⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
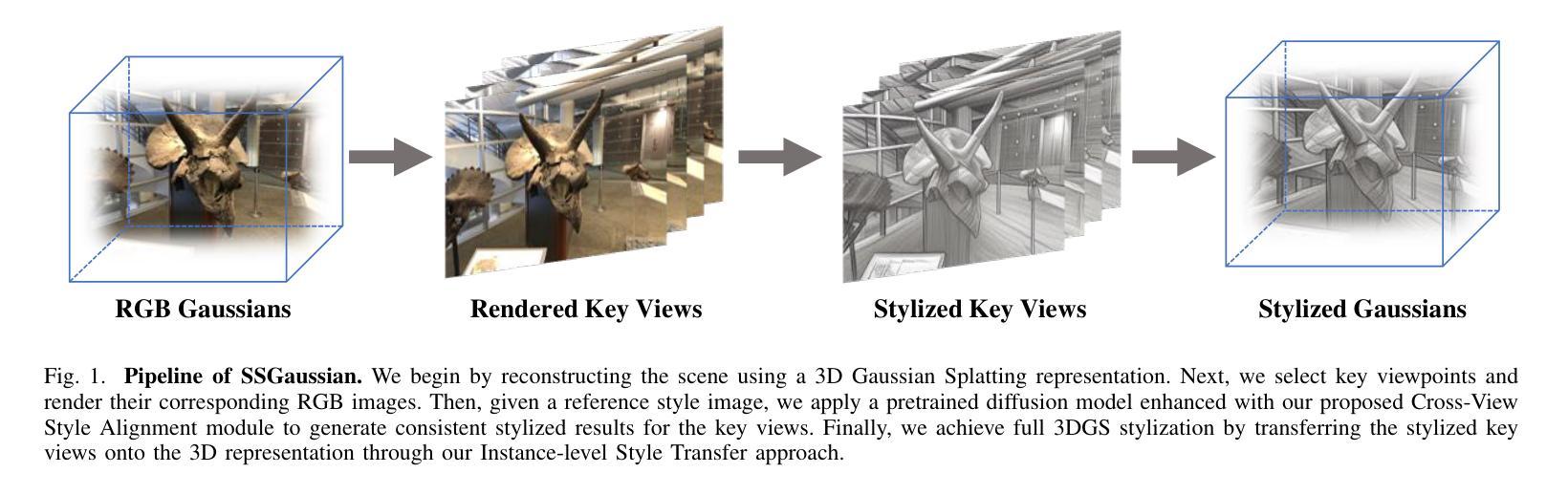
SSGaussian: Semantic-Aware and Structure-Preserving 3D Style Transfer
Authors:Jimin Xu, Bosheng Qin, Tao Jin, Zhou Zhao, Zhenhui Ye, Jun Yu, Fei Wu
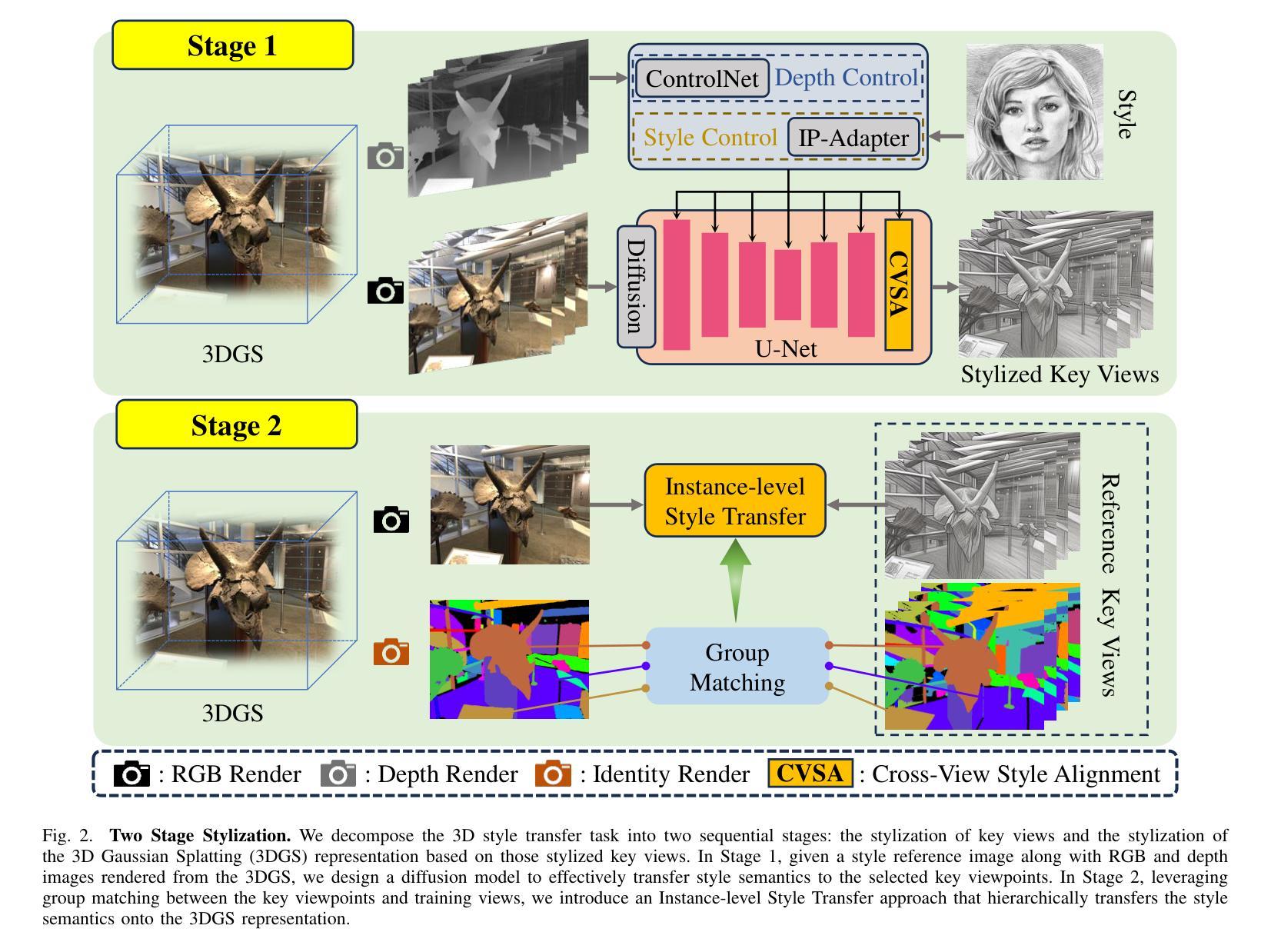
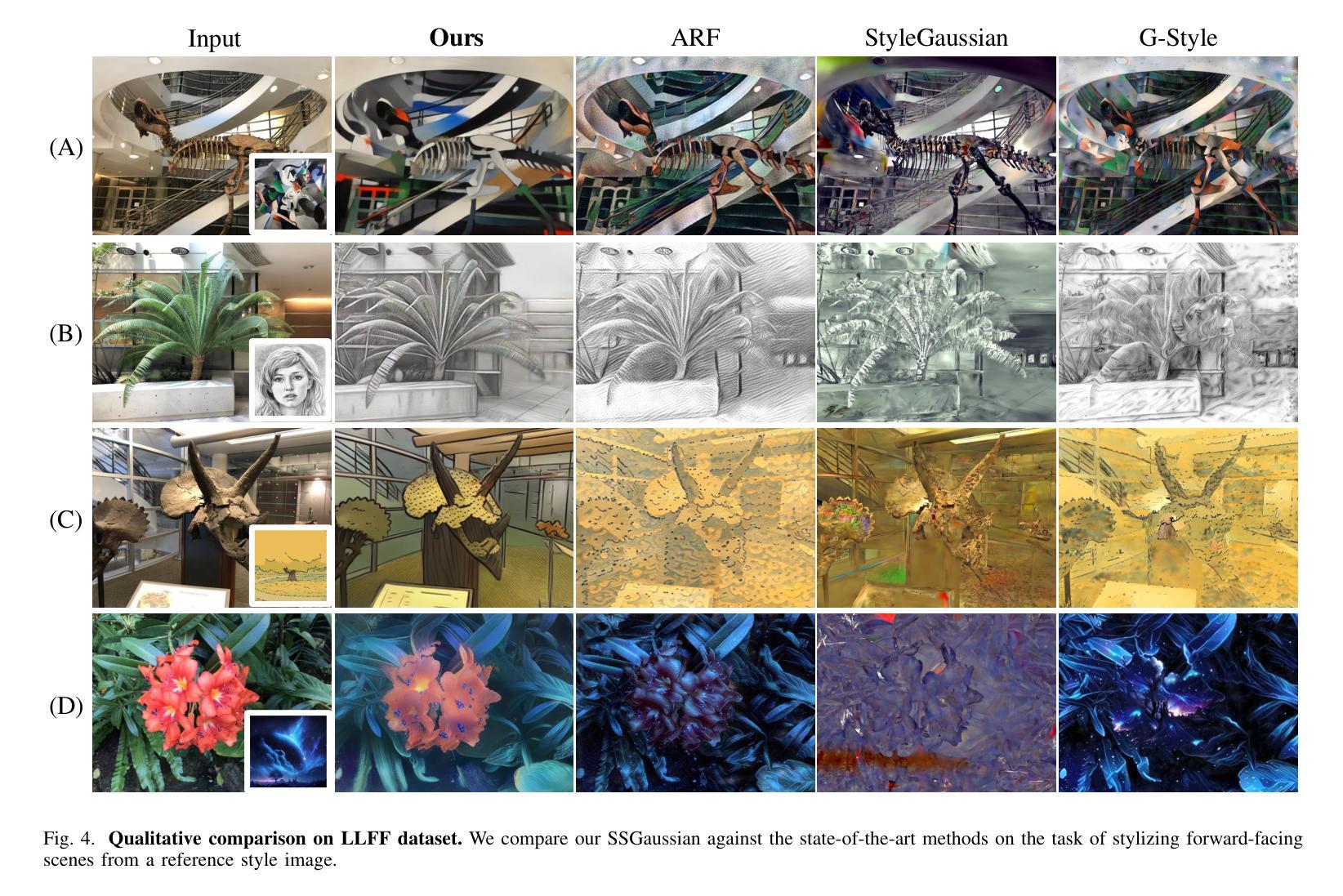
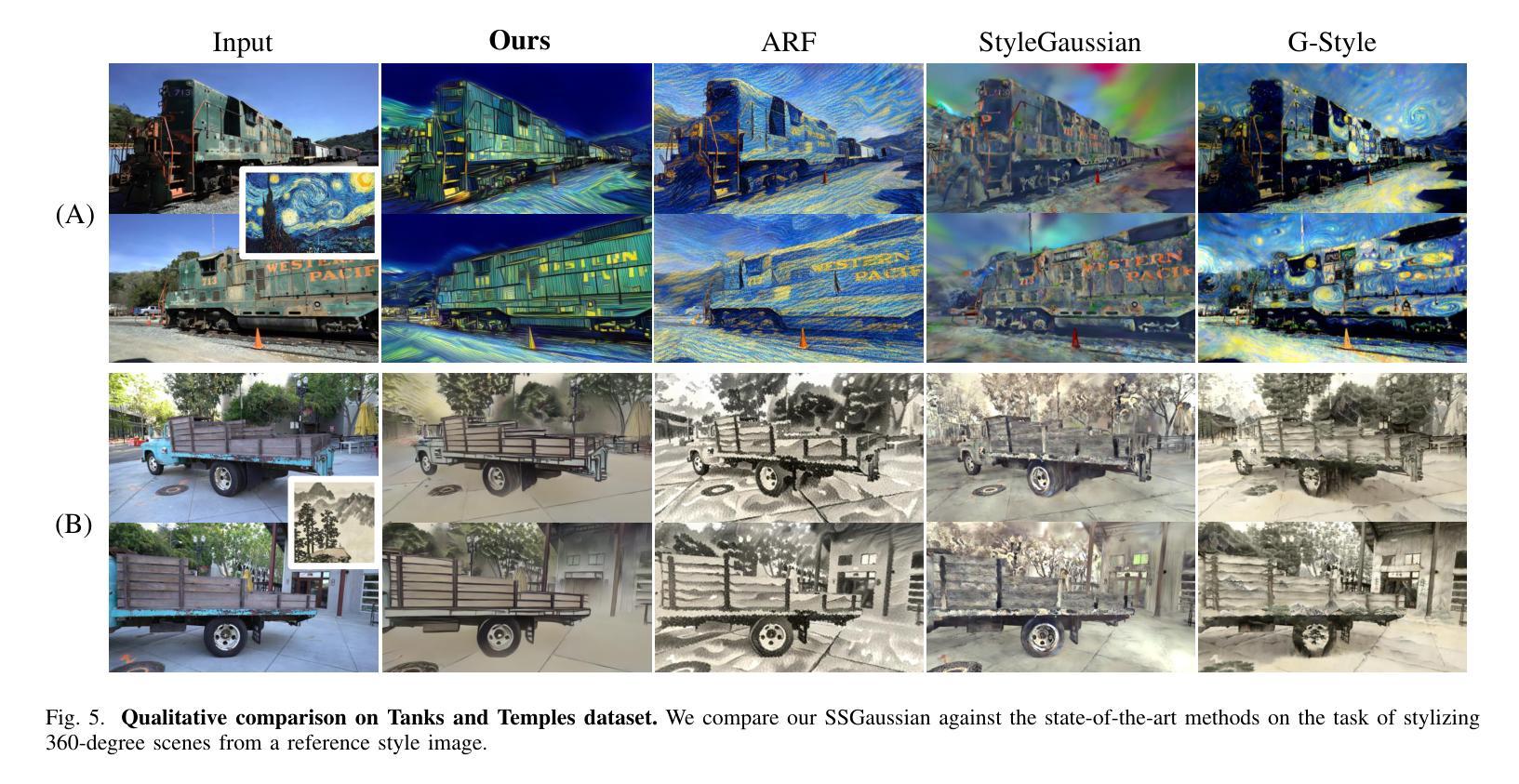
Recent advancements in neural representations, such as Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting, have increased interest in applying style transfer to 3D scenes. While existing methods can transfer style patterns onto 3D-consistent neural representations, they struggle to effectively extract and transfer high-level style semantics from the reference style image. Additionally, the stylized results often lack structural clarity and separation, making it difficult to distinguish between different instances or objects within the 3D scene. To address these limitations, we propose a novel 3D style transfer pipeline that effectively integrates prior knowledge from pretrained 2D diffusion models. Our pipeline consists of two key stages: First, we leverage diffusion priors to generate stylized renderings of key viewpoints. Then, we transfer the stylized key views onto the 3D representation. This process incorporates two innovative designs. The first is cross-view style alignment, which inserts cross-view attention into the last upsampling block of the UNet, allowing feature interactions across multiple key views. This ensures that the diffusion model generates stylized key views that maintain both style fidelity and instance-level consistency. The second is instance-level style transfer, which effectively leverages instance-level consistency across stylized key views and transfers it onto the 3D representation. This results in a more structured, visually coherent, and artistically enriched stylization. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our 3D style transfer pipeline significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods across a wide range of scenes, from forward-facing to challenging 360-degree environments. Visit our project page https://jm-xu.github.io/SSGaussian for immersive visualization.
近期神经表征领域的进展,如神经辐射场和3D高斯喷绘,增加了将风格迁移应用于3D场景的兴趣。尽管现有方法能够将风格模式转移到一致的3D神经表征上,但它们难以有效地从参考风格图像中提取并转移高级风格语义。此外,风格化的结果通常缺乏结构清晰度和分离度,使得难以区分3D场景中的不同实例或对象。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种新的3D风格迁移管道,该管道有效地结合了来自预训练的2D扩散模型的先验知识。我们的管道包括两个关键阶段:首先,我们利用扩散先验知识生成关键视点的风格化渲染。然后,我们将风格化的关键视图转移到3D表征上。这个过程包含两个创新的设计。第一个是跨视图风格对齐,它将跨视图注意力插入到UNet的最后一个上采样块中,允许跨多个关键视图进行特征交互。这确保扩散模型生成的风格化关键视图既保持风格忠实度又保持实例级一致性。第二个是实例级风格迁移,它有效地利用风格化关键视图之间的实例级一致性并将其转移到3D表征上。这产生了一个更具结构性的、视觉连贯的、艺术感增强的风格化结果。广泛的定性和定量实验表明,我们的3D风格迁移管道在广泛的场景上显著优于最先进的方法,从正面到具有挑战性的360度环境。请访问我们的项目页面https://jm-xu.github.io/SSGaussian以获取沉浸式可视化体验。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了将风格迁移应用于3D场景的新方法,该方法结合了预训练的二维扩散模型的先验知识。文章提出了一个新颖的3D风格迁移管道,分为两个阶段:首先利用扩散先验生成关键视角的风格化渲染,然后将风格化的关键视图转移到3D表示上。该管道包括两个创新设计:跨视图风格对齐和实例级风格迁移。跨视图风格对齐确保扩散模型生成的风格化关键视图既保持风格忠实度又保持实例级一致性;实例级风格迁移则将实例级一致性应用到风格化的关键视图上,实现更结构化、视觉连贯和艺术丰富的风格化效果。实验证明,该方法在多种场景上显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 风格迁移技术已应用于3D场景,但仍面临提取和转移高层次风格语义的挑战。
- 提出了一种新颖的3D风格迁移管道,结合了预训练的二维扩散模型的先验知识。
- 管道分为两个阶段:生成关键视角的风格化渲染,然后将风格化的关键视图转移到3D表示。
- 采用了两个创新设计:跨视图风格对齐和实例级风格迁移。
- 跨视图风格对齐确保风格化关键视图的风格忠实度和实例级一致性。
- 实例级风格迁移增强了风格化的结构化、视觉连贯性和艺术性。
- 该方法在多种场景上的表现显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


GRMM: Real-Time High-Fidelity Gaussian Morphable Head Model with Learned Residuals
Authors:Mohit Mendiratta, Mayur Deshmukh, Kartik Teotia, Vladislav Golyanik, Adam Kortylewski, Christian Theobalt
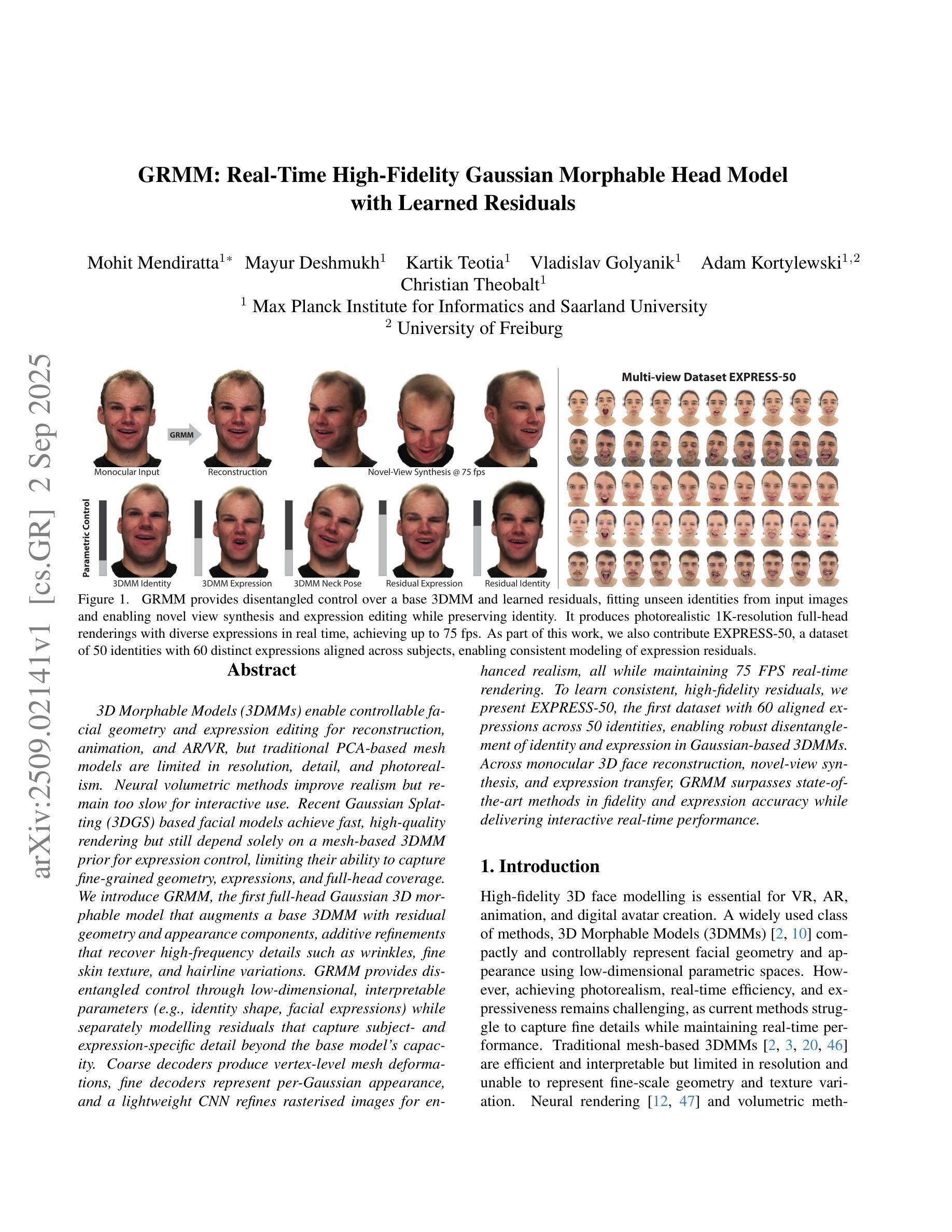
3D Morphable Models (3DMMs) enable controllable facial geometry and expression editing for reconstruction, animation, and AR/VR, but traditional PCA-based mesh models are limited in resolution, detail, and photorealism. Neural volumetric methods improve realism but remain too slow for interactive use. Recent Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) based facial models achieve fast, high-quality rendering but still depend solely on a mesh-based 3DMM prior for expression control, limiting their ability to capture fine-grained geometry, expressions, and full-head coverage. We introduce GRMM, the first full-head Gaussian 3D morphable model that augments a base 3DMM with residual geometry and appearance components, additive refinements that recover high-frequency details such as wrinkles, fine skin texture, and hairline variations. GRMM provides disentangled control through low-dimensional, interpretable parameters (e.g., identity shape, facial expressions) while separately modelling residuals that capture subject- and expression-specific detail beyond the base model’s capacity. Coarse decoders produce vertex-level mesh deformations, fine decoders represent per-Gaussian appearance, and a lightweight CNN refines rasterised images for enhanced realism, all while maintaining 75 FPS real-time rendering. To learn consistent, high-fidelity residuals, we present EXPRESS-50, the first dataset with 60 aligned expressions across 50 identities, enabling robust disentanglement of identity and expression in Gaussian-based 3DMMs. Across monocular 3D face reconstruction, novel-view synthesis, and expression transfer, GRMM surpasses state-of-the-art methods in fidelity and expression accuracy while delivering interactive real-time performance.
3D可变模型(3DMM)可实现面部几何形状和表情编辑的重建、动画以及AR/VR。但传统的基于PCA的网格模型在分辨率、细节和逼真度方面存在局限性。神经体积法提高了逼真度,但用于交互的速率仍然太慢。最近基于高斯涂抹(3DGS)的面部模型实现了快速高质量渲染,但仍然仅依赖于基于网格的3DMM先验进行表情控制,这限制了其捕捉精细几何形状、表情和全头覆盖的能力。我们介绍了GRMM,这是第一个全头高斯3D可变模型,它通过基础3DMM与残余几何和外观组件相结合,增加了附加精细度,可以恢复高频细节,如皱纹、皮肤纹理和发际线变化。GRMM通过低维度、可解释的参数(例如身份形状、面部表情)提供了解耦控制,同时分别对超出基础模型容量的特定主体和表情细节进行建模。粗糙解码器产生顶点级网格变形,精细解码器表示每个高斯的外观,一个轻量级的CNN对渲染的图像进行细化,以增强逼真度,同时保持75 FPS的实时渲染。为了学习一致的高保真残差,我们推出了EXPRESS-50数据集,该数据集包含50个身份的60个对齐表情,能够在基于高斯分布的3DMM中实现身份和表情的稳健解耦。在单眼3D面部重建、新视角合成和表情转移方面,GRMM在保真度和表情准确性方面超越了最先进的方法,同时提供了交互式实时性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://mohitm1994.github.io/GRMM/
摘要
本文提出一种全新的全头高斯三维可变形模型GRMM,它通过增加基础三维可变形模型(3DMM)的残余几何和外观成分,实现了快速高质量渲染,并能控制面部几何形状和表情。GRMM能够捕捉高频细节,如皱纹、皮肤纹理和头发线变化等。它通过低维度、可解释的参数(如身份形状、面部表情)提供了解耦控制,同时建立超出基础模型能力的残余模型。粗解码器产生顶点级网格变形,精细解码器表示每个高斯的外观,轻量级卷积神经网络对渲染图像进行微调,以增强真实感。此外,为了学习一致的高保真残余模型,本文引入了EXPRESS-50数据集,该数据集包含50个身份的60个对齐表情,使高斯基础三维可变形模型的身份和表情解耦更加稳健。在单目三维人脸重建、新视角合成和表情转移等方面,GRMM在保真度和表情准确性方面超越了现有方法,同时实现了交互式实时性能。
关键见解
- 提出了全新的全头高斯三维可变形模型GRMM,结合了基础三维可变形模型(3DMM)和残余几何及外观成分。
- GRMM能够实现快速高质量渲染,并控制面部几何形状和表情。
- GRMM可以捕捉高频细节,如皱纹、皮肤纹理和头发线变化。
- 通过低维度、可解释的参数进行解耦控制,同时建立残余模型以捕捉超出基础模型能力的细节。
- 引入了EXPRESS-50数据集,用于学习一致的高保真残余模型,实现身份和表情的稳健解耦。
- 在多项实验如单目三维人脸重建、新视角合成和表情转移中,GRMM的性能超越了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
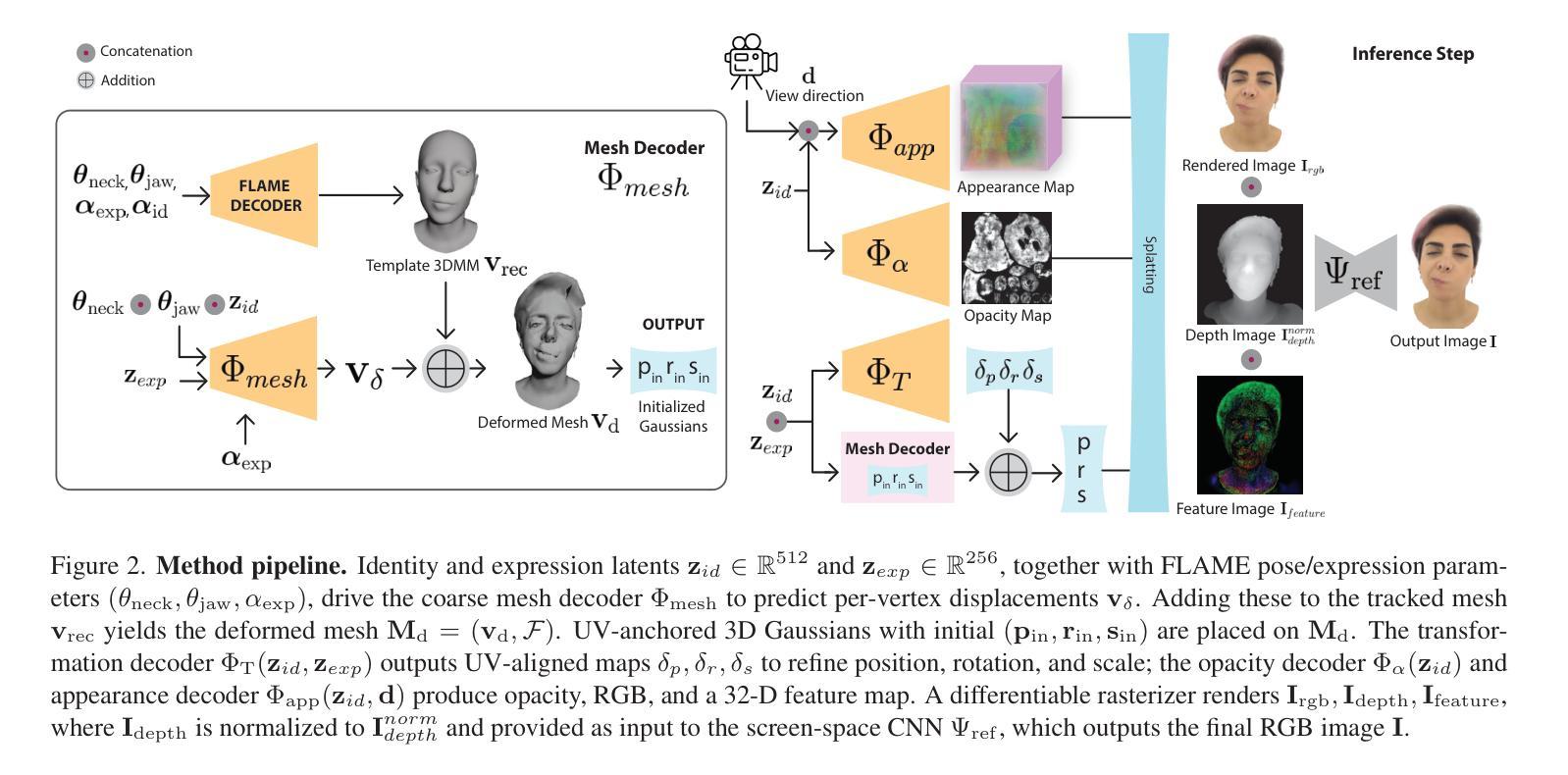
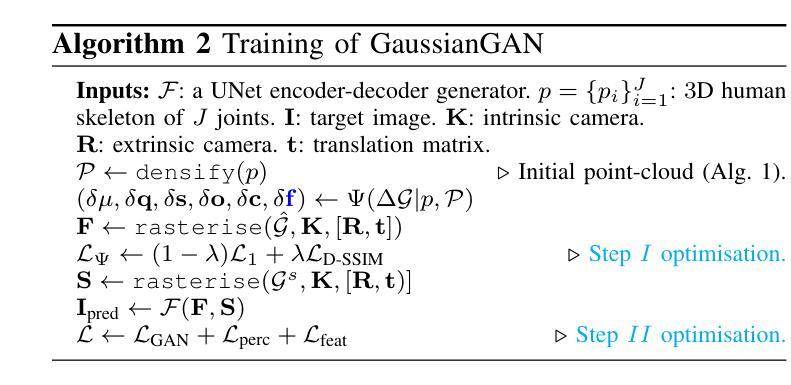
GaussianGAN: Real-Time Photorealistic controllable Human Avatars
Authors:Mohamed Ilyes Lakhal, Richard Bowden
Photorealistic and controllable human avatars have gained popularity in the research community thanks to rapid advances in neural rendering, providing fast and realistic synthesis tools. However, a limitation of current solutions is the presence of noticeable blurring. To solve this problem, we propose GaussianGAN, an animatable avatar approach developed for photorealistic rendering of people in real-time. We introduce a novel Gaussian splatting densification strategy to build Gaussian points from the surface of cylindrical structures around estimated skeletal limbs. Given the camera calibration, we render an accurate semantic segmentation with our novel view segmentation module. Finally, a UNet generator uses the rendered Gaussian splatting features and the segmentation maps to create photorealistic digital avatars. Our method runs in real-time with a rendering speed of 79 FPS. It outperforms previous methods regarding visual perception and quality, achieving a state-of-the-art results in terms of a pixel fidelity of 32.94db on the ZJU Mocap dataset and 33.39db on the Thuman4 dataset.
真实感和可控的人类化身由于神经渲染的快速发展而提供了快速和真实的合成工具,因此在研究社区中受到了欢迎。然而,当前解决方案的一个限制是存在明显的模糊。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了GaussianGAN,这是一种为实时真人照片渲染而开发的可动态化身方法。我们引入了一种新颖的高斯喷射点密化策略,用于从估计的骨骼肢体周围的柱状结构表面构建高斯点。给定相机校准,我们使用全新的视图分割模块进行准确的语义分割。最后,UNet生成器使用渲染的高斯喷射特征和分割图来创建真实感的数字化身。我们的方法在实时运行,渲染速度为79 FPS。在视觉感知和质量方面,它优于以前的方法,在ZJU Mocap数据集上实现了像素保真度32.94db,在Thuman4数据集上实现了33.39db,达到了最新技术水平的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE conference series on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition 2025
Summary
神经渲染技术的快速发展为人类提供了快速而逼真的合成工具,推动了逼真可控的人类角色(avatars)的研究。然而,当前解决方案存在明显的模糊问题。为解决这一问题,本文提出GaussianGAN方法,该方法用于实时渲染逼真的人物角色。通过引入高斯点生成策略,结合相机校准和新型视图分割模块,实现了准确渲染。使用UNet生成器结合渲染的高斯点和分割图,生成逼真的数字角色。该方法实时运行,渲染速度达到79 FPS,在ZJU Mocap和Thuman4数据集上的像素保真度达到业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 神经渲染技术的快速发展促进了逼真可控的人类角色的研究。
- 当前解决方案存在明显的模糊问题,需要新方法解决。
- GaussianGAN方法用于实时渲染逼真的人物角色。
- GaussianGAN引入了高斯点生成策略来解决模糊问题。
- 结合相机校准和新型视图分割模块,实现了准确渲染。
- 使用UNet生成器结合渲染的高斯点和分割图,生成数字角色。
点此查看论文截图

