⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-26 更新
Through the Looking Glass: A Dual Perspective on Weakly-Supervised Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Jiaqi Ma, Guo-Sen Xie, Fang Zhao, Zechao Li
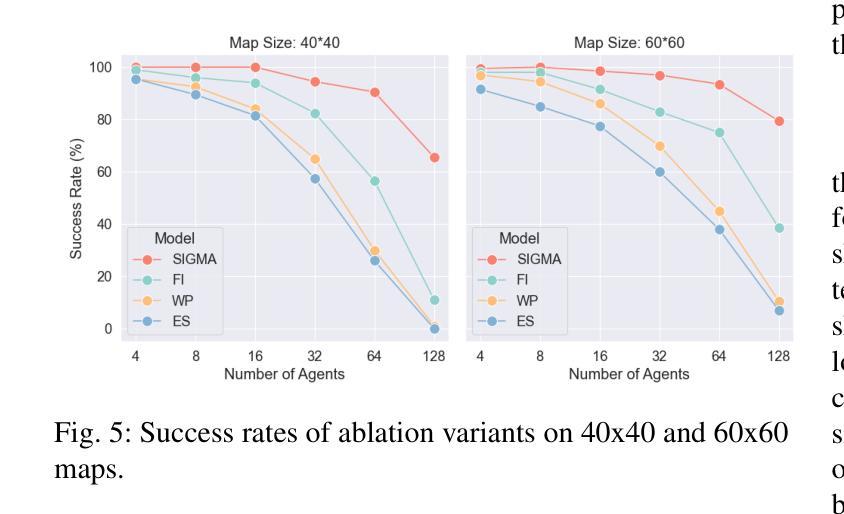
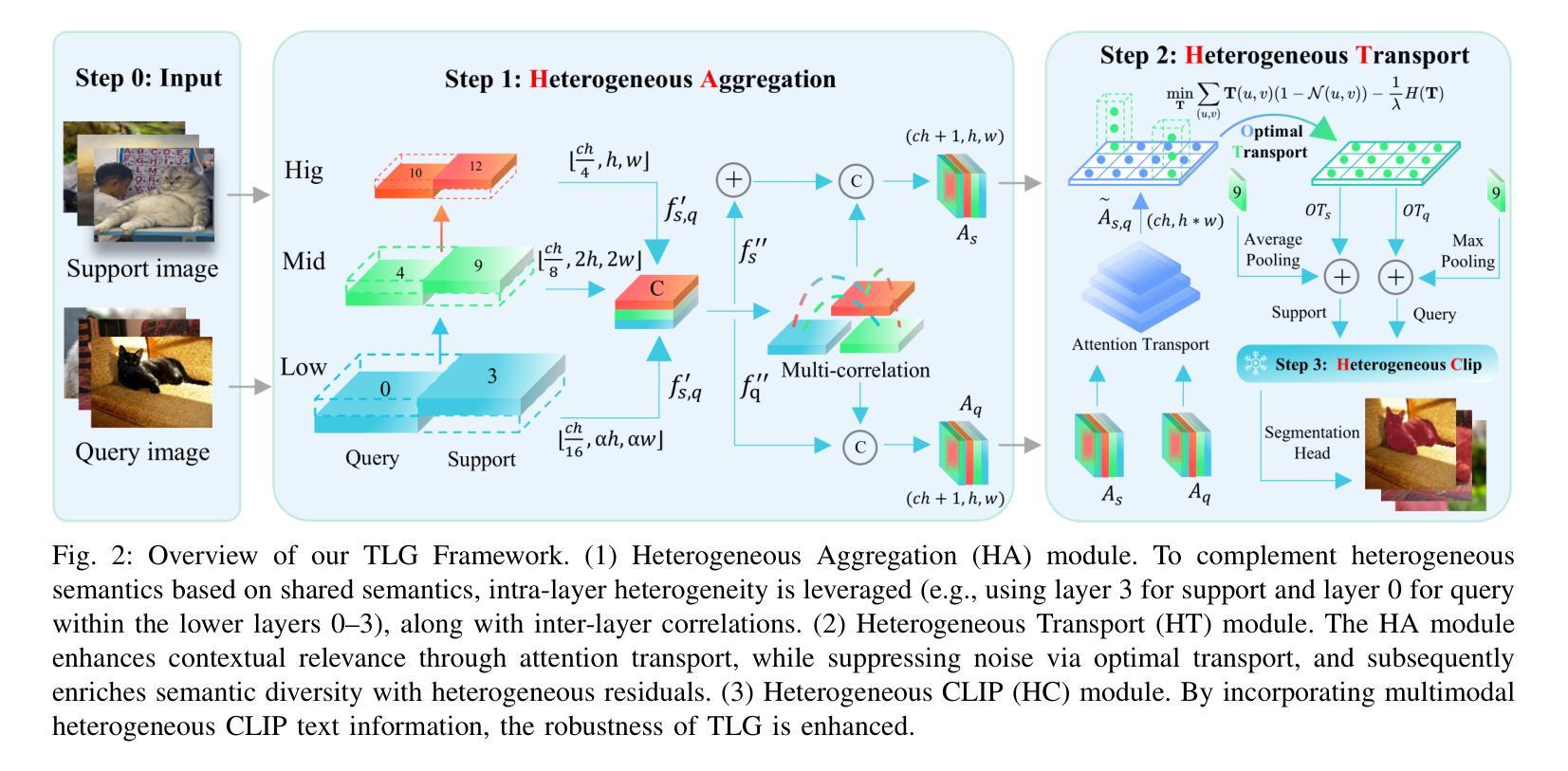
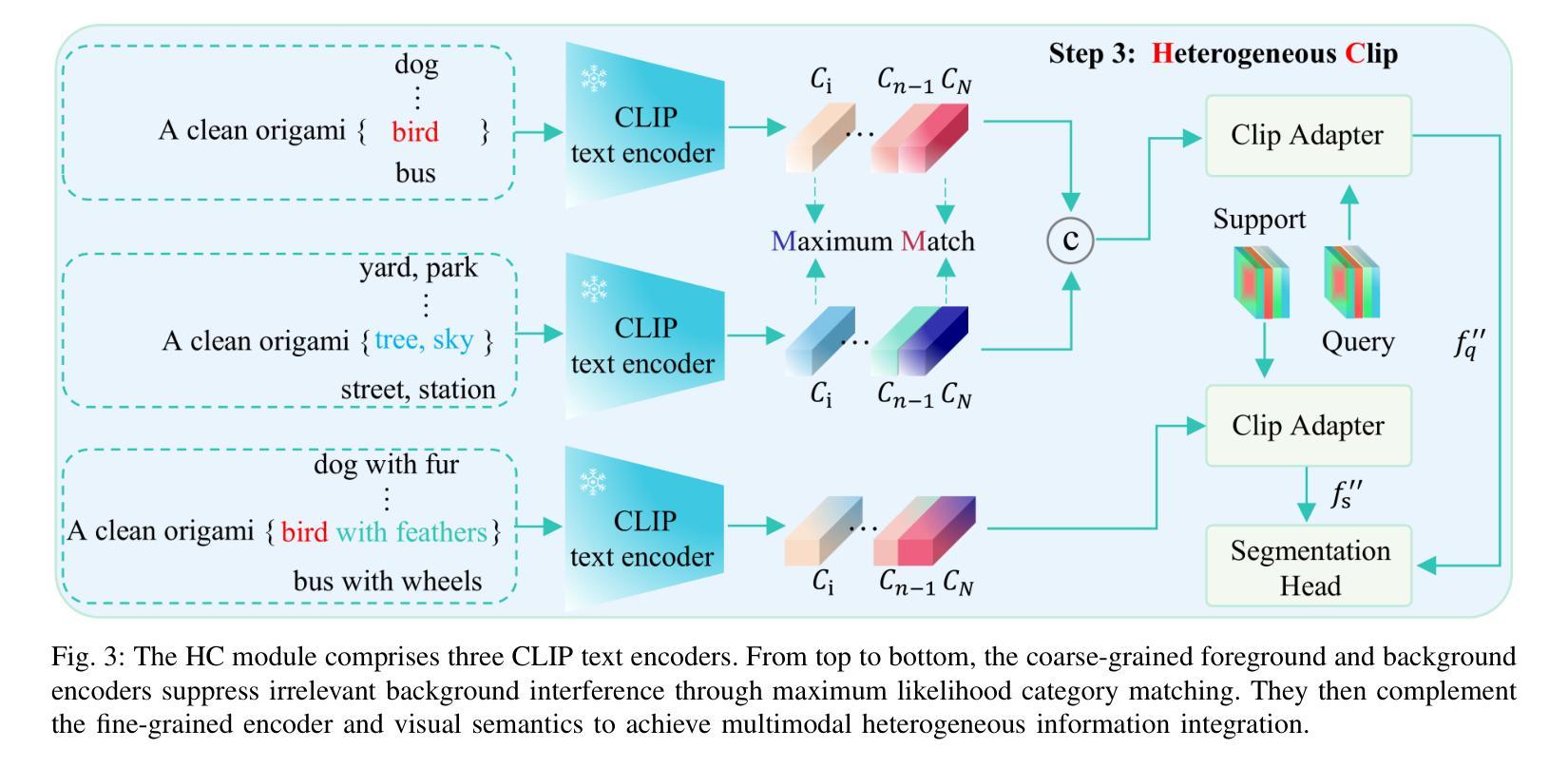
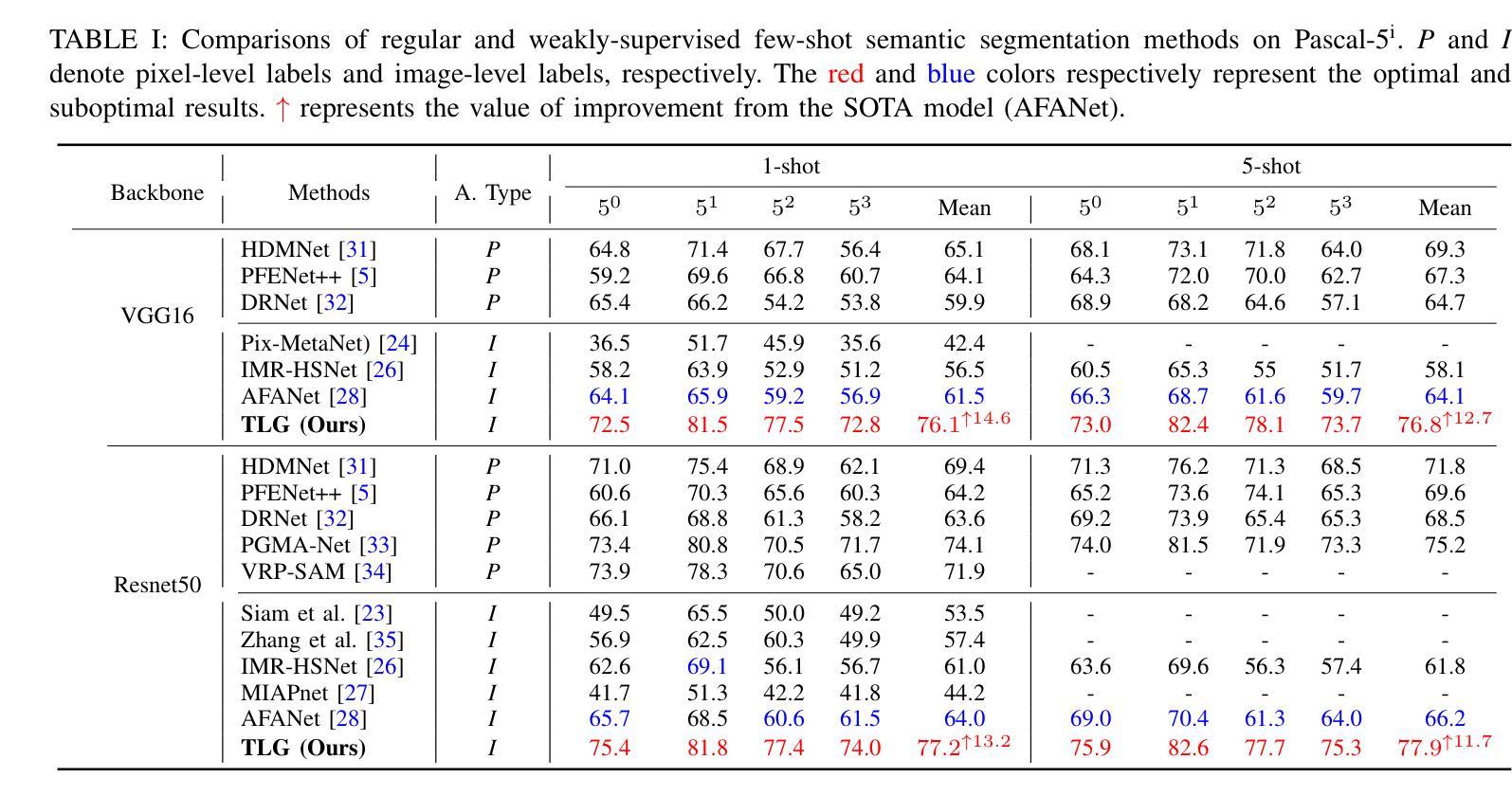
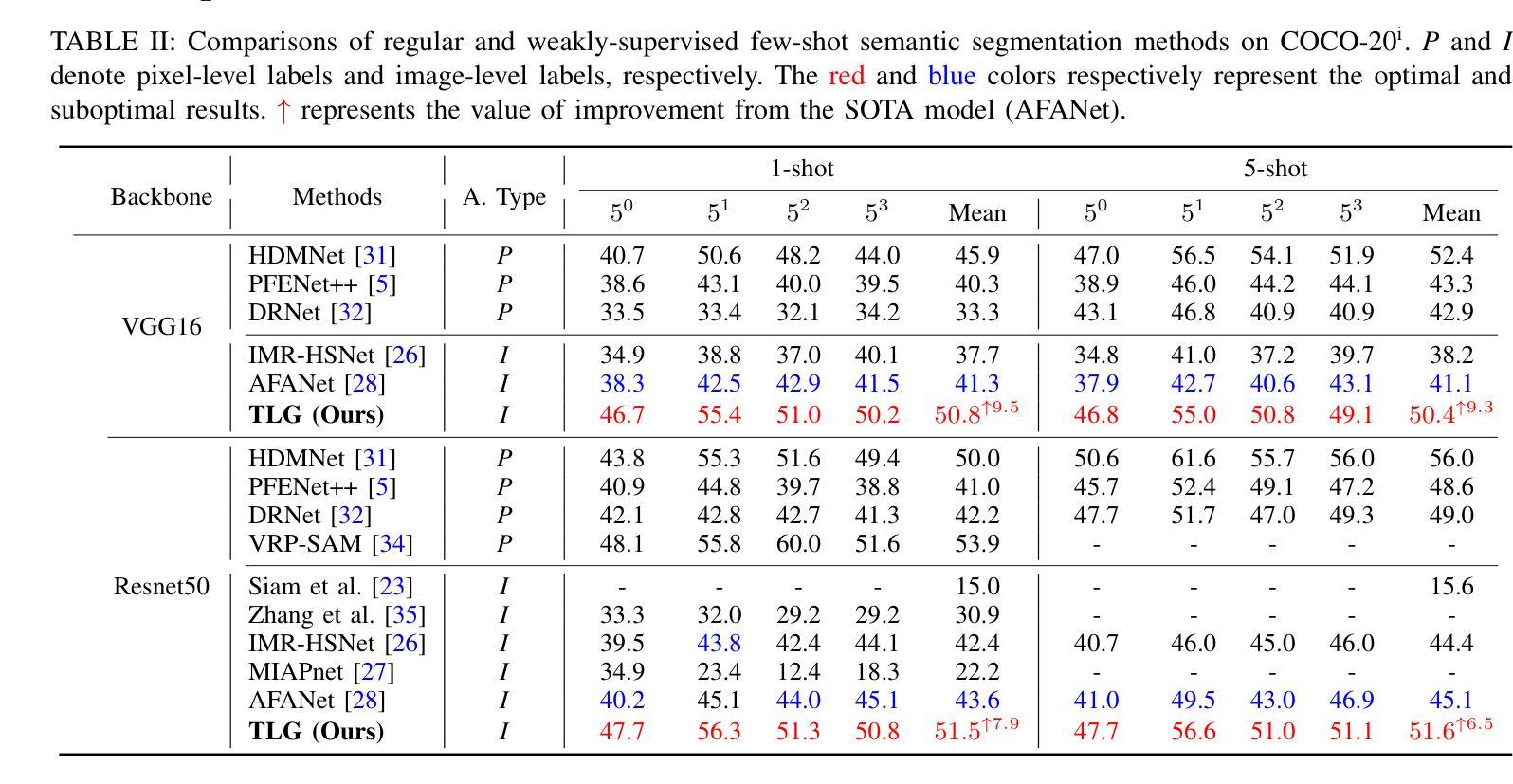
Meta-learning aims to uniformly sample homogeneous support-query pairs, characterized by the same categories and similar attributes, and extract useful inductive biases through identical network architectures. However, this identical network design results in over-semantic homogenization. To address this, we propose a novel homologous but heterogeneous network. By treating support-query pairs as dual perspectives, we introduce heterogeneous visual aggregation (HA) modules to enhance complementarity while preserving semantic commonality. To further reduce semantic noise and amplify the uniqueness of heterogeneous semantics, we design a heterogeneous transfer (HT) module. Finally, we propose heterogeneous CLIP (HC) textual information to enhance the generalization capability of multimodal models. In the weakly-supervised few-shot semantic segmentation (WFSS) task, with only 1/24 of the parameters of existing state-of-the-art models, TLG achieves a 13.2% improvement on Pascal-5\textsuperscript{i} and a 9.7% improvement on COCO-20\textsuperscript{i}. To the best of our knowledge, TLG is also the first weakly supervised (image-level) model that outperforms fully supervised (pixel-level) models under the same backbone architectures. The code is available at https://github.com/jarch-ma/TLG.
元学习旨在均匀采样具有相同类别和相似属性的同质支持-查询对,并通过相同的网络架构提取有用的归纳偏见。然而,这种相同的网络设计导致了过度语义同质化。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的同源但异构图网络。我们将支持-查询对视为双重视角,引入异构图视觉聚合(HA)模块,以增强互补性同时保留语义共性。为了进一步减少语义噪声并放大异质语义的独特性,我们设计了异质转移(HT)模块。最后,我们提出异质CLIP(HC)文本信息,以增强多模式模型的泛化能力。在弱监督少样本语义分割(WFSS)任务中,TLG仅使用现有最先进的模型参数的1/24,就在Pascal-5i上实现了13.2%的提升,在COCO-20i上实现了9.7%的提升。据我们所知,TLG还是第一个在相同骨干架构下,弱监督(图像级)模型优于全监督(像素级)模型的实例。代码可访问https://github.com/jarch-ma/TLG。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种解决少样本语义分割任务的方法,通过引入同源异构网络和模块,增强模型对同质支持查询对的采样效果,并提升模型的泛化能力。同时,该方法在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i任务上取得了显著的改进效果,并提供了可用代码。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种基于元学习的方法,旨在通过统一采样同质支持查询对,提取有用的归纳偏见。
