⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-08-26 更新
Cross-Modal Prototype Augmentation and Dual-Grained Prompt Learning for Social Media Popularity Prediction
Authors:Ao Zhou, Mingsheng Tu, Luping Wang, Tenghao Sun, Zifeng Cheng, Yafeng Yin, Zhiwei Jiang, Qing Gu
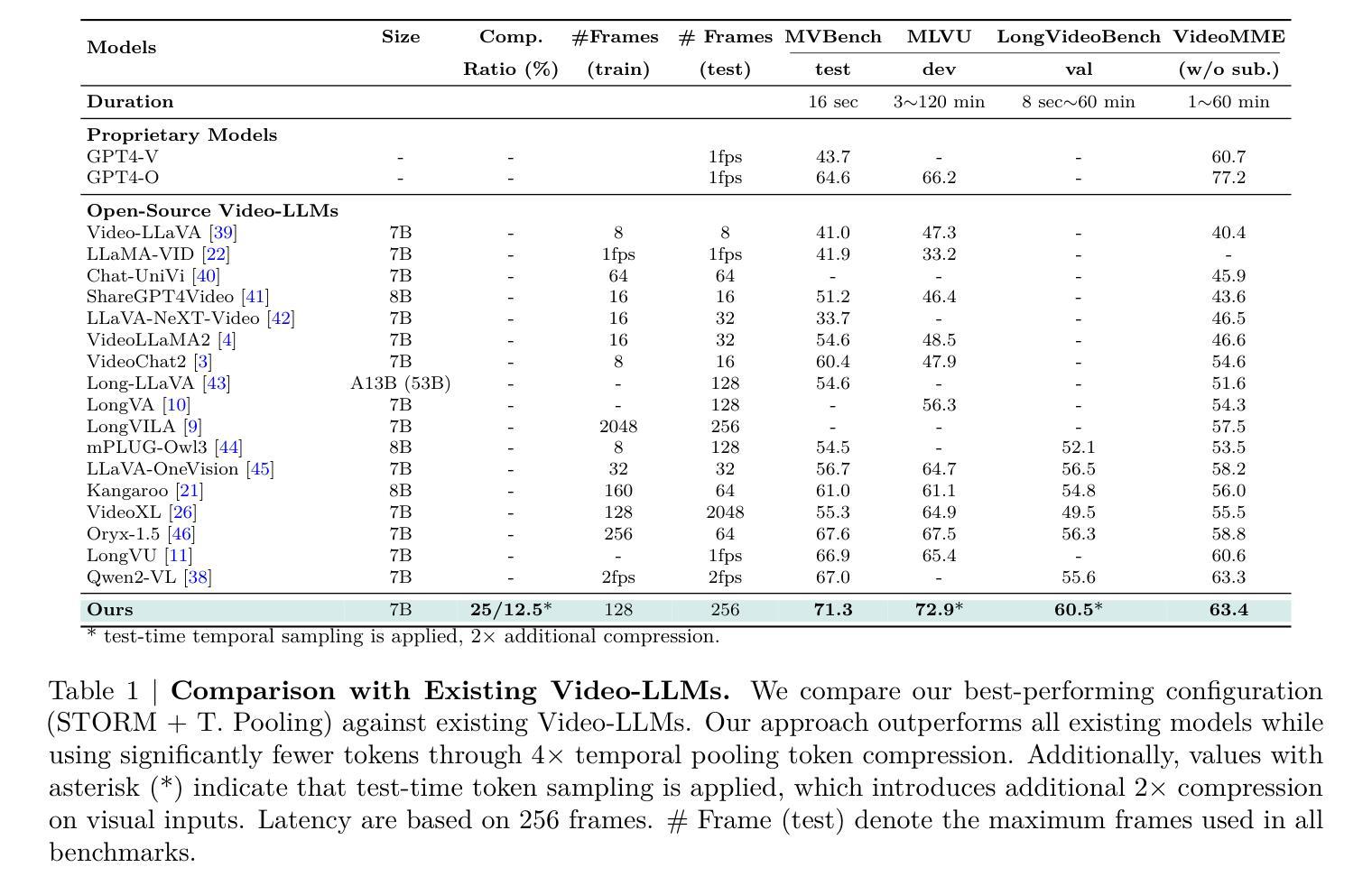
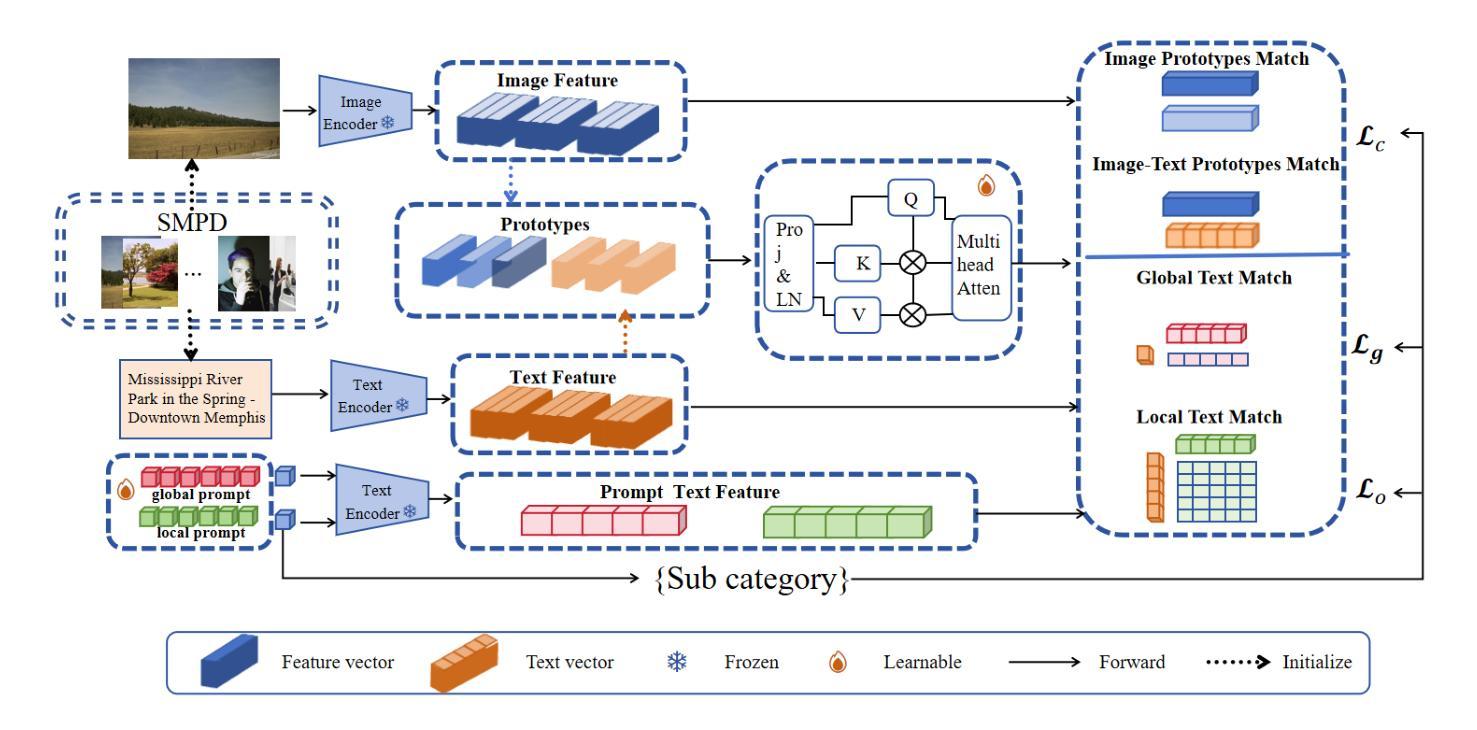
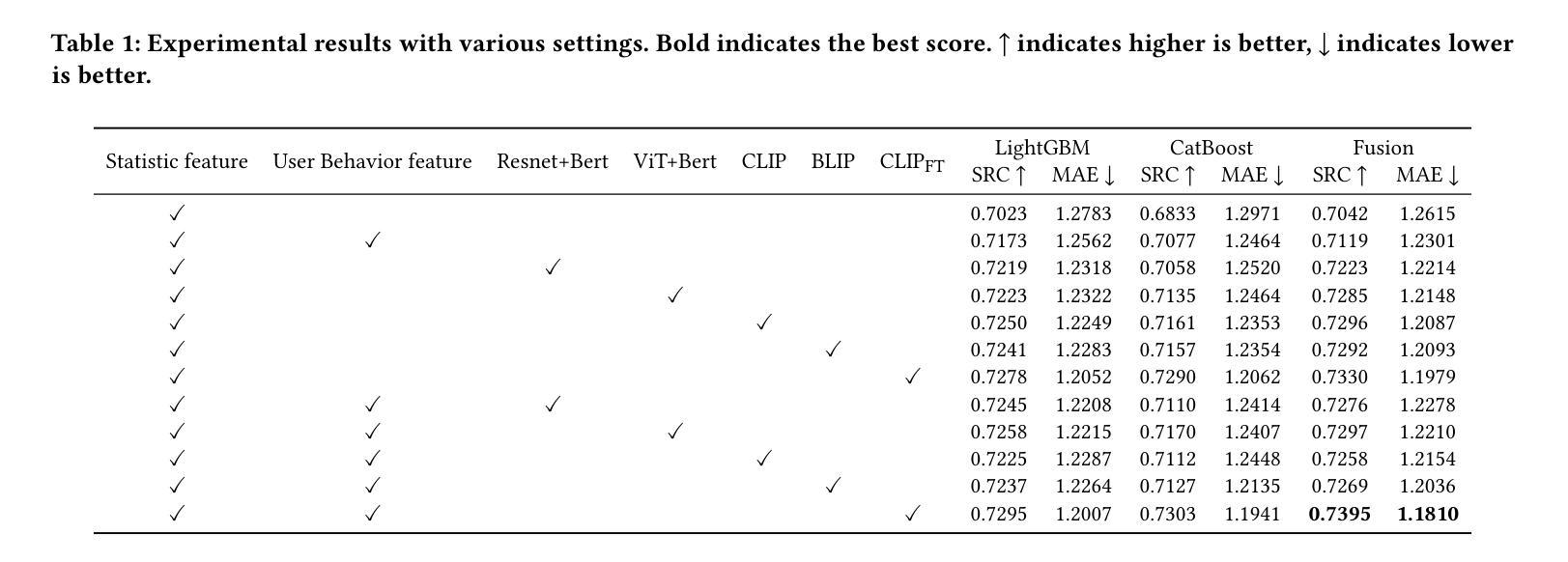
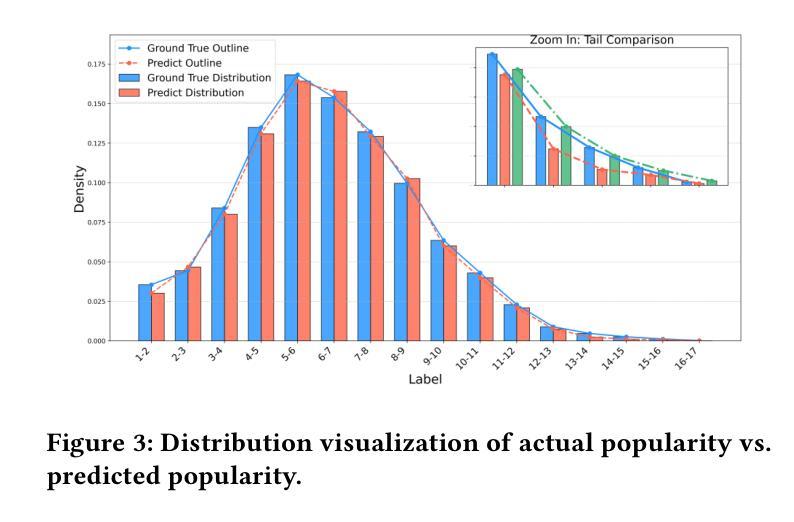
Social Media Popularity Prediction is a complex multimodal task that requires effective integration of images, text, and structured information. However, current approaches suffer from inadequate visual-textual alignment and fail to capture the inherent cross-content correlations and hierarchical patterns in social media data. To overcome these limitations, we establish a multi-class framework , introducing hierarchical prototypes for structural enhancement and contrastive learning for improved vision-text alignment. Furthermore, we propose a feature-enhanced framework integrating dual-grained prompt learning and cross-modal attention mechanisms, achieving precise multimodal representation through fine-grained category modeling. Experimental results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on benchmark metrics, establishing new reference standards for multimodal social media analysis.
