⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
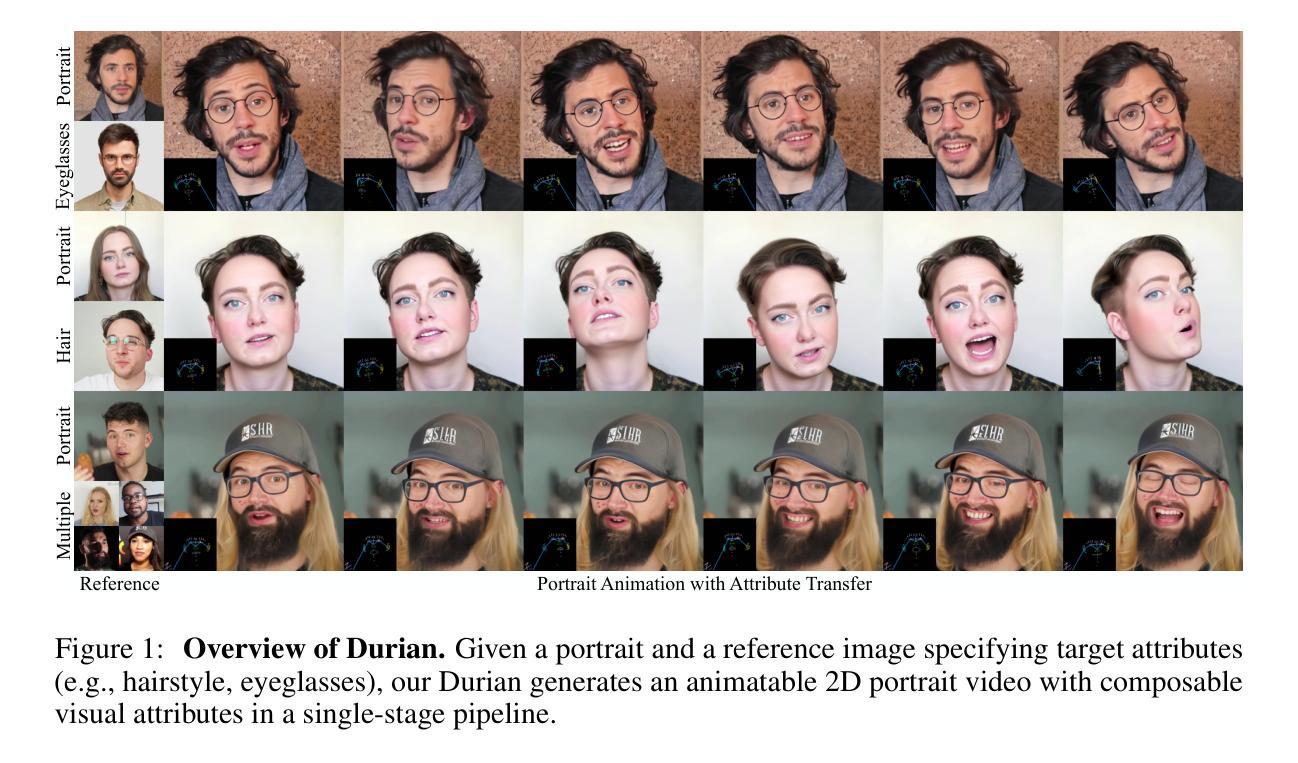
Durian: Dual Reference-guided Portrait Animation with Attribute Transfer
Authors:Hyunsoo Cha, Byungjun Kim, Hanbyul Joo
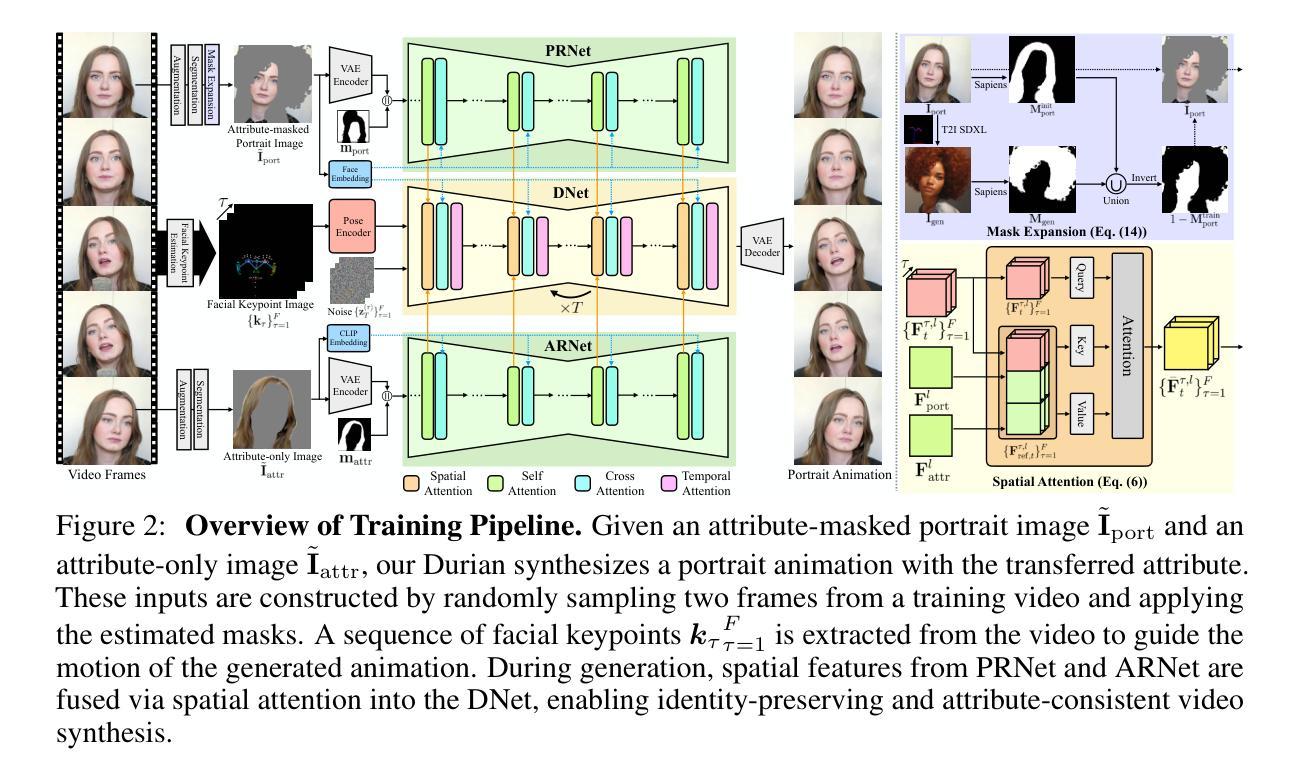
We present Durian, the first method for generating portrait animation videos with facial attribute transfer from a given reference image to a target portrait in a zero-shot manner. To enable high-fidelity and spatially consistent attribute transfer across frames, we introduce dual reference networks that inject spatial features from both the portrait and attribute images into the denoising process of a diffusion model. We train the model using a self-reconstruction formulation, where two frames are sampled from the same portrait video: one is treated as the attribute reference and the other as the target portrait, and the remaining frames are reconstructed conditioned on these inputs and their corresponding masks. To support the transfer of attributes with varying spatial extent, we propose a mask expansion strategy using keypoint-conditioned image generation for training. In addition, we further augment the attribute and portrait images with spatial and appearance-level transformations to improve robustness to positional misalignment between them. These strategies allow the model to effectively generalize across diverse attributes and in-the-wild reference combinations, despite being trained without explicit triplet supervision. Durian achieves state-of-the-art performance on portrait animation with attribute transfer, and notably, its dual reference design enables multi-attribute composition in a single generation pass without additional training.
我们提出了Durian方法,这是第一种零样本方式生成肖像动画视频的方法,可以将给定参考图像的面部属性转移到目标肖像上。为了实现跨帧的高保真和空间一致的属性转移,我们引入了双参考网络,它将肖像和属性图像的空间特征注入扩散模型的去噪过程中。我们使用自我重建公式对模型进行训练,从同一肖像视频中采样两帧:一帧作为属性参考,另一帧作为目标肖像,然后根据这些输入及其相应的掩码对剩余帧进行重建。为了支持具有不同空间范围的属性转移,我们提出了使用关键点条件图像生成的掩膜扩展策略进行训练。此外,我们进一步使用空间和外观级别的变换来增强属性和肖像图像,以提高它们之间位置不对齐的鲁棒性。这些策略使得模型能够在不同的属性和野外参考组合中有效推广,即使在没有明确的三元组监督的情况下也是如此。Durian在带有属性转移的肖像动画方面达到了最先进的性能,值得注意的是,其双参考设计能够在单次生成过程中实现多属性组合,无需额外的训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://hyunsoocha.github.io/durian
Summary
本文介绍了名为Durian的方法,它能在零样本情况下从给定的参考图像向目标肖像生成动画视频。通过引入双重参考网络,实现了跨帧的高保真和空间一致性的属性转移。采用自重建训练模式,通过关键点的条件图像生成进行掩膜扩展策略支持不同空间范围的属性转移。通过增强属性和肖像图像的空间和外观级别的转换,提高了对它们之间位置不匹配问题的稳健性。尽管没有明确的三个样本监督,但Durian在肖像动画属性转移方面达到了最先进的性能,其双重参考设计能够在单次生成过程中实现多属性组合。
Key Takeaways
- Durian是第一种能够在零样本情况下实现从给定参考图像向目标肖像生成动画视频的方法。
- 双重参考网络被引入以实现高保真和空间一致性的跨帧属性转移。
- 采用自重建训练模式,通过相同肖像视频采样的两个帧,一个作为属性参考,另一个作为目标肖像,进行训练。
- 引入掩膜扩展策略,支持不同空间范围的属性转移,并通过关键点的条件图像生成进行训练。
- 通过增强属性和肖像图像的空间和外观级别的转换,提高模型稳健性,应对位置不匹配问题。
- Durian在肖像动画属性转移方面表现出最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图


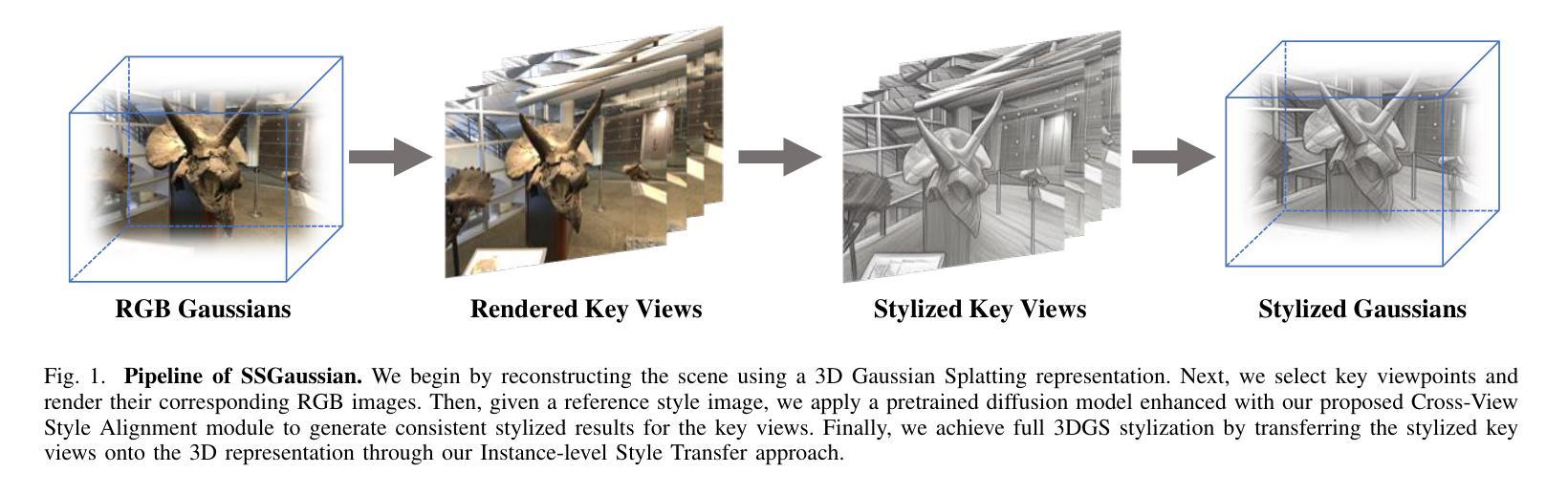
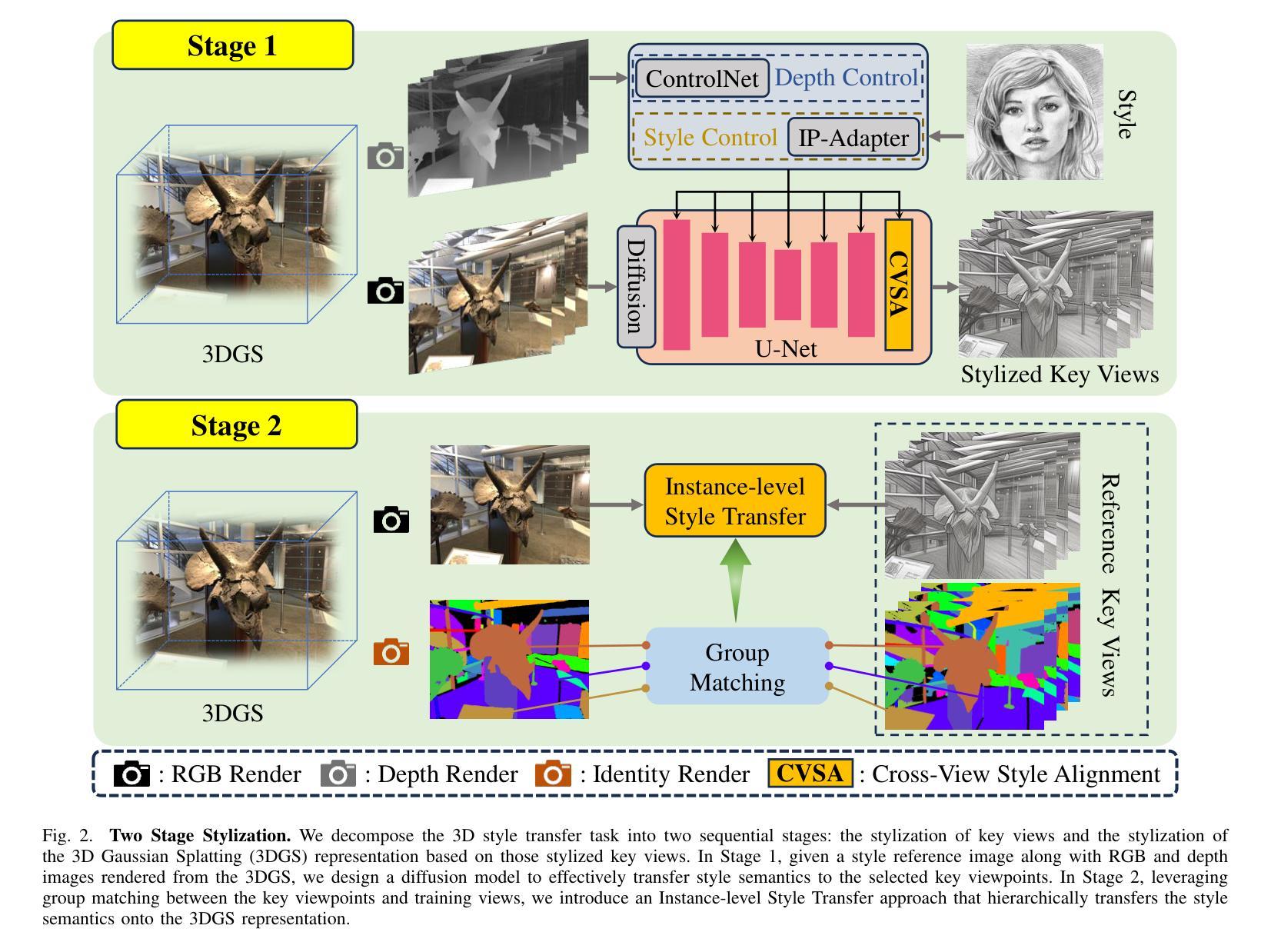
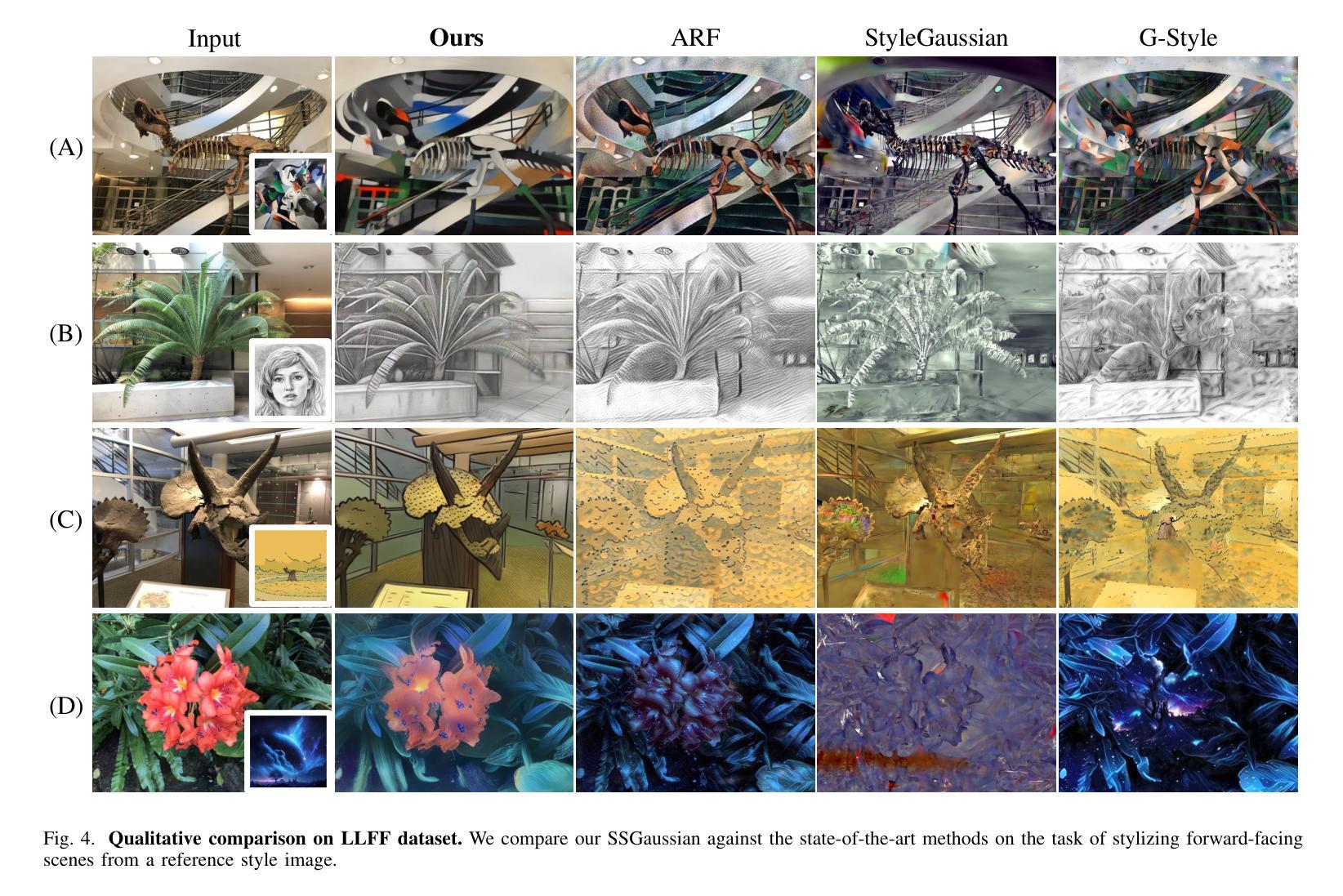
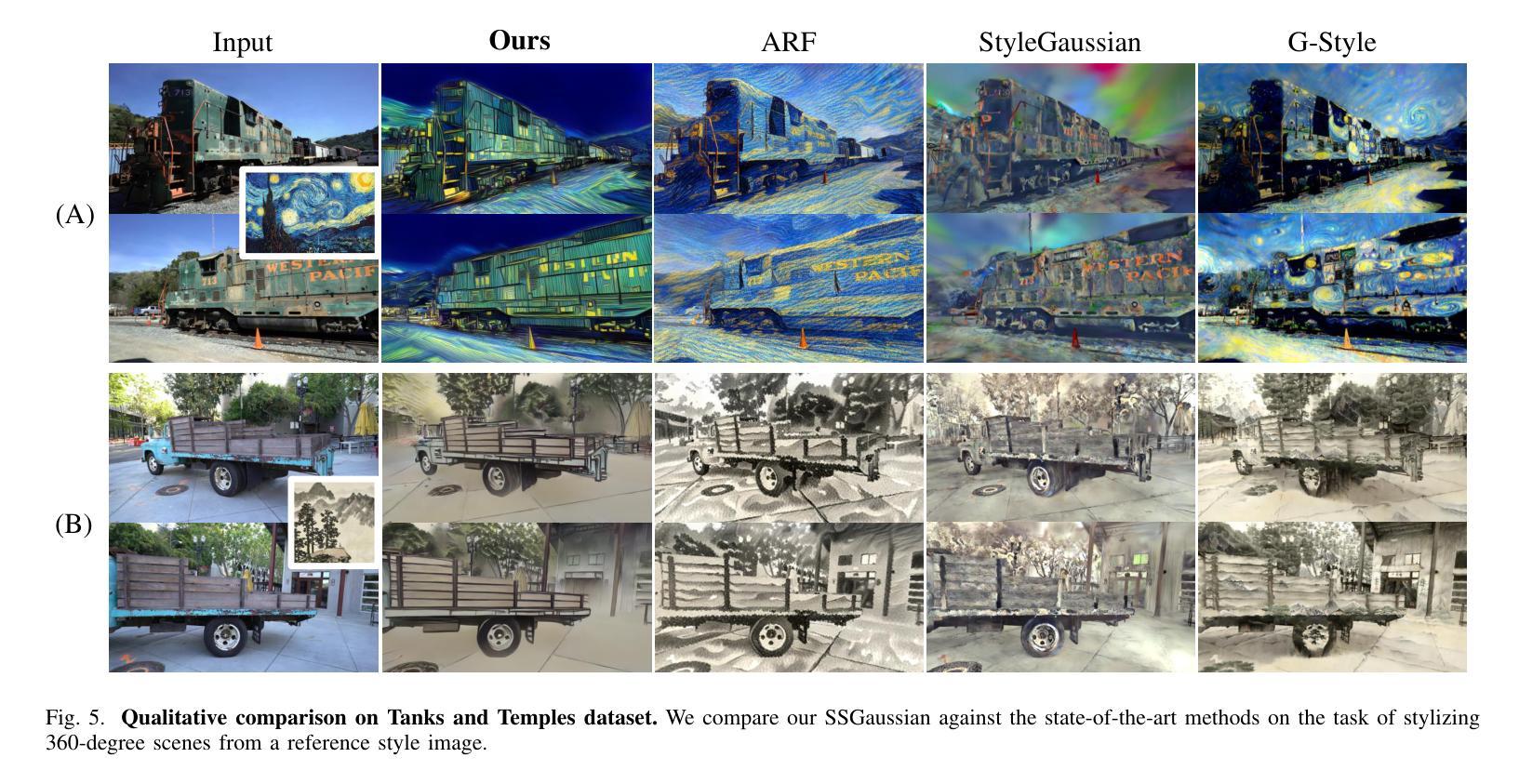
SSGaussian: Semantic-Aware and Structure-Preserving 3D Style Transfer
Authors:Jimin Xu, Bosheng Qin, Tao Jin, Zhou Zhao, Zhenhui Ye, Jun Yu, Fei Wu
Recent advancements in neural representations, such as Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting, have increased interest in applying style transfer to 3D scenes. While existing methods can transfer style patterns onto 3D-consistent neural representations, they struggle to effectively extract and transfer high-level style semantics from the reference style image. Additionally, the stylized results often lack structural clarity and separation, making it difficult to distinguish between different instances or objects within the 3D scene. To address these limitations, we propose a novel 3D style transfer pipeline that effectively integrates prior knowledge from pretrained 2D diffusion models. Our pipeline consists of two key stages: First, we leverage diffusion priors to generate stylized renderings of key viewpoints. Then, we transfer the stylized key views onto the 3D representation. This process incorporates two innovative designs. The first is cross-view style alignment, which inserts cross-view attention into the last upsampling block of the UNet, allowing feature interactions across multiple key views. This ensures that the diffusion model generates stylized key views that maintain both style fidelity and instance-level consistency. The second is instance-level style transfer, which effectively leverages instance-level consistency across stylized key views and transfers it onto the 3D representation. This results in a more structured, visually coherent, and artistically enriched stylization. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our 3D style transfer pipeline significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods across a wide range of scenes, from forward-facing to challenging 360-degree environments. Visit our project page https://jm-xu.github.io/SSGaussian for immersive visualization.
最近,神经表征领域的进展,如神经辐射场和3D高斯喷涂等技术,增加了将风格迁移应用于3D场景的兴趣。尽管现有方法能够将风格模式转移到一致的3D神经表征上,但它们难以有效地从参考风格图像中提取并转移高级风格语义。此外,风格化的结果通常缺乏结构清晰度和分离度,使得难以在3D场景中区分不同的实例或对象。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新颖的3D风格迁移管道,该管道有效地整合了来自预训练的2D扩散模型的先验知识。我们的管道由两个阶段组成:首先,我们利用扩散先验知识生成关键视点的风格化渲染。然后,我们将风格化的关键视图转移到3D表征上。这一过程采用了两项创新设计。首先是跨视图风格对齐,它将跨视图注意力插入到UNet的最后一个上采样块中,允许跨多个关键视图进行特征交互。这确保扩散模型生成的风格化关键视图既保持风格忠实度又保持实例级一致性。其次是实例级风格迁移,它有效地利用风格化关键视图之间的实例级一致性,并将其转移到3D表征上。这导致了一种更具结构、视觉连贯性和艺术丰富性的风格化。广泛的定性和定量实验表明,我们的3D风格迁移管道在各种场景中显著优于现有最先进的管道,无论是正面场景还是具有挑战性的360度环境。请访问我们的项目页面:链接地址以获取沉浸式可视化体验。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
近期神经网络表示技术如Neural Radiance Fields和3D Gaussian Splatting的发展,引发了将风格迁移应用于3D场景的兴趣。现有方法虽能将风格模式转移到3D一致的神经网络表示上,但难以有效提取和转移参考风格图像的高级语义。此外,风格化的结果往往缺乏结构清晰度和分离度,难以区分3D场景中的不同实例或对象。为此,我们提出一种新颖的3D风格迁移管道,有效整合了预训练的2D扩散模型的先验知识。该管道包括两个阶段:首先,我们利用扩散先验生成关键视角的风格化渲染;然后,将这些风格化的关键视图转移到3D表示上。这一过程融入了两项创新设计。首先是跨视图风格对齐,将跨视图注意力插入UNet的最后一个上采样块中,允许跨多个关键视图进行特征交互。这确保扩散模型生成的风格化关键视图既保持风格忠实度又保持实例级一致性。其次是实例级风格迁移,它有效地利用风格化关键视图之间的实例级一致性,并将其转移到3D表示上。这产生了一种更具结构、视觉连贯且艺术感更强的风格化。广泛的定性和定量实验表明,我们的3D风格迁移管道在多种场景上显著优于最先进的方法,包括正面和具有挑战性的360度环境。沉浸式可视化请访问我们的项目页面:https://jm-xu.github.io/SSGaussian。
关键见解
- 现有3D风格迁移方法在提取和转移高级风格语义方面存在困难。
- 提出的3D风格迁移管道包含两个阶段:生成风格化渲染的关键视角,并将其转移到3D表示。
- 管道融入了两项创新设计:跨视图风格对齐和实例级风格迁移。
- 跨视图风格对齐通过跨视图注意力确保风格化关键视图的风格忠实度和实例级一致性。
- 实例级风格迁移利用风格化关键视图之间的实例级一致性,实现更具结构、视觉连贯且艺术感强的风格化。
- 该方法在多种场景上显著优于现有最先进的方法,包括处理正面和360度环境等具有挑战性的场景。
点此查看论文截图


