⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
Delta Activations: A Representation for Finetuned Large Language Models
Authors:Zhiqiu Xu, Amish Sethi, Mayur Naik, Ser-Nam Lim
The success of powerful open source Large Language Models (LLMs) has enabled the community to create a vast collection of post-trained models adapted to specific tasks and domains. However, navigating and understanding these models remains challenging due to inconsistent metadata and unstructured repositories. We introduce Delta Activations, a method to represent finetuned models as vector embeddings by measuring shifts in their internal activations relative to a base model. This representation allows for effective clustering by domain and task, revealing structure in the model landscape. Delta Activations also demonstrate desirable properties: it is robust across finetuning settings and exhibits an additive property when finetuning datasets are mixed. In addition, we show that Delta Activations can embed tasks via few-shot finetuning, and further explore its use for model selection and merging. We hope Delta Activations can facilitate the practice of reusing publicly available models. Code is available at https://github.com/OscarXZQ/delta_activations.
强大的开源大型语言模型(LLM)的成功使得社区能够创建大量适应特定任务和领域的后训练模型。然而,由于元数据不一致和非结构化仓库,浏览和理解这些模型仍然具有挑战性。我们引入了Delta Activations,一种通过测量微调模型的内部激活相对于基础模型的移动来将其表示为向量嵌入的方法。这种表示方法允许按领域和任务进行有效聚类,揭示模型景观中的结构。Delta Activations还显示出理想的属性:它在微调设置中是稳健的,并且在混合微调数据集时表现出累加属性。此外,我们展示了Delta Activations可以通过几次微调嵌入任务,并进一步探索其在模型选择和合并中的使用。我们希望Delta Activations能够推动重新使用公开可用模型的实践。代码可在https://github.com/OscarXZQ/delta_activations获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
开源大型语言模型(LLM)的成功促使社区创建了众多针对特定任务和领域的后训练模型。然而,由于元数据的不一致性和仓库的结构化不足,理解和导航这些模型仍然具有挑战性。本文介绍Delta Activations,一种通过测量相对于基础模型的内部激活的变化来表示微调模型的方法,将其表示为向量嵌入。这种表示方法允许按领域和任务进行有效聚类,揭示模型景观中的结构。Delta Activations还具有令人满意的特性:它适用于各种微调设置,并在混合微调数据集时表现出可加性。此外,本文展示了Delta Activations可以通过少样本微调嵌入任务,并进一步探索其在模型选择和合并中的应用。本文希望Delta Activations能促进公开模型的复用实践。
Key Takeaways
- 开源大型语言模型(LLM)社区已经创建了众多针对特定任务和领域的后训练模型。
- 理解和导航这些模型由于元数据的不一致性和仓库的结构化不足而具有挑战性。
- Delta Activations是一种通过测量内部激活的变化来表示微调模型的方法,允许按领域和任务有效聚类。
- Delta Activations具有稳健性和可加性,适用于各种微调设置和混合数据集。
- Delta Activations可以通过少样本微调嵌入任务,并用于模型选择和合并。
- Delta Activations有望促进公开模型的复用实践。
点此查看论文截图







CANDY: Benchmarking LLMs’ Limitations and Assistive Potential in Chinese Misinformation Fact-Checking
Authors:Ruiling Guo, Xinwei Yang, Chen Huang, Tong Zhang, Yong Hu
The effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) to fact-check misinformation remains uncertain, despite their growing use. To this end, we present CANDY, a benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in fact-checking Chinese misinformation. Specifically, we curate a