社交媒体流行度预测是一项复杂的跨模态任务,需要有效地整合图像、文本和结构化信息。然而,当前的方法在视觉和文本对齐方面存在不足,无法捕捉社交媒体数据中固有的跨内容关联和层次模式。为了克服这些局限性,我们建立了多类框架,引入层次原型进行结构增强和对比学习,以改进视觉文本对齐。此外,我们提出了一个特征增强的框架,融合了双粒度提示学习和跨模态注意力机制,通过精细粒度的类别建模实现精确的多模态表示。实验结果表明,我们在基准指标上达到了最先进的性能,为跨模态社交媒体分析建立了新的参考标准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
社交媒体热度预测是一个复杂的跨模态任务,需要结合图像、文本和结构化信息。当前方法存在视觉与文本对齐不足的问题,无法捕捉社交媒体数据中的内在跨内容关联和层次模式。为解决这些问题,我们建立了多类框架,引入层次原型进行结构增强和对比学习以改进视觉文本对齐。同时,我们提出了一个特征增强的框架,融合了双粒度提示学习和跨模态注意力机制,通过精细粒度类别建模实现精确的多模态表示。实验结果表明,该方法在基准指标上达到了领先水平,为多媒体社交媒体分析建立了新的参考标准。
Key Takeaways
- 社交媒体热度预测是跨模态任务,需结合图像、文本和结构化信息。
- 当前方法存在视觉与文本对齐不足的问题。
- 引入层次原型进行结构增强和对比学习以改进视觉文本对齐。
- 提出特征增强的框架,融合双粒度提示学习和跨模态注意力机制。
- 通过精细粒度类别建模实现精确的多模态表示。
- 实验结果在基准指标上达到了领先水平。
点此查看论文截图


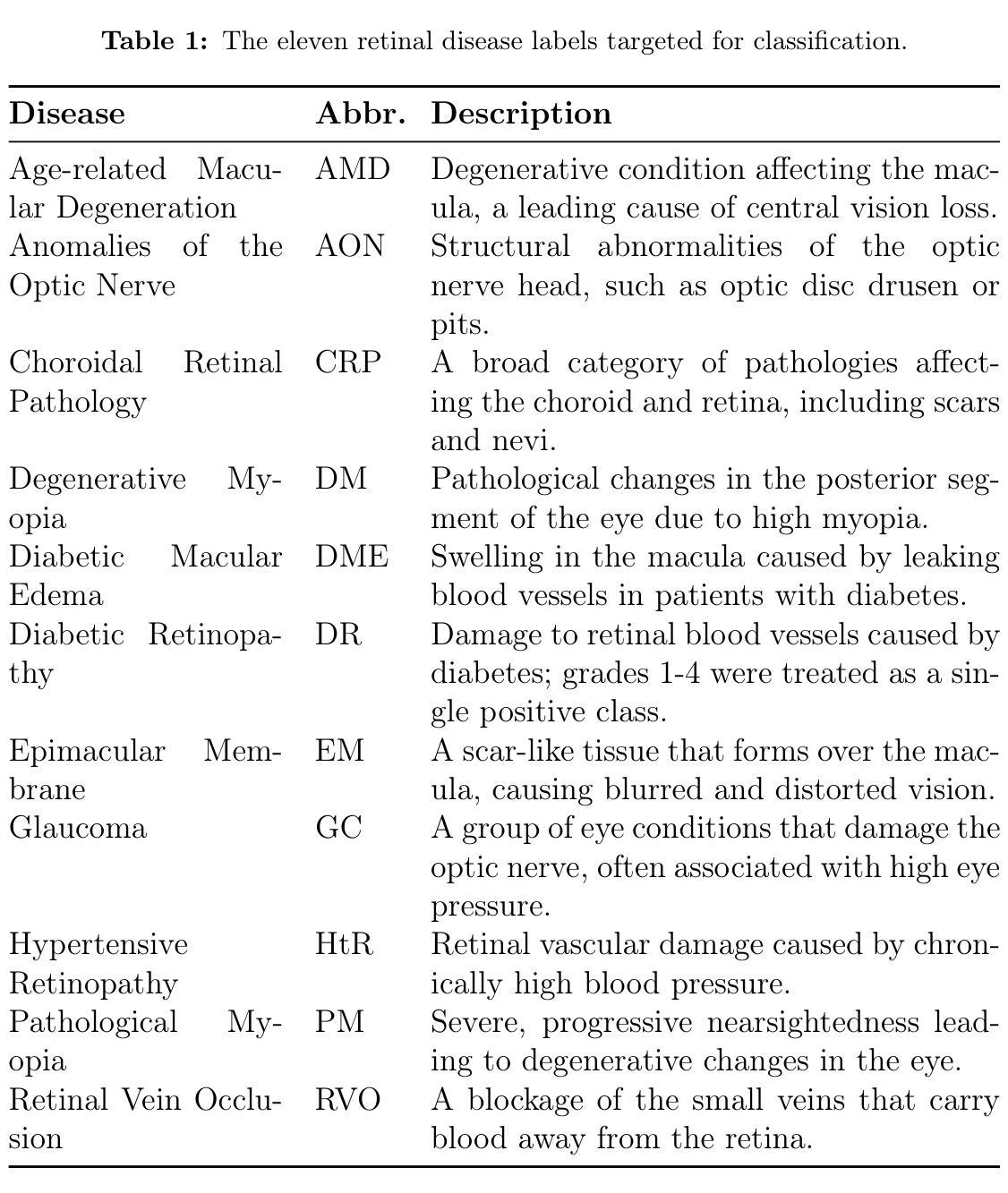
Automated Multi-label Classification of Eleven Retinal Diseases: A Benchmark of Modern Architectures and a Meta-Ensemble on a Large Synthetic Dataset
Authors:Jerry Cao-Xue, Tien Comlekoglu, Keyi Xue, Guanliang Wang, Jiang Li, Gordon Laurie
The development of multi-label deep learning models for retinal disease classification is often hindered by the scarcity of large, expertly annotated clinical datasets due to patient privacy concerns and high costs. The recent release of SynFundus-1M, a high-fidelity synthetic dataset with over one million fundus images, presents a novel opportunity to overcome these barriers. To establish a foundational performance benchmark for this new resource, we developed an end-to-end deep learning pipeline, training six modern architectures (ConvNeXtV2, SwinV2, ViT, ResNet, EfficientNetV2, and the RETFound foundation model) to classify eleven retinal diseases using a 5-fold multi-label stratified cross-validation strategy. We further developed a meta-ensemble model by stacking the out-of-fold predictions with an XGBoost classifier. Our final ensemble model achieved the highest performance on the internal validation set, with a macro-average Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC) of 0.9973. Critically, the models demonstrated strong generalization to three diverse, real-world clinical datasets, achieving an AUC of 0.7972 on a combined DR dataset, an AUC of 0.9126 on the AIROGS glaucoma dataset and a macro-AUC of 0.8800 on the multi-label RFMiD dataset. This work provides a robust baseline for future research on large-scale synthetic datasets and establishes that models trained exclusively on synthetic data can accurately classify multiple pathologies and generalize effectively to real clinical images, offering a viable pathway to accelerate the development of comprehensive AI systems in ophthalmology.