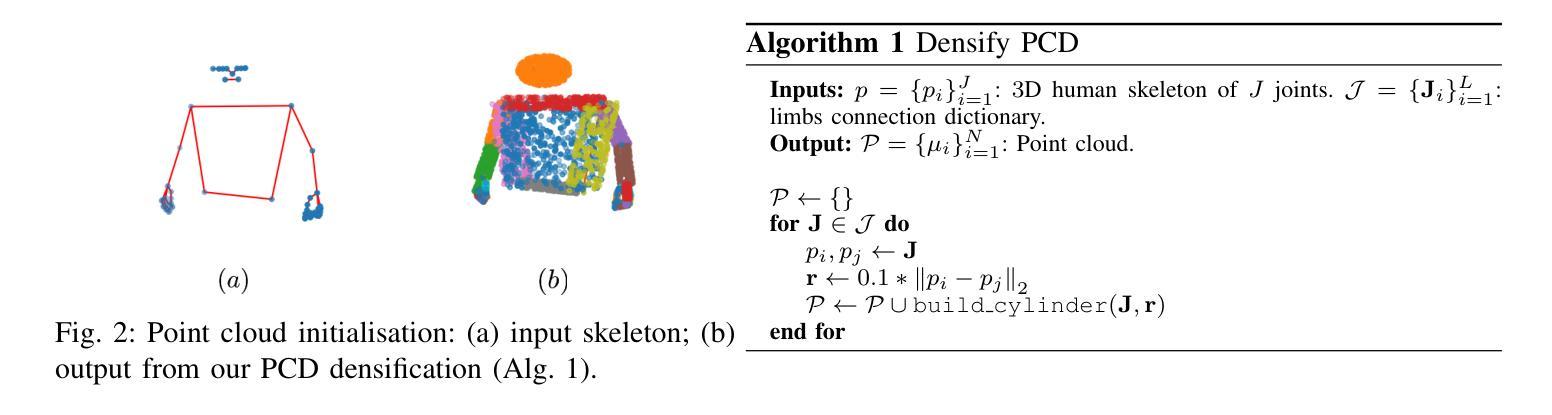
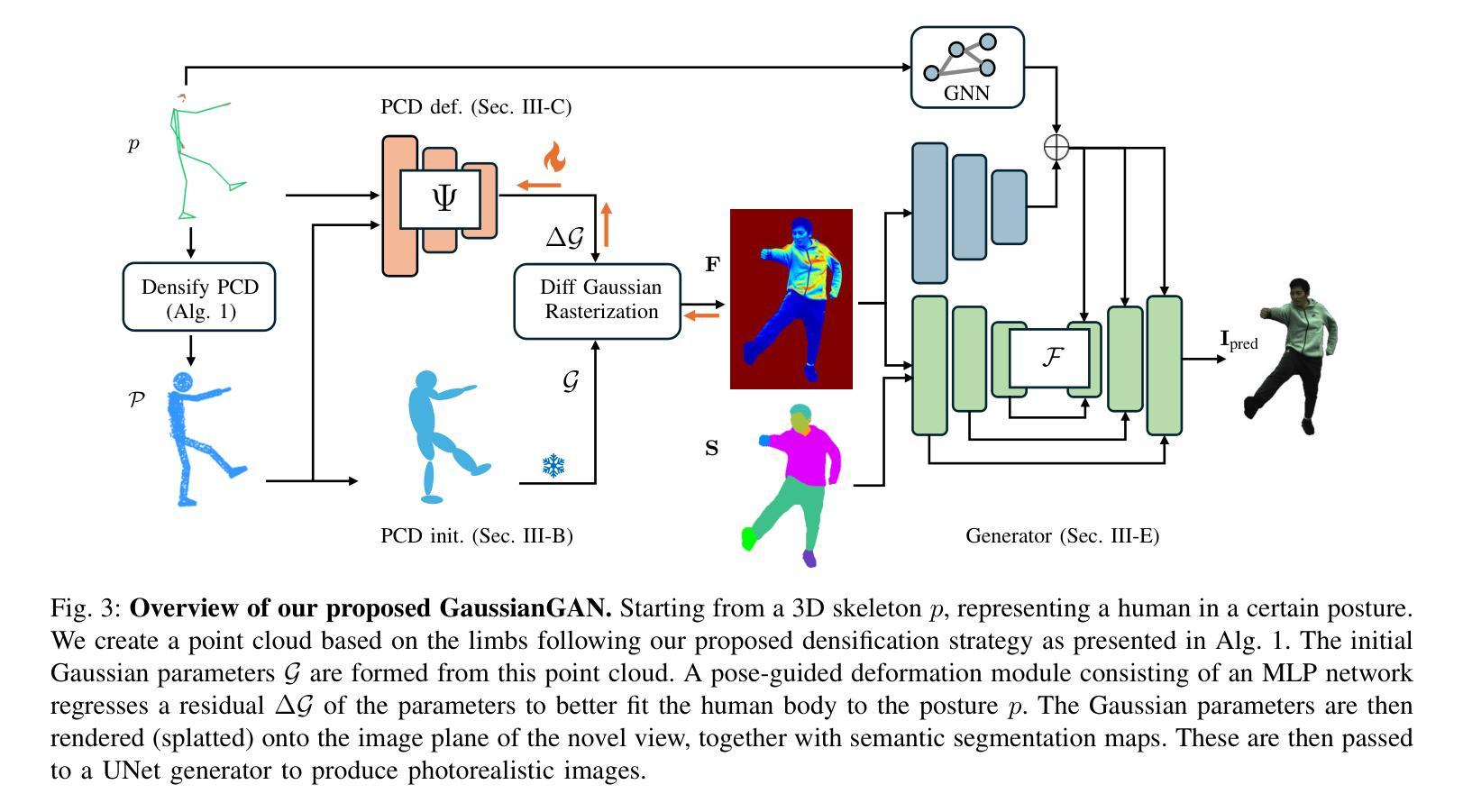
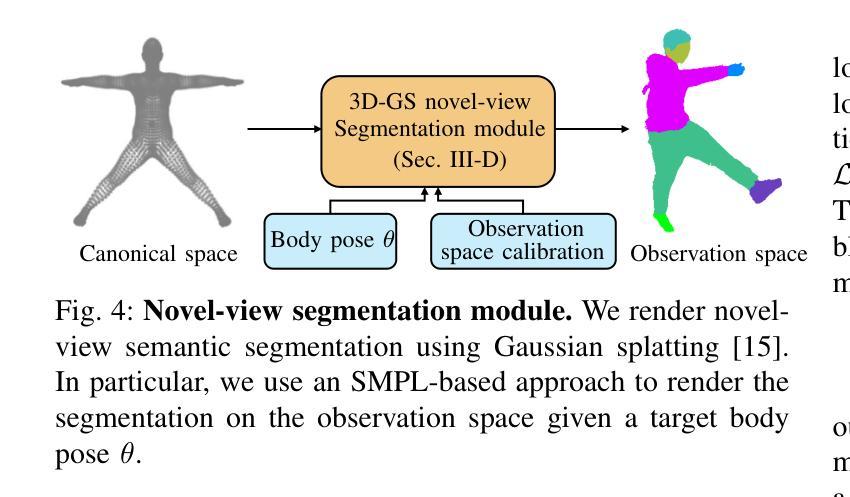

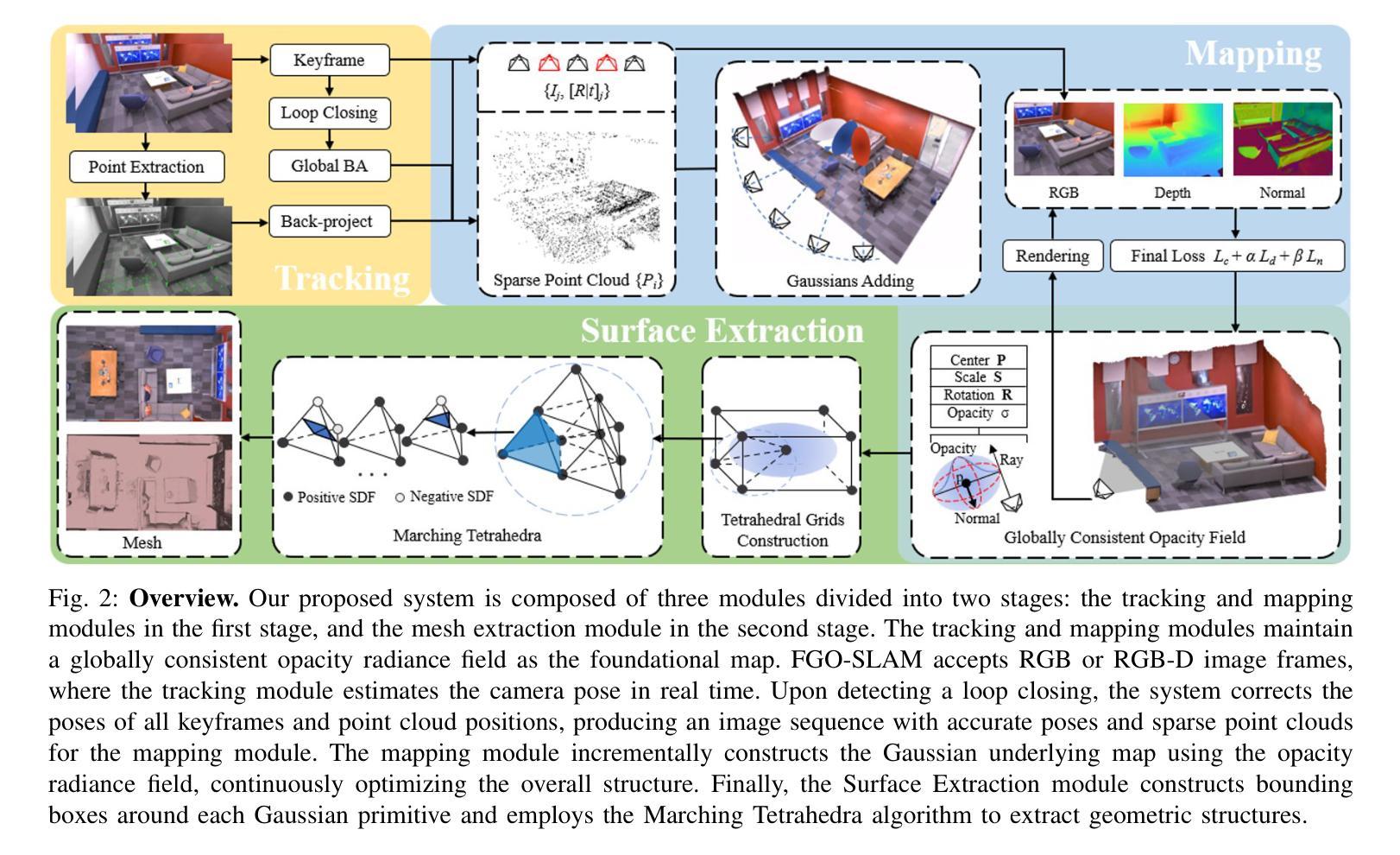
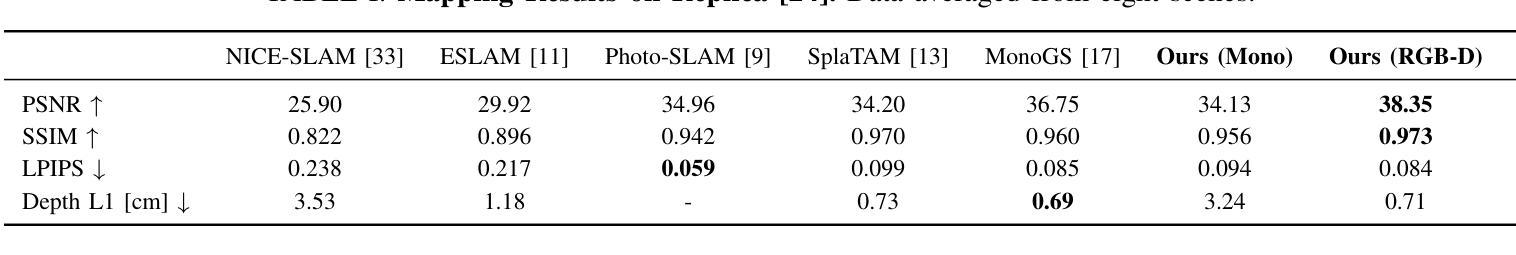
FGO-SLAM: Enhancing Gaussian SLAM with Globally Consistent Opacity Radiance Field
Authors:Fan Zhu, Yifan Zhao, Ziyu Chen, Biao Yu, Hui Zhu
Visual SLAM has regained attention due to its ability to provide perceptual capabilities and simulation test data for Embodied AI. However, traditional SLAM methods struggle to meet the demands of high-quality scene reconstruction, and Gaussian SLAM systems, despite their rapid rendering and high-quality mapping capabilities, lack effective pose optimization methods and face challenges in geometric reconstruction. To address these issues, we introduce FGO-SLAM, a Gaussian SLAM system that employs an opacity radiance field as the scene representation to enhance geometric mapping performance. After initial pose estimation, we apply global adjustment to optimize camera poses and sparse point cloud, ensuring robust tracking of our approach. Additionally, we maintain a globally consistent opacity radiance field based on 3D Gaussians and introduce depth distortion and normal consistency terms to refine the scene representation. Furthermore, after constructing tetrahedral grids, we identify level sets to directly extract surfaces from 3D Gaussians. Results across various real-world and large-scale synthetic datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art tracking accuracy and mapping performance.
视觉SLAM因其能为嵌入式人工智能提供感知能力和模拟测试数据而重新受到关注。然而,传统SLAM方法难以满足高质量场景重建的需求,而高斯SLAM系统尽管具有快速渲染和高品质映射能力,但缺乏有效的姿态优化方法,在几何重建方面面临挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了FGO-SLAM,这是一个采用不透明度辐射场作为场景表示的高斯SLAM系统,以提高几何映射性能。在完成初始姿态估计后,我们应用全局调整来优化相机姿态和稀疏点云,确保我们的方法的稳健跟踪。此外,我们基于三维高斯维持全局一致的不透明度辐射场,并引入深度失真和正常一致性术语来优化场景表示。此外,在构建四面体网格后,我们确定水平集以直接从三维高斯提取表面。在各种现实世界和大规模合成数据集上的结果表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的跟踪精度和映射性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICRA 2025
Summary
视觉SLAM因其能为嵌入式人工智能提供感知能力和模拟测试数据而备受关注。针对传统SLAM方法难以满足高质量场景重建需求,以及高斯SLAM系统在姿态优化和几何重建方面存在的问题,我们提出FGO-SLAM,采用基于高斯分布的透明度辐射场作为场景表示,增强几何映射性能。通过初始姿态估计、全局调整优化相机姿态和稀疏点云,实现稳健的跟踪。此外,我们基于高斯分布维持全局一致的透明度辐射场,引入深度失真和法线一致性项优化场景表示。在构建四面体格网后,我们通过识别等值线直接从高斯分布中提取表面。实验结果在多组真实和大规模合成数据集上显示出本方法达到了最先进的跟踪精度和映射性能。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉SLAM因其对Embodied AI的感知能力和模拟测试数据的贡献而备受关注。
- 传统SLAM方法难以满足高质量场景重建需求。
- 高斯SLAM系统虽具有快速渲染和高精度映射能力,但在姿态优化和几何重建方面存在挑战。
- FGO-SLAM是一个采用透明度辐射场的高斯SLAM系统,旨在增强几何映射性能。
- FGO-SLAM通过初始姿态估计和全局调整优化相机姿态和稀疏点云,实现稳健的跟踪。
- 方法引入深度失真和法线一致性项,以优化场景表示并基于高斯分布直接提取表面。
点此查看论文截图



Im2Haircut: Single-view Strand-based Hair Reconstruction for Human Avatars
Authors:Vanessa Sklyarova, Egor Zakharov, Malte Prinzler, Giorgio Becherini, Michael J. Black, Justus Thies
We present a novel approach for 3D hair reconstruction from single photographs based on a global hair prior combined with local optimization. Capturing strand-based hair geometry from single photographs is challenging due to the variety and geometric complexity of hairstyles and the lack of ground truth training data. Classical reconstruction methods like multi-view stereo only reconstruct the visible hair strands, missing the inner structure of hairstyles and hampering realistic hair simulation. To address this, existing methods leverage hairstyle priors trained on synthetic data. Such data, however, is limited in both quantity and quality since it requires manual work from skilled artists to model the 3D hairstyles and create near-photorealistic renderings. To address this, we propose a novel approach that uses both, real and synthetic data to learn an effective hairstyle prior. Specifically, we train a transformer-based prior model on synthetic data to obtain knowledge of the internal hairstyle geometry and introduce real data in the learning process to model the outer structure. This training scheme is able to model the visible hair strands depicted in an input image, while preserving the general 3D structure of hairstyles. We exploit this prior to create a Gaussian-splatting-based reconstruction method that creates hairstyles from one or more images. Qualitative and quantitative comparisons with existing reconstruction pipelines demonstrate the effectiveness and superior performance of our method for capturing detailed hair orientation, overall silhouette, and backside consistency. For additional results and code, please refer to https://im2haircut.is.tue.mpg.de.
我们提出了一种从单张照片重建三维头发的新方法,该方法基于全局头发先验结合局部优化。从单张照片捕捉基于发丝的发几何结构是一项挑战,因为发型的多样性和几何复杂性以及缺乏真实训练数据。传统的重建方法,如多视角立体法,只能重建可见的发丝,忽略了发型的内部结构并阻碍了真实感的头发模拟。为解决这一问题,现有方法利用在合成数据上训练的发型先验。然而,这种数据在数量和质量上都是有限的,因为它需要熟练艺术家的手工工作来建立三维发型并创建接近照片级的渲染。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种结合真实和合成数据的有效发型先验学习方法。具体来说,我们在合成数据上训练基于转换器的先验模型,以获得发型内部几何的知识,并在学习过程中引入真实数据来模拟外部结构。这种训练方案能够模拟输入图像中描绘的可见发丝,同时保留发型的一般三维结构。我们利用这一先验信息创建了一种基于高斯平铺的重建方法,可以从一张或多张图像创建发型。与现有重建管道的质量和数量比较表明,我们的方法在捕捉详细的头发方向、整体轮廓和背面一致性方面非常有效且性能优越。更多结果和代码请参考:https://im2haircut.is.tue.mpg.de。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF For more results please refer to the project page https://im2haircut.is.tue.mpg.de
Summary
本文提出了一种基于全球头发先验与局部优化相结合的单照片3D头发重建新方法。该方法结合了真实和合成数据来训练发型先验模型,能捕捉发型内部几何结构,并通过高斯贴图技术从一张或多张照片重建发型。相比现有重建流程,该方法更有效地捕捉头发细节方向、整体轮廓和背面一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的3D头发重建方法,结合全球头发先验和局部优化。
- 通过结合真实和合成数据,训练发型先验模型。
- 模型能捕捉发型内部几何结构。
- 采用高斯贴图技术从一张照片或多张照片重建发型。
- 方法能有效捕捉头发细节方向、整体轮廓和背面一致性。
- 提供了定量和定性的评估,证明该方法优于现有重建流程。
点此查看论文截图
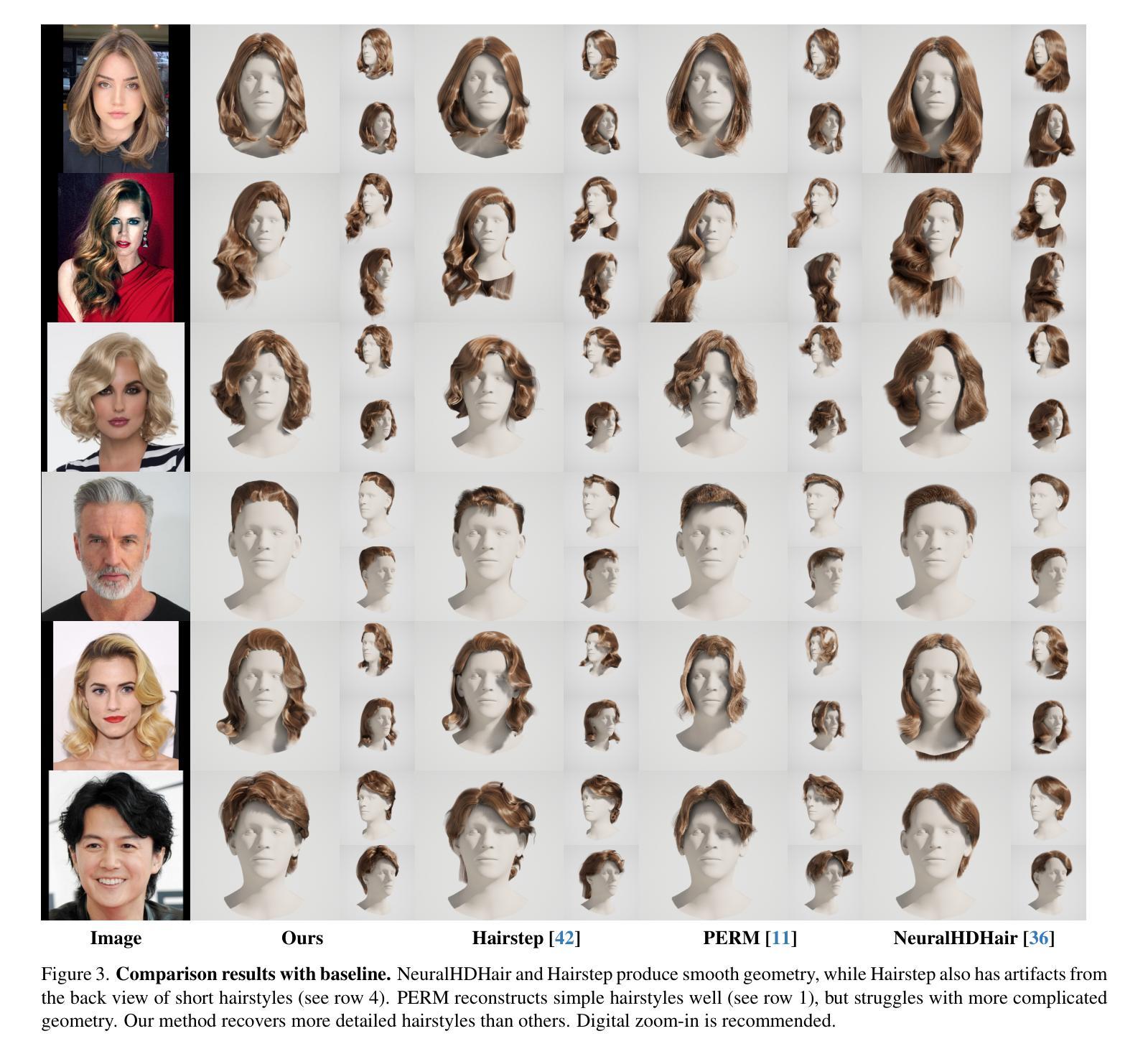


