⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
DeepSeek performs better than other Large Language Models in Dental Cases
Authors:Hexian Zhang, Xinyu Yan, Yanqi Yang, Lijian Jin, Ping Yang, Junwen Wang
Large language models (LLMs) hold transformative potential in healthcare, yet their capacity to interpret longitudinal patient narratives remains inadequately explored. Dentistry, with its rich repository of structured clinical data, presents a unique opportunity to rigorously assess LLMs’ reasoning abilities. While several commercial LLMs already exist, DeepSeek, a model that gained significant attention earlier this year, has also joined the competition. This study evaluated four state-of-the-art LLMs (GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0 Flash, Copilot, and DeepSeek V3) on their ability to analyze longitudinal dental case vignettes through open-ended clinical tasks. Using 34 standardized longitudinal periodontal cases (comprising 258 question-answer pairs), we assessed model performance via automated metrics and blinded evaluations by licensed dentists. DeepSeek emerged as the top performer, demonstrating superior faithfulness (median score = 0.528 vs. 0.367-0.457) and higher expert ratings (median = 4.5/5 vs. 4.0/5), without significantly compromising readability. Our study positions DeepSeek as the leading LLM for case analysis, endorses its integration as an adjunct tool in both medical education and research, and highlights its potential as a domain-specific agent.
大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗保健领域具有变革性潜力,然而它们解释患者长期叙事的能力尚未得到充分探索。牙科拥有丰富的结构化临床数据仓库,为严格评估LLM的推理能力提供了独特机会。虽然已有几个商业LLM存在,但今年早些时候引起人们极大关注的DeepSeek模型也加入了竞争。本研究评估了四种最先进的大型语言模型(GPT-4o、Gemini 2.0 Flash、Copilot和DeepSeek V3)在分析纵向牙科案例故事的能力,通过开放式临床任务进行。我们使用了34个标准化的纵向牙周病案例(包含258个问题答案对),通过自动化指标和执业牙医的盲评来评估模型性能。DeepSeek表现出最佳性能,展现出更高的忠实度(中位数得分=0.528比0.367-0.457)和更高的专家评分(中位数= 4.5/5比4.0/5),同时不会显著损害可读性。我们的研究将DeepSeek定位为案例分析的领先大型语言模型,支持其在医学教育和研究中的集成辅助工具的地位,并突出了其作为特定领域的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Abstract word count: 171; Total word count: 3130; Total number of tables: 2; Total number of figures: 3; Number of references: 32
摘要
