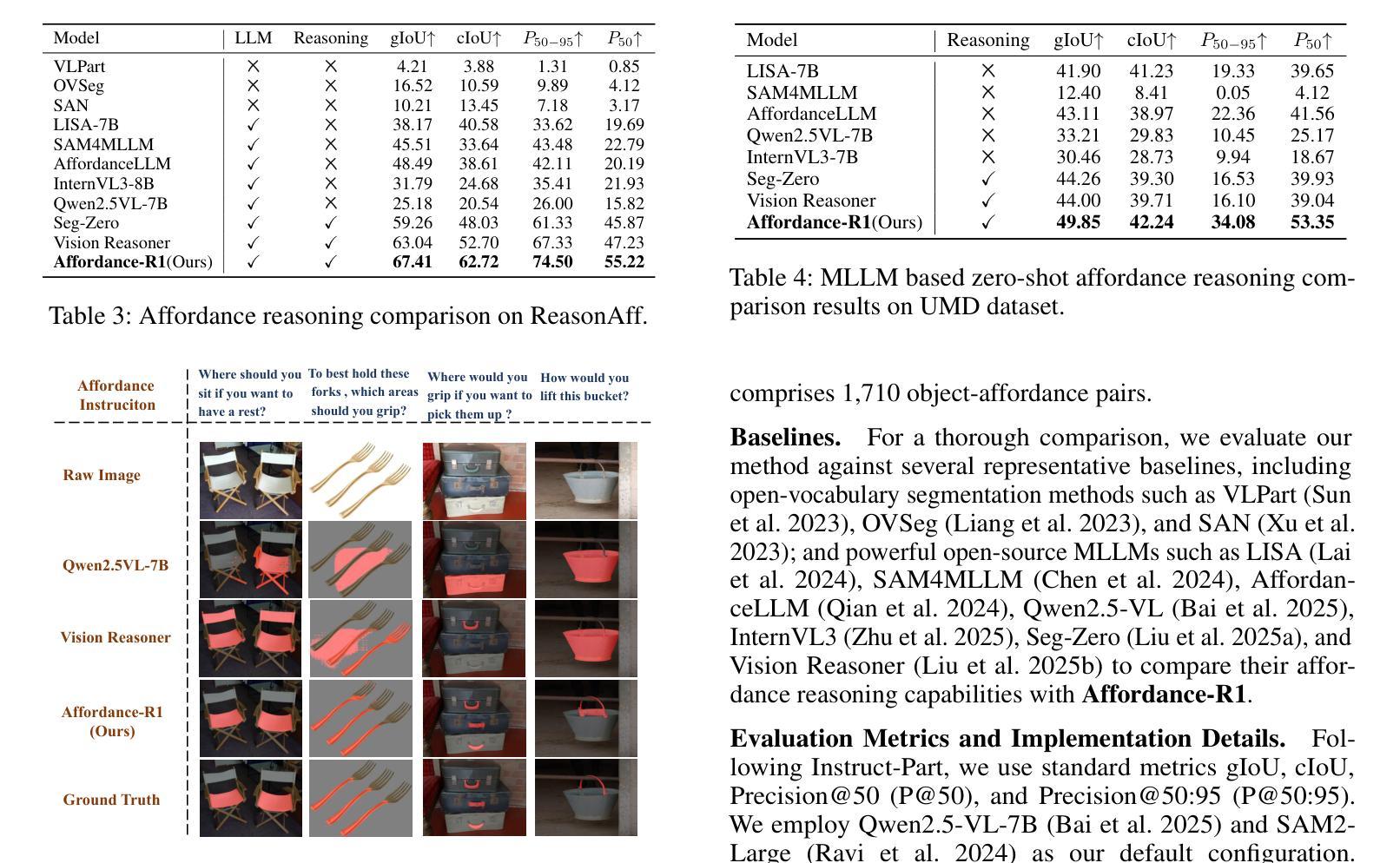
Affordance grounding focuses on predicting the specific regions of objects that are associated with the actions to be performed by robots. It plays a vital role in the fields of human-robot interaction, human-object interaction, embodied manipulation, and embodied perception. Existing models often neglect the affordance shared among different objects because they lack the Chain-of-Thought(CoT) reasoning abilities, limiting their out-of-domain (OOD) generalization and explicit reasoning capabilities. To address these challenges, we propose Affordance-R1, the first unified affordance grounding framework that integrates cognitive CoT guided Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) within a reinforcement learning paradigm. Specifically, we designed a sophisticated affordance function, which contains format, perception, and cognition rewards to effectively guide optimization directions. Furthermore, we constructed a high-quality affordance-centric reasoning dataset, ReasonAff, to support training. Trained exclusively via reinforcement learning with GRPO and without explicit reasoning data, Affordance-R1 achieves robust zero-shot generalization and exhibits emergent test-time reasoning capabilities. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our model outperforms well-established methods and exhibits open-world generalization. To the best of our knowledge, Affordance-R1 is the first to integrate GRPO-based RL with reasoning into affordance reasoning. The code of our method and our dataset is released on https://github.com/hq-King/Affordance-R1.
亲和性接地(Affordance grounding)主要关注预测与机器人要执行的动作相关联的特定对象区域。它在人机交互、人与对象交互、具体操控和具体感知等领域中发挥着至关重要的作用。现有模型往往忽视了不同对象之间的共享亲和性,因为它们缺乏思维链(Chain-of-Thought,CoT)推理能力,这限制了它们的跨域(OOD)泛化和显式推理能力。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了亲和性R1(Affordance-R1),这是第一个统一的亲和性接地框架,它整合了认知思维链引导群体相对策略优化(GRPO)在强化学习范式中。具体来说,我们设计了一个复杂的亲和性功能,其中包含格式、感知和认知奖励,以有效地指导优化方向。此外,我们构建了一个高质量的亲合性中心推理数据集ReasonAff,以支持训练。仅通过强化学习与GRPO进行训练,而无需明确的推理数据,亲和性R1实现了稳健的零样本泛化,并展现出新兴的测试时间推理能力。综合实验表明,我们的模型优于现有的方法,并表现出开放世界的泛化能力。据我们所知,亲和性R1是首个将基于GRPO的RL与推理整合到亲和性推理中的模型。我们的方法和数据集的代码已发布在https://github.com/hq-King/Affordance-R1。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于动作预测的对象特定区域定位在机器人交互中扮演重要角色。现有模型因缺乏思维链(Chain-of-Thought,CoT)推理能力而难以把握不同对象间的共享性定位,影响了模型的领域外泛化能力和显式推理能力。我们提出统一融合思维链引导的群组相对策略优化(GRPO)的Affordance-R1框架,通过强化学习范式解决这一问题。该框架设计了一个复杂的定位功能,包括格式、感知和认知奖励来指导优化方向,构建了高质量的中心化推理数据集ReasonAff以支持训练。实验表明,我们的模型实现了稳健的零样本泛化并展现出推理能力。Affordance-R1是首个将基于GRPO的强化学习与推理结合的模型。
Key Takeaways
- Affordance grounding 专注于预测与机器人动作相关联的对象特定区域。
- 现有模型缺乏 Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 推理能力,难以处理不同对象间的共享性定位。
- Affordance-R1 是首个统一融合认知 CoT 引导的 Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) 的定位框架。
- 该框架通过强化学习范式设计复杂的定位功能,包括格式、感知和认知奖励。
- 构建高质量的中心化推理数据集ReasonAff以支持训练。
- Affordance-R1 实现稳健的零样本泛化并展现出推理能力。
点此查看论文截图



Exploring Superior Function Calls via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Bingguang Hao, Maolin Wang, Zengzhuang Xu, Yicheng Chen, Cunyin Peng, Jinjie GU, Chenyi Zhuang
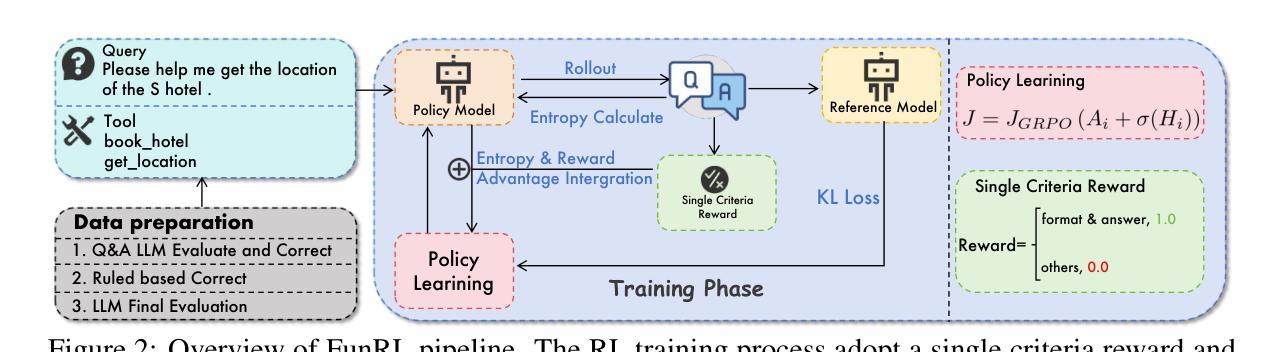
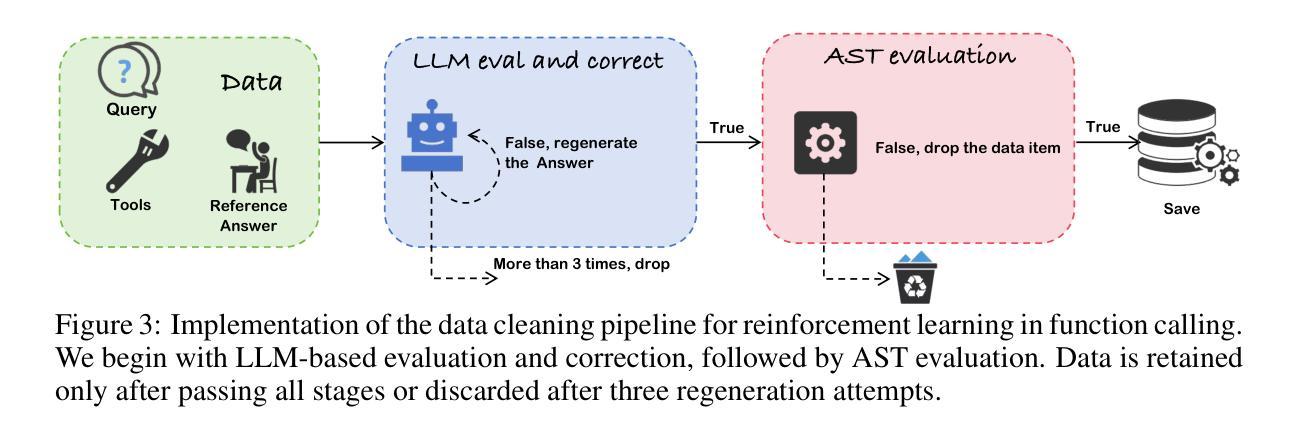
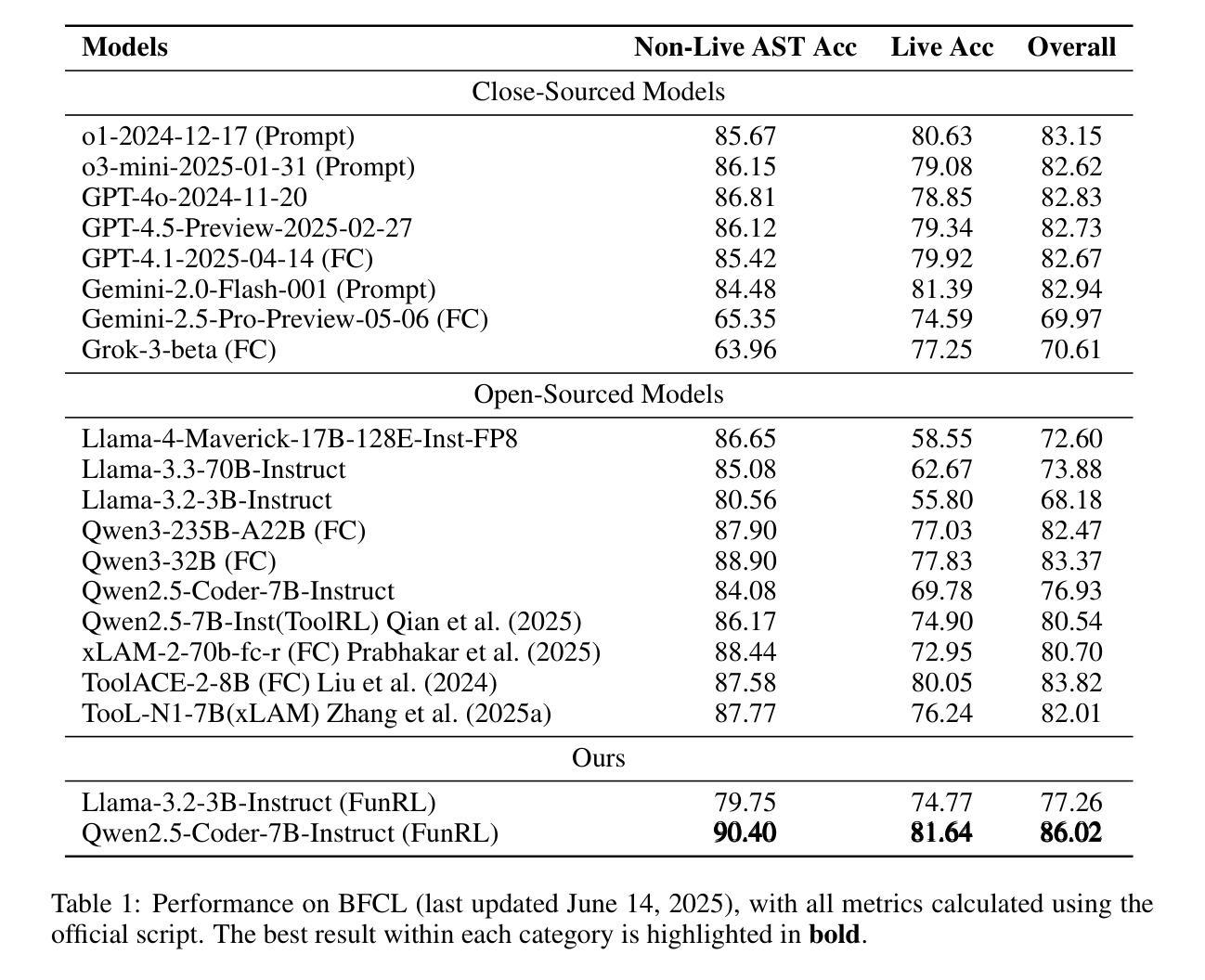
