⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
Ultrasound-based detection and malignancy prediction of breast lesions eligible for biopsy: A multi-center clinical-scenario study using nomograms, large language models, and radiologist evaluation
Authors:Ali Abbasian Ardakani, Afshin Mohammadi, Taha Yusuf Kuzan, Beyza Nur Kuzan, Hamid Khorshidi, Ashkan Ghorbani, Alisa Mohebbi, Fariborz Faeghi, Sepideh Hatamikia, U Rajendra Acharya
To develop and externally validate integrated ultrasound nomograms combining BIRADS features and quantitative morphometric characteristics, and to compare their performance with expert radiologists and state of the art large language models in biopsy recommendation and malignancy prediction for breast lesions. In this retrospective multicenter, multinational study, 1747 women with pathologically confirmed breast lesions underwent ultrasound across three centers in Iran and Turkey. A total of 10 BIRADS and 26 morphological features were extracted from each lesion. A BIRADS, morphometric, and fused nomogram integrating both feature sets was constructed via logistic regression. Three radiologists (one senior, two general) and two ChatGPT variants independently interpreted deidentified breast lesion images. Diagnostic performance for biopsy recommendation (BIRADS 4,5) and malignancy prediction was assessed in internal and two external validation cohorts. In pooled analysis, the fused nomogram achieved the highest accuracy for biopsy recommendation (83.0%) and malignancy prediction (83.8%), outperforming the morphometric nomogram, three radiologists and both ChatGPT models. Its AUCs were 0.901 and 0.853 for the two tasks, respectively. In addition, the performance of the BIRADS nomogram was significantly higher than the morphometric nomogram, three radiologists and both ChatGPT models for biopsy recommendation and malignancy prediction. External validation confirmed the robust generalizability across different ultrasound platforms and populations. An integrated BIRADS morphometric nomogram consistently outperforms standalone models, LLMs, and radiologists in guiding biopsy decisions and predicting malignancy. These interpretable, externally validated tools have the potential to reduce unnecessary biopsies and enhance personalized decision making in breast imaging.
为了开发和外部验证结合BIRADS特征和定量形态特征的集成超声列线图(nomograms),并将它们与专家放射科医生以及最先进的自然语言模型在乳腺病变的活检推荐和恶性预测方面的表现进行比较。在这项回顾性多中心、多国研究中,1747名经病理证实患有乳腺病变的女性在伊朗和土耳其的三个中心接受了超声检查。从每个病变中提取了10个BIRADS特征和26个形态特征。通过逻辑回归构建了结合这两组特征的BIRADS、形态学和融合列线图。三位放射科医生(一位高级,两位普通)和两个ChatGPT变体独立解释了匿名乳腺病变图像。在内部和两个外部验证队列中评估了活检推荐(BIRADS 4、5)和恶性预测的诊断性能。在综合分析中,融合列图在活检推荐(83.0%)和恶性预测(83.8%)方面达到了最高准确度,优于形态学列图、三位放射科医生和两个ChatGPT模型。其AUC分别为0.901和0.853。另外,BIRADS列图的表现在活检推荐和恶性预测方面都显著高于形态学列图、三位放射科医生和两个ChatGPT模型。外部验证证实了其在不同超声平台和人群中的稳健性。集成的BIRADS形态学列图在指导活检决策和预测恶性方面始终优于独立模型、大型语言模型(LLMs)和放射科医生。这些可解释、经过外部验证的工具有可能减少不必要的活检,提高乳腺影像的个性化和决策制定水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38 pages, 8 figures, 12 tables
摘要
一项多国多中心研究结合了乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BIRADS)特征和定量形态学特征,开发了集成的超声预测图,用于对乳腺病变进行活检推荐和恶性预测。该研究在伊朗和土耳其的三个中心进行,共有1747名病理证实乳腺病变的女性接受了超声检查。通过逻辑回归构建了一个结合BIRADS、形态测量和融合预测图的模型。对活检推荐(BIRADS 4、5)和恶性预测的诊断性能在内部和两个外部验证队列中进行了评估。融合预测图在活检推荐和恶性预测方面的准确性最高,分别达到了83.0%和83.8%,优于形态测量预测图、三位放射科医生以及两种ChatGPT模型。此外,BIRADS预测图在活检推荐和恶性预测方面的性能也显著优于形态测量预测图、放射科医生和ChatGPT模型。外部验证证实了其在不同超声平台和人群中的稳健性。集成的BIRADS形态测量预测图在指导活检决策和预测恶性方面表现优于单一模型、大型语言模型和放射科医生。这些可解释且经过外部验证的工具有望减少不必要的活检,提高个性化决策在乳腺影像中的制定。
关键见解
- 研究结合了BIRADS特征和定量形态学特征,开发了融合的超声预测图。
- 融合预测图在活检推荐和恶性预测方面表现出最高准确性。
- 融合预测图的性能优于形态测量预测图、放射科医生及ChatGPT模型。
- BIRADS预测图在指导活检决策和预测恶性方面也有优异表现。
- 外部验证显示了预测图在不同超声平台和人群中的稳健性。
- 这些预测图有望减少不必要的活检,提高乳腺影像的个性化决策制定。
- 该研究为乳腺超声诊断提供了一种新的、性能优越的工具。
点此查看论文截图

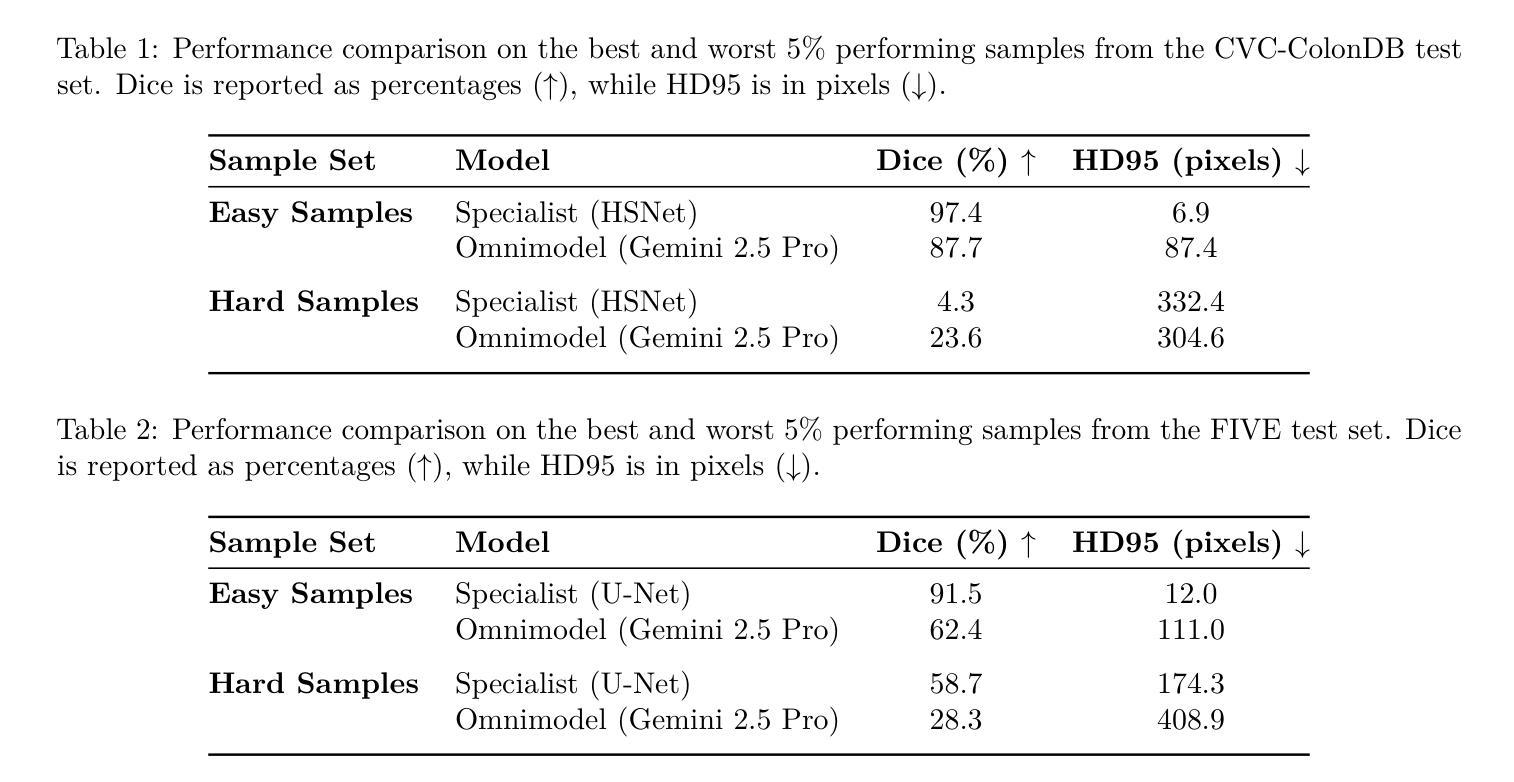
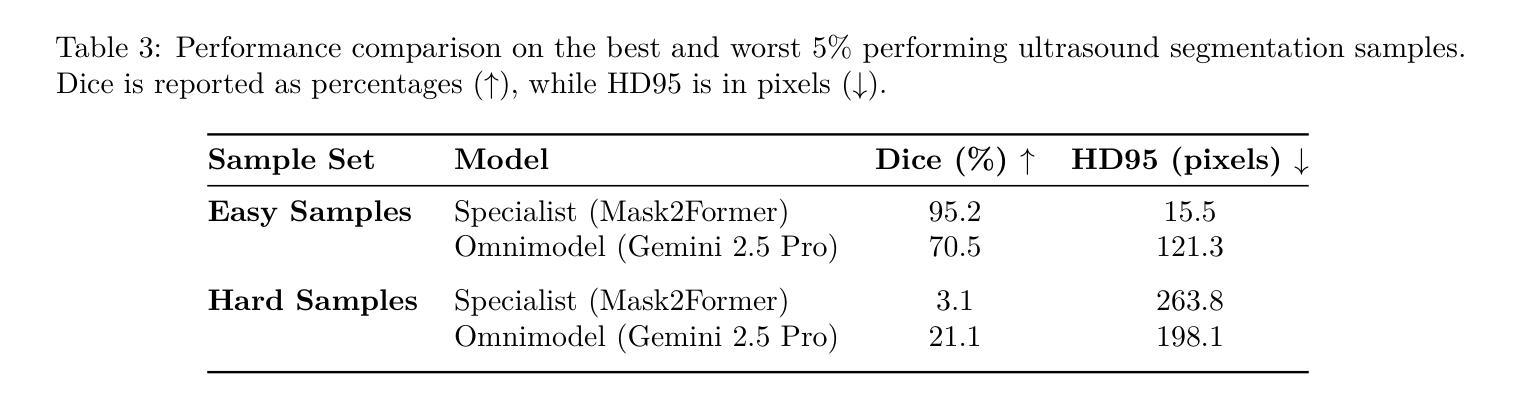
Can General-Purpose Omnimodels Compete with Specialists? A Case Study in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yizhe Zhang, Qiang Chen, Tao Zhou
The emergence of powerful, general-purpose omnimodels capable of processing diverse data modalities has raised a critical question: can these jack-of-all-trades'' systems perform on par with highly specialized models in knowledge-intensive domains? This work investigates this question within the high-stakes field of medical image segmentation. We conduct a comparative study analyzing the zero-shot performance of a state-of-the-art omnimodel (Gemini 2.5 Pro, the Nano Banana’’ model) against domain-specific deep learning models on three distinct tasks: polyp (endoscopy), retinal vessel (fundus), and breast tumor segmentation (ultrasound). Our study focuses on performance at the extremes by curating subsets of the easiest'' and hardest’’ cases based on the specialist models’ accuracy. Our findings reveal a nuanced and task-dependent landscape. For polyp and breast tumor segmentation, specialist models excel on easy samples, but the omnimodel demonstrates greater robustness on hard samples where specialists fail catastrophically. Conversely, for the fine-grained task of retinal vessel segmentation, the specialist model maintains superior performance across both easy and hard cases. Intriguingly, qualitative analysis suggests omnimodels may possess higher sensitivity, identifying subtle anatomical features missed by human annotators. Our results indicate that while current omnimodels are not yet a universal replacement for specialists, their unique strengths suggest a potential complementary role with specialist models, particularly in enhancing robustness on challenging edge cases.
