⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
Adaptive Contrast Adjustment Module: A Clinically-Inspired Plug-and-Play Approach for Enhanced Fetal Plane Classification
Authors:Yang Chen, Sanglin Zhao, Baoyu Chen, Mans Gustaf
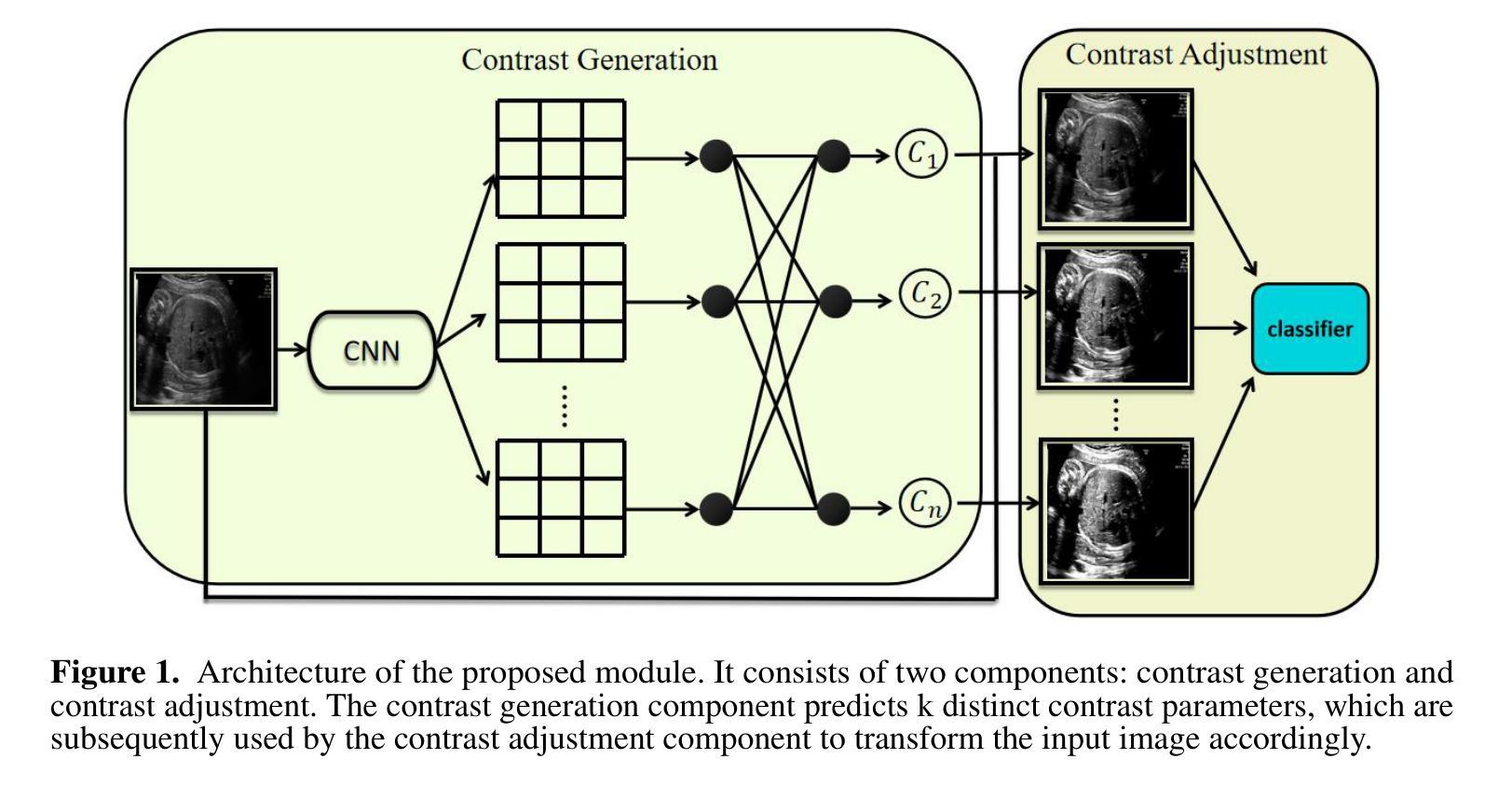
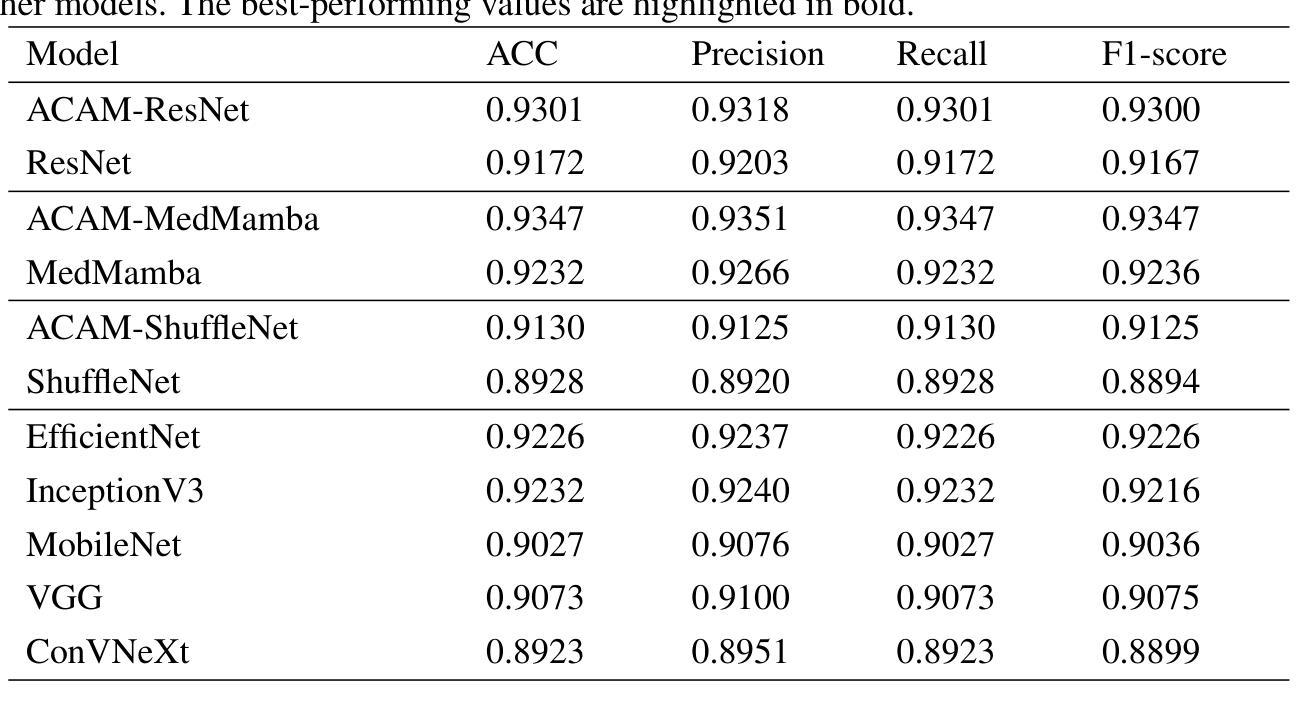
Fetal ultrasound standard plane classification is essential for reliable prenatal diagnosis but faces inherent challenges, including low tissue contrast, boundary ambiguity, and operator-dependent image quality variations. To overcome these limitations, we propose a plug-and-play adaptive contrast adjustment module (ACAM), whose core design is inspired by the clinical practice of doctors adjusting image contrast to obtain clearer and more discriminative structural information. The module employs a shallow texture-sensitive network to predict clinically plausible contrast parameters, transforms input images into multiple contrast-enhanced views through differentiable mapping, and fuses them within downstream classifiers. Validated on a multi-center dataset of 12,400 images across six anatomical categories, the module consistently improves performance across diverse models, with accuracy of lightweight models increasing by 2.02 percent, accuracy of traditional models increasing by 1.29 percent, and accuracy of state-of-the-art models increasing by 1.15 percent. The innovation of the module lies in its content-aware adaptation capability, replacing random preprocessing with physics-informed transformations that align with sonographer workflows while improving robustness to imaging heterogeneity through multi-view fusion. This approach effectively bridges low-level image features with high-level semantics, establishing a new paradigm for medical image analysis under real-world image quality variations.
胎儿超声标准平面分类对于可靠的产前诊断至关重要,但面临着固有的挑战,包括组织对比度低、边界模糊和依赖于操作员的图像质量变化。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种即插即用的自适应对比度调整模块(ACAM),其核心设计灵感来源于医生调整图像对比度以获取更清晰、更具区分度的结构信息的临床实践。该模块采用浅纹理敏感网络来预测临床上合理的对比度参数,通过可微分映射将输入图像转换为多个对比度增强的视图,并在下游分类器中融合它们。在多中心数据集(涵盖12400张图像和六个解剖类别)上进行验证,该模块在各种模型上的表现始终有所提升,轻量级模型的准确率提高2.02%,传统模型的准确率提高1.29%,先进模型的准确率提高1.15%。该模块的创新之处在于其基于内容感知的自适应能力,用基于物理的转换替代了随机预处理,这与超声医师的工作流程相符,同时通过多视图融合提高了对成像异质性的稳健性。这种方法有效地将低级图像特征与高级语义相结合,为现实世界中图像质量变化的医学图像分析建立了新的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种即插即用的自适应对比度调整模块(ACAM),用于解决胎儿超声标准平面分类在产前诊断中的挑战。该模块通过调整图像对比度,获得更清晰、更具辨识度的结构信息,采用浅纹理敏感网络预测合理的对比度参数,将输入图像转化为多种对比度增强视图,并在下游分类器中融合。在多中心数据集上验证,该模块在不同模型上的性能均有所提升。
Key Takeaways
- 胎儿超声标准平面分类对产前诊断至关重要,但存在组织对比度低、边界模糊和图像质量操作者差异等挑战。
- 提出自适应对比度调整模块(ACAM),灵感来源于医生调整图像对比度以获取更清晰结构信息的临床实践。
- ACAM使用浅纹理敏感网络预测合理的对比度参数,将输入图像转化为多种对比度增强视图。
- ACAM通过可微映射实现多种视图融合,并在下游分类器中使用。
- 在包含12,400张图像的多中心数据集上进行验证,ACAM提升了不同模型的性能。
- ACAM的创新之处在于其内容感知适应能力,能替换随机预处理,采用符合超声工作者工作流程的物理信息转换。
点此查看论文截图

HCCM: Hierarchical Cross-Granularity Contrastive and Matching Learning for Natural Language-Guided Drones
Authors:Hao Ruan, Jinliang Lin, Yingxin Lai, Zhiming Luo, Shaozi Li
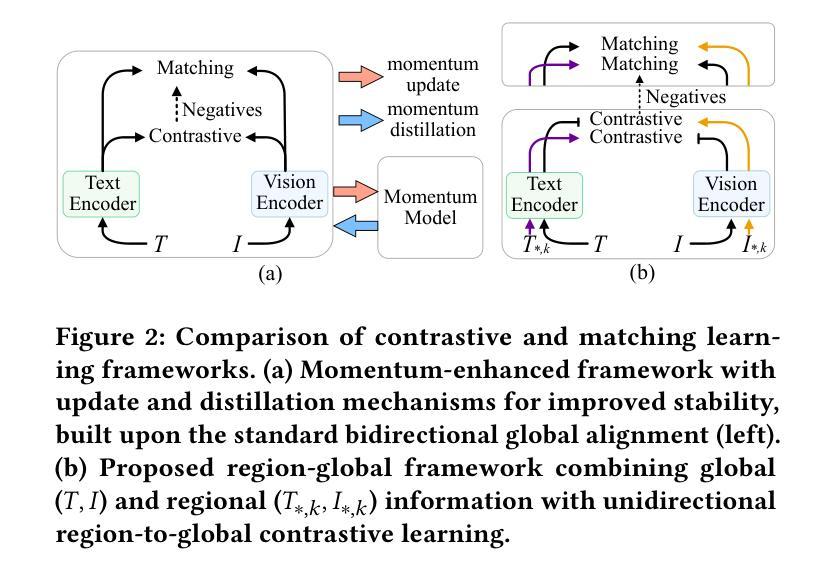
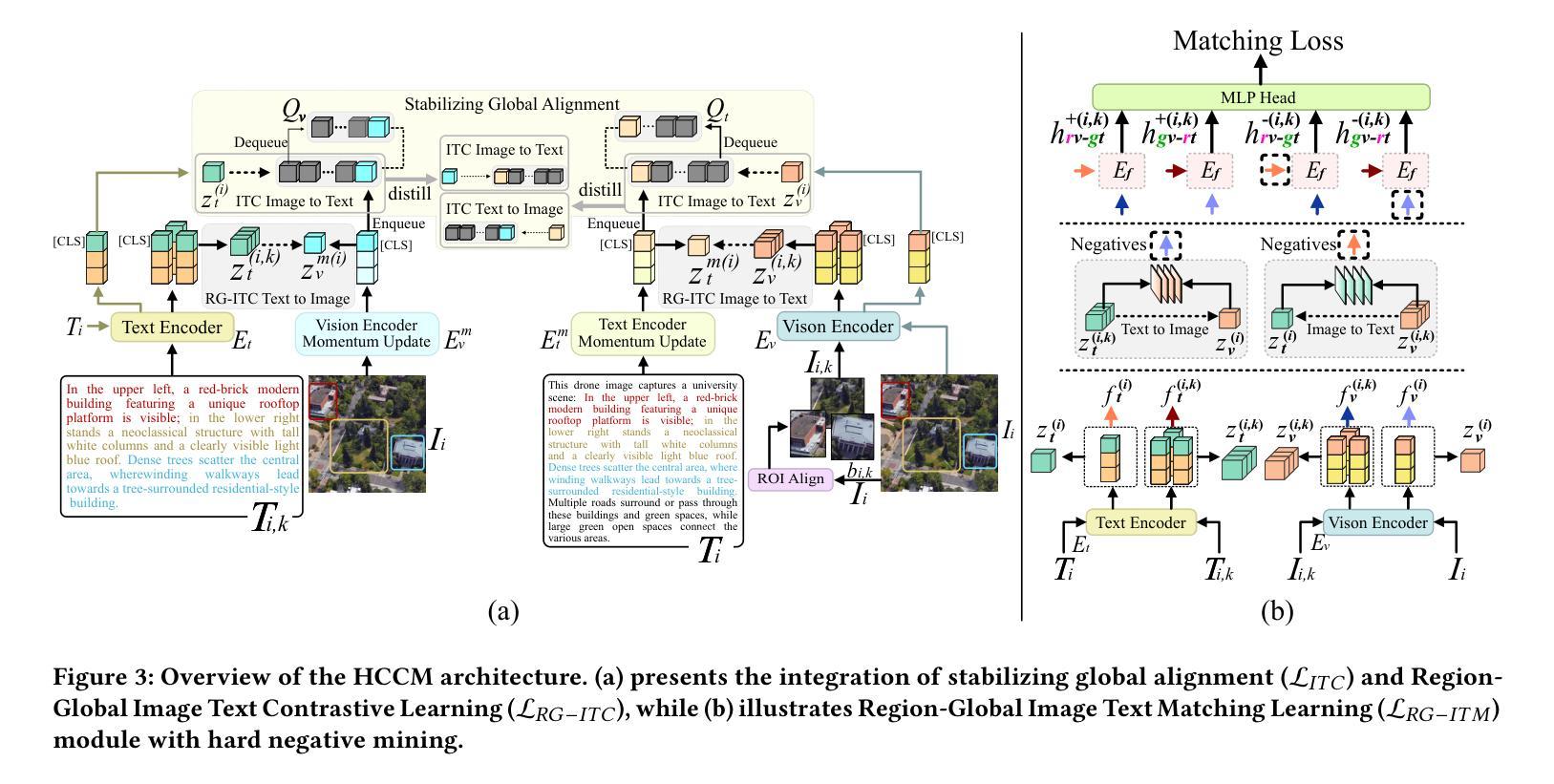
Natural Language-Guided Drones (NLGD) provide a novel paradigm for tasks such as target matching and navigation. However, the wide field of view and complex compositional semantics in drone scenarios pose challenges for vision-language understanding. Mainstream Vision-Language Models (VLMs) emphasize global alignment while lacking fine-grained semantics, and existing hierarchical methods depend on precise entity partitioning and strict containment, limiting effectiveness in dynamic environments. To address this, we propose the Hierarchical Cross-Granularity Contrastive and Matching learning (HCCM) framework with two components: (1) Region-Global Image-Text Contrastive Learning (RG-ITC), which avoids precise scene partitioning and captures hierarchical local-to-global semantics by contrasting local visual regions with global text and vice versa; (2) Region-Global Image-Text Matching (RG-ITM), which dispenses with rigid constraints and instead evaluates local semantic consistency within global cross-modal representations, enhancing compositional reasoning. Moreover, drone text descriptions are often incomplete or ambiguous, destabilizing alignment. HCCM introduces a Momentum Contrast and Distillation (MCD) mechanism to improve robustness. Experiments on GeoText-1652 show HCCM achieves state-of-the-art Recall@1 of 28.8% (image retrieval) and 14.7% (text retrieval). On the unseen ERA dataset, HCCM demonstrates strong zero-shot generalization with 39.93% mean recall (mR), outperforming fine-tuned baselines.