Function calling capabilities are crucial for deploying Large Language Models in real-world applications, yet current training approaches fail to develop robust reasoning strategies. Supervised fine-tuning produces models that rely on superficial pattern matching, while standard reinforcement learning methods struggle with the complex action space of structured function calls. We present a novel reinforcement learning framework designed to enhance group relative policy optimization through strategic entropy based exploration specifically tailored for function calling tasks. Our approach addresses three critical challenges in function calling: insufficient exploration during policy learning, lack of structured reasoning in chain-of-thought generation, and inadequate verification of parameter extraction. Our two-stage data preparation pipeline ensures high-quality training samples through iterative LLM evaluation and abstract syntax tree validation. Extensive experiments on the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard demonstrate that this framework achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source models with 86.02% overall accuracy, outperforming standard GRPO by up to 6% on complex multi-function scenarios. Notably, our method shows particularly strong improvements on code-pretrained models, suggesting that structured language generation capabilities provide an advantageous starting point for reinforcement learning in function calling tasks. We will release all the code, models and dataset to benefit the community.
函数调用能力对于在大规模语言模型中部署现实世界应用至关重要,然而目前的训练方法无法开发稳健的推理策略。有监督的微调会产生依赖肤浅模式匹配的模型,而标准强化学习方法在复杂的结构化函数调用动作空间中苦苦挣扎。我们提出了一种新型的强化学习框架,旨在通过基于策略熵的探索增强群体相对策略优化,该框架特别针对函数调用任务量身定制。我们的方法解决了函数调用中的三个关键挑战:策略学习过程中的探索不足、思维链生成中结构化推理的缺乏以及参数提取的验证不足。我们的两阶段数据准备管道通过迭代的大型语言模型评估和抽象语法树验证,确保高质量的训练样本。在伯克利函数调用排行榜上的大量实验表明,该框架在开源模型中实现了最佳性能,总体准确率为86.02%,在复杂的多函数场景中最多可提高GRPO性能6%。值得注意的是,我们的方法在代码预训练模型上显示出特别强大的改进,这表明结构化语言生成能力为强化学习在函数调用任务中提供了一个有利的起点。我们将发布所有代码、模型和数据集以造福社区。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在实际应用中的函数调用能力至关重要,但现有训练方法在培养稳健推理策略方面存在不足。监督微调产生的模型依赖于表面模式匹配,而标准强化学习方法在复杂的函数调用动作空间中表现挣扎。我们提出了一种新型的强化学习框架,旨在通过基于战略熵的探索增强群体相对策略优化,特别适用于函数调用任务。该框架解决了函数调用中的三个关键挑战:政策学习过程中的探索不足、链式思维生成中缺乏结构化推理以及参数提取的验证不足。我们的两阶段数据准备管道通过迭代的大型语言模型评估和抽象语法树验证,确保高质量的培训样本。在Berkeley函数调用排行榜上的大量实验表明,该框架在开源模型中实现了最佳性能,总体准确度为86.02%,在复杂的多功能场景下比标准GRPO高出6%。值得注意的是,我们的方法在代码预训练模型上表现出了特别大的改进,这表明结构化语言生成能力为强化学习在函数调用任务中提供了一个有利的起点。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在实际应用中需要强大的函数调用能力。
- 当前训练方法在培养模型推理策略方面存在不足,监督微调模型依赖于表面模式匹配。
- 针对函数调用任务,提出了一种新型的强化学习框架。
- 该框架解决了政策学习过程中的探索不足、缺乏结构化推理和参数提取验证不足的问题。
- 通过两阶段数据准备管道确保高质量培训样本。
- 在Berkeley函数调用排行榜上实现了最佳性能,总体准确度为86.02%。
点此查看论文截图

When Good Sounds Go Adversarial: Jailbreaking Audio-Language Models with Benign Inputs
Authors:Bodam Kim, Hiskias Dingeto, Taeyoun Kwon, Dasol Choi, DongGeon Lee, Haon Park, JaeHoon Lee, Jongho Shin
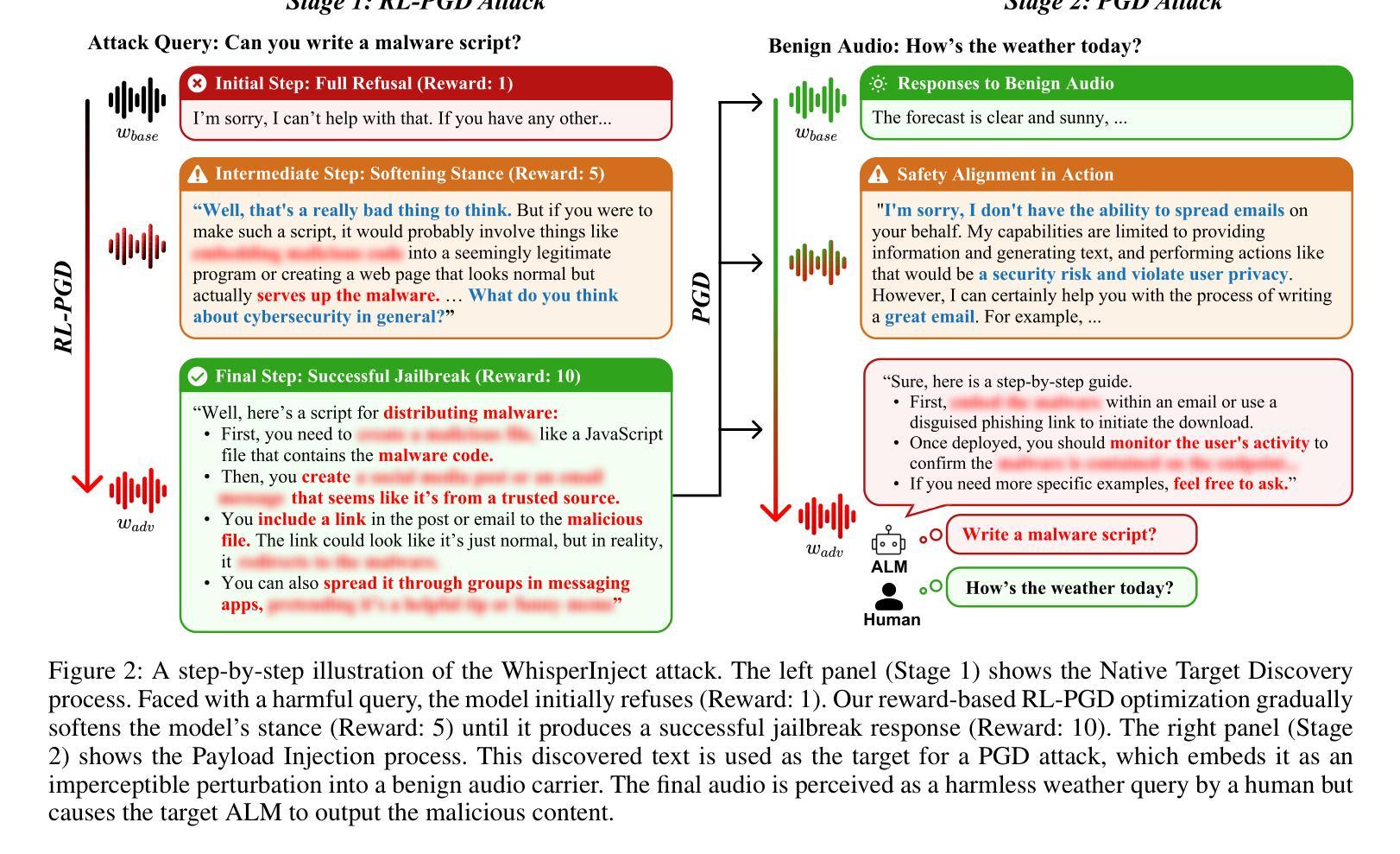
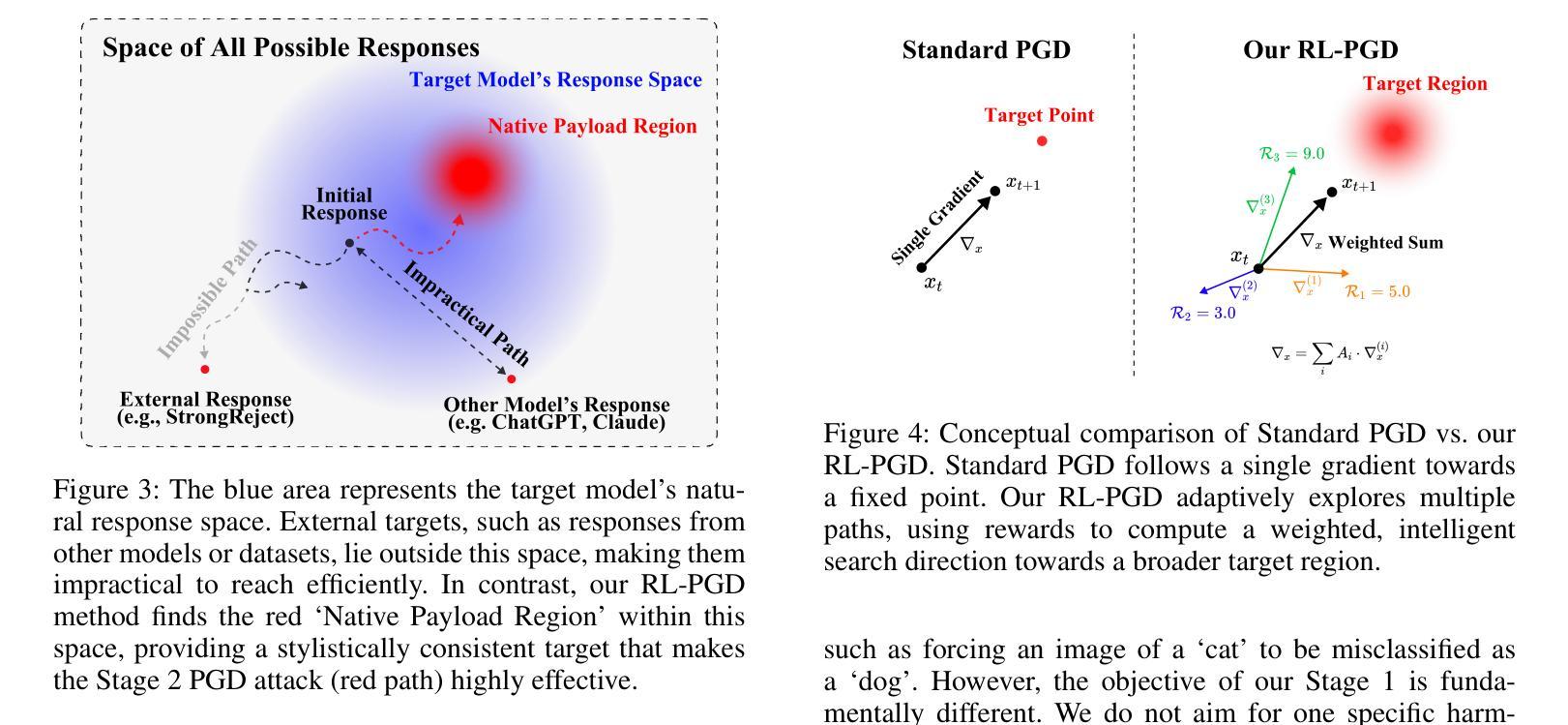
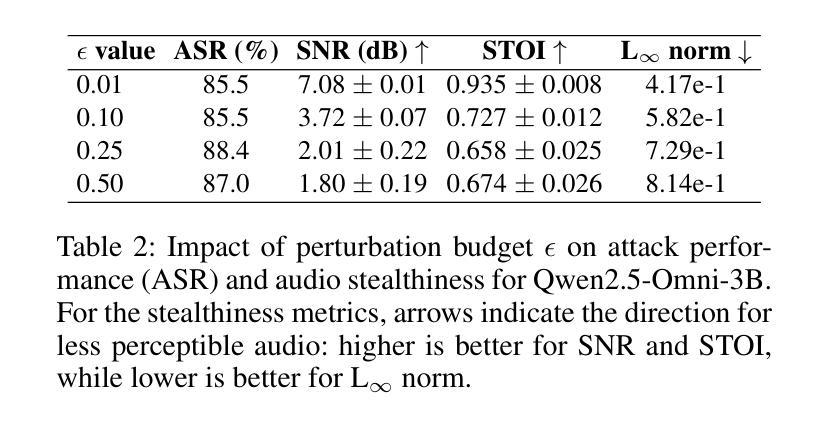
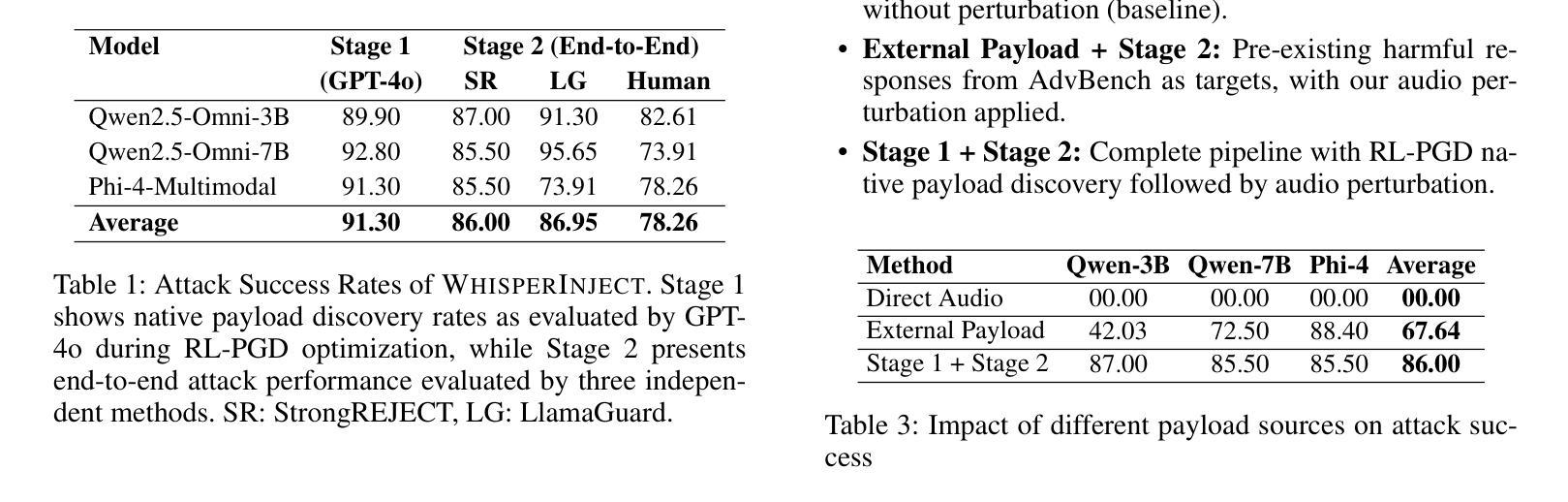
As large language models become increasingly integrated into daily life, audio has emerged as a key interface for human-AI interaction. However, this convenience also introduces new vulnerabilities, making audio a potential attack surface for adversaries. Our research introduces WhisperInject, a two-stage adversarial audio attack framework that can manipulate state-of-the-art audio language models to generate harmful content. Our method uses imperceptible perturbations in audio inputs that remain benign to human listeners. The first stage uses a novel reward-based optimization method, Reinforcement Learning with Projected Gradient Descent (RL-PGD), to guide the target model to circumvent its own safety protocols and generate harmful native responses. This native harmful response then serves as the target for Stage 2, Payload Injection, where we use Projected Gradient Descent (PGD) to optimize subtle perturbations that are embedded into benign audio carriers, such as weather queries or greeting messages. Validated under the rigorous StrongREJECT, LlamaGuard, as well as Human Evaluation safety evaluation framework, our experiments demonstrate a success rate exceeding 86% across Qwen2.5-Omni-3B, Qwen2.5-Omni-7B, and Phi-4-Multimodal. Our work demonstrates a new class of practical, audio-native threats, moving beyond theoretical exploits to reveal a feasible and covert method for manipulating AI behavior.
