⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
Differential Morphological Profile Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:David Huangal, J. Alex Hurt
Semantic segmentation of overhead remote sensing imagery enables applications in mapping, urban planning, and disaster response. State-of-the-art segmentation networks are typically developed and tuned on ground-perspective photographs and do not directly address remote sensing challenges such as extreme scale variation, foreground-background imbalance, and large image sizes. We explore the incorporation of the differential morphological profile (DMP), a multi-scale shape extraction method based on grayscale morphology, into modern segmentation networks. Prior studies have shown that the DMP can provide critical shape information to Deep Neural Networks to enable superior detection and classification performance in overhead imagery. In this work, we extend prior DMPNet work beyond classification and object detection by integrating DMP features into three state-of-the-art convolutional and transformer semantic segmentation architectures. We utilize both direct input, which adapts the input stem of feature extraction architectures to accept DMP channels, and hybrid architectures, a dual-stream design that fuses RGB and DMP encoders. Using the iSAID benchmark dataset, we evaluate a variety of DMP differentials and structuring element shapes to more effectively provide shape information to the model. Our results show that while non-DMP models generally outperform the direct-input variants, hybrid DMP consistently outperforms direct-input and is capable of surpassing a non-DMP model on mIoU, F1, and Recall.
高空遥感影像的语义分割在地图绘制、城市规划和灾害应对等方面都有广泛应用。最先进的分割网络通常是在地面照片上开发和调整的,并没有直接解决遥感面临的挑战,如极端尺度变化、前景背景不平衡和图像尺寸大等。我们探索将差分形态剖面(DMP)这一基于灰度形态学的多尺度形状提取方法融入现代分割网络。先前的研究表明,DMP可以为深度神经网络提供关键形状信息,从而在高空图像中实现卓越的检测和分类性能。在这项工作中,我们通过将DMP特征集成到三种最先进的卷积和transformer语义分割架构中,将先前的DMPNet工作从分类和对象检测扩展。我们采用直接输入的方式,即调整特征提取架构的输入干以接受DMP通道,以及混合架构(一种双流设计,融合了RGB和DMP编码器)。我们使用iSAID基准数据集评估了各种DMP差异和结构元素形状,以更有效地为模型提供形状信息。我们的结果表明,虽然非DMP模型通常表现优于直接输入变体,但混合DMP始终优于直接输入,并在mIoU、F1和召回率方面能够超越非DMP模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文探讨了将差分形态学轮廓(DMP)融入现代分割网络,以应对遥感影像语义分割的挑战。通过在iSAID基准数据集上评估,发现混合DMP架构在性能上超越了直接输入和非DMP模型。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在遥感影像中的应用广泛,包括地图绘制、城市规划和灾害响应等领域。
- 当前先进的分割网络主要在地面照片上开发和调整,未能直接应对遥感影像中的极端尺度变化、前景与背景不平衡及大图像尺寸等问题。
- DMP作为一种多尺度形状提取方法,能基于灰度形态学提供关键形状信息。
- 本文将DMP特征融入三种先进的卷积和transformer语义分割架构中。
- 采用直接输入和混合架构两种方法整合DMP特征,其中混合架构采用双流设计,融合RGB和DMP编码器。
- 在iSAID基准数据集上的实验结果显示,非DMP模型通常优于直接输入变体,而混合DMP在mIoU、F1和Recall等方面表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图

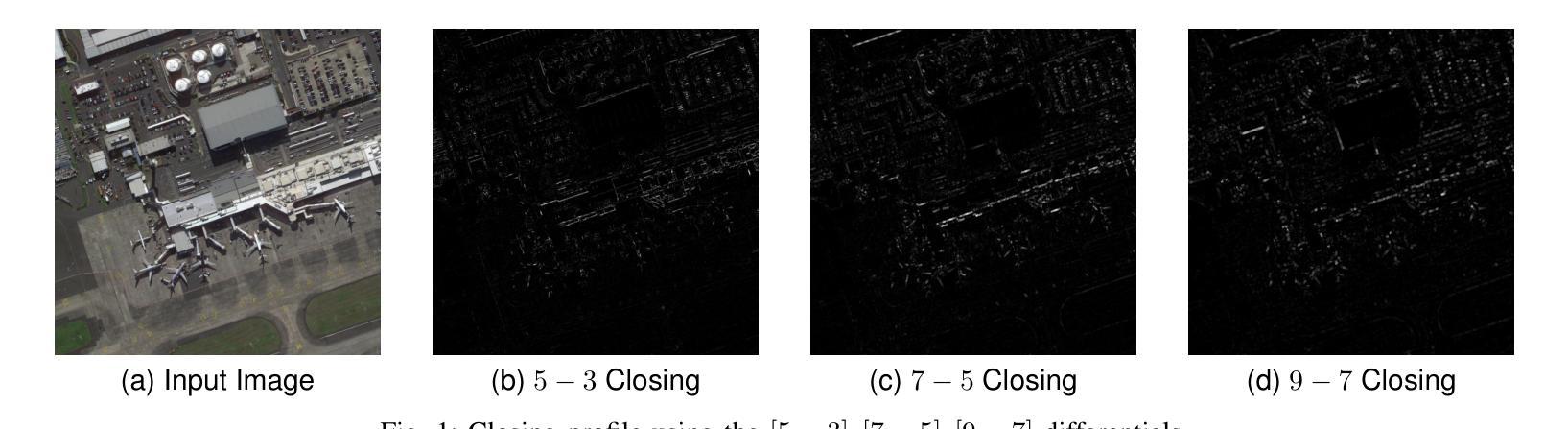
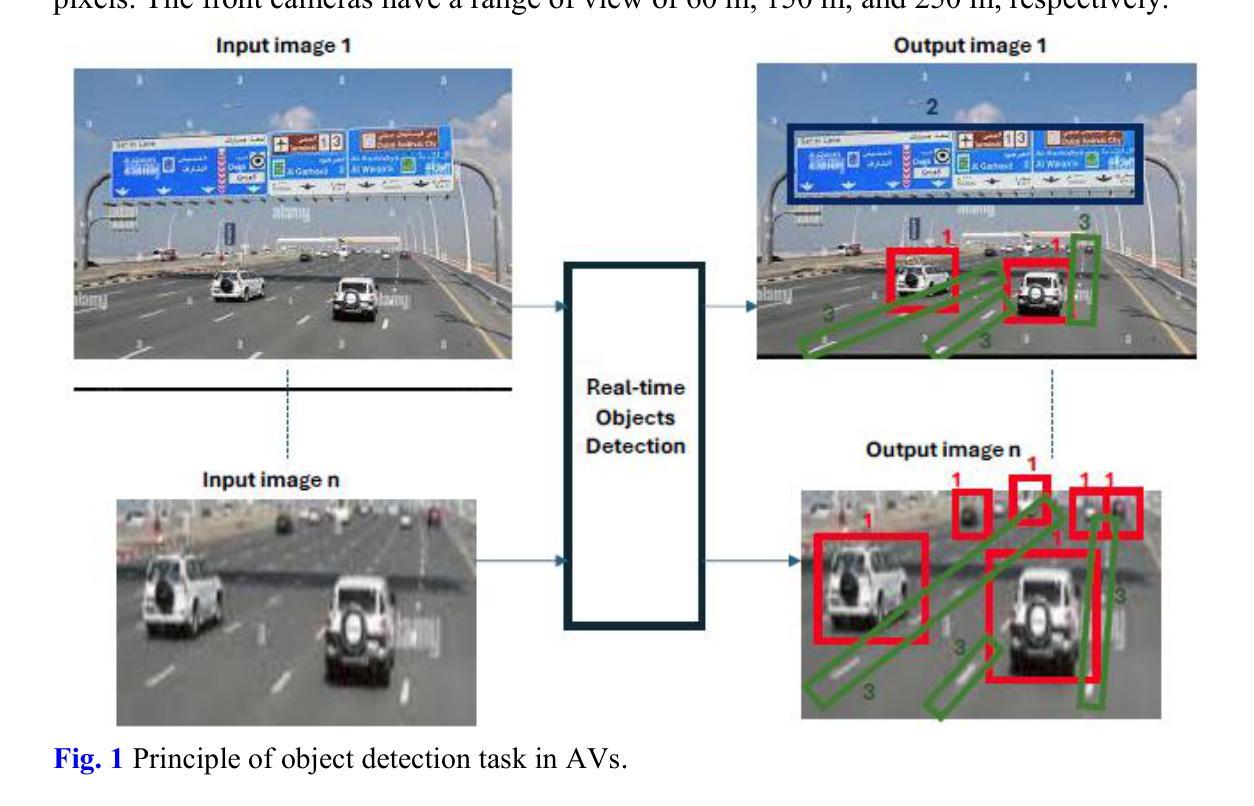
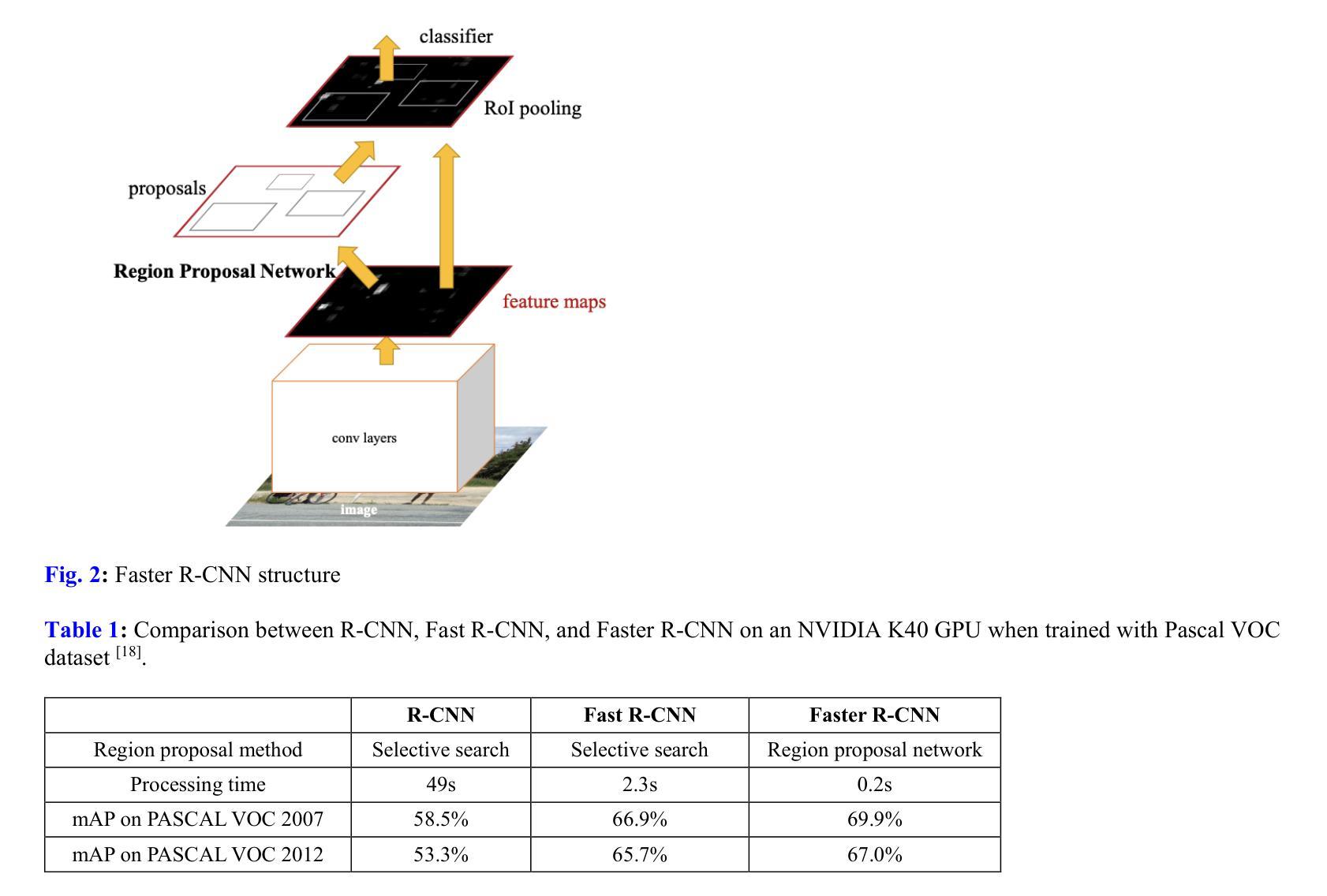
Real-time Object Detection and Associated Hardware Accelerators Targeting Autonomous Vehicles: A Review
Authors:Safa Sali, Anis Meribout, Ashiyana Majeed, Mahmoud Meribout, Juan Pablo, Varun Tiwari, Asma Baobaid
The efficiency of object detectors depends on factors like detection accuracy, processing time, and computational resources. Processing time is crucial for real-time applications, particularly for autonomous vehicles (AVs), where instantaneous responses are vital for safety. This review paper provides a concise yet comprehensive survey of real-time object detection (OD) algorithms for autonomous cars delving into their hardware accelerators (HAs). Non-neural network-based algorithms, which use statistical image processing, have been entirely substituted by AI algorithms, such as different models of convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Their intrinsically parallel features led them to be deployable into edge-based HAs of various types, where GPUs and, to a lesser extent, ASIC (application-specific integrated circuit) remain the most widely used. Throughputs of hundreds of frames/s (fps) could be reached; however, handling object detection for all the cameras available in a typical AV requires further hardware and algorithmic improvements. The intensive competition between AV providers has limited the disclosure of algorithms, firmware, and even hardware platform details. This remains a hurdle for researchers, as commercial systems provide valuable insights while academics undergo lengthy training and testing on restricted datasets and road scenarios. Consequently, many AV research papers may not be reflected in end products, being developed under limited conditions. This paper surveys state-of-the-art OD algorithms and aims to bridge the gap with technologies in commercial AVs. To our knowledge, this aspect has not been addressed in earlier surveys. Hence, the paper serves as a tangible reference for researchers designing future generations of vehicles, expected to be fully autonomous for comfort and safety.
目标检测器的效率取决于检测精度、处理时间和计算资源等因素。处理时间对于实时应用至关重要,特别是在自动驾驶汽车中,瞬时响应对安全至关重要。这篇综述论文对自动驾驶汽车的实时目标检测算法进行了简明而全面的调查,深入探讨了其硬件加速器。基于非神经网络算法的统计图像处理已经被AI算法所取代,如各种卷积神经网络模型。它们固有的并行特性使其可以部署到各种类型的边缘基于HAs中,其中GPU和较小程度的ASIC仍然是最广泛使用的。可以达到数百帧每秒的吞吐量;然而,处理典型自动驾驶汽车上所有摄像头上的目标检测需要进一步的硬件和算法改进。自动驾驶提供商之间的激烈竞争限制了算法、固件甚至是硬件平台细节的披露。这对于研究人员来说是一个挑战,因为商业系统提供了有价值的见解,而学术界则在有限的数据集和道路场景上进行冗长的训练和测试。因此,许多自动驾驶汽车研究论文可能无法反映在最终产品中,这些产品是在有限条件下开发的。这篇论文调查了最新的目标检测算法,旨在弥补与商业自动驾驶汽车技术的差距。据我们所知,这方面的内容在之前的调查中尚未得到重视。因此,该论文对于设计未来几代汽车的研究人员具有重要的参考价值,未来的汽车预计会实现完全的自动化,以提高舒适性和安全性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文综述了面向自动驾驶车辆的实时目标检测算法及其硬件加速器。文章指出目标检测效率依赖于检测准确性、处理时间和计算资源。对于自动驾驶车辆,处理时间尤为关键。当前,神经网络算法已替代非神经网络算法,其中卷积神经网络模型因其并行特性广泛应用于边缘型硬件加速器。然而,处理所有摄像头的数据仍需要硬件和算法的进一步改进。文章强调商业系统提供有价值信息的同时,学术界面临的限制阻碍了研究的发展。本文旨在填补现有调查中的空白,为未来车辆设计提供实际参考。
Key Takeaways:
- 目标检测效率依赖于检测准确性、处理时间和计算资源。
- 自动驾驶车辆需要瞬时响应,处理时间至关重要。
- 非神经网络算法已被AI算法如卷积神经网络模型替代。
- 卷积神经网络模型的并行特性使其适用于各种边缘型硬件加速器,尤其是GPU和ASIC。
- 目标检测仍需进一步改进,以处理自动驾驶车辆上所有摄像头的数据。
- 商业系统对自动驾驶目标检测算法的信息披露有限,阻碍了学术研究的发展。
点此查看论文截图

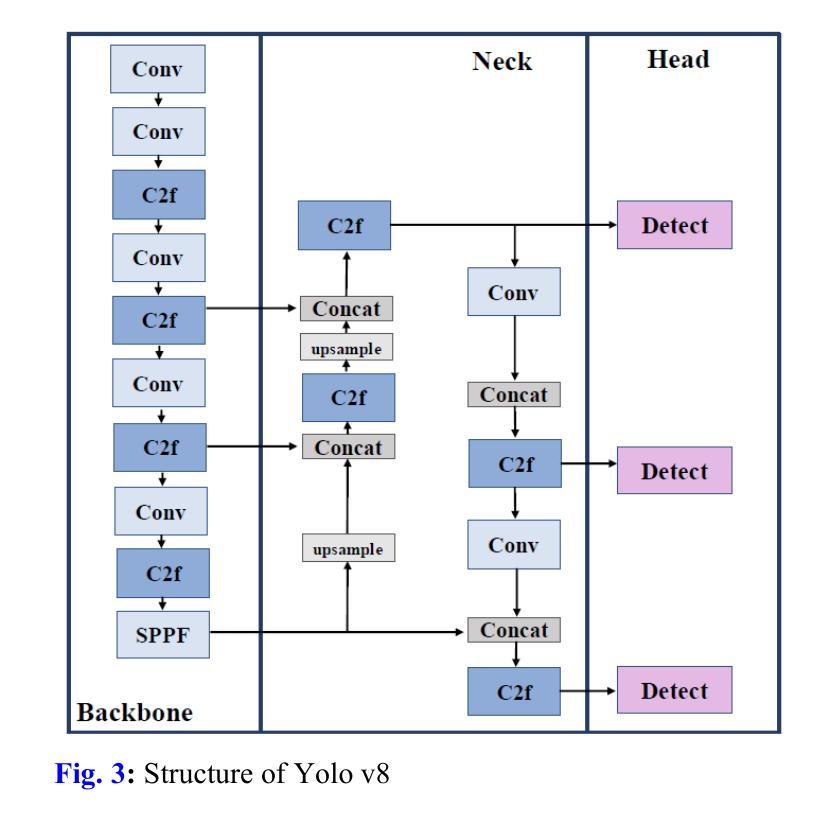
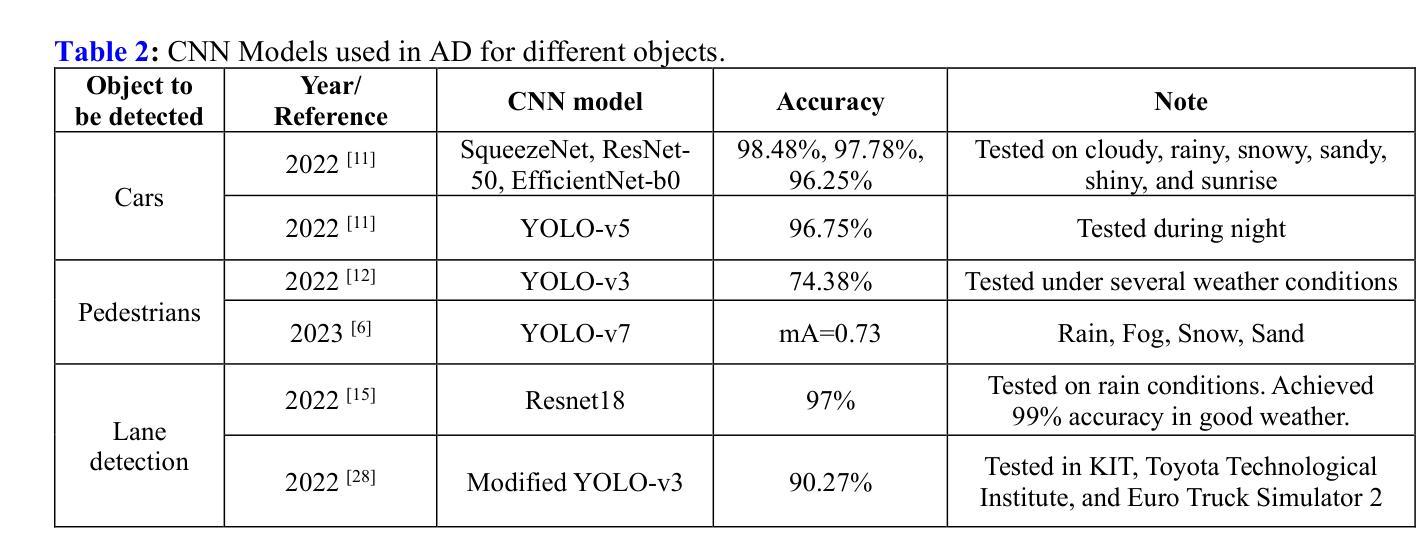
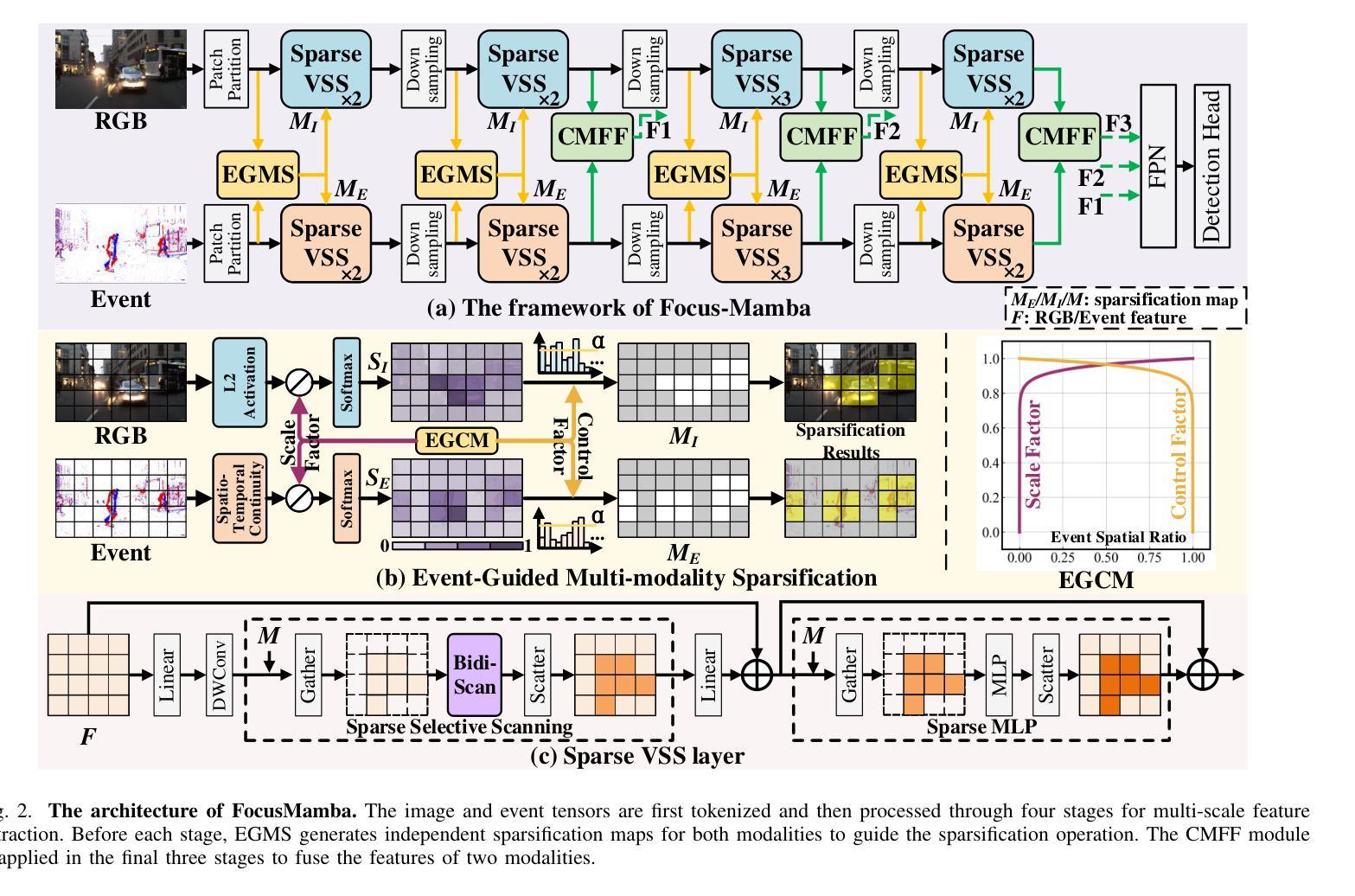
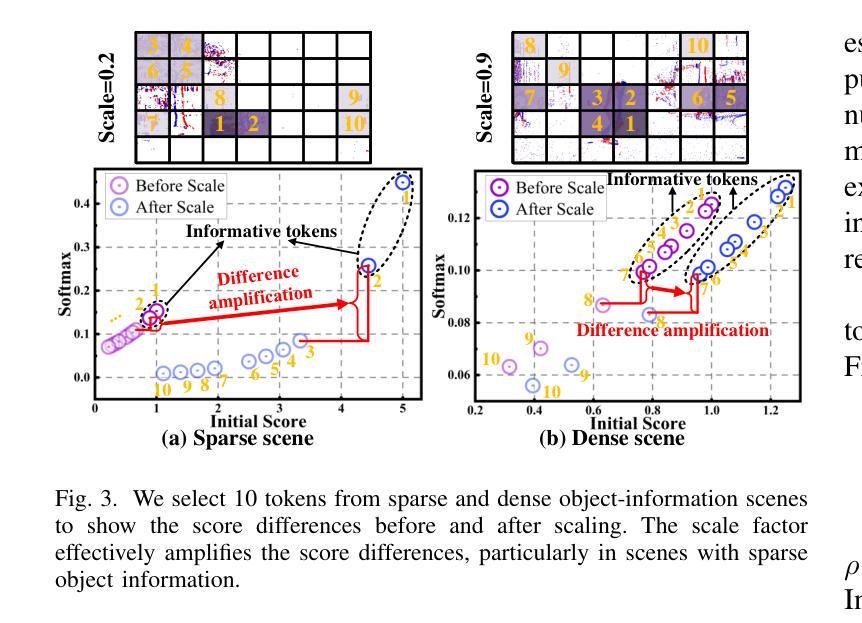
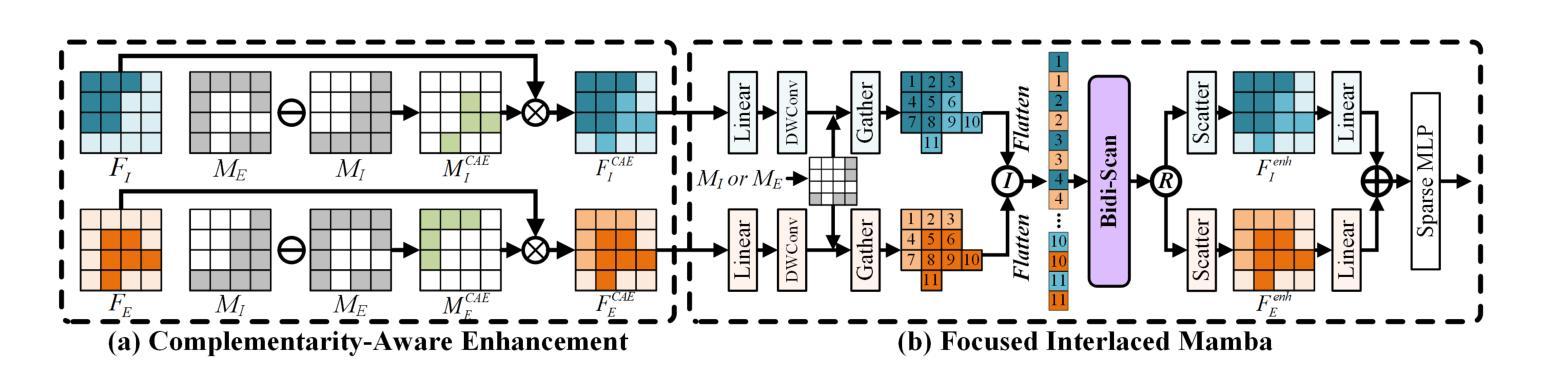
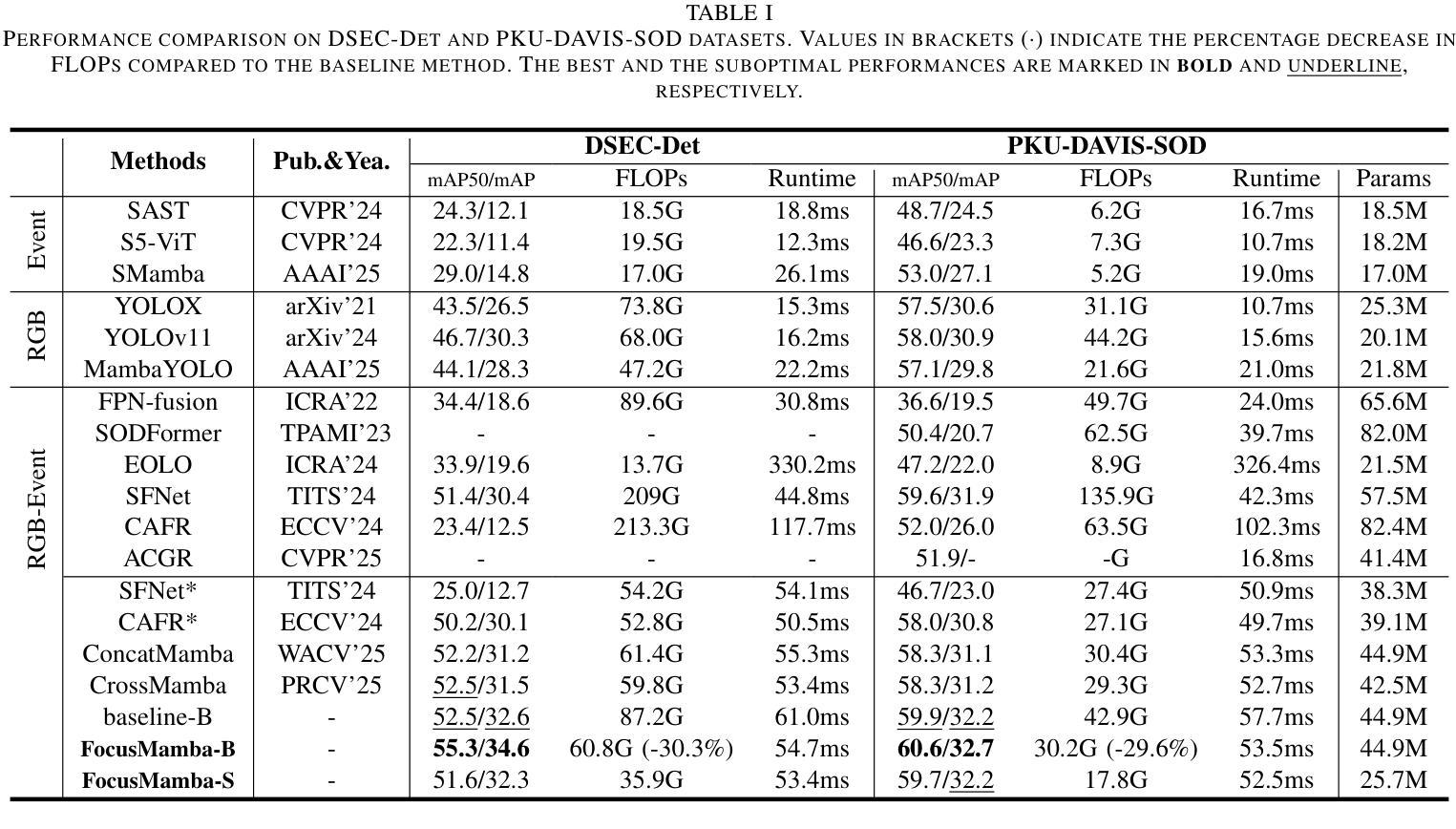
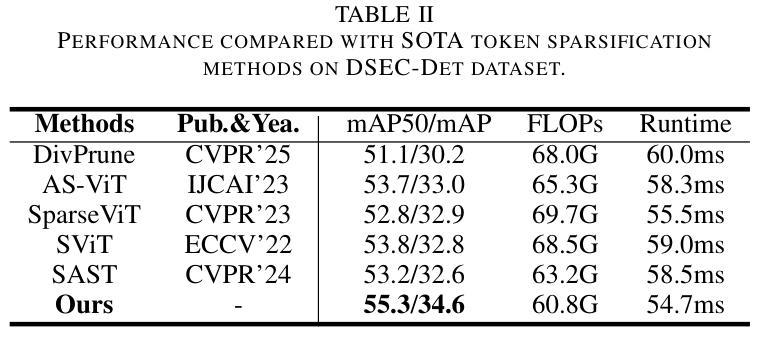
Focus Through Motion: RGB-Event Collaborative Token Sparsification for Efficient Object Detection
Authors:Nan Yang, Yang Wang, Zhanwen Liu, Yuchao Dai, Yang Liu, Xiangmo Zhao
Existing RGB-Event detection methods process the low-information regions of both modalities (background in images and non-event regions in event data) uniformly during feature extraction and fusion, resulting in high computational costs and suboptimal performance. To mitigate the computational redundancy during feature extraction, researchers have respectively proposed token sparsification methods for the image and event modalities. However, these methods employ a fixed number or threshold for token selection, hindering the retention of informative tokens for samples with varying complexity. To achieve a better balance between accuracy and efficiency, we propose FocusMamba, which performs adaptive collaborative sparsification of multimodal features and efficiently integrates complementary information. Specifically, an Event-Guided Multimodal Sparsification (EGMS) strategy is designed to identify and adaptively discard low-information regions within each modality by leveraging scene content changes perceived by the event camera. Based on the sparsification results, a Cross-Modality Focus Fusion (CMFF) module is proposed to effectively capture and integrate complementary features from both modalities. Experiments on the DSEC-Det and PKU-DAVIS-SOD datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior performance in both accuracy and efficiency compared to existing methods. The code will be available at https://github.com/Zizzzzzzz/FocusMamba.
现有RGB-事件检测方法在特征提取和融合过程中会统一处理两种模态的低信息区域(图像中的背景事件数据中非事件区域),这导致了较高的计算成本和性能下降。为了减少特征提取过程中的计算冗余,研究人员分别针对图像和事件模态提出了令牌稀疏化方法。然而,这些方法使用固定的数量或阈值来进行令牌选择,阻碍了不同复杂度样本的信息令牌的保留。为了平衡准确性和效率,我们提出了FocusMamba,它能够对多模态特征进行自适应协同稀疏化,并有效地融合互补信息。具体来说,设计了一种事件引导的多模态稀疏化(EGMS)策略,通过利用事件相机感知的场景内容变化来识别和自适应丢弃每个模态中的低信息区域。基于稀疏化结果,提出了跨模态焦点融合(CMFF)模块,以有效捕获并融合两种模态的互补特征。在DSEC-Det和PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上的实验表明,该方法在准确性和效率上均优于现有方法。代码将在https://github.com/Zizzzzzzz/FocusMamba上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文指出传统RGB-Event检测方法在处理图像和事件数据的低信息区域时存在计算成本高、性能不佳的问题。为解决此问题,研究者提出进行特征提取时的令牌稀疏化方法。但当前的方法在令牌选择时采用固定的数值或阈值,无法保留样本不同复杂性下的信息令牌。本文提出的FocusMamba方法能够实现多模态特征的自适应协同稀疏化,并有效地融合互补信息。具体而言,通过事件引导的多模态稀疏化策略,自适应地丢弃各模态的低信息区域,利用事件相机感知的场景内容变化来实现这一目的。根据稀疏化结果,提出跨模态聚焦融合模块,以捕捉并融合两种模态的互补特征。在DSEC-Det和PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上的实验表明,该方法在准确性和效率上均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- RGB-Event检测方法面临计算成本高和性能不佳的问题,特别是在处理低信息区域时。
- 当前的特征提取方法采用固定的令牌选择机制,不利于处理复杂度不同的样本。
- FocusMamba方法通过自适应协同稀疏化多模态特征来解决上述问题。
- 事件引导的多模态稀疏化策略能够自适应地识别并丢弃低信息区域。
- 跨模态聚焦融合模块有效捕捉并融合了两种模态的互补特征。
- 在DSEC-Det和PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上的实验显示,FocusMamba方法较现有方法更具优势和效率。
点此查看论文截图