- 提出了一种新型的同源异构网络设计,通过处理支持查询对作为双重视角,增强互补性并保留语义共性。
- 引入了异构视觉聚合模块(HA),用于增强语义共同性并减少语义噪声。
- 设计了异构传输模块(HT),以进一步突出异构语义的独特性。
- 通过引入异构CLIP(HC)文本信息,增强了多模态模型的泛化能力。
- 在弱监督少样本语义分割任务上取得了显著成果,包括在Pascal-5i和COCO-20i上的改进。
点此查看论文截图

Beyond Human-prompting: Adaptive Prompt Tuning with Semantic Alignment for Anomaly Detection
Authors:Pi-Wei Chen, Jerry Chun-Wei Lin, Wei-Han Chen, Jia Ji, Zih-Ching Chen, Feng-Hao Yeh, Chao-Chun Chen
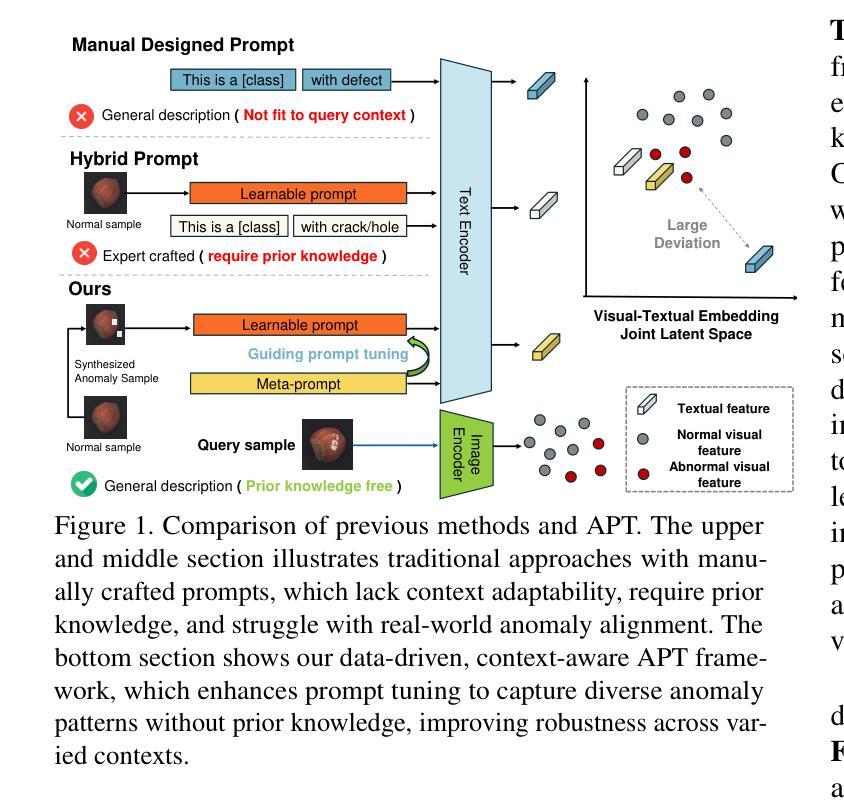
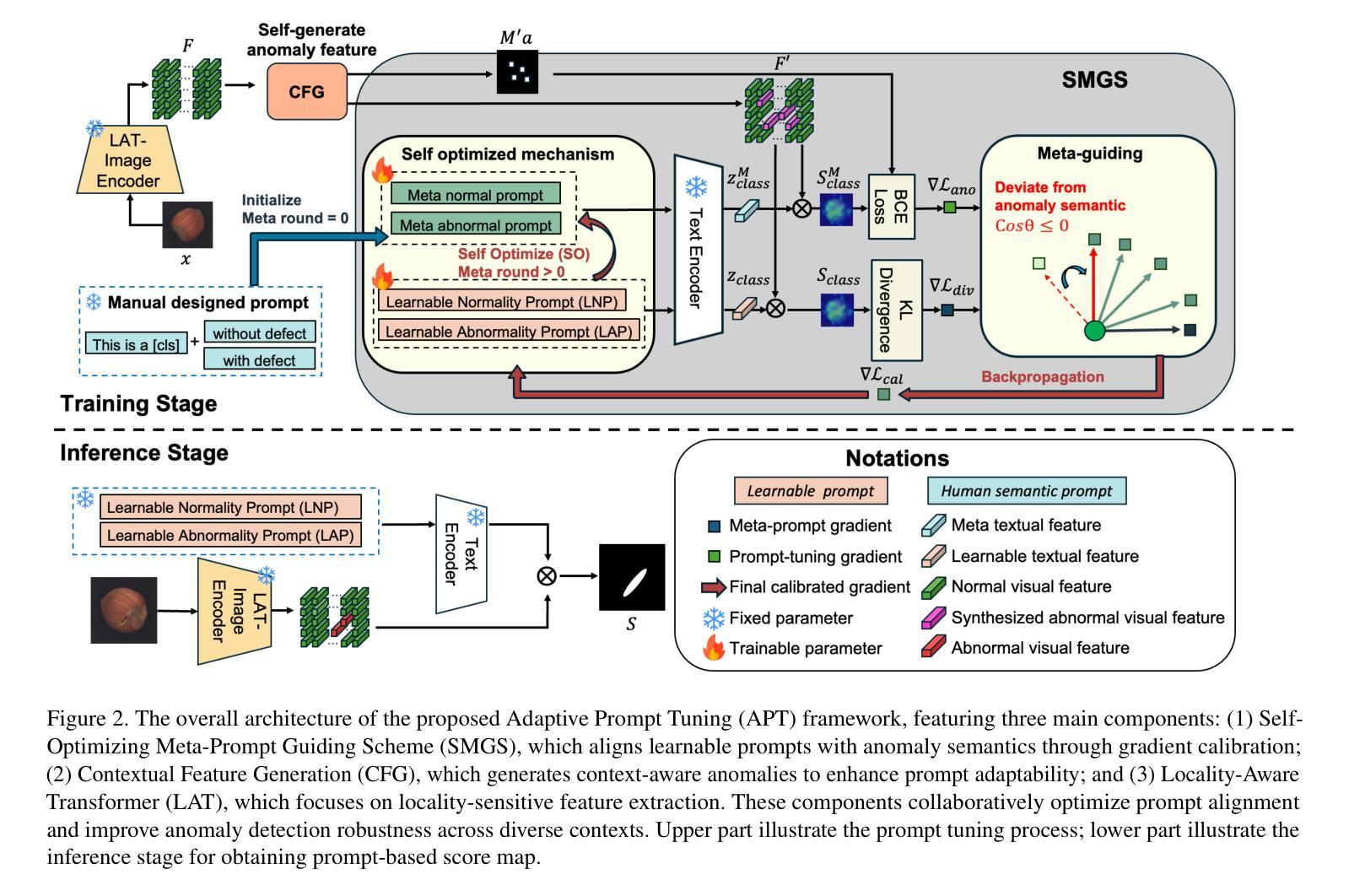
Pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have recently shown promise in detecting anomalies. However, previous approaches are fundamentally limited by their reliance on human-designed prompts and the lack of accessible anomaly samples, leading to significant gaps in context-specific anomaly understanding. In this paper, we propose \textbf{A}daptive \textbf{P}rompt \textbf{T}uning with semantic alignment for anomaly detection (APT), a groundbreaking prior knowledge-free, few-shot framework and overcomes the limitations of traditional prompt-based approaches. APT uses self-generated anomaly samples with noise perturbations to train learnable prompts that capture context-dependent anomalies in different scenarios. To prevent overfitting to synthetic noise, we propose a Self-Optimizing Meta-prompt Guiding Scheme (SMGS) that iteratively aligns the prompts with general anomaly semantics while incorporating diverse synthetic anomaly. Our system not only advances pixel-wise anomaly detection, but also achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmark datasets without requiring prior knowledge for prompt crafting, establishing a robust and versatile solution for real-world anomaly detection.
预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)最近在异常检测方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,之前的方法从根本上受限于其依赖于人为设计的提示和缺乏可访问的异常样本,导致在特定上下文中的异常理解上存在较大差距。在本文中,我们提出了用于异常检测的基于语义对齐的自适应提示调整(APT)方法。APT是一种突破性的无先验知识、小样例框架,克服了传统基于提示的方法的限制。APT使用带有噪声扰动的自生成异常样本,训练学习提示,以捕获不同场景中与上下文相关的异常。为了防止对合成噪声的过拟合,我们提出了一种自优化元提示引导方案(SMGS),该方案通过迭代方式将提示与通用异常语义对齐,同时融入多样化的合成异常。我们的系统不仅推动了像素级的异常检测,而且在多个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能,无需为提示设计提供先验知识,为实际异常检测提供了稳健且通用的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型在异常检测中展现出潜力,但受限于人工设计的提示和缺乏可访问的异常样本,导致对特定上下文中的异常理解存在差距。本文提出无需先验知识的少样本框架APT(自适应提示调整与语义对齐异常检测法),通过生成带有噪声扰动的异常样本训练可学习提示,以捕获不同场景中的上下文相关异常。为防止过度拟合合成噪声,提出自优化元提示引导方案SMGS,该方案可迭代地对齐提示与常规异常语义,同时融入多样的合成异常。APT不仅推动了像素级的异常检测,还在多个基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能,无需事先了解提示制作知识,为实际异常检测提供了稳健且通用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型在异常检测领域具有潜力。