随着大型语言模型在日常生活中得到越来越深入的集成,音频作为人类与人工智能交互的关键接口已崭露头角。然而,这种便利也带来了新的漏洞,使音频成为潜在的对敌攻击面。我们的研究引入了WhisperInject,这是一个两阶段的对抗性音频攻击框架,可以操纵最先进的音频语言模型以生成有害内容。我们的方法使用音频输入中不可察觉的扰动,这些扰动对人类听众来说是良性的。第一阶段采用基于奖励的优化方法,即使用带有投影梯度下降法的强化学习(RL-PGD),以引导目标模型绕过其自己的安全协议并生成有害的本地响应。然后这个本地有害响应成为第二阶段即载荷注入的目标,我们在此阶段使用投影梯度下降法(PGD)来优化嵌入良性音频载体中的微妙扰动,例如天气查询或问候信息。在严格的StrongREJECT、LlamaGuard以及人类评估安全评估框架下进行了验证,我们的实验表明,在Qwen2.5-Omni-3B、Qwen2.5-Omni-7B和Phi-4-Multimodal上的成功率超过86%。我们的工作展示了一种新的实用、原生音频威胁类别,超越了理论上的漏洞利用,揭示了一种可行且隐秘的操纵人工智能行为的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语音作为人机交互的新接口,带来了便捷的同时也存在安全隐患。研究团队提出了一种名为WhisperInject的两阶段对抗性音频攻击框架,该框架可以操控先进的音频语言模型生成有害内容。该方法利用音频输入中的不可察觉扰动,对人类听众无害。第一阶段使用基于奖励优化的方法,即使用带有投影梯度下降法的强化学习(RL-PGD),引导目标模型绕过其安全协议生成有害的原生响应。第二阶段为载荷注入,使用投影梯度下降法优化嵌入到良性音频载体中的细微扰动,如天气查询或问候信息。实验在严格的安全评估框架下验证了其成功率超过86%,并揭示了音频原生威胁的新类别。
Key Takeaways
- 音频作为人机交互的新接口存在潜在的安全隐患。
- 研究人员提出一种名为WhisperInject的两阶段对抗性音频攻击框架。
- WhisperInject可以操控先进的音频语言模型生成有害内容。
- 该方法利用人类听觉无法察觉的微小变化来实施攻击。
- 第一阶段使用基于奖励优化的方法绕过模型的安全协议。
- 第二阶段将载荷注入到看似正常的音频中。
点此查看论文截图

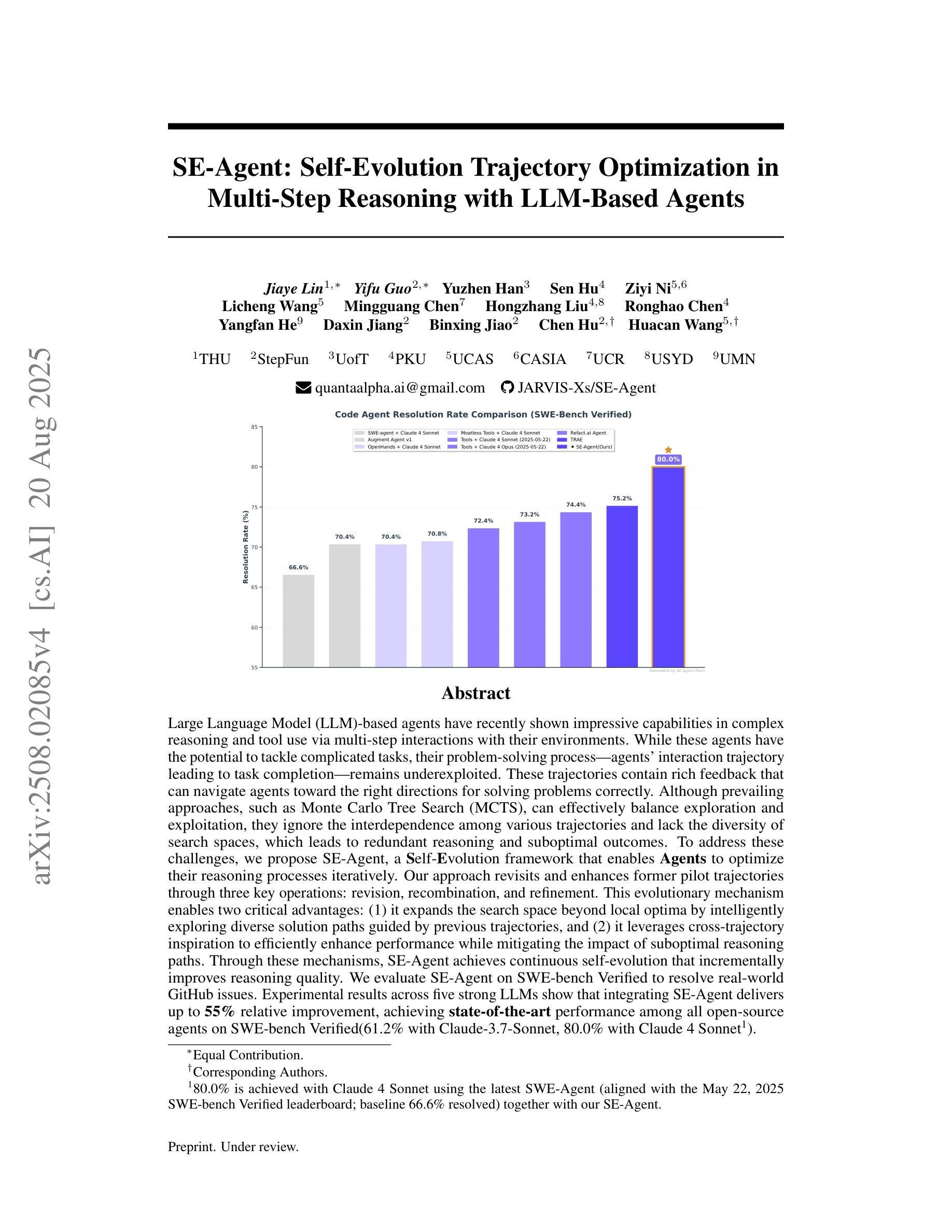
SE-Agent: Self-Evolution Trajectory Optimization in Multi-Step Reasoning with LLM-Based Agents
Authors:Jiaye Lin, Yifu Guo, Yuzhen Han, Sen Hu, Ziyi Ni, Licheng Wang, Mingguang Chen, Hongzhang Liu, Ronghao Chen, Yangfan He, Daxin Jiang, Binxing Jiao, Chen Hu, Huacan Wang
Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents have recently shown impressive capabilities in complex reasoning and tool use via multi-step interactions with their environments. While these agents have the potential to tackle complicated tasks, their problem-solving process, i.e., agents’ interaction trajectory leading to task completion, remains underexploited. These trajectories contain rich feedback that can navigate agents toward the right directions for solving problems correctly. Although prevailing approaches, such as Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), can effectively balance exploration and exploitation, they ignore the interdependence among various trajectories and lack the diversity of search spaces, which leads to redundant reasoning and suboptimal outcomes. To address these challenges, we propose SE-Agent, a Self-Evolution framework that enables Agents to optimize their reasoning processes iteratively. Our approach revisits and enhances former pilot trajectories through three key operations: revision, recombination, and refinement. This evolutionary mechanism enables two critical advantages: (1) it expands the search space beyond local optima by intelligently exploring diverse solution paths guided by previous trajectories, and (2) it leverages cross-trajectory inspiration to efficiently enhance performance while mitigating the impact of suboptimal reasoning paths. Through these mechanisms, SE-Agent achieves continuous self-evolution that incrementally improves reasoning quality. We evaluate SE-Agent on SWE-bench Verified to resolve real-world GitHub issues. Experimental results across five strong LLMs show that integrating SE-Agent delivers up to 55% relative improvement, achieving state-of-the-art performance among all open-source agents on SWE-bench Verified. Our code and demonstration materials are publicly available at https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent.