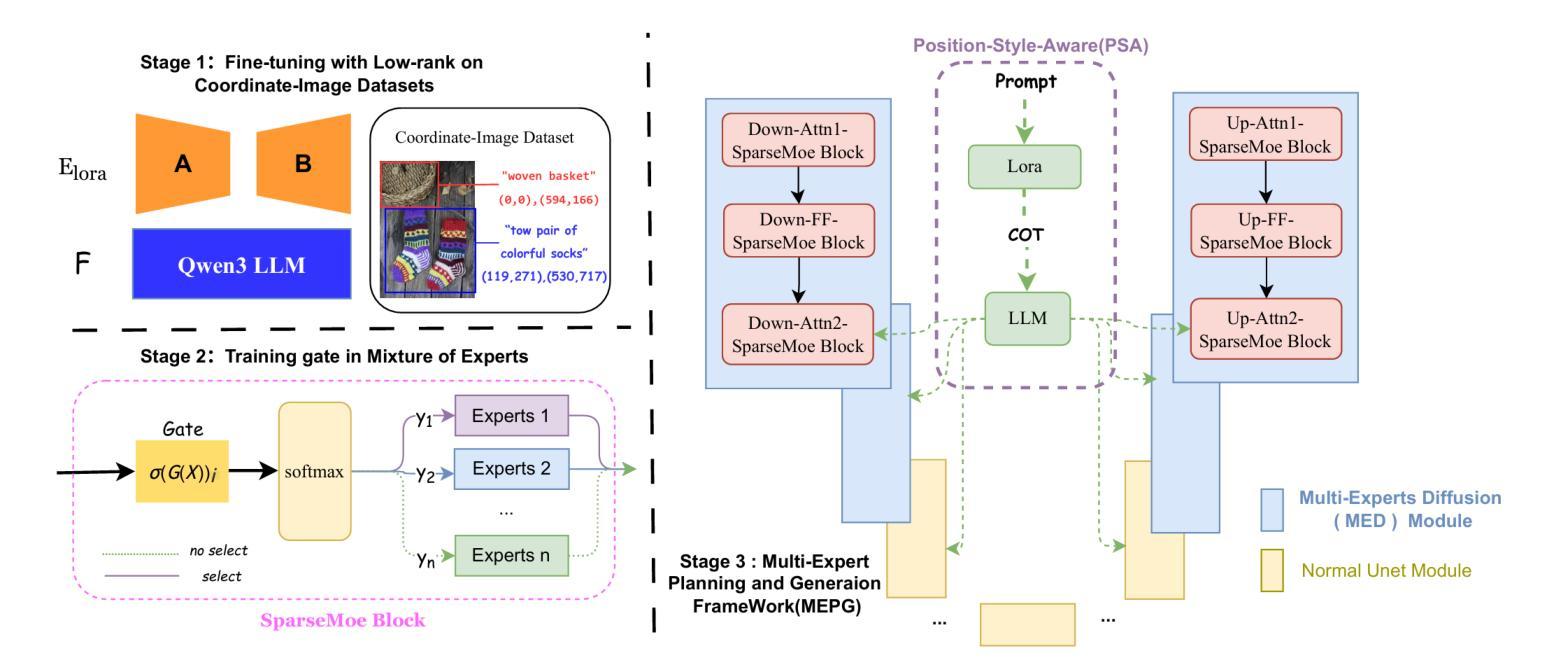
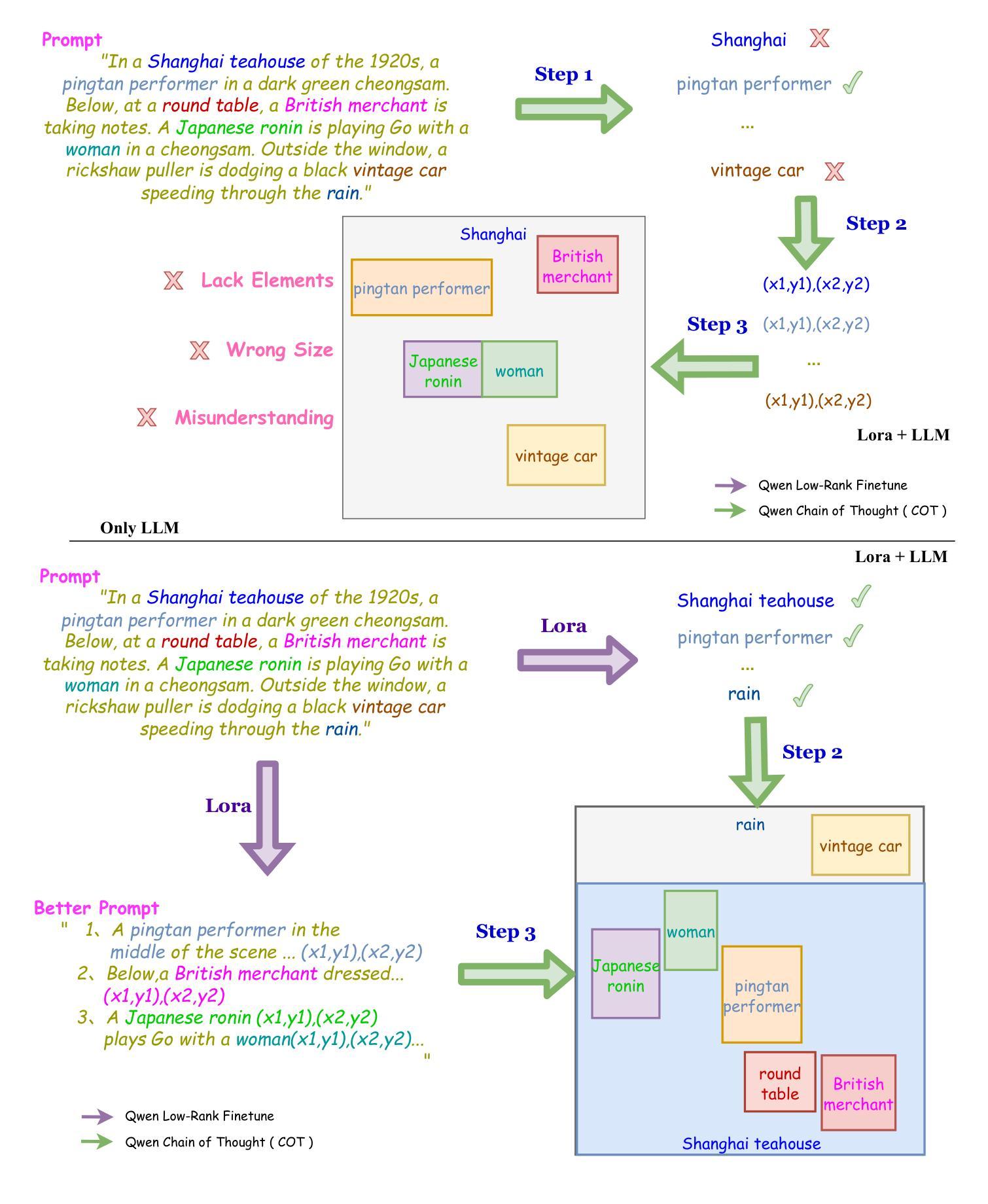
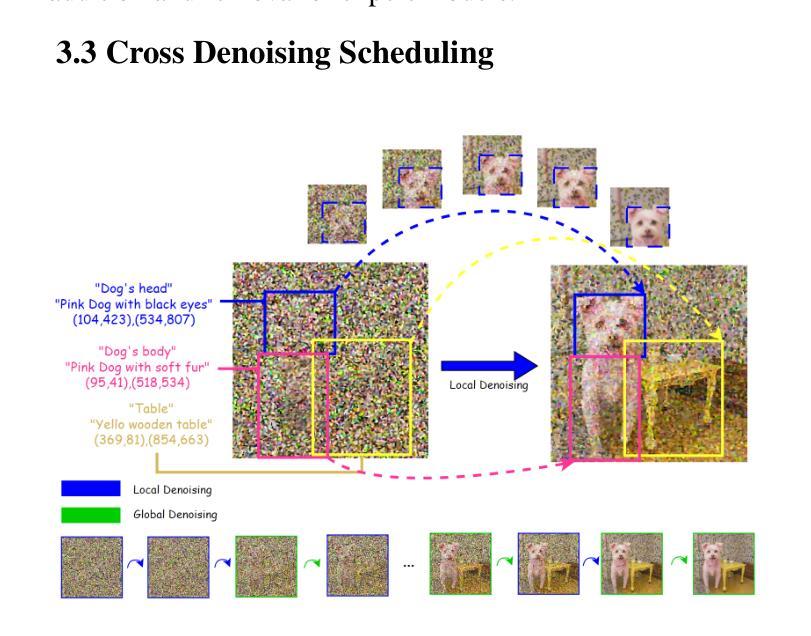
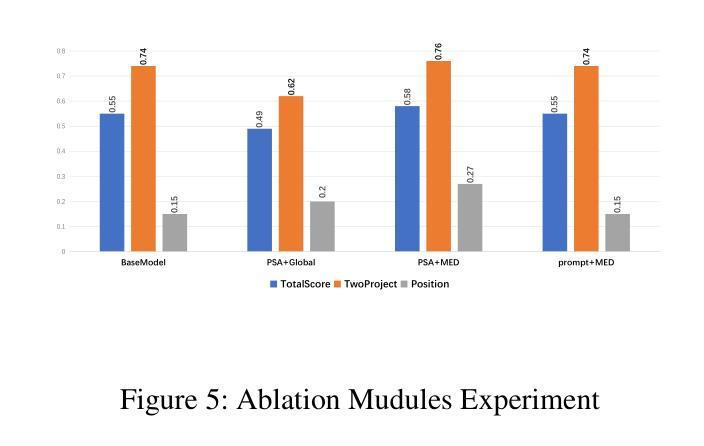
MEPG:Multi-Expert Planning and Generation for Compositionally-Rich Image Generation
Authors:Yuan Zhao, Liu Lin
Text-to-image diffusion models have achieved remarkable image quality, but they still struggle with complex, multiele ment prompts, and limited stylistic diversity. To address these limitations, we propose a Multi-Expert Planning and Gen eration Framework (MEPG) that synergistically integrates position- and style-aware large language models (LLMs) with spatial-semantic expert modules. The framework comprises two core components: (1) a Position-Style-Aware (PSA) module that utilizes a supervised fine-tuned LLM to decom pose input prompts into precise spatial coordinates and style encoded semantic instructions; and (2) a Multi-Expert Dif fusion (MED) module that implements cross-region genera tion through dynamic expert routing across both local regions and global areas. During the generation process for each lo cal region, specialized models (e.g., realism experts, styliza tion specialists) are selectively activated for each spatial par tition via attention-based gating mechanisms. The architec ture supports lightweight integration and replacement of ex pert models, providing strong extensibility. Additionally, an interactive interface enables real-time spatial layout editing and per-region style selection from a portfolio of experts. Ex periments show that MEPG significantly outperforms base line models with the same backbone in both image quality and style diversity.
文本到图像的扩散模型已经取得了显著的图像质量,但它们仍然面临复杂、多元素提示和风格多样性有限的挑战。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一个多专家规划和生成框架(MEPG),该框架协同整合了位置感知和风格感知的大型语言模型(LLM)与空间语义专家模块。该框架包括两个核心组件:(1)位置风格感知(PSA)模块,它利用监督微调LLM将输入提示分解为精确的空间坐标和风格编码语义指令;(2)多专家扩散(MED)模块,通过局部区域和全局区域的动态专家路由实现跨区域生成。针对每个局部区域的生成过程,通过基于注意力的门控机制,有选择地激活特殊模型(例如,现实主义者专家、风格化专家)等。该架构支持专家模型的轻松集成和替换,具有很强的可扩展性。此外,交互式界面允许实时空间布局编辑和从专家组合中选择每个区域的风格。实验表明,MEPG在图像质量和风格多样性方面都显著优于具有相同背景的基线模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本内容关于图像扩散模型,其面临复杂多元素提示和风格多样性受限的问题。为此,提出了多专家规划和生成框架(MEPG),该框架结合了位置感知和风格感知的大型语言模型(LLM)与空间语义专家模块。MEPG包含两个核心组件:一是位置风格感知(PSA)模块,用于将输入提示分解为精确的空间坐标和风格编码语义指令;二是多专家扩散(MED)模块,通过动态专家路由在本地区域和全局区域之间实现跨区域生成。MEPG能够实时编辑空间布局并为每个区域选择专家风格,因此其图像质量和风格多样性均优于基线模型。
Key Takeaways
- 文本内容主要介绍了图像扩散模型在处理复杂多元素提示和风格多样性方面的挑战。
- 提出了一种名为多专家规划和生成框架(MEPG)的解决方案,该框架结合了大型语言模型和空间语义专家模块。
- MEPG包含两个核心组件:位置风格感知模块(PSA)和多专家扩散模块(MED)。
- PSA模块能够将输入提示分解为精确的空间坐标和风格编码语义指令。
- MED模块通过动态专家路由在本地和全局区域之间实现跨区域生成,提高图像质量和风格多样性。
- MEPG支持轻松集成和替换专家模型,具有强大的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图


