⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
A Primer on Causal and Statistical Dataset Biases for Fair and Robust Image Analysis
Authors:Charles Jones, Ben Glocker
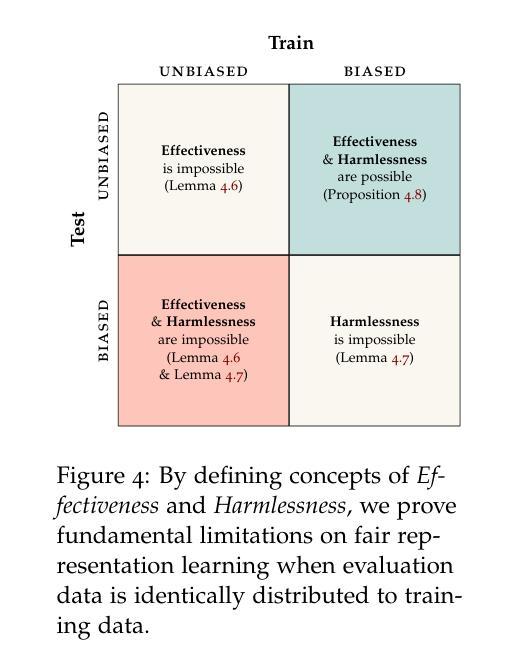
Machine learning methods often fail when deployed in the real world. Worse still, they fail in high-stakes situations and across socially sensitive lines. These issues have a chilling effect on the adoption of machine learning methods in settings such as medical diagnosis, where they are arguably best-placed to provide benefits if safely deployed. In this primer, we introduce the causal and statistical structures which induce failure in machine learning methods for image analysis. We highlight two previously overlooked problems, which we call the \textit{no fair lunch} problem and the \textit{subgroup separability} problem. We elucidate why today’s fair representation learning methods fail to adequately solve them and propose potential paths forward for the field.
机器学习在实际部署时经常出现失效的情况。更为严重的是,它们在关键时刻和涉及社会敏感问题的情境中也会出现失误。这些问题严重影响了机器学习在医疗诊断等领域的应用推广,在那些如果能安全部署的话,机器学习可发挥出最好的优势。在这篇基础教程中,我们介绍了导致图像分析机器学习方法失败的因果和统计结构。我们重点介绍了两个之前被忽视的问题,我们称之为“没有免费午餐”问题和“子组可分性”问题。我们阐述了目前的公平表示学习方法为何无法充分解决这两个问题,并提出了未来解决该领域问题的潜在途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Excerpt from C. Jones’ PhD thesis. Winner of the G-Research PhD prize 2025
Summary
本文介绍了机器学习在图像分析中的失败原因,强调了当前公平表示学习方法无法解决的两个问题:“无公平午餐”问题和“子组可分性”问题。文章指出这些问题在高风险和社会敏感领域尤为突出,并建议未来解决方向。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习在实际部署中经常失败,特别是在高风险和社会敏感领域。
- 在医疗诊断等场景中,机器学习方法的失败对其应用产生了负面影响。
- 介绍了导致机器学习在图像分析失败的原因,包括两个被忽视的问题:“无公平午餐”和“子组可分性”。
- 现有的公平表示学习方法无法解决这两个新问题。
- 文章指出了这两个问题的严重性,并强调了解决它们的必要性。
- 文章为机器学习领域的未来发展提出了潜在的方向和建议。
点此查看论文截图

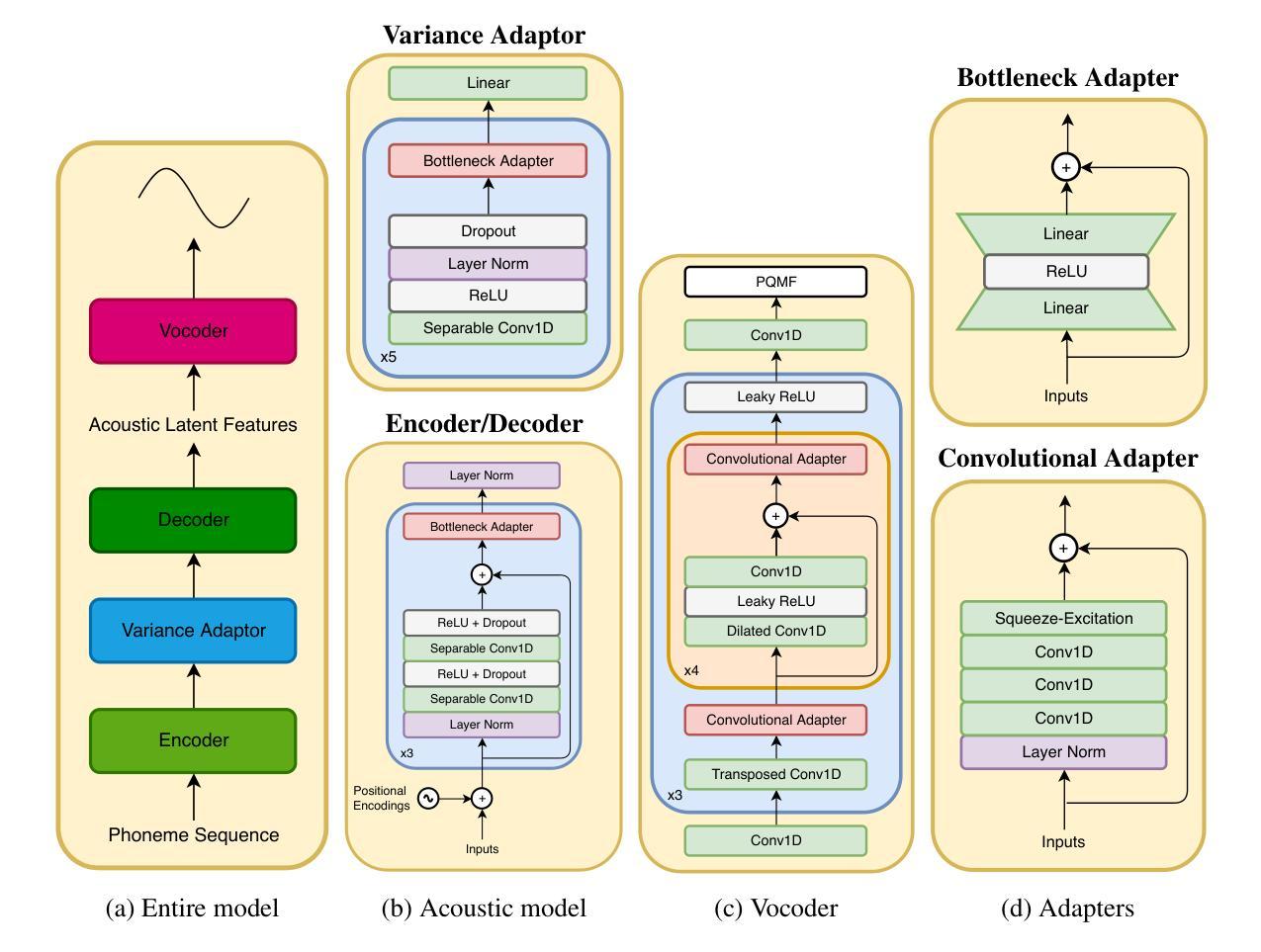
Dual-Scale Volume Priors with Wasserstein-Based Consistency for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Junying Meng, Gangxuan Zhou, Jun Liu, Weihong Guo
Despite signi cant progress in semi-supervised medical image segmentation, most existing segmentation networks overlook e ective methodological guidance for feature extraction and important prior information from datasets. In this paper, we develop a semi-supervised medical image segmentation framework that e ectively integrates spatial regularization methods and volume priors. Speci cally, our approach integrates a strong explicit volume prior at the image scale and Threshold Dynamics spatial regularization, both derived from variational models, into the backbone segmentation network. The target region volumes for each unlabeled image are estimated by a regression network, which e ectively regularizes the backbone segmentation network through an image-scale Wasserstein distance constraint, ensuring that the class ratios in the segmentation results for each unlabeled image match those predicted by the regression network. Additionally, we design a dataset-scale Wasserstein distance loss function based on a weak implicit volume prior, which enforces that the volume distribution predicted for the unlabeled dataset is similar to that of labeled dataset. Experimental results on the 2017 ACDC dataset, PROMISE12 dataset, and thigh muscle MR image dataset show the superiority of the proposed method.
尽管半监督医学图像分割取得了显著进展,但大多数现有的分割网络忽视了特征提取的有效方法指导以及数据集中重要的先验信息。在本文中,我们开发了一个半监督医学图像分割框架,该框架有效地集成了空间正则化方法和体积先验。具体来说,我们的方法将图像尺度的强显式体积先验和阈值动态空间正则化(两者均来自变分模型)集成到主干分割网络中。回归网络估计每张未标记图像的目标区域体积,通过图像尺度的Wasserstein距离约束有效地对主干分割网络进行正则化,确保每张未标记图像的分割结果中的类别比例与回归网络的预测相匹配。此外,我们基于弱隐式体积先验设计了一个数据集尺度的Wasserstein距离损失函数,该函数强制未标记数据集的体积分布与标记数据集的体积分布相似。在2017年ACDC数据集、PROMISE12数据集和大腿肌肉MR图像数据集上的实验结果证明了所提出方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割领域现有网络忽略有效的特征提取和先验信息。本文提出一种半监督医学图像分割框架,整合空间正则化方法和体积先验。通过回归网络估计未标记图像的目标区域体积,通过图像尺度的Wasserstein距离约束有效正则化分割网络。同时设计基于弱隐式体积先验的数据集尺度Wasserstein距离损失函数。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明该方法优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有医学图像分割网络忽略特征提取和先验信息的重要性。
- 本文提出一种半监督医学图像分割框架,整合空间正则化方法和体积先验。
- 通过回归网络估计未标记图像的目标区域体积。
- 通过图像尺度的Wasserstein距离约束正则化分割网络。
- 设计基于弱隐式体积先验的数据集尺度Wasserstein距离损失函数。
- 框架在多个数据集上的实验结果表明其优越性。
点此查看论文截图

Error Detection Schemes for Barrett Reduction of CT-BU on FPGA in Post Quantum Cryptography
Authors:Paresh Baidya, Rourab Paul, Vikas Srivastava, Sumit Kumar Debnath
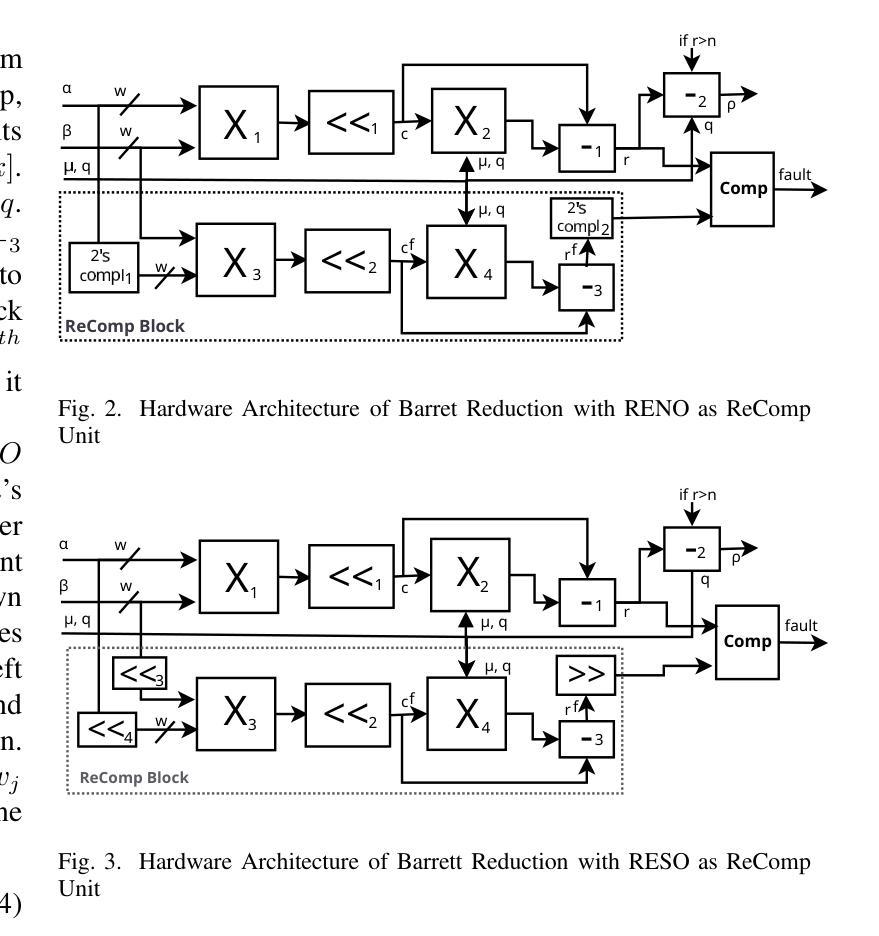
A fault can occur naturally or intentionally. However, intentionally injecting faults into hardware accelerators of Post-Quantum Cryptographic (PQC) algorithms may leak sensitive information. This intentional fault injection in side-channel attacks compromises the reliability of PQC implementations. The recently NIST-standardized key encapsulation mechanism (KEM), Kyber may also leak information at the hardware implementation level. This work proposes three efficient and lightweight recomputation-based fault detection methods for Barrett Reduction in the Cooley-Tukey Butterfly Unit (CT-BU) of Kyber on a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). The CT-BU and Barrett Reduction are fundamental components in structured lattice-based PQC algorithms, including Kyber, NTRU, Falcon, CRYSTALS-Dilithium, etc. This paper introduces a new algorithm, Recomputation with Swapped Operand (RESWO), for fault detection. While Recomputation with Negated Operand (RENO) and Recomputation with Shifted Operand (RESO) are existing methods used in other PQC hardware algorithms. To the best of our knowledge, RENO and RESO have never been used in Barrett Reduction before. The proposed RESWO method consumes a similar number of slices compared to RENO and RESO. However, RESWO shows lesser delay compared to both RENO and RESO. The fault detection efficiency of RESWO, RENO, and RESO is nearly 100%.
故障可能自然发生或人为造成。然而,故意向后量子密码(PQC)算法的硬件加速器注入故障可能会泄露敏感信息。这种在侧信道攻击中的故意故障注入会损害PQC实现的可靠性。最近被NIST标准化的密钥封装机制(KEM)Kyber在硬件实现层面也可能泄露信息。针对Kyber的Cooley-Tukey蝶形运算单元(CT-BU)中的Barrett规约,本文提出了三种高效且轻量级的基于重新计算的故障检测方法,该检测手段可在现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)上实施。CT-BU和Barrett规约是基于结构格的后量子密码算法(包括Kyber、NTRU、Falcon、CRYSTALS-Dilithium等)的基本组成部分。本文介绍了一种新的用于故障检测的算法——交换操作数重新计算(RESWO)。而否定操作数重新计算(RENO)和移位操作数重新计算(RESO)是已应用于其他PQC硬件算法的方法。据我们所知,在Barrett规约中从未使用过RENO和RESO。所提出的RESWO方法与RENO和RESO相比,消耗相似的切片数量。但RESWO相对于RENO和RESO表现出更短的延迟时间。RESWO、RENO和RESO的故障检测效率接近100%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在加密系统中存在天然或人为注入的错误。人为将错误注入到量子密码算法的后量子密码学硬件加速器中可能会泄露敏感信息。这些侧信道攻击中的有意错误注入破坏了后量子密码学实现的可靠性。最近标准化的密钥封装机制Kyber在硬件实现层面也可能泄露信息。本文提出了三种高效轻量级的基于重构的错误检测方法,用于Kyber中的库伊-图基蝴蝶单位中的巴雷特规约算法(FPGA)。该单位和巴雷特规约算法是基于结构化网格的后量子密码算法的核心组件,包括Kyber、NTRU、Falcon、CRYSTALS-Dilithium等。本文引入了一种新的错误检测算法Recomputation with Swapped Operand (RESWO)。虽然现有的方法包括Recomputation with Negated Operand (RENO)和Recomputation with Shifted Operand (RESO),但据我们所知,它们以前从未在巴雷特规约中使用过。新的RESWO方法消耗的切片数量与RENO和RESO相似,但延迟更少。这三种方法的错误检测效率几乎达到了百分之百。重点在于简化这些机制并提高效率和运行速度,从而增强其在实际硬件部署中的实用性。这在设计和实现可靠的后量子密码学硬件解决方案中至关重要。对于保障量子密码学安全性和完整性具有重大意义。
关键要点:
- 有意将错误注入到量子密码硬件加速器中会引发敏感信息的泄露问题,影响到后量子密码算法的可靠性。对于加密领域构成了重大的潜在威胁和风险挑战。应对相关设计环节和后续完善改进措施实施提出了需求和挑战应对的客观必要。具备推进具体安全保障机制研究的重要意义。
- Kyber密钥封装机制在硬件实现层面也存在信息泄露风险,亟需解决相关漏洞问题以保障数据安全性和可靠性。
- 针对库伊-图基蝴蝶单位中的巴雷特规约算法提出了三种新的错误检测方法(RESWO、RENO和RESO),具备高效且轻量级的特点,对故障的检测率近百分之百准确率高能进一步提升巴雷特归约的性能可靠性防止因误引发的故障危害影响到其他重要的PQC算法的落地使用奠定了坚实的技术基础。
- 上述三种方法具备相似的计算资源消耗水平,但RESWO在延迟方面表现更优,表明其在实时系统中的应用潜力更大。
点此查看论文截图



Learning from Majority Label: A Novel Problem in Multi-class Multiple-Instance Learning
Authors:Shiku Kaito, Shinnosuke Matsuo, Daiki Suehiro, Ryoma Bise
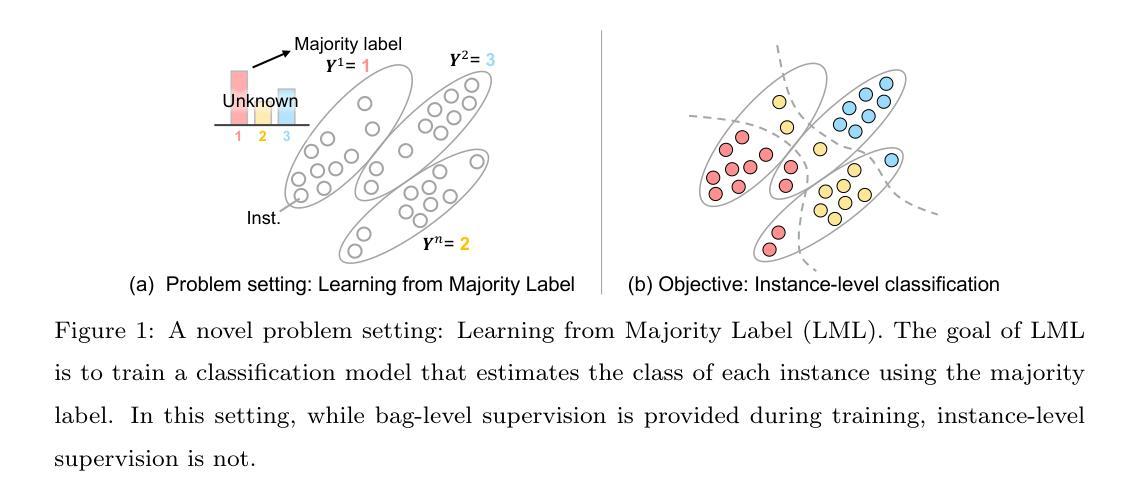
The paper proposes a novel multi-class Multiple-Instance Learning (MIL) problem called Learning from Majority Label (LML). In LML, the majority class of instances in a bag is assigned as the bag-level label. The goal of LML is to train a classification model that estimates the class of each instance using the majority label. This problem is valuable in a variety of applications, including pathology image segmentation, political voting prediction, customer sentiment analysis, and environmental monitoring. To solve LML, we propose a Counting Network trained to produce bag-level majority labels, estimated by counting the number of instances in each class. Furthermore, analysis experiments on the characteristics of LML revealed that bags with a high proportion of the majority class facilitate learning. Based on this result, we developed a Majority Proportion Enhancement Module (MPEM) that increases the proportion of the majority class by removing minority class instances within the bags. Experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method on four datasets compared to conventional MIL methods. Moreover, ablation studies confirmed the effectiveness of each module. The code is available at \href{https://github.com/Shiku-Kaito/Learning-from-Majority-Label-A-Novel-Problem-in-Multi-class-Multiple-Instance-Learning}{here}.
本文提出了一种新的多类多实例学习(MIL)问题,称为从多数标签学习(LML)。在LML中,将一个包中的多数实例类分配为包级标签。LML的目标是利用多数标签训练一个分类模型,以估计每个实例的类别。该问题在各种应用中都具有价值,包括病理学图像分割、政治投票预测、客户情感分析和环境监测。为了解决LML问题,我们提出了一种计数网络,该网络经过训练以计算每个类的实例数量来产生包级多数标签。此外,对LML特性的分析实验表明,包含多数类实例比例较高的袋子有助于学习。基于这一结果,我们开发了一个多数比例增强模块(MPEM),通过移除袋子内的少数类实例来增加多数类的比例。实验表明,与常规MIL方法相比,所提出的方法在四个数据集上表现优越。此外,消融研究证实了每个模块的有效性。代码可从https://github.com/Shiku-Kaito/Learning-from-Majority-label-A-Novel-Problem-in-Multi-class-Multiple-Instance-Learning获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 9 figures, Accepted in Pattern recognition
Summary
本文提出了一种新的多类多实例学习问题,称为基于多数标签的学习(LML)。LML将袋子中的多数类实例作为袋级标签,旨在训练一个分类模型,利用多数标签来估计每个实例的类别。此方法在病理学图像分割、政治投票预测、客户情感分析和环境监测等多种应用中具有应用价值。为解决LML问题,本文提出了计数网络,通过计算每个类别的实例数量来产生袋级多数标签。分析实验表明,多数类实例比例较高的袋子有助于学习。基于此,开发了一个多数比例增强模块(MPEM),通过移除袋子中的少数类实例来增加多数类的比例。实验证明,该方法在四个数据集上的表现优于传统的MIL方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了新型的多类多实例学习问题——基于多数标签的学习(LML)。
- LML方法将袋子中的多数类实例作为袋级标签,用于训练分类模型。
- LML在多种应用领域中具有实用性,如病理学图像分割、政治投票预测等。
- 计数网络用于生成袋级多数标签,通过计算各类的实例数量来实现。
- 多数类实例比例较高的袋子有助于学习,基于此开发了MPEM模块。
- 实验证明,所提方法在四个数据集上的表现优于传统MIL方法。
点此查看论文截图