AutoDetect: Designing an Autoencoder-based Detection Method for Poisoning Attacks on Object Detection Applications in the Military Domain
Authors:Alma M. Liezenga, Stefan Wijnja, Puck de Haan, Niels W. T. Brink, Jip J. van Stijn, Yori Kamphuis, Klamer Schutte
Poisoning attacks pose an increasing threat to the security and robustness of Artificial Intelligence systems in the military domain. The widespread use of open-source datasets and pretrained models exacerbates this risk. Despite the severity of this threat, there is limited research on the application and detection of poisoning attacks on object detection systems. This is especially problematic in the military domain, where attacks can have grave consequences. In this work, we both investigate the effect of poisoning attacks on military object detectors in practice, and the best approach to detect these attacks. To support this research, we create a small, custom dataset featuring military vehicles: MilCivVeh. We explore the vulnerability of military object detectors for poisoning attacks by implementing a modified version of the BadDet attack: a patch-based poisoning attack. We then assess its impact, finding that while a positive attack success rate is achievable, it requires a substantial portion of the data to be poisoned – raising questions about its practical applicability. To address the detection challenge, we test both specialized poisoning detection methods and anomaly detection methods from the visual industrial inspection domain. Since our research shows that both classes of methods are lacking, we introduce our own patch detection method: AutoDetect, a simple, fast, and lightweight autoencoder-based method. Our method shows promising results in separating clean from poisoned samples using the reconstruction error of image slices, outperforming existing methods, while being less time- and memory-intensive. We urge that the availability of large, representative datasets in the military domain is a prerequisite to further evaluate risks of poisoning attacks and opportunities patch detection.
中毒攻击对军事领域人工智能系统的安全和稳健性构成日益严重的威胁。开源数据集和预训练模型的广泛使用加剧了这一风险。尽管这一威胁十分严重,但关于物体检测系统中毒攻击的应用和检测的研究却十分有限。在军事领域中,攻击可能带来严重后果,这一问题尤为严重。
在这项工作中,我们不仅对实践中中毒攻击对军事物体检测器的影响进行了调查,还研究了检测这些攻击的最佳方法。为了支持这项研究,我们创建了一个包含军用车辆的小型自定义数据集:MilCivVeh。我们通过实现一种基于补丁的中毒攻击——BadDet攻击的改进版,来探索军事物体检测器对中毒攻击的脆弱性。然后,我们评估了它的影响,发现虽然可以实现积极的攻击成功率,但需要大量数据被毒害——这引发了对其实际可行性的质疑。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be presented at SPIE: Sensors + Imaging, Artificial Intelligence for Security and Defence Applications II
Summary
针对军事人工智能系统的中毒攻击威胁日益严重,特别是在对象检测系统中。研究团队调查了中毒攻击对军事对象检测器的影响,并探索了检测这些攻击的最佳方法。为此,他们创建了一个军事车辆专用的小型数据集MilCivVeh,并实现了基于补丁的中毒攻击BadDet的修改版。评估发现,虽然攻击成功率高,但需要大量数据被篡改,实用性存疑。针对检测难题,他们测试了专门的毒药检测方法和来自视觉工业检测领域的异常检测方法,但效果不佳。因此,他们提出了一种基于自动编码器的补丁检测方法AutoDetect,能够利用图像切片的重建误差来区分清洁样本和中毒样本,表现出优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 中毒攻击对军事人工智能系统的威胁日益严重,特别是在对象检测系统中。
- 目前针对军事对象检测系统的中毒攻击研究有限。
- 创建一个军事车辆专用的小型数据集MilCivVeh以支持研究。
- 实现了基于补丁的中毒攻击BadDet的修改版,并评估了其影响。
- 检测中毒攻击的挑战在于现有方法的效果不佳。
- 提出的AutoDetect方法表现出优越的性能,能够利用图像切片的重建误差来区分清洁样本和中毒样本。
点此查看论文截图

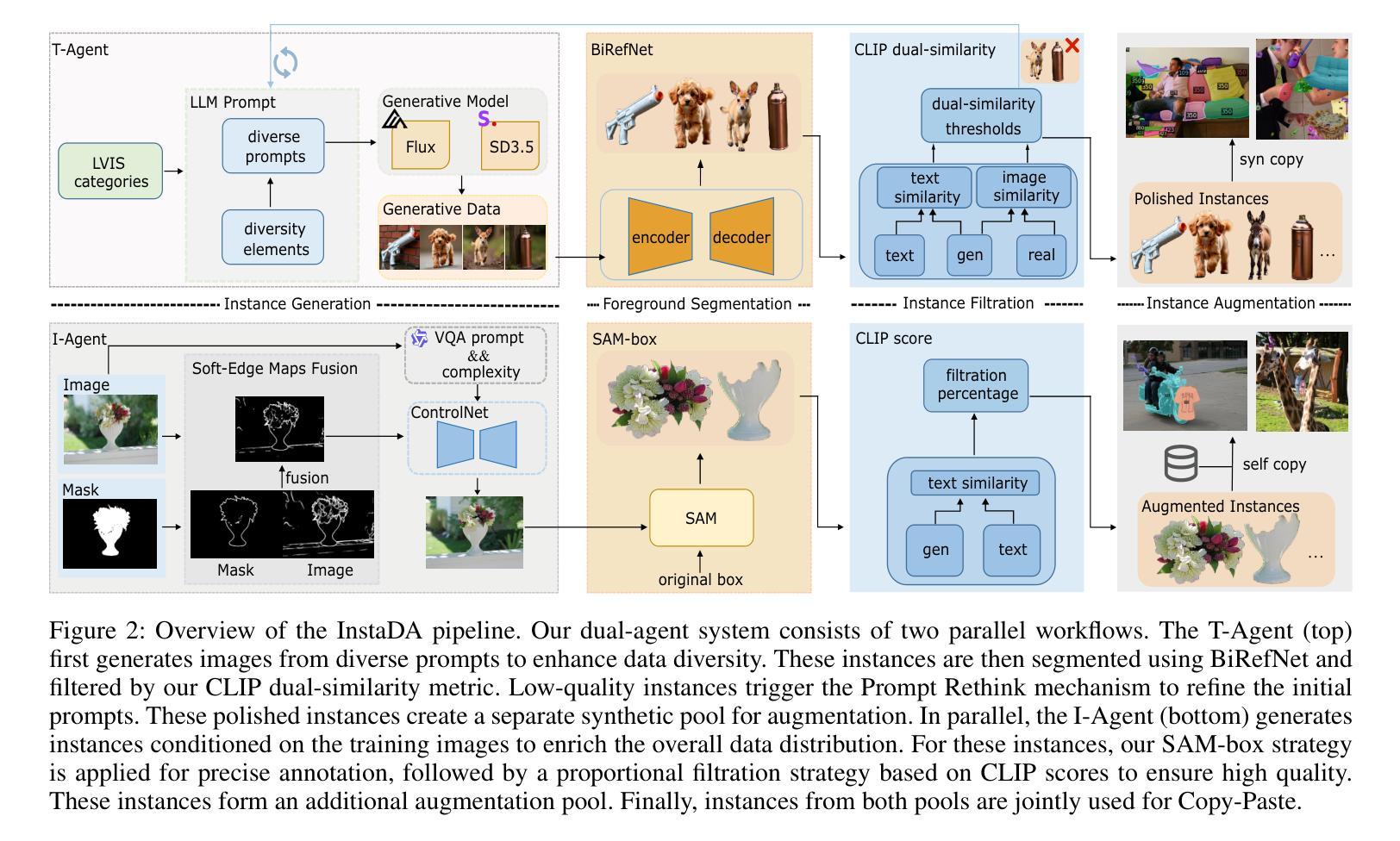
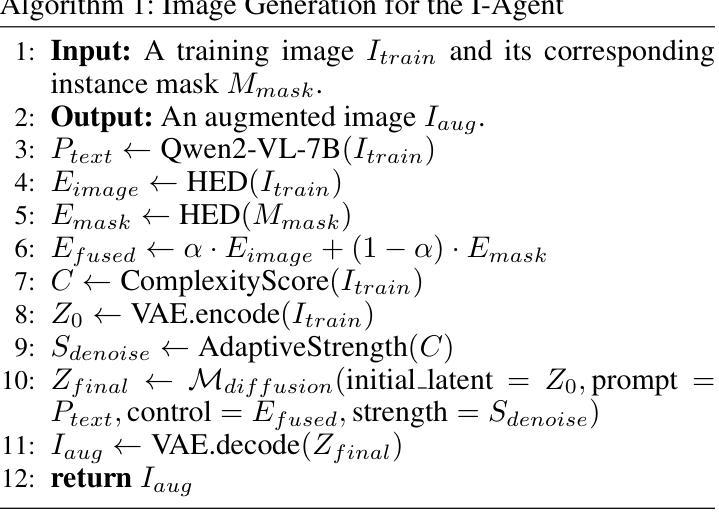
InstaDA: Augmenting Instance Segmentation Data with Dual-Agent System
Authors:Xianbao Hou, Yonghao He, Zeyd Boukhers, John See, Hu Su, Wei Sui, Cong Yang
Acquiring high-quality instance segmentation data is challenging due to the labor-intensive nature of the annotation process and significant class imbalances within datasets. Recent studies have utilized the integration of Copy-Paste and diffusion models to create more diverse datasets. However, these studies often lack deep collaboration between large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models, and underutilize the rich information within the existing training data. To address these limitations, we propose InstaDA, a novel, training-free Dual-Agent system designed to augment instance segmentation datasets. First, we introduce a Text-Agent (T-Agent) that enhances data diversity through collaboration between LLMs and diffusion models. This agent features a novel Prompt Rethink mechanism, which iteratively refines prompts based on the generated images. This process not only fosters collaboration but also increases image utilization and optimizes the prompts themselves. Additionally, we present an Image-Agent (I-Agent) aimed at enriching the overall data distribution. This agent augments the training set by generating new instances conditioned on the training images. To ensure practicality and efficiency, both agents operate as independent and automated workflows, enhancing usability. Experiments conducted on the LVIS 1.0 validation set indicate that InstaDA achieves significant improvements, with an increase of +4.0 in box average precision (AP) and +3.3 in mask AP compared to the baseline. Furthermore, it outperforms the leading model, DiverGen, by +0.3 in box AP and +0.1 in mask AP, with a notable +0.7 gain in box AP on common categories and mask AP gains of +0.2 on common categories and +0.5 on frequent categories.
获取高质量的实例分割数据是一项挑战,因为标注过程劳动密集且数据集中存在严重的类别不平衡问题。最近的研究通过结合Copy-Paste和扩散模型来创建更多样化的数据集。然而,这些研究往往缺乏大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型之间的深度协作,并且未能充分利用现有训练数据中的丰富信息。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了InstaDA,这是一种无需训练的新型双代理系统,旨在增强实例分割数据集。首先,我们引入了一个文本代理(T-Agent),它通过LLM和扩散模型的协作来提高数据多样性。该代理具有新颖的提示反思机制,可以根据生成的图像迭代优化提示。这个过程不仅促进了协作,还提高了图像利用率并优化了提示本身。此外,我们还推出了图像代理(I-Agent),旨在丰富整体数据分布。该代理通过基于训练图像生成新实例来丰富训练集。为确保实用性和效率,两个代理作为独立、自动化的工作流程进行操作,增强了易用性。在LVIS 1.0验证集上进行的实验表明,InstaDA实现了显著的改进,框平均精度(AP)提高了+4.0,掩码AP提高了+3.3,超过了基线。此外,它超越了领先模型DiverGen,在框AP上提高了+0.3,在掩码AP上提高了+0.1。在常见类别上框AP增加了+0.7,掩码AP在常见类别上增加了+0.2,在频繁类别上增加了+0.5。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对实例分割数据获取困难的问题,提出了InstaDA训练免费双代理系统,通过文本代理和图像代理增强数据多样性和丰富性。实验表明,InstaDA在LVIS 1.0验证集上取得了显著改进,提高了盒子平均精度(AP)和掩膜AP。
Key Takeaways
- InstaDA是一个训练免费的双代理系统,旨在增强实例分割数据集。
- 通过文本代理(T-Agent)和图像代理(I-Agent)增强数据多样性和丰富性。
- T-Agent引入了一种新颖的Prompt Rethink机制,该机制可以迭代优化提示并增加图像利用率。
- I-Agent旨在丰富整体数据分布,通过基于训练图像生成新实例来实现。
- 两个代理作为独立自动化工作流程运行,提高了实用性。
- 实验表明,InstaDA在LVIS 1.0验证集上取得了改进,包括盒子平均精度和掩膜AP的显著提高。
点此查看论文截图


Explaining What Machines See: XAI Strategies in Deep Object Detection Models
Authors:FatemehSadat Seyedmomeni, Mohammad Ali Keyvanrad
In recent years, deep learning has achieved unprecedented success in various computer vision tasks, particularly in object detection. However, the black-box nature and high complexity of deep neural networks pose significant challenges for interpretability, especially in critical domains such as autonomous driving, medical imaging, and security systems. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) aims to address this challenge by providing tools and methods to make model decisions more transparent, interpretable, and trust-worthy for humans. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of state-of-the-art explain-ability methods specifically applied to object detection models. The paper be-gins by categorizing existing XAI techniques based on their underlying mechanisms-perturbation-based, gradient-based, backpropagation-based, and graph-based methods. Notable methods such as D-RISE, BODEM, D-CLOSE, and FSOD are discussed in detail. Furthermore, the paper investigates their applicability to various object detection architectures, including YOLO, SSD, Faster R-CNN, and EfficientDet. Statistical analysis of publication trends from 2022 to mid-2025 shows an accelerating interest in explainable object detection, indicating its increasing importance. The study also explores common datasets and evaluation metrics, and highlights the major challenges associated with model interpretability. By providing a structured taxonomy and a critical assessment of existing methods, this review aims to guide researchers and practitioners in selecting suitable explainability techniques for object detection applications and to foster the development of more interpretable AI systems.
近年来,深度学习在各种计算机视觉任务中取得了前所未有的成功,特别是在目标检测领域。然而,深度神经网络的黑盒性和高复杂性给可解释性带来了重大挑战,特别是在自动驾驶、医疗成像和安全系统等关键领域。可解释人工智能(XAI)旨在通过提供工具和方法来解决这一挑战,使模型决策更加透明、可解释和值得信赖。这篇综述对专门应用于目标检测模型的最先进解释方法进行了综合分析。文章首先根据现有XAI技术的底层机制进行分类,包括基于扰动的方法、基于梯度的方法、基于反向传播的方法和基于图的方法。对D-RISE、BODEM、D-CLOSE和FSOD等值得注意的方法进行了详细介绍。此外,文章还探讨了它们在各种目标检测架构(包括YOLO、SSD、Faster R-CNN和EfficientDet)中的适用性。从2022年到2025年中期关于解释性目标检测的出版物趋势统计分析显示,人们对解释性目标检测的兴趣正在加速增长,这表明其重要性日益增加。该研究还探讨了常见数据集和评估指标,并指出了与模型解释性相关的重大挑战。通过提供现有方法的结构化分类和批判性评估,本综述旨在指导研究者和实践者为目标检测应用选择合适的解释技术,并推动开发更具解释性的AI系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 71 pages, 47 figures
Summary
本文综述了应用于对象检测模型的最新解释性人工智能(XAI)方法,旨在解决深度神经网络模型决策的不透明和不可解释性问题。文章分类介绍了基于扰动、梯度、反向传播和图形机制的XAI技术,并详细讨论了几种著名方法,如D-RISE、BODEM、D-CLOSE和FSOD。此外,文章还研究了这些方法在YOLO、SSD、Faster R-CNN和EfficientDet等对象检测架构中的应用。统计数据显示,从2022年到2025年中,对可解释性对象检测的兴趣正在加速增长。本文旨在通过提供结构化的分类和重要评估,指导研究者和实践者选择适合对象检测应用的解释技术,推动更可解释的AI系统的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络在对象检测任务中的成功带来了模型决策透明性和解释性的挑战。
- 解释性人工智能(XAI)方法旨在解决这一挑战,使模型决策更加透明、可解释和值得信赖。
- 综述对当前应用于对象检测模型的XAI技术进行了全面分析,包括基于扰动、梯度、反向传播和图形的方法。
- 文章详细讨论了几种著名的XAI方法,如D-RISE、BODEM、D-CLOSE和FSOD。
- XAI技术在多种对象检测架构(如YOLO、SSD、Faster R-CNN和EfficientDet)中有广泛应用。
- 统计数据显示,对可解释性对象检测的研究兴趣正在加速增长。
点此查看论文截图