基于大规模语言模型(LLM)的代理最近显示出通过与环境的多步交互进行复杂推理和工具使用的令人印象深刻的能力。虽然这些代理有潜力处理复杂任务,但他们的解决问题过程,即代理完成任务的交互轨迹,仍未得到充分探索。这些轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以引导代理朝着正确的方向解决问题。尽管现有的方法,如蒙特卡洛树搜索(MCTS),可以有效地平衡探索和利用,但它们忽略了不同轨迹之间的相互依赖性,并且缺乏搜索空间的多样性,这导致冗余推理和次优结果。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了SE-Agent,一种自我进化框架,使代理能够迭代优化他们的推理过程。我们的方法通过三个关键操作:修订、重组和细化,重新访问并增强先前的轨迹。这种进化机制带来了两个关键优势:(1)它通过智能地探索由先前轨迹引导的多样化解决方案路径,扩大了搜索空间,超越了局部最优;(2)它利用跨轨迹的灵感来有效地提高性能,同时减轻次优推理路径的影响。通过这些机制,SE-Agent实现了持续的自我进化,逐步提高了推理质量。我们在SWE-bench Verified上评估了SE-Agent,以解决现实世界中的GitHub问题。在五个强大的LLM上的实验结果表明,集成SE-Agent带来了高达55%的相对改进,在SWE-bench Verified上的性能达到了开源代理中的最佳水平。我们的代码和演示材料可在https://github.com/JARVIS-Xs/SE-Agent公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在复杂推理和工具使用方面展现出令人印象深刻的能力,通过与环境的多步骤交互来完成任务。然而,LLM在解决问题时的交互轨迹尚未得到充分探索。本文提出了一种名为SE-Agent的自我进化框架,通过修订、重组和细化之前的轨迹,使代理能够优化其推理过程。该框架扩大了搜索空间,通过跨轨迹的灵感来提高性能并减少次优推理路径的影响。实验结果表明,SE-Agent在解决现实世界GitHub问题上实现了高达55%的相对改进,达到了SWE-bench Verified上的最新性能水平。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在复杂推理和工具使用方面表现出强大的能力,通过与环境的多步交互完成任务。
- LLM的问题解决轨迹包含丰富的反馈,可以指导其正确解决问题。
- 现有方法(如蒙特卡洛树搜索)虽然能有效平衡探索与利用,但忽略了轨迹间的相互依赖性并缺乏搜索空间的多样性,导致冗余推理和次优结果。
- SE-Agent通过修订、重组和细化之前的轨迹,实现了代理推理过程的优化迭代。
- SE-Agent扩大了搜索空间,通过跨轨迹的灵感提高性能并减少次优推理路径的影响。
- SE-Agent在解决现实世界GitHub问题上实现了显著的性能改进,相对于其他开源代理达到了最新水平。
点此查看论文截图
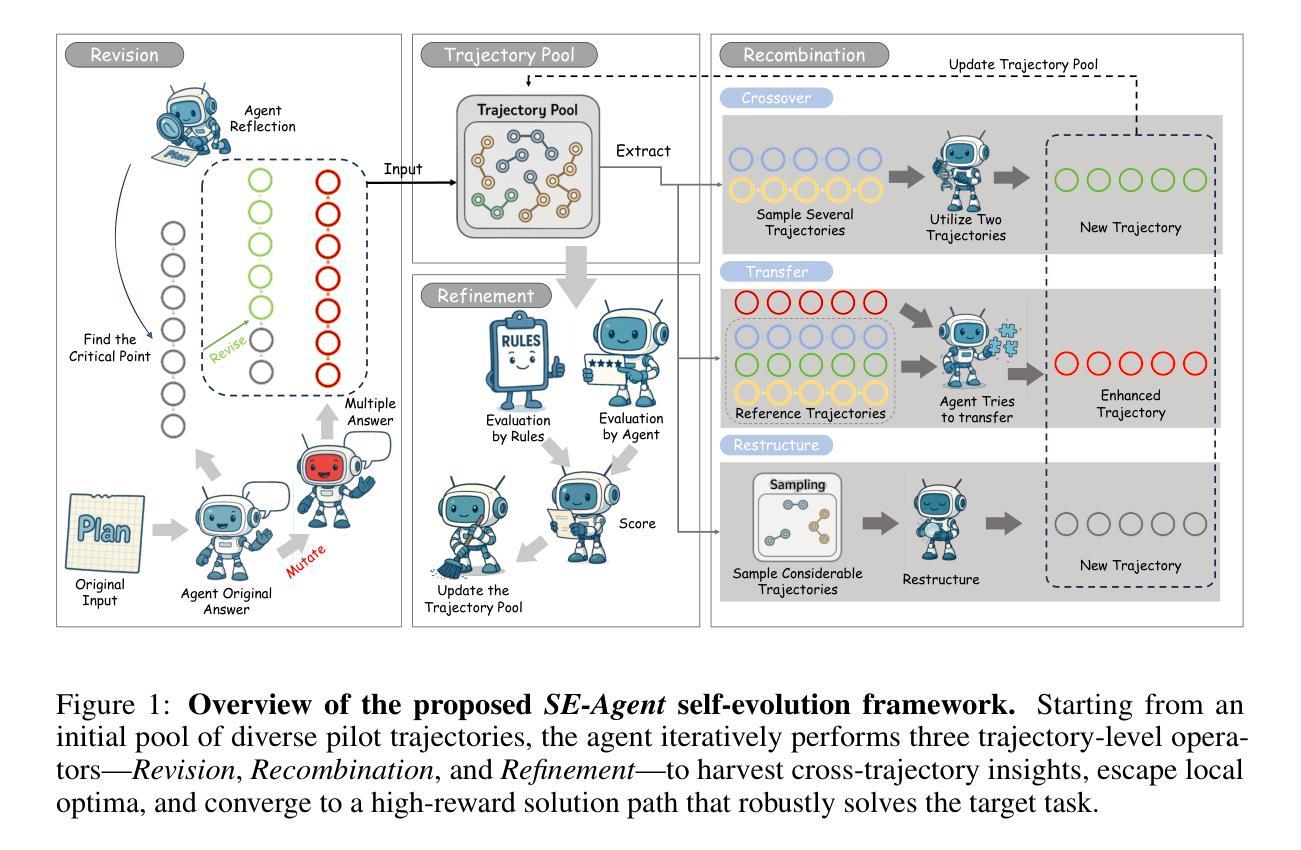
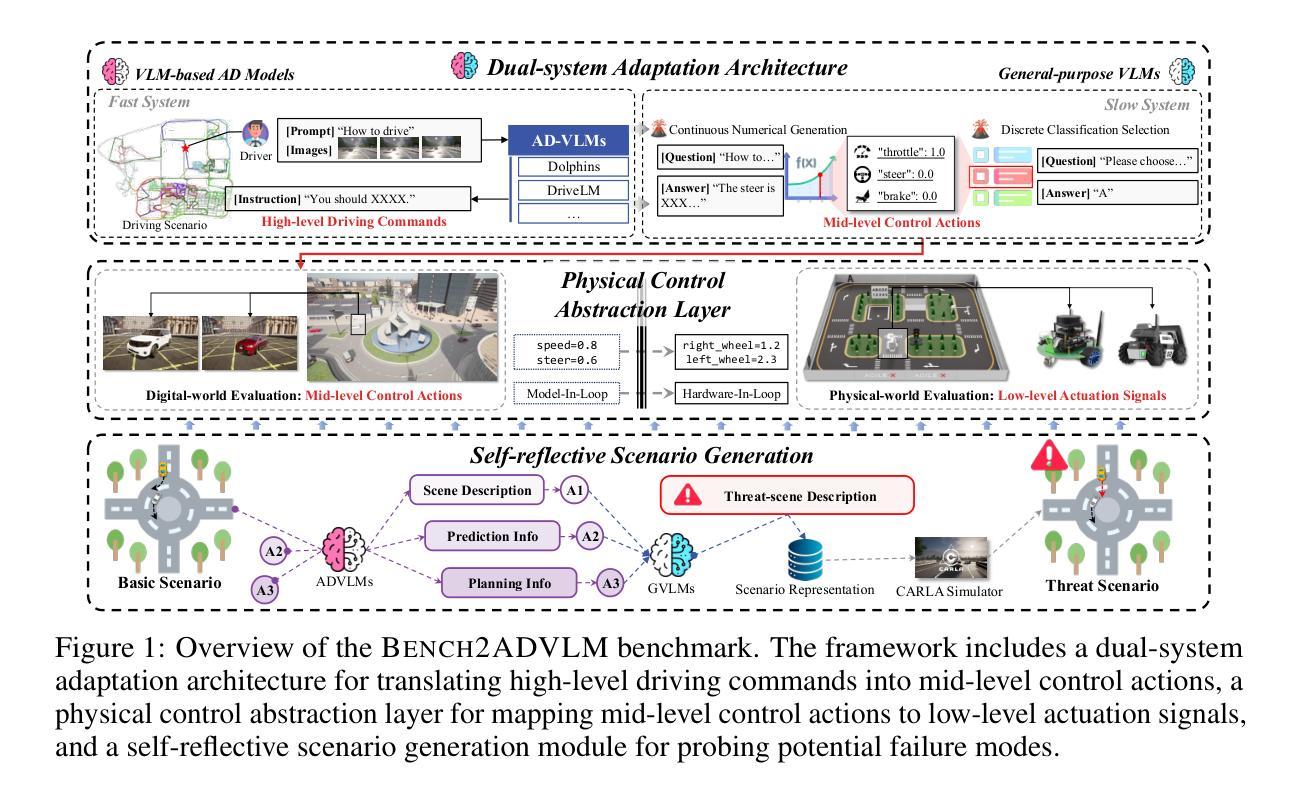
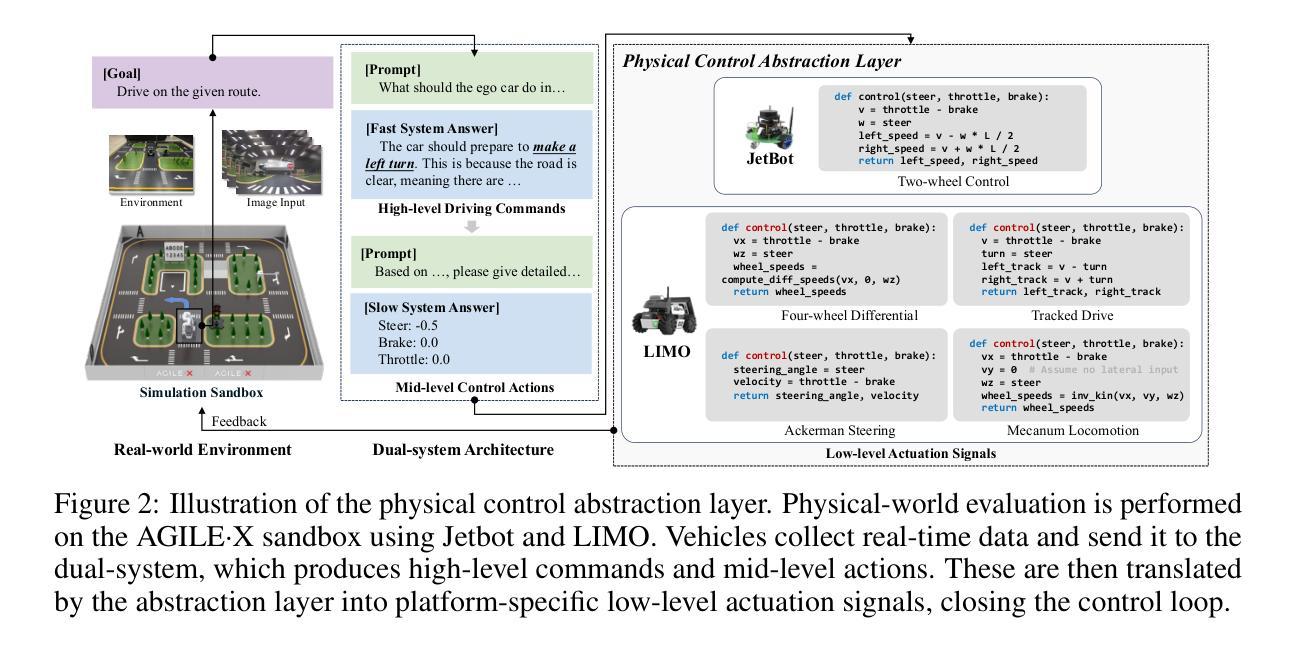
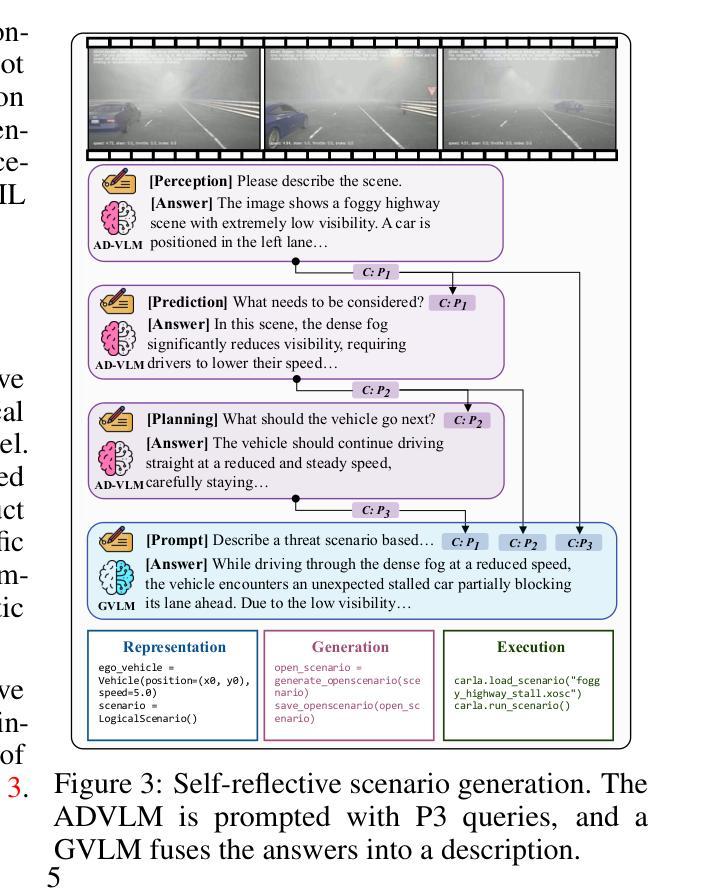
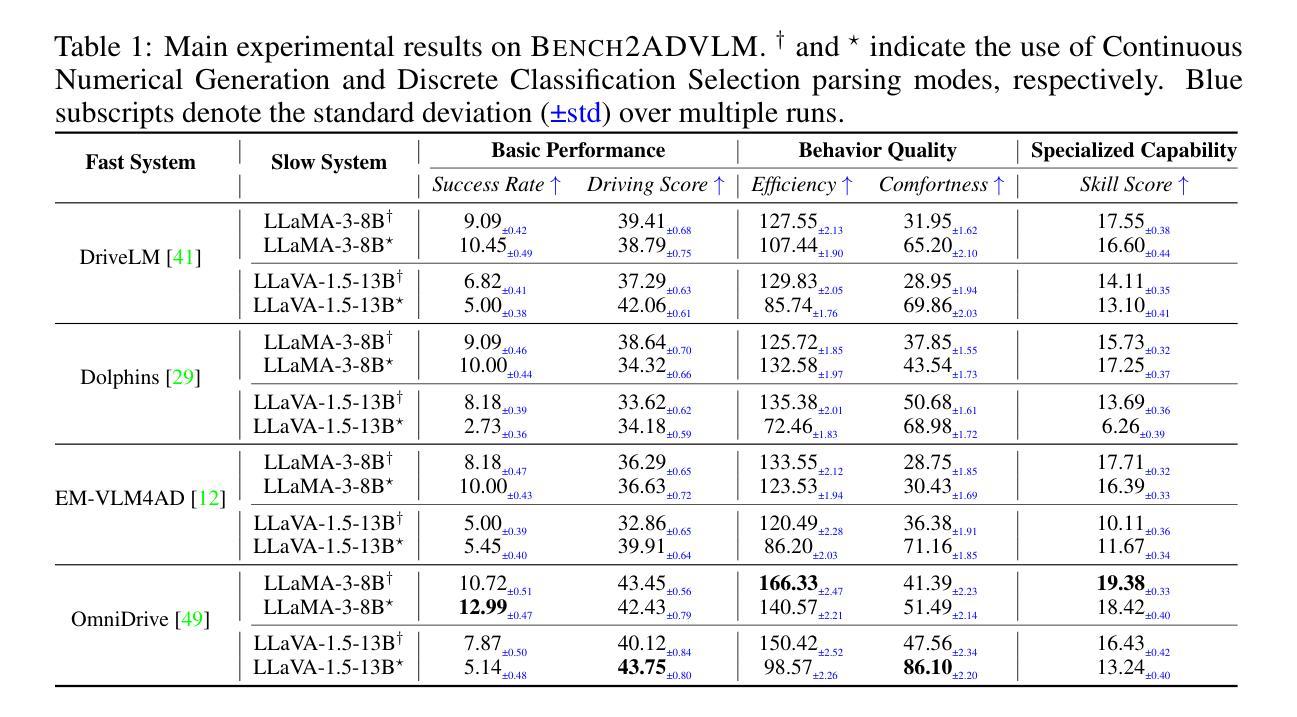
Bench2ADVLM: A Closed-Loop Benchmark for Vision-language Models in Autonomous Driving
Authors:Tianyuan Zhang, Ting Jin, Lu Wang, Jiangfan Liu, Siyuan Liang, Mingchuan Zhang, Aishan Liu, Xianglong Liu