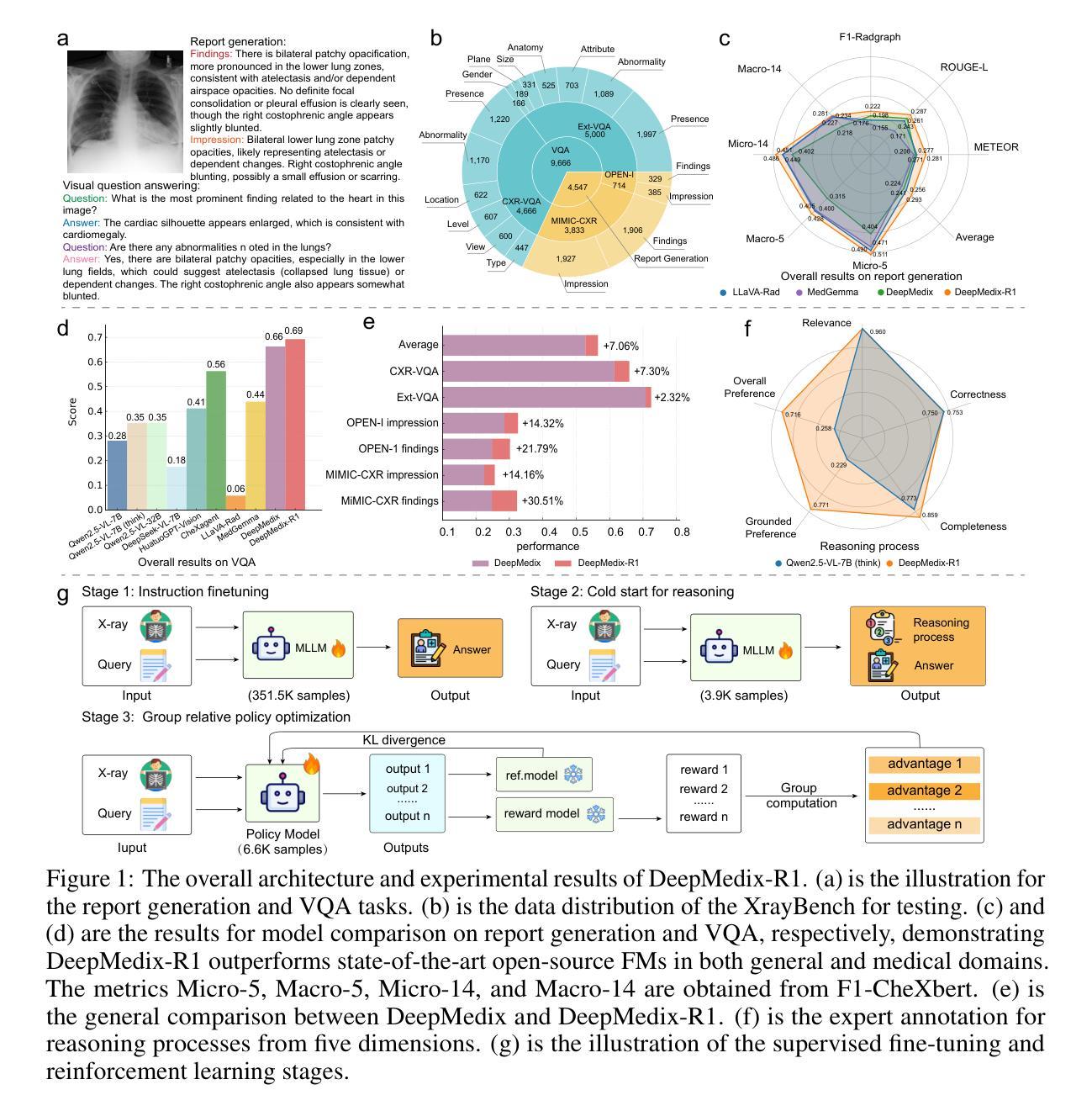
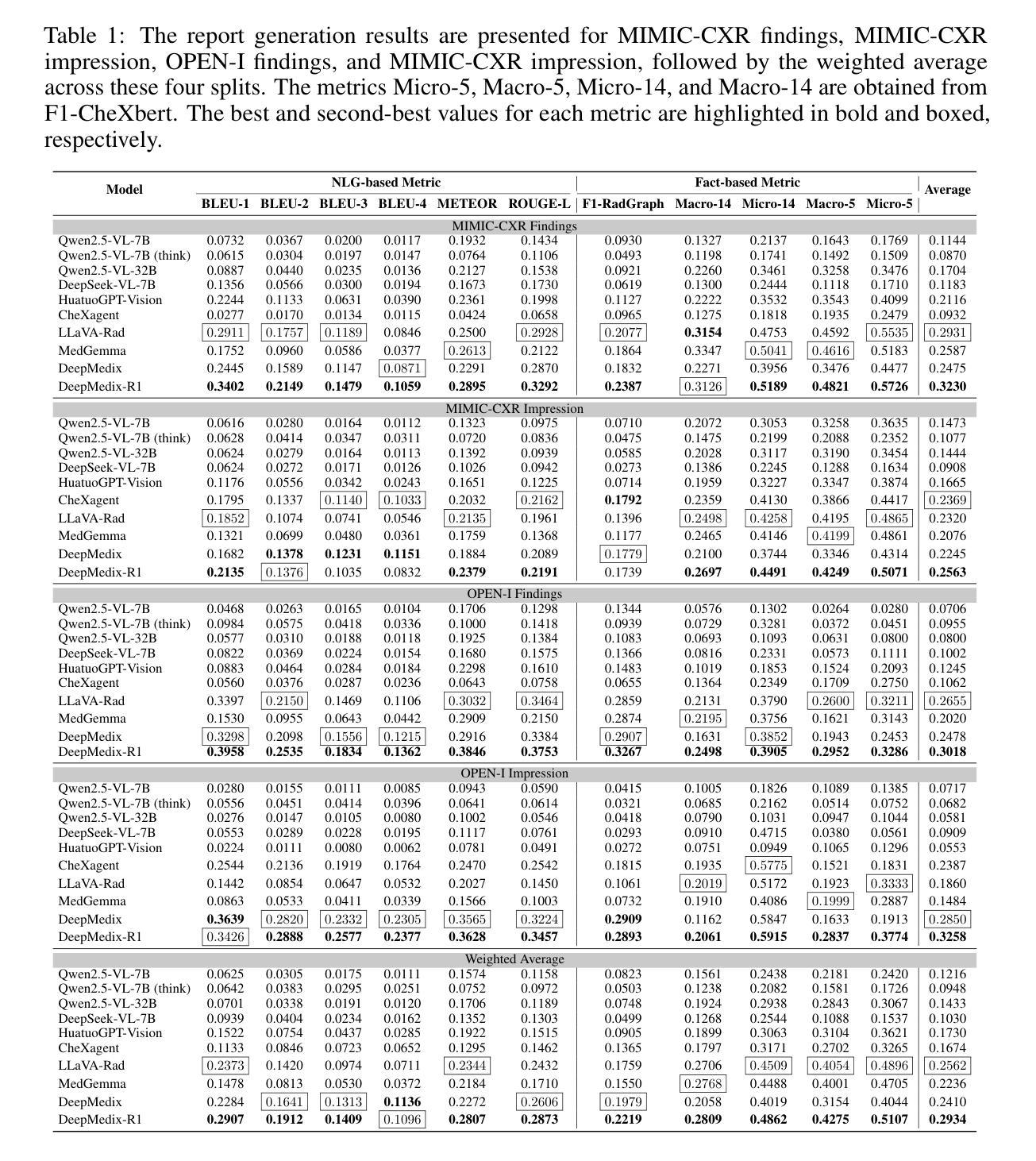
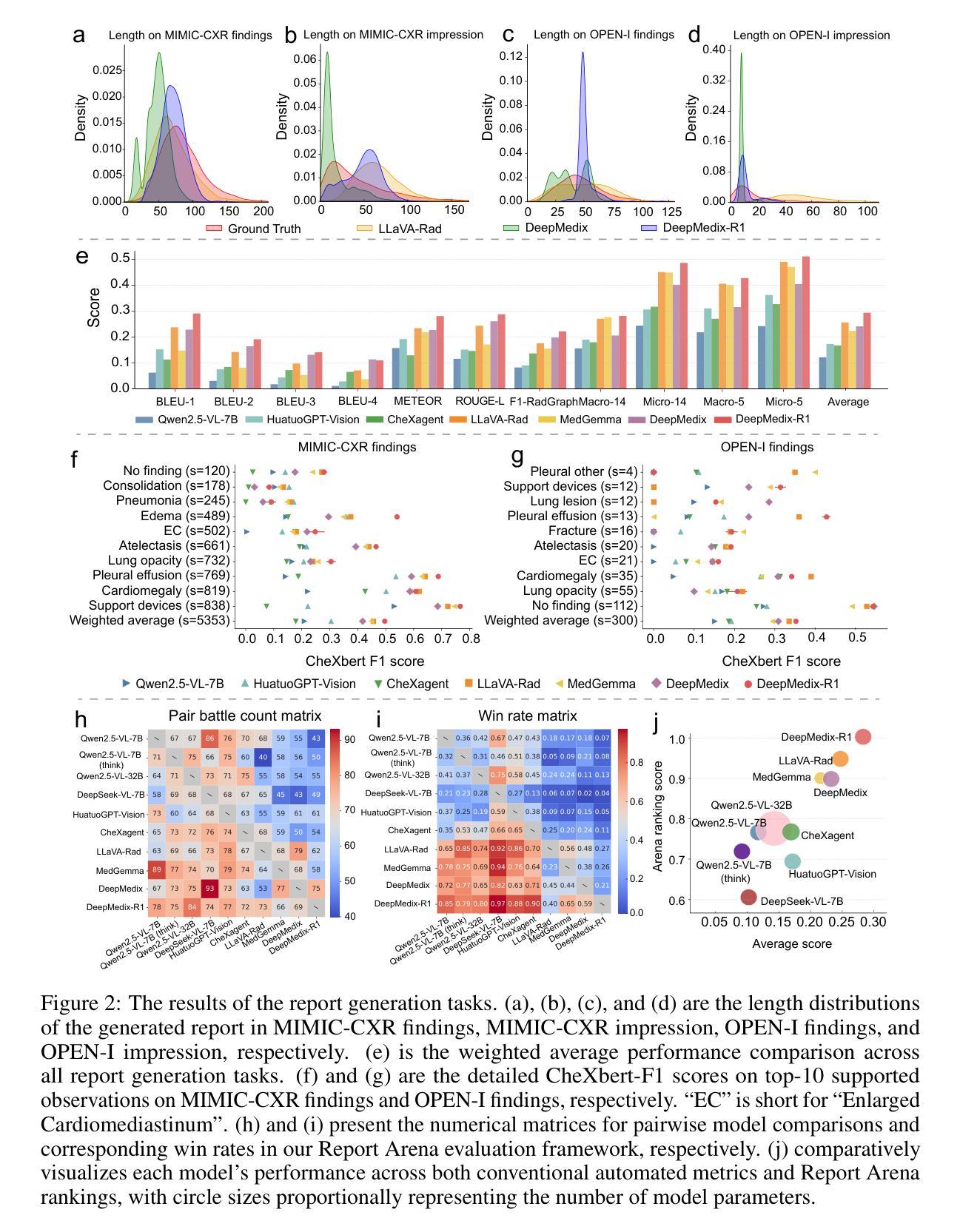
A Foundation Model for Chest X-ray Interpretation with Grounded Reasoning via Online Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Qika Lin, Yifan Zhu, Bin Pu, Ling Huang, Haoran Luo, Jingying Ma, Zhen Peng, Tianzhe Zhao, Fangzhi Xu, Jian Zhang, Kai He, Zhonghong Ou, Swapnil Mishra, Mengling Feng
Medical foundation models (FMs) have shown tremendous promise amid the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. However, current medical FMs typically generate answers in a black-box manner, lacking transparent reasoning processes and locally grounded interpretability, which hinders their practical clinical deployments. To this end, we introduce DeepMedix-R1, a holistic medical FM for chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation. It leverages a sequential training pipeline: initially fine-tuned on curated CXR instruction data to equip with fundamental CXR interpretation capabilities, then exposed to high-quality synthetic reasoning samples to enable cold-start reasoning, and finally refined via online reinforcement learning to enhance both grounded reasoning quality and generation performance. Thus, the model produces both an answer and reasoning steps tied to the image’s local regions for each query. Quantitative evaluation demonstrates substantial improvements in report generation (e.g., 14.54% and 31.32% over LLaVA-Rad and MedGemma) and visual question answering (e.g., 57.75% and 23.06% over MedGemma and CheXagent) tasks. To facilitate robust assessment, we propose Report Arena, a benchmarking framework using advanced language models to evaluate answer quality, further highlighting the superiority of DeepMedix-R1. Expert review of generated reasoning steps reveals greater interpretability and clinical plausibility compared to the established Qwen2.5-VL-7B model (0.7416 vs. 0.2584 overall preference). Collectively, our work advances medical FM development toward holistic, transparent, and clinically actionable modeling for CXR interpretation.
医疗基础模型(FMs)在人工智能(AI)技术的快速发展中显示出巨大的潜力。然而,当前的医疗FM通常以黑箱方式生成答案,缺乏透明的推理过程和基于本地的可解释性,这阻碍了其在实际临床部署中的应用。为此,我们引入了DeepMedix-R1,这是一个全面的用于胸部X射线(CXR)解读的医疗FM。它利用了一个序列训练管道:首先,在精选的CXR指令数据上进行微调,以具备基本的CXR解读能力;然后,暴露于高质量合成推理样本中以启动冷启动推理;最后,通过在线强化学习进行精炼,以提高基于本地的推理质量和生成性能。因此,该模型为每一个查询生成与图像局部区域相关联的答案和推理步骤。定量评估表明,在报告生成(例如,相较于LLaVA-Rad和MedGemma分别提高14.54%和31.32%)和视觉问答(例如,相较于MedGemma和CheXagent分别提高57.75%和23.06%)的任务中实现了显著改进。为了进行稳健的评估,我们提出了Report Arena,这是一个使用先进语言模型来评估答案质量的基准框架,进一步突显了DeepMedix-R1的优越性。对生成推理步骤的专家评审显示,与已建立的Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型相比,其解释性和临床可信度更高(整体偏好为0.7416对0.2584)。总的来说,我们的工作推动了医疗FM向全面、透明且临床可行的CXR解读模型发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
摘要
随着人工智能技术的快速发展,医疗基础模型(FMs)在医疗图像解读方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,当前医疗FMs通常采用黑盒方式生成答案,缺乏透明的推理过程和本地化的解释性,这阻碍了其在临床实践中的应用。为此,我们提出了DeepMedix-R1,一个全面的用于胸部X光(CXR)解读的医疗FM。它采用序贯训练管道:首先,在精选的CXR指令数据上进行微调,以具备基本的CXR解读能力;然后,通过高质量合成推理样本进行冷启动推理;最后,通过在线强化学习进行细化,提高基于图像的本地推理质量和生成性能。因此,该模型为每一个查询生成答案和与图像局部区域相关的推理步骤。定量评估显示,在报告生成和视觉问答任务方面,DeepMedix-R1较LLaVA-Rad和MedGemma有显著改善。为便于评估,我们提出了Report Arena,一个使用先进语言模型评估答案质量的基准框架,进一步突显DeepMedix-R1的优越性。与已建立的Qwen2.5-VL-7B模型相比,专家对生成的推理步骤的审查显示出更高的可解释性和临床可信度。总体上,我们的研究推动了医疗FM在CXR解读方面朝着全面、透明和临床可操作的方向发展。
关键见解
- 医疗基础模型(FMs)在人工智能驱动的胸部X光(CXR)解读中具有巨大潜力。
- 当前医疗FMs存在缺乏透明推理和本地解释性的问题,限制了其在临床实践中的应用。
- DeepMedix-R1是一个全面的用于CXR解读的医疗FM,采用序贯训练管道提高性能。
- DeepMedix-R1在报告生成和视觉问答任务上较其他模型有显著改善。
- 为评估答案质量,提出了Report Arena基准框架。
- DeepMedix-R1的推理步骤具有更高的可解释性和临床可信度。
点此查看论文截图

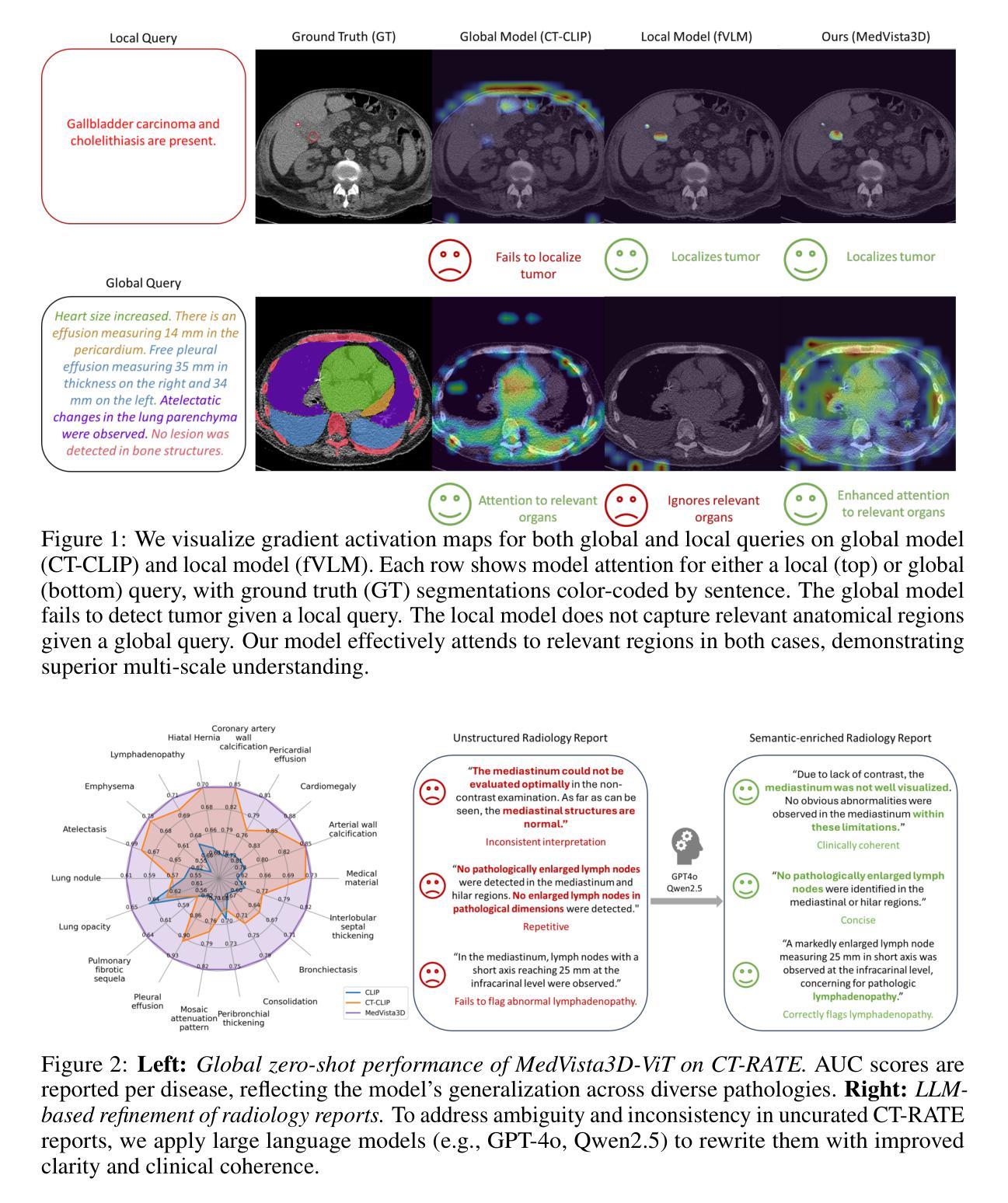
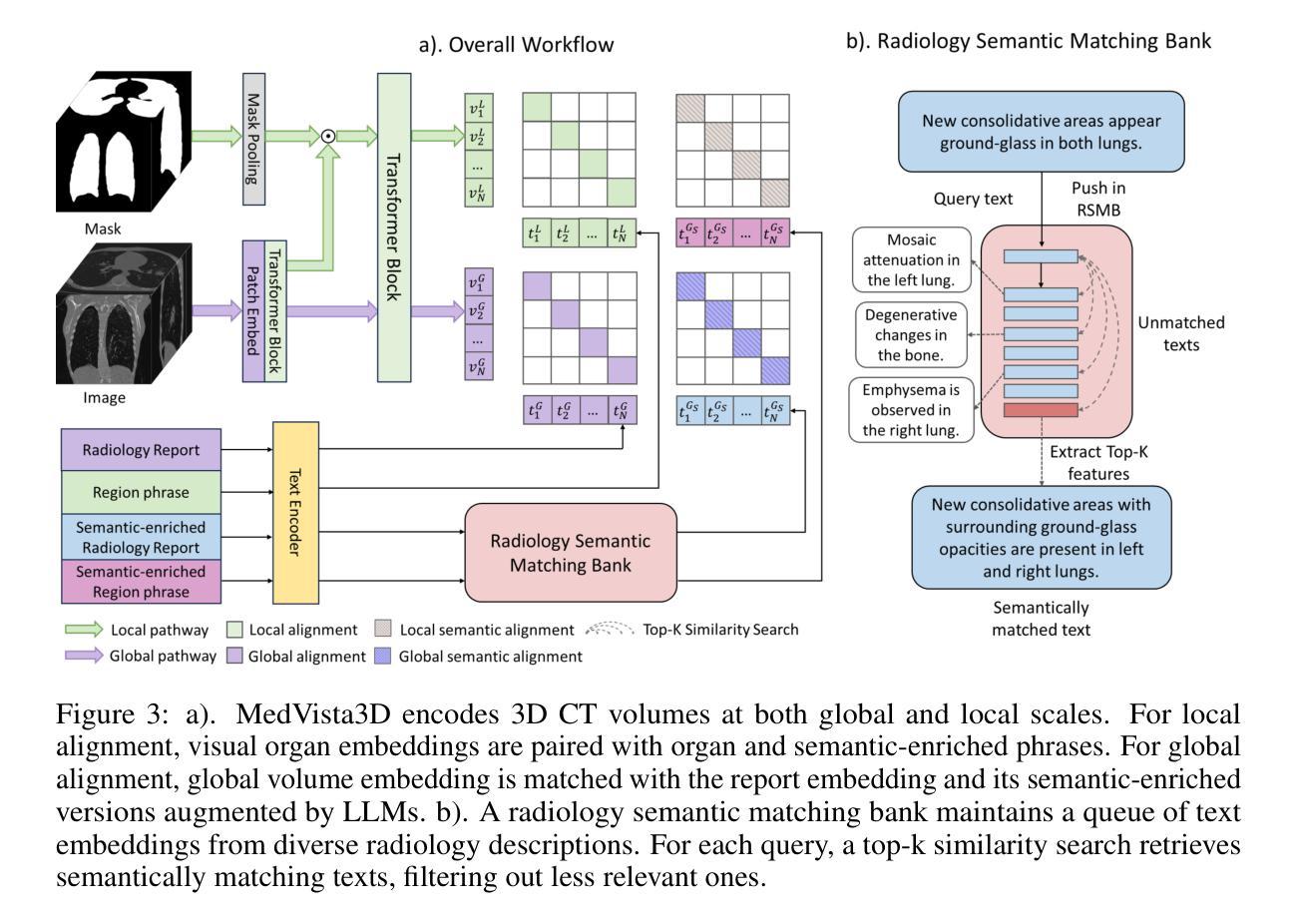
MedVista3D: Vision-Language Modeling for Reducing Diagnostic Errors in 3D CT Disease Detection, Understanding and Reporting
Authors:Yuheng Li, Yenho Chen, Yuxiang Lai, Jike Zhong, Vanessa Wildman, Xiaofeng Yang
Radiologic diagnostic errors-under-reading errors, inattentional blindness, and communication failures-remain prevalent in clinical practice. These issues often stem from missed localized abnormalities, limited global context, and variability in report language. These challenges are amplified in 3D imaging, where clinicians must examine hundreds of slices per scan. Addressing them requires systems with precise localized detection, global volume-level reasoning, and semantically consistent natural language reporting. However, existing 3D vision-language models are unable to meet all three needs jointly, lacking local-global understanding for spatial reasoning and struggling with the variability and noise of uncurated radiology reports. We present MedVista3D, a multi-scale semantic-enriched vision-language pretraining framework for 3D CT analysis. To enable joint disease detection and holistic interpretation, MedVista3D performs local and global image-text alignment for fine-grained representation learning within full-volume context. To address report variability, we apply language model rewrites and introduce a Radiology Semantic Matching Bank for semantics-aware alignment. MedVista3D achieves state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot disease classification, report retrieval, and medical visual question answering, while transferring well to organ segmentation and prognosis prediction. Code and datasets will be released.
在临床实践中,放射学诊断错误(包括漏读错误、注意力缺失性失明和沟通失败)仍然普遍存在。这些问题通常源于局部异常的遗漏、全局情境的局限以及报告语言的差异。在三维成像中,医生每次扫描需要检查数百个切片,这些挑战被进一步放大。要解决这些问题,需要拥有精确局部检测、全局体积级推理和语义连贯的自然语言报告的系统。然而,现有的3D视觉语言模型无法同时满足所有三个需求,缺乏局部全局理解来进行空间推理,并且难以应对未整理的放射学报告的变体和噪声。我们推出了MedVista3D,这是一个用于3D CT分析的多尺度语义丰富视觉语言预训练框架。为了实现联合疾病检测和整体解释,MedVista3D执行局部和全局图像文本对齐,以在全卷积背景下进行精细粒度表示学习。为了解决报告差异问题,我们应用了语言模型重写,并引入放射学语义匹配银行进行语义感知对齐。MedVista3D在零样本疾病分类、报告检索和医学视觉问答方面达到了最先进的性能,同时很好地应用于器官分割和预后预测。代码和数据集将予以公开。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在医学影像诊断中常见的一些错误和挑战,如忽略局部异常、注意力缺失、沟通障碍等。为解决这些问题,提出了一种名为MedVista3D的多尺度语义增强视觉语言预训练框架,用于进行三维CT分析。该框架通过局部和全局图像文本对齐,实现精细粒度表示学习,在整体语境下达到联合疾病检测和整体解释的目标。同时引入语言模型重写和放射学语义匹配银行,以解决报告差异和语义对齐问题。MedVista3D在零样本疾病分类、报告检索、医学影像问答等方面取得了最佳性能,并能很好地应用于器官分割和预后预测。
Key Takeaways
- 医学影像诊断中存在常见的错误和挑战,包括忽略局部异常、注意力缺失和沟通障碍等。
- 这些挑战在3D成像中更加突出,因为临床医生需要检查的切片数量非常多。
- MedVista3D是一个多尺度的语义增强视觉语言预训练框架,旨在解决这些问题。
- MedVista3D通过局部和全局图像文本对齐,实现精细粒度表示学习,在整体语境下达到联合疾病检测和整体解释的目标。
- 该框架解决了报告差异问题,通过语言模型重写和放射学语义匹配银行实现语义对齐。
- MedVista3D在多项任务上表现出最佳性能,包括零样本疾病分类、报告检索、医学影像问答等。
点此查看论文截图