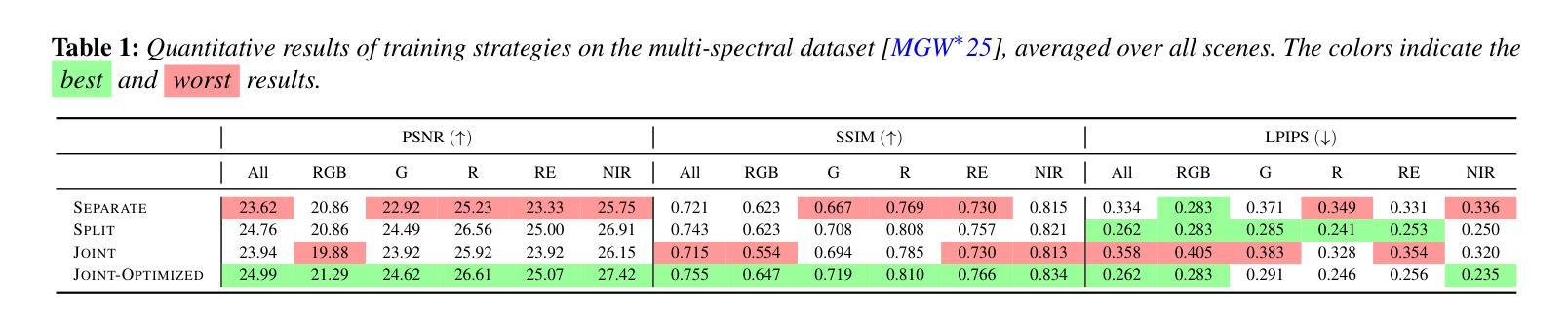
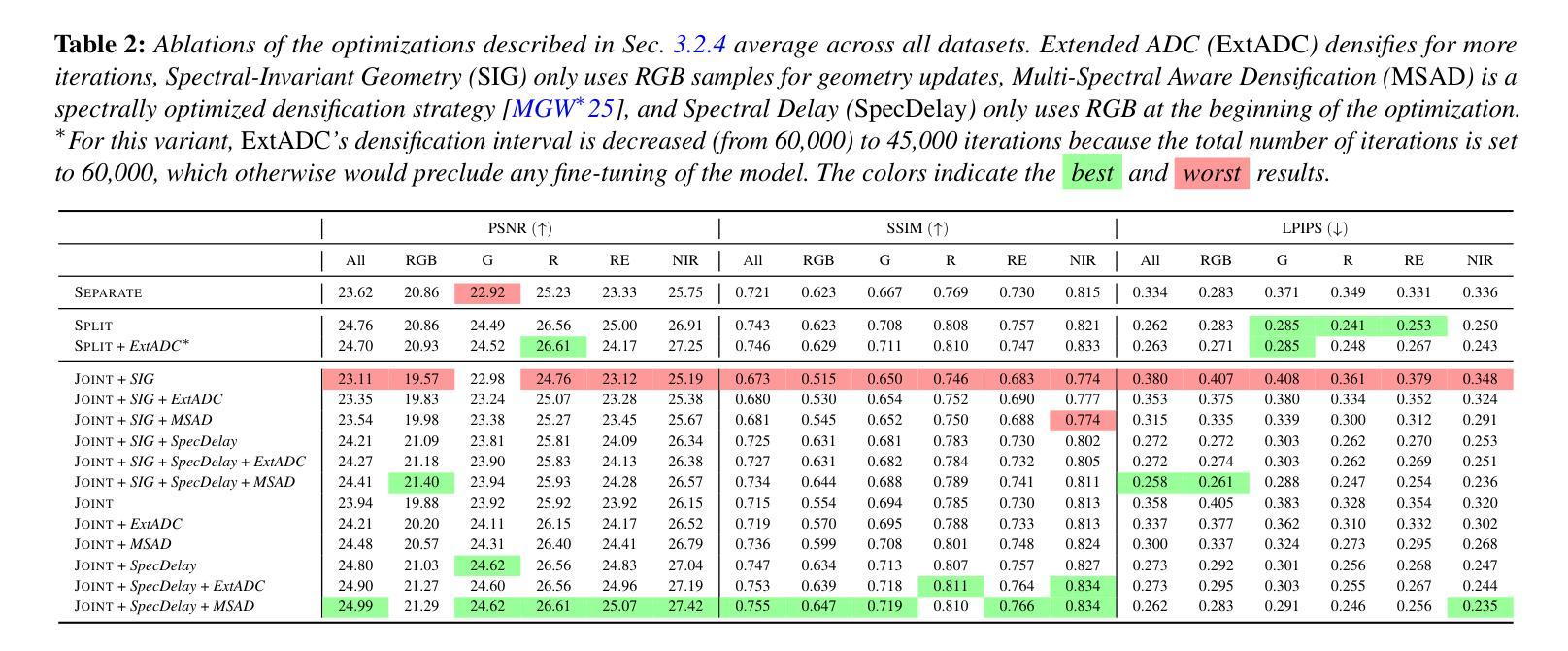
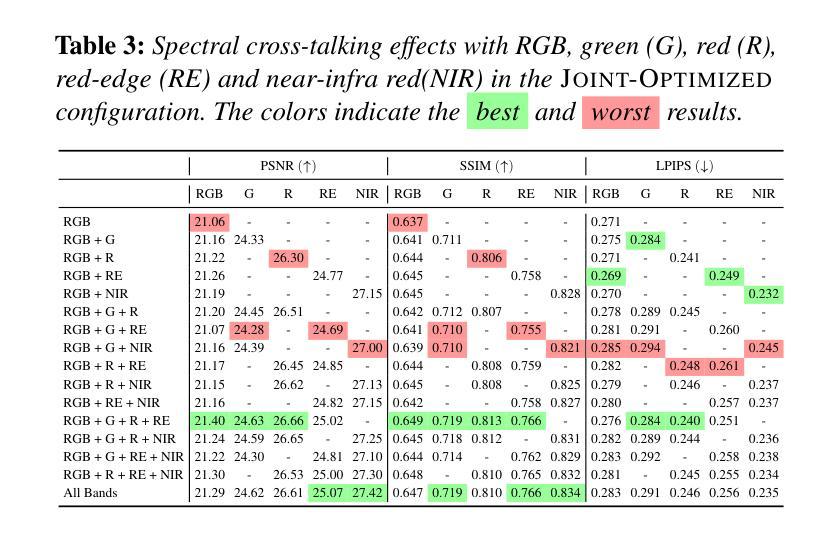
Towards Integrating Multi-Spectral Imaging with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Josef Grün, Lukas Meyer, Maximilian Weiherer, Bernhard Egger, Marc Stamminger, Linus Franke
We present a study of how to integrate color (RGB) and multi-spectral imagery (red, green, red-edge, and near-infrared) into the 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework, a state-of-the-art explicit radiance-field-based method for fast and high-fidelity 3D reconstruction from multi-view images. While 3DGS excels on RGB data, naive per-band optimization of additional spectra yields poor reconstructions due to inconsistently appearing geometry in the spectral domain. This problem is prominent, even though the actual geometry is the same, regardless of spectral modality. To investigate this, we evaluate three strategies: 1) Separate per-band reconstruction with no shared structure. 2) Splitting optimization, in which we first optimize RGB geometry, copy it, and then fit each new band to the model by optimizing both geometry and band representation. 3) Joint, in which the modalities are jointly optimized, optionally with an initial RGB-only phase. We showcase through quantitative metrics and qualitative novel-view renderings on multi-spectral datasets the effectiveness of our dedicated optimized Joint strategy, increasing overall spectral reconstruction as well as enhancing RGB results through spectral cross-talk. We therefore suggest integrating multi-spectral data directly into the spherical harmonics color components to compactly model each Gaussian’s multi-spectral reflectance. Moreover, our analysis reveals several key trade-offs in when and how to introduce spectral bands during optimization, offering practical insights for robust multi-modal 3DGS reconstruction.
我们研究如何将颜色(RGB)和多光谱图像(红色、绿色、红边和近红外)集成到三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)框架中。3DGS是一种基于显式辐射场的先进方法,能够从多视角图像快速进行高保真三维重建。虽然3DGS在RGB数据上表现卓越,但对额外光谱的盲目波段优化会导致重建效果较差,因为在光谱域中几何形状会出现不一致。即使实际几何形状相同,无论光谱模式如何,这个问题仍然突出。为了研究这个问题,我们评估了三种策略:1)无共享结构的单独波段重建。2)分割优化,我们首先优化RGB几何形状,进行复制,然后通过优化几何形状和波段表示来适应每个新波段。3)联合优化,其中模态联合优化,可选择初始的仅RGB阶段。我们通过多光谱数据集上的定量指标和定性新颖视图渲染,展示了我们专门优化的联合策略的有效性,它提高了整体光谱重建效果,并通过光谱交叉增强了RGB结果。因此,我们建议在球形谐波颜色组件中直接集成多光谱数据,以紧凑地模拟每个高斯的多光谱反射。此外,我们的分析揭示了何时以及如何在优化过程中引入光谱波段的几个关键权衡,为稳健的多模式3DGS重建提供了实用见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF for project page, see https://meyerls.github.io/towards_multi_spec_splat/
Summary
本研究探讨了如何将颜色(RGB)和多光谱图像(红、绿、红边和近红外)集成到基于三维高斯展平的框架中,实现对多视角图像进行快速而高精度的三维重建。针对多光谱数据在集成时面临的挑战,研究提出了三种策略,最终通过优化联合策略实现了多光谱重建的有效性,提高了RGB结果的光谱交叉效果。建议直接集成多光谱数据到球面谐波颜色成分中,为每个高斯光谱反射提供紧凑模型。同时,分析提供了在优化过程中引入光谱带的时机和方法的关键权衡,为稳健的多模态三维重建提供了实践见解。
Key Takeaways
- 研究展示了如何将多光谱数据集成到三维高斯展平框架中,以实现高精度三维重建。
- 在处理多光谱数据时面临了不一致几何的挑战。
- 提出了三种策略来解决这一挑战,并通过实验评估了它们的性能。
- 优化联合策略能有效提高多光谱重建效果,并增强RGB结果的光谱交叉效果。
- 建议将多光谱数据直接集成到球面谐波颜色成分中,为高斯光谱反射提供紧凑模型。
点此查看论文截图


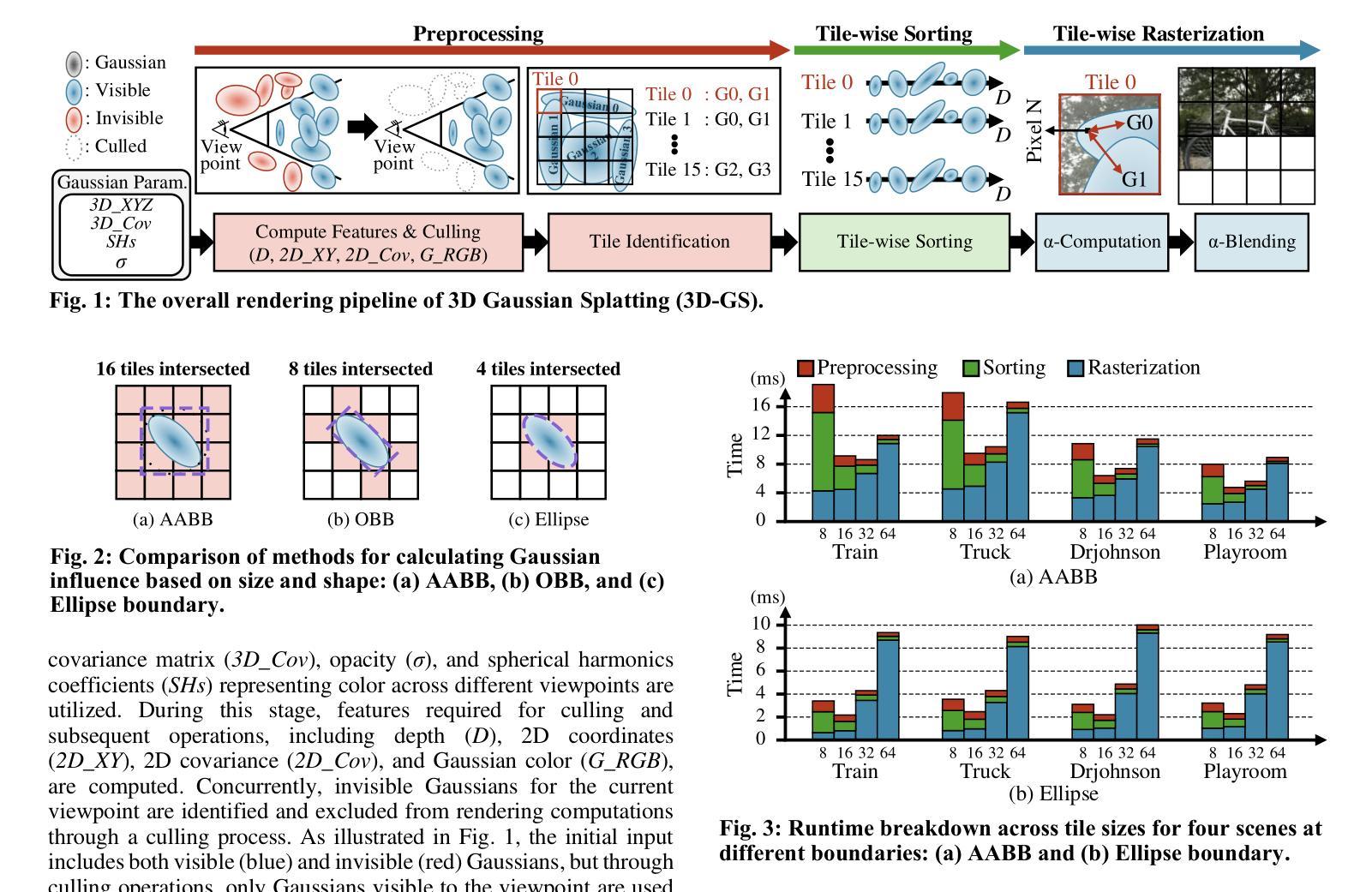
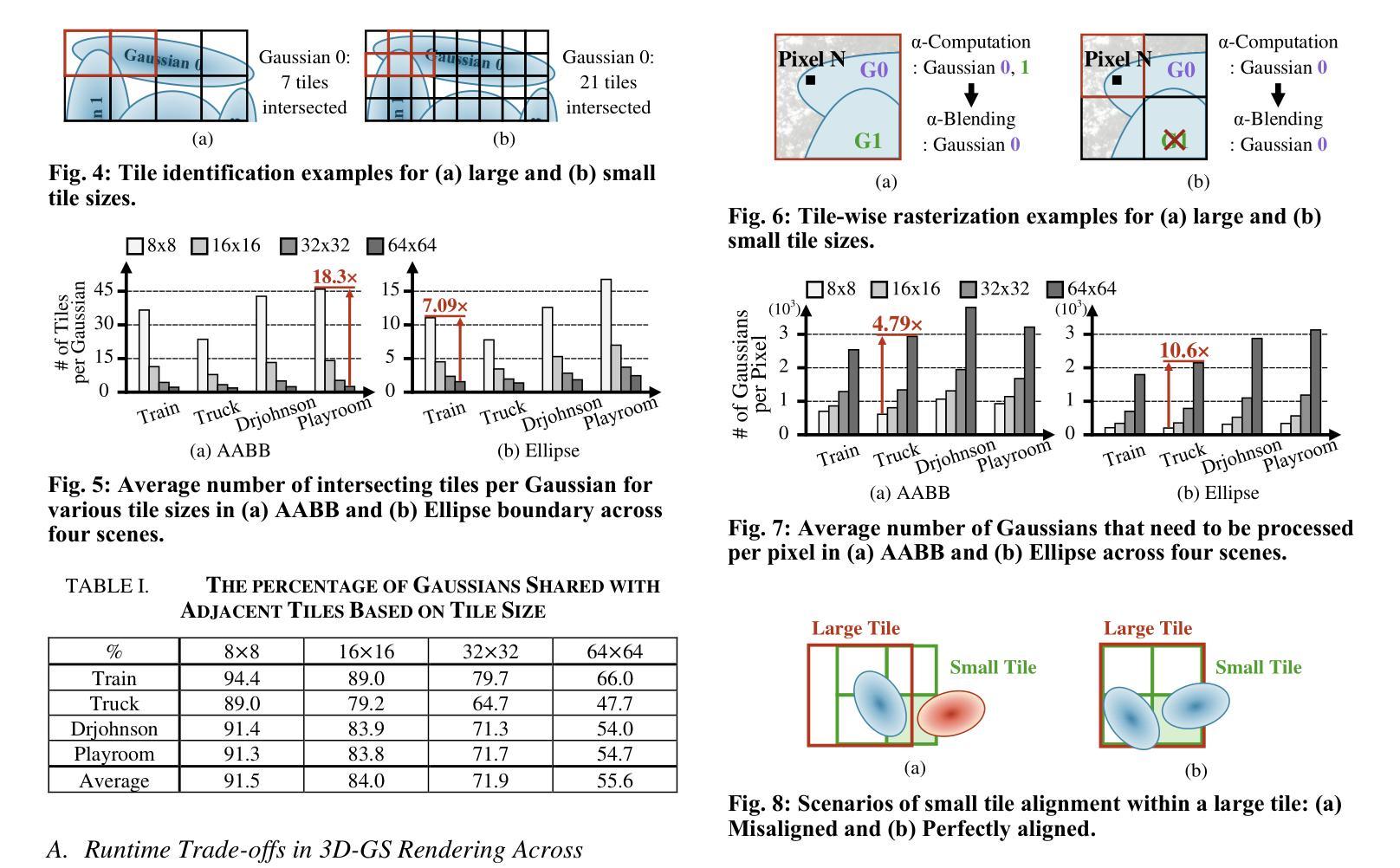
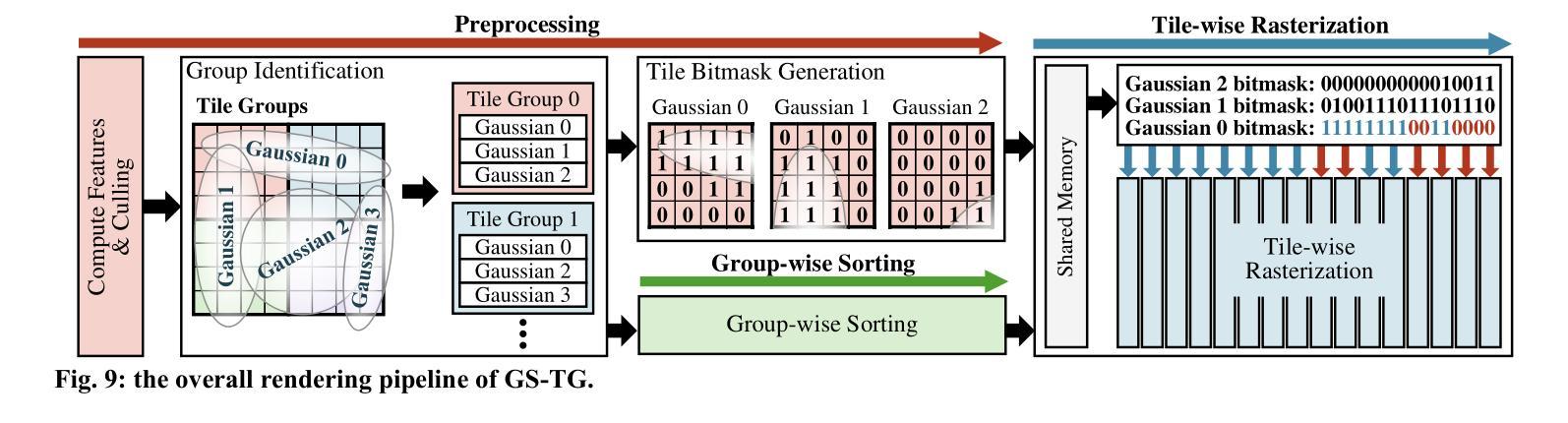
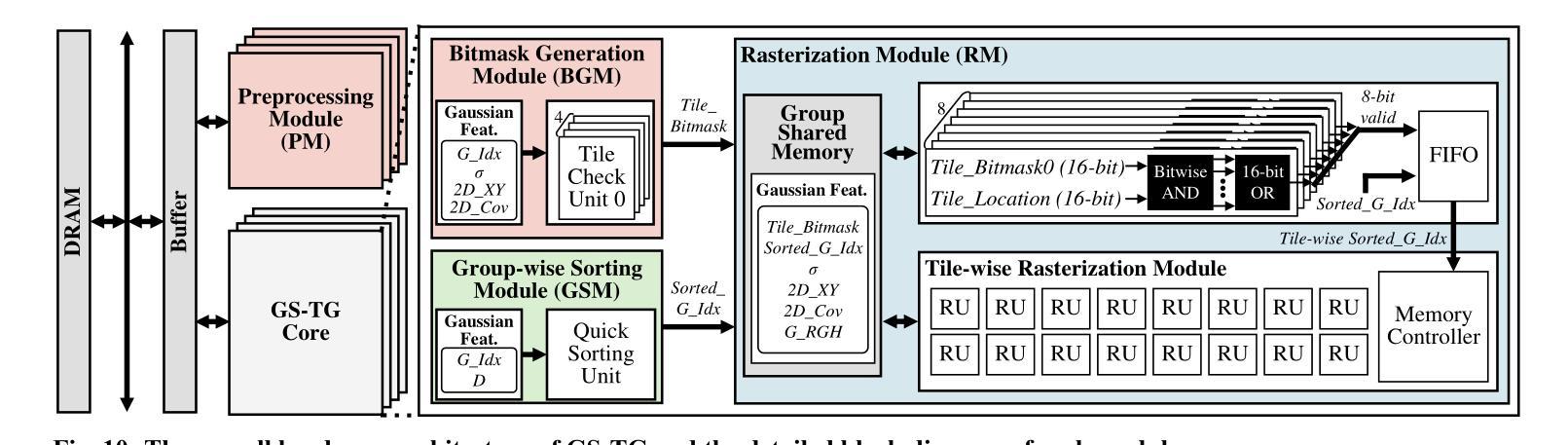
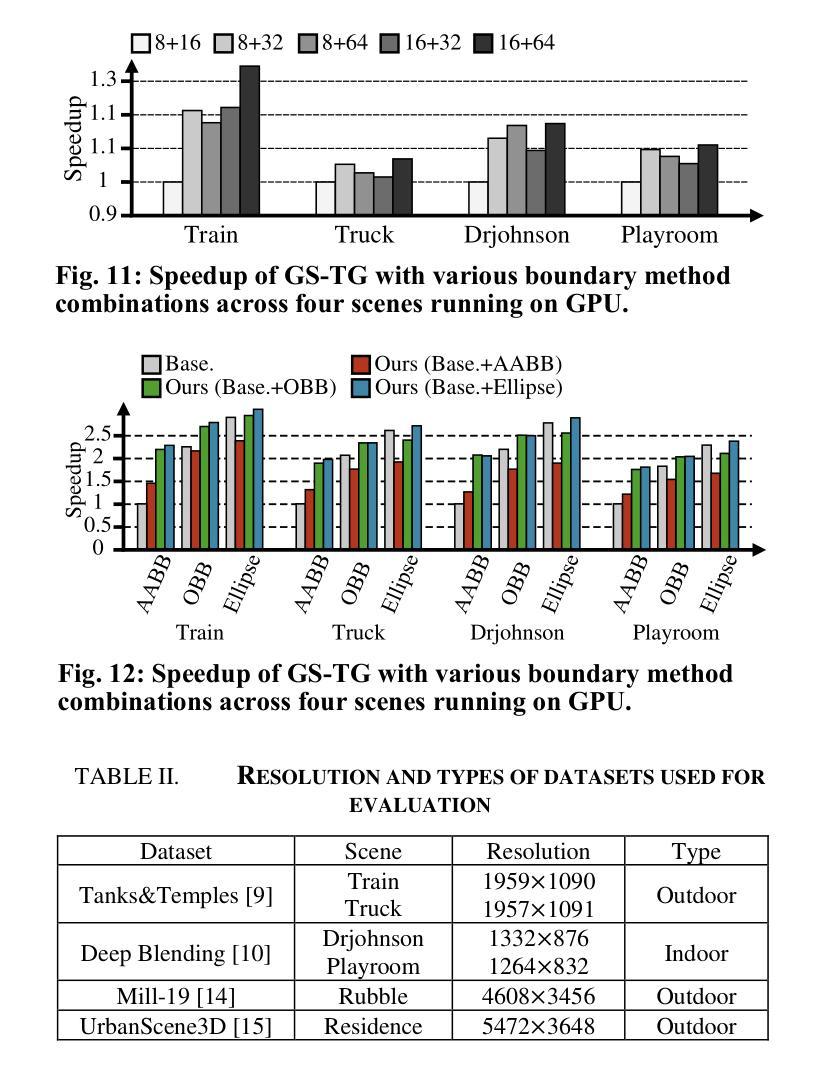
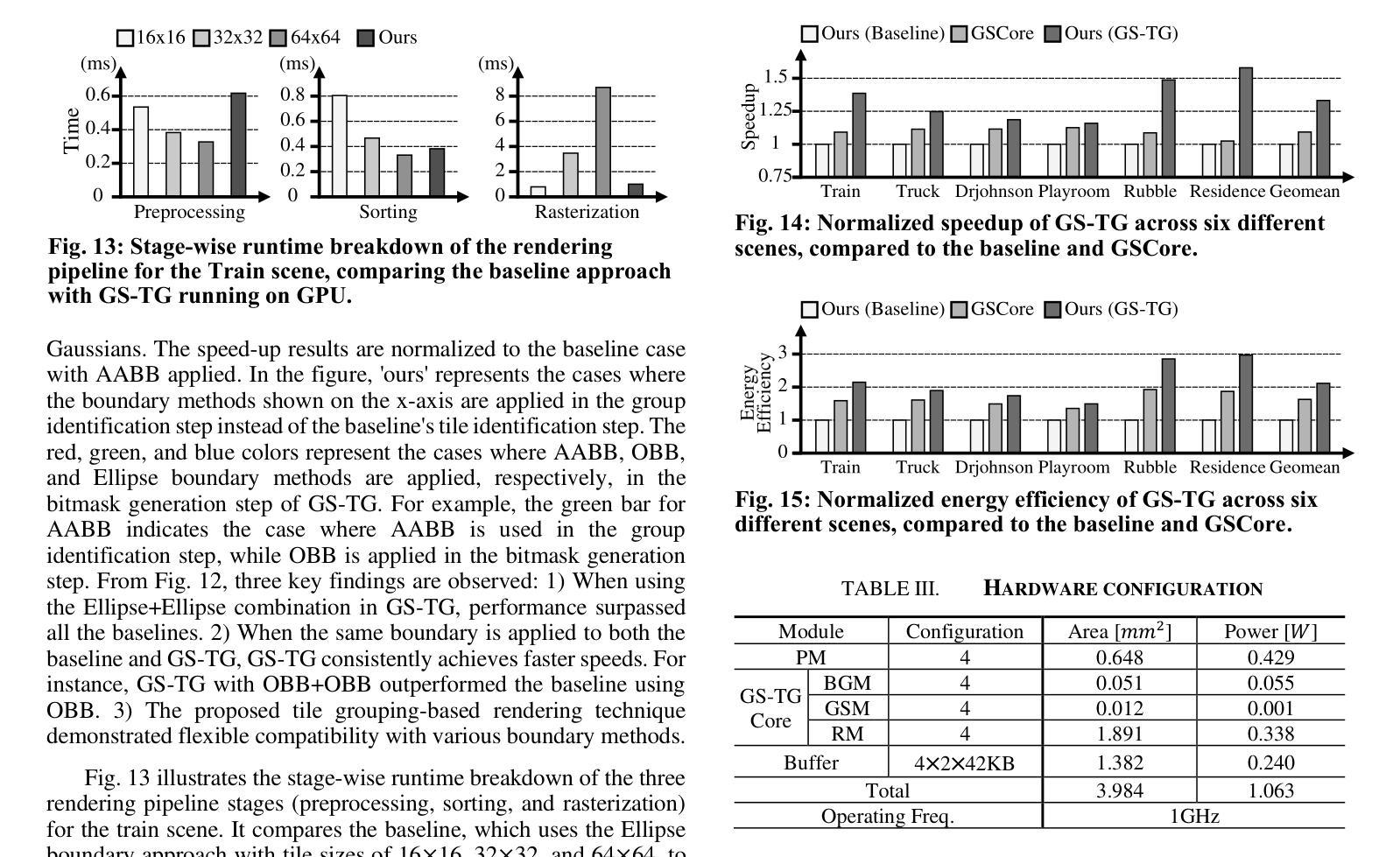
GS-TG: 3D Gaussian Splatting Accelerator with Tile Grouping for Reducing Redundant Sorting while Preserving Rasterization Efficiency
Authors:Joongho Jo, Jongsun Park
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has emerged as a promising alternative to neural radiance fields (NeRF) as it offers high speed as well as high image quality in novel view synthesis. Despite these advancements, 3D-GS still struggles to meet the frames per second (FPS) demands of real-time applications. In this paper, we introduce GS-TG, a tile-grouping-based accelerator that enhances 3D-GS rendering speed by reducing redundant sorting operations and preserving rasterization efficiency. GS-TG addresses a critical trade-off issue in 3D-GS rendering: increasing the tile size effectively reduces redundant sorting operations, but it concurrently increases unnecessary rasterization computations. So, during sorting of the proposed approach, GS-TG groups small tiles (for making large tiles) to share sorting operations across tiles within each group, significantly reducing redundant computations. During rasterization, a bitmask assigned to each Gaussian identifies relevant small tiles, to enable efficient sharing of sorting results. Consequently, GS-TG enables sorting to be performed as if a large tile size is used by grouping tiles during the sorting stage, while allowing rasterization to proceed with the original small tiles by using bitmasks in the rasterization stage. GS-TG is a lossless method requiring no retraining or fine-tuning and it can be seamlessly integrated with previous 3D-GS optimization techniques. Experimental results show that GS-TG achieves an average speed-up of 1.54 times over state-of-the-art 3D-GS accelerators.
三维高斯渲染(3D-GS)作为神经辐射场(NeRF)的一种有前途的替代方案已经出现,因为它在新型视图合成中提供了高速和高图像质量。尽管有了这些进展,但3D-GS仍然难以满足实时应用中的每秒帧数(FPS)需求。在本文中,我们介绍了GS-TG,一种基于瓦片分组技术的加速器,它通过减少冗余排序操作并保持光栅化效率来提高3D-GS的渲染速度。GS-TG解决了在渲染过程中存在的关键问题,即对于实现优化的运行速度有着平衡需求的冲突问题。GS-TG提出了一种创新的策略:增大瓦片尺寸能有效减少冗余排序操作,但同时也会增加不必要的光栅化计算量。因此,在排序过程中,GS-TG会将小瓦片分组(用于制作大瓦片),使每组瓦片共享排序操作,从而显著减少冗余计算。在光栅化过程中,分配给每个高斯值的位掩码用于识别相关的小瓦片,从而实现高效的排序结果共享。因此,通过分组瓦片进行排序阶段,就好像使用较大的瓦片尺寸进行排序一样快,同时通过位掩码在光栅化阶段进行小瓦片的处理来保持原有的性能优势。GS-TG是一种无损方法,无需重新训练或微调,它可以无缝集成到先前的3D-GS优化技术中。实验结果表明,GS-TG相对于先进的加速器的速度提高了平均大约一倍以上(速度为原来1.54倍)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF DAC 2025
Summary
本文介绍了GS-TG,一种基于瓦片分组技术的加速器,用于提升3D高斯喷绘(3D-GS)的渲染速度。GS-TG通过减少冗余排序操作并保持光栅化效率,解决了3D-GS在实时应用中面临的帧率需求挑战。它通过分组瓦片共享排序操作来减少冗余计算,并在光栅化过程中使用位掩码识别相关瓦片,从而实现了高效的排序结果共享。该方法无需重新训练或微调,可无缝集成到先前的3D-GS优化技术中,平均提速达到1.54倍。
Key Takeaways
- GS-TG是一种基于瓦片分组技术的加速器,旨在提高3D高斯喷绘(3D-GS)的渲染速度。
- GS-TG解决了3D-GS在实时应用中面临的帧率需求挑战,满足了高速和高图像质量的要求。
- GS-TG通过减少冗余排序操作和优化光栅化效率来提高渲染速度。
- GS-TG通过分组瓦片共享排序操作来减少计算量,并利用位掩码在光栅化过程中识别相关瓦片,实现高效的排序结果共享。
- GS-TG可以无缝集成到现有的3D-GS优化技术中,并且不需要重新训练或微调。
- 实验结果表明,GS-TG相比现有的3D-GS加速器实现了平均1.54倍的提速。
点此查看论文截图