Fitting Image Diffusion Models on Video Datasets
Authors:Juhun Lee, Simon S. Woo
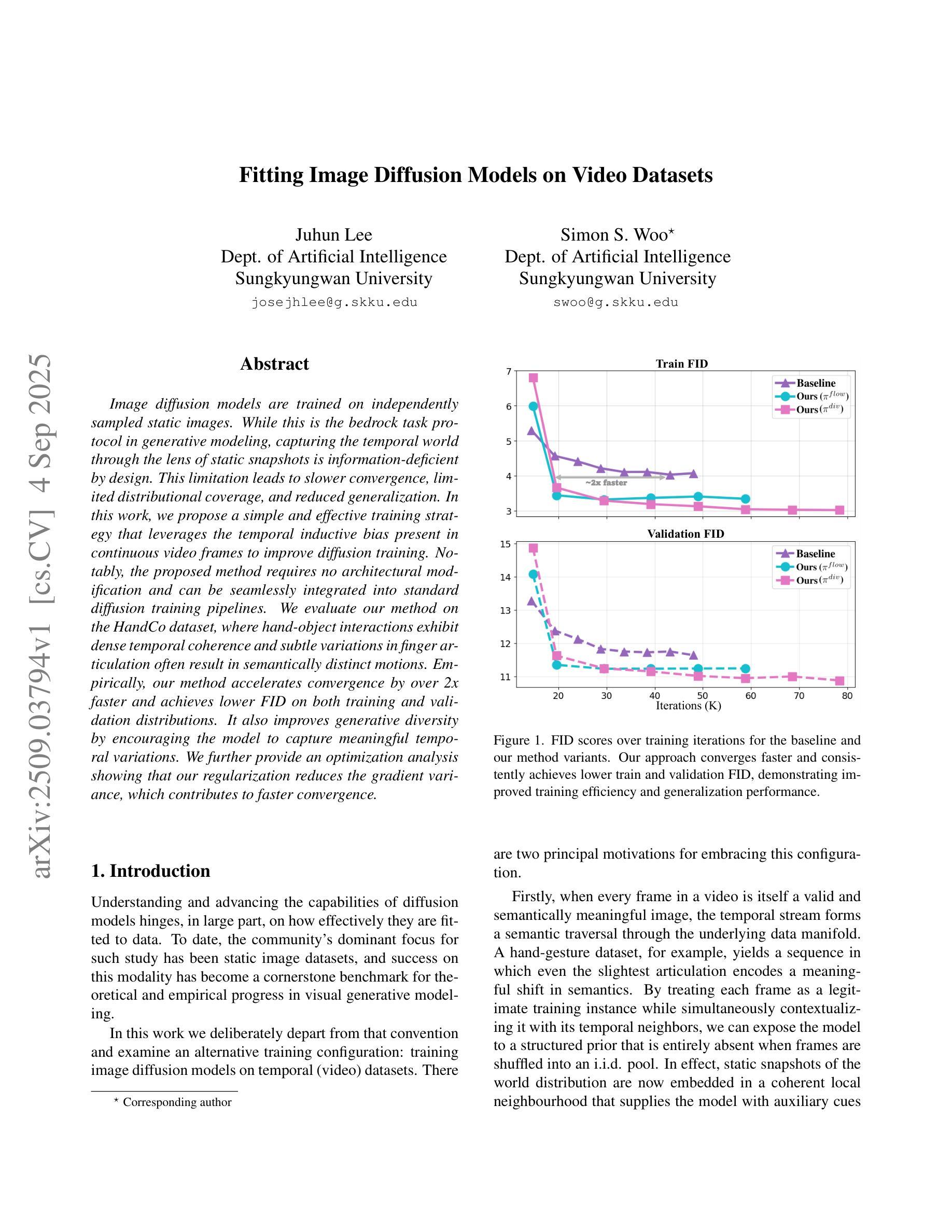
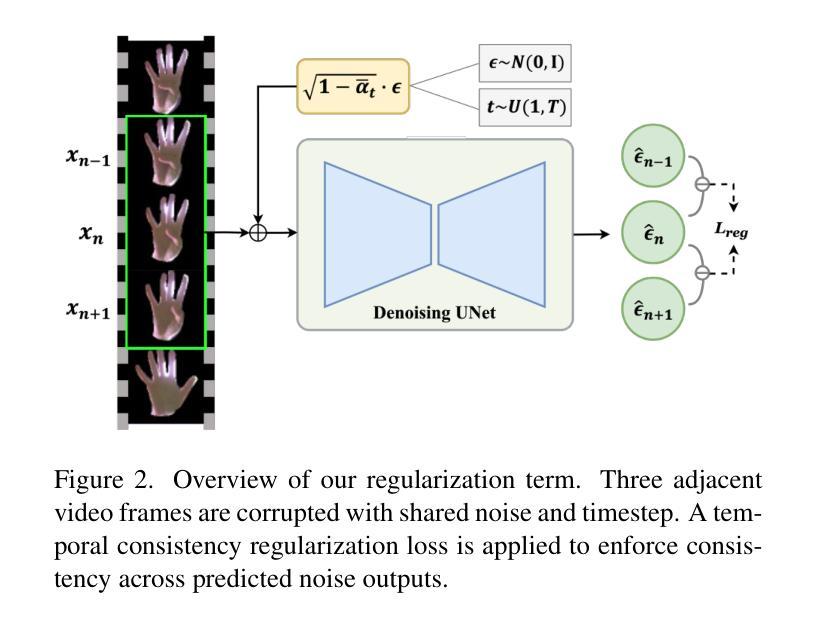
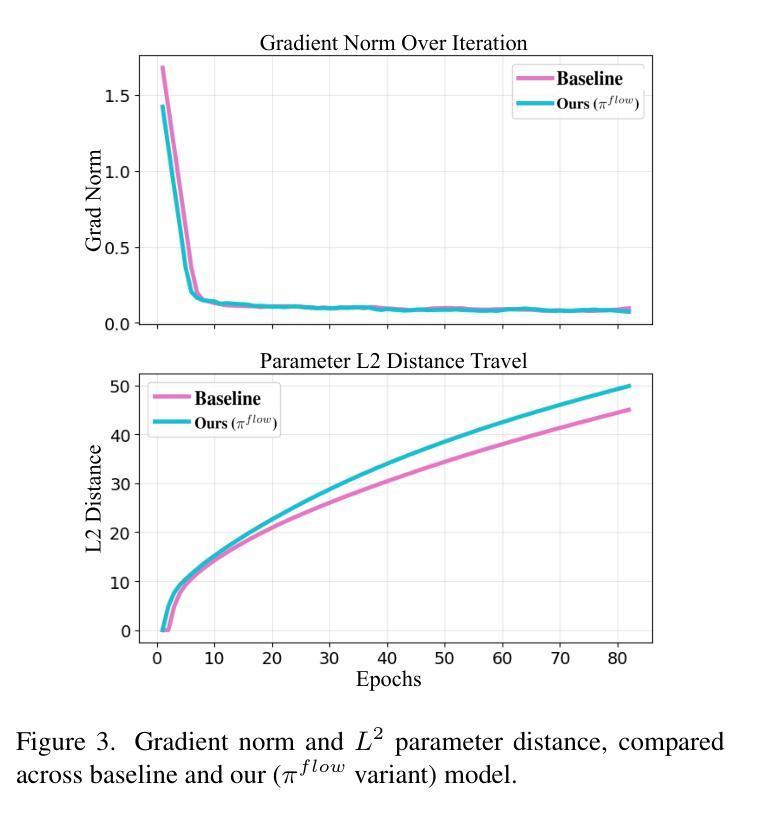
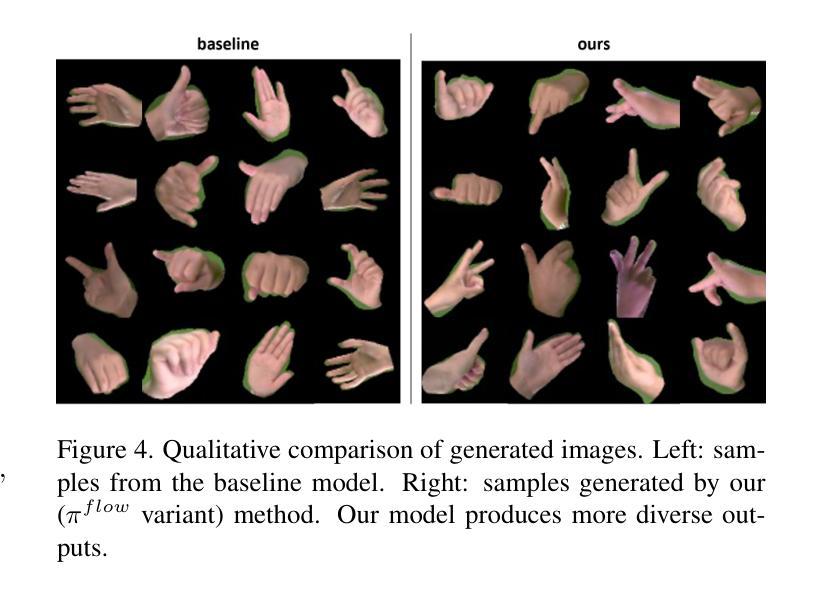
Image diffusion models are trained on independently sampled static images. While this is the bedrock task protocol in generative modeling, capturing the temporal world through the lens of static snapshots is information-deficient by design. This limitation leads to slower convergence, limited distributional coverage, and reduced generalization. In this work, we propose a simple and effective training strategy that leverages the temporal inductive bias present in continuous video frames to improve diffusion training. Notably, the proposed method requires no architectural modification and can be seamlessly integrated into standard diffusion training pipelines. We evaluate our method on the HandCo dataset, where hand-object interactions exhibit dense temporal coherence and subtle variations in finger articulation often result in semantically distinct motions. Empirically, our method accelerates convergence by over 2$\text{x}$ faster and achieves lower FID on both training and validation distributions. It also improves generative diversity by encouraging the model to capture meaningful temporal variations. We further provide an optimization analysis showing that our regularization reduces the gradient variance, which contributes to faster convergence.
图像扩散模型是在独立采样的静态图像上进行训练的。虽然这是生成模型中的基本任务协议,但通过静态快照捕捉现实世界的时间轴在设计上本身就存在信息缺失。这一局限性导致了收敛速度较慢、分布覆盖有限以及泛化能力降低。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单有效的训练策略,利用连续视频帧中存在的时间归纳偏见来改善扩散训练。值得注意的是,所提出的方法不需要对架构进行修改,并且可以无缝集成到标准扩散训练管道中。我们在HandCo数据集上评估了我们的方法,该数据集的手动交互表现出密集的时间连贯性,手指关节的细微变化通常会导致语义上截然不同的动作。从经验上看,我们的方法将收敛速度提高了两倍以上,并在训练和验证分布上实现了更低的FID。它还能通过鼓励模型捕捉有意义的时序变化来提高生成多样性。我们还进一步提供了优化分析,表明我们的正则化降低了梯度方差,从而有助于更快的收敛。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV25 Workshop
Summary
本文提出一种利用连续视频帧中的时间归纳偏见改进扩散训练的策略。该策略无需对架构进行修改,可无缝集成到标准扩散训练管道中。在HandCo数据集上评估表明,该方法加速了收敛速度,降低了FID值,提高了生成多样性,并鼓励模型捕捉有意义的时间变化。优化分析显示,正则化降低了梯度方差,有助于加快收敛。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在独立采样的静态图像上进行训练,但在捕捉时间世界时存在信息缺失的问题。
- 提出一种利用视频帧中的时间归纳偏见来改善扩散训练的策略。
- 该方法无需修改架构,可顺利融入标准扩散训练流程。
- 在HandCo数据集上测试显示,该方法加速了收敛速度超过2倍。
- 方法降低了FID值,在训练和验证分布上都表现出更好的性能。
- 通过鼓励捕捉有意义的时间变化,提高了生成多样性。
点此查看论文截图
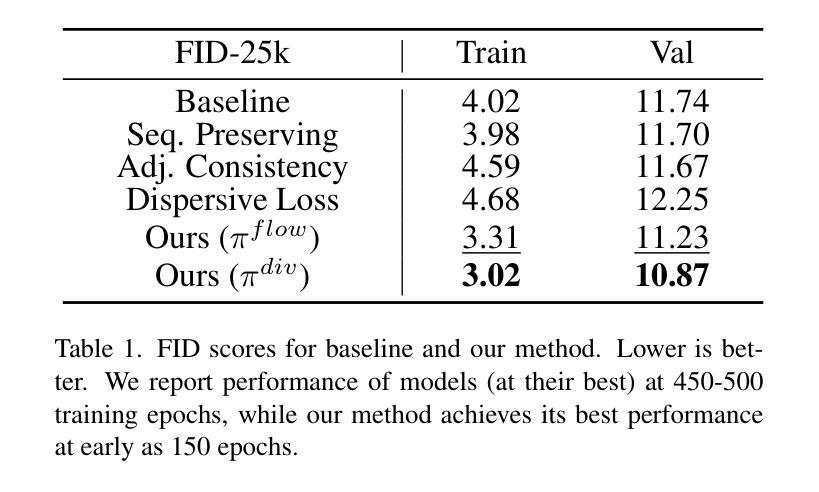
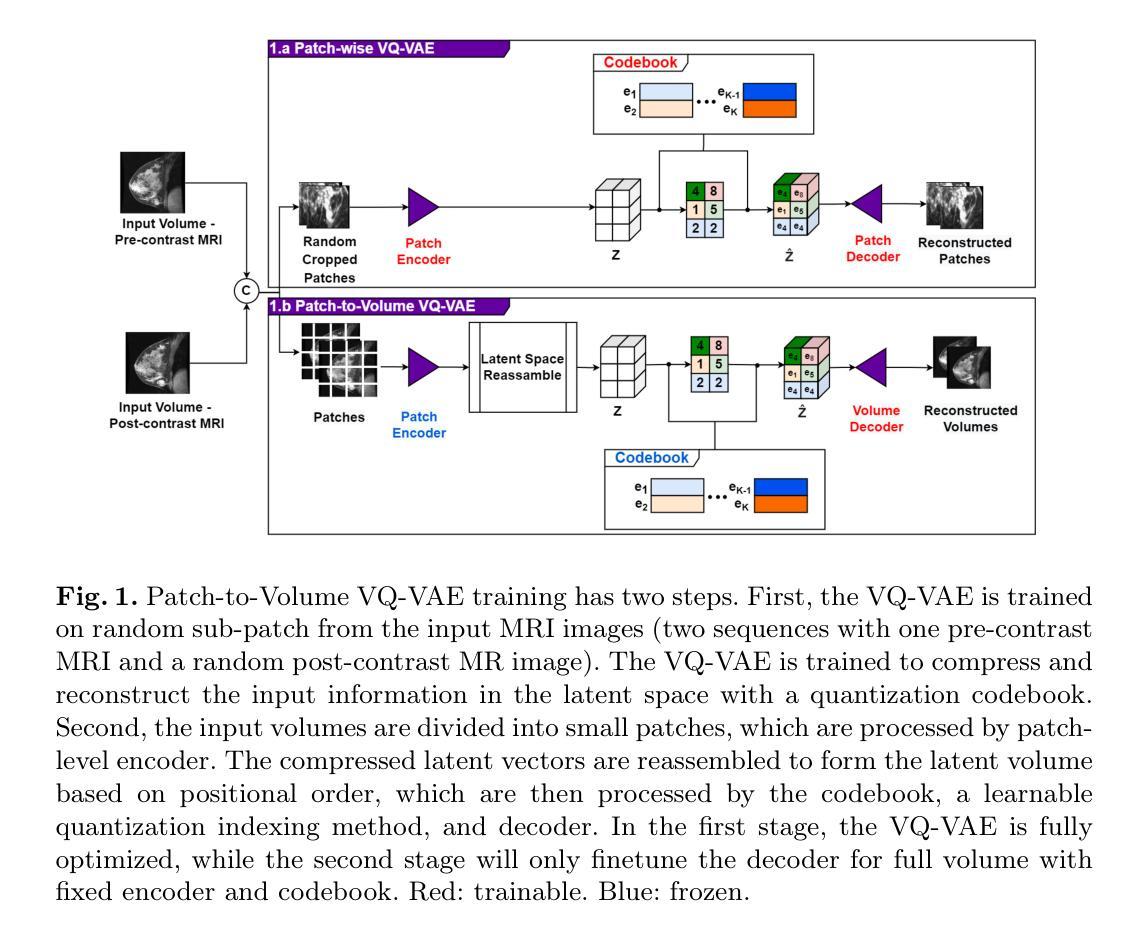
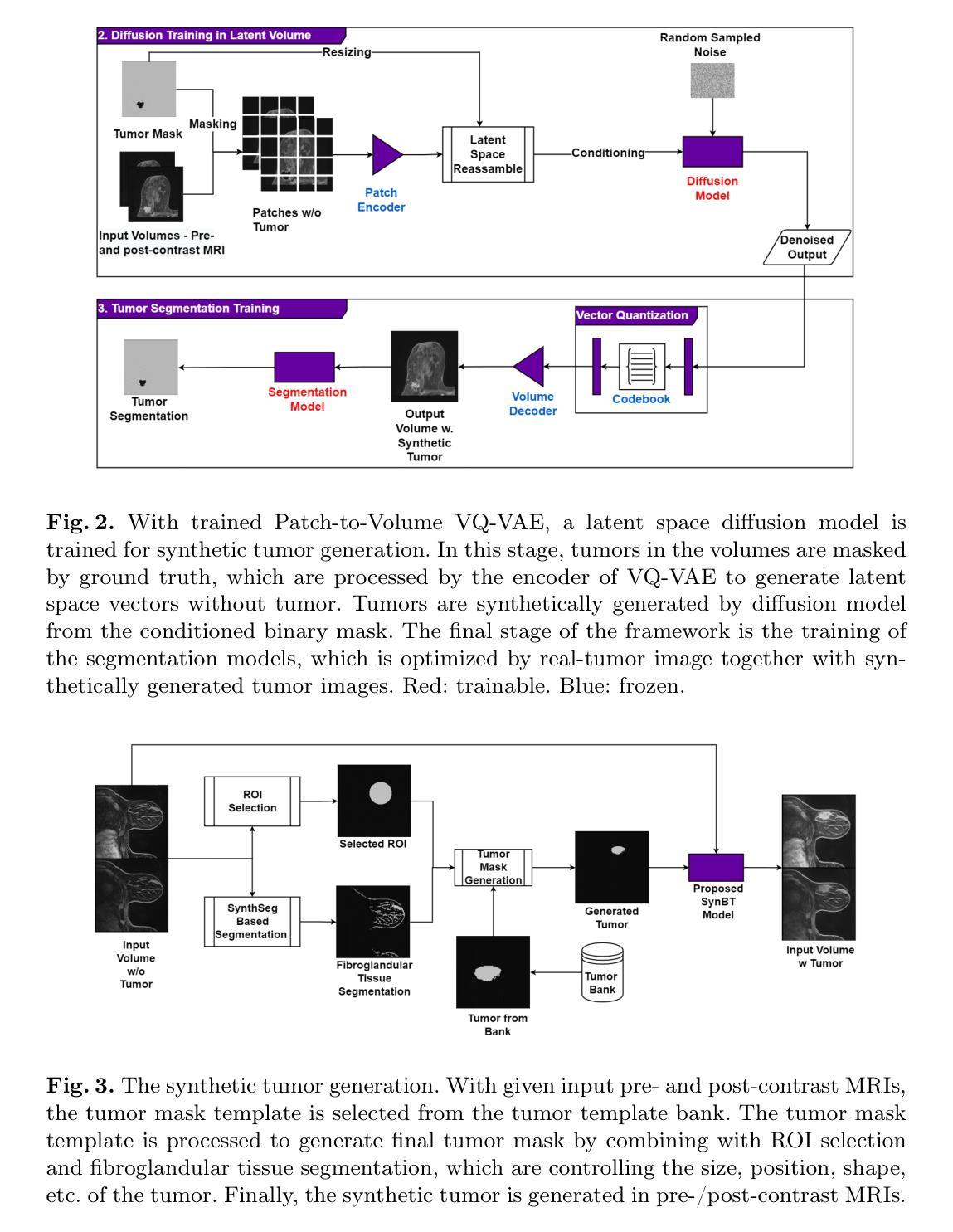
SynBT: High-quality Tumor Synthesis for Breast Tumor Segmentation by 3D Diffusion Model
Authors:Hongxu Yang, Edina Timko, Levente Lippenszky, Vanda Czipczer, Lehel Ferenczi
Synthetic tumors in medical images offer controllable characteristics that facilitate the training of machine learning models, leading to an improved segmentation performance. However, the existing methods of tumor synthesis yield suboptimal performances when tumor occupies a large spatial volume, such as breast tumor segmentation in MRI with a large field-of-view (FOV), while commonly used tumor generation methods are based on small patches. In this paper, we propose a 3D medical diffusion model, called SynBT, to generate high-quality breast tumor (BT) in contrast-enhanced MRI images. The proposed model consists of a patch-to-volume autoencoder, which is able to compress the high-resolution MRIs into compact latent space, while preserving the resolution of volumes with large FOV. Using the obtained latent space feature vector, a mask-conditioned diffusion model is used to synthesize breast tumors within selected regions of breast tissue, resulting in realistic tumor appearances. We evaluated the proposed method for a tumor segmentation task, which demonstrated the proposed high-quality tumor synthesis method can facilitate the common segmentation models with performance improvement of 2-3% Dice Score on a large public dataset, and therefore provides benefits for tumor segmentation in MRI images.
医学图像中的合成肿瘤具有可控特性,有助于训练机器学习模型,从而提高分割性能。然而,当肿瘤占据较大空间体积时,现有的肿瘤合成方法表现不佳,例如在具有大视野(FOV)的MRI中进行乳腺癌分割。而常用的肿瘤生成方法基于小斑块。本文提出了一种名为SynBT的3D医学扩散模型,用于在增强MRI图像中生成高质量乳腺癌。所提出的模型包括一个从斑块到体积的自编码器,能够将高分辨率MRI压缩成紧凑的潜在空间,同时保留大视野体积的分辨率。利用获得的潜在空间特征向量,使用带掩膜条件的扩散模型在选定区域的乳腺组织中合成乳腺癌,产生逼真的肿瘤外观。我们对所提出的方法进行了肿瘤分割任务评估,结果表明,高质量肿瘤合成方法能够促进公共数据集上Dice得分提高2-3%,因此,对MRI图像的肿瘤分割具有益处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI 2025 Deep-Breath Workshop. Supported by IHI SYNTHIA project
Summary
本文提出一种名为SynBT的3D医学扩散模型,用于生成高质量对比增强MRI图像中的乳腺癌肿瘤。该模型包括一个由补丁到体积的自编码器,能够压缩高分辨率MRI到紧凑的潜在空间,同时保留大视野的体积分辨率。利用获得的潜在空间特征向量,采用掩膜条件扩散模型在乳腺组织选定区域合成乳腺癌,产生逼真的肿瘤外观。在大型公共数据集上的肿瘤分割任务评估表明,该高质量肿瘤合成方法能提高常见的分割模型的性能,提高Dice得分率为2-3%,从而为MRI图像中的肿瘤分割提供了优势。
Key Takeaways
- 合成医学图像中的肿瘤具有可控特性,有助于训练机器学习模型,提高分割性能。
- 现有肿瘤合成方法在肿瘤占据较大空间体积时表现不佳,如在大视野MRI中的乳腺癌分割。
- 提出的SynBT模型是一个3D医学扩散模型,旨在生成高质量的对比增强MRI图像中的乳腺癌肿瘤。
- SynBT模型包括一个由补丁到体积的自编码器,能够压缩高分辨率MRI到紧凑的潜在空间,同时保留大视野的体积分辨率。
- 使用获得的潜在空间特征向量,SynBT模型可以在乳腺组织选定区域合成乳腺癌,产生逼真的肿瘤外观。
- 评估显示,SynBT模型有助于提高肿瘤分割任务的性能,特别是在大型公共数据集上。
点此查看论文截图

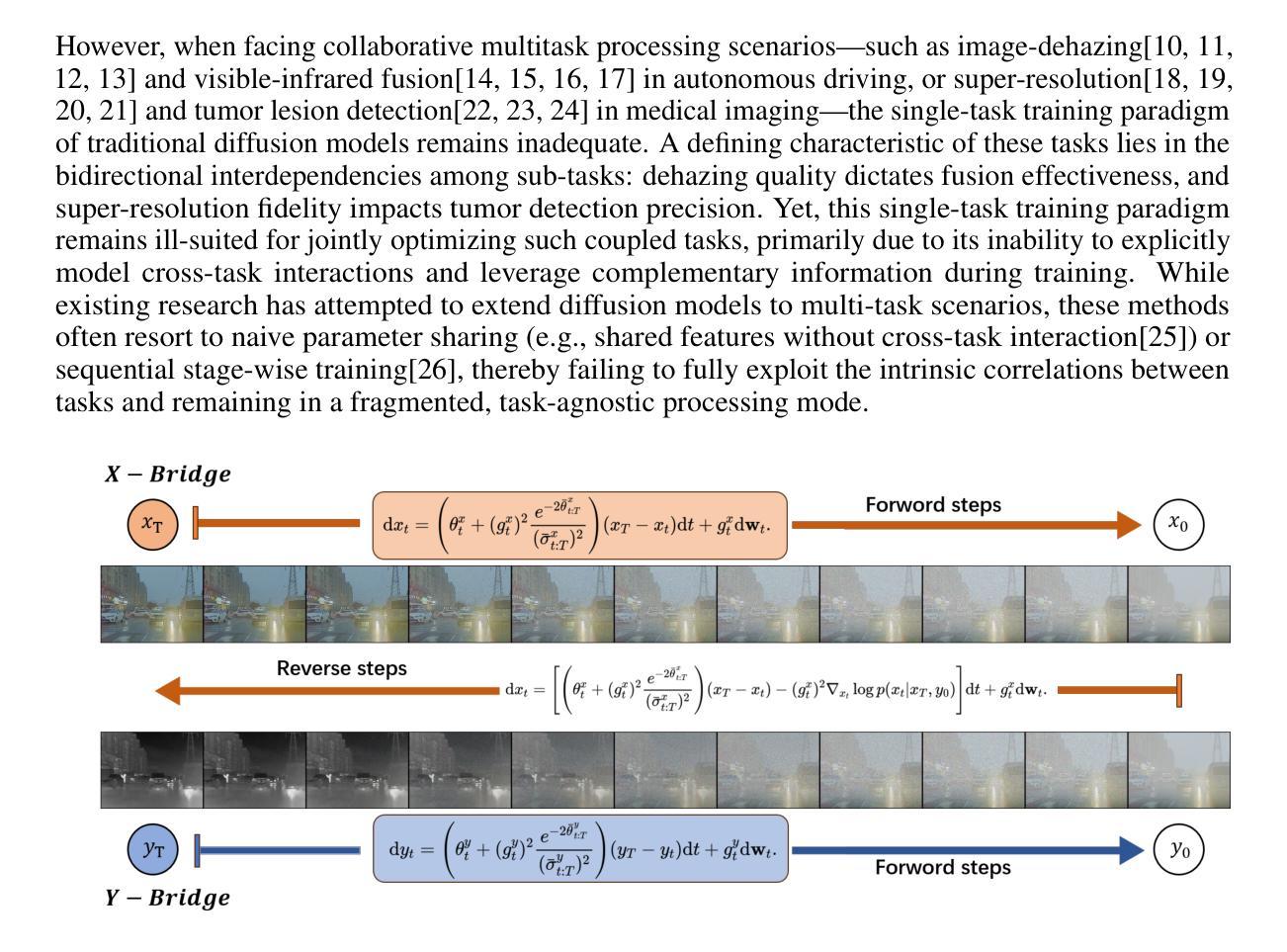
DCDB: Dynamic Conditional Dual Diffusion Bridge for Ill-posed Multi-Tasks
Authors:Chengjie Huang, Jiafeng Yan, Jing Li, Lu Bai
Conditional diffusion models have made impressive progress in the field of image processing, but the characteristics of constructing data distribution pathways make it difficult to exploit the intrinsic correlation between tasks in multi-task scenarios, which is even worse in ill-posed tasks with a lack of training data. In addition, traditional static condition control makes it difficult for networks to learn in multi-task scenarios with its dynamically evolving characteristics. To address these challenges, we propose a dynamic conditional double diffusion bridge training paradigm to build a general framework for ill-posed multi-tasks. Firstly, this paradigm decouples the diffusion and condition generation processes, avoiding the dependence of the diffusion model on supervised data in ill-posed tasks. Secondly, generated by the same noise schedule, dynamic conditions are used to gradually adjust their statistical characteristics, naturally embed time-related information, and reduce the difficulty of network learning. We analyze the learning objectives of the network under different conditional forms in the single-step denoising process and compare the changes in its attention weights in the network, demonstrating the superiority of our dynamic conditions. Taking dehazing and visible-infrared fusion as typical ill-posed multi-task scenarios, we achieve the best performance in multiple indicators on public datasets. The code has been publicly released at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCDB-D3C2.
在图像处理领域,条件扩散模型已经取得了令人瞩目的进展。然而,构建数据分布途径的特征使得在多任务场景中利用任务之间的内在关联变得困难,在缺乏训练数据的病态任务中这种情况更为严重。另外,传统的静态条件控制使得网络在具有动态演变特征的多任务场景中学习变得困难。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种动态条件双重扩散桥训练范式,以建立一个适用于病态多任务的通用框架。首先,该范式解耦了扩散和条件生成过程,避免了在病态任务中扩散模型对监督数据的依赖。其次,通过相同的噪声调度生成动态条件,逐步调整其统计特征,自然嵌入与时间相关的信息,降低网络学习的难度。我们分析了单步去噪过程中不同条件下网络的学习目标,并比较了网络中注意力权重的变化,证明了我们的动态条件的优越性。以去雾和可见光-红外融合作为典型的病态多任务场景,我们在公共数据集上的多个指标上实现了最佳性能。代码已公开发布在:[https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DCDB-D3C2。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages,6 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个动态条件双重扩散桥训练范式,构建了一个针对复杂多任务问题的通用框架。通过解耦扩散和条件生成过程,解决了缺乏监督数据的问题,并采用动态条件逐步调整统计特征,减少网络学习难度。在公开数据集上实现了去雾和可见光红外融合等典型复杂多任务场景的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 动态条件双重扩散桥训练范式解决了在图像处理的复杂多任务场景中,传统静态条件控制难以应对的问题。
- 解耦扩散和条件生成过程使得模型在缺乏监督数据的任务中表现更好。
- 动态条件能够根据噪声时间表进行调整,自然嵌入时间相关信息,降低网络学习难度。
- 该训练范式在公开数据集上实现了去雾和可见光红外融合等任务的最佳性能。
- 该方法的网络学习目标在不同条件下进行了分析,证明了其优越性。
- 注意力权重在网络中的变化表明动态条件有助于提高模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