Learning functions through Diffusion Maps
Authors:Alvaro Almeida Gomez
We propose a data-driven method for approximating real-valued functions on smooth manifolds, building on the Diffusion Maps framework under the manifold hypothesis. Given pointwise evaluations of a function, the method constructs a smooth extension to the ambient space by exploiting diffusion geometry and its connection to the heat equation and the Laplace-Beltrami operator. To address the computational challenges of high-dimensional data, we introduce a dimensionality reduction strategy based on the low-rank structure of the distance matrix, revealed via singular value decomposition (SVD). In addition, we develop an online updating mechanism that enables efficient incorporation of new data, thereby improving scalability and reducing computational cost. Numerical experiments, including applications to sparse CT reconstruction, demonstrate that the proposed methodology outperforms classical feedforward neural networks and interpolation methods in terms of both accuracy and efficiency.
我们提出了一种基于数据驱动的方法,用于在平滑流形上近似实值函数。该方法建立在流形假设下的扩散图框架之上。给定函数的点态评估,该方法通过利用扩散几何及其与热方程和Laplace-Beltrami算子的联系,在环境空间中构建平滑扩展。为了解决高维数据的计算挑战,我们提出了一种基于奇异值分解(SVD)揭示的距离矩阵低秩结构的降维策略。此外,我们开发了一种在线更新机制,能够高效地融入新数据,从而提高可扩展性并降低计算成本。数值实验表明,包括在稀疏CT重建中的应用在内,所提出的方法在准确性和效率方面都优于经典的前馈神经网络和插值方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Comments are welcome
Summary
本文提出一种基于数据驱动的方法,用于在平滑流形上近似实值函数。该方法在流形假设下构建在扩散映射框架上的扩散几何结构,并利用其与热方程和Laplace-Beltrami算子的联系进行平滑扩展。为了应对高维数据的计算挑战,引入基于距离矩阵低秩结构的降维策略,通过奇异值分解(SVD)揭示。此外,开发了在线更新机制,能够高效融入新数据,从而提高方法的可扩展性并降低计算成本。数值实验包括稀疏CT重建的应用,表明该方法在准确性和效率方面都优于经典的前馈神经网络和插值方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种基于数据驱动的方法,利用扩散映射框架在平滑流形上近似实值函数。
- 利用扩散几何结构,结合热方程和Laplace-Beltrami算子的联系进行平滑扩展。
- 引入基于距离矩阵低秩结构的降维策略,以提高计算效率。
- 通过奇异值分解(SVD)揭示距离矩阵的低秩结构。
- 开发在线更新机制,以便高效融入新数据。
- 方法具有优秀的可扩展性,可以降低计算成本。
点此查看论文截图

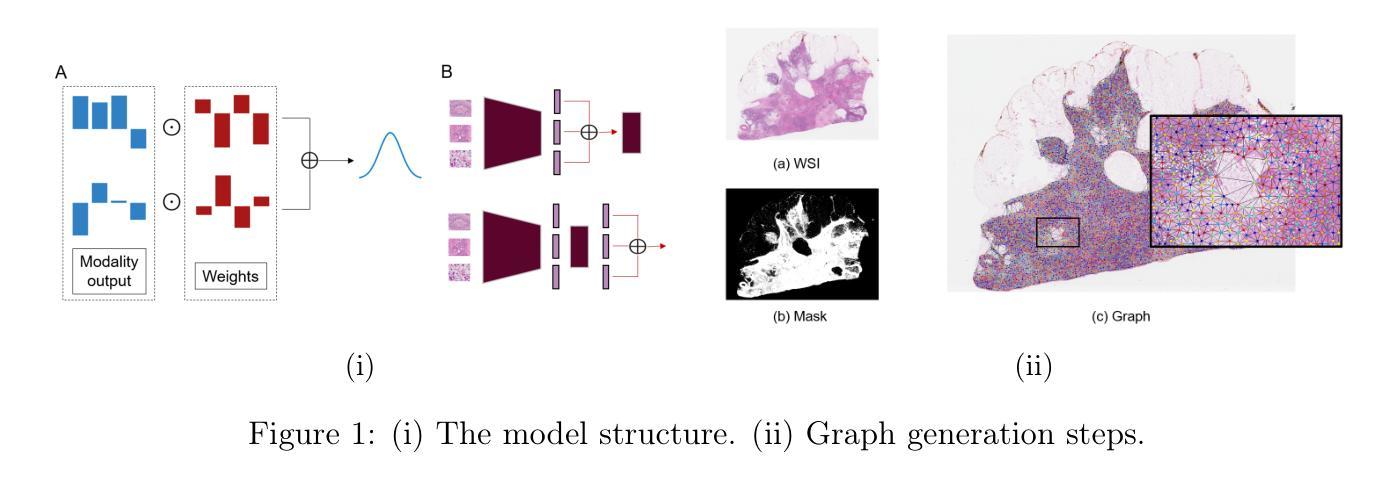
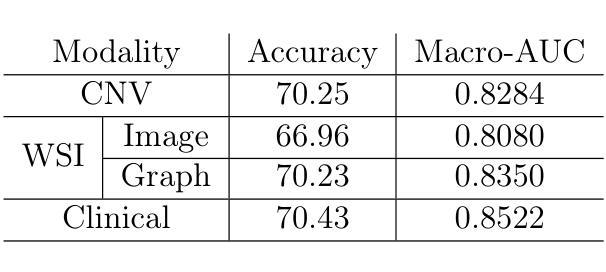
Scalable and Loosely-Coupled Multimodal Deep Learning for Breast Cancer Subtyping
Authors:Mohammed Amer, Mohamed A. Suliman, Tu Bui, Nuria Garcia, Serban Georgescu
Healthcare applications are inherently multimodal, benefiting greatly from the integration of diverse data sources. However, the modalities available in clinical settings can vary across different locations and patients. A key area that stands to gain from multimodal integration is breast cancer molecular subtyping, an important clinical task that can facilitate personalized treatment and improve patient prognosis. In this work, we propose a scalable and loosely-coupled multimodal framework that seamlessly integrates data from various modalities, including copy number variation (CNV), clinical records, and histopathology images, to enhance breast cancer subtyping. While our primary focus is on breast cancer, our framework is designed to easily accommodate additional modalities, offering the flexibility to scale up or down with minimal overhead without requiring re-training of existing modalities, making it applicable to other types of cancers as well. We introduce a dual-based representation for whole slide images (WSIs), combining traditional image-based and graph-based WSI representations. This novel dual approach results in significant performance improvements. Moreover, we present a new multimodal fusion strategy, demonstrating its ability to enhance performance across a range of multimodal conditions. Our comprehensive results show that integrating our dual-based WSI representation with CNV and clinical health records, along with our pipeline and fusion strategy, outperforms state-of-the-art methods in breast cancer subtyping.
医疗健康应用程序本质上是多模式的,大大受益于不同数据源的集成。然而,临床环境中可用的模式可以在不同的地点和患者之间变化。从多模式集成中受益的关键领域之一是乳腺癌分子分型,这是一项重要的临床任务,可以促进个性化治疗并改善患者预后。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个可扩展且松散耦合的多模式框架,该框架无缝集成了各种模式的数据,包括拷贝数变异(CNV)、临床记录和组病理图像,以提高乳腺癌的分型能力。虽然我们的重点是在乳腺癌上,但我们的框架设计易于容纳其他模式,提供灵活的可伸缩性,无需对现有模式进行重新训练,使其也适用于其他类型的癌症。我们引入了基于双表示的整张幻灯片图像(WSI),结合了传统的图像和基于图的WSI表示。这种新型双路径方法带来了显著的性能提升。此外,我们提出了一种新的多模式融合策略,展示了其在各种多模式条件下的增强性能的能力。我们的综合结果表明,将我们的基于双路径的WSI表示与CNV和临床健康记录相结合,以及我们的管道和融合策略,在乳腺癌分型方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一个可扩展的、松散耦合的多模态框架,该框架无缝集成了拷贝数变异、临床记录和病理图像等多种数据,以改进乳腺癌分子分型。采用双重基于表示的全幻灯片图像技术,结合传统图像和基于图的幻灯片表示法,取得显著性能提升。新的多模态融合策略能增强各种多模态条件下的性能。整合双重基于全幻灯片图像表示的方法与拷贝数变异和临床健康记录,配合管道和融合策略,在乳腺癌分型方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗保健应用具有多模态特性,从整合多样数据源中获益巨大。
- 乳腺癌分子分型是多模态整合的关键应用领域之一,有助于个性化治疗和改善患者预后。
- 提出一种可扩展的、松散耦合的多模态框架,能够灵活适应不同模态的增减,无需对现有模态进行重新训练。
- 采用双重基于表示的全幻灯片图像技术,结合传统图像和基于图的表示法,提高了性能。
- 引入新的多模态融合策略,能够增强在各种多模态条件下的性能。
- 该框架在乳腺癌分型方面的性能优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

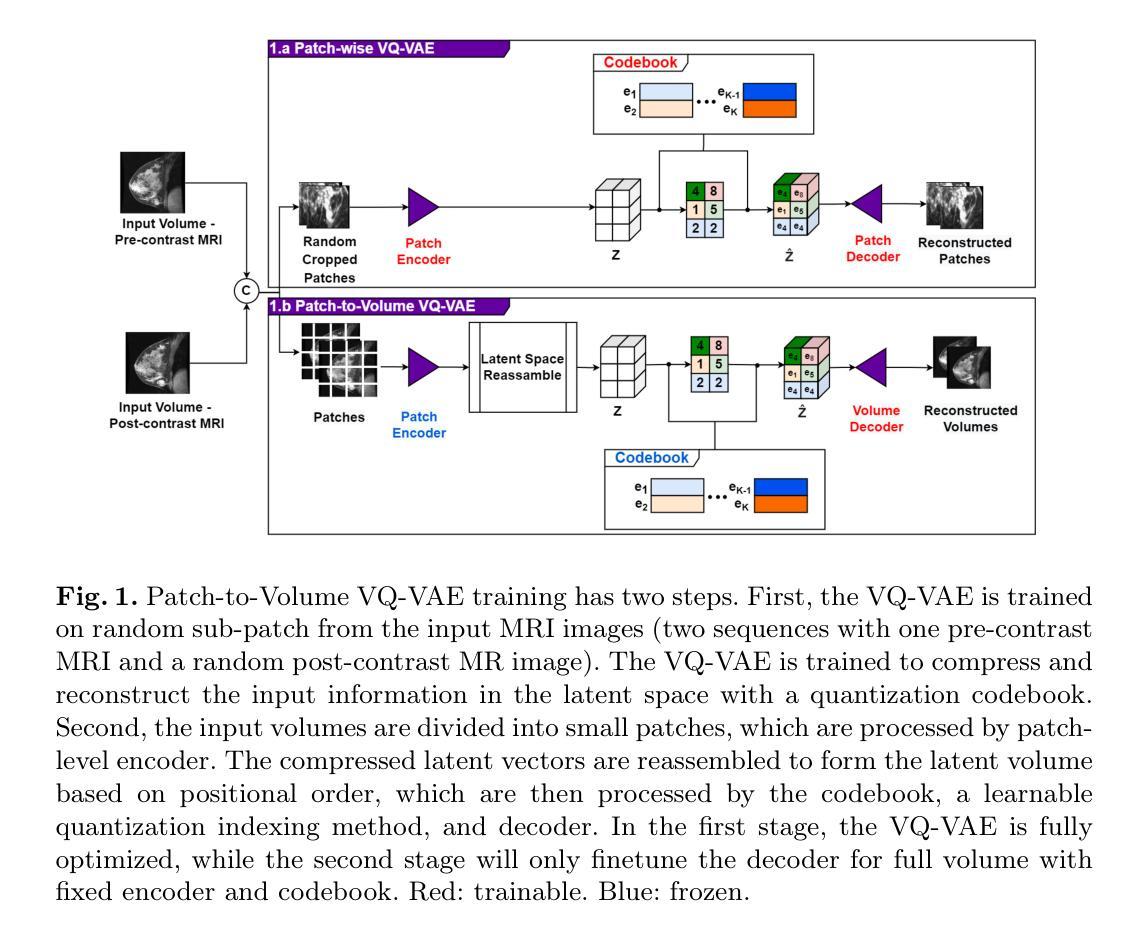
SynBT: High-quality Tumor Synthesis for Breast Tumor Segmentation by 3D Diffusion Model
Authors:Hongxu Yang, Edina Timko, Levente Lippenszky, Vanda Czipczer, Lehel Ferenczi
Synthetic tumors in medical images offer controllable characteristics that facilitate the training of machine learning models, leading to an improved segmentation performance. However, the existing methods of tumor synthesis yield suboptimal performances when tumor occupies a large spatial volume, such as breast tumor segmentation in MRI with a large field-of-view (FOV), while commonly used tumor generation methods are based on small patches. In this paper, we propose a 3D medical diffusion model, called SynBT, to generate high-quality breast tumor (BT) in contrast-enhanced MRI images. The proposed model consists of a patch-to-volume autoencoder, which is able to compress the high-resolution MRIs into compact latent space, while preserving the resolution of volumes with large FOV. Using the obtained latent space feature vector, a mask-conditioned diffusion model is used to synthesize breast tumors within selected regions of breast tissue, resulting in realistic tumor appearances. We evaluated the proposed method for a tumor segmentation task, which demonstrated the proposed high-quality tumor synthesis method can facilitate the common segmentation models with performance improvement of 2-3% Dice Score on a large public dataset, and therefore provides benefits for tumor segmentation in MRI images.
医学图像中的合成肿瘤具有可控特性,有助于训练机器学习模型,从而提高分割性能。然而,现有的肿瘤合成方法在肿瘤占据较大空间体积时,表现并不理想,例如在MRI中具有大视野(FOV)的乳腺癌分割。通常使用的肿瘤生成方法基于小补丁。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为SynBT的3D医学扩散模型,用于生成高质量对比增强MRI图像中的乳腺癌(BT)。所提出模型包括一个由补丁到体积的自编码器,能够将高分辨率MRI压缩成紧凑的潜在空间,同时保留大视野体积的分辨率。利用获得的潜在空间特征向量,使用掩模条件扩散模型在选定乳腺组织区域内合成乳腺癌,产生逼真的肿瘤外观。我们对所提出的方法进行了肿瘤分割任务评估,结果表明,高质量肿瘤合成方法能够促进公共大型数据集上的常见分割模型,提高2-3%的Dice得分。因此,该方法对MRI图像的肿瘤分割具有益处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025 Deep-Breath Workshop. Supported by IHI SYNTHIA project
Summary
医学图像中合成肿瘤具有可控特性,有助于训练机器学习模型,提高分割性能。针对现有肿瘤合成方法在肿瘤占据较大空间体积时性能不佳的问题,如MRI中视野较大的乳腺癌分割,本文提出了一种名为SynBT的3D医学扩散模型,用于生成高质量的乳腺癌对比增强MRI图像。该模型由patch-to-volume自编码器组成,能够压缩高分辨率MRI图像到紧凑的潜在空间,同时保留大视野的体积分辨率。使用获得的潜在空间特征向量,通过掩膜控制的扩散模型在选定乳腺组织区域合成肿瘤,产生逼真的肿瘤外观。评估用于肿瘤分割任务的方法表明,高质量肿瘤合成方法能促进公共数据集上的分割模型性能提高2-3%的Dice得分,因此在MRI图像肿瘤分割中提供优势。
Key Takeaways
- 合成肿瘤在医学图像中具有可控特性,有助于机器学习模型的训练,提升分割性能。
- 现有肿瘤合成方法在处理大空间体积的肿瘤时存在性能问题,特别是在MRI中的大视野乳腺癌分割。
- 提出了名为SynBT的3D医学扩散模型,用于生成高质量的对比增强MRI乳腺癌图像。
- 该模型包含patch-to-volume自编码器,能够压缩高分辨率MRI到紧凑潜在空间,同时保持大视野的体积分辨率。
- 使用潜在空间特征向量,通过掩膜控制的扩散模型在选定乳腺组织区域合成肿瘤。
- 评估显示,该方法能提高肿瘤分割模型的性能,在公共数据集上的Dice得分提高2-3%。
点此查看论文截图

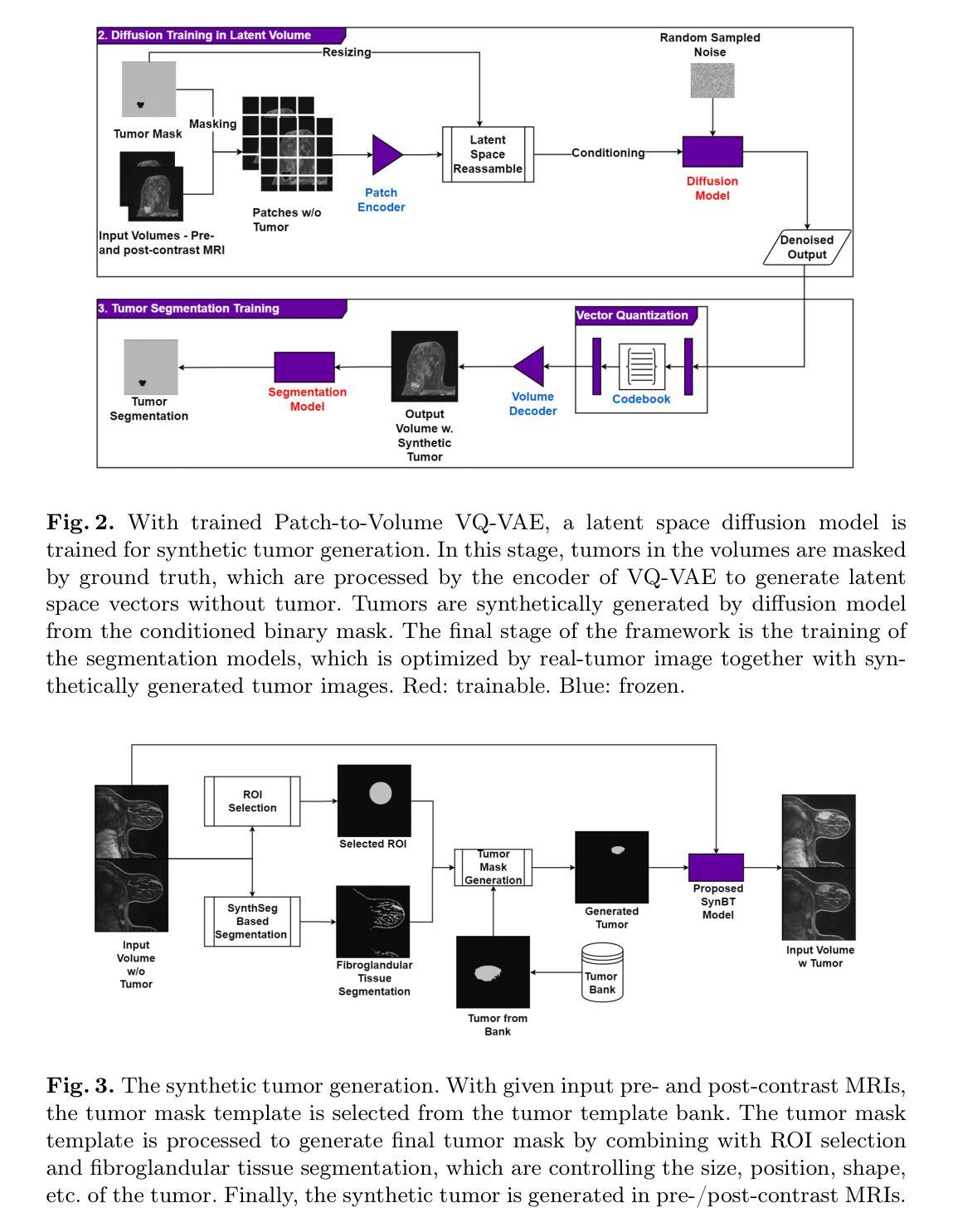
SPENet: Self-guided Prototype Enhancement Network for Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Chao Fan, Xibin Jia, Anqi Xiao, Hongyuan Yu, Zhenghan Yang, Dawei Yang, Hui Xu, Yan Huang, Liang Wang
Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation (FSMIS) aims to segment novel classes of medical objects using only a few labeled images. Prototype-based methods have made significant progress in addressing FSMIS. However, they typically generate a single global prototype for the support image to match with the query image, overlooking intra-class variations. To address this issue, we propose a Self-guided Prototype Enhancement Network (SPENet). Specifically, we introduce a Multi-level Prototype Generation (MPG) module, which enables multi-granularity measurement between the support and query images by simultaneously generating a global prototype and an adaptive number of local prototypes. Additionally, we observe that not all local prototypes in the support image are beneficial for matching, especially when there are substantial discrepancies between the support and query images. To alleviate this issue, we propose a Query-guided Local Prototype Enhancement (QLPE) module, which adaptively refines support prototypes by incorporating guidance from the query image, thus mitigating the negative effects of such discrepancies. Extensive experiments on three public medical datasets demonstrate that SPENet outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior performance.
少量医学图像分割(FSMIS)旨在仅使用少量标记图像对新型医学对象进行分割。基于原型的方法在解决FSMIS方面取得了重大进展。然而,它们通常只为支持图像生成一个全局原型,以与查询图像相匹配,从而忽略了类内变化。为了解决此问题,我们提出了一种自引导原型增强网络(SPENet)。具体来说,我们引入了多级原型生成(MPG)模块,该模块通过同时生成全局原型和自适应数量的局部原型,实现了支持图像和查询图像之间的多粒度度量。此外,我们观察到支持图像中的所有局部原型并不都有利于匹配,尤其是在支持图像和查询图像之间存在显著差异时。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了查询引导局部原型增强(QLPE)模块,该模块通过融入查询图像的指导信息自适应地优化支持原型,从而减轻了此类差异带来的负面影响。在三个公开医学数据集上的大量实验表明,SPENet优于现有最先进的方法,实现了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学图像分割的新方法——自我引导原型增强网络(SPENet)。针对现有原型方法忽略类内变化的问题,提出了多级别原型生成模块,能够生成全局原型和自适应数量的局部原型,以实现多粒度测量。同时,为解决支持图像与查询图像间差异导致的问题,提出了查询引导局部原型增强模块,通过融入查询图像的引导信息来优化支持原型。在三个公开医学数据集上的实验表明,SPENet优于现有方法,取得了优越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation (FSMIS)的目标是仅使用少量标记图像对新的医学对象进行分类。
- 原型方法已在FSMIS中取得显著进展,但通常只生成单一全局原型,忽略了类内变化。
- SPENet通过引入多级别原型生成模块来解决这一问题,该模块可以同时生成全局原型和自适应数量的局部原型。
- 在支持图像和查询图像之间存在差异时,并非所有局部原型都有益于匹配。
- SPENet通过查询引导局部原型增强模块来解决这一问题,该模块通过融入查询图像的引导信息来优化支持原型。
- 实验表明,SPENet在三个公开医学数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
- SPENet的实现结合了全局和局部原型,有效应对了医学图像中的复杂性和类内变化。
点此查看论文截图