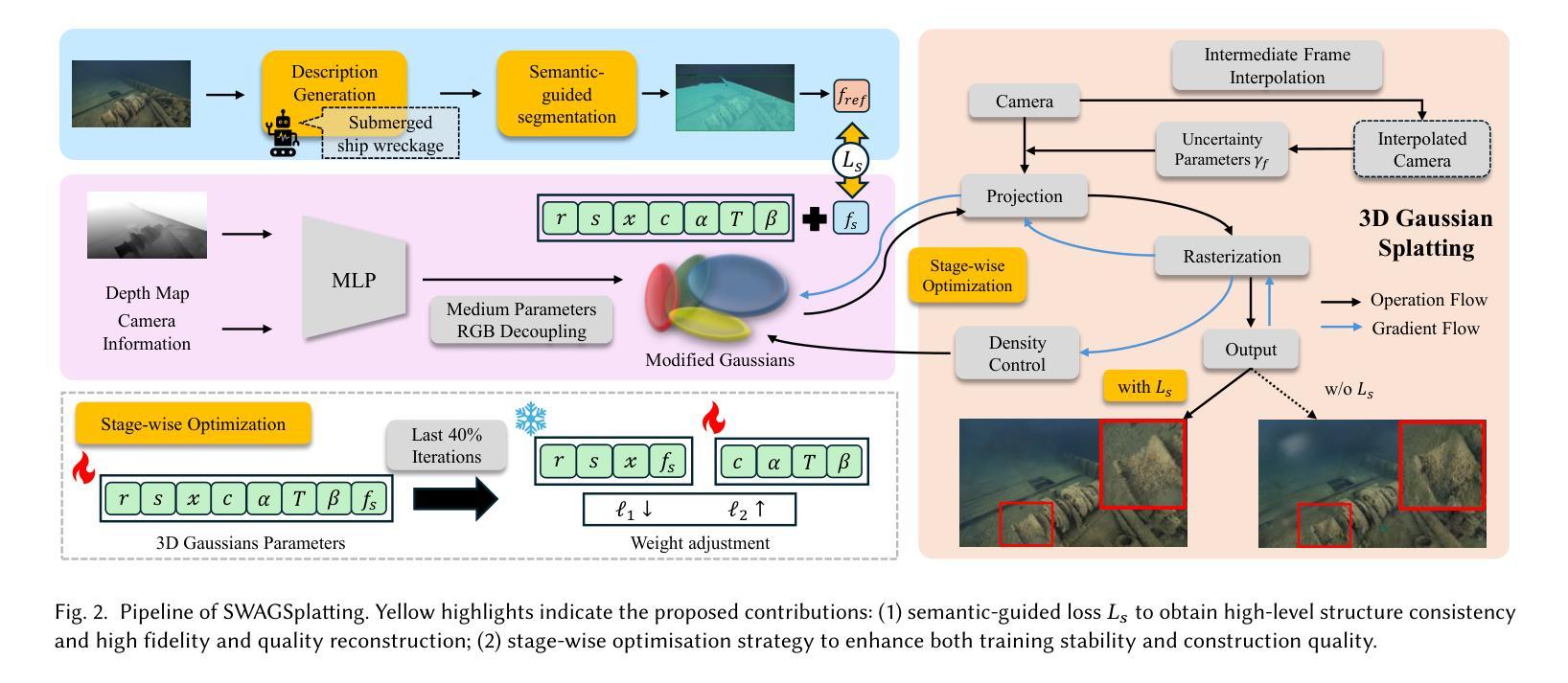
SWAGSplatting: Semantic-guided Water-scene Augmented Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhuodong Jiang, Haoran Wang, Guoxi Huang, Brett Seymour, Nantheera Anantrasirichai
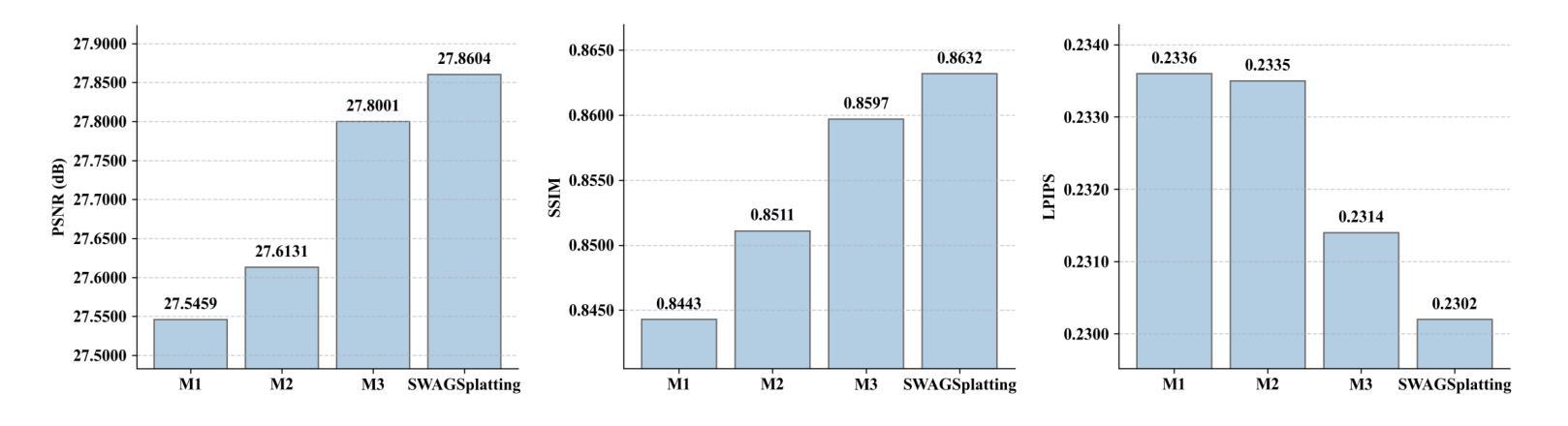
Accurate 3D reconstruction in underwater environments remains a complex challenge due to issues such as light distortion, turbidity, and limited visibility. AI-based techniques have been applied to address these issues, however, existing methods have yet to fully exploit the potential of AI, particularly in integrating language models with visual processing. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that leverages multimodal cross-knowledge to create semantic-guided 3D Gaussian Splatting for robust and high-fidelity deep-sea scene reconstruction. By embedding an extra semantic feature into each Gaussian primitive and supervised by the CLIP extracted semantic feature, our method enforces semantic and structural awareness throughout the training. The dedicated semantic consistency loss ensures alignment with high-level scene understanding. Besides, we propose a novel stage-wise training strategy, combining coarse-to-fine learning with late-stage parameter refinement, to further enhance both stability and reconstruction quality. Extensive results show that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on SeaThru-NeRF and Submerged3D datasets across three metrics, with an improvement of up to 3.09 dB on average in terms of PSNR, making it a strong candidate for applications in underwater exploration and marine perception.
在水下环境中实现精确的3D重建仍然是一个复杂的挑战,因为存在光畸变、浑浊和能见度有限等问题。虽然基于人工智能的技术已应用于解决这些问题,但现有方法尚未充分利用人工智能的潜力,特别是在将语言模型与视觉处理相结合方面。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用跨模态交叉知识创建语义引导的三维高斯拼贴的新框架,以实现稳健和高保真深海场景重建。通过将额外的语义特征嵌入每个高斯基本单位,并在CLIP提取的语义特征监督下,我们的方法在整个训练过程中强制进行语义和结构感知。专用的语义一致性损失确保与高级场景理解的对齐。此外,我们提出了一种新的分阶段训练策略,结合从粗到细的学习与后期参数优化,以进一步提高稳定性和重建质量。大量结果表明,我们的方法在海通透NeRF和淹没三维数据集上三项指标的表现均优于最新方法,在峰值信噪比方面平均提高了高达3.09分贝,使其成为水下探索和海洋感知应用的有力候选者。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to SIGGRAPH Asia 2025 Technical Communications
Summary
本论文提出了一种新型框架,结合多模态跨知识,利用语义引导的三维高斯Splatting技术,实现了深海场景的稳健与高保真重建。该方法通过嵌入额外的语义特征,监督CLIP提取的语义特征,实现了语义和结构感知的训练过程。同时,提出了阶段式训练策略,结合粗到细学习与后期参数优化,提高了模型的稳定性和重建质量。在SeaThru-NeRF和Submerged3D数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法在三项指标上均优于现有技术,平均峰值信噪比提高了高达3.09 dB,为水下探索和海洋感知应用提供了有力支持。
Key Takeaways
- 本论文针对水下环境的三维重建提出了一个新型框架。
- 利用AI技术解决水下环境的光畸变、混浊和有限可见性问题。
- 通过结合多模态知识和语义引导的三维高斯Splatting技术,实现了稳健和高保真的重建。
- 通过嵌入语义特征并结合CLIP技术,模型在训练过程中获得语义和结构感知能力。
- 引入了一种新的阶段式训练策略,结合了粗到细的学习和后期参数优化。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果显示,该方法在性能上显著优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

MarkSplatter: Generalizable Watermarking for 3D Gaussian Splatting Model via Splatter Image Structure
Authors:Xiufeng Huang, Ziyuan Luo, Qi Song, Ruofei Wang, Renjie Wan
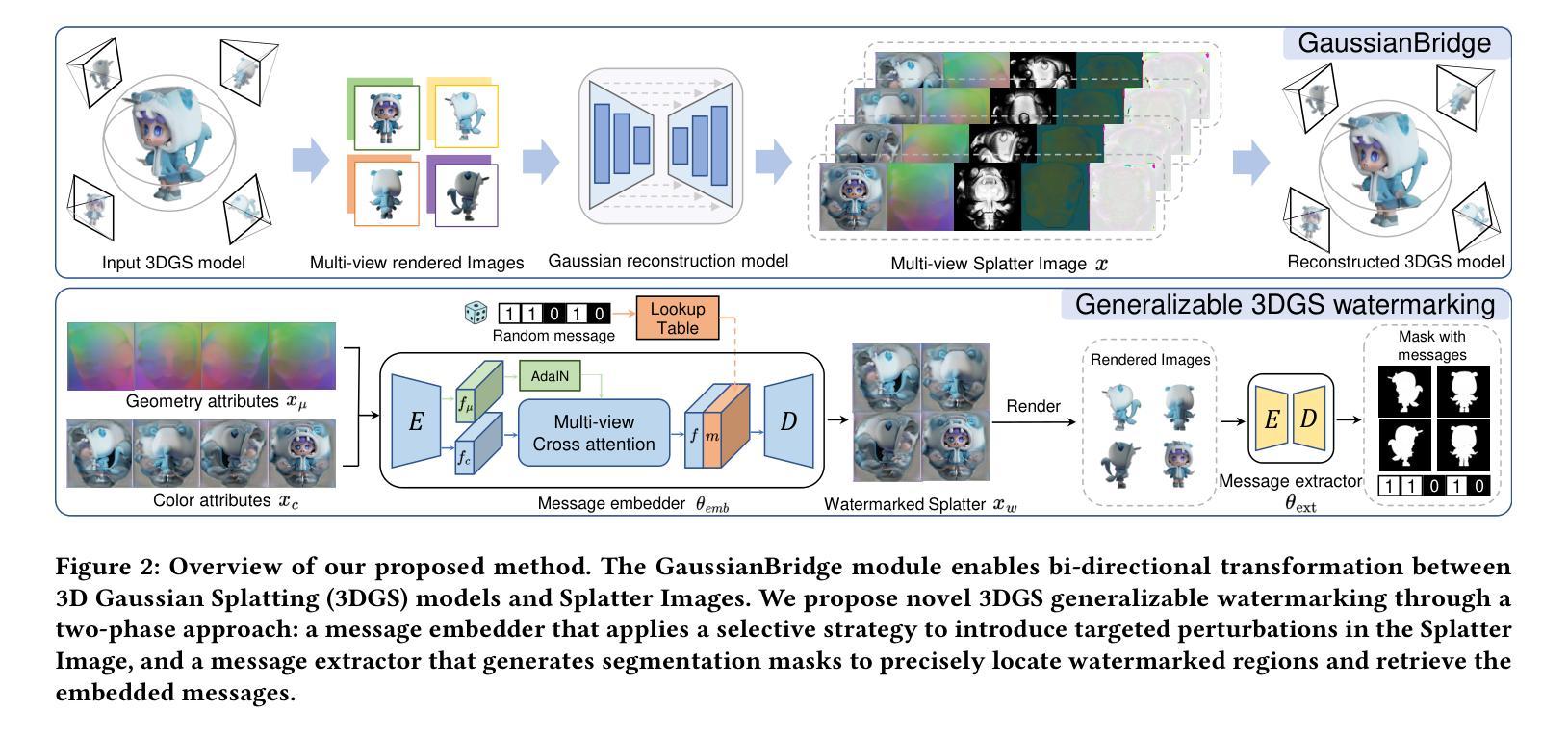
The growing popularity of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has intensified the need for effective copyright protection. Current 3DGS watermarking methods rely on computationally expensive fine-tuning procedures for each predefined message. We propose the first generalizable watermarking framework that enables efficient protection of Splatter Image-based 3DGS models through a single forward pass. We introduce GaussianBridge that transforms unstructured 3D Gaussians into Splatter Image format, enabling direct neural processing for arbitrary message embedding. To ensure imperceptibility, we design a Gaussian-Uncertainty-Perceptual heatmap prediction strategy for preserving visual quality. For robust message recovery, we develop a dense segmentation-based extraction mechanism that maintains reliable extraction even when watermarked objects occupy minimal regions in rendered views. Project page: https://kevinhuangxf.github.io/marksplatter.
随着三维高斯模糊(3DGS)的日益普及,对有效版权保护的需求也日益迫切。当前的3DGS水印方法依赖于针对每条预设信息进行的计算密集型的微调程序。我们提出了第一个通用水印框架,通过单次前向传递实现了基于Splatter图像格式的3DGS模型的有效保护。我们引入了GaussianBridge,它将非结构化的三维高斯转换为Splatter图像格式,实现了任意消息的嵌入式直接神经网络处理。为确保不可察觉性,我们设计了一种基于高斯不确定性感知图的预测策略,以保留视觉效果。为确保可靠地恢复消息,我们开发了一种基于密集分割的提取机制,即使在渲染视图中水印对象占据很小的区域时也能保持可靠的提取效果。项目页面:https://kevinhuangxf.github.io/marksplatter。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文关注于使用简化的方法保护流行技术如三维高斯映射(3DGS)中的版权问题。现有的水印技术复杂且计算量大,需针对每条预设信息调整优化。本研究提出了一种通用的水印框架,通过单次前向传递即可高效保护基于Splatter Image格式的3DGS模型。该研究引入GaussianBridge技术将非结构化的三维高斯转化为Splatter Image格式,使神经处理得以嵌入任意信息成为可能。为保留视觉效果同时保证不被觉察性,其提出了利用高斯不确定性预测策略保障图像质量。并且建立了一套密度分割技术以保障水印在微弱信息覆盖环境下仍能够被完整提取。项目页面链接:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
以下从文本中总结出关键的七点内容:
- 三维高斯映射(3DGS)逐渐成为热点,因此版权保护的需求加大。当前的水印技术难以满足现实需求,其需过于复杂精细的预处理。此项研究则创新性地推出了可一般化的解决方案用于应对这个问题。
- 提出了一种新的水印框架技术——GaussianBridge,能够将非结构化三维高斯数据转化为Splatter Image格式进行便捷处理。这提高了信息嵌入的效率并拓宽了其应用范围。
- 为了确保水印的隐蔽性,研究团队采用了基于高斯不确定性感知图的预测策略来保持图像质量不变。这确保了水印的嵌入不会破坏原始图像的视觉质量。
- 研究团队开发了一种基于密集分割的水印提取机制,这一机制在即使是微小区域内依然可以稳定地提取水印信息。这对于在各种视角获取图像的视觉效果进行了加强优化,且不易因变换视角导致水印失效或难以提取的问题。
- 项目提供了一个详细的项目页面,其中包括该研究的详细信息、成果展示等以供研究者和公众参考。该页面包含了进一步的实验结果和应用示例链接等资源以供共享与查询利用。
- 上述方法的优点体现在简单有效的一站式解决方案和能在几乎不受视场限制的复杂场景中发挥效果的能力上。
点此查看论文截图


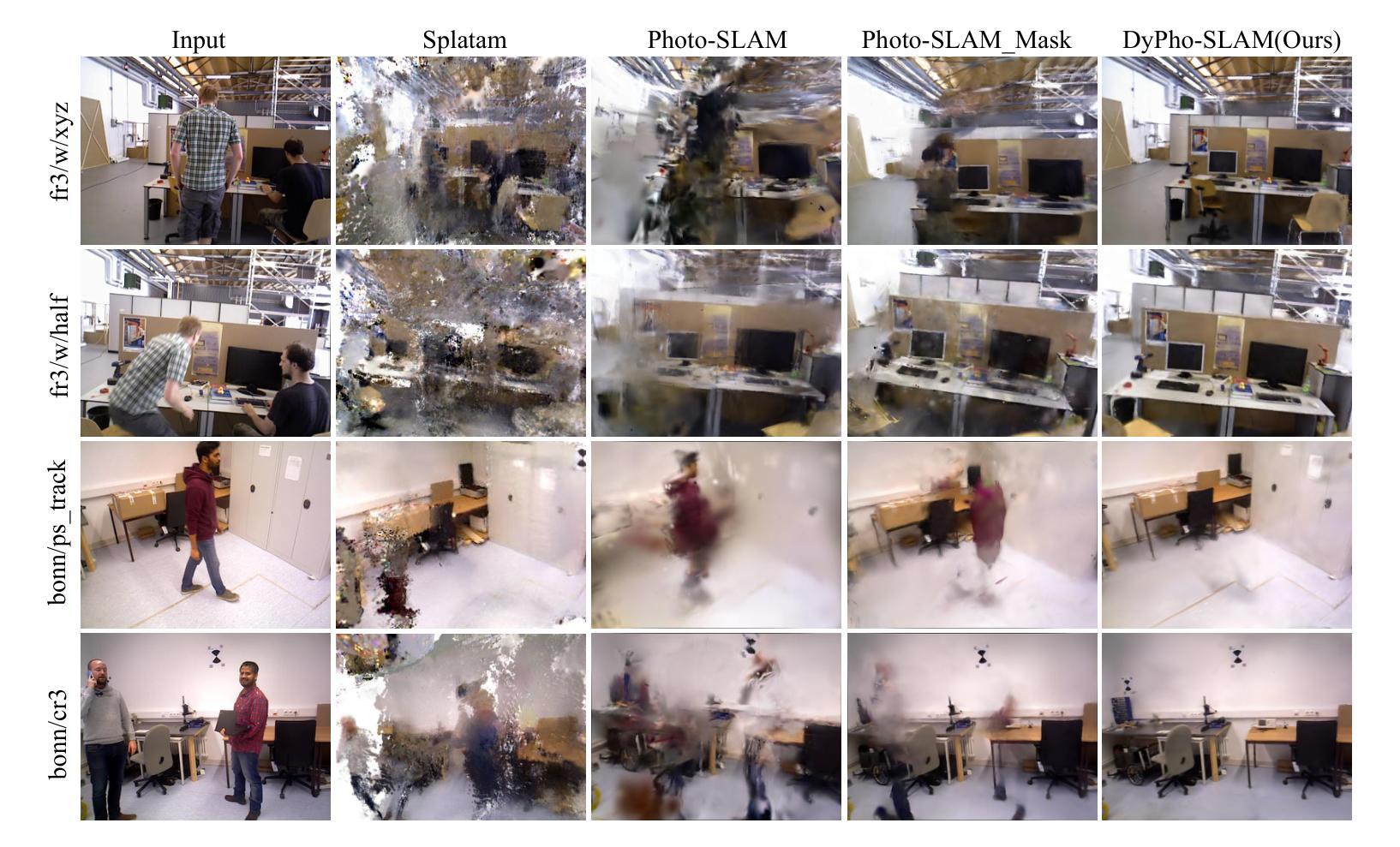
DyPho-SLAM : Real-time Photorealistic SLAM in Dynamic Environments
Authors:Yi Liu, Keyu Fan, Bin Lan, Houde Liu
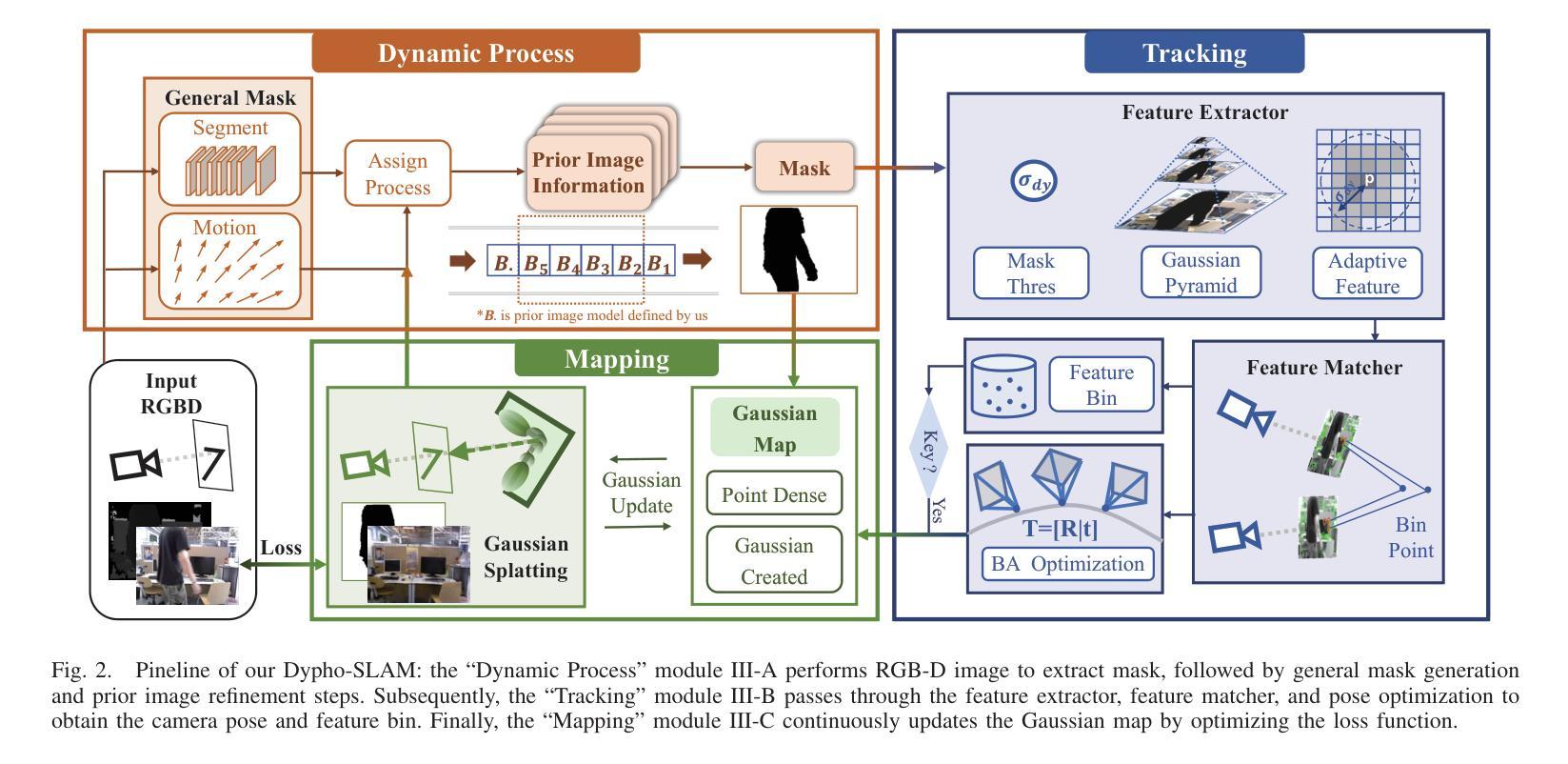
Visual SLAM algorithms have been enhanced through the exploration of Gaussian Splatting representations, particularly in generating high-fidelity dense maps. While existing methods perform reliably in static environments, they often encounter camera tracking drift and fuzzy mapping when dealing with the disturbances caused by moving objects. This paper presents DyPho-SLAM, a real-time, resource-efficient visual SLAM system designed to address the challenges of localization and photorealistic mapping in environments with dynamic objects. Specifically, the proposed system integrates prior image information to generate refined masks, effectively minimizing noise from mask misjudgment. Additionally, to enhance constraints for optimization after removing dynamic obstacles, we devise adaptive feature extraction strategies significantly improving the system’s resilience. Experiments conducted on publicly dynamic RGB-D datasets demonstrate that the proposed system achieves state-of-the-art performance in camera pose estimation and dense map reconstruction, while operating in real-time in dynamic scenes.
视觉SLAM算法通过探索高斯分布图(Gaussian Splatting)表示方法得到了增强,特别是在生成高保真稠密地图方面。尽管现有方法在静态环境中表现可靠,但在处理移动物体引起的干扰时,它们经常遇到摄像机跟踪漂移和模糊映射的问题。本文提出了DyPho-SLAM,这是一个用于解决动态对象环境中定位和逼真度映射挑战的实时、资源高效的视觉SLAM系统。具体来说,该系统结合了先前的图像信息来生成精细的掩膜,有效地减少了因掩膜误判而产生的噪声。此外,为了提高去除动态障碍后的优化约束,我们设计了自适应特征提取策略,大大提高了系统的恢复能力。在公开的动态RGB-D数据集上进行的实验表明,该系统在相机姿态估计和密集地图重建方面达到了最新技术水平,同时在动态场景中实现了实时运行。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICME 2025(Oral)
Summary
本文提出DyPho-SLAM系统,利用高斯Splatting表示法增强视觉SLAM算法,以应对动态环境下的定位和真实感映射挑战。该系统通过整合先前图像信息生成精细遮罩,减少来自遮罩误判的噪声,并采用自适应特征提取策略,提高系统对动态障碍去除后的优化约束的适应性。在公开动态RGB-D数据集上的实验表明,该系统在相机姿态估计和密集地图重建方面达到最新技术水平,可在动态场景中实时运行。
Key Takeaways
- DyPho-SLAM系统利用高斯Splatting表示法增强视觉SLAM算法。
- 系统旨在解决动态环境下的定位和真实感映射挑战。
- 通过整合先前图像信息生成精细遮罩,减少来自遮罩误判的噪声。
- 采用自适应特征提取策略,提高系统对动态障碍去除后的优化约束的适应性。
- 系统在相机姿态估计和密集地图重建方面表现优异。
- 实验结果在公开动态RGB-D数据集上验证。
点此查看论文截图

