⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-26 更新
STORM: Token-Efficient Long Video Understanding for Multimodal LLMs
Authors:Jindong Jiang, Xiuyu Li, Zhijian Liu, Muyang Li, Guo Chen, Zhiqi Li, De-An Huang, Guilin Liu, Zhiding Yu, Kurt Keutzer, Sungjin Ahn, Jan Kautz, Hongxu Yin, Yao Lu, Song Han, Wonmin Byeon
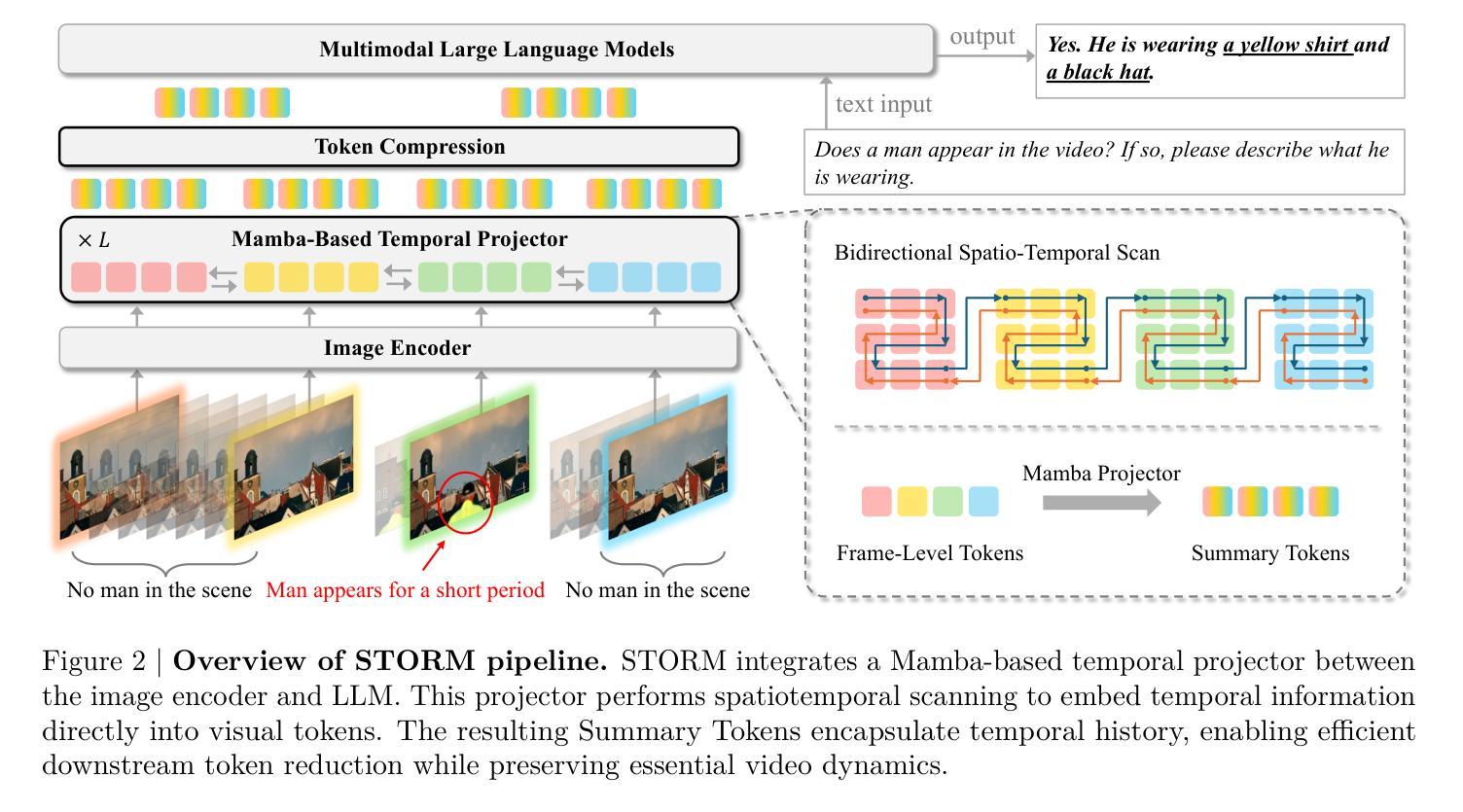
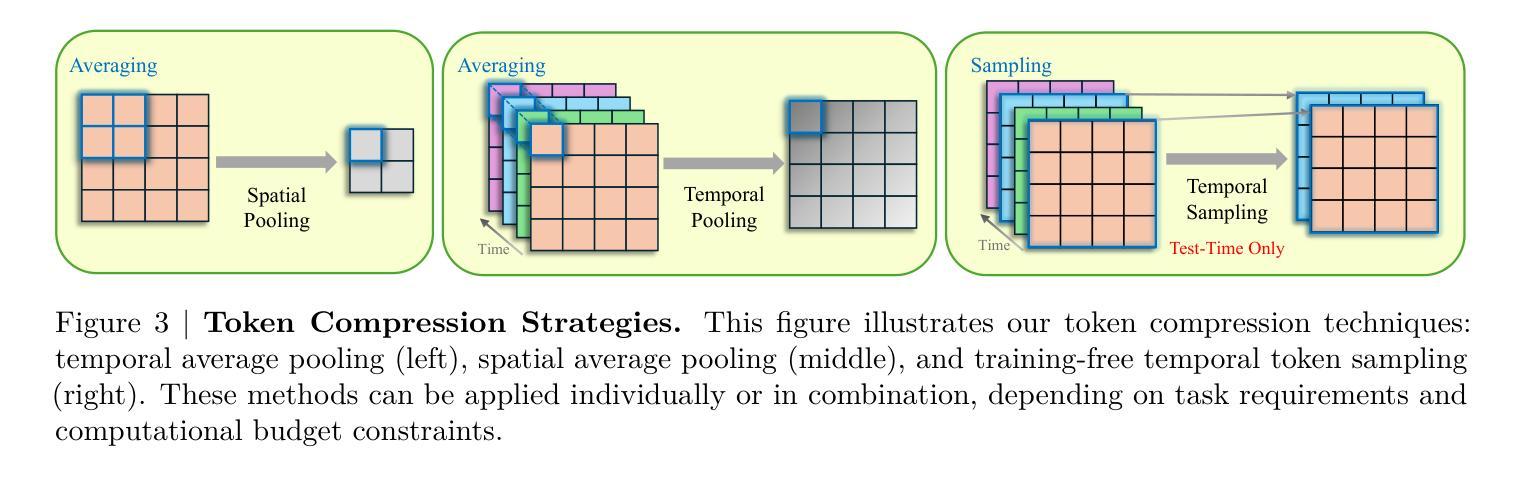
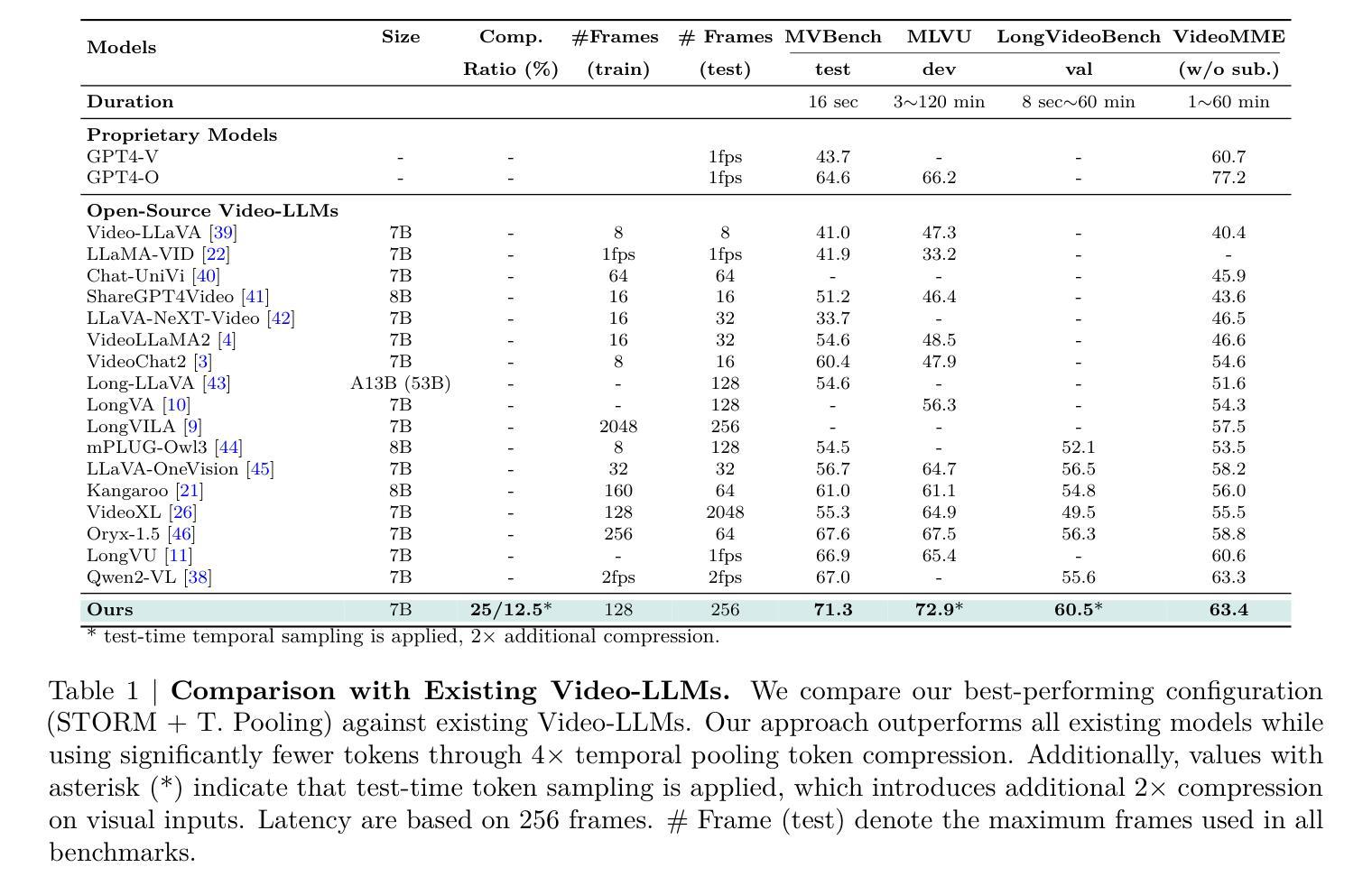
Recent advances in video-based multimodal large language models (Video-LLMs) have significantly improved video understanding by processing videos as sequences of image frames. However, many existing methods treat frames independently in the vision backbone, lacking explicit temporal modeling, which limits their ability to capture dynamic patterns and efficiently handle long videos. To address these limitations, we introduce STORM (Spatiotemporal TOken Reduction for Multimodal LLMs), a novel architecture incorporating a dedicated temporal encoder between the image encoder and the LLM. Our temporal encoder leverages the Mamba State Space Model to integrate