通用多模态全模型的出现,能够处理多种数据模态,引发了一个关键问题:这些“万金油”系统能否在知识密集型领域与高度专业化的模型表现相当?本文工作在医疗图像分割这一高风险领域对此问题进行了探讨。我们对最先进的全模型(Gemini 2.5 Pro,“Nano Banana”模型)的零样本性能进行了比较研究,与针对三个不同任务的领域特定深度学习模型进行对比:息肉(内窥镜)、视网膜血管(眼底)和乳腺癌肿瘤分割(超声)。我们的研究重点放在极端性能上,通过筛选专家模型准确率下的“最容易”和“最困难”的案例子集来进行分析。研究发现了一个微妙且任务依赖性的局面。在息肉和乳腺癌肿瘤分割方面,专业模型在简单样本上表现出色,但全模型在困难样本上表现出更大的稳健性,在这些样本上专家模型会出现灾难性的失败。相反,对于精细的视网膜血管分割任务,专业模型在简单和困难的情况下均保持卓越性能。有趣的是,定性分析表明全模型可能具有更高的敏感性,能够识别出人类注释器遗漏的细微解剖特征。我们的结果表明,虽然当前的全模型还无法普遍替代专家,但其独特的优势表明它们有可能与专家模型互补,特别是在提高对具有挑战性的边缘情况的稳健性方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 7 figures
摘要
新兴的强大通用omnimodels能够处理多种数据模态,引发了一个关键问题:这些“无所不能”的系统是否能在知识密集型领域中与高度专业化的模型表现相当?本研究在医疗图像分割等高风险领域探讨了这个问题。通过对比最先进的omnimodel(Gemini 2.5 Pro,“Nano Banana”模型)与特定领域的深度学习模型在三项不同任务上的零样本性能,研究发现在最容易和最困难的案例子集上,结果呈现出复杂且依赖于任务的格局。在息肉和乳腺肿瘤分割方面,专业模型在简单样本上表现出色,但omnimodel在复杂样本上表现出更大的稳健性,专业模型在这些样本上失败惨重。相反,对于精细的视网膜血管分割任务,专业模型在简单和困难的情况下都保持着卓越的性能。有趣的是,定性分析表明omnimodels可能具有更高的敏感性,能够识别出人类注释器遗漏的微妙解剖特征。我们的结果表明,虽然当前的omnimodels还不是专业模型的通用替代品,但它们的独特优势表明,它们可能与专业模型互补,特别是在提高挑战边缘案例的稳健性方面。
**关键见解**
1. Omnimodels(全能模型)在医疗图像分割等多样化任务中的性能表现引人关注。
2. 在息肉和乳腺肿瘤分割方面,专业模型在简单样本上表现优秀,而全能模型在复杂样本上展现出更高的稳健性。
3. 对于视网膜血管分割这类精细任务,专业模型的表现始终优于全能模型。
4. 定性分析显示全能模型具有更高的敏感性,能识别出人类注释器遗漏的细微解剖特征。
5. 当前的全能模型尚未成为专业模型的全面替代品。
6. 全能模型和专业模型之间具有潜在的互补性,特别是在处理具有挑战性的边缘案例时。
点此查看论文截图

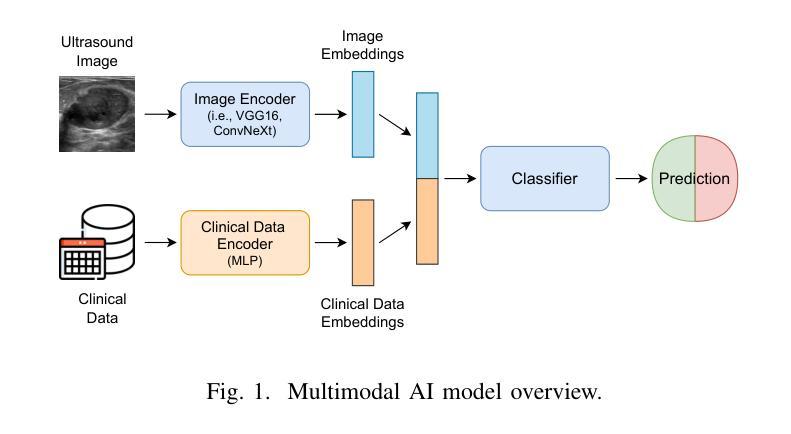
Multimodal Deep Learning for Phyllodes Tumor Classification from Ultrasound and Clinical Data
Authors:Farhan Fuad Abir, Abigail Elliott Daly, Kyle Anderman, Tolga Ozmen, Laura J. Brattain
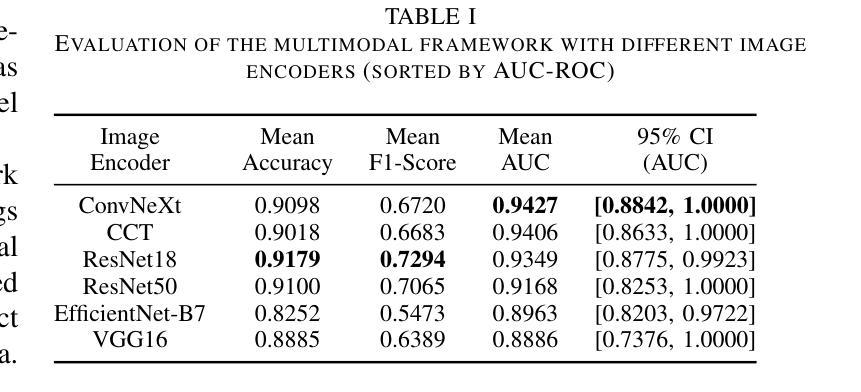
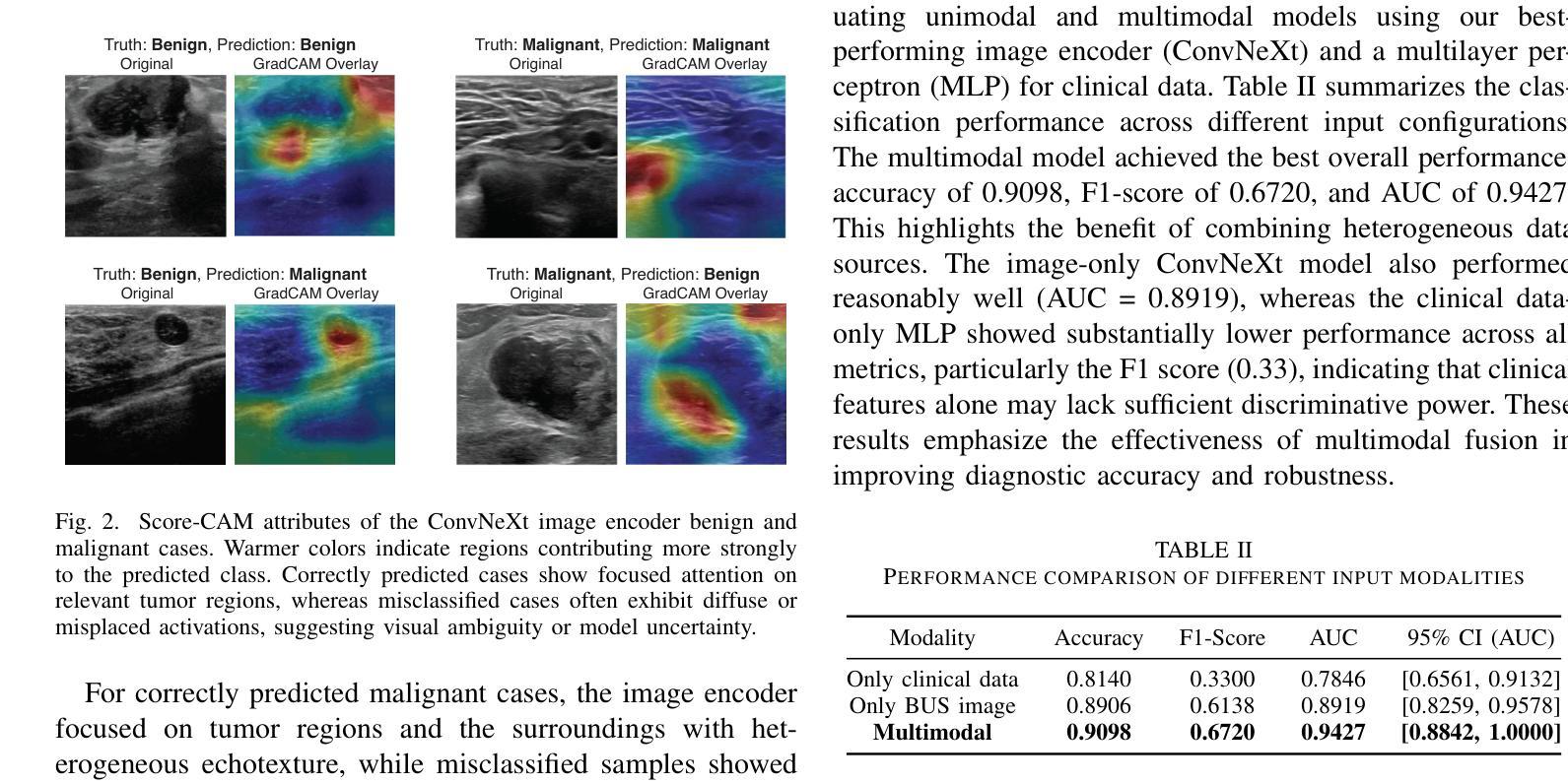
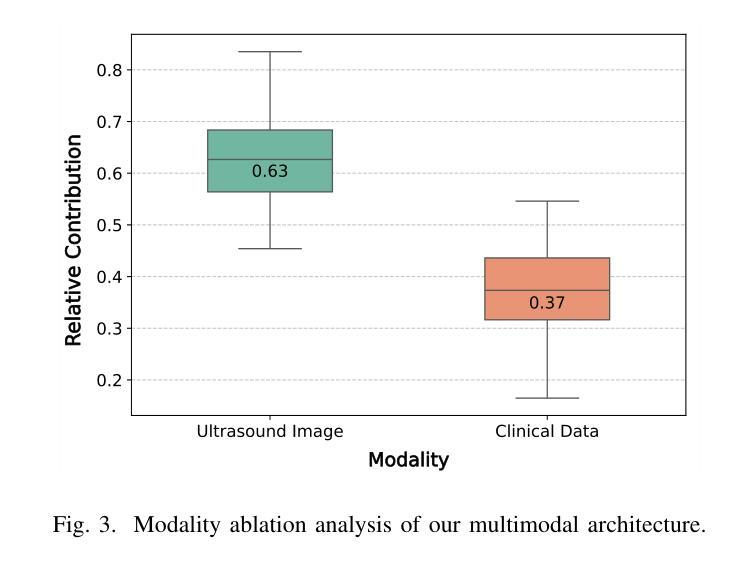
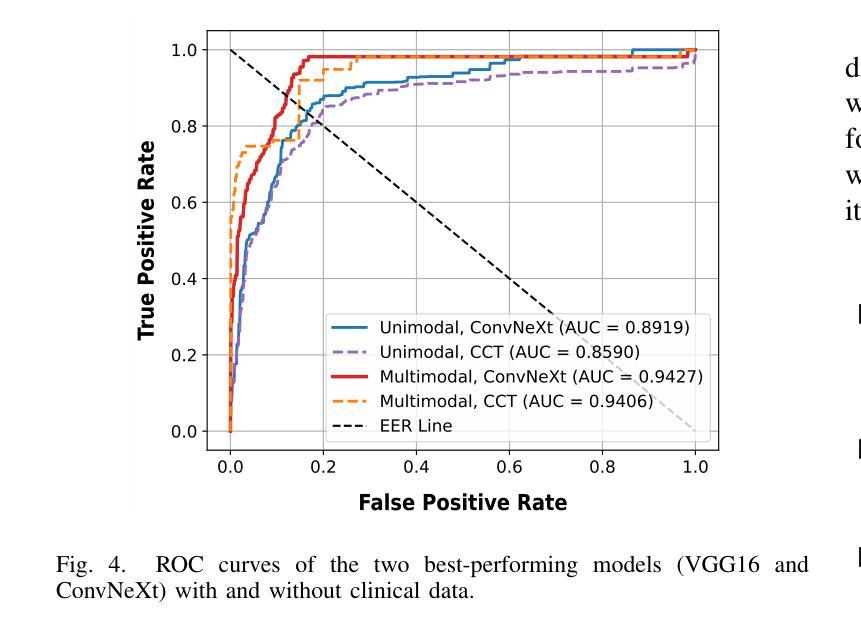