大型语言模型(LLMs)在医疗保健领域具有变革性潜力,但它们解读纵向患者叙述的能力尚未得到充分探索。牙科丰富的结构化临床数据为严格评估LLMs的推理能力提供了独特机会。本研究评估了四种最先进的LLMs(GPT-4o、Gemini 2.0 Flash、Copilot和DeepSeek V3)在分析纵向牙科病例概况的能力,通过开放式临床任务进行。DeepSeek表现最佳,在忠实度和专家评分上均优于其他模型,且未显著牺牲可读性。本研究确立了DeepSeek在病例分析领域的领先地位,支持其在医学教育和研究中的辅助工具地位,并凸显了其作为领域特定代理的潜力。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在牙科领域的应用为评估其推理能力提供了独特机会。
- 本研究评估了四种先进的LLMs在分析纵向牙科病例概况时的表现。
- DeepSeek在忠实度与专家评分上表现最佳。
- DeepSeek的优异表现未显著牺牲其输出的可读性。
- 本研究确立了DeepSeek在病例分析领域的领先地位。
- DeepSeek有潜力成为医学教育和研究中的辅助工具。
- LLMs在牙科领域的应用具有广阔的发展前景。
点此查看论文截图

Advanced Deep Learning Techniques for Classifying Dental Conditions Using Panoramic X-Ray Images
Authors:Alireza Golkarieh, Kiana Kiashemshaki, Sajjad Rezvani Boroujeni
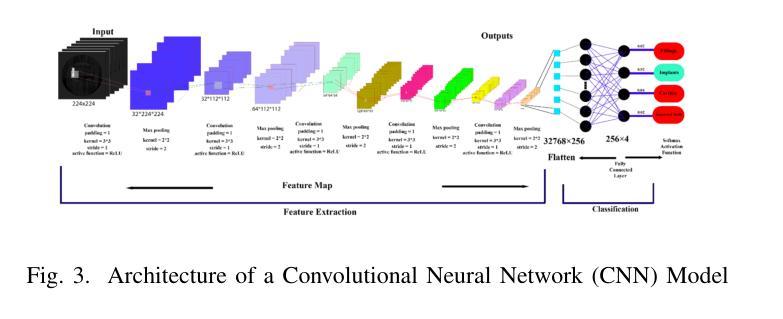
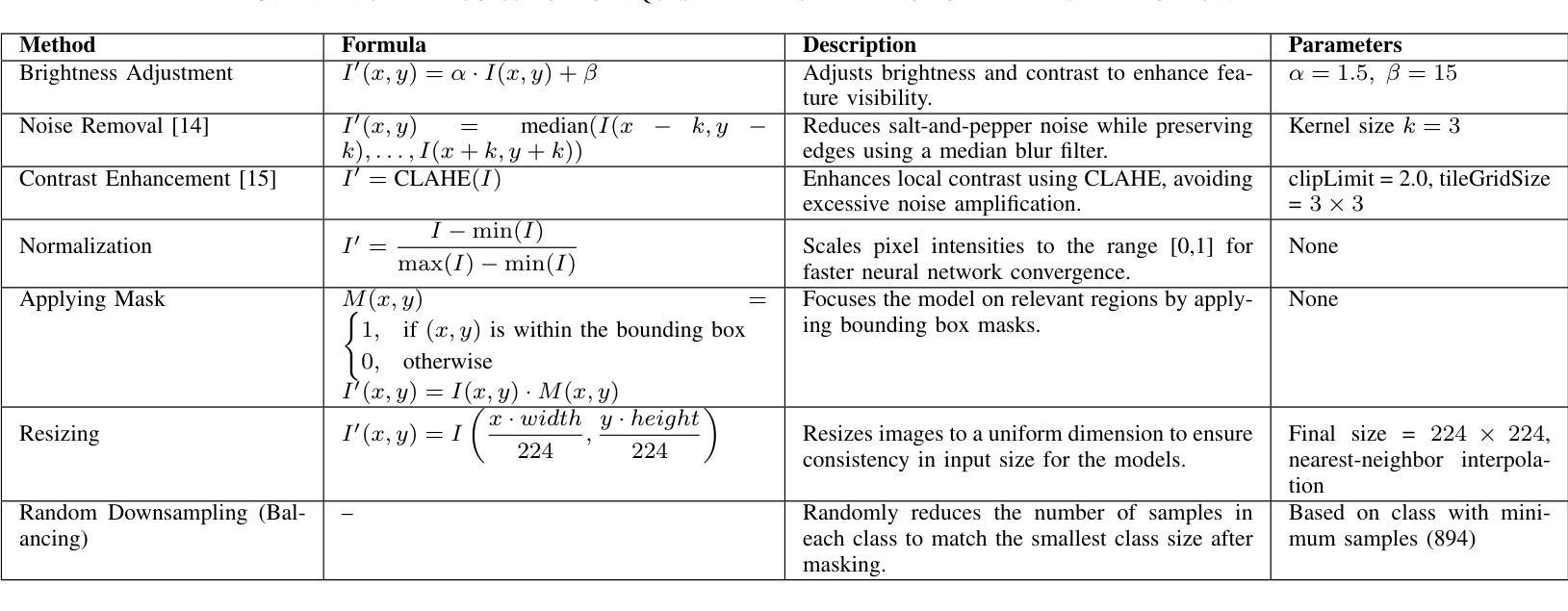
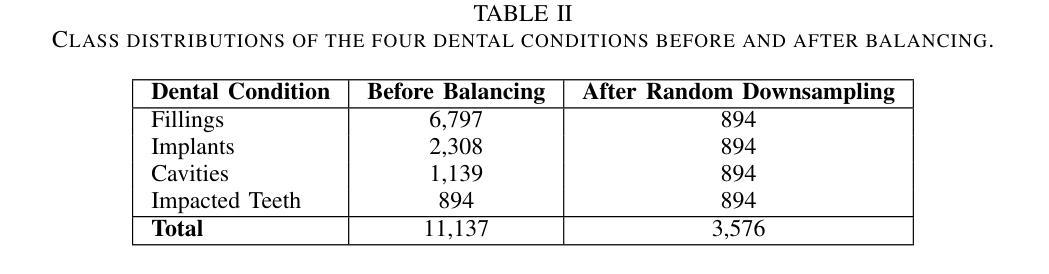
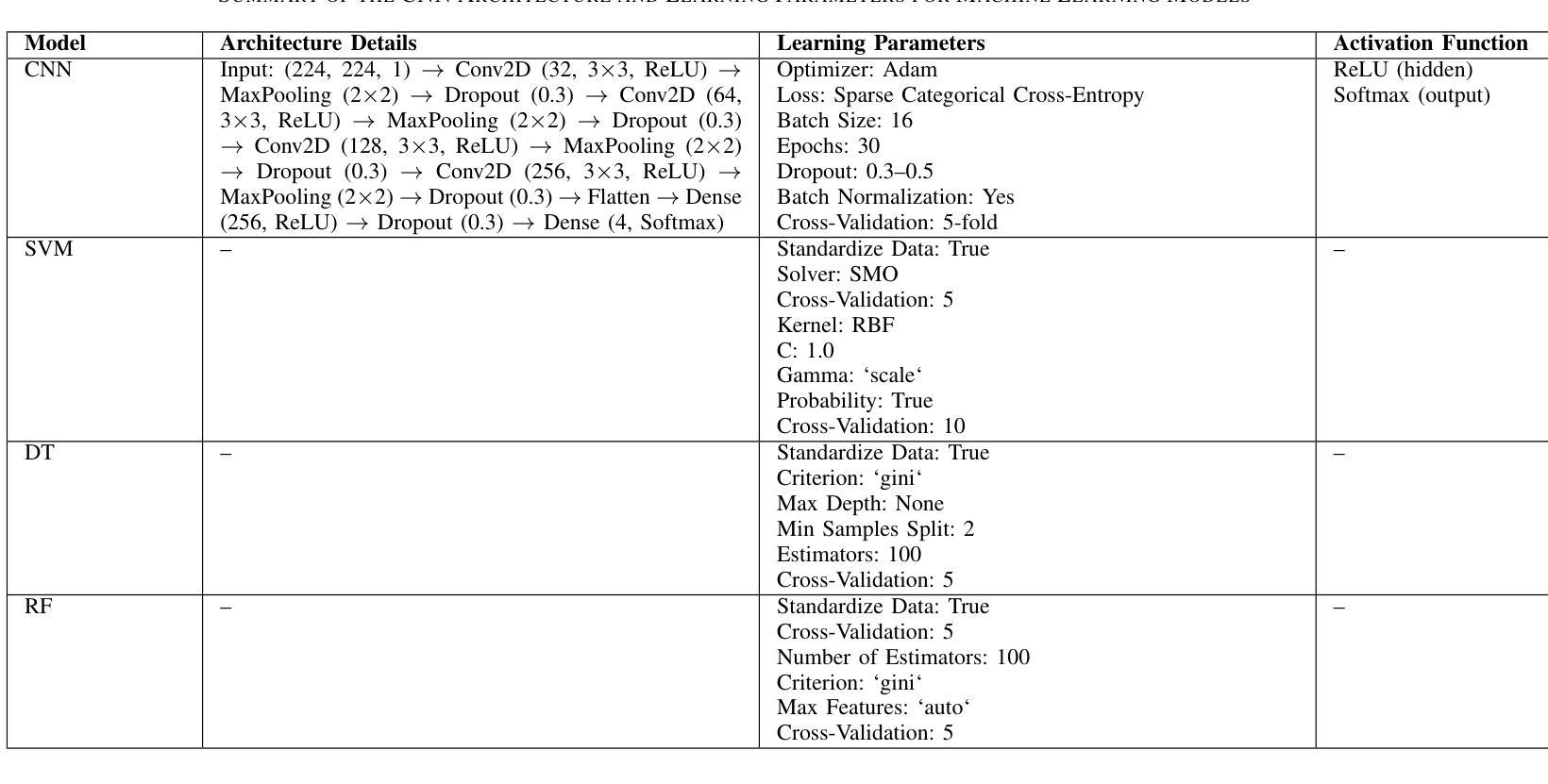
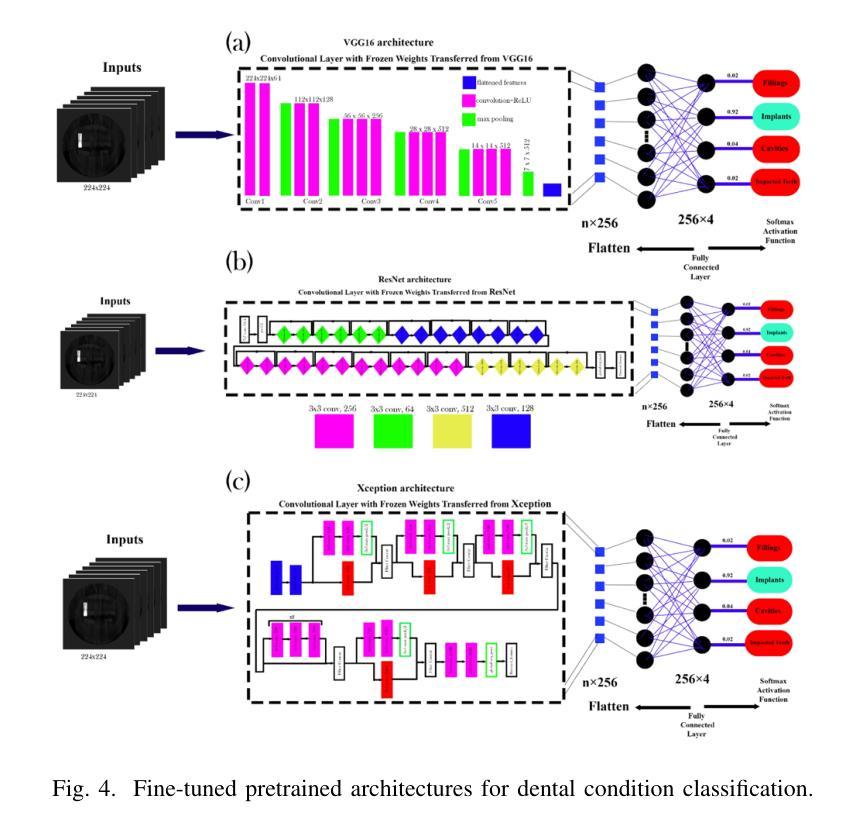
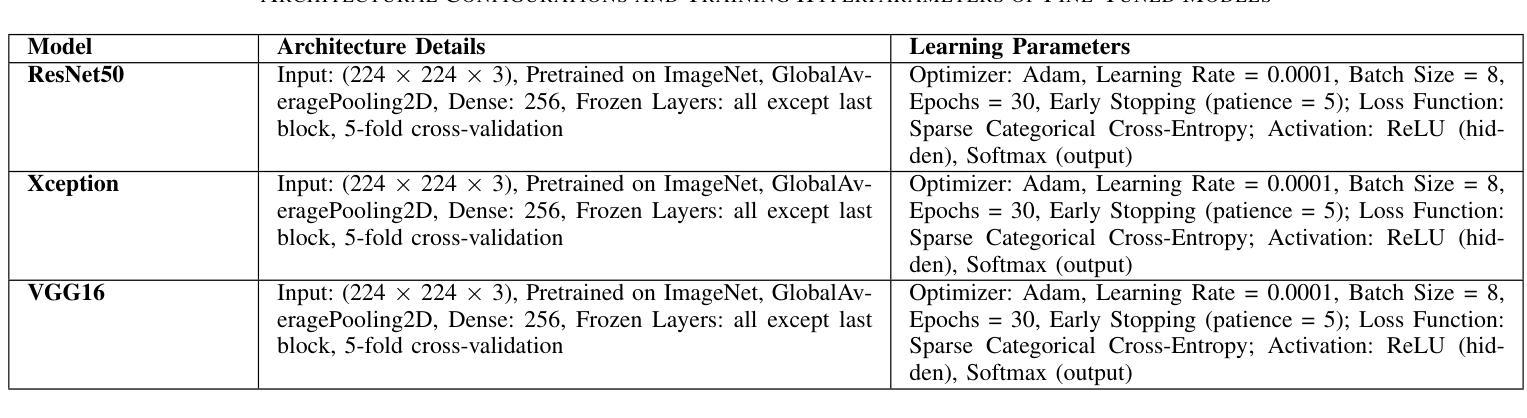
This study investigates deep learning methods for automated classification of dental conditions in panoramic X-ray images. A dataset of 1,512 radiographs with 11,137 expert-verified annotations across four conditions fillings, cavities, implants, and impacted teeth was used. After preprocessing and class balancing, three approaches were evaluated: a custom convolutional neural network (CNN), hybrid models combining CNN feature extraction with traditional classifiers, and fine-tuned pre-trained architectures. Experiments employed 5 fold cross validation with accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score as evaluation metrics. The hybrid CNN Random Forest model achieved the highest performance with 85.4% accuracy, surpassing the custom CNN baseline of 74.3%. Among pre-trained models, VGG16 performed best at 82.3% accuracy, followed by Xception and ResNet50. Results show that hybrid models improve discrimination of morphologically similar conditions and provide efficient, reliable performance. These findings suggest that combining CNN-based feature extraction with ensemble classifiers offers a practical path toward automated dental diagnostic support, while also highlighting the need for larger datasets and further clinical validation.