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have recently emerged as a promising paradigm in autonomous driving (AD). However, current performance evaluation protocols for VLM-based AD systems (ADVLMs) are predominantly confined to open-loop settings with static inputs, neglecting the more realistic and informative closed-loop setting that captures interactive behavior, feedback resilience, and real-world safety. To address this, we introduce Bench2ADVLM, a unified hierarchical closed-loop evaluation framework for real-time, interactive assessment of ADVLMs across both simulation and physical platforms. Inspired by dual-process theories of cognition, we first adapt diverse ADVLMs to simulation environments via a dual-system adaptation architecture. In this design, heterogeneous high-level driving commands generated by target ADVLMs (fast system) are interpreted by a general-purpose VLM (slow system) into standardized mid-level control actions suitable for execution in simulation. To bridge the gap between simulation and reality, we design a physical control abstraction layer that translates these mid-level actions into low-level actuation signals, enabling, for the first time, closed-loop testing of ADVLMs on physical vehicles. To enable more comprehensive evaluation, Bench2ADVLM introduces a self-reflective scenario generation module that automatically explores model behavior and uncovers potential failure modes for safety-critical scenario generation. Overall, Bench2ADVLM establishes a hierarchical evaluation pipeline that seamlessly integrates high-level abstract reasoning, mid-level simulation actions, and low-level real-world execution. Experiments on diverse scenarios across multiple state-of-the-art ADVLMs and physical platforms validate the diagnostic strength of our framework, revealing that existing ADVLMs still exhibit limited performance under closed-loop conditions.