Phyllodes tumors (PTs) are rare fibroepithelial breast lesions that are difficult to classify preoperatively due to their radiological similarity to benign fibroadenomas. This often leads to unnecessary surgical excisions. To address this, we propose a multimodal deep learning framework that integrates breast ultrasound (BUS) images with structured clinical data to improve diagnostic accuracy. We developed a dual-branch neural network that extracts and fuses features from ultrasound images and patient metadata from 81 subjects with confirmed PTs. Class-aware sampling and subject-stratified 5-fold cross-validation were applied to prevent class imbalance and data leakage. The results show that our proposed multimodal method outperforms unimodal baselines in classifying benign versus borderline/malignant PTs. Among six image encoders, ConvNeXt and ResNet18 achieved the best performance in the multimodal setting, with AUC-ROC scores of 0.9427 and 0.9349, and F1-scores of 0.6720 and 0.7294, respectively. This study demonstrates the potential of multimodal AI to serve as a non-invasive diagnostic tool, reducing unnecessary biopsies and improving clinical decision-making in breast tumor management.
叶状肿瘤(PTs)是一种罕见的乳腺纤维上皮病变,由于其放射学与良性纤维腺瘤相似,故术前难以分类,这经常导致不必要的手术切除。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种多模态深度学习框架,该框架结合了乳腺超声(BUS)图像与结构化临床数据,以提高诊断准确性。我们开发了一个双分支神经网络,从超声图像和患者元数据中提取特征,这些特征来自81名已确诊的PT患者。应用类别感知采样和分层主体5倍交叉验证,以防止类别不平衡和数据泄露。结果表明,我们提出的多模态方法在分类良性与边界性或恶性PT方面优于单模态基线方法。在六种图像编码器中,ConvNeXt和ResNet18在多模态环境中表现最佳,AUC-ROC得分分别为0.9427和0.9349,F1得分分别为0.6720和0.7294。本研究表明多模态人工智能的潜力,可以作为非侵入性诊断工具,减少不必要的活检,提高乳腺肿瘤管理的临床决策水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Body Sensor Networks (IEEE-EMBS BSN 2025)
Summary
一篇关于叶状肿瘤(PTs)的论文,提出了一个结合乳腺超声图像和结构化临床数据的多模态深度学习框架,以提高诊断准确性。研究开发了双分支神经网络,从超声图像和患者元数据中提取特征,并应用于81名已确诊的PTs患者。该研究展示了多模态人工智能作为非侵入性诊断工具在乳腺肿瘤管理中的潜力,能够减少不必要的活检,提高临床决策的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 叶状肿瘤是罕见的乳腺纤维上皮病变,术前难以分类,常与良性纤维腺瘤在放射学上相似,导致不必要的手术切除。
- 提出了一种多模态深度学习框架,结合了乳腺超声图像和结构化临床数据,以提高诊断准确性。
- 研究采用的双分支神经网络能够从超声图像和患者元数据中提取特征。
- 该框架应用于81名已确诊的叶状肿瘤患者。
- 为了解决类别不平衡和数据泄露问题,研究采用了类别感知采样和主体分层5折交叉验证。