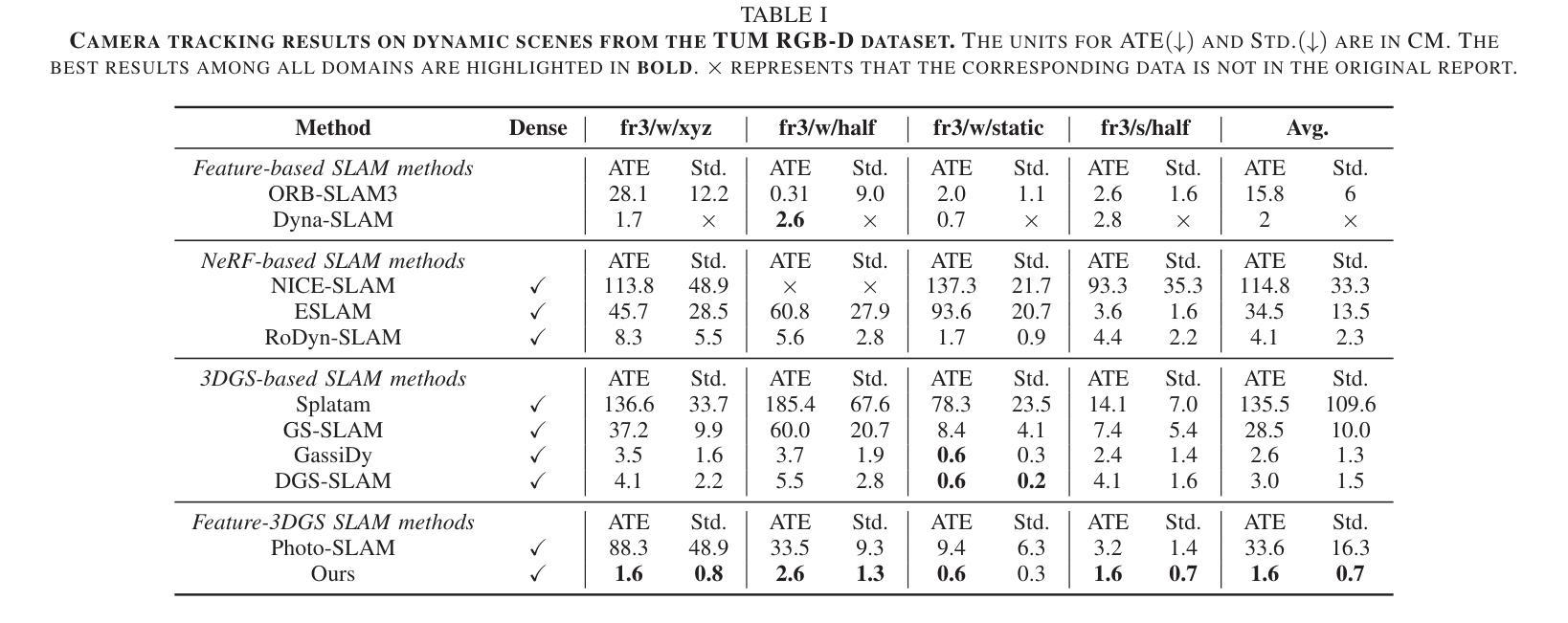

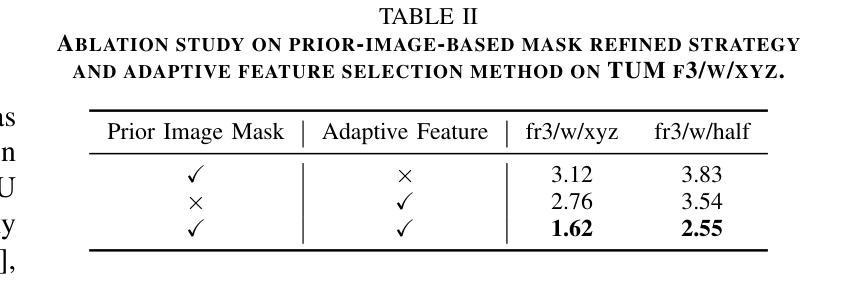
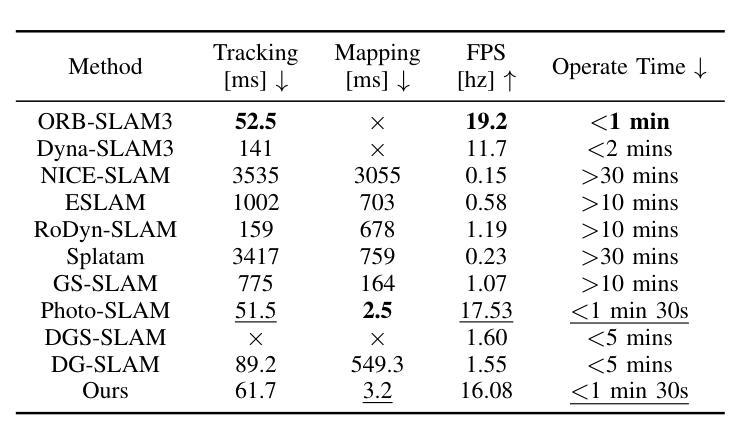
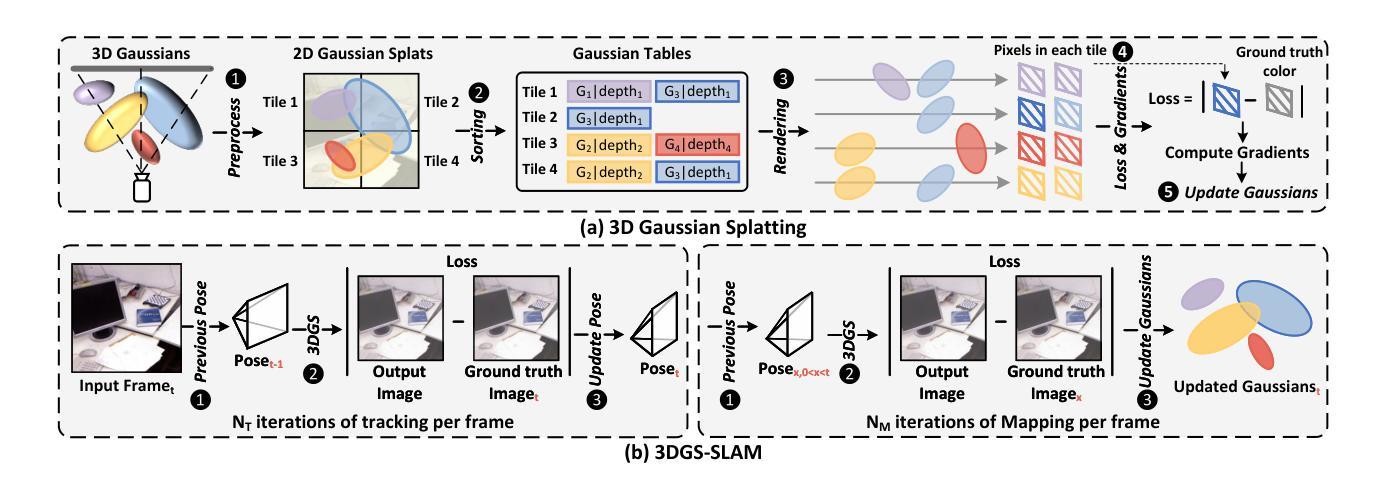
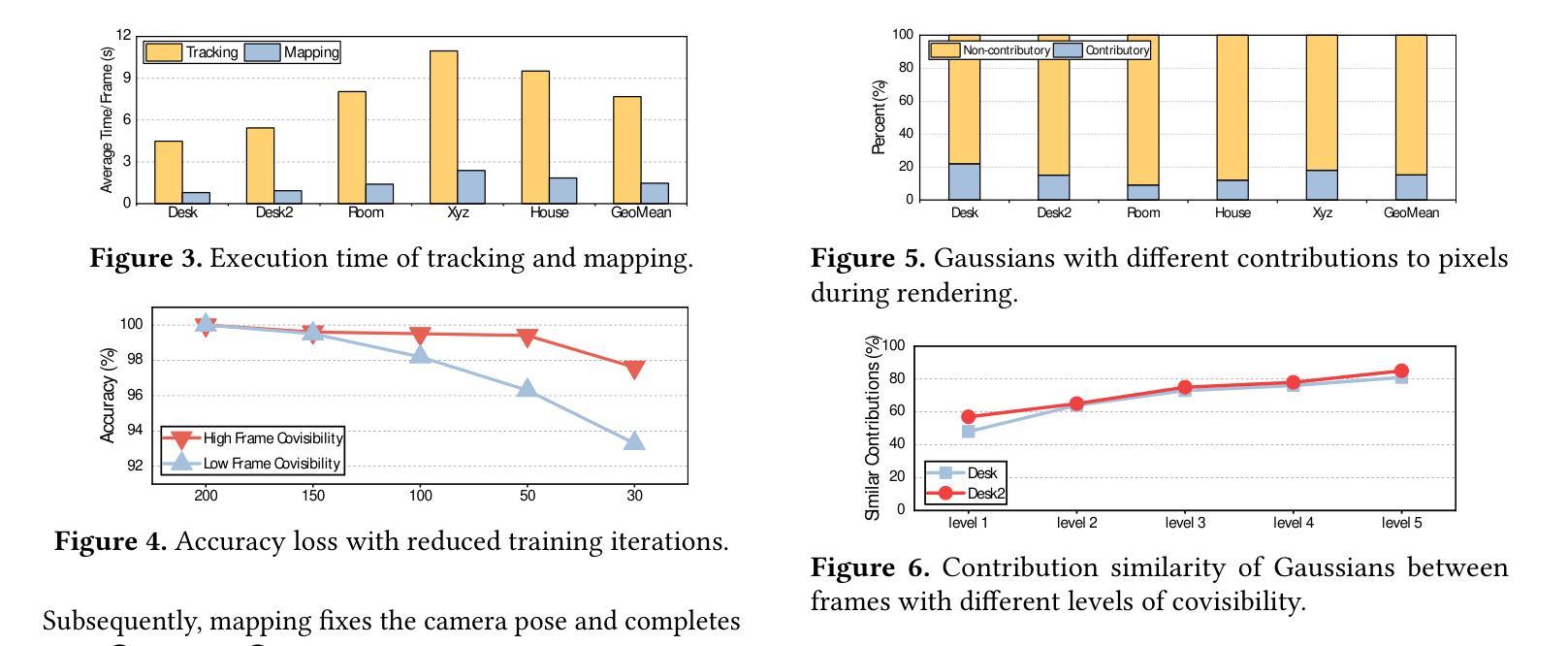
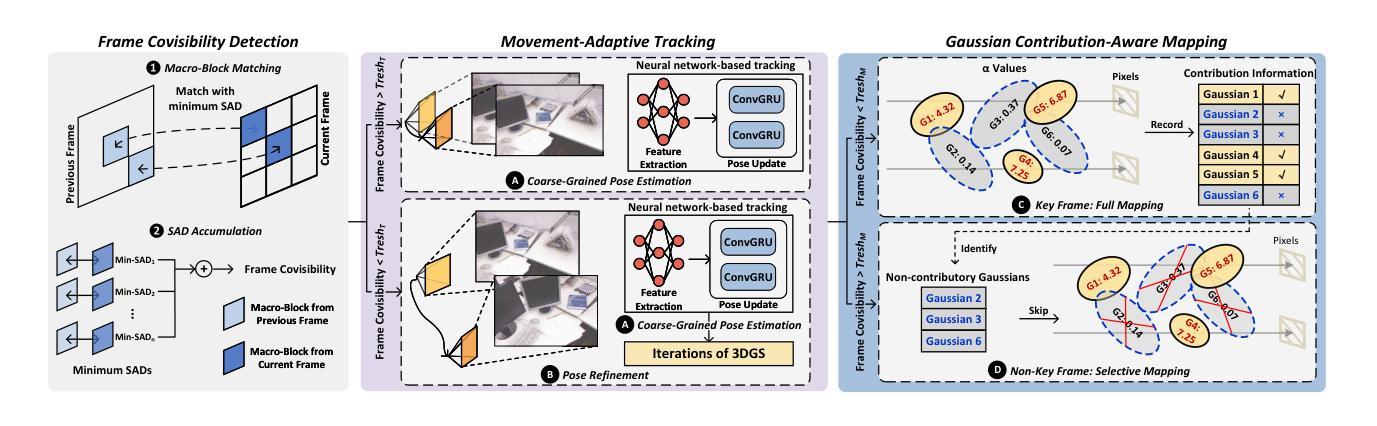
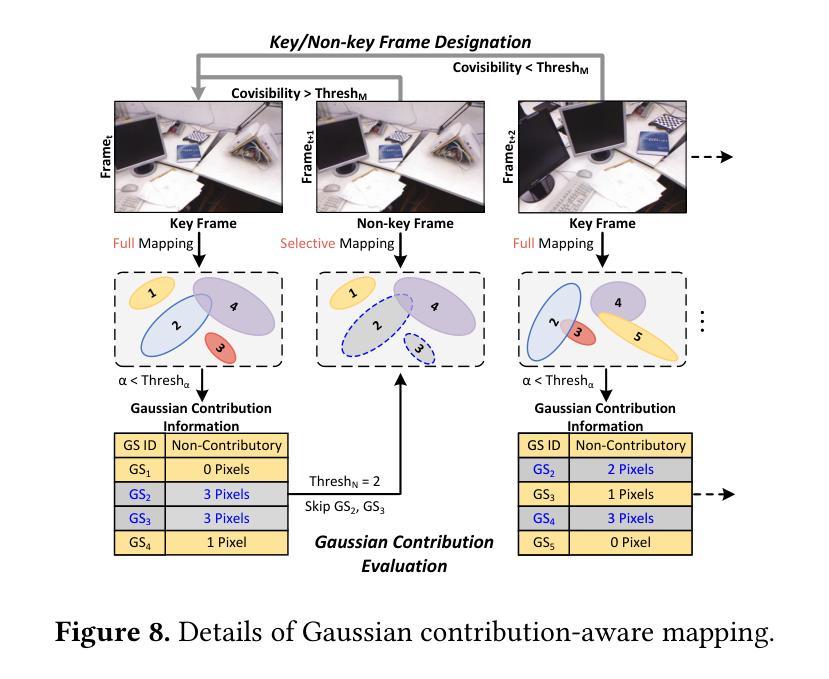
AGS: Accelerating 3D Gaussian Splatting SLAM via CODEC-Assisted Frame Covisibility Detection
Authors:Houshu He, Naifeng Jing, Li Jiang, Xiaoyao Liang, Zhuoran Song
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a critical task that enables autonomous vehicles to construct maps and localize themselves in unknown environments. Recent breakthroughs combine SLAM with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to achieve exceptional reconstruction fidelity. However, existing 3DGS-SLAM systems provide insufficient throughput due to the need for multiple training iterations per frame and the vast number of Gaussians. In this paper, we propose AGS, an algorithm-hardware co-design framework to boost the efficiency of 3DGS-SLAM based on the intuition that SLAM systems process frames in a streaming manner, where adjacent frames exhibit high similarity that can be utilized for acceleration. On the software level: 1) We propose a coarse-then-fine-grained pose tracking method with respect to the robot’s movement. 2) We avoid redundant computations of Gaussians by sharing their contribution information across frames. On the hardware level, we propose a frame covisibility detection engine to extract intermediate data from the video CODEC. We also implement a pose tracking engine and a mapping engine with workload schedulers to efficiently deploy the AGS algorithm. Our evaluation shows that AGS achieves up to $17.12\times$, $6.71\times$, and $5.41\times$ speedups against the mobile and high-end GPUs, and a state-of-the-art 3DGS accelerator, GSCore.
同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)是一项关键任务,它使自主车辆能够在未知环境中构建地图并定位自身。最近的突破结合了SLAM与三维高斯拼接(3DGS)技术,实现了卓越的重建保真度。然而,现有的基于3DGS的SLAM系统由于每帧需要多次训练迭代和大量的高斯数据,导致吞吐量不足。在本文中,我们提出了AGS算法,这是一种软硬件协同设计框架,旨在提高基于3DGS的SLAM的效率。我们的直觉是SLAM系统以流式方式处理帧,相邻帧之间具有高度的相似性,这可以用于加速。在软件层面:首先提出一种粗粒度到细粒度的机器人运动姿态跟踪方法;其次,我们通过共享高斯函数的贡献信息来避免冗余计算。在硬件层面,我们提出了一种帧共可见性检测引擎,能够从视频编解码器中提取中间数据。我们还实现了一个带有工作负载调度器的姿态跟踪引擎和映射引擎,以有效地部署AGS算法。我们的评估显示,与移动和高端GPU以及最先进的3DGS加速器GSCore相比,AGS分别实现了最高达17.12倍、6.71倍和5.41倍的加速效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种名为AGS的算法-硬件协同设计框架,旨在提高基于三维高斯混合模型(3DGS)的同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)系统的效率。通过利用相邻帧的高相似性进行加速,软件层面采用粗到细粒度的姿态跟踪方法,避免冗余计算,并分享高斯贡献信息跨帧传递;硬件层面,提出利用视频编解码器的帧共视检测引擎,并配以姿态跟踪引擎和映射引擎与任务调度器进行高效部署。实验结果显示,该方案在移动与高端GPU以及当前主流的三维高斯加速器GSCore上实现了显著的速度提升。
Key Takeaways
- AGS算法结合了软硬件设计提高基于3DGS的SLAM系统效率。
- 利用相邻帧的高相似性进行加速,提升了系统的实时性能。
- 软件层面采用粗到细粒度的姿态跟踪方法,避免冗余计算。
- 通过分享高斯贡献信息跨帧传递,优化了计算资源的使用。
- 硬件层面利用视频编解码器的帧共视检测引擎提取中间数据。
- 实现了高效的姿态跟踪引擎和映射引擎配合任务调度器。
点此查看论文截图

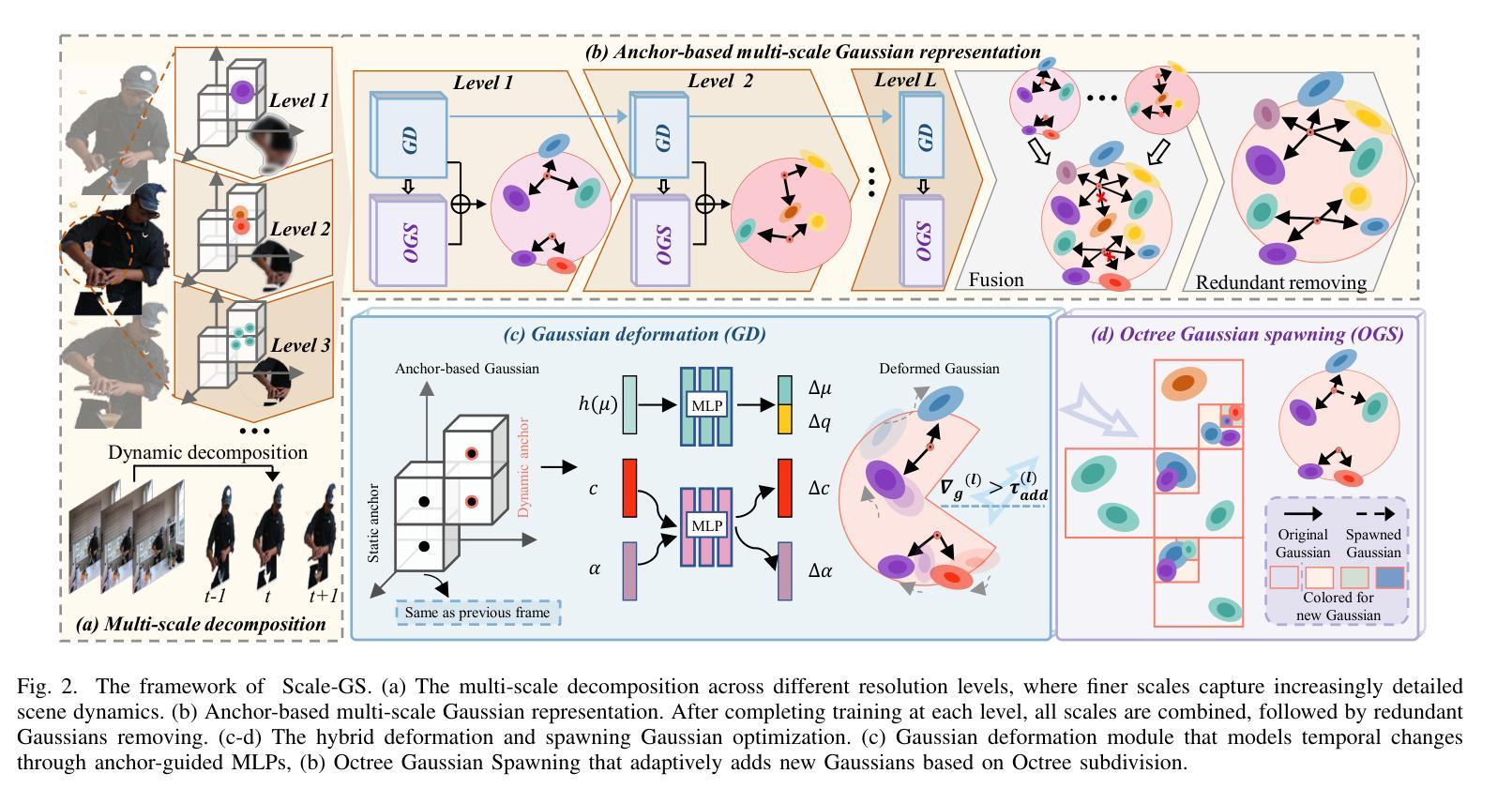
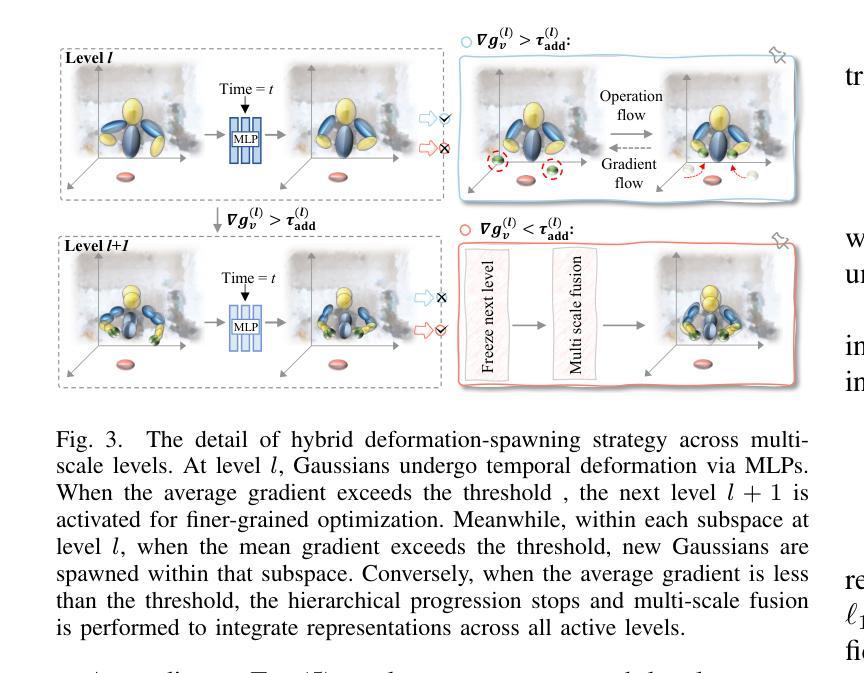
Scale-GS: Efficient Scalable Gaussian Splatting via Redundancy-filtering Training on Streaming Content
Authors:Jiayu Yang, Weijian Su, Songqian Zhang, Yuqi Han, Jinli Suo, Qiang Zhang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables high-fidelity real-time rendering, a key requirement for immersive applications. However, the extension of 3DGS to dynamic scenes remains limitations on the substantial data volume of dense Gaussians and the prolonged training time required for each frame. This paper presents \M, a scalable Gaussian Splatting framework designed for efficient training in streaming tasks. Specifically, Gaussian spheres are hierarchically organized by scale within an anchor-based structure. Coarser-level Gaussians represent the low-resolution structure of the scene, while finer-level Gaussians, responsible for detailed high-fidelity rendering, are selectively activated by the coarser-level Gaussians. To further reduce computational overhead, we introduce a hybrid deformation and spawning strategy that models motion of inter-frame through Gaussian deformation and triggers Gaussian spawning to characterize wide-range motion. Additionally, a bidirectional adaptive masking mechanism enhances training efficiency by removing static regions and prioritizing informative viewpoints. Extensive experiments demonstrate that \M~ achieves superior visual quality while significantly reducing training time compared to state-of-the-art methods.
3D高斯绘制(3DGS)能够实现高保真实时渲染,这是沉浸式应用的关键要求。然而,将3DGS扩展到动态场景时,密集高斯的大量数据体积和每帧所需的延长训练时间仍存在限制。本文提出了\M,一种面向流式任务高效训练的可扩展高斯绘制框架。具体而言,高斯球是按尺度在锚点基础上进行层次结构组织的。较粗级别的高斯表示场景的低分辨率结构,而较细级别的高斯负责详细的高保真渲染,并由较粗级别的高斯选择性地激活。为了进一步优化计算开销,我们引入了一种混合变形和生成策略,通过高斯变形对帧间运动进行建模,并触发高斯生成以表征大范围运动。此外,双向自适应掩码机制通过去除静态区域并优先处理信息丰富的视点,提高了训练效率。大量实验表明,\M~在达到优越视觉质量的同时,与最新方法相比显著减少了训练时间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对动态场景的高效渲染技术,提出了基于锚点的分层高斯球体框架,并结合混合变形与繁殖策略,实现高效训练。该技术提高了实时渲染的视觉效果,同时显著缩短了训练时间。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS可用于实现高保真实时渲染,适用于沉浸式应用。
- 现有的动态场景渲染技术在处理大规模数据时存在局限性,需要长时间训练。
- 提出的分层高斯球体框架能够高效处理动态场景,通过粗粒度高斯表示低分辨率场景结构,细粒度高斯负责高保真渲染。
- 混合变形和繁殖策略用于减少计算开销,通过高斯变形模拟帧间运动,通过高斯繁殖表征大范围运动。
- 双向自适应掩码机制提高训练效率,去除静态区域并优先关注信息丰富的视点。
点此查看论文截图



