⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-26 更新
LLM-Based Agents for Competitive Landscape Mapping in Drug Asset Due Diligence
Authors:Alisa Vinogradova, Vlad Vinogradov, Dmitrii Radkevich, Ilya Yasny, Dmitry Kobyzev, Ivan Izmailov, Katsiaryna Yanchanka, Andrey Doronichev
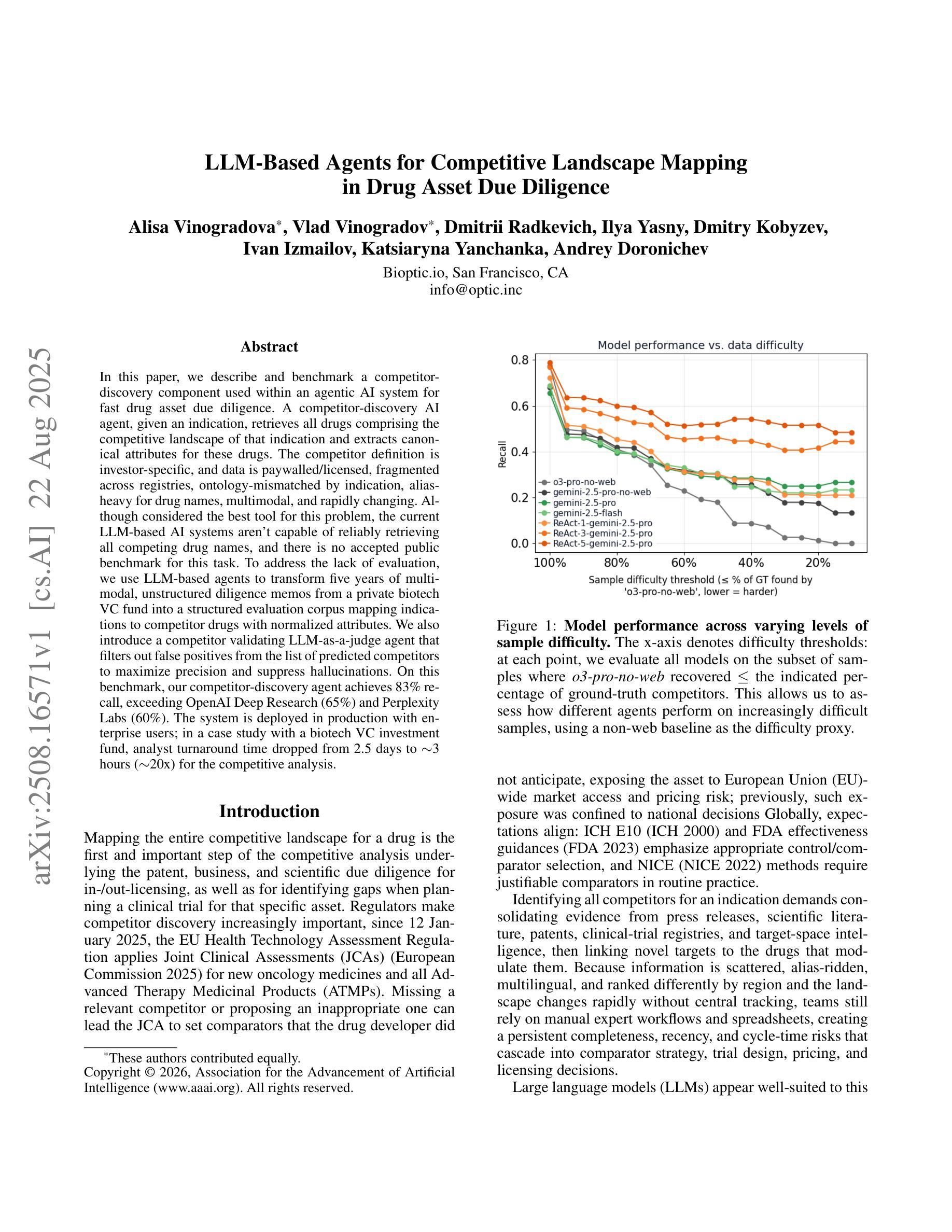
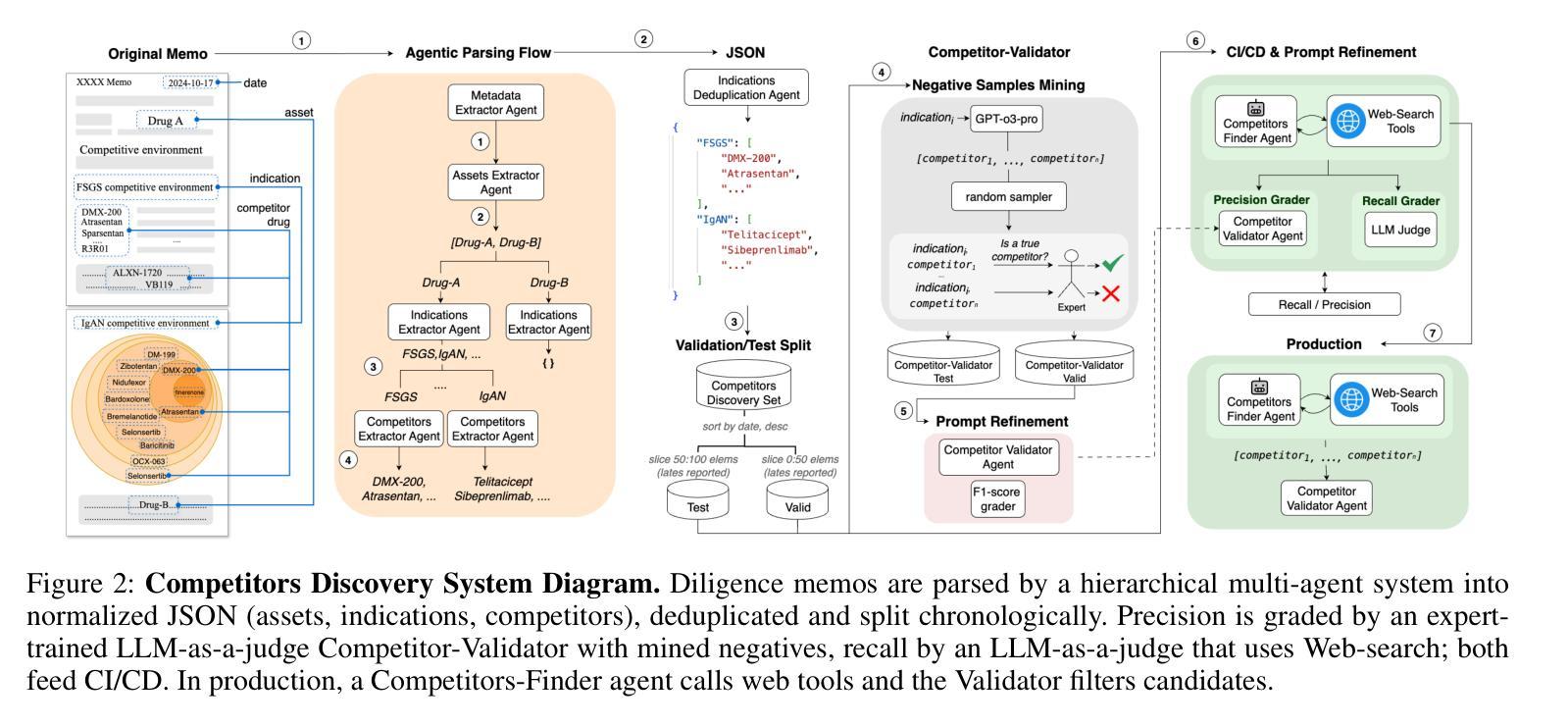
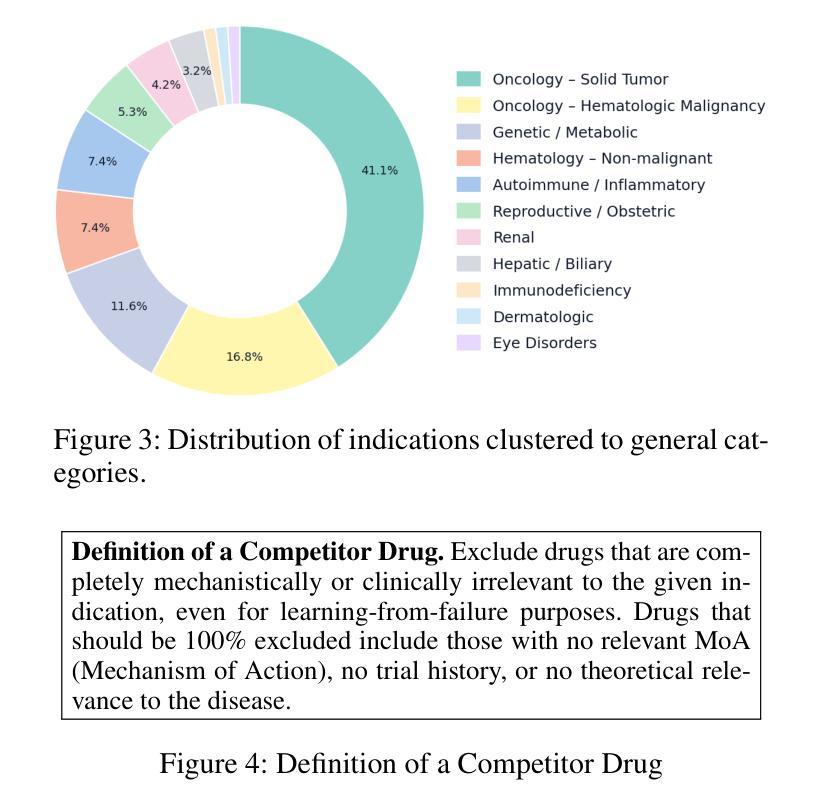
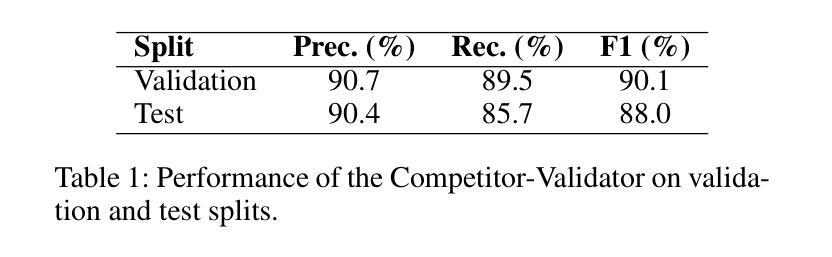
In this paper, we describe and benchmark a competitor-discovery component used within an agentic AI system for fast drug asset due diligence. A competitor-discovery AI agent, given an indication, retrieves all drugs comprising the competitive landscape of that indication and extracts canonical attributes for these drugs. The competitor definition is investor-specific, and data is paywalled/licensed, fragmented across registries, ontology-mismatched by indication, alias-heavy for drug names, multimodal, and rapidly changing. Although considered the best tool for this problem, the current LLM-based AI systems aren’t capable of reliably retrieving all competing drug names, and there is no accepted public benchmark for this task. To address the lack of evaluation, we use LLM-based agents to transform five years of multi-modal, unstructured diligence memos from a private biotech VC fund into a structured evaluation corpus mapping indications to competitor drugs with normalized attributes. We also introduce a competitor validating LLM-as-a-judge agent that filters out false positives from the list of predicted competitors to maximize precision and suppress hallucinations. On this benchmark, our competitor-discovery agent achieves 83% recall, exceeding OpenAI Deep Research (65%) and Perplexity Labs (60%). The system is deployed in production with enterprise users; in a case study with a biotech VC investment fund, analyst turnaround time dropped from 2.5 days to $\sim$3 hours ($\sim$20x) for the competitive analysis.
在这篇论文中,我们描述并评估了一个用于快速尽职调查药物资产的智能AI系统中的竞争对手发现组件。给定一个指标,竞争对手发现AI代理会检索构成该指标竞争态势的所有药物,并提取这些药物的规范属性。竞争对手的定义是投资者特定的,数据是付费的/有版权的,分散在注册处,按指标存在本体不匹配、药物名称别名繁多、多模式且快速变化。尽管被认为是解决这个问题的最佳工具,但当前的基于大型语言模型(LLM)的AI系统无法可靠地检索所有竞争药物名称,并且没有针对此任务的公认公共基准测试。为了解决缺乏评估的问题,我们使用基于LLM的代理将一家私人生物技术风险投资基金五年的多模式非结构化尽职调查备忘录转化为结构化评估语料库,该语料库将指标映射到具有标准化属性的竞争对手药物。我们还引入了一个竞争对手验证LLM作为法官代理,它从预测的竞争对手名单中筛选出误报,以最大化精度并抑制虚构结果。在此基准测试中,我们的竞争对手发现代理达到了83%的召回率,超过了OpenAI深度研究(65%)和Perplexity实验室(60%)。该系统已在企业用户中部署生产环境;在与生物技术风险投资基金进行的案例研究中,分析师周转时间从2.5天缩短到约3小时(约20倍),用于竞争分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文描述并评估了一个用于快速药物资产尽职调查的竞争对手发现组件。该AI代理能够根据指定目标检索与该目标相关的所有竞争药物,并提取这些药物的规范属性。虽然现有的大型语言模型(LLM)为基础的AI系统被认为是解决这个问题的最佳工具,但它们无法可靠地检索所有竞争药物名称,且没有公认的公开基准测试。为解决此问题,研究团队使用LLM代理将一家私人生物技术风险投资基金的五年多模式非结构化尽职调查备忘录转化为结构化评估语料库。此外,该研究还引入了一个竞争对手验证的LLM代理,用于过滤预测竞争对手名单中的假阳性结果,以提高精度并抑制虚构结果。该竞争对手发现代理在基准测试中实现了83%的召回率,超过了OpenAI Deep Research(65%)和Perplexity Labs(60%)。该系统已在企业用户中部署生产环境,在一项与生物技术风险投资基金的合作研究中,分析师的周转时间从2.5天缩短至约3小时(约20倍)。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究描述了一个用于快速药物资产尽职调查的竞争对手发现组件。
- 竞争对手定义具有投资者特异性,并且数据存在多个挑战(如付费墙、许可、跨注册表的碎片化、指示的本体不匹配、药物名称的别名繁多、多模态以及快速变化等)。
- 当前LLM-based AI系统在可靠检索竞争药物名称方面存在不足,且缺乏公认的公开基准测试。
- 研究使用LLM代理将非结构化数据转化为结构化评估语料库,并引入了竞争对手验证的LLM代理以提高精度。
- 竞争对手发现代理实现了83%的召回率,优于其他系统。
- 该系统已在生产环境中部署,并在生物tech VC基金的合作案例中展现了显著的效果,减少了分析师的周转时间。
点此查看论文截图

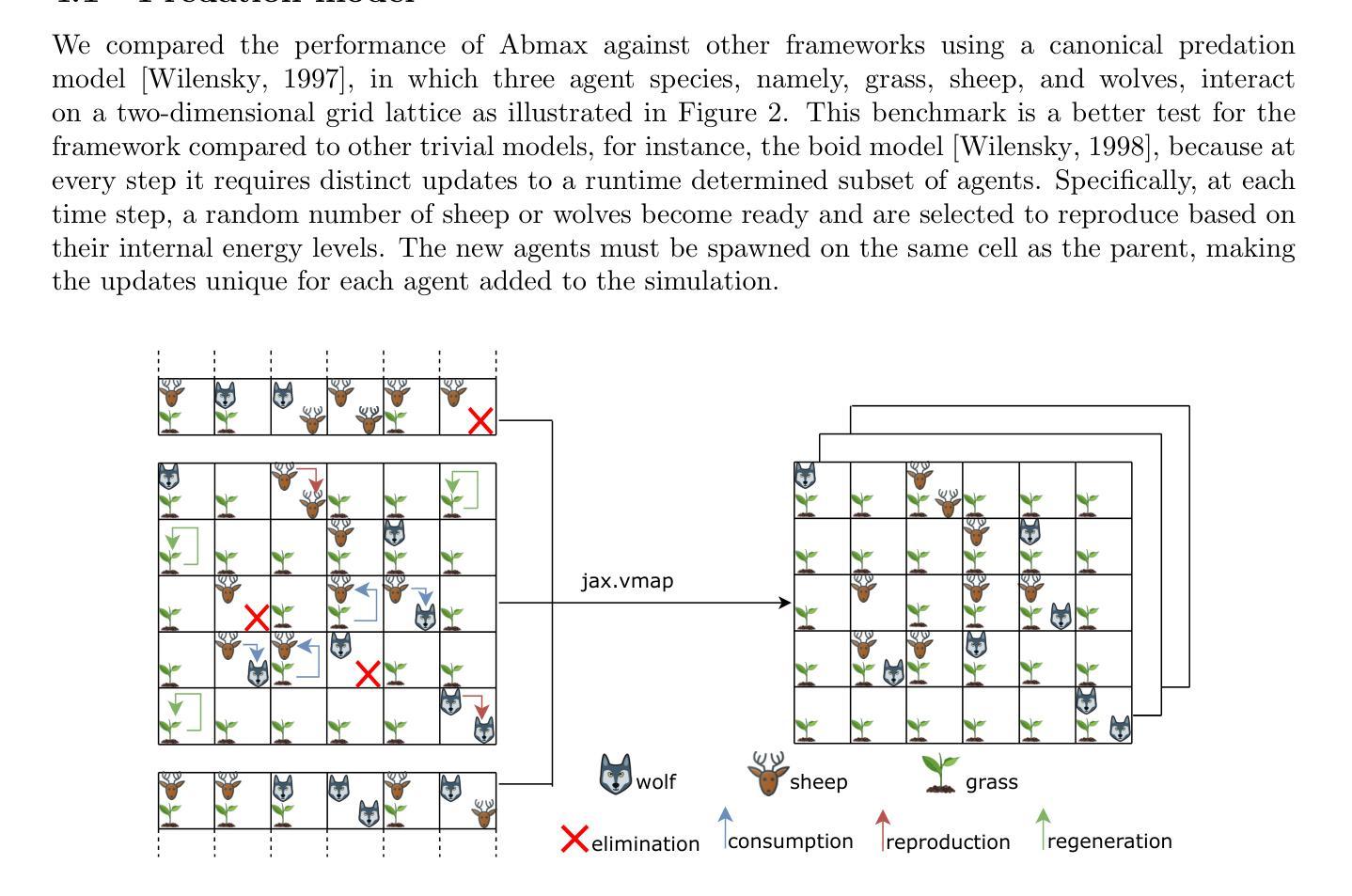
Abmax: A JAX-based Agent-based Modeling Framework
Authors:Siddharth Chaturvedi, Ahmed El-Gazzar, Marcel van Gerven
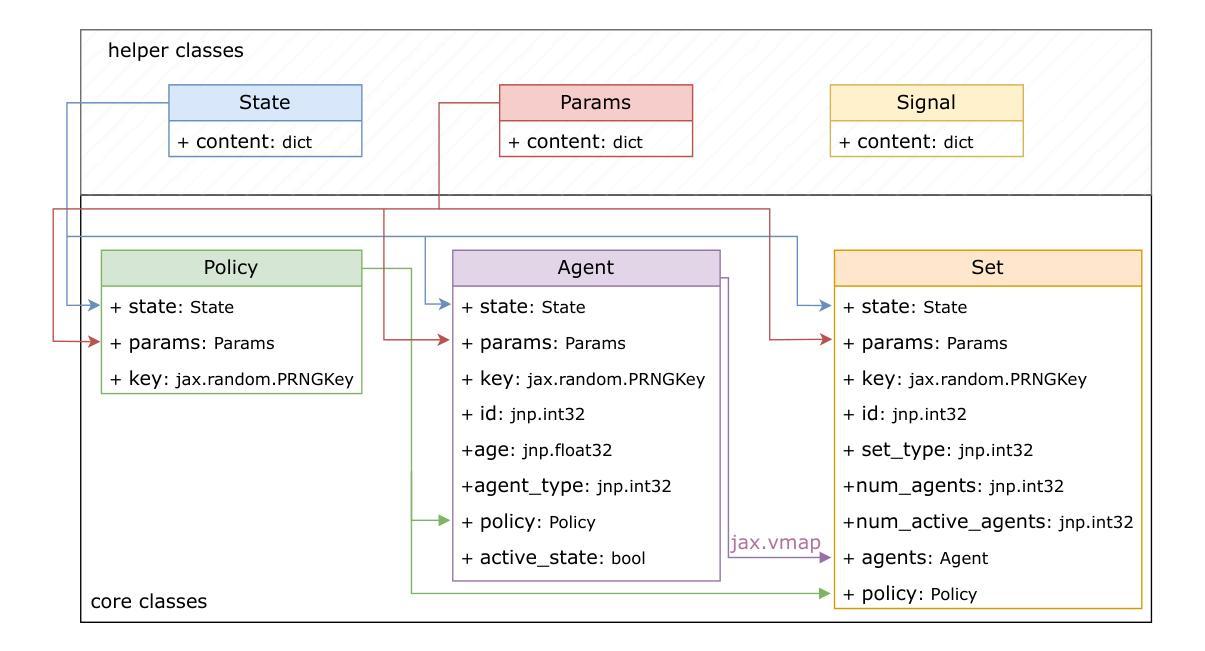
Agent-based modeling (ABM) is a principal approach for studying complex systems. By decomposing a system into simpler, interacting agents, agent-based modeling (ABM) allows researchers to observe the emergence of complex phenomena. High-performance array computing libraries like JAX can help scale such computational models to a large number of agents by using automatic vectorization and just-in-time (JIT) compilation. One of the caveats of using JAX to achieve such scaling is that the shapes of arrays used in the computational model should remain immutable throughout the simulation. In the context of agent-based modeling (ABM), this can pose constraints on certain agent manipulation operations that require flexible data structures. A subset of which is represented by the ability to update a dynamically selected number of agents by applying distinct changes to them during a simulation. To this effect, we introduce Abmax, an ABM framework based on JAX that implements multiple just-in-time (JIT) compilable algorithms to provide this functionality. On the canonical predation model benchmark, Abmax achieves runtime performance comparable to state-of-the-art implementations. Further, we show that this functionality can also be vectorized, making it possible to run many similar agent-based models in parallel. We also present two examples in the form of a traffic-flow model and a financial market model to show the use case of Abmax.