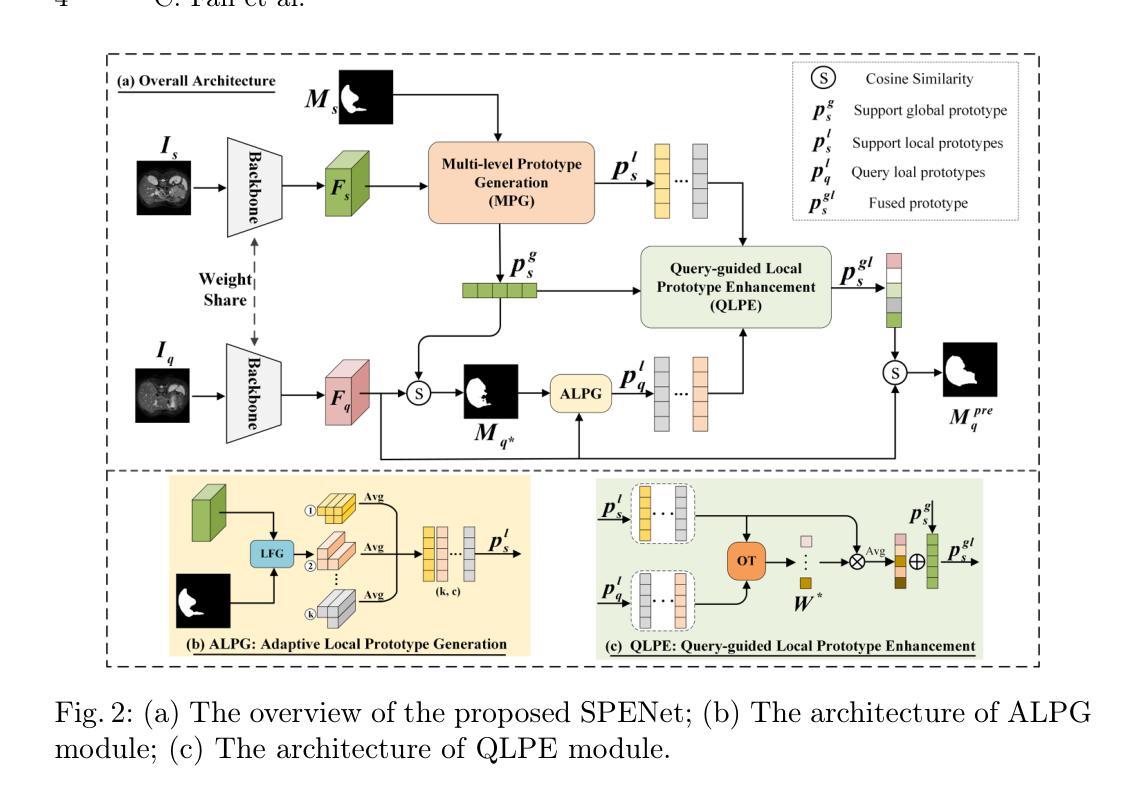
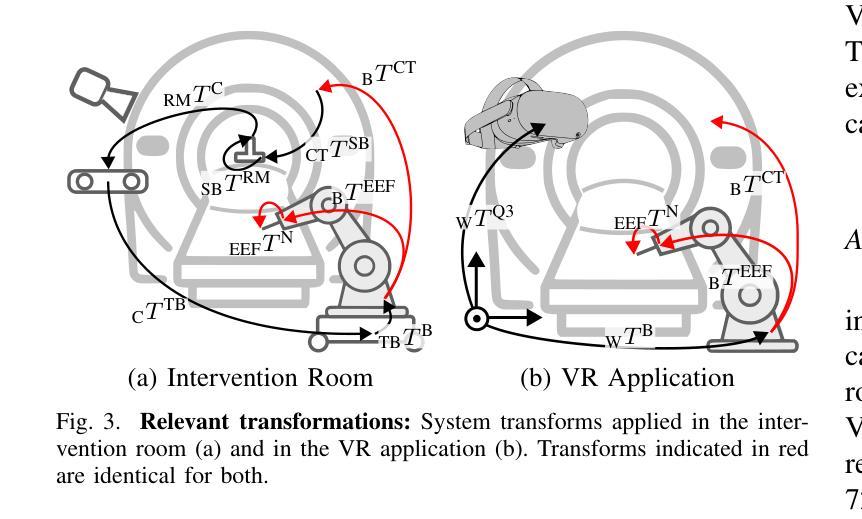
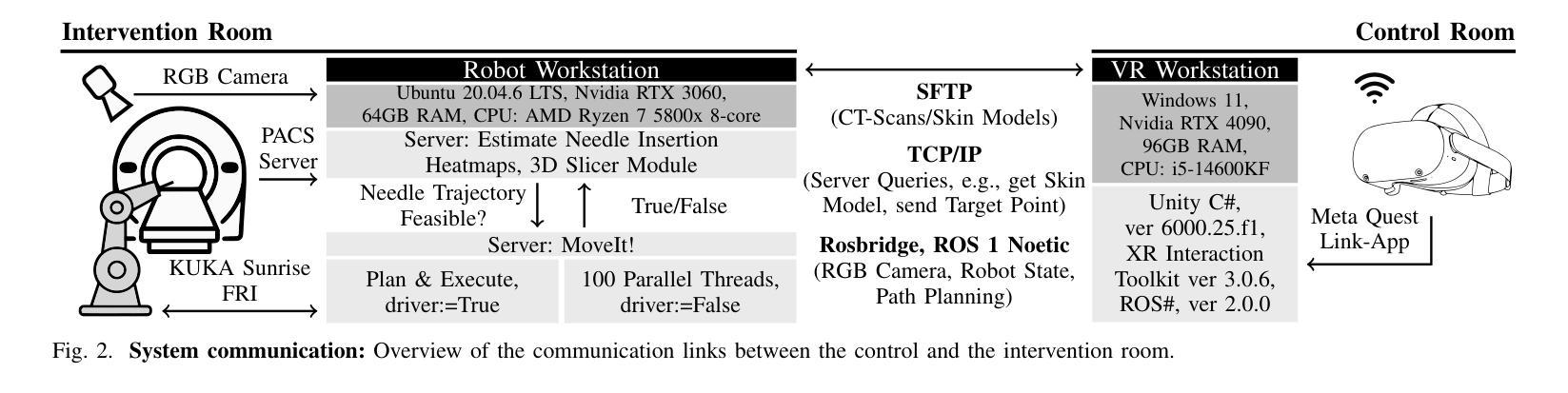
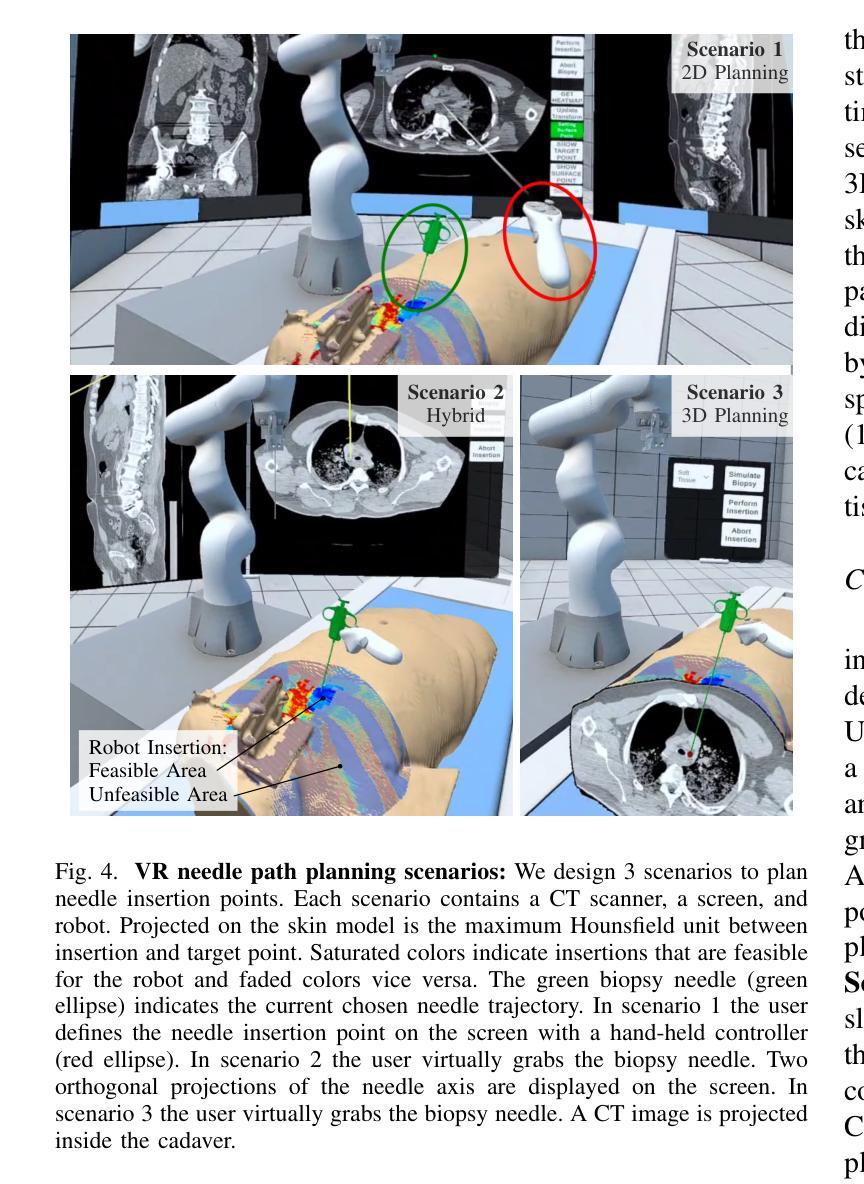
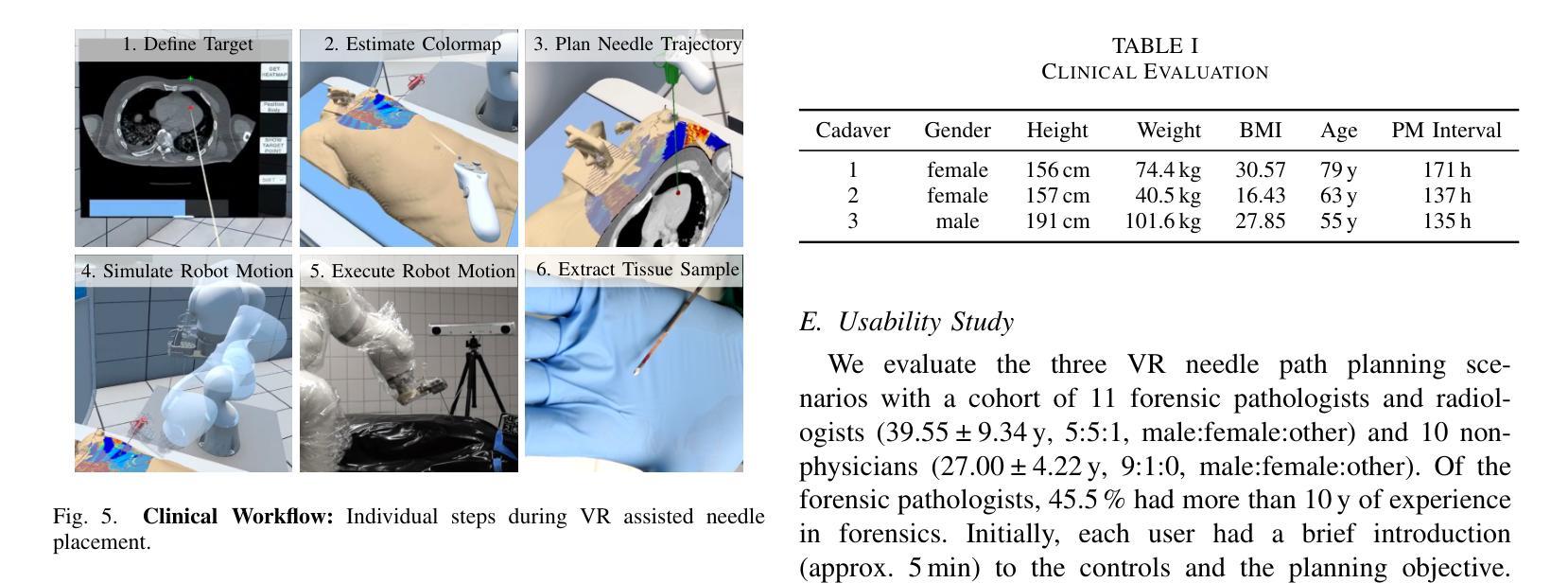
A Digital Twin for Robotic Post Mortem Tissue Sampling using Virtual Reality
Authors:Maximilian Neidhardt, Ludwig Bosse, Vidas Raudonis, Kristina Allgoewer, Axel Heinemann, Benjamin Ondruschka, Alexander Schlaefer
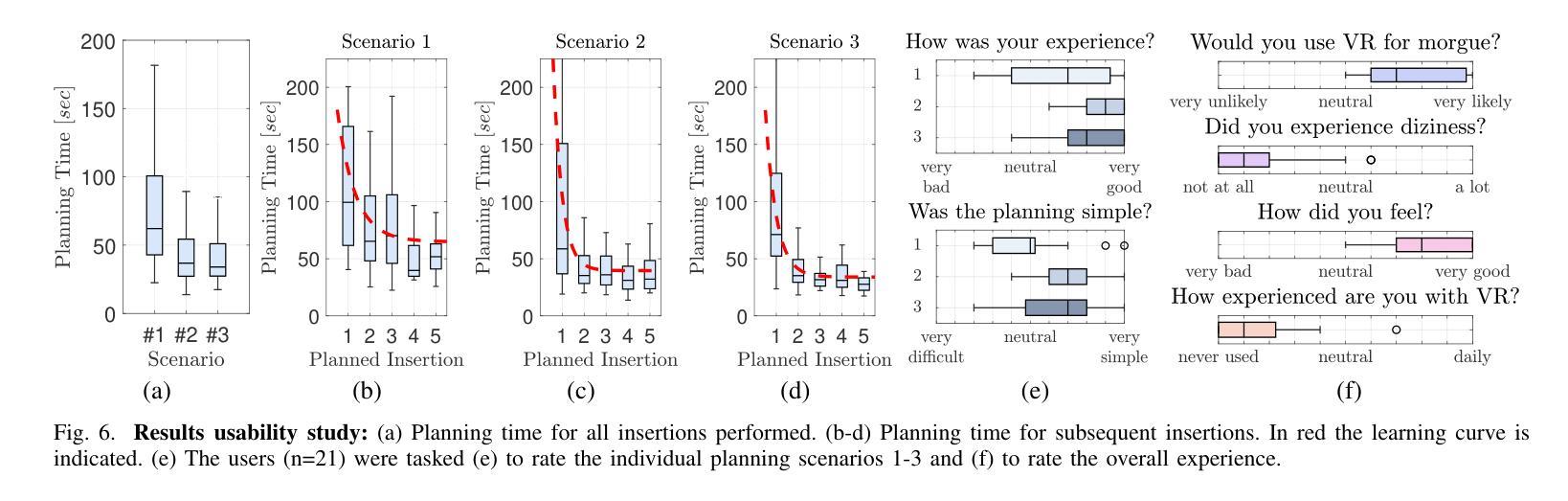
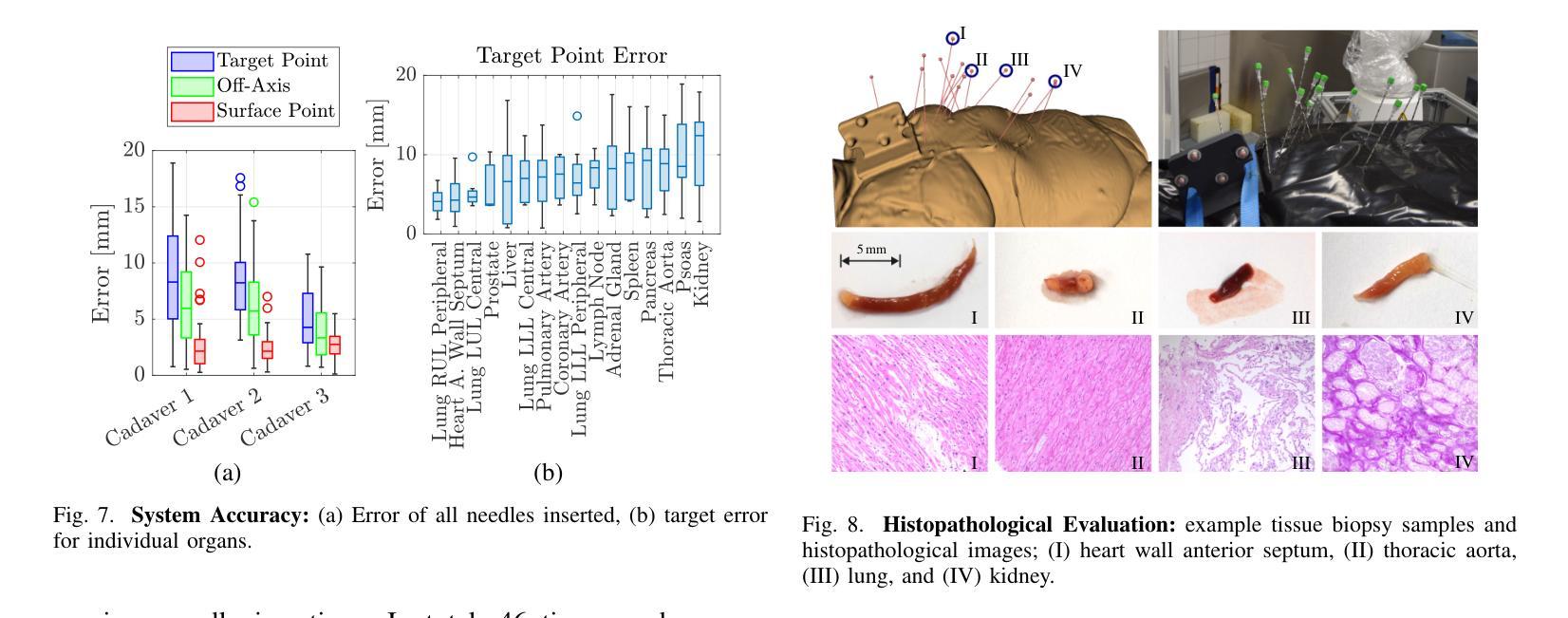
Studying tissue samples obtained during autopsies is the gold standard when diagnosing the cause of death and for understanding disease pathophysiology. Recently, the interest in post mortem minimally invasive biopsies has grown which is a less destructive approach in comparison to an open autopsy and reduces the risk of infection. While manual biopsies under ultrasound guidance are more widely performed, robotic post mortem biopsies have been recently proposed. This approach can further reduce the risk of infection for physicians. However, planning of the procedure and control of the robot need to be efficient and usable. We explore a virtual reality setup with a digital twin to realize fully remote planning and control of robotic post mortem biopsies. The setup is evaluated with forensic pathologists in a usability study for three interaction methods. Furthermore, we evaluate clinical feasibility and evaluate the system with three human cadavers. Overall, 132 needle insertions were performed with an off-axis needle placement error of 5.30+-3.25 mm. Tissue samples were successfully biopsied and histopathologically verified. Users reported a very intuitive needle placement approach, indicating that the system is a promising, precise, and low-risk alternative to conventional approaches.
研究在尸检过程中获得的组织样本是金标准,在诊断死亡原因和了解疾病病理生理学方面具有重要意义。最近,对死后微创活检的兴趣有所增加,这是一种与开放尸检相比破坏性较小的方法,并降低了感染的风险。虽然超声引导下手动活检更为普遍,但死后机器人活检最近已被提出。这种方法可以进一步降低医生感染的风险。然而,程序的规划和机器人的控制必须高效且易于使用。我们探索了使用数字双胞胎的虚拟现实设置,以实现远程规划和控制死后机器人活检。该设置通过法医病理学家对三种交互方法进行了可用性评估。此外,我们还评估了临床可行性,并用三具人类遗体对系统进行了评估。总体而言,进行了132次针刺插入,离轴针放置误差为5.30+-3.25毫米。成功进行了组织样本活检并进行病理组织学验证。用户报告了一种非常直观的针放置方法,表明该系统是一个有前途的、精确的、低风险的替代传统方法的选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在尸检过程中获取组织样本进行研究是诊断死亡原因和了解疾病病理生理学的金标准。近期,对尸检微创活检技术的兴趣日益浓厚,与开放性尸检相比,这是一种破坏程度较低的方法,降低了感染风险。虽然超声引导下手动活检更普遍,但机器人进行尸检活检的方法也已被提出。为降低医师感染风险,本文探索了使用虚拟现实设置和数字孪生技术实现远程规划和控制机器人进行尸检活检。通过法医病理学家进行可用性评估,并对三种交互方法进行了评估。此外,还评估了系统的临床可行性,并在三具人类尸体上进行了测试。总体上,进行了132次针头插入操作,离轴针头放置误差为5.30±3.25毫米。成功进行了组织样本活检并进行组织病理学验证。用户报告针头放置方法非常直观,表明该系统是一个有前途的、精确的、低风险的替代传统方法。
Key Takeaways
- 尸检中研究组织样本是诊断死亡原因和了解疾病病理生理学的金标准。
- 微创活检技术成为尸检的新趋势,以降低感染风险。
- 机器人进行尸检活检能够进一步降低医师感染风险。
- 使用虚拟现实设置和数字孪生技术可以实现远程规划和控制机器人进行尸检活检。
- 系统可用性得到了法医病理学家的评估。
- 在三具人类尸体上进行了系统的临床可行性评估,总体上的针头放置误差较小。
点此查看论文截图

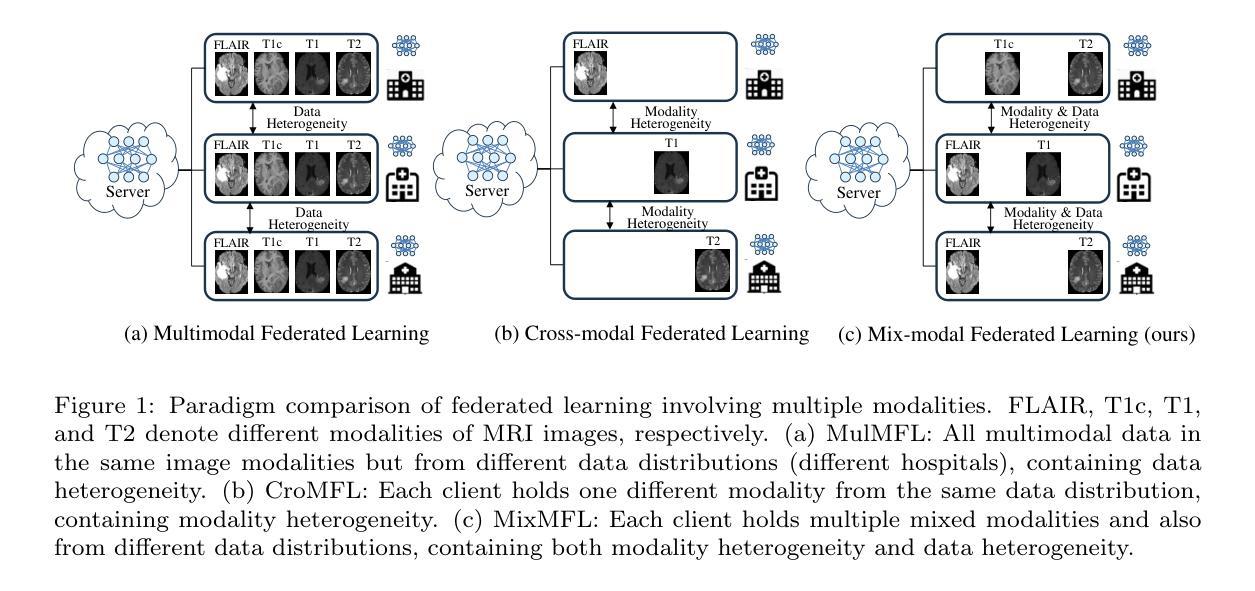
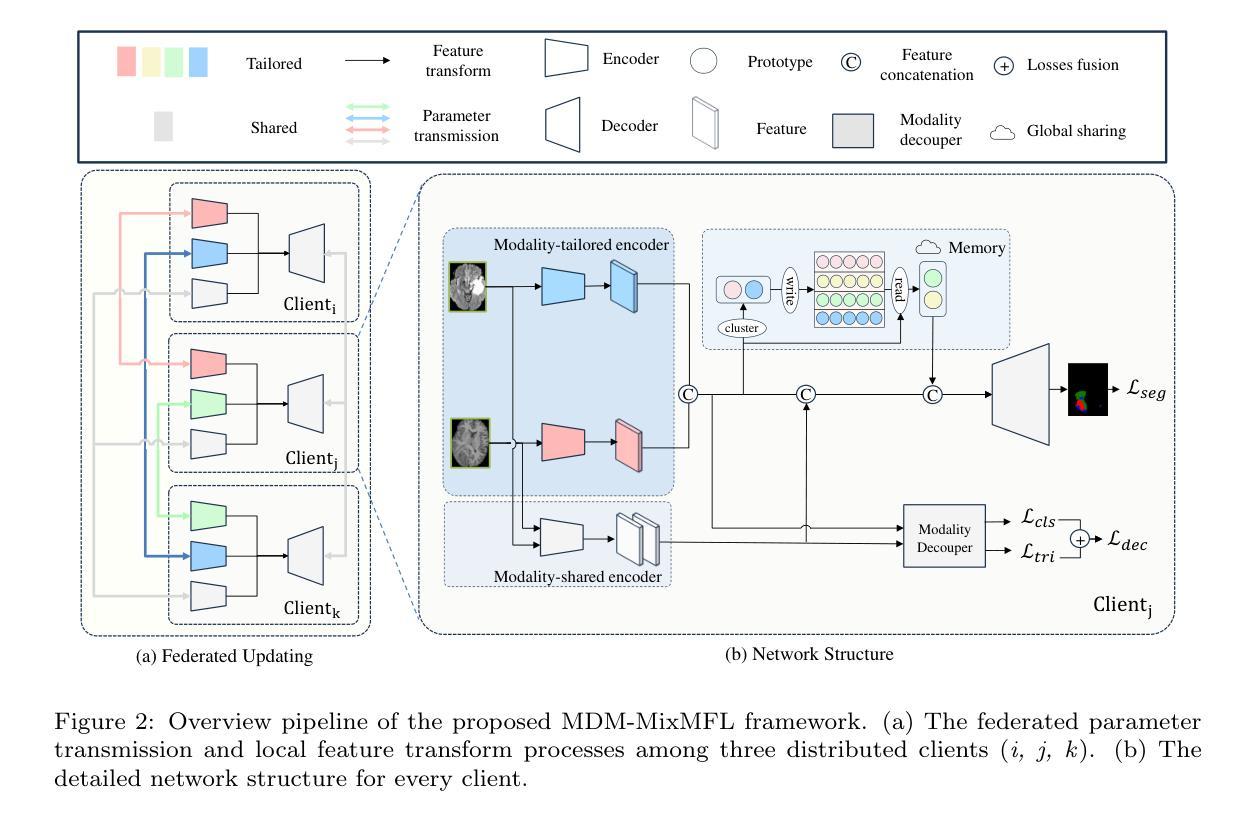
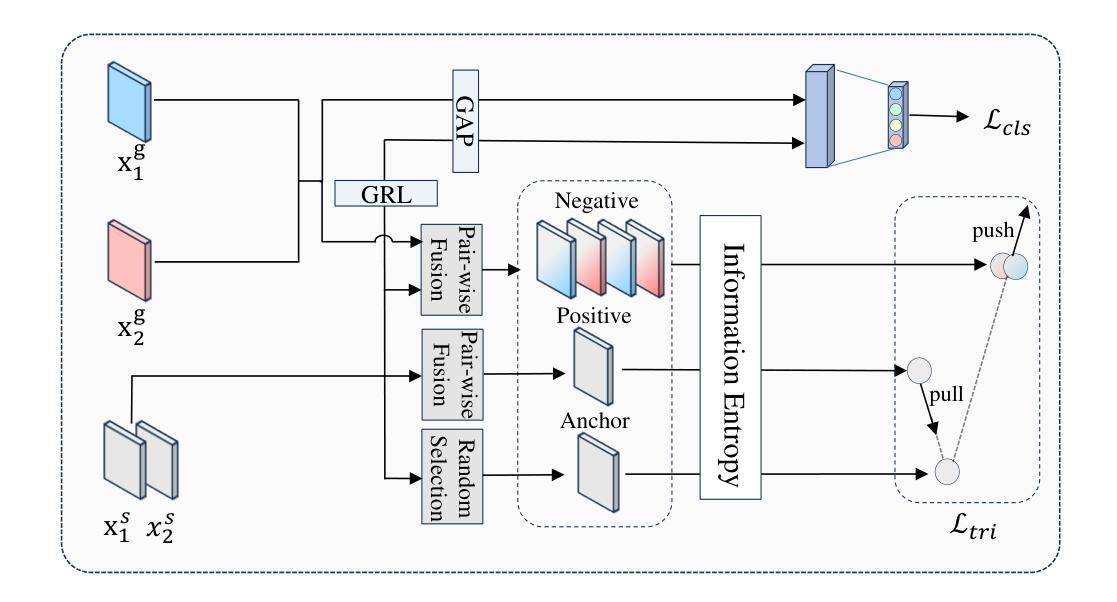
Mix-modal Federated Learning for MRI Image Segmentation
Authors:Guyue Hu, Siyuan Song, Jingpeng Sun, Zhe Jin, Chenglong Li, Jin Tang
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image segmentation is crucial in diagnosing and treating many diseases, such as brain tumors. Existing MRI image segmentation methods mainly fall into a centralized multimodal paradigm, which is inapplicable in engineering non-centralized mix-modal medical scenarios. In this situation, each distributed client (hospital) processes multiple mixed MRI modalities, and the modality set and image data for each client are diverse, suffering from extensive client-wise modality heterogeneity and data heterogeneity. In this paper, we first formulate non-centralized mix-modal MRI image segmentation as a new paradigm for federated learning (FL) that involves multiple modalities, called mix-modal federated learning (MixMFL). It distinguishes from existing multimodal federating learning (MulMFL) and cross-modal federating learning (CroMFL) paradigms. Then, we proposed a novel modality decoupling and memorizing mix-modal federated learning framework (MDM-MixMFL) for MRI image segmentation, which is characterized by a modality decoupling strategy and a modality memorizing mechanism. Specifically, the modality decoupling strategy disentangles each modality into modality-tailored and modality-shared information. During mix-modal federated updating, corresponding modality encoders undergo tailored and shared updating, respectively. It facilitates stable and adaptive federating aggregation of heterogeneous data and modalities from distributed clients. Besides, the modality memorizing mechanism stores client-shared modality prototypes dynamically refreshed from every modality-tailored encoder to compensate for incomplete modalities in each local client. It further benefits modality aggregation and fusion processes during mixmodal federated learning. Extensive experiments on two public datasets for MRI image segmentation demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our methods.
磁共振成像(MRI)图像分割在诊断和治疗许多疾病(如脑肿瘤)中起着至关重要的作用。现有的MRI图像分割方法主要集中在一个集中的多模态范式上,这在工程非集中混合模态医疗场景中并不适用。在这种情况下,每个分布式客户端(医院)处理多种混合MRI模态,每个客户端的模态集和图像数据各不相同,面临着广泛的客户端模态异质性和数据异质性。在本文中,我们首先制定了一种新的联邦学习(FL)范式,用于非集中混合模态MRI图像分割,称为混合模态联邦学习(MixMFL)。它与现有的多模态联邦学习(MulMFL)和跨模态联邦学习(CroMFL)范式有所不同。然后,我们针对MRI图像分割提出了一种新颖的模态解耦和记忆混合模态联邦学习框架(MDM-MixMFL),其特点是具有模态解耦策略和模态记忆机制。具体来说,模态解耦策略将每个模态分解为模态定制和模态共享的信息。在混合模态联邦更新过程中,相应的模态编码器分别进行定制和共享更新。它促进了来自分布式客户端的异构数据和模态的稳定和自适应联邦聚合。此外,模态记忆机制存储来自每个模态定制编码器的动态刷新客户端共享模态原型,以补偿每个本地客户端的不完整模态。这进一步有利于混合模态联邦学习过程中的模态聚合和融合过程。在MRI图像分割领域的两个公开数据集上进行的广泛实验证明了我们方法的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在非集中式的混合模态医疗场景中,MRI图像分割面临诸多挑战。本文提出一种新的混合模态联邦学习(MixMFL)范式,用于解决非集中式的混合模态MRI图像分割问题。同时,提出了一种新颖的模态解耦和记忆混合模态联邦学习框架(MDM-MixMFL),该框架具有模态解耦策略和模态记忆机制,可有效处理来自分布式客户端的异构数据和模态。
Key Takeaways
- MRI图像分割在许多疾病诊断和治疗中至关重要,如脑肿瘤。
- 现有MRI图像分割方法主要基于集中化的多模态范式,不适用于工程中的非集中化混合模态医疗场景。
- 本文提出一种新的混合模态联邦学习(MixMFL)范式,用于处理非集中化的混合模态MRI图像分割。
- MDM-MixMFL框架具有模态解耦策略和模态记忆机制,可处理来自分布式客户端的异构数据和模态。
- 模态解耦策略将每个模态分解为模态特定和模态共享的信息,便于在混合模态联邦更新中进行针对性的更新。
- 模态记忆机制有助于补偿本地客户端的不完整模态,并进一步促进模态聚合和融合过程。
点此查看论文截图