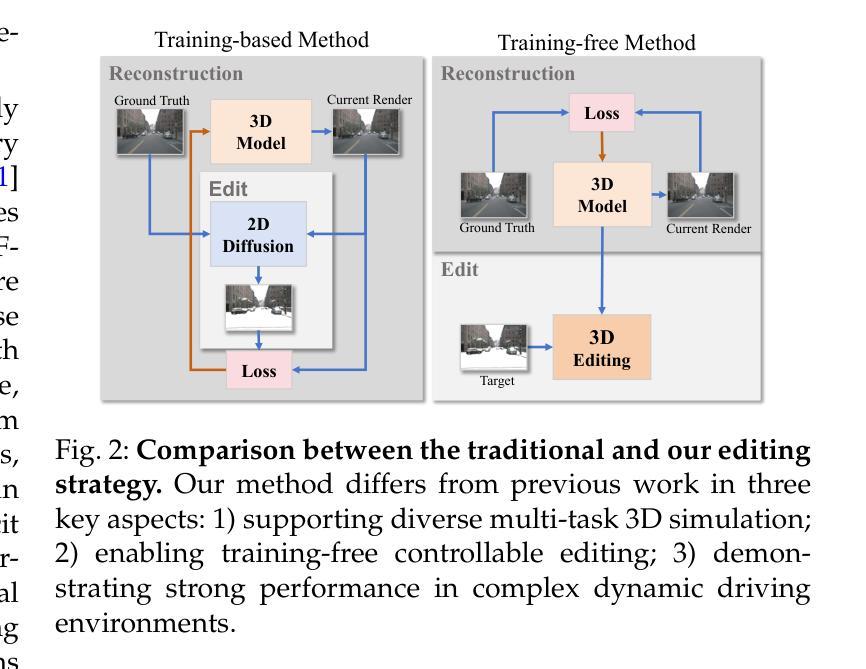
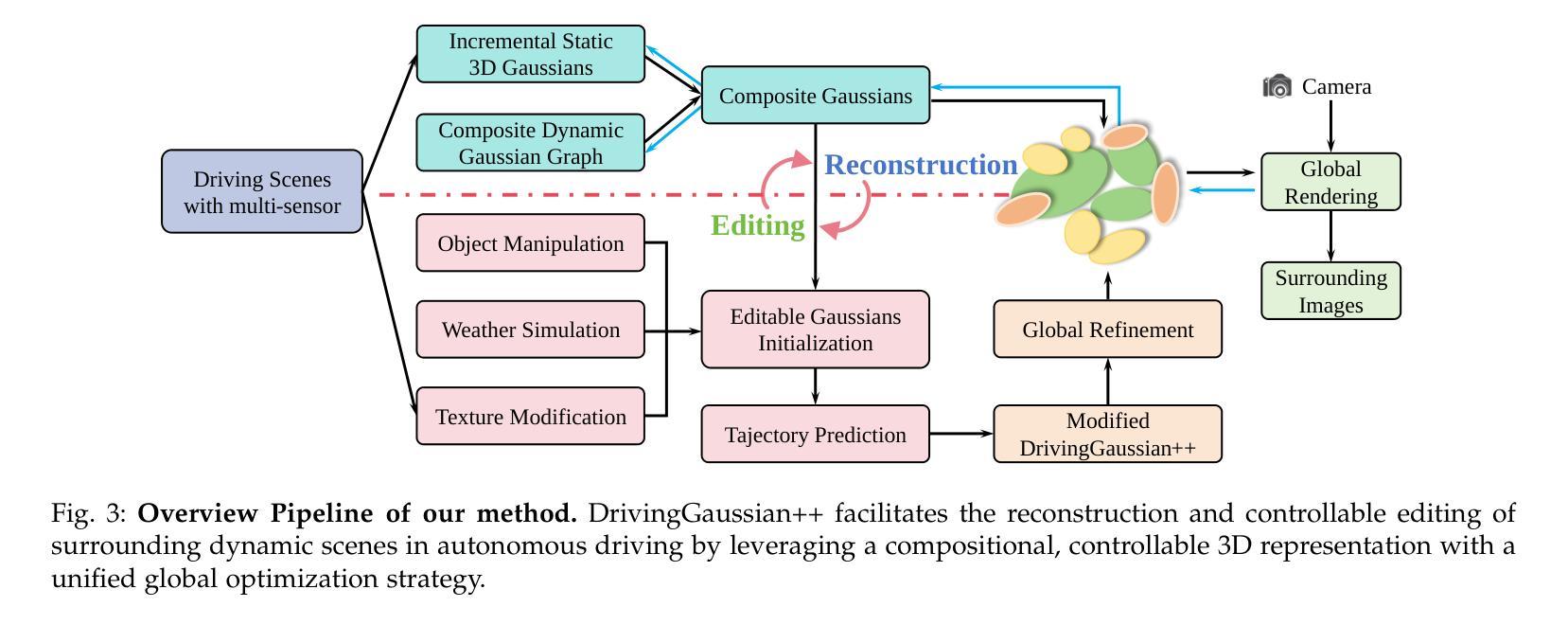
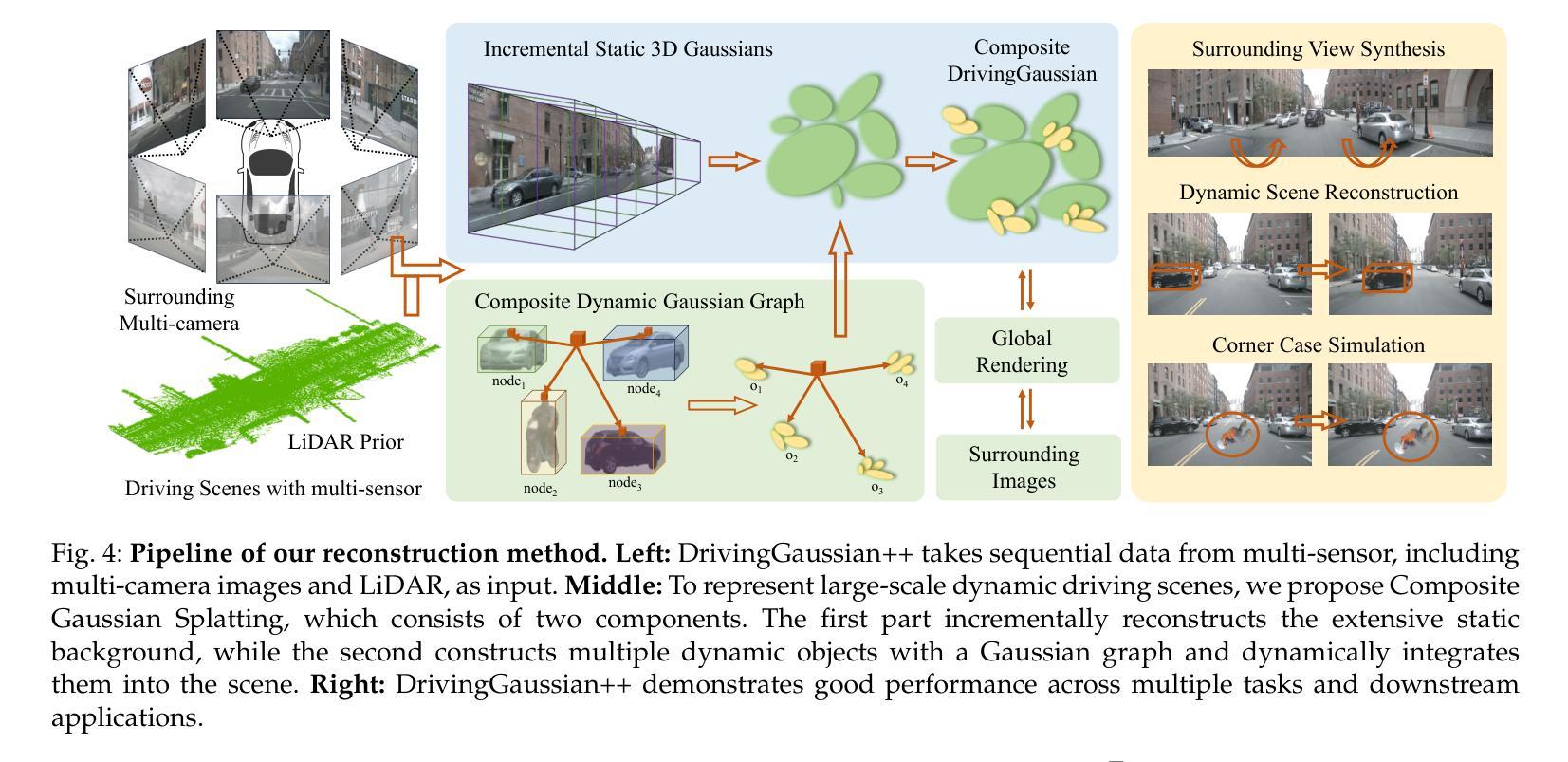
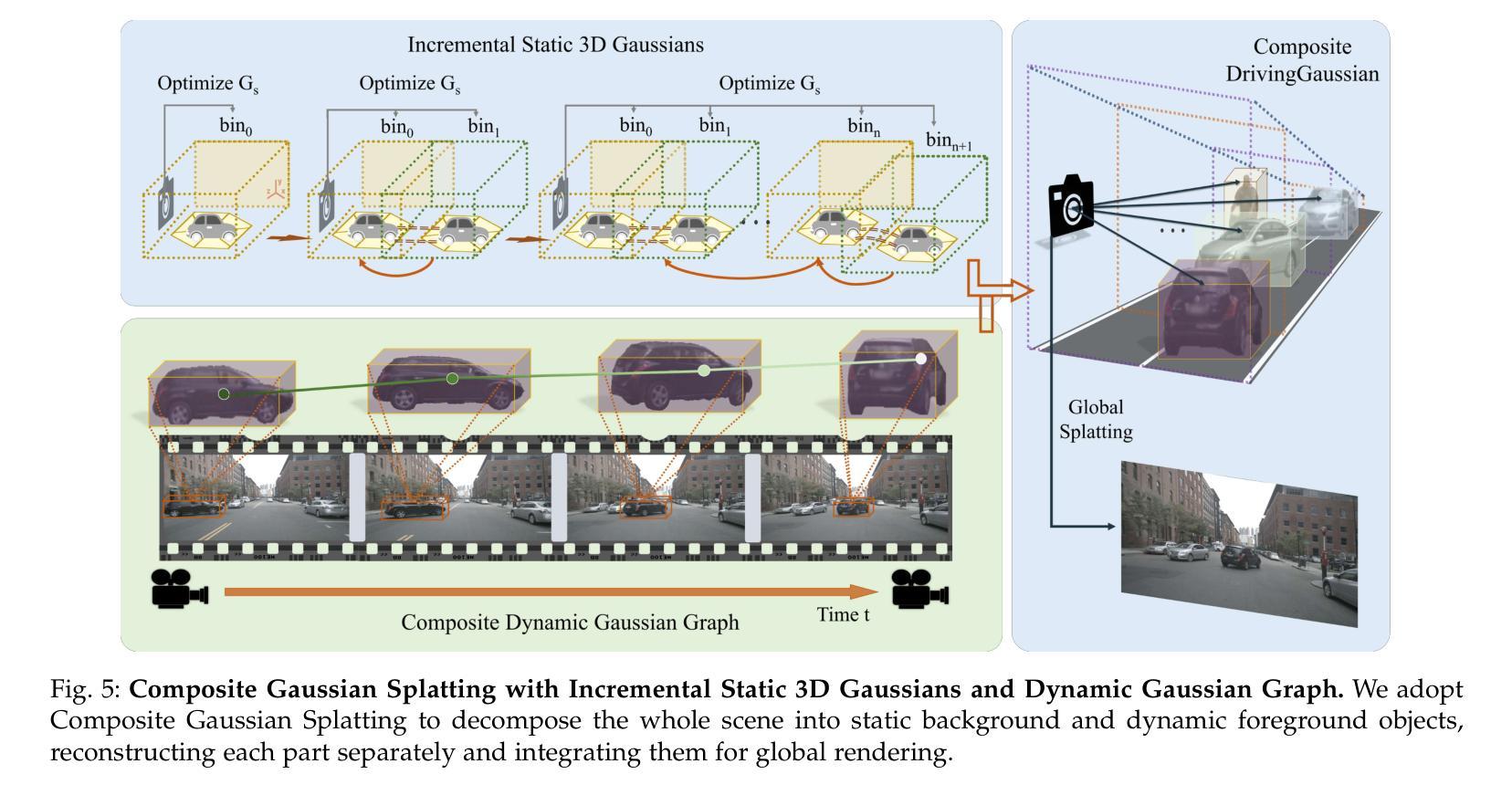
DrivingGaussian++: Towards Realistic Reconstruction and Editable Simulation for Surrounding Dynamic Driving Scenes
Authors:Yajiao Xiong, Xiaoyu Zhou, Yongtao Wan, Deqing Sun, Ming-Hsuan Yang
We present DrivingGaussian++, an efficient and effective framework for realistic reconstructing and controllable editing of surrounding dynamic autonomous driving scenes. DrivingGaussian++ models the static background using incremental 3D Gaussians and reconstructs moving objects with a composite dynamic Gaussian graph, ensuring accurate positions and occlusions. By integrating a LiDAR prior, it achieves detailed and consistent scene reconstruction, outperforming existing methods in dynamic scene reconstruction and photorealistic surround-view synthesis. DrivingGaussian++ supports training-free controllable editing for dynamic driving scenes, including texture modification, weather simulation, and object manipulation, leveraging multi-view images and depth priors. By integrating large language models (LLMs) and controllable editing, our method can automatically generate dynamic object motion trajectories and enhance their realism during the optimization process. DrivingGaussian++ demonstrates consistent and realistic editing results and generates dynamic multi-view driving scenarios, while significantly enhancing scene diversity. More results and code can be found at the project site: https://xiong-creator.github.io/DrivingGaussian_plus.github.io
我们推出了DrivingGaussian++,这是一个高效且实用的框架,用于现实主义的重建和可控编辑周围的动态自动驾驶场景。DrivingGaussian++使用增量3D高斯对静态背景进行建模,并用复合动态高斯图重建移动物体,确保准确的位置和遮挡。通过集成激光雷达先验信息,它实现了详细且一致的场景重建,在动态场景重建和真实感环绕视图合成方面优于现有方法。DrivingGaussian++支持对动态驾驶场景进行无训练控制编辑,包括纹理修改、天气模拟和对象操作,利用多视图图像和深度先验信息。通过集成大型语言模型(LLMs)和控制编辑,我们的方法可以自动生成动态对象运动轨迹,并在优化过程中增强它们的真实性。DrivingGaussian++展示了连贯和现实的编辑结果,生成动态多视图驾驶场景,同时显著增强了场景多样性。更多结果和代码可在项目网站找到:https://xiong-creator.github.io/DrivingGaussian_plus.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
驾驶场景重建与编辑的新框架DrivingGaussian++能够有效模拟并控制自主驾驶周围动态场景的重建。它利用增量3D高斯模型背景,并通过动态高斯图重建移动物体,确保准确的位置与遮挡处理。结合LiDAR先验信息,实现详细且一致的场景重建,并在动态场景重建和真实感环绕视图合成方面超越现有方法。DrivingGaussian++支持无训练可控编辑动态驾驶场景,包括纹理修改、天气模拟和物体操作等,利用多视角图像和深度先验信息。整合大型语言模型(LLMs)和可控编辑功能,能够自动产生动态物体运动轨迹,并在优化过程中提升真实感。DrivingGaussian++能生成连贯且真实的编辑结果和动态多视角驾驶场景,大幅增强场景多样性。
Key Takeaways
- DrivingGaussian++能有效重建自主驾驶周围的动态场景。
- 使用增量3D高斯建模静态背景,通过动态高斯图重建移动物体。
- 结合LiDAR先验信息实现详细且一致的场景重建。
- 支持无训练可控编辑,包括纹理修改、天气模拟和物体操作。
- 利用多视角图像和深度先验信息提升编辑的真实感。
- 整合大型语言模型(LLMs)以自动生成动态物体运动轨迹。
- 生成连贯且真实的编辑结果和动态多视角驾驶场景,增强场景多样性。
点此查看论文截图

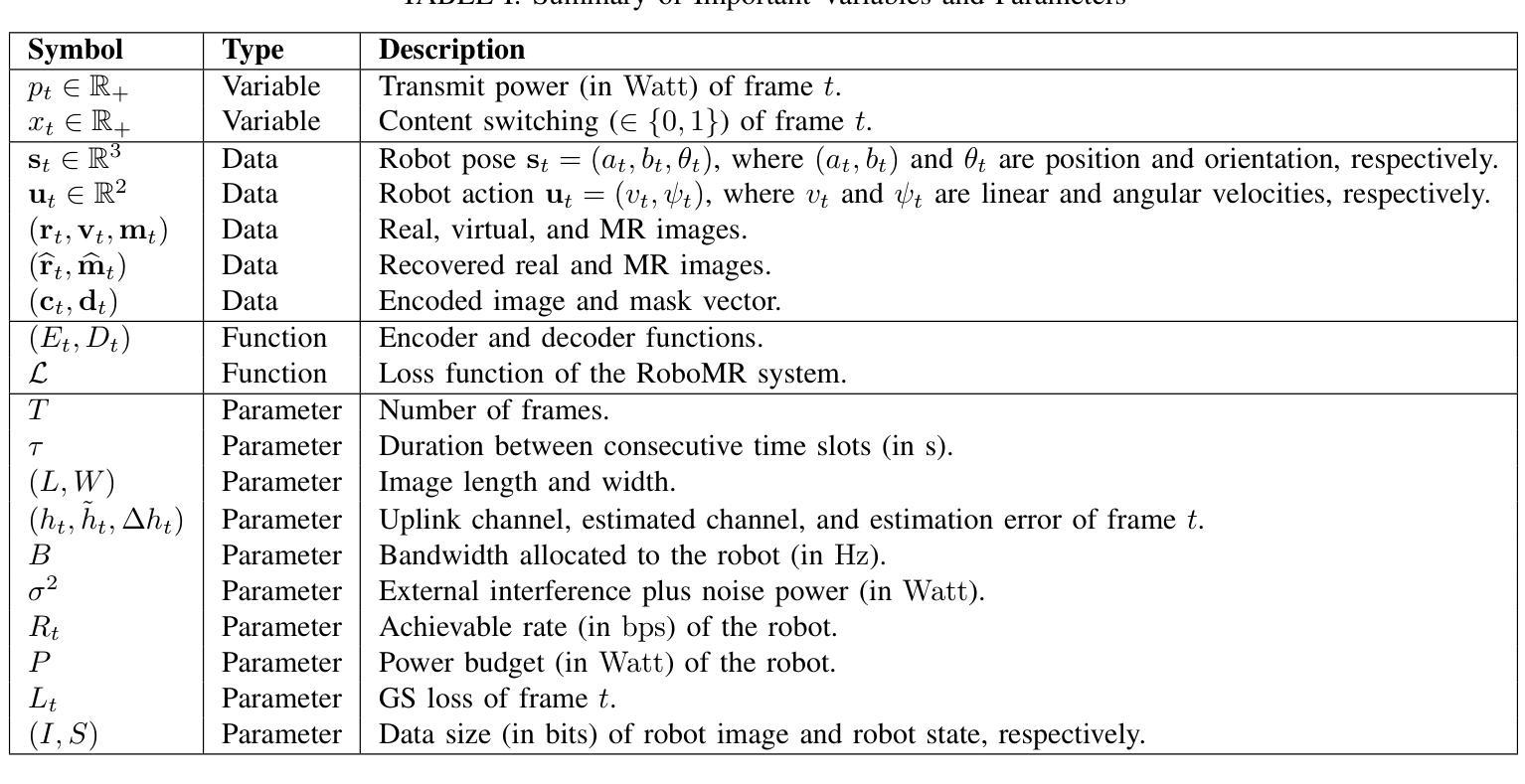
Communication Efficient Robotic Mixed Reality with Gaussian Splatting Cross-Layer Optimization
Authors:Chenxuan Liu, He Li, Zongze Li, Shuai Wang, Wei Xu, Kejiang Ye, Derrick Wing Kwan Ng, Chengzhong Xu
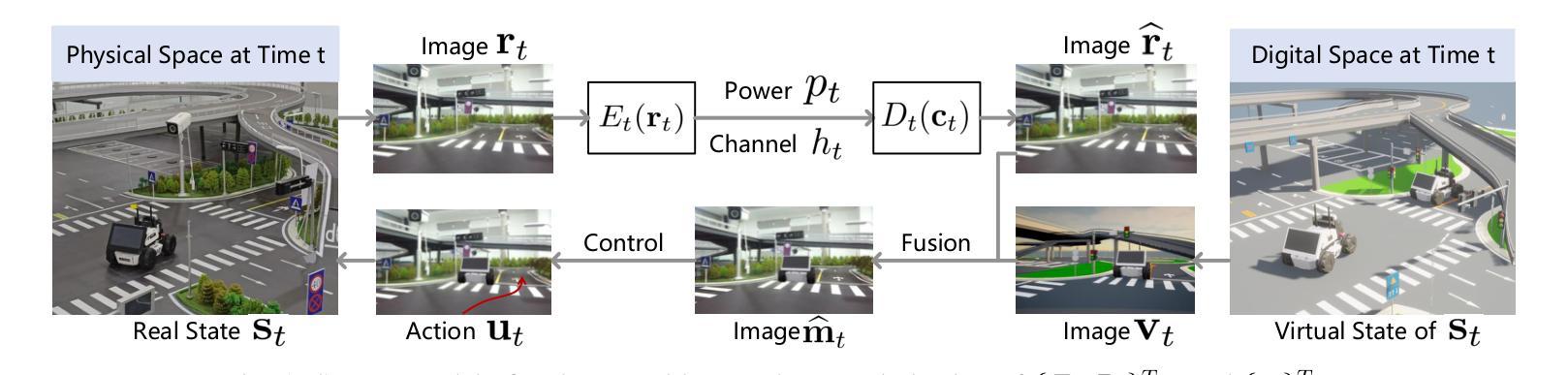
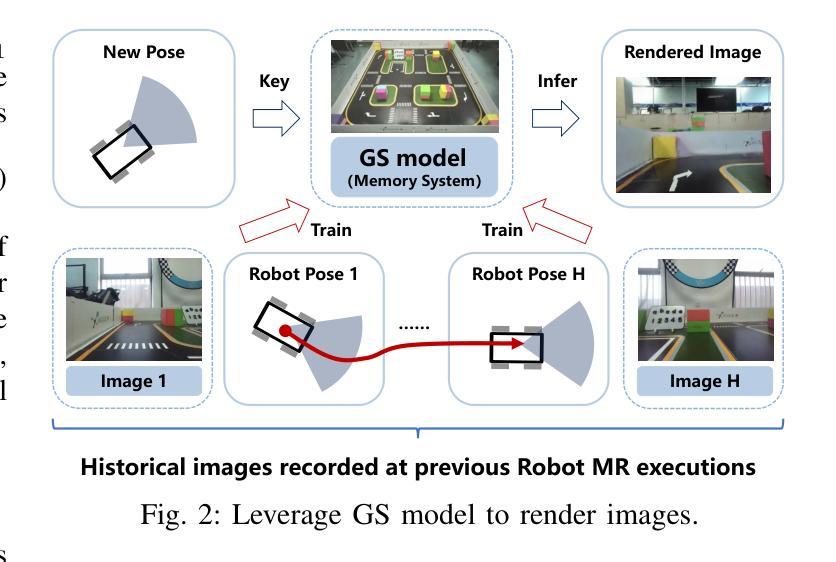
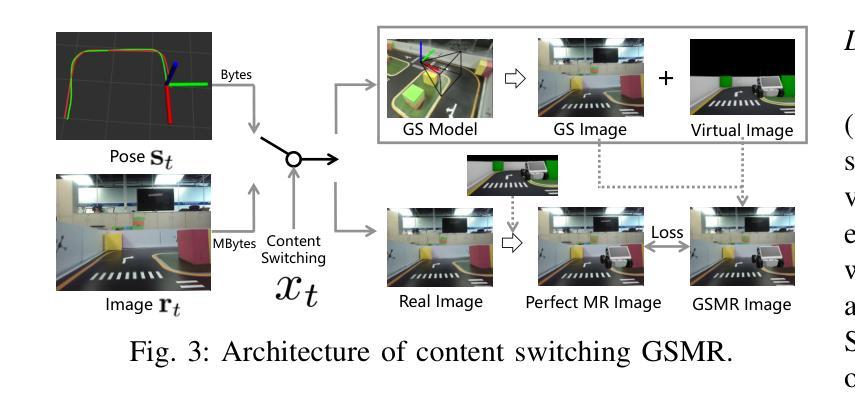
Realizing low-cost communication in robotic mixed reality (RoboMR) systems presents a challenge, due to the necessity of uploading high-resolution images through wireless channels. This paper proposes Gaussian splatting (GS) RoboMR (GSMR), which enables the simulator to opportunistically render a photo-realistic view from the robot’s pose by calling ``memory’’ from a GS model, thus reducing the need for excessive image uploads. However, the GS model may involve discrepancies compared to the actual environments. To this end, a GS cross-layer optimization (GSCLO) framework is further proposed, which jointly optimizes content switching (i.e., deciding whether to upload image or not) and power allocation (i.e., adjusting to content profiles) across different frames by minimizing a newly derived GSMR loss function. The GSCLO problem is addressed by an accelerated penalty optimization (APO) algorithm that reduces computational complexity by over $10$x compared to traditional branch-and-bound and search algorithms. Moreover, variants of GSCLO are presented to achieve robust, low-power, and multi-robot GSMR. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed GSMR paradigm and GSCLO method achieve significant improvements over existing benchmarks on both wheeled and legged robots in terms of diverse metrics in various scenarios. For the first time, it is found that RoboMR can be achieved with ultra-low communication costs, and mixture of data is useful for enhancing GS performance in dynamic scenarios.
在机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统中实现低成本通信是一项挑战,因为需要通过无线信道上传高分辨率图像。本文提出了高斯喷溅(GS)RoboMR(GSMR),使模拟器能够通过从GS模型中调用“内存”来随机呈现机器人的逼真视图,从而减少对过多图像上传的需求。然而,与真实环境相比,GS模型可能存在差异。为此,进一步提出了GS跨层优化(GSCLO)框架,通过最小化新推出的GSMR损失函数,联合优化内容切换(即决定是否上传图像)和功率分配(即适应内容配置文件)。不同帧的GSCLO问题通过加速惩罚优化(APO)算法来解决,该算法的计算复杂度比传统的分支界定和搜索算法降低了超过10倍。此外,还提出了多种GSCLO变体,以实现稳健、低功耗和多机器人GSMR。大量实验表明,所提出的GSMR范式和GSCLO方法在轮式机器人和步行机器人上,在各种场景的多个指标上均取得了显著的改进。首次发现,RoboMR可以实现超低通信成本,并且数据的混合对于提高动态场景中的GS性能很有用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 18 figures, to appear in IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯点云技术(GS)的机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统优化方法,通过调用GS模型的“记忆”功能,实现模拟器的实时渲染,减少了对高分辨率图像上传的依赖。为进一步提高性能,提出了GS跨层优化(GSCLO)框架,联合优化内容切换和功率分配,并通过加速惩罚优化(APO)算法解决计算复杂度问题。实验证明,该方法在轮式和步行机器人上均显著优于现有基准测试,实现了超低通信成本的混合现实应用。首次发现数据混合对动态场景中GS性能的提升有帮助。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯点云技术(GS)用于机器人混合现实(RoboMR)系统,实现实时渲染。
- GS模型调用“记忆”功能,降低对高分辨率图像上传的依赖。
- 提出GS跨层优化(GSCLO)框架,联合优化内容切换和功率分配。
- 使用加速惩罚优化(APO)算法解决计算复杂度问题。
- 实验证明该方法在轮式和步行机器人上均优于现有基准测试。
- 实现超低通信成本的混合现实应用。
点此查看论文截图

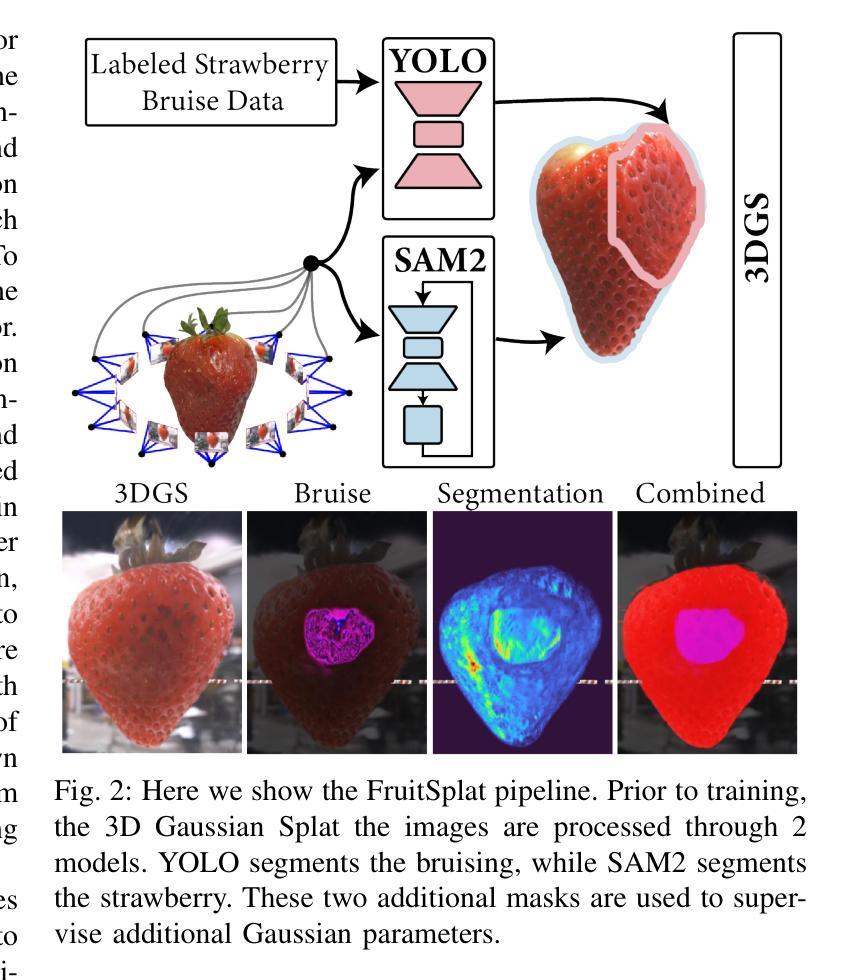
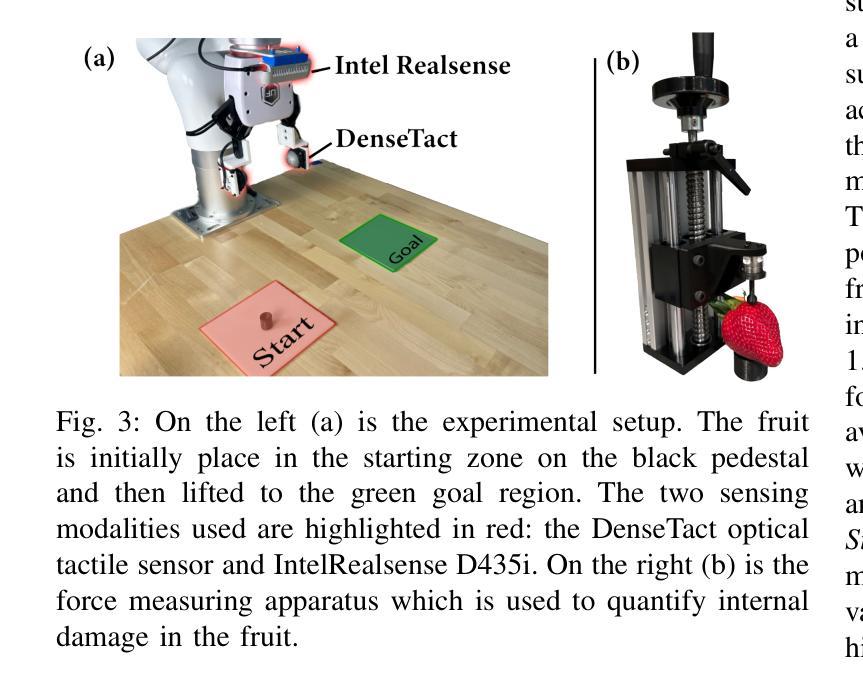
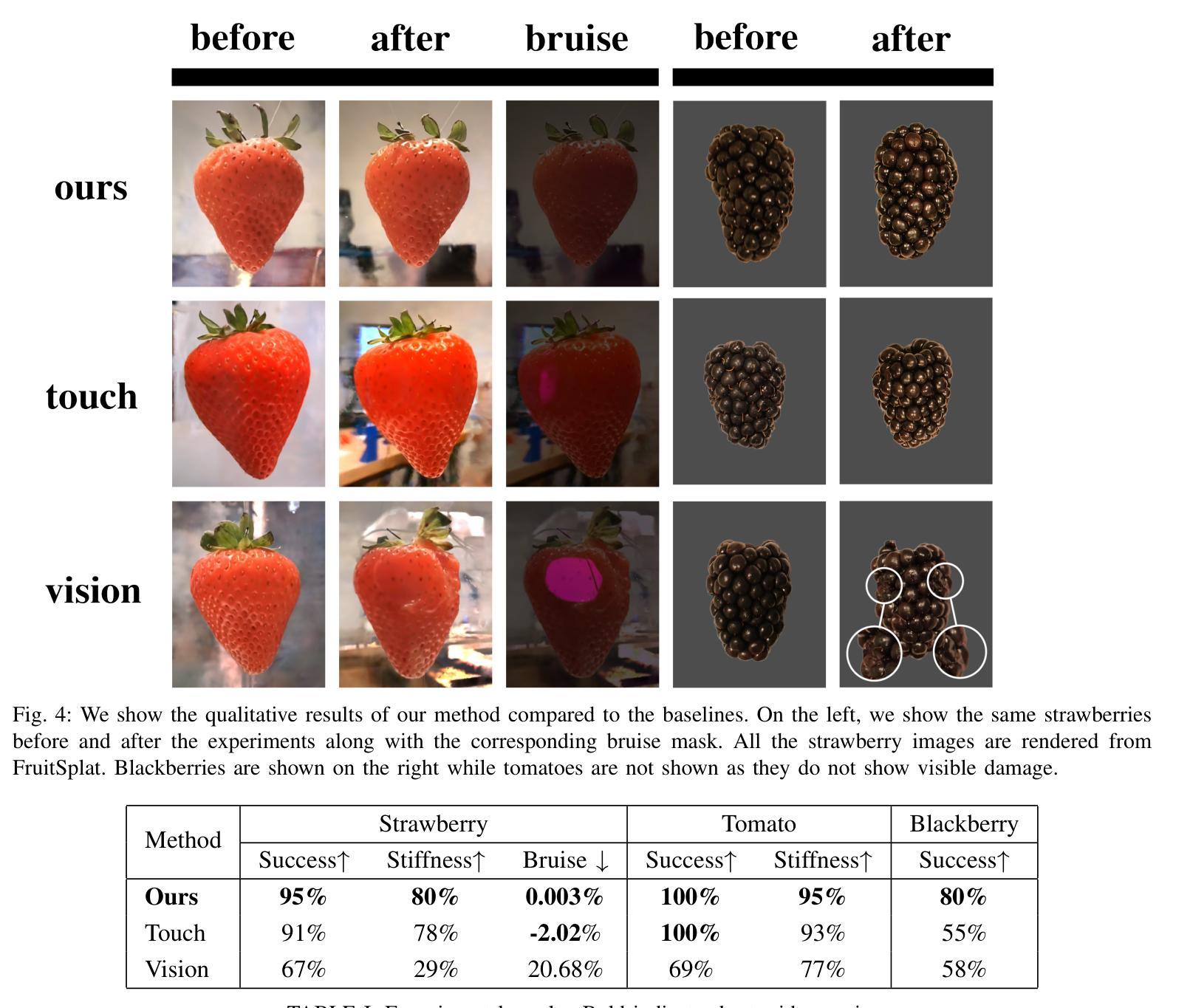
DexFruit: Dexterous Manipulation and Gaussian Splatting Inspection of Fruit
Authors:Aiden Swann, Alex Qiu, Matthew Strong, Angelina Zhang, Samuel Morstein, Kai Rayle, Monroe Kennedy III
DexFruit is a robotic manipulation framework that enables gentle, autonomous handling of fragile fruit and precise evaluation of damage. Many fruits are fragile and prone to bruising, thus requiring humans to manually harvest them with care. In this work, we demonstrate by using optical tactile sensing, autonomous manipulation of fruit with minimal damage can be achieved. We show that our tactile informed diffusion policies outperform baselines in both reduced bruising and pick-and-place success rate across three fruits: strawberries, tomatoes, and blackberries. In addition, we introduce FruitSplat, a novel technique to represent and quantify visual damage in high-resolution 3D representation via 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Existing metrics for measuring damage lack quantitative rigor or require expensive equipment. With FruitSplat, we distill a 2D strawberry mask as well as a 2D bruise segmentation mask into the 3DGS representation. Furthermore, this representation is modular and general, compatible with any relevant 2D model. Overall, we demonstrate a 92% grasping policy success rate, up to a 20% reduction in visual bruising, and up to an 31% improvement in grasp success rate on challenging fruit compared to our baselines across our three tested fruits. We rigorously evaluate this result with over 630 trials. Please checkout our website at https://dex-fruit.github.io .
DexFruit是一个机器人操作框架,能够实现脆弱水果的轻柔自主处理和损伤的精确评估。许多水果都是脆弱的,容易擦伤,因此需要人们小心地手工采摘它们。在这项工作中,我们通过使用光学触觉感应技术,展示了可以对水果进行自主操作,且能够尽量减少损伤。我们展示我们的触觉感知扩散策略在减少擦伤和取放成功率方面超过了基线标准,这一优势在草莓、番茄和黑莓三种水果上都得到了体现。此外,我们还推出了一种名为FruitSplat的新技术,该技术通过3D高斯展布(3DGS)以高分辨率的3D表现形式来呈现和量化视觉损伤。现有的损伤测量指标缺乏定量严谨性或需要昂贵的设备。借助FruitSplat,我们将一个二维草莓掩膜以及一个二维擦伤分割掩膜蒸馏到3DGS表示中。此外,这种表示是模块化和通用的,与任何相关的二维模型都兼容。总的来说,我们展示了高达92%的抓取策略成功率,视觉擦伤减少了20%,与我们基线标准相比,在具有挑战性的水果上抓取成功率提高了31%。我们在超过630次的试验中对这一结果进行了严格评估。请访问我们的网站 https://dex-fruit.github.io 了解更多信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
DexFruit框架实现了对脆弱水果的轻柔自主操作与损伤精确评估。该研究利用光学触觉感知技术,实现了自主操作水果时减少损伤的目标。在草莓、番茄和黑莓三种水果上的实验表明,其触觉感知引导的策略相较于基线方法在减少破损和提高拾取放置成功率上均有所超越。此外,研究还推出了FruitSplat技术,通过3D高斯喷溅(3DGS)实现高分辨率的3D损伤表示和量化。该技术可将二维水果掩膜和二维损伤分割掩膜转化为3DGS表示,模块化且通用性强,适用于任何相关二维模型。总体而言,该研究实现了高达92%的抓取策略成功率,相较于基线方法最多减少20%的视觉破损和提高了31%的挑战性水果抓取成功率。该研究通过了超过630次试验的严格评估。有关详细信息,请访问其官网链接:https://dex-fruit.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- DexFruit框架能够实现脆弱水果的自主操作和损伤评估。
- 利用光学触觉感知技术实现水果的低损伤自主操作。
- 在三种水果上的实验显示DexFruit策略相较于基线方法减少了破损并提高了拾取放置成功率。
- 引入FruitSplat技术,利用3D高斯喷溅实现高分辨率的3D损伤表示和量化。
- FruitSplat技术可将二维掩膜转化为三维表示,具有模块化、通用性强的特点。
- 研究实现了高成功率抓取策略,显著减少了视觉破损,提高了挑战性水果的抓取成功率。
点此查看论文截图