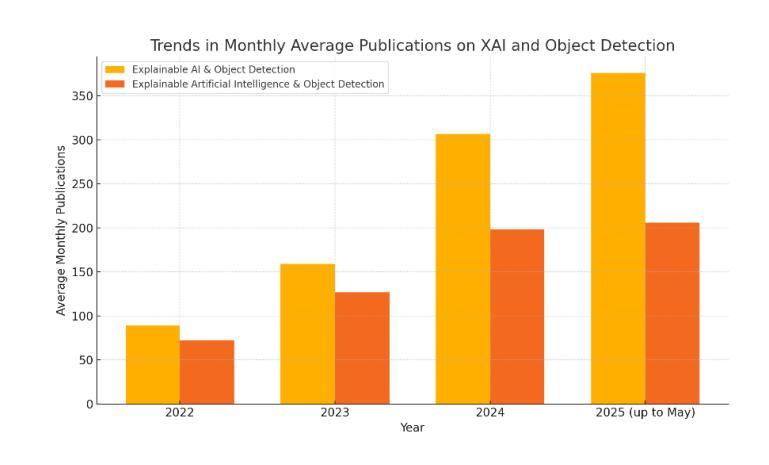
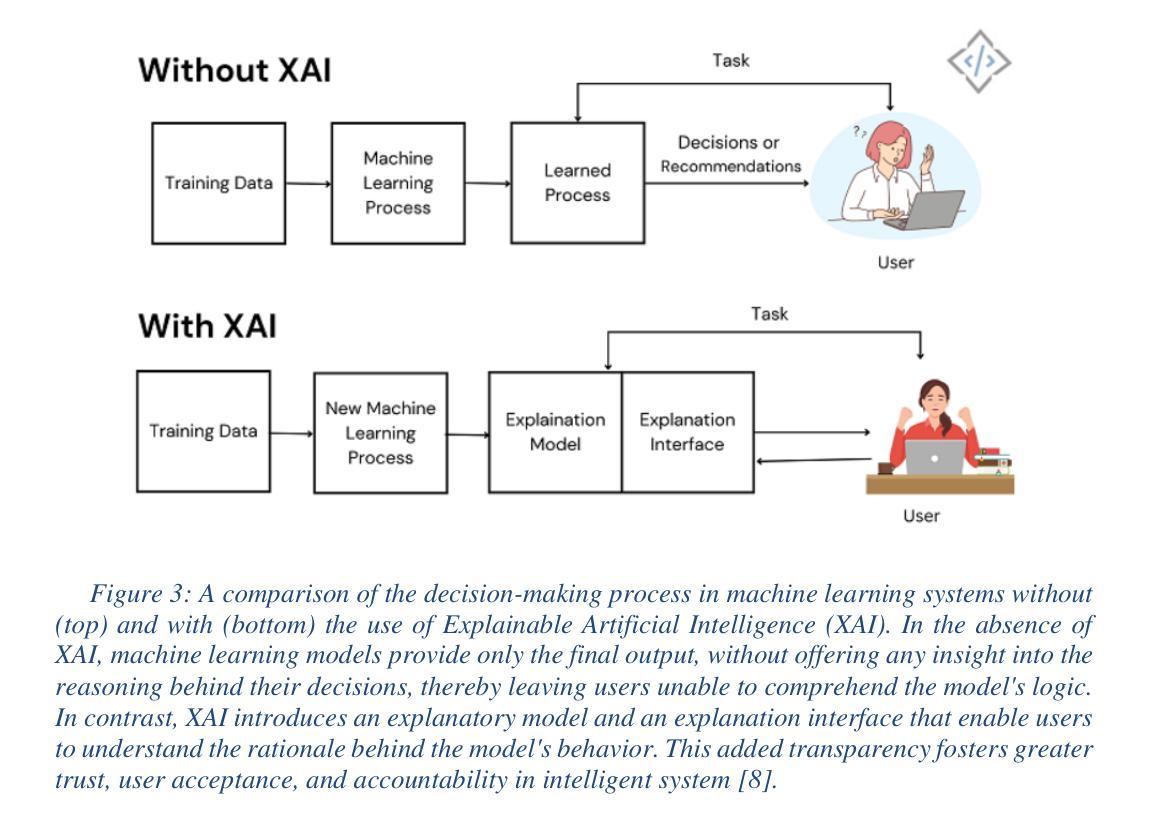
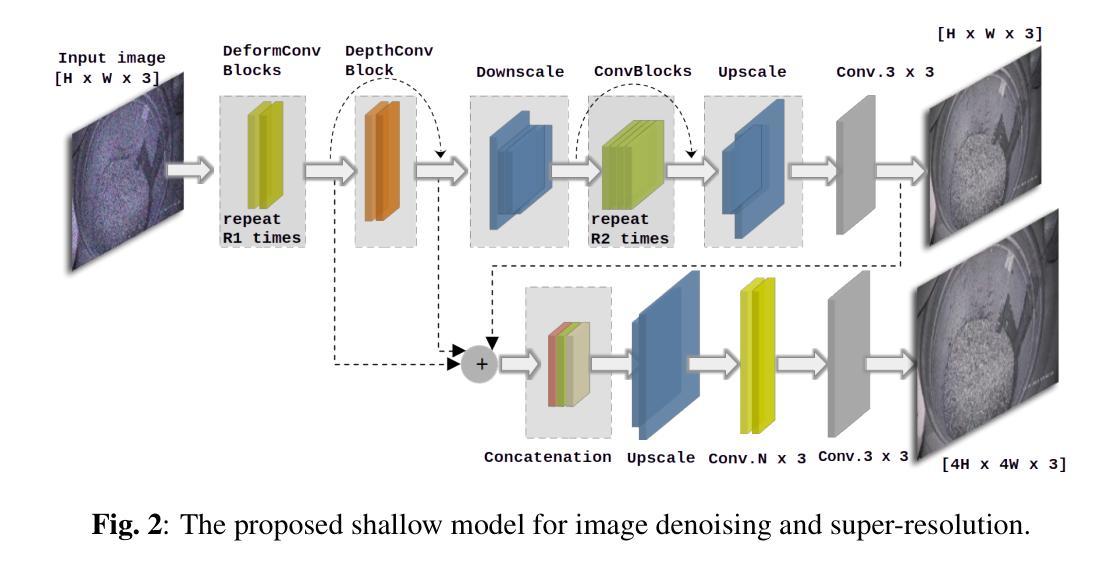
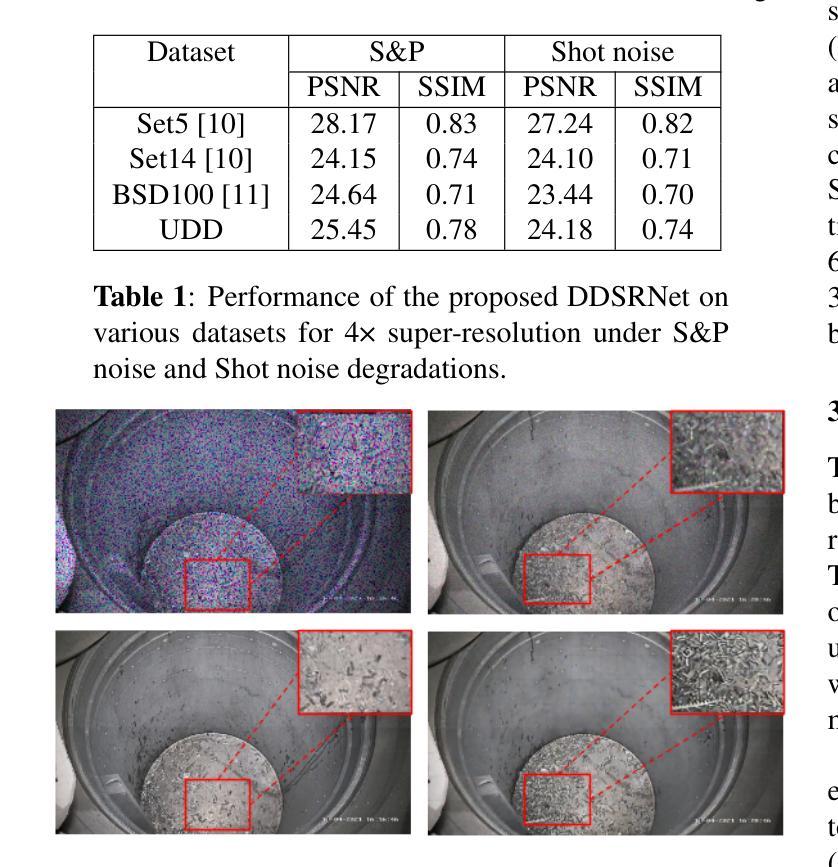
Image Quality Enhancement and Detection of Small and Dense Objects in Industrial Recycling Processes
Authors:Oussama Messai, Abbass Zein-Eddine, Abdelouahid Bentamou, Mickaël Picq, Nicolas Duquesne, Stéphane Puydarrieux, Yann Gavet
This paper tackles two key challenges: detecting small, dense, and overlapping objects (a major hurdle in computer vision) and improving the quality of noisy images, especially those encountered in industrial environments. [1, 2]. Our focus is on evaluating methods built on supervised deep learning. We perform an analysis of these methods, using a newly developed dataset comprising over 10k images and 120k instances. By evaluating their performance, accuracy, and computational efficiency, we identify the most reliable detection systems and highlight the specific challenges they address in industrial applications. This paper also examines the use of deep learning models to improve image quality in noisy industrial environments. We introduce a lightweight model based on a fully connected convolutional network. Additionally, we suggest potential future directions for further enhancing the effectiveness of the model. The repository of the dataset and proposed model can be found at: https://github.com/o-messai/SDOOD, https://github.com/o-messai/DDSRNet
本文解决了两个关键挑战:检测小、密集、重叠的物体(计算机视觉中的主要障碍)以及提高含噪图像的质量,尤其是工业环境中遇到的图像。 [1, 2]。我们的重点是对基于有监督深度学习的方法进行评估。我们使用新开发的包含超过10k张图像和12万个实例的数据集对这些方法进行分析。通过评估它们的性能、准确性和计算效率,我们确定了最可靠的检测系统,并强调了它们在工业应用中解决的具体挑战。本文还探讨了使用深度学习模型提高工业环境中含噪图像质量的可行性。我们提出了一种基于全连接卷积网络的轻量级模型。此外,我们还介绍了进一步提高模型有效性的潜在未来方向。数据集和所提出模型的存储库可以在以下链接找到:https://github.com/o-messai/SDOOD,https://github.com/o-messai/DDSRNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Event: Seventeenth International Conference on Quality Control by Artificial Vision (QCAV2025), 2025, Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan
Summary
本文解决了两个主要挑战:一是检测小、密集和重叠的物体(计算机视觉中的主要障碍),二是提高工业环境中噪声图像的质量。文章重点评估基于监督深度学习的方法,并使用新开发的包含超过10k图像和120k实例的数据集进行分析。通过评估其性能、准确性和计算效率,确定了最可靠的检测系统,并强调了它们在工业应用中的特定挑战。此外,文章还介绍了基于全卷积网络的轻量级模型来提高噪声工业环境中的图像质量,并提出了进一步提高模型有效性的潜在方向。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文解决了检测小、密集和重叠物体以及提高工业环境中噪声图像质量两个关键挑战。
- 文章使用了新开发的包含大量图像和实例的数据集来评估基于监督深度学习的检测方法。
- 通过对性能、准确性和计算效率的评估,确定了最可靠的检测系统。
- 论文强调了这些系统在工业应用中的特定挑战。
- 介绍了基于全卷积网络的轻量级模型,旨在提高噪声工业环境中的图像质量。
- 文章提出了进一步提高模型有效性的潜在方向。
点此查看论文截图

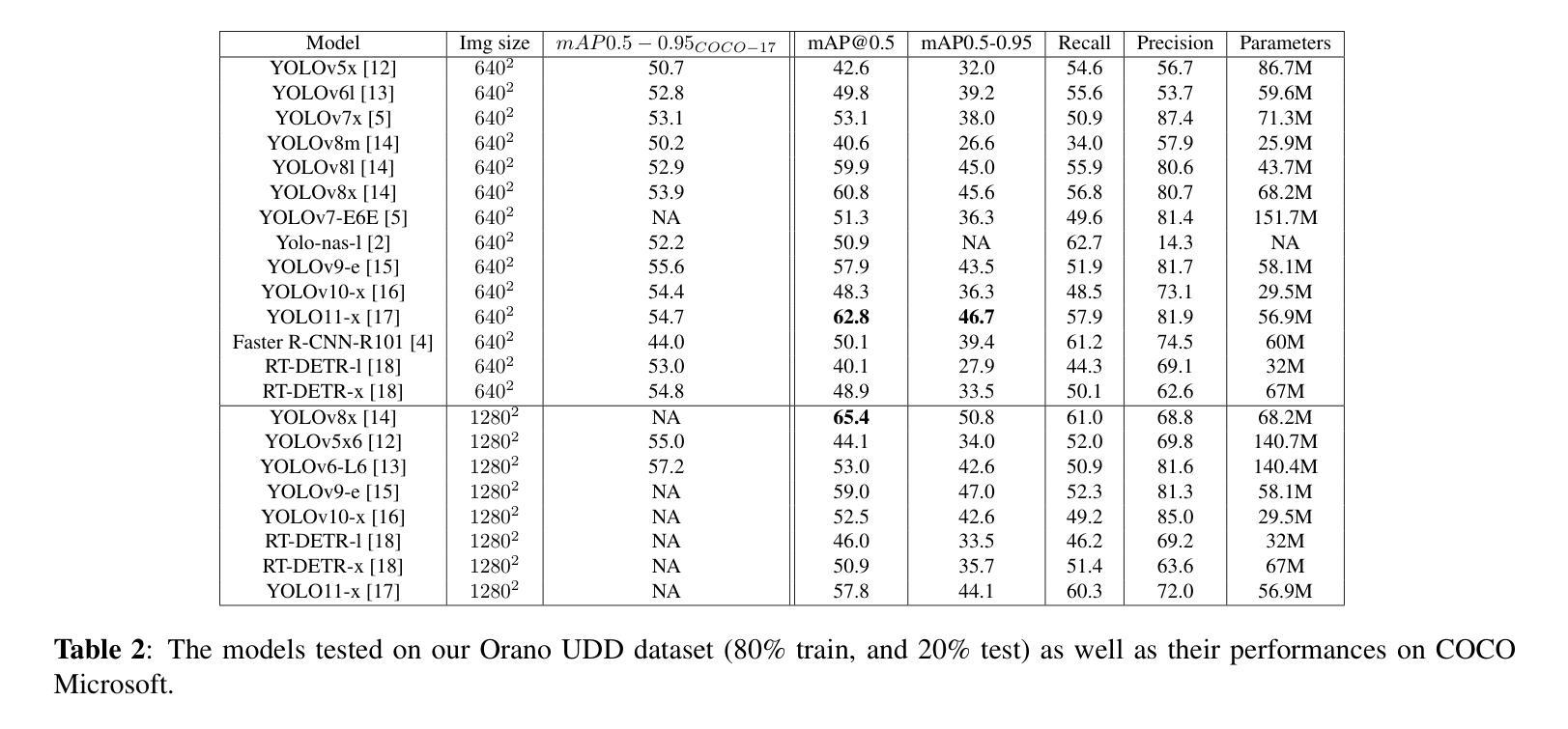
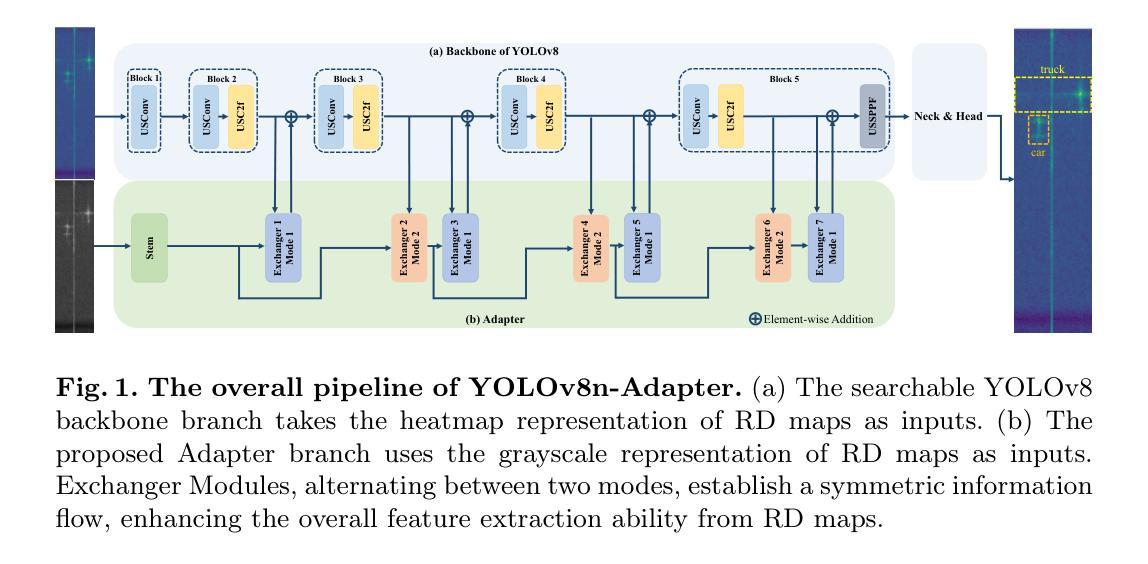
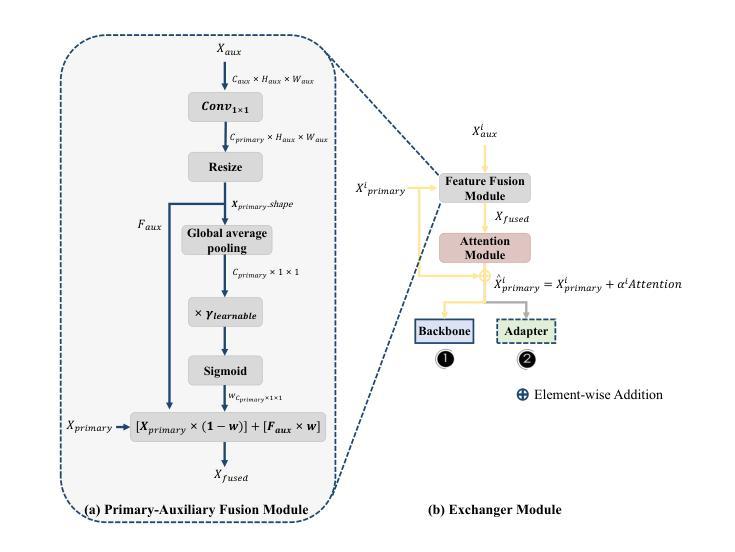
Multi-Representation Adapter with Neural Architecture Search for Efficient Range-Doppler Radar Object Detection
Authors:Zhiwei Lin, Weicheng Zheng, Yongtao Wang
Detecting objects efficiently from radar sensors has recently become a popular trend due to their robustness against adverse lighting and weather conditions compared with cameras. This paper presents an efficient object detection model for Range-Doppler (RD) radar maps. Specifically, we first represent RD radar maps with multi-representation, i.e., heatmaps and grayscale images, to gather high-level object and fine-grained texture features. Then, we design an additional Adapter branch, an Exchanger Module with two modes, and a Primary-Auxiliary Fusion Module to effectively extract, exchange, and fuse features from the multi-representation inputs, respectively. Furthermore, we construct a supernet with various width and fusion operations in the Adapter branch for the proposed model and employ a One-Shot Neural Architecture Search method to further improve the model’s efficiency while maintaining high performance. Experimental results demonstrate that our model obtains favorable accuracy and efficiency trade-off. Moreover, we achieve new state-of-the-art performance on RADDet and CARRADA datasets with mAP@50 of 71.9 and 57.1, respectively.
检测雷达传感器中的物体由于其对抗恶劣光照和天气条件的稳健性,与相机相比,最近成为了一个流行趋势。本文提出了一种针对Range-Doppler(RD)雷达图的高效目标检测模型。具体来说,我们首先使用多种表示方法(如热图和灰度图像)来表示RD雷达图,以获取高级目标和精细纹理特征。然后,我们设计了一个额外的适配器分支、一个具有两种模式的交换器模块以及一个主辅助融合模块,以有效地从多表示输入中提取、交换和融合特征。此外,我们在适配器分支中构建了具有不同宽度和融合操作的超网,为所提出的模型采用了一次性神经网络架构搜索方法,以进一步提高模型的效率并保持高性能。实验结果表明,我们的模型在准确性和效率之间取得了有利的平衡。此外,我们在RADDet和CARRADA数据集上实现了最新的性能,mAP@50分别为71.9和57.1。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICANN 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种针对Range-Doppler雷达地图的高效对象检测模型。该模型通过多表示方法(如热图和灰度图像)表示雷达地图,并设计了一个Adapter分支、一个带有两种模式的Exchanger模块以及一个Primary-Auxiliary融合模块,以有效地提取、交换和融合来自多表示输入的特征。此外,通过构建具有不同宽度和融合操作的supernet,并采用一次性神经网络架构搜索方法,进一步提高模型的效率并保持高性能。实验结果表明,该模型在RADDet和CARRADA数据集上取得了新的最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种针对Range-Doppler雷达地图的高效对象检测模型。
- 模型采用多表示方法(热图和灰度图像)来表示雷达地图,以获取高级对象特征和精细纹理特征。
- 论文设计了Adapter分支、Exchanger模块和Primary-Auxiliary融合模块,以有效地提取、交换和融合特征。
- 通过构建supernet并采用一次性神经网络架构搜索方法,模型在保持高性能的同时提高了效率。
- 实验结果表明,该模型在RADDet和CARRADA数据集上取得了优越的检测性能。
- 模型在RADDet数据集上的mAP@50达到了71.9,在CARRADA数据集上的mAP@50达到了57.1。
点此查看论文截图

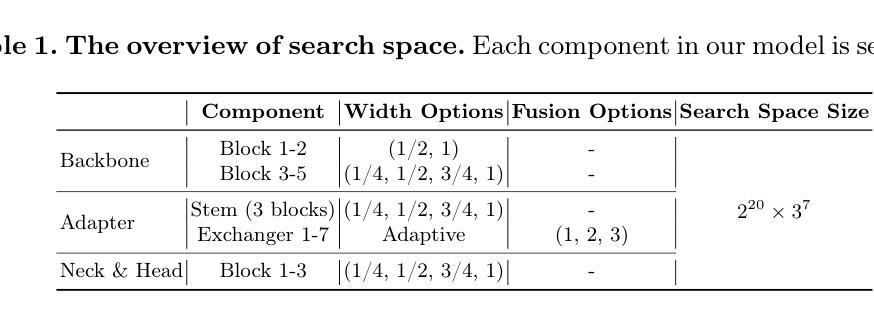
No More Sibling Rivalry: Debiasing Human-Object Interaction Detection
Authors:Bin Yang, Yulin Zhang, Hong-Yu Zhou, Sibei Yang
Detection transformers have been applied to human-object interaction (HOI) detection, enhancing the localization and recognition of human-action-object triplets in images. Despite remarkable progress, this study identifies a critical issue-“Toxic Siblings” bias-which hinders the interaction decoder’s learning, as numerous similar yet distinct HOI triplets interfere with and even compete against each other both input side and output side to the interaction decoder. This bias arises from high confusion among sibling triplets/categories, where increased similarity paradoxically reduces precision, as one’s gain comes at the expense of its toxic sibling’s decline. To address this, we propose two novel debiasing learning objectives-“contrastive-then-calibration” and “merge-then-split”-targeting the input and output perspectives, respectively. The former samples sibling-like incorrect HOI triplets and reconstructs them into correct ones, guided by strong positional priors. The latter first learns shared features among sibling categories to distinguish them from other groups, then explicitly refines intra-group differentiation to preserve uniqueness. Experiments show that we significantly outperform both the baseline (+9.18% mAP on HICO-Det) and the state-of-the-art (+3.59% mAP) across various settings.
检测转换器已应用于人机交互(HOI)检测,提高了图像中人类动作对象三元组的定位和识别能力。尽管有显著进展,但本研究发现了一个关键问题——“有毒同胞”偏见,它阻碍了交互解码器的学习。因为许多相似但又不同的HOI三元组在输入和输出方面都相互干扰和竞争,给交互解码器带来了干扰。这种偏见来源于同级三元组/类别之间的混淆程度很高,相似性增加反而降低了精度,因为一方的收益是以其有毒同胞的衰退为代价的。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了两种新的去偏学习目标:“对比校准”和“合并分割”,分别针对输入和输出角度。前者采样类似同胞的不正确HOI三元组,并在强位置先验的指导下重建为正确的三元组。后者首先学习同级类别之间的共享特征来区分它们与其他组别,然后显式改进组内差异以保留独特性。实验表明,我们在各种设置下显著优于基线(HICO-Det上的mAP提高9.18%)和最新技术(mAP提高3.59%)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accept to ICCV2025
Summary:
检测转换器已应用于人机交互(HOI)检测,提高了图像中人机交互三元组的定位和识别能力。本研究发现了一种名为“有毒兄弟”偏差的关键问题,阻碍了交互解码器的学习。众多相似但不同的HOI三元组在输入和输出方面都干扰甚至竞争交互解码器。为解决此问题,我们提出了两种新颖的偏差校正学习目标——“对比然后校准”和“合并然后拆分”,分别针对输入和输出视角。前者采样类似的不正确HOI三元组,并在强位置先验的指导下重建为正确的三元组。后者首先学习兄弟类别之间的共享特征,将它们与其他组区分开,然后显式地改进组内差异以保留唯一性。实验表明,我们在不同设置下显著优于基线(+9.18%的HICO-Det mAP)和最新技术(+3.59%的mAP)。
Key Takeaways:
- 检测转换器在人机交互检测中的应用提高了图像中三元组的定位和识别能力。
- 研究发现了一个名为“有毒兄弟”偏差的关键问题,影响交互解码器的学习。
- 相似但不同的HOI三元组在输入和输出方面对解码器造成干扰。
- 为解决“有毒兄弟”偏差问题,提出了两种新的偏差校正学习目标。
- “对比然后校准”方法通过采样并重建类似的不正确HOI三元组来校正偏差。
- “合并然后拆分”方法通过学习和区分兄弟类别及组内差异来提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

