⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-26 更新
LLM-Based Agents for Competitive Landscape Mapping in Drug Asset Due Diligence
Authors:Alisa Vinogradova, Vlad Vinogradov, Dmitrii Radkevich, Ilya Yasny, Dmitry Kobyzev, Ivan Izmailov, Katsiaryna Yanchanka, Andrey Doronichev
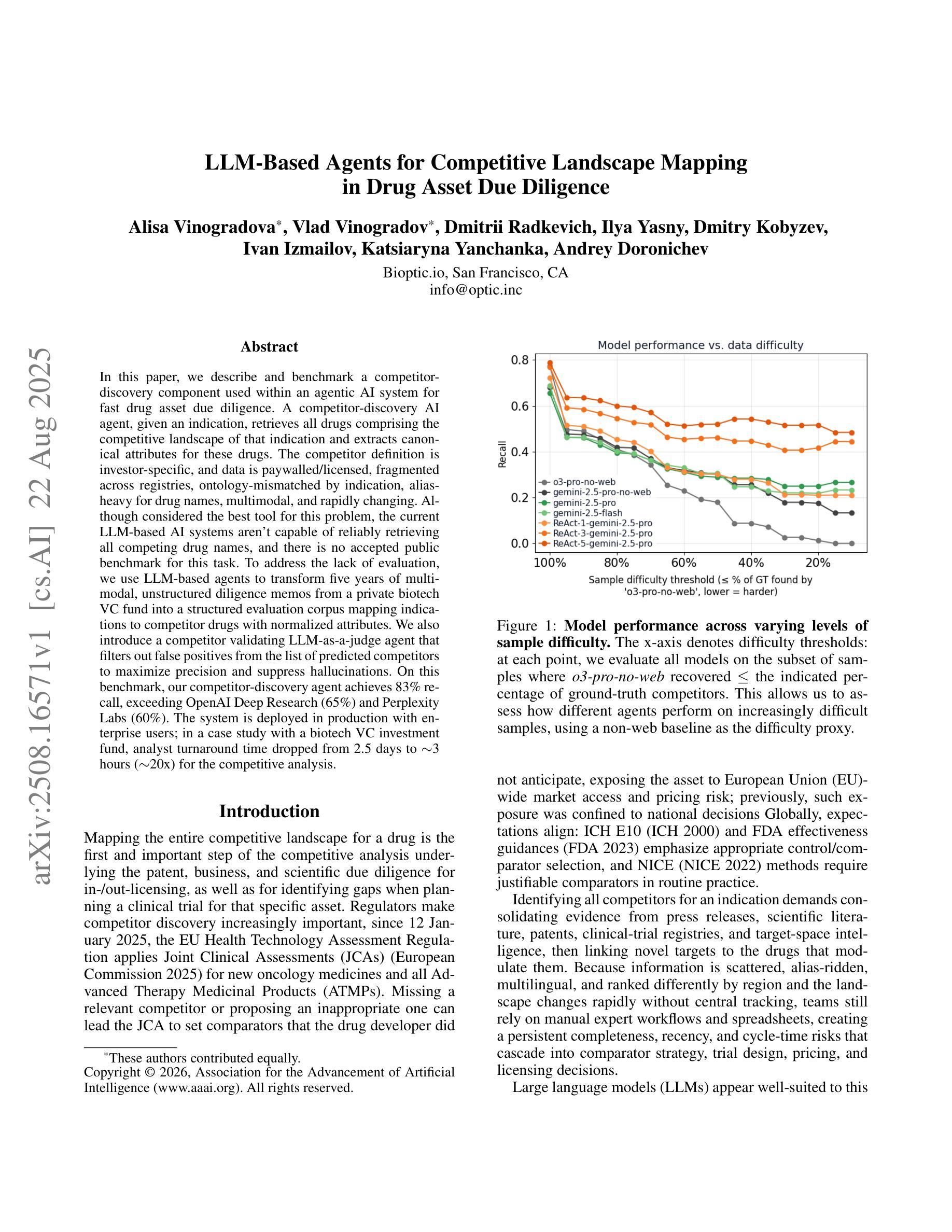
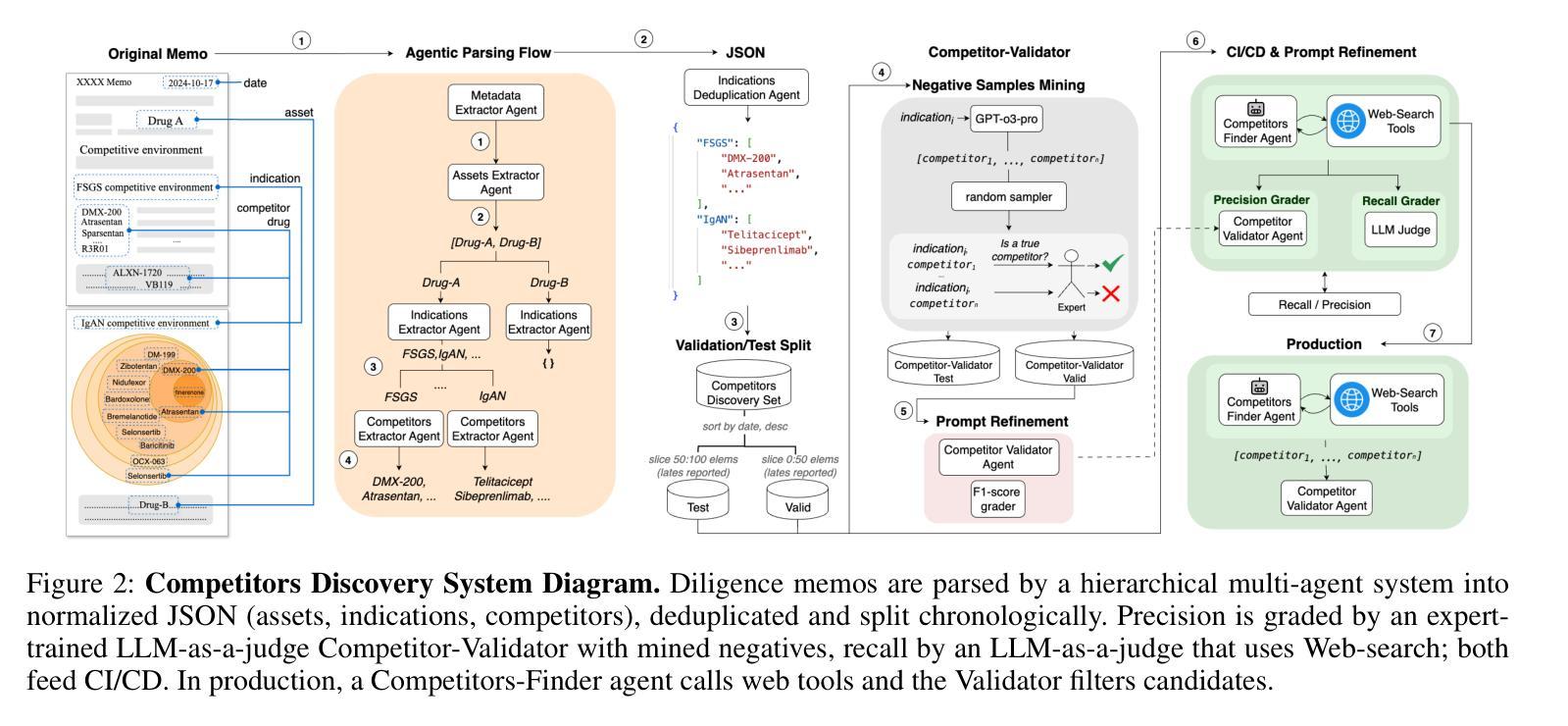
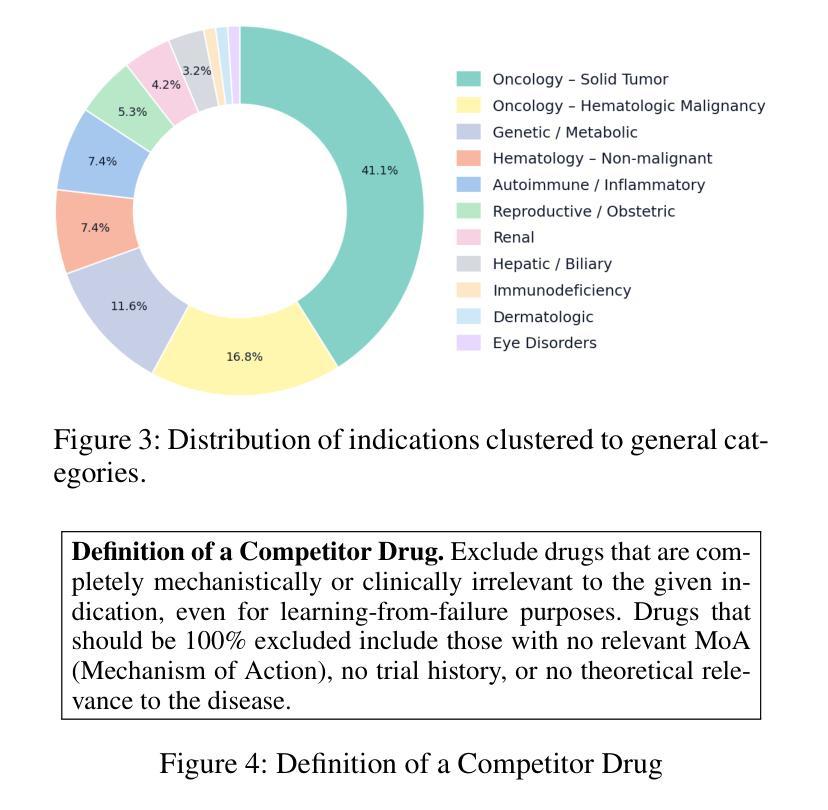
In this paper, we describe and benchmark a competitor-discovery component used within an agentic AI system for fast drug asset due diligence. A competitor-discovery AI agent, given an indication, retrieves all drugs comprising the competitive landscape of that indication and extracts canonical attributes for these drugs. The competitor definition is investor-specific, and data is paywalled/licensed, fragmented across registries, ontology-mismatched by indication, alias-heavy for drug names, multimodal, and rapidly changing. Although considered the best tool for this problem, the current LLM-based AI systems aren’t capable of reliably retrieving all competing drug names, and there is no accepted public benchmark for this task. To address the lack of evaluation, we use LLM-based agents to transform five years of multi-modal, unstructured diligence memos from a private biotech VC fund into a structured evaluation corpus mapping indications to competitor drugs with normalized attributes. We also introduce a competitor validating LLM-as-a-judge agent that filters out false positives from the list of predicted competitors to maximize precision and suppress hallucinations. On this benchmark, our competitor-discovery agent achieves 83% recall, exceeding OpenAI Deep Research (65%) and Perplexity Labs (60%). The system is deployed in production with enterprise users; in a case study with a biotech VC investment fund, analyst turnaround time dropped from 2.5 days to $\sim$3 hours ($\sim$20x) for the competitive analysis.
本文描述并评估了一个用于快速尽职调查药物资产的智能AI系统中的竞争对手发现组件。给定一个指标,竞争对手发现AI代理会检索构成该指标竞争态势的所有药物,并提取这些药物的规范属性。竞争对手的定义是投资者特定的,并且数据是付费的/许可的,跨注册机构分散,按指示存在本体不匹配,药物名称别名繁多,多模式且快速变化。尽管被认为是解决这个问题的最佳工具,但当前的基于大型语言模型(LLM)的AI系统无法可靠地检索所有竞争药物名称,并且没有针对此任务的公认公共基准测试。为了解决缺乏评估的问题,我们使用基于LLM的代理将一家私人生物技术VC基金的五年多模式非结构化尽职调查备忘录转化为结构化评估语料库,该语料库将指标映射到具有标准化属性的竞争对手药物。我们还引入了一个竞争对手验证LLM作为法官代理,从预测的竞争对手名单中筛选出假阳性结果,以最大限度地提高精度并抑制幻觉。在此基准测试中,我们的竞争对手发现代理实现了83%的召回率,超过了OpenAI深度研究(65%)和困惑实验室(60%)。该系统已在企业用户中部署生产环境;在与生物技术VC投资基金的案例研究中,分析师周转时间从2.5天缩短到约3小时(约20倍)用于竞争分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文描述并评估了一个用于快速药物资产尽职调查的竞争对手发现组件。该组件利用LLM(大型语言模型)为基础的人工智能代理,根据特定指标检索所有竞争对手药物并提取其规范属性。尽管是目前解决此问题的最佳工具,但现有LLM系统无法可靠地检索所有竞争对手药物名称,且缺乏公认的公共基准测试。为解决此问题,研究团队使用LLM代理将五年的多模式、非结构化尽职调查备忘录转化为结构化评估语料库,并引入竞争对手验证代理以过滤出预测中的假阳性结果,提高精度并抑制虚构结果。在基准测试中,竞争对手发现代理的召回率达到83%,超过了OpenAI Deep Research(65%)和Perplexity Labs(60%)。该系统已在企业用户中部署生产环境,并在与生物技术风险投资基金进行案例研究时,分析师的周转时间从2.5天缩短到约3小时(约减少20倍)。
Key Takeaways:
- 竞争对手发现组件被用于快速药物资产尽职调查。
- LLM为基础的人工智能代理用于检索竞争对手药物并提取其属性。
- 当前LLM系统在检索所有竞争对手药物名称方面存在不足。
- 研究团队利用LLM代理创建了一个结构化评估语料库以评估竞争对手发现性能。
- 引入竞争对手验证代理以提高精度并抑制虚构结果。
- 竞争对手发现代理的召回率达到83%,优于其他系统。
点此查看论文截图
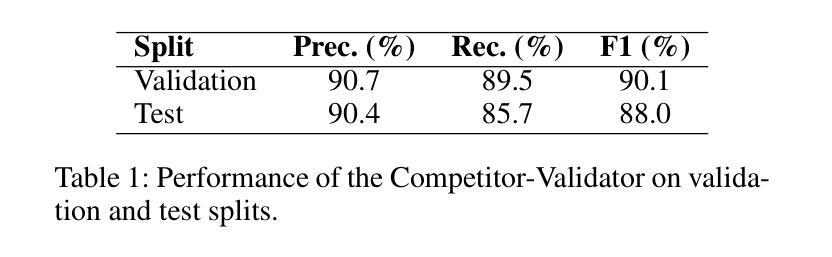

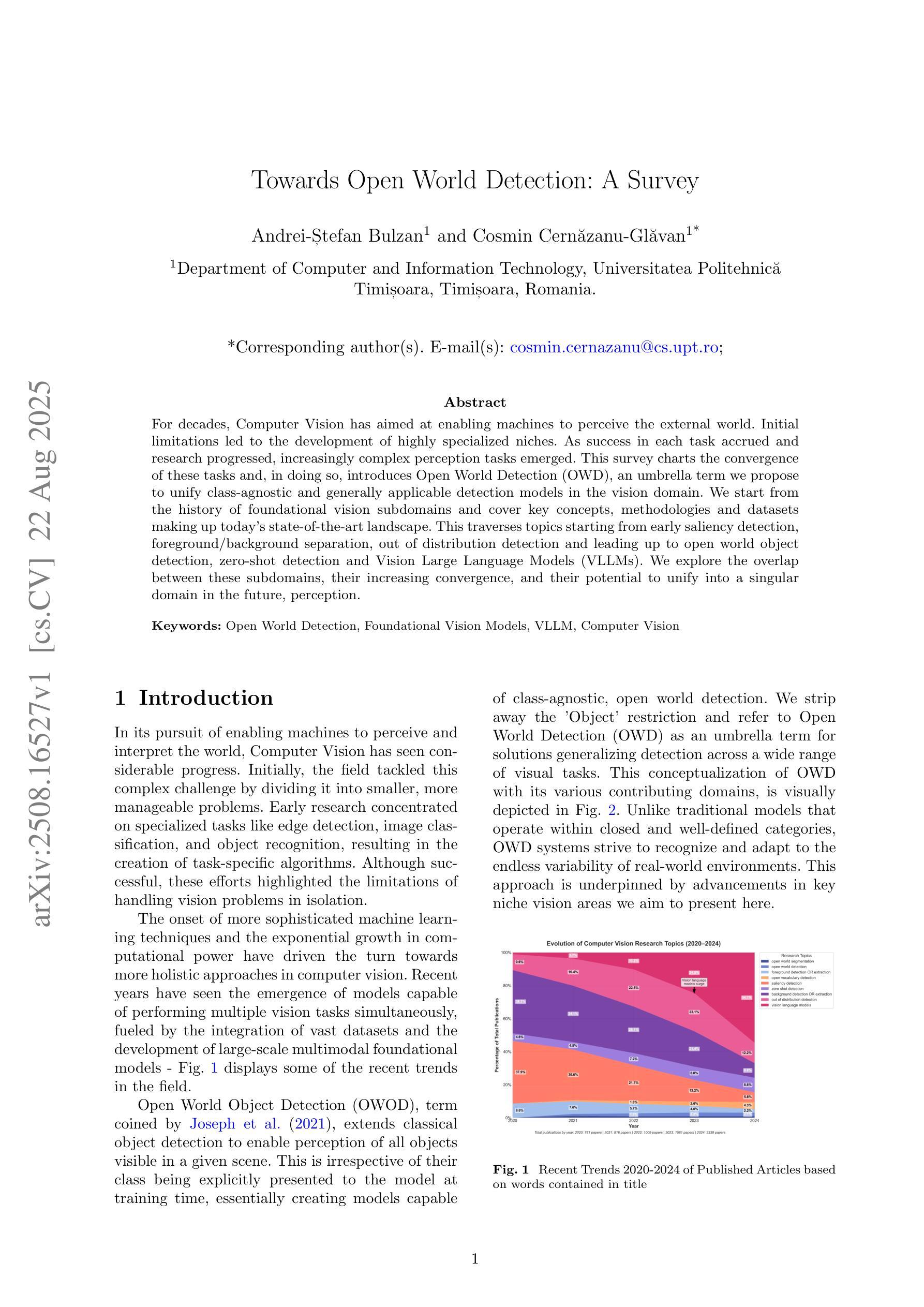
Towards Open World Detection: A Survey
Authors:Andrei-Stefan Bulzan, Cosmin Cernazanu-Glavan
For decades, Computer Vision has aimed at enabling machines to perceive the external world. Initial limitations led to the development of highly specialized niches. As success in each task accrued and research progressed, increasingly complex perception tasks emerged. This survey charts the convergence of these tasks and, in doing so, introduces Open World Detection (OWD), an umbrella term we propose to unify class-agnostic and generally applicable detection models in the vision domain. We start from the history of foundational vision subdomains and cover key concepts, methodologies and datasets making up today’s state-of-the-art landscape. This traverses topics starting from early saliency detection, foreground/background separation, out of distribution detection and leading up to open world object detection, zero-shot detection and Vision Large Language Models (VLLMs). We explore the overlap between these subdomains, their increasing convergence, and their potential to unify into a singular domain in the future, perception.
数十年来,计算机视觉的目标是使机器能够感知外部世界。最初的局限性导致了高度专业化的细分领域的开发。随着每个任务的成功累积和研究进展,出现了越来越复杂的感知任务。这篇综述描述了这些任务的融合,并在此过程中引入了开放世界检测(OWD),这是我们提出的一个总称,旨在统一视觉领域中的类无关和普遍适用的检测模型。我们从基础视觉子域的历史开始,涵盖了构成当今最新技术景观的关键概念、方法和数据集。这涵盖了从早期的显著性检测、前景/背景分离、离群检测,一直到开放世界目标检测、零样本检测和视觉大语言模型(VLLM)等主题。我们探索了这些子域之间的重叠,它们日益融合以及在将来可能统一为一个单独的感知领域的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 30 pages
Summary:
数十年以来,计算机视觉旨在让机器感知外部世界。随着研究任务的逐渐成功和研究进展的不断深化,出现了越来越复杂的感知任务。本文概述了这些任务的融合,并介绍了我们提出的开放世界检测(OWD)这一通用术语,以统一视觉领域中的类无关和普遍适用的检测模型。本文回顾了基础视觉子域的历史,涵盖了构成当今最新技术景观的关键概念、方法和数据集。涉及从早期的显著性检测、前景/背景分离、离群分布检测,到开放世界目标检测、零射击检测和视觉大型语言模型(VLLMs)等话题。本文探讨了这些子域之间的重叠性、其日益融合的趋势以及将来统一为单一感知域的可能性。
Key Takeaways:
- 计算机视觉旨在让机器感知外部世界,经历了从高度专业化的领域到越来越复杂的感知任务的转变。
- 开放世界检测(OWD)是一个新提出的通用术语,用于统一视觉领域中的类无关和普遍适用的检测模型。
- 文章回顾了计算机视觉的基础子域历史,包括显著性检测、前景/背景分离等早期话题。
- 文章介绍了当今最新的技术和数据集,这些技术和数据集构成了当前的计算机视觉技术景观。
- 计算机视觉的不同子域之间存在重叠,且这些子域正变得越来越融合。
- 文章探讨了这些子域未来的发展趋势,包括它们可能统一为一个单一的感知域。
点此查看论文截图
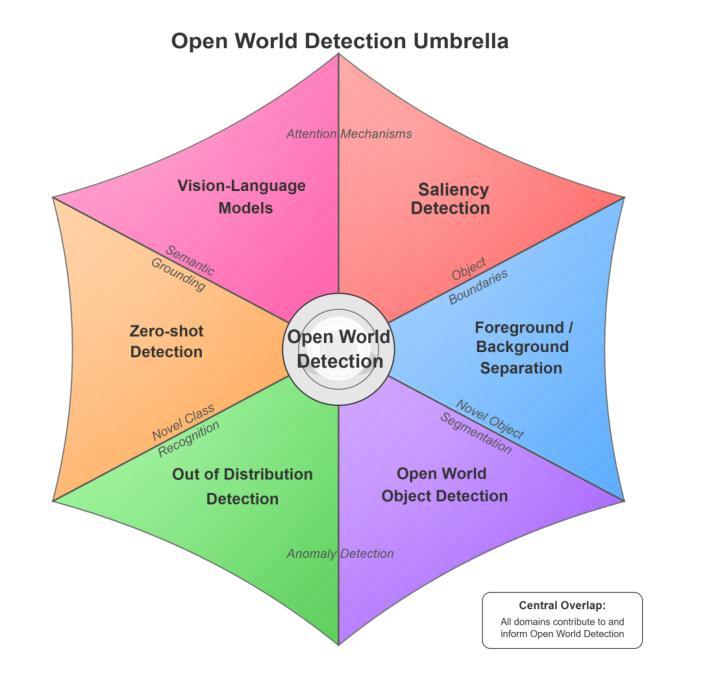