- 传统方法受限于人工设计的提示和缺乏异常样本。
- APT框架通过生成带有噪声扰动的异常样本训练可学习提示。
- APT利用自优化元提示引导方案SMGS,防止过度拟合合成噪声。
- APT可捕获不同场景中的上下文相关异常。
- APT在像素级异常检测方面取得进展。
点此查看论文截图

Integrating Time Series into LLMs via Multi-layer Steerable Embedding Fusion for Enhanced Forecasting
Authors:Zhuomin Chen, Dan Li, Jiahui Zhou, Shunyu Wu, Haozheng Ye, Jian Lou, See-Kiong Ng
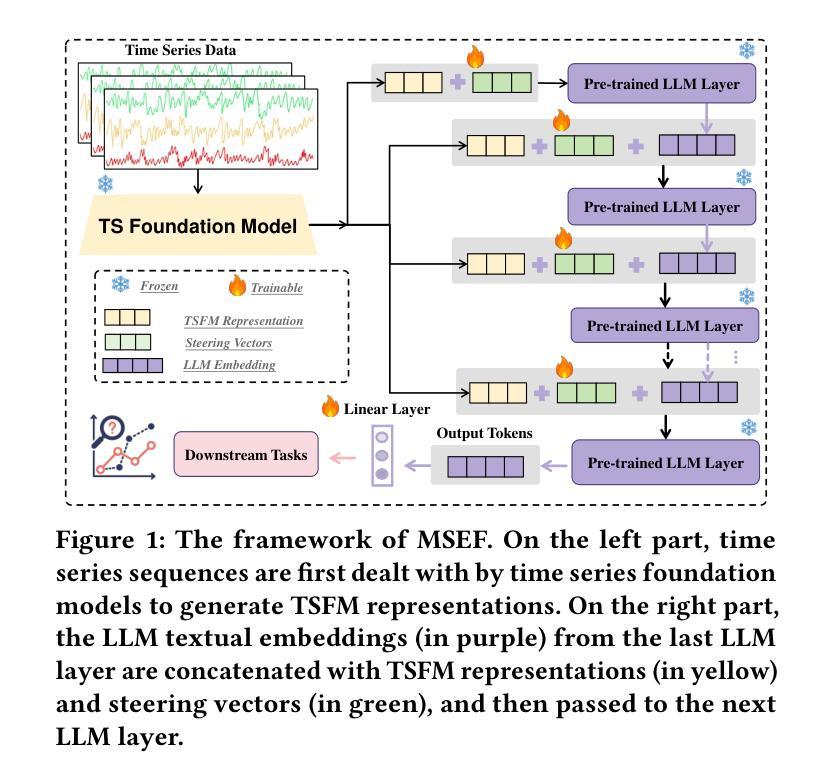
Time series (TS) data are ubiquitous across various application areas, rendering time series forecasting (TSF) a fundamental task. With the astounding advances in large language models (LLMs), a variety of methods have been developed to adapt LLMs for time series forecasting. Despite unlocking the potential of LLMs in comprehending TS data, existing methods are inherently constrained by their shallow integration of TS information, wherein LLMs typically access TS representations at shallow layers, primarily at the input layer. This causes the influence of TS representations to progressively fade in deeper layers and eventually leads to ineffective adaptation between textual embeddings and TS representations. In this paper, we propose the Multi-layer Steerable Embedding Fusion (MSEF), a novel framework that enables LLMs to directly access time series patterns at all depths, thereby mitigating the progressive loss of TS information in deeper layers. Specifically, MSEF leverages off-the-shelf time series foundation models to extract semantically rich embeddings, which are fused with intermediate text representations across LLM layers via layer-specific steering vectors. These steering vectors are designed to continuously optimize the alignment between time series and textual modalities and facilitate a layer-specific adaptation mechanism that ensures efficient few-shot learning capabilities. Experimental results on seven benchmarks demonstrate significant performance improvements by MSEF compared with baselines, with an average reduction of 31.8% in terms of MSE. The code is available at https://github.com/One1sAll/MSEF.