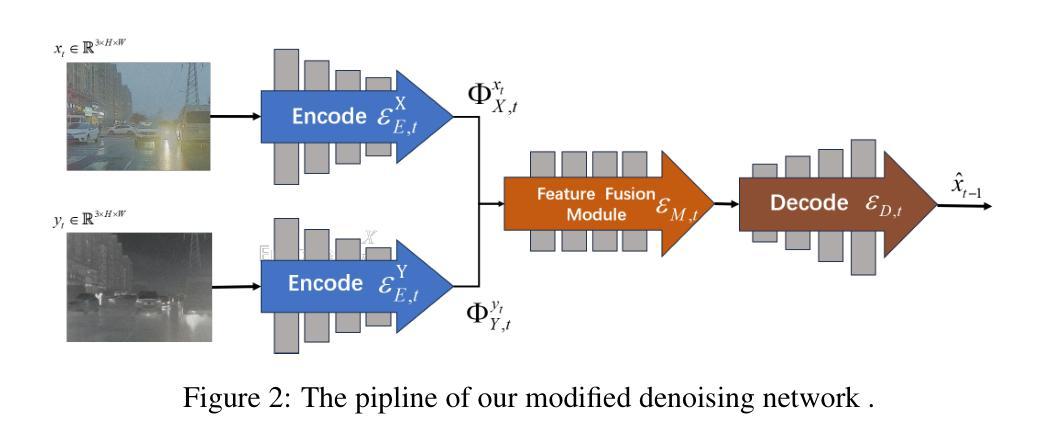
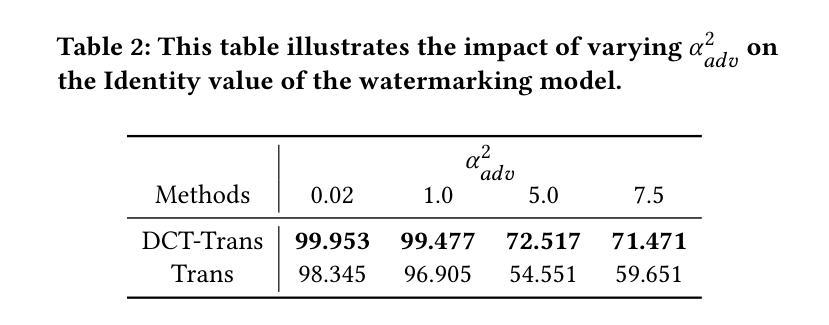
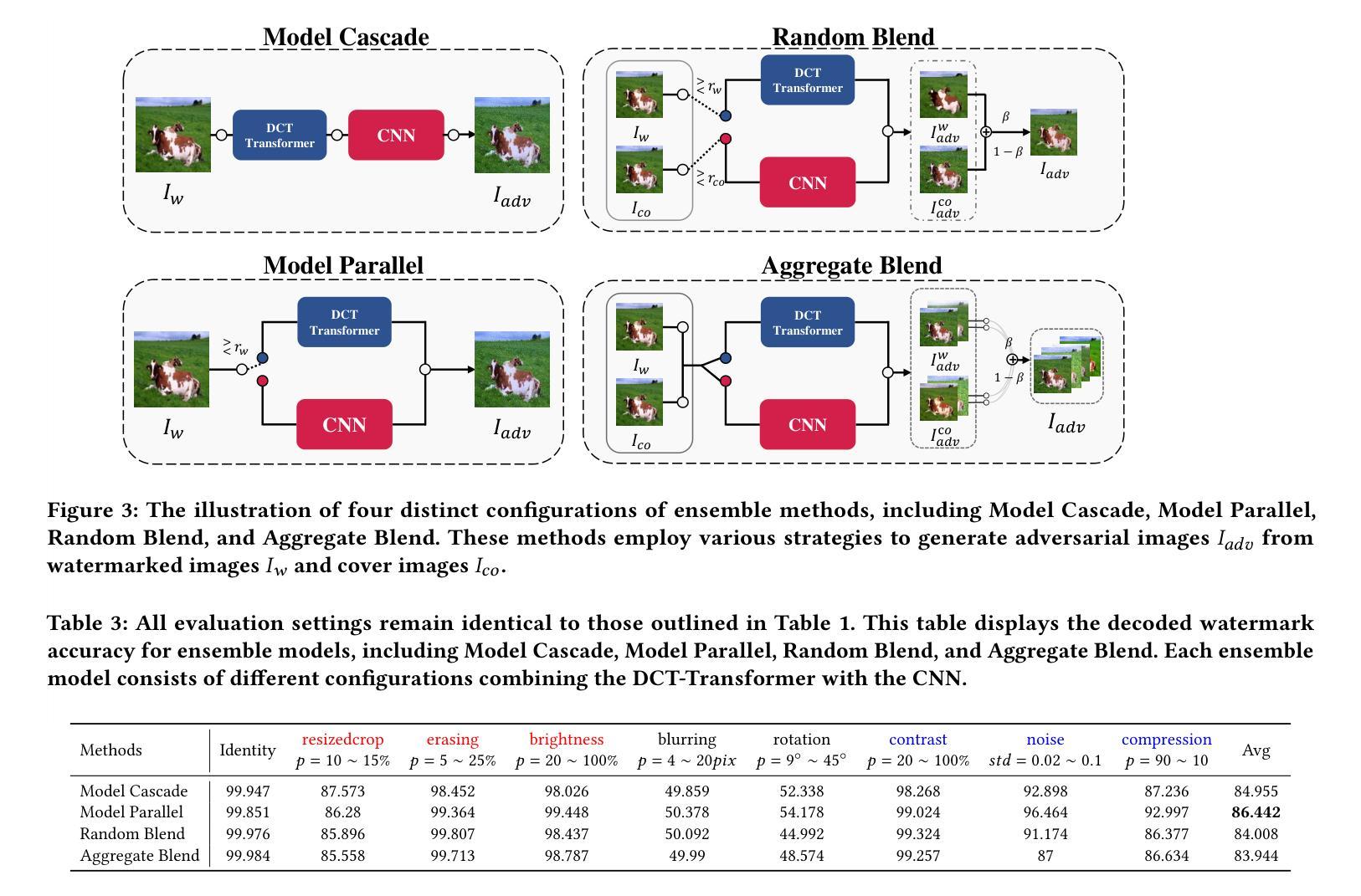
Enhancing Robustness in Post-Processing Watermarking: An Ensemble Attack Network Using CNNs and Transformers
Authors:Tzuhsuan Huang, Cheng Yu Yeo, Tsai-Ling Huang, Hong-Han Shuai, Wen-Huang Cheng, Jun-Cheng Chen
Recent studies on deep watermarking have predominantly focused on in-processing watermarking, which integrates the watermarking process into image generation. However, post-processing watermarking, which embeds watermarks after image generation, offers more flexibility. It can be applied to outputs from any generative model (e.g. GANs, diffusion models) without needing access to the model’s internal structure. It also allows users to embed unique watermarks into individual images. Therefore, this study focuses on post-processing watermarking and enhances its robustness by incorporating an ensemble attack network during training. We construct various versions of attack networks using CNN and Transformer in both spatial and frequency domains to investigate how each combination influences the robustness of the watermarking model. Our results demonstrate that combining a CNN-based attack network in the spatial domain with a Transformer-based attack network in the frequency domain yields the highest robustness in watermarking models. Extensive evaluation on the WAVES benchmark, using average bit accuracy as the metric, demonstrates that our ensemble attack network significantly enhances the robustness of baseline watermarking methods under various stress tests. In particular, for the Regeneration Attack defined in WAVES, our method improves StegaStamp by 18.743%. The code is released at:https://github.com/aiiu-lab/DeepRobustWatermark.
近期关于深度水印的研究主要集中于处理过程中的水印技术,这种技术将水印过程集成到图像生成中。然而,后处理水印技术能够在图像生成后嵌入水印,因此具有更大的灵活性。它可以应用于任何生成模型的输出(例如GANs、扩散模型),而无需访问模型的内部结构。它还允许用户将独特的水印嵌入到单独的图像中。因此,本研究专注于后处理水印技术,并通过在训练中结合集成攻击网络来提高其稳健性。我们利用CNN和Transformer在空间和频率领域构建了各种版本的攻击网络,以研究每种组合如何影响水印模型的稳健性。我们的结果表明,在空域使用CNN结合攻击网络,在频域使用Transformer结合攻击网络,能够在水印模型中实现最高的稳健性。我们在WAVES基准测试集上进行了广泛评估,以平均位准确率为指标,证明了我们的集成攻击网络在各种压力测试下显著提高了基线水印方法的稳健性。特别是在WAVES定义的再生攻击中,我们的方法提高了StegaStamp的准确率高达18.743%。代码已发布在:https://github.com/aiiu-lab/DeepRobustWatermark。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
本文研究了深度水印技术中的后处理水印技术,该技术能够在图像生成后嵌入水印,具有更大的灵活性。研究通过集成组合攻击网络提高了其稳健性,并探讨了不同攻击网络结构(包括CNN和Transformer)对水印模型稳健性的影响。实验结果表明,结合空间域CNN攻击网络与频率域Transformer攻击网络可获得最佳稳健性。在WAVES基准测试上的评估显示,该方法显著提高了基线水印方法的稳健性,特别是在WAVES定义的再生攻击中,提高了StegaStamp方法达18.743%。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注后处理水印技术,该技术能够在图像生成后嵌入水印,展现更大的灵活性。
- 提出集成组合攻击网络以提高水印模型的稳健性。
- 通过构建不同攻击网络结构(CNN和Transformer),探究其对水印模型稳健性的影响。
- 结合空间域CNN攻击网络与频率域Transformer攻击网络获得最佳稳健性结果。
- 在WAVES基准测试上,该方法显著提高基线水印方法的稳健性。
- 对于再生攻击,该方法改进了StegaStamp方法达18.743%。
点此查看论文截图

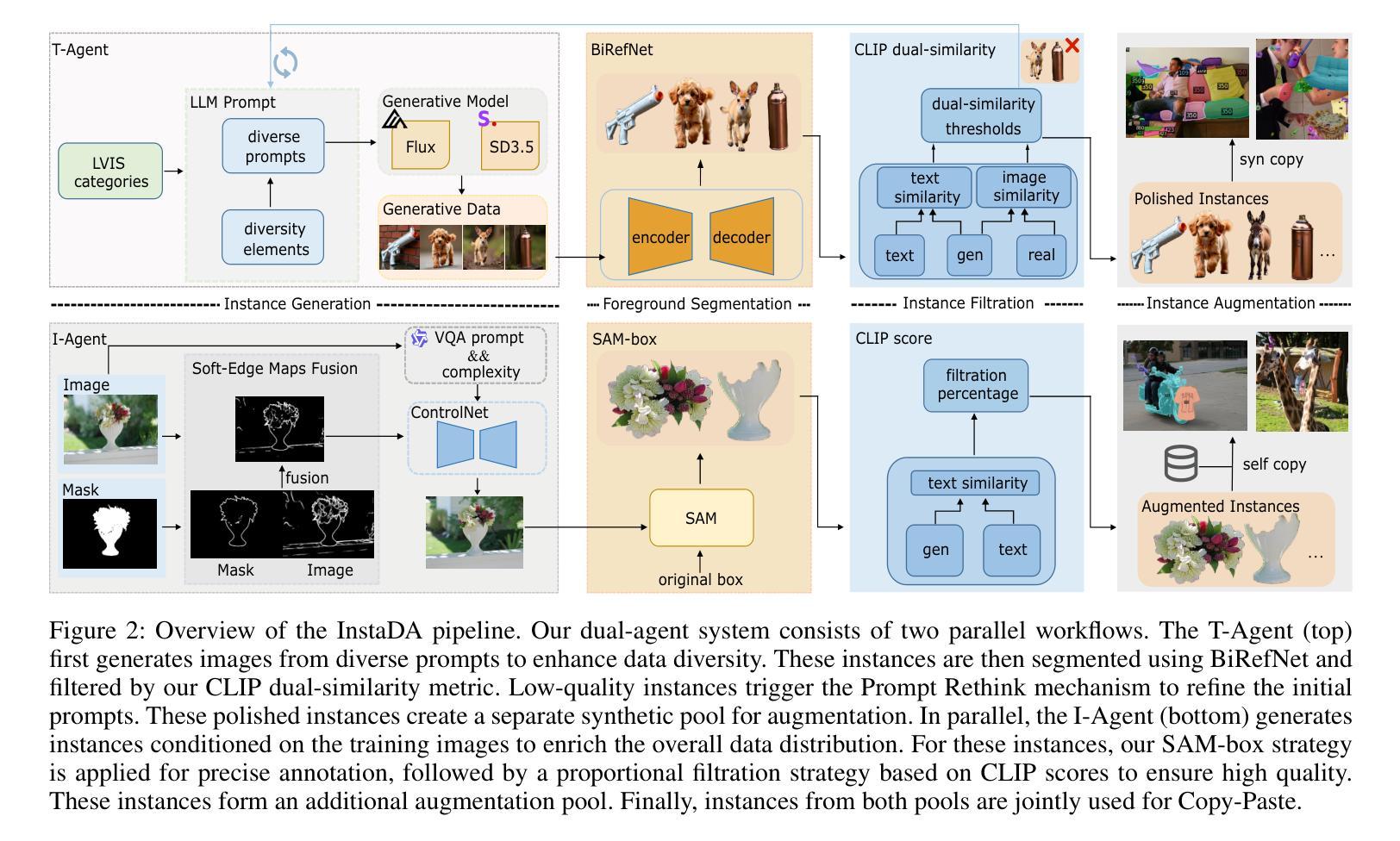
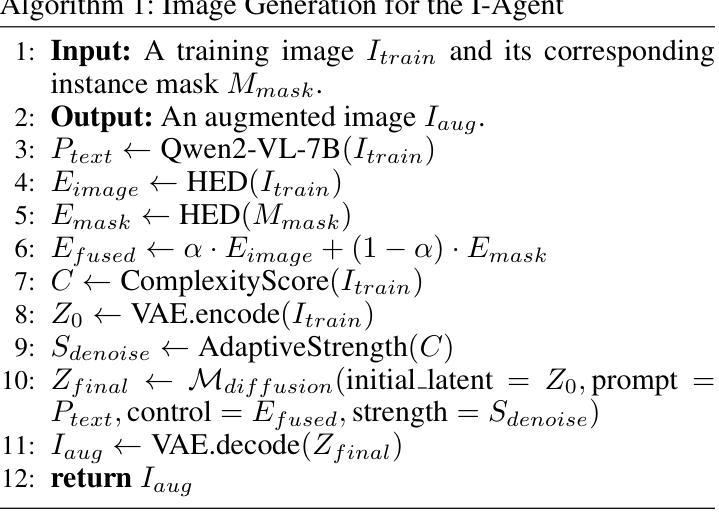
InstaDA: Augmenting Instance Segmentation Data with Dual-Agent System
Authors:Xianbao Hou, Yonghao He, Zeyd Boukhers, John See, Hu Su, Wei Sui, Cong Yang
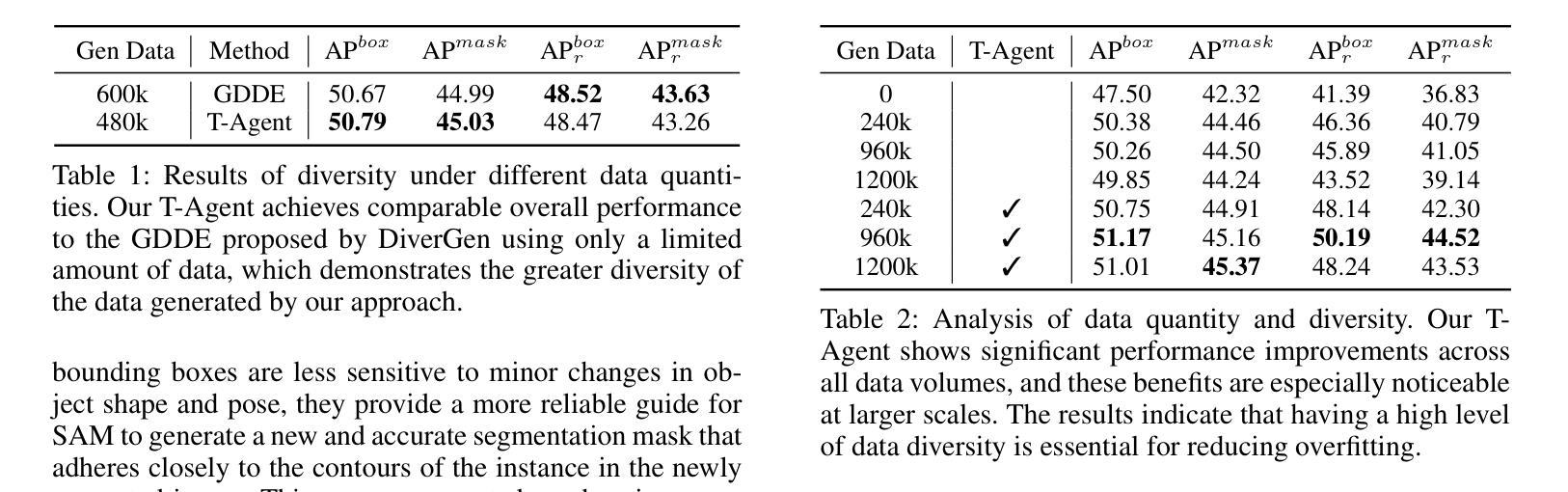
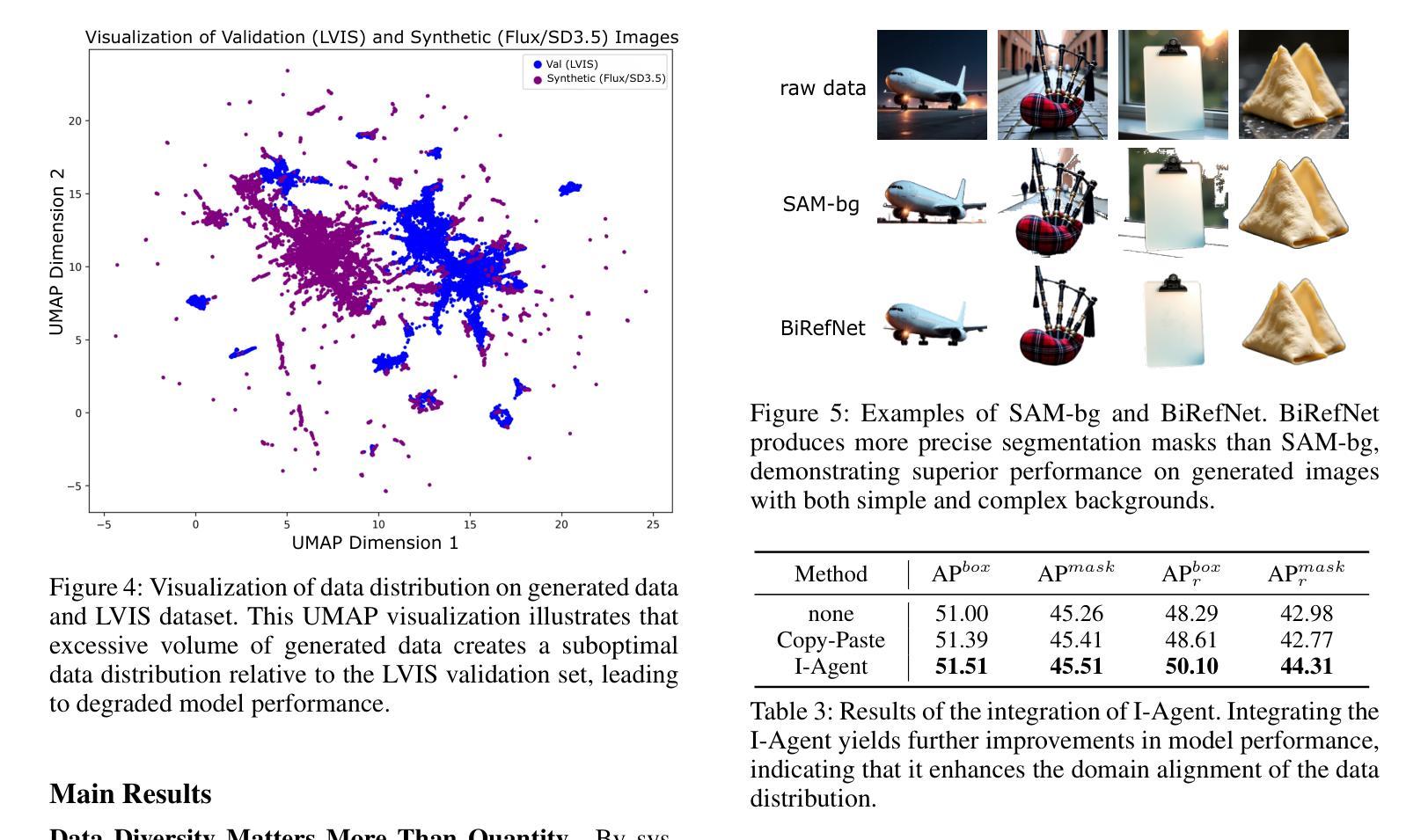
Acquiring high-quality instance segmentation data is challenging due to the labor-intensive nature of the annotation process and significant class imbalances within datasets. Recent studies have utilized the integration of Copy-Paste and diffusion models to create more diverse datasets. However, these studies often lack deep collaboration between large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models, and underutilize the rich information within the existing training data. To address these limitations, we propose InstaDA, a novel, training-free Dual-Agent system designed to augment instance segmentation datasets. First, we introduce a Text-Agent (T-Agent) that enhances data diversity through collaboration between LLMs and diffusion models. This agent features a novel Prompt Rethink mechanism, which iteratively refines prompts based on the generated images. This process not only fosters collaboration but also increases image utilization and optimizes the prompts themselves. Additionally, we present an Image-Agent (I-Agent) aimed at enriching the overall data distribution. This agent augments the training set by generating new instances conditioned on the training images. To ensure practicality and efficiency, both agents operate as independent and automated workflows, enhancing usability. Experiments conducted on the LVIS 1.0 validation set indicate that InstaDA achieves significant improvements, with an increase of +4.0 in box average precision (AP) and +3.3 in mask AP compared to the baseline. Furthermore, it outperforms the leading model, DiverGen, by +0.3 in box AP and +0.1 in mask AP, with a notable +0.7 gain in box AP on common categories and mask AP gains of +0.2 on common categories and +0.5 on frequent categories.
获取高质量的实例分割数据是一个挑战,因为标注过程劳动密集,且数据集中存在显著的类别不平衡问题。最近的研究通过结合Copy-Paste和扩散模型来创建更多样化的数据集。然而,这些研究往往缺乏大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型之间的深度协作,并且未能充分利用现有训练数据中的丰富信息。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了InstaDA,这是一种全新的、无需训练的双代理系统,旨在增强实例分割数据集。首先,我们引入了一个文本代理(T-Agent),它通过LLM和扩散模型之间的协作来提高数据多样性。该代理具有新颖的Prompt Rethink机制,该机制会根据生成的图像迭代优化提示。这个过程不仅促进了协作,还提高了图像利用率并优化了提示本身。此外,我们还推出了旨在丰富整体数据分布的图像代理(I-Agent)。该代理通过基于训练图像生成新实例来丰富训练集。为确保实用性和效率,两个代理都作为独立且自动化的工作流程运行,增强了易用性。在LVIS 1.0验证集上进行的实验表明,InstaDA取得了显著改进,相对于基线提高了+4.0的框平均精度(AP)和+3.3的掩模AP。此外,它在领先模型DiverGen的基础上提高了+0.3的框AP和+0.1的掩模AP,在常见类别上框AP提高了+0.7,掩模AP在常见类别上提高了+0.2,在频繁类别上提高了+0.5。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对高质量实例分割数据获取的挑战,如标注过程劳动强度高和数据集类别不平衡等问题,最近研究开始结合Copy-Paste和扩散模型来创建更多样化的数据集。然而,这些研究在大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型之间的深度合作方面存在不足,且未能充分利用现有训练数据的丰富信息。为解决这些局限,我们提出InstaDA,一种无需训练的新型双代理系统,旨在增强实例分割数据集。其中,我们引入Text-Agent(T-Agent)通过LLMs和扩散模型的协作提高数据多样性。该代理具有新颖的Prompt Rethink机制,可根据生成的图像迭代优化提示。这不仅促进了协作,还提高了图像利用率并优化了提示本身。此外,我们还推出了Image-Agent(I-Agent),旨在丰富整体数据分布。该代理通过基于训练图像生成新实例来丰富训练集。为确保实用性和效率,两个代理作为独立自动化工作流程运行,增强了易用性。在LVIS 1.0验证集上进行的实验表明,InstaDA在盒平均精度(AP)和掩膜AP方面取得了显著的提升,较基准方法分别提高了+4.0和+3.3的AP。并且与领先的模型DiverGen相比,在盒AP和掩膜AP上分别提高了+0.3和+0.1,在常见类别和频繁类别的盒AP和掩膜AP上分别取得了显著的增益。
关键见解
- 高质量实例分割数据获取具有挑战性,因标注过程劳动强度高和数据集类别不平衡等问题。
- 现有研究开始结合Copy-Paste和扩散模型创建多样化数据集,但在大型语言模型和扩散模型的深度合作方面存在不足。
- 提出InstaDA系统,包括Text-Agent和Image-Agent,分别通过文本和图像增强数据多样性和整体数据分布。
- Text-Agent中的Prompt Rethink机制可迭代优化提示,促进协作并提高图像利用率。
- Image-Agent旨在生成基于训练图像的新实例,以丰富数据集的多样性。
- 两个代理作为独立自动化工作流程运行,提高了实用性和效率。
点此查看论文截图