自然语言指导的无人机(NLGD)为目标匹配和导航等任务提供了新的范式。然而,无人机场景中的广阔视野和复杂的组合语义对视觉语言理解提出了挑战。主流的视觉语言模型(VLM)强调全局对齐,但缺乏精细的语义信息,而现有的层次方法依赖于精确实体分割和严格包含关系,在动态环境中的有效性受到限制。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了层次化跨粒度对比匹配学习(HCCM)框架,包含两个组件:(1)区域全局图像文本对比学习(RG-ITC),通过对比局部视觉区域与全局文本,避免精确场景分割,捕捉层次化的局部到全局语义; (2)区域全局图像文本匹配(RG-ITM),摒弃了刚性约束,转而评估全局跨模态表示中的局部语义一致性,增强了组合推理能力。此外,无人机文本描述往往不完整或模糊,导致对齐不稳定。HCCM引入了一种动量对比和蒸馏(MCD)机制,提高了稳健性。在GeoText-1 652上的实验表明,HCCM实现了最先进的Recall@1指标,图像检索为28.8%,文本检索为14.7%。在未见过的ERA数据集上,HCCM表现出强大的零样本泛化能力,平均召回率为39.93%(mR),超过了微调基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM’25
Summary
本文提出了一个名为Hierarchical Cross-Granularity Contrastive and Matching learning(HCCM)的框架,旨在解决自然语言引导无人机在视觉语言理解方面所面临的挑战。该框架包括两个组件:Region-Global Image-Text Contrastive Learning(RG-ITC)和Region-Global Image-Text Matching(RG-ITM)。RG-ITC通过对比局部视觉区域与全局文本,捕捉层次化的局部到全局语义;RG-ITM则评估局部语义一致性在全局跨模态表示中的表现,增强组合推理能力。此外,还引入了Momentum Contrast and Distillation(MCD)机制提高无人机文本描述的鲁棒性。实验结果表明,HCCM框架在GeoText-1652数据集上取得了最先进的召回率,并且在未见过的ERA数据集上展现了强大的零样本泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- NLGD(自然语言引导无人机)在目标匹配和导航等任务中代表了一种新的范式,但面临着视野广阔和场景语义复杂度的挑战。
- 主流Vision-Language Models(VLMs)强调全局对齐,但缺乏精细的语义粒度,而现有的分层方法依赖于精确实体分区和严格包含关系,这在动态环境中限制了其有效性。
- HCCM框架通过Region-Global Image-Text Contrastive Learning(RG-ITC)捕捉层次化的局部到全局语义,避免精确场景分割。
- HCCM框架中的Region-Global Image-Text Matching(RG-ITM)评估局部语义一致性在全局跨模态表示中的表现,增强了组合推理能力,并摒弃了刚性约束。
- 无人机文本描述常常不完整或模糊,HCCM框架引入了Momentum Contrast and Distillation(MCD)机制来提高鲁棒性。
- 在GeoText-1652数据集上的实验表明,HCCM框架实现了先进的召回率表现。
点此查看论文截图


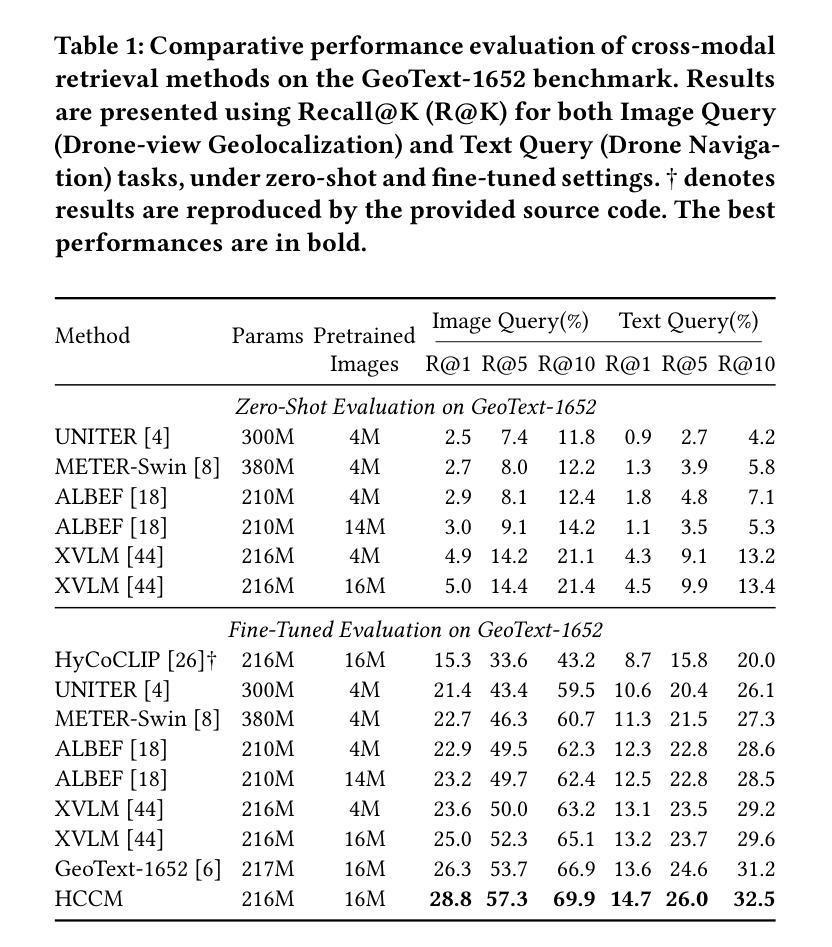
Contrastive Learning through Auxiliary Branch for Video Object Detection
Authors:Lucas Rakotoarivony
Video object detection is a challenging task because videos often suffer from image deterioration such as motion blur, occlusion, and deformable shapes, making it significantly more difficult than detecting objects in still images. Prior approaches have improved video object detection performance by employing feature aggregation and complex post-processing techniques, though at the cost of increased computational demands. To improve robustness to image degradation without additional computational load during inference, we introduce a straightforward yet effective Contrastive Learning through Auxiliary Branch (CLAB) method. First, we implement a constrastive auxiliary branch using a contrastive loss to enhance the feature representation capability of the video object detector’s backbone. Next, we propose a dynamic loss weighting strategy that emphasizes auxiliary feature learning early in training while gradually prioritizing the detection task as training converges. We validate our approach through comprehensive experiments and ablation studies, demonstrating consistent performance gains. Without bells and whistles, CLAB reaches a performance of 84.0% mAP and 85.2% mAP with ResNet-101 and ResNeXt-101, respectively, on the ImageNet VID dataset, thus achieving state-of-the-art performance for CNN-based models without requiring additional post-processing methods.