本研究探讨了深度学习在全景X射线图像自动分类牙科疾病的方法。使用包含四种情况(填充物、龋齿、植入物和阻生牙)的1512张放射影像数据集,共计有专家验证的注释11,137条。经过预处理和类别平衡后,评估了三种方法:自定义卷积神经网络(CNN)、结合CNN特征提取与传统分类器的混合模型,以及经过微调预训练的架构。实验采用五折交叉验证,以准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数作为评价指标。混合CNN随机森林模型性能最佳,准确率为85.4%,超过了自定义CNN基线(74.3%)。在预训练模型中,VGG16表现最佳,准确率为82.3%,其次是Xception和ResNet50。结果表明,混合模型在形态相似疾病的鉴别方面有所提高,能够提供高效可靠的性能。这些发现表明,将基于CNN的特征提取与集成分类器相结合为实现牙科诊断自动化的实用途径提供了可能,同时也强调了需要更大的数据集和进一步的临床验证。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 8 figures, 8 tables
摘要
牙齿修复研究中深度学习技术用于自动化分类全景X光图像的应用调查。该研究使用了包含牙体缺损、龋洞、种植牙及智齿埋伏等不同牙科病症的专业认证标注数据的包含大量样本的放射影像学数据集进行深度学习的分类验证研究。在数据预处理及类别平衡之后,分别进行了针对自定义卷积神经网络(CNN)模型,混合模型(将CNN特征提取和传统分类器相结合),以及对预先训练模型精细调节的方法进行研究。通过对这些模型的试验并运用了5折交叉验证以准确衡量精确度、精准度、召回率和F1分数等评价指标。研究结果表明混合CNN随机森林模型具有最高的性能表现,准确度达到了85.4%,超越了基准自定义CNN模型的准确度(仅达到74.3%)。在预先训练的模型中,VGG16表现最佳,准确度为82.3%,紧随其后的是Xception和ResNet50模型。总的来说,研究表明混合模型可以改善对形态上相似的疾病鉴别诊断的问题并提供有效可靠的支持功能,另外认为要想进一步优化实现牙科领域的全自动辅助诊断还有赖通过不断扩大的样本数量集以及相关结论在后续临床研究中的有效验证和完善调整改进优化改进相关策略思路以提升表现水平以便做出更优的贡献提供研究方面的合理方案助力技术发展普及从而更好地为广大口腔病患患者群体提供服务。。上述研究显示结果的优劣展现将对今后的自动精准化诊断提供重要依据和参考。
关键见解
- 研究探讨了深度学习在全景X光图像自动化分类牙科疾病中的应用。
- 采用包含多种牙科病症的放射影像学数据集进行实验。
- 评估了自定义CNN模型、混合模型以及预训练模型的性能。
- 混合CNN随机森林模型表现最佳,准确度高。
- 在预训练模型中,VGG16的准确度表现领先。
- 研究强调了大型数据集和进一步临床验证的必要性。
点此查看论文截图


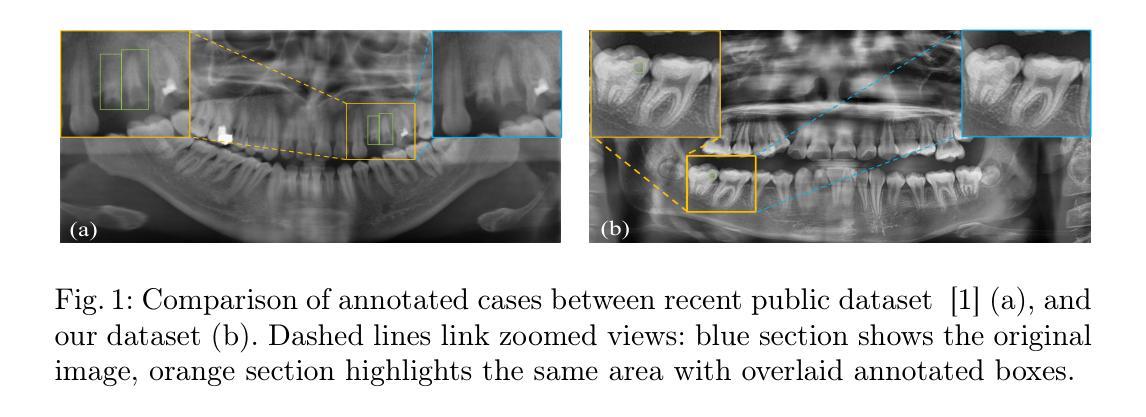
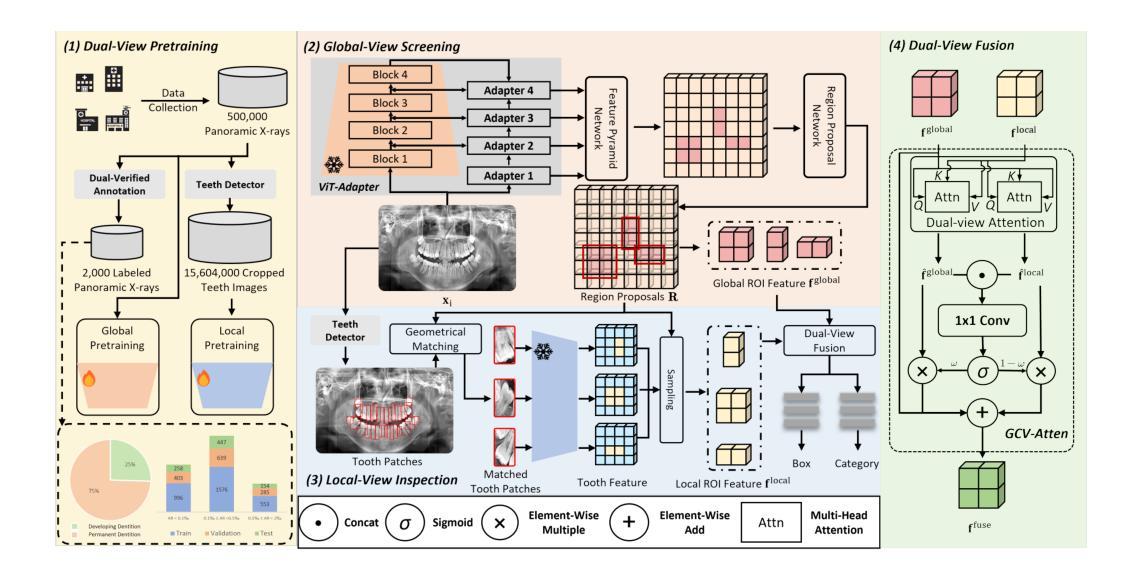
Adapting Foundation Model for Dental Caries Detection with Dual-View Co-Training
Authors:Tao Luo, Han Wu, Tong Yang, Dinggang Shen, Zhiming Cui