carefully annotated dataset of ~20k instances. Our analysis shows that current LLMs exhibit limitations in generating accurate fact-checking conclusions, even when enhanced with chain-of-thought reasoning and few-shot prompting. To understand these limitations, we develop a taxonomy to categorize flawed LLM-generated explanations for their conclusions and identify factual fabrication as the most common failure mode. Although LLMs alone are unreliable for fact-checking, our findings indicate their considerable potential to augment human performance when deployed as assistive tools in scenarios. Our dataset and code can be accessed at https://github.com/SCUNLP/CANDY
尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)的使用日益普遍,但它们核实误信息的有效性仍不确定。为此,我们推出了CANDY,这是一个旨在系统评估LLM在核实中文误信息方面的能力和局限性的基准测试。具体来说,我们精心标注了一个包含约20k实例的数据集。我们的分析表明,即使在采用思维链推理和少量提示的情况下,当前的LLM在生成准确的核实结论方面仍存在局限性。为了了解这些局限性,我们开发了一个分类法,对LLM生成的结论中的错误解释进行了分类,并确定了事实捏造是最常见的失败模式。虽然LLM单独用于核实信息并不可靠,但我们的研究结果表明,在作为辅助工具部署的情况下,它们对提高人类性能有很大的潜力。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/SCUNLP/CANDY访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Findings of EMNLP 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在检测中文错误信息方面的效能尚未明确。为此,我们推出CANDY基准测试,旨在系统地评估LLMs在事实核查方面的能力和局限性。我们精心标注了一个包含约2万个实例的数据集,分析表明,即使在采用思维链推理和少量提示的情况下,当前的LLMs在生成准确的事实核查结论方面仍存在局限性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在检测错误信息方面的效能尚不确定。