Enhancing Zero-Shot Pedestrian Attribute Recognition with Synthetic Data Generation: A Comparative Study with Image-To-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Pablo Ayuso-Albizu, Juan C. SanMiguel, Pablo Carballeira
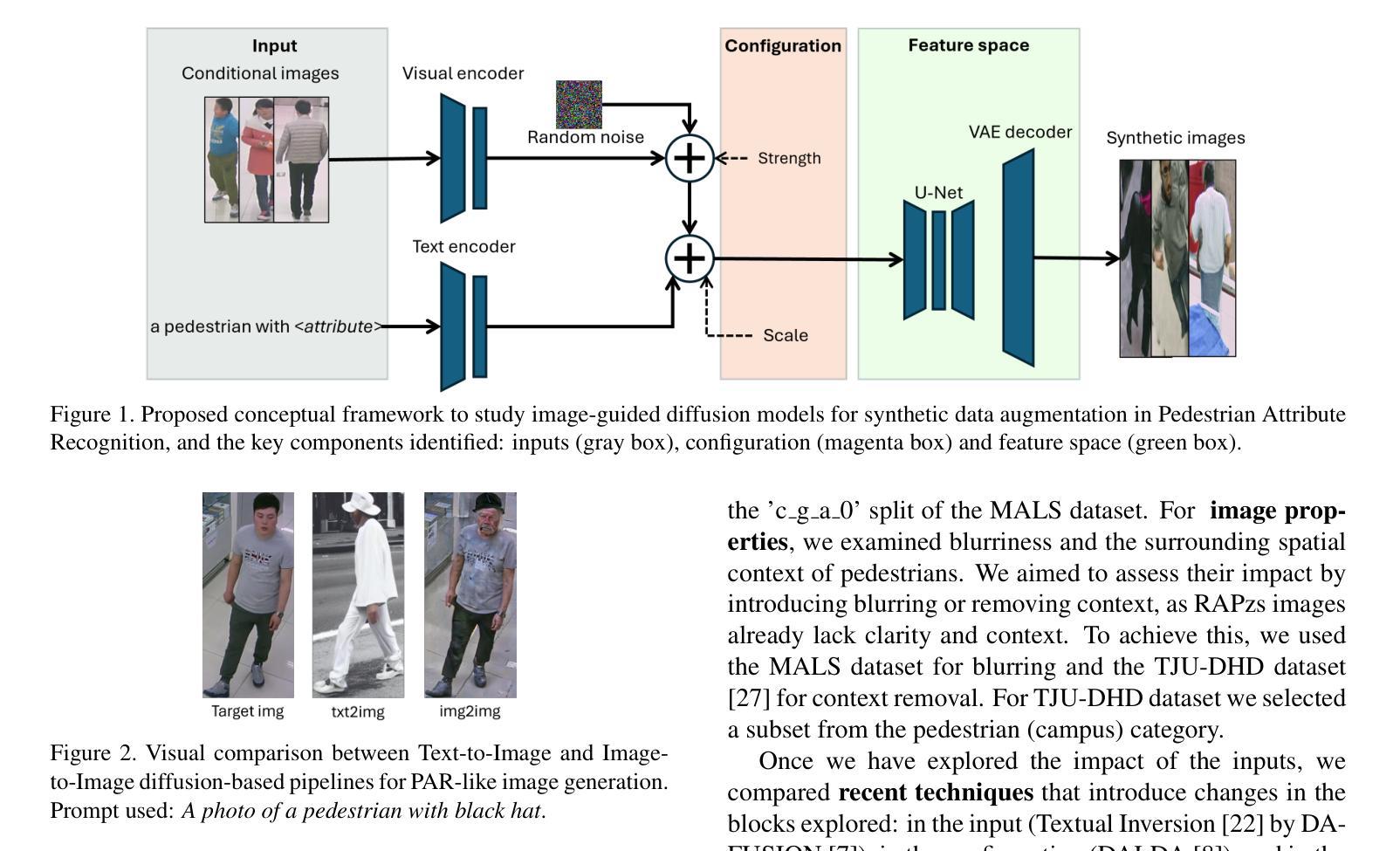
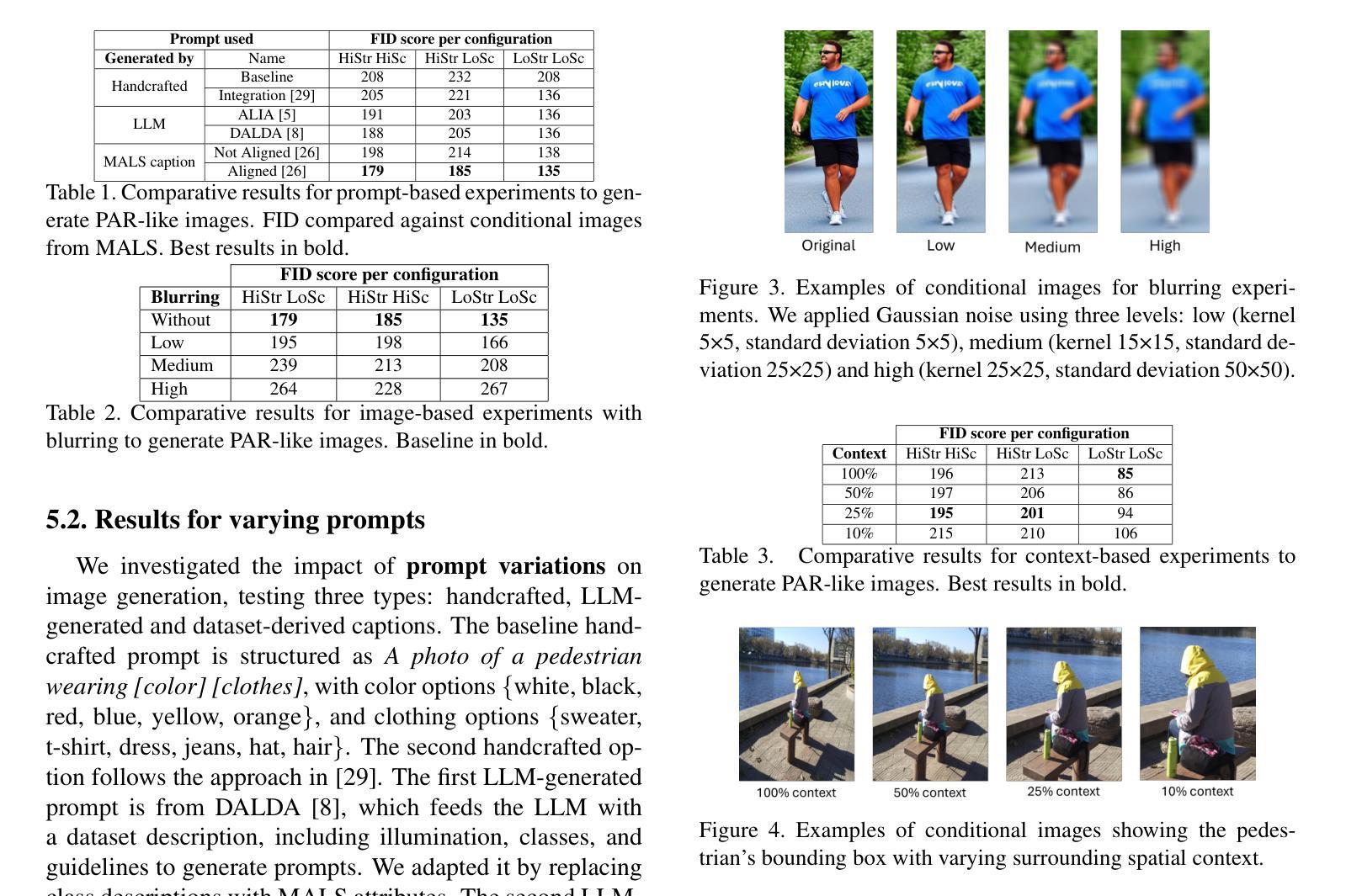
Pedestrian Attribute Recognition (PAR) involves identifying various human attributes from images with applications in intelligent monitoring systems. The scarcity of large-scale annotated datasets hinders the generalization of PAR models, specially in complex scenarios involving occlusions, varying poses, and diverse environments. Recent advances in diffusion models have shown promise for generating diverse and realistic synthetic images, allowing to expand the size and variability of training data. However, the potential of diffusion-based data expansion for generating PAR-like images remains underexplored. Such expansion may enhance the robustness and adaptability of PAR models in real-world scenarios. This paper investigates the effectiveness of diffusion models in generating synthetic pedestrian images tailored to PAR tasks. We identify key parameters of img2img diffusion-based data expansion; including text prompts, image properties, and the latest enhancements in diffusion-based data augmentation, and examine their impact on the quality of generated images for PAR. Furthermore, we employ the best-performing expansion approach to generate synthetic images for training PAR models, by enriching the zero-shot datasets. Experimental results show that prompt alignment and image properties are critical factors in image generation, with optimal selection leading to a 4.5% improvement in PAR recognition performance.
行人属性识别(PAR)涉及从图像中识别各种人类属性,在智能监控系统中有广泛应用。大规模标注数据集的稀缺阻碍了PAR模型在涉及遮挡、不同姿势和多样环境等复杂场景中的泛化能力。扩散模型的最新进展在生成多样且现实的合成图像方面显示出希望,从而可以扩大训练数据的大小和变化。然而,基于扩散的数据扩展在生成类似于PAR图像方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。这种扩展可能提高PAR模型在现实场景中的稳健性和适应性。本文旨在研究扩散模型在生成针对PAR任务的合成行人图像方面的有效性。我们确定了基于img2img扩散的数据扩展的关键参数,包括文本提示、图像属性和基于扩散的数据增强的最新改进,并研究了它们对生成的用于PAR的图像质量的影响。此外,我们通过丰富零样本数据集,采用表现最佳的扩展方法生成合成图像来训练PAR模型。实验结果表明,提示对齐和图像属性是图像生成的关键因素,最优选择导致PAR识别性能提高了4.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted at AVSS 2025 conference
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型在生成针对行人属性识别(PAR)任务的合成行人图像中的有效性。研究通过利用扩散模型进行数据扩展,增强PAR模型的鲁棒性和适应现实场景的能力。实验结果表明,提示对齐和图像属性是图像生成的关键因素,最优选择可提高PAR识别性能4.5%。
Key Takeaways
- 行人属性识别(PAR)在智能监控系统中有广泛应用,但缺乏大规模标注数据集限制了其模型的通用性。
- 扩散模型在生成多样且真实的合成图像上显示出潜力,可用于扩展PAR的训练数据集。
- 扩散模型在生成合成行人图像方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。
- 本文探讨了img2img扩散模型的关键参数,包括文本提示、图像属性以及最新的扩散模型增强技术。
- 实验发现,提示对齐和图像属性对生成图像的质量有重要影响。
- 最优的扩散模型方法可提高PAR识别性能达4.5%。
点此查看论文截图

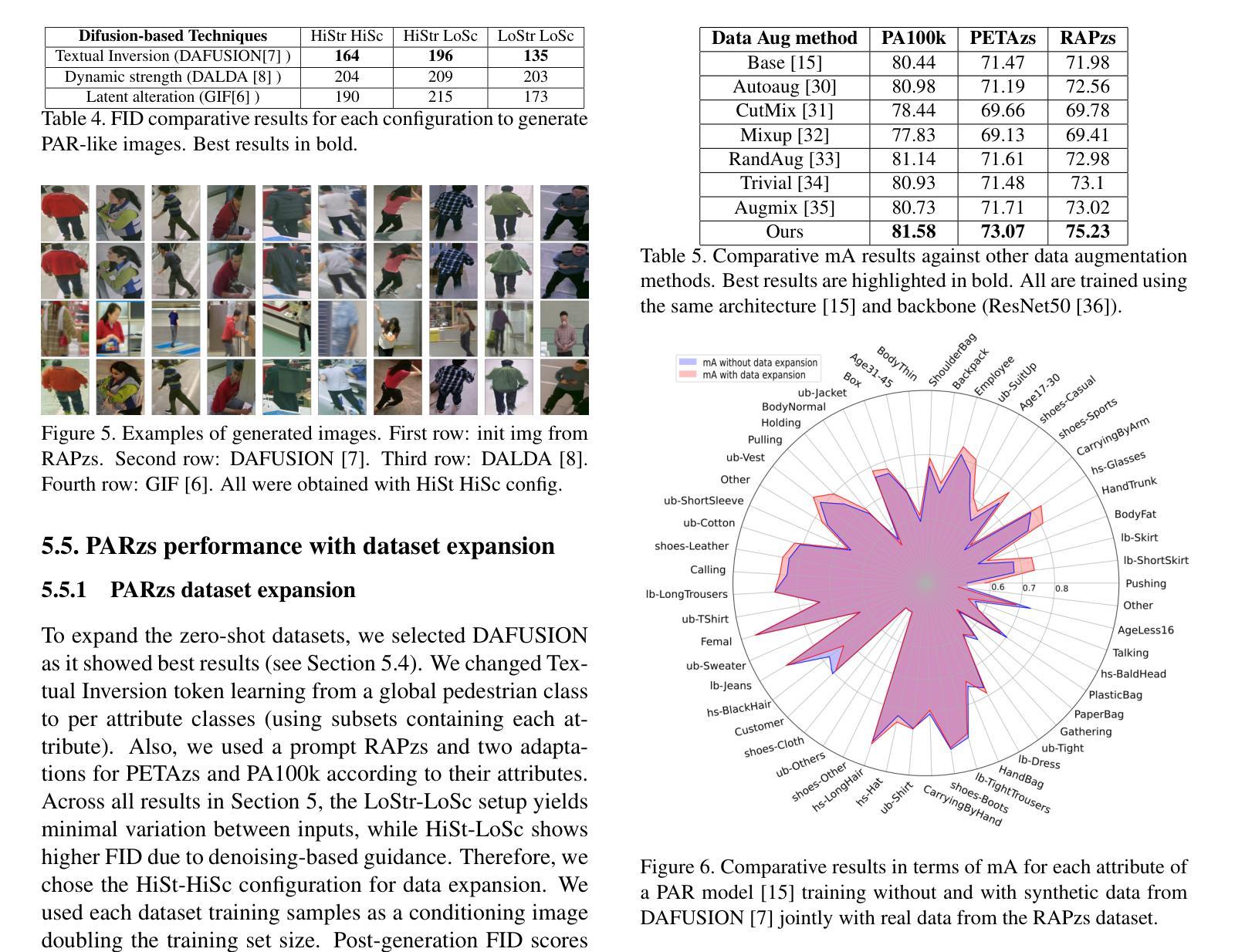
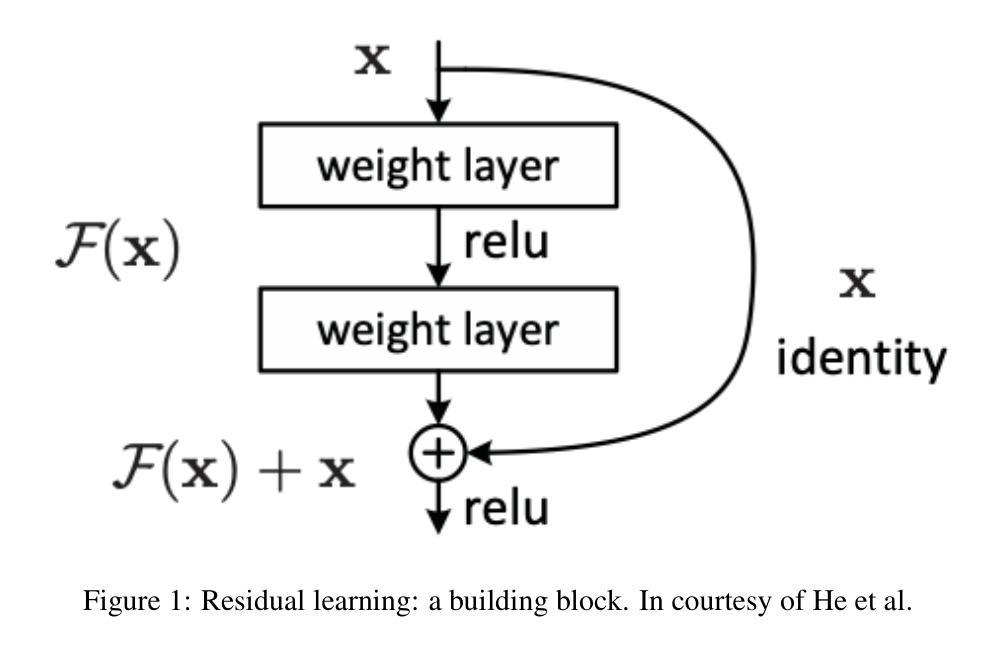
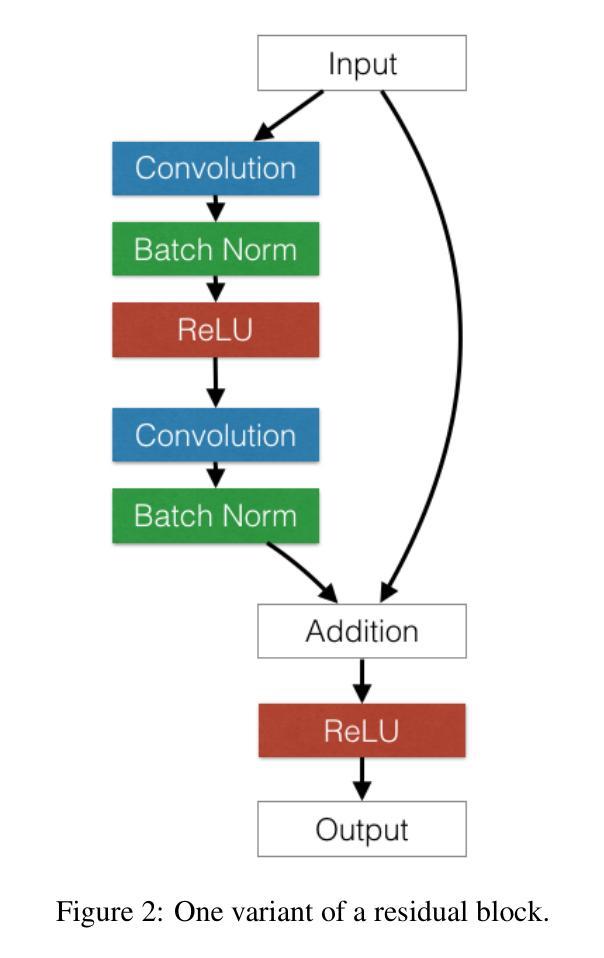
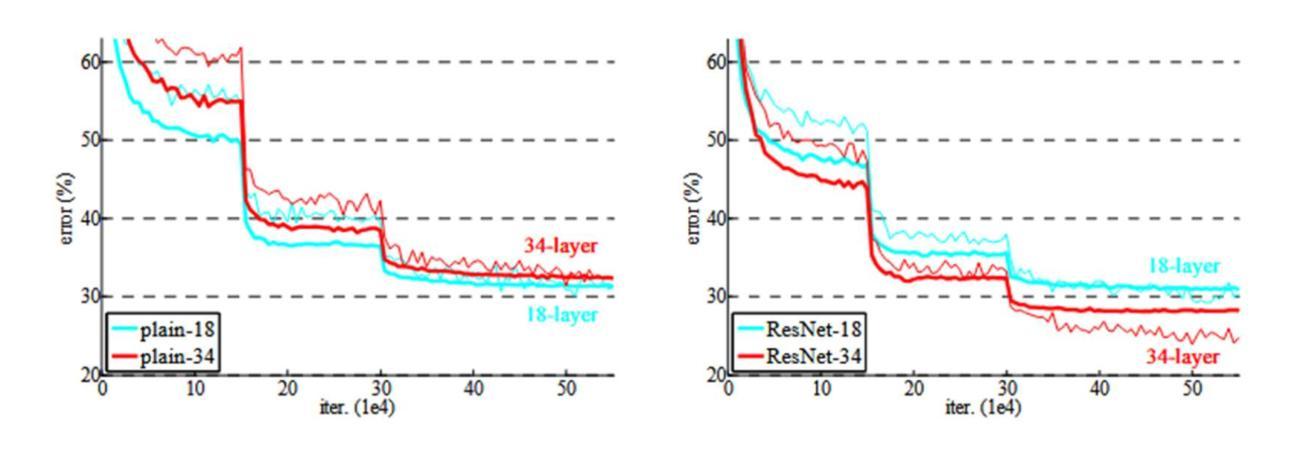
Foundations and Models in Modern Computer Vision: Key Building Blocks in Landmark Architectures
Authors:Radu-Andrei Bourceanu, Neil De La Fuente, Jan Grimm, Andrei Jardan, Andriy Manucharyan, Cornelius Weiss, Daniel Cremers, Roman Pflugfelder
This report analyzes the evolution of key design patterns in computer vision by examining six influential papers. The analysis begins with foundational architectures for image recognition. We review ResNet, which introduced residual connections to overcome the vanishing gradient problem and enable effective training of significantly deeper convolutional networks. Subsequently, we examine the Vision Transformer (ViT), which established a new paradigm by applying the Transformer architecture to sequences of image patches, demonstrating the efficacy of attention-based models for large-scale image recognition. Building on these visual representation backbones, we investigate generative models. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are analyzed for their novel adversarial training process, which challenges a generator against a discriminator to learn complex data distributions. Then, Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) are covered, which improve upon prior generative methods by performing a sequential denoising process in a perceptually compressed latent space. LDMs achieve high-fidelity synthesis with greater computational efficiency, representing the current state-of-the-art for image generation. Finally, we explore self-supervised learning techniques that reduce dependency on labeled data. DINO is a self-distillation framework in which a student network learns to match the output of a momentum-updated teacher, yielding features with strong k-NN classification performance. We conclude with Masked Autoencoders (MAE), which utilize an asymmetric encoder-decoder design to reconstruct heavily masked inputs, providing a highly scalable and effective method for pre-training large-scale vision models.
本报告通过分析六篇有影响力的论文,探讨了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变。分析从图像识别的基本架构开始。我们回顾了ResNet,它引入了残差连接,克服了梯度消失问题,实现了对深度卷积网络的有效训练。之后,我们研究了将Transformer架构应用于图像补丁序列的Vision Transformer(ViT),这开创了新的范式,证明了基于注意力的模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。基于这些视觉表示骨干,我们研究了生成模型。分析了生成对抗网络(GANs)的新型对抗训练过程,该过程通过生成器与鉴别器的对抗来学习复杂的数据分布。然后介绍了潜在扩散模型(LDMs),通过在感知压缩的潜在空间中进行连续的去噪过程,改进了先前的生成方法。LDMs实现了高保真度的合成,具有更高的计算效率,代表了当前图像生成的最新技术。最后,我们探索了减少对标定数据依赖性的自监督学习技术。DINO是一种自蒸馏框架,学生网络学习匹配动量更新的教师的输出,产生具有强大k-NN分类性能的特征。最后以Masked Autoencoders(MAE)为例,它采用对称的编码器-解码器设计来重建高度遮挡的输入,提供了一种可伸缩且有效的预训练大规模视觉模型的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文分析了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变,通过考察六篇有影响力的论文进行了深入研讨。文章首先介绍了图像识别的奠基架构ResNet,它引入残差连接克服了梯度消失问题,使训练更深的卷积网络变得有效。接着探讨了应用Transformer架构于图像补丁序列的Vision Transformer(ViT),展示了注意力模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。在此基础上,研究了生成模型,特别是生成对抗网络(GANs)的对抗训练过程。此外,还介绍了潜扩散模型(LDMs)如何在感知压缩的潜在空间中执行顺序去噪过程,实现了高保真合成和更高的计算效率。最后,探索了减少对标注数据依赖的自监督学习技术,如DINO和遮罩自动编码器(MAE)。
Key Takeaways
- ResNet通过引入残差连接解决了梯度消失问题,使训练深层网络更为有效。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)将Transformer架构应用于图像补丁序列,展示了注意力模型在图像识别中的优越性。
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)通过对抗训练过程学习复杂的数据分布。
- 潜扩散模型(LDMs)在感知压缩的潜在空间中进行去噪,实现了高保真合成和高效计算。
- 自监督学习技术减少了对标注数据的依赖,DINO和MAE是其中的代表方法。
- DINO利用自蒸馏框架,使学生网络学习匹配动量更新的教师输出,获得强大的k-NN分类性能。
点此查看论文截图

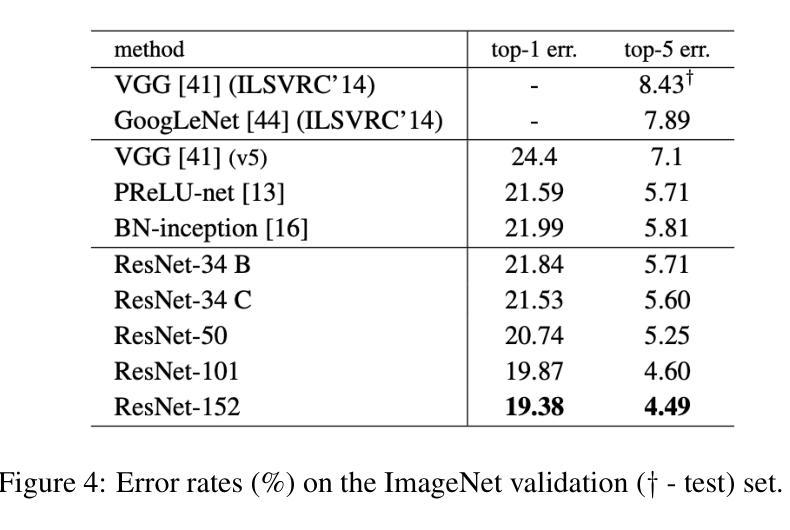
LOTS of Fashion! Multi-Conditioning for Image Generation via Sketch-Text Pairing
Authors:Federico Girella, Davide Talon, Ziyue Liu, Zanxi Ruan, Yiming Wang, Marco Cristani
Fashion design is a complex creative process that blends visual and textual expressions. Designers convey ideas through sketches, which define spatial structure and design elements, and textual descriptions, capturing material, texture, and stylistic details. In this paper, we present LOcalized Text and Sketch for fashion image generation (LOTS), an approach for compositional sketch-text based generation of complete fashion outlooks. LOTS leverages a global description with paired localized sketch + text information for conditioning and introduces a novel step-based merging strategy for diffusion adaptation. First, a Modularized Pair-Centric representation encodes sketches and text into a shared latent space while preserving independent localized features; then, a Diffusion Pair Guidance phase integrates both local and global conditioning via attention-based guidance within the diffusion model’s multi-step denoising process. To validate our method, we build on Fashionpedia to release Sketchy, the first fashion dataset where multiple text-sketch pairs are provided per image. Quantitative results show LOTS achieves state-of-the-art image generation performance on both global and localized metrics, while qualitative examples and a human evaluation study highlight its unprecedented level of design customization.
服装设计是一个复杂的创造性过程,融合了视觉和文本表达。设计师通过草图传达想法,这些草图定义了空间结构和设计元素,并通过文本描述捕捉材料、纹理和风格细节。在本文中,我们介绍了用于服装图像生成的本地化文本和草图(LOTS)方法,这是一种基于组合草图文本生成完整时尚外观的方法。LOTS利用全局描述与配对局部草图+文本信息进行条件设置,并引入了一种基于步骤的合并策略来进行扩散适应。首先,模块化配对中心表示法将草图和文本编码成共享潜在空间,同时保留独立局部特征;然后,扩散对指导阶段通过扩散模型多步去噪过程中的注意力导向机制将局部和全局条件相结合。为了验证我们的方法,我们在Fashionpedia的基础上构建了Sketchy数据集,这是第一个每张图像都提供多个文本草图对的数据集。定量结果表明,LOTS在全球和本地化指标上均达到了最先进的图像生成性能,而定性示例和人类评估研究则突出了其前所未有的设计定制水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICCV25 (Oral). Project page: https://intelligolabs.github.io/lots/
Summary
本文提出了基于局部文本和草图(LOTS)的时尚图像生成方法,该方法结合了全局描述与局部草图文本信息,通过扩散模型的多步去噪过程实现时尚设计的生成。LOTS方法采用模块化配对表示法,将草图与文本编码到共享潜在空间中,同时保留独立局部特征。通过扩散配对引导阶段,将局部和全局条件通过注意力机制引导集成到扩散模型中。该方法在Fashionpedia数据集上构建并发布了Sketchy数据集,实现了高水平的图像生成性能。
Key Takeaways
- 时尚设计是一个复杂的创意过程,结合了视觉和文本表达。
- LOTS方法利用全局描述与局部草图文本信息来实现时尚设计的生成。
- 模块化配对表示法将草图与文本编码到共享潜在空间,同时保留独立局部特征。
- 扩散配对引导阶段通过注意力机制集成局部和全局条件。
- 该方法在Fashionpedia数据集上构建并发布了Sketchy数据集。
- LOTS方法实现了高水平的图像生成性能,包括全球和局部指标。
点此查看论文截图