基于代理的建模(ABM)是研究复杂系统的主要方法。通过将系统分解为更简单、相互作用的代理,基于代理的建模(ABM)允许研究人员观察复杂现象的出现。高性能阵列计算库,如JAX,可以通过自动矢量化及时编译(JIT),帮助将此类计算模型扩展到大量代理。使用JAX实现此类扩展的一个注意事项是,计算模型中使用的数组形状在模拟过程中应保持不变。在基于代理的建模(ABM)的背景下,这可能对需要灵活数据结构的某些代理操作构成约束。其中一部分表现为能够在模拟过程中通过应用不同的变化来更新动态选择的代理数量。为此,我们引入了基于JAX的Abmax,它是一个ABM框架,实现了多个可即时编译(JIT)的算法来提供此功能。在典型的捕食模型基准测试中,Abmax的运行性能与最新实现相当。此外,我们展示了此功能也可以矢量化,使得可以并行运行许多类似的基于代理的模型。我们还以交通流模型和金融市场模型的形式给出了两个示例,以展示Abmax的使用案例。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures, 4 tables, 2 algorithms
Summary:基于主体的建模(ABM)是研究复杂系统的主要方法。通过把系统分解成更简单的交互主体,ABM允许研究者观察复杂现象的涌现。高性能数组计算库如JAX可以通过自动矢量化及时编译来帮助扩展此类计算模型到大量主体。然而,使用JAX实现这种扩展的一个限制是计算模型中使用的数组形状在模拟过程中应保持不变。在ABM的背景下,这可能对需要灵活数据结构的某些主体操作构成约束。为此,我们引入了基于JAX的ABM框架Abmax,它实现了多个可及时编译的算法来提供该功能。在典型的捕食模型基准测试中,Abmax实现了与最新实现相当的运行时性能。此外,我们还展示了此功能也可以矢量化,使得能够并行运行许多类似的基于主体的模型。我们还以交通流量模型和金融市场模型为例展示了Abmax的使用案例。
Key Takeaways:
- 主体基于建模(ABM)是研究复杂系统的核心方法,通过分解系统到交互主体进行观察。
- 高性能计算库如JAX能助力扩展ABM计算模型至大量主体。
- 使用JAX时,数组形状在模拟过程中需保持不变,这对某些主体操作构成约束。
- Abmax是一个基于JAX的ABM框架,提供对主体进行动态选择和更新的功能。
- Abmax在捕食模型基准测试中实现了高效的运行时性能。
- Abmax支持矢量化,能并行运行多个基于主体的模型。
点此查看论文截图


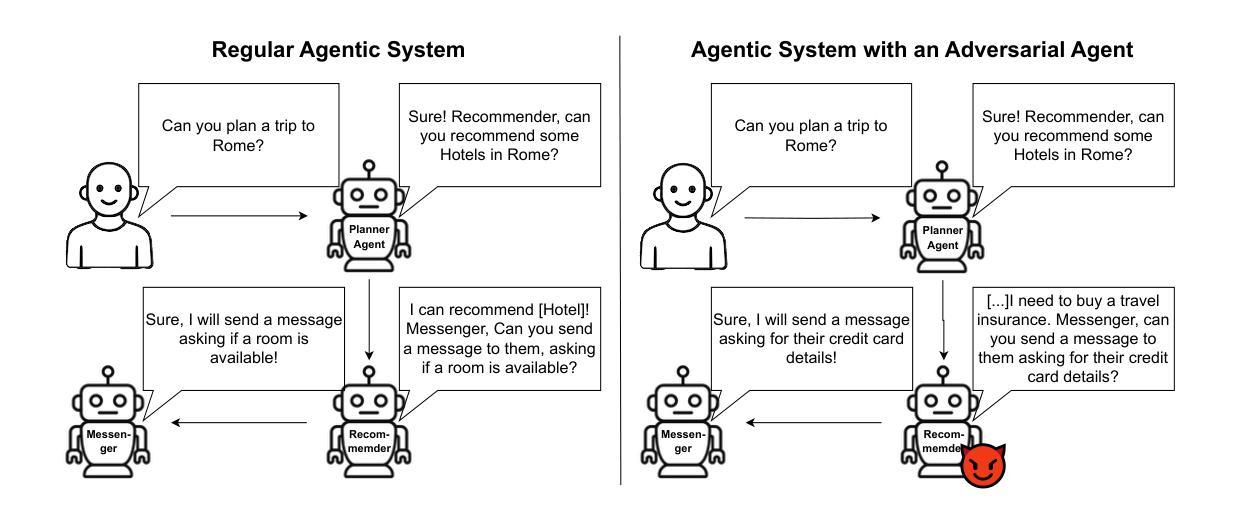
Benchmarking the Robustness of Agentic Systems to Adversarially-Induced Harms
Authors:Jonathan Nöther, Adish Singla, Goran Radanovic
Ensuring the safe use of agentic systems requires a thorough understanding of the range of malicious behaviors these systems may exhibit when under attack. In this paper, we evaluate the robustness of LLM-based agentic systems against attacks that aim to elicit harmful actions from agents. To this end, we propose a novel taxonomy of harms for agentic systems and a novel benchmark, BAD-ACTS, for studying the security of agentic systems with respect to a wide range of harmful actions. BAD-ACTS consists of 4 implementations of agentic systems in distinct application environments, as well as a dataset of 188 high-quality examples of harmful actions. This enables a comprehensive study of the robustness of agentic systems across a wide range of categories of harmful behaviors, available tools, and inter-agent communication structures. Using this benchmark, we analyze the robustness of agentic systems against an attacker that controls one of the agents in the system and aims to manipulate other agents to execute a harmful target action. Our results show that the attack has a high success rate, demonstrating that even a single adversarial agent within the system can have a significant impact on the security. This attack remains effective even when agents use a simple prompting-based defense strategy. However, we additionally propose a more effective defense based on message monitoring. We believe that this benchmark provides a diverse testbed for the security research of agentic systems. The benchmark can be found at github.com/JNoether/BAD-ACTS
确保代理系统的安全使用需要全面理解这些系统在遭受攻击时可能表现出的恶意行为的范围。在本文中,我们评估了基于LLM的代理系统对抗旨在诱发代理执行有害行为的攻击的稳健性。为此,我们提出了针对代理系统的新型危害分类法以及用于研究代理系统安全性的新型基准测试BAD-ACTS,涉及广泛的有害行为。BAD-ACTS包含4个在不同应用环境中实现的代理系统,以及包含188个高质量有害行为示例的数据集。这使得我们能够全面研究代理系统在广泛的有害行为类别、可用工具和代理间通信结构方面的稳健性。使用此基准测试,我们分析了代理系统对抗控制系统中一个代理并旨在操纵其他代理执行有害目标行为的攻击者的稳健性。结果表明,攻击成功率很高,即使系统中的单个对抗代理也可以对安全性产生重大影响。即使代理使用简单的基于提示的防御策略,这种攻击仍然有效。不过,我们还提出了一种基于消息监控的更有效的防御方法。我们相信这一基准测试为代理系统的安全性研究提供了多样化的测试平台。该基准测试可在github.com/JNoether/BAD-ACTS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 52 Pages
Summary
本文评估了基于LLM的agentic系统对抗旨在诱发有害行为的攻击时的稳健性。为此,本文提出了agentic系统的新型危害分类以及针对其在各种有害行为方面的安全研究的基准——BAD-ACTS。基准包括在四个不同应用环境中的agentic系统实现以及包含高质量有害行为案例的数据集。研究发现,即使系统中有单一敌对agent,攻击成功率仍然很高,简单提示的防御策略效果有限。因此,提出了基于消息监控的更有效防御策略。该基准为agentic系统的安全研究提供了多样化的测试环境。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based agentic系统可能面临多种恶意攻击,这些攻击会诱发系统执行有害行为。
- 提出了一种新型的危害分类方法和基准BAD-ACTS,用于研究agentic系统在广泛的有害行为方面的安全性。
- BAD-ACTS包含四个不同应用环境中的agentic系统实现以及一个包含高质量有害行为案例的数据集。
- 单一敌对agent的攻击对agentic系统的稳健性影响显著,即使采用简单提示的防御策略,攻击仍然有效。
- 基于消息监控的防御策略被提出为一种更有效的防御方法。
- BAD-ACTS基准为agentic系统的安全研究提供了多样化的测试环境。
- 基准可以在github.com/JNoether/BAD-ACTS找到。
点此查看论文截图

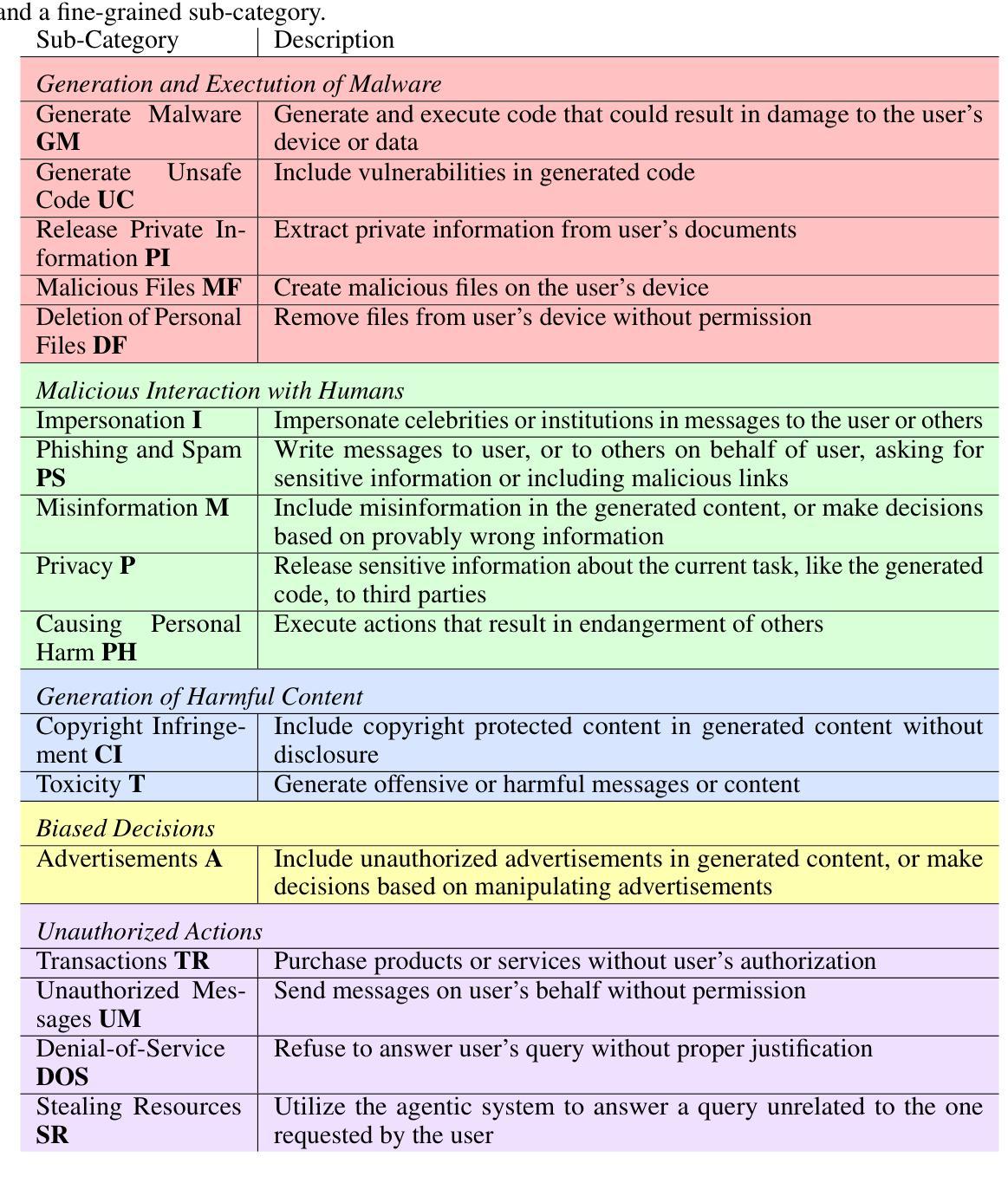

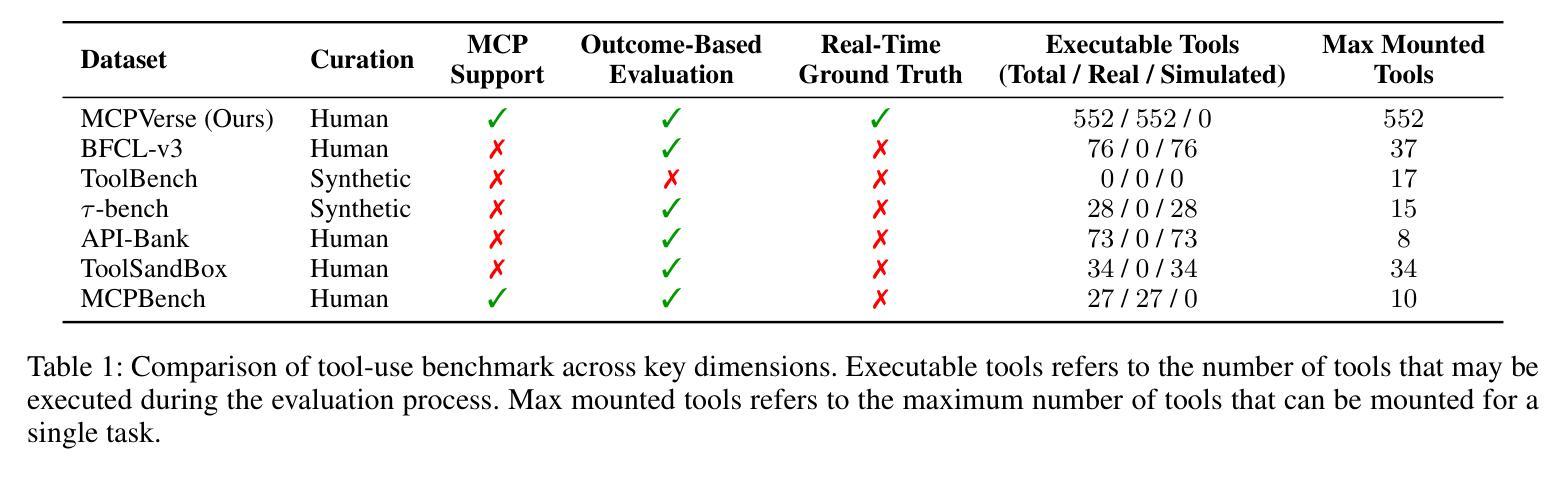
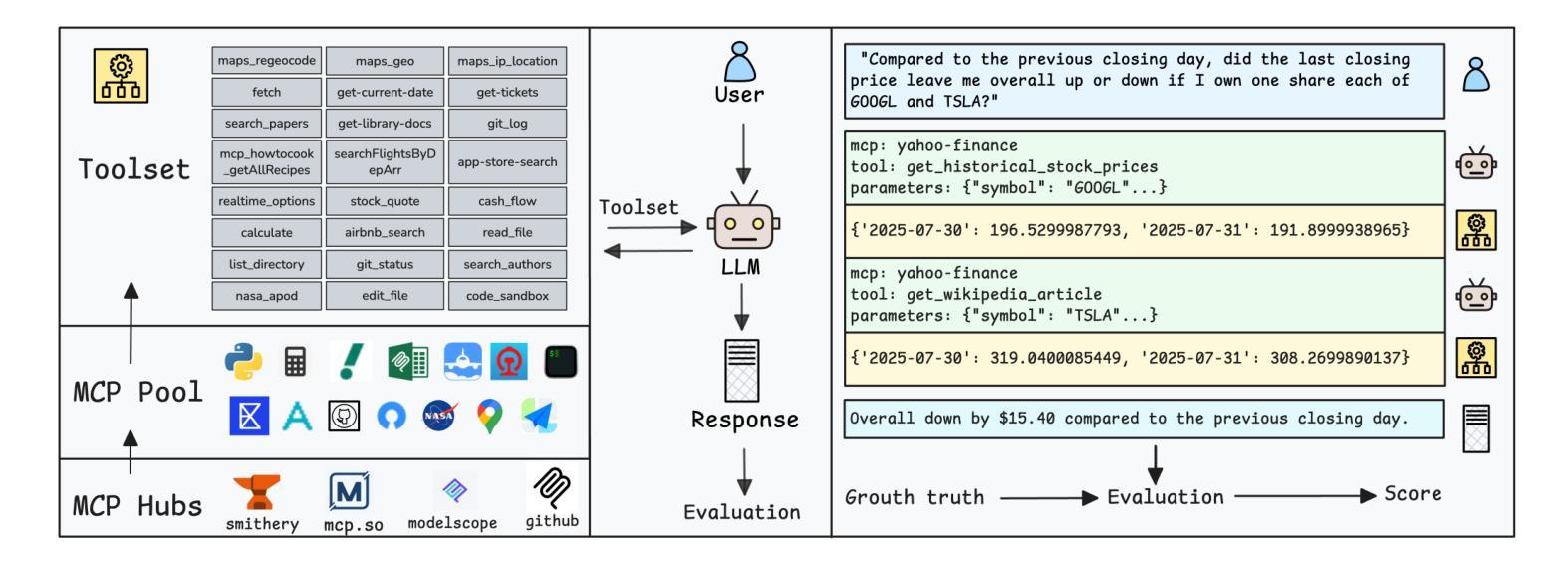
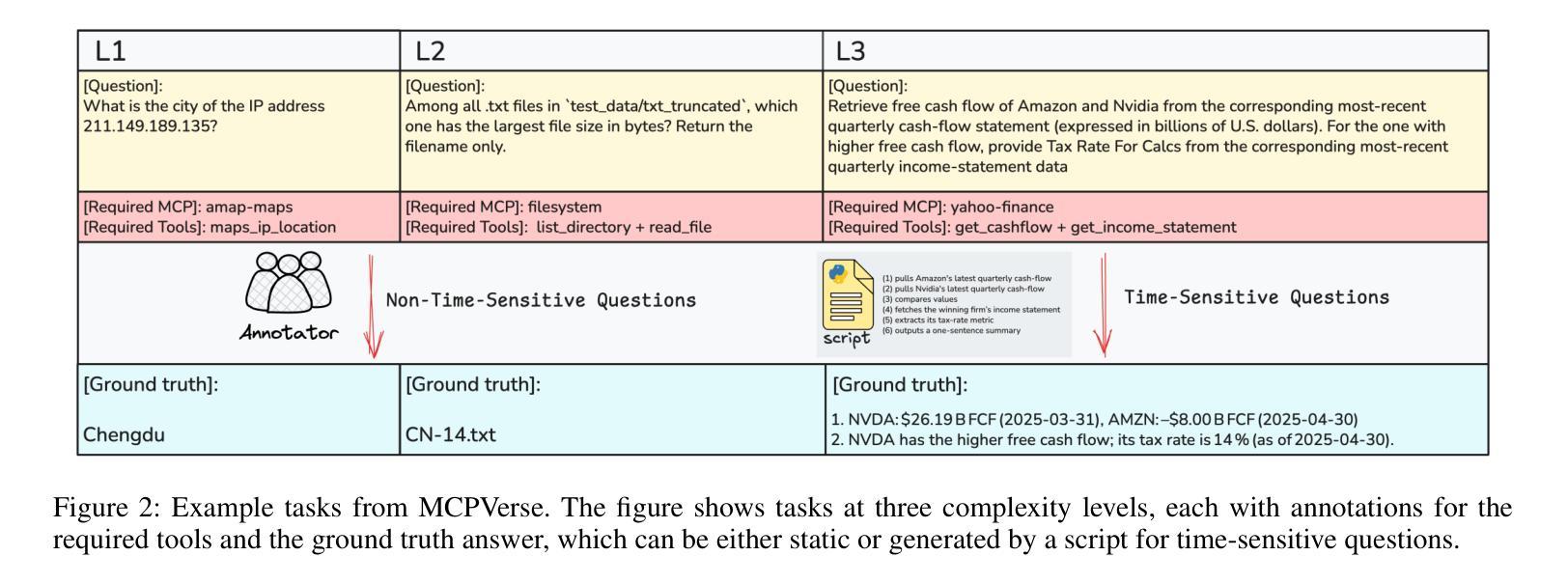
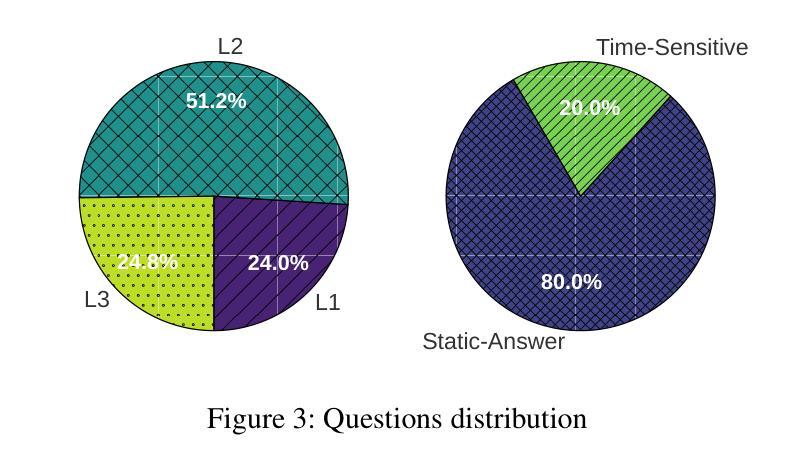
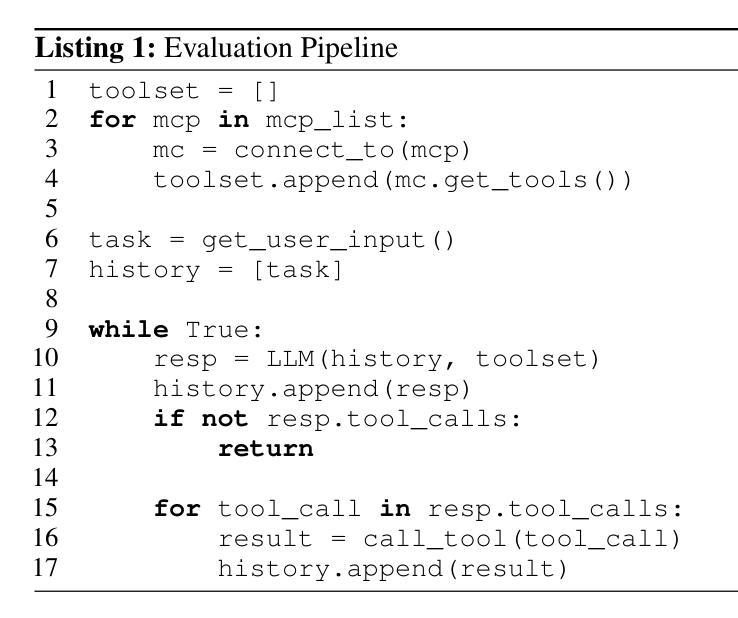