时间序列(TS)数据在各个应用领域都普遍存在,使得时间序列预测(TSF)成为一项基本任务。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的惊人发展,已经开发了许多方法来适应LLM进行时间序列预测。尽管现有方法已经挖掘出了LLM在理解TS数据方面的潜力,但它们固有的对TS信息浅层集成的限制也显现出来。在此,LLM通常仅在输入层访问TS表示,这导致TS表示的影响在深层中逐渐消失,并最终导致文本嵌入和TS表示之间的不适应。在本文中,我们提出了多层可转向嵌入融合(MSEF)这一新框架,使LLM能够直接在所有深度访问时间序列模式,从而减轻深层中TS信息的逐步损失。具体而言,MSEF利用现成的时间序列基础模型来提取语义丰富的嵌入,这些嵌入通过与LLM各层的中间文本表示相结合,通过特定层的转向向量进行融合。这些转向向量旨在持续优化时间序列和文本模式之间的对齐,并促进特定层的适应机制,确保有效的少样本学习能力。在七个基准测试上的实验结果表明,与基线相比,MSEF表现出显著的性能改进,在均方误差(MSE)方面平均降低了31.8%。代码可访问https://github.com/One1sAll/MSEF。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be published in CIKM 2025
Summary:针对时间序列数据(TS),基于大型语言模型(LLMs)的时间序列预测(TSF)方法在近年来不断出现,但由于传统方法局限于在浅层层面融合时间序列信息,导致其使用效率和深度有待提升。本论文提出了多层级可调整嵌入融合(MSEF)框架,它能够引导LLMs在不同深度层直接获取时间序列模式,进而缓解深层信息丢失的问题。该框架结合了预先训练的时间序列基础模型与文本表示模型,并借助特定层级的转向向量,在少样本场景下表现出了优越的性能。在七个基准测试上的实验结果表明,与基准模型相比,MSEF的性能显著提升了平均MSE减少达到惊人的高达近百分之三十。该项目开源的代码位于指定网址。
Key Takeaways:
- 时间序列数据在各领域应用广泛,时间序列预测成为关键任务。大型语言模型在时间序列预测中的应用逐渐显现。
- 传统方法对于时间序列信息的融合仅限于浅层层次,导致深层信息丢失的问题。为此,需要改进大型语言模型的融合策略以提升性能。
- MSEF框架的提出旨在引导大型语言模型在所有深度层次获取时间序列模式,以提高预测的精准度和广度。其主要结合时间信息和文本嵌入模型的联合优化方案来达到效果。这标志着针对大规模语言的时序数据分析走向更深层次的处理策略。
- MSEF框架通过利用预先训练的时间序列基础模型提取语义丰富的嵌入信息,并与文本表示模型相融合,实现了跨层级的融合效果。这种跨层融合有助于实现信息的有效利用和性能的进一步提高。其中特定层级的转向向量是其创新设计之一,它在融合时间信息和文本模态方面起到关键作用。同时促进了层级的特定适应性机制的形成与完善,极大程度上促进了少量数据的实际应用价值及其对未来业务模式的参考价值进一步提升及成长 。证明上述自适应调整策略和方案可以在更复杂的现实场景中获得更为出色的应用效果及市场表现。这也进一步增强了行业领域对该技术的期待和关注。具体应用场景涉及实际数据模拟场景分析及市场需求理解等 。其公开的代码可供进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

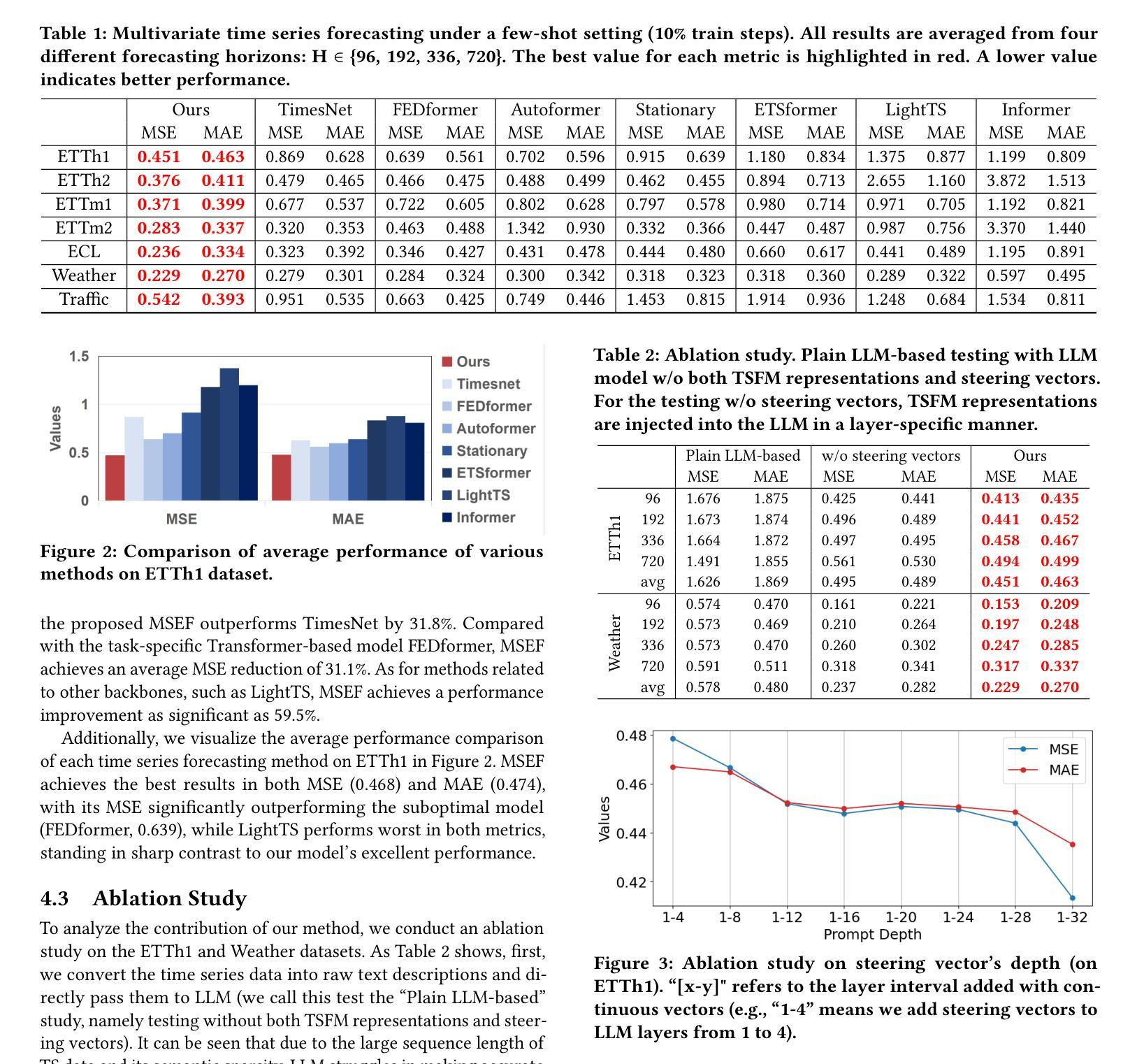
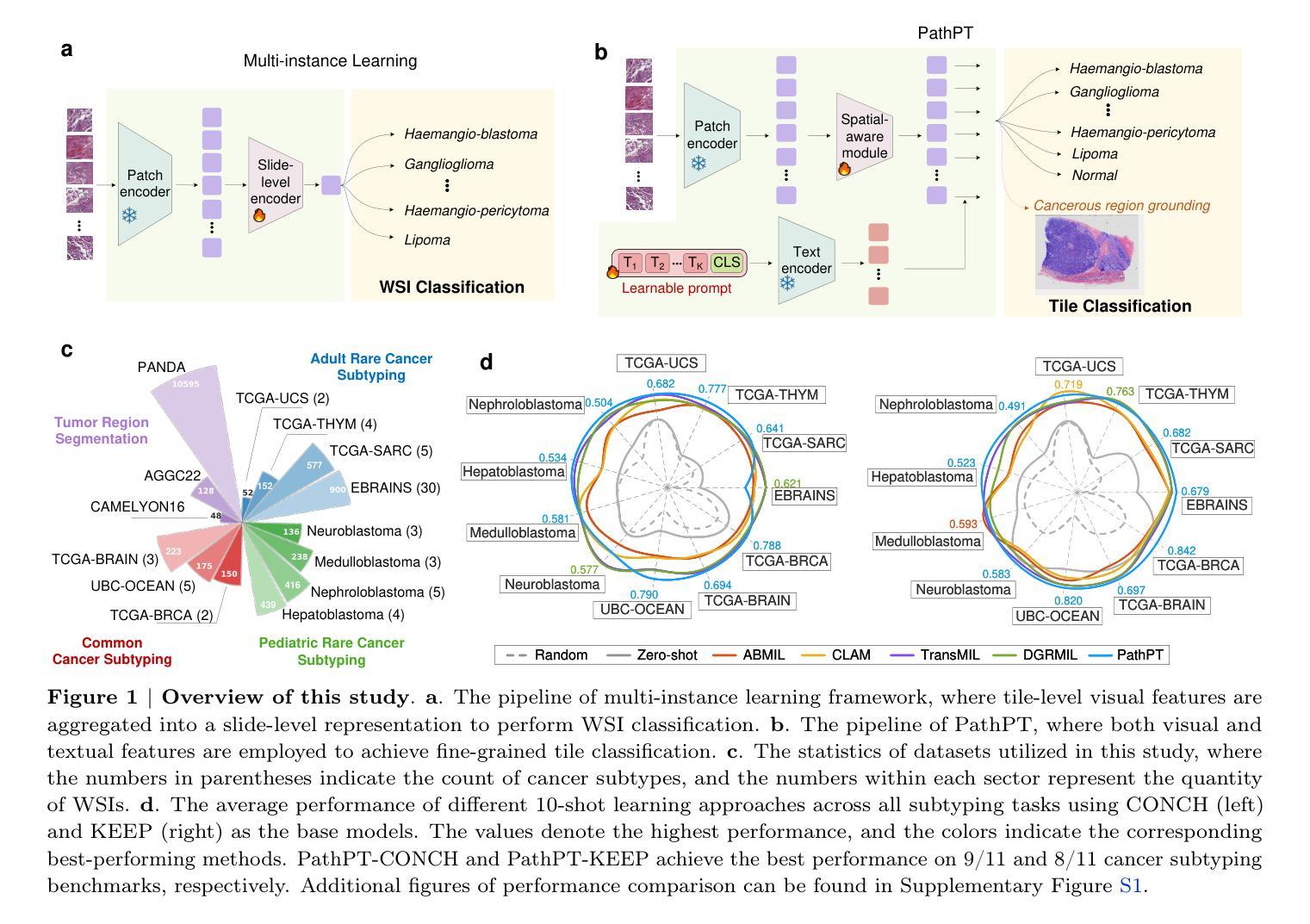
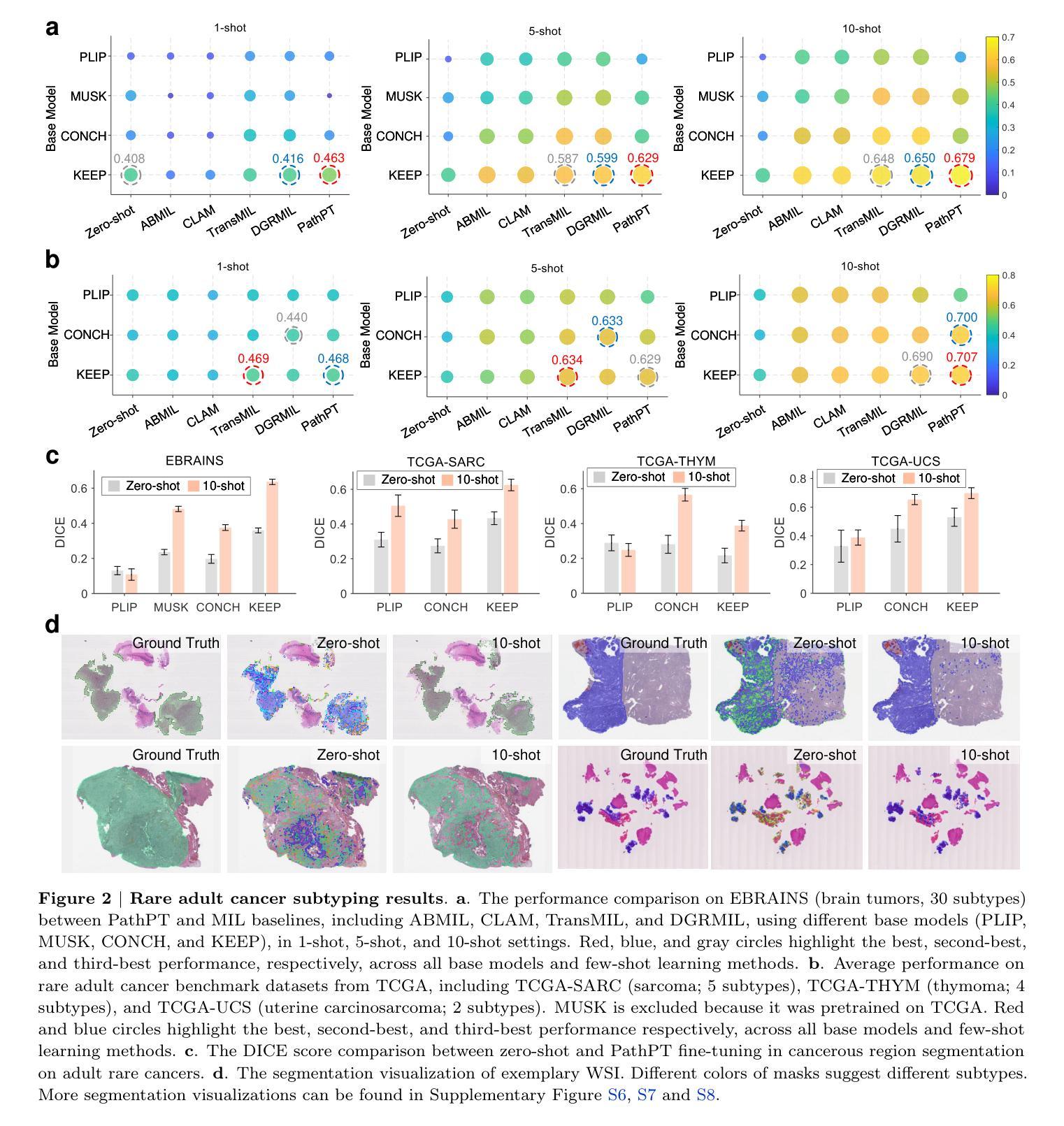
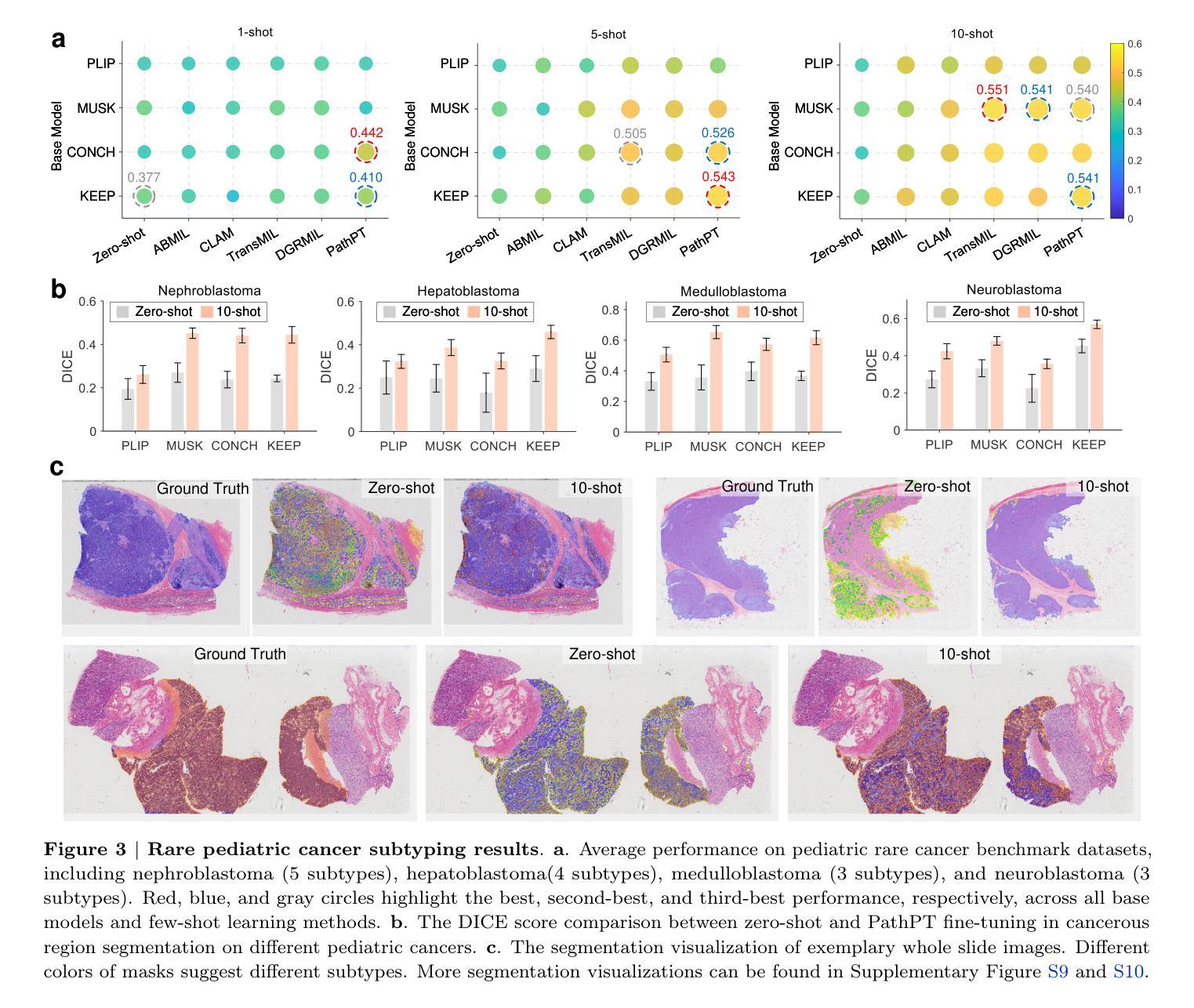
Boosting Pathology Foundation Models via Few-shot Prompt-tuning for Rare Cancer Subtyping