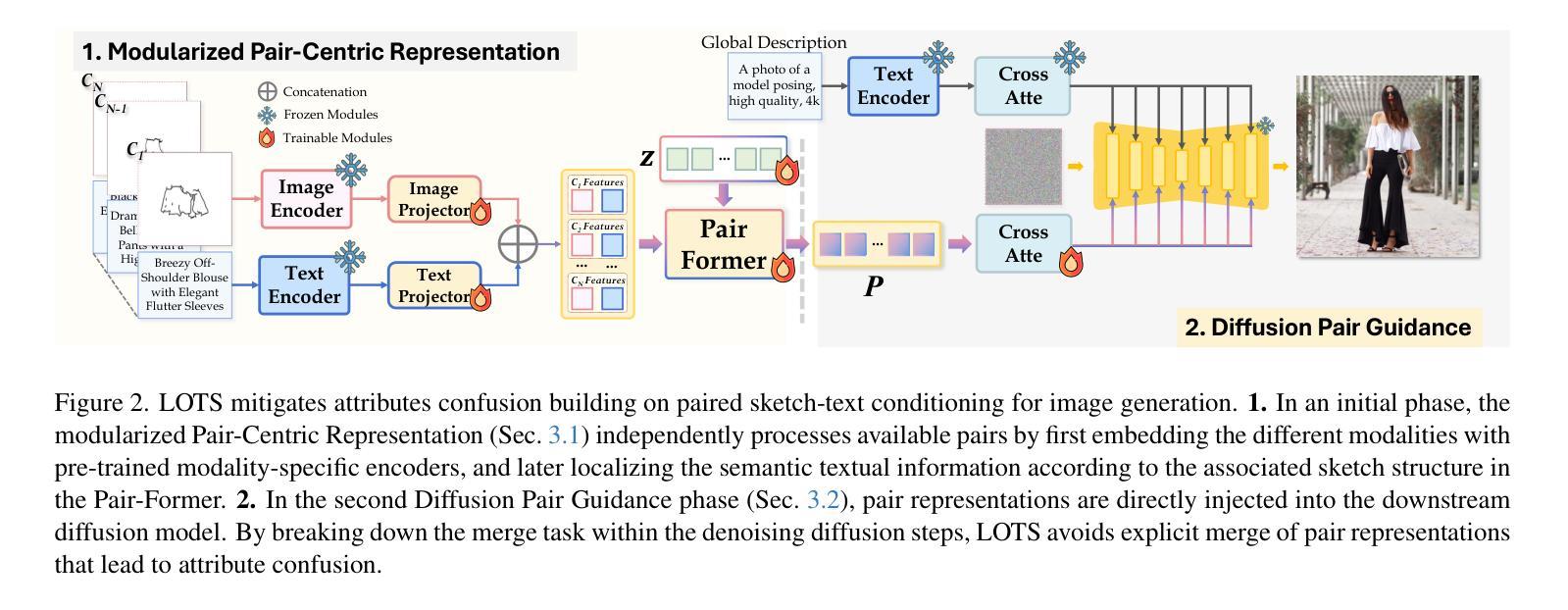
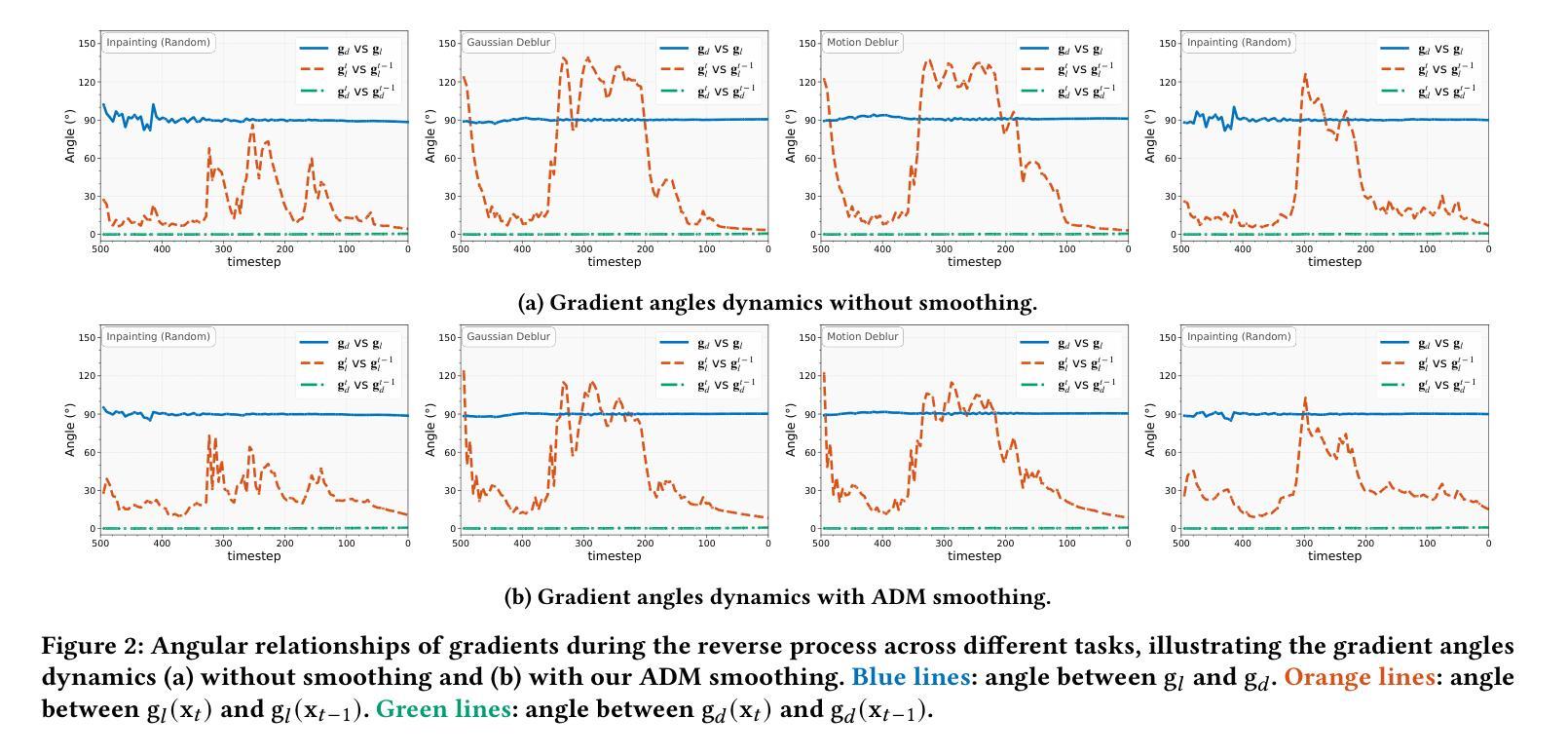
Enhancing Diffusion Model Stability for Image Restoration via Gradient Management
Authors:Hongjie Wu, Mingqin Zhang, Linchao He, Ji-Zhe Zhou, Jiancheng Lv
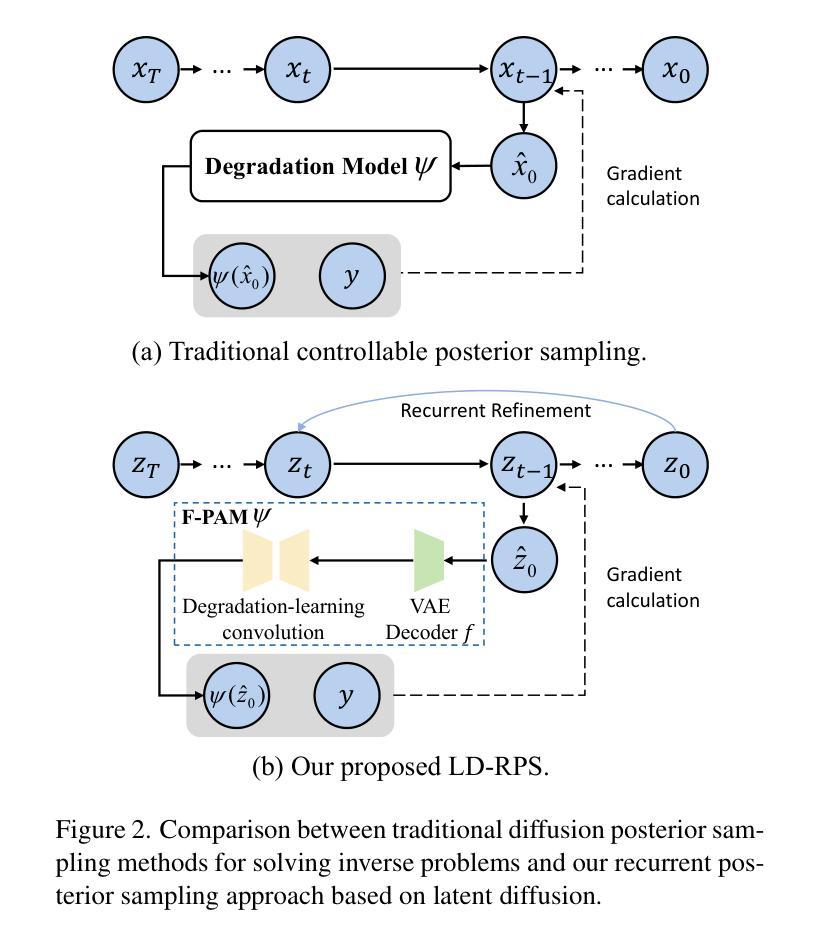
Diffusion models have shown remarkable promise for image restoration by leveraging powerful priors. Prominent methods typically frame the restoration problem within a Bayesian inference framework, which iteratively combines a denoising step with a likelihood guidance step. However, the interactions between these two components in the generation process remain underexplored. In this paper, we analyze the underlying gradient dynamics of these components and identify significant instabilities. Specifically, we demonstrate conflicts between the prior and likelihood gradient directions, alongside temporal fluctuations in the likelihood gradient itself. We show that these instabilities disrupt the generative process and compromise restoration performance. To address these issues, we propose Stabilized Progressive Gradient Diffusion (SPGD), a novel gradient management technique. SPGD integrates two synergistic components: (1) a progressive likelihood warm-up strategy to mitigate gradient conflicts; and (2) adaptive directional momentum (ADM) smoothing to reduce fluctuations in the likelihood gradient. Extensive experiments across diverse restoration tasks demonstrate that SPGD significantly enhances generation stability, leading to state-of-the-art performance in quantitative metrics and visually superior results. Code is available at https://github.com/74587887/SPGD.
扩散模型通过利用强大的先验知识在图像修复领域显示出巨大的潜力。显著的方法通常在一个贝叶斯推断框架内构建修复问题,该框架迭代地结合去噪步骤和可能性指导步骤。然而,生成过程中这两个组件之间的相互作用仍未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们分析了这些组件的底层梯度动态,并发现了重大不稳定现象。具体来说,我们展示了先验知识和可能性梯度方向之间的冲突,以及可能性梯度本身的暂时波动。我们表明,这些不稳定因素破坏了生成过程并影响了修复性能。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了稳定的渐进梯度扩散(SPGD),这是一种新型的梯度管理技术。SPGD集成两个协同组件:(1)渐进的可能性预热策略,以缓解梯度冲突;(2)自适应方向动量(ADM)平滑,以减少可能性梯度的波动。在多种修复任务上的广泛实验表明,SPGD显著增强了生成的稳定性,并在定量指标上达到了最先进的性能,视觉上结果也更为优越。代码可在https://github.com/74587887/SPGD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Multimedia 2025
摘要
扩散模型通过利用强大的先验知识在图像修复方面显示出显著的前景。主流方法通常将修复问题置于贝叶斯推断框架内,该框架通过去噪步骤和可能性引导步骤的迭代组合来工作。然而,生成过程中这两个组件之间的相互作用仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们分析了这些组件的潜在梯度动态,并发现了重大不稳定现象。具体来说,我们证明了先验和可能性梯度方向之间的冲突,以及可能性梯度本身的暂时波动。我们表明,这些不稳定现象破坏了生成过程并影响了修复性能。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了稳定的渐进梯度扩散(SPGD),这是一种新型梯度管理技术。SPGD集成了两个协同组件:(1)渐进的可能性预热策略,以缓解梯度冲突;(2)自适应方向动量(ADM)平滑,以减少可能性梯度的波动。在多种修复任务上的广泛实验表明,SPGD显著增强了生成稳定性,在定量指标方面达到了最先进的性能,并在视觉上产生了更好的结果。
要点
- 扩散模型在图像修复方面表现出显著前景,主要使用贝叶斯推断框架来解决修复问题。
- 当前方法中的生成过程存在重大不稳定现象,主要由于先验和可能性梯度方向的冲突,以及可能性梯度本身的暂时波动。
- 这些不稳定现象会影响生成过程和修复性能。
- 本文提出了稳定的渐进梯度扩散(SPGD)来解决这些问题。
- SPGD包括两个主要组件:渐进的可能性预热策略和自适应方向动量(ADM)平滑。
- 广泛实验证明SPGD能显著增强生成稳定性,并达到最先进的性能。
- 代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

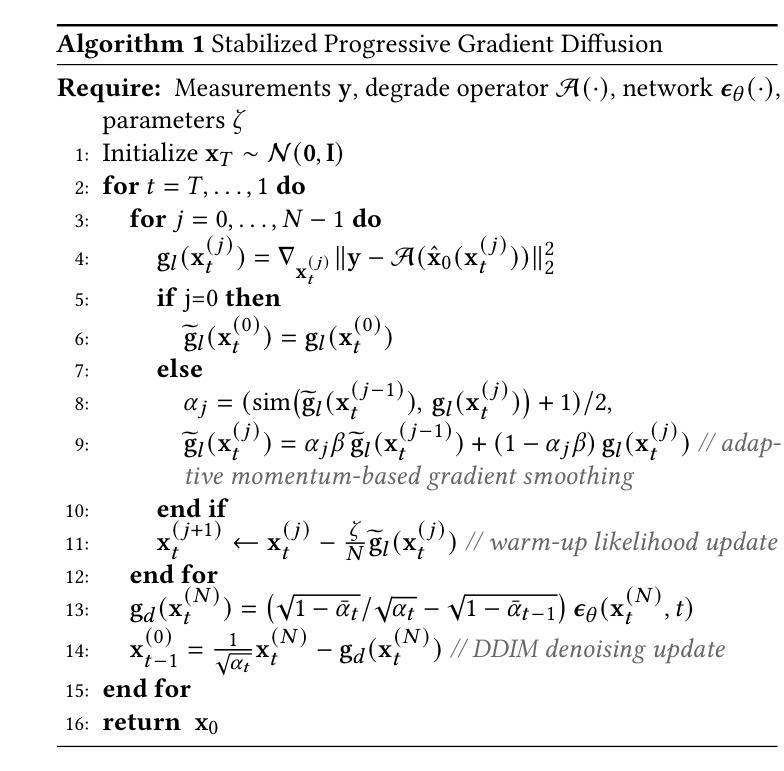
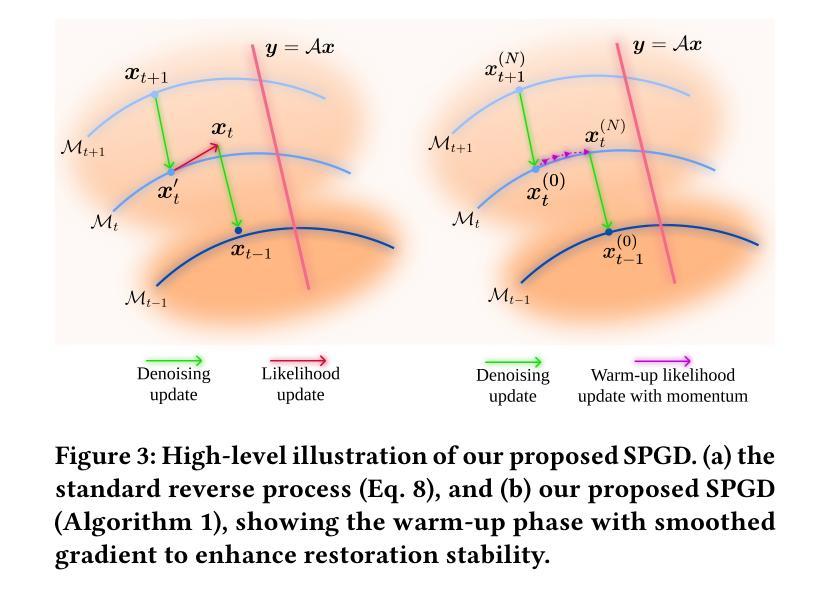

LD-RPS: Zero-Shot Unified Image Restoration via Latent Diffusion Recurrent Posterior Sampling
Authors:Huaqiu Li, Yong Wang, Tongwen Huang, Hailang Huang, Haoqian Wang, Xiangxiang Chu
Unified image restoration is a significantly challenging task in low-level vision. Existing methods either make tailored designs for specific tasks, limiting their generalizability across various types of degradation, or rely on training with paired datasets, thereby suffering from closed-set constraints. To address these issues, we propose a novel, dataset-free, and unified approach through recurrent posterior sampling utilizing a pretrained latent diffusion model. Our method incorporates the multimodal understanding model to provide sematic priors for the generative model under a task-blind condition. Furthermore, it utilizes a lightweight module to align the degraded input with the generated preference of the diffusion model, and employs recurrent refinement for posterior sampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods, validating its effectiveness and robustness. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/LD-RPS.
图像统一恢复是低级视觉中的一个具有挑战性的任务。现有方法要么针对特定任务进行定制设计,从而限制了其在不同类型退化中的泛化能力,要么依赖于配对数据集进行训练,从而受到封闭集约束的限制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新的、无需数据集的方法,通过利用预训练的潜在扩散模型进行递归后采样来实现图像统一恢复。我们的方法结合了多模式理解模型,为任务盲条件下的生成模型提供语义先验。此外,它还利用了一个轻量级模块来对退化输入与扩散模型的生成偏好进行对齐,并采用了递归细化进行后采样。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有先进技术,验证了其有效性和稳健性。我们的代码和数据可在https://github.com/AMAP-ML/LD-RPS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于预训练潜在扩散模型的统一图像恢复方法,无需数据集。该方法通过递归后采样技术,结合多模态理解模型,为生成模型提供语义先验,同时采用轻量级模块对齐退化输入与扩散模型的生成偏好,并通过递归优化进行后采样。实验证明该方法在统一图像恢复任务上优于现有技术,具有有效性和鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于预训练潜在扩散模型的统一图像恢复方法。
- 采用递归后采样技术,无需使用数据集。
- 结合多模态理解模型,为生成模型提供语义先验。
- 采用轻量级模块对齐退化输入与扩散模型的生成偏好。
- 通过递归优化进行后采样,提高图像恢复效果。
- 实验证明该方法在统一图像恢复任务上优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