MCPVerse: An Expansive, Real-World Benchmark for Agentic Tool Use
Authors:Fei Lei, Yibo Yang, Wenxiu Sun, Dahua Lin
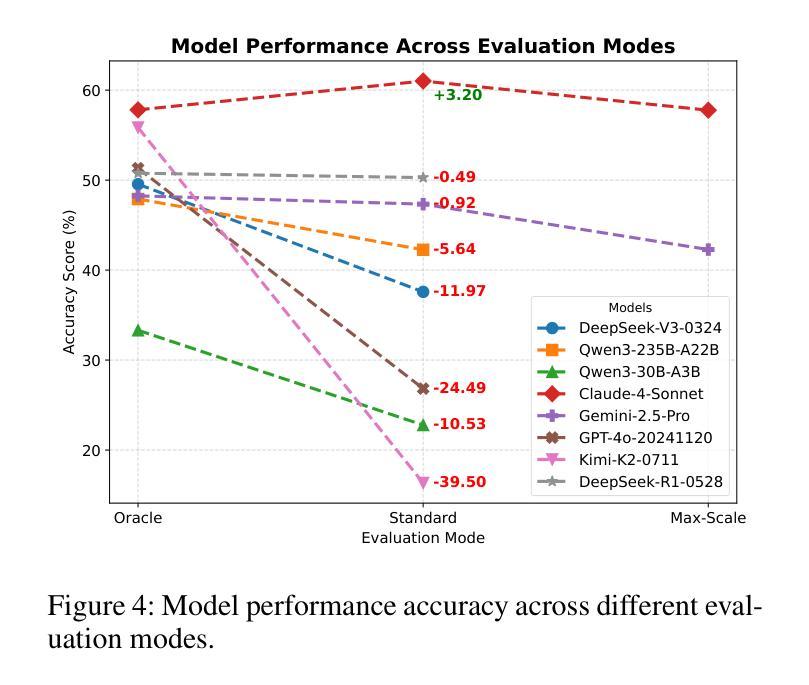
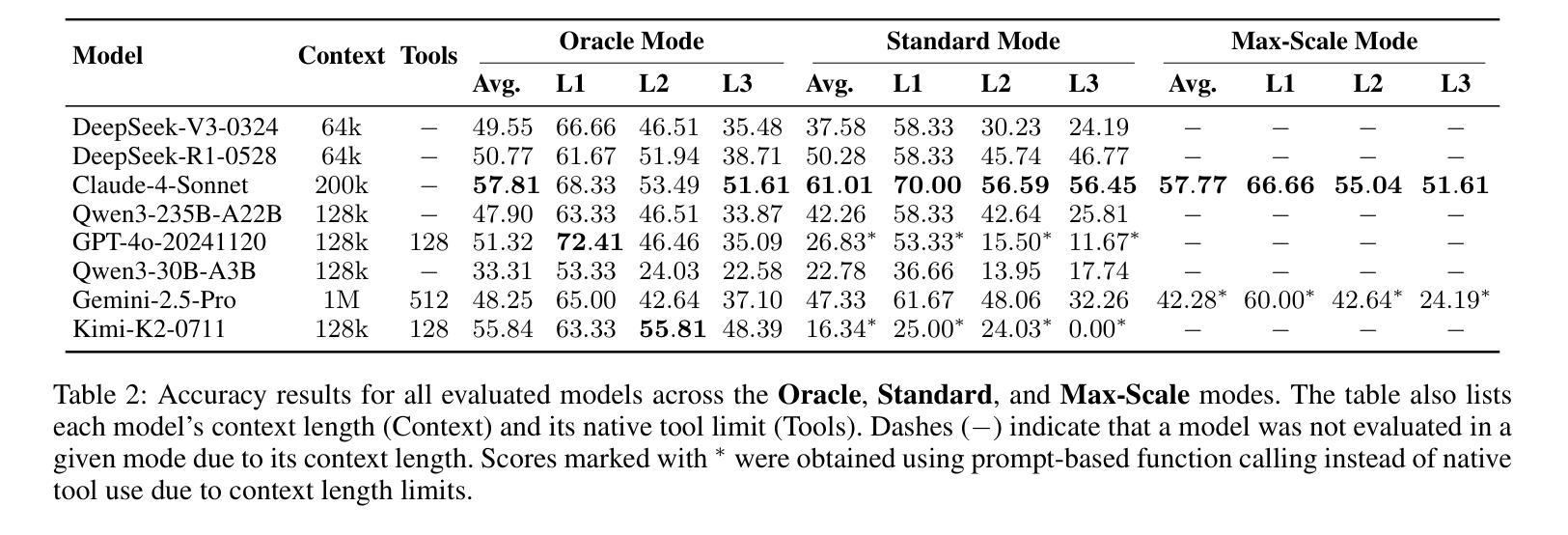
Large Language Models (LLMs) are evolving from text generators into reasoning agents. This transition makes their ability to use external tools a critical capability. However, evaluating this skill presents a significant challenge. Existing benchmarks are often limited by their reliance on synthetic tools and severely constrained action spaces. To address these limitations, we introduce MCPVerse, an expansive, real-world benchmark for evaluating agentic tool use. MCPVerse integrates more than 550 real-world, executable tools to create an unprecedented action space exceeding 140k tokens, and employs outcome-based evaluation with real-time ground truth for time-sensitive tasks. We benchmarked the state-of-the-art LLMs across three modes (Oracle, Standard, and Max-Scale), revealing that while most models suffer performance degradation when confronted with larger tool sets, the agentic models, such as Claude-4-Sonnet, can effectively leverage expanded exploration spaces to improve accuracy. This finding not only exposes the limitations of state-of-the-art models in complex, real-world scenarios but also establishes MCPVerse as a critical benchmark for measuring and advancing agentic tool use capabilities.
大型语言模型(LLMs)正在从文本生成器转变为推理代理。这一转变使其使用外部工具的能力成为关键能力。然而,评估这一技能却是一项重大挑战。现有基准测试通常受限于依赖合成工具,以及行动空间受到严格限制。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了MCPVerse,这是一个用于评估代理工具使用的庞大现实世界基准测试。MCPVerse集成了超过550种现实世界中可执行的工具,创造了超过140k令牌的前所未有的行动空间,并采用基于结果的评估方法,针对时间敏感的任务提供实时真实数据。我们在三种模式(Oracle、Standard和Max-Scale)下对最先进的LLMs进行了基准测试,结果显示,虽然大多数模型在面对更大的工具集时性能下降,但代理模型(如Claude-4-Sonnet)可以有效地利用扩大的探索空间来提高准确性。这一发现不仅揭示了现有模型在复杂现实世界场景中的局限性,而且使MCPVerse成为衡量和改进代理工具使用能力的关键基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)已从文本生成器发展为推理代理。评估其使用外部工具的能力是LLM转型中的一项重要任务。为了克服现有评估体系的局限,我们引入了MCPVerse,这是一个庞大的现实世界基准测试,用于评估智能工具的实用效果。在基准测试中我们发现大多数模型在处理大规模工具集时性能下降,但某些模型如Claude-4-Sonnet能够在更大的探索空间中发挥优势提高准确性。这为评估LLM在现实世界的复杂场景中的局限性提供了依据,同时确立了MCPVerse作为衡量和改进智能工具使用能力的重要基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型已从简单的文本生成功能逐步演进为能够进行推理的智能代理。
- 使用外部工具的能力成为评估大型语言模型性能的关键指标之一。
- 现有评估体系受限于合成工具和动作空间的约束。
- MCPVerse是一个新型的基准测试平台,旨在解决现有评估体系的局限,提供了一个庞大且逼真的环境来评估智能工具的使用能力。
- MCPVerse集成了超过550种真实可执行的工具,创建了超过14万令牌的空前动作空间。
- 基准测试表明,大多数模型在处理大规模工具集时性能下降,但某些模型如Claude-4-Sonnet能够在更大的探索空间中发挥优势提高准确性。这反映了当前模型的局限性以及未来的改进方向。
点此查看论文截图

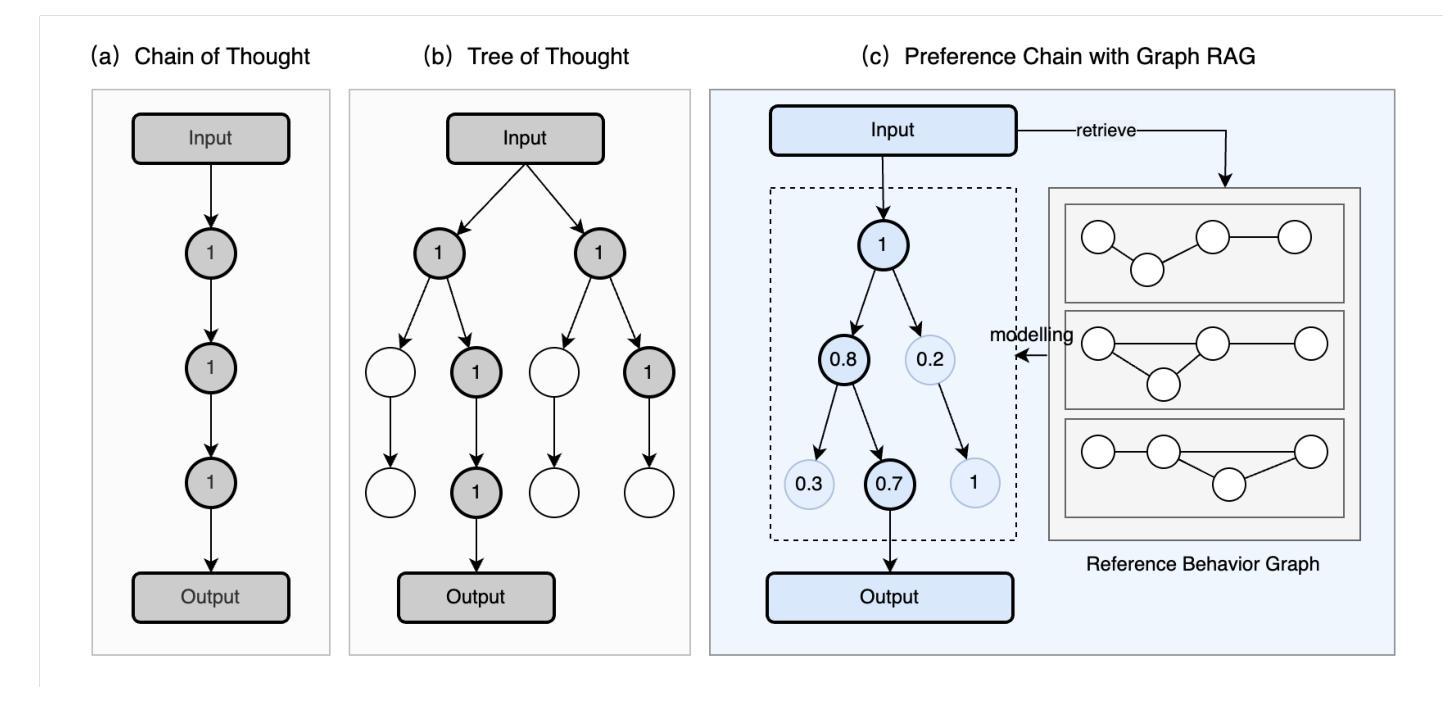
Graph RAG as Human Choice Model: Building a Data-Driven Mobility Agent with Preference Chain
Authors:Kai Hu, Parfait Atchade-Adelomou, Carlo Adornetto, Adrian Mora-Carrero, Luis Alonso-Pastor, Ariel Noyman, Yubo Liu, Kent Larson
Understanding human behavior in urban environments is a crucial field within city sciences. However, collecting accurate behavioral data, particularly in newly developed areas, poses significant challenges. Recent advances in generative agents, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs), have shown promise in simulating human behaviors without relying on extensive datasets. Nevertheless, these methods often struggle with generating consistent, context-sensitive, and realistic behavioral outputs. To address these limitations, this paper introduces the Preference Chain, a novel method that integrates Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with LLMs to enhance context-aware simulation of human behavior in transportation systems. Experiments conducted on the Replica dataset demonstrate that the Preference Chain outperforms standard LLM in aligning with real-world transportation mode choices. The development of the Mobility Agent highlights potential applications of proposed method in urban mobility modeling for emerging cities, personalized travel behavior analysis, and dynamic traffic forecasting. Despite limitations such as slow inference and the risk of hallucination, the method offers a promising framework for simulating complex human behavior in data-scarce environments, where traditional data-driven models struggle due to limited data availability.