视频目标检测是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为视频常常会受到图像退化问题的影响,如运动模糊、遮挡和可变形状,这使得视频中的目标检测比静态图像中的检测更为困难。先前的方法通过采用特征聚合和复杂的后处理技术提高了视频目标检测的性能,但同时也增加了计算需求。为了提高对图像退化的鲁棒性,同时在不增加推理过程中的计算负载的情况下,我们提出了一种简单有效的通过辅助分支进行对比学习(CLAB)的方法。首先,我们使用对比损失实现了一个对比辅助分支,以增强视频目标检测器主干特征表示的能力。接下来,我们提出了一种动态损失权重策略,该策略在训练早期强调辅助特征学习,随着训练的收敛逐渐优先考虑检测任务。我们通过全面的实验和消融研究验证了我们的方法,证明了其持续的性能提升。在不使用任何额外技巧的情况下,CLAB在ImageNet VID数据集上达到了使用ResNet-101和ResNeXt-101的84.0%和85.2%的mAP性能,从而在基于CNN的模型中实现了最先进的性能,且无需额外的后处理方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted paper for ACIVS 2025
Summary
视频目标检测是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为视频经常出现图像退化问题,如运动模糊、遮挡和可变形形状。为提高对图像退化的鲁棒性,同时不增加推理过程中的计算负担,我们提出了一种简单有效的对比学习辅助分支(CLAB)方法。通过实现对比辅助分支并使用对比损失增强视频目标检测器主干的特征表示能力,再提出动态损失权重策略,在训练初期强调辅助特征学习,随着训练收敛逐渐以检测任务为主。实验和消融研究表明,我们的方法表现稳健,性能提升明显。在ImageNet VID数据集上,CLAB使用ResNet-101和ResNeXt-101分别达到了84.0%和85.2%的mAP,实现了基于CNN模型的最新性能,无需额外的后处理方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视频目标检测面临图像退化挑战,如运动模糊、遮挡和形状变形。
- 对比学习辅助分支(CLAB)方法旨在提高视频目标检测性能并应对图像退化问题。
- CLAB方法通过实现对比辅助分支并使用对比损失来增强视频目标检测器的特征表示能力。
- 动态损失权重策略在训练过程中平衡了辅助特征学习与检测任务的优先级。
- CLAB方法在不增加计算负担的情况下提高了视频目标检测的鲁棒性。
- 在ImageNet VID数据集上,CLAB方法实现了最新性能,使用ResNet-101和ResNeXt-101达到较高的mAP值。
点此查看论文截图

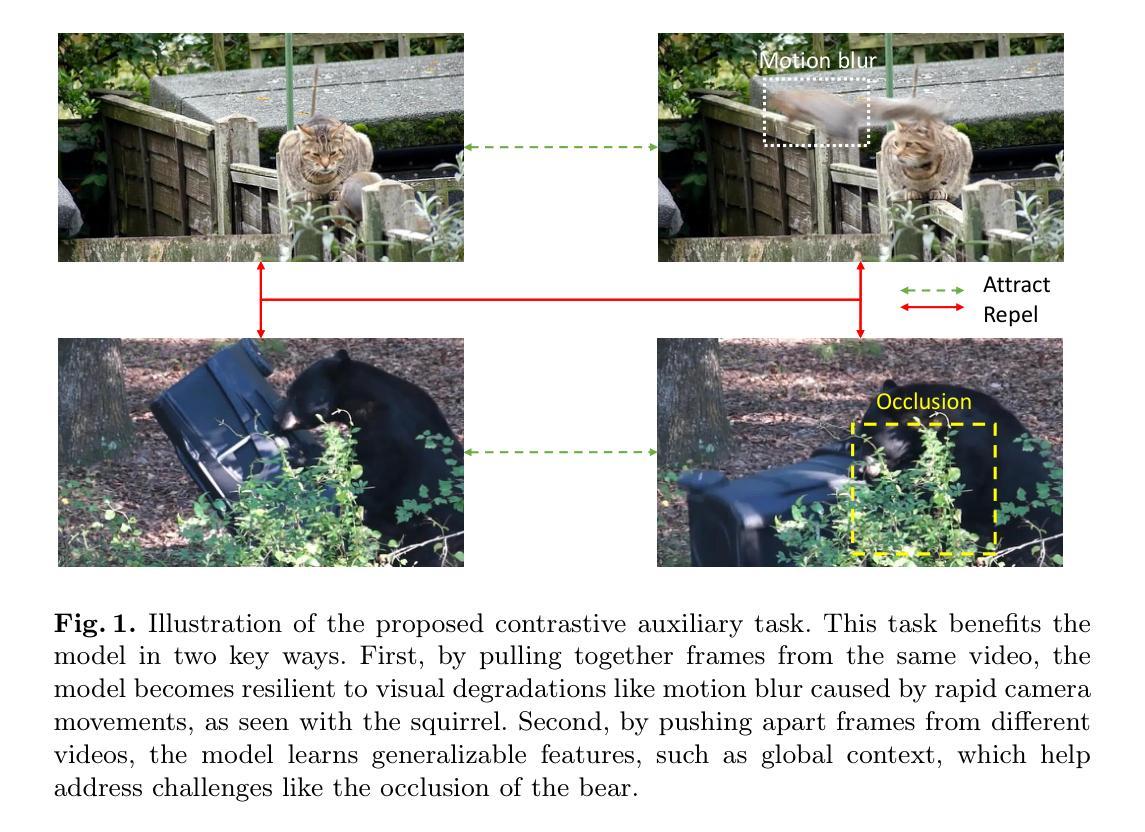
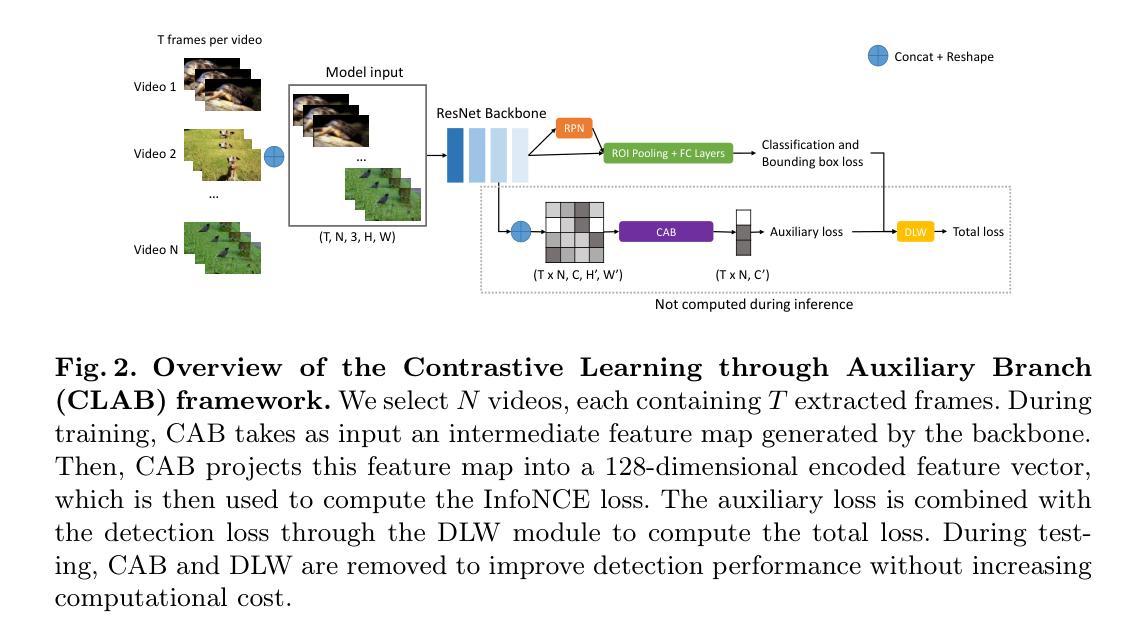
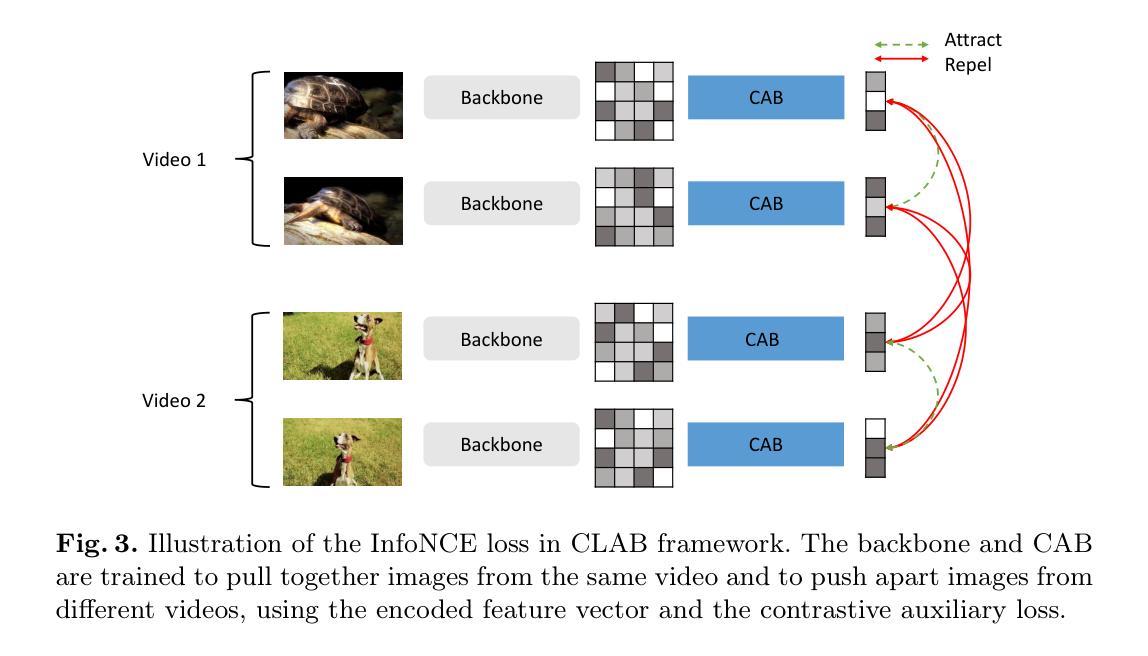
DNP-Guided Contrastive Reconstruction with a Reverse Distillation Transformer for Medical Anomaly Detection
Authors:Luhu Li, Bowen Lin, Mukhtiar Khan, Shujun Fu
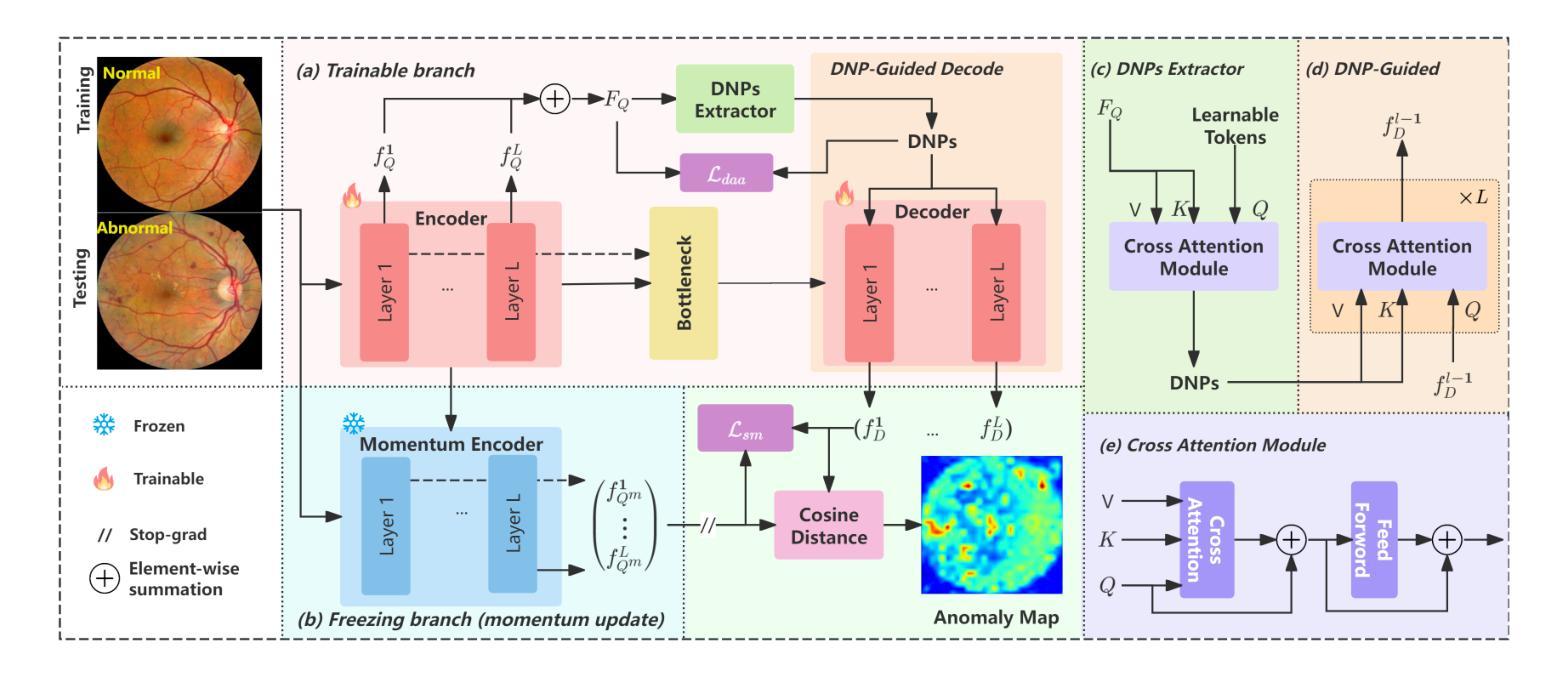
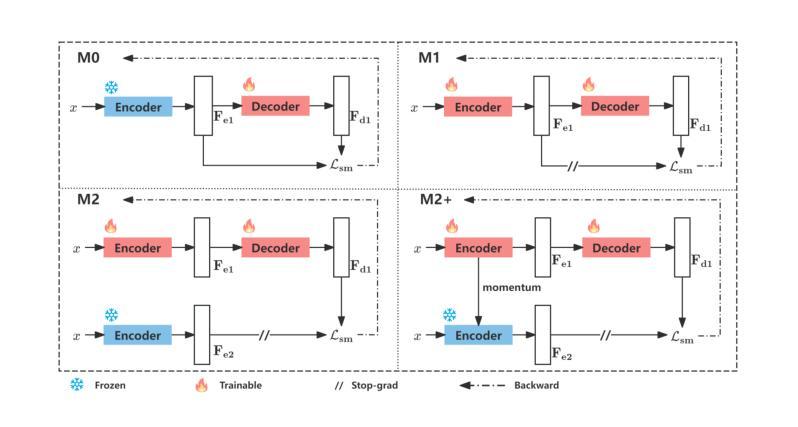
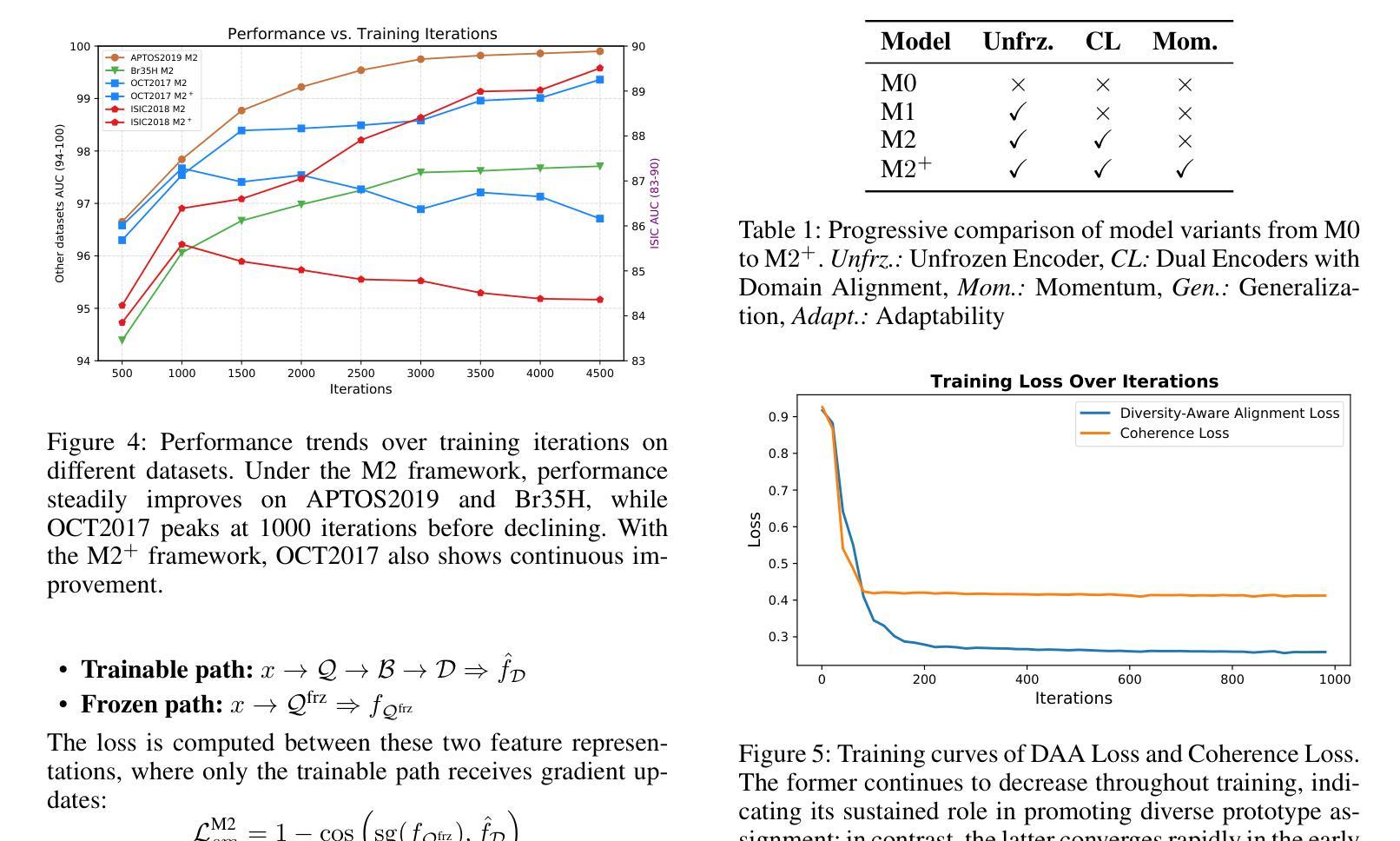
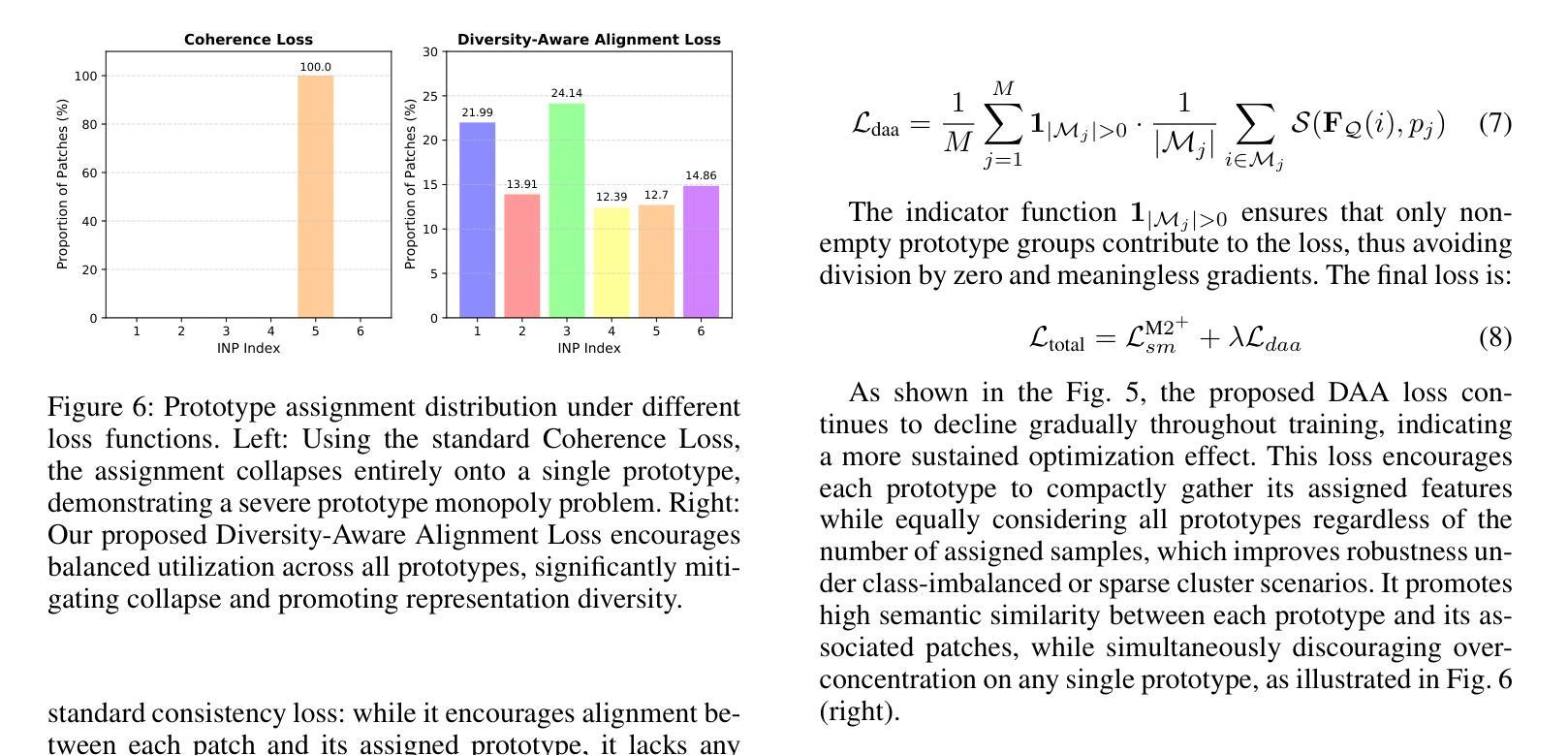
Anomaly detection in medical images is challenging due to limited annotations and a domain gap compared to natural images. Existing reconstruction methods often rely on frozen pre-trained encoders, which limits adaptation to domain-specific features and reduces localization accuracy. Prototype-based learning offers interpretability and clustering benefits but suffers from prototype collapse, where few prototypes dominate training, harming diversity and generalization. To address this, we propose a unified framework combining a trainable encoder with prototype-guided reconstruction and a novel Diversity-Aware Alignment Loss. The trainable encoder, enhanced by a momentum branch, enables stable domain-adaptive feature learning. A lightweight Prototype Extractor mines informative normal prototypes to guide the decoder via attention for precise reconstruction. Our loss enforces balanced prototype use through diversity constraints and per-prototype normalization, effectively preventing collapse. Experiments on multiple medical imaging benchmarks show significant improvements in representation quality and anomaly localization, outperforming prior methods. Visualizations and prototype assignment analyses further validate the effectiveness of our anti-collapse mechanism and enhanced interpretability.