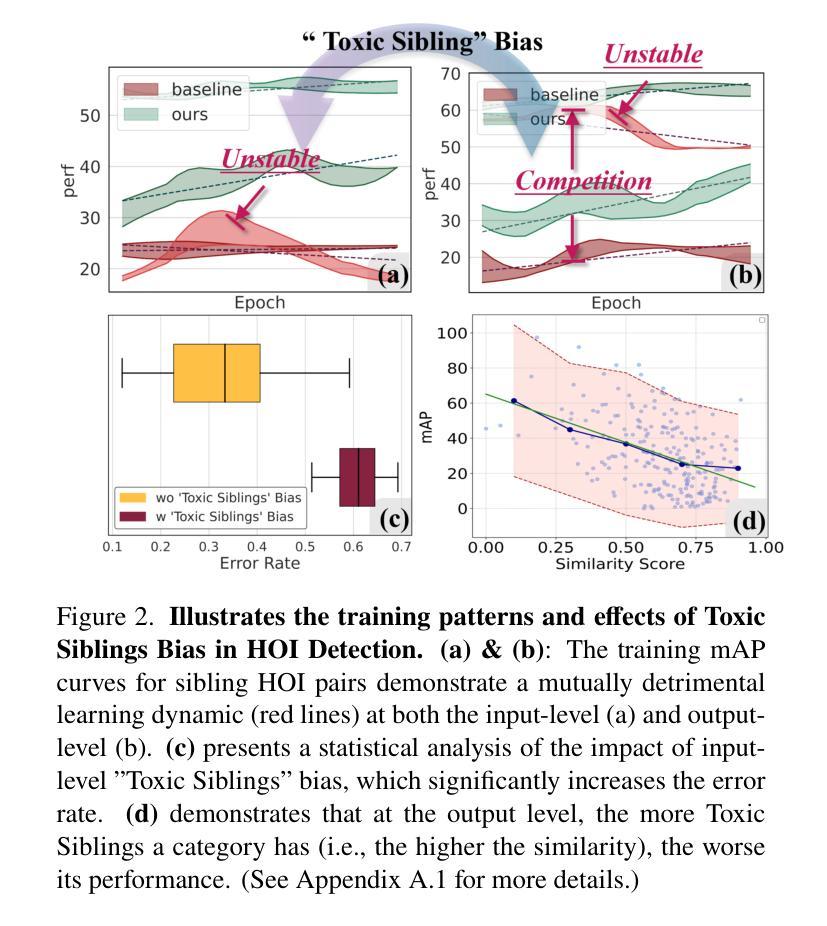
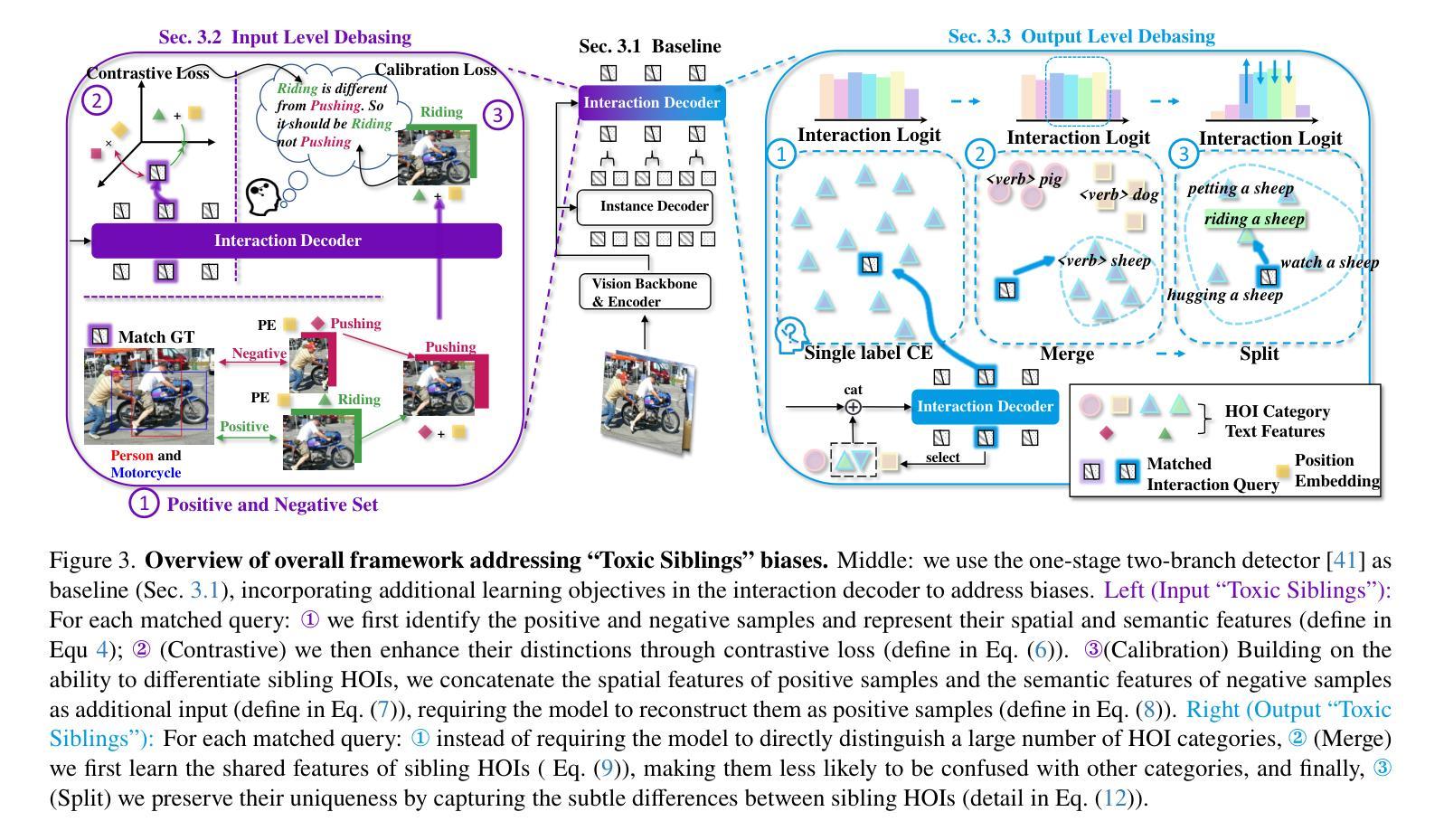
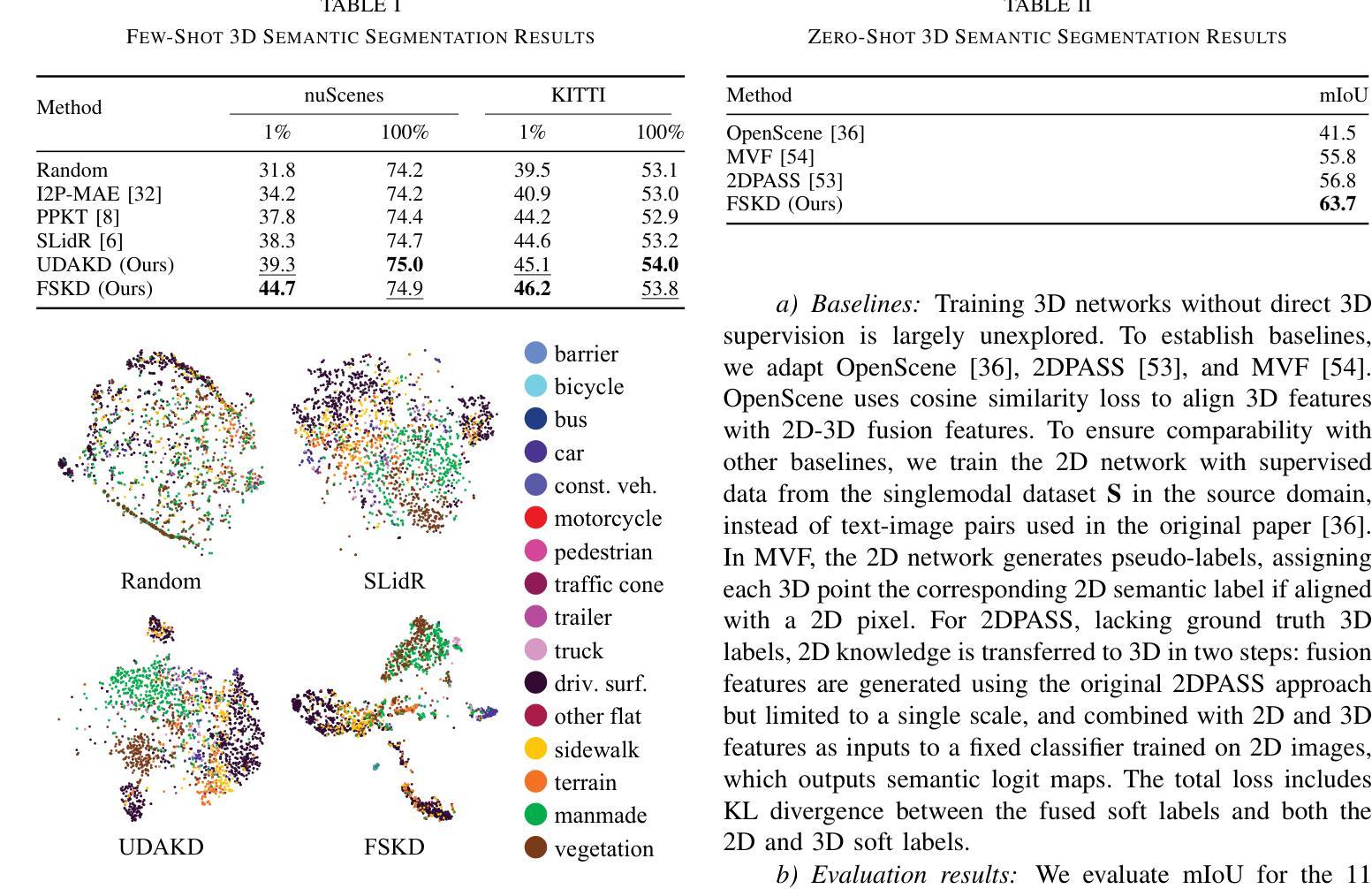
Domain Adaptation-Based Crossmodal Knowledge Distillation for 3D Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jialiang Kang, Jiawen Wang, Dingsheng Luo
Semantic segmentation of 3D LiDAR data plays a pivotal role in autonomous driving. Traditional approaches rely on extensive annotated data for point cloud analysis, incurring high costs and time investments. In contrast, realworld image datasets offer abundant availability and substantial scale. To mitigate the burden of annotating 3D LiDAR point clouds, we propose two crossmodal knowledge distillation methods: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Knowledge Distillation (UDAKD) and Feature and Semantic-based Knowledge Distillation (FSKD). Leveraging readily available spatio-temporally synchronized data from cameras and LiDARs in autonomous driving scenarios, we directly apply a pretrained 2D image model to unlabeled 2D data. Through crossmodal knowledge distillation with known 2D-3D correspondence, we actively align the output of the 3D network with the corresponding points of the 2D network, thereby obviating the necessity for 3D annotations. Our focus is on preserving modality-general information while filtering out modality-specific details during crossmodal distillation. To achieve this, we deploy self-calibrated convolution on 3D point clouds as the foundation of our domain adaptation module. Rigorous experimentation validates the effectiveness of our proposed methods, consistently surpassing the performance of state-of-the-art approaches in the field.
在自动驾驶中,3D激光雷达数据的语义分割扮演着至关重要的角色。传统方法依赖于大量的点云分析标注数据,需要大量的时间和资金投入。相比之下,现实世界图像数据集则更为丰富且规模庞大。为了减轻对3D激光雷达点云的标注负担,我们提出了两种跨模态知识蒸馏方法:无监督域自适应知识蒸馏(UDAKD)和基于特征和语义的知识蒸馏(FSKD)。我们利用自动驾驶场景中摄像头和激光雷达的时空同步数据,直接将预训练的2D图像模型应用于无标签的2D数据。通过具有已知2D-3D对应关系的跨模态知识蒸馏,我们主动将3D网络的输出与对应的2D网络的点对齐,从而避免了使用昂贵的3D注释的需要。我们的重点是在跨模态蒸馏过程中保留模态通用信息,同时过滤掉模态特定的细节。为了实现这一点,我们在三维点云上部署了自校准卷积作为我们的域自适应模块的基础。严格的实验验证了我们的方法的有效性,在相关领域内超越了最先进的方法的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICRA 2025
Summary
本文探讨了在自动驾驶领域中,利用语义分割对3D激光雷达数据进行处理的重要性。传统方法需要大量标注数据来进行点云分析,成本高昂且耗时。为减轻标注负担,本文提出了两种跨模态知识蒸馏方法:无监督域适应知识蒸馏(UDAKD)和特征语义知识蒸馏(FSKD)。利用自主驾驶场景中相机和激光雷达的时空同步数据,将预训练的2D图像模型直接应用于无标签的2D数据。通过跨模态知识蒸馏与已知的2D-3D对应关系,使3D网络的输出与对应的2D网络点对齐,无需3D标注。研究重点是保留模态通用信息,过滤掉模态特定细节,在跨模态蒸馏中部署自校准卷积在3D点云上作为域适应模块的基础。实验证明,所提方法效果显著,超越现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在自动驾驶中的3D激光雷达数据处理扮演重要角色。
- 传统方法依赖大量标注数据,成本高且耗时。
- 提出两种跨模态知识蒸馏方法:UDAKD和FSKD以减轻标注负担。
- 利用时空同步的相机和激光雷达数据,应用预训练的2D图像模型于无标签的2D数据。
- 通过跨模态知识蒸馏实现与已知的2D-3D对应关系对齐输出,无需额外的3D标注。
- 研究重点在于保留模态通用信息并过滤掉特定细节,部署自校准卷积于3D点云为基础构建域适应模块。
点此查看论文截图

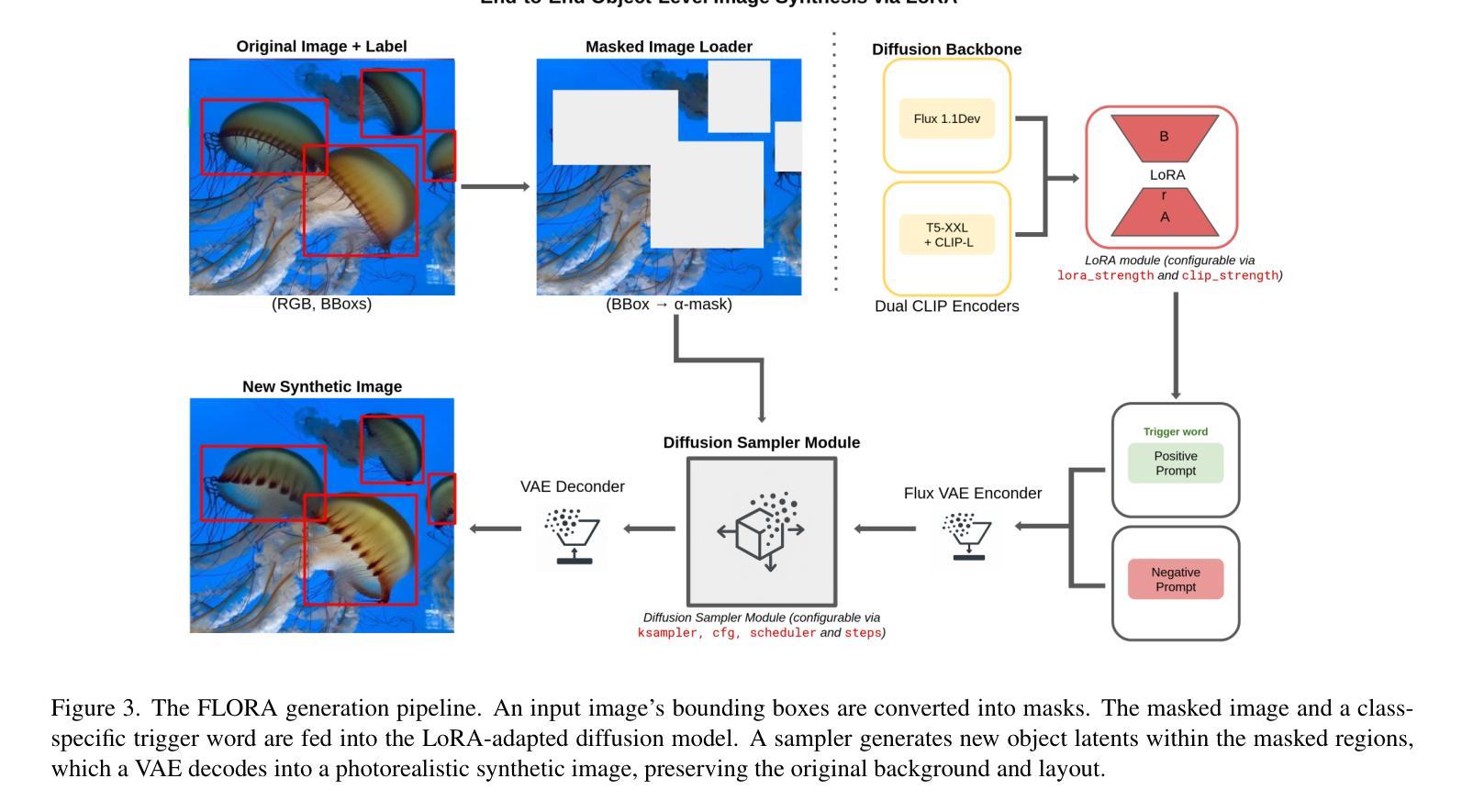
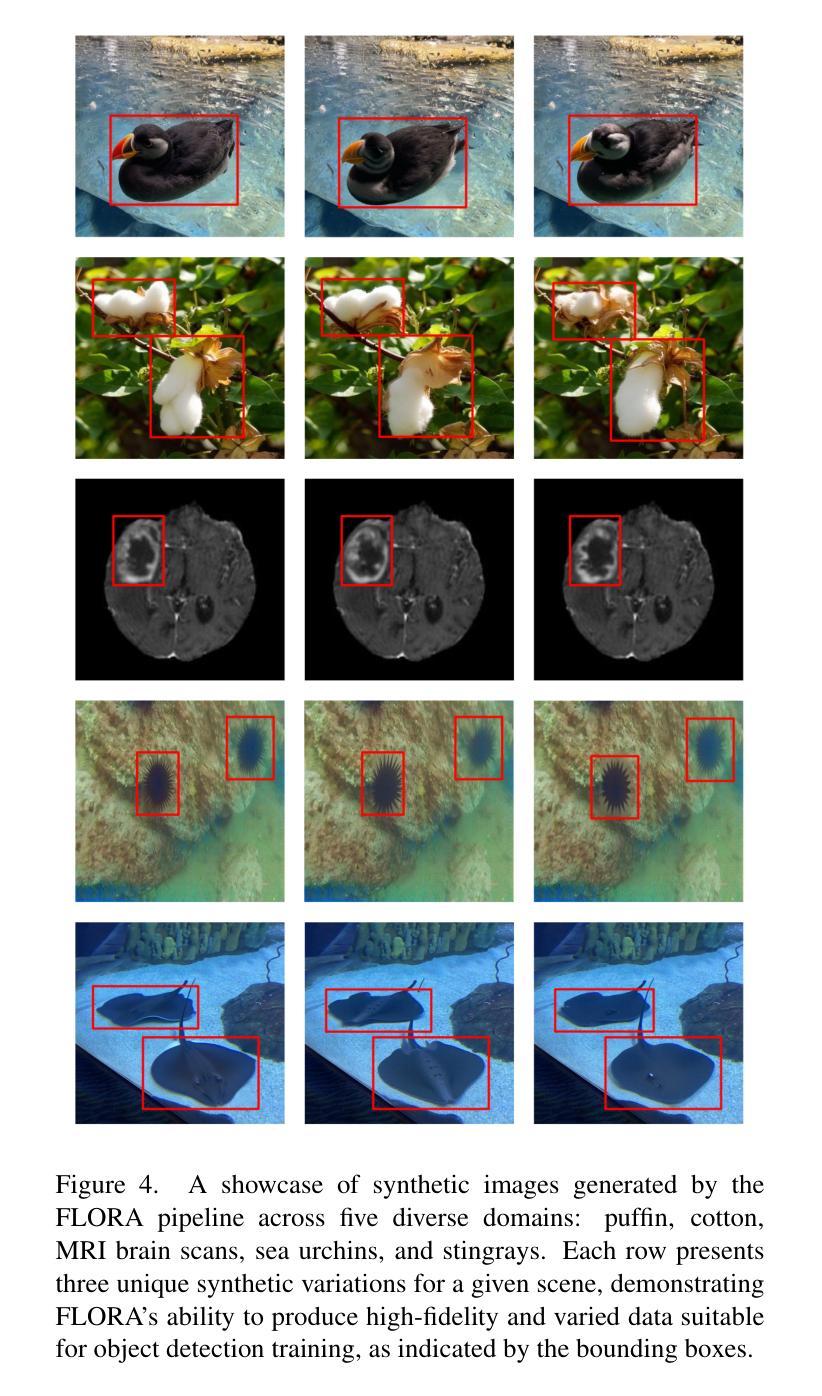
FLORA: Efficient Synthetic Data Generation for Object Detection in Low-Data Regimes via finetuning Flux LoRA
Authors:Alvaro Patricio, Atabak Dehban, Rodrigo Ventura
Recent advances in diffusion-based generative models have demonstrated significant potential in augmenting scarce datasets for object detection tasks. Nevertheless, most recent models rely on resource-intensive full fine-tuning of large-scale diffusion models, requiring enterprise-grade GPUs (e.g., NVIDIA V100) and thousands of synthetic images. To address these limitations, we propose Flux LoRA Augmentation (FLORA), a lightweight synthetic data generation pipeline. Our approach uses the Flux 1.1 Dev diffusion model, fine-tuned exclusively through Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). This dramatically reduces computational requirements, enabling synthetic dataset generation with a consumer-grade GPU (e.g., NVIDIA RTX 4090). We empirically evaluate our approach on seven diverse object detection datasets. Our results demonstrate that training object detectors with just 500 synthetic images generated by our approach yields superior detection performance compared to models trained on 5000 synthetic images from the ODGEN baseline, achieving improvements of up to 21.3% in mAP@.50:.95. This work demonstrates that it is possible to surpass state-of-the-art performance with far greater efficiency, as FLORA achieves superior results using only 10% of the data and a fraction of the computational cost. This work demonstrates that a quality and efficiency-focused approach is more effective than brute-force generation, making advanced synthetic data creation more practical and accessible for real-world scenarios.
近期基于扩散的生成模型的新进展已经显示出在增强稀缺数据集以进行目标检测任务方面的巨大潜力。然而,大多数最新模型依赖于大规模扩散模型的全精细调整,这需要企业级GPU(例如NVIDIA V100)和数千张合成图像,计算资源消耗大。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了Flux LoRA Augmentation(FLORA),这是一个轻量级的合成数据生成管道。我们的方法使用Flux 1.1 Dev扩散模型,仅通过低秩适应(LoRA)进行微调。这大大降低了计算要求,使用消费级GPU(例如NVIDIA RTX 4090)即可生成合成数据集。我们在七个不同的目标检测数据集上实证评估了我们的方法。结果表明,仅使用我们的方法生成500张合成图像训练目标检测器,其检测性能优于使用ODGEN基线生成的5000张合成图像训练的模型,在mAP@.50:.95指标上提高了高达21.3%。这项工作表明,以更高的效率超越最新技术性能是可能的,因为FLORA仅使用10%的数据和一小部分计算成本就取得了优越的结果。这项工作表明,以质量和效率为中心的方法比暴力生成更有效,使得高级合成数据的创建在现实世界场景中更加实用和可访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散的生成模型在对象检测任务的稀缺数据集增强方面展现出巨大潜力。针对大规模扩散模型的全面微调所带来的资源密集问题,提出Flux LoRA Augmentation(FLORA)轻量级合成数据生成管道。该方法使用Flux 1.1 Dev扩散模型,仅通过Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)进行微调,显著降低计算要求,可在消费级GPU上生成合成数据集。在七个不同的对象检测数据集上的实证评估表明,仅使用500张由该方法生成的合成图像训练的物体检测器,其检测性能优于使用ODGEN基线生成的5000张合成图像的模型,提高了高达21.3%的mAP@.50:.95。此工作证明了以质量和效率为导向的方法比暴力生成更有效,使高级合成数据创建在现实世界场景中更加实用和可访问。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散生成模型在对象检测数据集增强方面具有显著潜力。
- Flux LoRA Augmentation (FLORA)是一种轻量级的合成数据生成方法。
- FLORA使用Flux 1.1 Dev扩散模型并结合Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)进行微调,降低计算需求。
- FLORA可在消费级GPU上实施。
- 在七个对象检测数据集上的评估显示,FLORA生成的少量合成图像训练的检测器性能优越。
- FLORA方法实现了高效的数据使用,仅使用10%的数据和较少的计算成本就达到了优越的结果。
点此查看论文截图