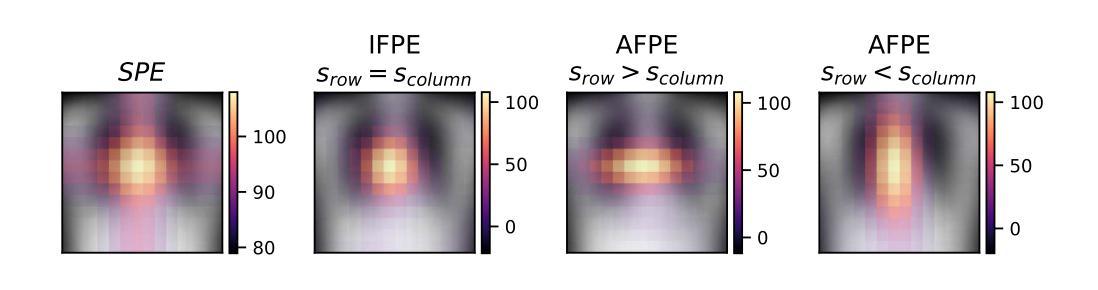
Anisotropic Fourier Features for Positional Encoding in Medical Imaging
Authors:Nabil Jabareen, Dongsheng Yuan, Dingming Liu, Foo-Wei Ten, Sören Lukassen
The adoption of Transformer-based architectures in the medical domain is growing rapidly. In medical imaging, the analysis of complex shapes - such as organs, tissues, or other anatomical structures - combined with the often anisotropic nature of high-dimensional images complicates these adaptations. In this study, we critically examine the role of Positional Encodings (PEs), arguing that commonly used approaches may be suboptimal for the specific challenges of medical imaging. Sinusoidal Positional Encodings (SPEs) have proven effective in vision tasks, but they struggle to preserve Euclidean distances in higher-dimensional spaces. Isotropic Fourier Feature Positional Encodings (IFPEs) have been proposed to better preserve Euclidean distances, but they lack the ability to account for anisotropy in images. To address these limitations, we propose Anisotropic Fourier Feature Positional Encoding (AFPE), a generalization of IFPE that incorporates anisotropic, class-specific, and domain-specific spatial dependencies. We systematically benchmark AFPE against commonly used PEs on multi-label classification in chest X-rays, organ classification in CT images, and ejection fraction regression in echocardiography. Our results demonstrate that choosing the correct PE can significantly improve model performance. We show that the optimal PE depends on the shape of the structure of interest and the anisotropy of the data. Finally, our proposed AFPE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art PEs in all tested anisotropic settings. We conclude that, in anisotropic medical images and videos, it is of paramount importance to choose an anisotropic PE that fits the data and the shape of interest.
在医学领域采用基于Transformer的架构正在迅速增长。在医学成像中,对器官、组织或其他解剖结构等复杂形状的分析,以及高维图像的常各向异性性质,使这些适应复杂化。在这项研究中,我们深入探讨了位置编码(PEs)的作用,认为常用的方法可能不适用于医学成像所面临的特定挑战。正弦位置编码(SPEs)在视觉任务中已被证明是有效的,但在高维空间中难以保持欧几里得距离。各向同性傅里叶特征位置编码(IFPEs)能更好地保持欧几里得距离,但它们无法考虑图像的各向异性。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了各向异性傅里叶特征位置编码(AFPE),它是IFPE的一种推广,结合了各向异性、特定类别和特定领域的空间依赖性。我们在胸部X射线的多标签分类、CT图像的器官分类和超声心动图的射血分数回归等方面系统地评估了AFPE与常用PEs的性能。我们的结果表明,选择正确的PE可以显著提高模型性能。我们证明了最佳PE取决于所关注结构的外形和数据的各向异性。最后,在所有的各向异性测试环境中,我们提出的AFPE显著优于最新的PEs。我们得出结论,在各向异性的医学图像和视频中,选择适合数据和关注形状的各向异性PE至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 3 figures, 2 tables, to be published in ShapeMI MICCAI 2025
摘要
在医学领域,采用基于Transformer的架构越来越受欢迎。在医学成像中,分析复杂的形状(如器官、组织或其他解剖结构)与图像的高维性结合使得这些适应性面临挑战。本研究对位置编码(PEs)的作用进行了批判性评估,认为常用方法可能不适用于医学成像所面临的特定挑战。正弦位置编码(SPEs)在视觉任务中表现出色,但在高维空间中难以保持欧几里得距离。等距傅里叶特征位置编码(IFPEs)能更好地保持欧几里得距离,但忽略了图像的各向异性。为解决这些局限性,我们提出了各向异性傅里叶特征位置编码(AFPE),它是IFPE的一种推广,结合了各向异性、类别特定和领域特定的空间依赖性。我们在胸部X射线的多标签分类、CT图像的器官分类和超声心动图的心功能分级等方面系统地评估了AFPE与常用PE的性能。结果表明,选择正确的PE可以显著提高模型性能。最佳PE的选择取决于关注结构的形状和数据各向异性。最后,在所有的测试各向异性设置中,我们提出的AFPE均显著优于最先进的PEs。我们得出结论,在各向异性的医学图像和视频中,选择适合数据和关注形状的各向异性PE至关重要。
关键见解
- Transformer架构在医学领域的应用正在快速增长,特别是在医学成像领域。
- 位置编码(PEs)在医学成像中的选择至关重要,因为图像复杂性对模型性能有影响。
- 常见位置编码方法可能在处理医学图像的特定挑战时表现不佳。
- 各向异性傅里叶特征位置编码(AFPE)是一种新型编码方法,能够结合各向异性、类别特定和领域特定的空间依赖性。
- AFPE在多种医学成像任务上显著优于其他位置编码方法。
- 选择最佳的位置编码取决于关注的结构形状和数据的各向异性。
点此查看论文截图

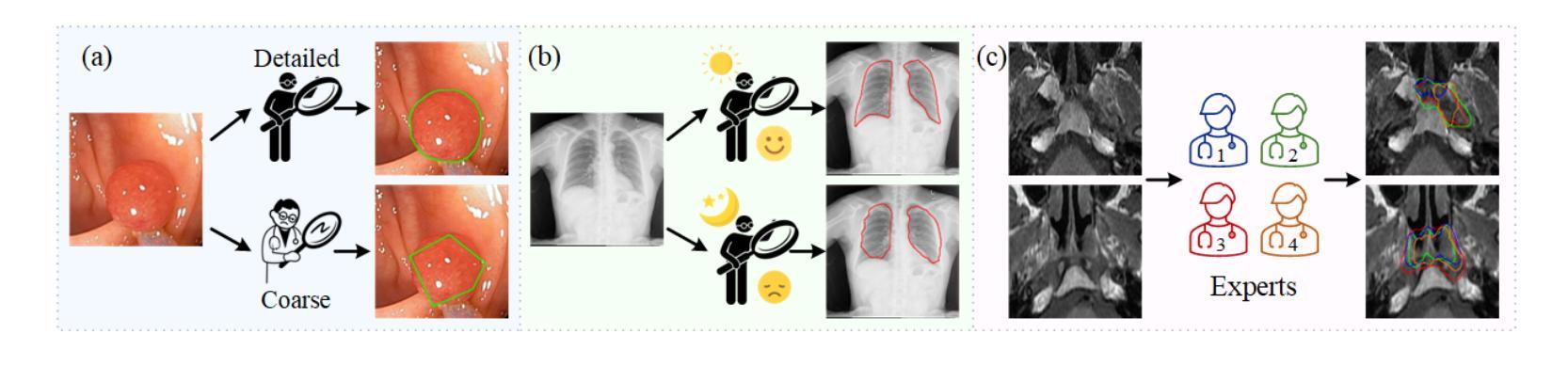
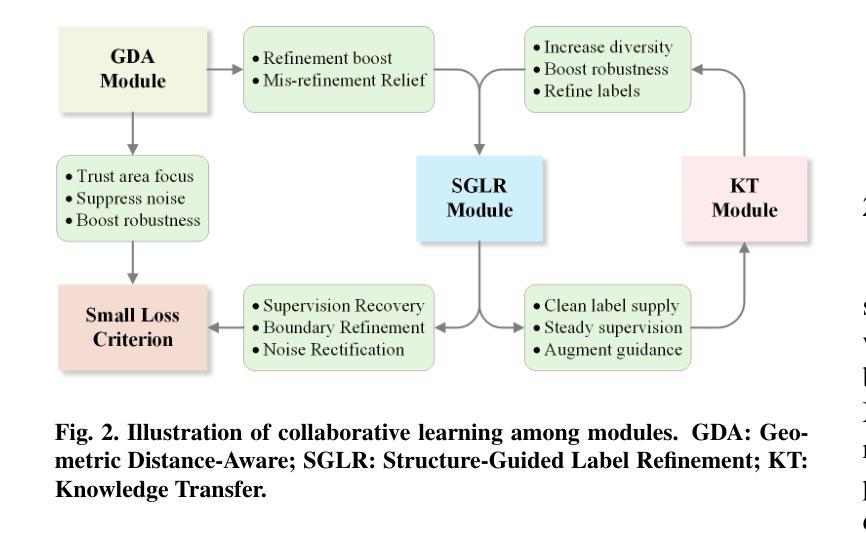
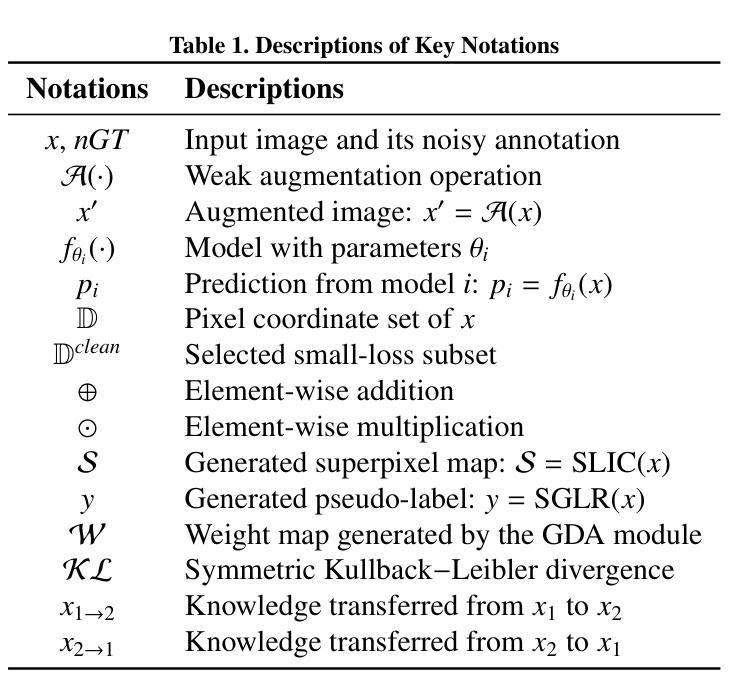
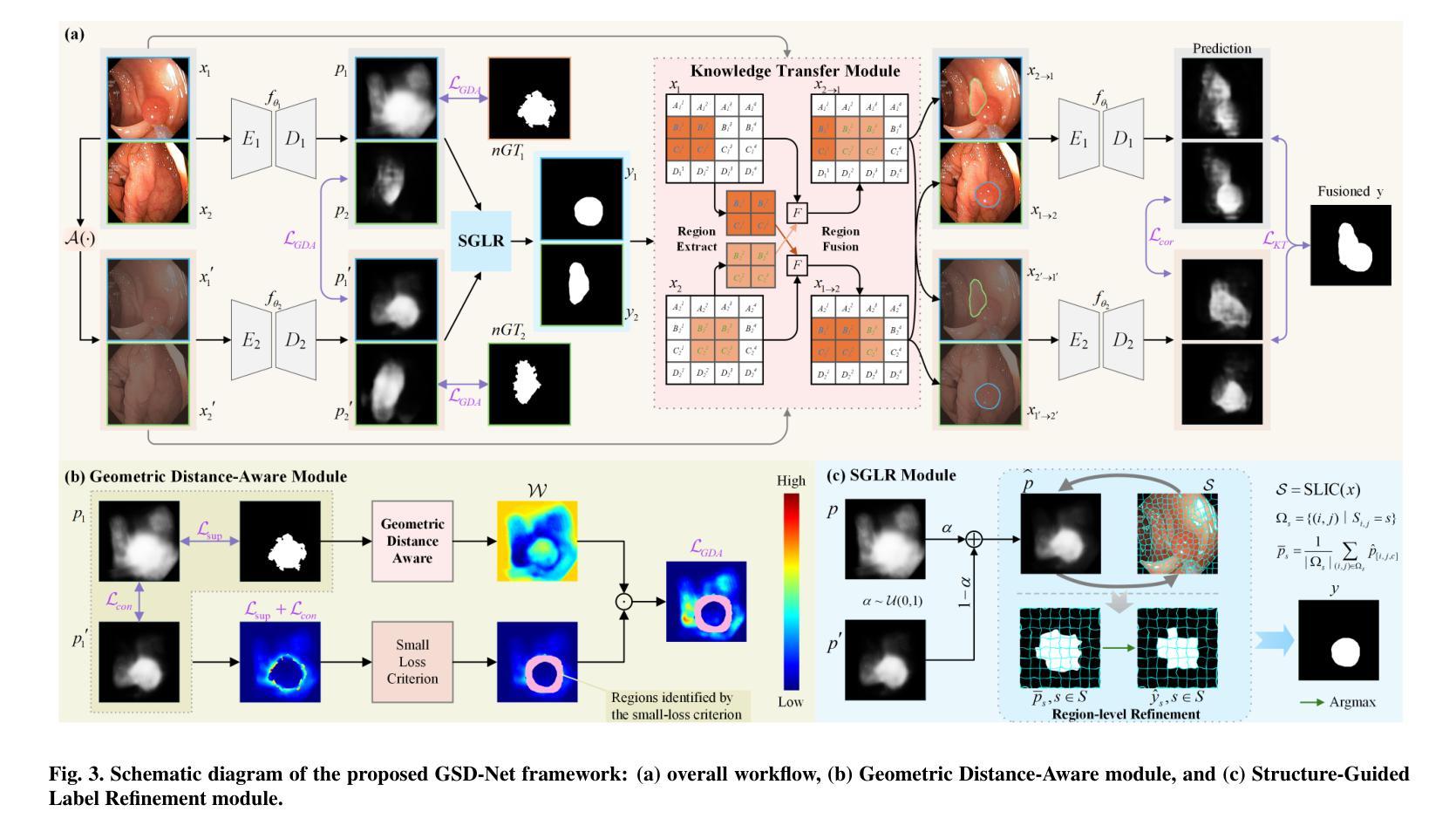
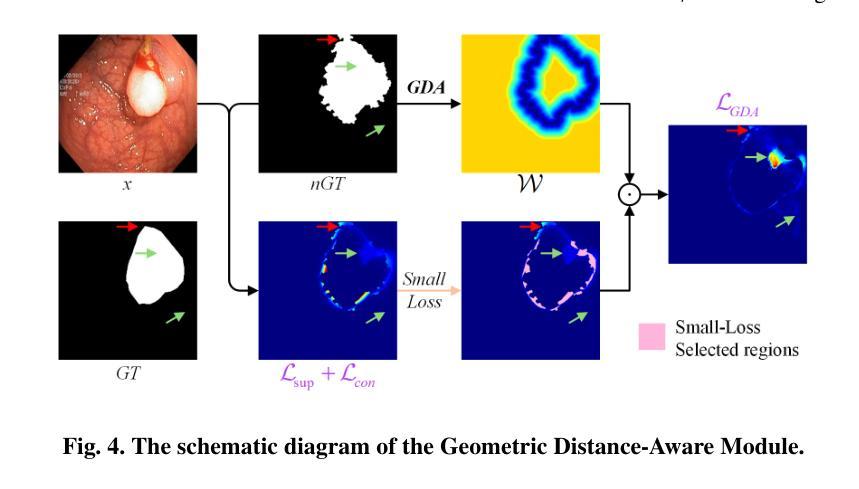
From Noisy Labels to Intrinsic Structure: A Geometric-Structural Dual-Guided Framework for Noise-Robust Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tao Wang, Zhenxuan Zhang, Yuanbo Zhou, Xinlin Zhang, Yuanbin Chen, Tao Tan, Guang Yang, Tong Tong
The effectiveness of convolutional neural networks in medical image segmentation relies on large-scale, high-quality annotations, which are costly and time-consuming to obtain. Even expert-labeled datasets inevitably contain noise arising from subjectivity and coarse delineations, which disrupt feature learning and adversely impact model performance. To address these challenges, this study propose a Geometric-Structural Dual-Guided Network (GSD-Net), which integrates geometric and structural cues to improve robustness against noisy annotations. It incorporates a Geometric Distance-Aware module that dynamically adjusts pixel-level weights using geometric features, thereby strengthening supervision in reliable regions while suppressing noise. A Structure-Guided Label Refinement module further refines labels with structural priors, and a Knowledge Transfer module enriches supervision and improves sensitivity to local details. To comprehensively assess its effectiveness, we evaluated GSD-Net on six publicly available datasets: four containing three types of simulated label noise, and two with multi-expert annotations that reflect real-world subjectivity and labeling inconsistencies. Experimental results demonstrate that GSD-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance under noisy annotations, achieving improvements of 2.52% on Kvasir, 22.76% on Shenzhen, 8.87% on BU-SUC, and 4.59% on BraTS2020 under SR simulated noise. The codes of this study are available at https://github.com/ortonwang/GSD-Net.
卷积神经网络在医学图像分割中的有效性依赖于大规模的高质量标注,而这些标注的获取成本高昂且耗时。即使是专家标注的数据集也不可避免地包含由于主观性和粗略描绘而产生的噪声,这些噪声会破坏特征学习并对模型性能产生不利影响。为了解决这些挑战,本研究提出了一种几何结构双重引导网络(GSD-Net),它融合了几何和结构线索,以提高对噪声标注的稳健性。它引入了一个几何距离感知模块,该模块使用几何特征动态调整像素级权重,从而在可靠的区域加强监督,同时抑制噪声。结构引导标签细化模块进一步使用结构先验来细化标签,知识传递模块丰富了监督并提高了对局部细节的敏感度。为了全面评估其有效性,我们在六个公开数据集上评估了GSD-Net的性能:四个数据集包含三种模拟标签噪声,两个数据集具有多专家注释,反映了现实世界中的主观性和标签不一致性。实验结果表明,在噪声标注下,GSD-Net达到了最先进的性能,在Kvasir上提高了2.52%,在Shenzhen上提高了22.76%,在BU-SUC上提高了8.87%,在BraTS2020的SR模拟噪声下提高了4.59%。该研究的代码可在https://github.com/ortonwang/GSD-Net获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大规模高质量注释的卷积神经网络在医学图像分割中的有效性是建立在其成本高昂且耗时的获取过程之上的。专家标注的数据集不可避免地存在由于主观性和粗略描绘而产生的噪声,这破坏了特征学习并对模型性能产生负面影响。本研究提出一种几何结构双重引导网络(GSD-Net),它整合几何和结构线索,提高对抗噪声注释的稳健性。通过几何距离感知模块动态调整像素级权重,利用结构先验进一步细化标签,并丰富监督和提高对局部细节的敏感性。在六个公开数据集上的评估表明,GSD-Net在噪声标注下实现了最佳性能,在Kvasir、Shenzhen、BU-SUC和BraTS2020等数据集上的改进率分别为2.52%、22.76%、8.87%和4.59%。
Key Takeaways
- 卷积神经网络在医学图像分割中的有效性依赖于大规模高质量注释,但获取这些注释成本高昂且耗时。
- 专家标注的数据集存在由于主观性和粗略描绘而产生的噪声,影响模型性能。
- 本研究提出GSD-Net,通过整合几何和结构线索,提高对抗噪声注释的稳健性。
- GSD-Net包含几何距离感知模块、结构引导标签细化模块和知识转移模块。
- 几何距离感知模块能动态调整像素级权重,强化可靠区域的监督,抑制噪声。
- 结构引导标签细化模块利用结构先验细化标签。
- GSD-Net在多个公开数据集上实现最佳性能,展现出对噪声标注的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