- 在分类良性与边界性或恶性叶状肿瘤方面,多模态方法优于单模态基线。
点此查看论文截图

ModAn-MulSupCon: Modality-and Anatomy-Aware Multi-Label Supervised Contrastive Pretraining for Medical Imaging
Authors:Eichi Takaya, Ryusei Inamori
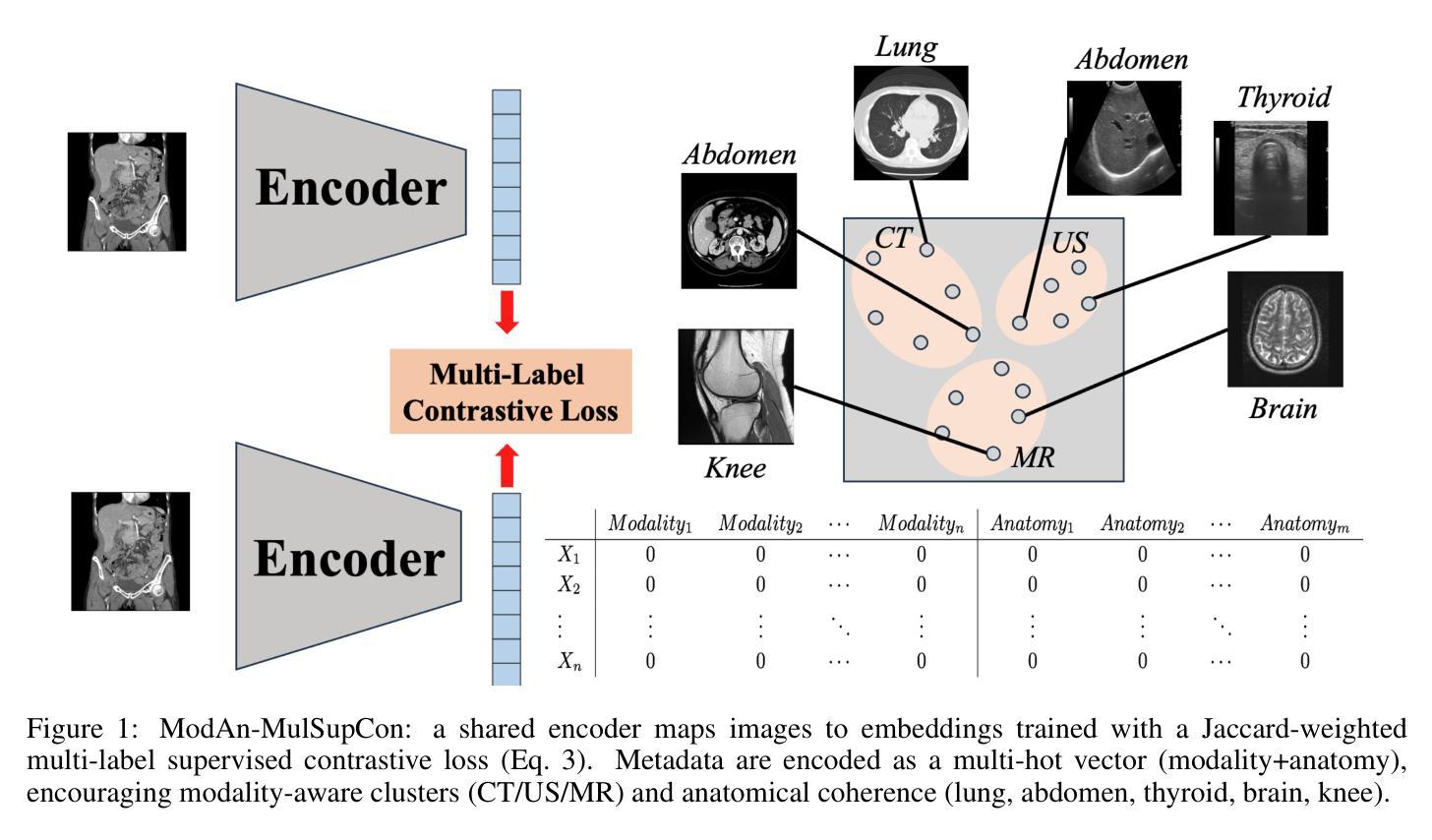
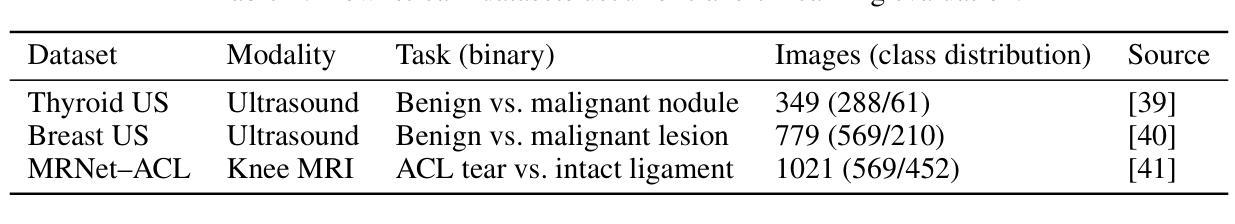
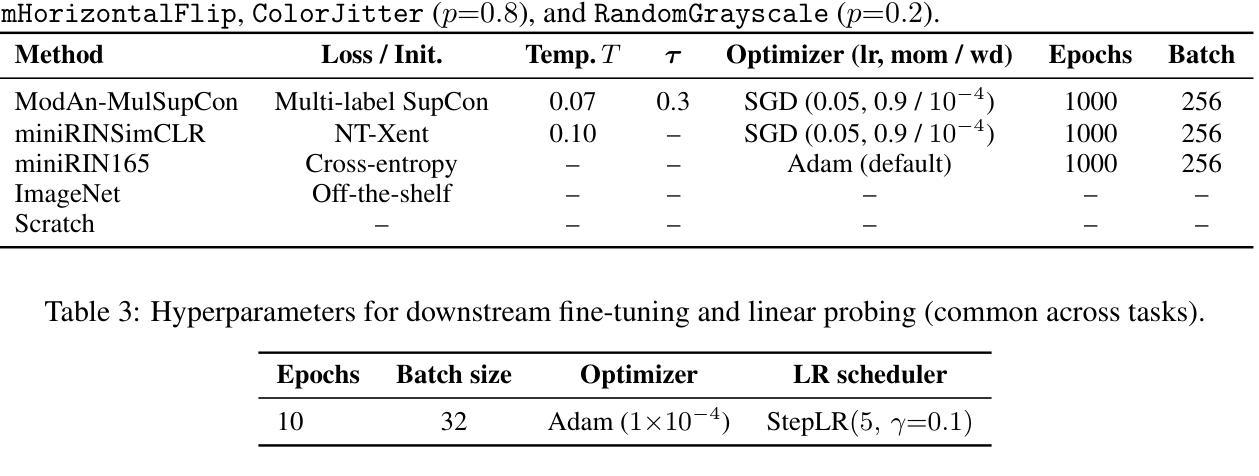
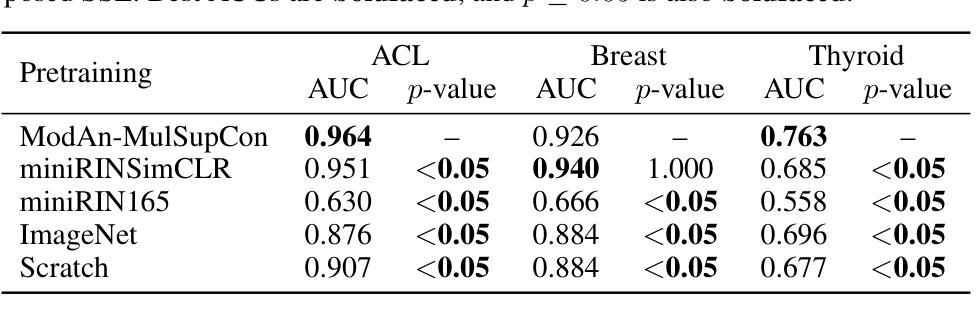
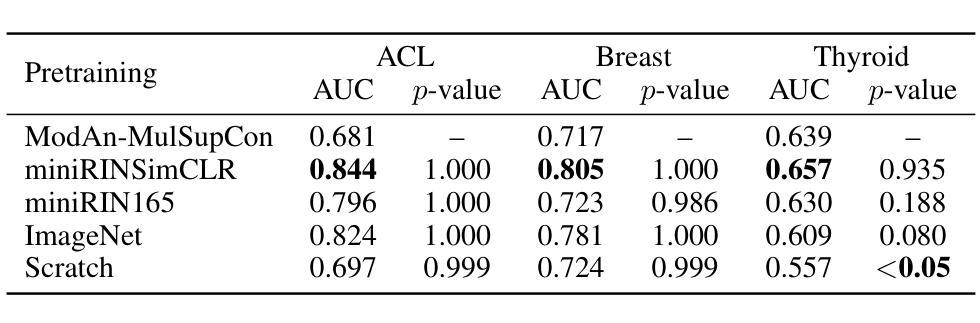
Background and objective: Expert annotations limit large-scale supervised pretraining in medical imaging, while ubiquitous metadata (modality, anatomical region) remain underused. We introduce ModAn-MulSupCon, a modality- and anatomy-aware multi-label supervised contrastive pretraining method that leverages such metadata to learn transferable representations. Method: Each image’s modality and anatomy are encoded as a multi-hot vector. A ResNet-18 encoder is pretrained on a mini subset of RadImageNet (miniRIN, 16,222 images) with a Jaccard-weighted multi-label supervised contrastive loss, and then evaluated by fine-tuning and linear probing on three binary classification tasks–ACL tear (knee MRI), lesion malignancy (breast ultrasound), and nodule malignancy (thyroid ultrasound). Result: With fine-tuning, ModAn-MulSupCon achieved the best AUC on MRNet-ACL (0.964) and Thyroid (0.763), surpassing all baselines ($p<0.05$), and ranked second on Breast (0.926) behind SimCLR (0.940; not significant). With the encoder frozen, SimCLR/ImageNet were superior, indicating that ModAn-MulSupCon representations benefit most from task adaptation rather than linear separability. Conclusion: Encoding readily available modality/anatomy metadata as multi-label targets provides a practical, scalable pretraining signal that improves downstream accuracy when fine-tuning is feasible. ModAn-MulSupCon is a strong initialization for label-scarce clinical settings, whereas SimCLR/ImageNet remain preferable for frozen-encoder deployments.