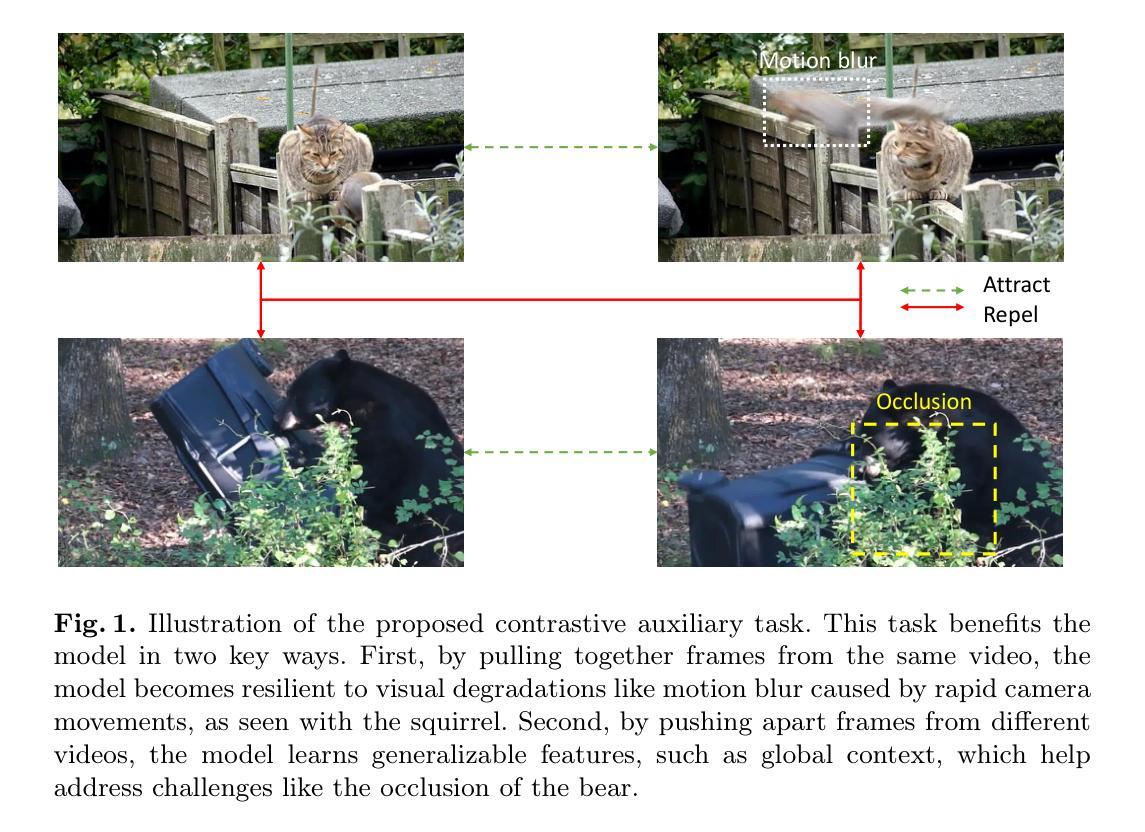
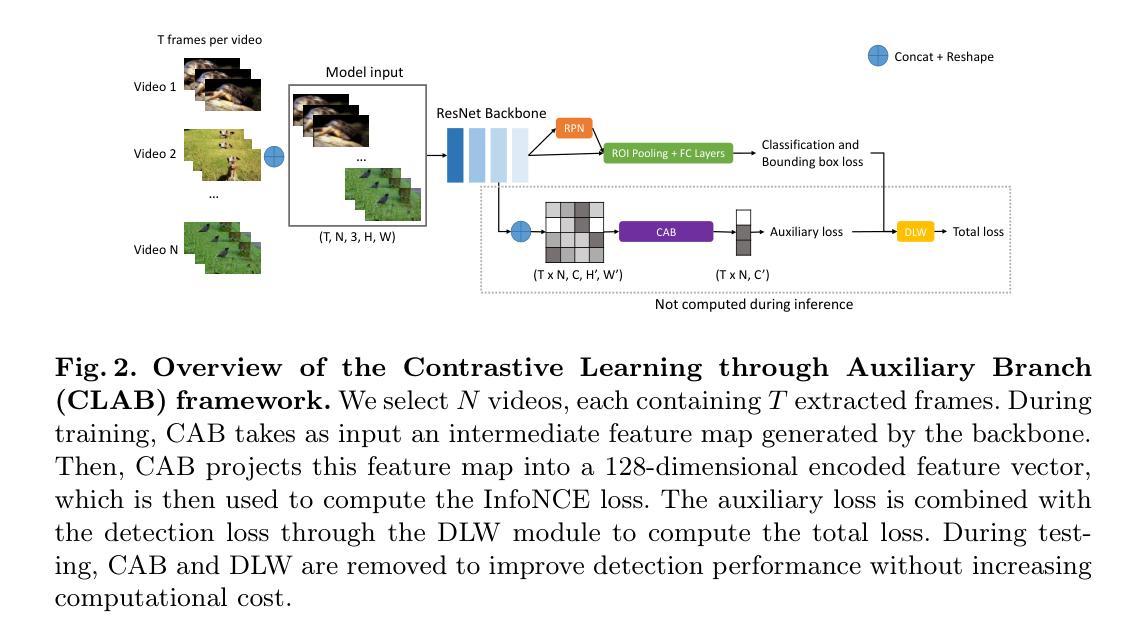
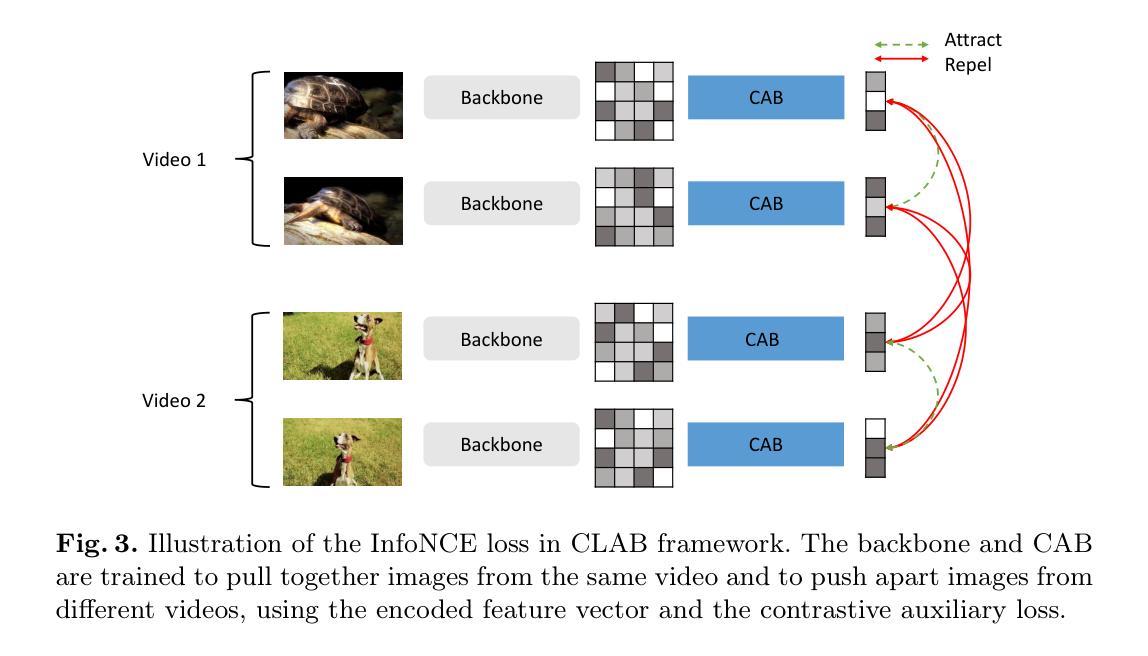
Contrastive Learning through Auxiliary Branch for Video Object Detection
Authors:Lucas Rakotoarivony
Video object detection is a challenging task because videos often suffer from image deterioration such as motion blur, occlusion, and deformable shapes, making it significantly more difficult than detecting objects in still images. Prior approaches have improved video object detection performance by employing feature aggregation and complex post-processing techniques, though at the cost of increased computational demands. To improve robustness to image degradation without additional computational load during inference, we introduce a straightforward yet effective Contrastive Learning through Auxiliary Branch (CLAB) method. First, we implement a constrastive auxiliary branch using a contrastive loss to enhance the feature representation capability of the video object detector’s backbone. Next, we propose a dynamic loss weighting strategy that emphasizes auxiliary feature learning early in training while gradually prioritizing the detection task as training converges. We validate our approach through comprehensive experiments and ablation studies, demonstrating consistent performance gains. Without bells and whistles, CLAB reaches a performance of 84.0% mAP and 85.2% mAP with ResNet-101 and ResNeXt-101, respectively, on the ImageNet VID dataset, thus achieving state-of-the-art performance for CNN-based models without requiring additional post-processing methods.
视频目标检测是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为视频经常受到图像退化问题的影响,如运动模糊、遮挡和可变形形状,这使得它比在静止图像中检测目标更加困难。先前的方法通过采用特征聚合和复杂的后处理技术提高了视频目标检测的性能,但增加了计算需求。为了提高对图像退化的鲁棒性,在推理过程中不需要增加计算负载,我们引入了一种简单有效的通过辅助分支进行对比学习(CLAB)的方法。首先,我们使用对比损失实现了一个对比辅助分支,以增强视频目标检测器主干特征表示的能力。接下来,我们提出了一种动态损失加权策略,该策略强调在早期训练阶段学习辅助特征,随着训练的收敛,逐渐优先重视检测任务。我们通过全面的实验和消融研究验证了我们的方法,证明了其持续的性能提升。没有额外的修饰和附加组件,CLAB在ImageNet VID数据集上使用ResNet-101和ResNeXt-101分别达到了84.0%和85.2%的mAP性能,从而在不需要额外后处理方法的情况下,实现了基于CNN的模型的最先进性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted paper for ACIVS 2025
Summary
视频目标检测任务具有挑战性,因为视频常常存在图像退化问题,如运动模糊、遮挡和变形等。本文引入了一种简单有效的对比学习辅助分支(CLAB)方法,以提高视频对象检测器对图像退化的鲁棒性,同时不增加推理过程中的计算负担。通过实施对比辅助分支和使用动态损失加权策略,该方法在训练初期强调辅助特征学习,随着训练的收敛逐渐侧重于检测任务。在ImageNet VID数据集上,CLAB方法达到了使用ResNet-101和ResNeXt-101时的84.0%和85.2%的mAP,实现了基于CNN的模型的最佳性能,无需额外的后处理方法。
Key Takeaways
- 视频目标检测面临图像退化挑战,如运动模糊、遮挡和变形。
- 对比学习辅助分支(CLAB)方法通过增强特征表示能力提高视频对象检测性能。
- CLAB方法实施了一个对比辅助分支和动态损失加权策略,以优化训练过程。
- CLAB方法在ImageNet VID数据集上实现了卓越性能,使用ResNet-101和ResNeXt-101时分别达到84.0%和85.2%的mAP。
- CLAB方法不增加额外的计算负担,且不需要额外的后处理方法。
点此查看论文截图

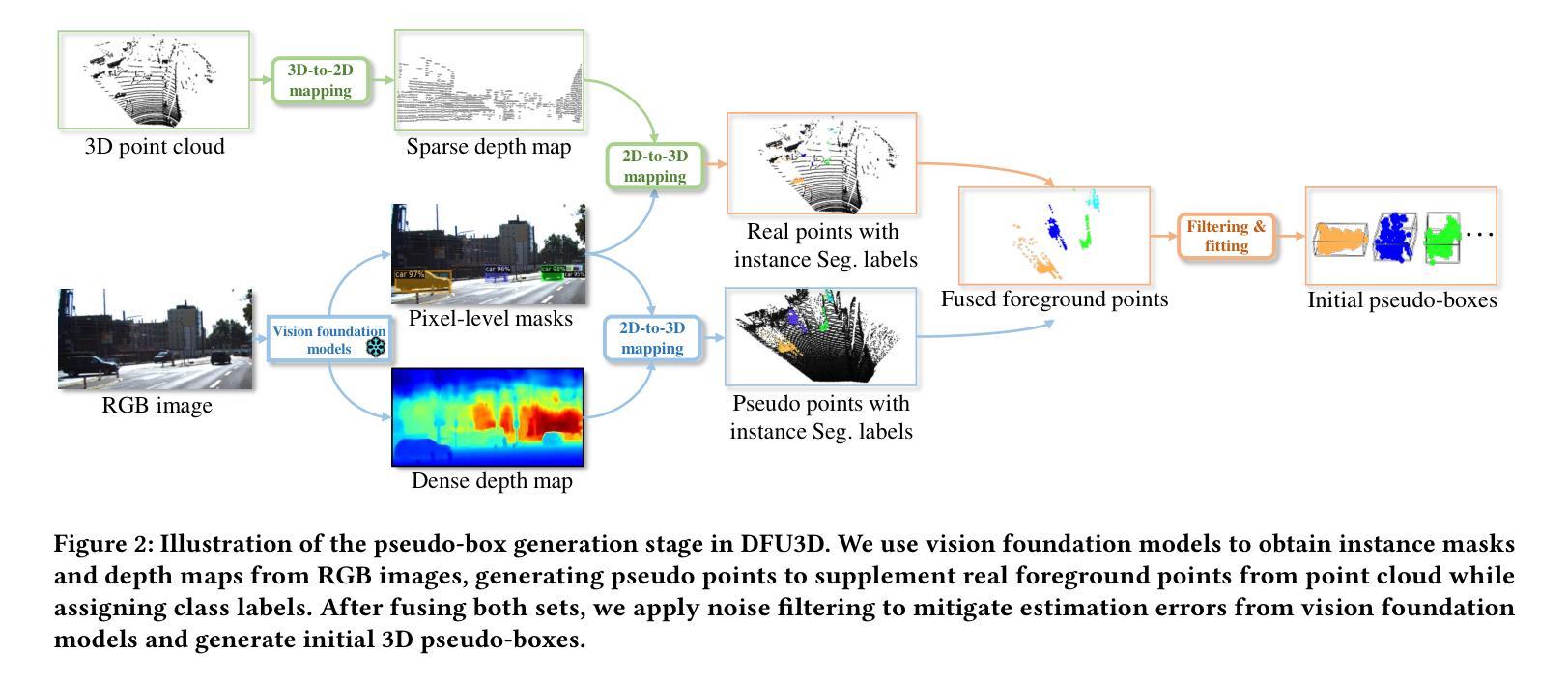
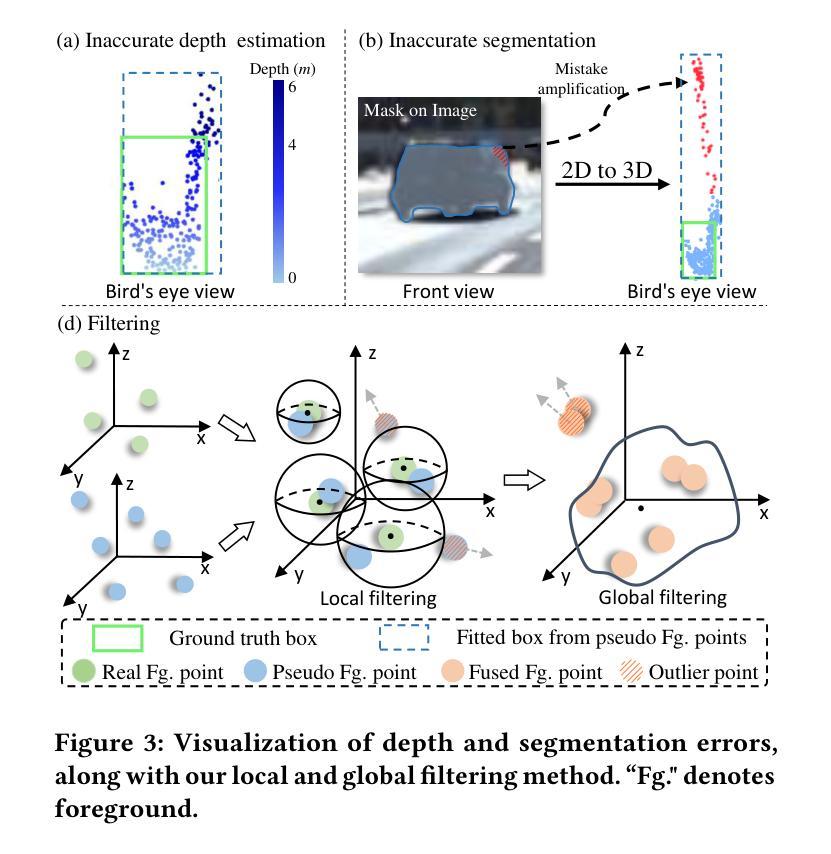
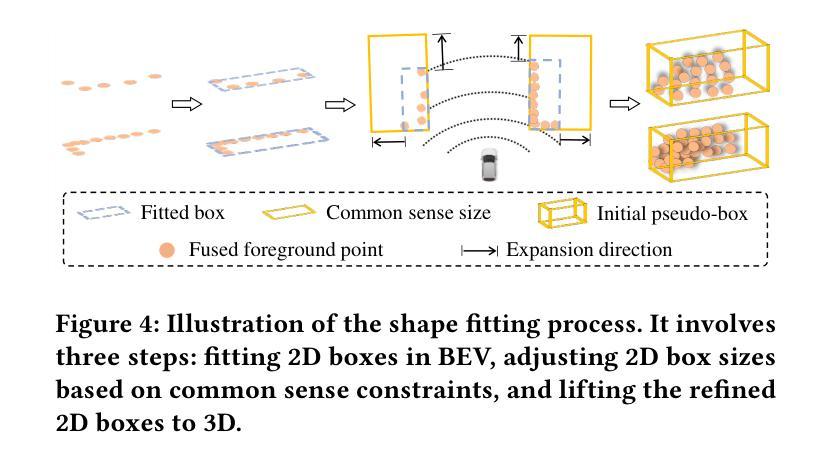
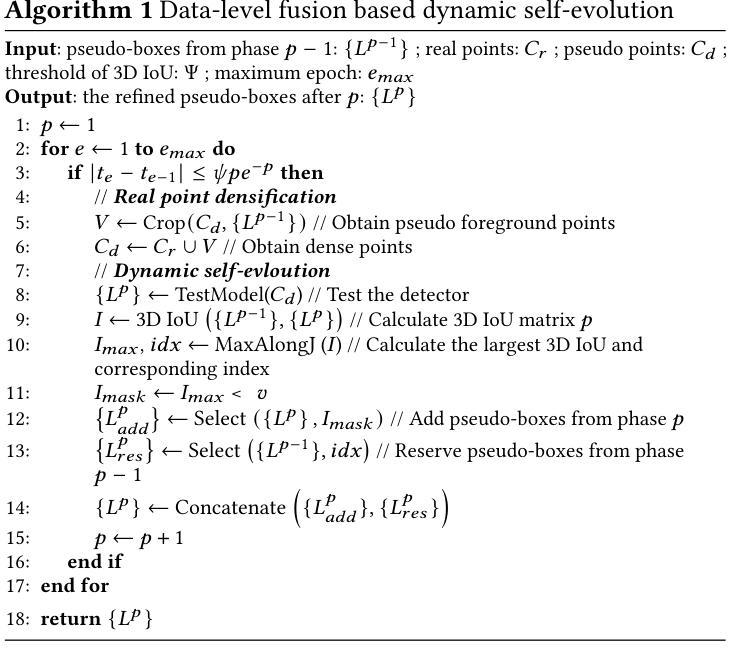
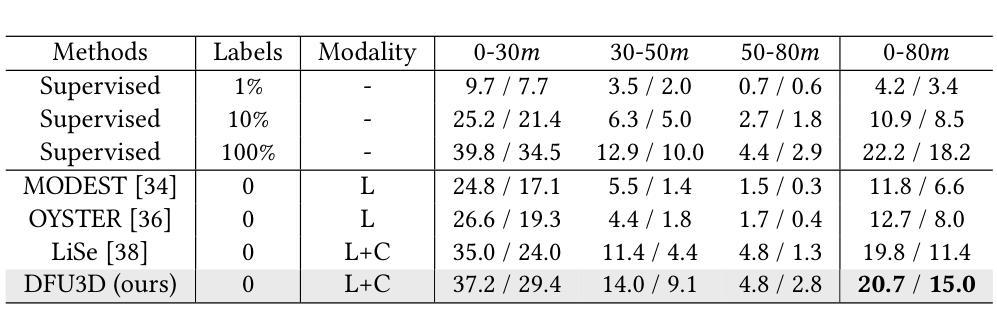
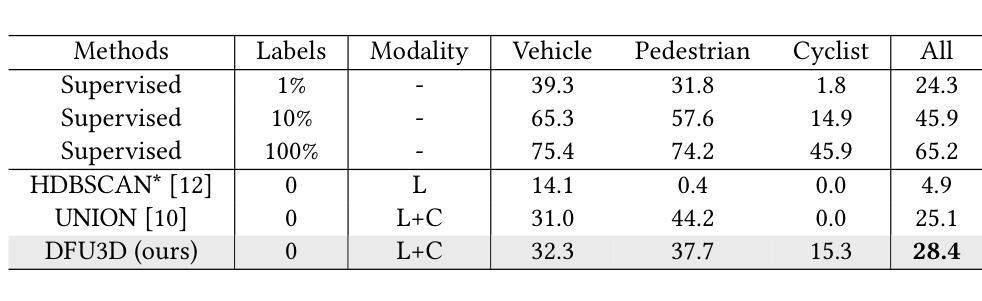
Enhancing Pseudo-Boxes via Data-Level LiDAR-Camera Fusion for Unsupervised 3D Object Detection
Authors:Mingqian Ji, Jian Yang, Shanshan Zhang
Existing LiDAR-based 3D object detectors typically rely on manually annotated labels for training to achieve good performance. However, obtaining high-quality 3D labels is time-consuming and labor-intensive. To address this issue, recent works explore unsupervised 3D object detection by introducing RGB images as an auxiliary modal to assist pseudo-box generation. However, these methods simply integrate pseudo-boxes generated by LiDAR point clouds and RGB images. Yet, such a label-level fusion strategy brings limited improvements to the quality of pseudo-boxes, as it overlooks the complementary nature in terms of LiDAR and RGB image data. To overcome the above limitations, we propose a novel data-level fusion framework that integrates RGB images and LiDAR data at an early stage. Specifically, we utilize vision foundation models for instance segmentation and depth estimation on images and introduce a bi-directional fusion method, where real points acquire category labels from the 2D space, while 2D pixels are projected onto 3D to enhance real point density. To mitigate noise from depth and segmentation estimations, we propose a local and global filtering method, which applies local radius filtering to suppress depth estimation errors and global statistical filtering to remove segmentation-induced outliers. Furthermore, we propose a data-level fusion based dynamic self-evolution strategy, which iteratively refines pseudo-boxes under a dense representation, significantly improving localization accuracy. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that the detector trained by our method significantly outperforms that trained by previous state-of-the-art methods with 28.4$%$ mAP on the nuScenes validation benchmark.
现有的基于激光雷达的3D目标检测器通常依赖于手动标注的标签进行训练,以实现良好的性能。然而,获取高质量的3D标签是耗时且劳动密集型的。为了解决这一问题,最近的研究通过引入RGB图像作为辅助模式来辅助伪框生成,从而探索了无监督的3D目标检测。然而,这些方法只是将激光雷达点云和RGB图像生成的伪框进行简单整合。然而,这种标签层面的融合策略对伪框质量的提高有限,因为它忽视了激光雷达和RGB图像数据之间的互补性。为了克服上述局限性,我们提出了一种新的数据层面融合框架,该框架在早期阶段就将RGB图像和激光雷达数据进行整合。具体来说,我们利用视觉基础模型对图像进行实例分割和深度估计,并引入了一种双向融合方法,其中真实点从二维空间获取类别标签,而二维像素则投影到三维以增强真实点的密度。为了减轻深度和分割估计中的噪声,我们提出了一种局部和全局滤波方法,采用局部半径滤波来抑制深度估计误差,全局统计滤波来去除由分割引起的异常值。此外,我们提出了一种基于数据层面融合的动态自演化策略,该策略在密集表示下迭代优化伪框,显著提高了定位精度。在nuScenes数据集上的大量实验表明,采用我们方法训练的检测器在nuScenes验证基准测试上的mAP为28.4%,显著优于采用之前最先进方法训练的检测器。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ACM MM 2025
Summary
基于激光雷达的3D对象检测通常依赖手动标注的标签进行训练以达到良好的性能,但获取高质量的3D标签耗时耗力。为解决这个问题,近期研究尝试引入RGB图像作为辅助模态以促进伪箱生成,但简单融合伪箱数据与RGB图像效果有限。本文提出一种新型数据级别融合框架,在初期阶段融合RGB图像和激光雷达数据。利用视觉基础模型进行图像实例分割和深度估计,引入双向融合方法,实现2D点与3D点的相互标注增强。通过局部和全局滤波方法减少深度估计和分割引起的噪声,并提出基于数据级别融合的动态自演化策略,迭代优化伪箱在密集表示下的定位精度。在nuScenes数据集上的实验表明,本文方法训练的检测器较先前顶尖方法有明显的性能提升,mAP提高至28.4%。
Key Takeaways
- 现有基于激光雷达的3D对象检测依赖手动标注,成本高昂且耗时。
- 引入RGB图像作为辅助模态的方法虽然出现,但融合策略有限,改善不明显。
- 本文提出一种新型数据级别融合框架,在初期阶段结合RGB图像和激光雷达数据。
- 利用视觉基础模型进行实例分割和深度估计,并采用双向融合方法增强2D与3D点的标注。
- 通过局部和全局滤波减少估计误差和噪声,并引入动态自演化策略迭代优化伪箱定位精度。
点此查看论文截图