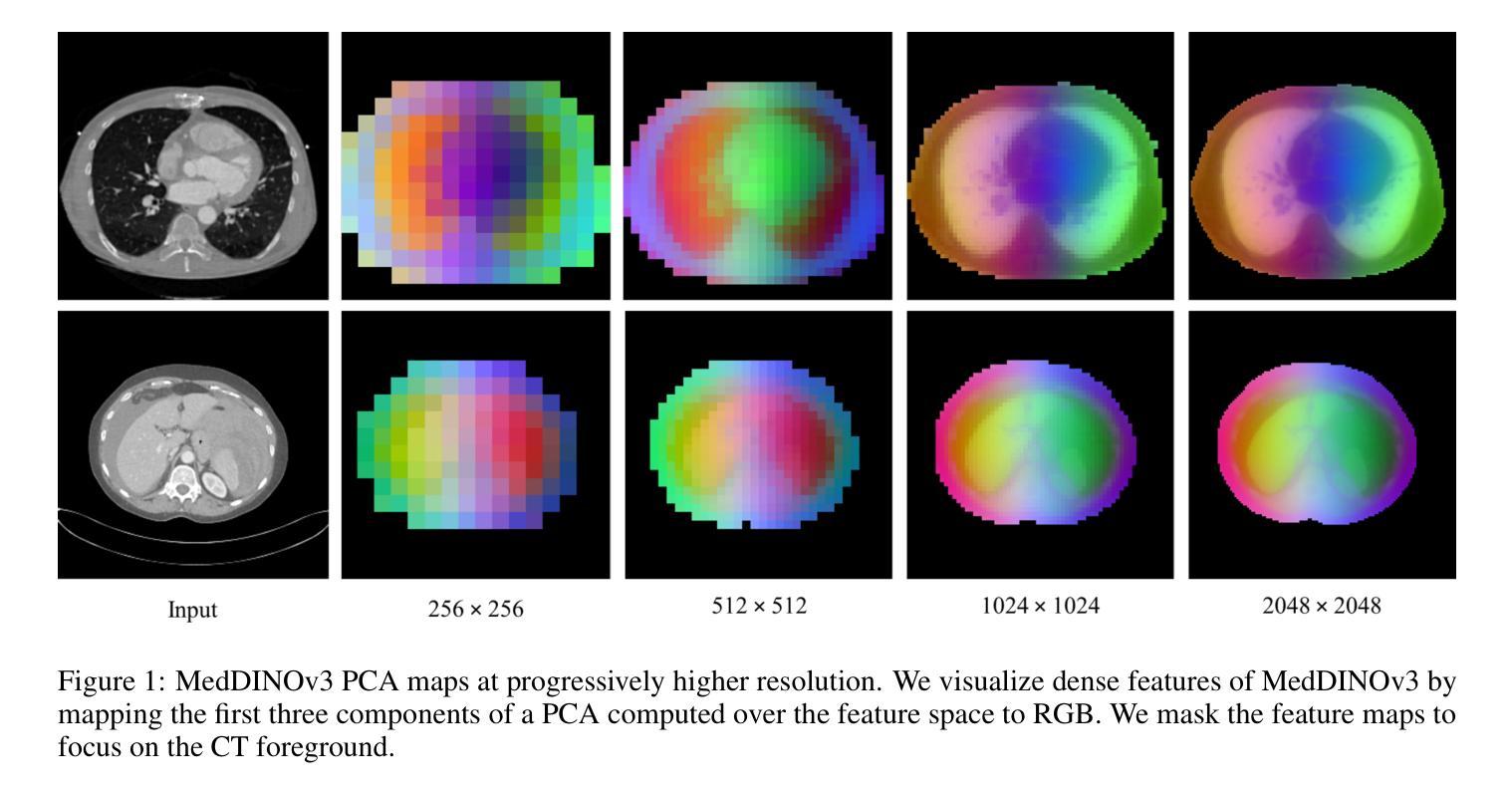
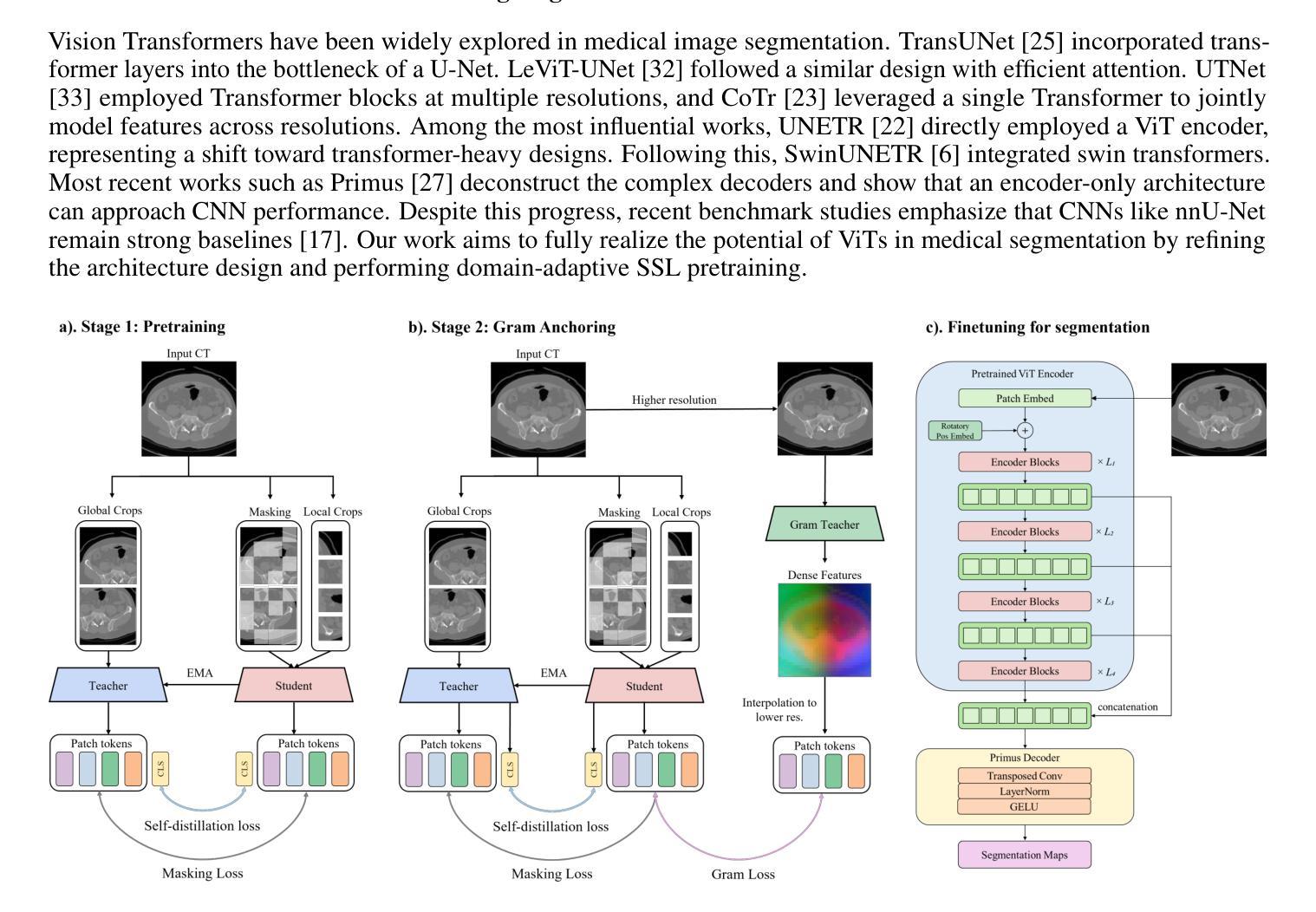
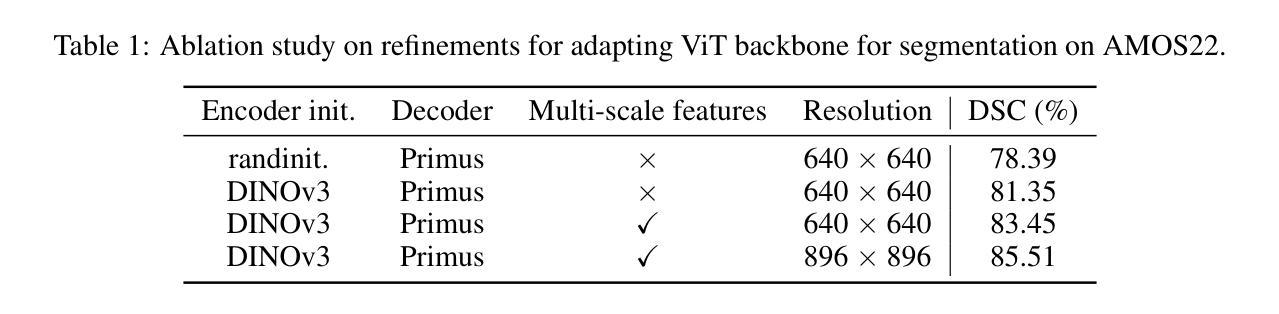
MedDINOv3: How to adapt vision foundation models for medical image segmentation?
Authors:Yuheng Li, Yizhou Wu, Yuxiang Lai, Mingzhe Hu, Xiaofeng Yang
Accurate segmentation of organs and tumors in CT and MRI scans is essential for diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease monitoring. While deep learning has advanced automated segmentation, most models remain task-specific, lacking generalizability across modalities and institutions. Vision foundation models (FMs) pretrained on billion-scale natural images offer powerful and transferable representations. However, adapting them to medical imaging faces two key challenges: (1) the ViT backbone of most foundation models still underperform specialized CNNs on medical image segmentation, and (2) the large domain gap between natural and medical images limits transferability. We introduce MedDINOv3, a simple and effective framework for adapting DINOv3 to medical segmentation. We first revisit plain ViTs and design a simple and effective architecture with multi-scale token aggregation. Then, we perform domain-adaptive pretraining on CT-3M, a curated collection of 3.87M axial CT slices, using a multi-stage DINOv3 recipe to learn robust dense features. MedDINOv3 matches or exceeds state-of-the-art performance across four segmentation benchmarks, demonstrating the potential of vision foundation models as unified backbones for medical image segmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/ricklisz/MedDINOv3.
在CT和MRI扫描中,器官和肿瘤的精确分割对于诊断、治疗规划和疾病监测至关重要。深度学习虽然推动了自动化分割技术的发展,但大多数模型仍然是针对特定任务,在不同模态和机构之间缺乏通用性。视觉基础模型(FMs),在百亿级自然图像上进行预训练,提供了强大且可迁移的表示能力。然而,将其适应医学成像面临两个主要挑战:(1)大多数基础模型的ViT骨干网在医学图像分割方面仍不如专业化的CNN表现良好;(2)自然图像和医学图像之间的领域差距限制了可迁移性。我们引入了MedDINOv3,这是一个简单有效的框架,用于将DINOv3适应医学分割。我们首先回顾了简单的ViTs,并设计了一个简单有效的具有多尺度令牌聚合的架构。然后,我们在CT-3M(一个精选的包含387万张轴向CT切片的集合)上进行域自适应预训练,采用多阶段的DINOv3配方来学习稳健的密集特征。MedDINOv3在四个分割基准测试中达到了或超过了最先进的性能,证明了视觉基础模型作为医学图像分割统一骨干的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/ricklisz/MedDINOv3获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了MedDINOv3框架,该框架将DINOv3适应于医学图像分割。通过重新审视普通ViTs并设计简洁有效的多尺度令牌聚合架构,以及使用CT-3M上的域自适应预训练,MedDINOv3在四个分割基准测试上达到了或超越了最新性能,证明了视觉基础模型作为医学图像分割的统一骨干网的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像中器官和肿瘤的精确分割对诊断、治疗规划和疾病监测至关重要。
- 深度学习已推进了自动化分割,但大多数模型仍缺乏跨模态和机构的通用性。
- 视觉基础模型(FMs)在医学成像中面临两大挑战:ViT主干在医学图像分割上性能不足以及自然与医学图像之间的域差距限制了可转移性。
- MedDINOv3框架旨在解决上述问题,通过适应DINOv3至医学分割领域。
- MedDINOv3设计了一种简洁有效的多尺度令牌聚合架构,并使用了CT-3M数据集上的域自适应预训练。
- MedDINOv3在四个分割基准测试中表现优异,证明了其在医学图像分割中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

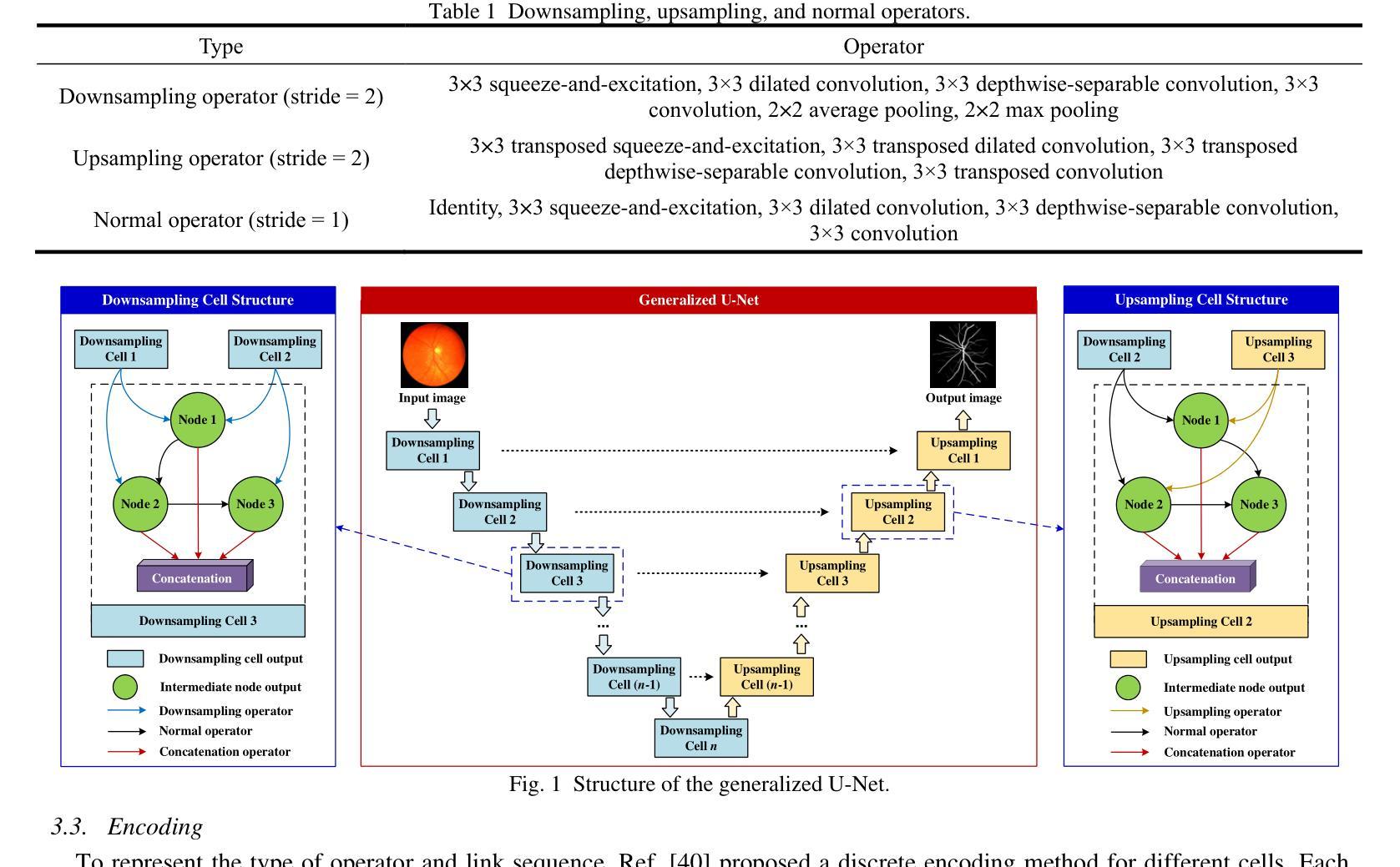
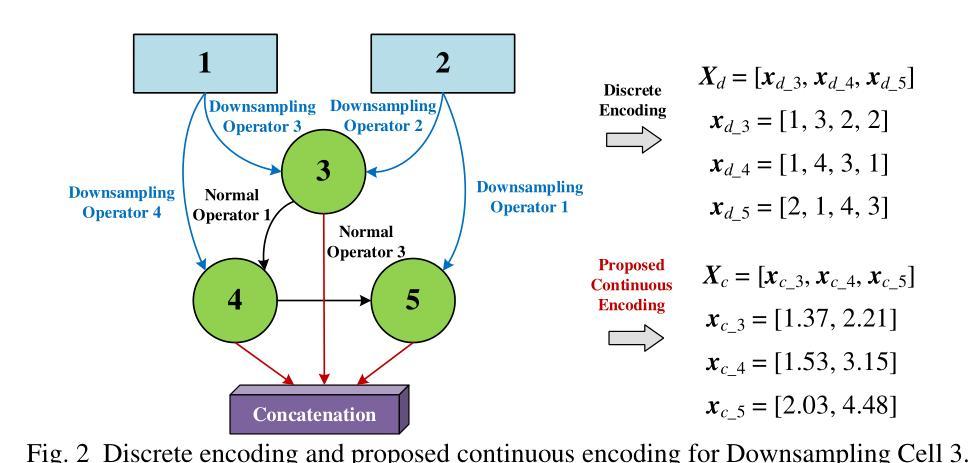
A Continuous Encoding-Based Representation for Efficient Multi-Fidelity Multi-Objective Neural Architecture Search
Authors:Zhao Wei, Chin Chun Ooi, Yew-Soon Ong
Neural architecture search (NAS) is an attractive approach to automate the design of optimized architectures but is constrained by high computational budget, especially when optimizing for multiple, important conflicting objectives. To address this, an adaptive Co-Kriging-assisted multi-fidelity multi-objective NAS algorithm is proposed to further reduce the computational cost of NAS by incorporating a clustering-based local multi-fidelity infill sampling strategy, enabling efficient exploration of the search space for faster convergence. This algorithm is further accelerated by the use of a novel continuous encoding method to represent the connections of nodes in each cell within a generalized cell-based U-Net backbone, thereby decreasing the search dimension (number of variables). Results indicate that the proposed NAS algorithm outperforms previously published state-of-the-art methods under limited computational budget on three numerical benchmarks, a 2D Darcy flow regression problem and a CHASE_DB1 biomedical image segmentation problem. The proposed method is subsequently used to create a wind velocity regression model with application in urban modelling, with the found model able to achieve good prediction with less computational complexity. Further analysis revealed that the NAS algorithm independently identified principles undergirding superior U-Net architectures in other literature, such as the importance of allowing each cell to incorporate information from prior cells.
神经网络架构搜索(NAS)是一种吸引人的自动化设计优化架构的方法,但受到高计算预算的限制,尤其是在针对多个重要且相互冲突的目标进行优化时。为了解决这一问题,提出了一种自适应协同克里格辅助多保真多目标NAS算法,通过引入基于聚类的局部多保真填充采样策略,进一步降低了NAS的计算成本,实现了搜索空间的高效探索,从而加快了收敛速度。该算法通过使用一种新的连续编码方法来表示基于通用单元U-Net骨干网中每个单元的连接,从而降低了搜索维度(变量数),进一步加速了算法。结果表明,在有限的计算预算下,所提出的NAS算法在三个数值基准测试、一个2D Darcy流回归问题和一个CHASE_DB1生物医学图像分割问题上优于之前发表的最先进方法。随后,该方法被用于创建风速回归模型,应用于城市建模,所发现的模型能够以较低的计算复杂度实现良好的预测。进一步分析表明,NAS算法独立地发现了其他文献中支撑优越U-Net架构的原则,例如允许每个单元从前序单元中获取信息的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对神经网络架构搜索(NAS)在计算预算高且需要优化多个重要冲突目标时存在的挑战,提出了一种自适应协同克里格辅助的多保真多目标NAS算法。该算法通过引入基于聚类的局部多保真填充采样策略,实现了搜索空间的高效探索,从而加快了收敛速度。此外,通过使用新型连续编码方法表示通用单元基U-Net骨架中每个单元的连接,进一步加速了算法,并降低了搜索维度(变量数)。在三个数值基准测试、一个二维达西流回归问题和CHASE_DB1生物医学图像分割问题上,所提NAS算法在有限计算预算下表现出优于先前最先进方法的效果。此外,利用该方法创建了用于城市建模的风速回归模型,所建模型在降低计算复杂性的同时,具有良好的预测能力。研究还发现,NAS算法独立地揭示了其他文献中支撑优秀U-Net架构的原则,如允许每个单元从前单元获取信息的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- NAS算法可以通过自适应协同克里格辅助的多保真多目标优化策略来降低计算成本。
- 通过引入基于聚类的局部多保真填充采样策略,该算法能高效探索搜索空间并加快收敛速度。
- 使用新型连续编码方法表示单元连接,降低搜索维度并提高算法效率。
- 所提NAS算法在多个基准测试上表现优于现有技术,特别是在有限的计算预算下。
- 该算法可应用于创建城市模型中的风速回归模型,具有良好的预测能力且计算复杂性较低。
点此查看论文截图