- CANDY基准测试旨在评估LLMs在事实核查中文错误信息方面的能力。
- 我们标注了一个包含约2万个实例的数据集用于评估。
- 当前LLMs在生成准确事实核查结论方面存在局限性。
- LLMs生成的解释存在缺陷,并分类了常见的失败模式。
- 事实编造是最常见的失败模式。
点此查看论文截图





Attn-Adapter: Attention Is All You Need for Online Few-shot Learner of Vision-Language Model
Authors:Phuoc-Nguyen Bui, Khanh-Binh Nguyen, Hyunseung Choo
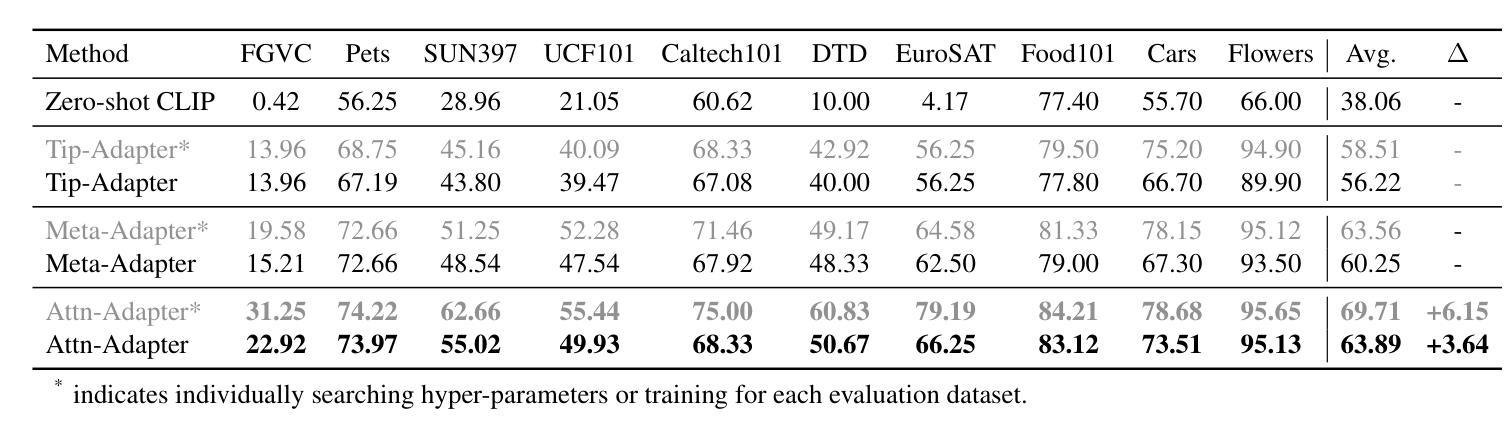
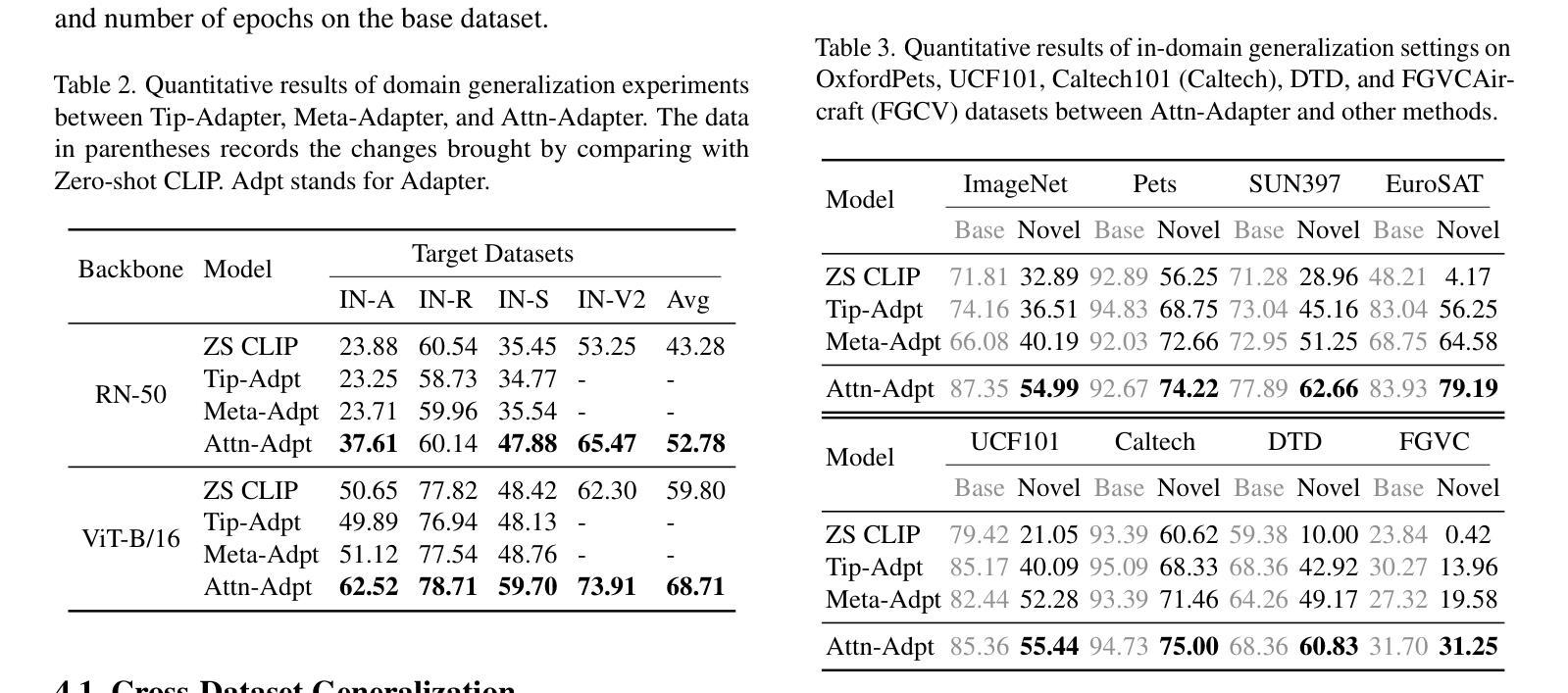
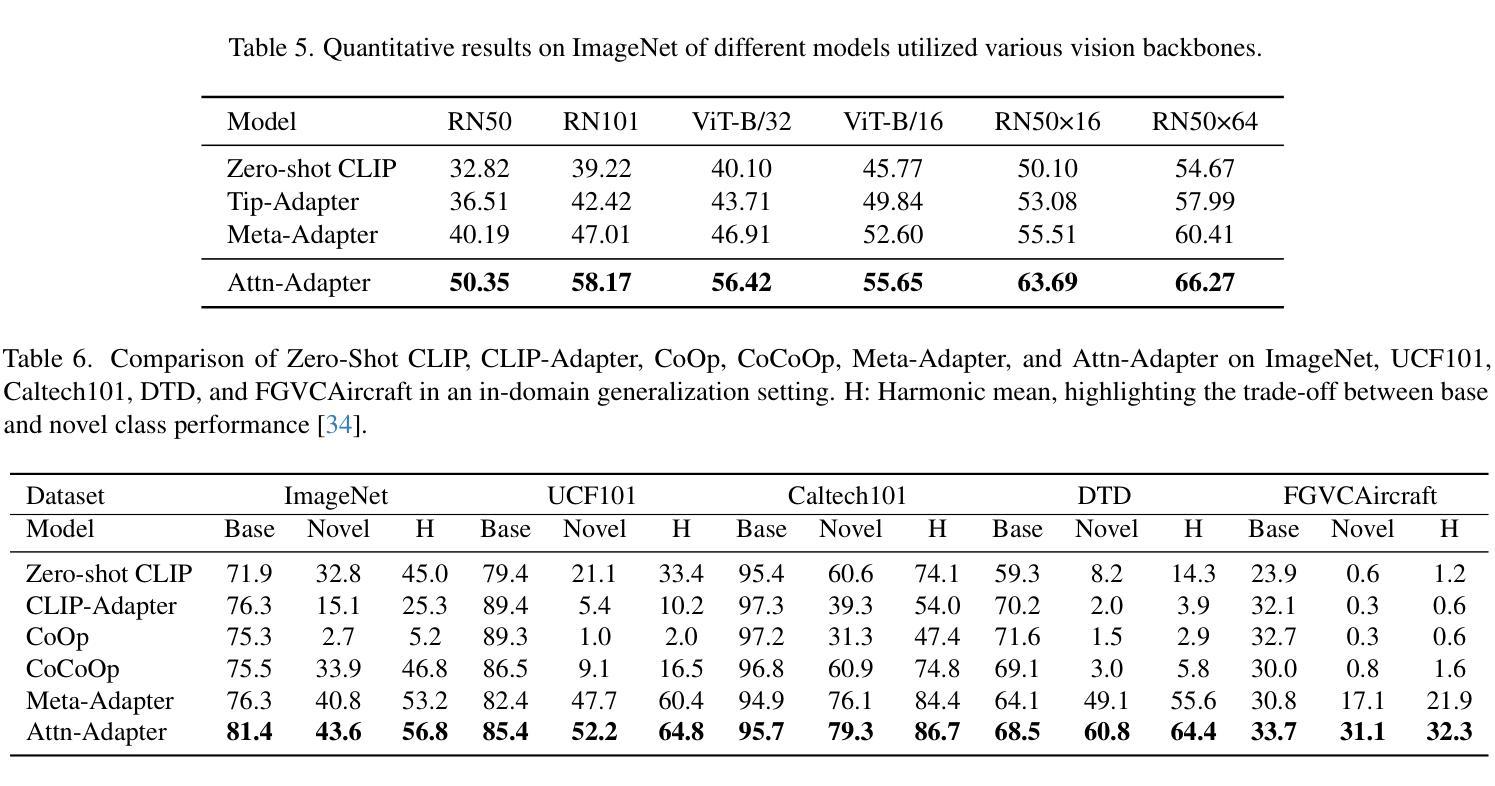
Contrastive vision-language models excel in zero-shot image recognition but face challenges in few-shot scenarios due to computationally intensive offline fine-tuning using prompt learning, which risks overfitting. To overcome these limitations, we propose Attn-Adapter, a novel online few-shot learning framework that enhances CLIP’s adaptability via a dual attention mechanism. Our design incorporates dataset-specific information through two components: the Memory Attn-Adapter, which refines category embeddings using support examples, and the Local-Global Attn-Adapter, which enriches image embeddings by integrating local and global features. This architecture enables dynamic adaptation from a few labeled samples without retraining the base model. Attn-Adapter outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cross-category and cross-dataset generalization, maintaining efficient inference and scaling across CLIP backbones.