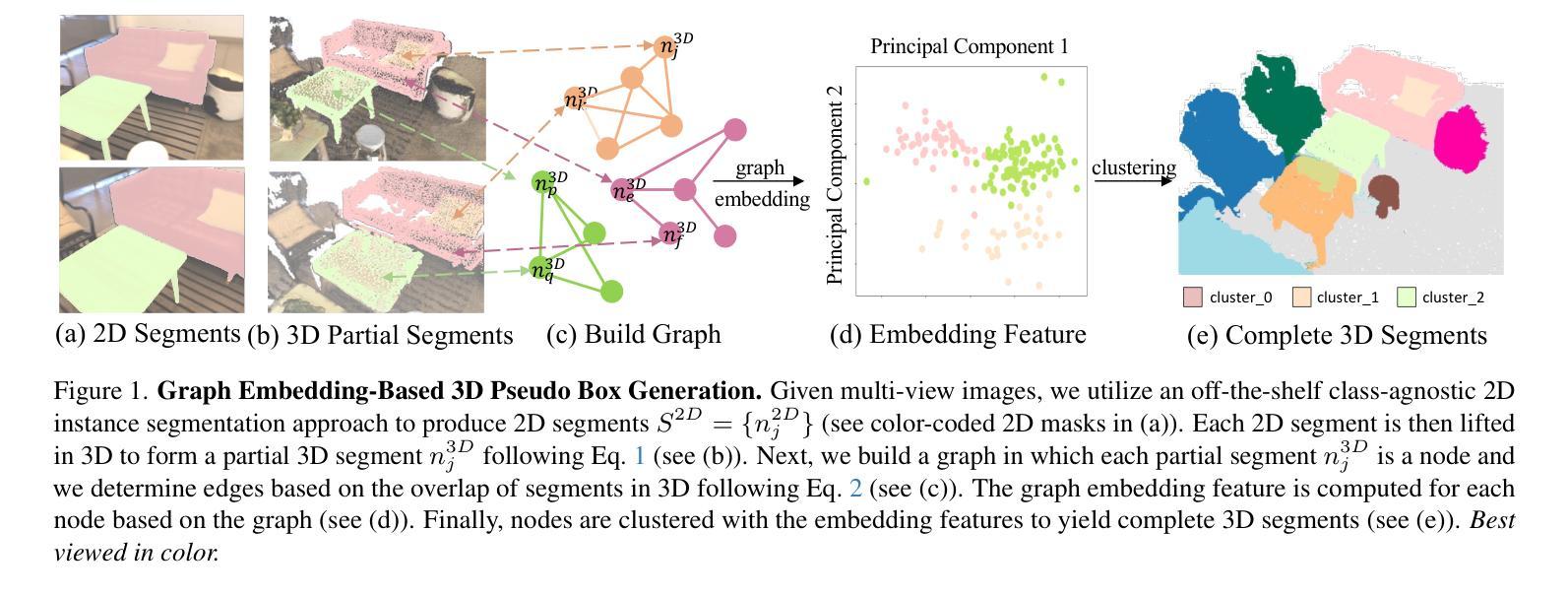
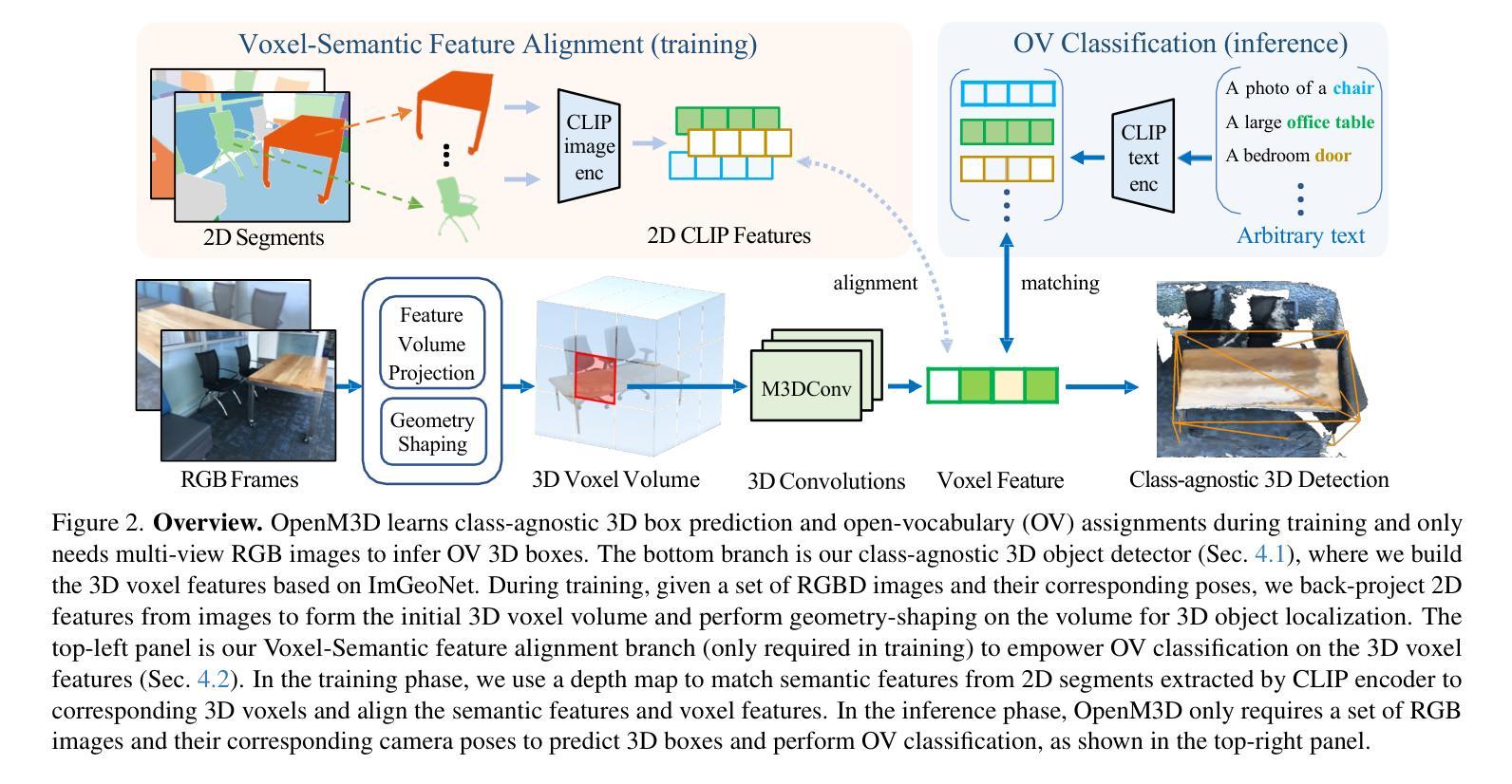
OpenM3D: Open Vocabulary Multi-view Indoor 3D Object Detection without Human Annotations
Authors:Peng-Hao Hsu, Ke Zhang, Fu-En Wang, Tao Tu, Ming-Feng Li, Yu-Lun Liu, Albert Y. C. Chen, Min Sun, Cheng-Hao Kuo
Open-vocabulary (OV) 3D object detection is an emerging field, yet its exploration through image-based methods remains limited compared to 3D point cloud-based methods. We introduce OpenM3D, a novel open-vocabulary multi-view indoor 3D object detector trained without human annotations. In particular, OpenM3D is a single-stage detector adapting the 2D-induced voxel features from the ImGeoNet model. To support OV, it is jointly trained with a class-agnostic 3D localization loss requiring high-quality 3D pseudo boxes and a voxel-semantic alignment loss requiring diverse pre-trained CLIP features. We follow the training setting of OV-3DET where posed RGB-D images are given but no human annotations of 3D boxes or classes are available. We propose a 3D Pseudo Box Generation method using a graph embedding technique that combines 2D segments into coherent 3D structures. Our pseudo-boxes achieve higher precision and recall than other methods, including the method proposed in OV-3DET. We further sample diverse CLIP features from 2D segments associated with each coherent 3D structure to align with the corresponding voxel feature. The key to training a highly accurate single-stage detector requires both losses to be learned toward high-quality targets. At inference, OpenM3D, a highly efficient detector, requires only multi-view images for input and demonstrates superior accuracy and speed (0.3 sec. per scene) on ScanNet200 and ARKitScenes indoor benchmarks compared to existing methods. We outperform a strong two-stage method that leverages our class-agnostic detector with a ViT CLIP-based OV classifier and a baseline incorporating multi-view depth estimator on both accuracy and speed.
开放词汇(OV)3D对象检测是一个新兴领域,与基于3D点云的检测方法相比,基于图像的方法的探索仍然有限。我们介绍了OpenM3D,这是一种新型开放词汇的多视角室内3D对象检测器,无需人工注释即可进行训练。特别是,OpenM3D是一个单阶段检测器,适应于从ImGeoNet模型诱导的2Dvoxel特征。为了支持OV,它与类无关的3D定位损失和高质量的3D伪盒一起联合训练,以及与需要各种预训练CLIP特征的voxel语义对齐损失。我们遵循OV-3DET的训练设置,提供有姿态的RGB-D图像,但不可用3D框或类的手工注释。我们提出了一种使用图嵌入技术的3D伪盒生成方法,将2D段组合成连贯的3D结构。我们的伪盒子在精度和召回率方面优于其他方法,包括OV-3DET中提出的方法。我们进一步从与每个连贯的3D结构相关的2D段中采样各种CLIP特征,以与相应的voxel特征对齐。训练高度准确的单阶段检测器的关键是需要同时学习这两种损失以达到高质量目标。在推理阶段,OpenM3D是一种高效的检测器,仅需要多视角图像作为输入,并在ScanNet200和ARKitScenes室内基准测试上表现出卓越的性能和速度(每秒0.3秒)。我们在使用基于ViT CLIP的OV分类器融入我们的类无关检测器和多视角深度估计器的强大两阶段方法上,在准确性和速度方面都表现出超越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV2025
Summary
本文介绍了OpenM3D,一种无需人工标注的开放词汇室内3D目标检测器。它采用单阶段检测器,通过ImGeoNet模型诱导的二维体素特征进行训练。为支持开放词汇,它与类无关的3D定位损失和高质量的三维伪装箱以及体素语义对齐损失进行联合训练。提出一种使用图嵌入技术的三维伪装箱生成方法,将二维片段组合成连贯的三维结构。在ScanNet200和ARKitScenes室内基准测试中,与现有方法相比,OpenM3D表现出更高的准确性和速度。本文还探讨了一种结合单阶段检测器、基于ViT CLIP的开放词汇分类器和多视图深度估计器的基准方案。此方法能进一步提升准确性与速度。总结为一句话即:“研究团队提出无需人工标注的开放式室内三维目标检测器OpenM3D,基于图嵌入技术和多种特征对齐技术,提高了检测精度和速度。”
Key Takeaways
- OpenM3D是一种无需人工标注的开放词汇室内三维目标检测器。
- OpenM3D使用单阶段检测器结合二维体素特征进行训练。它联合训练支持开放词汇技术并与类无关的3D定位损失以及体素语义对齐损失进行结合。
- 提出一种利用图嵌入技术生成三维伪装箱的方法,该方法结合了二维片段形成连贯的三维结构,并实现了较高的精确度和召回率。
- OpenM3D利用多种CLIP特征来对齐每个连贯的三维结构对应的体素特征。这一关键步骤有助于提高单阶段检测器的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

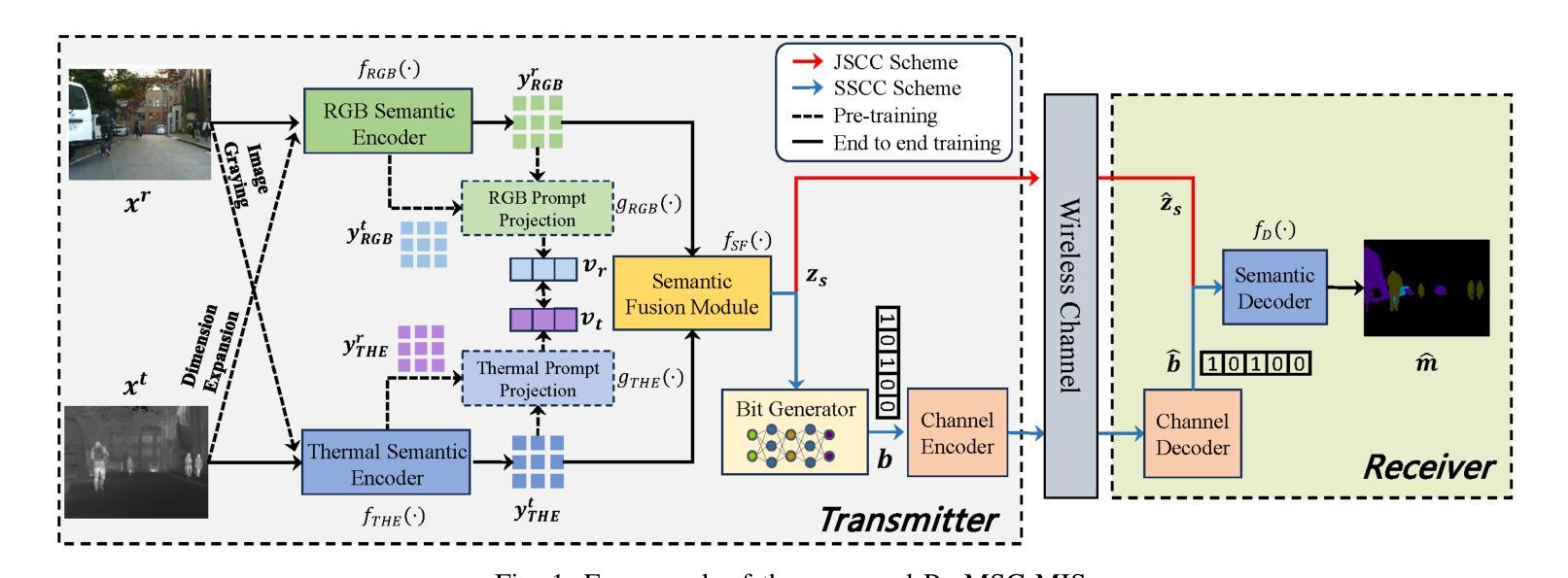
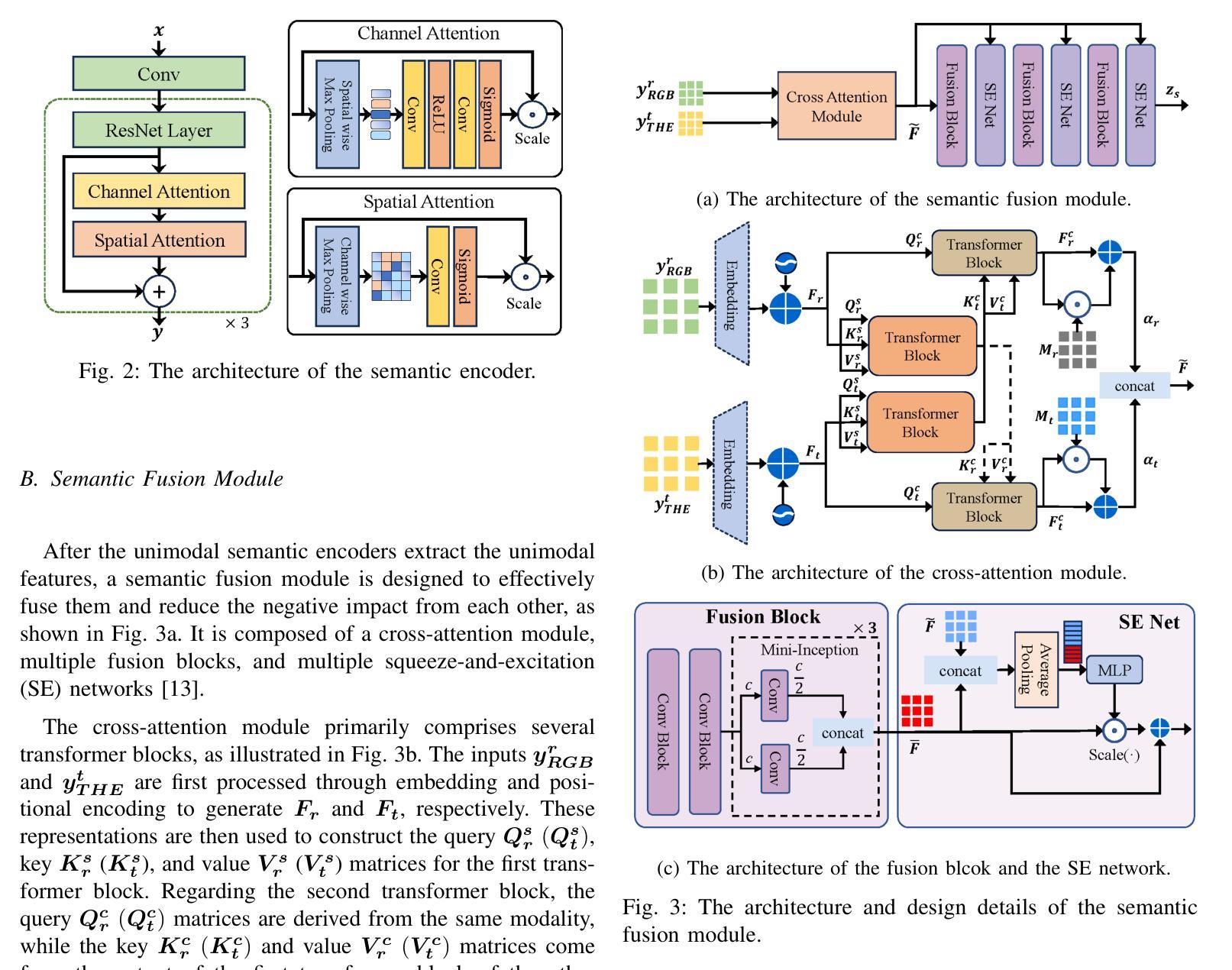
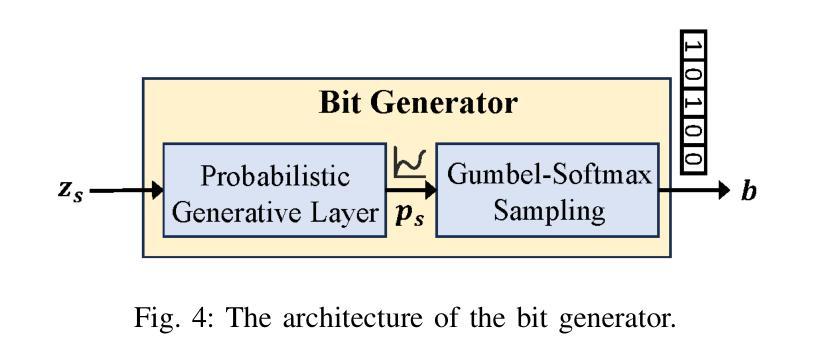
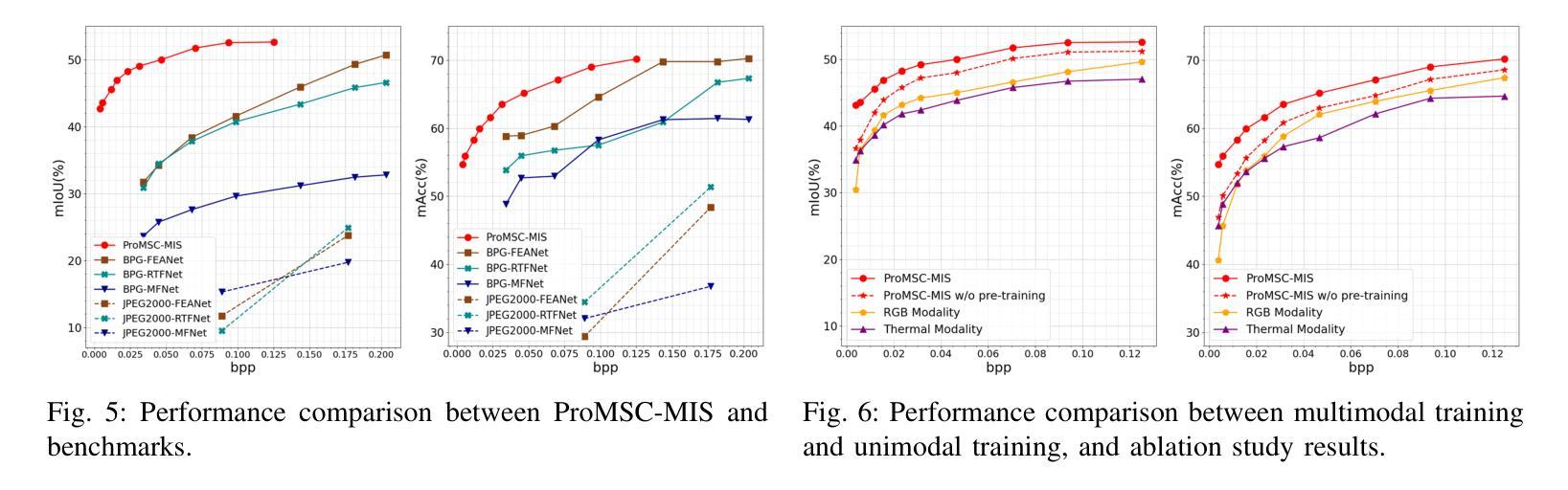
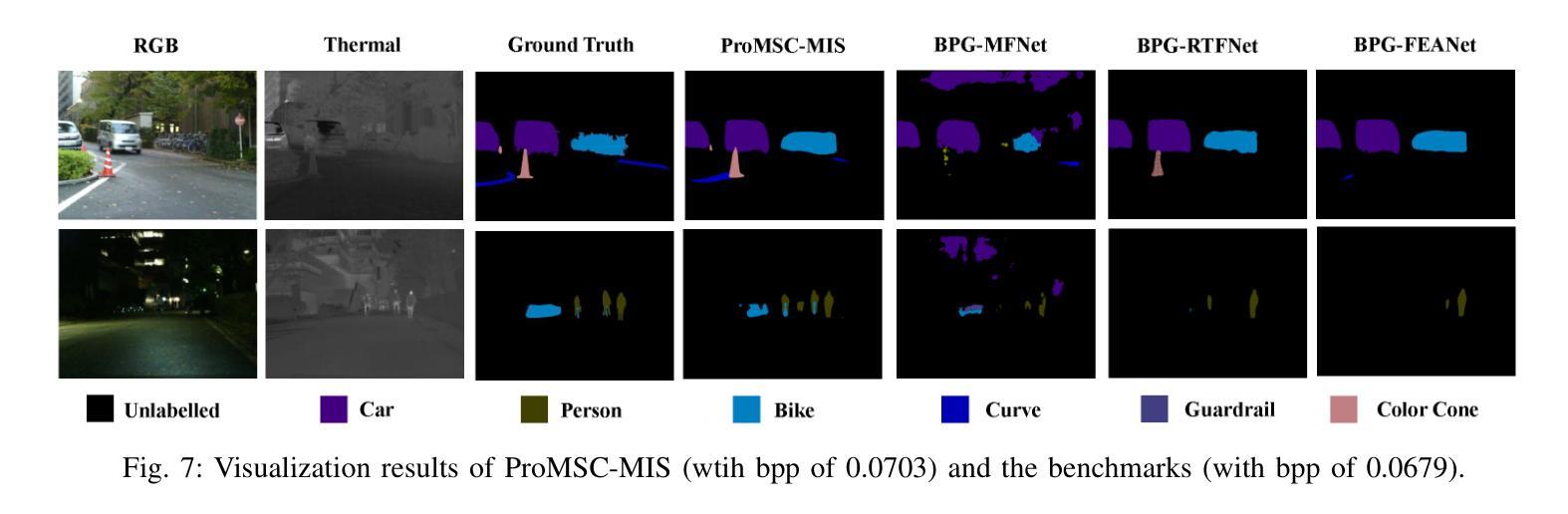
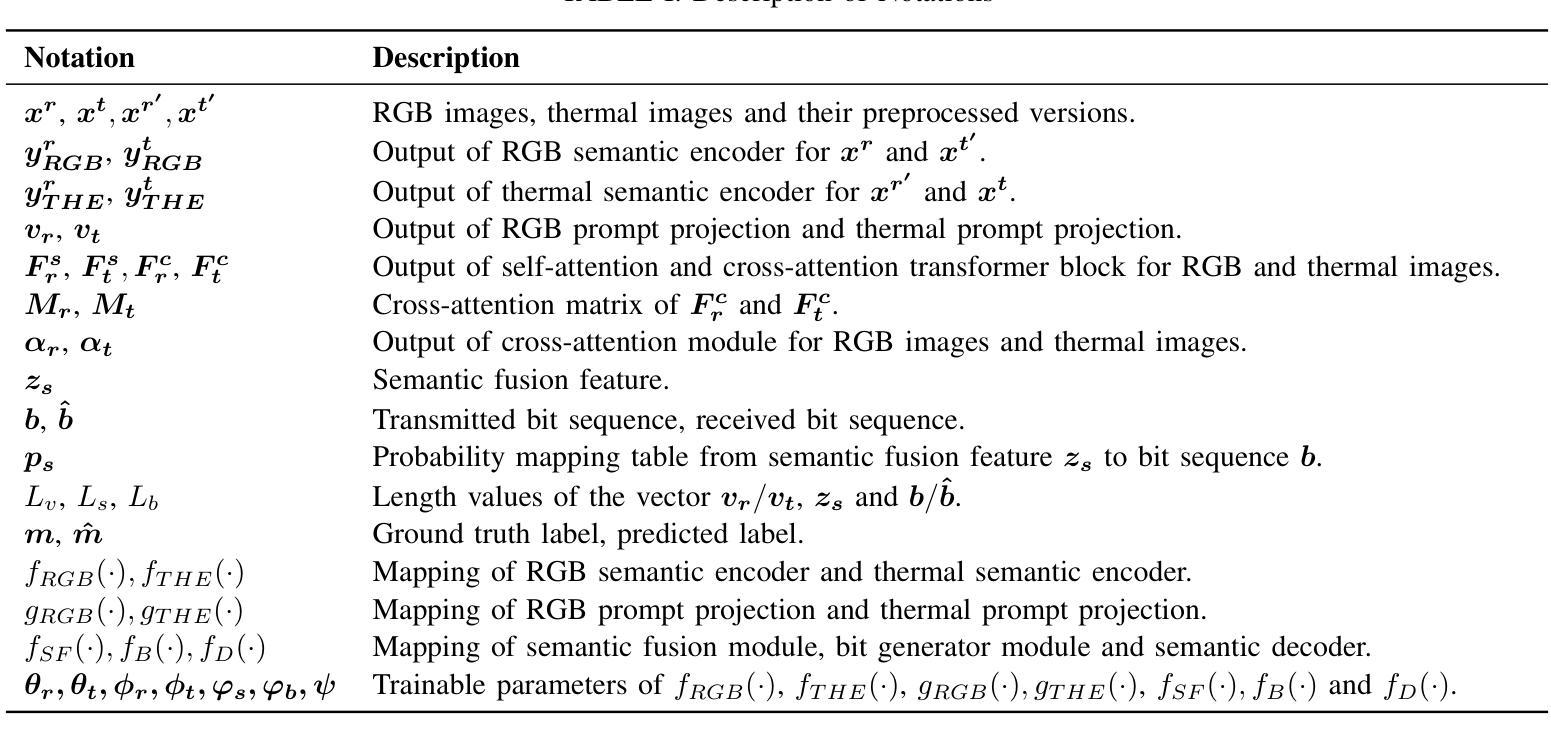
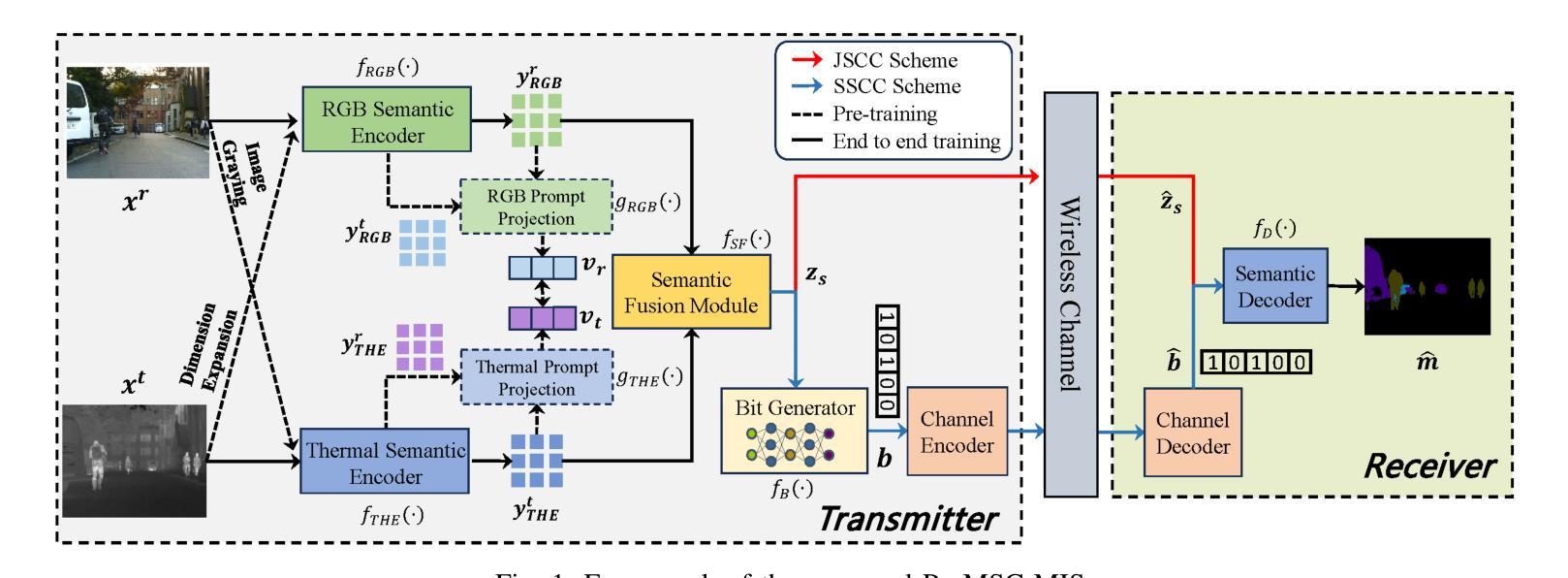
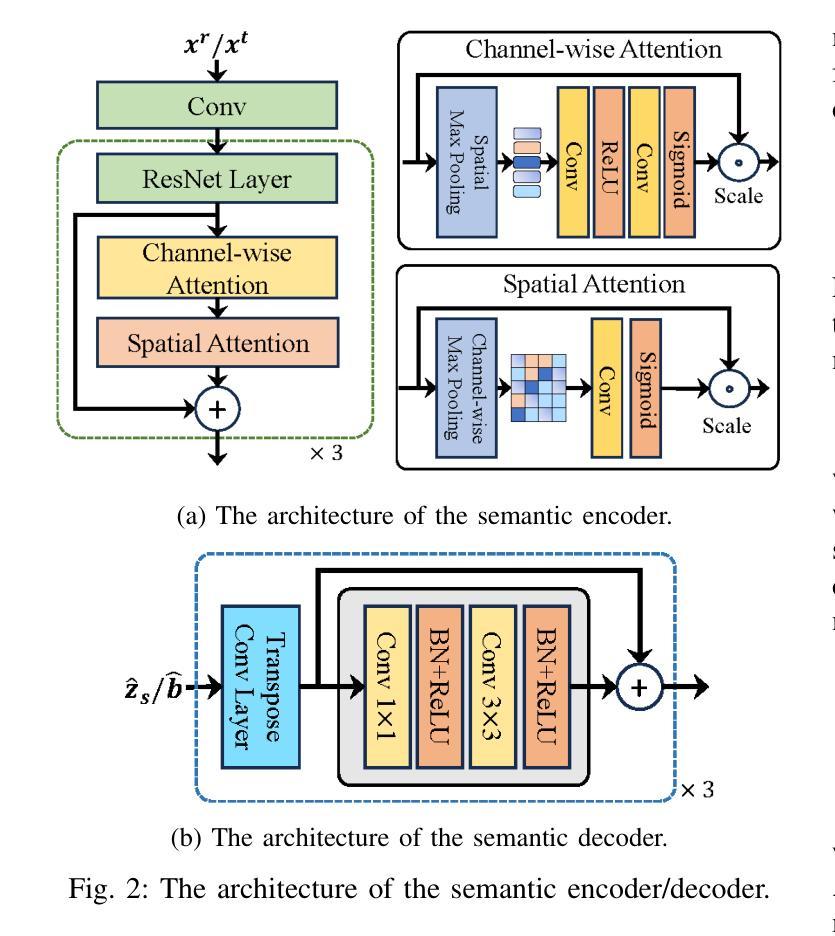
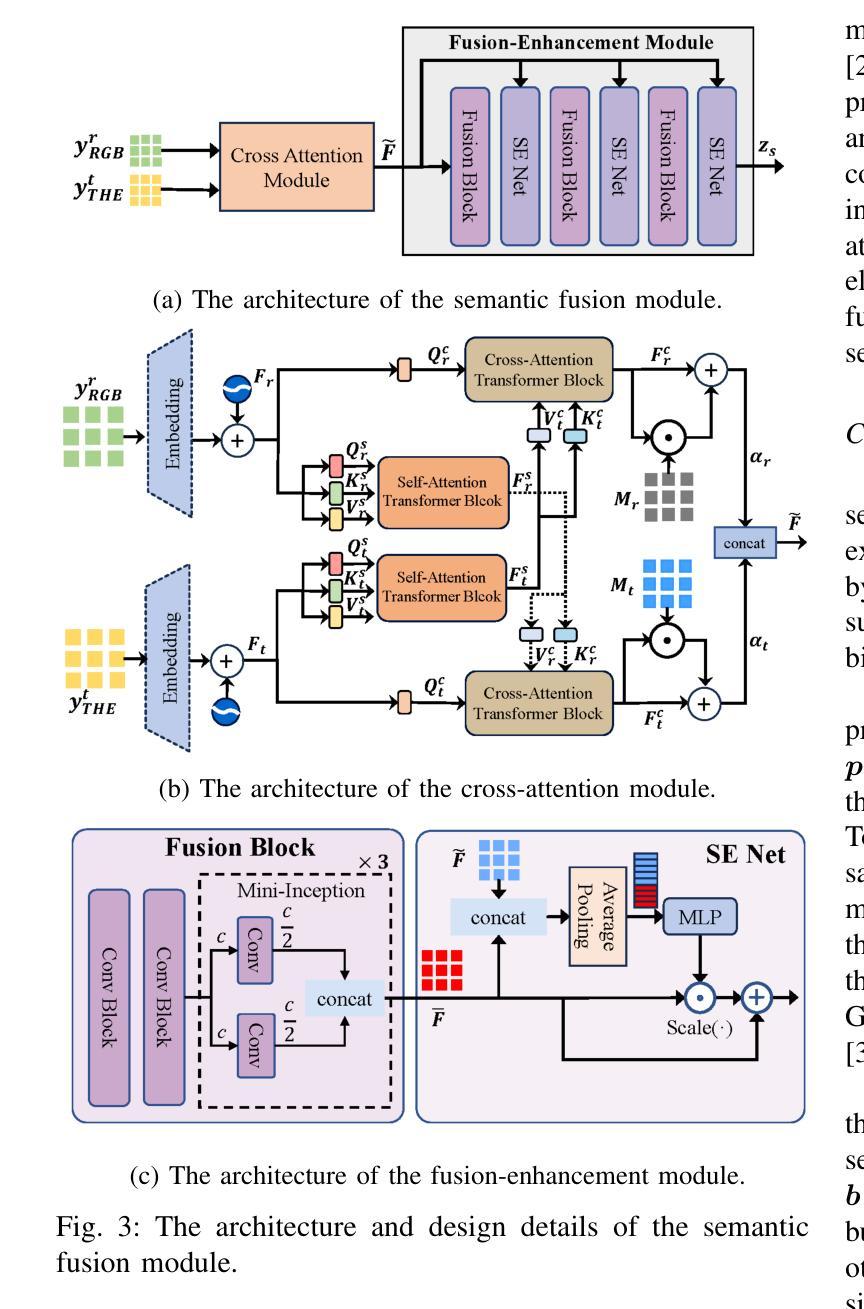
ProMSC-MIS: Prompt-based Multimodal Semantic Communication for Multi-Spectral Image Segmentation
Authors:Haoshuo Zhang, Yufei Bo, Meixia Tao
Multimodal semantic communication has great potential to enhance downstream task performance by integrating complementary information across modalities. This paper introduces ProMSC-MIS, a novel Prompt-based Multimodal Semantic Communication framework for Multi-Spectral Image Segmentation. It enables efficient task-oriented transmission of spatially aligned RGB and thermal images over band-limited channels. Our framework has two main design novelties. First, by leveraging prompt learning and contrastive learning, unimodal semantic encoders are pre-trained to learn diverse and complementary semantic representations by using features from one modality as prompts for another. Second, a semantic fusion module that combines cross-attention mechanism and squeeze-and-excitation (SE) networks is designed to effectively fuse cross-modal features. Experimental results demonstrate that ProMSC-MIS substantially outperforms conventional image transmission combined with state-of-the-art segmentation methods. Notably, it reduces the required channel bandwidth by 50%–70% at the same segmentation performance, while also decreasing the storage overhead and computational complexity by 26% and 37%, respectively. Ablation studies also validate the effectiveness of the proposed pre-training and semantic fusion strategies. Our scheme is highly suitable for applications such as autonomous driving and nighttime surveillance.
多模态语义通信通过整合各模态的互补信息,具有巨大的潜力来提升下游任务性能。本文介绍了ProMSC-MIS,一个基于提示的新型多模态语义通信框架,用于多光谱图像分割。它能够实现空间对齐的RGB和热图像在带宽受限通道上的高效任务导向传输。我们的框架有两个主要的设计新颖之处。首先,通过利用提示学习和对比学习,单模态语义编码器被预训练以使用一种模态的特征作为另一种模态的提示来学习多样且互补的语义表示。其次,设计了一个语义融合模块,它结合了交叉注意机制和挤压激励(SE)网络,以有效地融合跨模态特征。实验结果表明,ProMSC-MIS在相同的分割性能下,相较于传统图像传输结合最先进的分割方法,大幅降低了所需的信道带宽达50%-70%,同时减少了存储开销和计算复杂度分别为26%和37%。消融研究也验证了所提出预训练和语义融合策略的有效性。我们的方案非常适合自动驾驶和夜间监控等应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2508.17920
Summary
基于多模态语义通信的多光谱图像分割方法取得了突破性进展。本研究引入了一种基于提示的ProMSC-MIS框架,能有效整合不同模态间的互补信息以提升下游任务性能。该研究的关键创新在于利用提示学习和对比学习,训练单模态语义编码器以学习多样且互补的语义表示,并采用融合跨注意力机制和挤压激励网络的语义融合模块,以实现跨模态特征的有效融合。实验结果显示,ProMSC-MIS在降低信道带宽需求的同时,实现了与传统图像传输结合的最先进分割方法的显著性能提升。此外,该方案还降低了存储开销和计算复杂度,具有很高的实际应用价值,如自动驾驶和夜间监控等领域。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态语义通信能增强下游任务性能,通过整合不同模态的互补信息。
- ProMSC-MIS框架是一种基于提示的多媒体语义通信框架,用于多光谱图像分割。
- 利用提示学习和对比学习训练单模态语义编码器,学习多样且互补的语义表示。
- 语义融合模块结合了跨注意力机制和挤压激励网络,有效融合跨模态特征。
- ProMSC-MIS在降低信道带宽需求的同时实现了出色的分割性能。
- 与传统方法相比,ProMSC-MIS降低了存储开销和计算复杂度。
点此查看论文截图