医学图像中的异常检测面临诸多挑战,原因就在于与天然图像相比,医学图像的注解有限且领域差距较大。现有的重建方法通常依赖于固定的预训练编码器,这就限制了其对特定领域的特征适应,并降低了定位精度。基于原型的学习提供了可解释性和聚类优势,但却存在原型坍塌的问题,少数原型会主导训练过程,从而损害多样性和泛化能力。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种结合可训练编码器、原型引导重建和新型多样性感知对齐损失的统一框架。可训练的编码器通过动量分支增强功能,可实现稳定的域自适应特征学习。轻量级原型提取器能够挖掘出信息丰富的正常原型,通过注意力引导解码器进行精确重建。我们的损失通过多样性和每个原型的归一化强制平衡原型的使用,有效地防止了原型的坍塌。在多个医学影像基准测试上的实验表明,我们的方法在表示质量和异常定位方面都有显著提高,优于以前的方法。可视化和原型分配分析进一步验证了我们防坍塌机制和增强可解释性的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文解决了医学图像异常检测中的标注有限和领域差异问题。针对现有重建方法依赖冻结预训练编码器的问题,提出结合可训练编码器、原型引导重建和新型多样性感知对齐损失的统一框架。可训练编码器通过动量分支增强,实现稳定的领域自适应特征学习。轻量级原型提取器挖掘正常原型信息,通过注意力引导解码器进行精确重建。损失函数通过多样性和每个原型的归一化强制平衡原型使用,有效防止原型崩溃。在多个医学图像基准测试上的实验表明,该方法在表示质量和异常定位方面显著提高,优于先前方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像异常检测面临标注有限和领域差异的挑战。
- 现有重建方法依赖冻结的预训练编码器,限制了领域特定特征的适应和定位精度。
- 提出结合可训练编码器、原型引导重建和多样性感知对齐损失的统一框架。
- 可训练编码器通过动量分支增强,实现稳定的领域自适应特征学习。
- 原型提取器挖掘正常原型信息,通过注意力引导精确重建。
- 损失函数设计强制平衡原型使用,有效防止原型崩溃。
点此查看论文截图

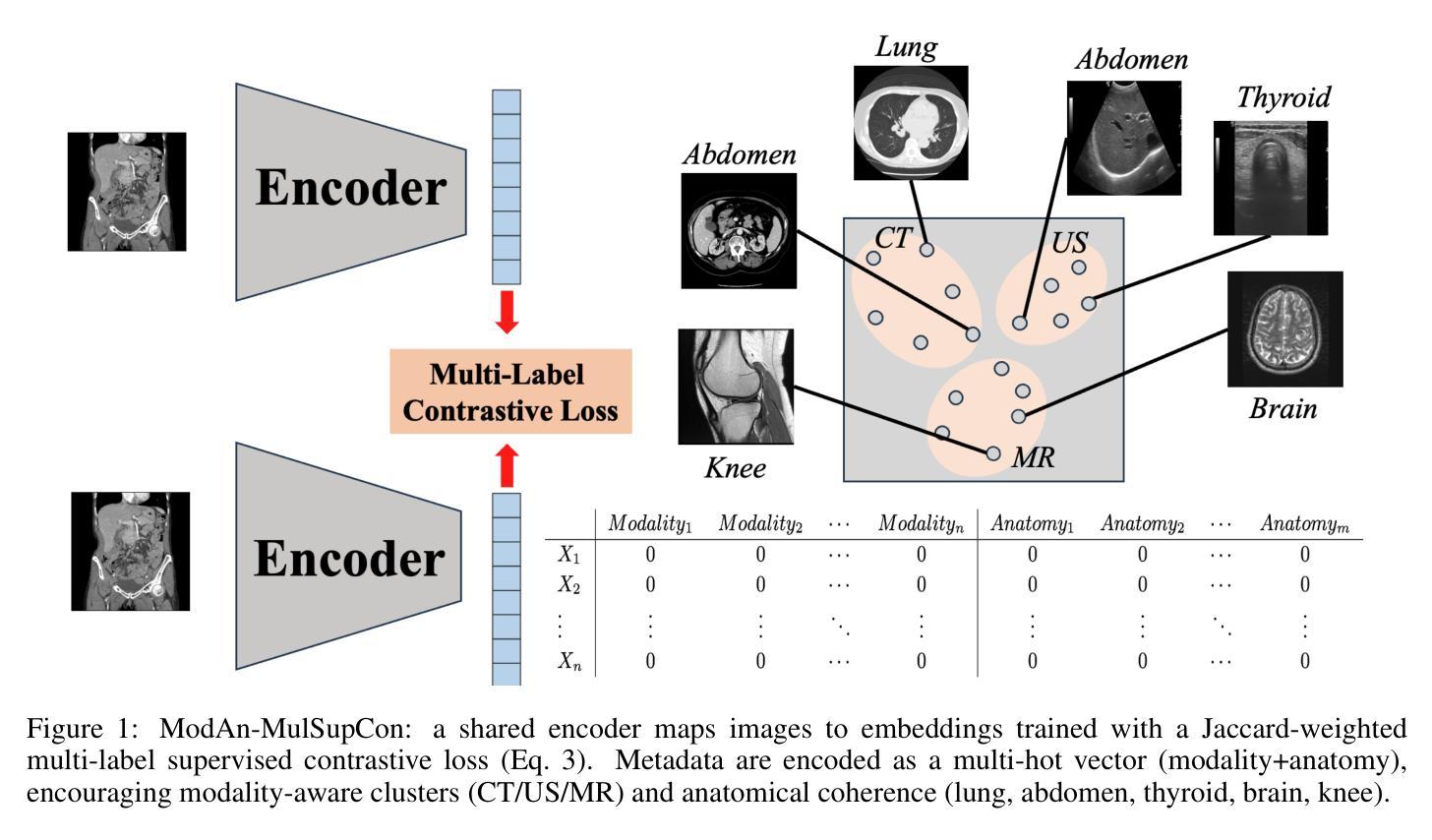
ModAn-MulSupCon: Modality-and Anatomy-Aware Multi-Label Supervised Contrastive Pretraining for Medical Imaging
Authors:Eichi Takaya, Ryusei Inamori
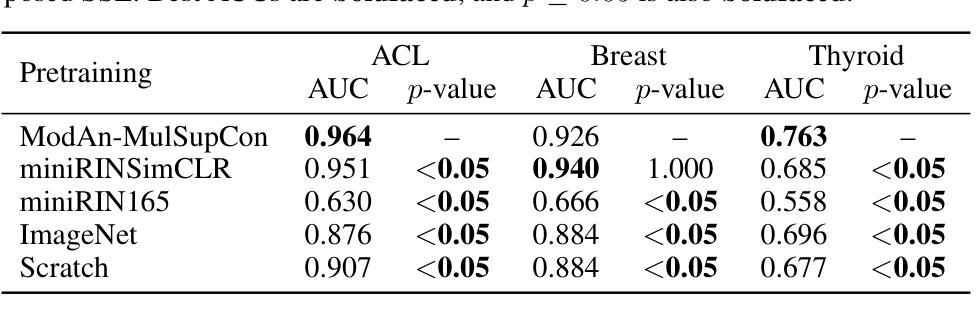
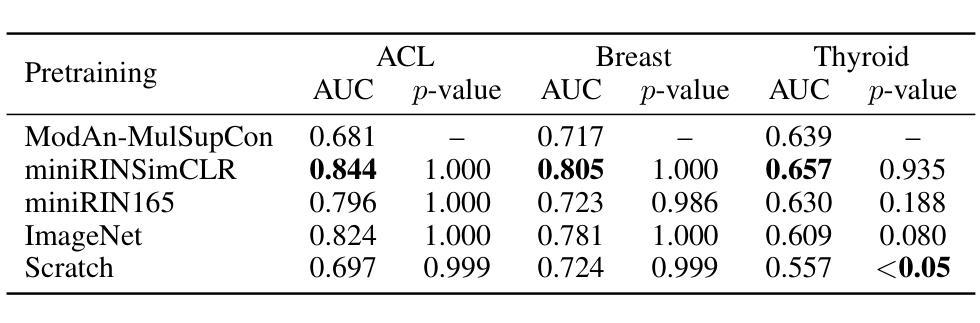
Background and objective: Expert annotations limit large-scale supervised pretraining in medical imaging, while ubiquitous metadata (modality, anatomical region) remain underused. We introduce ModAn-MulSupCon, a modality- and anatomy-aware multi-label supervised contrastive pretraining method that leverages such metadata to learn transferable representations. Method: Each image’s modality and anatomy are encoded as a multi-hot vector. A ResNet-18 encoder is pretrained on a mini subset of RadImageNet (miniRIN, 16,222 images) with a Jaccard-weighted multi-label supervised contrastive loss, and then evaluated by fine-tuning and linear probing on three binary classification tasks–ACL tear (knee MRI), lesion malignancy (breast ultrasound), and nodule malignancy (thyroid ultrasound). Result: With fine-tuning, ModAn-MulSupCon achieved the best AUC on MRNet-ACL (0.964) and Thyroid (0.763), surpassing all baselines ($p<0.05$), and ranked second on Breast (0.926) behind SimCLR (0.940; not significant). With the encoder frozen, SimCLR/ImageNet were superior, indicating that ModAn-MulSupCon representations benefit most from task adaptation rather than linear separability. Conclusion: Encoding readily available modality/anatomy metadata as multi-label targets provides a practical, scalable pretraining signal that improves downstream accuracy when fine-tuning is feasible. ModAn-MulSupCon is a strong initialization for label-scarce clinical settings, whereas SimCLR/ImageNet remain preferable for frozen-encoder deployments.