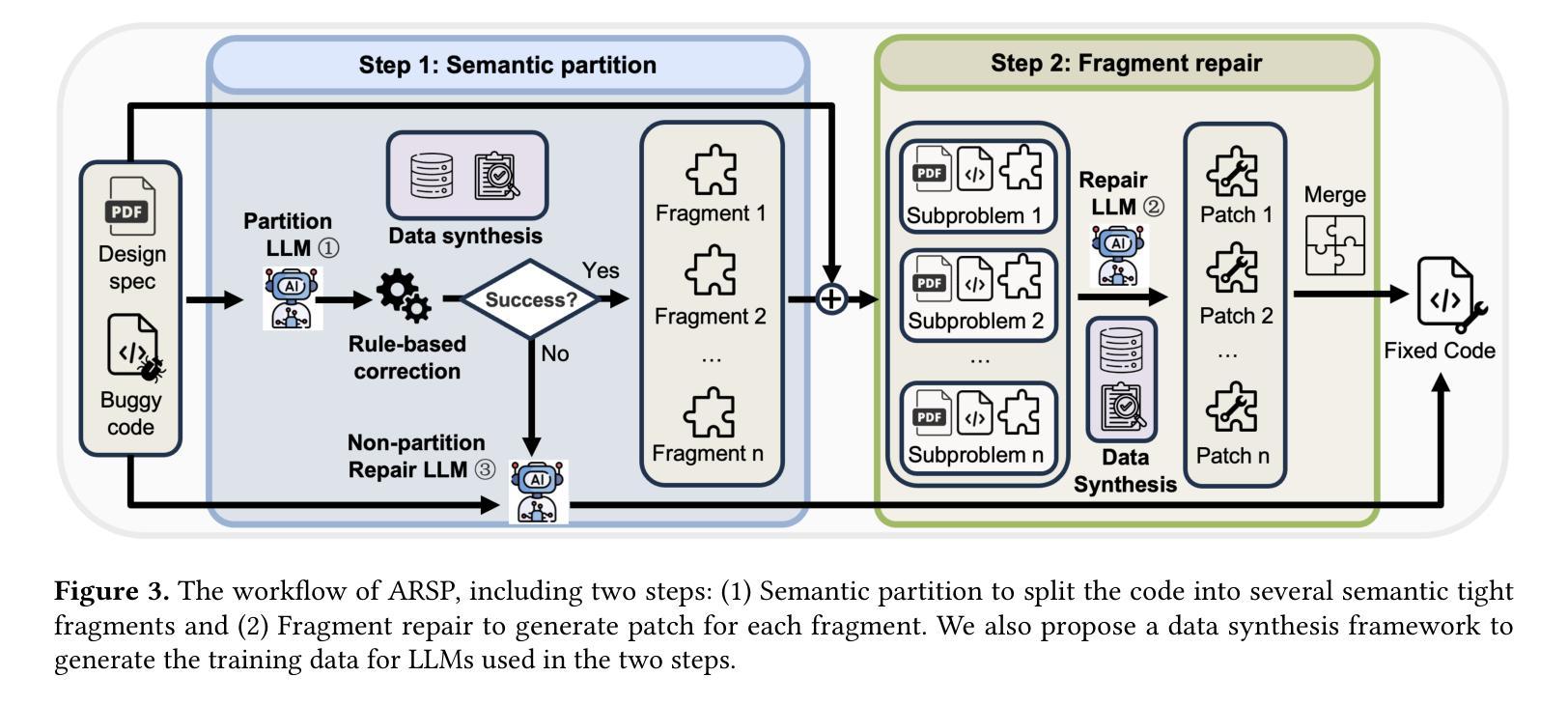
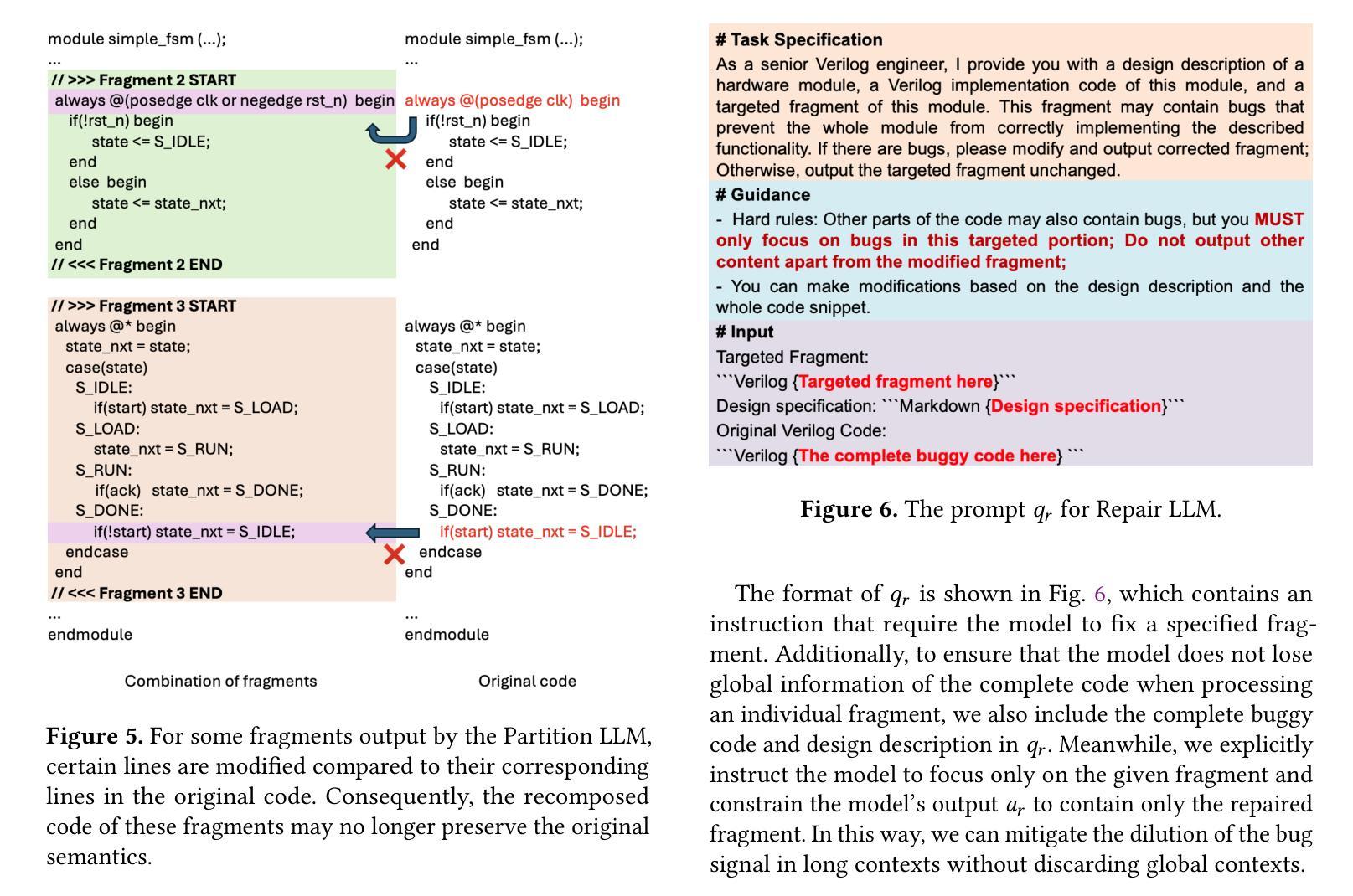
ARSP: Automated Repair of Verilog Designs via Semantic Partitioning
Authors:Bingkun Yao, Ning Wang, Xiangfeng Liu, Yuxin Du, Yuchen Hu, Hong Gao, Zhe Jiang, Nan Guan
Debugging functional Verilog bugs consumes a significant portion of front-end design time. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated great potential in mitigating this effort, existing LLM-based automated debugging methods underperform on industrial-scale modules. A major reason for this is bug signal dilution in long contexts, where a few bug-relevant tokens are overwhelmed by hundreds of unrelated lines, diffusing the model’s attention. To address this issue, we introduce ARSP, a two-stage system that mitigates dilution via semantics-guided fragmentation. A Partition LLM splits a module into semantically tight fragments; a Repair LLM patches each fragment; edits are merged without altering unrelated logic. A synthetic data framework generates fragment-level training pairs spanning bug types, design styles, and scales to supervise both models. Experiments show that ARSP achieves 77.92% pass@1 and 83.88% pass@5, outperforming mainstream commercial LLMs including Claude-3.7 and SOTA automated Verilog debugging tools Strider and MEIC. Also, semantic partitioning improves pass@1 by 11.6% and pass@5 by 10.2% over whole-module debugging, validating the effectiveness of fragment-level scope reduction in LLM-based Verilog debugging.
调试功能Verilog错误会消耗前端设计的大量时间。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在缓解这一努力方面显示出巨大潜力,但基于LLM的现有自动化调试方法在工业规模模块上的表现不佳。主要原因是长上下文中的错误信号稀释,其中几个与错误相关的令牌被数百行无关代码淹没,分散了模型的注意力。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了ARSP,这是一个两阶段的系统,通过语义引导的碎片化来缓解稀释问题。一个分区LLM将模块分割成语义紧密的片段;一个修复LLM对每个片段进行修复;编辑在不改变无关逻辑的情况下合并。合成数据框架生成涵盖错误类型、设计风格和规模的片段级训练对,以监督两个模型。实验表明,ARSP达到了77.92%的pass@1和83.88%的pass@5,优于主流商业LLM(包括Claude-3.7)以及最先进的Verilog自动化调试工具Strider和MEIC。此外,语义分区在pass@1上提高了11.6%,在pass@5上提高了10.2%,优于全模块调试,验证了片段级范围缩减在LLM基于Verilog调试中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ARSP是一个两阶段系统,通过语义引导分段缓解调试信息稀释问题,提高LLM在Verilog自动化调试中的性能。系统包括分割LLM和修复LLM,可针对模块进行语义紧密分段,并对每段进行修复。合成数据框架生成片段级训练对,涵盖错误类型、设计风格和规模,以监督两个模型。实验表明,ARSP在Verilog自动化调试中表现出优异性能,优于主流商业LLM和最新自动化Verilog调试工具。
Key Takeaways
- ARSP是一个针对Verilog自动化调试的两阶段系统,旨在解决大型语言模型在调试工业规模模块时的性能不足。
- ARSP通过语义引导分段(semantic-guided fragmentation)来缓解调试信息稀释问题。
- ARSP包括分割LLM和修复LLM,分别对模块进行语义紧密分段并修复每段。
- 合成数据框架用于生成涵盖各种错误类型、设计风格和规模的片段级训练对,以监督LLM。
- 实验结果表明,ARSP在Verilog自动化调试方面表现出色,优于主流商业LLM以及Strider和MEIC等最新自动化Verilog调试工具。
- 语义分段显著提高了ARSP的调试性能,验证了片段级别范围缩减在LLM基于Verilog调试中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图



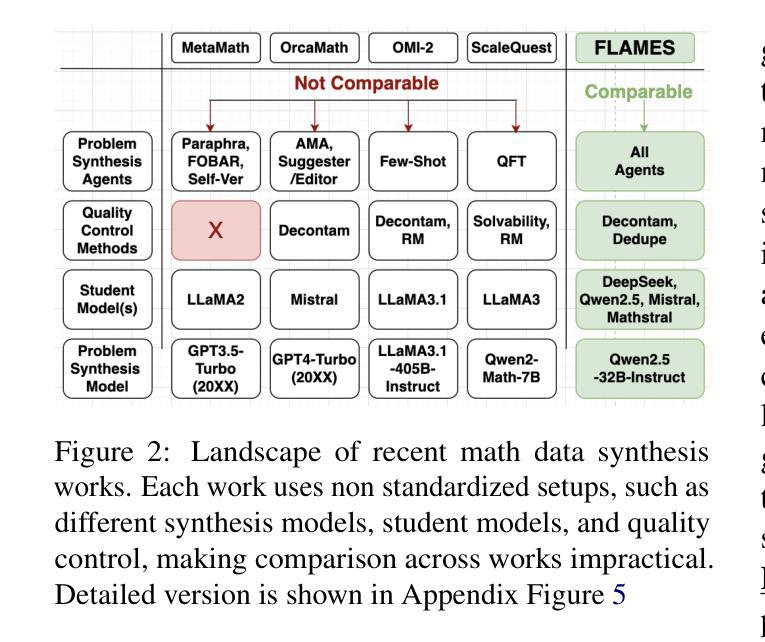
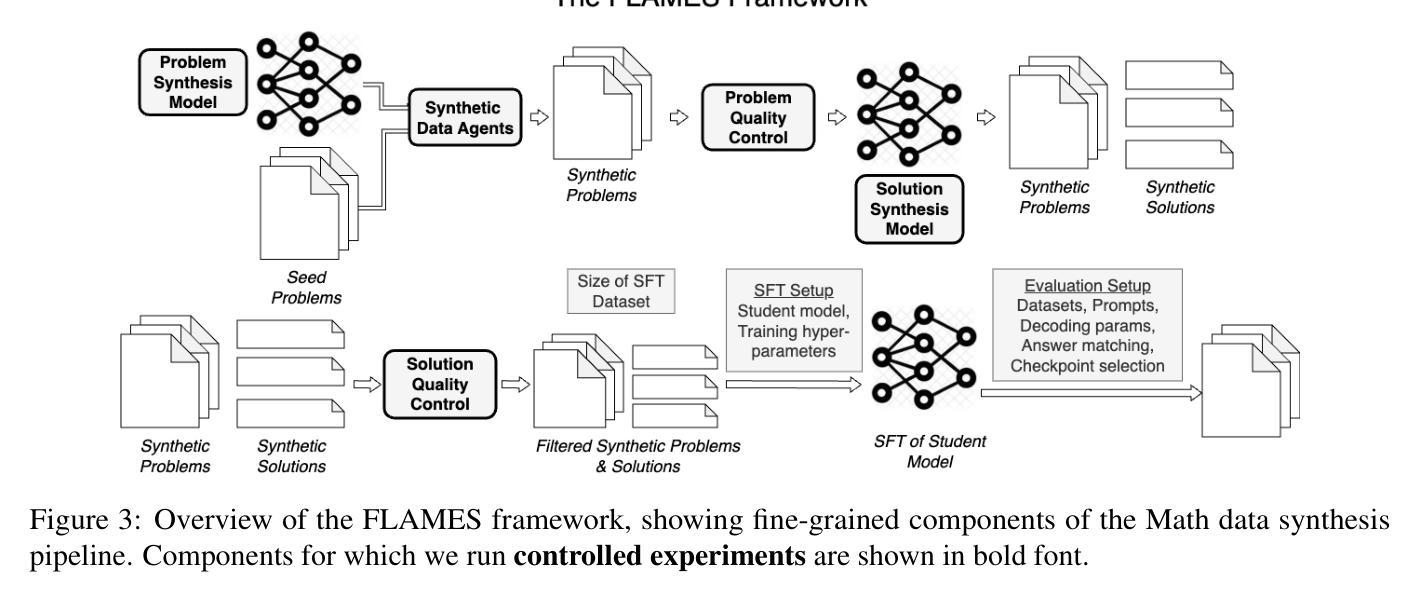
FLAMES: Improving LLM Math Reasoning via a Fine-Grained Analysis of the Data Synthesis Pipeline
Authors:Parker Seegmiller, Kartik Mehta, Soumya Saha, Chenyang Tao, Shereen Oraby, Arpit Gupta, Tagyoung Chung, Mohit Bansal, Nanyun Peng
Recent works improving LLM math reasoning with synthetic data have used unique setups, making comparison of data synthesis strategies impractical. This leaves many unanswered questions about the roles of different factors in the synthetic data pipeline, such as the impact of filtering low-quality problems. To address this gap, we introduce FLAMES, a Framework for LLM Assessment of Math rEasoning Data Synthesis, and perform a systematic study of 10 existing data synthesis strategies and multiple other factors impacting the performance of synthetic math reasoning data. Our FLAMES experiments provide several valuable insights about the optimal balance of difficulty and diversity of synthetic data. First, data agents designed to increase problem complexity lead to best improvements on most math metrics. Second, with a fixed data generation budget, keeping higher problem coverage is more important than keeping only problems with reliable solutions. Third, GSM8K- and MATH-based synthetic data can lead to improvements on competition-level benchmarks, showcasing easy-to-hard generalization. Leveraging insights from our FLAMES experiments, we design two novel data synthesis strategies for improving out-of-domain generalization and robustness. Further, we develop the FLAMES dataset, an effective blend of our novel and existing data synthesis strategies, outperforming public datasets on OlympiadBench (+15.7), CollegeMath (+4.5), GSMPlus (+6.5), and MATH (+3.1). Fine-tuning Qwen2.5-Math-7B on the FLAMES dataset achieves 81.4% on MATH, surpassing larger Llama3 405B, GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
近期使用合成数据改进LLM数学推理的研究采用了独特的设置,这使得数据合成策略的对比变得不切实际。这留下了许多关于合成数据管道中不同因素作用的问题悬而未决,例如过滤低质量问题的影响。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了FLAMES,一个用于LLM数学推理数据合成的评估框架,并对现有的10种数据合成策略和多种影响合成数学推理数据性能的其他因素进行了系统研究。我们的FLAMES实验提供了关于合成数据的难度和多样性之间最佳平衡的宝贵见解。首先,旨在增加问题复杂性的数据代理在大多数数学指标上取得了最佳改进效果。其次,在固定的数据生成预算下,保持更高的问题覆盖面比只保留具有可靠解决方案的问题更重要。第三,基于GSM8K和MATH的合数据可以在竞赛水平的基准测试上取得改进,展示了从易到难的泛化能力。利用我们从FLAMES实验中获得的见解,我们设计了两种新型数据合成策略,以提高跨域泛化和稳健性。此外,我们开发了FLAMES数据集,它是我们新颖和现有数据合成策略的有效融合,在OlympiadBench(高出+15.7)、CollegeMath(+4.5)、GSMPlus(+6.5)和MATH(+3.1)等公共数据集上表现出色。对FLAMES数据集进行微调后,Qwen2.5-Math-7B在MATH上达到了81.4%,超过了更大的Llama3 405B、GPT-4o和Claude 3.5 Sonnet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at EMNLP 2025
摘要
本文介绍了FLAMES框架,用于评估数学推理数据合成策略。作者对10种现有的数据合成策略和多种影响合成数学推理数据性能的因素进行了系统研究,提供了关于合成数据难度和多样性平衡方面的宝贵见解。研究结果表明,设计增加问题复杂性的数据代理可在大多数数学指标上获得最佳改进;在固定数据生成预算下,保持更高的问题覆盖面比保持只有可靠解决方案的问题更重要;基于GSM8K和MATH的合成数据可在竞赛级别的基准测试上实现改进,展示从易到难的泛化能力。
关键见解
- 设计增加问题复杂性的数据代理在提升数学指标上表现最佳。
- 在有限的数据生成预算下,广泛覆盖不同问题比只关注有可靠解决方案的问题更重要。
- GSM8K和MATH基础上的合成数据在竞赛级基准测试上展现出良好的改进效果,证明了从简单到复杂问题的泛化能力。
- 利用FLAMES实验中的见解,提出了两种新的数据合成策略,旨在提高跨域泛化和鲁棒性。
- 开发的FLAMES数据集融合了新颖和现有的数据合成策略,在多个基准测试上表现优异。
- 对QWEN2.5-MATH-7B模型进行微调,使用FLAMES数据集在MATH任务上达到了81.4%的准确率,超过了其他大型模型如Llama3 405B、GPT-4o和Claude 3.5 Sonnet。
- FLAMES框架为评估和改进LLM数学推理数据合成策略提供了一个重要工具。
点此查看论文截图

Beyond Interpretability: Exploring the Comprehensibility of Adaptive Video Streaming through Large Language Models
Authors:Lianchen Jia, Chaoyang Li, Ziqi Yuan, Jiahui Chen, Tianchi Huang, Jiangchuan Liu, Lifeng Sun
Over the past decade, adaptive video streaming technology has witnessed significant advancements, particularly driven by the rapid evolution of deep learning techniques. However, the black-box nature of deep learning algorithms presents challenges for developers in understanding decision-making processes and optimizing for specific application scenarios. Although existing research has enhanced algorithm interpretability through decision tree conversion, interpretability does not directly equate to developers’ subjective comprehensibility. To address this challenge, we introduce \texttt{ComTree}, the first bitrate adaptation algorithm generation framework that considers comprehensibility. The framework initially generates the complete set of decision trees that meet performance requirements, then leverages large language models to evaluate these trees for developer comprehensibility, ultimately selecting solutions that best facilitate human understanding and enhancement. Experimental results demonstrate that \texttt{ComTree} significantly improves comprehensibility while maintaining competitive performance, showing potential for further advancement. The source code is available at https://github.com/thu-media/ComTree.
过去十年来,自适应视频流媒体技术取得了重大进展,尤其是受到深度学习技术迅速发展的推动。然而,深度学习算法的黑盒性质给开发者带来了理解决策过程和针对特定应用场景进行优化方面的挑战。尽管现有研究已通过决策树转换提高了算法的可解释性,但可解释性并不直接等同于开发者的主观可理解性。为了解决这一挑战,我们引入了
ComTree',这是第一个考虑可理解性的比特率自适应算法生成框架。该框架首先生成满足性能要求的完整决策树集合,然后利用大型语言模型对开发者的可理解性对这些树进行评估,最终选择最有利于人类理解和优化的解决方案。实验结果表明,ComTree’在保持竞争力的情况下显著提高了可理解性,显示出进一步发展的潜力。源代码可在https://github.com/thu-media/ComTree获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM Multimedia2025
Summary
近年来,自适应视频流媒体技术受到深度学习的推动取得了显著进步。然而,深度学习算法的黑盒性质使得开发者难以了解决策过程并优化特定应用场景。为解决此问题,我们推出了一款考虑可理解性的比特率自适应算法生成框架——ComTree。它首先生成满足性能要求的完整决策树集,再利用大型语言模型评估这些树的可理解性程度,最终选择最能促进人类理解和优化的解决方案。实验结果显示,ComTree在保持竞争力的同时显著提高了可理解性,展现出进一步发展的潜力。源码可访问:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 自适应视频流媒体技术受益于深度学习技术的快速发展。
- 深度学习算法的黑盒性质导致开发者在理解和优化决策过程方面面临挑战。
- ComTree是首个考虑可理解性的比特率自适应算法生成框架。
- ComTree通过生成决策树集并利用大型语言模型评估其可理解性来解决上述问题。
- 实验结果证明ComTree在保持性能竞争力的同时,显著提高了算法的可理解性。
- ComTree具有进一步发展的潜力。
点此查看论文截图