背景与目标:专家注释限制了医学影像的大规模监督预训练,而普遍的元数据(模态、解剖部位)仍未得到充分利用。我们引入了ModAn-MulSupCon,这是一种模态和解剖结构感知的多标签监督对比预训练方法,它利用此类元数据来学习可迁移的表示。方法:将每幅图像的模态和解剖结构编码为多热向量。使用Jaccard加权多标签监督对比损失在RadImageNet的一个小子集(miniRIN,16222张图像)上对ResNet-18编码器进行预训练,然后通过微调线性探针针对三个二分类任务(ACL撕裂(膝关节MRI)、病变恶性(乳腺超声)和结节恶性(甲状腺超声))进行评估。结果:通过微调,ModAn-MulSupCon在MRNet-ACL上取得最佳AUC(0.964),甲状腺(0.763)超越所有基线(p<0.05),并在乳房上排名第二(0.926),仅次于SimCLR(0.940;不显著)。冻结编码器后,SimCLR/ImageNet表现更佳,表明ModAn-MulSupCon的表示形式更受益于任务适应而非线性可分性。结论:将易于获得的模态/解剖结构元数据编码为多标签目标,提供了一个实用、可扩展的预训练信号,在可行的情况下微调能改善下游精度。ModAn-MulSupCon是标签稀缺的临床环境的良好初始化方法,而SimCLR/ImageNet更适合于冻结编码器的部署。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为ModAn-MulSupCon的方法,该方法利用医学图像中的模态和解剖结构信息,进行多标签监督对比预训练,学习可迁移的表示。该方法在RadImageNet的一个小子集上进行预训练,并通过微调线性探测在三个二分类任务上进行了评估。结果显示,当微调时,ModAn-MulSupCon在MRNet-ACL和甲状腺超声结节恶性任务上表现最佳,超过了所有基线;而在乳腺超声病变恶性任务上排名第二。结论表明,将易于获得的模态/解剖结构信息编码为多标签目标,提供了一个实用的、可扩展的预训练信号,在微调可行的情况下,可以提高下游任务的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- ModAn-MulSupCon是一种利用模态和解剖结构信息的多标签监督对比预训练方法。
- 该方法在RadImageNet的一个小子集上进行预训练,学习图像表示。
- 在三个二分类任务上的评估显示,ModAn-MulSupCon在部分任务上表现最佳,尤其在MRNet-ACL和甲状腺超声结节恶性任务上。
- 相较于SimCLR/ImageNet,ModAn-MulSupCon在微调时表现更佳,但在冻结编码器部署时稍逊一筹。
- 编码模态/解剖结构信息作为多标签目标可以提供实用的、可扩展的预训练信号。
- ModAn-MulSupCon适用于标签稀缺的临床环境。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Trustworthy Breast Tumor Segmentation in Ultrasound using Monte Carlo Dropout and Deep Ensembles for Epistemic Uncertainty Estimation
Authors:Toufiq Musah, Chinasa Kalaiwo, Maimoona Akram, Ubaida Napari Abdulai, Maruf Adewole, Farouk Dako, Adaobi Chiazor Emegoakor, Udunna C. Anazodo, Prince Ebenezer Adjei, Confidence Raymond
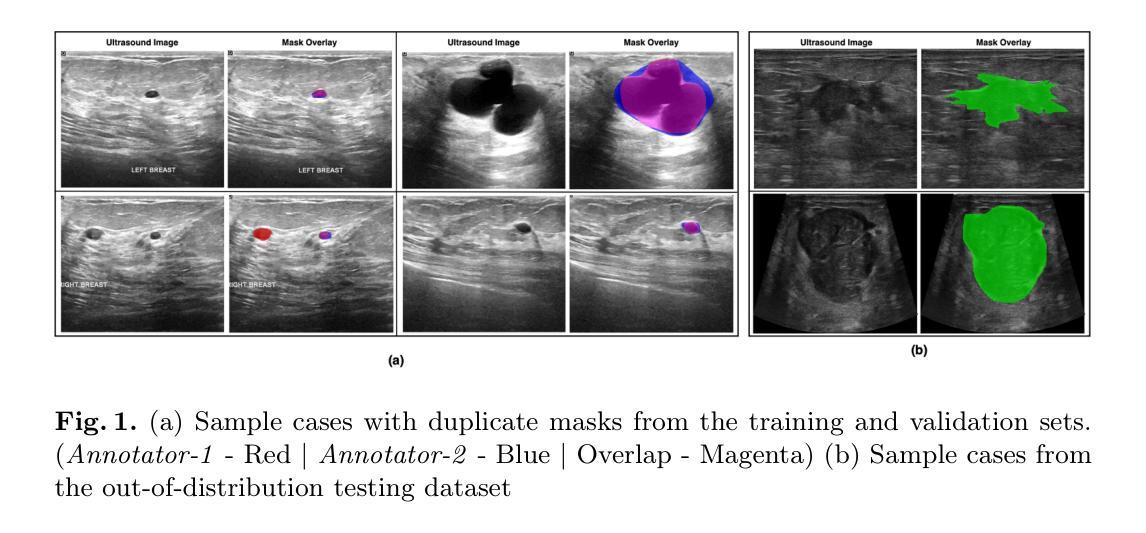
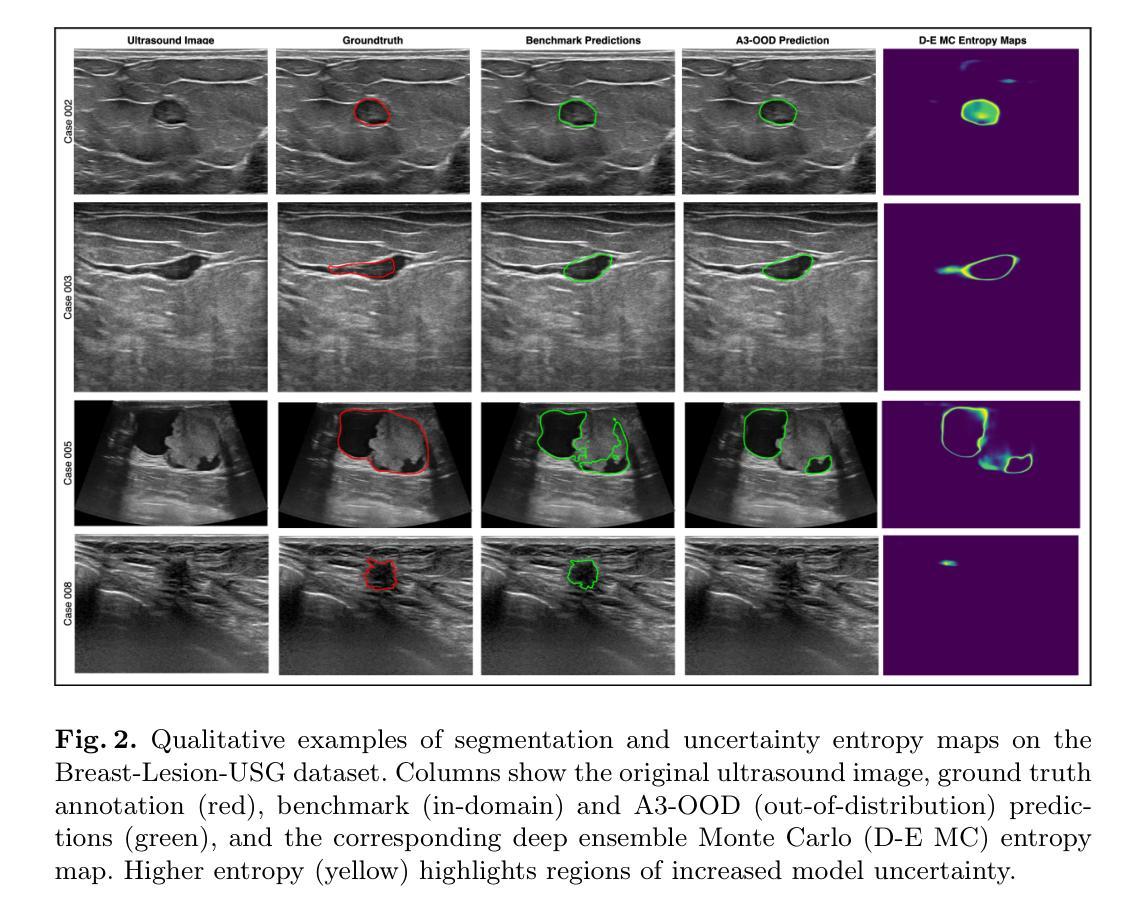
Automated segmentation of BUS images is important for precise lesion delineation and tumor characterization, but is challenged by inherent artifacts and dataset inconsistencies. In this work, we evaluate the use of a modified Residual Encoder U-Net for breast ultrasound segmentation, with a focus on uncertainty quantification. We identify and correct for data duplication in the BUSI dataset, and use a deduplicated subset for more reliable estimates of generalization performance. Epistemic uncertainty is quantified using Monte Carlo dropout, deep ensembles, and their combination. Models are benchmarked on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets to demonstrate how they generalize to unseen cross-domain data. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy on the Breast-Lesion-USG dataset with in-distribution validation, and provides calibrated uncertainty estimates that effectively signal regions of low model confidence. Performance declines and increased uncertainty observed in out-of-distribution evaluation highlight the persistent challenge of domain shift in medical imaging, and the importance of integrated uncertainty modeling for trustworthy clinical deployment. \footnote{Code available at: https://github.com/toufiqmusah/nn-uncertainty.git}