背景与目标:专家注释限制了医学影像的大规模有监督预训练,而普遍存在的元数据(模态、解剖部位)却被使用不足。我们引入了ModAn-MulSupCon,这是一种模态和解剖结构感知的多标签监督对比预训练方法,它利用此类元数据来学习可迁移的表示。方法:将每张图像的模态和解剖结构编码为多热向量。使用Jaccard加权多标签监督对比损失在RadImageNet的一个小子集(miniRIN,包含16,222张图像)上对ResNet-18编码器进行预训练,然后通过微调线性探测在三项二分类任务(膝关节MRI的ACL撕裂、乳腺超声的病变恶性程度以及甲状腺超声的结节恶性程度)上对其进行评估。结果:通过微调,ModAn-MulSupCon在MRNet-ACL(AUC为0.964)和甲状腺(AUC为0.763)上的表现最佳,超过了所有基线(p<0.05),并在乳腺(AUC为0.926)上排名第二,仅次于SimCLR(AUC为0.940,无显著差异)。当编码器冻结时,SimCLR/ImageNet表现更佳,这表明ModAn-MulSupCon的表示形式更受益于任务适应性而非线性可分性。结论:将易于获得的模态/解剖结构元数据编码为多标签目标提供了一种实用且可扩展的预训练信号,在微调可行的情况下可提高下游准确性。ModAn-MulSupCon是标签稀缺的临床环境中的强大初始化方法,而SimCLR/ImageNet对于冻结编码器部署更为可取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了ModAn-MulSupCon方法,这是一种利用模态和解剖结构信息的有监督对比预训练方法。该方法将图像的模态和解剖结构编码为多热向量,并使用Jaccard加权多标签监督对比损失在RadImageNet的一个小子集上进行预训练。通过微调,该方法在三个二分类任务上取得了最佳AUC值。结论表明,将易于获得的模态/解剖结构信息编码为多标签目标,提供了一种实用且可扩展的预训练信号,在微调可行的情况下,能提高下游任务的准确性。
关键见解
- ModAn-MulSupCon是一种利用模态和解剖结构信息的有监督对比预训练方法。
- 该方法利用多热向量编码图像的模态和解剖结构信息。
- 使用Jaccard加权多标签监督对比损失在RadImageNet的一个小子集上进行预训练。
- 通过微调,ModAn-MulSupCon在三个二分类任务上取得了最佳AUC值。
- ModAn-MulSupCon在标签稀缺的临床环境中是一个强大的初始化方法。
- 在冻结编码器部署时,SimCLR/ImageNet仍然是更理想的选择。
点此查看论文截图

CATformer: Contrastive Adversarial Transformer for Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Qinyi Tian, Spence Cox, Laura E. Dalton
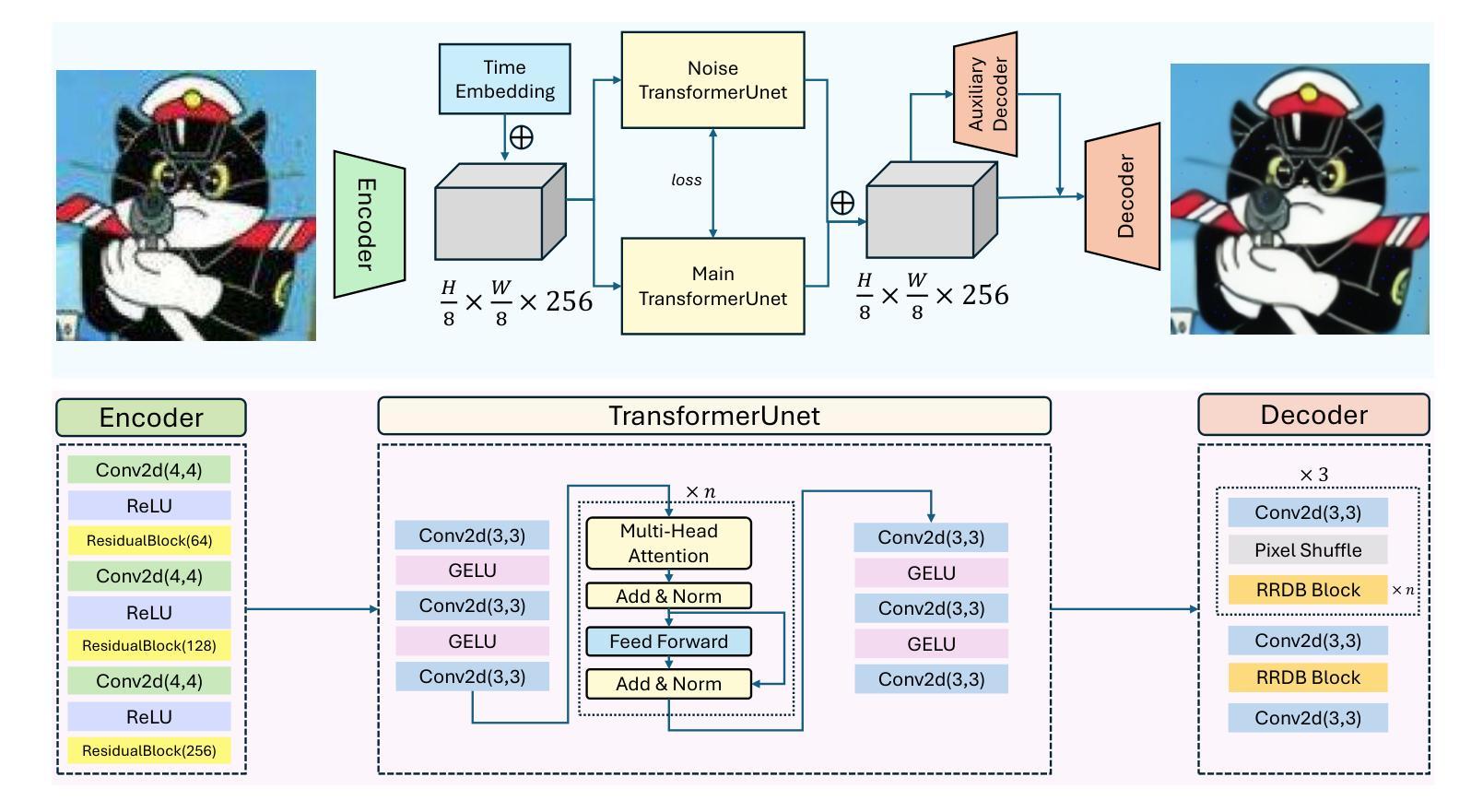
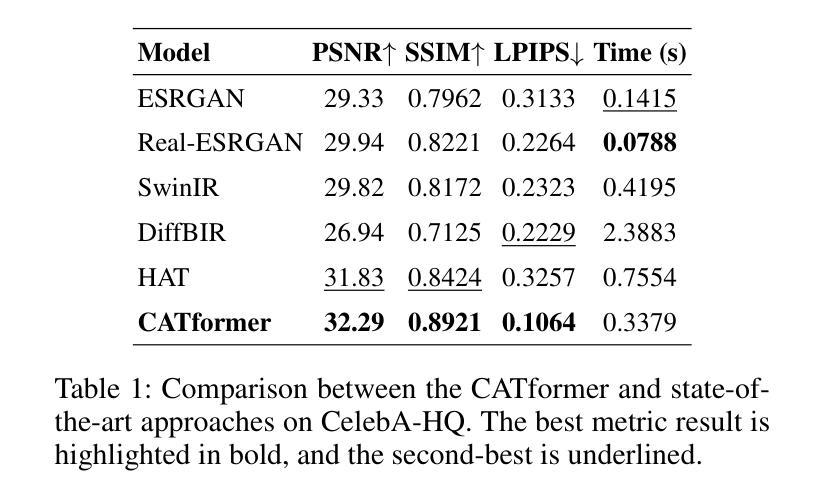
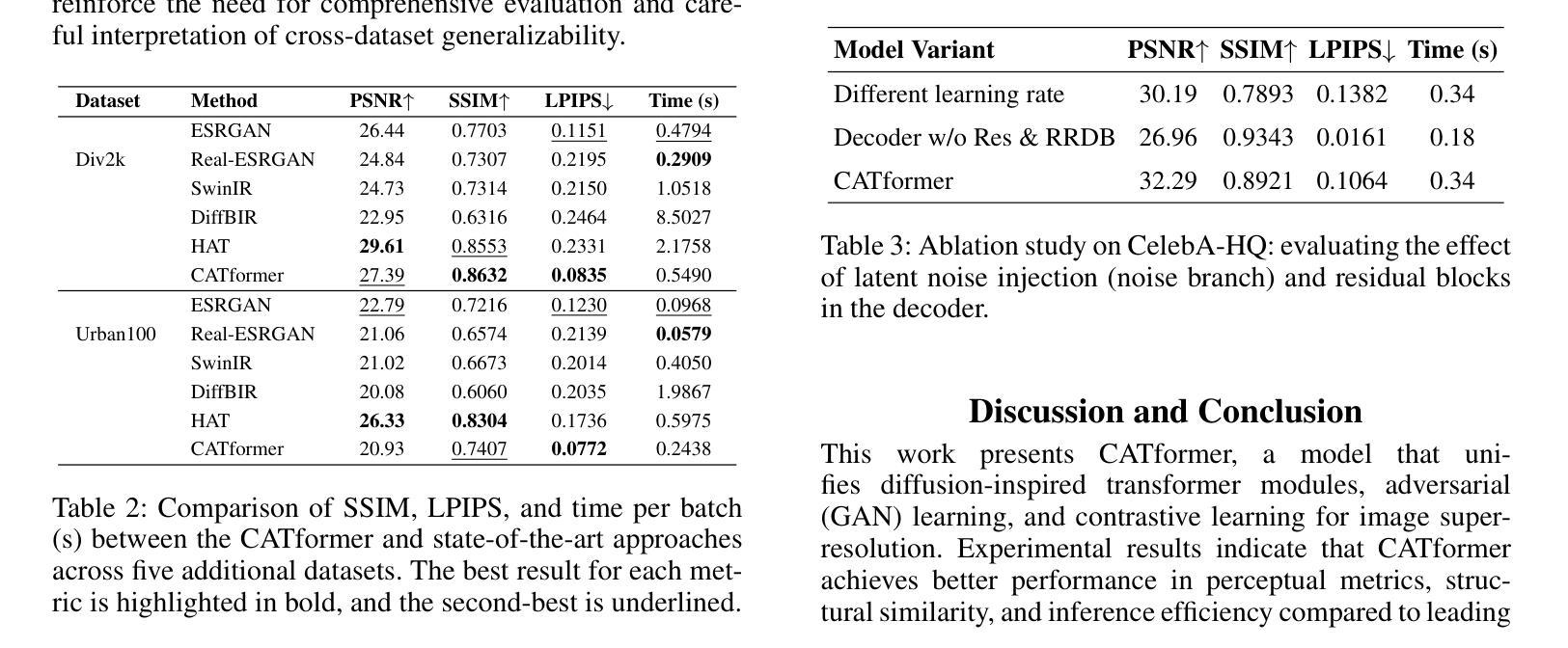
Super-resolution remains a promising technique to enhance the quality of low-resolution images. This study introduces CATformer (Contrastive Adversarial Transformer), a novel neural network integrating diffusion-inspired feature refinement with adversarial and contrastive learning. CATformer employs a dual-branch architecture combining a primary diffusion-inspired transformer, which progressively refines latent representations, with an auxiliary transformer branch designed to enhance robustness to noise through learned latent contrasts. These complementary representations are fused and decoded using deep Residual-in-Residual Dense Blocks for enhanced reconstruction quality. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that CATformer outperforms recent transformer-based and diffusion-inspired methods both in efficiency and visual image quality. This work bridges the performance gap among transformer-, diffusion-, and GAN-based methods, laying a foundation for practical applications of diffusion-inspired transformers in super-resolution.
超分辨率技术依然是一种可以提升低分辨率图像质量的颇具前景的技术。本研究介绍了CATformer(对比对抗性转换器),这是一种新型神经网络,融合了扩散启发特征细化、对抗性学习与对比学习。CATformer采用双分支架构,结合主要扩散启发转换器,逐步优化潜在表示,以及一个辅助转换器分支,通过学习潜在对比增强对噪声的鲁棒性。这些互补表示通过深度残差残差密集块进行融合和解码,以提高重建质量。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,CATformer在效率和视觉图像质量方面超越了最近的基于转换器和扩散的方法。这项工作缩小了基于转换器、扩散和GAN的方法之间的性能差距,为扩散启发转换器的实际应用在超分辨率领域奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CATformer是一种新型神经网络,结合了扩散启发特征优化、对抗学习和对比学习,用于提高低分辨率图像的超分辨率。它采用双分支架构,主分支为扩散启发变压器,用于逐步优化潜在表示,辅助分支为增强噪声鲁棒性的对比辅助变压器。两者融合并使用深度Residual-in-Residual Dense Blocks进行解码,以提高重建质量。在基准数据集上的实验表明,CATformer在效率和视觉图像质量方面优于最新的基于变压器和扩散的方法。
Key Takeaways
- CATformer是一种结合扩散启发特征优化、对抗学习和对比学习的新型神经网络。
- 采用双分支架构,主分支用于优化潜在表示,辅助分支增强噪声鲁棒性。
- 通过结合这两种表示并使用深度Residual-in-Residual Dense Blocks解码,提高图像重建质量。
- CATformer在基准数据集上的实验表现优于其他基于变压器和扩散的方法。
- 该研究缩小了基于变压器、扩散和GAN的方法之间的性能差距。
- CATformer为扩散启发变压器在超分辨率实际应用中的应用奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图


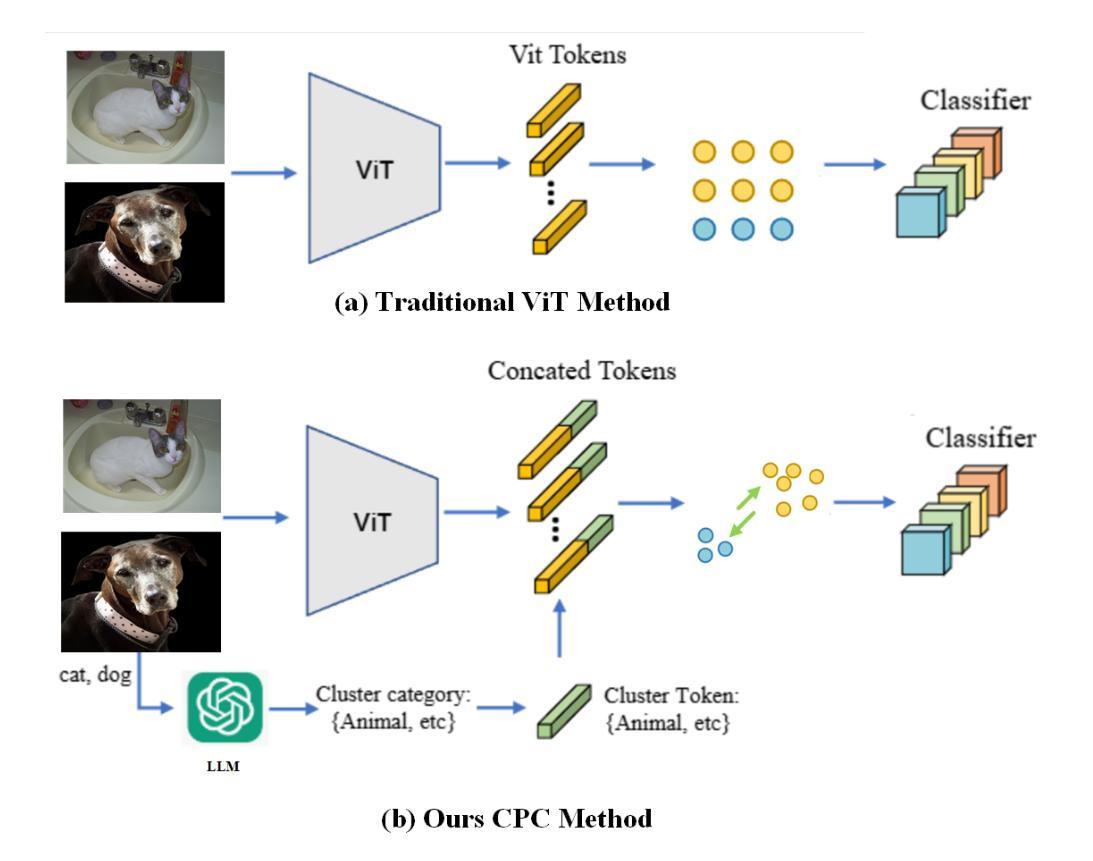
Contrastive Prompt Clustering for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowen Ma, Wenqiao Zhang, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels has gained attention for its cost-effectiveness. Most existing methods emphasize inter-class separation, often neglecting the shared semantics among related categories and lacking fine-grained discrimination. To address this, we propose Contrastive Prompt Clustering (CPC), a novel WSSS framework. CPC exploits Large Language Models (LLMs) to derive category clusters that encode intrinsic inter-class relationships, and further introduces a class-aware patch-level contrastive loss to enforce intra-class consistency and inter-class separation. This hierarchical design leverages clusters as coarse-grained semantic priors while preserving fine-grained boundaries, thereby reducing confusion among visually similar categories. Experiments on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 demonstrate that CPC surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in WSSS.