Accurate dental caries detection from panoramic X-rays plays a pivotal role in preventing lesion progression. However, current detection methods often yield suboptimal accuracy due to subtle contrast variations and diverse lesion morphology of dental caries. In this work, inspired by the clinical workflow where dentists systematically combine whole-image screening with detailed tooth-level inspection, we present DVCTNet, a novel Dual-View Co-Training network for accurate dental caries detection. Our DVCTNet starts with employing automated tooth detection to establish two complementary views: a global view from panoramic X-ray images and a local view from cropped tooth images. We then pretrain two vision foundation models separately on the two views. The global-view foundation model serves as the detection backbone, generating region proposals and global features, while the local-view model extracts detailed features from corresponding cropped tooth patches matched by the region proposals. To effectively integrate information from both views, we introduce a Gated Cross-View Attention (GCV-Atten) module that dynamically fuses dual-view features, enhancing the detection pipeline by integrating the fused features back into the detection model for final caries detection. To rigorously evaluate our DVCTNet, we test it on a public dataset and further validate its performance on a newly curated, high-precision dental caries detection dataset, annotated using both intra-oral images and panoramic X-rays for double verification. Experimental results demonstrate DVCTNet’s superior performance against existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods on both datasets, indicating the clinical applicability of our method. Our code and labeled dataset are available at https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DVCTNet.