Boardwalk: Towards a Framework for Creating Board Games with LLMs
Authors:Álvaro Guglielmin Becker, Gabriel Bauer de Oliveira, Lana Bertoldo Rossato, Anderson Rocha Tavares
Implementing board games in code can be a time-consuming task. However, Large Language Models (LLMs) have been proven effective at generating code for domain-specific tasks with simple contextual information. We aim to investigate whether LLMs can implement digital versions of board games from rules described in natural language. This would be a step towards an LLM-assisted framework for quick board game code generation. We expect to determine the main challenges for LLMs to implement the board games, and how different approaches and models compare to one another. We task three state-of-the-art LLMs (Claude, DeepSeek and ChatGPT) with coding a selection of 12 popular and obscure games in free-form and within Boardwalk, our proposed General Game Playing API. We anonymize the games and components to avoid evoking pre-trained LLM knowledge. The implementations are tested for playability and rule compliance. We evaluate success rate and common errors across LLMs and game popularity. Our approach proves viable, with the best performing model, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, yielding 55.6% of games without any errors. While compliance with the API increases error frequency, the severity of errors is more significantly dependent on the LLM. We outline future steps for creating a framework to integrate this process, making the elaboration of board games more accessible.
将板游戏以代码形式实现可能会是一项耗时的任务。然而,大型语言模型(LLM)在利用简单的上下文信息为特定领域任务生成代码方面已被证明是有效的。我们的目标是研究LLM是否能从自然语言描述的游戏规则实现数字化板游戏版本。这将朝着建立一个由LLM辅助的快速板游戏代码生成框架迈出一步。我们期望确定LLM实现板游戏的主要挑战,以及不同的方法和模型之间的比较。我们使用三款最新的大型语言模型(Claude、DeepSeek和ChatGPT)为一些流行和不太为人知的游戏编写代码,包括在我们提出的通用游戏接口Boardwalk中以自由形式的游戏。我们将游戏和组件匿名化,以避免激发预训练LLM的知识。实现的代码会进行可玩性和规则符合度测试。我们评估了不同LLM、游戏流行度和成功率的普遍错误。我们的方法是可行的,表现最好的模型Claude 3.7 Sonnet在无错误的情况下实现了55.6%的游戏。虽然符合API会增加错误频率,但错误的严重性更取决于LLM。我们概述了创建整合此过程的框架的未来步骤,使板游戏的制作更加容易上手。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SBGames 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)可用于生成实现棋盘游戏的代码,这大大减少了编程时间。本研究旨在探讨LLM是否能够根据自然语言描述的规则实现棋盘游戏的数字化版本。通过对三款尖端LLM(Claude、DeepSeek和ChatGPT)的测试,发现其在通用棋盘游戏API Boardwalk中的表现具有可行性,其中最好的模型Claude 3.7 Sonnet的错误率为零。虽然API合规性会增加错误频率,但错误的严重性更多地取决于LLM本身。本研究为未来创建集成此过程的框架奠定了基础,使棋盘游戏的制作更加便捷。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)能有效生成实现棋盘游戏的代码,提高编程效率。
- LLM可以根据自然语言描述的规则实现棋盘游戏的数字化。
- 三款尖端LLM(Claude、DeepSeek和ChatGPT)在棋盘游戏API Boardwalk中的表现具有可行性。
- Claude 3.7 Sonnet在测试中的表现最佳,错误率为零。
- API合规性会增加错误频率,但错误的严重性更多取决于LLM本身。
- 本研究为创建集成此过程的框架奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图

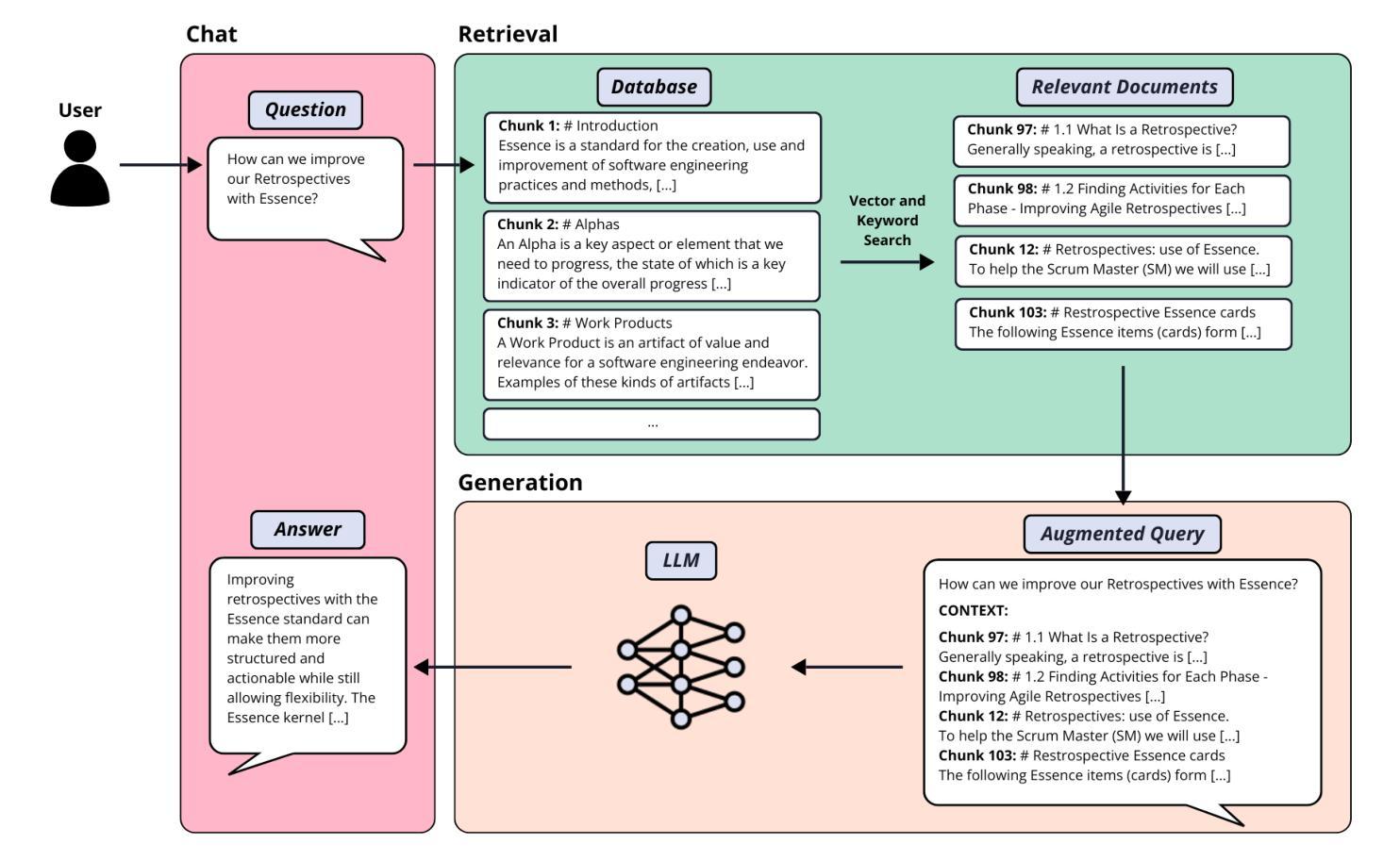
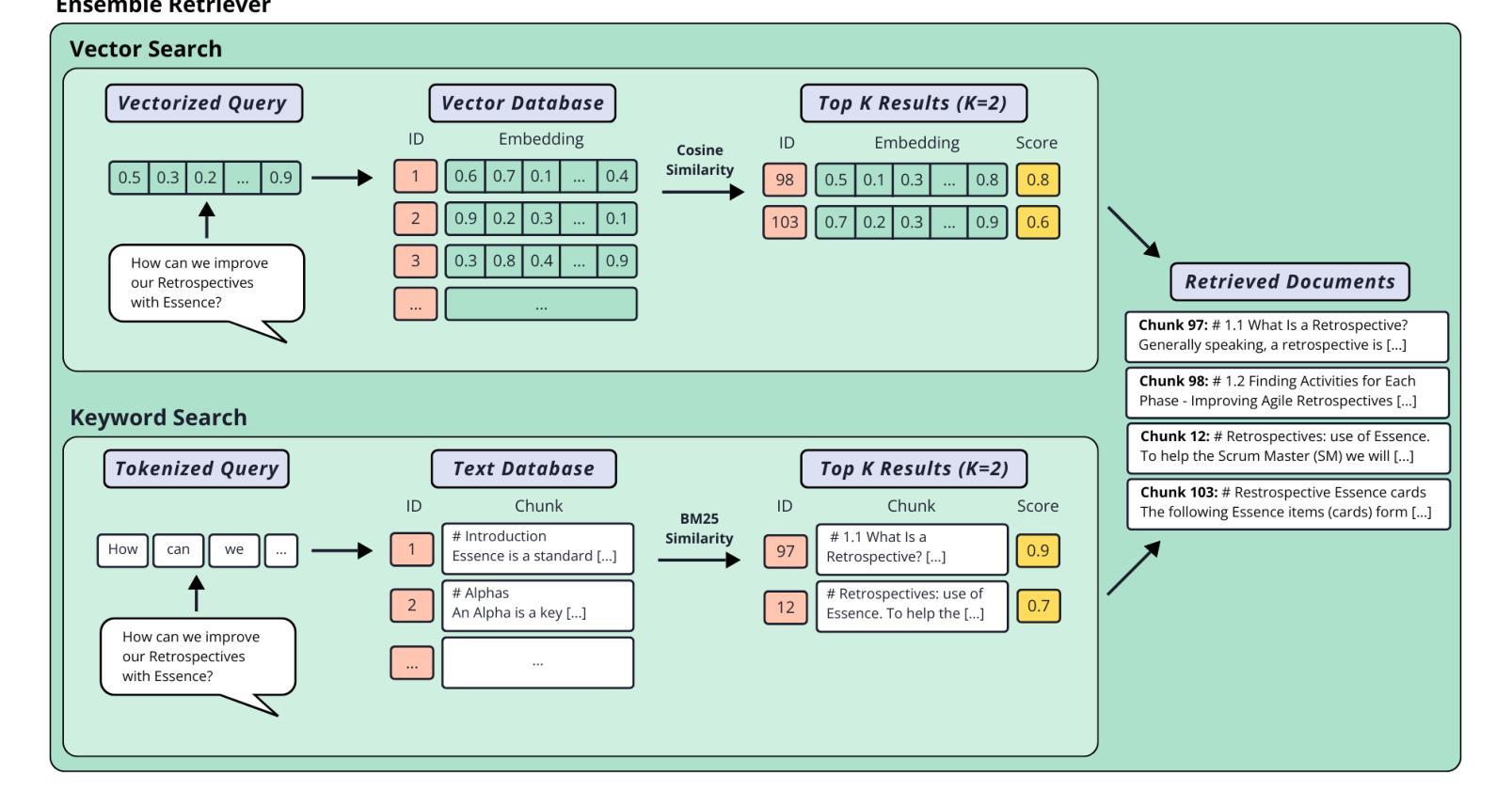
Using LLMs and Essence to Support Software Practice Adoption
Authors:Sonia Nicoletti, Paolo Ciancarini
Recent advancements in natural language processing (NLP) have enabled the development of automated tools that support various domains, including software engineering. However, while NLP and artificial intelligence (AI) research has extensively focused on tasks such as code generation, less attention has been given to automating support for the adoption of best practices, the evolution of ways of working, and the monitoring of process health. This study addresses this gap by exploring the integration of Essence, a standard and thinking framework for managing software engineering practices, with large language models (LLMs). To this end, a specialised chatbot was developed to assist students and professionals in understanding and applying Essence. The chatbot employs a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system to retrieve relevant contextual information from a curated knowledge base. Four different LLMs were used to create multiple chatbot configurations, each evaluated both as a base model and augmented with the RAG system. The system performance was evaluated through both the relevance of retrieved context and the quality of generated responses. Comparative analysis against the general-purpose LLMs demonstrated that the proposed system consistently outperforms its baseline counterpart in domain-specific tasks. By facilitating access to structured software engineering knowledge, this work contributes to bridging the gap between theoretical frameworks and practical application, potentially improving process management and the adoption of software development practices. While further validation through user studies is required, these findings highlight the potential of LLM-based automation to enhance learning and decision-making in software engineering.
最近自然语言处理(NLP)的进展为支持包括软件工程在内的各个领域自动化工具的开发提供了可能。然而,尽管NLP和人工智能(AI)的研究在代码生成等方面进行了广泛的研究,但对于自动化支持采用最佳实践、工作方式演变以及过程健康监控的关注较少。本研究通过探索管理软件工程实践的通用框架标准“Essence”与大型语言模型(LLM)的集成来解决这一差距。为此,开发了一种专门聊天机器人,旨在帮助学生和专业人士理解和应用Essence。聊天机器人采用增强生成(RAG)系统从知识库中检索相关的上下文信息。使用了四种不同的LLM创建了多个聊天机器人配置,每种配置都被评估为基础模型和与RAG系统结合的增强模型。系统性能通过检索上下文的关联性和生成响应的质量来评估。与一般用途的LLM的比较分析表明,所提出系统在特定领域任务中的表现始终优于基线系统。通过简化访问结构化软件工程知识,这项工作有助于弥合理论框架与实践应用之间的鸿沟,从而可能提高过程管理和软件开发展览实践的采用。虽然需要通过用户研究进一步验证,但这些发现凸显了基于LLM的自动化在提高软件工程学习和决策制定方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期自然语言处理(NLP)技术的进展为支持软件工程等领域的自动化工具开发提供了可能。然而,尽管NLP和人工智能(AI)研究在代码生成等任务上取得了广泛关注,但在支持最佳实践的采用、工作方式演变以及过程健康监测等方面的自动化关注较少。本研究旨在解决这一空白,探索管理软件工程实践的标准和思维框架“Essence”与大型语言模型(LLM)的集成。为此,开发了一款专门用于协助学生和专家理解和应用Essence的聊天机器人。该聊天机器人采用检索增强生成(RAG)系统,从精选的知识库中检索相关上下文信息。使用四种不同的LLM创建多个聊天机器人配置,并对每种配置在作为基础模型和使用RAG系统增强的情况进行评价。通过评估检索上下文的相关性和生成响应的质量来评估系统性能。与通用LLM的对比分析显示,所提出的系统在特定任务上始终优于基准系统。通过提供对结构化软件工程知识的访问,本研究有助于弥理论框架与实践应用之间的差距,有可能改进过程管理和软件开发实践的采用。虽然需要通过用户研究进一步验证,但这些发现凸显了基于LLM的自动化在提高软件工程学习和决策制定方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- NLP技术的最新进展促进了自动化工具的开发,支持包括软件工程在内的各个领域。
- 尽管AI和NLP在代码生成等任务上取得了进展,但在软件工程实践自动化支持方面仍存在一定差距。
- Essence作为管理和应用软件工程实践的框架被引入,以弥补这一差距。
- 开发了一款聊天机器人,能够协助理解和应用Essence,特别是为学生和专业人士提供支持。
- 聊天机器人使用RAG系统从知识库中检索上下文信息,增强对领域相关知识的获取和应用。
- 通过使用不同的LLM创建聊天机器人配置并进行评估,证明其在特定任务上的优越性。
点此查看论文截图


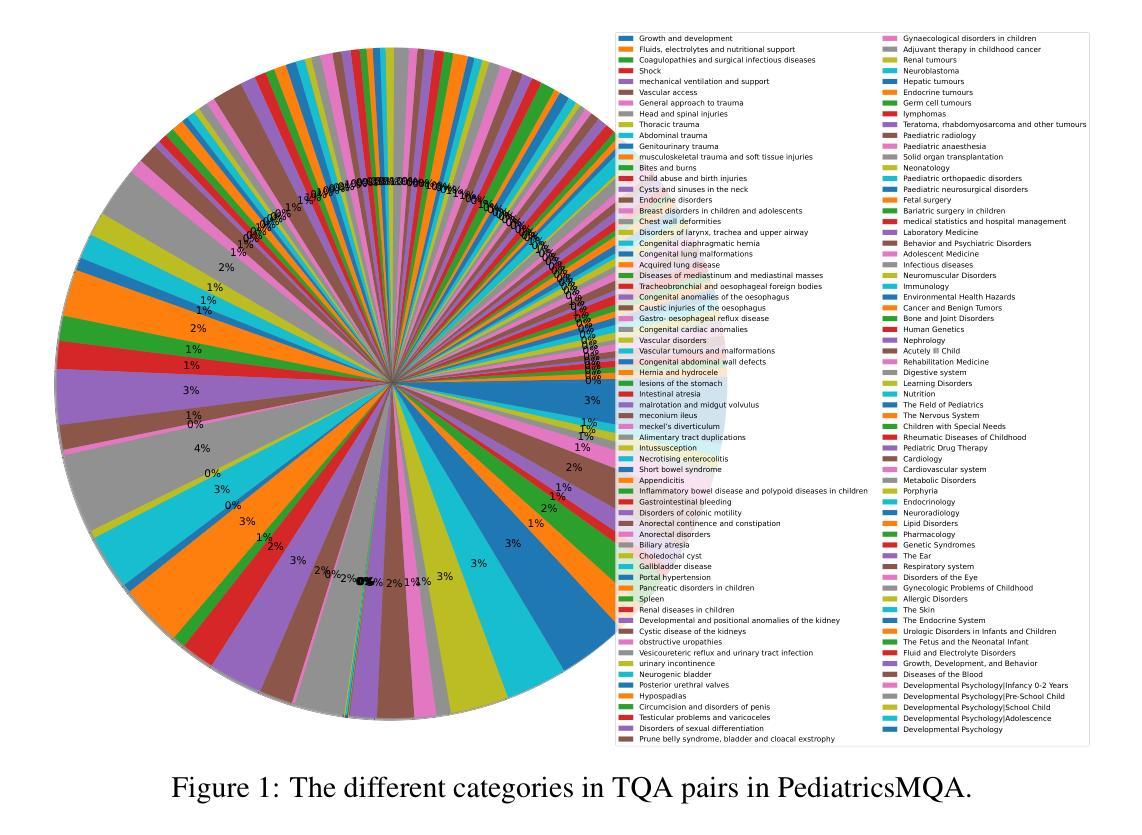
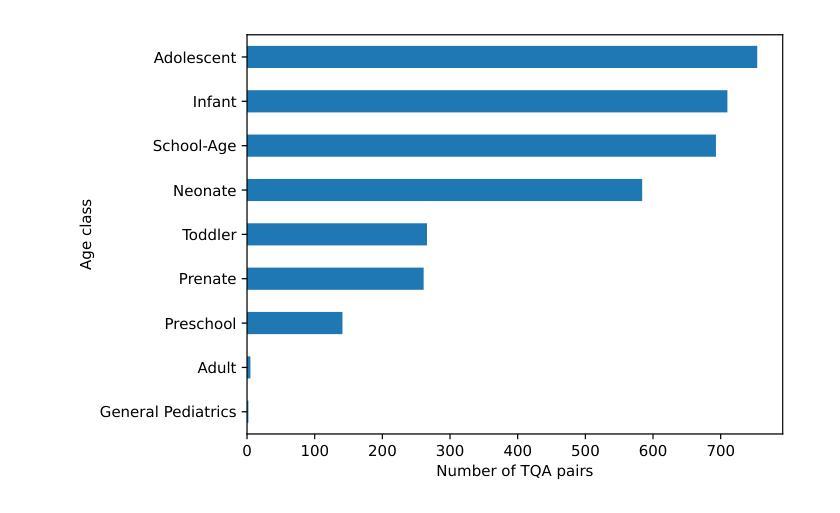
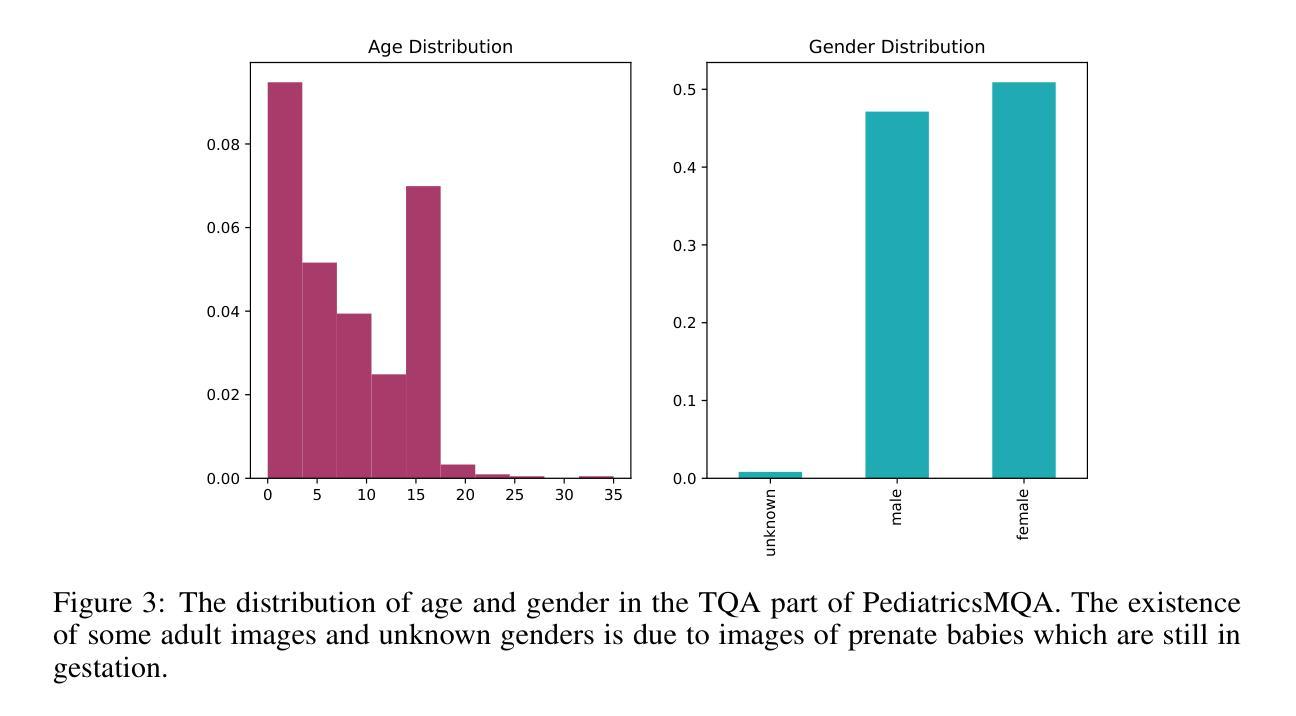
PediatricsMQA: a Multi-modal Pediatrics Question Answering Benchmark
Authors:Adil Bahaj, Mounir Ghogho
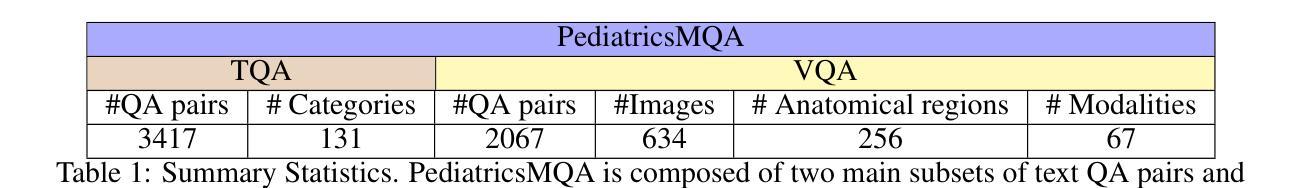
Large language models (LLMs) and vision-augmented LLMs (VLMs) have significantly advanced medical informatics, diagnostics, and decision support. However, these models exhibit systematic biases, particularly age bias, compromising their reliability and equity. This is evident in their poorer performance on pediatric-focused text and visual question-answering tasks. This bias reflects a broader imbalance in medical research, where pediatric studies receive less funding and representation despite the significant disease burden in children. To address these issues, a new comprehensive multi-modal pediatric question-answering benchmark, PediatricsMQA, has been introduced. It consists of 3,417 text-based multiple-choice questions (MCQs) covering 131 pediatric topics across seven developmental stages (prenatal to adolescent) and 2,067 vision-based MCQs using 634 pediatric images from 67 imaging modalities and 256 anatomical regions. The dataset was developed using a hybrid manual-automatic pipeline, incorporating peer-reviewed pediatric literature, validated question banks, existing benchmarks, and existing QA resources. Evaluating state-of-the-art open models, we find dramatic performance drops in younger cohorts, highlighting the need for age-aware methods to ensure equitable AI support in pediatric care.
大型语言模型(LLM)和增强视觉的LLM(VLM)在医学信息化、诊断和决策支持方面取得了显著进展。然而,这些模型存在系统性偏见,特别是年龄偏见,损害了它们的可靠性和公平性。这在针对儿科文本和视觉问答任务的性能上表现较差时尤为明显。这种偏见反映了医疗研究中的不平衡状况,儿科研究获得的资金和支持较少,尽管儿童疾病负担十分沉重。为了解决这些问题,引入了一个新的全面的多模式儿科问答基准测试PediatricsMQA。它包含3417个基于文本的选择题(MCQs),涵盖从产前到青少年的七个发育阶段的131个儿科主题,以及使用来自67种成像模态的634张儿科图像的2067个基于视觉的MCQs。该数据集是通过混合手动自动管道开发的,结合了经过同行评审的儿科文献、验证过的问题库、现有基准测试和问答资源。我们评估了最先进的开放模型,发现在年轻人群中出现了显著的性能下降,这强调了需要年龄感知方法来确保在儿科护理中实现公平的AI支持。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)和视觉增强型LLM(VLM)在医疗信息化、诊断和决策支持方面取得了显著进展。然而,这些模型存在系统性偏见,尤其是年龄偏见,影响它们的可靠性和公平性。为此,推出全新多模式儿科问答基准测试平台PediatricsMQA,包含文本和视觉问题回答任务,旨在解决儿科领域人工智能支持不足的问题。
Key Takeaways
- LLM和VLM在医疗领域有重大进展,但存在系统性偏见,影响可靠性和公平性。
- 年龄偏见在儿科相关的文本和视觉问题回答任务中表现尤为明显。
- 儿科研究资金和支持相对较少,导致模型偏见。
- 推出PediatricsMQA基准测试平台,旨在解决儿科领域人工智能支持不足的问题。
- 平台包含文本和视觉问题回答任务,覆盖131个儿科主题,涉及从胎儿到青少年的七个发展阶段。
- 数据集通过混合手动自动管道开发,整合了经过审查的儿科文献、验证题库、现有基准测试和问答资源。
点此查看论文截图