利用图像级标签进行弱监督语义分割(WSSS)因其成本效益而受到关注。大多数现有方法强调类间分离,往往忽略了相关类别之间的共享语义,且缺乏精细的粒度鉴别。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了对比提示聚类(CPC),这是一种新型的WSSS框架。CPC利用大型语言模型(LLM)来推导编码内在类间关系的类别聚类,并进一步引入了一种类感知的补丁级对比损失,以加强类内一致性和类间分离。这种层次化的设计利用聚类作为粗粒度的语义先验,同时保留精细的边界,从而减少视觉上相似类别之间的混淆。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014上的实验表明,CPC在WSSS中超越了现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的新框架——对比提示聚类(CPC)。CPC利用大型语言模型(LLM)推导类别聚类,编码类别间的内在关系,并引入类感知补丁级对比损失,以加强类内一致性和类间分离。这种层次设计利用聚类作为粗粒度语义先验,同时保留精细边界,减少视觉相似类别之间的混淆。实验表明,CPC在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的表现超越了现有的WSSS先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)因成本效益而受到关注。
- 现有WSSS方法往往忽视相关类别之间的共享语义,缺乏精细粒度鉴别。
- 提出了一种新的WSSS框架——对比提示聚类(CPC)。
- CPC利用大型语言模型(LLM)推导类别聚类,编码类别间的内在关系。
- CPC引入类感知补丁级对比损失,以加强类内一致性和类间分离。
- 层次设计利用聚类作为粗粒度语义先验,同时保留精细边界。
点此查看论文截图

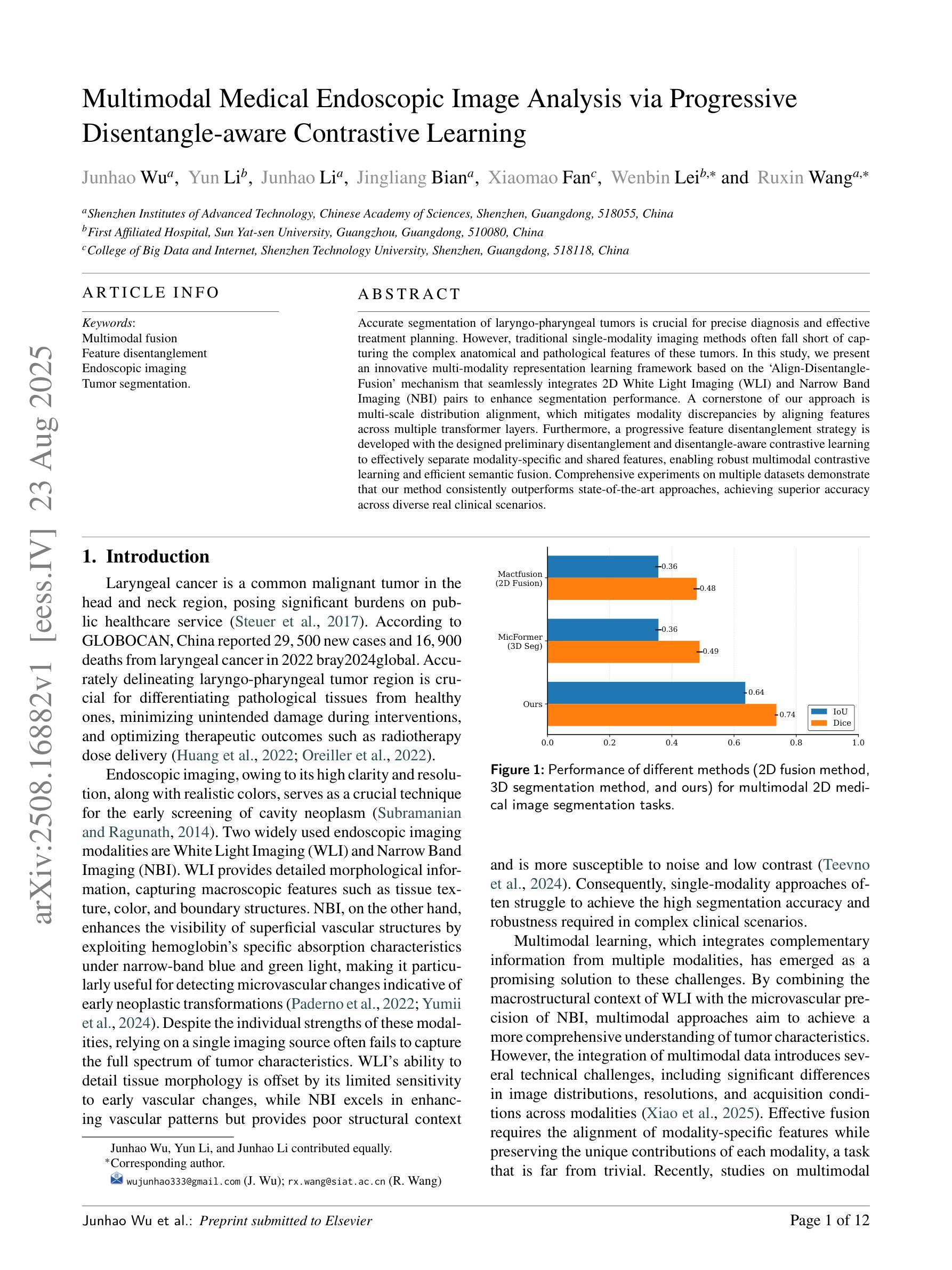
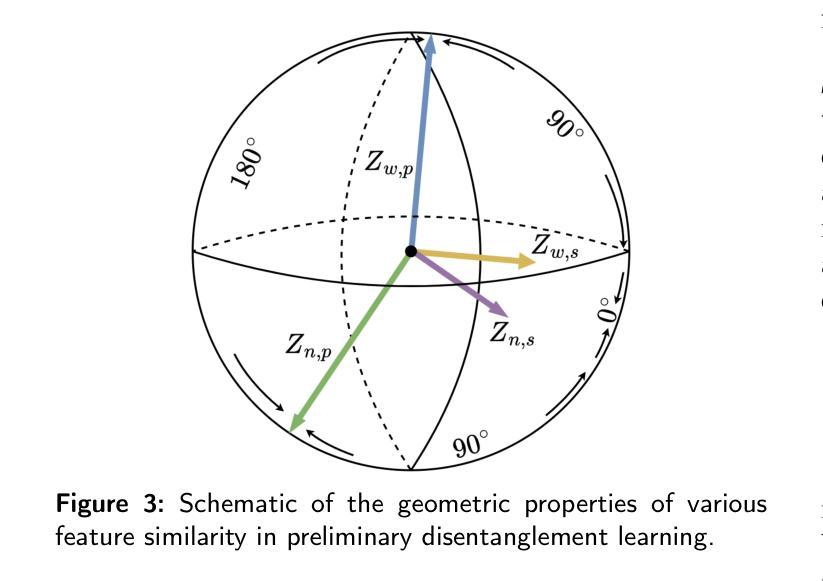
Multimodal Medical Endoscopic Image Analysis via Progressive Disentangle-aware Contrastive Learning
Authors:Junhao Wu, Yun Li, Junhao Li, Jingliang Bian, Xiaomao Fan, Wenbin Lei, Ruxin Wang
Accurate segmentation of laryngo-pharyngeal tumors is crucial for precise diagnosis and effective treatment planning. However, traditional single-modality imaging methods often fall short of capturing the complex anatomical and pathological features of these tumors. In this study, we present an innovative multi-modality representation learning framework based on the `Align-Disentangle-Fusion’ mechanism that seamlessly integrates 2D White Light Imaging (WLI) and Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) pairs to enhance segmentation performance. A cornerstone of our approach is multi-scale distribution alignment, which mitigates modality discrepancies by aligning features across multiple transformer layers. Furthermore, a progressive feature disentanglement strategy is developed with the designed preliminary disentanglement and disentangle-aware contrastive learning to effectively separate modality-specific and shared features, enabling robust multimodal contrastive learning and efficient semantic fusion. Comprehensive experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving superior accuracy across diverse real clinical scenarios.
喉咽肿瘤准确分割对于精确诊断和治疗计划至关重要。然而,传统的单一成像方法往往难以捕捉这些肿瘤的复杂解剖和病理特征。在本研究中,我们提出了一种基于“对齐-分离-融合”机制的创新多模态表示学习框架,无缝集成了2D白光成像(WLI)和窄带成像(NBI)配对,以提高分割性能。我们的方法的核心是多尺度分布对齐,它通过对齐多个transformer层中的特征来减轻模态差异。此外,还开发了一种渐进的特征分离策略,通过设计初步分离和解纠缠感知对比学习,有效地分离了模态特定特征和共享特征,实现了稳健的多模态对比学习和高效的语义融合。在多个数据集上的综合实验表明,我们的方法一直优于最先进的方法,并在多种实际临床场景中实现了更高的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages,6 figures, 6 tables
摘要
本文提出了一种基于“对齐-分离-融合”机制的多模态表示学习框架,该框架无缝集成了2D白光成像(WLI)和窄带成像(NBI)配对,以提高喉咽肿瘤分割的性能。该方法的核心是多尺度分布对齐,通过对齐多层transformer的特征来减少模态差异。同时,开发了一种渐进式特征分离策略,通过初步分离和分离感知对比学习,有效地分离了模态特定和共享特征,实现了稳健的多模态对比学习和高效的语义融合。在多个数据集上的综合实验表明,该方法一致优于最新技术,在多种真实临床场景下具有卓越准确性。
关键见解
- 提出了一种基于多模态表示学习的框架,集成了2D白光成像和窄带成像,以提高喉咽肿瘤分割性能。
- 多尺度分布对齐是该方法的核心,通过对齐多层transformer的特征来减少模态差异。
- 采用了渐进式特征分离策略,通过初步分离和分离感知对比学习有效分离模态特定和共享特征。
- 该方法实现了稳健的多模态对比学习和高效的语义融合。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,该方法在多种真实临床场景下具有卓越性能。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法具有更好的准确性。
点此查看论文截图
Predicting brain tumour enhancement from non-contrast MR imaging with artificial intelligence
Authors:James K Ruffle, Samia Mohinta, Guilherme Pombo, Asthik Biswas, Alan Campbell, Indran Davagnanam, David Doig, Ahmed Hamman, Harpreet Hyare, Farrah Jabeen, Emma Lim, Dermot Mallon, Stephanie Owen, Sophie Wilkinson, Sebastian Brandner, Parashkev Nachev
Brain tumour imaging assessment typically requires both pre- and post-contrast MRI, but gadolinium administration is not always desirable, such as in frequent follow-up, renal impairment, allergy, or paediatric patients. We aimed to develop and validate a deep learning model capable of predicting brain tumour contrast enhancement from non-contrast MRI sequences alone. We assembled 11089 brain MRI studies from 10 international datasets spanning adult and paediatric populations with various neuro-oncological states, including glioma, meningioma, metastases, and post-resection appearances. Deep learning models (nnU-Net, SegResNet, SwinUNETR) were trained to predict and segment enhancing tumour using only non-contrast T1-, T2-, and T2/FLAIR-weighted images. Performance was evaluated on 1109 held-out test patients using patient-level detection metrics and voxel-level segmentation accuracy. Model predictions were compared against 11 expert radiologists who each reviewed 100 randomly selected patients. The best-performing nnU-Net achieved 83% balanced accuracy, 91.5% sensitivity, and 74.4% specificity in detecting enhancing tumour. Enhancement volume predictions strongly correlated with ground truth (R2 0.859). The model outperformed expert radiologists, who achieved 69.8% accuracy, 75.9% sensitivity, and 64.7% specificity. 76.8% of test patients had Dice over 0.3 (acceptable detection), 67.5% had Dice over 0.5 (good detection), and 50.2% had Dice over 0.7 (excellent detection). Deep learning can identify contrast-enhancing brain tumours from non-contrast MRI with clinically relevant performance. These models show promise as screening tools and may reduce gadolinium dependence in neuro-oncology imaging. Future work should evaluate clinical utility alongside radiology experts.