视网膜疾病分类的多标签深度学习模型的发展常常因缺乏大规模的专业标注临床数据集而受到阻碍,这主要是由于患者隐私担忧和成本高昂。最近发布的SynFundus-1M,一个高保真度的合成数据集,包含超过一百万张眼底图像,为解决这些障碍提供了新的机会。为了为这个新资源建立基础性能基准,我们开发了一个端到端的深度学习管道,训练了六种现代架构(ConvNeXtV2、SwinV2、ViT、ResNet、EfficientNetV2和RETFound基础模型)来使用5倍多标签分层交叉验证策略对十一种视网膜疾病进行分类。我们进一步通过堆叠跨折叠预测并使用XGBoost分类器开发了一个元集成模型。我们的最终集成模型在内部验证集上取得了最高性能,宏观平均接收器操作特性曲线下面积(AUC)为0.9973。重要的是,这些模型在三个不同的现实世界临床数据集上表现出了强大的泛化能力,在合并的糖尿病视网膜病变数据集上的AUC为0.7972,在AIROGS青光眼数据集上的AUC为0.9126,在多标签RFMiD数据集的宏观AUC为0.8800。这项工作为未来的大规模合成数据集研究提供了稳健的基线,并证明仅接受合成数据训练的模型可以准确地分类多种病理情况,并有效地泛化到真实临床图像,这为加速眼科综合人工智能系统的开发提供了可行的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages, 6 figures, 8 tables
摘要
视网膜疾病分类的多标签深度学习模型发展常受限于缺乏大量专业标注的临床数据集,原因在于患者隐私问题和成本高昂。SynFundus-1M这一高保真合成数据集的发布,为克服这些障碍提供了新的机会。为了建立这一新资源的基础性能基准,我们开发了一种端到端的深度学习管道,训练了六种现代架构(ConvNeXtV2、SwinV2、ViT、ResNet、EfficientNetV2和RETFound基础模型)以进行多标签分类的视网膜疾病。我们采用五折多标签分层交叉验证策略。通过堆叠出折预测与XGBoost分类器,我们进一步开发了元集成模型。最终集成模型在内部验证集上取得了最高性能,宏观平均受试者工作特征曲线下的面积(AUC)为0.9973。这些模型在三个不同的现实世界临床数据集上展现出强大的泛化能力,在组合糖尿病视网膜病变数据集上的AUC为0.7972,在AIROGS青光眼数据集上的AUC为0.9126,在多标签RFMiD数据集上的宏观AUC为0.8800。这项工作为未来的大规模合成数据集研究提供了稳健的基线,并证明了仅通过合成数据训练的模型能够准确分类多种病理学并有效地泛化到真实临床图像,这为加速眼科综合人工智能系统的开发提供了可行的途径。
关键见解
- 视网膜疾病分类的多标签深度学习模型发展受限,主要因为缺乏大规模、专业标注的临床数据集。
- SynFundus-1M数据集为高保真合成数据集,包含超过一百万张眼底图像,为解决这一难题提供了新的途径。
- 通过训练六种现代架构,建立了基于这一新资源的基础性能基准。
- 采用五折多标签分层交叉验证策略进行模型训练。
- 开发元集成模型以提高性能,通过堆叠出折预测与XGBoost分类器实现。
- 最终集成模型在内部验证集上取得高AUC值(宏观平均AUC为0.9973)。
点此查看论文截图

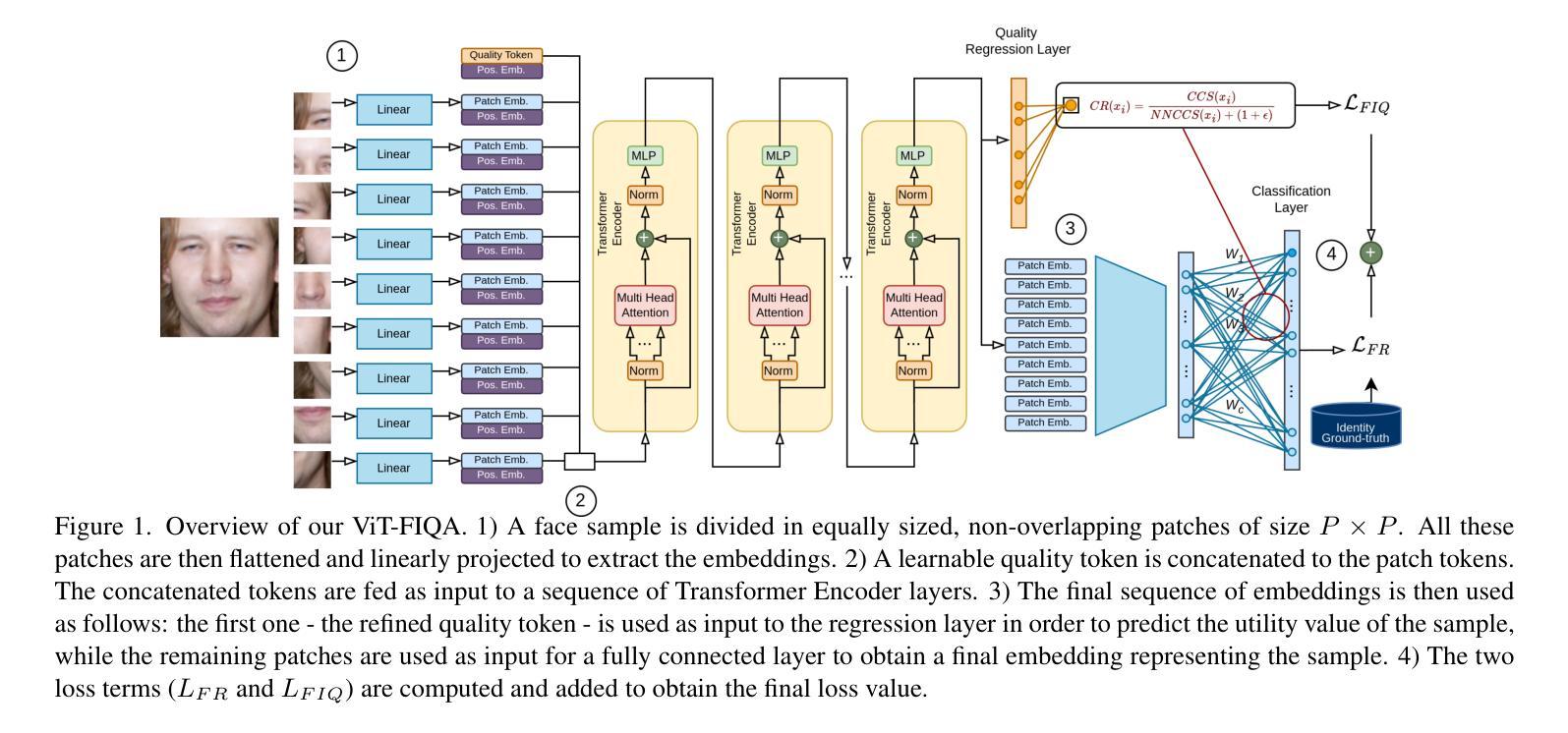
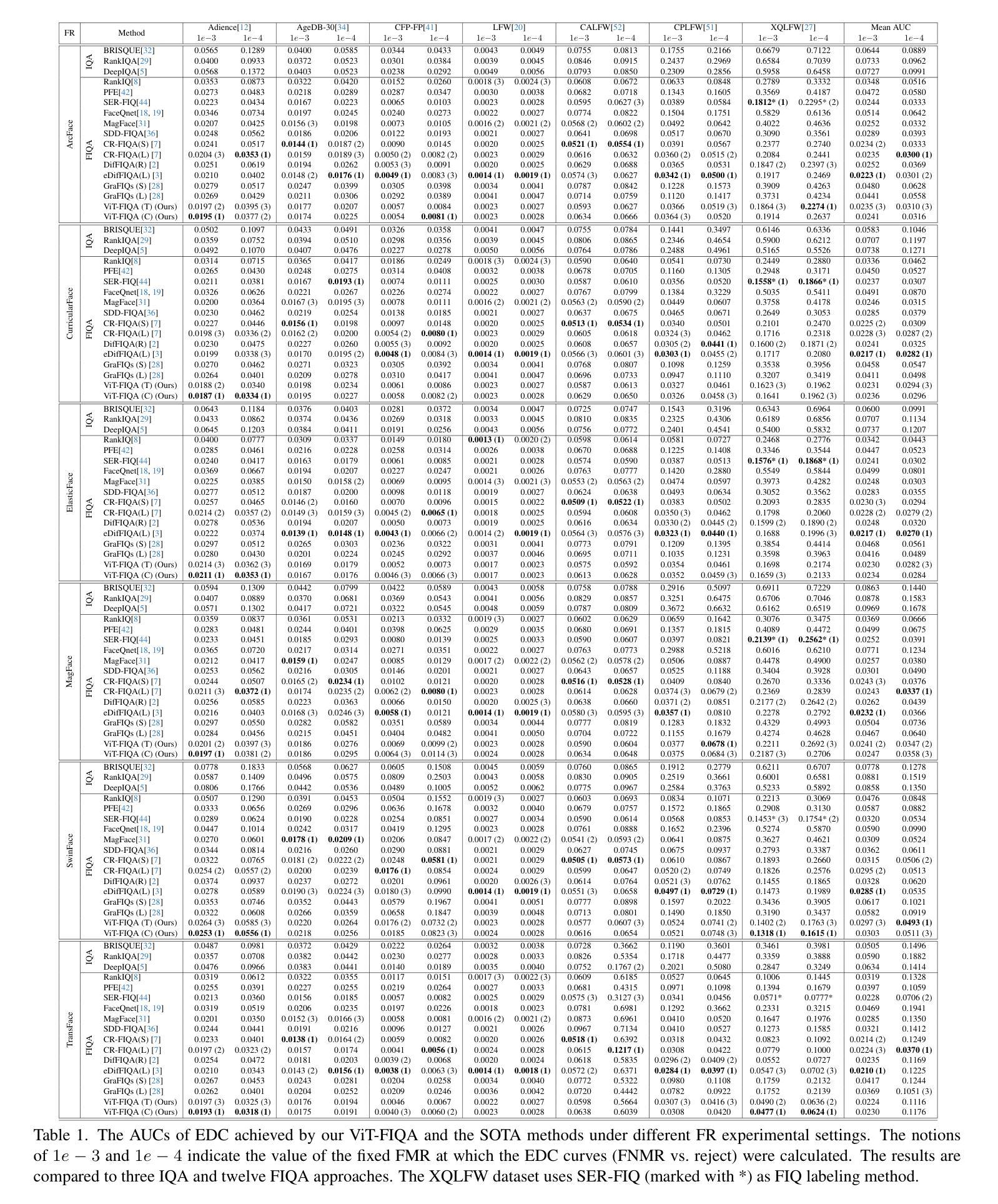
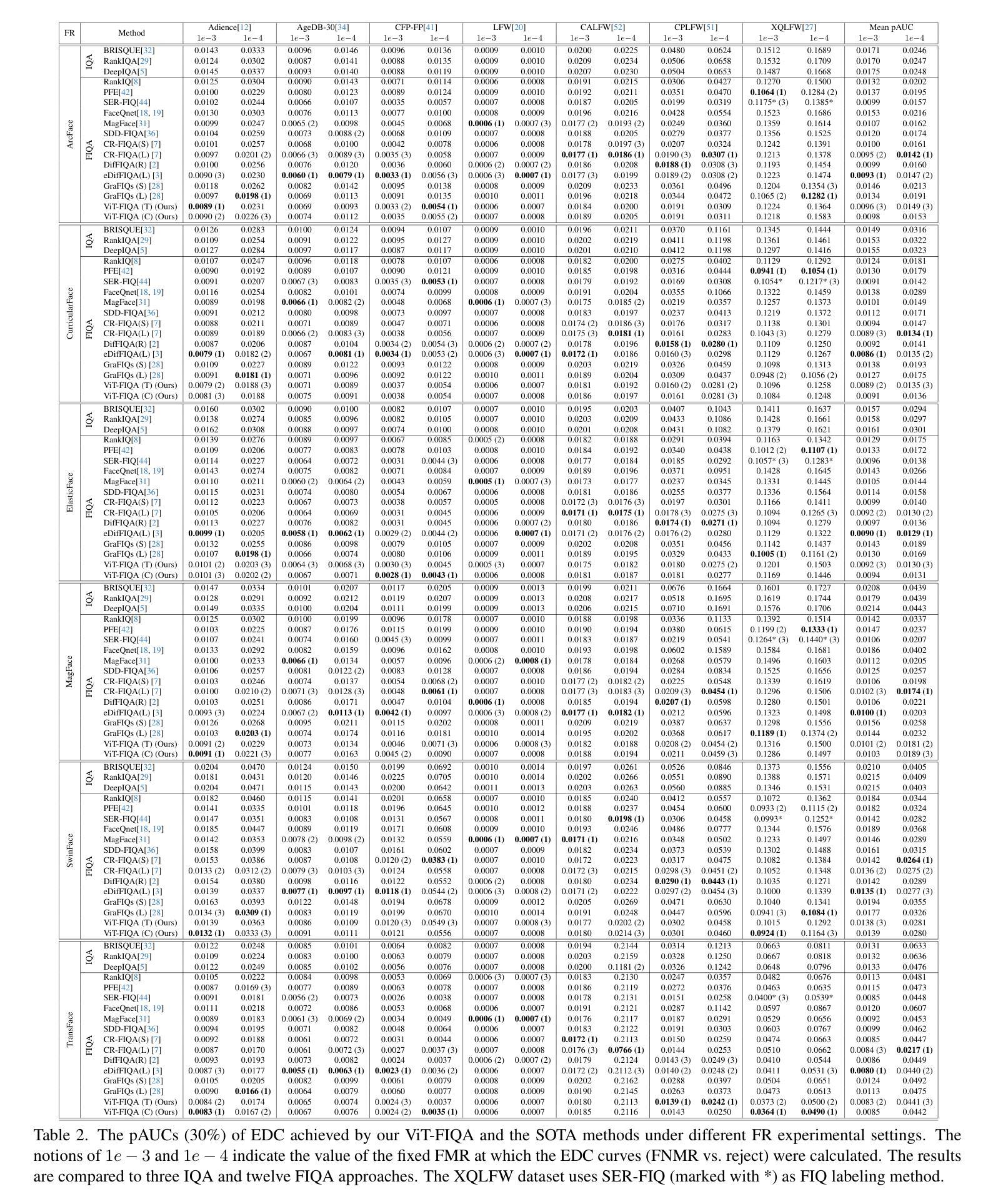