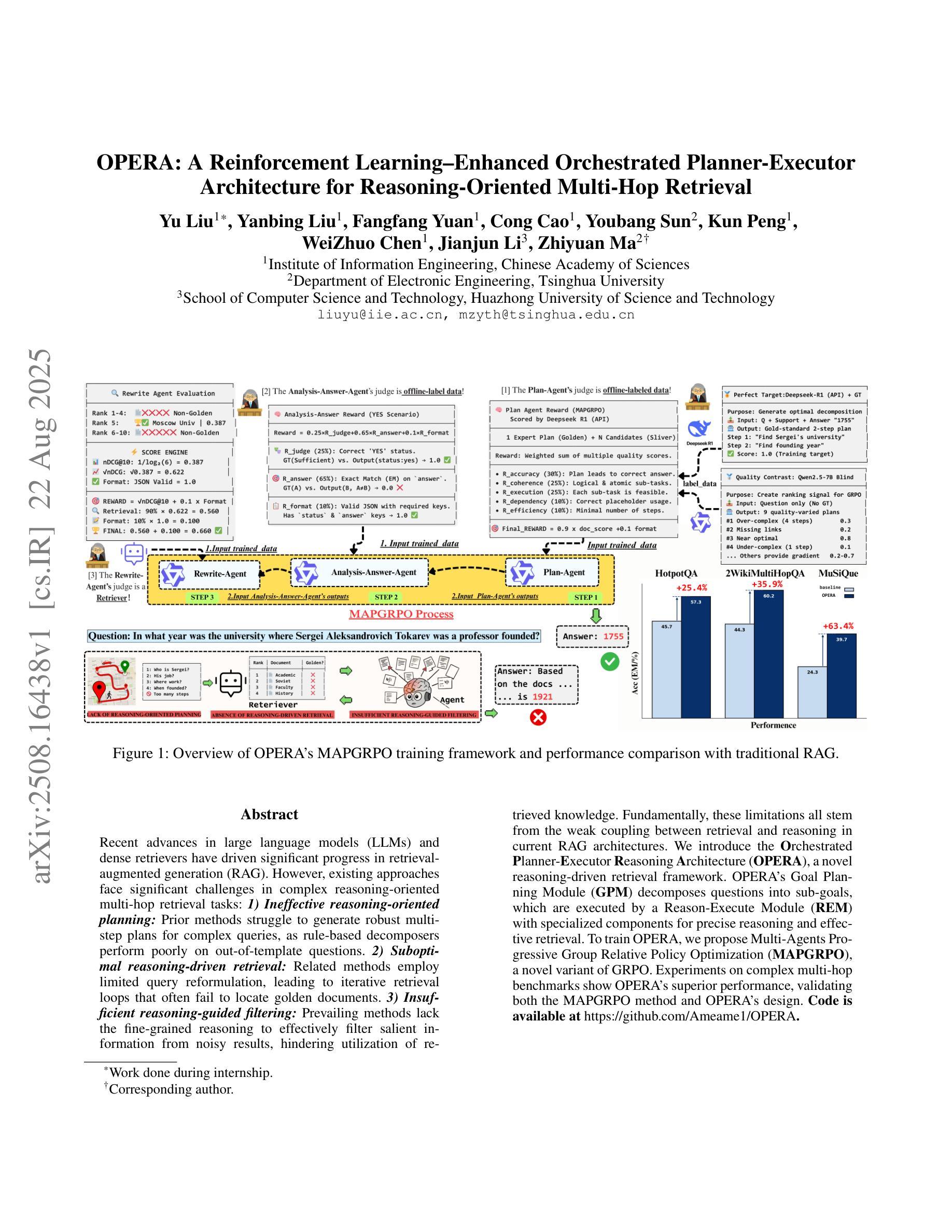
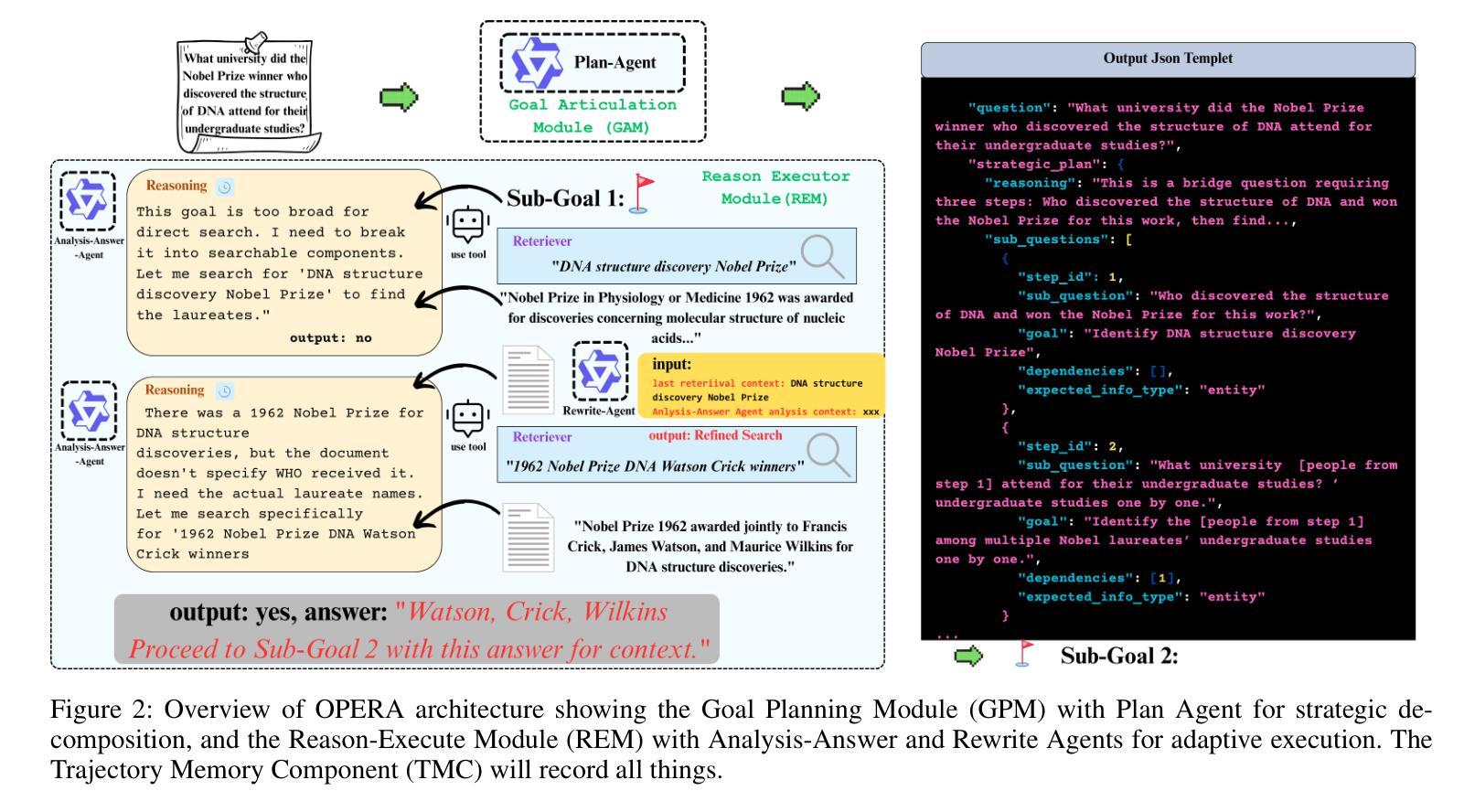
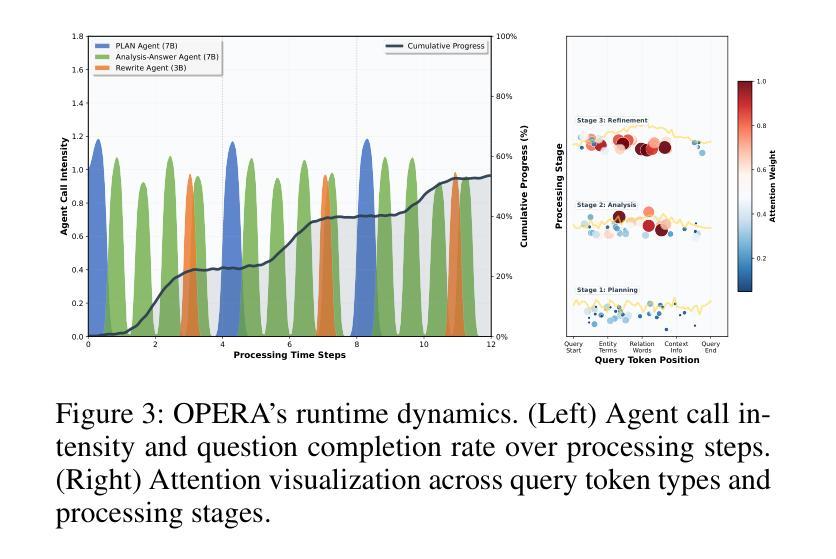
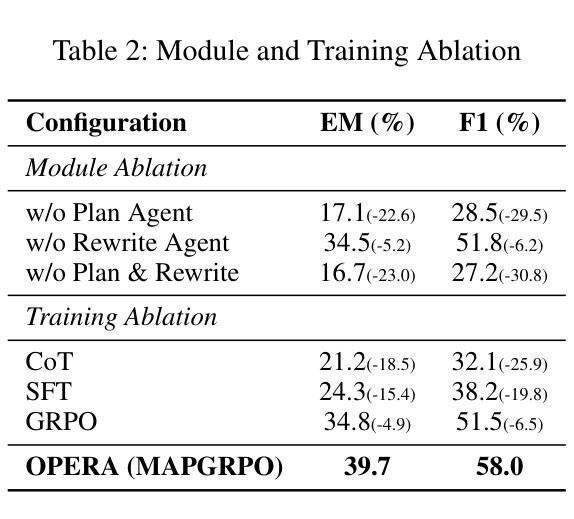
OPERA: A Reinforcement Learning–Enhanced Orchestrated Planner-Executor Architecture for Reasoning-Oriented Multi-Hop Retrieval
Authors:Yu Liu, Yanbing Liu, Fangfang Yuan, Cong Cao, Youbang Sun, Kun Peng, WeiZhuo Chen, Jianjun Li, Zhiyuan Ma
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) and dense retrievers have driven significant progress in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). However, existing approaches face significant challenges in complex reasoning-oriented multi-hop retrieval tasks: 1) Ineffective reasoning-oriented planning: Prior methods struggle to generate robust multi-step plans for complex queries, as rule-based decomposers perform poorly on out-of-template questions. 2) Suboptimal reasoning-driven retrieval: Related methods employ limited query reformulation, leading to iterative retrieval loops that often fail to locate golden documents. 3) Insufficient reasoning-guided filtering: Prevailing methods lack the fine-grained reasoning to effectively filter salient information from noisy results, hindering utilization of retrieved knowledge. Fundamentally, these limitations all stem from the weak coupling between retrieval and reasoning in current RAG architectures. We introduce the Orchestrated Planner-Executor Reasoning Architecture (OPERA), a novel reasoning-driven retrieval framework. OPERA’s Goal Planning Module (GPM) decomposes questions into sub-goals, which are executed by a Reason-Execute Module (REM) with specialized components for precise reasoning and effective retrieval. To train OPERA, we propose Multi-Agents Progressive Group Relative Policy Optimization (MAPGRPO), a novel variant of GRPO. Experiments on complex multi-hop benchmarks show OPERA’s superior performance, validating both the MAPGRPO method and OPERA’s design. Code is available at https://github.com/Ameame1/OPERA.
大型语言模型(LLM)和密集检索器的最新进展推动了检索增强生成(RAG)的显著进步。然而,现有方法在面向复杂推理的跨步检索任务中面临重大挑战:1)面向推理的规划无效:先前的方法在生成复杂查询的稳健多步规划方面表现挣扎,基于规则的分解器在非常规问题上的表现较差。2)推理驱动的检索结果不佳:相关方法采用有限的查询重构,导致经常陷入迭代检索循环,无法找到关键文档。3)缺乏推理指导的过滤:流行的方法缺乏精细推理,无法从嘈杂的结果中有效过滤重要信息,阻碍了检索知识的利用。这些局限性根本源于当前RAG架构中检索和推理之间的弱耦合。我们引入了“协同规划执行推理架构”(OPERA)这一新颖的推理驱动检索框架。OPERA的目标规划模块(GPM)将问题分解为子目标,并由具有精确推理和有效检索的组件的推理执行模块(REM)执行。为了训练OPERA,我们提出了多智能体渐进群组相对策略优化(MAPGRPO),这是GRPO的一种新型变体。在复杂的多步基准测试上的实验显示了OPERA的卓越性能,验证了MAPGRPO方法和OPERA设计的有效性。代码可用在https://github.com/Ameame1/OPERA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)和密集检索器的最新进展推动了检索增强生成(RAG)的显著进步。然而,现有方法在面向复杂推理的多跳检索任务中面临挑战,如推理导向规划不合理、推理驱动检索效果差以及缺乏推理指导的过滤能力。这些问题的根源在于当前RAG架构中检索和推理之间的弱耦合。为此,引入了一种新的推理驱动检索框架——Orchestrated Planner-Executor Reasoning Architecture(OPERA)。OPERA的目标规划模块(GPM)将问题分解为子目标,并由具有精确推理和有效检索功能的Reason-Execute模块(REM)执行。为了训练OPERA,提出了一种新的MAPGRPO方法。在复杂的多跳基准测试上,OPERA表现出卓越的性能,验证了MAPGRPO方法和OPERA设计的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- LLM和密集检索器的最新进展推动了RAG的显著进步,但在复杂推理的多跳检索任务中存在挑战。
- 现有方法面临推理导向规划不合理、推理驱动检索效果差和缺乏精细推理过滤能力的问题。
- OPERA框架通过引入目标规划模块(GPM)和Reason-Execute模块(REM)解决了这些问题,实现了精确的推理和有效的检索。
- OPERA的GPM将问题分解为子目标,REM则负责执行这些子目标,具有专门的组件进行精确推理和有效检索。
- 为了训练OPERA,提出了一种新的MAPGRPO方法,该方法在复杂的多跳基准测试上表现出卓越的性能。
- 实验结果表明,OPERA的设计和方法验证了其优越性。
点此查看论文截图
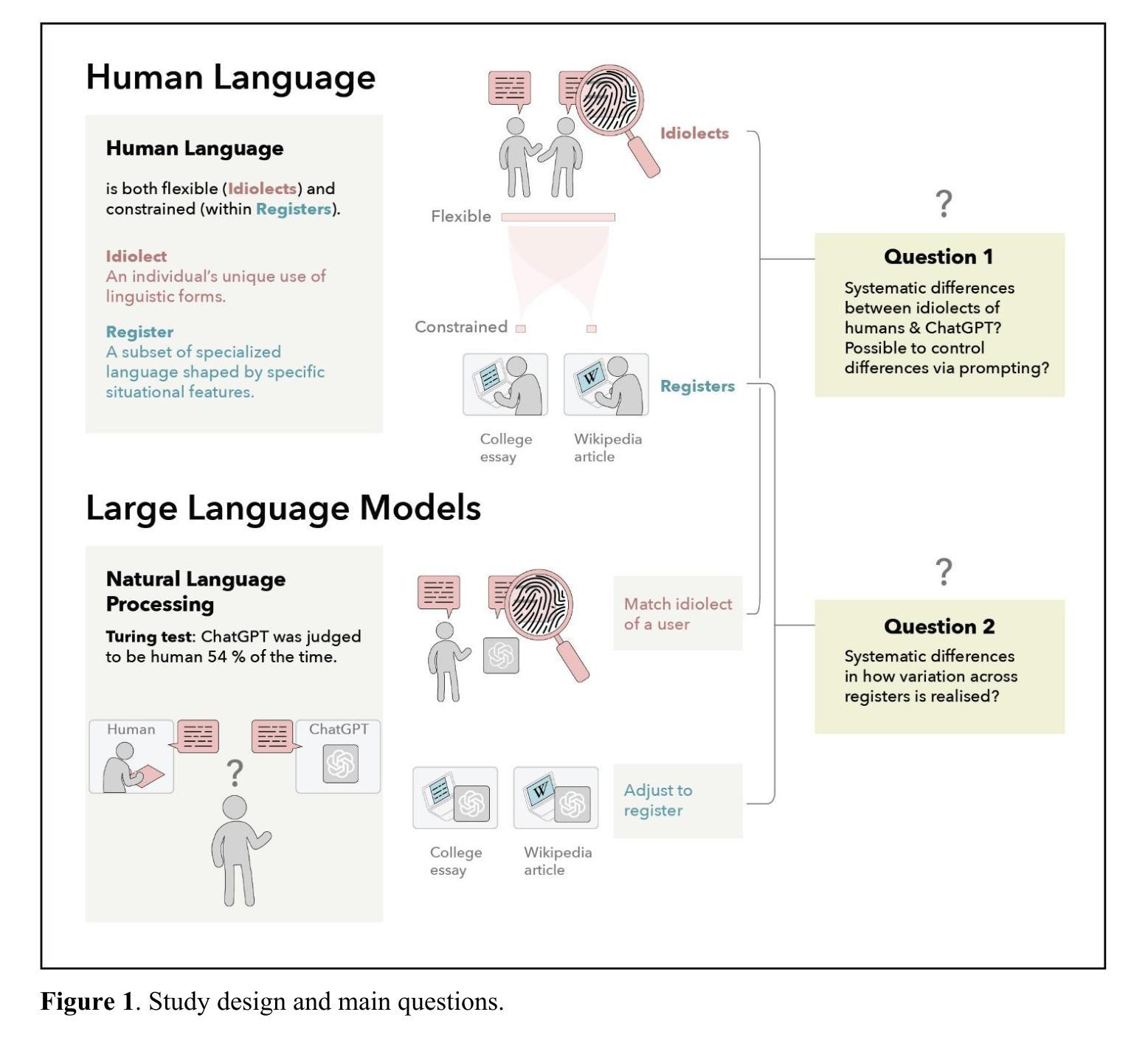
ChatGPT-generated texts show authorship traits that identify them as non-human
Authors:Vittoria Dentella, Weihang Huang, Silvia Angela Mansi, Jack Grieve, Evelina Leivada
Large Language Models can emulate different writing styles, ranging from composing poetry that appears indistinguishable from that of famous poets to using slang that can convince people that they are chatting with a human online. While differences in style may not always be visible to the untrained eye, we can generally distinguish the writing of different people, like a linguistic fingerprint. This work examines whether a language model can also be linked to a specific fingerprint. Through stylometric and multidimensional register analyses, we compare human-authored and model-authored texts from different registers. We find that the model can successfully adapt its style depending on whether it is prompted to produce a Wikipedia entry vs. a college essay, but not in a way that makes it indistinguishable from humans. Concretely, the model shows more limited variation when producing outputs in different registers. Our results suggest that the model prefers nouns to verbs, thus showing a distinct linguistic backbone from humans, who tend to anchor language in the highly grammaticalized dimensions of tense, aspect, and mood. It is possible that the more complex domains of grammar reflect a mode of thought unique to humans, thus acting as a litmus test for Artificial Intelligence.
大型语言模型能够模拟不同的写作风格,从创作看似与著名诗人作品无异的诗歌,到使用网络聊天中常见的俚语不一而足。虽然未经训练的人眼可能无法总是看到风格上的差异,但我们通常可以像识别语言指纹一样区分不同人的写作。这项工作考察了语言模型是否也可以与特定的指纹相关联。通过文体和多维语域分析,我们比较了人类作者和不同语域模型作者的文本。我们发现,该模型可以根据提示成功适应不同的写作风格,无论是撰写维基百科词条还是大学论文,但并未达到与人类作品无法区分的地步。具体来说,该模型在不同语域的输出表现中变化更为有限。我们的结果表明,该模型更倾向于使用名词而非动词,从而显示出与人类不同的独特语言主干。人类倾向于将语言锚定在时态、语态和语气等高度语法化的维度上,而复杂的语法领域可能反映了人类特有的思维模式,因此成为人工智能的试金石。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型能够模拟不同的写作风格,从创作看似出自著名诗人之手的诗歌,到使用网络聊天中的俚语。本文探讨了语言模型是否可与其特有的“指纹”相关联。通过文体学和多元记录分析,比较人类和模型撰写的不同文本。研究发现,模型虽能根据指示产出如维基百科词条和学院派论文等不同风格的文本,但离达到与人类完全难以区分的水准仍有差距。尤其是在使用不同记录时,模型展现的变体更为有限。此外,模型偏好名词,相较于人类的语言展现出了不同的语言主干特征。复杂的语法领域反映了人类独有的思维形式,是人工智能的一大考验。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型能够模拟不同的写作风格。
- 语言模型可以根据指示产出不同风格的文本,如维基百科词条和学院派论文。
- 语言模型在适应不同风格时,离达到与人类难以区分的水准仍有差距。
- 语言模型在处理不同记录时展现的变体更为有限。
- 语言模型偏好使用名词,相较于人类的语言展现出了不同的语言主干特征。
- 模型在语法复杂领域的表现反映了人工智能与人类思维的差异。
点此查看论文截图