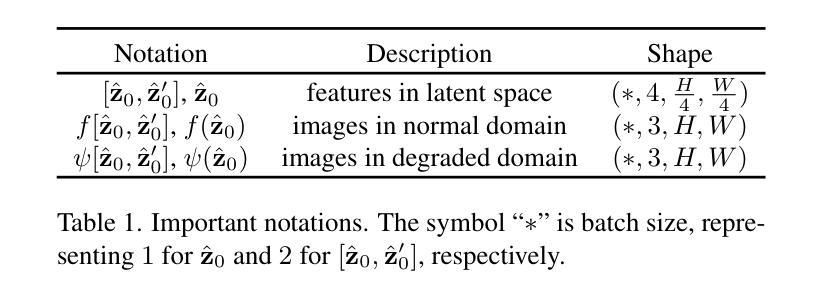

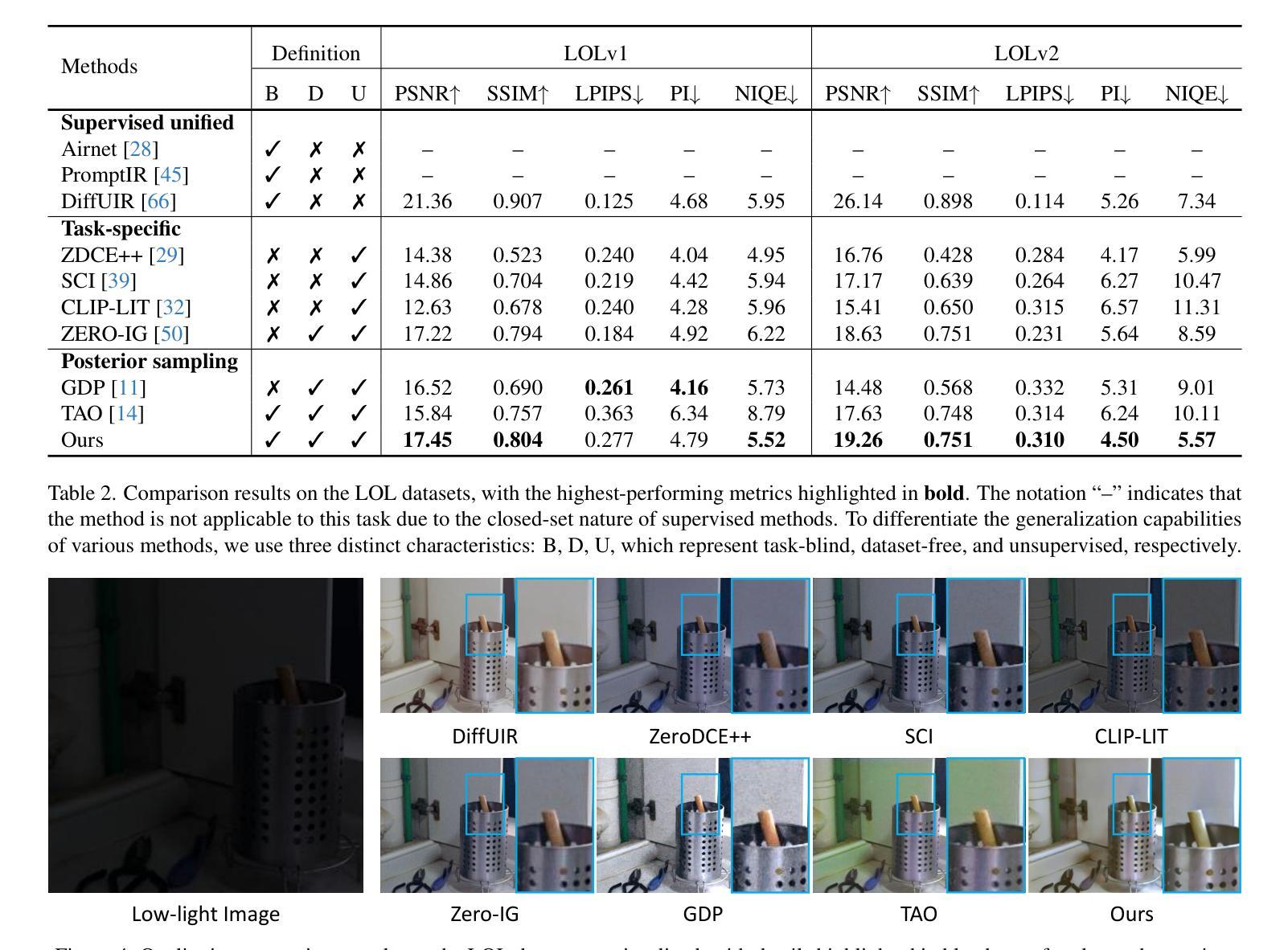
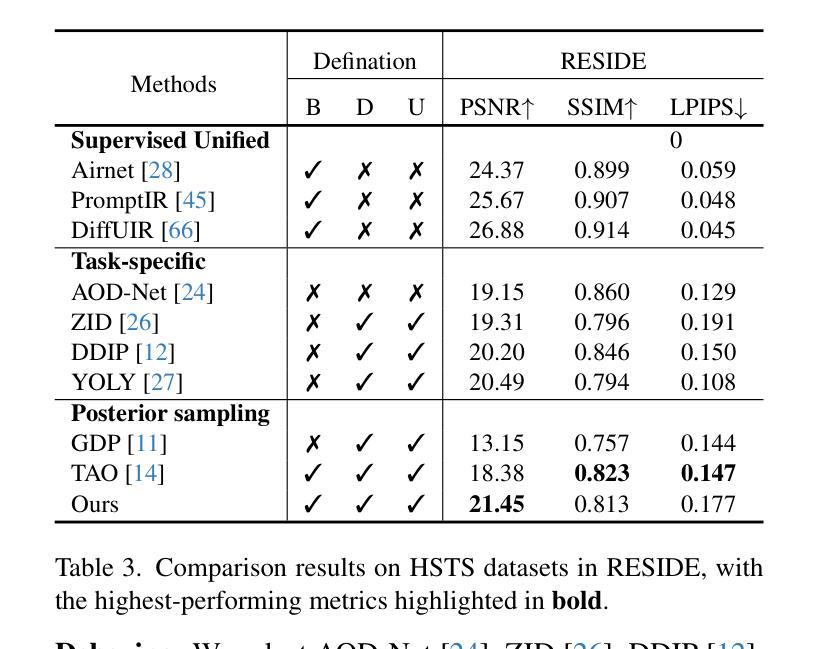
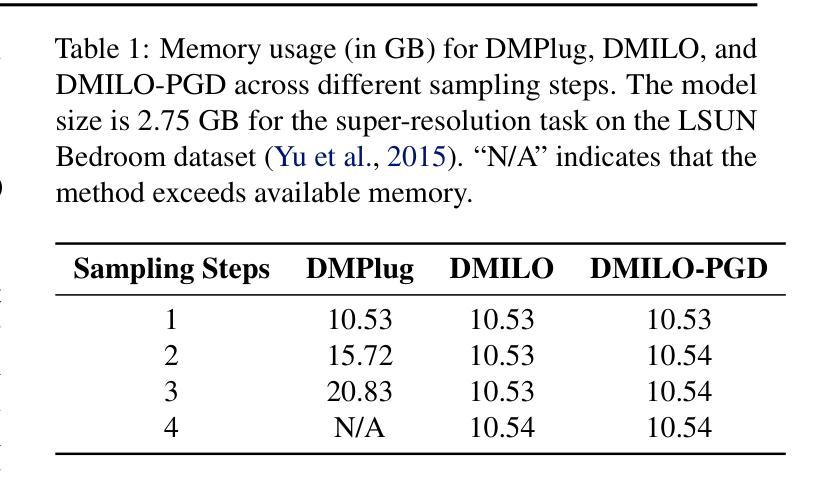
Integrating Intermediate Layer Optimization and Projected Gradient Descent for Solving Inverse Problems with Diffusion Models
Authors:Yang Zheng, Wen Li, Zhaoqiang Liu
Inverse problems (IPs) involve reconstructing signals from noisy observations. Recently, diffusion models (DMs) have emerged as a powerful framework for solving IPs, achieving remarkable reconstruction performance. However, existing DM-based methods frequently encounter issues such as heavy computational demands and suboptimal convergence. In this work, building upon the idea of the recent work DMPlug, we propose two novel methods, DMILO and DMILO-PGD, to address these challenges. Our first method, DMILO, employs intermediate layer optimization (ILO) to alleviate the memory burden inherent in DMPlug. Additionally, by introducing sparse deviations, we expand the range of DMs, enabling the exploration of underlying signals that may lie outside the range of the diffusion model. We further propose DMILO-PGD, which integrates ILO with projected gradient descent (PGD), thereby reducing the risk of suboptimal convergence. We provide an intuitive theoretical analysis of our approaches under appropriate conditions and validate their superiority through extensive experiments on diverse image datasets, encompassing both linear and nonlinear IPs. Our results demonstrate significant performance gains over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting the effectiveness of DMILO and DMILO-PGD in addressing common challenges in DM-based IP solvers.
逆问题(IPs)涉及从噪声观察中重建信号。最近,扩散模型(DMs)作为一种解决IPs的强大框架崭露头角,实现了令人印象深刻的重建性能。然而,现有的基于DM的方法经常面临计算量大和收敛不佳等问题。在这项工作中,我们基于近期工作DMPlug的思想,提出了两种新方法DMILO和DMILO-PGD,以应对这些挑战。我们的第一种方法DMILO采用中间层优化(ILO)来缓解DMPlug所固有的内存负担。此外,通过引入稀疏偏差,我们扩大了DMs的范围,能够探索可能位于扩散模型范围之外的潜在信号。我们进一步提出了DMILO-PGD,它将ILO与投影梯度下降法(PGD)相结合,从而降低了收敛不佳的风险。我们在适当条件下对方法进行了直观的理论分析,并通过对各种图像数据集的大量实验验证了其优越性,这些实验涵盖了线性和非线性IPs。我们的结果证明了DMILO和DMILO-PGD相较于最新技术方法的显著性能提升,突显了它们在解决基于DM的IP求解器中的常见挑战方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
扩散模型在解决反问题中展现出强大的性能,但存在计算量大和收敛性不佳的问题。本文提出两种新方法DMILO和DMILO-PGD,前者通过中间层优化和稀疏偏差来扩展模型的探索范围,后者结合了中间层优化与投影梯度下降法,以降低次优收敛的风险。实验证明,两种方法在图像数据集上的表现均优于现有先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在解决反问题中表现出强大的性能。
- 现有扩散模型方法面临计算量大和收敛性不佳的挑战。
- DMILO方法通过中间层优化和稀疏偏差来扩展模型的探索范围,减轻内存负担。
- DMILO-PGD结合了中间层优化与投影梯度下降法,提高收敛性能。
- 本文对两种方法进行了直观的理论分析。
- 实验证明,两种方法在多种图像数据集上的表现均优于现有先进方法。
点此查看论文截图

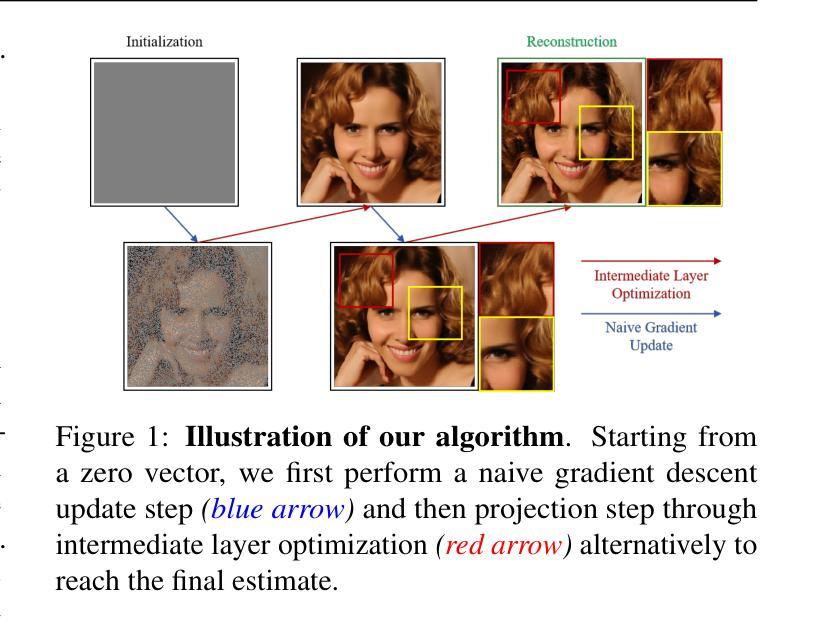


Res-MoCoDiff: Residual-guided diffusion models for motion artifact correction in brain MRI
Authors:Mojtaba Safari, Shansong Wang, Qiang Li, Zach Eidex, Richard L. J. Qiu, Chih-Wei Chang, Hui Mao, Xiaofeng Yang
Objective. Motion artifacts in brain MRI, mainly from rigid head motion, degrade image quality and hinder downstream applications. Conventional methods to mitigate these artifacts, including repeated acquisitions or motion tracking, impose workflow burdens. This study introduces Res-MoCoDiff, an efficient denoising diffusion probabilistic model specifically designed for MRI motion artifact correction.Approach.Res-MoCoDiff exploits a novel residual error shifting mechanism during the forward diffusion process to incorporate information from motion-corrupted images. This mechanism allows the model to simulate the evolution of noise with a probability distribution closely matching that of the corrupted data, enabling a reverse diffusion process that requires only four steps. The model employs a U-net backbone, with attention layers replaced by Swin Transformer blocks, to enhance robustness across resolutions. Furthermore, the training process integrates a combined l1+l2 loss function, which promotes image sharpness and reduces pixel-level errors. Res-MoCoDiff was evaluated on both an in-silico dataset generated using a realistic motion simulation framework and an in-vivo MR-ART dataset. Comparative analyses were conducted against established methods, including CycleGAN, Pix2pix, and a diffusion model with a vision transformer backbone, using quantitative metrics such as PSNR, SSIM, and NMSE.Main results. The proposed method demonstrated superior performance in removing motion artifacts across minor, moderate, and heavy distortion levels. Res-MoCoDiff consistently achieved the highest SSIM and the lowest NMSE values, with a PSNR of up to 41.91+-2.94 dB for minor distortions. Notably, the average sampling time was reduced to 0.37 seconds per batch of two image slices, compared with 101.74 seconds for conventional approaches.
目标:脑MRI中的运动伪影,主要来自头部刚性运动,会降低图像质量并阻碍下游应用。传统的方法,包括重复采集或运动跟踪,会给工作流程带来负担。本研究介绍了Res-MoCoDiff,这是一种专为MRI运动伪影校正设计的高效去噪扩散概率模型。
方法:Res-MoCoDiff在正向扩散过程中利用新颖残差误差转移机制,融入运动伪影图像的信息。这种机制允许模型模拟噪声演变,其概率分布与受干扰数据相匹配,实现仅需要四个步骤的反向扩散过程。模型采用U-net骨干网,用Swin Transformer块替换注意力层,以增强跨分辨率的稳健性。此外,训练过程结合了l1+l2损失函数,这有助于提高图像清晰度和减少像素级错误。Res-MoCoDiff在利用现实运动模拟框架生成的模拟数据集和体内MR-ART数据集上进行了评估。与CycleGAN、Pix2pix和具有视觉转换器骨干的扩散模型进行了比较性分析,使用了PSNR、SSIM和NMSE等定量指标。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对MRI运动伪影校正的高效去噪扩散概率模型——Res-MoCoDiff。该方法通过新颖的残差误差移位机制在正向扩散过程中融入运动受干扰图像的信息。它能模拟噪声演变,并与受干扰数据的概率分布相匹配,使反向扩散过程仅需四步。模型采用U-net架构,并用Swin Transformer块增强跨分辨率的稳健性。在模拟和真实MR数据中,与现有方法相比,Res-MoCoDiff在去除各级运动伪影方面表现出卓越性能,采样时间大大减少。
Key Takeaways
- Res-MoCoDiff是一种针对MRI运动伪影校正的扩散概率模型。
- 该方法通过新颖的残差误差移位机制在正向扩散过程中融入运动受干扰图像的信息。
- 模型采用U-net架构,并用Swin Transformer块提高跨分辨率的稳健性。
- 在模拟和真实MR数据中,Res-MoCoDiff在去除各级运动伪影方面表现出卓越性能。
- 与其他方法相比,Res-MoCoDiff的采样时间大大减少。
- 该模型采用结合l1+l2损失函数进行训练,有助于提高图像清晰度和减少像素级误差。
点此查看论文截图

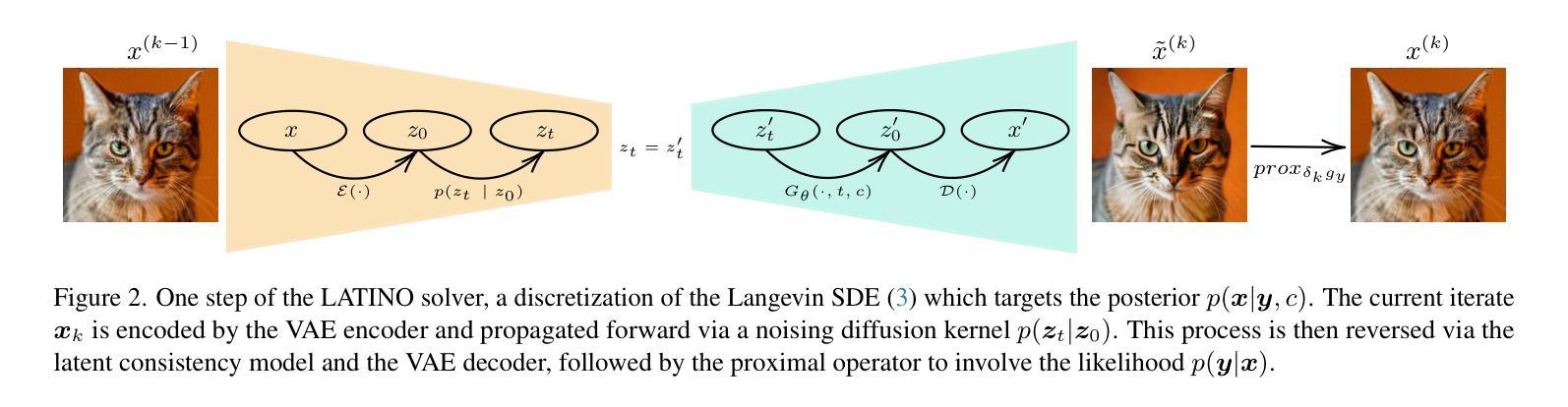
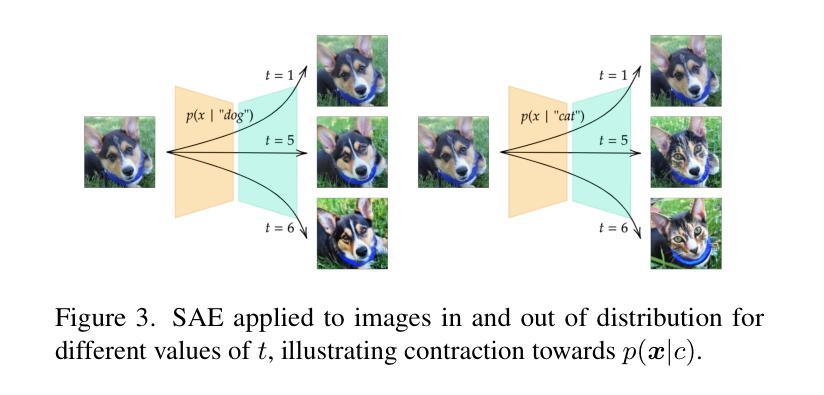
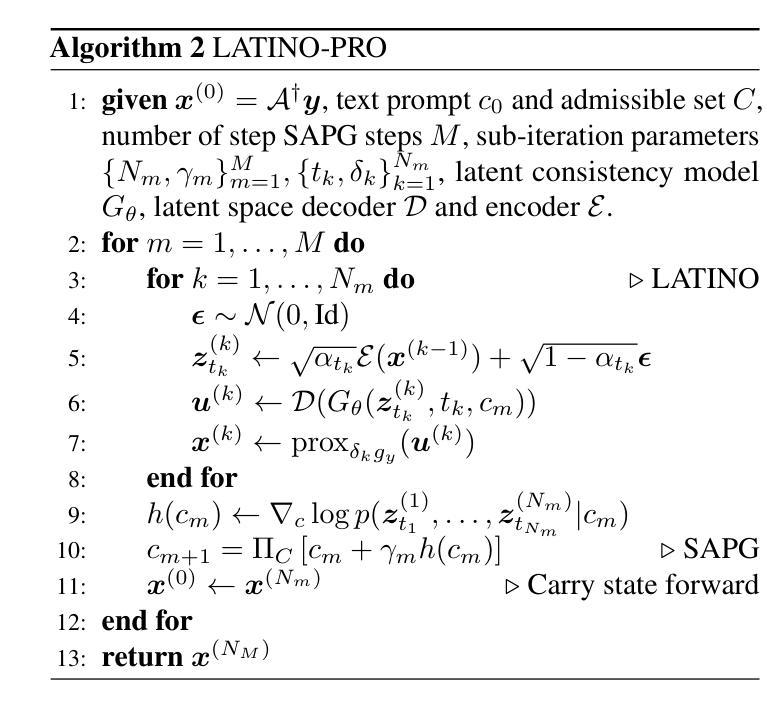
LATINO-PRO: LAtent consisTency INverse sOlver with PRompt Optimization
Authors:Alessio Spagnoletti, Jean Prost, Andrés Almansa, Nicolas Papadakis, Marcelo Pereyra
Text-to-image latent diffusion models (LDMs) have recently emerged as powerful generative models with great potential for solving inverse problems in imaging. However, leveraging such models in a Plug & Play (PnP), zero-shot manner remains challenging because it requires identifying a suitable text prompt for the unknown image of interest. Also, existing text-to-image PnP approaches are highly computationally expensive. We herein address these challenges by proposing a novel PnP inference paradigm specifically designed for embedding generative models within stochastic inverse solvers, with special attention to Latent Consistency Models (LCMs), which distill LDMs into fast generators. We leverage our framework to propose LAtent consisTency INverse sOlver (LATINO), the first zero-shot PnP framework to solve inverse problems with priors encoded by LCMs. Our conditioning mechanism avoids automatic differentiation and reaches SOTA quality in as little as 8 neural function evaluations. As a result, LATINO delivers remarkably accurate solutions and is significantly more memory and computationally efficient than previous approaches. We then embed LATINO within an empirical Bayesian framework that automatically calibrates the text prompt from the observed measurements by marginal maximum likelihood estimation. Extensive experiments show that prompt self-calibration greatly improves estimation, allowing LATINO with PRompt Optimization to define new SOTAs in image reconstruction quality and computational efficiency. The code is available at https://latino-pro.github.io
文本到图像的潜在扩散模型(LDM)最近作为强大的生成模型出现,在成像中的逆问题解决方案方面具有巨大潜力。然而,以Plug & Play(PnP)的方式利用这些模型仍然具有挑战性,因为这需要针对感兴趣的未知图像确定合适的文本提示。此外,现有的文本到图像PnP方法在计算上非常昂贵。我们通过提出一种新型PnP推理范式来解决这些挑战,该范式专门设计用于将生成模型嵌入随机逆求解器中,特别关注潜在一致性模型(LCMs),它将LDM蒸馏成快速生成器。我们利用我们的框架提出了LAtent consisTency INverse sOlver(LATINO),这是第一个以零射击方式解决逆问题的PnP框架,其先验由LCMs编码。我们的调节机制避免了自动微分,并在仅8个神经网络功能评估中达到了最新技术水平。因此,LATINO提供了非常准确的解决方案,并且在内存和计算效率方面显著优于以前的方法。然后我们将LATINO嵌入经验贝叶框架中,该框架通过边际最大似然估计自动校准文本提示来自观察到的测量值。大量实验表明,提示自我校准极大地提高了估计值,使得LATINO与PRompt Optimization一起在图像重建质量和计算效率方面定义了新的最新技术。代码可在https://latino-pro.github.io找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 24 figures, International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV 2025
Summary
文本到图像的潜在扩散模型(LDM)是新兴的强大的生成模型,具有解决成像逆问题的巨大潜力。然而,以Plug & Play(PnP)即插即用方式和零样本方式利用此类模型具有挑战性,因为需要为未知图像选择合适的文本提示。现有文本到图像的PnP方法计算量大。本文提出一种新型的PnP推理范式,专为将生成模型嵌入随机逆求解器而设计,特别关注潜在一致性模型(LCMs),它将LDM蒸馏为快速生成器。我们利用该框架提出LAtent consisTency INverse sOlver(LATINO),这是第一个零样本PnP框架,使用LCMs编码的先验知识解决逆问题。其调节机制避免了自动微分,并在仅8个神经网络功能评估中达到了最佳质量。LATINO提供了精准解决方案,并且在内存和计算方面比以前的方法更有效率。然后,我们将LATINO嵌入经验贝叶斯框架中,通过边际最大似然估计自动校准文本提示。大量实验表明,提示自我校准大大提高了估算效果,使LATINO with PRompt Optimization在图像重建质量和计算效率方面定义了新的最佳水平。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的潜在扩散模型(LDM)是强大的生成模型,能解决成像逆问题。
2.Plug & Play方式利用此类模型具有挑战性,需找到合适的文本提示。 - 提出一种新型的PnP推理范式,嵌入随机逆求解器,特别关注潜在一致性模型(LCMs)。
- 引入LAtent consisTency INverse sOlver(LATINO),能在零样本PnP框架下解决逆问题。
- LATINO调节机制避免自动微分,达到高质量解决方案且计算效率高。
- 将LATINO嵌入经验贝叶斯框架进行文本提示的自我校准。
- 实验显示,自我校准的提示提高了估算效果,使LATINO在图像重建质量和计算效率上达到新的最佳水平。
点此查看论文截图