Authors:Dexuan He, Xiao Zhou, Wenbin Guan, Liyuan Zhang, Xiaoman Zhang, Sinuo Xu, Ge Wang, Lifeng Wang, Xiaojun Yuan, Xin Sun, Yanfeng Wang, Kun Sun, Ya Zhang, Weidi Xie
Rare cancers comprise 20-25% of all malignancies but face major diagnostic challenges due to limited expert availability-especially in pediatric oncology, where they represent over 70% of cases. While pathology vision-language (VL) foundation models show promising zero-shot capabilities for common cancer subtyping, their clinical performance for rare cancers remains limited. Existing multi-instance learning (MIL) methods rely only on visual features, overlooking cross-modal knowledge and compromising interpretability critical for rare cancer diagnosis. To address this limitation, we propose PathPT, a novel framework that fully exploits the potential of vision-language pathology foundation models through spatially-aware visual aggregation and task-specific prompt tuning. Unlike conventional MIL, PathPT converts WSI-level supervision into fine-grained tile-level guidance by leveraging the zero-shot capabilities of VL models, thereby preserving localization on cancerous regions and enabling cross-modal reasoning through prompts aligned with histopathological semantics. We benchmark PathPT on eight rare cancer datasets(four adult and four pediatric) spanning 56 subtypes and 2,910 WSIs, as well as three common cancer datasets, evaluating four state-of-the-art VL models and four MIL frameworks under three few-shot settings. Results show that PathPT consistently delivers superior performance, achieving substantial gains in subtyping accuracy and cancerous region grounding ability. This work advances AI-assisted diagnosis for rare cancers, offering a scalable solution for improving subtyping accuracy in settings with limited access to specialized expertise.