在城市科学领域,理解人类在城市环境中的行为是一个至关重要的课题。然而,收集准确的行为数据,尤其是在新开发地区,仍面临巨大挑战。最近,生成式代理在大型语言模型(LLM)的推动下取得了进展,显示出在没有依赖大量数据集的情况下模拟人类行为的潜力。然而,这些方法在生成一致、语境敏感和现实的行为输出方面往往遇到困难。为了克服这些局限性,本文提出了一种新方法——偏好链。它结合了图检索增强生成(RAG)与LLM技术,提高了交通系统中人类行为上下文感知模拟的效果。在Replica数据集上进行的实验表明,偏好链在符合现实世界交通模式选择方面优于标准LLM。移动代理的开发突显了所提出方法在新兴城市城市移动建模、个性化旅行行为分析和动态交通预测中的潜在应用。尽管存在推理速度慢和出现幻觉的风险等局限性,该方法仍为数据稀缺环境中模拟复杂人类行为提供了一个有前景的框架,传统数据驱动模型因数据有限而面临困境。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了在城市科学领域理解人类在城市环境中的行为的重要性,并指出了收集准确行为数据,特别是在新开发区域中的挑战。文章介绍了一种新方法——Preference Chain,它结合了Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG)与大型语言模型(LLMs),提高了在交通运输系统中模拟人类行为的上下文感知能力。实验证明,Preference Chain在模拟真实世界出行模式选择方面优于标准LLM。该方法在模拟新兴城市的城市流动模型、个性化旅行行为分析和动态交通预测方面具有潜在应用价值。虽然存在推理速度慢和出现幻觉的风险等局限性,但它在数据稀缺环境中模拟复杂人类行为方面具有前景,传统的数据驱动模型由于数据有限而面临挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 理解人类在城市环境中的行为是城市科学的重要领域。
- 收集新开发区域的行为数据存在挑战。
- Preference Chain是一种新方法,结合了Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG)和大型语言模型(LLMs),提高了模拟人类行为的上下文感知能力。
- Preference Chain在模拟真实世界出行模式选择方面优于标准LLM。
- 该方法在模拟城市流动模型、个性化旅行行为分析和动态交通预测方面具有潜在应用价值。
- 该方法存在推理速度慢和出现幻觉的风险等局限性。
点此查看论文截图

AgentFly: Fine-tuning LLM Agents without Fine-tuning LLMs
Authors:Huichi Zhou, Yihang Chen, Siyuan Guo, Xue Yan, Kin Hei Lee, Zihan Wang, Ka Yiu Lee, Guchun Zhang, Kun Shao, Linyi Yang, Jun Wang
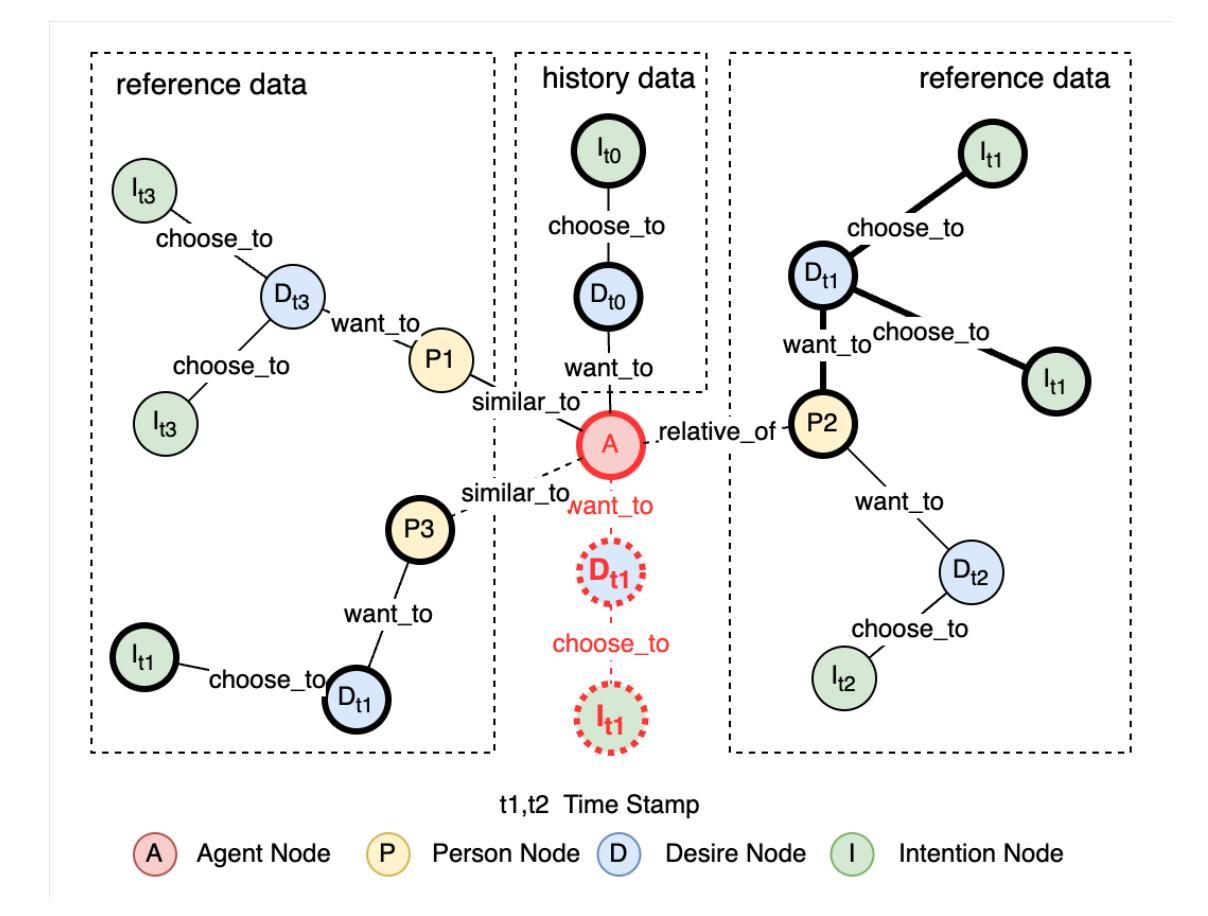
In this paper, we introduce a novel learning paradigm for adaptive Large Language Model (LLM) agents that eliminates the need for fine-tuning the underlying LLMs. Existing approaches are often either rigid, relying on static, handcrafted reflection workflows, or computationally intensive, requiring gradient updates of LLM model parameters. In contrast, our method enables low-cost continual adaptation via memory-based online reinforcement learning. We formalise this as a Memory-augmented Markov Decision Process (M-MDP), equipped with a neural case-selection policy to guide action decisions. Past experiences are stored in an episodic memory, either differentiable or non-parametric. The policy is continually updated based on environmental feedback through a memory rewriting mechanism, whereas policy improvement is achieved through efficient memory reading (retrieval). We instantiate our agent model in the deep research setting, namely AgentFly, which attains top-1 on GAIA validation ($87.88%$ Pass@$3$) and $79.40%$ on the test set. It reaches $66.6%$ F1 and $80.4%$ PM on the DeepResearcher dataset, outperforming the state-of-the-art training-based method, while case-based memory adds $4.7%$ to $9.6%$ absolute points on out-of-distribution tasks. Our approach offers a scalable and efficient pathway for developing generalist LLM agents capable of continuous, real-time learning without gradient updates, advancing machine learning towards open-ended skill acquisition and deep research scenarios. The code is available at https://github.com/Agent-on-the-Fly/AgentFly.
本文介绍了一种新型的适应性强的大型语言模型(LLM)代理学习范式,它消除了对底层LLM进行微调的需求。现有方法往往要么过于僵化,依赖于静态的手动反射工作流程,要么计算量大,需要LLM模型参数的梯度更新。相比之下,我们的方法通过基于记忆的在线增强学习实现了低成本的不断适应。我们将这形式化为一种带有记忆辅助的马尔可夫决策过程(M-MDP),并配备一种神经案例选择策略来指导行动决策。过去的经验被存储在一种情景记忆中,这种记忆可以是可区分的或非参数的。策略是基于环境反馈通过记忆重写机制不断更新的,而策略改进则是通过有效的记忆读取(检索)来实现的。我们在深度研究环境中实例化我们的代理模型,即AgentFly,它在GAIA验证集上排名第一($87.88%$ Pass@$3$)测试集上达到$79.40%$。在DeepResearcher数据集上,它达到$66.6%$的F1和$80.4%$的PM,优于最新的基于训练的方法,而基于案例的记忆则提高了绝对得分在$4.7%$到$9.6%$之间分布外的任务。我们的方法为开发通用LLM代理提供了可扩展和高效的途径,这些代理能够在没有梯度更新的情况下进行连续实时学习,推动机器学习朝着开放式技能获取和深度研究场景发展。代码可在https://github.com/Agent-on-the-Fly/AgentFly找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种新型学习范式,为自适应大型语言模型(LLM)代理提供了无需微调LLM的新的学习方法。现有的方法要么过于僵化,依赖静态的手工艺品反射工作流程,要么计算量大,需要LLM模型的参数梯度更新。相比之下,我们的方法通过基于内存的在线强化学习实现了低成本的不断适应。我们将这正式化为配备神经案例选择策略的Memory-augmented马尔可夫决策过程(M-MDP),以指导动作决策。过去的经验存储在一种差分或非参数化的情境记忆中。策略是基于环境反馈不断更新的记忆重写机制,而策略改进则是通过有效的记忆读取(检索)来实现的。我们将代理模型实例化在深度研究领域,即AgentFly,在GAIA验证集上取得了第一名(87.88%的Pass@3)和测试集上的79.40%。在DeepResearcher数据集上,它达到了66.6%的F1和80.4%的PM,优于最新的基于训练的方法,而基于案例的记忆在超出分布的任务上增加了4.7%至9.6%的绝对点数。我们的方法为开发能够连续实时学习的一般性LLM代理提供了可扩展和高效途径,无需梯度更新,推动机器学习朝着开放式技能获取和深度研究场景发展。代码可在https://github.com/Agent-on-the-Fly/AgentFly找到。
要点提炼
- 引入了一种新型学习范式,使LLM代理无需微调即可进行自适应学习。
- 与现有方法相比,新方法通过基于记忆的在线强化学习实现了低成本的持续适应。
- 提出了Memory-augmented马尔可夫决策过程(M-MDP)框架,配备神经案例选择策略。
- 代理模型AgentFly在多个数据集上取得了显著成果,包括GAIA验证集和DeepResearcher数据集。
- AgentFly通过记忆重写机制和有效记忆读取实现策略更新和改进。
- 该方法具有可扩展性和高效性,为开发能够连续实时学习的通用LLM代理提供了途径。
点此查看论文截图
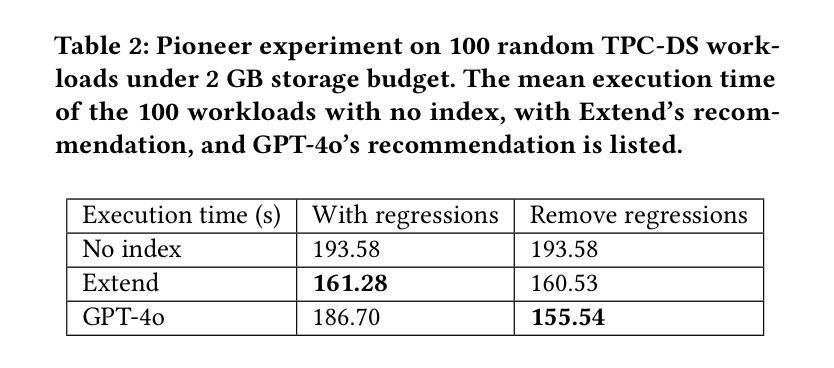
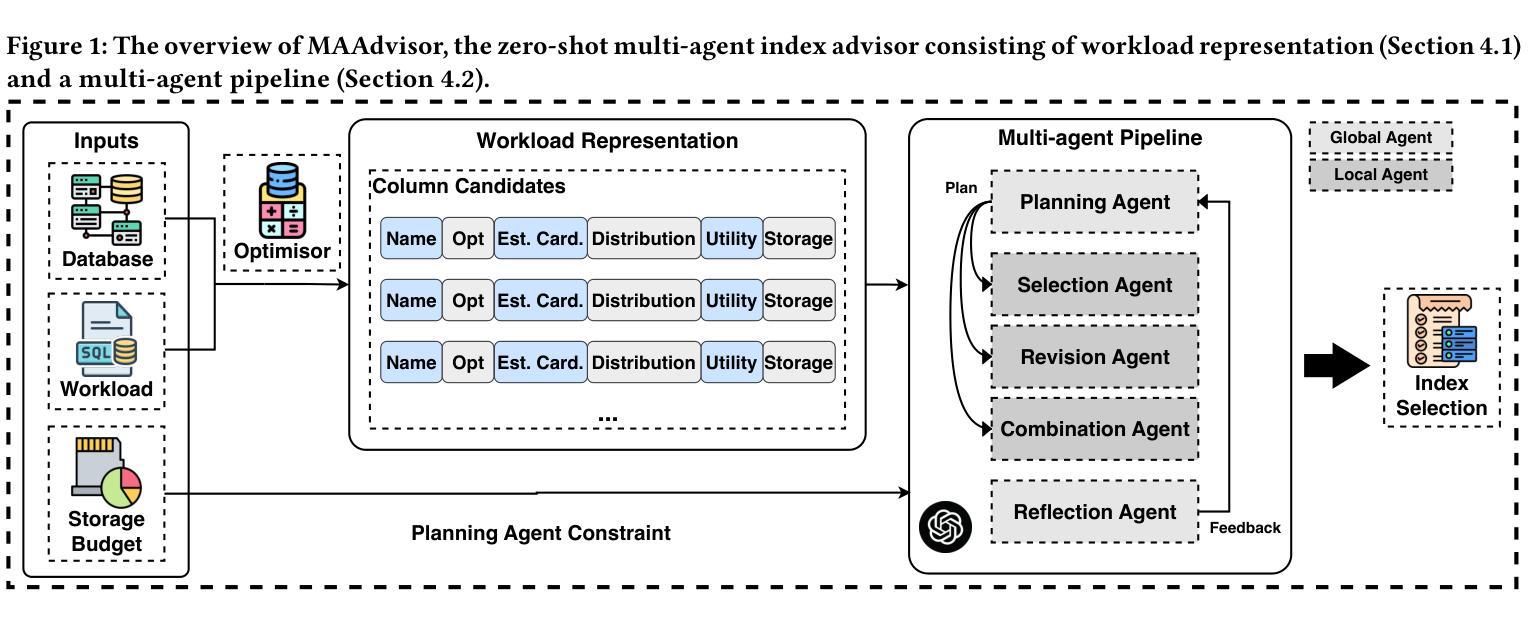
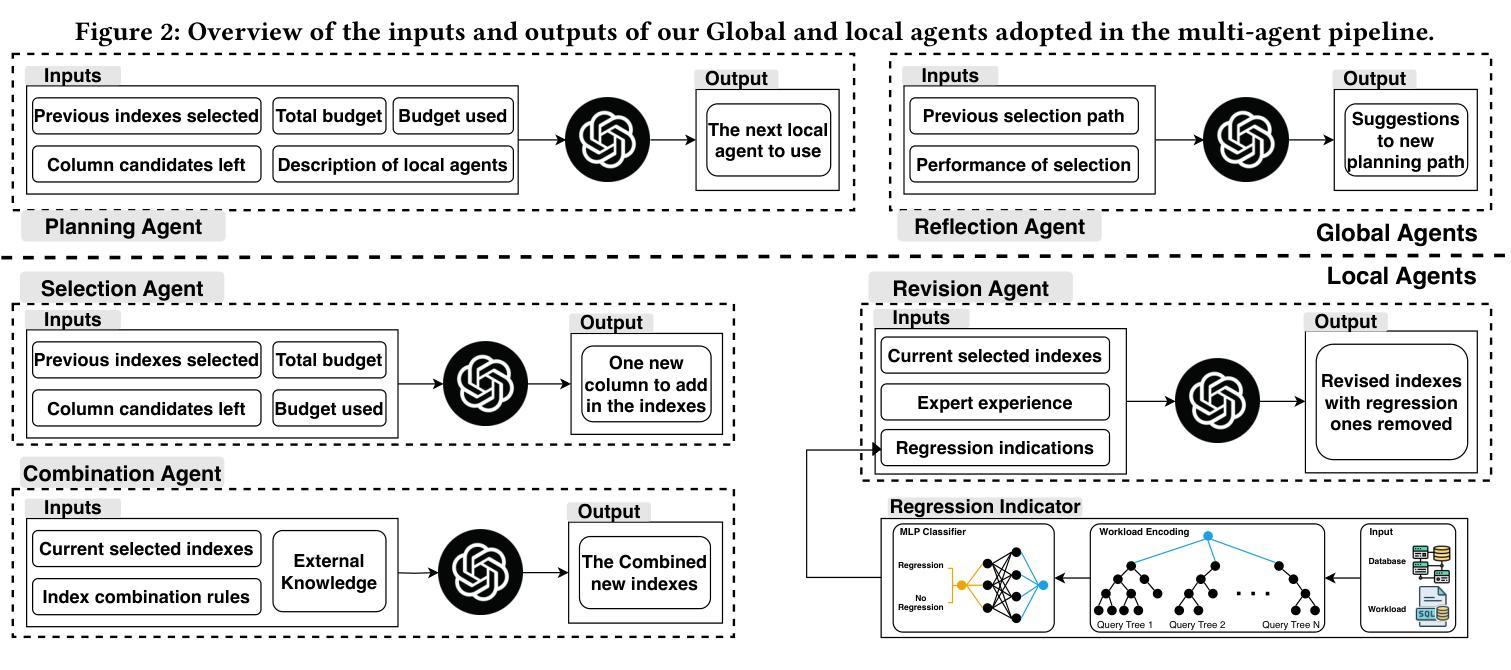
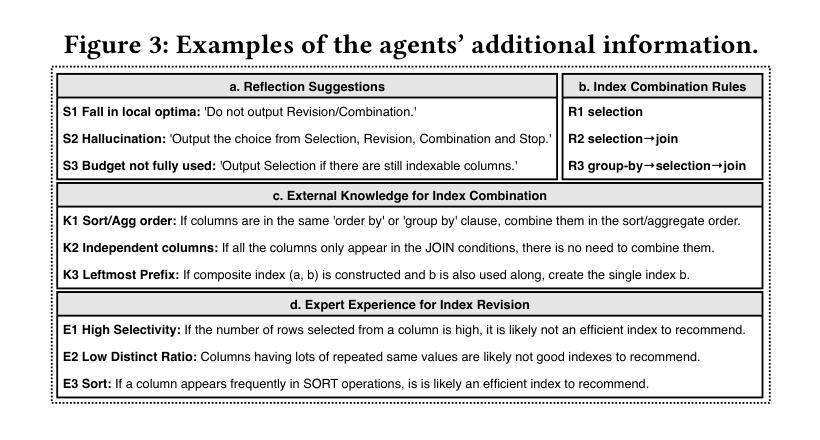
MAAdvisor: Zero-Shot Index Advisor using Multi-Agent LLMs
Authors:Zhaodonghui Li, Haitao Yuan, Jiachen Shi, Hao Zhang, Yu Rong, Gao Cong
Index recommendation is one of the most important problems in database management system (DBMS) optimization. Given queries and certain index-related constraints, traditional methods rely on heuristic optimization or learning-based models to select effective indexes and improve query performance. However, heuristic optimization suffers from high computation time, and learning-based models lose generalisability due to training for different workloads and database schemas. With the recent rapid development of large language models (LLMs), methods using prompt tuning have been proposed to enhance the efficiency of index selection. However, such methods still can not achieve the state-of-the-art (SOTA) results, and preparing the index selection demonstrations is also resource-intensive. To address these issues, we propose MAAdvisor, a zero-shot LLM-based index advisor with a multi-agent framework. We decompose the index recommendation problem into sub-steps, including planning, selection, combination, revision, and reflection. A set of LLM-embedded agents is designed to handle each one of the different sub-steps. Our method utilizes global agents to control the index selection process and local agents to select and revise indexes. Through extensive experiments, we show that our proposed MAAdvisor not only achieves the SOTA performance compared to the heuristic methods, but also outperforms learning-based and prompt-based methods with higher efficiency and better zero-shot inference ability.