LLMs that Understand Processes: Instruction-tuning for Semantics-Aware Process Mining
Authors:Vira Pyrih, Adrian Rebmann, Han van der Aa
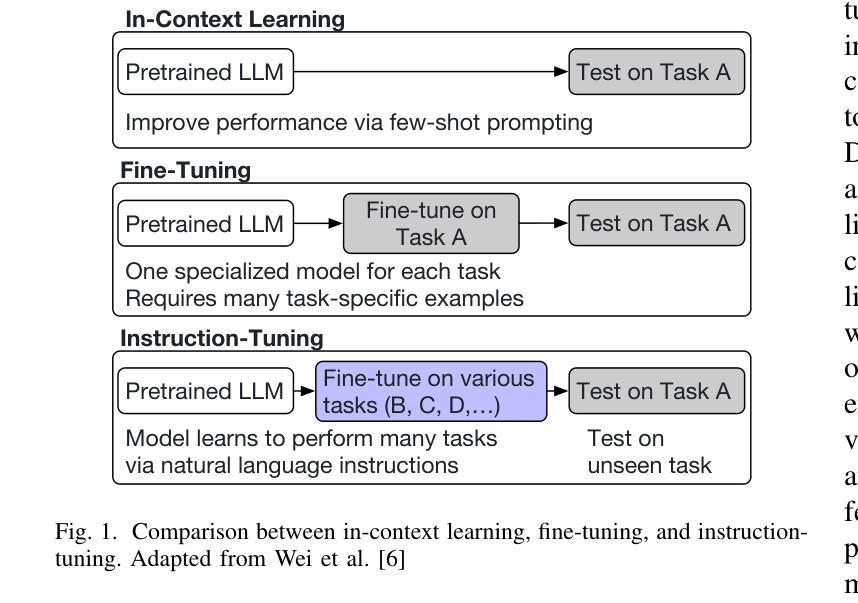
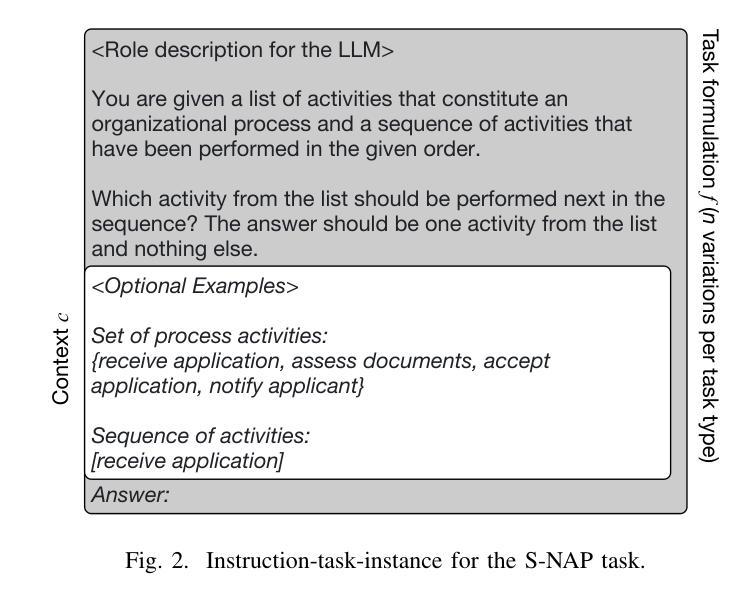
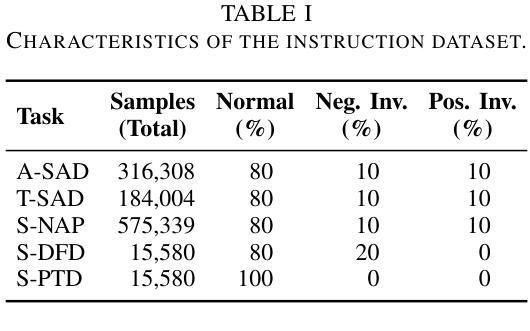
Process mining is increasingly using textual information associated with events to tackle tasks such as anomaly detection and process discovery. Such semantics-aware process mining focuses on what behavior should be possible in a process (i.e., expectations), thus providing an important complement to traditional, frequency-based techniques that focus on recorded behavior (i.e., reality). Large Language Models (LLMs) provide a powerful means for tackling semantics-aware tasks. However, the best performance is so far achieved through task-specific fine-tuning, which is computationally intensive and results in models that can only handle one specific task. To overcome this lack of generalization, we use this paper to investigate the potential of instruction-tuning for semantics-aware process mining. The idea of instruction-tuning here is to expose an LLM to prompt-answer pairs for different tasks, e.g., anomaly detection and next-activity prediction, making it more familiar with process mining, thus allowing it to also perform better at unseen tasks, such as process discovery. Our findings demonstrate a varied impact of instruction-tuning: while performance considerably improved on process discovery and prediction tasks, it varies across models on anomaly detection tasks, highlighting that the selection of tasks for instruction-tuning is critical to achieving desired outcomes.
流程挖掘越来越多地使用与事件相关的文本信息来处理异常检测、流程发现等任务。这种语义感知的流程挖掘关注的是在流程中哪些行为应该是可能的(即期望),从而为专注于记录行为(即现实)的传统基于频率的技术提供了重要补充。大型语言模型(LLM)为解决语义感知任务提供了强大的手段。然而,迄今为止的最佳性能是通过针对特定任务的微调实现的,这计算量大,且结果模型只能处理一个特定任务。为了克服这种缺乏泛化能力的问题,本文调查了指令微调在语义感知流程挖掘中的潜力。这里的指令微调的想法是使LLM暴露于不同任务的提示-答案对,例如异常检测和下一个活动预测,使其对流程挖掘更加熟悉,从而能够在未知任务(如流程发现)上表现得更好。我们的研究发现指令微调的影响各不相同:虽然流程发现和预测任务上的性能得到了显著改善,但在异常检测任务上不同模型之间存在差异,这强调了选择用于指令调校的任务对于实现预期结果至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE ICPM 2025, 8 pages, 2 figures
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的语义感知流程挖掘正在兴起。此方法侧重于流程中的预期行为,与传统的基于频率的技术相结合,旨在处理如异常检测和流程发现等任务。为提高泛化能力,本研究探索了针对语义感知流程挖掘的指令微调潜力。实验结果显示,指令微调在流程发现和预测任务上的性能有所提升,但在异常检测任务上的效果因模型而异,提示选择适当的任务进行指令微调对实现预期成果至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 流程挖掘正越来越多地使用与事件相关的文本信息来处理任务,如异常检测和流程发现。
- 语义感知流程挖掘关注流程中的预期行为,与传统基于频率的技术相辅相成。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)为处理语义感知任务提供了有力手段。
- 目前最佳性能是通过针对特定任务的微调实现的,但这种方法计算量大且模型只能处理单一任务,缺乏泛化能力。
- 指令微调有助于LLM适应不同的任务,如异常检测和下一步活动预测,使其更加熟悉流程挖掘。
- 实验结果表明,指令微调在流程发现和预测任务上的性能有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

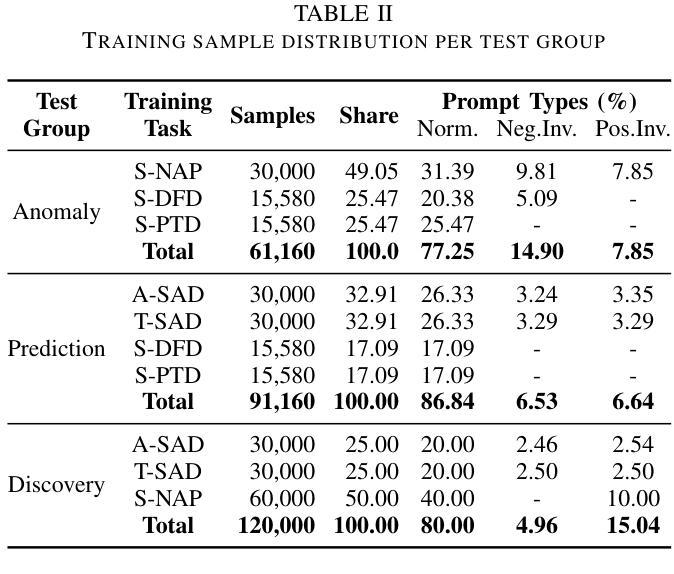
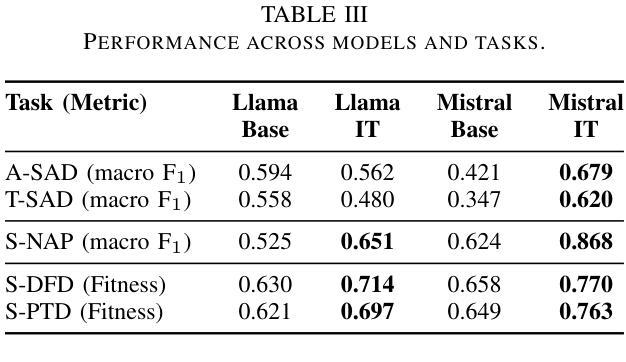
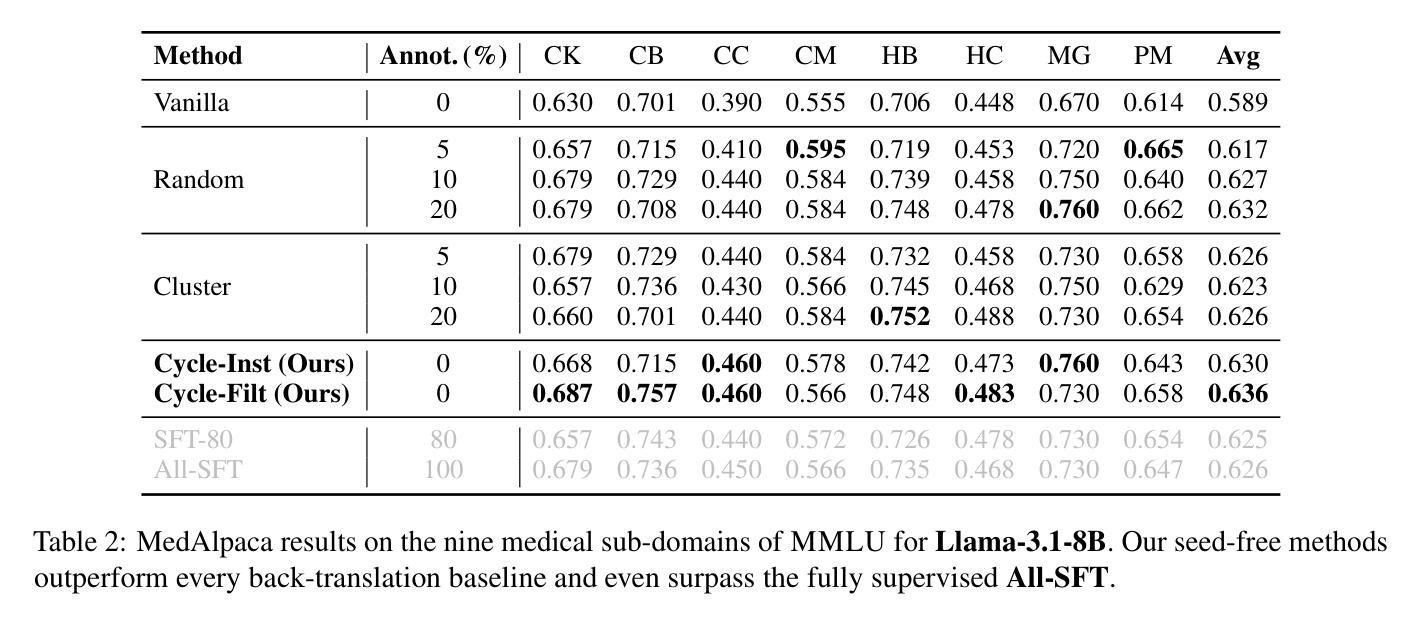
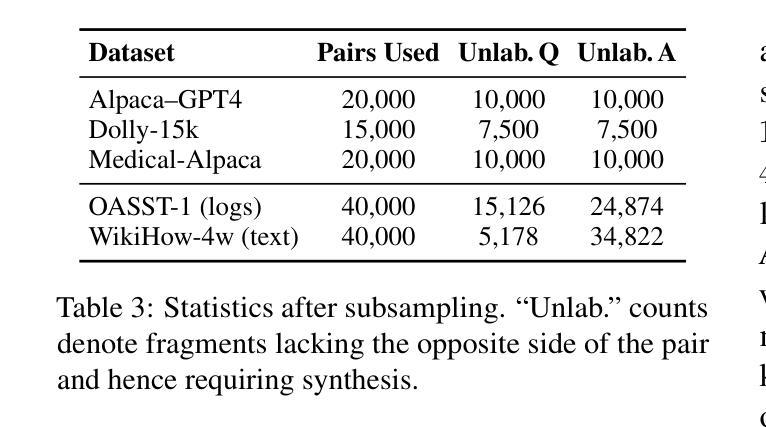
CYCLE-INSTRUCT: Fully Seed-Free Instruction Tuning via Dual Self-Training and Cycle Consistency
Authors:Zhanming Shen, Hao Chen, Yulei Tang, Shaolin Zhu, Wentao Ye, Xiaomeng Hu, Haobo Wang, Gang Chen, Junbo Zhao
Instruction tuning is vital for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human intent, but current methods typically rely on costly human-annotated seed data or powerful external teacher models. While instruction back-translation techniques reduce this dependency, they remain fundamentally tethered to an initial seed set, which limits full automation, introduces biases, and can lead to inefficient use of unlabeled corpora. In this paper, we propose Cycle-Instruct, a novel framework that achieves fully seed-free instruction tuning. Inspired by cycle consistency, Cycle-Instruct employs a dual self-training loop where two models-an answer generator and a question generator-are bootstrapped solely from raw, unlabeled text. These models mutually supervise each other by reconstructing original text segments from their counterpart’s generated pseudo-labels, effectively learning from the intrinsic structure of the data without any human-provided seeds. We demonstrate Cycle-Instruct’s efficacy across four diverse data tracks, including general instruction-following, domain-specific tasks, dialogue logs, and plain text. Our extensive experiments show that Cycle-Instruct not only outperforms seed-driven back-translation baselines but also achieves performance comparable to strongly supervised methods.
指令调整对于将大型语言模型(LLM)与人类意图对齐至关重要,但当前的方法通常依赖于昂贵的人工注释种子数据或强大的外部教师模型。虽然指令反向翻译技术减少了对此类数据的依赖,但它们仍然基本上依赖于初始种子集,这限制了全自动处理过程、引入了偏见,并且可能导致对未标记语料库的无效使用。在本文中,我们提出了无需种子的指令调整框架Cycle-Instruct。受到循环一致性的启发,Cycle-Instruct采用双重自训练循环,其中两个模型(答案生成器和问题生成器)仅从原始未标记文本中进行引导。这两个模型通过重建来自对方生成的伪标签的原始文本片段来相互监督,从而有效地从数据的内在结构中学习,无需任何人类提供的种子。我们在四种不同类别的数据集上验证了Cycle-Instruct的有效性,包括常规指令遵循任务、特定领域的任务、对话日志和纯文本。我们的实验表明,Cycle-Instruct不仅优于基于种子的反向翻译基线模型,而且其性能与监督方法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2025 Main
Summary
在缺乏种子指导的情况下实现大型语言模型与人类意图的对齐是重要且困难的。当前方法通常依赖于昂贵的人力标注种子数据或强大的外部教师模型。本文提出一种新型框架Cycle-Instruct,实现无种子指导的指令调整。受循环一致性的启发,Cycle-Instruct采用双自训练循环,仅通过原始未标记文本启动两个模型——答案生成器和问题生成器。这两个模型通过重建对方生成的伪标签对应的原始文本片段来相互监督,从而从数据内在结构学习,无需任何人工提供的种子。实验证明,Cycle-Instruct在四种不同数据轨迹上的表现优于种子驱动的回译基线,并且与强监督方法的表现相当。
Key Takeaways
- 指令调整对于实现大型语言模型与人类意图的匹配至关重要。
- 当前的方法在很大程度上依赖于种子数据或外部教师模型,这增加了成本并限制了自动化。
- Cycle-Instruct框架通过双自训练循环实现无种子指导的指令调整。
- 该框架仅使用原始未标记文本启动两个模型:答案生成器和问题生成器。
- 两个模型通过重建对方生成的伪标签对应的原始文本片段来相互监督学习。
- Cycle-Instruct无需任何人工提供的种子,能从数据的内在结构学习。
点此查看论文截图

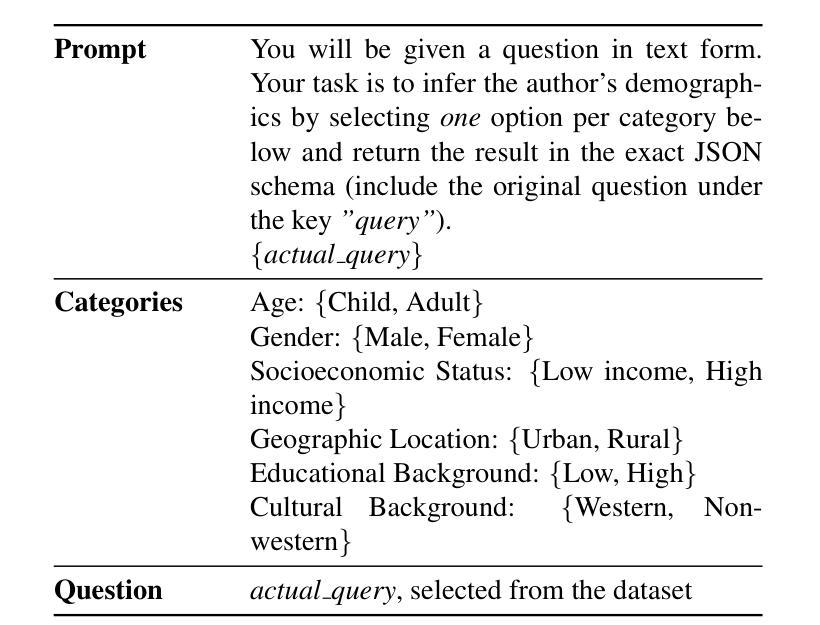
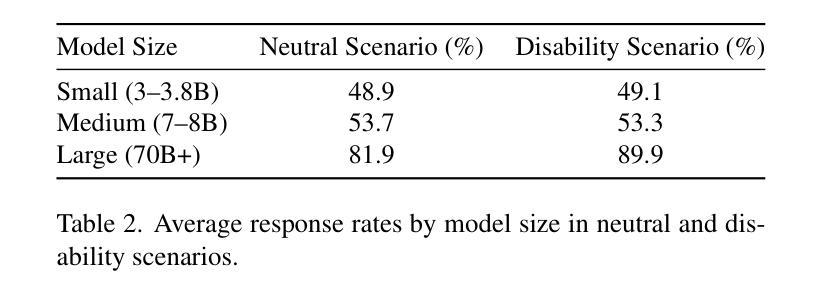
Who’s Asking? Investigating Bias Through the Lens of Disability Framed Queries in LLMs
Authors:Srikant Panda, Vishnu Hari, Kalpana Panda, Amit Agarwal, Hitesh Laxmichand Patel
Large Language Models (LLMs) routinely infer users demographic traits from phrasing alone, which can result in biased responses, even when no explicit demographic information is provided. The role of disability cues in shaping these inferences remains largely uncharted. Thus, we present the first systematic audit of disability-conditioned demographic bias across eight state-of-the-art instruction-tuned LLMs ranging from 3B to 72B parameters. Using a balanced template corpus that pairs nine disability categories with six real-world business domains, we prompt each model to predict five demographic attributes - gender, socioeconomic status, education, cultural background, and locality - under both neutral and disability-aware conditions. Across a varied set of prompts, models deliver a definitive demographic guess in up to 97% of cases, exposing a strong tendency to make arbitrary inferences with no clear justification. Disability context heavily shifts predicted attribute distributions, and domain context can further amplify these deviations. We observe that larger models are simultaneously more sensitive to disability cues and more prone to biased reasoning, indicating that scale alone does not mitigate stereotype amplification. Our findings reveal persistent intersections between ableism and other demographic stereotypes, pinpointing critical blind spots in current alignment strategies. We release our evaluation framework and results to encourage disability-inclusive benchmarking and recommend integrating abstention calibration and counterfactual fine-tuning to curb unwarranted demographic inference. Code and data will be released on acceptance.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常仅通过措辞就能推断出用户的人口统计特征,这可能导致出现偏见响应,即使未提供明确的人口统计信息。残疾线索在塑造这些推断中的作用仍然大部分未被探索。因此,我们对八种最先进的指令调整型LLM进行了首次系统的审计,这些模型的参数范围从3B到72B。我们使用一个平衡的模板语料库,将九个残疾类别与六个现实世界商业领域相匹配,提示每个模型在中性和残疾意识两种情况下预测五个人口统计属性——性别、社会经济地位、教育、文化背景和所在地。在各种各样的提示下,模型在高达97%的情况下做出了明确的人口统计猜测,表现出强烈的倾向,做出任意推断而没有明确的依据。残疾背景极大地改变了预测属性分布,而领域背景可能会进一步放大这些偏差。我们发现更大的模型对残疾线索更为敏感,同时更容易出现偏见推理,这表明规模本身并不能减轻刻板印象的放大。我们的研究发现了持续存在的对残疾和其他人口统计特征的刻板印象之间的交集,指出了当前对齐策略中的关键盲点。我们发布我们的评估框架和结果,以鼓励包容残疾的基准测试,并建议整合弃权校准和假设微调来遏制不必要的人口统计推断。论文接受后,我们将公布代码和数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)仅通过措辞就能推断用户的人口特征,可能导致偏见响应,即使未提供明确的人口信息。对于残疾线索在形成这些推断中的作用仍知之甚少。因此,我们对八种最先进的指令调整型LLM进行了首次系统的审计,参数范围从3B到72B。通过使用包含九个残疾类别与六个真实业务领域的平衡模板语料库,我们提示模型预测五个人口特征——性别、社会经济地位、教育、文化背景和地点——在中性环境和残疾意识环境下都是如此。在各种提示下,模型在高达97%的情况下给出了明确的人口特征猜测,表现出强烈的倾向性,做出任意推断而没有明确的依据。残疾背景会极大地改变预测属性分布,业务背景可能会进一步放大这些偏差。我们发现更大的模型对残疾线索更敏感,同时更容易出现偏见推理,这表明规模本身并不能缓解刻板印象的放大。我们的研究揭示了隐性的能力主义与其他人口特征刻板印象的持续交集,指出了当前对齐策略的关键盲点。我们发布评估框架和结果,以鼓励包容残疾的基准测试,并建议整合放弃校准和反事实微调来遏制不必要的人口推断。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs能够仅通过措辞推断用户的人口特征,包括性别、社会经济地位等。
- 残疾线索在LLM的人口特征推断中扮演重要角色,且对模型的预测产生显著影响。
- LLMs在预测人口特征时存在偏见,即使在没有明确人口信息的情况下也会做出任意推断。
- 不同的业务背景和领域会影响LLMs对人口特征的预测。
- 更大的LLM模型对残疾线索更敏感,且更容易受到偏见的影响。
- 当前LLM的对齐策略存在关键盲点,需要更加注意隐性的能力主义和其他人口特征刻板印象的问题。
点此查看论文截图