ViT-FIQA: Assessing Face Image Quality using Vision Transformers
Authors:Andrea Atzori, Fadi Boutros, Naser Damer
Face Image Quality Assessment (FIQA) aims to predict the utility of a face image for face recognition (FR) systems. State-of-the-art FIQA methods mainly rely on convolutional neural networks (CNNs), leaving the potential of Vision Transformer (ViT) architectures underexplored. This work proposes ViT-FIQA, a novel approach that extends standard ViT backbones, originally optimized for FR, through a learnable quality token designed to predict a scalar utility score for any given face image. The learnable quality token is concatenated with the standard image patch tokens, and the whole sequence is processed via global self-attention by the ViT encoders to aggregate contextual information across all patches. At the output of the backbone, ViT-FIQA branches into two heads: (1) the patch tokens are passed through a fully connected layer to learn discriminative face representations via a margin-penalty softmax loss, and (2) the quality token is fed into a regression head to learn to predict the face sample’s utility. Extensive experiments on challenging benchmarks and several FR models, including both CNN- and ViT-based architectures, demonstrate that ViT-FIQA consistently achieves top-tier performance. These results underscore the effectiveness of transformer-based architectures in modeling face image utility and highlight the potential of ViTs as a scalable foundation for future FIQA research https://cutt.ly/irHlzXUC.