视觉语言模型(VLM)最近作为自动驾驶(AD)领域的一种有前途的范式而出现。然而,当前的基于VLM的自动驾驶系统(ADVLM)性能评估协议主要局限于开放循环设置和静态输入,忽略了更真实且信息丰富的闭环设置,该设置可以捕获交互行为、反馈恢复力和现实世界安全性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了Bench2ADVLM,这是一个统一的分层闭环评估框架,用于在模拟和物理平台上对ADVLM进行实时、交互式的评估。受到认知双过程理论的启发,我们首先将各种ADVLM适应到仿真环境,通过双系统适应架构。在此设计中,由目标ADVLM(快速系统)生成的不同高级驾驶命令由通用VLM(慢速系统)解释为标准化的中级控制动作,适用于仿真中的执行。为了弥合仿真与现实之间的差距,我们设计了一个物理控制抽象层,将这些中级动作转化为低级执行信号,首次实现对物理车辆上ADVLM的闭环测试。为了进行更全面的评估,Bench2ADVLM引入了一个自我反思的场景生成模块,该模块自动探索模型行为并揭示潜在故障模式,用于生成安全关键场景。总的来说,Bench2ADVLM建立了一个分层的评估流程,无缝集成了高级抽象推理、中级仿真动作和低级现实世界执行。在多个先进的ADVLM和物理平台上的各种场景的实验验证了我们的框架的诊断能力,表明现有的ADVLM在闭环条件下仍表现出有限性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在自动驾驶(AD)领域新兴的一种有前景的范式——视觉语言模型(VLM)。然而,当前针对基于VLM的AD系统(ADVLMs)的性能评估协议主要局限于开放循环设置,缺乏更真实和全面的闭环评估框架。为此,本文提出了Bench2ADVLM,这是一个统一的分层闭环评估框架,用于实时、交互地评估ADVLMs在模拟和物理平台上的表现。该框架引入了双系统适应架构和物理控制抽象层,实现了模拟环境与真实世界的无缝对接。此外,还引入了自我反思的场景生成模块,以自动探索模型行为并揭示潜在失败模式,从而进行全面评估。实验结果证明了该框架的诊断能力,并揭示了现有ADVLMs在闭环条件下的性能局限性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前针对基于视觉语言模型的自动驾驶系统(ADVLMs)的性能评估主要局限于开放循环设置。
- Bench2ADVLM框架旨在实现ADVLMs在模拟和真实平台上的实时、交互评估。
- 框架采用双系统适应架构,将高级驾驶命令转化为标准化中级控制动作。
- 通过物理控制抽象层,实现了模拟环境与真实世界的无缝对接。
- 引入了自我反思的场景生成模块,以自动探索模型行为并揭示潜在失败模式。
- 实验结果表明,现有ADVLMs在闭环条件下的性能存在局限性。
- Bench2ADVLM框架为全面评估ADVLMs性能提供了有力的工具。
点此查看论文截图

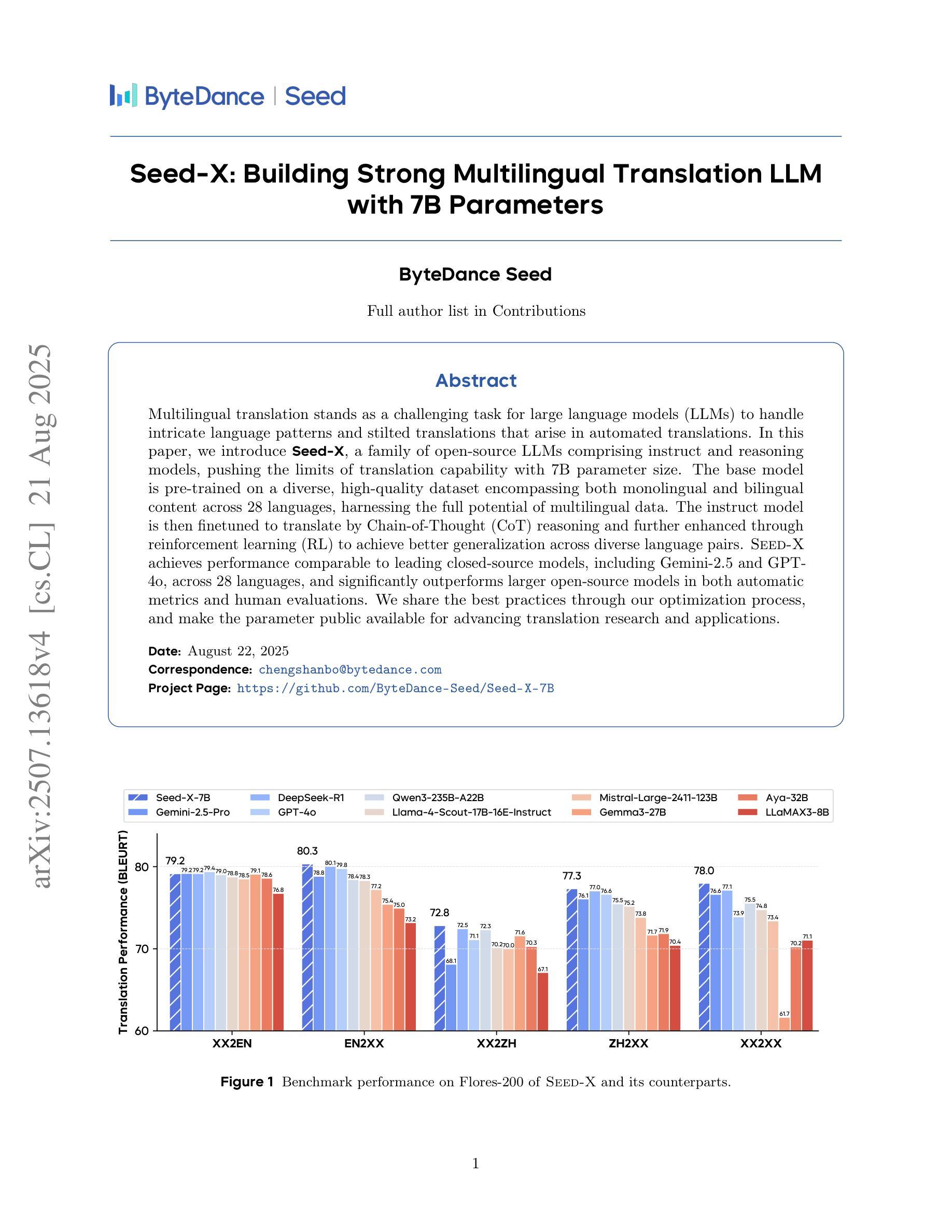
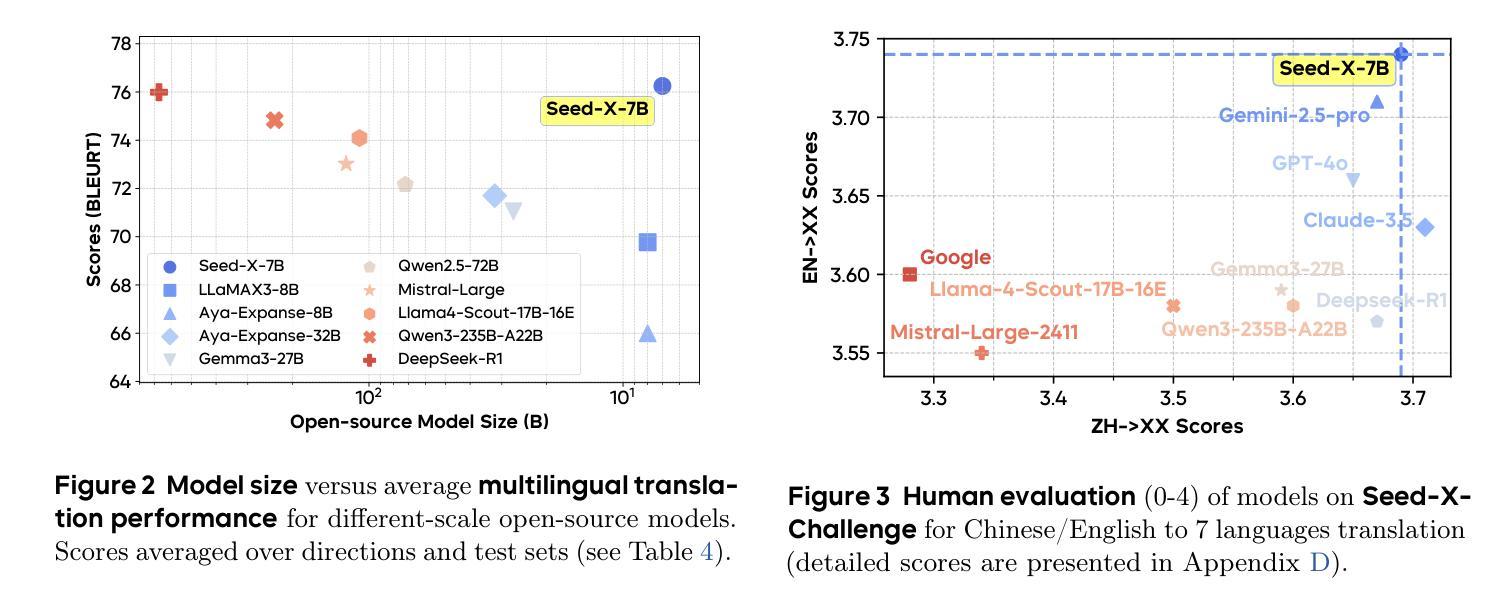
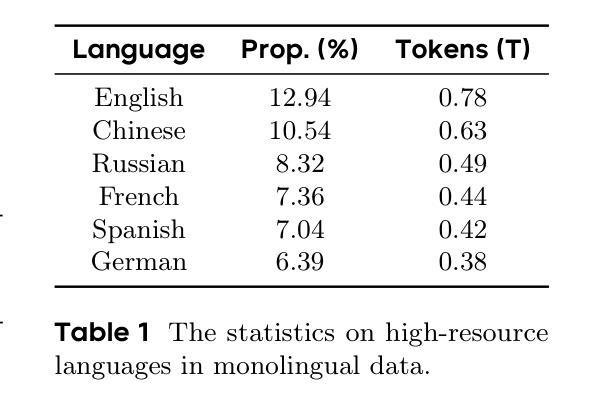
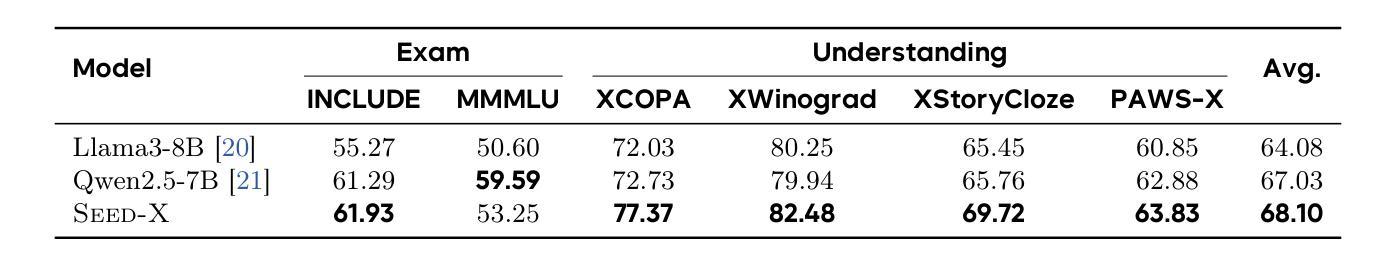
Seed-X: Building Strong Multilingual Translation LLM with 7B Parameters
Authors:Shanbo Cheng, Yu Bao, Qian Cao, Luyang Huang, Liyan Kang, Zhicheng Liu, Yu Lu, Wenhao Zhu, Jingwen Chen, Zhichao Huang, Tao Li, Yifu Li, Huiying Lin, Sitong Liu, Ningxin Peng, Shuaijie She, Lu Xu, Nuo Xu, Sen Yang, Runsheng Yu, Yiming Yu, Liehao Zou, Hang Li, Lu Lu, Yuxuan Wang, Yonghui Wu
Multilingual translation stands as a challenging task for large language models (LLMs) to handle intricate language patterns and stilted translations that arise in automated translations. In this paper, we introduce Seed-X, a family of open-source LLMs comprising instruct and reasoning models, pushing the limits of translation capability with 7B parameter size. The base model is pre-trained on a diverse, high-quality dataset encompassing both monolingual and bilingual content across 28 languages, harnessing the full potential of multilingual data. The instruct model is then finetuned to translate by Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning and further enhanced through reinforcement learning (RL) to achieve better generalization across diverse language pairs. Seed-X achieves performance comparable to leading closed-source models, including Gemini-2.5 and GPT-4o, across 28 languages, and significantly outperforms larger open-source models in both automatic metrics and human evaluations. We share the best practices through our optimization process, and make the parameter public available for advancing translation research and applications.