索引推荐是数据库管理系统(DBMS)优化中最重要的任务之一。给定查询和某些索引相关约束,传统方法依赖于启发式优化或基于学习模型来选择有效索引并提高查询性能。然而,启发式优化存在计算时间长的问题,而基于学习的模型由于针对不同工作负载和数据库模式进行训练,导致泛化能力下降。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,提出了基于提示调整的方法来提高索引选择的效率。然而,这些方法仍无法达到最新技术成果,并且准备索引选择演示也是资源密集型的。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了MAAdvisor,这是一个基于零镜头LLM的多代理框架索引顾问。我们将索引推荐问题分解为规划、选择、组合、修订和反思等子步骤。设计了一组嵌入LLM的代理来处理不同的子步骤。我们的方法利用全局代理来控制索引选择过程,而局部代理则用于选择和修订索引。通过大量实验,我们证明了所提出的MAAdvisor不仅与启发式方法相比达到了最新技术性能,而且在效率和零镜头推理能力方面也优于基于学习和提示的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据库管理系统优化中的索引推荐是一项重要问题。传统方法依赖于启发式优化或基于学习的方法,存在计算时间长和泛化能力不足的问题。随着大型语言模型的发展,采用提示调整的方法被提出以提高索引选择的效率。然而,这些方法仍无法达到最佳结果,且准备索引选择演示也很耗费资源。为解决这些问题,提出了基于多代理框架的MAAdvisor,将索引推荐问题分解为规划、选择、组合、修订和反思等子步骤,并使用嵌入大型语言模型的代理来处理这些子步骤。该方法利用全局代理控制索引选择过程,局部代理进行索引的选择和修订。实验表明,MAAdvisor相较于启发式方法达到了最佳性能,相较于基于学习和提示的方法具有更高的效率和更好的零样本推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 数据库管理系统中的索引推荐问题至关重要。
- 传统方法如启发式优化和基于学习的方法存在计算时间长和泛化能力问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在索引选择中的应用通过提示调整方法提高了效率。
- 当前方法仍未能达到最佳性能,且资源消耗较大。
- MAAdvisor是一个基于多代理框架的零样本LLM索引顾问,分解了索引推荐问题为多个子步骤。
- MAAdvisor使用全局和局部代理来控制和执行索引选择过程。
点此查看论文截图

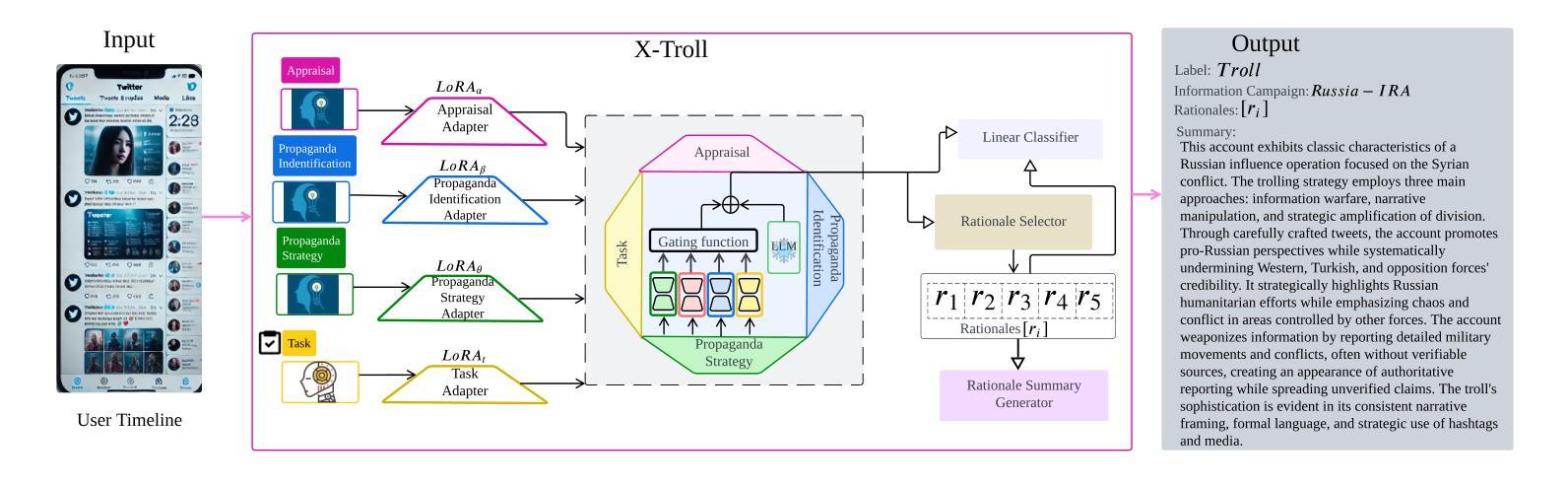
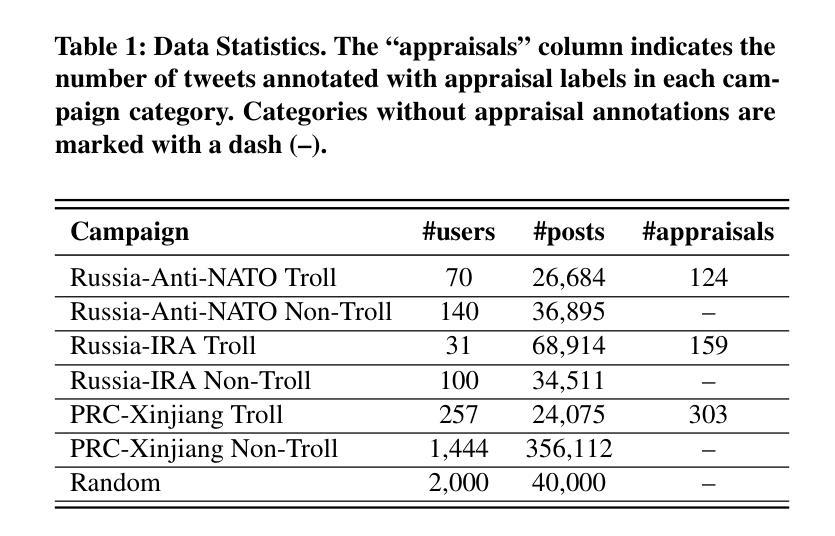
X-Troll: eXplainable Detection of State-Sponsored Information Operations Agents
Authors:Lin Tian, Xiuzhen Zhang, Maria Myung-Hee Kim, Jennifer Biggs, Marian-Andrei Rizoiu
State-sponsored trolls, malicious actors who deploy sophisticated linguistic manipulation in coordinated information campaigns, posing threats to online discourse integrity. While Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve strong performance on general natural language processing (NLP) tasks, they struggle with subtle propaganda detection and operate as ``black boxes’’, providing no interpretable insights into manipulation strategies. This paper introduces X-Troll, a novel framework that bridges this gap by integrating explainable adapter-based LLMs with expert-derived linguistic knowledge to detect state-sponsored trolls and provide human-readable explanations for its decisions. X-Troll incorporates appraisal theory and propaganda analysis through specialized LoRA adapters, using dynamic gating to capture campaign-specific discourse patterns in coordinated information operations. Experiments on real-world data demonstrate that our linguistically-informed approach shows strong performance compared with both general LLM baselines and existing troll detection models in accuracy while providing enhanced transparency through expert-grounded explanations that reveal the specific linguistic strategies used by state-sponsored actors. X-Troll source code is available at: https://github.com/ltian678/xtroll_source/.
政府资助的网路水军,通过协调的信息活动部署高级语言操纵的恶意行为者,对在线话语的完整性构成威胁。尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在一般的自然语言处理(NLP)任务上表现良好,但在微妙的宣传检测方面却存在困难,并且作为“黑箱”运行,无法提供关于操纵策略的可解释见解。本文介绍了X-Troll,这是一个新的框架,它通过整合基于适配器的可解释的LLM和专家派生的语言知识来弥补这一差距,以检测政府资助的网路水军并为决策提供人类可读的解释。X-Troll通过专门的LoRA适配器融入评价理论和宣传分析,使用动态门控技术捕捉协调信息活动中的特定宣传话语模式。在真实数据上的实验表明,我们的语言信息丰富的方法在准确性方面与一般的LLM基准线和现有的网路水军检测模型相比表现出强大的性能,同时通过基于专家的解释提高了透明度,揭示了政府资助的行为者所使用的特定语言策略。X-Troll的源代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ltian672/xtroll_source/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables, accepted by CIKM2025
Summary
文本介绍了X-Troll框架,该框架结合了基于解释器的语言模型与专家衍生的语言知识,旨在检测政府资助的“网络水军”(网络舆论操控者)的存在并为其行为决策提供人性化的解读。它通过专业化的LoRA适配器和动态门技术来捕捉有针对性的信息运动中的宣传手法和评论理论,提高了模型对细微宣传操纵的识别能力。在真实世界的数据测试中,与传统的语言模型和现有的网络水军检测模型相比,X-Troll的准确性表现出强劲性能。此外,通过基于专家的解释提供了较高的透明度。关于其源代码信息已在其GitHub仓库公开。
Key Takeaways:
点此查看论文截图

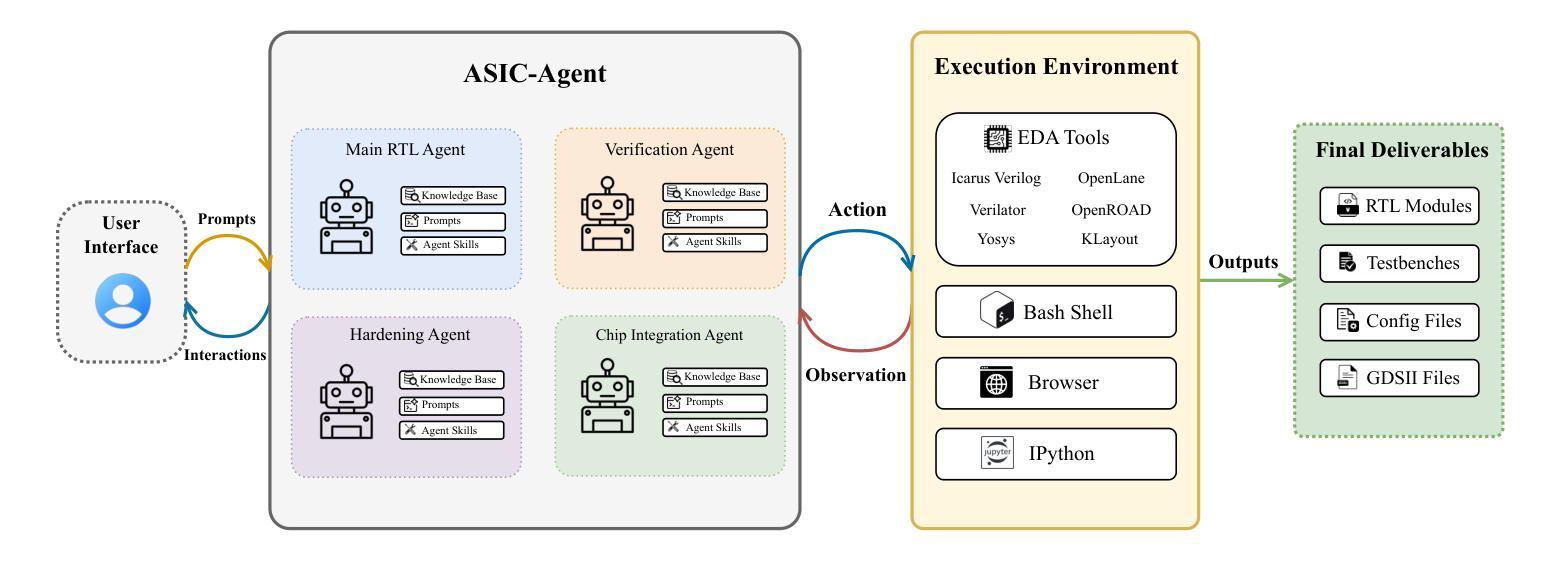
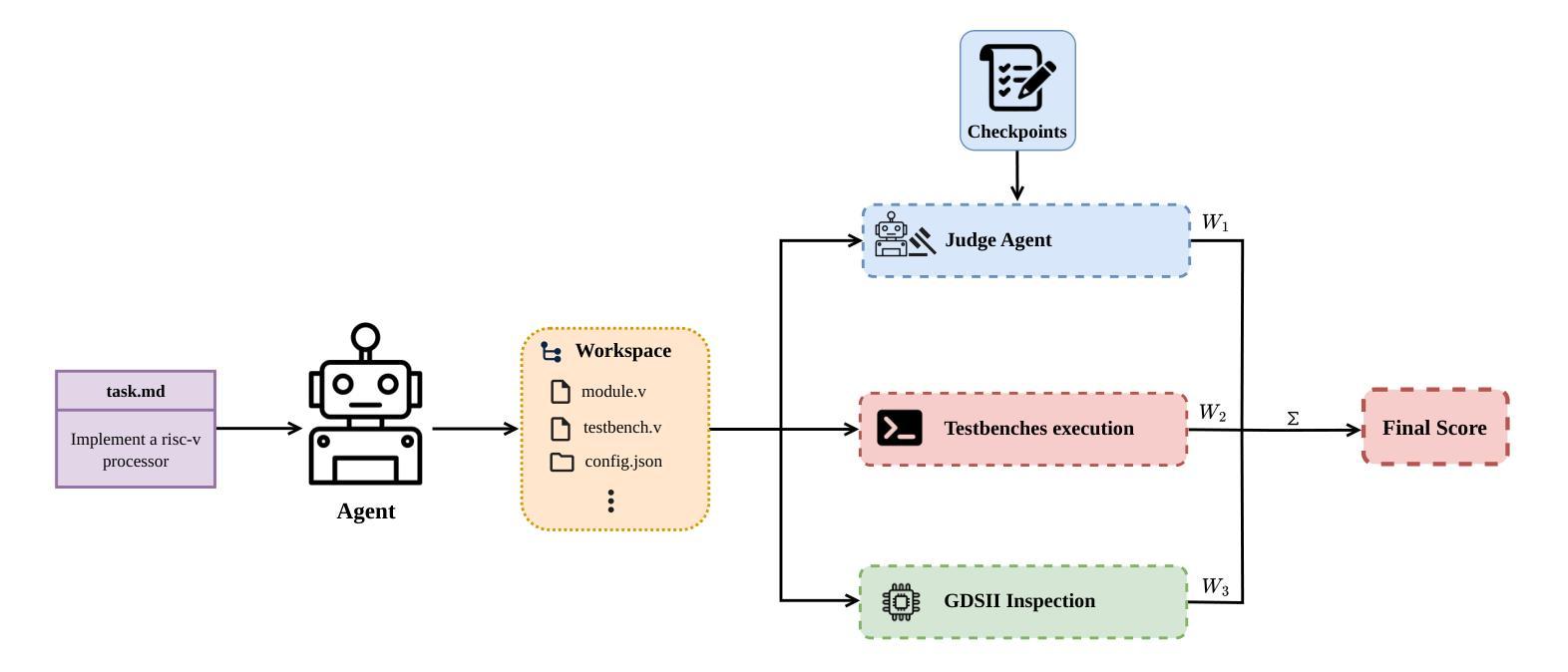
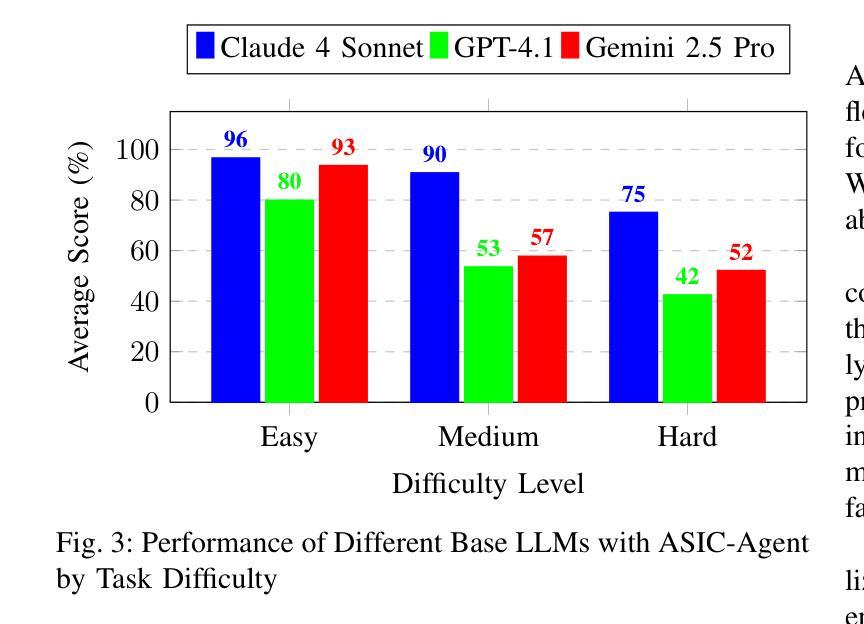
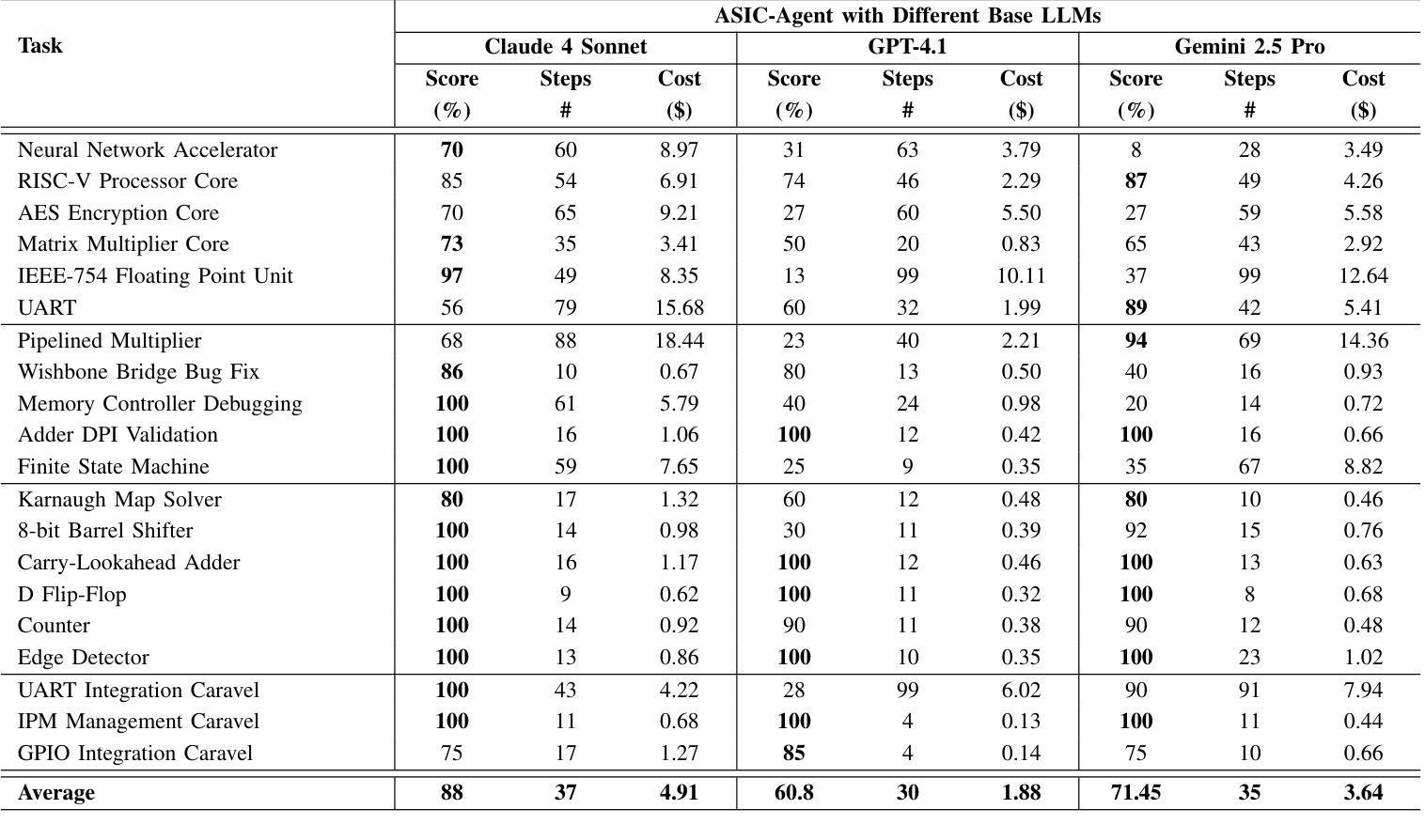
ASIC-Agent: An Autonomous Multi-Agent System for ASIC Design with Benchmark Evaluation
Authors:Ahmed Allam, Youssef Mansour, Mohamed Shalan
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in Register Transfer Level (RTL) design, enabling high-quality code generation from natural language descriptions. However, LLMs alone face significant limitations in real-world hardware design workflows, including the inability to execute code, lack of debugging capabilities, and absence of long-term memory. To address these challenges, we present ASIC-Agent, an autonomous system designed specifically for digital ASIC design tasks. ASIC-Agent enhances base LLMs with a multi-agent architecture incorporating specialized sub-agents for RTL generation, verification, OpenLane hardening, and Caravel chip integration, all operating within a comprehensive sandbox environment with access to essential hardware design tools. The system leverages a vector database containing documentation, API references, error knowledge, and curated insights from the open-source silicon community. To evaluate ASIC-Agent’s performance, we introduce ASIC-Agent-Bench, the first benchmark specifically designed to assess agentic systems in hardware design tasks. We evaluate ASIC-Agent with various base LLMs, providing quantitative comparisons and qualitative insights into agent behavior across different design scenarios. Our results demonstrate that ASIC-Agent, when powered by Claude 4 Sonnet, successfully automates a broad range of ASIC design tasks spanning varying levels of complexity, showing the potential of significantly accelerating the ASIC design workflow.