罕见癌症占所有恶性肿瘤的20-25%,但由于专家资源有限,特别是在儿童肿瘤学中(罕见癌症占病例的70%以上),其诊断面临重大挑战。虽然病理学视觉语言(VL)基础模型在常见的癌症分型中显示出有前景的零样本能力,但它们在罕见癌症的临床表现仍然有限。现有的多实例学习(MIL)方法仅依赖于视觉特征,忽视了跨模态知识,这对罕见癌症诊断至关重要。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了PathPT,这是一个全新的框架,它充分利用了视觉语言病理学基础模型的潜力,通过空间感知的视觉聚合和特定任务的提示调整。与传统的MIL不同,PathPT通过将WSI级别的监督转化为精细的瓦片级别的指导,利用VL模型的零样本能力,从而保留对癌变区域的定位,并通过与病理语义对齐的提示实现跨模态推理。我们在涵盖56种亚型和2910个WSI的八个罕见癌症数据集(四个成人和四个儿科)以及三个常见癌症数据集上测试了PathPT,在三种小样例设置下评估了四种最先进的VL模型和四种MIL框架。结果表明,PathPT始终表现出卓越的性能,在分型准确性和癌变区域定位能力方面实现了显著的改进。这项工作推动了人工智能在罕见癌症诊断方面的应用,为在缺乏专业专家的情况下提高分型准确性提供了可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了罕见癌症诊断面临的挑战,尤其是儿科肿瘤学中罕见癌症占比超过70%的情况。虽然病理视觉语言基础模型对常见癌症分型表现出零样本能力,但对罕见癌症的临床表现仍然有限。为此,提出了一种名为PathPT的新框架,该框架充分利用了视觉语言病理学基础模型的潜力,通过空间感知的视觉聚合和特定任务的提示调整来解决这个问题。PathPT将WSI级别的监督转化为精细的瓷砖级别的指导,利用VL模型的零样本能力,从而保留对癌变区域的定位,并通过与病理语义对齐的提示实现跨模态推理。在多个罕见癌症数据集上的实验表明,PathPT在子类型准确性和癌变区域定位能力方面表现出卓越的性能。这项工作为罕见癌症的AI辅助诊断提供了可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 罕见癌症占所有恶性肿瘤的20-25%,在儿科肿瘤学中占比更高,达到70%以上,诊断面临重大挑战。
- 病理视觉语言基础模型对常见癌症分型具有零样本能力,但对罕见癌症的临床表现有限。
- PathPT框架充分利用视觉语言病理学基础模型的潜力,通过空间感知的视觉聚合和特定任务的提示调整来解决上述问题。
- PathPT将WSI级别的监督转化为精细瓷砖级别的指导,利用VL模型的零样本能力保留癌变区域定位并实现跨模态推理。
- PathPT在多个罕见癌症数据集上的实验表现优越,显著提高子类型准确性和癌变区域定位能力。
- PathPT为罕见癌症的AI辅助诊断提供了可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

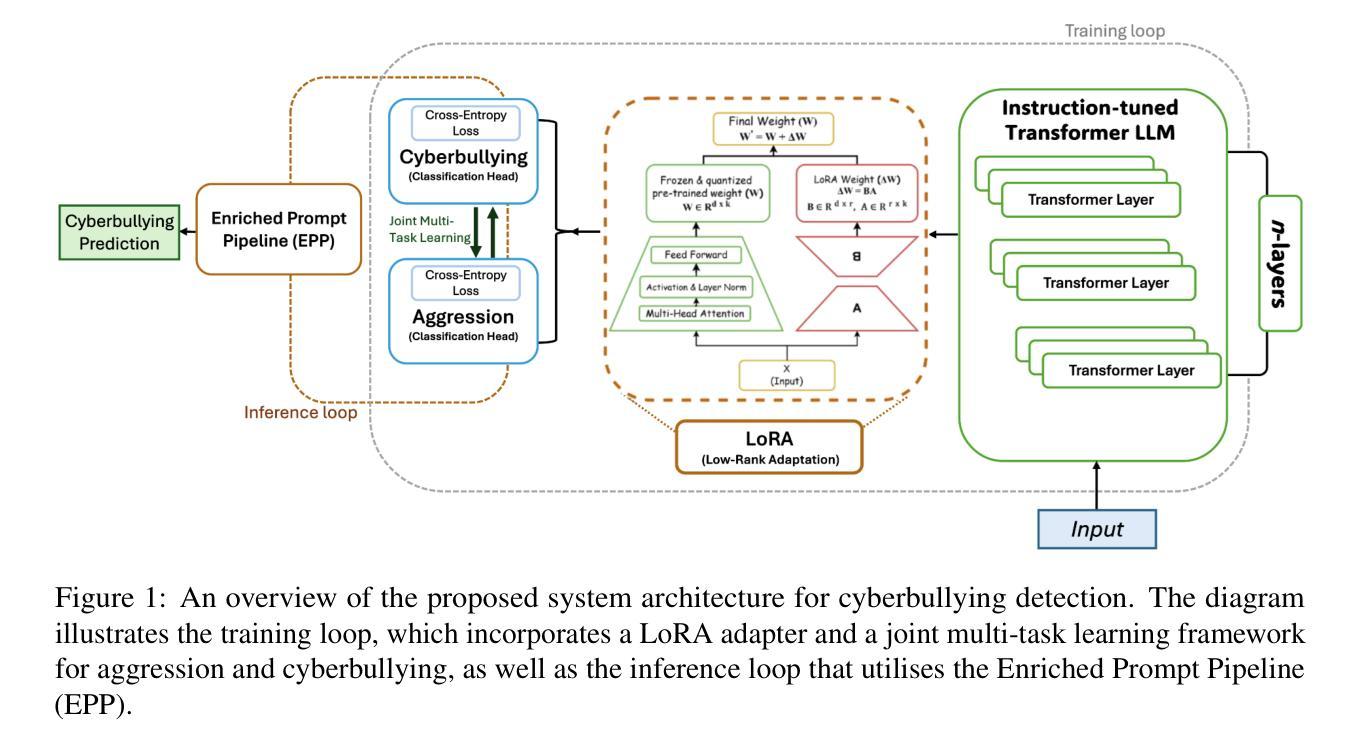
Cyberbullying Detection via Aggression-Enhanced Prompting
Authors:Aisha Saeid, Anu Sabu, Girish A. Koushik, Ferrante Neri, Diptesh Kanojia
Detecting cyberbullying on social media remains a critical challenge due to its subtle and varied expressions. This study investigates whether integrating aggression detection as an auxiliary task within a unified training framework can enhance the generalisation and performance of large language models (LLMs) in cyberbullying detection. Experiments are conducted on five aggression datasets and one cyberbullying dataset using instruction-tuned LLMs. We evaluated multiple strategies: zero-shot, few-shot, independent LoRA fine-tuning, and multi-task learning (MTL). Given the inconsistent results of MTL, we propose an enriched prompt pipeline approach in which aggression predictions are embedded into cyberbullying detection prompts to provide contextual augmentation. Preliminary results show that the enriched prompt pipeline consistently outperforms standard LoRA fine-tuning, indicating that aggression-informed context significantly boosts cyberbullying detection. This study highlights the potential of auxiliary tasks, such as aggression detection, to improve the generalisation of LLMs for safety-critical applications on social networks.
检测社交媒体上的网络欺凌仍然是一个关键挑战,因为其表达微妙且多样。本研究旨在探讨在统一训练框架内将攻击检测作为辅助任务是否可以提高大型语言模型(LLM)在网络欺凌检测中的通用性和性能。实验采用五个攻击数据集和一个网络欺凌数据集,使用指令调整的大型语言模型。我们评估了多种策略:零样本、少样本、独立LoRA微调和多任务学习(MTL)。鉴于多任务学习的不一致结果,我们提出了一种丰富的提示管道方法,其中攻击预测被嵌入到网络欺凌检测提示中以提供上下文增强。初步结果表明,丰富的提示管道始终优于标准的LoRA微调,这表明攻击检测上下文可显著提高网络欺凌检测能力。该研究突出了辅助任务(如攻击检测)的潜力,可以改进大型语言模型在社交网络安全关键应用的通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to RANLP 2025
Summary:本研究探讨了将攻击检测作为辅助任务,在一个统一的训练框架内,是否能够提升大型语言模型在网络欺凌检测中的通用性和性能。实验在五个攻击数据集和一个网络欺凌数据集上进行,评估了零样本、少样本、独立LoRA微调以及多任务学习的策略。在此基础上提出了增强提示管道方法,其中将攻击预测嵌入到网络欺凌检测提示中提供上下文增强。初步结果显示增强提示管道方法的性能优于标准LoRA微调方法,证明了攻击信息上下文对网络欺凌检测的重要性。这突出展示了将攻击检测作为辅助任务,对于提高大型语言模型在社交网络安全关键应用中的通用性潜力。
Key Takeaways:
- 网络欺凌检测面临挑战,因其表达形式微妙多变。
- 集成攻击检测作为辅助任务能提高大型语言模型在网络欺凌检测中的性能。