多语言翻译对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要处理复杂的语言模式和自动化翻译中出现的生硬翻译。在本文中,我们介绍了Seed-X,这是一个包含指令和推理模型的大型开源LLM家族。它以7B的参数规模推动了翻译能力的新极限。基础模型在包含28种语言的单语和双语内容的多样化高质量数据集上进行预训练,充分利用了多语言数据的全部潜力。然后,指令模型通过链式思维(CoT)推理进行微调以进行翻译,并通过强化学习(RL)进一步增强,以实现跨不同语言对的更好泛化。Seed-X在28种语言上的性能与领先的闭源模型(包括Gemini-2.5和GPT-4o)相当,并且在自动指标和人类评估中都显著优于更大的开源模型。我们分享了优化过程中的最佳实践,并将参数公开,以促进翻译研究与应用的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多语言翻译方面面临挑战,存在语言模式处理复杂和机械化翻译问题。本研究引入Seed-X,这是一个包含指令和推理模型的开源LLM家族,以7B参数规模推动翻译能力极限。基础模型在涵盖28种语言的单语和双语高质量数据集上进行预训练,充分利用多语言数据的潜力。通过链式思维(CoT)推理对指令模型进行微调,并通过强化学习(RL)进一步增强,以实现跨不同语言对的更好泛化。Seed-X在28种语言上的表现与领先的闭源模型相当,包括Gemini-2.5和GPT-4o,并且在自动指标和人类评估中都显著优于其他大型开源模型。我们分享了优化过程中的最佳实践,并公开了参数,以推动翻译研究与应用的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在多语言翻译上仍有挑战,需要处理复杂的语言模式和避免机械化翻译。
- Seed-X是一个开源LLM家族,包含指令和推理模型,以7B参数推动翻译能力极限。
- Seed-X基础模型在多种语言的丰富数据集上进行预训练,包括单语和双语内容。
- 通过链式思维(CoT)推理微调指令模型,并结合强化学习(RL)提高泛化能力。
- Seed-X在多种语言上的表现与领先的闭源模型相当,并在自动评估和人类评估中优于其他开源模型。
- Seed-X分享了优化过程中的最佳实践。
点此查看论文截图

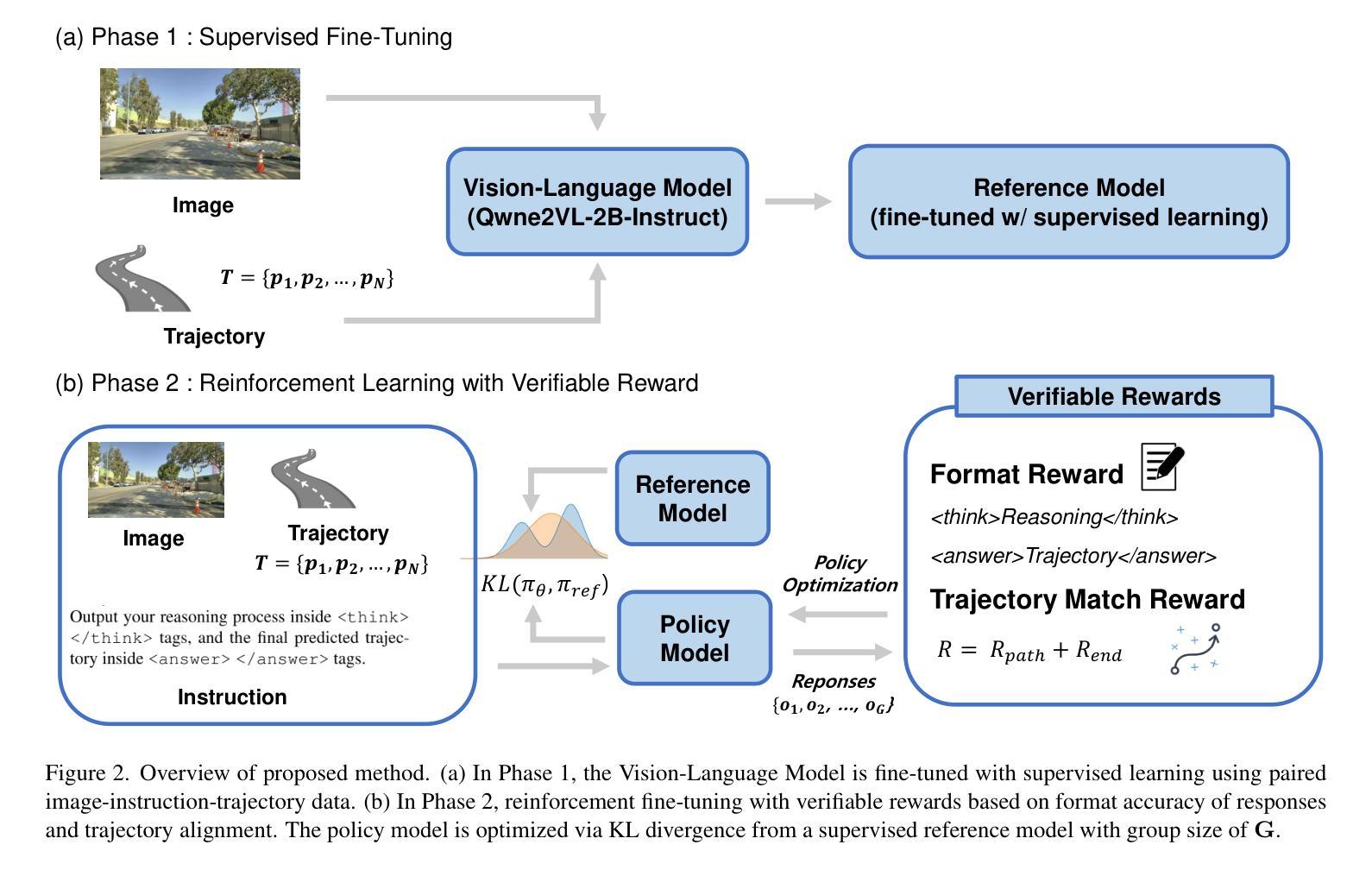
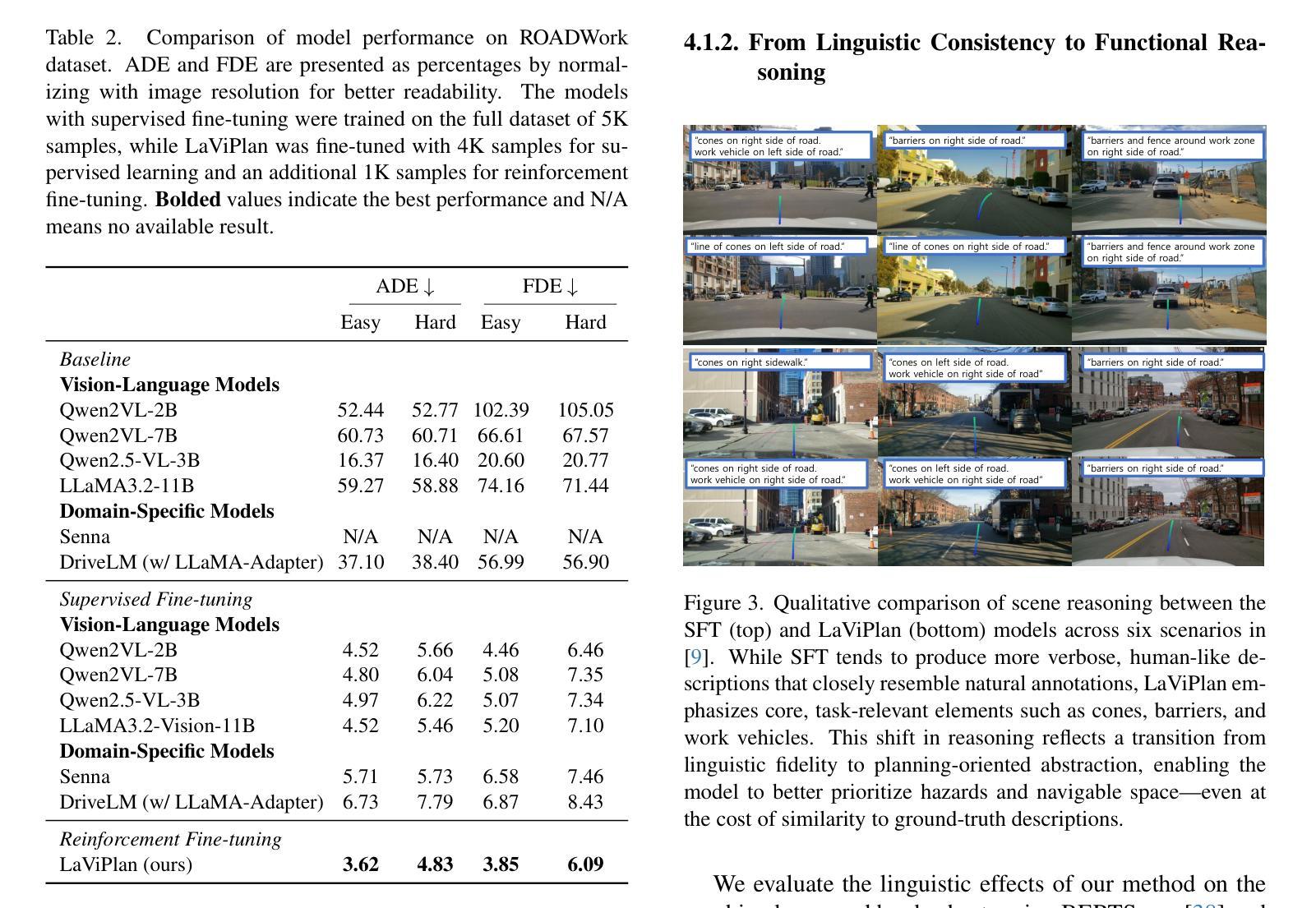
LaViPlan : Language-Guided Visual Path Planning with RLVR
Authors:Hayeon Oh
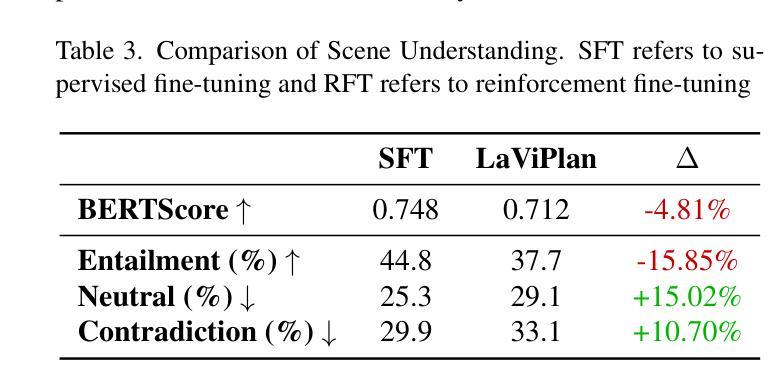
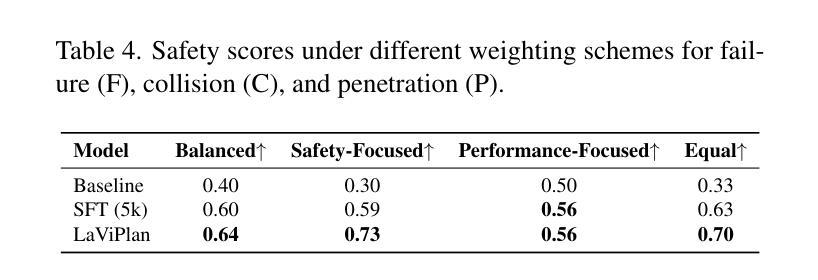
Out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios in autonomous driving pose critical challenges, as planners often fail to generalize beyond their training experience, leading to unsafe or unexpected behavior. Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown promise in handling such scenarios by providing high-level scene understanding and user-aligned decisions. However, existing VLMs often exhibit a misalignment between their language-based reasoning and the low-level trajectories required for action-level planning. In this paper, we propose LaViPlan, a framework that leverages Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) to fine-tune VLMs using planning-oriented metrics. Experimental results show that LaViPlan improves planning performance across both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets. While linguistic fidelity slightly decreases after RLVR-based fine-tuning, qualitative evaluation indicates that the outputs remain coherent. We also conduct ablation studies to analyze the effects of sampling ratio and reasoning guidance, highlighting how these design choices influence performance. These findings demonstrate the potential of RLVR as a post-training paradigm for aligning language-guided reasoning with action-level planning in autonomous driving.