自动分割BUS图像对于精确病灶界定和肿瘤特征描述非常重要,但面临着固有的伪像和数据集不一致性的挑战。在这项工作中,我们评估了使用修改后的残差编码器U-Net进行乳腺超声分割的可行性,重点关注不确定性量化。我们识别并纠正了BUSI数据集中的数据重复问题,并使用去重子集进行更可靠的总体化性能估计。使用蒙特卡洛失活法和深度集成及其组合来量化知识不确定性。模型在内部和外部数据集上进行了评估,以展示它们如何适应未见过的跨域数据。我们的方法在实现Breast-Lesion-USG数据集上的最新分割准确性方面具有最佳性能,提供了校准的不确定性估计,有效标记了模型不确定的区域。在外部评估中观察到的性能下降和不确定性增加突显了医学成像领域转移的持续挑战,以及集成不确定性建模对于可信赖的临床部署的重要性。注释:代码可在https://github.com/toufiqmusah/nn-uncertainty.git获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Medical Image Computing in Resource Constrained Settings Workshop & Knowledge Interchange
Summary
本文探讨了在乳腺超声图像(BUS)中,使用改良的残差编码器U-Net进行自动分割的重要性及所面临的挑战。文章重点关注不确定性量化,并识别并修正了BUSI数据集的数据重复问题。通过蒙特卡洛dropout、深度集成及其组合来量化认知不确定性。模型在内部和跨域数据集上的表现证明了其在未见数据上的泛化能力。本文方法实现了在Breast-Lesion-USG数据集上的最新分割精度,并提供校准的不确定性估计,有效指示低模型置信区域。在跨域评估中的性能下降和不确定性增加突显了医学成像中的领域转换挑战,以及综合不确定性建模对于可靠临床部署的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化乳腺超声图像分割对于精确病变识别和肿瘤特征化至关重要,但面临内在伪像和数据集不一致性的挑战。
- 使用改良的Residual Encoder U-Net进行乳腺超声分割,并重点关注不确定性量化。
- 识别并解决了BUSI数据集的数据重复问题,以确保更可靠的性能估计。
- 通过蒙特卡洛dropout和深度集成等方法量化认知不确定性。
- 模型在内部和跨域数据集上的表现证明了其在未见数据上的泛化能力。
- 达到了在Breast-Lesion-USG数据集上的最新分割精度,且不确定性估计有效。
点此查看论文截图

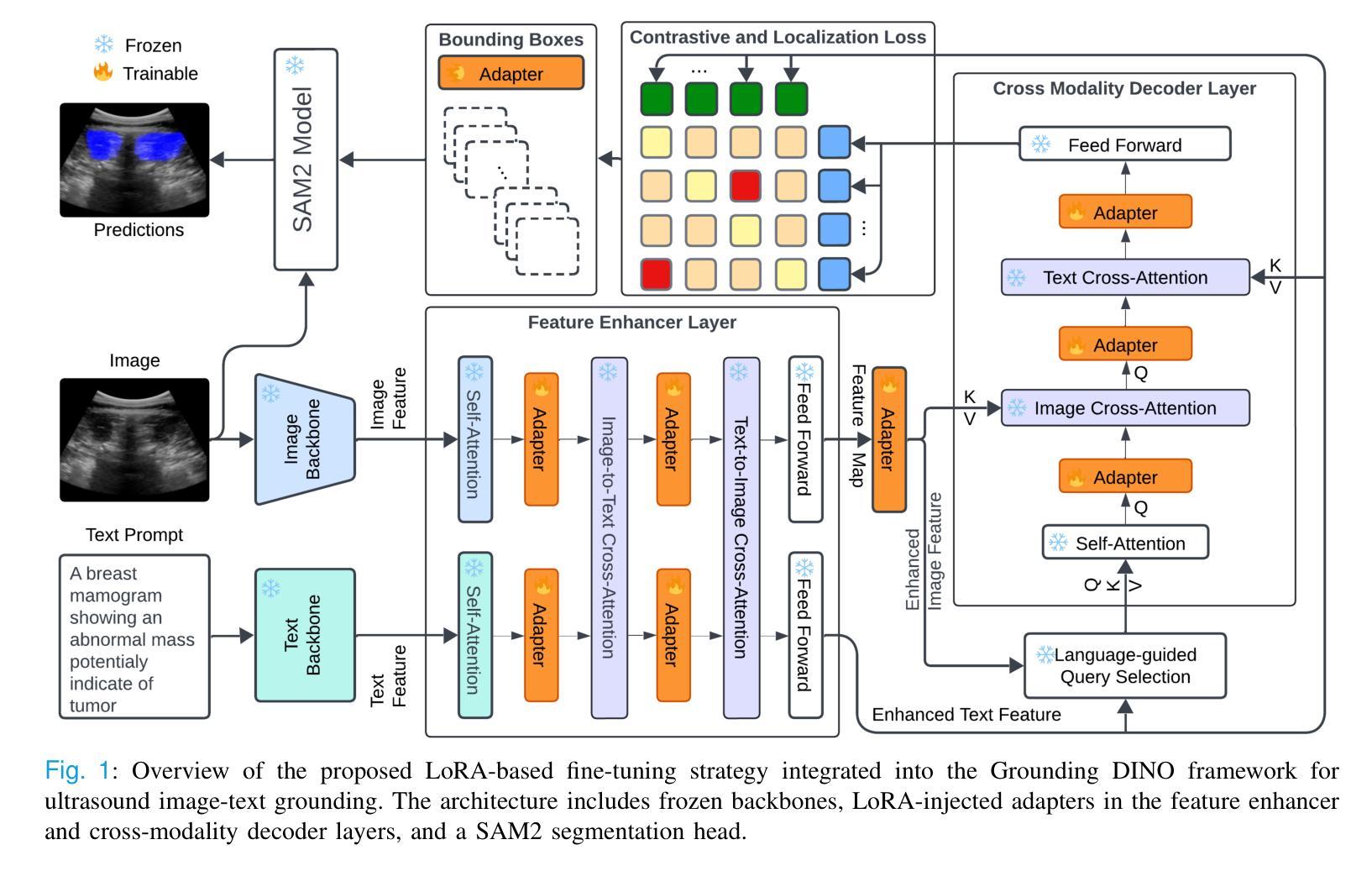
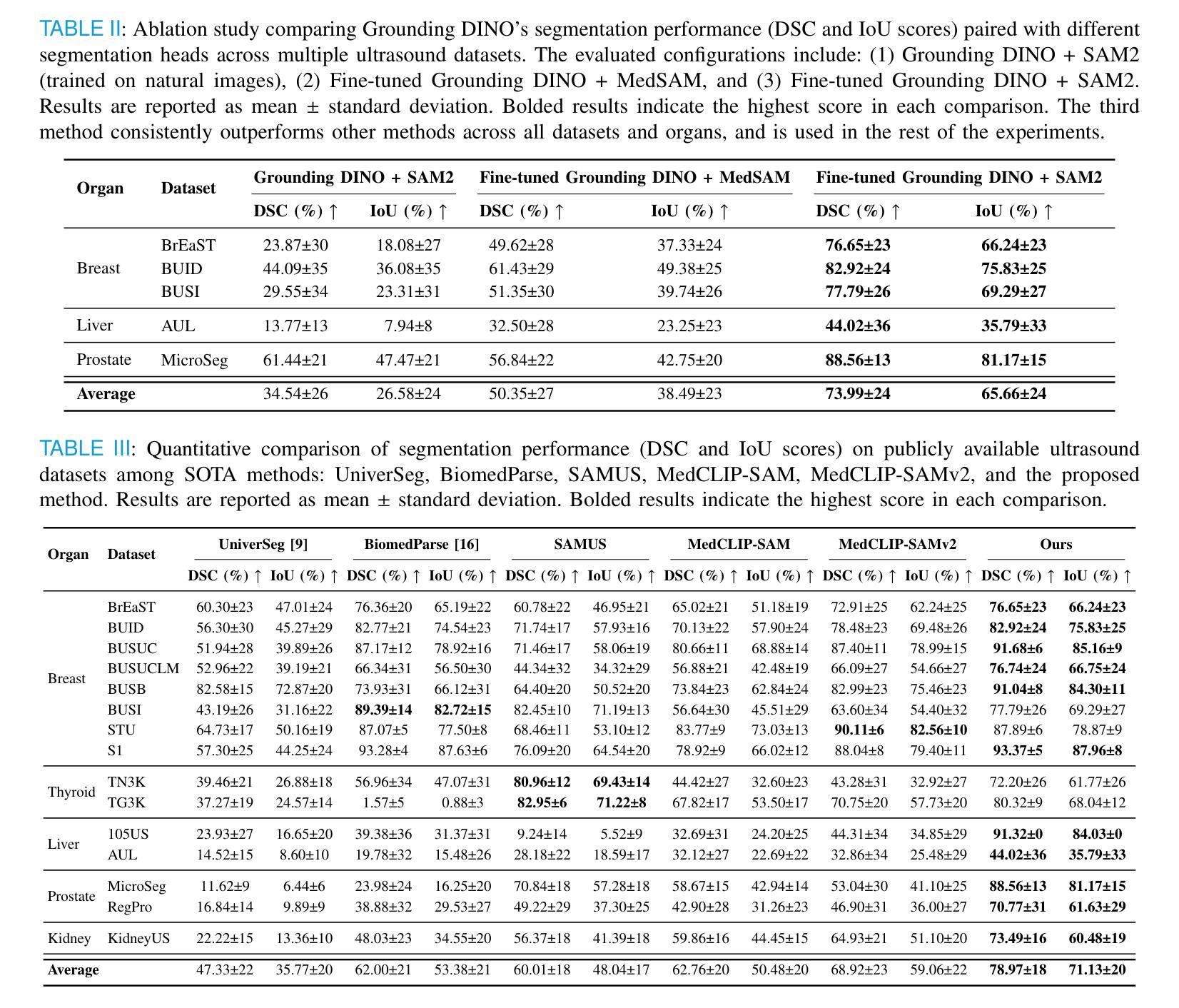
GroundingDINO-US-SAM: Text-Prompted Multi-Organ Segmentation in Ultrasound with LoRA-Tuned Vision-Language Models
Authors:Hamza Rasaee, Taha Koleilat, Hassan Rivaz
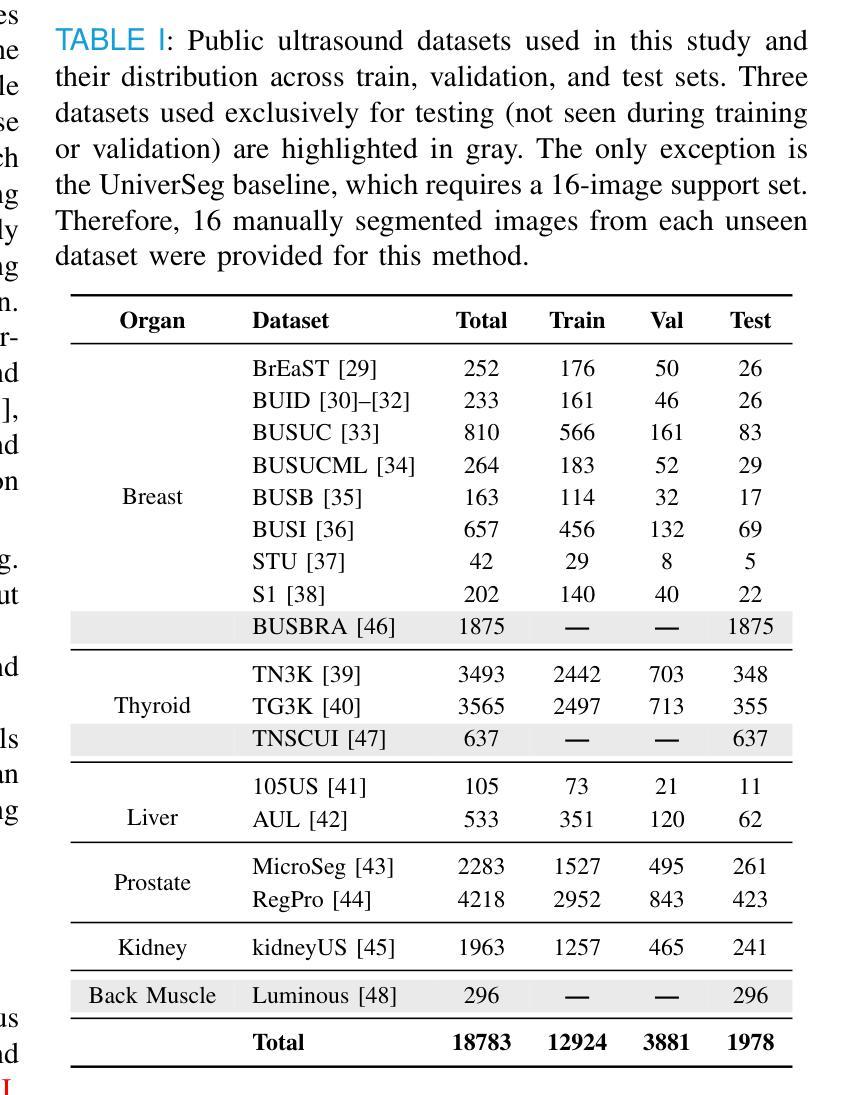
Accurate and generalizable object segmentation in ultrasound imaging remains a significant challenge due to anatomical variability, diverse imaging protocols, and limited annotated data. In this study, we propose a prompt-driven vision-language model (VLM) that integrates Grounding DINO with SAM2 to enable object segmentation across multiple ultrasound organs. A total of 18 public ultrasound datasets, encompassing the breast, thyroid, liver, prostate, kidney, and paraspinal muscle, were utilized. These datasets were divided into 15 for fine-tuning and validation of Grounding DINO using Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) to the ultrasound domain, and 3 were held out entirely for testing to evaluate performance in unseen distributions. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art segmentation methods, including UniverSeg, MedSAM, MedCLIP-SAM, BiomedParse, and SAMUS on most seen datasets while maintaining strong performance on unseen datasets without additional fine-tuning. These results underscore the promise of VLMs in scalable and robust ultrasound image analysis, reducing dependence on large, organ-specific annotated datasets. We will publish our code on code.sonography.ai after acceptance.