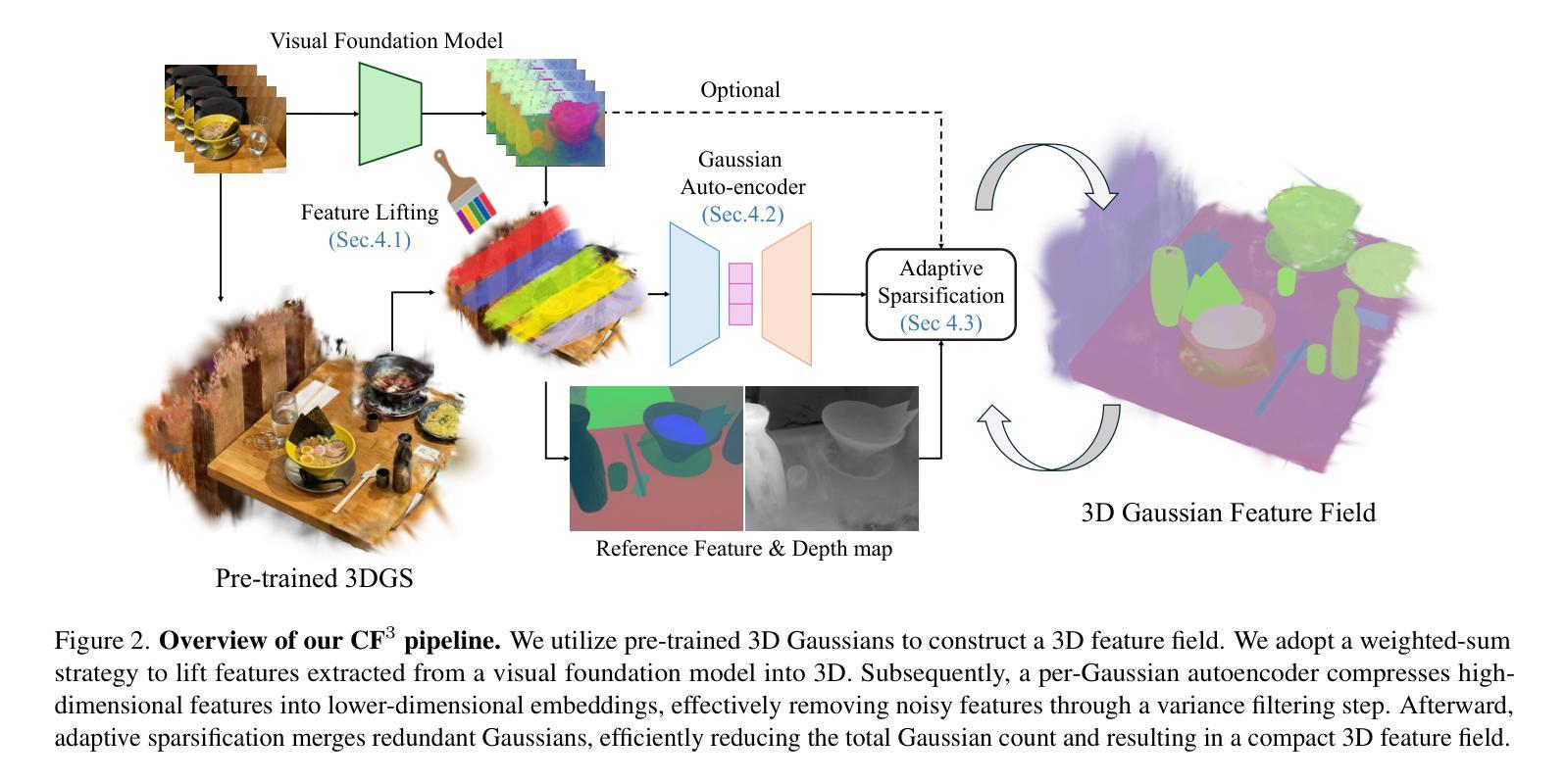
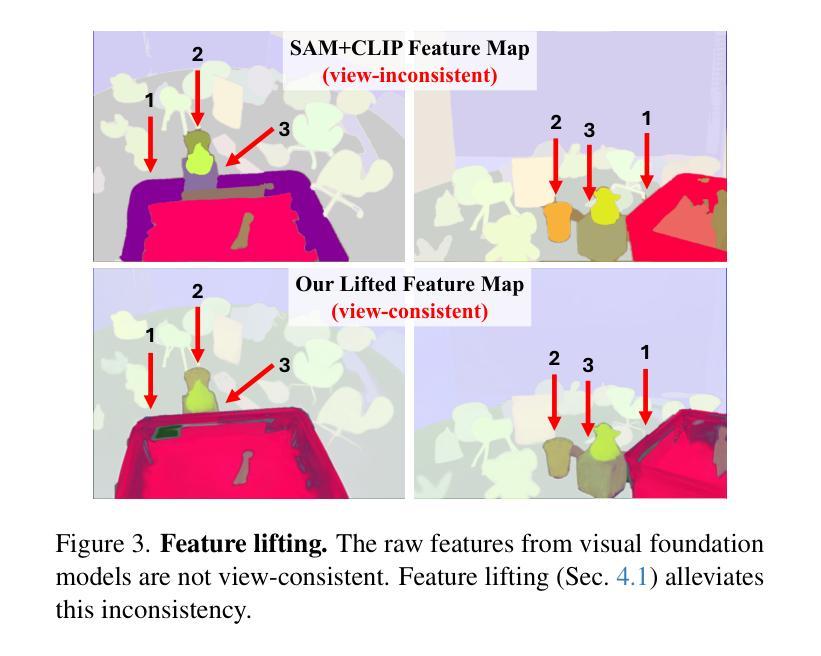
CF3: Compact and Fast 3D Feature Fields
Authors:Hyunjoon Lee, Joonkyu Min, Jaesik Park
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has begun incorporating rich information from 2D foundation models. However, most approaches rely on a bottom-up optimization process that treats raw 2D features as ground truth, incurring increased computational costs. We propose a top-down pipeline for constructing compact and fast 3D Gaussian feature fields, namely, CF3. We first perform a fast weighted fusion of multi-view 2D features with pre-trained Gaussians. This approach enables training a per-Gaussian autoencoder directly on the lifted features, instead of training autoencoders in the 2D domain. As a result, the autoencoder better aligns with the feature distribution. More importantly, we introduce an adaptive sparsification method that optimizes the Gaussian attributes of the feature field while pruning and merging the redundant Gaussians, constructing an efficient representation with preserved geometric details. Our approach achieves a competitive 3D feature field using as little as 5% of the Gaussians compared to Feature-3DGS.
3D高斯延展(3DGS)已经开始融入来自二维基础模型的丰富信息。然而,大多数方法依赖于自下而上的优化过程,将原始二维特征视为真实依据,从而增加了计算成本。我们提出了一种构建紧凑且快速的3D高斯特征场的自上而下流程,即CF3。我们首先使用预训练的高斯对多视角二维特征进行快速加权融合。这种方法可以直接在提取的特征上训练每个高斯自编码器,而不是在二维域中训练自编码器。因此,自编码器能更好地与特征分布对齐。更重要的是,我们引入了一种自适应稀疏化方法,该方法在剔除和合并冗余高斯的同时优化特征场的高斯属性,从而构建了一个保留几何细节的有效表示。我们的方法仅使用与Feature-3DGS相比的5%的高斯数就能实现具有竞争力的3D特征场。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025, Project Page: https://jjoonii.github.io/cf3-website/
Summary
本文介绍了将二维特征模型信息融入三维高斯融合技术(3DGS)的新方法。针对现有方法主要依赖自下而上的优化过程,将原始二维特征视为真实值,导致计算成本增加的问题,本文提出了一种自上而下的构建紧凑快速三维高斯特征场的方法,即CF3。该方法通过快速加权融合多角度二维特征与预训练高斯模型,直接在提升的特征上训练每个高斯自编码器,使自编码器更好地适应特征分布。此外,还引入了一种自适应稀疏化方法,在优化特征场的高斯属性时能够剔除并合并冗余高斯,实现高效表示并保留几何细节。与Feature-3DGS相比,该方法仅使用5%的高斯即可获得具有竞争力的三维特征场。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了三维高斯融合技术(3DGS)融入二维特征模型信息的新发展。
- 现有方法主要依赖自下而上的优化过程,导致计算成本增加。
- 提出了一种自上而下的构建紧凑快速三维高斯特征场的方法——CF3。
- 通过快速加权融合多角度二维特征与预训练高斯模型来优化计算效率。
- 直接在提升的特征上训练每个高斯自编码器,提高自编码器与特征分布的适应性。
- 引入自适应稀疏化方法,优化特征场的高斯属性并保留几何细节。
点此查看论文截图

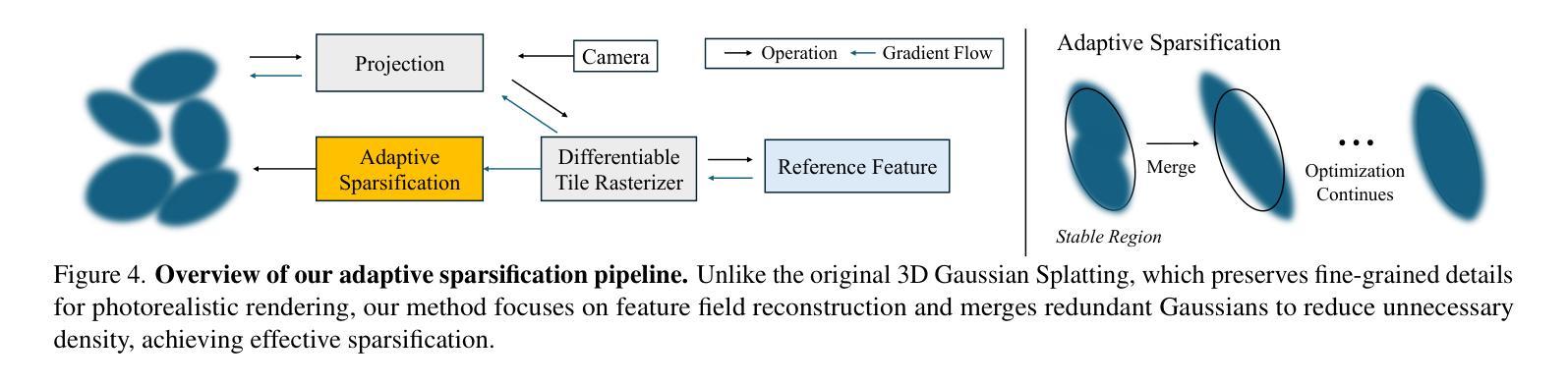

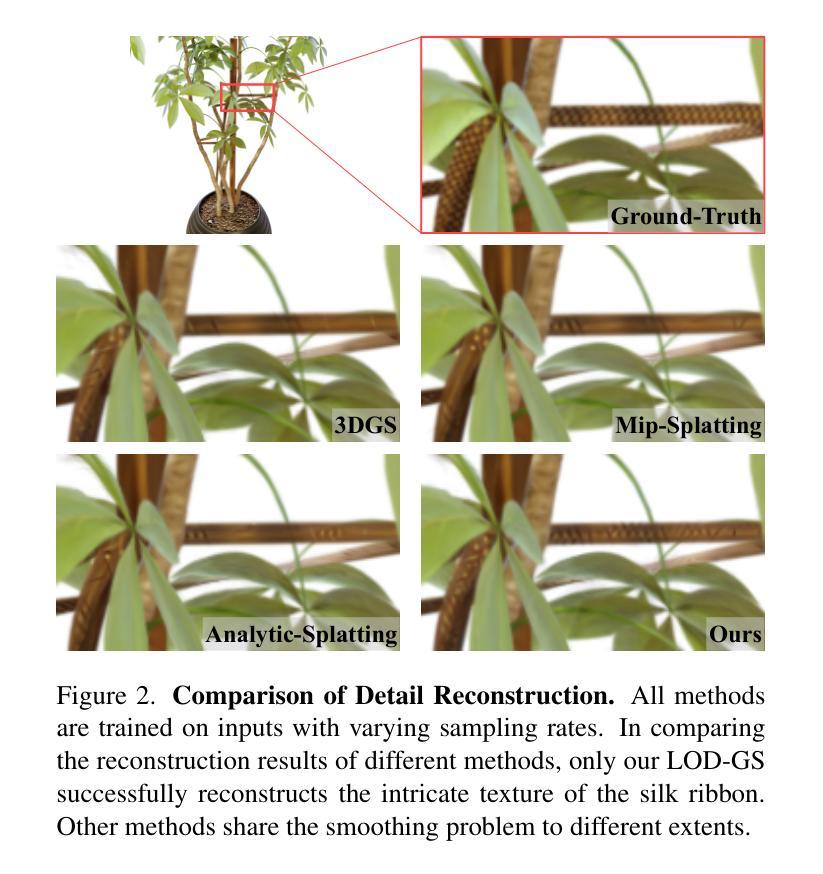
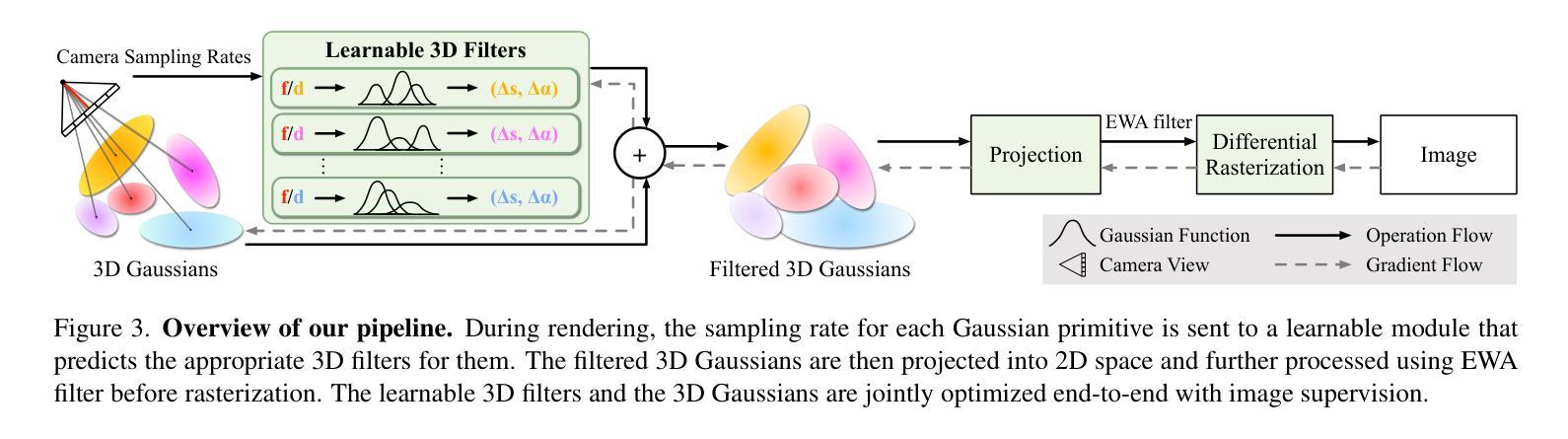
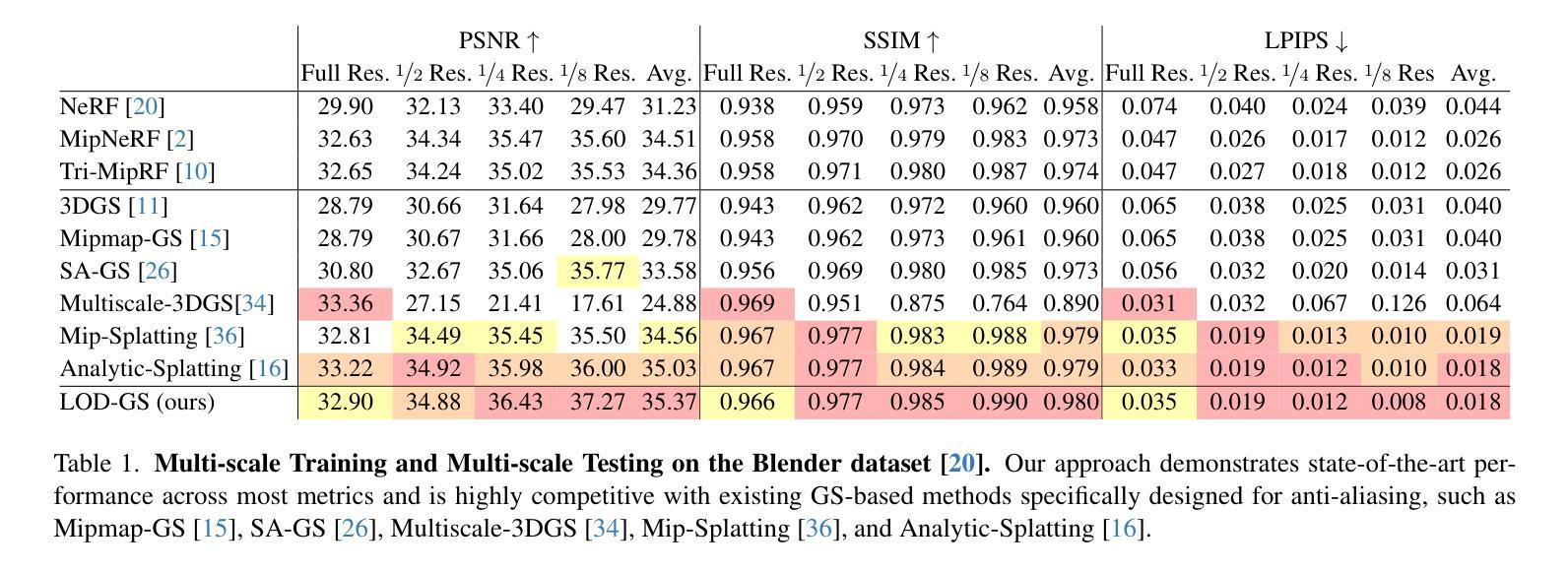
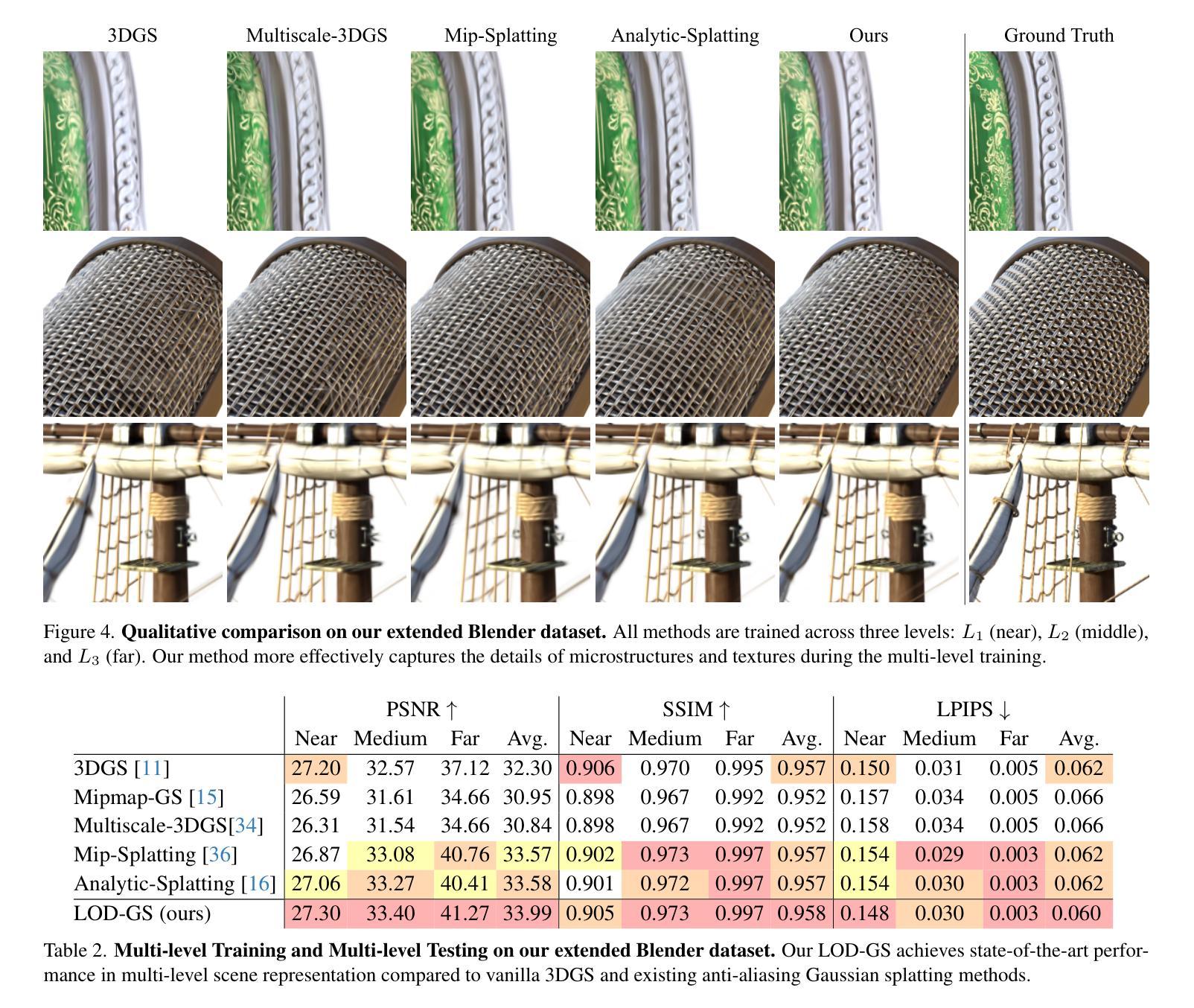
LOD-GS: Level-of-Detail-Sensitive 3D Gaussian Splatting for Detail Conserved Anti-Aliasing
Authors:Zhenya Yang, Bingchen Gong, Kai Chen
Despite the advancements in quality and efficiency achieved by 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in 3D scene rendering, aliasing artifacts remain a persistent challenge. Existing approaches primarily rely on low-pass filtering to mitigate aliasing. However, these methods are not sensitive to the sampling rate, often resulting in under-filtering and over-smoothing renderings. To address this limitation, we propose LOD-GS, a Level-of-Detail-sensitive filtering framework for Gaussian Splatting, which dynamically predicts the optimal filtering strength for each 3D Gaussian primitive. Specifically, we introduce a set of basis functions to each Gaussian, which take the sampling rate as input to model appearance variations, enabling sampling-rate-sensitive filtering. These basis function parameters are jointly optimized with the 3D Gaussian in an end-to-end manner. The sampling rate is influenced by both focal length and camera distance. However, existing methods and datasets rely solely on down-sampling to simulate focal length changes for anti-aliasing evaluation, overlooking the impact of camera distance. To enable a more comprehensive assessment, we introduce a new synthetic dataset featuring objects rendered at varying camera distances. Extensive experiments on both public datasets and our newly collected dataset demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA rendering quality while effectively eliminating aliasing. The code and dataset have been open-sourced.
尽管三维高斯贴图技术(3DGS)在三维场景渲染方面取得了质量和效率的提升,但混叠伪影仍然是一个持续存在的挑战。现有的方法主要依赖低通滤波来减轻混叠现象。然而,这些方法对采样率并不敏感,往往导致滤波不足和过度平滑的渲染结果。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了LOD-GS,一种针对高斯贴图的细节层次敏感滤波框架,它能动态预测每个三维高斯基元的最佳滤波强度。具体来说,我们为每个高斯引入了一组基函数,以采样率作为输入来模拟外观变化,从而实现采样率敏感滤波。这些基函数的参数与三维高斯以端到端的方式进行联合优化。采样率受到焦距和相机距离的影响。然而,现有方法和数据集仅依赖下采样来模拟焦距变化以进行抗混叠评估,忽略了相机距离的影响。为了进行更全面的评估,我们引入了一个新的合成数据集,其中包含在不同相机距离下渲染的物体。在公共数据集和我们新收集的数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的渲染质量,同时有效地消除了混叠。代码和数据集已经开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在三维场景渲染中,尽管有3D高斯绘制技术(3DGS)的应用大大提高了质量和效率,但存在走样现象一直是个难题。目前通常采用低通滤波方法来缓解走样现象,然而这些办法缺乏对采样率的敏感度,易导致走样或过度平滑的结果。本研究提出了一种新型的Level of Detail敏感的高斯绘制滤波器框架LOD-GS。此框架会针对每个三维高斯几何图形预测最优滤波强度。特别的是,我们引入了基于采样率的基函数来调整每个高斯模型的表现差异,使滤波更加敏感于采样率。参数通过端到端的优化方式联合优化三维高斯和基函数。我们创建了一个新合成数据集,用于全面评估相机距离对图像的影响,并实验证明我们的方法在消除走样现象的同时实现了业界领先的渲染质量。代码和数据集已开源。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术在渲染质量提升方面取得了进展,但走样现象仍然是一个挑战。
- 当前采用低通滤波的方法缓解走样问题,但这种方法缺乏对采样率的敏感度。
- LOD-GS框架引入了对采样率敏感的基函数来调整高斯模型的性能。每个高斯模型都有一个预测的过滤强度参数集用于应对采样率的动态变化。此框架能有效处理现有方法的局限性并增强抗走样能力。
- 基函数参数与三维高斯模型通过端到端的优化方式联合优化,提升了渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图