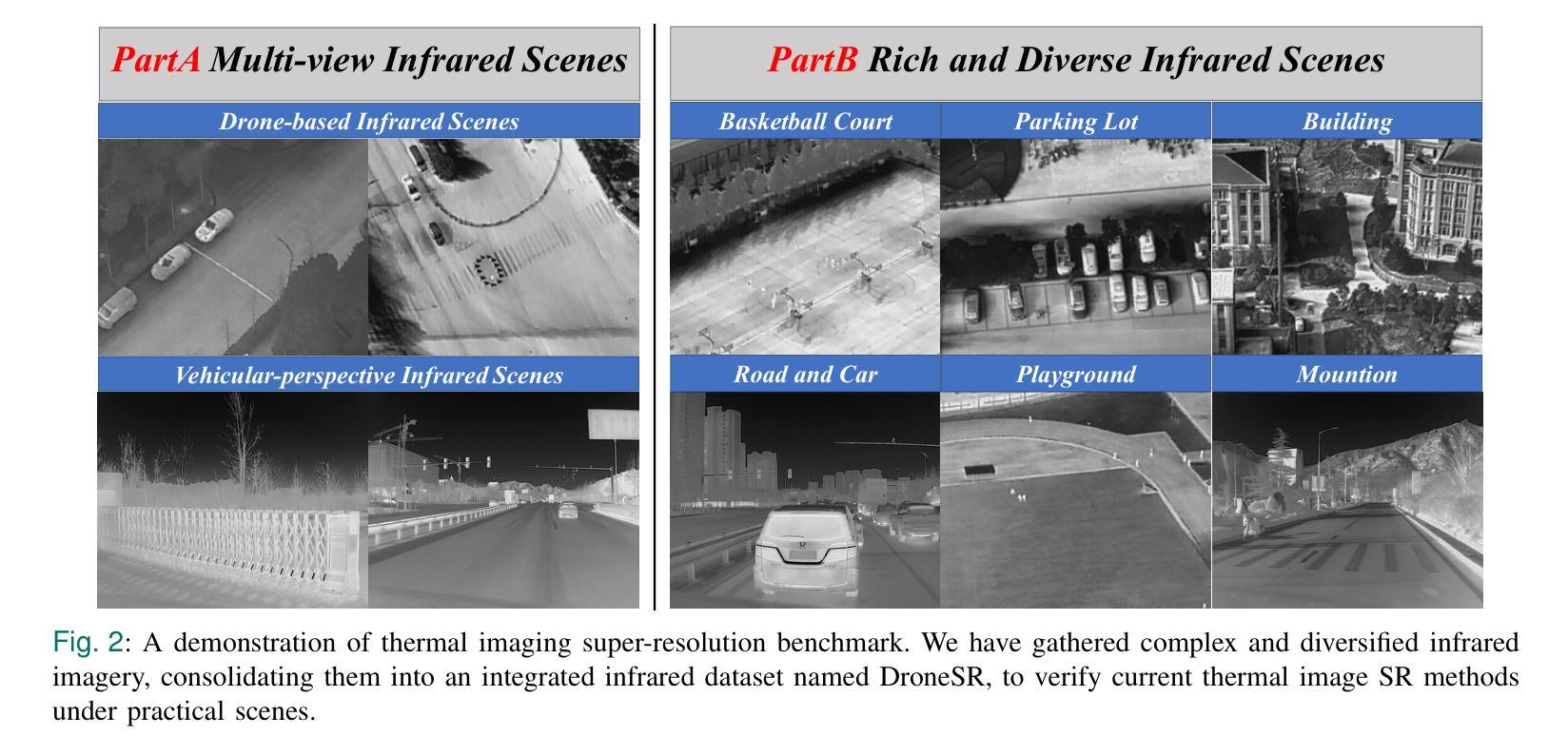
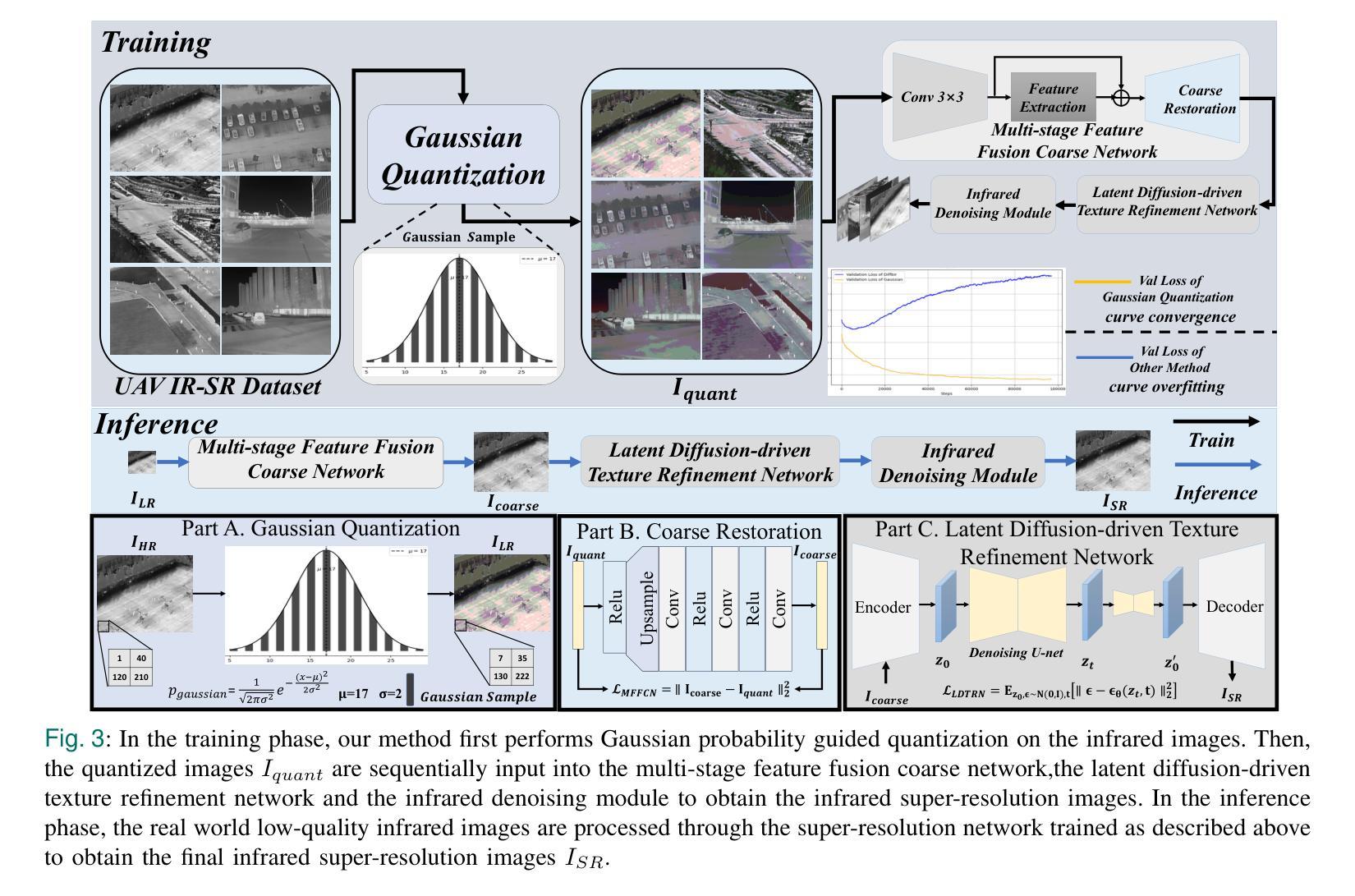
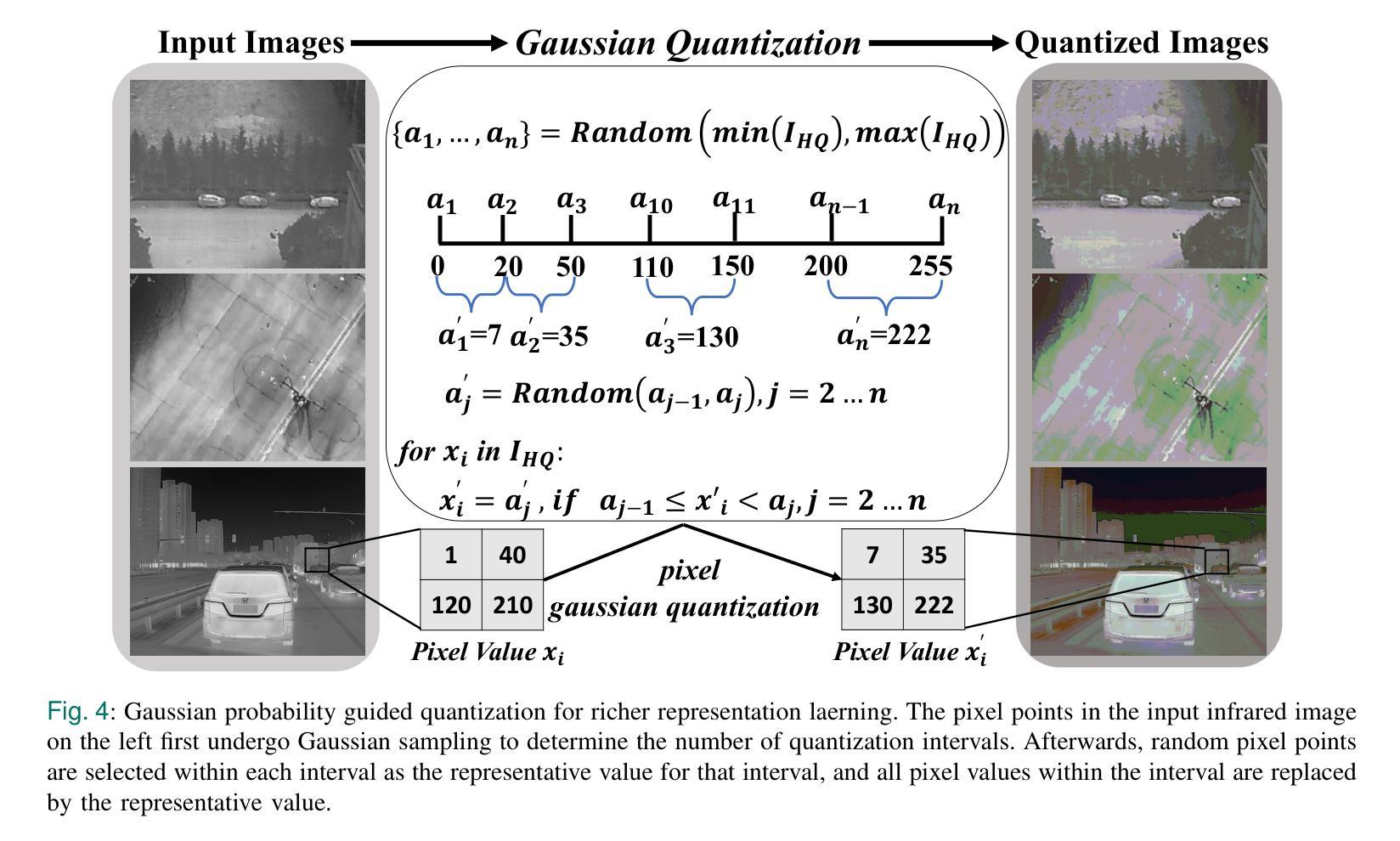
DroneSR: Rethinking Few-shot Thermal Image Super-Resolution from Drone-based Perspective
Authors:Zhipeng Weng, Xiaopeng Liu, Ce Liu, Xingyuan Guo, Yukai Shi, Liang Lin
Although large scale models achieve significant improvements in performance, the overfitting challenge still frequently undermines their generalization ability. In super resolution tasks on images, diffusion models as representatives of generative models typically adopt large scale architectures. However, few-shot drone-captured infrared training data frequently induces severe overfitting in large-scale architectures. To address this key challenge, our method proposes a new Gaussian quantization representation learning method oriented to diffusion models that alleviates overfitting and enhances robustness. At the same time, an effective monitoring mechanism tracks large scale architectures during training to detect signs of overfitting. By introducing Gaussian quantization representation learning, our method effectively reduces overfitting while maintaining architecture complexity. On this basis, we construct a multi source drone-based infrared image benchmark dataset for detection and use it to emphasize overfitting issues of large scale architectures in few sample, drone-based diverse drone-based image reconstruction scenarios. To verify the efficacy of the method in mitigating overfitting, experiments are conducted on the constructed benchmark. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing super resolution approaches and significantly mitigates overfitting of large scale architectures under complex conditions. The code and DroneSR dataset will be available at: https://github.com/wengzp1/GARLSR.
虽然大规模模型在性能上取得了显著改进,但过拟合问题仍然经常破坏它们的泛化能力。在图像超分辨率任务中,扩散模型作为生成模型的代表通常采用大规模架构。然而,对于少量无人机捕获的红外训练数据,这往往导致大规模架构中的严重过拟合问题。为了应对这一关键挑战,我们的方法提出了一种面向扩散模型的新型高斯量化表示学习方法,可以缓解过拟合问题并增强模型的稳健性。同时,有效的监控机制可以跟踪训练过程中的大规模架构,以检测过拟合的迹象。通过引入高斯量化表示学习,我们的方法在保持架构复杂性的同时,有效地减少了过拟合。在此基础上,我们构建了一个用于检测的多源无人机红外图像基准数据集,并用来强调在少量样本、基于无人机的多样化图像重建场景中大规模架构的过拟合问题。为了验证该方法在缓解过拟合方面的有效性,我们在构建的基准数据集上进行了实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于现有的超分辨率方法,并在复杂条件下显著减轻了大规模架构的过拟合问题。代码和DroneSR数据集可在以下网址获取:https://github.com/wengzp1/GARLSR。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模模型在性能上取得了显著的提升,但过拟合问题仍然频繁地影响了其泛化能力。在图像超分辨率任务中,扩散模型等生成模型通常采用大规模架构,但对于无人机捕获的红外训练数据,这种架构往往会出现严重的过拟合现象。为解决这一挑战,本文提出了一种面向扩散模型的高斯量化表示学习方法,该方法可缓解过拟合问题并增强模型的稳健性。同时,通过引入有效的监控机制,在训练过程中跟踪大规模架构以检测过拟合的迹象。实验结果表明,该方法在复杂条件下优于现有的超分辨率方法,并显著缓解了大规模架构的过拟合问题。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模模型在性能上有所提升,但过拟合问题仍影响其泛化能力。
- 扩散模型在图像超分辨率任务中常采用大规模架构。
- 无人机捕获的红外训练数据对大规模架构容易产生过拟合。
- 提出了一种面向扩散模型的高斯量化表示学习方法,以缓解过拟合并增强模型稳健性。
- 引入监控机制来跟踪大规模架构的训练过程,以检测过拟合的迹象。
- 构建的基于多源无人机的红外图像基准数据集用于强调大规模架构在少量样本下的过拟合问题。
点此查看论文截图


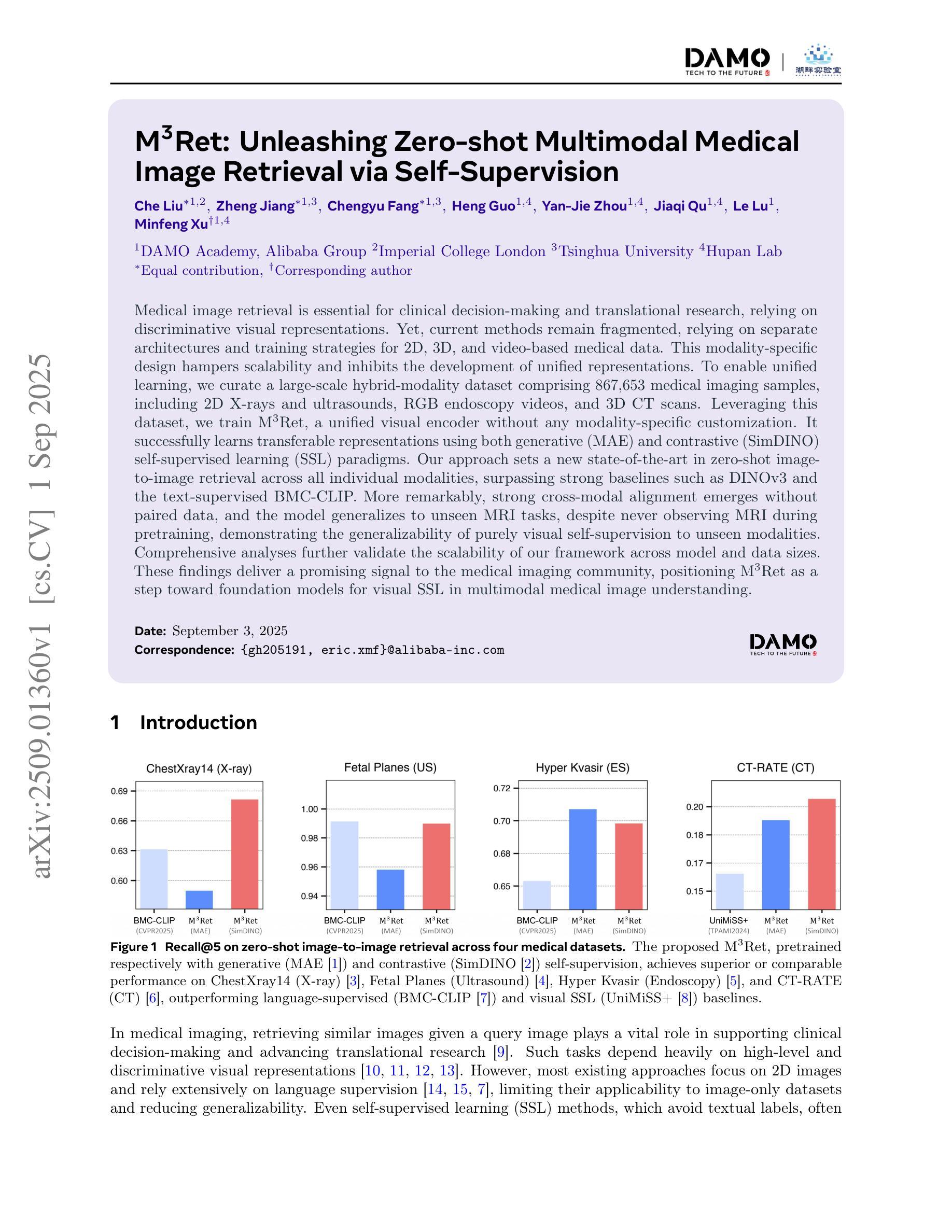
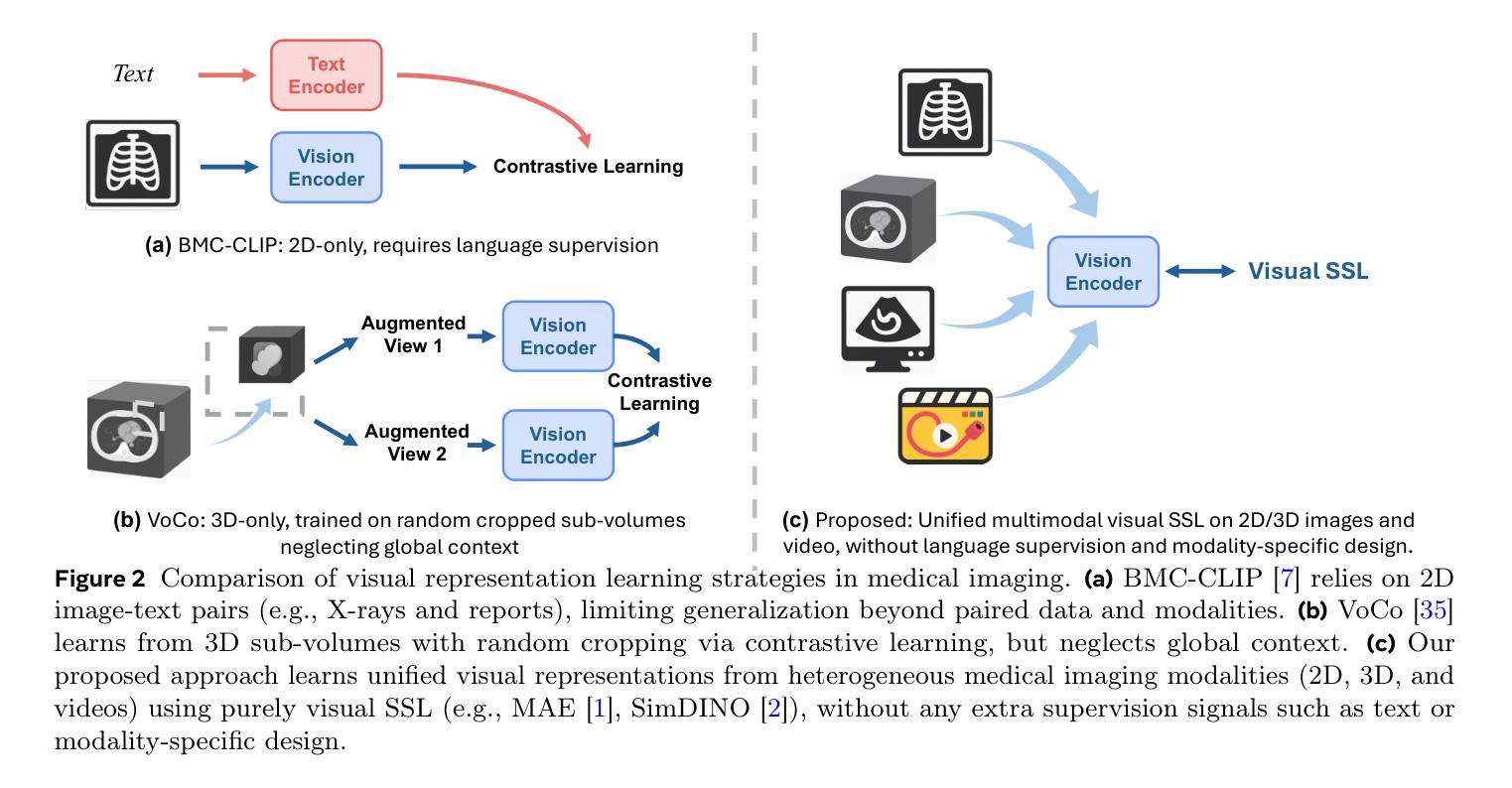
M3Ret: Unleashing Zero-shot Multimodal Medical Image Retrieval via Self-Supervision
Authors:Che Liu, Zheng Jiang, Chengyu Fang, Heng Guo, Yan-Jie Zhou, Jiaqi Qu, Le Lu, Minfeng Xu
Medical image retrieval is essential for clinical decision-making and translational research, relying on discriminative visual representations. Yet, current methods remain fragmented, relying on separate architectures and training strategies for 2D, 3D, and video-based medical data. This modality-specific design hampers scalability and inhibits the development of unified representations. To enable unified learning, we curate a large-scale hybrid-modality dataset comprising 867,653 medical imaging samples, including 2D X-rays and ultrasounds, RGB endoscopy videos, and 3D CT scans. Leveraging this dataset, we train M3Ret, a unified visual encoder without any modality-specific customization. It successfully learns transferable representations using both generative (MAE) and contrastive (SimDINO) self-supervised learning (SSL) paradigms. Our approach sets a new state-of-the-art in zero-shot image-to-image retrieval across all individual modalities, surpassing strong baselines such as DINOv3 and the text-supervised BMC-CLIP. More remarkably, strong cross-modal alignment emerges without paired data, and the model generalizes to unseen MRI tasks, despite never observing MRI during pretraining, demonstrating the generalizability of purely visual self-supervision to unseen modalities. Comprehensive analyses further validate the scalability of our framework across model and data sizes. These findings deliver a promising signal to the medical imaging community, positioning M3Ret as a step toward foundation models for visual SSL in multimodal medical image understanding.
医学图像检索对临床决策和转化研究至关重要,依赖于区分性的视觉表示。然而,当前的方法仍然支离破碎,针对2D、3D和基于视频的医疗数据,依赖于独立的架构和训练策略。这种针对特定模态的设计阻碍了可扩展性,并抑制了统一表示的发展。为了实现统一学习,我们创建了一个大规模混合模态数据集,包含867,653个医学成像样本,包括2D X光片和超声波、RGB内窥镜视频和3D CT扫描。利用该数据集,我们训练了M3Ret,这是一种统一的视觉编码器,无需任何针对特定模态的定制。它成功地利用生成式(MAE)和对比式(SimDINO)自监督学习(SSL)范式学习可迁移的表示。我们的方法在所有单个模态的零样本图像到图像检索中树立了新的标杆,超越了强大的基线模型,如DINOv3和文本监督的BMC-CLIP。更值得一提的是,尽管在预训练阶段从未接触过MRI,但在没有配对数据的情况下出现了强大的跨模态对齐,并且该模型能够推广到未见过的MRI任务,证明了纯视觉自监督在未见模态中的通用性。全面的分析进一步验证了我们的框架在模型和数据规模方面的可扩展性。这些发现向医学成像领域传递了积极的信号,表明M3Ret是朝着视觉SSL多模态医学图像理解基础模型迈出的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
本文介绍了医学图像检索在临床决策和转化研究中的重要性,指出当前方法因针对2D、3D和视频医学数据的独立架构和训练策略而存在局限性。为解决这个问题,本文建立了一个大规模混合模态数据集,并在此基础上训练了M3Ret统一视觉编码器,无需任何特定模态的定制,通过生成式(MAE)和对比式(SimDINO)自监督学习范式成功学习可迁移表示。该模型在零样本图像检索方面达到了新的先进水平,具有跨模态对齐能力和泛化能力。本文研究结果标志着向多模态医学图像理解的视觉自监督基础模型迈进了重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像检索在临床决策和转化研究中具有重要意义,依赖于判别性视觉表示。
- 当前医学图像处理方法存在局限性,缺乏统一的多模态表示方法。
- 建立了一个大规模混合模态数据集,包含多种医学成像样本。
- 训练了M3Ret统一视觉编码器,无需特定模态定制。
- 通过生成式和对比式自监督学习范式成功训练模型。
- 模型在零样本图像检索方面表现优秀,具有跨模态对齐能力和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
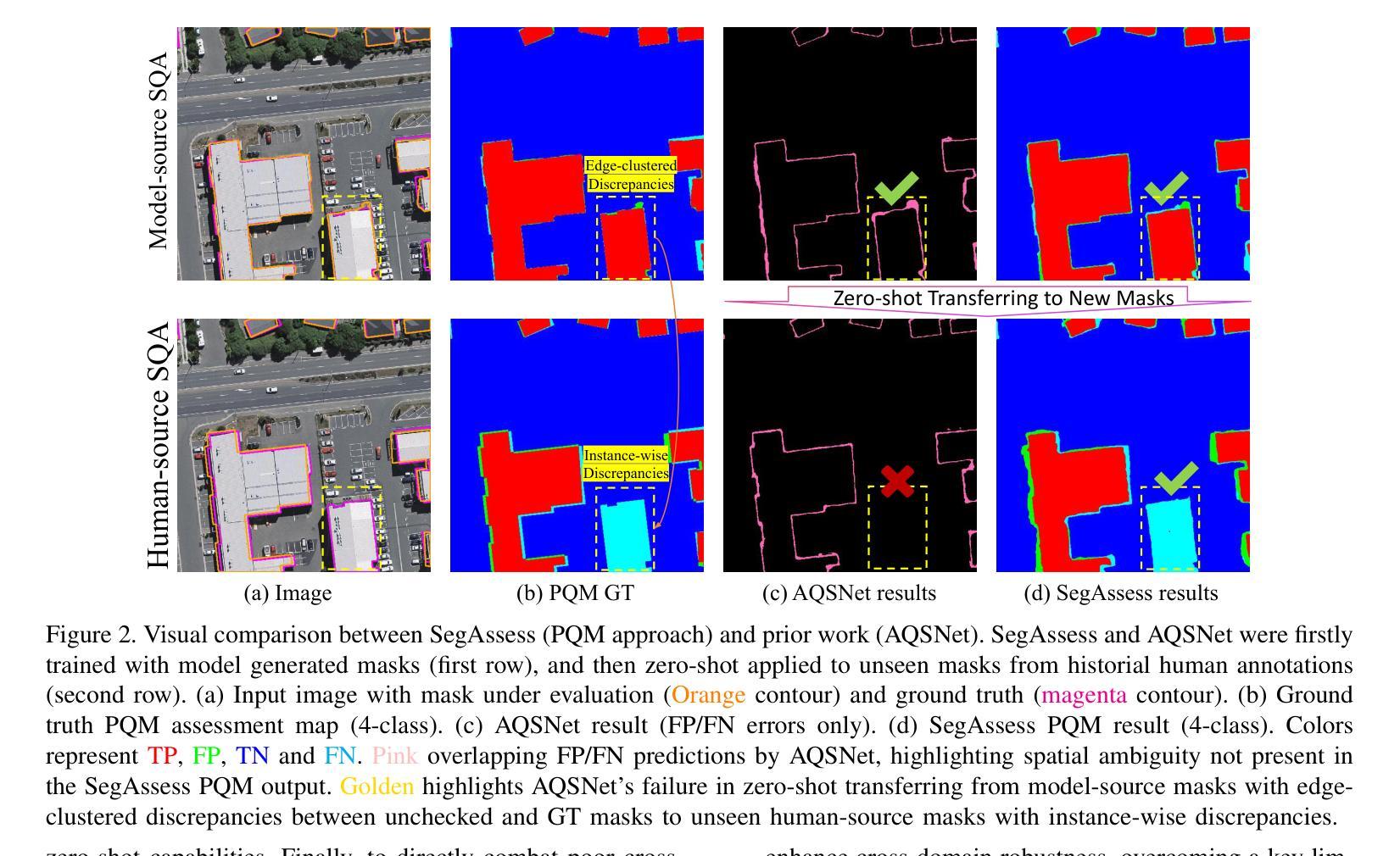
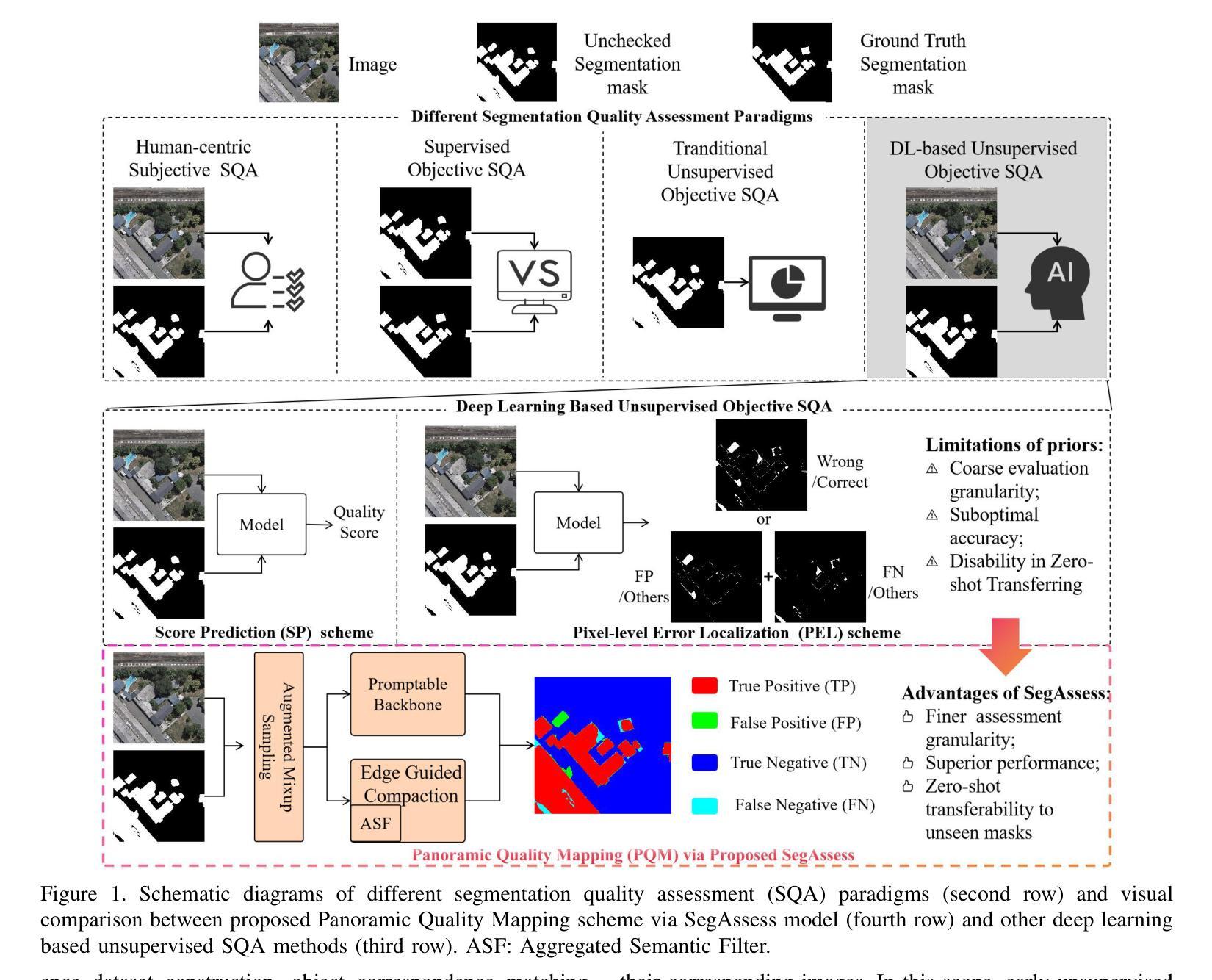
SegAssess: Panoramic quality mapping for robust and transferable unsupervised segmentation assessment
Authors:Bingnan Yang, Mi Zhang, Zhili Zhang, Zhan Zhang, Yuanxin Zhao, Xiangyun Hu, Jianya Gong
High-quality image segmentation is fundamental to pixel-level geospatial analysis in remote sensing, necessitating robust segmentation quality assessment (SQA), particularly in unsupervised settings lacking ground truth. Although recent deep learning (DL) based unsupervised SQA methods show potential, they often suffer from coarse evaluation granularity, incomplete assessments, and poor transferability. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces Panoramic Quality Mapping (PQM) as a new paradigm for comprehensive, pixel-wise SQA, and presents SegAssess, a novel deep learning framework realizing this approach. SegAssess distinctively formulates SQA as a fine-grained, four-class panoramic segmentation task, classifying pixels within a segmentation mask under evaluation into true positive (TP), false positive (FP), true negative (TN), and false negative (FN) categories, thereby generating a complete quality map. Leveraging an enhanced Segment Anything Model (SAM) architecture, SegAssess uniquely employs the input mask as a prompt for effective feature integration via cross-attention. Key innovations include an Edge Guided Compaction (EGC) branch with an Aggregated Semantic Filter (ASF) module to refine predictions near challenging object edges, and an Augmented Mixup Sampling (AMS) training strategy integrating multi-source masks to significantly boost cross-domain robustness and zero-shot transferability. Comprehensive experiments across 32 datasets derived from 6 sources demonstrate that SegAssess achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance and exhibits remarkable zero-shot transferability to unseen masks, establishing PQM via SegAssess as a robust and transferable solution for unsupervised SQA. The code is available at https://github.com/Yangbn97/SegAssess.
高质量图像分割对于遥感中的像素级地理空间分析至关重要,需要进行稳健的分割质量评估(SQA)。特别是在缺乏真实地面信息的情况下进行无监督设置时更是如此。尽管最近基于深度学习的无监督SQA方法显示出潜力,但它们通常存在评估粒度粗糙、评估不完整以及迁移性差等局限性。为了克服这些局限性,本文引入了全景质量映射(PQM)作为用于全面像素级SQA的新范式,并提出了SegAssess,这是一个实现该方法的深度学习框架。SegAssess独特地将SQA制定为精细粒度的四分类全景分割任务,将评估中的分割掩膜内的像素分类为真正阳性(TP)、假阳性(FP)、真阴性(TN)和假阴性(FN)类别,从而生成一个完整的质量图。SegAssess利用增强的Segment Anything Model(SAM)架构,采用输入掩膜作为通过交叉注意进行有效特征集成的提示。关键创新包括带有聚合语义过滤器(ASF)模块的边缘引导压实(EGC)分支,以改进在具有挑战性的对象边缘附近的预测,以及结合了多源掩膜的增强混合采样(AMS)训练策略,以显著提高跨域鲁棒性和零样本迁移能力。在来自六个源的32个数据集上进行的综合实验表明,SegAssess达到了最先进的性能水平,并对未见过的掩膜表现出显著的零样本迁移能力,证明了通过SegAssess实现的PQM是一种稳健且可迁移的无监督SQA解决方案。代码可从https://github.com/Yangbn97/SegAssess获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的遥感图像分割质量评估方法——全景质量映射(PQM),并实现了基于此方法的深度学习框架SegAssess。SegAssess将分割质量评估精细化为四分类全景分割任务,生成完整的质量图。通过增强型Segment Anything Model架构,实现有效特征整合。关键创新包括带有聚合语义过滤器的边缘引导紧缩分支,以及通过混合采样策略提升跨域稳健性和零样本迁移能力。实验证明SegAssess达到最佳性能,并在未见过的掩膜上展现出显著的零样本迁移能力。
Key Takeaways
- 引入全景质量映射(PQM)作为全面的像素级分割质量评估新方法。
- SegAssess框架实现了精细粒度的四分类全景分割质量评估。
- SegAssess利用增强的Segment Anything Model架构,通过交叉注意机制实现有效特征整合。
- 边缘引导紧缩分支和聚合语义过滤器用于改进在挑战性边缘附近的预测。
- 采用增强混合采样策略提升模型跨域稳健性和零样本迁移能力。
- 在多个数据集上的实验证明SegAssess达到最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