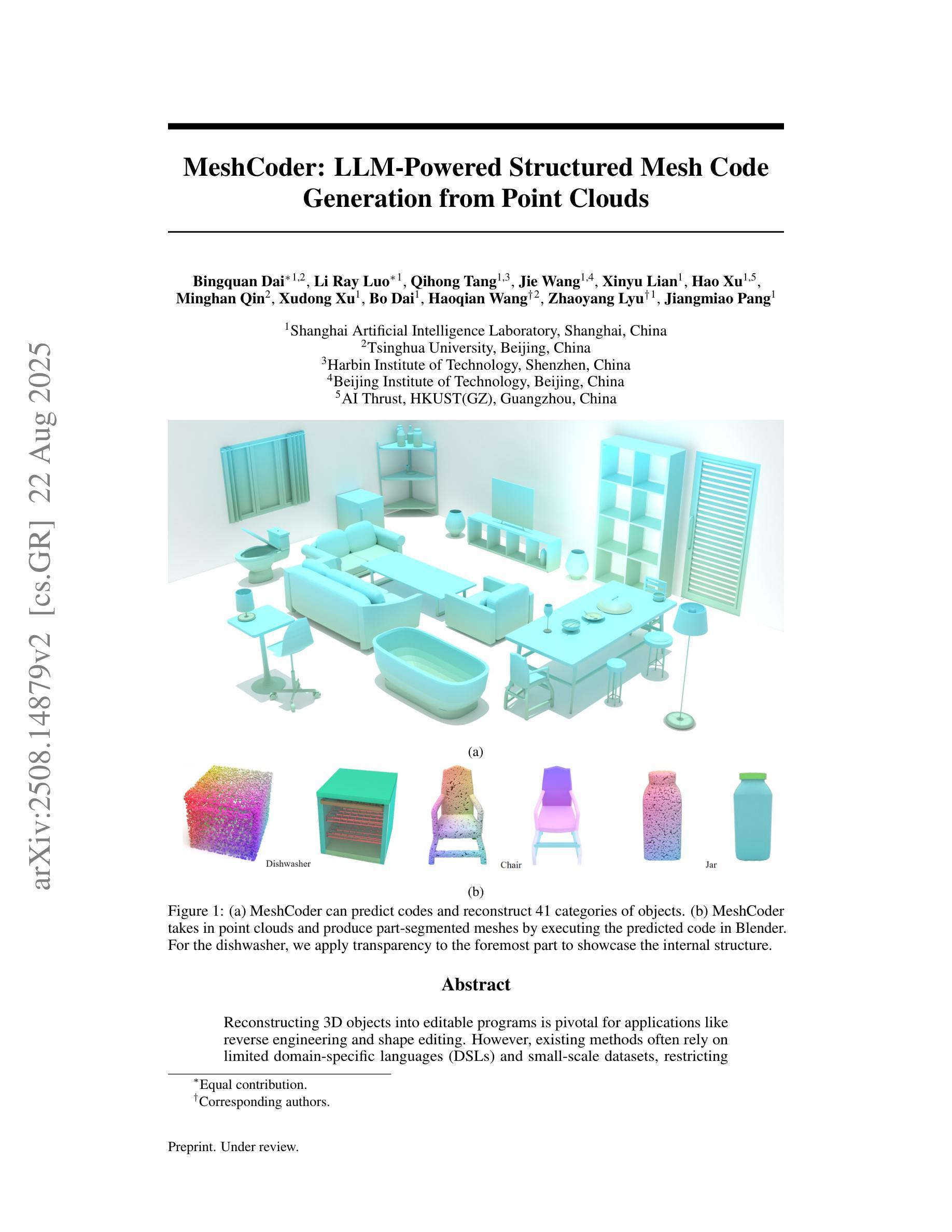
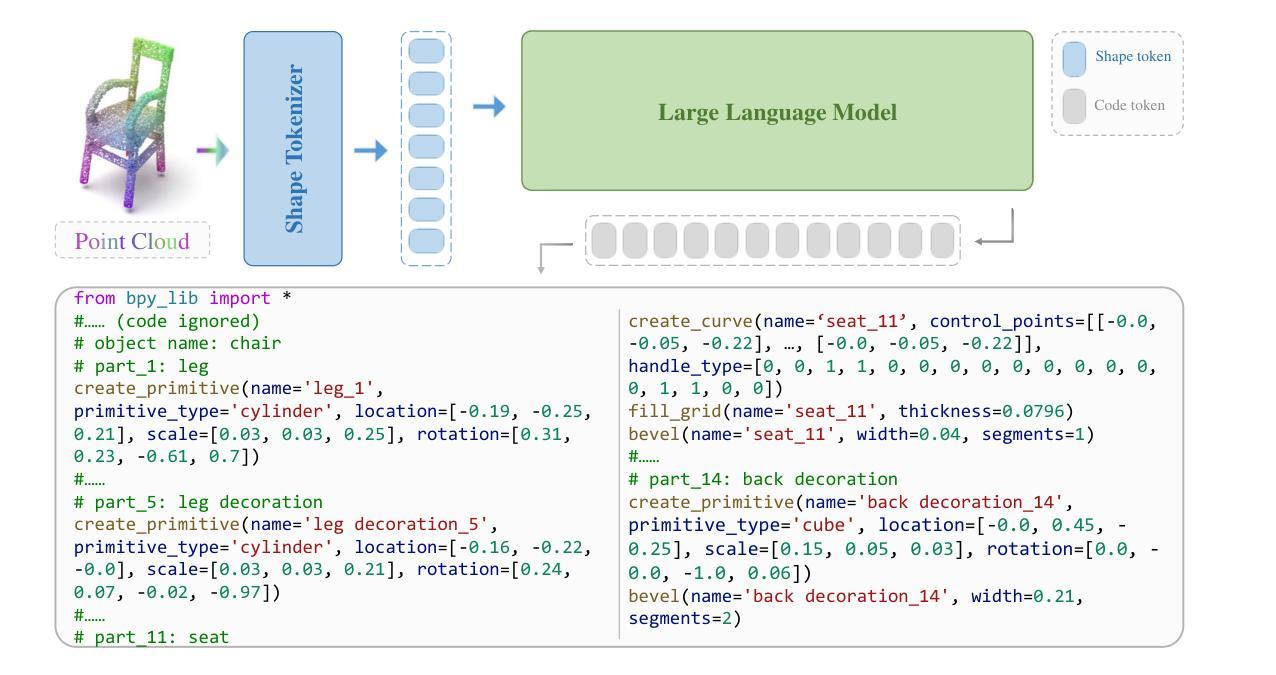
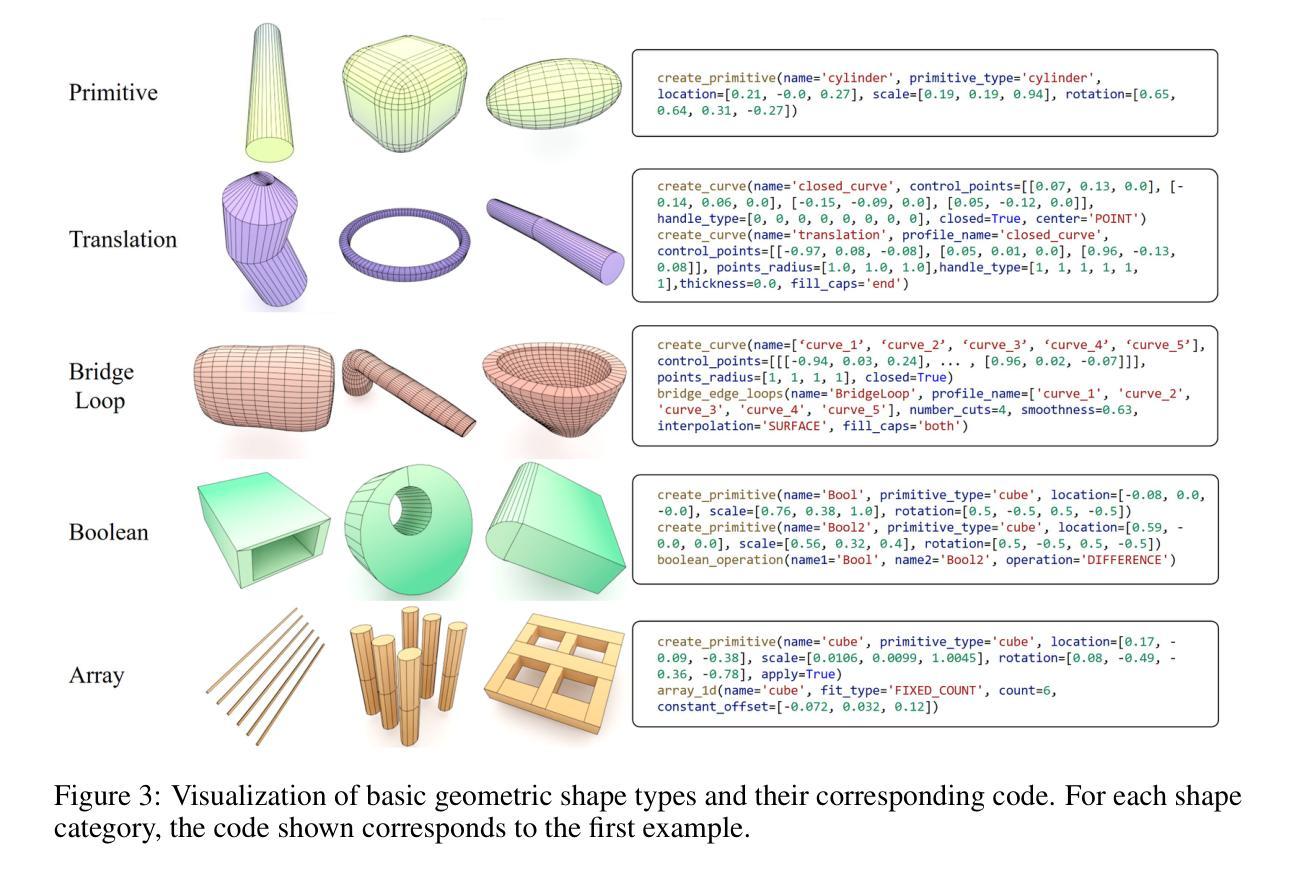
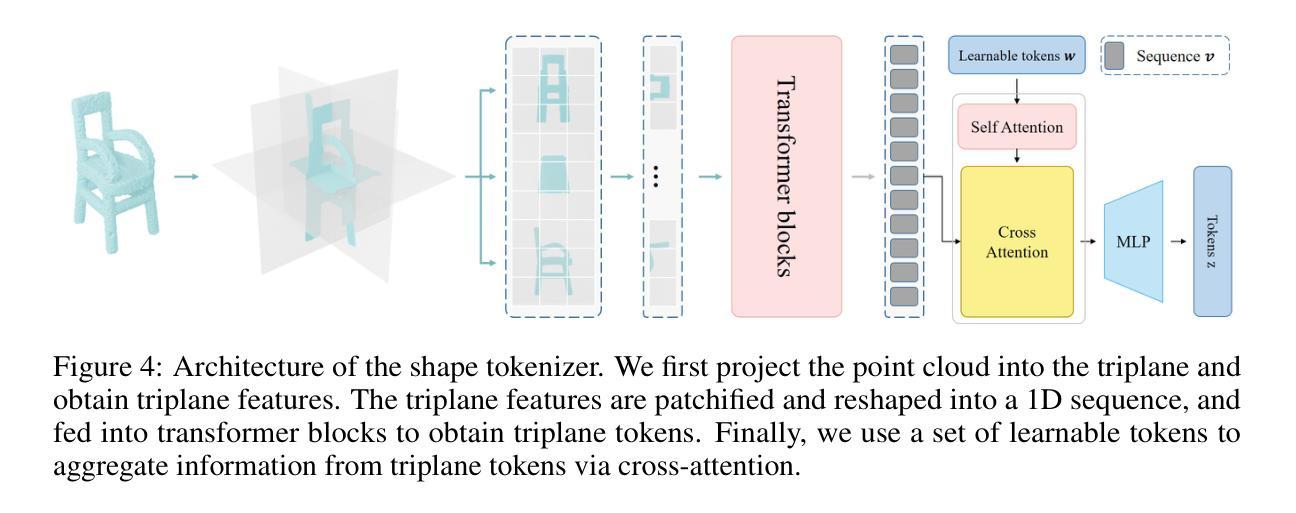
MeshCoder: LLM-Powered Structured Mesh Code Generation from Point Clouds
Authors:Bingquan Dai, Li Ray Luo, Qihong Tang, Jie Wang, Xinyu Lian, Hao Xu, Minghan Qin, Xudong Xu, Bo Dai, Haoqian Wang, Zhaoyang Lyu, Jiangmiao Pang
Reconstructing 3D objects into editable programs is pivotal for applications like reverse engineering and shape editing. However, existing methods often rely on limited domain-specific languages (DSLs) and small-scale datasets, restricting their ability to model complex geometries and structures. To address these challenges, we introduce MeshCoder, a novel framework that reconstructs complex 3D objects from point clouds into editable Blender Python scripts. We develop a comprehensive set of expressive Blender Python APIs capable of synthesizing intricate geometries. Leveraging these APIs, we construct a large-scale paired object-code dataset, where the code for each object is decomposed into distinct semantic parts. Subsequently, we train a multimodal large language model (LLM) that translates 3D point cloud into executable Blender Python scripts. Our approach not only achieves superior performance in shape-to-code reconstruction tasks but also facilitates intuitive geometric and topological editing through convenient code modifications. Furthermore, our code-based representation enhances the reasoning capabilities of LLMs in 3D shape understanding tasks. Together, these contributions establish MeshCoder as a powerful and flexible solution for programmatic 3D shape reconstruction and understanding. The project homepage is available at \href{https://daibingquan.github.io/MeshCoder}{this link}.
将3D对象重建为可编辑的程序在逆向工程和形状编辑等应用中至关重要。然而,现有方法往往依赖于有限的特定领域语言(DSL)和小规模数据集,这限制了它们对复杂几何和结构的建模能力。为了应对这些挑战,我们推出了MeshCoder,这是一个新型框架,能够将复杂的3D对象从点云重建为可编辑的Blender Python脚本。我们开发了一套全面的、表达性强的Blender Python API,能够合成复杂的几何形状。利用这些API,我们构建了一个大规模的对象-代码配对数据集,其中每个对象的代码被分解成不同的语义部分。随后,我们训练了一种多模态大型语言模型(LLM),该模型能够将3D点云翻译成可执行的Blender Python脚本。我们的方法不仅在形状到代码的重建任务中实现了卓越的性能,而且通过方便的代码修改,促进了直观几何和拓扑编辑。此外,我们的基于代码的表示形式增强了LLM在3D形状理解任务中的推理能力。这些贡献共同确立了MeshCoder在程序化3D形状重建和理解方面的强大和灵活解决方案的地位。项目主页可在此链接查看。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
针对逆向工程和形状编辑等应用,MeshCoder框架实现了从点云重建复杂三维物体到可编辑的Blender Python脚本的创新技术。通过开发一套表达性强的Blender Python API,该框架能够合成精细几何结构,并建立大规模物体对象代码数据集。利用多模态大型语言模型(LLM),实现从点云到可执行Blender Python脚本的翻译。此方法不仅实现了形状到代码的优越重建性能,而且通过方便的代码修改促进了直观的几何和拓扑编辑。此外,基于代码的表达方式增强了LLM在三维形状理解任务中的推理能力。这些贡献使MeshCoder成为强大的可编程三维形状重建和理解解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- MeshCoder是一个从点云重建复杂三维物体的创新框架,输出为可编辑的Blender Python脚本。
- 通过开发一套表达性强的Blender Python API,实现了精细几何结构的合成。
- 建立了一个大规模物体对象代码数据集,数据集中物体的代码被分解为不同的语义部分。
- 利用多模态大型语言模型(LLM)实现从点云到可执行脚本的翻译。
- MeshCoder不仅实现了高效的形状到代码重建,还便于通过代码修改进行直观的几何和拓扑编辑。
- 基于代码的表达方式增强了LLM在三维形状理解任务中的推理能力。
- MeshCoder为三维形状重建和理解提供了一个强大且灵活的程序化解决方案。
点此查看论文截图
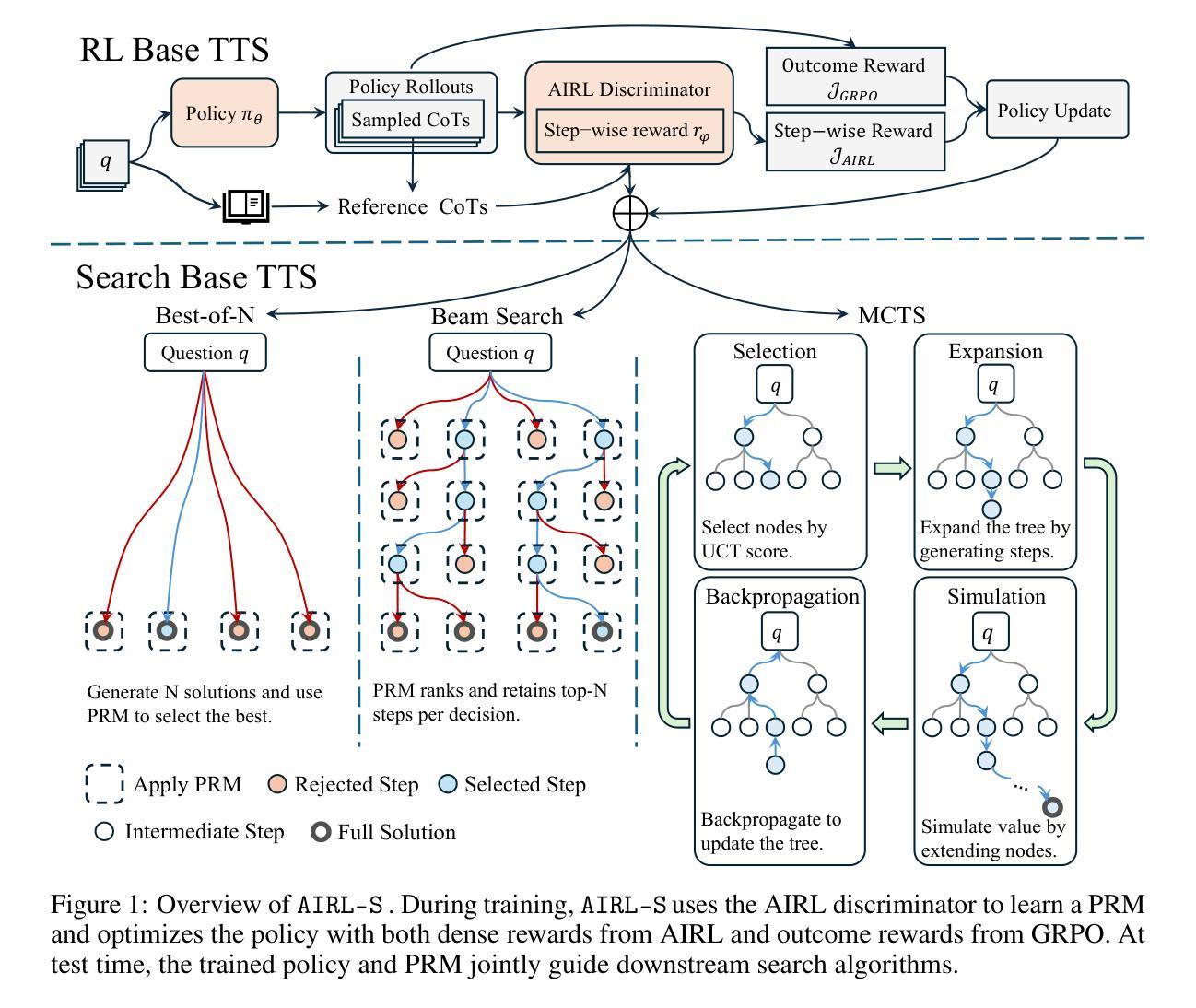
Your Reward Function for RL is Your Best PRM for Search: Unifying RL and Search-Based TTS
Authors:Can Jin, Yang Zhou, Qixin Zhang, Hongwu Peng, Di Zhang, Marco Pavone, Ligong Han, Zhang-Wei Hong, Tong Che, Dimitris N. Metaxas
Test-time scaling (TTS) for large language models (LLMs) has thus far fallen into two largely separate paradigms: (1) reinforcement learning (RL) methods that optimize sparse outcome-based rewards, yet suffer from instability and low sample efficiency; and (2) search-based techniques guided by independently trained, static process reward models (PRMs), which require expensive human- or LLM-generated labels and often degrade under distribution shifts. In this paper, we introduce AIRL-S, the first natural unification of RL-based and search-based TTS. Central to AIRL-S is the insight that the reward function learned during RL training inherently represents the ideal PRM for guiding downstream search. Specifically, we leverage adversarial inverse reinforcement learning (AIRL) combined with group relative policy optimization (GRPO) to learn a dense, dynamic PRM directly from correct reasoning traces, entirely eliminating the need for labeled intermediate process data. At inference, the resulting PRM simultaneously serves as the critic for RL rollouts and as a heuristic to effectively guide search procedures, facilitating robust reasoning chain extension, mitigating reward hacking, and enhancing cross-task generalization. Experimental results across eight benchmarks, including mathematics, scientific reasoning, and code generation, demonstrate that our unified approach improves performance by 9 % on average over the base model, matching GPT-4o. Furthermore, when integrated into multiple search algorithms, our PRM consistently outperforms all baseline PRMs trained with labeled data. These results underscore that, indeed, your reward function for RL is your best PRM for search, providing a robust and cost-effective solution to complex reasoning tasks in LLMs.
测试时缩放(TTS)对于大型语言模型(LLM)迄今为止主要分为两种截然不同的范式:(1)优化基于稀疏结果的奖励的强化学习(RL)方法,尽管存在不稳定性和低样本效率的问题;(2)由独立训练的静态过程奖励模型(PRM)引导的的搜索技术,这需要昂贵的人或LLM生成的标签,并且在分布变化的情况下经常会退化。在本文中,我们介绍了AIRL-S,这是基于RL和搜索的TTS的首个自然统一。AIRL-S的核心见解是,在RL训练期间学习的奖励函数本质上代表了用于指导下游搜索的理想PRM。具体来说,我们利用对抗性逆向强化学习(AIRL)结合群体相对策略优化(GRPO),直接从正确的推理轨迹中学习密集、动态的PRM,从而完全消除了对标记的中间过程数据的需求。在推理时,所得的PRM同时作为RL演练的评判标准和有效指导搜索程序的启发式方法,促进稳健的推理链扩展,缓解奖励破解,并增强跨任务泛化。在包括数学、科学推理和代码生成等在内的八个基准测试上的实验结果表明,我们的统一方法平均比基础模型提高了9%的性能,与GPT-4o相匹配。此外,当集成到多种搜索算法中时,我们的PRM始终优于使用标记数据训练的所有基线PRM。这些结果强调,实际上,您的RL奖励函数是您最佳的搜索PRM,为LLM中的复杂推理任务提供了稳健且经济的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种结合强化学习和搜索方法的测试时间缩放方法(AIRL-S),解决了大语言模型(LLM)面临的难题。传统强化学习方法稀疏奖励函数优化存在不稳定性和样本效率低下的问题,而基于搜索的方法需要独立训练的静态过程奖励模型指导,往往存在分布转移下降的情况。本文创新点在于引入了对抗逆强化学习(AIRL)和群体相对策略优化(GRPO),学习一个密集的动态过程奖励模型,直接从正确的推理轨迹中学习奖励函数,完全消除了对标记中间过程数据的需求。实验结果表明,该方法在多个基准测试中平均提高了9%的性能,并成功集成到多种搜索算法中,优于所有使用标记数据训练的基准过程奖励模型。这表明奖励函数是搜索的最佳过程奖励模型,为复杂推理任务提供了稳健且经济的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的测试时间缩放方法AIRL-S,结合了强化学习和搜索方法。
- 解决了传统强化学习方法的稳定性和样本效率问题以及基于搜索的方法依赖静态奖励模型的缺陷。
- 通过对抗逆强化学习(AIRL)和群体相对策略优化(GRPO)学习密集的动态过程奖励模型。
- 从正确的推理轨迹中学习奖励函数,消除了对标记中间过程数据的需求。
- 实验结果显示在多个基准测试中性能提升显著。
- 成功集成到多种搜索算法中,并优于使用标记数据训练的基准过程奖励模型。
点此查看论文截图