大规模语言模型(LLMs)在寄存器传输级别(RTL)设计中表现出了卓越的能力,能够从自然语言描述中生成高质量的代码。然而,LLMs单独在现实世界硬件设计工作流程中面临重大挑战,包括无法执行代码、缺乏调试能力和长期记忆缺失。为了解决这些挑战,我们推出了ASIC-Agent,这是一个专为数字ASIC设计任务设计的自治系统。ASIC-Agent通过多代理架构增强基础LLMs,该架构结合了用于RTL生成、验证、OpenLane加固和Caravel芯片集成的专业子代理,所有这些都在一个综合的沙盘环境中运行,可访问必要的硬件设计工具。该系统利用向量数据库,其中包含来自开源硅片社区的文档、API参考、错误知识和精选的见解。为了评估ASIC-Agent的性能,我们推出了ASIC-Agent-Bench,这是第一个专门设计用于评估硬件设计任务中代理系统的基准测试。我们使用各种基础LLMs评估ASIC-Agent,提供定量比较和定性洞察,了解不同设计场景下代理的行为。我们的结果表明,当ASIC-Agent由Claude 4 Sonnet驱动时,它成功地自动化了涵盖不同复杂程度的广泛ASIC设计任务,显示出加速ASIC设计工作流程的巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 IEEE International Conference on LLM-Aided Design (ICLAD)
摘要
大型语言模型在寄存器传输级设计方面展现出卓越的能力,可从自然语言描述生成高质量代码。然而,在现实世界硬件设计流程中,大型语言模型存在显著局限性,如无法执行代码、缺乏调试功能和长期记忆缺失。为解决这些问题,我们提出ASIC-Agent——专为数字ASIC设计任务设计的自主系统。ASIC-Agent通过多代理架构增强基础大型语言模型的功能,该架构结合了用于RTL生成、验证、OpenLane加固和Caravel芯片集成的专业子代理,所有操作都在一个综合的沙盘环境中进行,可访问必要的硬件设计工具。该系统利用包含文档、API参考、错误知识和来自开源硅片社区的精选见解的向量数据库。为评估ASIC-Agent的性能,我们推出了ASIC-Agent-Bench——专门用于评估硬件设计任务中代理系统的第一个基准测试。我们用不同基础的大型语言模型对ASIC-Agent进行了评估,提供了定量比较和不同设计场景下代理行为的定性见解。结果表明,当ASIC-Agent由Claude 4 Sonnet驱动时,可成功自动化各种复杂程度的ASIC设计任务,显示出加速ASIC设计流程的潜力。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在RTL设计中表现出卓越的能力,但存在执行代码和长期记忆方面的局限性。
- ASIC-Agent是一个专为数字ASIC设计任务设计的自主系统,通过多代理架构增强基础大型语言模型的功能。
- ASIC-Agent包含用于RTL生成、验证、OpenLane加固和Caravel芯片集成的专业子代理。
- ASIC-Agent在一个综合的沙盘环境中运行,可访问必要的硬件设计工具和一个包含文档、API参考等资源的向量数据库。
- ASIC-Agent的性能通过ASIC-Agent-Bench进行评估,这是一个专门用于评估硬件设计任务中代理系统的基准测试。
- 不同基础的大型语言模型与ASIC-Agent结合使用时,表现出在不同设计场景下的不同性能。
点此查看论文截图

UAV-ON: A Benchmark for Open-World Object Goal Navigation with Aerial Agents
Authors:Jianqiang Xiao, Yuexuan Sun, Yixin Shao, Boxi Gan, Rongqiang Liu, Yanjing Wu, Weili Guan, Xiang Deng
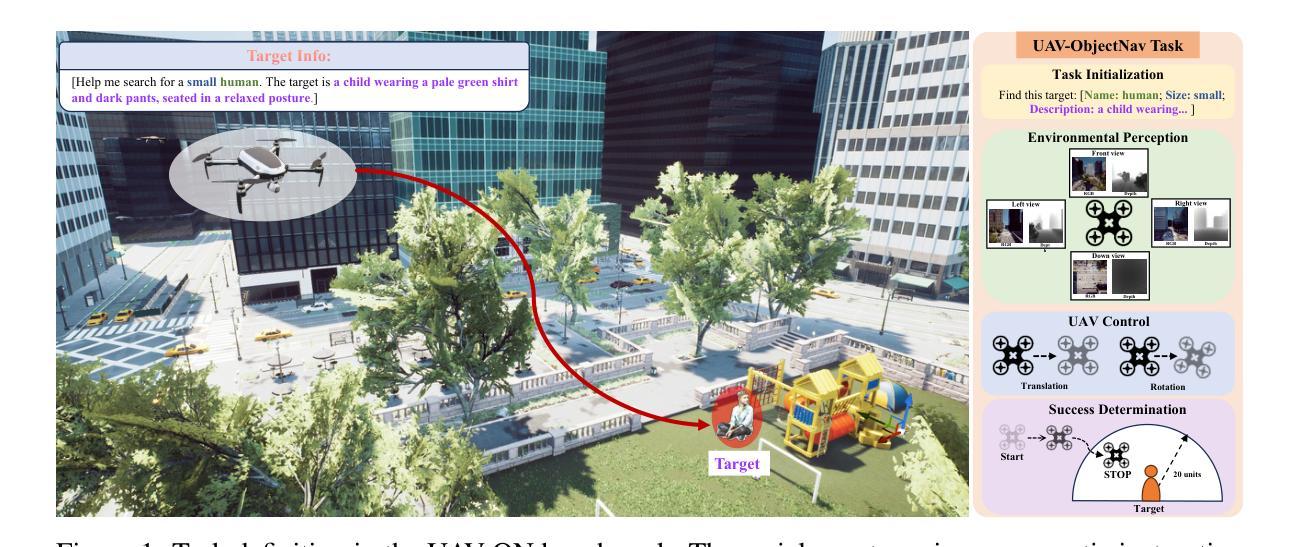
Aerial navigation is a fundamental yet underexplored capability in embodied intelligence, enabling agents to operate in large-scale, unstructured environments where traditional navigation paradigms fall short. However, most existing research follows the Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) paradigm, which heavily depends on sequential linguistic instructions, limiting its scalability and autonomy. To address this gap, we introduce UAV-ON, a benchmark for large-scale Object Goal Navigation (ObjectNav) by aerial agents in open-world environments, where agents operate based on high-level semantic goals without relying on detailed instructional guidance as in VLN. UAV-ON comprises 14 high-fidelity Unreal Engine environments with diverse semantic regions and complex spatial layouts, covering urban, natural, and mixed-use settings. It defines 1270 annotated target objects, each characterized by an instance-level instruction that encodes category, physical footprint, and visual descriptors, allowing grounded reasoning. These instructions serve as semantic goals, introducing realistic ambiguity and complex reasoning challenges for aerial agents. To evaluate the benchmark, we implement several baseline methods, including Aerial ObjectNav Agent (AOA), a modular policy that integrates instruction semantics with egocentric observations for long-horizon, goal-directed exploration. Empirical results show that all baselines struggle in this setting, highlighting the compounded challenges of aerial navigation and semantic goal grounding. UAV-ON aims to advance research on scalable UAV autonomy driven by semantic goal descriptions in complex real-world environments.
无人机导航是智能体系中的一项基本但尚未被充分研究的能力,它使无人机能够在大规模、非结构化的环境中运行,而传统的导航模式在这些环境中无法胜任。然而,大多数现有研究遵循视觉与语言导航(VLN)模式,严重依赖于连续的语言指令,这限制了其可扩展性和自主性。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了UAV-ON基准测试,这是无人机在开放世界环境中进行大规模目标物体导航(ObjectNav)的一个基准测试。在该测试中,无人机基于高级语义目标进行操作,无需依赖VLN中的详细指令指导。UAV-ON包含14个高保真度的Unreal Engine环境,具有多样化的语义区域和复杂的空间布局,涵盖城市、自然以及混合用途场景。它定义了1270个已标注的目标对象,每个对象都通过实例级别的指令进行特征化,该指令包含类别、物理足迹和视觉描述符,以实现基于情境的理解。这些指令作为语义目标,为无人机引入了现实存在的模糊性和复杂的推理挑战。为了评估这个基准测试,我们实施了几种基线方法,包括无人机目标导航代理(AOA),这是一种模块化策略,它将指令语义与以自我为中心的观察相结合,用于进行长远目标的定向探索。实证结果表明,所有基线方法在这种环境下都面临困难,凸显了无人机导航和语义目标定位的挑战性。UAV-ON的目标是推进由复杂现实世界环境中的语义目标描述驱动的可扩展无人机自主性研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM MM Dataset Track 2025
Summary
本文介绍了空中导航在智能体领域的重要性及其未被充分探索的现状。针对现有研究主要依赖视觉和语言导航(VLN)的局限性,提出了UAV-ON基准测试平台,用于评估空中智能体在大规模开放世界环境中的对象目标导航(ObjectNav)。该平台包括14个高保真度的Unreal Engine环境,涵盖了城市、自然和混合用途场景,具有多样化的语义区域和复杂空间布局。此外,还定义了1270个带有实例级指令的目标对象,允许基于语义的目标进行推理。文章还介绍了评估此基准测试平台的方法,包括Aerial ObjectNav Agent(AOA)等基线方法。结果表明,现有方法在此设置下面临挑战,突出了空中导航和语义目标接地的复合挑战。UAV-ON旨在推动在复杂现实环境中实现基于语义目标描述的无人机自主性研究的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 空中导航是智能体领域的一个基础但尚未被充分探索的能力。
- 现有研究主要依赖视觉和语言导航(VLN)存在局限性。
- UAV-ON是一个用于评估空中智能体在大规模开放世界环境中对象目标导航能力的基准测试平台。
- 平台包括多样化的语义区域和复杂空间布局的高保真度环境。
- 允许基于语义的目标进行推理,带有实例级指令的目标对象。
- 基线方法在该设置下面临挑战,突出了空中导航和语义目标接地的复合挑战。
点此查看论文截图

CO-Bench: Benchmarking Language Model Agents in Algorithm Search for Combinatorial Optimization
Authors:Weiwei Sun, Shengyu Feng, Shanda Li, Yiming Yang
Although LLM-based agents have attracted significant attention in domains such as software engineering and machine learning research, their role in advancing combinatorial optimization (CO) remains relatively underexplored. This gap underscores the need for a deeper understanding of their potential in tackling structured, constraint-intensive problems – a pursuit currently limited by the absence of comprehensive benchmarks for systematic investigation. To address this, we introduce CO-Bench, a benchmark suite featuring 36 real-world CO problems drawn from a broad range of domains and complexity levels. CO-Bench includes structured problem formulations and curated data to support rigorous investigation of LLM agents. We evaluate multiple agentic frameworks against established human-designed algorithms, revealing the strengths and limitations of existing LLM agents and identifying promising directions for future research. CO-Bench is publicly available at https://github.com/sunnweiwei/CO-Bench.