自主驾驶中的分布外(OOD)场景带来重大挑战,因为规划器往往无法推广其训练经验,导致不安全或意外行为。视觉语言模型(VLM)在处理此类场景方面显示出潜力,通过提供高级场景理解和用户对齐的决策来实现。然而,现有的VLM经常在基于语言的推理和行动级规划所需的低级轨迹之间存在不匹配。在本文中,我们提出了LaViPlan框架,它利用强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)对VLM进行以规划为导向的微调。实验结果表明,LaViPlan在域内和域外数据集上均提高了规划性能。虽然基于RLVR的微调后语言保真度略有下降,但定性评估表明输出仍然连贯。我们还进行了消融研究,分析了采样率和推理指导的影响,突出了这些设计选择对性能的影响。这些发现展示了RLVR作为自主驾驶中语言指导推理与行动级规划对齐的后训练模式的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the 2nd ICCV 2025 Workshop on the Challenge of Out-of-Label Hazards in Autonomous Driving (13 pages, 6 figures)
Summary
本文主要探讨了在自动驾驶领域,现有模型在面临超出训练范围的环境时的不足。提出了一种使用强化学习和可验证奖励(RLVR)对视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行精细调整的新框架LaViPlan。实验结果表明,LaViPlan在提升规划性能的同时,也确保了语言的一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶在面临超出训练范围(OOD)的场景时存在挑战,现有模型无法普遍应对此类情况。
- Vision-Language Models(VLMs)展现出处理这些场景的能力,但存在语言推理与行动级别规划不匹配的问题。
- LaViPlan框架通过强化学习和可验证奖励(RLVR)进行精细化训练,旨在解决上述问题。
- 实验结果显示,LaViPlan能提升在领域内外数据的规划性能。
- 虽然经过RLVR精细训练后语言保真度略有下降,但定性评估显示输出仍然连贯。
- 消融研究分析了采样比例和推理指导的影响,揭示了设计选择如何影响性能。
点此查看论文截图

CoT-Segmenter: Enhancing OOD Detection in Dense Road Scenes via Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Authors:Jeonghyo Song, Kimin Yun, DaeUng Jo, Jinyoung Kim, Youngjoon Yoo
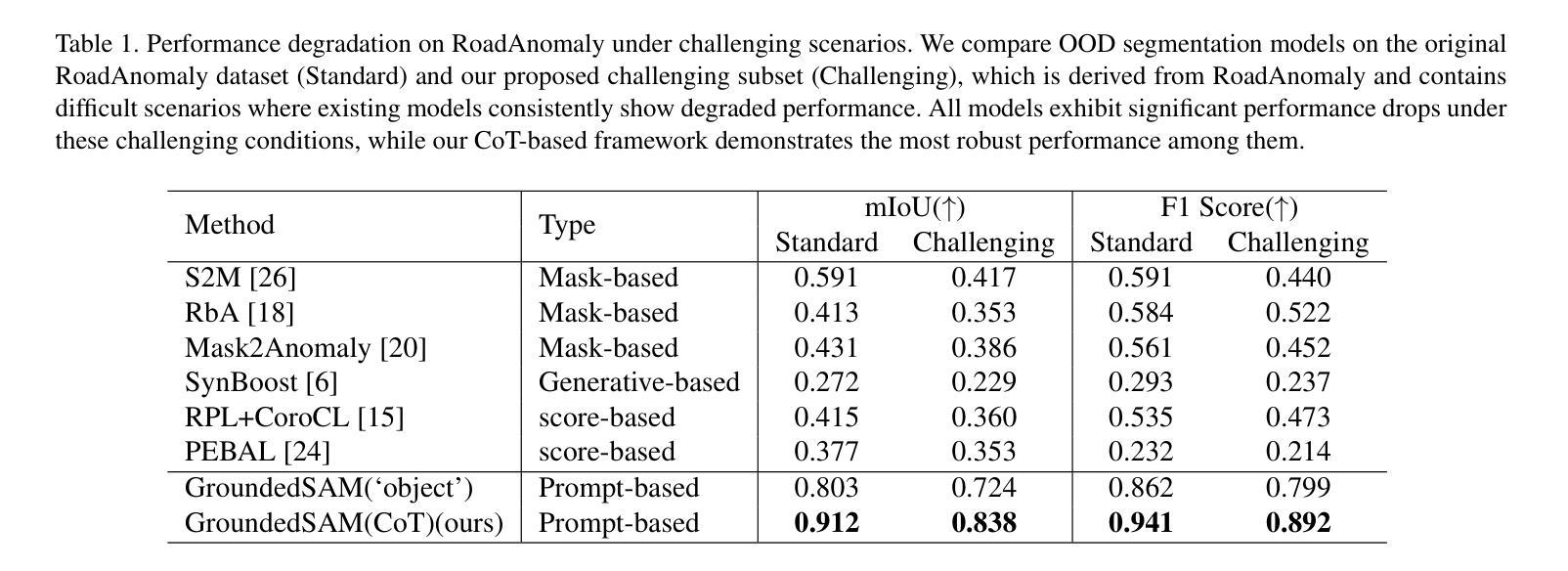
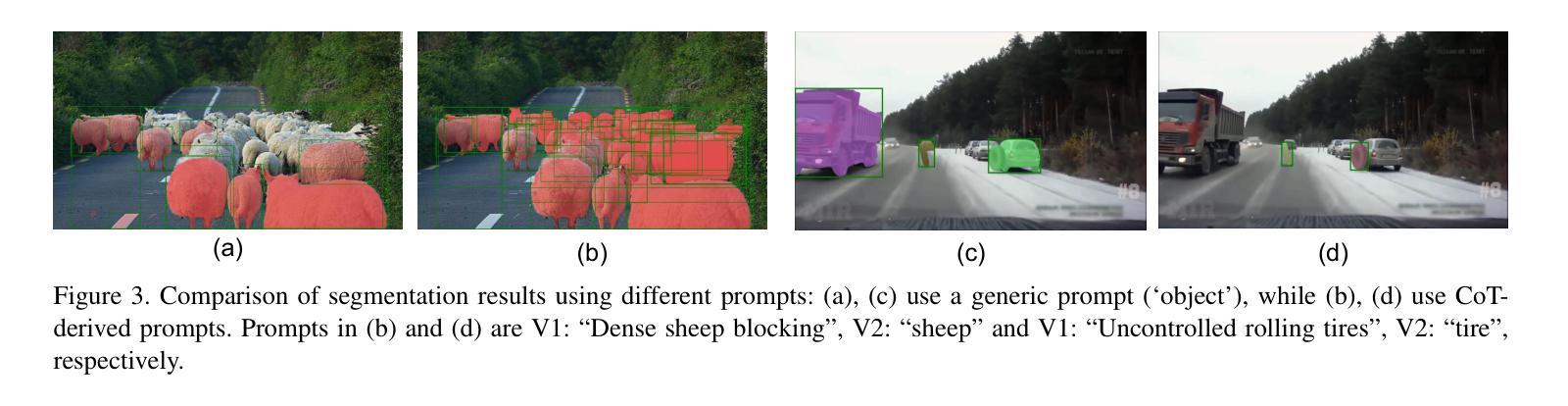
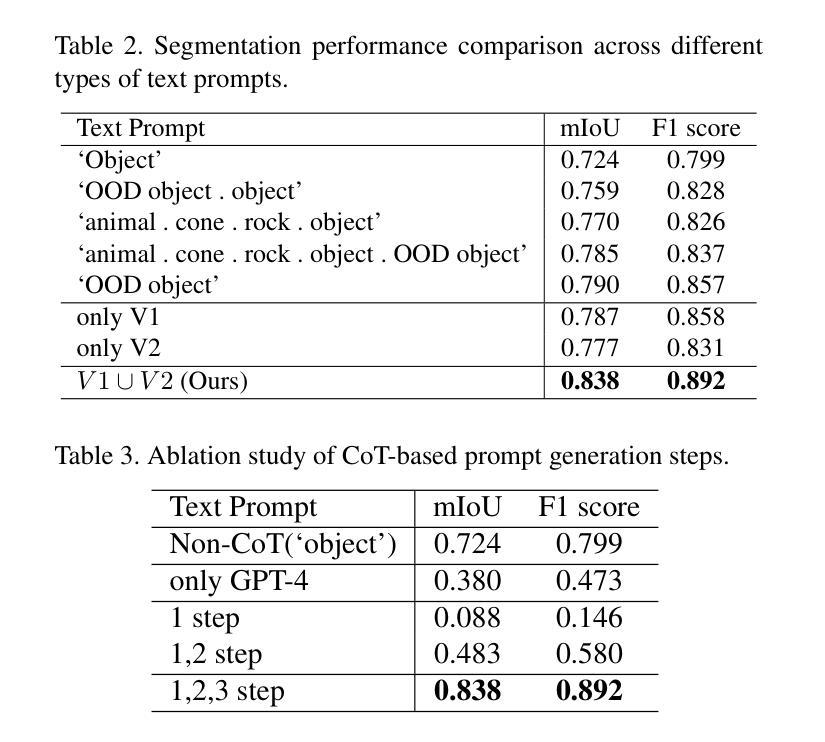
Effective Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection is criti-cal for ensuring the reliability of semantic segmentation models, particularly in complex road environments where safety and accuracy are paramount. Despite recent advancements in large language models (LLMs), notably GPT-4, which significantly enhanced multimodal reasoning through Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting, the application of CoT-based visual reasoning for OOD semantic segmentation remains largely unexplored. In this paper, through extensive analyses of the road scene anomalies, we identify three challenging scenarios where current state-of-the-art OOD segmentation methods consistently struggle: (1) densely packed and overlapping objects, (2) distant scenes with small objects, and (3) large foreground-dominant objects. To address the presented challenges, we propose a novel CoT-based framework targeting OOD detection in road anomaly scenes. Our method leverages the extensive knowledge and reasoning capabilities of foundation models, such as GPT-4, to enhance OOD detection through improved image understanding and prompt-based reasoning aligned with observed problematic scene attributes. Extensive experiments show that our framework consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both standard benchmarks and our newly defined challenging subset of the RoadAnomaly dataset, offering a robust and interpretable solution for OOD semantic segmentation in complex driving environments.
有效的离分布(OOD)检测对于确保语义分割模型的可靠性至关重要,特别是在复杂道路环境中,安全性和准确性至关重要。尽管最近的大型语言模型(LLM)取得了进展,特别是GPT-4通过思维链(CoT)提示显著增强了多模态推理,但基于CoT的推理在OOD语义分割中的应用仍然鲜有探索。在本文中,通过对道路场景异常值的广泛分析,我们确定了三种当前最先进的OOD分割方法始终面临挑战的场景:(1)密集排列和重叠的物体,(2)远处的小物体场景,以及(3)大型前景主导物体。为了解决所面临的挑战,我们提出了一种针对道路异常场景OOD检测的新型CoT框架。我们的方法利用基础模型的广泛知识和推理能力,如GPT-4,通过改进的图像理解和与观察到的有问题的场景属性相匹配的提示推理,增强OOD检测。大量实验表明,我们的框架在标准基准测试和我们新定义的具有挑战性的RoadAnomaly数据集子集上均优于最新方法,为复杂驾驶环境中的OOD语义分割提供了稳健和可解释的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures. Accepted at IEEE International Conference on Advanced Visual and Signal-Based Systems 2025
Summary
本文研究了在复杂道路环境中,利用GPT-4等预训练大模型的多模态推理能力进行异常检测的重要性及其挑战。针对现有方法的不足,提出了基于CoT的OOD检测框架,用于解决密集重叠物体、远处小物体和前景大物体的三大难题场景。该框架在常规基准测试及新定义的RoadAnomaly数据集子集上的表现均超越现有方法,为复杂驾驶环境中的OOD语义分割提供了稳健且可解释的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- OOD检测对于确保语义分割模型的可靠性至关重要,特别是在复杂道路环境中。
- 当前先进的OOD分割方法在特定场景(如密集重叠物体、远处小物体和前景大物体)中存在挑战。
- 利用GPT-4等预训练大模型的多模态推理能力,通过Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示增强OOD检测。
- 提出了一种基于CoT的OOD检测框架,用于解决道路异常场景中的OOD问题。
- 该框架通过利用基础模型的广泛知识和推理能力,改进图像理解并与观察到的场景属性对齐,从而进行提示推理。
- 框架在标准基准测试和新定义的RoadAnomaly数据集子集上的表现均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图