对比视觉语言模型在零样本图像识别方面表现优异,但在小样本场景中面临挑战,这是由于使用提示学习进行离线精细调整计算量大,存在过拟合的风险。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了Attn-Adapter,这是一种新型在线小样本学习框架,通过双注意力机制提高CLIP的适应性。我们的设计通过两个组件融入了数据集特定信息:Memory Attn-Adapter使用支持样例细化类别嵌入,而Local-Global Attn-Adapter通过整合局部和全局特征丰富图像嵌入。该架构能够从未标注的样本中动态适应,无需重新训练基础模型。Attn-Adapter在跨类别和跨数据集泛化方面优于现有最新方法,同时保持高效的推理和跨CLIP骨干网的扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 - LIMIT Workshop
Summary
基于对比视觉语言模型在零样本图像识别中的卓越表现,针对其在小样本场景下面临的挑战,提出了Attn-Adapter这一全新的在线小样本学习框架。它通过双重注意力机制增强CLIP模型的适应性,通过Memory Attn-Adapter和Local-Global Attn-Adapter两个组件,利用支持实例和集成局部与全局特征的方式,实现数据集特定信息的融入。这一架构能够在少量标注样本的基础上实现动态适应,无需重新训练基础模型。Attn-Adapter在跨类别和跨数据集泛化方面表现出卓越性能,同时保持高效推理和跨CLIP骨架的扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 对比视觉语言模型在零样本图像识别上表现优秀,但在小样本场景下面临挑战。
- Attn-Adapter是一个在线小样本学习框架,旨在增强CLIP模型的适应性。
- Attn-Adapter通过双重注意力机制实现动态适应,无需重新训练基础模型。
- Memory Attn-Adapter通过支持实例优化类别嵌入。
- Local-Global Attn-Adapter通过集成局部和全局特征丰富图像嵌入。
- Attn-Adapter在跨类别和跨数据集泛化方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图



Singular Value Few-shot Adaptation of Vision-Language Models
Authors:Taha Koleilat, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP have shown impressive zero-shot and few-shot learning capabilities across diverse applications. However, adapting these models to new fine-grained domains remains difficult due to reliance on prompt engineering and the high cost of full model fine-tuning. Existing adaptation approaches rely on augmented components, such as prompt tokens and adapter modules, which could limit adaptation quality, destabilize the model, and compromise the rich knowledge learned during pretraining. In this work, we present \textbf{CLIP-SVD}, a novel \textit{multi-modal} and \textit{parameter-efficient} adaptation technique that leverages Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to modify the internal parameter space of CLIP without injecting additional modules. Specifically, we fine-tune only the singular values of the CLIP parameter matrices to rescale the basis vectors for domain adaptation while retaining the pretrained model. This design enables enhanced adaptation performance using only \textbf{0.04%} of the model’s total parameters and better preservation of its generalization ability. CLIP-SVD achieves state-of-the-art classification results on 11 natural and 10 biomedical datasets, outperforming previous methods in both accuracy and generalization under few-shot settings. Additionally, we leverage a natural language-based approach to analyze the effectiveness and dynamics of the CLIP adaptation to allow interpretability of CLIP-SVD. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/CLIP-SVD.