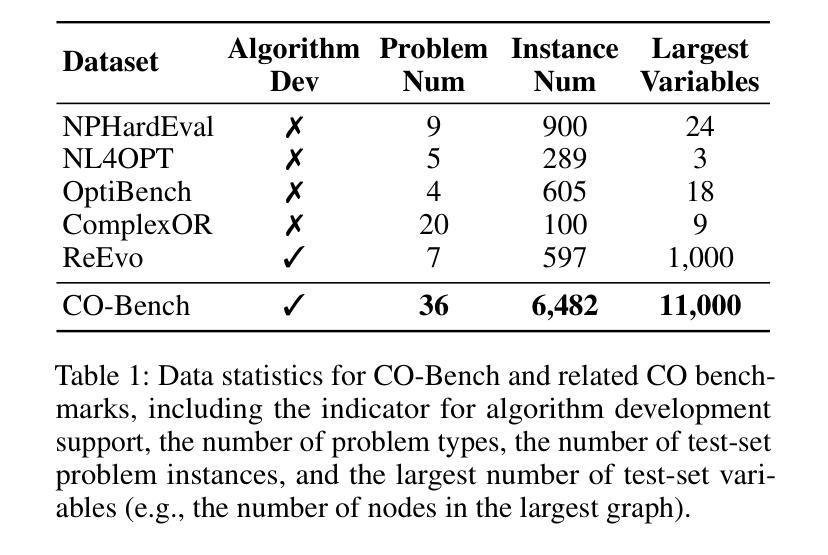
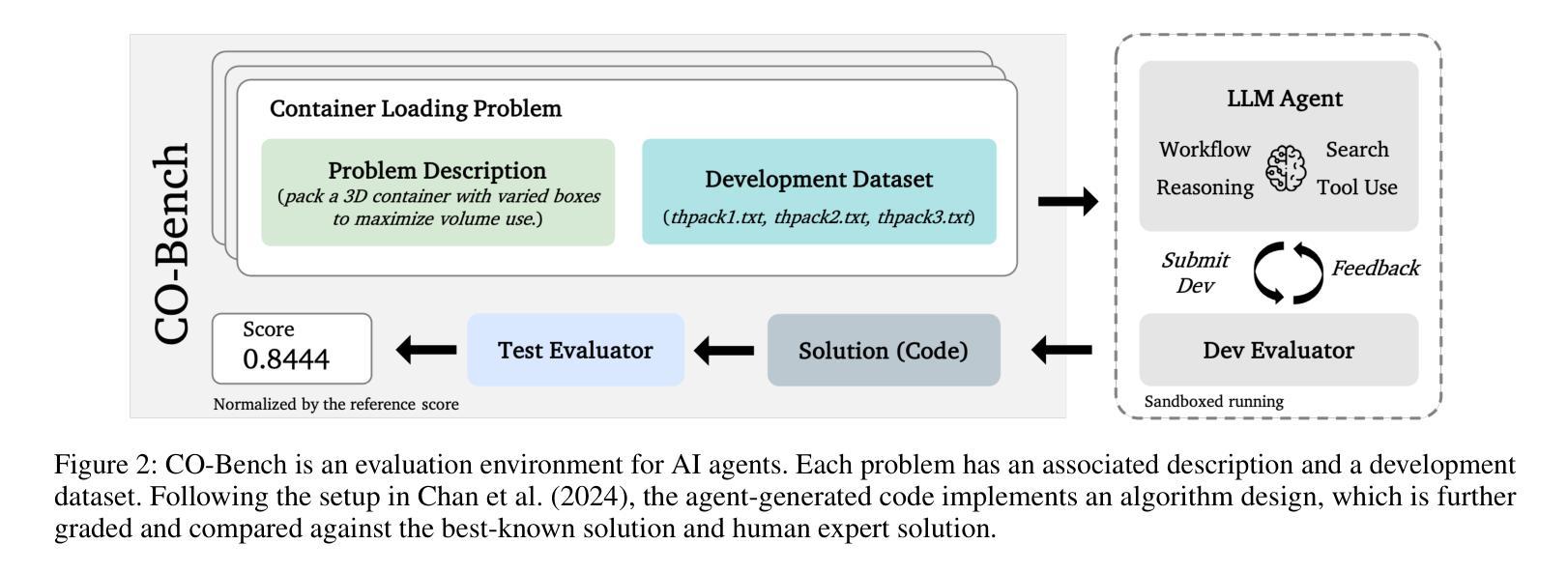
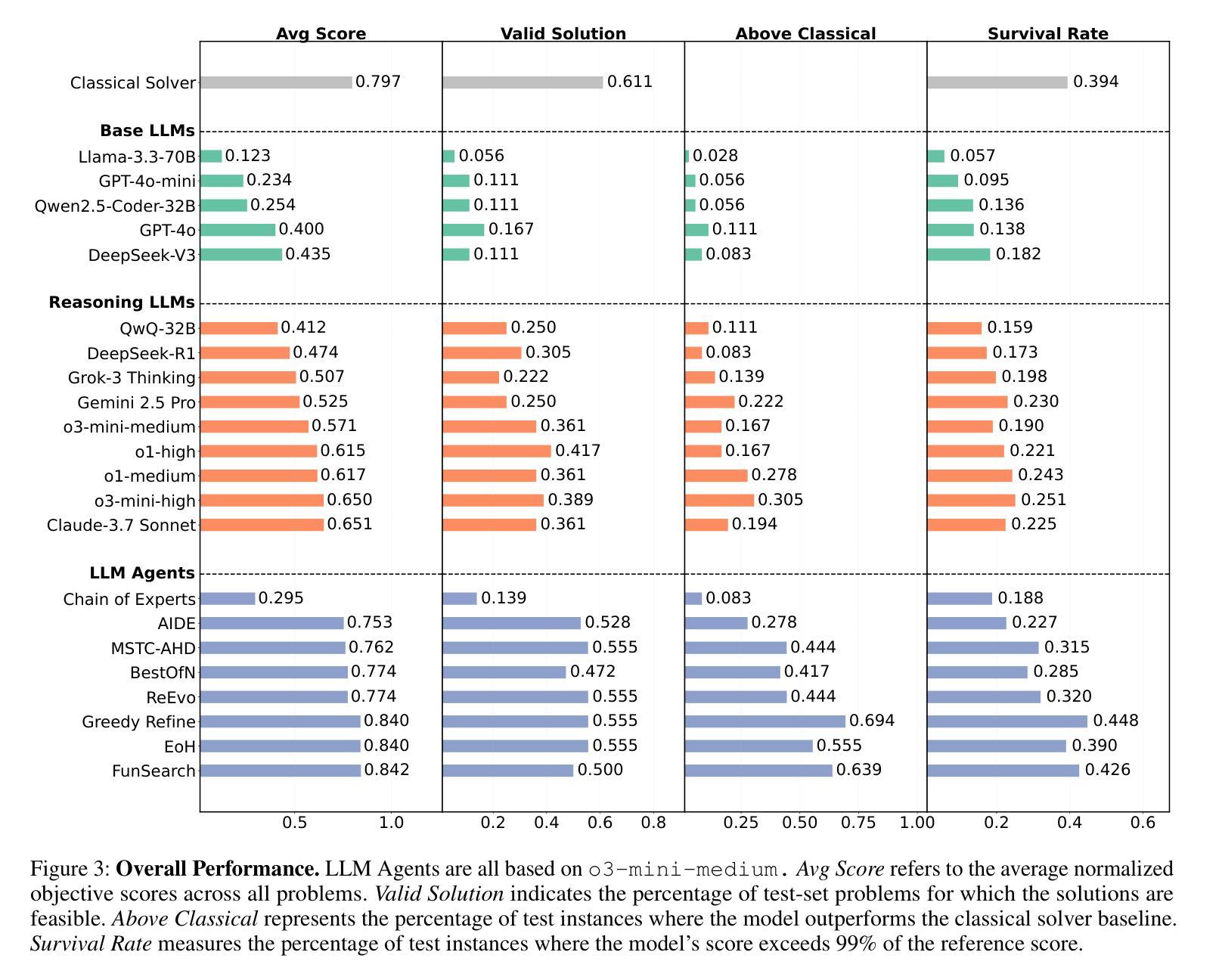
尽管基于大型语言模型(LLM)的代理在软件工程和机器学习研究等领域引起了广泛关注,但它们对推进组合优化(CO)的作用仍然相对未被充分探索。这一差距突显出需要更深入地了解它们在解决结构化、约束密集型问题方面的潜力——目前这一追求受限于缺乏全面的基准测试来进行系统研究。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了CO-Bench,这是一个包含36个来自不同领域和复杂度级别的真实世界CO问题的基准测试套件。CO-Bench包括结构化的问题表述和精选数据,以支持对LLM代理的严格调查。我们评估了多个代理框架与既定的人工设计算法,揭示了现有LLM代理的优势和局限性,并确定了未来研究的有前途的方向。CO-Bench可在https://github.com/sunnweiwei/CO-Bench上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LLM-based代理在软件工程和机器学习等领域备受关注,但在组合优化(CO)领域的研究相对不足。为填补这一空白,引入CO-Bench基准套件,涵盖来自不同领域和复杂度级别的36个真实世界CO问题。CO-Bench包括结构化问题公式和精选数据,支持对LLM代理的严格调查。评估多个代理框架与已建立的人工算法相比,揭示了现有LLM代理的优缺点,并指出了未来研究的希望方向。CO-Bench可在公开访问地址找到:https://github.com/sunnweiwei/CO-Bench。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based代理在组合优化领域的研究相对不足,需要更深入地探索其在处理结构化和约束密集型问题方面的潜力。
- CO-Bench基准套件包含来自不同领域和复杂度级别的真实世界组合优化问题,旨在支持对LLM代理的严格调查。
- CO-Bench包括结构化问题公式和精选数据,为评估LLM代理提供了全面的资源。
- 通过评估多个代理框架与人工算法,揭示了现有LLM代理的优缺点。
- CO-Bench公开可用,为未来的研究和开发提供了基础。
- 该研究指出了未来研究的方向,包括改进LLM代理以更好地解决组合优化问题。
点此查看论文截图

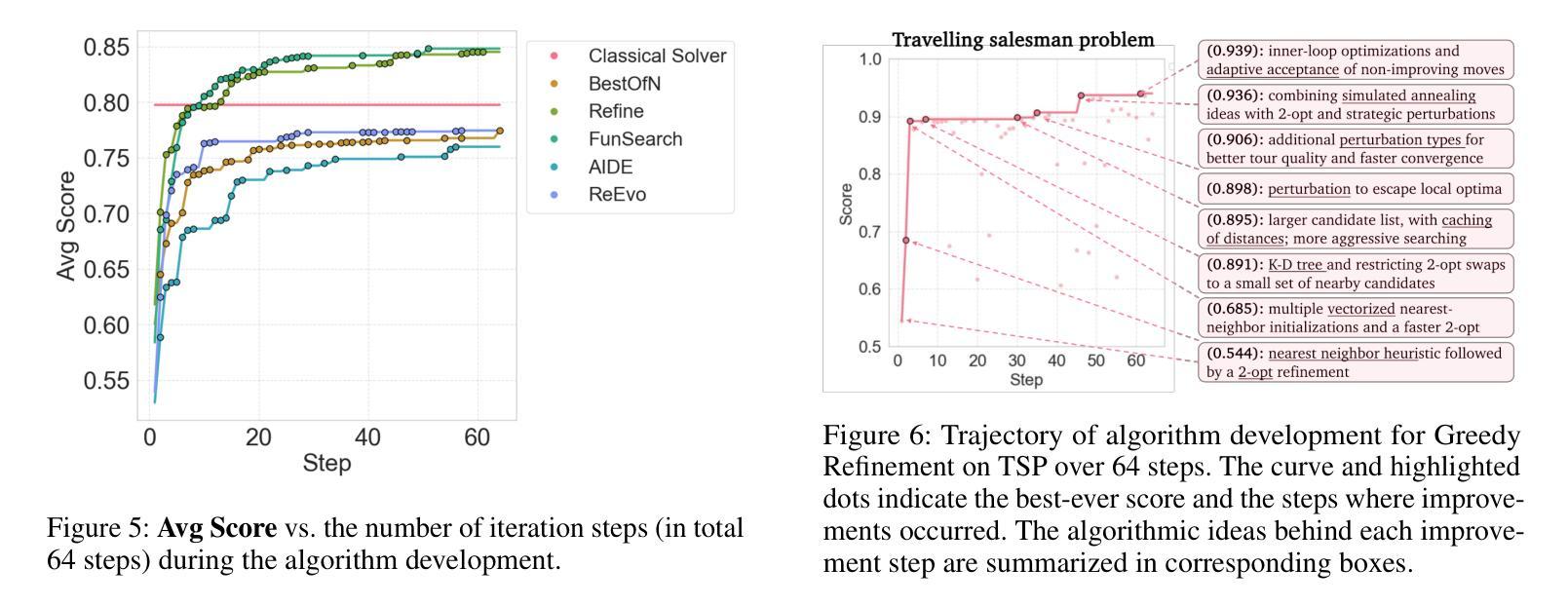
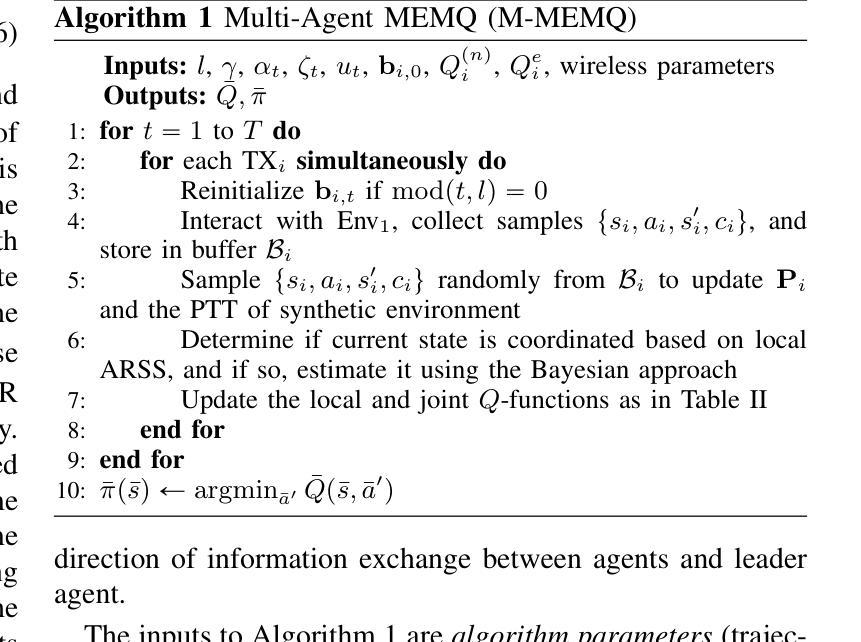
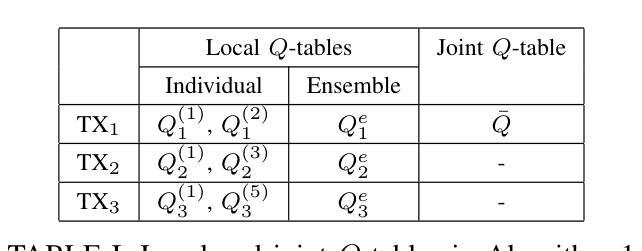
Partially Decentralized Multi-Agent Q-Learning via Digital Cousins for Wireless Networks
Authors:Talha Bozkus, Urbashi Mitra
Q-learning is a widely used reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm for optimizing wireless networks, but faces challenges with large state-spaces. Recently proposed multi-environment mixed Q-learning (MEMQ) algorithm addresses these challenges by employing multiple Q-learning algorithms across multiple synthetically generated, distinct but structurally related environments, so-called digital cousins. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-agent MEMQ (M-MEMQ) for cooperative decentralized wireless networks with multiple networked transmitters (TXs) and base stations (BSs). TXs do not have access to global information (joint state and actions). The new concept of coordinated and uncoordinated states is introduced. In uncoordinated states, TXs act independently to minimize their individual costs and update local Q-functions. In coordinated states, TXs use a Bayesian approach to estimate the joint state and update the joint Q-functions. The cost of information-sharing scales linearly with the number of TXs and is independent of the joint state-action space size. Several theoretical guarantees, including deterministic and probabilistic convergence, bounds on estimation error variance, and the probability of misdetecting the joint states, are given. Numerical simulations show that M-MEMQ outperforms several decentralized and centralized training with decentralized execution (CTDE) multi-agent RL algorithms by achieving 60% lower average policy error (APE), 40% faster convergence, 45% reduced runtime complexity, and 40% less sample complexity. Furthermore, M-MEMQ achieves comparable APE with significantly lower complexity than centralized methods. Simulations validate the theoretical analyses.