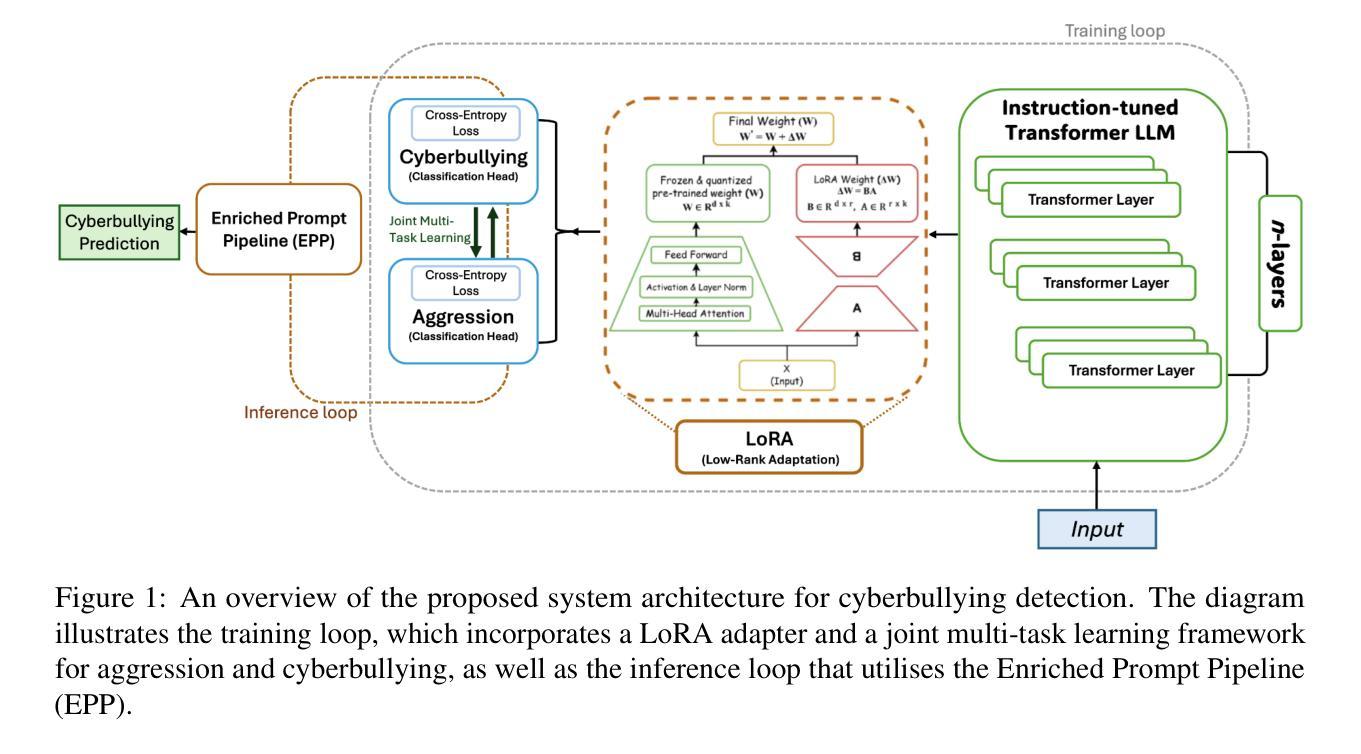
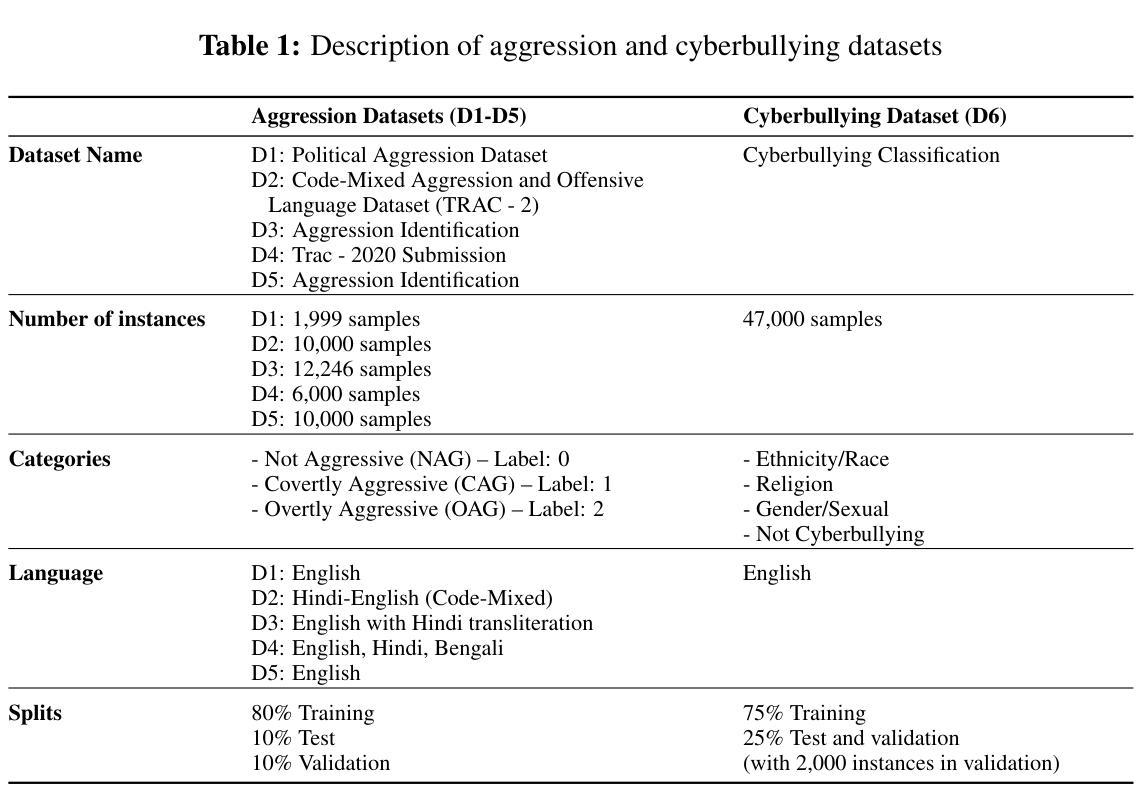
Cyberbullying Detection via Aggression-Enhanced Prompting
Authors:Aisha Saeid, Anu Sabu, Girish A. Koushik, Ferrante Neri, Diptesh Kanojia
Detecting cyberbullying on social media remains a critical challenge due to its subtle and varied expressions. This study investigates whether integrating aggression detection as an auxiliary task within a unified training framework can enhance the generalisation and performance of large language models (LLMs) in cyberbullying detection. Experiments are conducted on five aggression datasets and one cyberbullying dataset using instruction-tuned LLMs. We evaluated multiple strategies: zero-shot, few-shot, independent LoRA fine-tuning, and multi-task learning (MTL). Given the inconsistent results of MTL, we propose an enriched prompt pipeline approach in which aggression predictions are embedded into cyberbullying detection prompts to provide contextual augmentation. Preliminary results show that the enriched prompt pipeline consistently outperforms standard LoRA fine-tuning, indicating that aggression-informed context significantly boosts cyberbullying detection. This study highlights the potential of auxiliary tasks, such as aggression detection, to improve the generalisation of LLMs for safety-critical applications on social networks.
检测社交媒体上的网络欺凌仍然是一个关键挑战,因为网络欺凌的表达方式很微妙且多种多样。本研究旨在探究在统一训练框架内将攻击检测作为辅助任务整合,是否能提升大型语言模型(LLM)在网络欺凌检测中的通用性和性能。研究使用指令调整的大型语言模型对五个攻击数据集和一个网络欺凌数据集进行了实验。我们评估了多种策略:零样本、少样本、独立LoRA微调以及多任务学习(MTL)。鉴于多任务学习的结果不一致,我们提出了一种丰富的提示管道方法,其中攻击预测被嵌入到网络欺凌检测提示中以提供上下文增强。初步结果表明,丰富的提示管道始终优于标准的LoRA微调,这表明攻击检测提供的上下文信息可大大增强网络欺凌检测。本研究强调了辅助任务(如攻击检测)的潜力,可以改进LLM在社交网络安全关键应用的通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to RANLP 2025
Summary
社交媒体上的网络欺凌行为检测是一个重大挑战,因其表达方式多样且隐蔽。本研究探讨了在一个统一的训练框架内整合攻击检测作为辅助任务,是否能提高大型语言模型(LLM)在网络欺凌检测中的通用性和性能。实验采用五个攻击数据集和一个网络欺凌数据集,对LLM进行了指令调优。我们评估了零样本、少样本、独立LoRA微调以及多任务学习(MTL)等多种策略。鉴于MTL的不一致结果,我们提出了一种丰富的提示管道方法,其中攻击预测被嵌入到网络欺凌检测提示中以提供上下文增强。初步结果表明,丰富的提示管道始终优于标准的LoRA微调,表明攻击信息上下文对网络欺凌检测有显著改善。本研究强调了辅助任务(如攻击检测)在社交媒体安全关键应用中提高LLM通用性的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 网络欺凌行为在社交媒体上的检测具有挑战性,因其表达方式多样且隐蔽。
- 研究探索了在统一的训练框架内整合攻击检测作为辅助任务,以提高LLM在网络欺凌检测中的性能。
- 实验采用了多个数据集并对LLM进行了指令调优,评估了不同策略。
- 多任务学习的结果不一致,提出了一种丰富的提示管道方法,其中攻击预测作为上下文增强嵌入到网络欺凌检测提示中。
- 初步结果表明,丰富的提示管道方法优于标准微调方法。
- 攻击信息上下文对网络欺凌检测的改善有重要作用。
点此查看论文截图

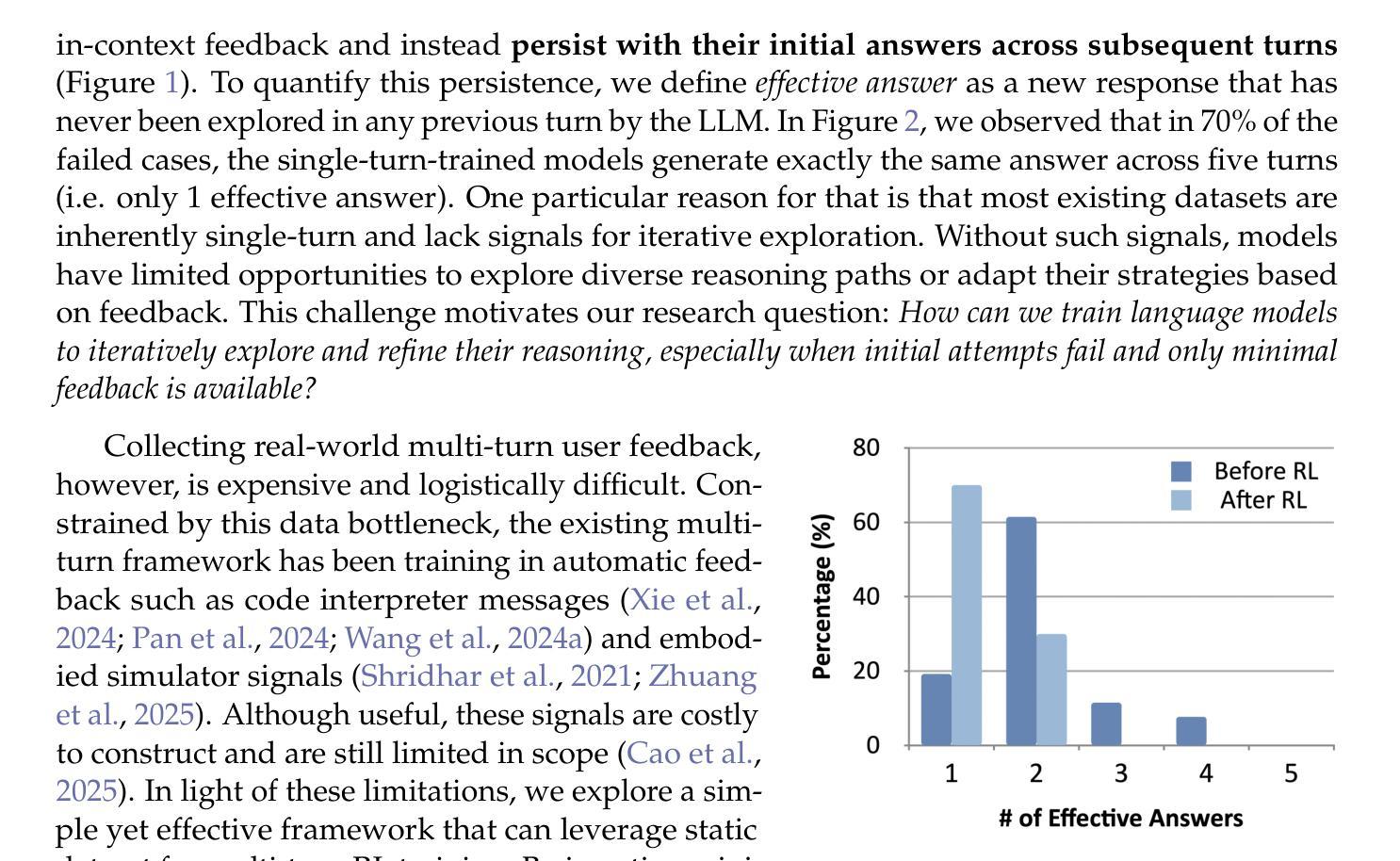
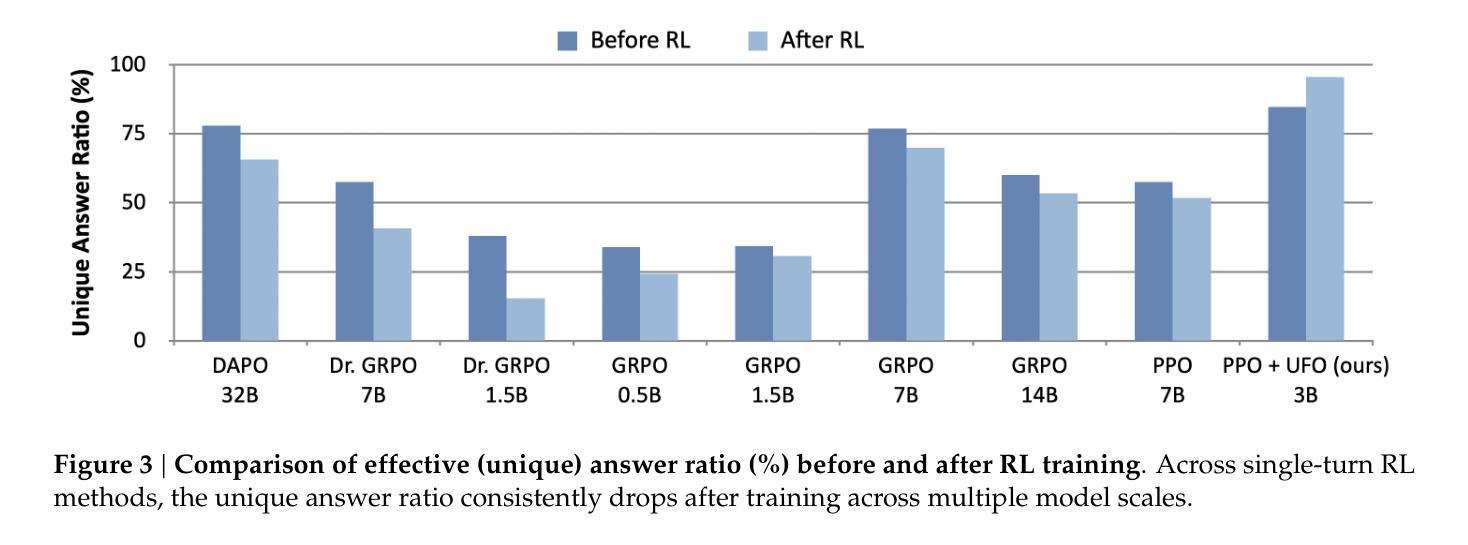
A Simple “Try Again” Can Elicit Multi-Turn LLM Reasoning
Authors:Licheng Liu, Zihan Wang, Linjie Li, Chenwei Xu, Yiping Lu, Han Liu, Avirup Sil, Manling Li
Multi-turn problem solving is critical yet challenging for Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) to reflect on their reasoning and revise from feedback. Existing Reinforcement Learning (RL) methods train large reasoning models on a single-turn paradigm with verifiable rewards. However, we observe that models trained with existing RL paradigms often lose their ability to solve problems across multiple turns and struggle to revise answers based on contextual feedback, leading to repetitive responses. We ask: can LRMs learn to reflect their answers in a multi-turn context? In this work, we find that training models with multi-turn RL using only unary feedback (e.g., “Let’s try again”) after wrong answers can improve both single-turn performance and multi-turn reasoning. We introduce Unary Feedback as Observation (UFO) for reinforcement learning, which uses minimal yet common unary user feedback during iterative problem solving. It can be easily applied to existing single-turn RL training setups. Experimental results show that RL training with UFO keeps single-turn performance and improves multi-turn reasoning accuracy by up to 14%, enabling language models to better react to feedback in multi-turn problem solving. To further minimize the number of turns needed for a correct answer while encouraging diverse reasoning when mistakes occur, we design reward structures that guide models to produce careful and deliberate answers in each turn. Code: https://github.com/lichengliu03/unary-feedback
多轮问题求解对于大型推理模型(LRM)来说是至关重要的,但也颇具挑战性,要求它们能够反思自己的推理并根据反馈进行修改。现有的强化学习(RL)方法是在单轮范式上训练大型推理模型,并辅以可验证的奖励。然而,我们观察到,采用现有RL范式训练的模型往往丧失了多轮问题求解的能力,并且在基于上下文反馈修正答案时遇到困难,导致重复响应。我们的问题是:LRM能否在多轮情境下学会反思自己的答案?在这项工作中,我们发现使用多轮强化学习训练模型,仅在错误答案后提供一元反馈(例如,“让我们再试一次”),可以提高单轮性能和多轮推理能力。我们为强化学习引入了作为观察的一元反馈(UFO),在迭代问题求解过程中使用最少但常见的一元用户反馈。它可以轻松应用于现有的单轮RL训练设置。实验结果表明,使用UFO的RL训练保持了单轮性能,并通过提高多轮推理准确性最多达14%,使语言模型能够在多轮问题求解中更好地应对反馈。为了尽量减少得到正确答案所需的轮数,并在出现错误时鼓励多样化的推理,我们设计了奖励结构,以引导模型在每轮中给出谨慎和慎重的答案。代码链接:https://github.com/lichengliu03/unary-feedback
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型推理模型(LRMs)在多轮问题解决中面临挑战,需要反思并基于反馈进行修订。现有强化学习(RL)方法主要基于单轮模式进行训练,虽然能验证奖励,但模型往往缺乏多轮问题解决的能力,难以根据上下文反馈修订答案,导致重复响应。本研究发现,通过多轮强化学习训练模型,仅利用错误答案后的一元反馈(如“再试一次”),即可提高单轮和多轮推理性能。本研究引入用于强化学习的一元反馈观测(UFO),在迭代问题解决过程中使用最小且常见的一元用户反馈。它可轻松应用于现有的单轮RL训练设置。实验结果显示,结合UFO的RL训练在保持单轮性能的同时,提高了多轮推理的准确性,最多可提高14%。为减少获得正确答案所需的轮次并在出错时鼓励多样化推理,我们设计了奖励结构,引导模型每轮给出谨慎和慎重的答案。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理模型(LRMs)在多轮问题解决中需要反思和修订能力。
- 现有强化学习(RL)方法主要基于单轮模式训练,导致模型缺乏多轮问题解决的能力。
- 通过多轮强化学习训练模型,利用一元反馈(如“再试一次”)可以提高单轮和多轮推理性能。
- 一元反馈观测(UFO)可轻松应用于现有单轮RL训练设置。
- UFO结合RL训练在保持单轮性能的同时,提高多轮推理准确性达14%。
- 为提高效率和多样化推理,设计了新的奖励结构。
- 该研究鼓励模型在每轮给出谨慎和慎重的答案。
点此查看论文截图