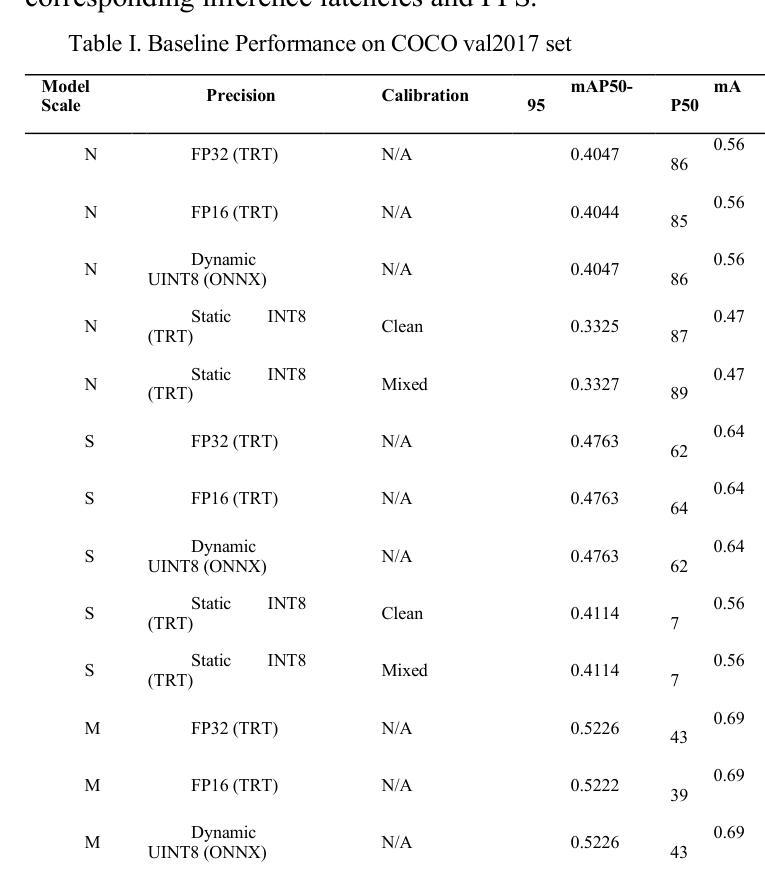
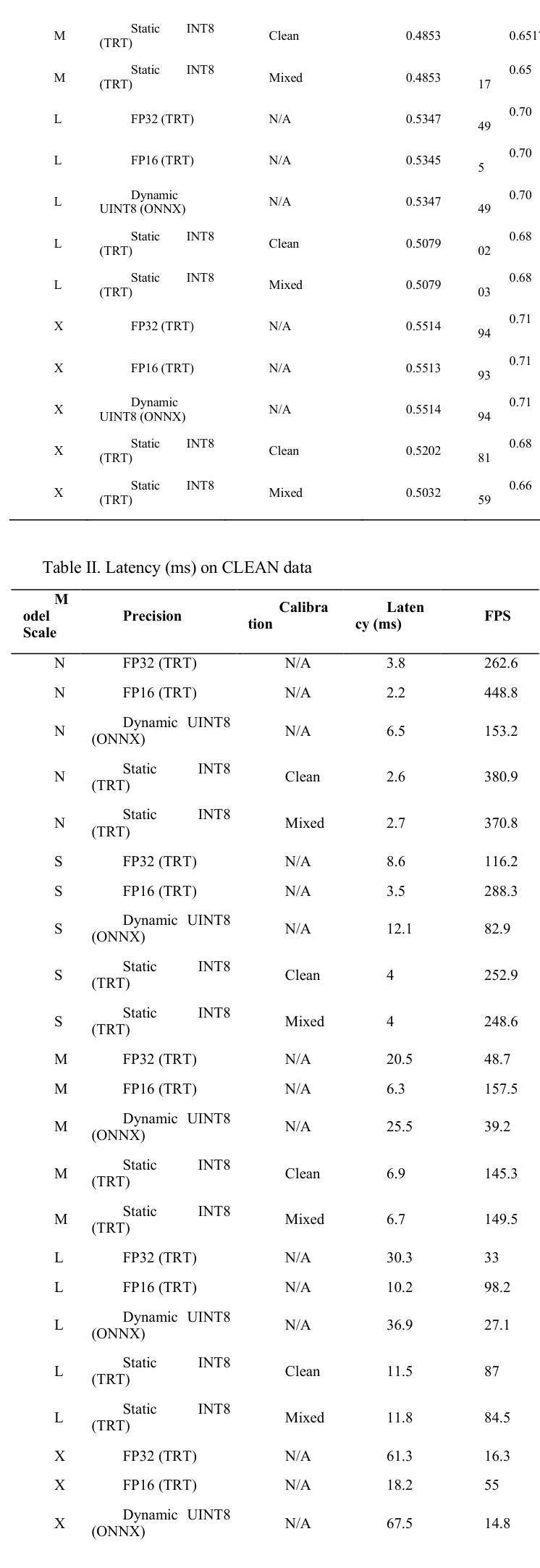
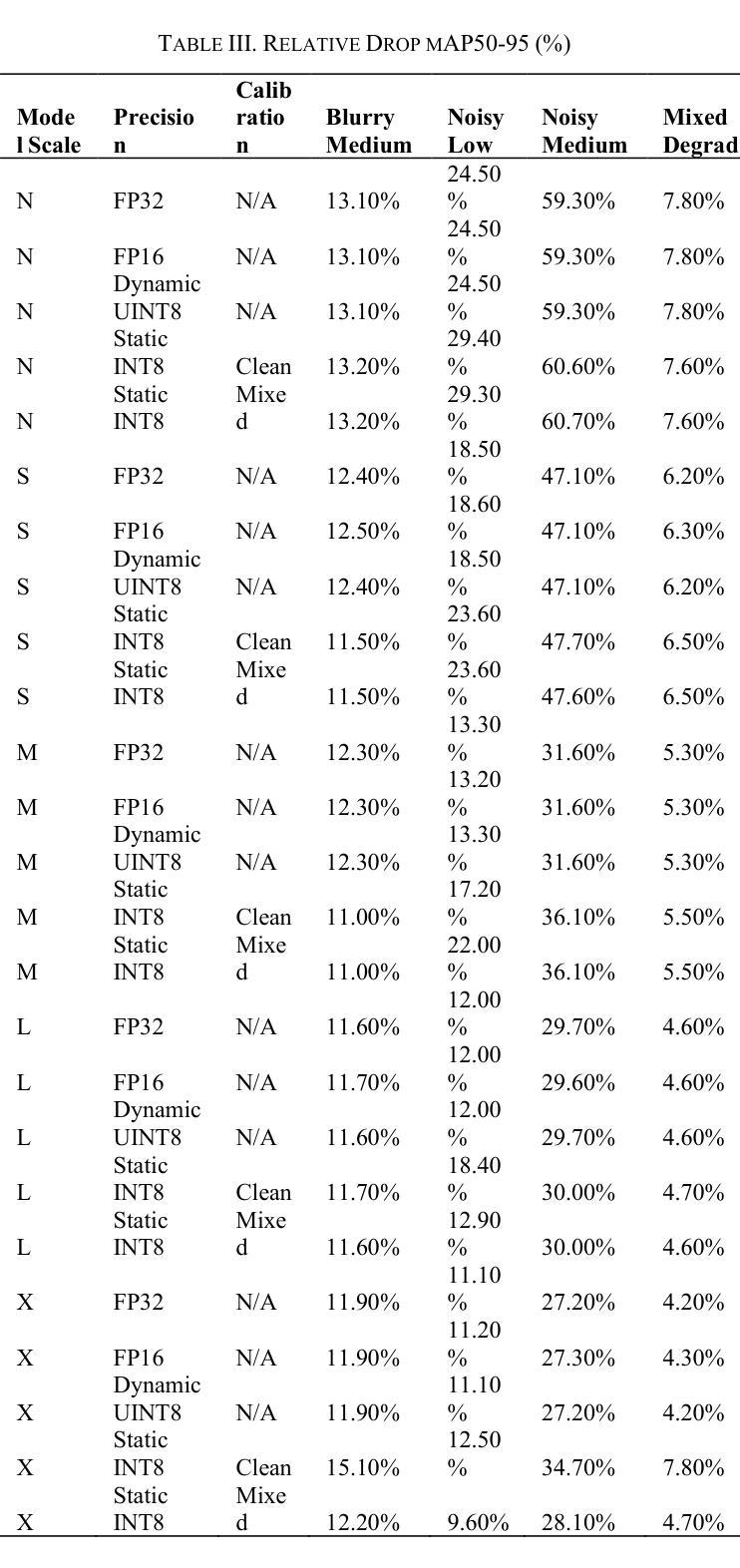
Quantization Robustness to Input Degradations for Object Detection
Authors:Toghrul Karimov, Hassan Imani, Allan Kazakov
Post-training quantization (PTQ) is crucial for deploying efficient object detection models, like YOLO, on resource-constrained devices. However, the impact of reduced precision on model robustness to real-world input degradations such as noise, blur, and compression artifacts is a significant concern. This paper presents a comprehensive empirical study evaluating the robustness of YOLO models (nano to extra-large scales) across multiple precision formats: FP32, FP16 (TensorRT), Dynamic UINT8 (ONNX), and Static INT8 (TensorRT). We introduce and evaluate a degradation-aware calibration strategy for Static INT8 PTQ, where the TensorRT calibration process is exposed to a mix of clean and synthetically degraded images. Models were benchmarked on the COCO dataset under seven distinct degradation conditions (including various types and levels of noise, blur, low contrast, and JPEG compression) and a mixed-degradation scenario. Results indicate that while Static INT8 TensorRT engines offer substantial speedups (1.5-3.3x) with a moderate accuracy drop (3-7% mAP50-95) on clean data, the proposed degradation-aware calibration did not yield consistent, broad improvements in robustness over standard clean-data calibration across most models and degradations. A notable exception was observed for larger model scales under specific noise conditions, suggesting model capacity may influence the efficacy of this calibration approach. These findings highlight the challenges in enhancing PTQ robustness and provide insights for deploying quantized detectors in uncontrolled environments. All code and evaluation tables are available at https://github.com/AllanK24/QRID.
针对在资源受限设备上部署高效的物体检测模型(如YOLO)而言,训练后量化(PTQ)是非常关键的。然而,减少精度对模型在现实世界中面对输入退化(如噪声、模糊和压缩伪影)的稳健性的影响是一个重大关注点。本文进行了一项全面的实证研究,评估了YOLO模型(从纳米到超大尺度)在不同精度格式下的稳健性,包括FP32、FP16(TensorRT)、动态UINT8(ONNX)和静态INT8(TensorRT)。我们针对静态INT8 PTQ引入并评估了一种退化感知校准策略,该策略将TensorRT校准过程暴露于干净图像和合成退化图像的混合体中。在COCO数据集上,模型在七种不同的退化条件(包括各种类型和级别的噪声、模糊、低对比度和JPEG压缩)以及混合退化场景下面进行了测试。结果表明,静态INT8 TensorRT引擎在干净数据上实现了显著的速度提升(约1.5-3.3倍),同时精度下降幅度适中(约3-7% mAP50-95)。然而,提出的退化感知校准并未在所有模型和退化情况下实现一致且广泛的稳健性改进。值得注意的是,在特定噪声条件下,较大的模型尺度表现出了改进,这表明模型容量可能影响此校准方法的有效性。这些发现突出了提高PTQ稳健性的挑战,并为在不受控环境中部署量化检测器提供了见解。所有代码和评估表格均可在https://github.com/AllanK24/QRID找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对在资源受限设备上部署YOLO等高效目标检测模型的问题,本文研究了量化训练(PTQ)对模型鲁棒性的影响。文章对YOLO模型在不同精度格式下的鲁棒性进行了全面的实证研究,包括FP32、FP16(TensorRT)、动态UINT8(ONNX)和静态INT8(TensorRT)。文章提出了一种针对静态INT8 PTQ的退化感知校准策略,在TensorRT校准过程中使用干净和合成退化图像的组合。模型在COCO数据集上进行了七种不同的退化条件下的基准测试(包括各种类型的噪声、模糊、低对比度以及JPEG压缩等),结果表明静态INT8 TensorRT引擎在清洁数据上实现了显著的速度提升(约1.5-3.3倍),精度下降幅度约为中等(约3-7% mAP50-95)。然而,退化感知校准并未在所有模型和退化条件下产生一致性的稳健性改进。文章指出,在某些特定噪声条件下的大型模型可能会有显著改进,这暗示模型的容量可能会影响校准方法的有效性。该研究突出了增强PTQ鲁棒性的挑战,并为在不受控制的环境中部署量化检测器提供了见解。代码和评估表均可在链接中找到:https://github.com/AllanK24/QRID。
关键见解
- 研究对YOLO模型在不同精度格式下的鲁棒性进行了全面的实证研究。
- 介绍了针对静态INT8 PTQ的退化感知校准策略,涉及TensorRT校准过程中使用干净和合成退化图像的组合。
- 模型在多种退化条件下进行了基准测试,包括各种类型的噪声、模糊、低对比度以及JPEG压缩等。
- 静态INT8 TensorRT引擎在清洁数据上实现了显著的速度提升和中等精度损失。
- 退化感知校准在某些特定条件下(如大型模型面对特定噪声条件)可能会有明显改进效果,但在所有情况下未产生一致性改善。
- 模型容量可能影响校准方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