从全景X射线准确检测龋齿对于防止病变进展起着至关重要的作用。然而,由于龋齿的细微对比度变化和多样的病变形态,当前检测方法往往准确性不佳。在这项工作中,我们受到牙医临床工作流程的启发,牙医会系统地结合全图筛选和详细的牙齿级别检查,我们提出了DVCTNet,这是一种用于准确检测龋齿的新型双视图协同训练网络。我们的DVCTNet开始于使用自动化牙齿检测来建立两个互补的视图:来自全景X射线图像的全局视图和来自裁剪后的牙齿图像局部视图。然后,我们分别在两个视图上预训练两个视觉基础模型。全局视图基础模型作为检测骨干,生成区域建议和全局特征,而局部视图模型则从与区域建议匹配的相应裁剪牙齿斑块中提取详细特征。为了有效地整合两个视图的信息,我们引入了一个门控跨视图注意力(GCV-Atten)模块,该模块动态融合双视图特征,通过将融合的特征回传给检测模型来增强检测流程,从而实现最终的龋齿检测。为了严格评估我们的DVCTNet,我们在公共数据集上进行了测试,并在新整理的高精度龋齿检测数据集上进一步验证了其性能,该数据集使用口腔内图像和全景X射线进行双重验证标注。实验结果表明,DVCTNet在这两个数据集上的性能均优于现有最先进的(SOTA)方法,表明了我们方法在临床上的适用性。我们的代码和标记数据集可在https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DVCTNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
全景X射线准确检测龋齿对于预防病变进展至关重要。然而,由于龋齿的细微对比度变化和多样的形态变化,当前检测方法的准确性常常不尽人意。本研究受牙医结合全景图像筛选和详细牙齿级别检查的常规工作流程启发,提出了一种新型的Dual-View Co-Training网络(DVCTNet)以实现准确的龋齿检测。DVCTNet首先通过自动牙齿检测建立两个互补视图:来自全景X射线的全局视图和来自裁剪牙齿图像的局部视图。然后,我们分别在两个视图上预训练两个视觉基础模型。全局视图模型作为检测骨干,生成区域建议和全局特征,而局部视图模型则从与区域建议匹配的裁剪牙齿斑块中提取详细特征。为了有效地整合两个视图的信息,我们引入了门控跨视图注意力(GCV-Atten)模块,该模块可以动态融合双视图特征,通过将融合的特征回传到检测模型来增强检测管道,从而实现最终的龋齿检测。为了严格评估DVCTNet的性能,我们在公共数据集上进行了测试,并进一步在全新精心策划的高精度龋齿检测数据集上验证了其性能,该数据集使用口腔内图像和全景X射线进行双重验证标注。实验结果表明,DVCTNet在数据集上的性能优于现有最先进的(SOTA)方法,表明我们的方法在临床上的适用性。我们的代码和标记数据集可在https://github.com/ShanghaiTech-IMPACT/DVCTNet获得。
关键见解
1.全景X射线在龋齿检测中起关键作用,但当前方法因细微对比度和形态变化而准确性有限。
2.提出DVCTNet模型,结合全景X射线的全局视图和裁剪牙齿图像的局部视图进行龋齿检测。
3.使用全局视图模型进行区域建议生成和全局特征提取,而局部视图模型则专注于详细特征提取。
4.引入门控跨视图注意力模块(GCV-Atten),动态融合双视图特征以增强检测性能。
5.在公共数据集和自定义数据集上的实验结果表明DVCTNet优于现有方法。
- DVCTNet具有临床适用性潜力。
点此查看论文截图