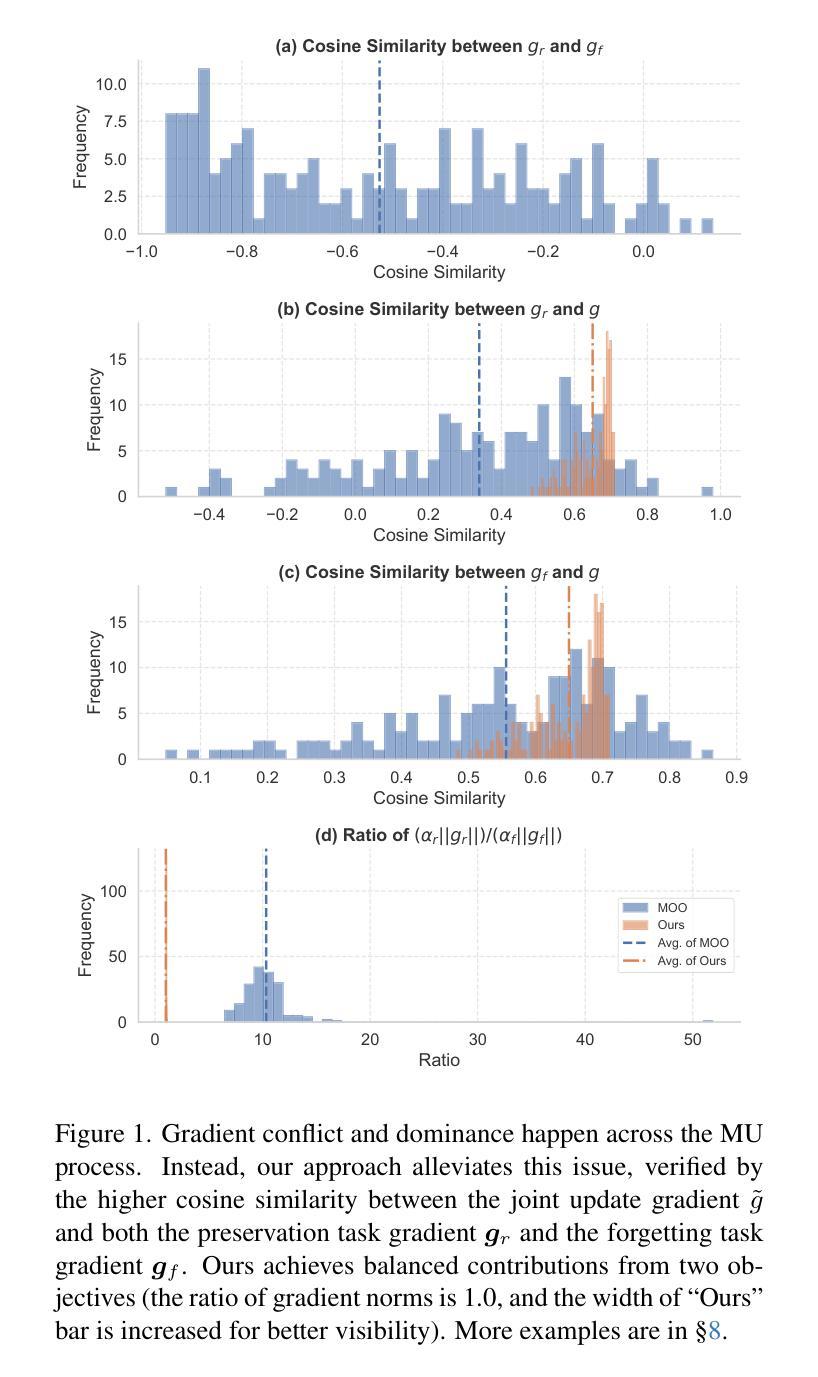
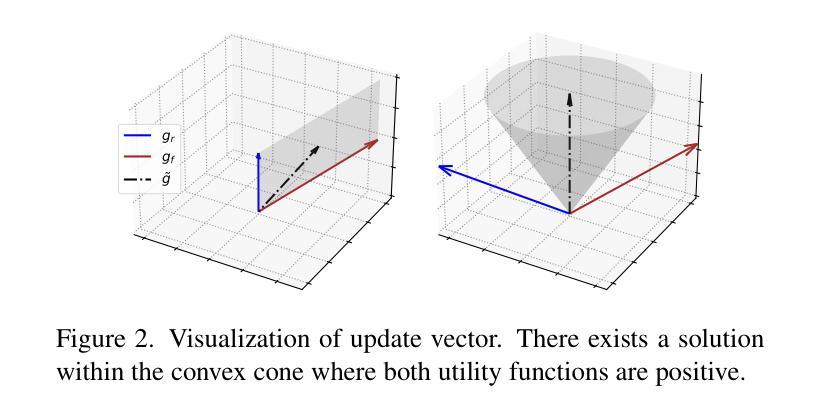
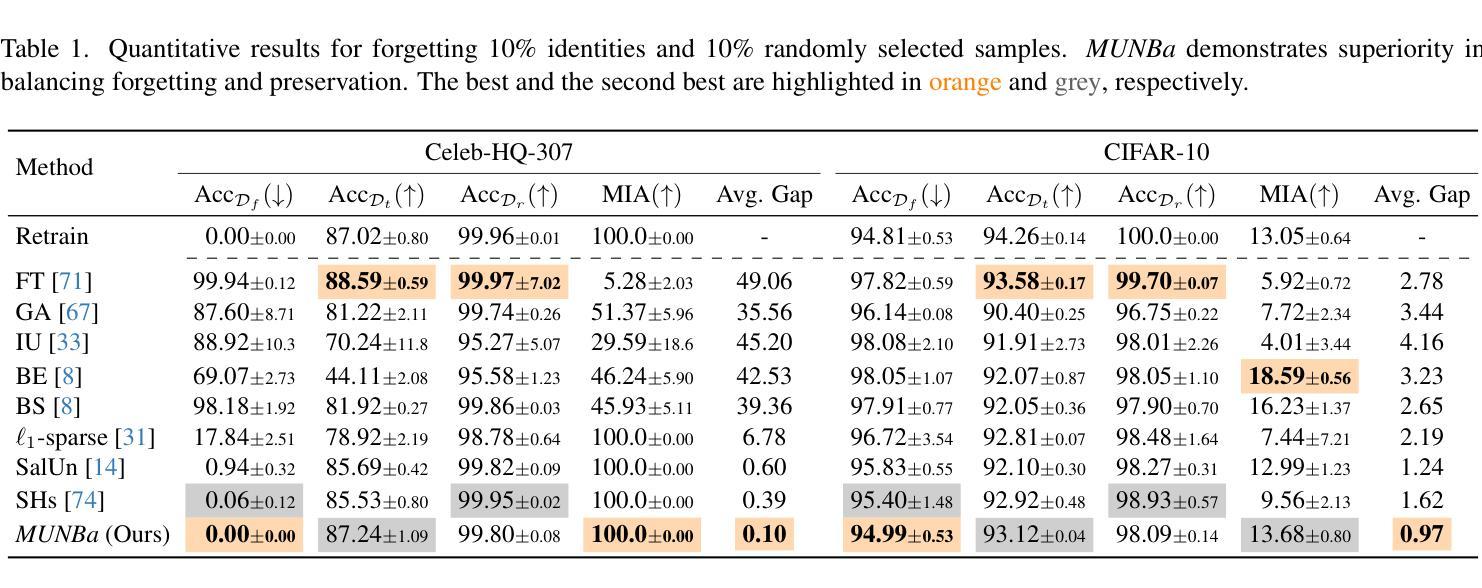
MUNBa: Machine Unlearning via Nash Bargaining
Authors:Jing Wu, Mehrtash Harandi
Machine Unlearning (MU) aims to selectively erase harmful behaviors from models while retaining the overall utility of the model. As a multi-task learning problem, MU involves balancing objectives related to forgetting specific concepts/data and preserving general performance. A naive integration of these forgetting and preserving objectives can lead to gradient conflicts and dominance, impeding MU algorithms from reaching optimal solutions. To address the gradient conflict and dominance issue, we reformulate MU as a two-player cooperative game, where the two players, namely, the forgetting player and the preservation player, contribute via their gradient proposals to maximize their overall gain and balance their contributions. To this end, inspired by the Nash bargaining theory, we derive a closed-form solution to guide the model toward the Pareto stationary point. Our formulation of MU guarantees an equilibrium solution, where any deviation from the final state would lead to a reduction in the overall objectives for both players, ensuring optimality in each objective. We evaluate our algorithm’s effectiveness on a diverse set of tasks across image classification and image generation. Extensive experiments with ResNet, vision-language model CLIP, and text-to-image diffusion models demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art MU algorithms, achieving a better trade-off between forgetting and preserving. Our results also highlight improvements in forgetting precision, preservation of generalization, and robustness against adversarial attacks.
机器遗忘(MU)旨在选择性地从模型中删除有害行为,同时保留模型的总体效用。作为多任务学习问题,MU涉及平衡与遗忘特定概念/数据相关的目标和保持整体性能的目标。这些遗忘和保留目标的简单集成可能导致梯度冲突和主导,阻碍MU算法达到最优解。为了解决梯度冲突和主导问题,我们将MU重新表述为一个两人合作游戏,其中两个玩家,即遗忘玩家和保留玩家,通过他们的梯度提案做出贡献,以最大化他们的整体收益并平衡他们的贡献。为此,受纳什谈判理论的启发,我们推导出一个封闭形式的解决方案,以引导模型走向帕累托稳定点。我们对MU的表述保证了均衡解,任何偏离最终状态都会导致两个玩家的整体目标减少,从而确保每个目标的最优性。我们在图像分类和图像生成的各种任务上评估了我们算法的有效性。使用ResNet、视觉语言模型CLIP和文本到图像扩散模型的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在遗忘和保留之间取得了更好的平衡,优于最新的MU算法。我们的结果还突出了在遗忘精度、保持泛化能力和对抗攻击的稳健性方面的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
机器学习模型中的机器遗忘(MU)旨在选择性删除模型中的有害行为,同时保留模型的总体效用。MU作为一个多任务学习问题,涉及平衡遗忘特定概念/数据和保持整体性能的目标。然而,简单地将这些遗忘和保留目标集成在一起可能导致梯度冲突和主导问题,阻碍MU算法达到最优解。为解决梯度冲突和主导问题,我们将MU重新构建为一个双人合作游戏,其中遗忘玩家和保留玩家通过其梯度提案来最大化其整体收益并平衡其贡献。为此,我们受到纳什谈判理论的启发,推导出一个封闭形式的解决方案来指导模型走向帕累托稳定点。我们的MU公式保证了均衡解,任何偏离最终状态都会导致整体目标减少,从而确保每个目标的优化。我们在图像分类和图像生成等任务上评估了算法的有效性。使用ResNet、视觉语言模型CLIP和文本到图像扩散模型的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于最先进的MU算法,在遗忘和保留之间取得了更好的平衡。我们的结果还显示了在遗忘精度、保持泛化能力和对抗攻击的稳健性方面的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 机器遗忘(MU)旨在从机器学习模型中删除有害行为,同时保持模型的整体效用。
- MU面临梯度冲突和主导问题的挑战。
- 将MU重新构建为双人合作游戏,其中遗忘玩家和保留玩家通过梯度提案进行合作。
- 受纳什谈判理论启发,推导出一个封闭形式的解决方案来指导模型走向帕累托稳定点。
- 方法在图像分类和图像生成等任务上表现优异。
- 与最先进的MU算法相比,在遗忘和保留之间取得了更好的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

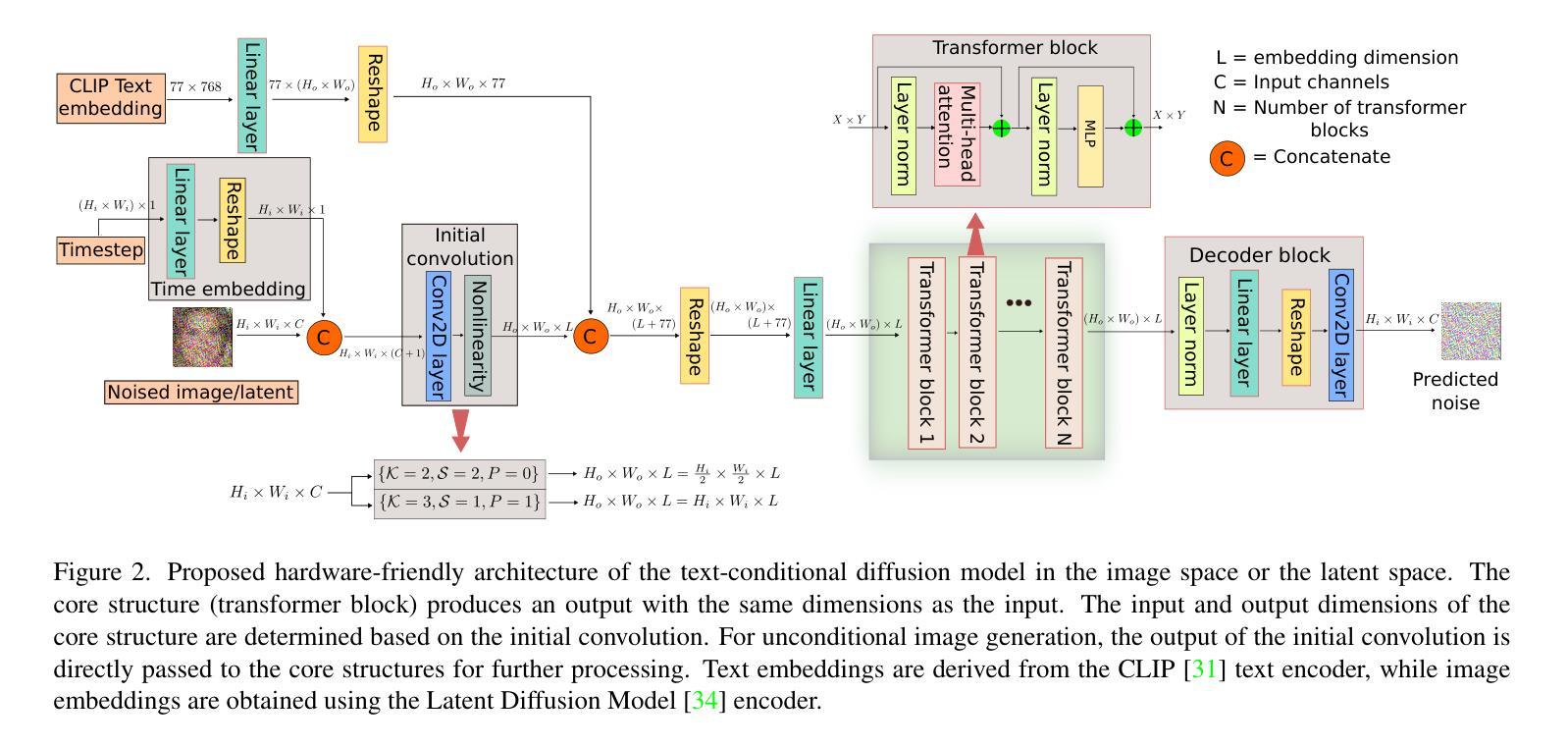
Hardware-Friendly Diffusion Models with Fixed-Size Reusable Structures for On-Device Image Generation
Authors:Sanchar Palit, Sathya Veera Reddy Dendi, Mallikarjuna Talluri, Raj Narayana Gadde
Vision Transformers and U-Net architectures have been widely adopted in the implementation of Diffusion Models. However, each architecture presents specific challenges while realizing them on-device. Vision Transformers require positional embedding to maintain correspondence between the tokens processed by the transformer, although they offer the advantage of using fixed-size, reusable repetitive blocks following tokenization. The U-Net architecture lacks these attributes, as it utilizes variable-sized intermediate blocks for down-convolution and up-convolution in the noise estimation backbone for the diffusion process. To address these issues, we propose an architecture that utilizes a fixed-size, reusable transformer block as a core structure, making it more suitable for hardware implementation. Our architecture is characterized by low complexity, token-free design, absence of positional embeddings, uniformity, and scalability, making it highly suitable for deployment on mobile and resource-constrained devices. The proposed model exhibit competitive and consistent performance across both unconditional and conditional image generation tasks. The model achieved a state-of-the-art FID score of 1.6 on unconditional image generation with the CelebA.
在Diffusion Models的实现过程中,Vision Transformers和U-Net架构已被广泛应用。然而,每种架构在设备上实现时都面临着特定的挑战。Vision Transformers需要位置嵌入来保持经过变压器处理的令牌之间的对应关系,尽管它们提供了使用固定大小的、可重复使用的重复块进行令牌化后的优势。U-Net架构缺少这些属性,因为它使用可变大小的中间块来进行去卷积和扩散过程中的噪声估计主干中的上卷积。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种利用固定大小的、可重复使用的变压器块作为核心结构的架构,使其更适合硬件实现。我们的架构特点是复杂度低、无令牌设计、无需位置嵌入、通用性强和可扩展性高,非常适合在移动设备和资源受限的设备上部署。所提出模型的性能在无条件图像生成任务和条件图像生成任务中都具有竞争力和一致性。该模型在无条件图像生成方面达到了最先进的FID分数1.6,使用CelebA数据集的模型效果最佳。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF presented at IJCNN 2025 poster track
Summary
本文探讨了Vision Transformers和U-Net架构在Diffusion Models中的应用及其面临的挑战。针对这些问题,提出了一种利用固定大小、可重用transformer块作为核心结构的新架构,具有低复杂度、无令牌设计、无需位置嵌入、通用性和可扩展性等特点,非常适合在移动和资源受限设备上部署。该模型在无条件图像生成任务上取得了最先进的FID分数。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers和U-Net架构在Diffusion Models中得到广泛应用。
- Vision Transformers需要位置嵌入来保持令牌间的对应关系。
- U-Net架构缺乏固定大小的中间块,适用于噪声估计主干进行扩散过程。
- 新提出的架构利用固定大小、可重用的transformer块作为核心结构。
- 新架构具有低复杂度、无令牌设计、无需位置嵌入、通用性和可扩展性。
- 新模型适合在移动和资源受限设备上部署。
点此查看论文截图



Enhanced Generative Data Augmentation for Semantic Segmentation via Stronger Guidance
Authors:Quang-Huy Che, Duc-Tri Le, Bich-Nga Pham, Duc-Khai Lam, Vinh-Tiep Nguyen
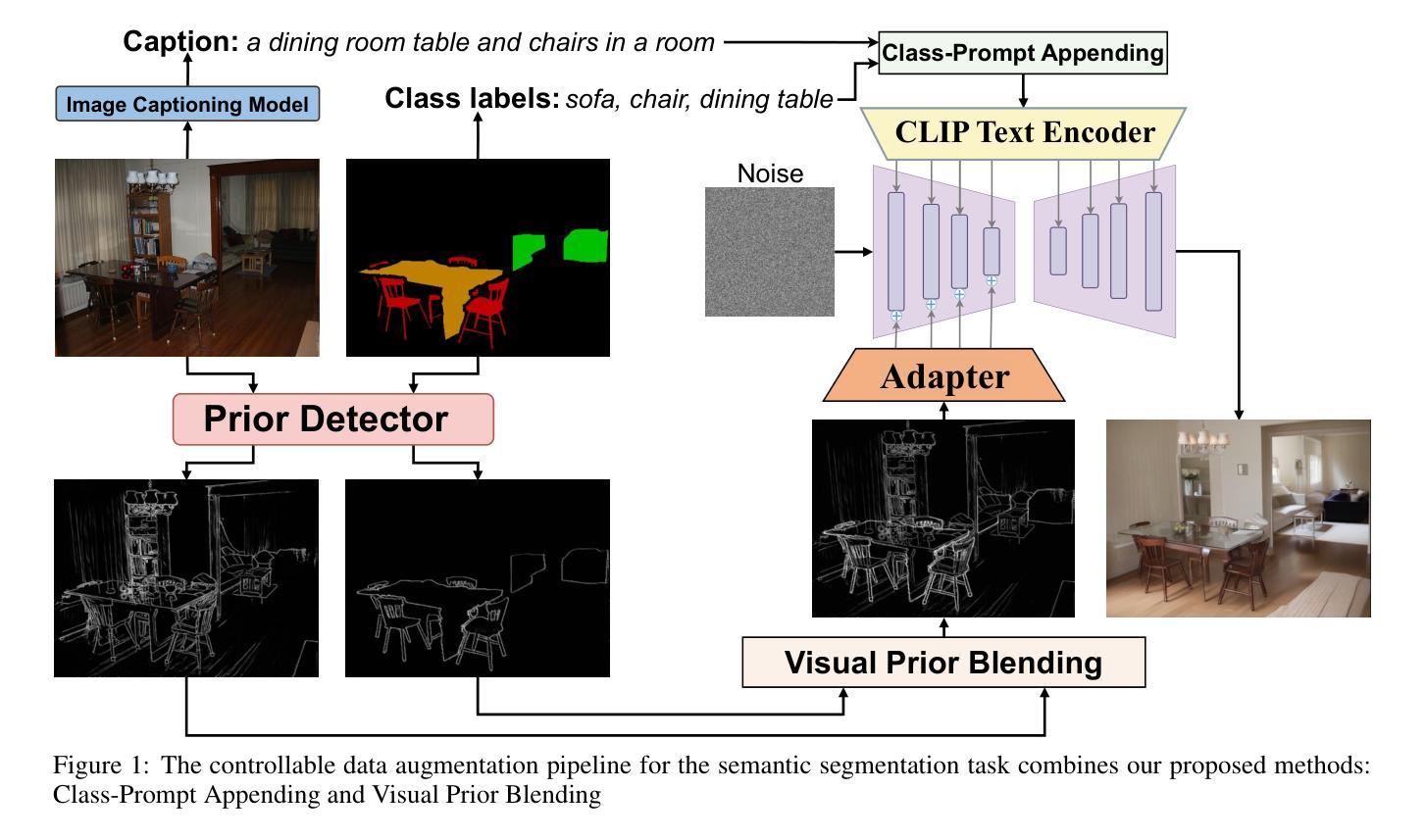
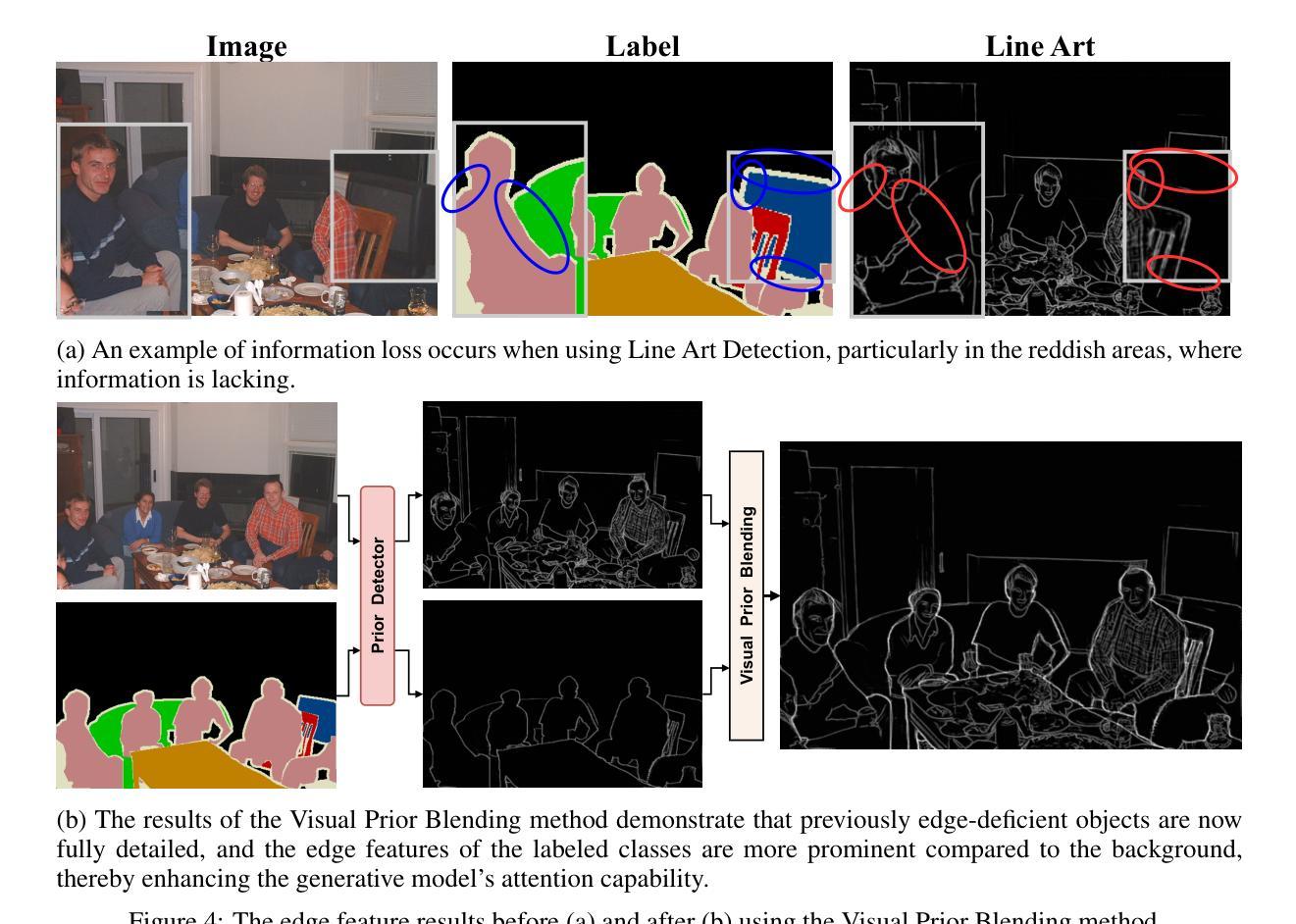
Data augmentation is crucial for pixel-wise annotation tasks like semantic segmentation, where labeling requires significant effort and intensive labor. Traditional methods, involving simple transformations such as rotations and flips, create new images but often lack diversity along key semantic dimensions and fail to alter high-level semantic properties. To address this issue, generative models have emerged as an effective solution for augmenting data by generating synthetic images. Controllable Generative models offer data augmentation methods for semantic segmentation tasks by using prompts and visual references from the original image. However, these models face challenges in generating synthetic images that accurately reflect the content and structure of the original image due to difficulties in creating effective prompts and visual references. In this work, we introduce an effective data augmentation pipeline for semantic segmentation using Controllable Diffusion model. Our proposed method includes efficient prompt generation using Class-Prompt Appending and Visual Prior Blending to enhance attention to labeled classes in real images, allowing the pipeline to generate a precise number of augmented images while preserving the structure of segmentation-labeled classes. In addition, we implement a class balancing algorithm to ensure a balanced training dataset when merging the synthetic and original images. Evaluation on PASCAL VOC datasets, our pipeline demonstrates its effectiveness in generating high-quality synthetic images for semantic segmentation. Our code is available at https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance.
数据增强对于像素级标注任务(如语义分割)至关重要,这些任务需要大量标注工作。传统的方法,如旋转和翻转等简单变换,虽然可以生成新图像,但往往在关键的语义维度上缺乏多样性,并且无法改变高级语义属性。为了解决这一问题,生成模型作为一种有效的数据增强方法,通过生成合成图像来增强数据。可控生成模型通过原始图像的提示和视觉参考,为语义分割任务提供数据增强方法。然而,这些模型在生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像时面临挑战,因为创建有效的提示和视觉参考具有难度。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种使用可控扩散模型的有效数据增强管道,用于语义分割。我们提出的方法包括使用类提示附加和视觉先验融合来有效生成提示,以增强对真实图像中标记类的关注,使管道能够在保持分割标记类结构的同时,生成精确数量的增强图像。此外,我们实现了一种类平衡算法,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时,训练数据集是平衡的。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估表明,我们的管道在生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割方面非常有效。我们的代码可在https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in ICPRAM 2025, ISBN 978-989-758-730-6, ISSN 2184-4313
Summary
针对像素级标注任务(如语义分割)中的数据增强至关重要,传统方法简单转换图像,但缺乏多样性。生成模型可生成合成图像,成为解决此问题的有效方法。可控生成模型可通过提示和原始图像的视觉参考进行数据增强。本工作使用可控扩散模型,通过Class-Prompt Appending和Visual Prior Blending技术提高真实图像中标记类的关注度,生成精确数量的增强图像并保留分割标记类的结构。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估证明了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强对像素级标注任务至关重要,尤其对于需要大量标注的语义分割任务。
- 传统数据增强方法如旋转和翻转虽然能创建新图像,但缺乏关键语义维度的多样性。
- 生成模型,特别是可控生成模型,通过生成合成图像为解决数据增强问题提供了有效方法。
- 引入可控扩散模型进行数据增强,使用Class-Prompt Appending和Visual Prior Blending技术提高真实图像中标记类的关注度。
- 方法能生成精确数量的增强图像,同时保留分割标记类的结构。
- 通过类平衡算法确保合成和原始图像的合并时数据集平衡。
- 在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估证明了该数据增强管道的有效性。
点此查看论文截图