- 实验在多个数据集上进行,评估了不同策略,包括零样本、少样本、独立LoRA微调及多任务学习。
- 提出增强提示管道方法,将攻击预测嵌入网络欺凌检测提示中。
- 初步结果显示增强提示管道方法性能优越,证明攻击信息上下文对网络欺凌检测的重要性。
- 辅助任务如攻击检测对于提高大型语言模型在社交网络安全关键应用中的通用性有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

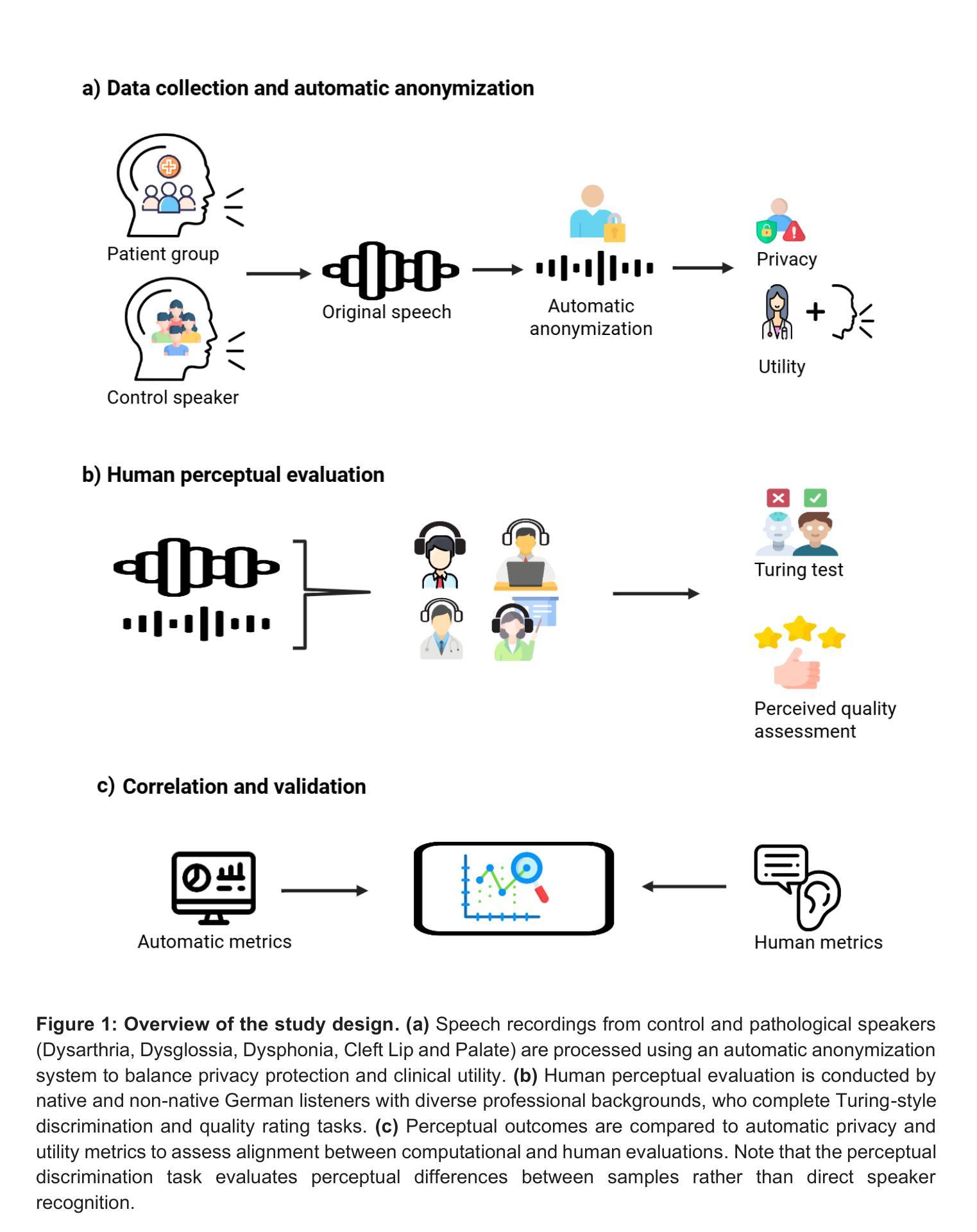
Perceptual Implications of Automatic Anonymization in Pathological Speech
Authors:Soroosh Tayebi Arasteh, Saba Afza, Tri-Thien Nguyen, Lukas Buess, Maryam Parvin, Tomas Arias-Vergara, Paula Andrea Perez-Toro, Hiu Ching Hung, Mahshad Lotfinia, Thomas Gorges, Elmar Noeth, Maria Schuster, Seung Hee Yang, Andreas Maier
Automatic anonymization techniques are essential for ethical sharing of pathological speech data, yet their perceptual consequences remain understudied. We present a comprehensive human-centered analysis of anonymized pathological speech, using a structured protocol involving ten native and non-native German listeners with diverse linguistic, clinical, and technical backgrounds. Listeners evaluated anonymized-original utterance pairs from 180 speakers spanning Cleft Lip and Palate, Dysarthria, Dysglossia, Dysphonia, and healthy controls. Speech was anonymized using state-of-the-art automatic methods (equal error rates in the range of 30-40%). Listeners completed Turing-style discrimination and quality rating tasks under zero-shot (single-exposure) and few-shot (repeated-exposure) conditions. Discrimination accuracy was high overall (91% zero-shot; 93% few-shot), but varied by disorder (repeated-measures ANOVA: p=0.007), ranging from 96% (Dysarthria) to 86% (Dysphonia). Anonymization consistently reduced perceived quality across groups (from 83% to 59%, p<0.001), with pathology-specific degradation patterns (one-way ANOVA: p=0.005). Native listeners showed a non-significant trend toward higher original speech ratings (Delta=4%, p=0.199), but this difference was minimal after anonymization (Delta=1%, p=0.724). No significant gender-based bias was observed. Perceptual outcomes did not correlate with automatic metrics; intelligibility was linked to perceived quality in original speech but not after anonymization. These findings underscore the need for listener-informed, disorder-specific anonymization strategies that preserve both privacy and perceptual integrity.
自动匿名化技术在病理语音数据的伦理共享中至关重要,但其感知后果仍研究不足。我们采用以人为中心的综合分析方法,对匿名病理语音进行研究,使用涉及十位德语本地人和非本地听众的结构化协议,这些听众具有不同的语言、临床和技术背景。听众评估了来自180名演讲者的匿名原始语句对,包括唇裂和腭裂、口齿不清、嗓音异常和正常对照。语音采用最先进的自动方法进行匿名处理(误差率范围为30%-40%)。听众在零样本(单次曝光)和少样本(多次曝光)条件下完成了图灵风格的辨别和质量评估任务。总体鉴别准确率较高(零样本91%;少样本93%),但不同疾病的鉴别准确率有所不同(重复测量方差分析:p=0.007),范围从96%(口齿不清)到86%(嗓音异常)。匿名处理一致地降低了各组感知质量(从83%降至59%,p<0.001),并呈现出针对特定病理的退化模式(单向方差分析:p=0.005)。本地听众对原始语音的评分有非显著性上升趋势(Delta=4%,p=0.199),但这一差异在匿名处理后变得微乎其微(Delta=1%,p=0.724)。未观察到基于性别的显著偏见。感知结果与自动度量指标不相关;可理解性与原始语音的感知质量有关,但与匿名处理后的感知质量无关。这些发现强调需要基于听众和特定疾病的匿名化策略,既保护隐私又保持感知完整性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了自动匿名化技术在病理语音数据共享中的重要作用,并进行了以人为中心的分析。实验邀请了不同语言、临床和技术背景的听众,对来自不同语音障碍人群的匿名化语音进行辨识和评分。研究发现,尽管匿名化技术的错误率在可接受范围内,但它仍然会降低语音的感知质量,并可能影响听众对语音障碍的辨识准确度。因此,需要针对听众和特定障碍的匿名化策略来同时保护隐私和感知完整性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动匿名化技术在病理语音数据共享中至关重要,但其感知影响尚待研究。
- 通过结构化协议邀请多种背景的听众参与评估匿名化病理语音。
- 匿名化技术虽减少了隐私泄露风险,但会降低语音感知质量。
- 不同语音障碍在匿名化后的辨识准确度存在差异。
- 听众对原始语音的评分在匿名化后趋于一致,性别差异在感知中不显著。
- 自动度量与感知结果不相关,而可懂度与原始语音的感知质量有关。
- 需要开发兼顾隐私保护和感知完整性的听众特定匿名化策略。
点此查看论文截图

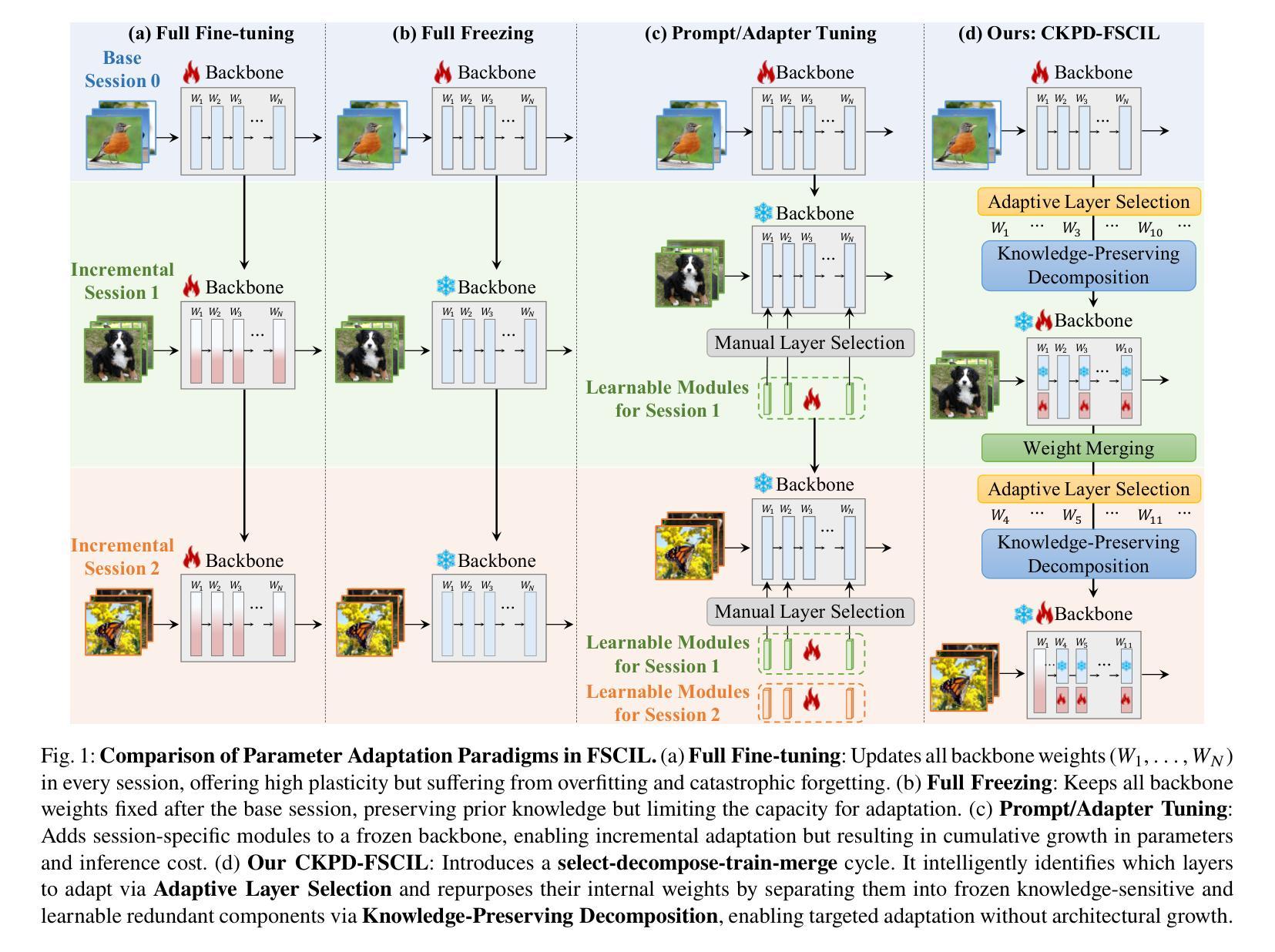