面部图像质量评估(FIQA)旨在预测面部图像对人脸识别(FR)系统的实用性。最先进的FIQA方法主要依赖于卷积神经网络(CNN),而忽视了视觉变压器(ViT)架构的潜力。这项工作提出了ViT-FIQA,这是一种新方法,它通过扩展标准ViT骨干网络来评估给定面部图像的实用性,并通过设计可学习的质量令牌进行优化,最初是为人脸识别而优化的。这种可学习的质量令牌与标准的图像补丁令牌相连接,整个序列通过ViT编码器的全局自注意力机制来处理,以聚合所有补丁的上下文信息。在骨干网络的输出端,ViT-FIQA分为两个分支:(1)补丁令牌通过全连接层学习鉴别面部表示,通过带有边界惩罚的softmax损失;(2)质量令牌被送入回归头以学习预测面部样本的效用。在具有挑战性的基准测试和各种人脸识别模型上的广泛实验,包括基于CNN和ViT的架构,都证明了ViT-FIQA始终达到了顶尖的性能。这些结果证明了基于变换器的架构在建模面部图像效用方面的有效性,并突出了ViT作为未来FIQA研究的可扩展基础的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops 2025 (ICCVW 2025)
Summary
本文提出了ViT-FIQA,这是一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)架构的新方法,用于面部图像质量评估(FIQA)。它通过设计一个可学习的质量令牌来扩展标准的ViT骨干网,该令牌可以预测给定面部图像的效用得分。在多个具有挑战性的基准测试和一些面部识别(FR)模型上进行的广泛实验表明,ViT-FIQA在性能上达到了一流的水平。
Key Takeaways
- ViT-FIQA是基于Vision Transformer的新方法,旨在进行面部图像质量评估(FIQA)。
- 通过设计可学习的质量令牌来扩展ViT骨干网,以预测面部图像的效用得分。
- 该方法通过全局自注意力机制处理图像补丁令牌和质量令牌,以聚合所有补丁的上下文信息。
- ViT-FIQA有两个分支头:一个用于学习面部表示,另一个用于预测面部样本的效用。
- 广泛实验表明,ViT-FIQA在多个具有挑战性的基准测试中性能达到一流水平。
- 实验结果证明了基于变压器的架构在建模面部图像效用方面的有效性。
- 这项工作突出了Vision Transformer在未来FIQA研究中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

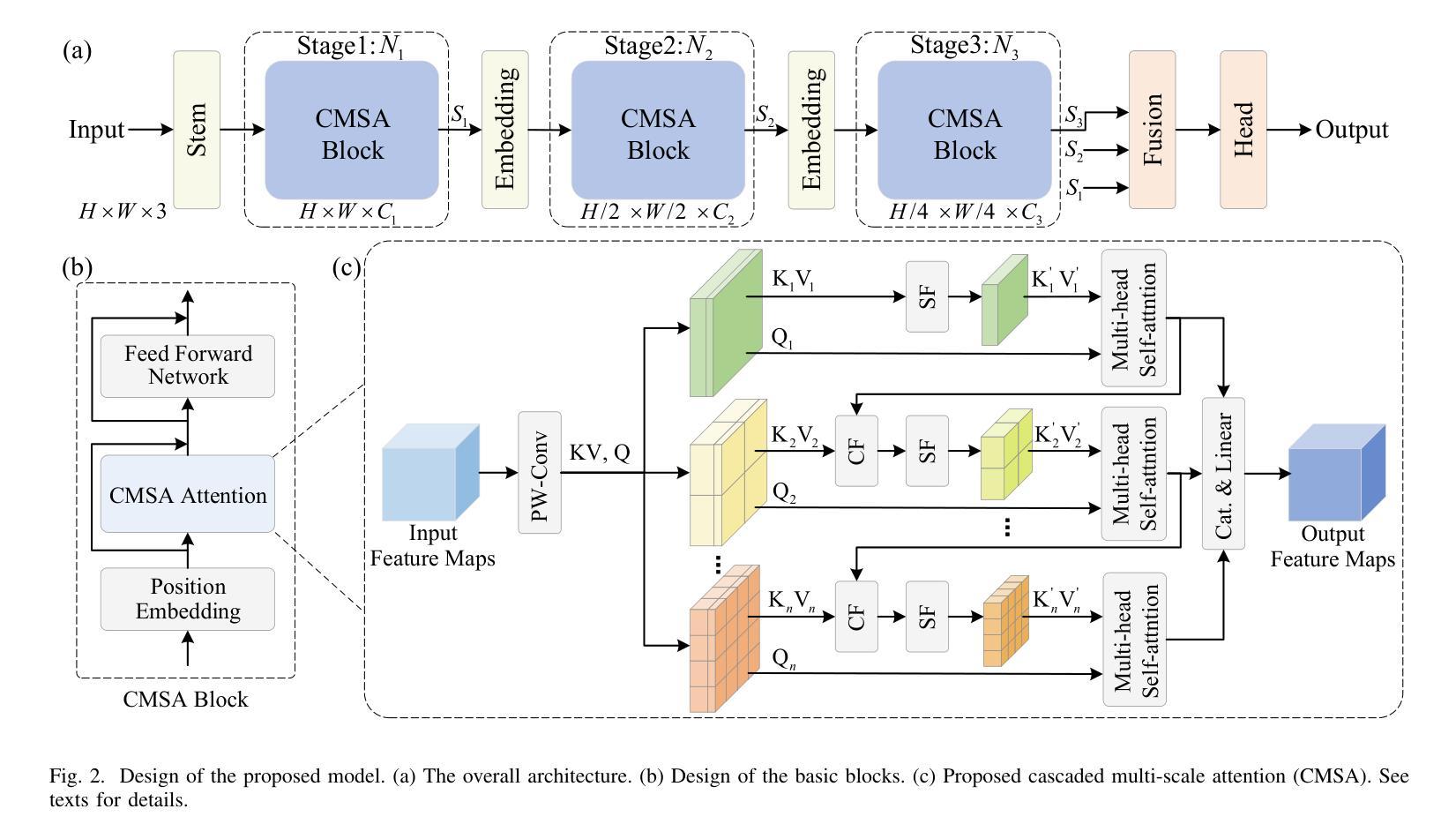
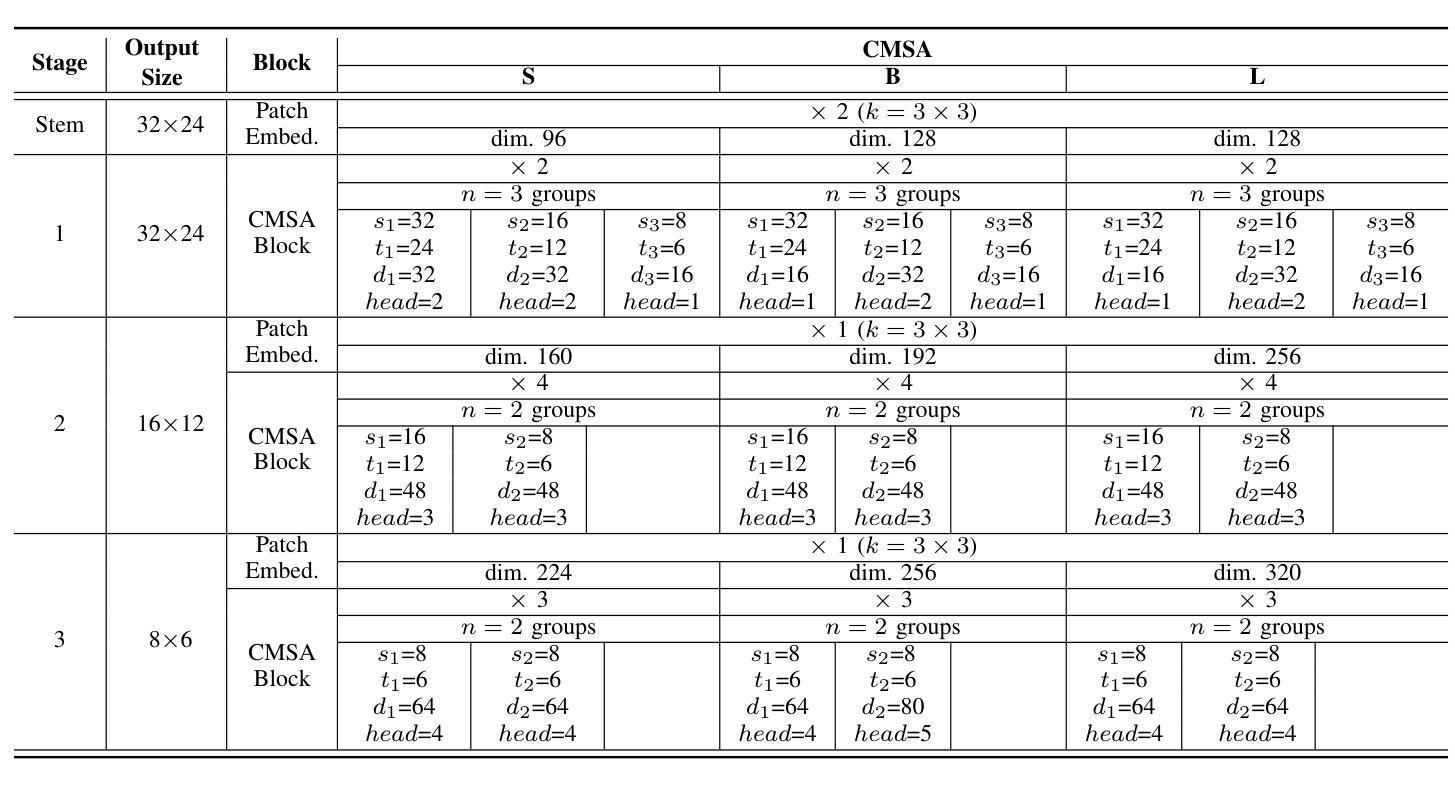
Cascaded Multi-Scale Attention for Enhanced Multi-Scale Feature Extraction and Interaction with Low-Resolution Images