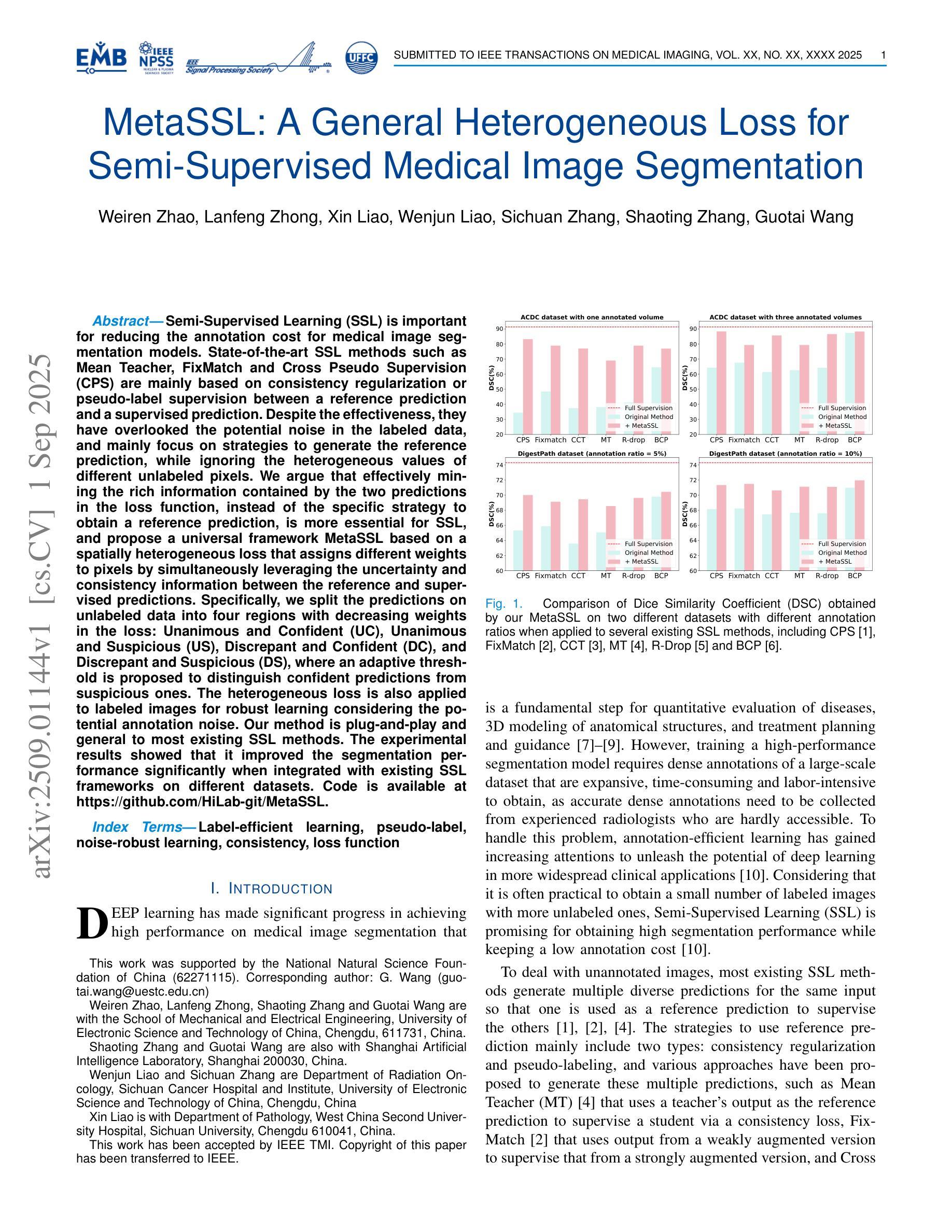
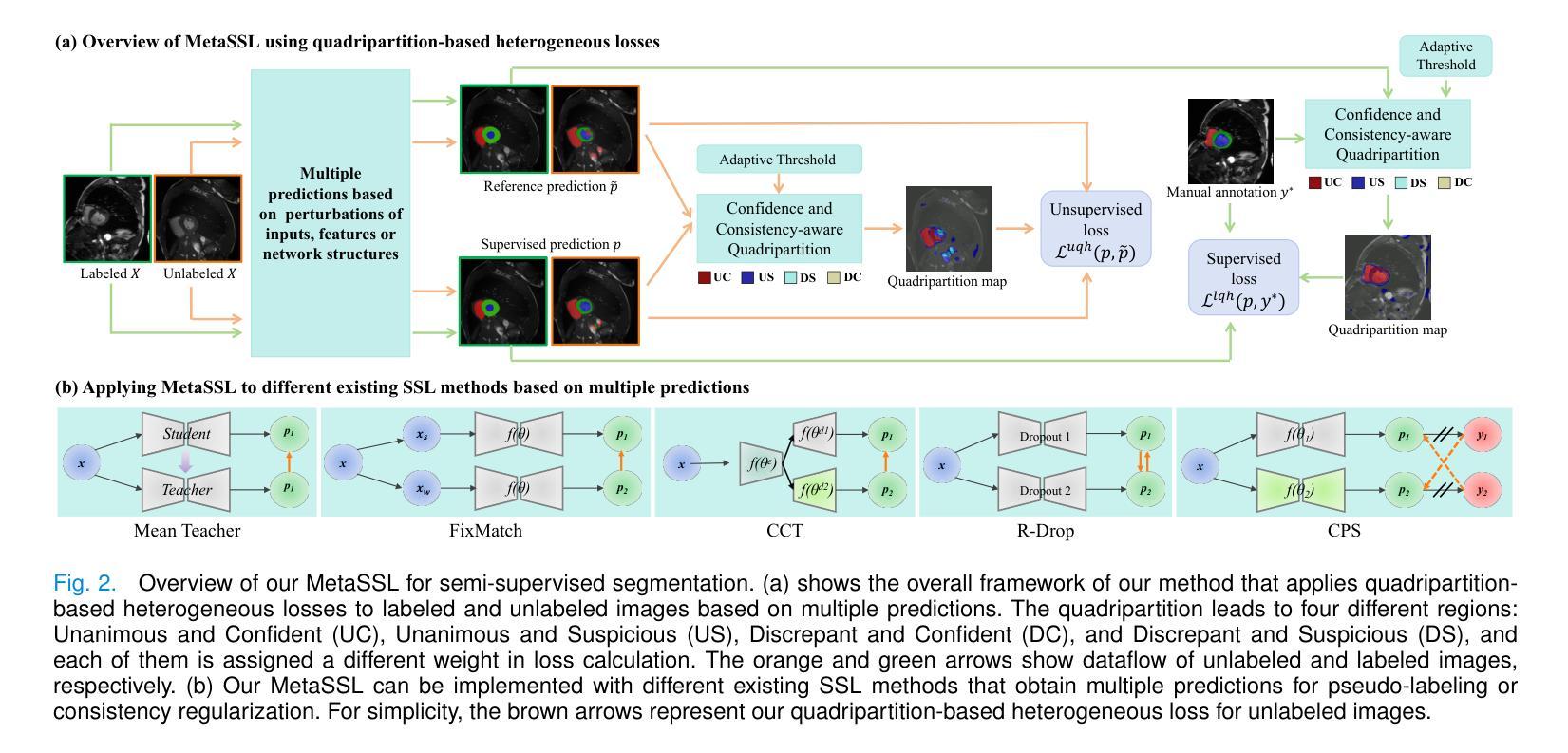
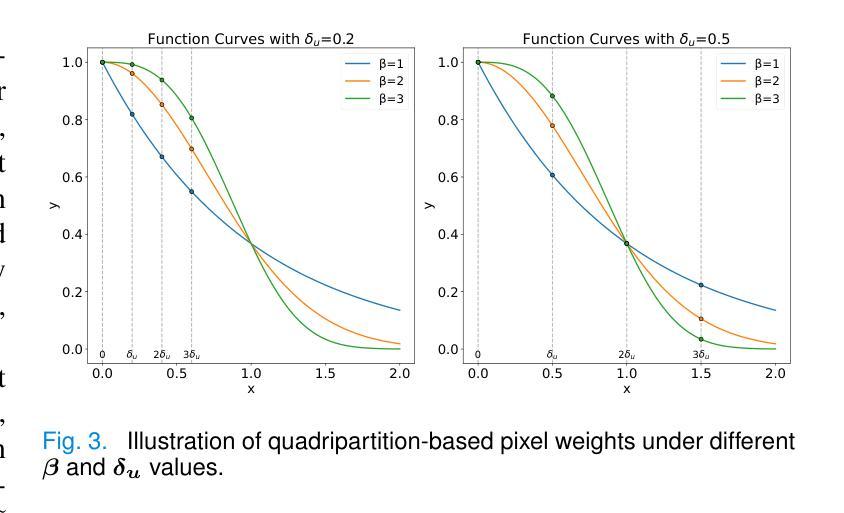
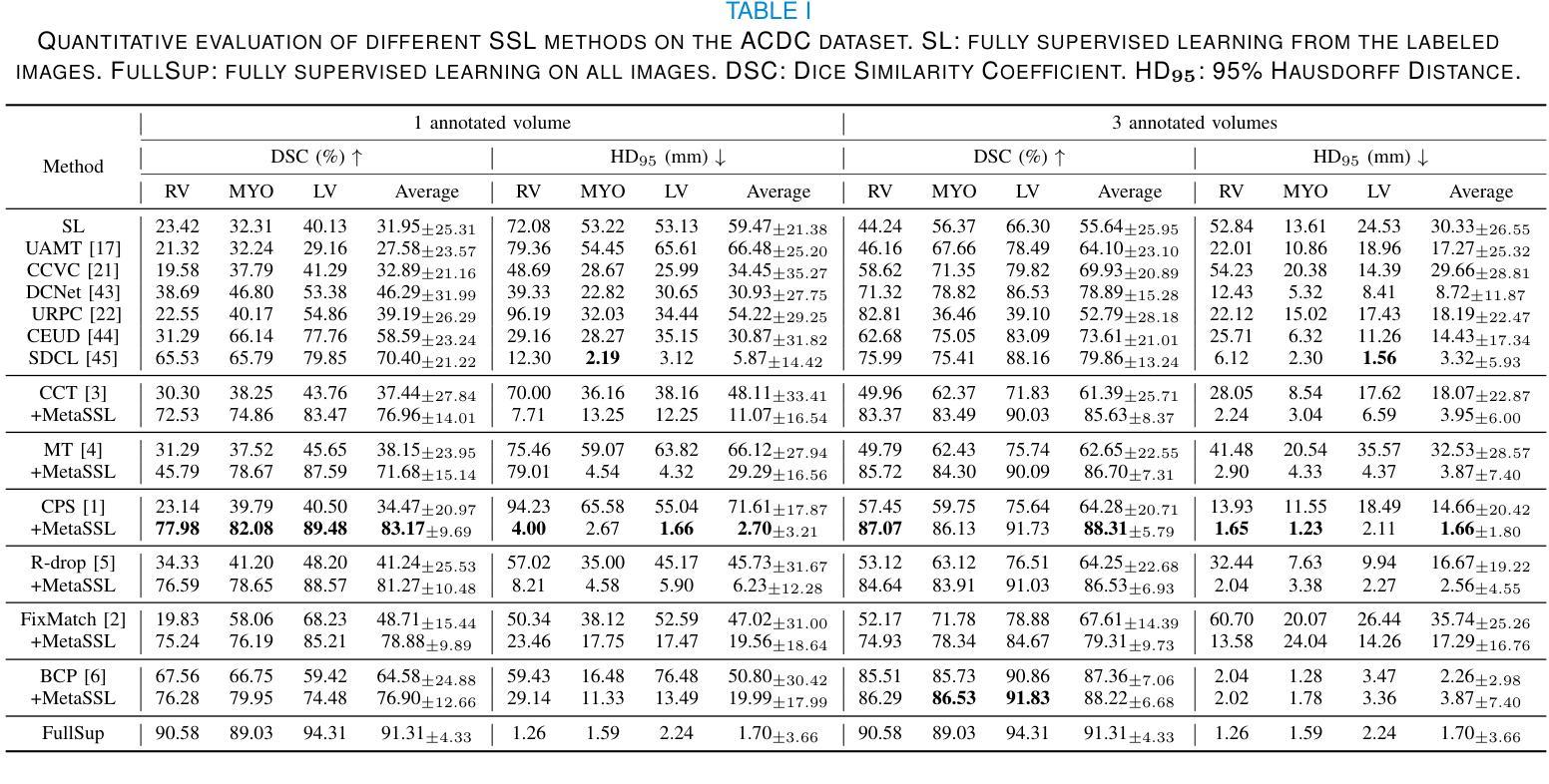
MetaSSL: A General Heterogeneous Loss for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Weiren Zhao, Lanfeng Zhong, Xin Liao, Wenjun Liao, Sichuan Zhang, Shaoting Zhang, Guotai Wang
Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) is important for reducing the annotation cost for medical image segmentation models. State-of-the-art SSL methods such as Mean Teacher, FixMatch and Cross Pseudo Supervision (CPS) are mainly based on consistency regularization or pseudo-label supervision between a reference prediction and a supervised prediction. Despite the effectiveness, they have overlooked the potential noise in the labeled data, and mainly focus on strategies to generate the reference prediction, while ignoring the heterogeneous values of different unlabeled pixels. We argue that effectively mining the rich information contained by the two predictions in the loss function, instead of the specific strategy to obtain a reference prediction, is more essential for SSL, and propose a universal framework MetaSSL based on a spatially heterogeneous loss that assigns different weights to pixels by simultaneously leveraging the uncertainty and consistency information between the reference and supervised predictions. Specifically, we split the predictions on unlabeled data into four regions with decreasing weights in the loss: Unanimous and Confident (UC), Unanimous and Suspicious (US), Discrepant and Confident (DC), and Discrepant and Suspicious (DS), where an adaptive threshold is proposed to distinguish confident predictions from suspicious ones. The heterogeneous loss is also applied to labeled images for robust learning considering the potential annotation noise. Our method is plug-and-play and general to most existing SSL methods. The experimental results showed that it improved the segmentation performance significantly when integrated with existing SSL frameworks on different datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/HiLab-git/MetaSSL.
半监督学习(SSL)对于降低医学图像分割模型的标注成本非常重要。最先进的SSL方法,如Mean Teacher、FixMatch和Cross Pseudo Supervision(CPS),主要基于参考预测和有监督预测之间的一致性正则化或伪标签监督。尽管这些方法有效,但它们忽略了标记数据中的潜在噪声,主要关注生成参考预测的策略,而忽略了不同未标记像素的异质值。我们认为,有效挖掘损失函数中两个预测所包含的丰富信息,而不是获得参考预测的具体策略,对于SSL更为重要。因此,我们提出了基于空间异质损失的通用框架MetaSSL,该框架通过同时利用参考和监督预测之间的不确定性和一致性信息,为像素分配不同的权重。具体来说,我们将未标记数据上的预测分为四个区域,在损失中的权重逐渐减小:一致且自信(UC)、一致且可疑(US)、不一致且自信(DC)和不一致且可疑(DS),其中提出自适应阈值来区分自信预测和可疑预测。异质损失也应用于带标签的图像,以实现稳健学习,考虑潜在的标注噪声。我们的方法是即插即用型,适用于大多数现有的SSL方法。实验结果表明,在与不同数据集的现有SSL框架集成时,它显著提高了分割性能。代码可在https://github.com/HiLab-git/MetaSSL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 12 figures. This work has been accepted by IEEE TMI
Summary
半监督学习(SSL)在降低医学图像分割模型的标注成本方面至关重要。最新的SSL方法主要基于一致性正则化或伪标签监督生成参考预测值。然而,它们忽视了标签数据中潜在的噪声,并主要关注生成参考预测的策略,而忽略了未标记像素的异质值。文章建议有效挖掘损失函数中两个预测值之间丰富的信息比获得参考预测值的特定策略更重要,并提出了基于空间异质损失的通用框架MetaSSL。该框架通过同时利用参考和监督预测之间的不确定性和一致性信息,对像素分配不同的权重。此外,该异质损失也应用于标记图像,以实现稳健学习,考虑潜在的标注噪声。实验结果在多个数据集上证明了该方法与现有SSL框架集成后,能提高分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- SSL在医学图像分割中对于降低标注成本至关重要。
- 最新的SSL方法主要基于一致性正则化和伪标签监督。
- 现有方法忽视了标签数据中的潜在噪声和未标记像素的异质值。
- 文章强调有效挖掘两种预测值间的信息比生成参考预测的策略更重要。
- 提出了基于空间异质损失的通用框架MetaSSL,对像素分配不同权重。
- MetaSSL框架同时利用参考和监督预测之间的不确定性和一致性信息。
- 该异质损失也应用于标记图像以实现稳健学习。
点此查看论文截图