在超声成像中,实现准确且普遍适用的目标分割仍然是一个巨大的挑战,这主要是由于解剖结构多样性、成像协议差异以及标注数据有限所造成的。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种基于提示的视觉语言模型(VLM),它集成了基于地形的DINO与SAM2,以在多个超声器官中实现目标分割。我们共使用了18个公开超声数据集,涵盖了乳腺、甲状腺、肝脏、前列腺、肾脏和腰背部肌肉等部位。这些数据集被分为两部分,其中15个用于微调基于地形的DINO并使用低秩适应(LoRA)对其进行超声领域的适应验证,另外3个则完全保留用于测试,以评估在未见分布中的性能表现。全面的实验表明,我们的方法在某些已见数据集上的表现优于最先进的分割方法,包括UniverSeg、MedSAM、MedCLIP-SAM、BiomedParse和SAMUS等,并且在未见数据集上无需额外微调即可保持强大的性能表现。这些结果突显了视觉语言模型在可扩展和稳健的超声图像分析中的潜力,并降低了对大型特定器官标注数据集的依赖。接受后,我们将在code.sonography.ai上发布我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures, 7 tables
Summary
该研究表明,超声成像中的目标分割仍然存在挑战,因解剖结构变化、成像协议多样性和标注数据有限等因素制约。本研究提出了一种基于提示驱动的视觉语言模型(VLM),通过整合Grounding DINO与SAM2,实现对多个超声器官的目标分割。研究使用了涵盖乳房、甲状腺、肝脏、前列腺、肾脏和背肌的共18个公开超声数据集。通过低秩适应(LoRA)对Grounding DINO进行微调验证,并采用三个未见数据集进行测试性能评估。实验表明,该方法在多数已见数据集上优于当前最先进的分割方法,包括UniverSeg、MedSAM、MedCLIP-SAM、BiomedParse和SAMUS等,同时在未见数据集上无需额外微调即可保持强劲性能。此研究突显了VLM在可扩展性和稳健性超声图像分析中的潜力,减少了大规模特定器官标注数据集的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种基于提示驱动的视觉语言模型(VLM),用于超声成像的目标分割。
- 整合了Grounding DINO与SAM2,实现对多个超声器官的目标分割。
- 研究使用了涵盖多个器官的共18个公开超声数据集进行实验。
- 通过低秩适应(LoRA)对模型进行微调验证。
- 该方法在多数已见数据集上的性能优于其他先进方法。
- 在未见数据集上无需额外微调即可保持强劲性能。
点此查看论文截图
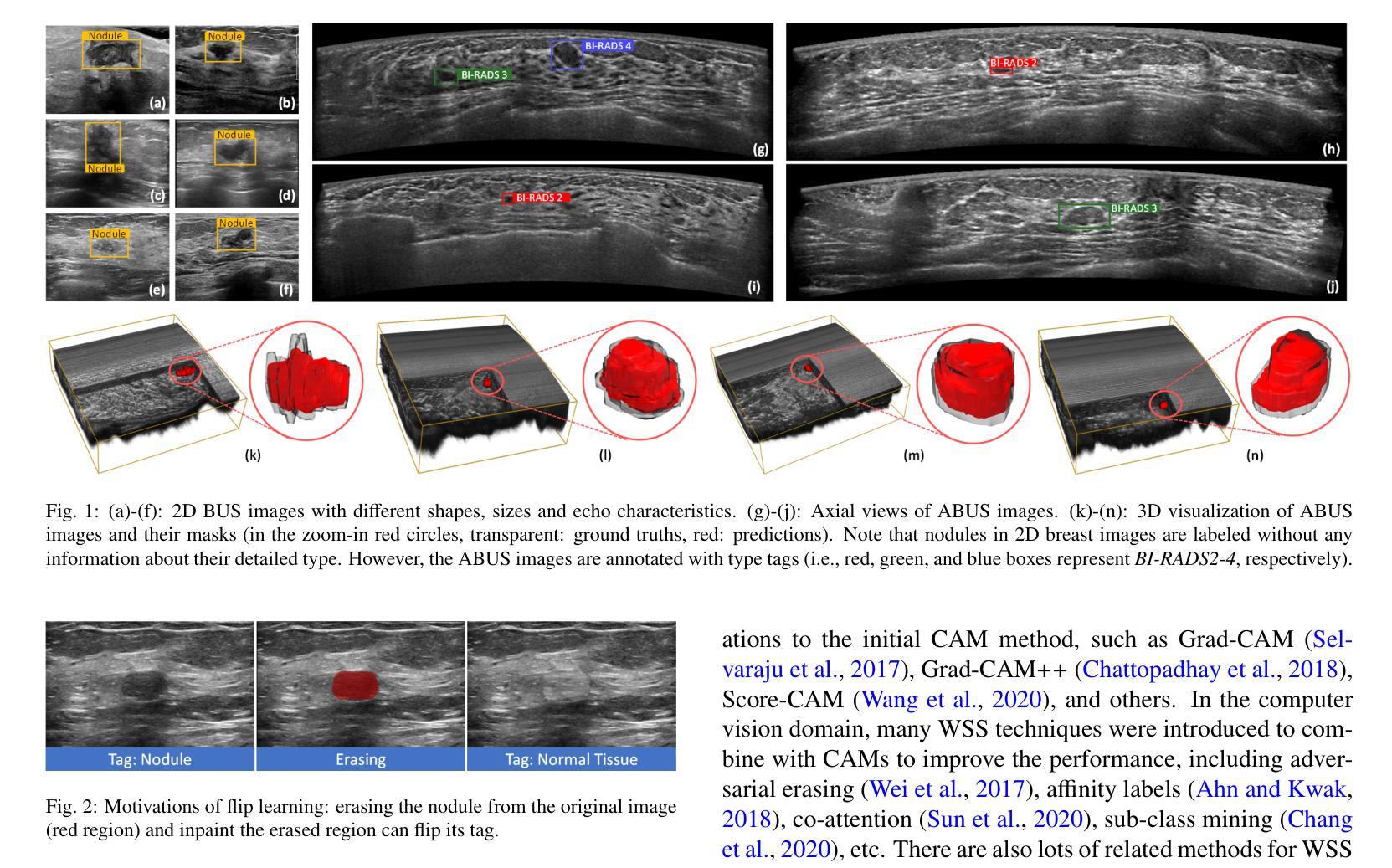
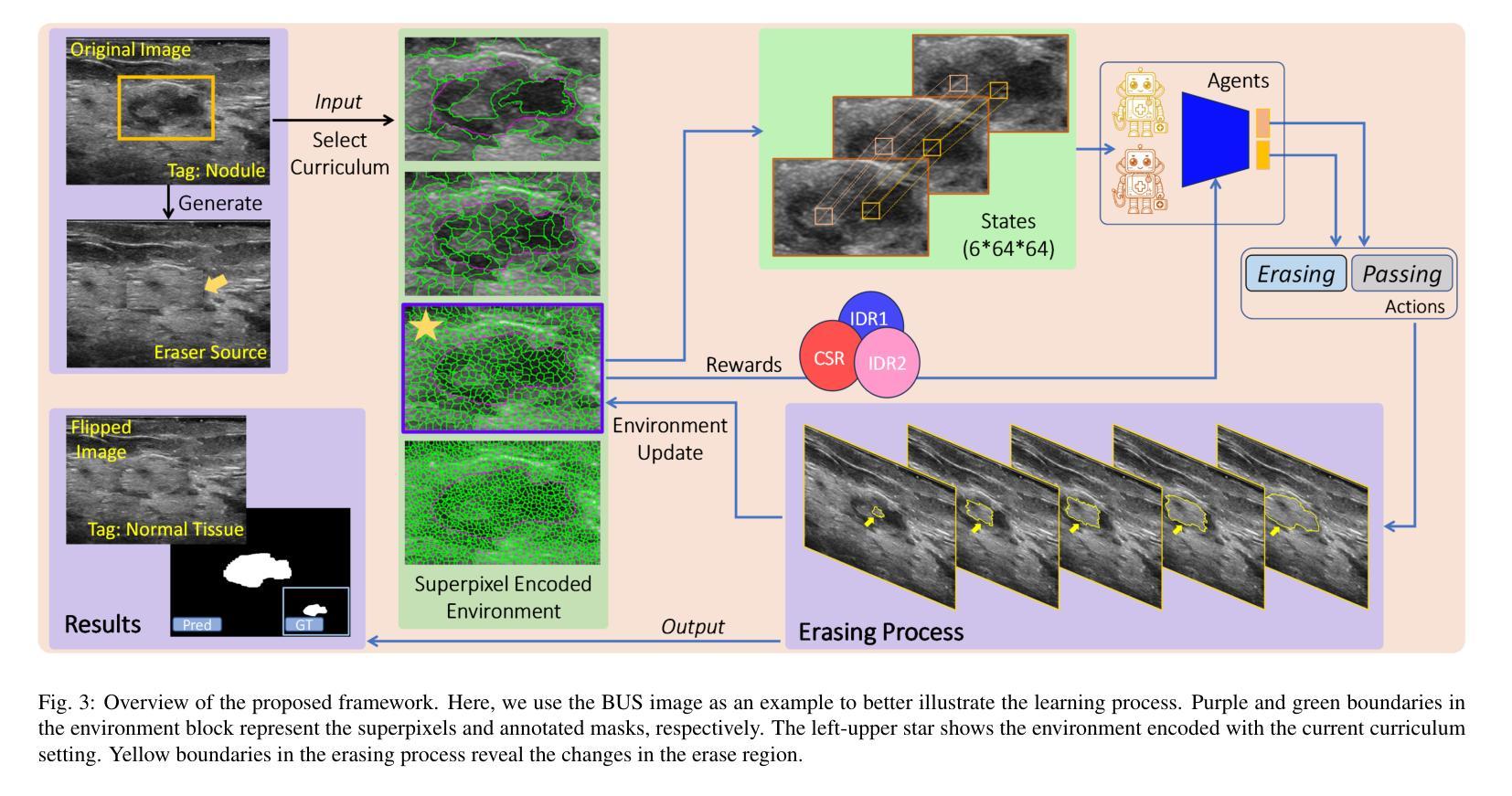
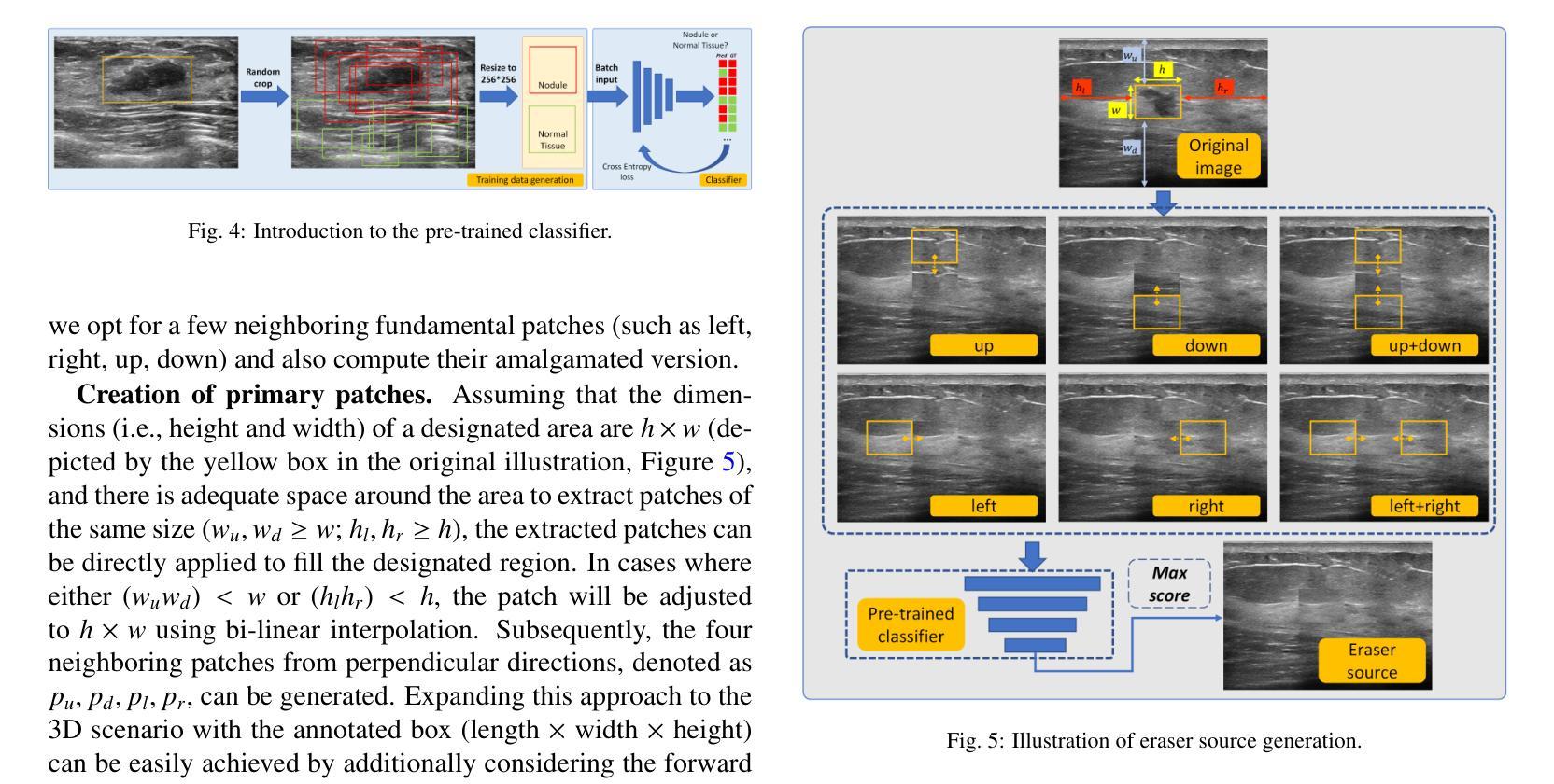
Flip Learning: Weakly Supervised Erase to Segment Nodules in Breast Ultrasound
Authors:Yuhao Huang, Ao Chang, Haoran Dou, Xing Tao, Xinrui Zhou, Yan Cao, Ruobing Huang, Alejandro F Frangi, Lingyun Bao, Xin Yang, Dong Ni
Accurate segmentation of nodules in both 2D breast ultrasound (BUS) and 3D automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) is crucial for clinical diagnosis and treatment planning. Therefore, developing an automated system for nodule segmentation can enhance user independence and expedite clinical analysis. Unlike fully-supervised learning, weakly-supervised segmentation (WSS) can streamline the laborious and intricate annotation process. However, current WSS methods face challenges in achieving precise nodule segmentation, as many of them depend on inaccurate activation maps or inefficient pseudo-mask generation algorithms. In this study, we introduce a novel multi-agent reinforcement learning-based WSS framework