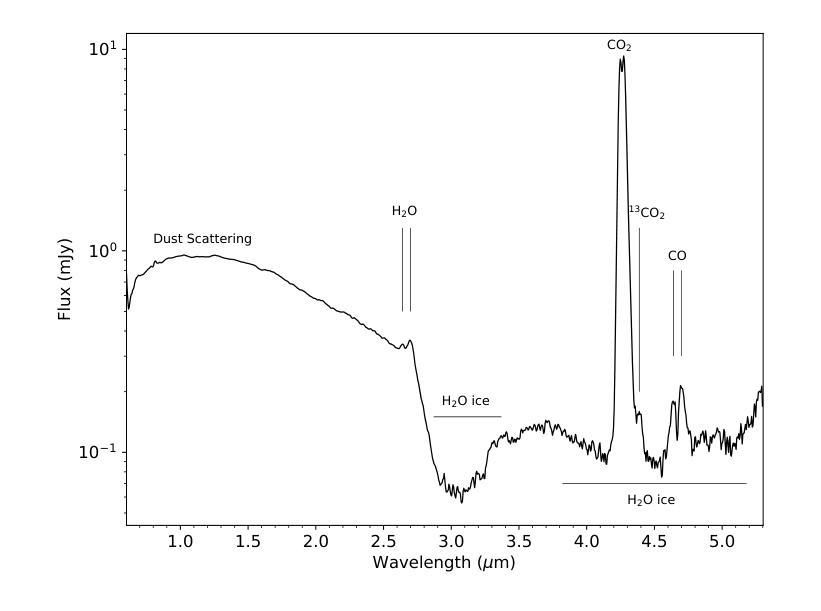
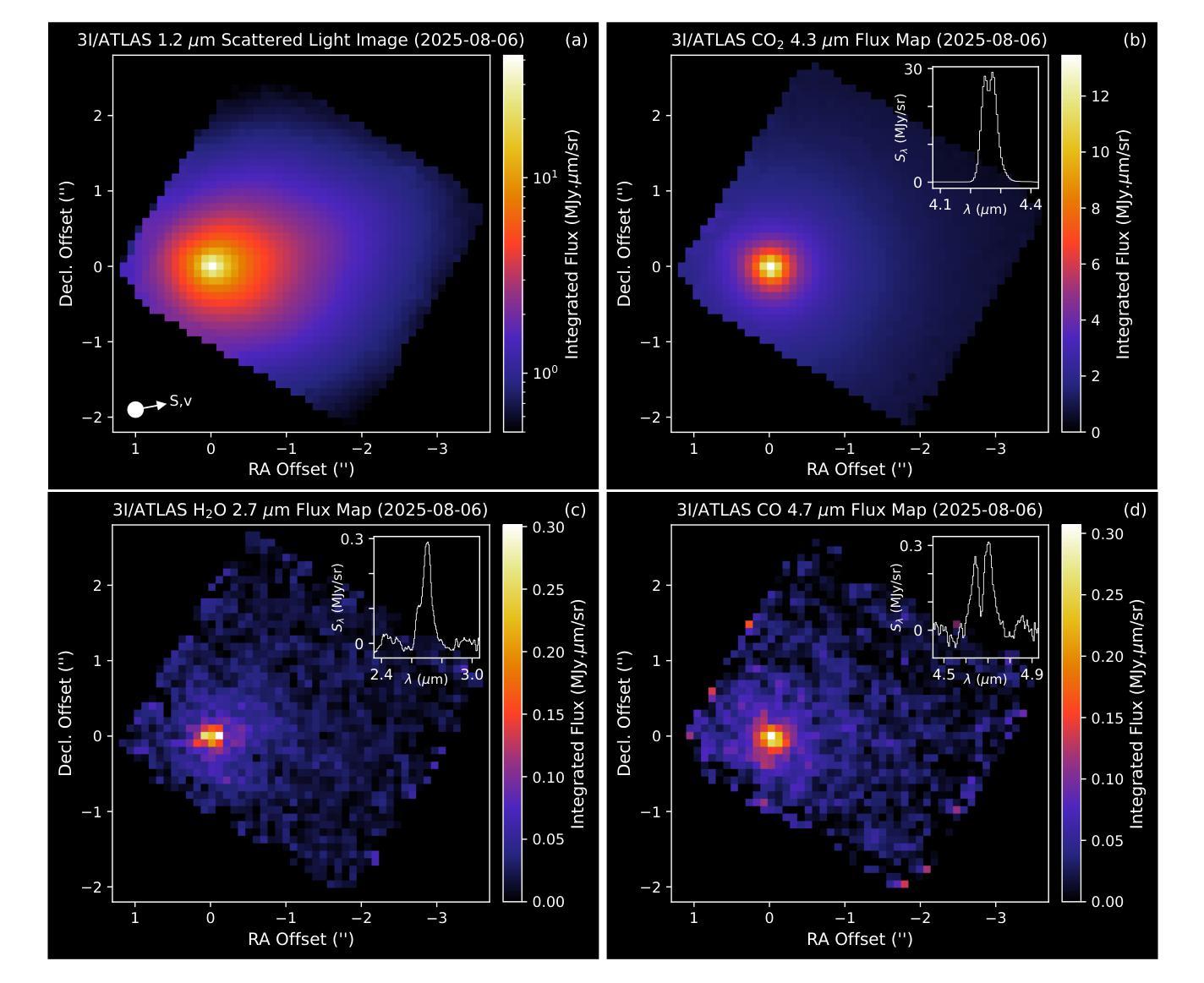
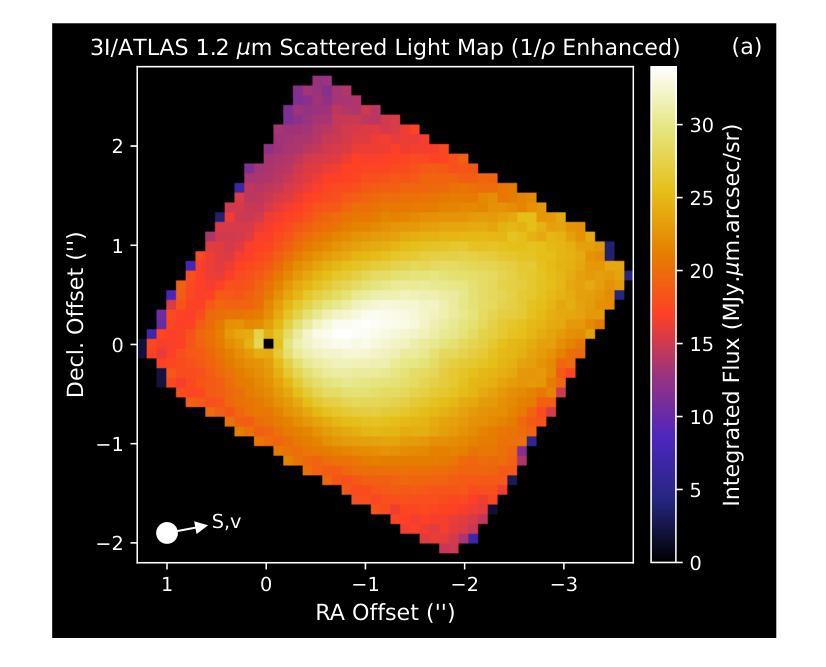
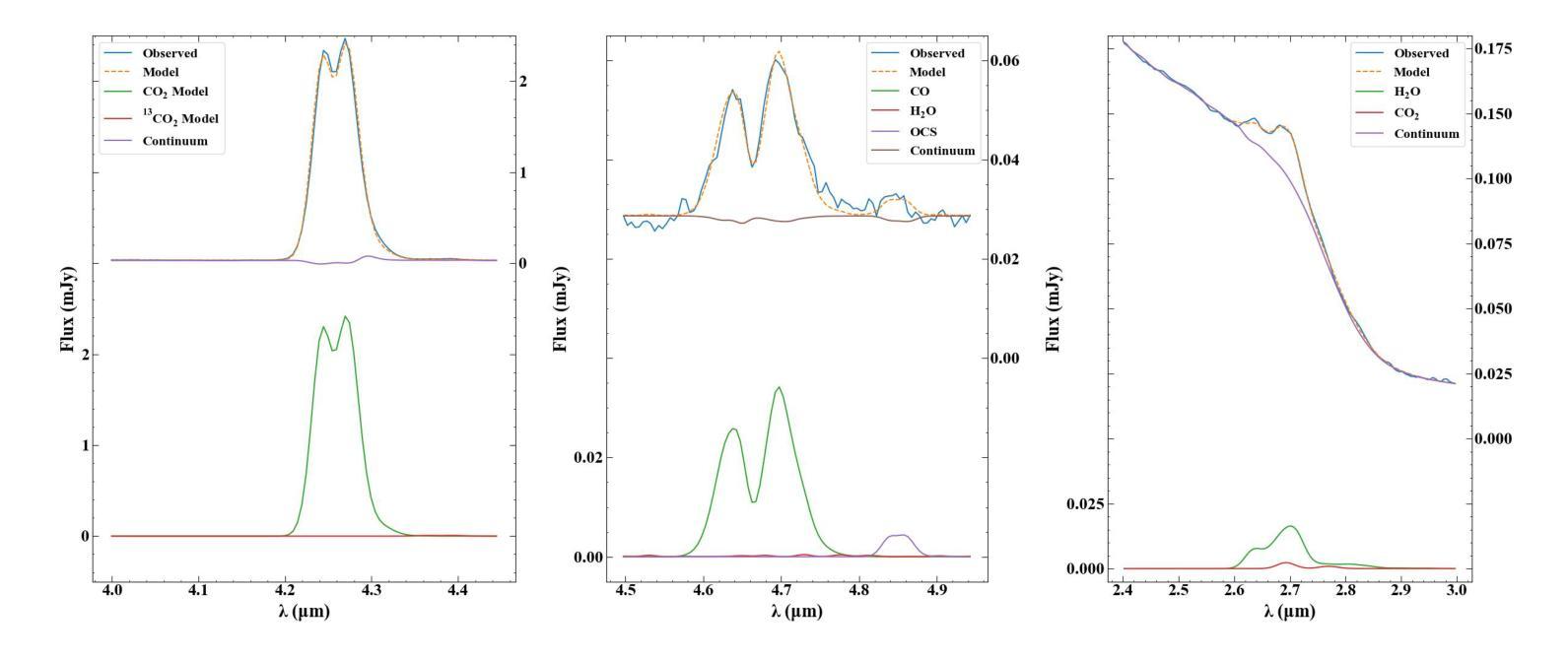
JWST detection of a carbon dioxide dominated gas coma surrounding interstellar object 3I/ATLAS
Authors:Martin A. Cordiner, Nathaniel X. Roth, Michael S. P. Kelley, Dennis Bodewits, Steven B. Charnley, Maria N. Drozdovskaya, Davide Farnocchia, Marco Micheli, Stefanie N. Milam, Cyrielle Opitom, Megan E. Schwamb, Cristina A. Thomas
3I/ATLAS is the third confirmed interstellar object to visit our Solar System, and only the second to display a clear coma. Infrared spectroscopy with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) provides the opportunity to measure its coma composition and determine the primary activity drivers. We report the first results from our JWST NIRSpec campaign for 3I/ATLAS, at an inbound heliocentric distance of $r_H=3.32$ au. The spectral images (spanning 0.6-5.3 $\mu$m) reveal a CO2 dominated coma, with enhanced outgassing in the sunward direction, and the presence of H2O, CO, OCS, water ice and dust. The coma CO2/H2O mixing ratio of $8.0\pm1.0$ is among the highest ever observed in a comet, and is 4.4-sigma above the trend as a function of heliocentric distance for long-period and Jupiter-family comets (excluding the outlier C/2016 R2). Our observations are compatible with an intrinsically CO2-rich nucleus, which may indicate that 3I/ATLAS contains ices exposed to higher levels of radiation than Solar System comets, or that it formed close to the CO2 ice line in its parent protoplanetary disk. A low coma H2O gas abundance may also be implied, for example, due to inhibited heat penetration into the nucleus, which could suppress the H2O sublimation rate relative to CO2 and CO.
3I/ATLAS是第三个确认访问我们太阳系的星际物体,也是第二个显示出清晰彗发的物体。通过詹姆斯·韦伯太空望远镜(JWST)的红外光谱提供了测量其彗发成分并确定主要活动驱动因素的机会。我们报告了使用JWST NIRSpec对3I/ATLAS的首次结果,其向地心距离为r_H=3.32天文单位。光谱图像(覆盖0.6-5.3微米)显示以CO2为主的彗发,在向阳方向出现增强出气现象,并存在H2O、CO、OCS、水冰和尘埃。彗发中的CO2/H2O混合比为8.0±1.0,这是在彗星中观察到的最高值之一,并且高于长周期和木星家族彗星随向心距离变化的趋势(排除异常值C/2016 R2)。我们的观测结果与固有的CO2丰富的核心相一致,这可能表明3I/ATLAS包含的冰暴露于比太阳系彗星更高的辐射水平下,或者它在其母行星盘附近形成于CO2冰线附近。彗发的H2O气体含量较低可能是由于热量难以穿透核心,这可能会抑制相对于CO2和CO的H2O升华速率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ApJ Letters 2025-08-25
Summary:
3I/ATLAS是第三个确认访问太阳系的外太阳系天体,使用詹姆斯韦伯太空望远镜(JWST)的红外光谱分析其组成,揭示其以二氧化碳为主的彗发,并发现其他成分如H2O、CO、OCS等。其CO2与H2O的混合比例极高,可能暗示其暴露在更高水平的辐射下或形成于接近二氧化碳冰线的位置。观测结果也可能暗示其水蒸气的含量较低。
Key Takeaways:
- 3I/ATLAS是第三个确认访问太阳系的外太阳系对象,第二个显示清晰彗发的对象。
- 使用JWST的NIRSpec对其进行了观测,揭示了以CO2为主的彗发组成。
- 发现彗发中包括H2O、CO、OCS等组分。
- CO2与H2O的混合比例极高,这可能是其与众不同的特征之一。
- 这种高混合比例可能暗示其暴露在更高水平的辐射下,或者是在其形成的行星盘内更接近二氧化碳冰线的地方形成。
- 观测结果也可能暗示其水蒸气的含量较低。
点此查看论文截图

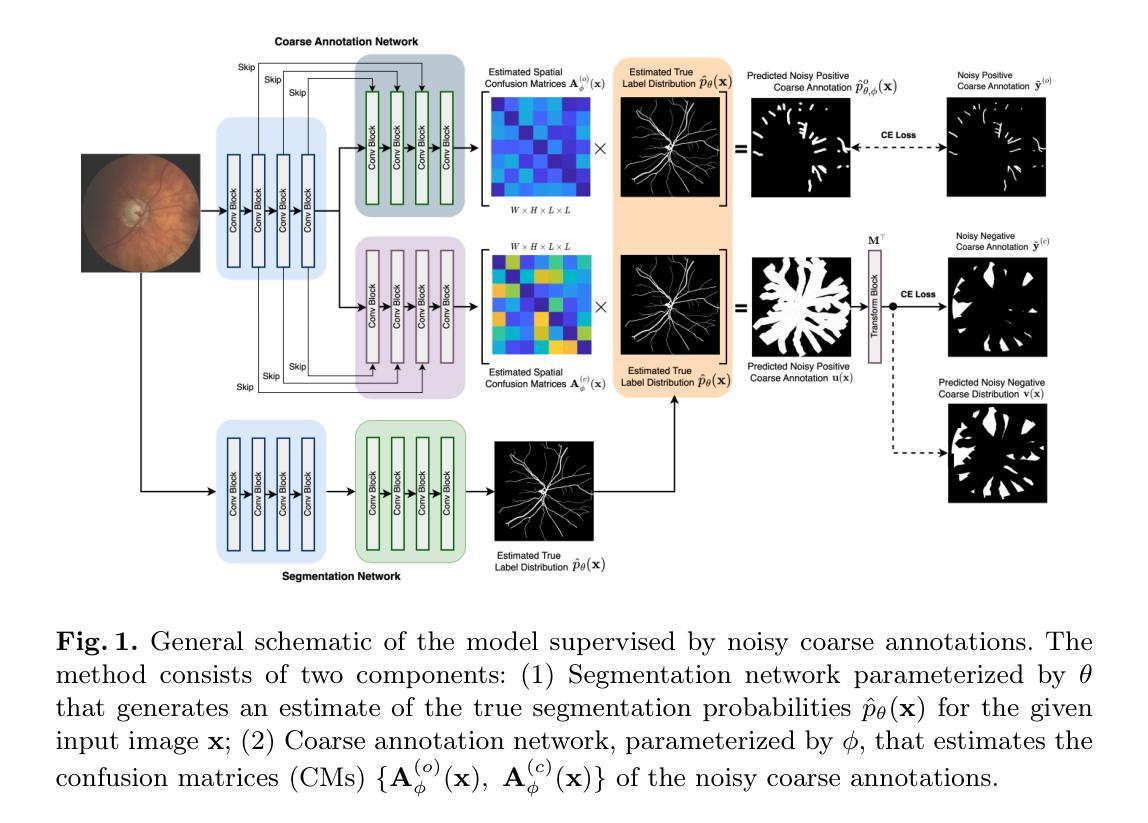
Emerging Semantic Segmentation from Positive and Negative Coarse Label Learning
Authors:Le Zhang, Fuping Wu, Arun Thirunavukarasu, Kevin Bronik, Thomas Nichols, Bartlomiej W. Papiez
Large annotated datasets are vital for training segmentation models, but pixel-level labeling is time-consuming, error-prone, and often requires scarce expert annotators, especially in medical imaging. In contrast, coarse annotations are quicker, cheaper, and easier to produce, even by non-experts. In this paper, we propose to use coarse drawings from both positive (target) and negative (background) classes in the image, even with noisy pixels, to train a convolutional neural network (CNN) for semantic segmentation. We present a method for learning the true segmentation label distributions from purely noisy coarse annotations using two coupled CNNs. The separation of the two CNNs is achieved by high fidelity with the characters of the noisy training annotations. We propose to add a complementary label learning that encourages estimating negative label distribution. To illustrate the properties of our method, we first use a toy segmentation dataset based on MNIST. We then present the quantitative results of experiments using publicly available datasets: Cityscapes dataset for multi-class segmentation, and retinal images for medical applications. In all experiments, our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in the cases where the ratio of coarse annotations is small compared to the given dense annotations.
大规模标注数据集对于训练分割模型至关重要,但是像素级标注耗时、易出错,并且经常需要稀缺的专家标注者,特别是在医学影像领域。相比之下,粗略标注更快、更便宜、更容易生成,甚至非专家也可以进行。在本文中,我们提出使用图像中正类(目标)和负类(背景)的粗略绘图,即使有噪声像素,来训练用于语义分割的卷积神经网络(CNN)。我们提出了一种方法,从纯粹的噪声粗略标注中学习真正的分割标签分布,使用两个耦合的CNN。两个CNN的高保真分离是通过噪声训练标注的特征来实现的。我们提出添加一种互补标签学习,鼓励估计负标签分布。为了说明我们方法的特性,我们首先在基于MNIST的玩具分割数据集上使用它。然后,我们展示了使用公开可用数据集进行的实验的定量结果:用于多类分割的Cityscapes数据集和用于医学应用的视网膜图像。在所有实验中,我们的方法都优于最先进的方法,特别是在与给定密集标注相比,粗略标注的比例较小的情况下。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大规模标注数据集对于训练分割模型至关重要,但像素级标注耗时、易出错,且通常需要稀缺的专家标注者,特别是在医学影像中。相比之下,粗略标注更快、更便宜,甚至非专家也能轻松制作。本文提出使用图像中正负类(目标及背景)的粗略绘图,甚至带有噪声像素,来训练卷积神经网络(CNN)进行语义分割。我们提出了一种从纯粹的噪声粗略标注中学习真正的分割标签分布的方法,使用两个耦合的CNN。两个CNN的高保真分离是由噪声训练标注的特征实现的。我们提出添加一种补充标签学习,以鼓励估计负标签分布。为了说明我们方法的特性,我们首先使用基于MNIST的玩具分割数据集。然后,我们展示了在公开数据集上实验的数量结果:用于多类分割的Cityscapes数据集和用于医学应用的视网膜图像。所有实验中,我们的方法都优于最先进的方法,特别是在粗略标注与给定密集标注相比所占比例较小的情况下。
关键见解
- 像素级标注对于训练分割模型至关重要,但存在时间成本高、易出错和缺乏专家标注者的问题。
- 相比像素级标注,使用粗略标注更加快速、经济且易于制作。
- 提出了一种利用图像中的正负类粗略绘图来训练卷积神经网络进行语义分割的方法。
- 通过两个耦合的CNN从噪声粗略标注中学习真正的分割标签分布。
- 噪声训练标注的特征决定了两个CNN的高保真分离。
- 添加了一种补充标签学习以鼓励估计负标签分布。
点此查看论文截图

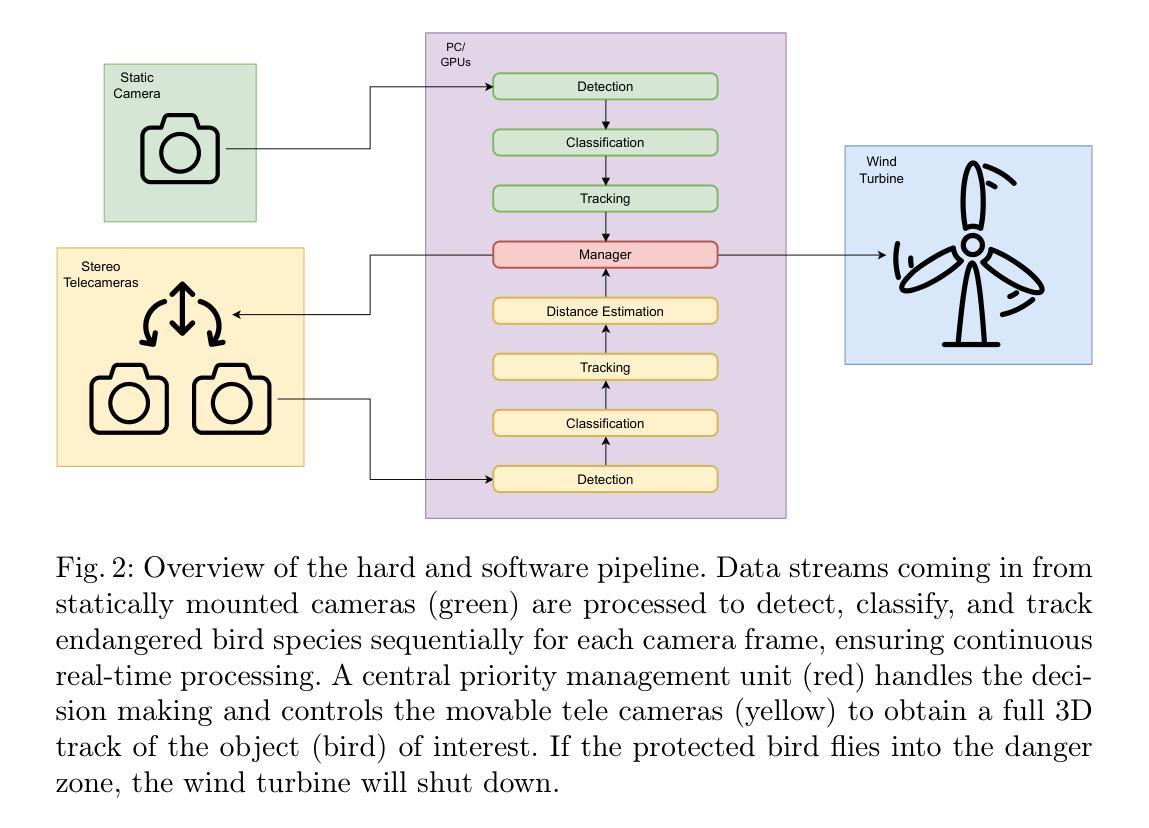
BirdRecorder’s AI on Sky: Safeguarding birds of prey by detection and classification of tiny objects around wind turbines
Authors:Nico Klar, Nizam Gifary, Felix P. G. Ziegler, Frank Sehnke, Anton Kaifel, Eric Price, Aamir Ahmad
The urgent need for renewable energy expansion, particularly wind power, is hindered by conflicts with wildlife conservation. To address this, we developed BirdRecorder, an advanced AI-based anti-collision system to protect endangered birds, especially the red kite (Milvus milvus). Integrating robotics, telemetry, and high-performance AI algorithms, BirdRecorder aims to detect, track, and classify avian species within a range of 800 m to minimize bird-turbine collisions. BirdRecorder integrates advanced AI methods with optimized hardware and software architectures to enable real-time image processing. Leveraging Single Shot Detector (SSD) for detection, combined with specialized hardware acceleration and tracking algorithms, our system achieves high detection precision while maintaining the speed necessary for real-time decision-making. By combining these components, BirdRecorder outperforms existing approaches in both accuracy and efficiency. In this paper, we summarize results on field tests and performance of the BirdRecorder system. By bridging the gap between renewable energy expansion and wildlife conservation, BirdRecorder contributes to a more sustainable coexistence of technology and nature.
对于可再生能源的扩张,尤其是风力发电的迫切需求,与野生动物保护之间存在冲突。为了解决这一问题,我们开发了BirdRecorder,这是一种先进的基于AI的防撞系统,旨在保护濒危鸟类,尤其是红鸢(Milvus milvus)。BirdRecorder融合了机器人技术、遥测技术和高性能AI算法,旨在在800米的范围内检测、跟踪和分类鸟类物种,以尽量减少鸟类与涡轮机的碰撞。BirdRecorder结合了先进的AI方法,并优化了硬件和软件架构,以实现实时图像处理。它利用单镜头检测器(SSD)进行检测,结合专门的硬件加速和跟踪算法,我们的系统在保持实时决策所需速度的同时,实现了高检测精度。通过结合这些组件,BirdRecorder在准确性和效率方面都优于现有方法。本文总结了BirdRecorder系统在实际测试和性能方面的成果。通过弥补可再生能源扩张和野生动物保护之间的鸿沟,BirdRecorder为技术与自然的更可持续共存做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 1 figures, to appear in Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Intelligent Autonomous Systems (IAS-19), Genoa, Italy, 2025
Summary
风力发电等可再生能源扩张与野生动物保护存在冲突。为解决这一问题,我们开发了BirdRecorder系统,利用AI技术保护濒危鸟类如红鸢。该系统结合机器人技术、遥测和先进的人工智能算法,在800米范围内检测、跟踪和分类鸟类,最小化鸟与风力涡轮的碰撞。BirdRecorder系统采用先进的AI方法,结合优化的软硬件架构,实现实时图像处理。利用SSD检测器结合硬件加速和跟踪算法,系统具有高检测精度和实时决策的速度。BirdRecorder在准确性和效率方面超越了现有方法。本文总结了BirdRecorder系统的现场测试结果和性能表现,为可再生能源扩张与野生动物保护之间的平衡做出了贡献。
Key Takeaways
- BirdRecorder是一种先进的人工智能防碰撞系统,旨在保护濒危鸟类免受风力涡轮机的伤害。
- 系统结合了机器人技术、遥测和AI算法来检测、跟踪和分类鸟类。
- BirdRecorder具有实时图像处理功能,采用SSD检测器实现高检测精度和快速决策。
- 系统在准确性和效率方面超越了现有方法。
- BirdRecorder的现场测试结果和性能表现得到了总结。
- 该系统有助于平衡可再生能源扩张和野生动物保护之间的关系。
点此查看论文截图



Prompt-based Multimodal Semantic Communication for Multi-spectral Image Segmentation
Authors:Haoshuo Zhang, Yufei Bo, Hongwei Zhang, Meixia Tao
Multimodal semantic communication has gained widespread attention due to its ability to enhance downstream task performance. A key challenge in such systems is the effective fusion of features from different modalities, which requires the extraction of rich and diverse semantic representations from each modality. To this end, we propose ProMSC-MIS, a Prompt-based Multimodal Semantic Communication system for Multi-spectral Image Segmentation. Specifically, we propose a pre-training algorithm where features from one modality serve as prompts for another, guiding unimodal semantic encoders to learn diverse and complementary semantic representations. We further introduce a semantic fusion module that combines cross-attention mechanisms and squeeze-and-excitation (SE) networks to effectively fuse cross-modal features. Simulation results show that ProMSC-MIS significantly outperforms benchmark methods across various channel-source compression levels, while maintaining low computational complexity and storage overhead. Our scheme has great potential for applications such as autonomous driving and nighttime surveillance.
多模态语义通信因其能增强下游任务性能而备受关注。此类系统的关键挑战在于有效地融合不同模态的特征,这需要从每个模态中提取丰富和多样化的语义表示。为此,我们提出了ProMSC-MIS,一个基于提示的多模态语义通信系统,用于多光谱图像分割。具体来说,我们提出了一种预训练算法,其中某一模态的特征为另一模态提供提示,引导单模态语义编码器学习多样化和互补的语义表示。我们还引入了一个语义融合模块,该模块结合了交叉注意机制和挤压激发(SE)网络,以有效地融合跨模态特征。仿真结果表明,在各种通道源压缩级别上,ProMSC-MIS的性能均优于基准方法,同时保持较低的计算复杂性和存储开销。我们的方案在自动驾驶和夜间监控等应用中具有巨大潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The full-length version, arXiv:2508.20057, has been updated
Summary
多模态语义通信因其能提高下游任务性能而受到广泛关注。关键挑战在于如何有效融合不同模态的特征,这需要从每种模态中提取丰富多样的语义表示。为此,我们提出了基于提示的多模态语义通信系统ProMSC-MIS,用于多光谱图像分割。我们提出了一种预训练算法,其中一种模态的特征为另一种模态提供提示,引导单模态语义编码器学习多样且互补的语义表示。我们还引入了一个语义融合模块,结合交叉注意机制和挤压激励网络,有效地融合了跨模态特征。仿真结果表明,ProMSC-MIS在多种通道源压缩水平上显著优于基准方法,同时保持较低的计算复杂度和存储开销。该方案在自动驾驶和夜间监控等领域具有广阔的应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态语义通信能增强下游任务性能,关键挑战在于不同模态特征的融合。
- ProMSC-MIS是一个基于提示的多模态语义通信系统,用于多光谱图像分割。
- 提出了预训练算法,通过一种模态的特征提示另一种模态,学习多样且互补的语义表示。
- 引入了语义融合模块,结合交叉注意机制和挤压激励网络,有效融合跨模态特征。
- 仿真结果显示ProMSC-MIS在多种压缩水平上表现优异。
- ProMSC-MIS具有较低的计算复杂度和存储开销。
点此查看论文截图