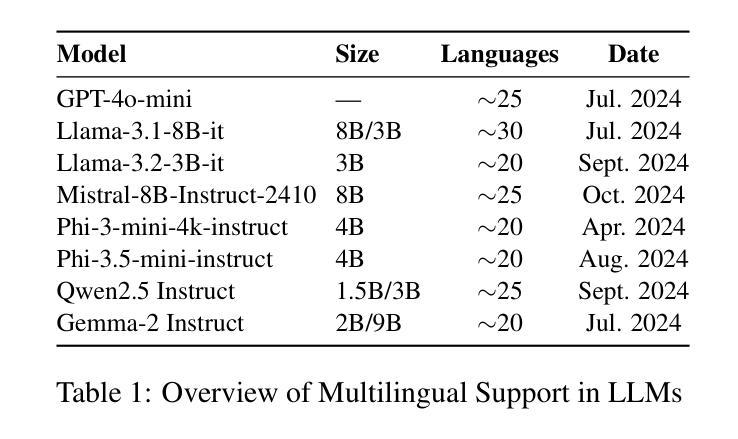
Is Small Language Model the Silver Bullet to Low-Resource Languages Machine Translation?
Authors:Yewei Song, Lujun Li, Cedric Lothritz, Saad Ezzini, Lama Sleem, Niccolo Gentile, Radu State, Tegawendé F. Bissyandé, Jacques Klein
Low-resource languages (LRLs) lack sufficient linguistic resources and are underrepresented in benchmark datasets, resulting in persistently lower translation quality than high-resource languages, especially in privacy-sensitive and resource-limited contexts. Firstly, this study systematically evaluates state-of-the-art smaller Large Language Models in 200 languages using the FLORES-200 benchmark, highlighting persistent deficiencies and disparities in the translation of LRLs. To mitigate these limitations, we investigate knowledge distillation from large pre-trained teacher models to Small Language Models (SLMs) through supervised fine-tuning. The results show substantial improvements; for example, the translation performance of English to Luxembourgish (EN to LB), measured by the LLM-as-a-Judge score, increases from 0.36 to 0.89 in the validation set for Llama-3.2-3B. We further investigate various fine-tuning configurations and tasks to clarify the trade-offs between data scale and training efficiency, verify that the model retains its general capabilities without significant catastrophic forgetting after training, and explore the distillation benefits to other LRLs on SLMs (Khasi, Assamese, and Ukrainian). In general, this work exposes the limitations and fairness issues of current SLMs in LRL translation and systematically explores the potential of using the distillation of knowledge from large to small models, offering practical, empirically grounded recommendations to improve LRL translation systems
低资源语言(LRLs)缺乏足够的语言资源,在基准数据集中的代表性不足,导致翻译质量持续低于高资源语言,尤其是在隐私敏感和资源有限的情境中尤为明显。首先,本研究使用FLORES-200基准数据集系统评估了200种语言的最新小型大型语言模型,突出了低资源语言翻译中的持续缺陷和差异。为了缓解这些限制,我们调查了通过有监督的微调从大型预训练教师模型向小型语言模型(SLM)进行知识蒸馏的方法。结果表明,在验证集上,英语到卢森堡语(EN到LB)的翻译性能得到了显著提高,以大型语言模型作为评判者的分数从0.36提高到0.89(以Llama-3.2-3B为例)。我们还进一步研究了各种微调配置和任务,以明确数据规模和训练效率之间的权衡,验证模型在训练后是否保持其一般能力而没有显著的灾难性遗忘,并探索了对其他低资源语言(如卡塔克语、阿萨姆语和乌克兰语)的小型语言模型上的蒸馏好处。总的来说,这项工作揭示了当前低资源语言翻译中小型语言模型的局限性和公平性问题,并系统地探索了从大型模型到小型模型进行知识蒸馏的潜力,为改进低资源语言翻译系统提供了实用且基于实证的建议。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本研究评估了小型语言模型在多种低资源语言(LRLs)上的翻译性能,并指出其在隐私敏感和资源受限环境中的持续问题。为了克服这些局限,该研究尝试从大型预训练教师模型通过知识蒸馏技术对小型语言模型(SLM)进行微调来提升翻译性能。研究发现这种方法可以显著改善翻译性能,比如在英语到卢森堡语的翻译中,LLM评分从0.36提高到0.89。此外,该研究还探讨了不同微调配置和任务之间的权衡,验证了模型在训练后不会丧失其通用能力,并探索了其他低资源语言(如卡奇语、阿萨姆语和乌克兰语)的小型语言模型的蒸馏效益。这项研究为改进低资源语言的翻译系统提供了实用的经验依据。
Key Takeaways:
- 低资源语言在基准数据集上缺乏足够的语言资源,导致翻译质量持续低于高资源语言。
- 研究采用FLORES-200基准对最新小型语言模型进行200种语言的系统评估。
- 知识蒸馏技术用于通过大型预训练教师模型提高小型语言模型的翻译性能。
- 知识蒸馏显著提高翻译性能,例如在英语到卢森堡语的翻译中LLM评分显著提高。
- 研究探讨了不同微调配置和任务之间的权衡,验证了模型的通用能力和防止灾难性遗忘的能力。
- 研究还探索了其他低资源语言的小型语言模型的蒸馏效益。
点此查看论文截图

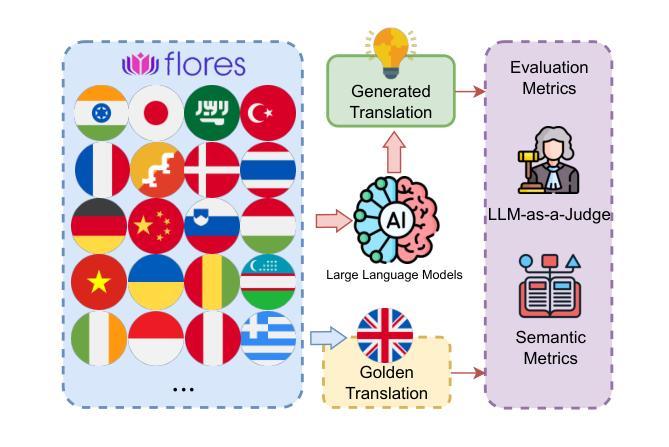

Can Large Language Models Simulate Human Responses? A Case Study of Stated Preference Experiments in the Context of Heating-related Choices
Authors:Han Wang, Jacek Pawlak, Aruna Sivakumar
Stated preference (SP) surveys are a key method to research how individuals make trade-offs in hypothetical, also futuristic, scenarios. In energy context this includes key decarbonisation enablement contexts, such as low-carbon technologies, distributed renewable energy generation, and demand-side response [1,2]. However, they tend to be costly, time-consuming, and can be affected by respondent fatigue and ethical constraints. Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating human-like textual responses, prompting growing interest in their application to survey research. This study investigates the use of LLMs to simulate consumer choices in energy-related SP surveys and explores their integration into data analysis workflows. A series of test scenarios were designed to systematically assess the simulation performance of several LLMs (LLaMA 3.1, Mistral, GPT-3.5 and DeepSeek-R1) at both individual and aggregated levels, considering contexts factors such as prompt design, in-context learning (ICL), chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, LLM types, integration with traditional choice models, and potential biases. Cloud-based LLMs do not consistently outperform smaller local models. In this study, the reasoning model DeepSeek-R1 achieves the highest average accuracy (77%) and outperforms non-reasoning LLMs in accuracy, factor identification, and choice distribution alignment. Across models, systematic biases are observed against the gas boiler and no-retrofit options, with a preference for more energy-efficient alternatives. The findings suggest that previous SP choices are the most effective input factor, while longer prompts with additional factors and varied formats can cause LLMs to lose focus, reducing accuracy.
陈述偏好(SP)调查是研究个体如何在假设的、未来的场景中做出权衡的关键方法。在能源领域,这包括关键的脱碳赋能环境,如低碳技术、分布式可再生能源发电和需求侧响应[1,2]。然而,它们往往成本高昂、耗费时间,并可能受到受访者疲劳和伦理约束的影响。大型语言模型(LLM)在生成类似人类的文本响应方面表现出令人瞩目的能力,促使人们对其应用于调查研究的兴趣日益浓厚。本研究探讨了使用LLM模拟能源相关SP调查中的消费者选择,并探讨了它们融入数据分析工作流程的方法。设计了一系列测试场景,以系统地评估几种LLM(LLaMA 3.1、Mistral、GPT-3.5和DeepSeek-R1)在个体和聚合层面的模拟性能,考虑上下文因素,如提示设计、上下文学习(ICL)、思维链(CoT)推理、LLM类型、与传统选择模型的集成以及潜在偏见。基于云的LLM并不总是优于较小的本地模型。在这项研究中,推理模型DeepSeek-R1达到了最高的平均准确率(77%),在准确率、因素识别和选择分布对齐方面优于非推理LLM。在所有模型中,都存在对燃气锅炉和无改造选择的系统性偏见,更倾向于选择更节能的替代方案。研究结果表明,先前的SP选择是最有效的输入因素,而较长的提示和带有额外因素和不同格式的提示可能会使LLM失去焦点,降低准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)在模拟消费者能源相关偏好选择中的应用,本文探讨了利用LLM进行假设偏好调查的新方法。研究对比了不同LLM在不同情境下的模拟性能,包括DeepSeek-R1在内的多种模型在模拟消费者选择方面展现出较高准确性。研究还发现,之前的选择偏好是最有效的输入因素,而更长的提示与多样化的格式可能会影响LLM的精确度。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)可用于模拟能源相关的消费者偏好选择。
- LLM在模拟消费者选择方面展现出高准确性,其中DeepSeek-R1模型表现最佳,平均准确度达到77%。
- 相较于非推理LLM,推理LLM在准确性、因素识别和选择分布对齐方面表现更优。
- 在模型中存在对能源效率更高选项的偏好和对燃气锅炉以及无改造选项的系统性偏见。
- 之前的选择偏好是模拟消费者决策中最有效的输入因素。
- 更长的提示和多样化的格式可能会影响LLM的精确度。
点此查看论文截图

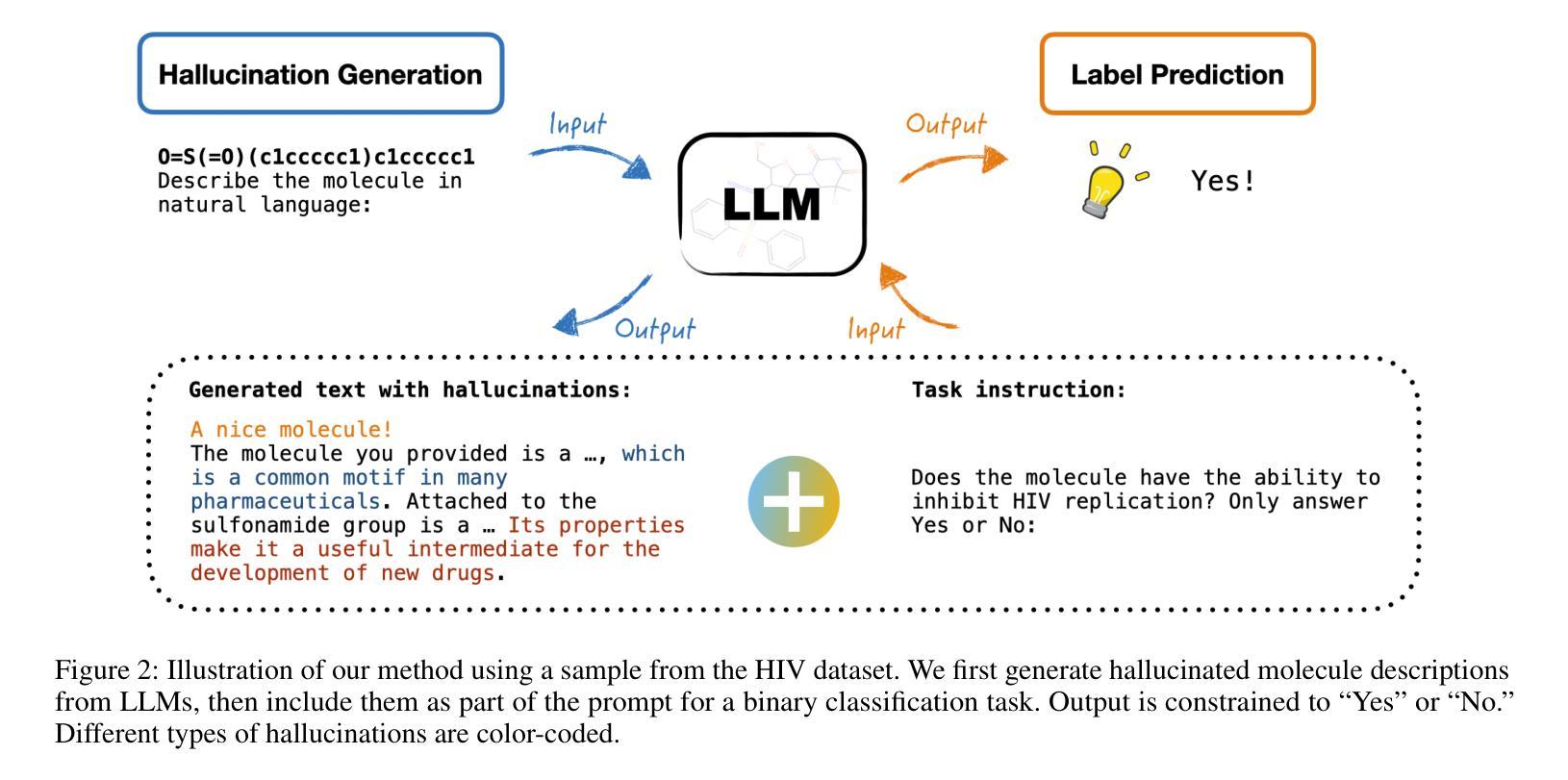
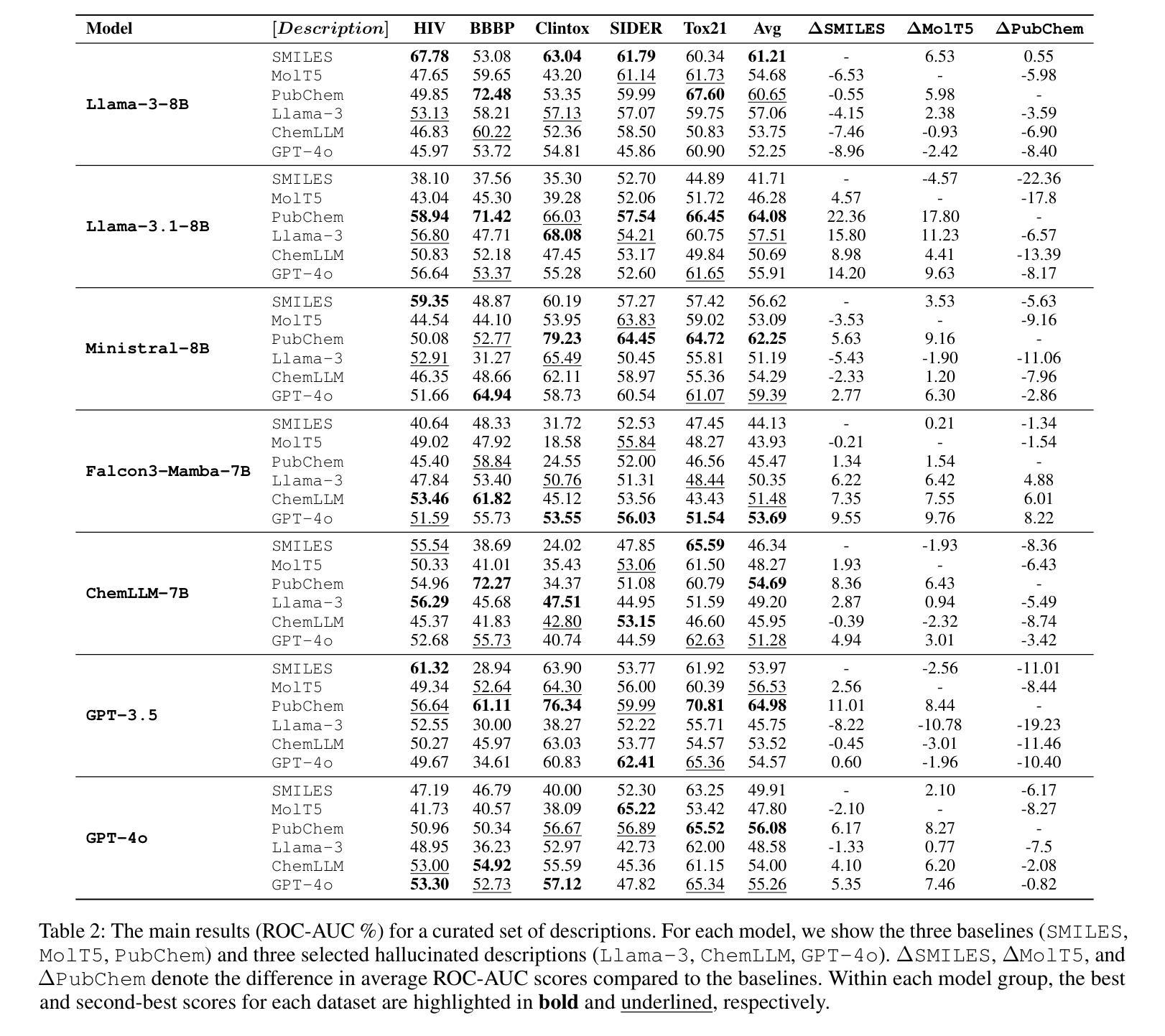
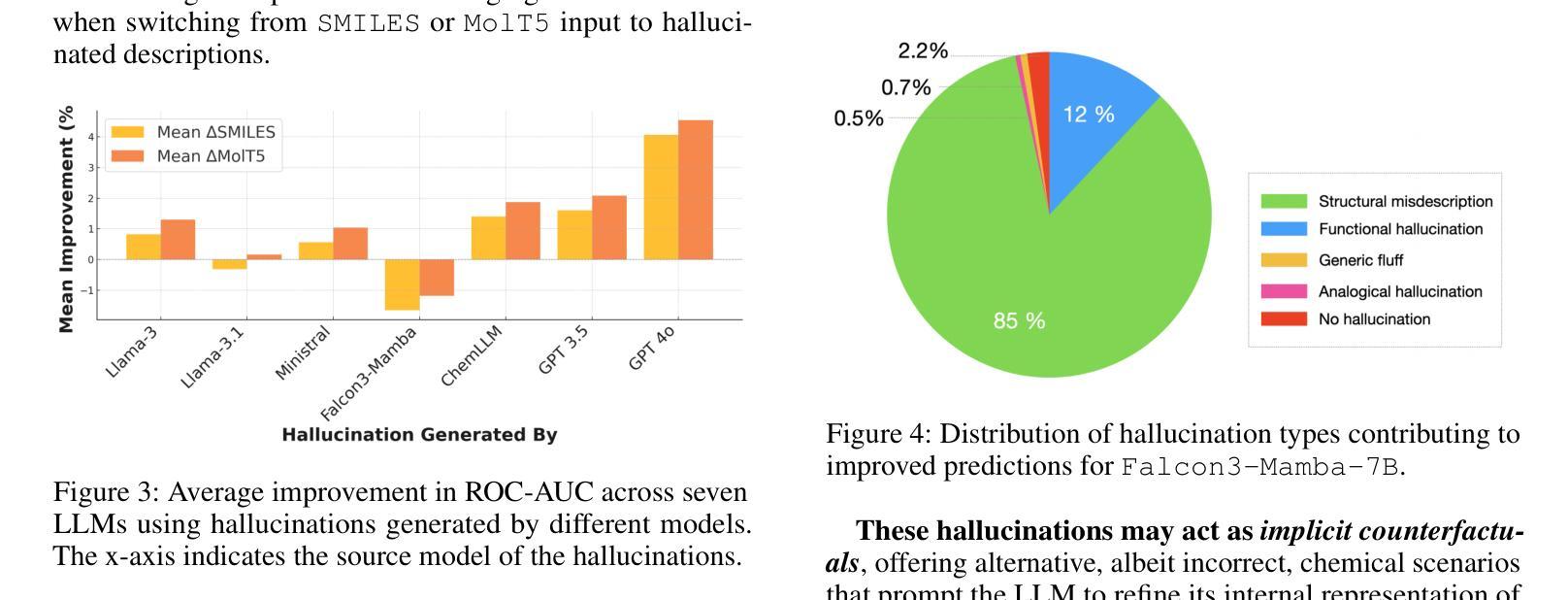
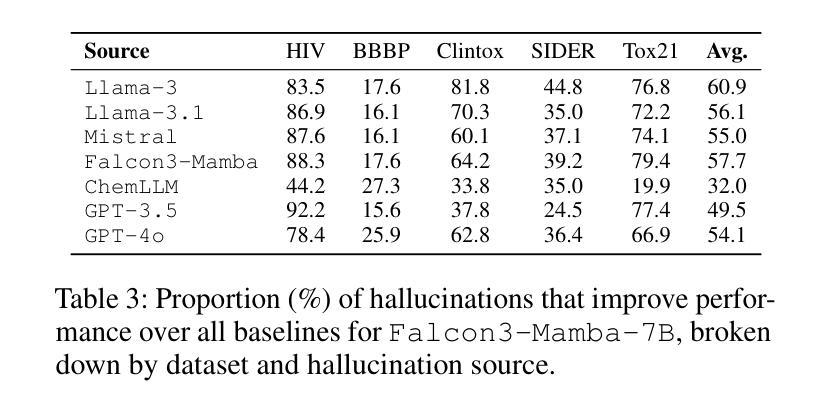
Can Hallucinations Help? Boosting LLMs for Drug Discovery
Authors:Shuzhou Yuan, Zhan Qu, Ashish Yashwanth Kangen, Michael Färber
Hallucinations in large language models (LLMs), plausible but factually inaccurate text, are often viewed as undesirable. However, recent work suggests that such outputs may hold creative potential. In this paper, we investigate whether hallucinations can improve LLMs on molecule property prediction, a key task in early-stage drug discovery. We prompt LLMs to generate natural language descriptions from molecular SMILES strings and incorporate these often hallucinated descriptions into downstream classification tasks. Evaluating seven instruction-tuned LLMs across five datasets, we find that hallucinations significantly improve predictive accuracy for some models. Notably, Falcon3-Mamba-7B outperforms all baselines when hallucinated text is included, while hallucinations generated by GPT-4o consistently yield the greatest gains between models. We further identify and categorize over 18,000 beneficial hallucinations, with structural misdescriptions emerging as the most impactful type, suggesting that hallucinated statements about molecular structure may increase model confidence. Ablation studies show that larger models benefit more from hallucinations, while temperature has a limited effect. Our findings challenge conventional views of hallucination as purely problematic and suggest new directions for leveraging hallucinations as a useful signal in scientific modeling tasks like drug discovery.
大型语言模型(LLM)中的幻觉,即看似合理但事实上不准确的文本,通常被视为不受欢迎。然而,最近的研究表明,这样的输出可能具有创造性潜力。在本文中,我们调查了幻觉是否可以提高LLM在分子属性预测方面的表现,这是早期药物发现中的一项关键任务。我们引导LLM根据分子的SMILES字符串生成自然语言描述,并将这些通常带有幻觉的描述纳入下游分类任务。在五个数据集上评估了七个指令调整过的LLM,我们发现幻觉显著提高了某些模型的预测精度。值得注意的是,当包含幻觉文本时,Falcon3-Mamba-7B超越了所有基线,而GPT-4o产生的幻觉始终在模型之间产生了最大的收益。我们进一步识别和分类了18000多个有益幻觉,结构上的错误描述是最有影响的一类,这表明关于分子结构的幻觉陈述可能会增加模型的信心。消融研究表明,较大的模型从幻觉中获益更多,而温度的影响有限。我们的研究结果挑战了幻觉仅被视为问题的传统观点,并为利用幻觉作为科学建模任务(如药物发现)中的有用信号提供了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型中的幻觉文本(hallucinations)虽然可能不准确,但近期研究表明其具备创造性潜力。本研究探讨了幻觉文本在预测分子属性方面的作用,这是早期药物发现中的关键任务。通过引导大型语言模型生成分子SMILES字符串的自然语言描述,并将其纳入下游分类任务中,研究发现幻觉文本对部分模型的预测准确性有显著改善。尤其是Falcon3-Mamba-7B模型在包含幻觉文本时表现最佳,而GPT-4o产生的幻觉文本在不同模型中始终带来最大收益。研究还识别和分类了超过18,000种有益幻觉,其中结构误描述影响最为显著,表明关于分子结构的幻觉陈述可能增加模型信心。研究还发现更大的模型更能从幻觉中受益,而温度对幻觉的影响有限。该研究挑战了幻觉仅被视为问题的传统观点,并为在药物发现等科学建模任务中利用幻觉作为有用信号提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型中的幻觉文本具备创造性潜力。
- 幻觉文本在预测分子属性方面对部分模型有显著改善。
- Falcon3-Mamba-7B模型在包含幻觉文本时表现最佳。
- GPT-4o产生的幻觉文本在不同模型中带来最大收益。
- 结构误描述的幻觉对模型预测的影响最为显著。
- 更大的模型更能从幻觉中受益。
点此查看论文截图