视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在多种应用中表现出了令人印象深刻的零样本和少样本学习能力。然而,将这些模型适应到新的细粒度领域仍然很困难,这主要是因为它们依赖于提示工程和高昂的完全模型微调成本。现有的适应方法依赖于增强组件,如提示令牌和适配器模块,这可能会限制适应质量,使模型不稳定,并可能破坏在预训练期间学到的丰富知识。在这项工作中,我们提出了\textbf{CLIP-SVD},这是一种新颖的多模态和参数有效的适应技术,它利用奇异值分解(SVD)来修改CLIP的内部参数空间,而无需注入额外的模块。具体来说,我们只微调CLIP参数矩阵的奇异值,以重新缩放用于领域适应的基向量,同时保留预训练模型。这种设计仅使用模型总参数的\textbf{0.04%}就能实现增强的适应性能,并更好地保持其泛化能力。CLIP-SVD在11个自然和10个生物医学数据集上实现了最先进的分类结果,在少样本设置下在准确性和泛化方面均优于以前的方法。此外,我们还利用基于自然语言的方法来分析CLIP适应的有效性和动态性,以实现CLIP-SVD的可解释性。代码可在https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/CLIP-SVD上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 8 tables
Summary
本文提出了基于奇异值分解(SVD)的CLIP模型适应新方法——CLIP-SVD。该方法利用SVD修改CLIP的内部参数空间,实现多模态和参数高效的模型适应。通过微调CLIP参数矩阵的奇异值来调整基础向量,以适应新领域,同时保留预训练模型的丰富知识。该方法仅使用模型总参数的0.04%,实现优秀的适应性能并保持良好的泛化能力。CLIP-SVD在多种数据集上取得了最先进的分类结果,并在少样本设置下展现出卓越的性能和泛化能力。此外,本文还采用自然语言分析方法研究CLIP适应的有效性及其动态变化,为CLIP-SVD提供可解释性。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP-SVD是一种新型的CLIP模型适应方法,利用奇异值分解(SVD)修改模型内部参数空间,实现多模态和参数高效的适应。
- 该方法通过微调CLIP参数矩阵的奇异值来适应新领域,同时保留预训练模型的丰富知识,实现优秀的适应性能并保持良好的泛化能力。
- CLIP-SVD使用仅模型总参数的0.04%,可增强适应性能同时保持模型的泛化能力。
- CLIP-SVD在多种数据集上取得了最先进的分类结果,包括自然和生物医学数据集。
点此查看论文截图



Are We SOLID Yet? An Empirical Study on Prompting LLMs to Detect Design Principle Violations
Authors:Fatih Pehlivan, Arçin Ülkü Ergüzen, Sahand Moslemi Yengejeh, Mayasah Lami, Anil Koyuncu
Traditional static analysis methods struggle to detect semantic design flaws, such as violations of the SOLID principles, which require a strong understanding of object-oriented design patterns and principles. Existing solutions typically focus on individual SOLID principles or specific programming languages, leaving a gap in the ability to detect violations across all five principles in multi-language codebases. This paper presents a new approach: a methodology that leverages tailored prompt engineering to assess LLMs on their ability to detect SOLID violations across multiple languages. We present a benchmark of four leading LLMs-CodeLlama, DeepSeekCoder, QwenCoder, and GPT-4o Mini-on their ability to detect violations of all five SOLID principles. For this evaluation, we construct a new benchmark dataset of 240 manually validated code examples. Using this dataset, we test four distinct prompt strategies inspired by established zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought techniques to systematically measure their impact on detection accuracy. Our emerging results reveal a stark hierarchy among models, with GPT-4o Mini decisively outperforming others, yet even struggles with challenging principles like DIP. Crucially, we show that prompt strategy has a dramatic impact, but no single strategy is universally best; for instance, a deliberative ENSEMBLE prompt excels at OCP detection while a hint-based EXAMPLE prompt is superior for DIP violations. Across all experiments, detection accuracy is heavily influenced by language characteristics and degrades sharply with increasing code complexity. These initial findings demonstrate that effective, AI-driven design analysis requires not a single best model, but a tailored approach that matches the right model and prompt to the specific design context, highlighting the potential of LLMs to support maintainability through AI-assisted code analysis.