Authors:Xiangyong Lu, Masanori Suganuma, Takayuki Okatani
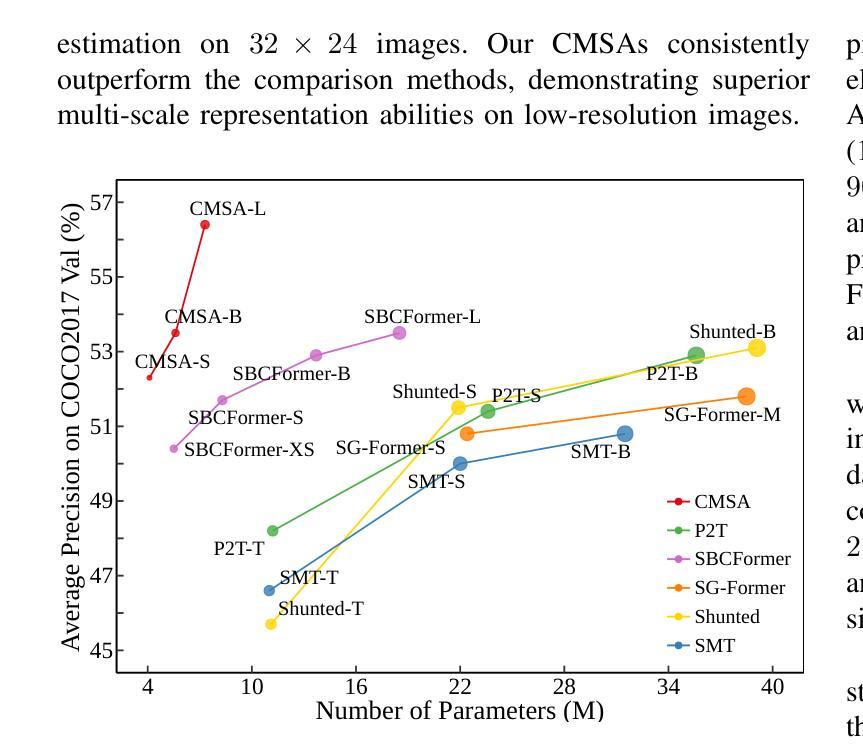
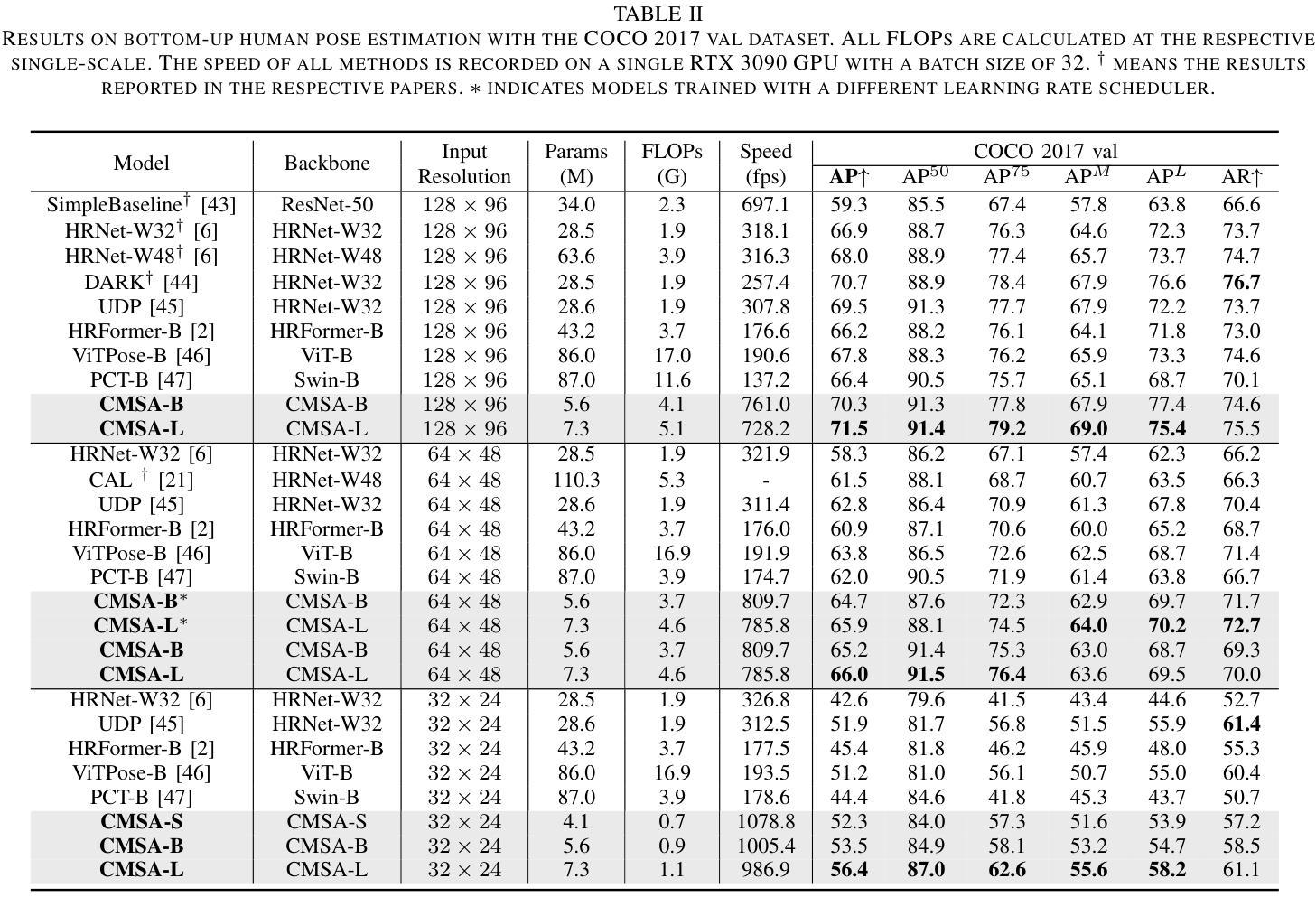
In real-world applications of image recognition tasks, such as human pose estimation, cameras often capture objects, like human bodies, at low resolutions. This scenario poses a challenge in extracting and leveraging multi-scale features, which is often essential for precise inference. To address this challenge, we propose a new attention mechanism, named cascaded multi-scale attention (CMSA), tailored for use in CNN-ViT hybrid architectures, to handle low-resolution inputs effectively. The design of CMSA enables the extraction and seamless integration of features across various scales without necessitating the downsampling of the input image or feature maps. This is achieved through a novel combination of grouped multi-head self-attention mechanisms with window-based local attention and cascaded fusion of multi-scale features over different scales. This architecture allows for the effective handling of features across different scales, enhancing the model’s ability to perform tasks such as human pose estimation, head pose estimation, and more with low-resolution images. Our experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in these areas with fewer parameters, showcasing its potential for broad application in real-world scenarios where capturing high-resolution images is not feasible. Code is available at https://github.com/xyongLu/CMSA.
在图像识别任务的现实应用(如人体姿态估计)中,相机通常会以低分辨率捕获物体(如人体)。这种情况在提取和利用多尺度特征方面提出了挑战,而对于精确推断,这往往是必不可少的。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的注意力机制,名为级联多尺度注意力(CMSA),它针对CNN-ViT混合架构定制,可有效处理低分辨率输入。CMSA的设计实现了跨不同尺度的特征提取和无缝集成,无需对输入图像或特征图进行降采样。这是通过分组多头自注意力机制与基于窗口的局部注意力相结合,以及在不同尺度上多级融合多尺度特征来实现的。该架构可有效地处理不同尺度的特征,增强模型在人体姿态估计、头部姿态估计等任务上的能力,适用于低分辨率图像。实验结果表明,该方法在参数较少的情况下,在这些领域的性能优于现有先进技术,展示了其在无法捕获高分辨率图像的现实场景中的广泛应用潜力。代码可在 https://github.com/xyongLu/CMSA 中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文提出一种名为级联多尺度注意力(CMSA)的新型注意力机制,适用于CNN-ViT混合架构,有效处理低分辨率输入。CMSA设计能够提取并无缝融合多尺度特征,无需对输入图像或特征图进行降采样。通过分组多头自注意力机制与基于窗口的局部注意力的新颖结合,以及在不同尺度上的多尺度特征的级联融合,该架构能够处理不同尺度的特征,提高模型在人体姿态估计、头部姿态估计等任务上的性能。实验结果表明,该方法在较少的参数下,优于现有先进技术,展现出在高分辨率图像捕获不可行的实际场景中应用的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种名为级联多尺度注意力(CMSA)的新型注意力机制,适用于处理低分辨率图像。
- CMSA适用于CNN-ViT混合架构,能够提取并融合多尺度特征。
- CMSA设计无需对输入图像或特征图进行降采样。
- 通过结合分组多头自注意力与窗口局部注意力,实现多尺度特征的提取与融合。
- 级联融合多尺度特征,提高模型在人体姿态估计等任务上的性能。
- 实验结果显示,CMSA在较少的参数下,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图