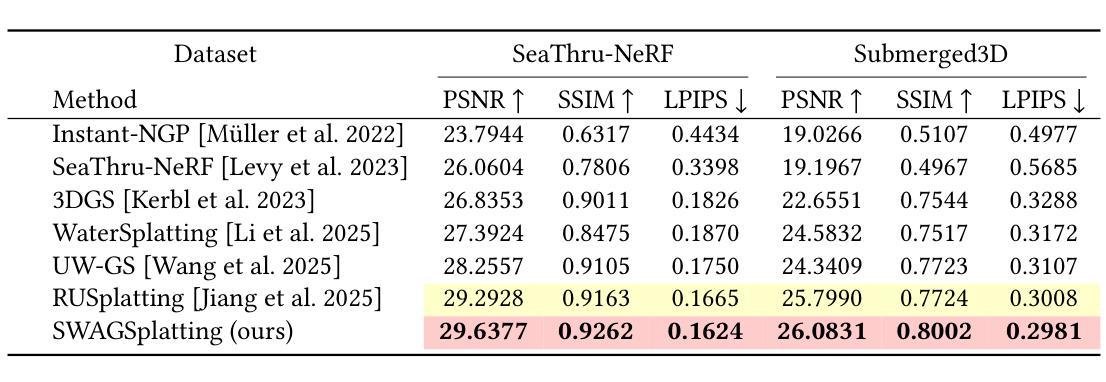
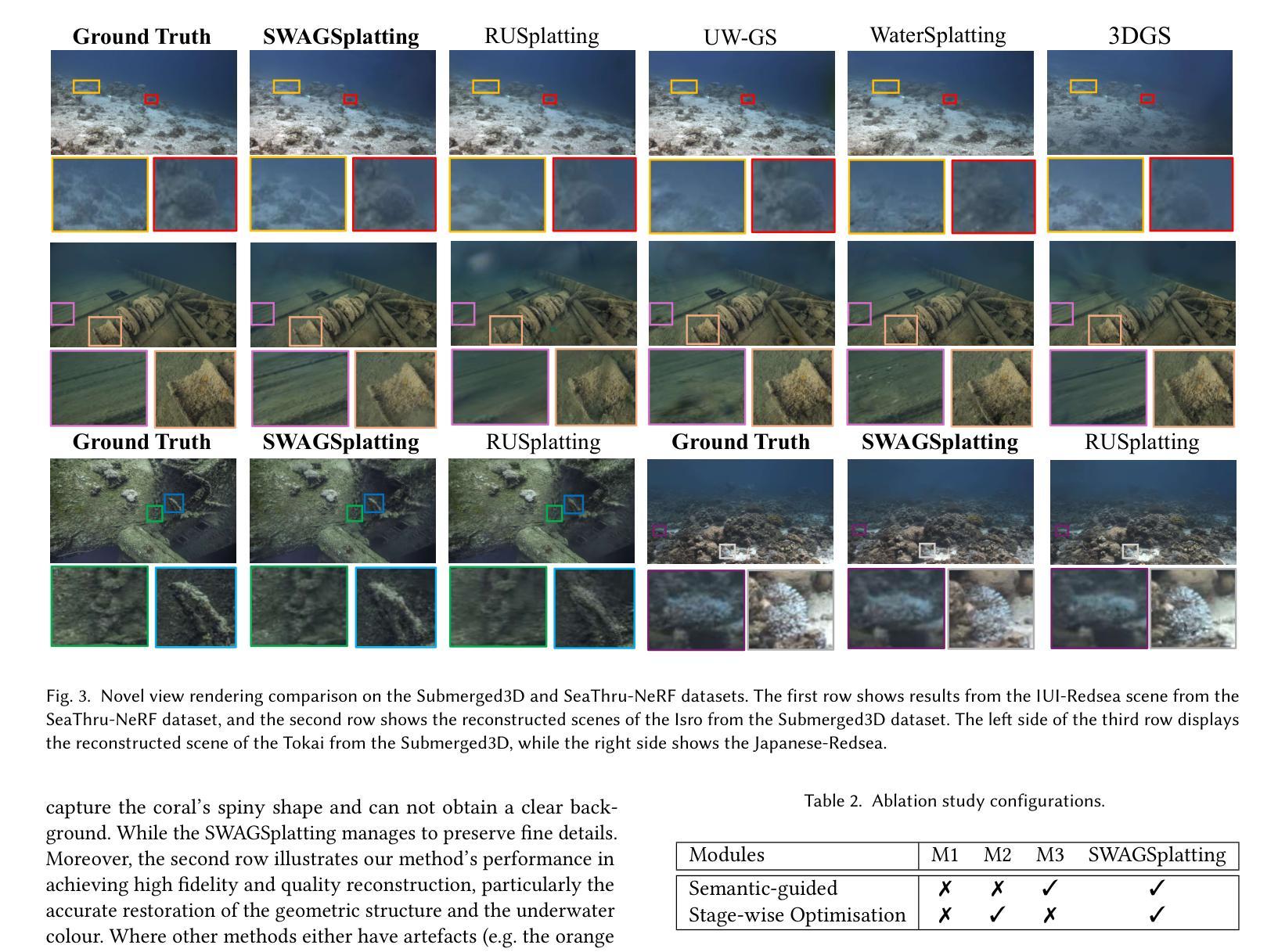
RUSplatting: Robust 3D Gaussian Splatting for Sparse-View Underwater Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Zhuodong Jiang, Haoran Wang, Guoxi Huang, Brett Seymour, Nantheera Anantrasirichai
Reconstructing high-fidelity underwater scenes remains a challenging task due to light absorption, scattering, and limited visibility inherent in aquatic environments. This paper presents an enhanced Gaussian Splatting-based framework that improves both the visual quality and geometric accuracy of deep underwater rendering. We propose decoupled learning for RGB channels, guided by the physics of underwater attenuation, to enable more accurate colour restoration. To address sparse-view limitations and improve view consistency, we introduce a frame interpolation strategy with a novel adaptive weighting scheme. Additionally, we introduce a new loss function aimed at reducing noise while preserving edges, which is essential for deep-sea content. We also release a newly collected dataset, Submerged3D, captured specifically in deep-sea environments. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods with PSNR gains up to 1.90dB, delivering superior perceptual quality and robustness, and offering promising directions for marine robotics and underwater visual analytics. The code of RUSplatting is available at https://github.com/theflash987/RUSplatting and the dataset Submerged3D can be downloaded at https://zenodo.org/records/15482420.
重建高保真水下场景仍然是一个充满挑战的任务,这是由于水下环境固有的光吸收、散射和有限的可见度造成的。本文针对基于高斯拼贴技术的框架进行增强,提高了水下深度渲染的视觉质量和几何精度。我们提出了针对RGB通道的解耦学习,以水下衰减的物理特性为指导,以实现更准确的颜色恢复。为了解决稀疏视图限制并提高视图一致性,我们引入了一种带有新型自适应加权方案的新帧插值策略。此外,我们引入了一种新的损失函数,旨在减少噪声的同时保留边缘,这对于深海内容至关重要。我们还发布了一个新收集的特定于深海环境的数据集Submerged3D。实验结果表明,我们的框架始终优于最新技术,PSNR增益高达1.90dB,提供卓越的感知质量和稳健性,并为海洋机器人技术和水下视觉分析提供了有前景的方向。RUSplatting的代码可在https://github.com/theflash987/RUSplatting上获取,数据集Submerged3D可在https://zenodo.org/records/15482420上下载。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by BMVC 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于高斯摊铺的增强框架,旨在提高水下场景的渲染质量和几何精度。通过解耦RGB通道学习、引入基于物理的水下衰减指导,实现了更准确的颜色复原。针对稀疏视图的问题,采取帧插值策略并结合新型自适应加权方案,提升了视图的连贯性。同时,设计新的损失函数,旨在降噪的同时保留边缘,这对深海内容至关重要。此外,还发布了一个专门在深海环境中采集的新数据集Submerged3D。实验结果表明,该框架较现有技术有明显优势,峰值信噪比提升达1.90dB,感知质量和稳健性上乘,为海洋机器人和水下视觉分析提供了有前景的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的增强高斯摊铺框架提高了水下场景的渲染质量和几何精度。
- 通过解耦RGB通道学习,结合水下衰减的物理指导,实现更准确的颜色复原。
- 采用帧插值策略及自适应加权方案应对稀疏视图问题,增强视图连贯性。
- 新设计的损失函数能在降噪的同时保留边缘,适用于深海内容处理。
- 发布了专门在深海环境下采集的新数据集Submerged3D。
- 实验结果显示,该框架较现有技术有显著提升,峰值信噪比最高提升达1.90dB。
点此查看论文截图

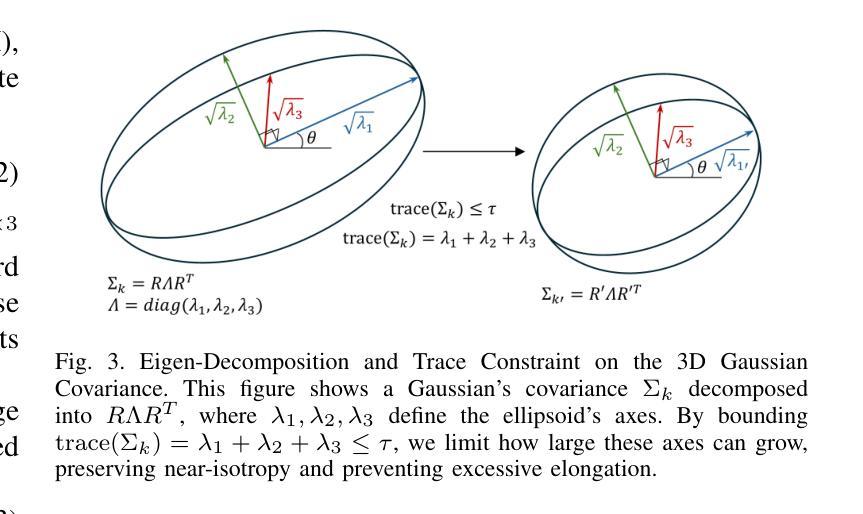
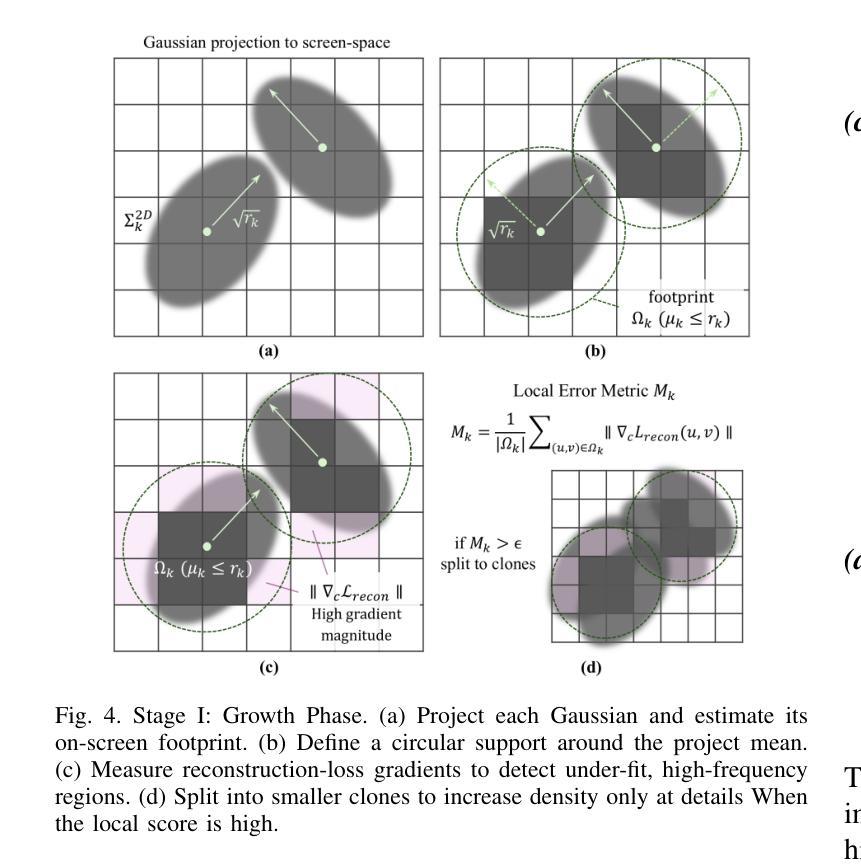
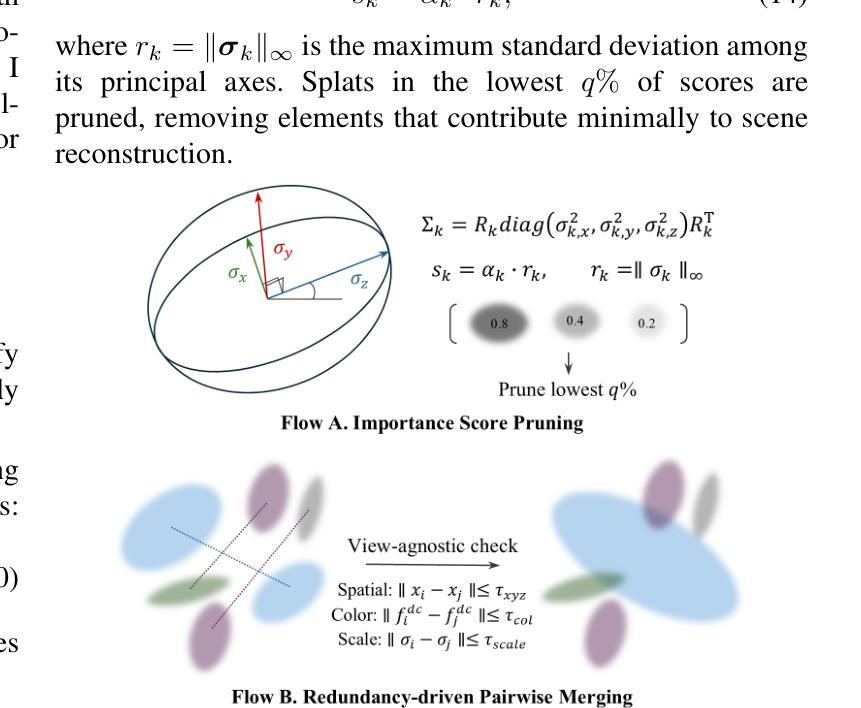
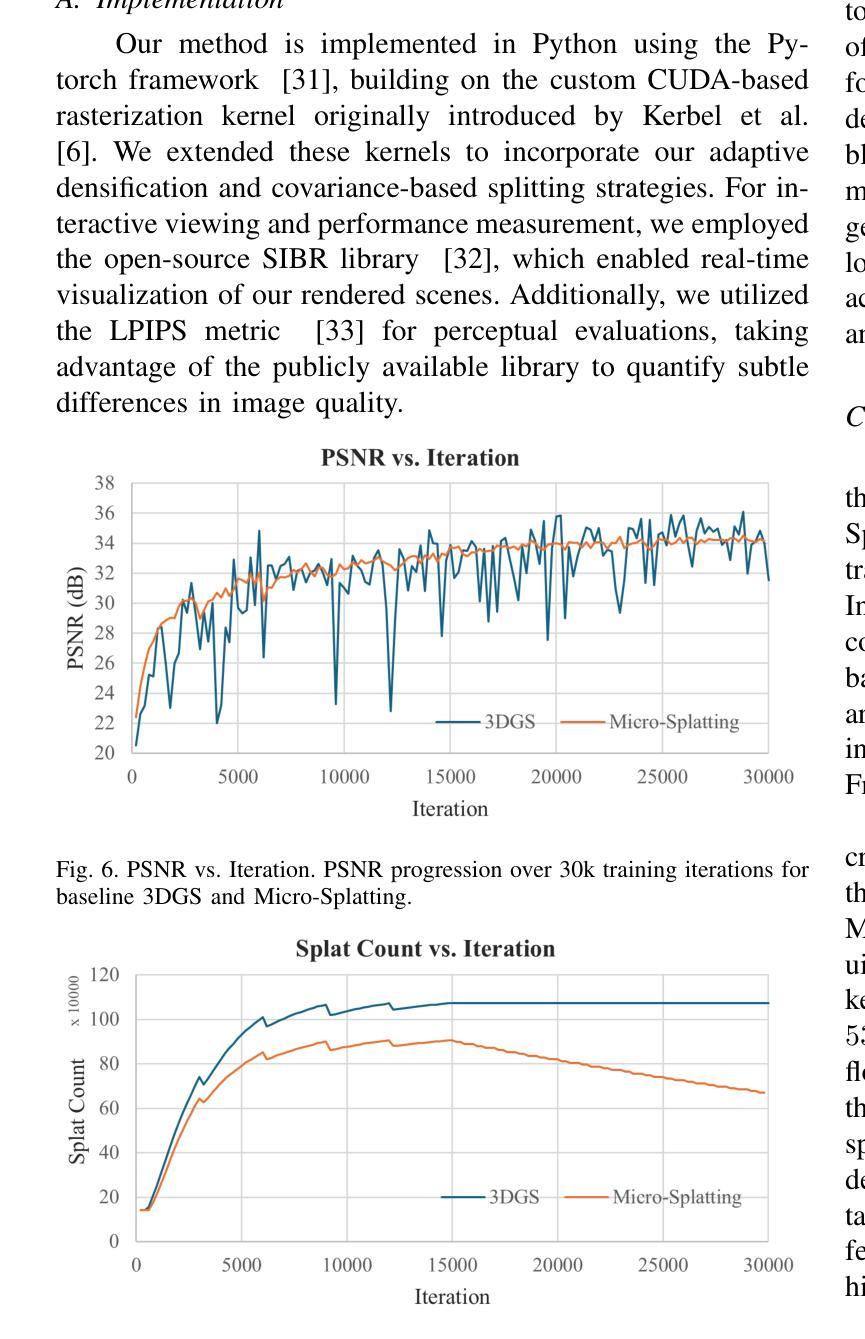
Micro-splatting: Multistage Isotropy-informed Covariance Regularization Optimization for High-Fidelity 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jee Won Lee, Hansol Lim, Sooyeun Yang, Jongseong Brad Choi
High-fidelity 3D Gaussian Splatting methods excel at capturing fine textures but often overlook model compactness, resulting in massive splat counts, bloated memory, long training, and complex post-processing. We present Micro-Splatting: Two-Stage Adaptive Growth and Refinement, a unified, in-training pipeline that preserves visual detail while drastically reducing model complexity without any post-processing or auxiliary neural modules. In Stage I (Growth), we introduce a trace-based covariance regularization to maintain near-isotropic Gaussians, mitigating low-pass filtering in high-frequency regions and improving spherical-harmonic color fitting. We then apply gradient-guided adaptive densification that subdivides splats only in visually complex regions, leaving smooth areas sparse. In Stage II (Refinement), we prune low-impact splats using a simple opacity-scale importance score and merge redundant neighbors via lightweight spatial and feature thresholds, producing a lean yet detail-rich model. On four object-centric benchmarks, Micro-Splatting reduces splat count and model size by up to 60% and shortens training by 20%, while matching or surpassing state-of-the-art PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS in real-time rendering. These results demonstrate that Micro-Splatting delivers both compactness and high fidelity in a single, efficient, end-to-end framework.
高保真3D高斯摊铺方法擅长捕捉精细纹理,但往往会忽略模型紧凑性,导致大量的摊铺计数、内存膨胀、训练时间长和复杂的后期处理。我们提出了Micro-Splatting:两阶段自适应增长与细化,这是一个统一的、在训练过程中的管道,能够保留视觉细节,同时大幅度减少模型复杂性,无需任何后期处理或辅助神经网络模块。在第一阶段(增长阶段),我们引入基于轨迹的协方差正则化,以维持接近等向的高斯分布,缓解高频区域的低通滤波,并改进球面谐波颜色拟合。然后,我们应用梯度引导的自适应密集化,只在视觉复杂区域细分摊铺,而让平滑区域保持稀疏。在第二阶段(细化阶段),我们利用简单的透明度尺度重要性评分剔除影响较小的摊铺,并通过轻量级的空间和特征阈值合并冗余的邻居,从而产生一个精简而细节丰富的模型。在四个以对象为中心的基准测试中,Micro-Splatting将摊铺计数和模型大小减少了高达60%,将训练时间缩短了20%,同时在实时渲染中匹配或超越了最先进的PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS。这些结果证明,Micro-Splatting在单一、高效、端到端的框架中实现了紧凑性和高保真度的兼顾。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to journal for potential publication
Summary
本文介绍了Micro-Splatting技术,这是一种在训练过程中统一的两阶段自适应增长与细化方法,旨在保留视觉细节的同时大幅降低模型复杂度。在第一阶段(增长阶段),通过引入基于轨迹的协方差正则化来维持接近等向的高斯分布,并应用梯度引导的自适应密集化。在第二阶段(细化阶段),通过简单的透明度尺度重要性评分剔除低影响的高斯点,并通过轻量级的空间和特征阈值合并冗余邻居。Micro-Splatting在四个以物体为中心的基准测试中,减少了高达60%的高斯点数和模型大小,缩短了20%的训练时间,同时在实时渲染中匹配或超越了最先进的技术指标。证明Micro-Splatting在一个高效、端到端的框架中同时实现了紧凑性和高保真度。
Key Takeaways
- Micro-Splatting是一种在训练过程中统一的两阶段自适应增长与细化方法,旨在解决传统3D高斯分裂方法在模型紧凑性和纹理捕捉上的不足。
- 第一阶段(增长阶段)通过引入基于轨迹的协方差正则化和梯度引导的自适应密集化,维持了高斯分布的等向性并提高了视觉复杂性区域的模型精度。
- 第二阶段(细化阶段)通过剔除低影响的高斯点和合并冗余邻居,实现了模型的大小和复杂度的显著降低。
- Micro-Splatting在四个物体为中心的基准测试中,显著减少了高斯点数、模型大小以及训练时间。
- 该方法在保证模型紧凑性的同时,达到了高保真度的效果,匹配或超越了现有技术的实时渲染性能。
- Micro-Splatting提供了一个高效、端到端的框架,能够在实际应用中实现模型的优化和性能的提升。
点此查看论文截图

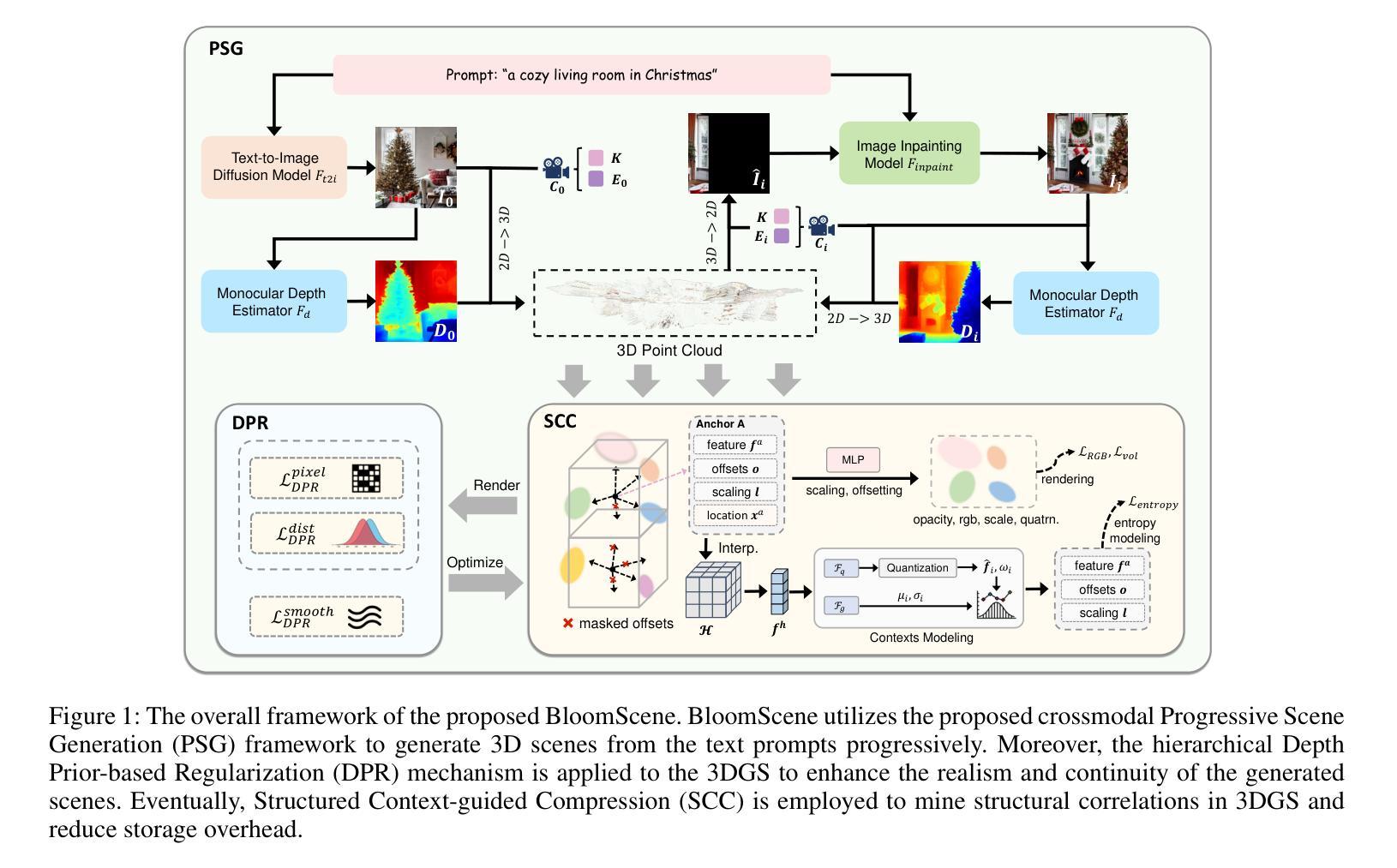
BloomScene: Lightweight Structured 3D Gaussian Splatting for Crossmodal Scene Generation
Authors:Xiaolu Hou, Mingcheng Li, Dingkang Yang, Jiawei Chen, Ziyun Qian, Xiao Zhao, Yue Jiang, Jinjie Wei, Qingyao Xu, Lihua Zhang
With the widespread use of virtual reality applications, 3D scene generation has become a new challenging research frontier. 3D scenes have highly complex structures and need to ensure that the output is dense, coherent, and contains all necessary structures. Many current 3D scene generation methods rely on pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models and monocular depth estimators. However, the generated scenes occupy large amounts of storage space and often lack effective regularisation methods, leading to geometric distortions. To this end, we propose BloomScene, a lightweight structured 3D Gaussian splatting for crossmodal scene generation, which creates diverse and high-quality 3D scenes from text or image inputs. Specifically, a crossmodal progressive scene generation framework is proposed to generate coherent scenes utilizing incremental point cloud reconstruction and 3D Gaussian splatting. Additionally, we propose a hierarchical depth prior-based regularization mechanism that utilizes multi-level constraints on depth accuracy and smoothness to enhance the realism and continuity of the generated scenes. Ultimately, we propose a structured context-guided compression mechanism that exploits structured hash grids to model the context of unorganized anchor attributes, which significantly eliminates structural redundancy and reduces storage overhead. Comprehensive experiments across multiple scenes demonstrate the significant potential and advantages of our framework compared with several baselines.
随着虚拟现实应用的广泛使用,3D场景生成已成为一个新的具有挑战性的研究前沿。3D场景具有复杂的结构,需要确保输出是密集的、连贯的,并包含所有必要的结构。目前许多3D场景生成方法依赖于预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型和单目深度估计器。然而,生成的场景占用大量的存储空间,并且常常缺乏有效的正则化方法,导致几何失真。为此,我们提出了BloomScene,这是一种轻量级的3D高斯飞溅结构化方法,用于跨模态场景生成,可以从文本或图像输入创建多样且高质量的3D场景。具体来说,我们提出了一种跨模态渐进场景生成框架,利用增量点云重建和3D高斯飞溅生成连贯场景。此外,我们提出了一种基于层次深度先验的正则化机制,利用深度精度和平滑度的多级约束,提高生成场景的真实感和连续性。最后,我们提出了一种结构化上下文引导压缩机制,利用结构化哈希网格对未组织锚点属性进行建模,这极大地消除了结构冗余并降低了存储开销。在多个场景的综合实验表明,我们的框架与几个基准相比具有显著潜力和优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025. Code: https://github.com/SparklingH/BloomScene
Summary
本文介绍了随着虚拟现实的广泛应用,3D场景生成成为新的研究前沿。文章提出了一种轻量级的结构化3D高斯描点法——BloomScene,用于跨模态场景生成,可以从文本或图像创建多样化、高质量的3D场景。该方法采用增量点云重建和3D高斯描点技术构建连贯场景,并提出层次深度先验正则化机制和多级深度约束增强场景真实性和连续性。最后,文章提出了一种结构化上下文引导压缩机制,利用结构化哈希网格建模无序锚点属性上下文,减少结构冗余并降低存储开销。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟现实的广泛应用推动了3D场景生成成为新的研究热点。
- 当前3D场景生成方法存在的问题包括场景结构复杂度高、存储空间占用大以及缺乏有效的正则化方法导致的几何失真。
- 提出了一种新的跨模态场景生成方法——BloomScene,结合文本或图像创建高质量、多样化的3D场景。
- BloomScene采用增量点云重建和3D高斯描点技术构建连贯场景,确保场景的连贯性和完整性。
- 提出了一种层次深度先验正则化机制,通过多级深度约束增强场景的真实感和连续性。
- 采用了结构化上下文引导压缩机制来减少结构冗余并降低存储开销。
点此查看论文截图