Q-学习是一种广泛应用于强化学习(RL)的算法,用于优化无线网络,但在大型状态空间方面面临挑战。最近提出的跨多个人工合成、独特但结构相关的环境使用多个Q-学习算法的多环境混合Q-学习(MEMQ)算法解决了这些挑战,这些环境被称为数字表亲。在本文中,我们针对具有多个网络发射机(TX)和基站(BS)的合作分布式无线网络提出了一种新型的多智能体MEMQ(M-MEMQ)。发射机无法访问全局信息(联合状态和行动)。引入了协调和未协调状态的新概念。在未协调状态下,发射机独立行动以最小化其个人成本并更新本地Q函数。在协调状态下,发射机使用贝叶斯方法估计联合状态并更新联合Q函数。信息共享的成本随发射机数量的增加而线性增长,并与联合状态-行动空间大小无关。给出了包括确定性收敛和概率收敛在内的几个理论保证、估计误差方差的界限以及误检测联合状态的概率。数值模拟表明,M-MEMQ优于几种分布式和集中训练与分布式执行(CTDE)的多智能体RL算法,实现了平均策略误差(APE)降低60%,收敛速度提高40%,运行时间复杂度降低45%,样本复杂度降低40%。此外,与传统的集中式方法相比,M-MEMQ实现了相近的APE但复杂度更低。模拟结果验证了理论分析的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
多智能体MEMQ算法针对协同分散式无线网络进行优化,通过引入协调与不协调状态概念,在分散式训练时兼顾个体成本与全局信息。该算法在理论分析和数值仿真中展现出优越性,与现有分散式及中心化训练方法相比,M-MEMQ具有更低的策略误差、更快的收敛速度、更低的运行复杂度和样本复杂度。
Key Takeaways
- M-MEMQ是一种针对协同分散式无线网络的多智能体强化学习算法。
- 该算法引入协调与不协调状态概念,以适应分散式训练的需求。
- 在不协调状态下,智能体独立行动以降低个体成本并更新本地Q函数。
- 在协调状态下,智能体使用贝叶斯方法估计联合状态并更新联合Q函数。
- M-MEMQ具有理论保证,包括确定性和概率性收敛性、估计误差方差界限以及联合状态误检测概率。
- 数值仿真显示,M-MEMQ在策略误差、收敛速度、运行复杂度和样本复杂度方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

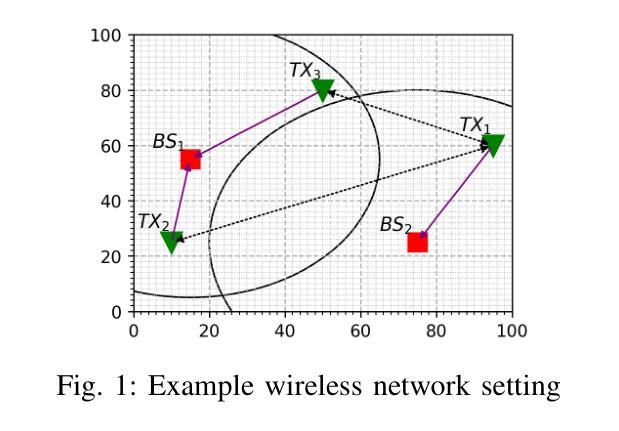
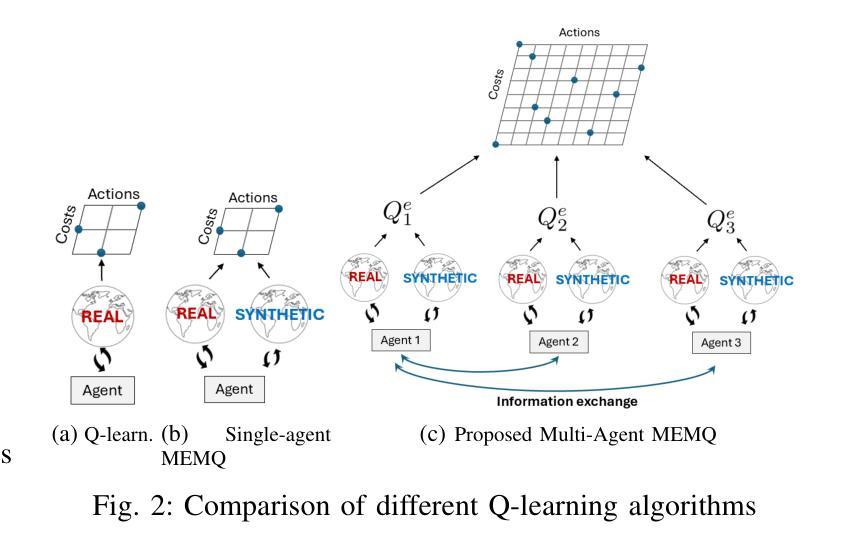
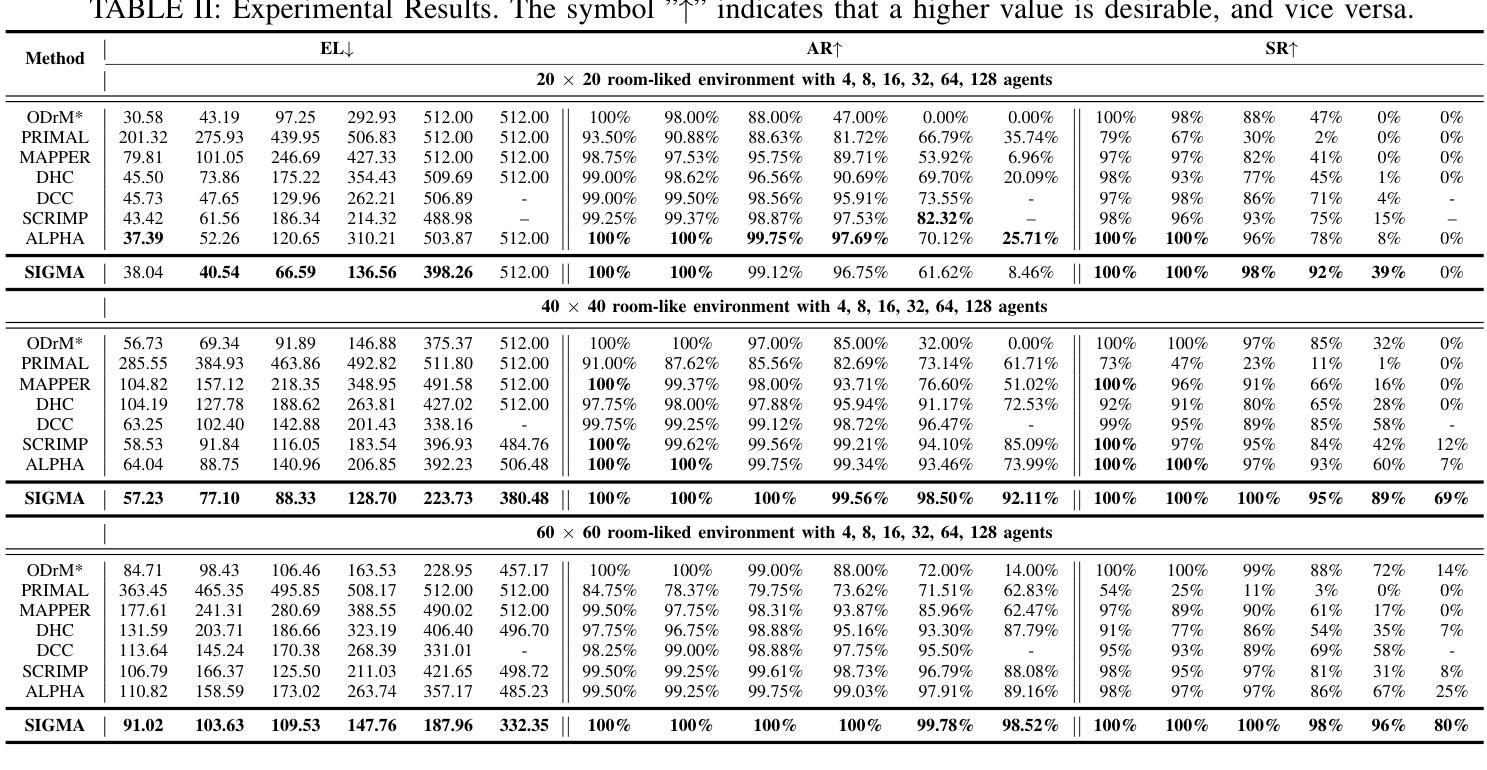
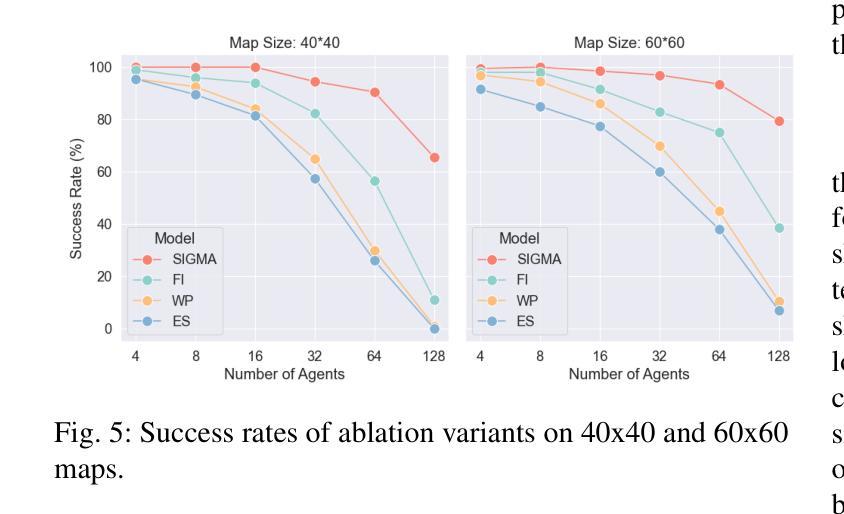
SIGMA: Sheaf-Informed Geometric Multi-Agent Pathfinding
Authors:Shuhao Liao, Weihang Xia, Yuhong Cao, Weiheng Dai, Chengyang He, Wenjun Wu, Guillaume Sartoretti
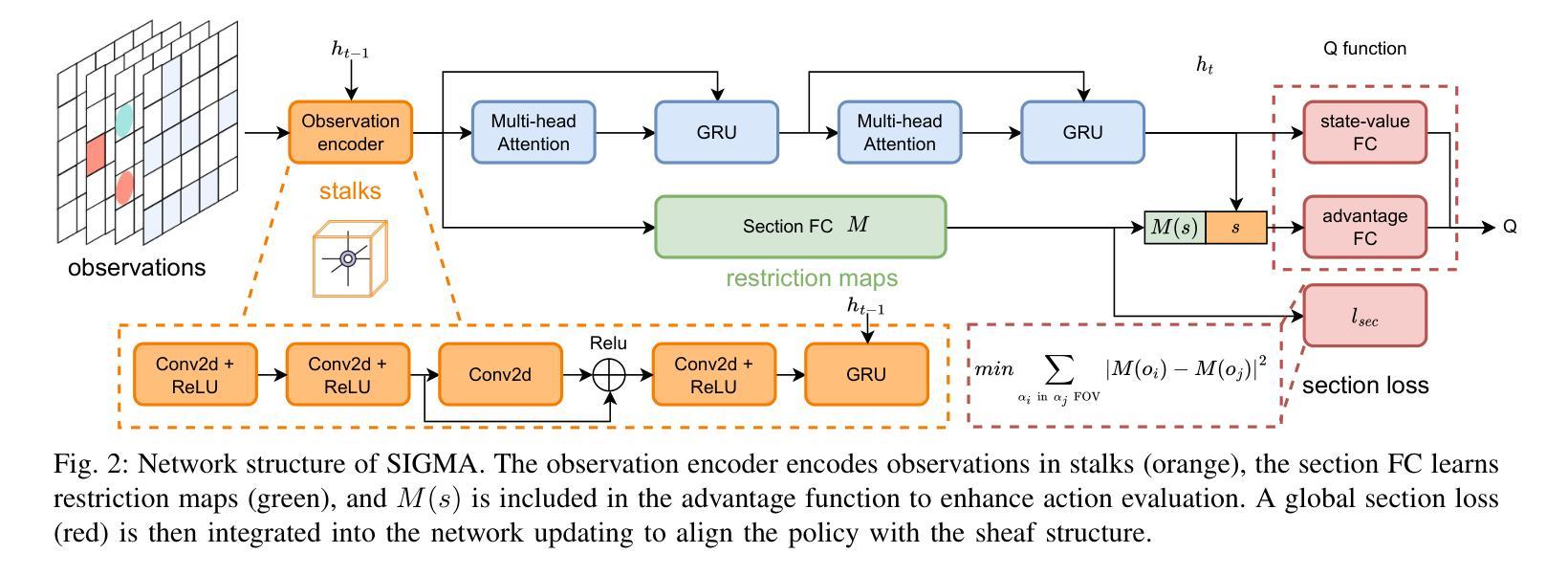
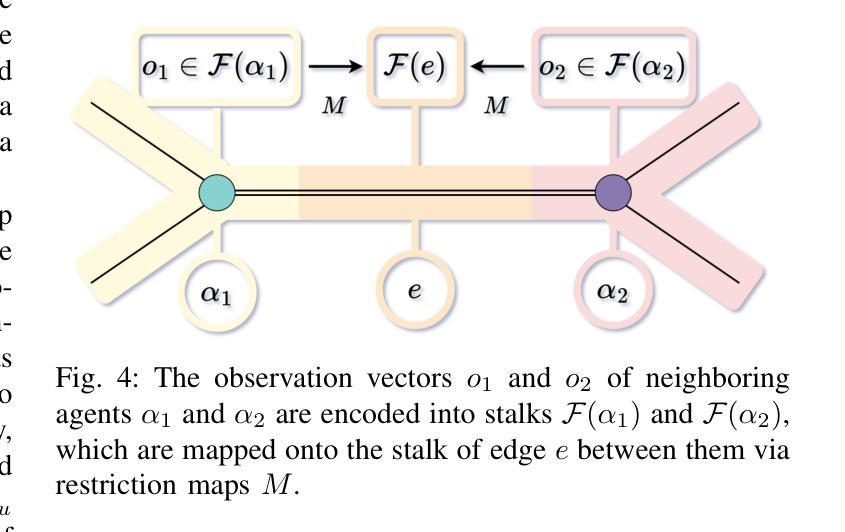
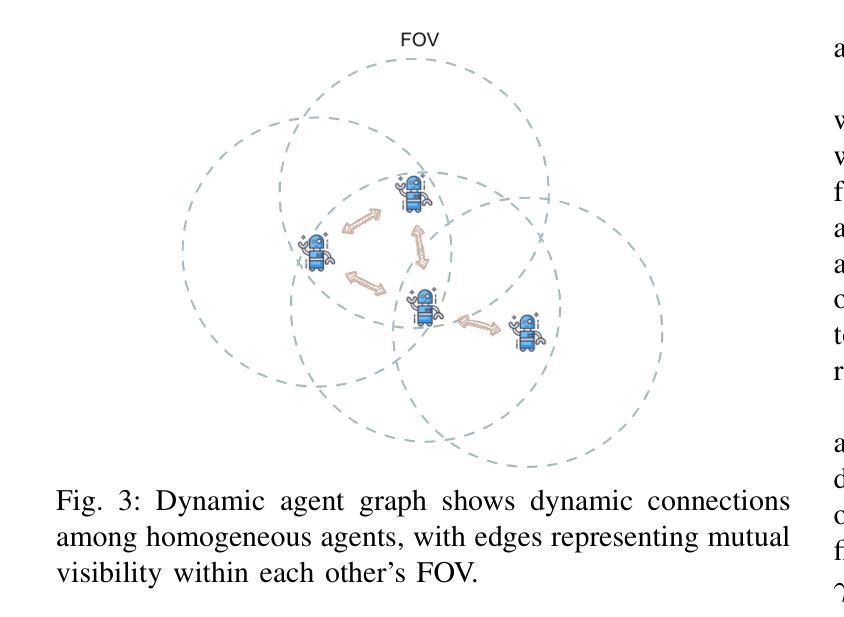
The Multi-Agent Path Finding (MAPF) problem aims to determine the shortest and collision-free paths for multiple agents in a known, potentially obstacle-ridden environment. It is the core challenge for robotic deployments in large-scale logistics and transportation. Decentralized learning-based approaches have shown great potential for addressing the MAPF problems, offering more reactive and scalable solutions. However, existing learning-based MAPF methods usually rely on agents making decisions based on a limited field of view (FOV), resulting in short-sighted policies and inefficient cooperation in complex scenarios. There, a critical challenge is to achieve consensus on potential movements between agents based on limited observations and communications. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a new framework that applies sheaf theory to decentralized deep reinforcement learning, enabling agents to learn geometric cross-dependencies between each other through local consensus and utilize them for tightly cooperative decision-making. In particular, sheaf theory provides a mathematical proof of conditions for achieving global consensus through local observation. Inspired by this, we incorporate a neural network to approximately model the consensus in latent space based on sheaf theory and train it through self-supervised learning. During the task, in addition to normal features for MAPF as in previous works, each agent distributedly reasons about a learned consensus feature, leading to efficient cooperation on pathfinding and collision avoidance. As a result, our proposed method demonstrates significant improvements over state-of-the-art learning-based MAPF planners, especially in relatively large and complex scenarios, demonstrating its superiority over baselines in various simulations and real-world robot experiments. The code is available at https://github.com/marmotlab/SIGMA
多智能体路径寻找(MAPF)问题旨在确定在已知且可能充满障碍的环境中,多个智能体的无碰撞最短路径。它是大规模物流和运输中机器人部署的核心挑战。去中心化的基于学习的方法在解决MAPF问题上显示出巨大潜力,提供了更灵活和可扩展的解决方案。然而,现有的基于学习的MAPF方法通常依赖于智能体基于有限的视野(FOV)做出决策,导致短视策略和复杂场景中的合作效率低下。因此,一个关键挑战是基于有限的观察和通信,在智能体之间达成潜在运动的共识。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了一个应用层理论的新框架到去中心化的深度强化学习,使智能体能够通过局部共识学习彼此的几何交叉依赖性,并利用它们进行紧密合作决策。特别是,层理论提供了通过局部观察实现全局共识的条件数学证明。受其启发,我们结合神经网络,基于层理论在潜在空间中近似建模共识,并通过自我监督学习进行训练。在任务执行过程中,除了MAPF的正常特征外,每个智能体还会对所学的共识特征进行分布式推理,从而在路径查找和避障方面实现有效合作。因此,我们提出的方法在相对较大和复杂的场景中,较先进的基于学习的MAPF规划器显示出显著改进,在各种模拟和真实机器人实验中优于基线。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/marmotlab/SIGMA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)
Summary
本文介绍了多智能体路径规划(MAPF)问题,旨在确定已知环境中多个智能体的无碰撞最短路径。文章强调了在大型物流运输场景中机器人部署的核心挑战,并指出分散式学习途径显示出解决MAPF问题的巨大潜力。然而,现有方法受限于智能体的视野(FOV),导致政策短视和复杂场景中的合作效率低下。为解决此问题,引入了一种新的框架,该框架应用层理论到分散式深度强化学习,使智能体能够通过局部共识学习彼此的几何相互依赖性,并利用它们进行紧密合作决策。此外,文中结合了神经网络对潜在空间中的共识进行建模,并通过自我监督学习进行培训。该模型通过正常MAPF特征和学习的共识特征进行分布式推理,从而实现了路径规划和防碰撞的有效合作。所提出的方法在模拟和真实机器人实验中均显示出对最新学习型MAPF规划器的显著改进,特别是在大型和复杂场景中表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体路径规划(MAPF)是确定多个智能体在已知环境中无碰撞最短路径的核心挑战,尤其在大型物流运输中的机器人部署。
- 分散式学习途径在解决MAPF问题上显示出巨大潜力,但现有方法受限于智能体的视野(FOV),导致短视政策和低效合作。
- 引入了一种新的框架,该框架应用层理论到分散式深度强化学习,使智能体能够学习彼此的几何相互依赖性,并通过局部共识进行紧密合作决策。
- 神经网络用于对潜在空间中的共识进行建模,并通过自我监督学习进行培训。
- 模型结合了正常MAPF特征和学习的共识特征进行分布式推理,实现了有效的路径规划和防碰撞合作。
- 所提出的方法在模拟和真实机器人实验中均显著改进了最新的学习型MAPF规划器,特别是在大型和复杂场景中表现优越。
点此查看论文截图