called Flip Learning, which relies solely on 2D/3D boxes for accurate segmentation. Specifically, multiple agents are employed to erase the target from the box to facilitate classification tag flipping, with the erased region serving as the predicted segmentation mask. The key contributions of this research are as follows: (1) Adoption of a superpixel/supervoxel-based approach to encode the standardized environment, capturing boundary priors and expediting the learning process. (2) Introduction of three meticulously designed rewards, comprising a classification score reward and two intensity distribution rewards, to steer the agents’ erasing process precisely, thereby avoiding both under- and over-segmentation. (3) Implementation of a progressive curriculum learning strategy to enable agents to interact with the environment in a progressively challenging manner, thereby enhancing learning efficiency. Extensively validated on the large in-house BUS and ABUS datasets, our Flip Learning method outperforms state-of-the-art WSS methods and foundation models, and achieves comparable performance as fully-supervised learning algorithms.
二维乳腺超声(BUS)和三维自动乳腺超声(ABUS)中结节的精确分割对于临床诊断和治疗计划至关重要。因此,开发一种自动化结节分割系统可以提高用户独立性并加快临床分析速度。与全监督学习不同,弱监督分割(WSS)可以简化繁琐且复杂的注释过程。然而,当前的WSS方法在实现精确结节分割方面面临挑战,因为它们中的许多方法依赖于不准确的激活图或低效的伪掩膜生成算法。在本研究中,我们引入了一种基于多智能体强化学习的新型WSS框架,称为Flip Learning,它仅依赖于2D/3D框进行精确分割。具体来说,使用多个智能体从框中擦除目标,以促进分类标签翻转,擦除区域作为预测的分割掩膜。本研究的关键贡献如下:(1)采用基于超像素/监督体素的方法对标准化环境进行编码,捕捉边界先验并加速学习过程。(2)引入了三种精心设计的奖励措施,包括分类分数奖励和两个强度分布奖励,以精确引导智能体的擦除过程,从而避免欠分割和过分割。(3)实施渐进式课程学习策略,使智能体能够以越来越具有挑战性的方式与环境进行交互,从而提高学习效率。在我们的Flip Learning方法的大规模内部BUS和ABUS数据集上进行广泛验证表明,它优于最新的WSS方法和基础模型,并且其性能与全监督学习算法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Medical Image Analysis. 24 pages, 13 figures, 20 tabels
Summary
本文介绍了基于多智能体的强化学习弱监督分割框架Flip Learning,用于二维和三维乳腺超声中的结节分割。该方法利用超像素/监督体素技术,通过设计三种奖励来指导智能体的擦除过程,并采用渐进的课程学习策略提高学习效率。在大量内部BUS和ABUS数据集上的验证表明,Flip Learning方法优于其他先进的WSS方法和基础模型,其性能与全监督学习算法相当。
Key Takeaways
- Flip Learning是一个基于多智能体的强化学习框架,用于乳腺超声中的结节分割。
- Flip Learning采用超像素/监督体素技术,以加快学习过程并捕捉边界先验信息。
- 通过设计三种奖励(包括分类得分奖励和两个强度分布奖励)来精确指导智能体的擦除过程。
- Flip Learning方法避免了过分割和欠分割的问题。
- 渐进的课程学习策略使智能体能够以逐渐挑战的方式与环境互动,从而提高学习效率。
- 在大量内部数据集上的验证显示,Flip Learning性能优于其他先进的弱监督分割方法和基础模型。
点此查看论文截图