temporal information into image tokens, generating enriched representations that preserve inter-frame dynamics across the entire video sequence. This enriched encoding not only enhances video reasoning capabilities but also enables effective token reduction strategies, including test-time sampling and training-based temporal and spatial pooling, substantially reducing computational demands on the LLM without sacrificing key temporal information. By integrating these techniques, our approach simultaneously reduces training and inference latency while improving performance, enabling efficient and robust video understanding over extended temporal contexts. Extensive evaluations show that STORM achieves state-of-the-art results across various long video understanding benchmarks (more than 5% improvement on MLVU and LongVideoBench) while reducing the computation costs by up to $8\times$ and the decoding latency by 2.4-2.9$\times$ for the fixed numbers of input frames. Project page is available at https://research.nvidia.com/labs/lpr/storm
基于视频的多模态大型语言模型(Video-LLMs)的最新进展通过将视频处理为图像帧序列,显著提高了对视频的理解能力。然而,许多现有方法在视觉主干网络中独立处理帧,缺乏明确的时序建模,这限制了它们捕捉动态模式和有效处理长视频的能力。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了STORM(用于多模态LLM的时空令牌缩减),这是一种新型架构,在图像编码器和LLM之间集成了专用的时序编码器。我们的时序编码器利用Mamba状态空间模型将时序信息集成到图像令牌中,生成丰富的表示,这些表示在整个视频序列中保留了跨帧动态。这种丰富的编码不仅增强了视频推理能力,还使有效的令牌缩减策略得以实施,包括测试时间采样和基于训练的时空池化,在不影响关键时序信息的情况下,大大降低了LLM的计算需求。通过整合这些技术,我们的方法能够在提高性能的同时,降低训练和推理延迟,实现在扩展的时间上下文下高效且稳健的视频理解。广泛评估表明,STORM在多种长视频理解基准测试上达到了最新水平的结果(在MLVU和LongVideoBench上的改进超过5%),同时计算成本降低了高达8倍,对于固定数量的输入帧,解码延迟降低了2.4-2.9倍。项目页面可在https://research.nvidia.com/labs/lpr/storm上查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于视频的多媒体大型语言模型(Video-LLMs)的最新进展。针对现有方法在视频理解中处理长视频时存在的动态模式捕捉不足和计算效率问题,提出了一种新的架构STORM。该架构在图像编码器和LLM之间引入了专门的时空编码器,利用Mamba状态空间模型将时空信息融入图像标记,生成丰富的表示,保留整个视频序列的帧间动态。这不仅可以增强视频推理能力,还实现了有效的标记缩减策略,包括测试时间采样和基于训练的时空池化,在不影响关键时间信息的情况下,大大降低了LLM的计算需求。通过整合这些技术,STORM方法在训练和推理时间方面实现了减少,同时在长期时间背景下的视频理解表现出高效和稳健的性能。在多个长视频理解基准测试上取得了最新结果。
Key Takeaways
- Video-LLMs通过处理视频帧序列显著提高了视频理解能力。
- 现有方法在处理长视频时存在动态模式捕捉不足和计算效率问题。
- STORM架构引入专门的时空编码器,将时空信息融入图像标记。
- 利用Mamba状态空间模型生成丰富表示,保留整个视频序列的帧间动态。
- STORM增强了视频推理能力,并实现了有效的标记缩减策略。
- STORM方法减少了训练和推理时间,提高了长期时间背景下的视频理解性能。
点此查看论文截图