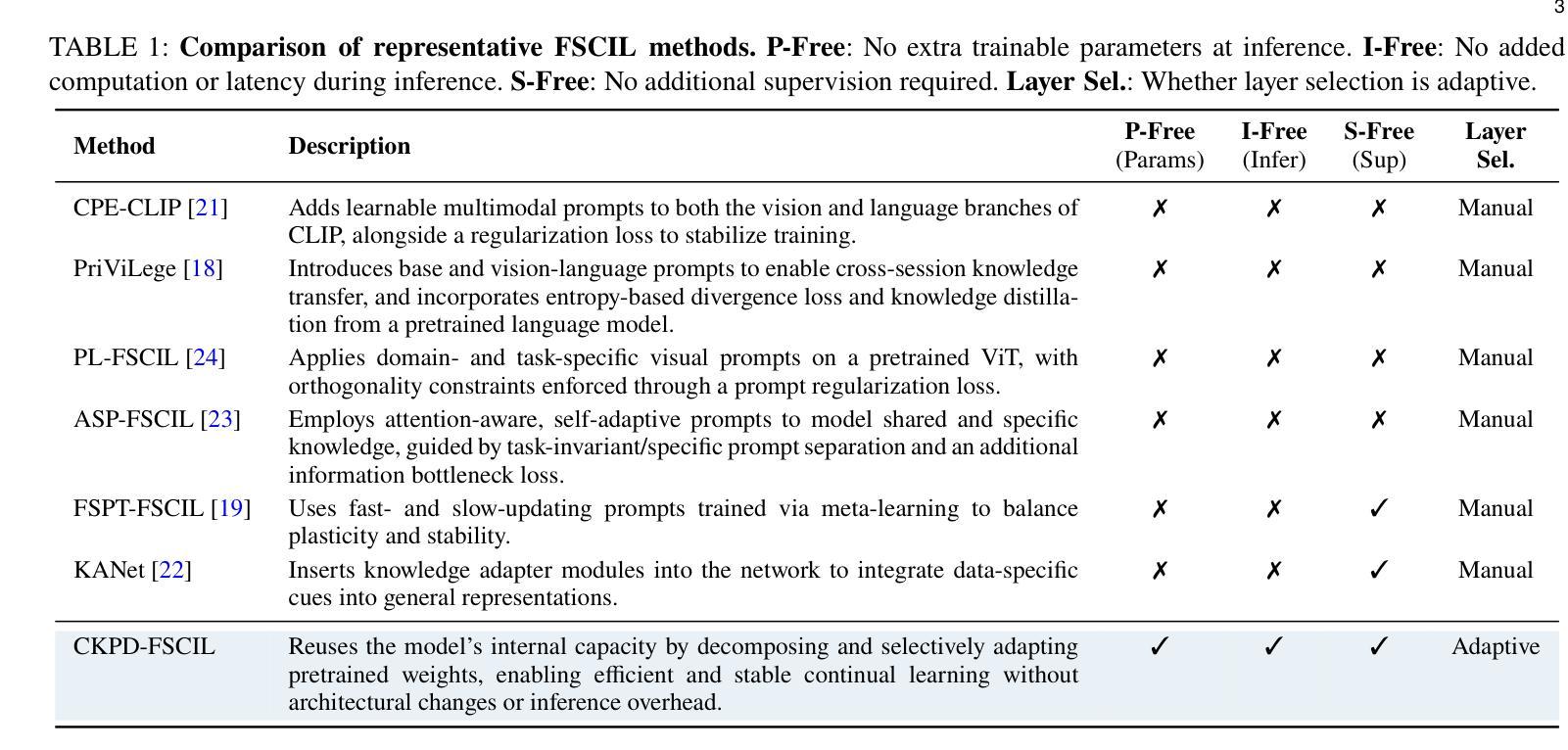
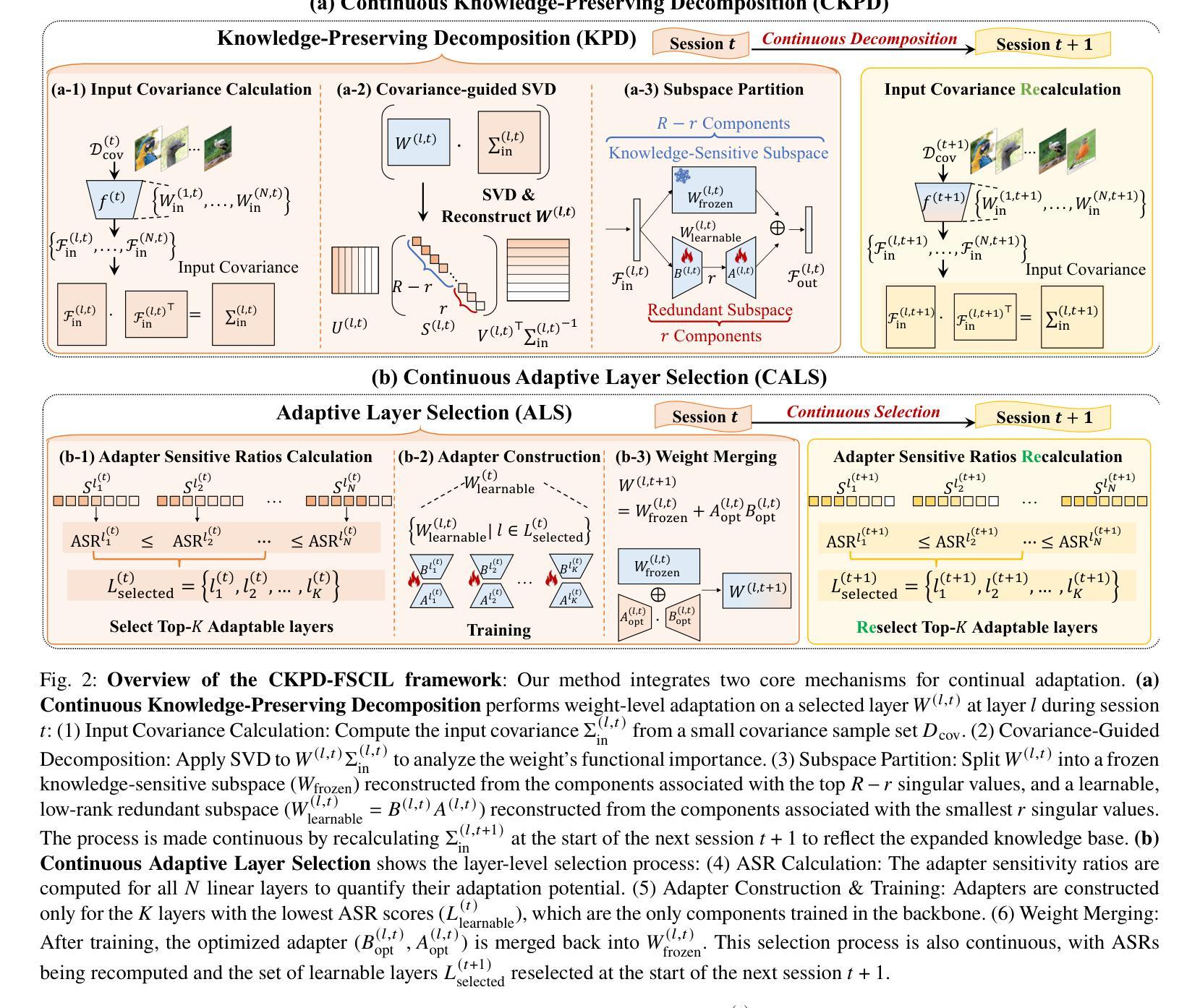
Continuous Knowledge-Preserving Decomposition with Adaptive Layer Selection for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Xiaojie Li, Jianlong Wu, Yue Yu, Liqiang Nie, Min Zhang
Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) faces a critical challenge: balancing the retention of prior knowledge with the acquisition of new classes. Existing methods either freeze the backbone to prevent catastrophic forgetting, sacrificing plasticity, or add new modules, incurring high costs. These approaches treat pretrained models as black boxes, overlooking two key opportunities to exploit their internal capacity: reusing redundant representational space within layers and selectively adapting layers based on their sensitivity to forgetting. We propose CKPD-FSCIL, a unified framework that unlocks the underutilized capacity of pretrained weights, achieving a superior stability-plasticity balance with zero inference overhead. Our design integrates two continuously adapting mechanisms: At the weight level, a Continuous Knowledge-Preserving Decomposition mechanism uses feature covariance to split each weight matrix into a frozen subspace that safeguards prior knowledge and a learnable, redundant subspace for new tasks. At the layer level, a Continuous Adaptive Layer Selection mechanism leverages an Adapter Sensitivity Ratio to automatically select layers with the highest redundant capacity and lowest forgetting risk for adaptation. By targeting only safe, high-potential subspaces and layers, CKPD-FSCIL enables efficient adaptation. After each session, the learned adapters are merged back into the original weights, ensuring zero additional parameters or FLOPs during inference. Extensive experiments on multiple FSCIL benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both adaptability and knowledge retention. The code is available at https://github.com/xiaojieli0903/CKPD-FSCIL.
Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning(FSCIL)面临一个关键挑战:如何在保留先前知识的同时学习新类别。现有方法要么冻结主干以防止灾难性遗忘,牺牲可塑性,要么添加新模块,产生高昂成本。这些方法将预训练模型视为黑箱,忽略了利用其内部容量的两个关键机会:在层内重新使用冗余的表示空间以及根据它们对遗忘的敏感性选择性地适应层。我们提出了CKPD-FSCIL,这是一个解锁预训练权重未充分利用容量的统一框架,以零推理开销实现了卓越的稳定性和可塑性平衡。我们的设计集成了两种连续适应机制:在权重层面,连续知识保留分解机制利用特征协方差将每个权重矩阵分割成一个保护先前知识的冻结子空间和一个用于新任务的可学习冗余子空间。在层层面,连续自适应层选择机制利用适配器敏感度比率自动选择具有最高冗余容量和最低遗忘风险的层进行适应。通过仅针对安全、高潜力的子空间和层进行定位,CKPD-FSCIL能够实现高效适应。在每个会话结束后,学习的适配器都会合并回原始权重,确保推理过程中没有额外的参数或浮点运算。在多个FSCIL基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在不断适应和保留知识方面均优于最新技术。代码可在https://github.com/xiaojieli0903/CKPD-FSCIL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/xiaojieli0903/CKPD-FSCIL
Summary
该文探讨了Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)中的关键问题,即在保留先前知识与学习新类别之间取得平衡。现有方法要么冻结主干网络以防止灾难性遗忘,牺牲可塑性,要么增加新模块,导致成本上升。本文提出CKPD-FSCIL框架,解锁了预训练权重的未充分利用容量,实现了稳定性与可塑性的卓越平衡,且无需推理开销。该框架设计了两种连续适应机制:在权重层面,通过特征协方差将每个权重矩阵分解为冻结子空间(保护先验知识)和可学习冗余子空间(用于新任务);在层面层面,通过适配器敏感度比率自动选择冗余容量最高、遗忘风险最低的图层进行适应。CKPD-FSCIL仅针对安全、潜力高的子空间和图层进行高效适应。实验表明,该方法在适应性和知识保留方面均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot类增量学习(FSCIL)面临保留先前知识与学习新类别的平衡挑战。
- 现有方法存在缺点:冻结主干网络会牺牲可塑性,增加新模块则会导致成本上升。
- CKPD-FSCIL框架利用预训练模型的未充分利用容量,实现稳定性与可塑性的平衡。
- CKPD-FSCIL通过两种连续适应机制进行工作:权重层面的知识保留分解和层面层面的自适应层选择。
- CKPD-FSCIL仅针对安全、潜力高的子空间和图层进行高效适应,提高了效率。
- CKPD-FSCIL实现了零推理开销,且实验表明其在适应性和知识保留方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图