脑肿瘤成像评估通常需要对比剂前后的MRI,但在频繁随访、肾功能受损、过敏或儿科患者中,钆的给药并不总是理想的。我们的目标是开发和验证一个深度学习模型,该模型能够仅从非对比MRI序列中预测脑肿瘤的对比增强效果。我们汇集了来自成人和儿科等不同神经肿瘤状态的国际数据集,包括胶质瘤、脑膜瘤、转移瘤和术后表现,共涉及10个数据集的11089个脑MRI研究。深度学习模型(nnU-Net、SegResNet、SwinUNETR)经过训练,仅使用非对比T1、T2和T2 / FLAIR加权图像来预测和分割增强肿瘤。在1109名独立测试患者上的性能评估采用了患者级别的检测指标和体素级别的分割准确性。模型预测与11位专家放射科医生进行了比较,每位放射科医生均审查了随机选择的100名患者。表现最佳的nnU-Net在检测增强肿瘤方面的平衡准确度为83%,敏感度为91.5%,特异度为74.4%。增强体积预测与真实值高度相关(R² 0.859)。该模型的性能优于专家放射科医生,后者的准确度为69.8%,敏感度为75.9%,特异度为64.7%。76.8%的测试患者的Dice系数大于0.3(可接受检测),67.5%的Dice系数大于0.5(良好检测),50.2%的Dice系数大于0.7(优良检测)。深度学习可以从非对比MRI中识别出对比增强的脑肿瘤,并具有临床意义。这些模型作为筛查工具显示出一定的前景,并可能减少神经肿瘤学成像中对钆的依赖。未来的工作应与放射学专家一起评估其临床实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38 pages
Summary
基于非对比MRI序列预测脑肿瘤对比增强的深度学习模型研究。该研究利用多种深度学习模型(如nnU-Net、SegResNet和SwinUNETR)训练模型,仅使用非对比T1、T2和T2/FLAIR加权图像来预测和分割增强肿瘤。模型性能通过患者级别的检测指标和体素级别的分割精度进行评估,并与专家放射科医生的评估结果进行比较。结果显示,深度学习模型在检测增强肿瘤方面表现出良好的性能,并有望作为筛查工具减少神经肿瘤学中钆的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- 研究旨在开发并验证一种能够从非对比MRI序列预测脑肿瘤对比增强的深度学习模型。
- 使用了多种深度学习模型进行训练和预测,数据来源涵盖成人和儿童的不同神经肿瘤状态患者。
- 模型性能通过严格的患者级别和体素级别评估指标进行评估。
- 最佳模型nnU-Net在检测增强肿瘤方面表现出良好性能,与专家放射科医生相比具有优势。
- 模型预测结果与真实结果高度相关,增强体积预测与真实值的相关性达到R² 0.859。
- 该模型有望作为筛查工具,减少神经肿瘤学中对钆的依赖。
点此查看论文截图

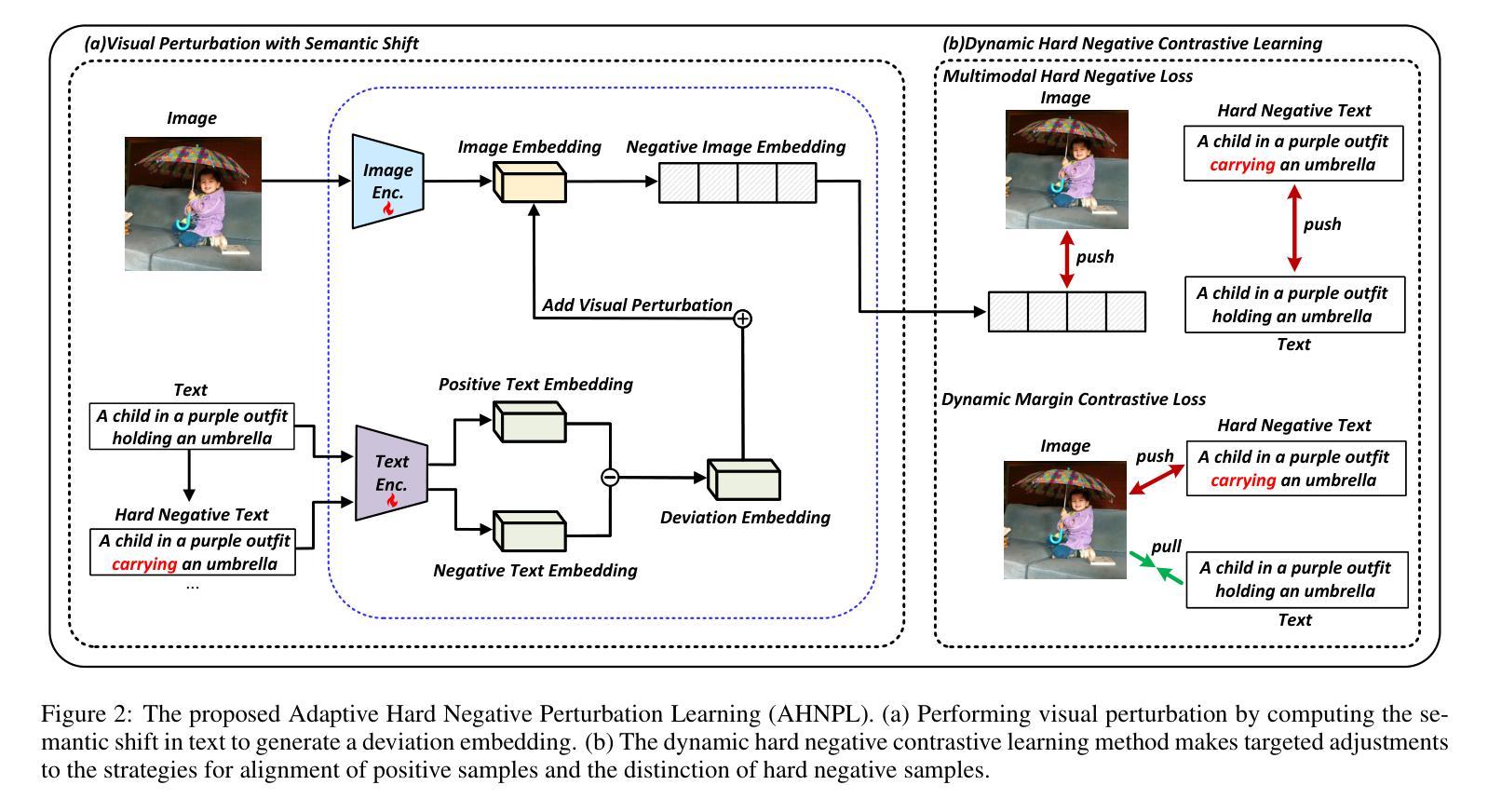
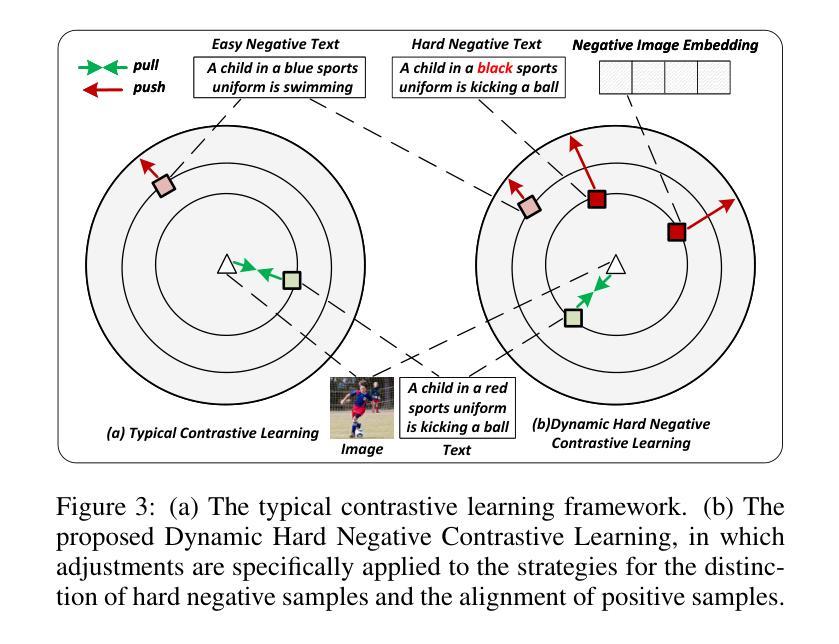
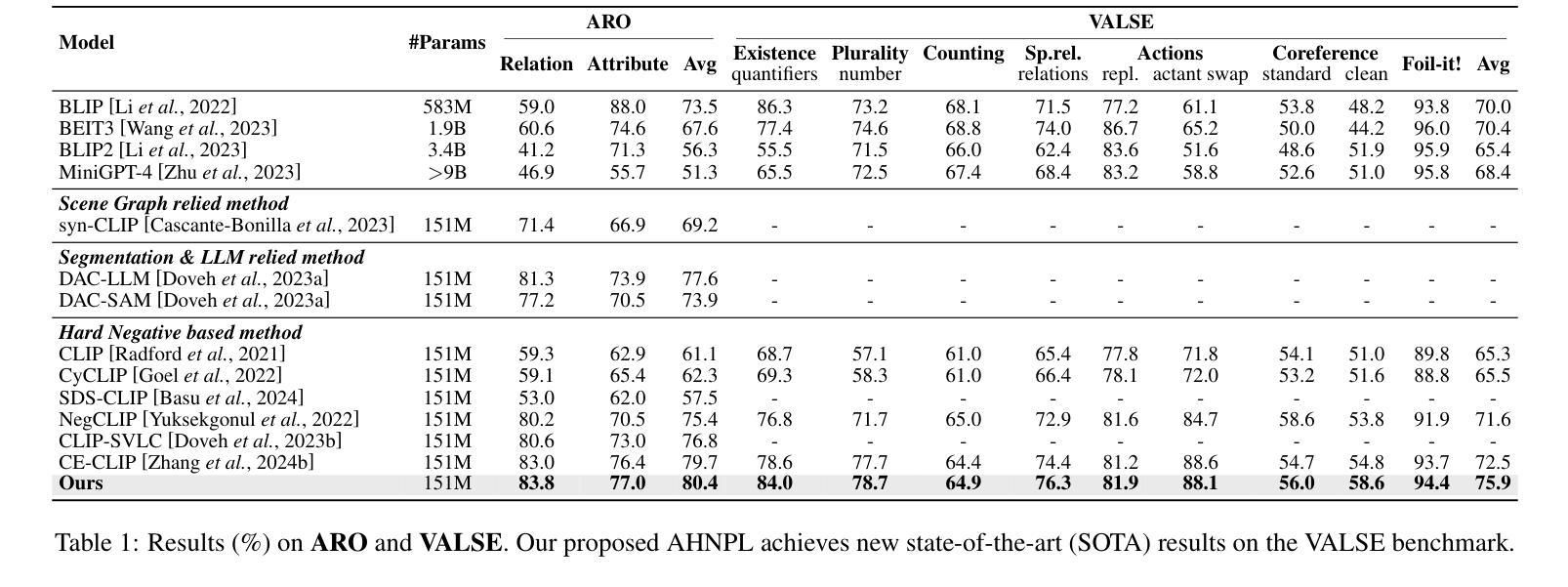
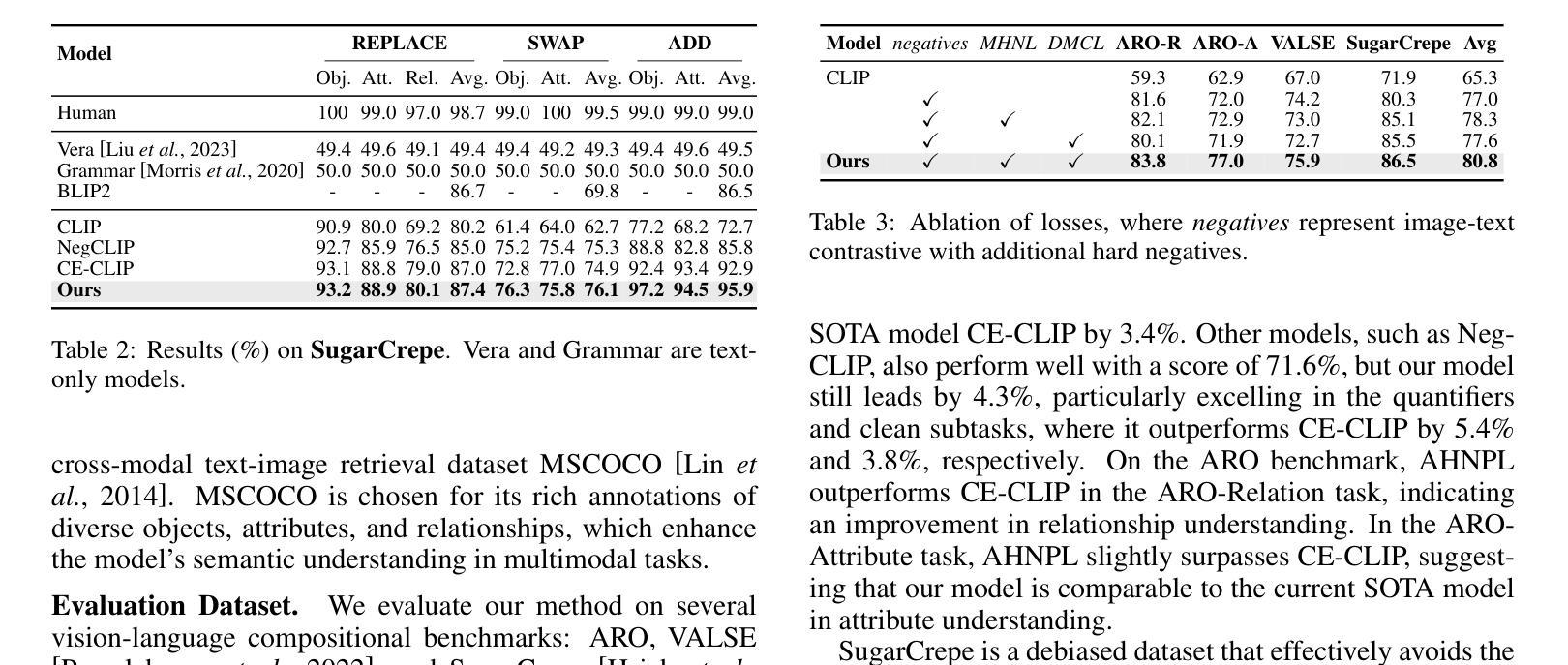
Visual Perturbation and Adaptive Hard Negative Contrastive Learning for Compositional Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Xin Huang, Ruibin Li, Tong Jia, Wei Zheng, Ya Wang
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are essential for multimodal tasks, especially compositional reasoning (CR) tasks, which require distinguishing fine-grained semantic differences between visual and textual embeddings. However, existing methods primarily fine-tune the model by generating text-based hard negative samples, neglecting the importance of image-based negative samples, which results in insufficient training of the visual encoder and ultimately impacts the overall performance of the model. Moreover, negative samples are typically treated uniformly, without considering their difficulty levels, and the alignment of positive samples is insufficient, which leads to challenges in aligning difficult sample pairs. To address these issues, we propose Adaptive Hard Negative Perturbation Learning (AHNPL). AHNPL translates text-based hard negatives into the visual domain to generate semantically disturbed image-based negatives for training the model, thereby enhancing its overall performance. AHNPL also introduces a contrastive learning approach using a multimodal hard negative loss to improve the model’s discrimination of hard negatives within each modality and a dynamic margin loss that adjusts the contrastive margin according to sample difficulty to enhance the distinction of challenging sample pairs. Experiments on three public datasets demonstrate that our method effectively boosts VLMs’ performance on complex CR tasks. The source code is available at https://github.com/nynu-BDAI/AHNPL.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)对于多模态任务至关重要,特别是需要区分视觉和文本嵌入之间细微语义差异的组合推理(CR)任务。然而,现有方法主要通过生成基于文本的硬负样本来微调模型,忽略了基于图像的负样本的重要性,这导致视觉编码器的训练不足,并最终影响模型的总体性能。此外,负样本通常被一视同仁,没有考虑其难度水平,正样本的对齐也不足,这导致难以对齐样本对。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了自适应硬负扰动学习(AHNPL)。AHNPL将基于文本的硬负样本转换为视觉领域,以生成用于训练模型的在语义上受干扰的基于图像的负样本,从而提高模型的总体性能。AHNPL还介绍了一种对比学习方法,使用多模态硬负损失来提高模型在每个模态内对硬负样本的辨别能力,以及一种动态边距损失,根据样本难度调整对比边距,以提高具有挑战性的样本对的区分度。在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法有效地提高了VLM在复杂的CR任务上的性能。源代码可在https://github.com/nynu-BDAI/AHNPL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2025)
Summary
本文主要探讨视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态任务中的关键挑战,特别是在处理需要区分视觉和文本嵌入细微语义差异的组成推理(CR)任务时。针对现有方法主要依赖文本生成硬负样本进行微调的问题,本文提出了一种自适应硬负扰动学习(AHNPL)的方法。该方法将文本生成的硬负样本转化为图像领域的负样本,以提高模型的性能。同时,AHNPL还引入了对比学习方法和动态边界损失来优化模型对困难样本的区分能力。实验证明,该方法能有效提升VLMs在复杂CR任务上的性能。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在处理多模态任务时面临区分视觉和文本嵌入细微语义差异的挑战。
- 现有方法主要依赖文本生成的硬负样本进行模型微调,忽略了图像负样本的重要性。
- AHNPL方法将文本生成的硬负样本转化为图像领域的负样本,以提高模型的训练效果。
- AHNPL引入了对比学习方法和多模态硬负损失来优化模型性能。
- 动态边界损失能根据样本难度调整对比边界,提高困难样本的区分能力。
- 实验证明,AHNPL方法在复杂组成推理任务上能有效提升VLMs的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Accurate and lightweight dehazing via multi-receptive-field non-local network and novel contrastive regularization
Authors:Zewei He, Zixuan Chen, Jinlei Li, Ziqian Lu, Xuecheng Sun, Hao Luo, Zhe-Ming Lu, Evangelos K. Markakis
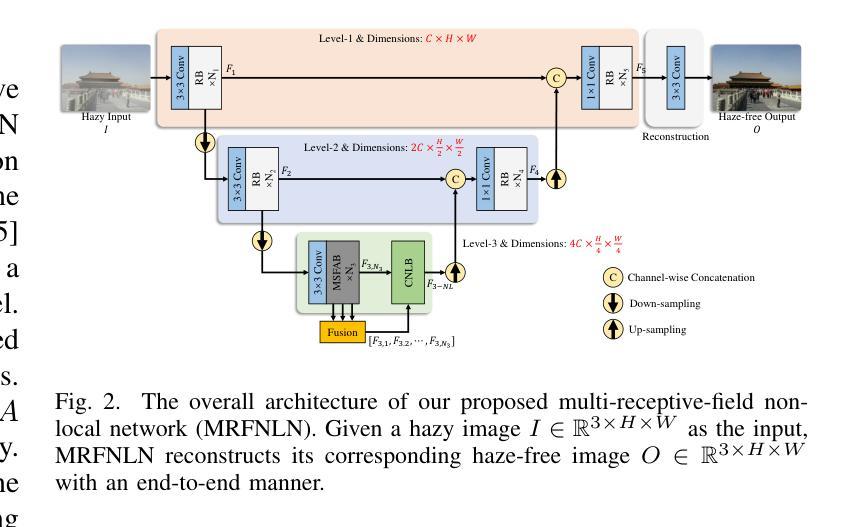
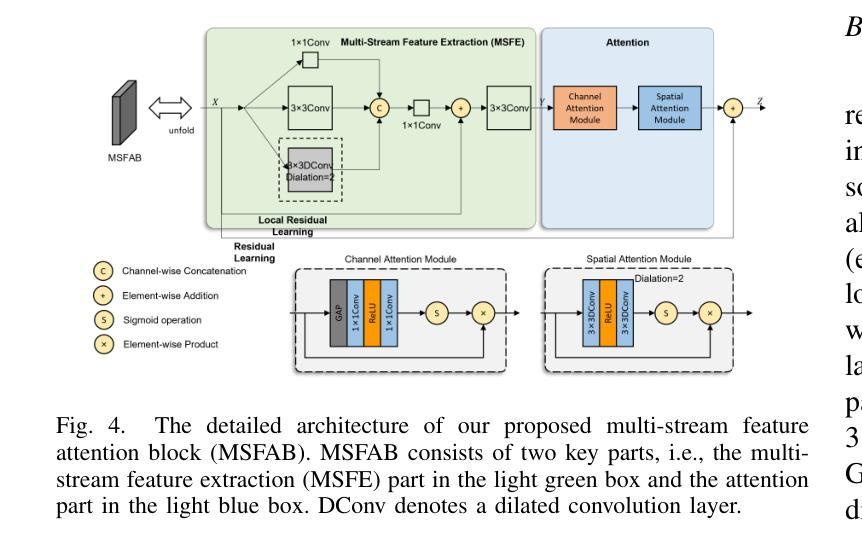
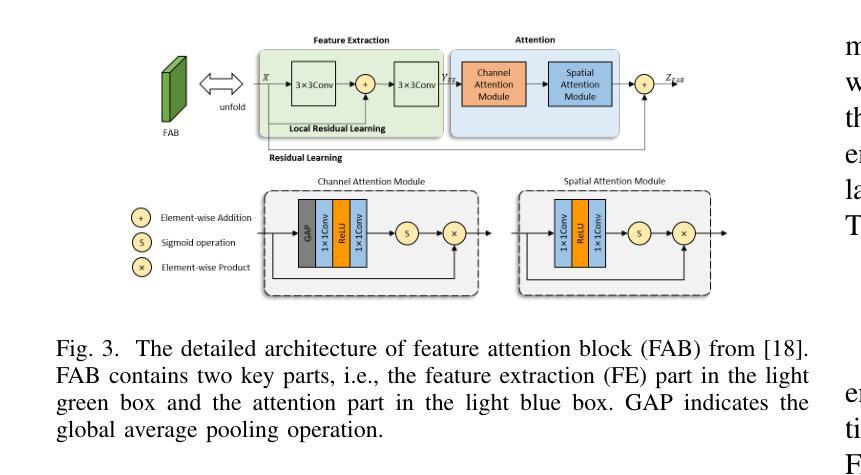
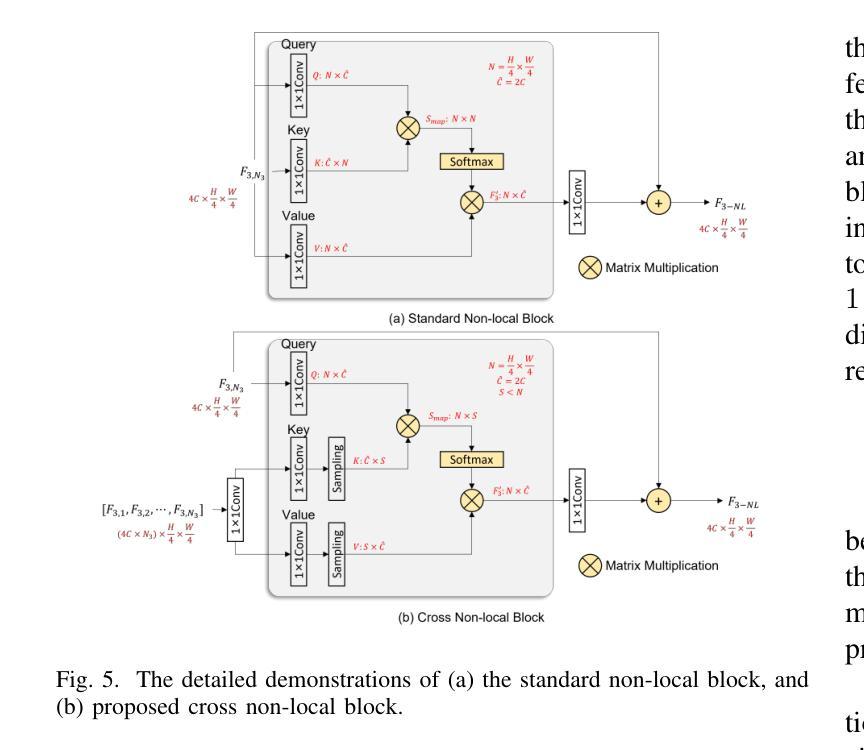
Recently, deep learning-based methods have dominated image dehazing domain. A multi-receptive-field non-local network (MRFNLN) consisting of the multi-stream feature attention block (MSFAB) and the cross non-local block (CNLB) is presented in this paper to further enhance the performance. We start with extracting richer features for dehazing. Specifically, a multi-stream feature extraction (MSFE) sub-block, which contains three parallel convolutions with different receptive fields (i.e., $1\times 1$, $3\times 3$, $5\times 5$), is designed for extracting multi-scale features. Following MSFE, an attention sub-block is employed to make the model adaptively focus on important channels/regions. These two sub-blocks constitute our MSFAB. Then, we design a cross non-local block (CNLB), which can capture long-range dependencies beyond the query. Instead of the same input source of query branch, the key and value branches are enhanced by fusing more preceding features. CNLB is computation-friendly by leveraging a spatial pyramid down-sampling (SPDS) strategy to reduce the computation and memory consumption without sacrificing the performance. Last but not least, a novel detail-focused contrastive regularization (DFCR) is presented by emphasizing the low-level details and ignoring the high-level semantic information in a representation space specially designed for dehazing. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MRFNLN model outperforms recent state-of-the-art dehazing methods with less than 1.5 Million parameters.
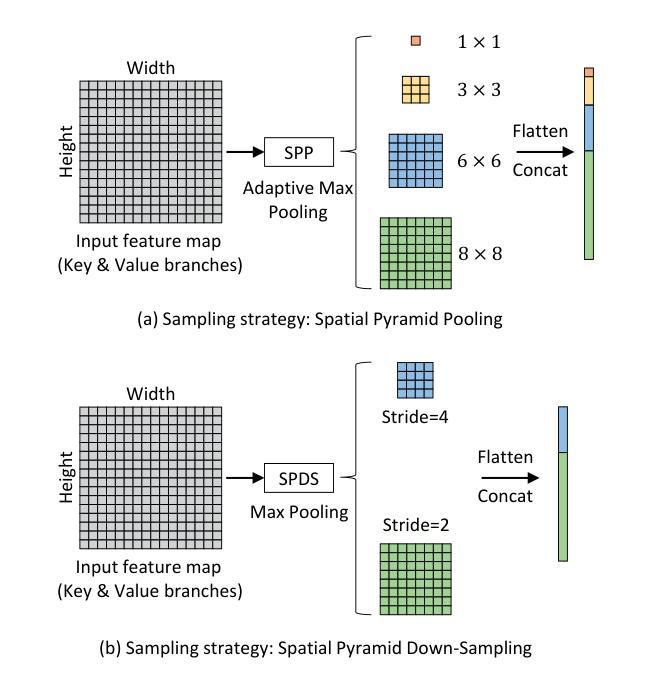
最近,基于深度学习的方法在图像去雾领域占据了主导地位。本文提出了一种由多流特征注意力块(MSFAB)和交叉非局部块(CNLB)组成的多感受野非局部网络(MRFNLN),以进一步提高性能。我们从提取更丰富用于去雾的特征开始。具体来说,设计了一个多流特征提取(MSFE)子块,其中包含三个具有不同感受野(即1×1、3×3、5×5)的并行卷积,用于提取多尺度特征。在MSFE之后,采用注意力子块使模型能够自适应地关注重要的通道/区域。这两个子块构成了我们的MSFAB。然后,我们设计了一个交叉非局部块(CNLB),它能够捕获查询之外的长距离依赖关系。与查询分支的相同输入源不同,关键值和分支通过融合更多的先前特征进行增强。CNLB通过利用空间金字塔下采样(SPDS)策略在计算和内存消耗方面更加友好,同时不会牺牲性能。最后但并非最不重要的是,提出了一种新的细节聚焦对比正则化(DFCR),它通过强调去雾表示空间中的低级细节并忽略高级语义信息来实现。综合实验结果表明,所提出MRFNLN模型在参数少于150万的情况下,性能优于最新的先进去雾方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to the IEEE Journal for possible publication
Summary
本论文提出了一种基于深度学习的图像去雾方法,采用多感受野非局部网络(MRFNLN),包含多流特征注意力块(MSFAB)和交叉非局部块(CNLB)。通过设计多流特征提取子块以提取更丰富的去雾特征,并引入注意力子块使模型自适应关注重要通道/区域。同时,设计了一种新型的细节聚焦对比正则化(DFCR),在专门设计的去雾表示空间中强调低层次细节而忽略高层次语义信息。实验结果表明,所提出的MRFNLN模型在参数少于150万的情况下,优于最新的去雾方法。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种多感受野非局部网络(MRFNLN)用于图像去雾,结合了多流特征注意力块(MSFAB)和交叉非局部块(CNLB)。
- 多流特征提取子块(MSFE)包含不同感受野的并行卷积,以提取多尺度特征。
- 注意力子块使模型能够自适应关注重要的通道/区域。
- 交叉非局部块(CNLB)能够捕捉超出查询的长程依赖性,并通过融合更多先前特征来增强关键和值分支。
- 采用空间金字塔下采样(SPDS)策略,降低计算量和内存消耗,不影响性能。
- 引入了一种新型细节聚焦对比正则化(DFCR),在去雾的专门表示空间中强调低层次细节。
点此查看论文截图