传统静态分析方法在检测语义设计缺陷方面存在困难,如违反SOLID原则等,这需要深入理解面向对象的设计模式和原则。现有解决方案通常专注于单个SOLID原则或特定编程语言,因此在多语言代码库中的所有五个原则违反检测方面存在空白。本文提出了一种新方法:一种利用定制提示工程来评估大型语言模型在多种语言下检测SOLID违反能力的方法。我们展示了四个领先的大型语言模型CodeLlama、DeepSeekCoder、QwenCoder和GPT-4o Mini在检测所有五个SOLID原则违反方面的能力。为此评估,我们构建了包含240个手动验证的代码示例的新基准数据集。使用该数据集,我们测试了四种不同的提示策略,这些策略灵感来自于已建立的零样本、少样本和思维链技术,以系统地测量它们对检测准确率的影响。我们的初步结果揭示了模型之间的鲜明层次结构,GPT-4o Mini在性能方面明显超越了其他模型,但在DIP等挑战性原理方面仍然面临困难。关键的是,我们表明提示策略具有巨大影响,但没有一种单一策略是普遍适用的最佳策略;例如,一个深思熟虑的ENSEMBL提示在OCP检测方面表现出色,而一个基于提示的EXAMPLE提示在DIP违规方面更胜一筹。在所有实验中,检测准确率受到语言特性的强烈影响,随着代码复杂性的增加,准确率急剧下降。这些初步结果表明,有效、AI驱动的设计分析需要一种定制的方法,该方法将正确的模型和提示与特定的设计上下文相匹配,突显了大型语言模型在通过AI辅助代码分析支持可维护性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ASE2025
摘要
本研究针对传统静态分析方法在语义设计缺陷检测中的不足,提出了一种新的方法。该方法利用定制提示工程评估大型语言模型在多语言代码库中检测SOLID原则违反的能力。本研究对四款领先的LLMs-CodeLlama、DeepSeekCoder、QwenCoder和GPT-4o Mini进行了评估,构建了一个包含240个手动验证的代码示例的新基准数据集,并测试了四种不同的提示策略。结果显示,GPT-4o Mini表现最佳,但仍面临一些挑战。提示策略对检测效果有很大影响,但没有一种策略是普遍适用的。总体而言,语言特性对检测结果有很大影响,随着代码复杂性的增加,检测精度会急剧下降。这些初步结果表明,有效的AI驱动设计分析需要匹配特定设计上下文的定制方法,突显了大型语言模型在支持可维护性方面的潜力。
关键见解
- 传统静态分析方法在检测语义设计缺陷(如SOLID原则违反)方面存在困难,需要深入理解面向对象的设计模式和原则。
- 现有解决方案主要关注单个SOLID原则或特定编程语言,缺乏在多语言代码库中检测所有五个原则违反的能力。
- 本研究提出了一种新的方法,利用定制提示工程评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在检测SOLID原则违反方面的能力。
- 对四款领先的LLMs进行了评估,发现GPT-4o Mini在检测SOLID原则违反方面表现最佳,但仍面临一些挑战。
- 提示策略对检测效果有很大影响,没有一种策略是普遍适用的。
- 语言特性和代码复杂性对检测结果有很大影响,随着代码复杂性的增加,检测精度会急剧下降。
点此查看论文截图



SPENet: Self-guided Prototype Enhancement Network for Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Chao Fan, Xibin Jia, Anqi Xiao, Hongyuan Yu, Zhenghan Yang, Dawei Yang, Hui Xu, Yan Huang, Liang Wang
Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation (FSMIS) aims to segment novel classes of medical objects using only a few labeled images. Prototype-based methods have made significant progress in addressing FSMIS. However, they typically generate a single global prototype for the support image to match with the query image, overlooking intra-class variations. To address this issue, we propose a Self-guided Prototype Enhancement Network (SPENet). Specifically, we introduce a Multi-level Prototype Generation (MPG) module, which enables multi-granularity measurement between the support and query images by simultaneously generating a global prototype and an adaptive number of local prototypes. Additionally, we observe that not all local prototypes in the support image are beneficial for matching, especially when there are substantial discrepancies between the support and query images. To alleviate this issue, we propose a Query-guided Local Prototype Enhancement (QLPE) module, which adaptively refines support prototypes by incorporating guidance from the query image, thus mitigating the negative effects of such discrepancies. Extensive experiments on three public medical datasets demonstrate that SPENet outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods, achieving superior performance.
少量医疗图像分割(FSMIS)旨在仅使用少量标记图像对新型医疗对象进行分割。基于原型的方法在解决FSMIS方面取得了显著进展。然而,它们通常只为支持图像生成一个全局原型,以与查询图像进行匹配,从而忽略了类内变化。为了解决此问题,我们提出了自引导原型增强网络(SPENet)。具体来说,我们引入了一个多层次原型生成(MPG)模块,该模块通过同时生成全局原型和自适应数量的局部原型,实现了支持图像和查询图像之间的多粒度测量。此外,我们观察到支持图像中的所有局部原型并不都有利于匹配,尤其是在支持图像和查询图像之间存在显著差异时。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了查询引导局部原型增强(QLPE)模块,该模块通过融入查询图像的指导来自适应地优化支持原型,从而减轻了这种差异带来的负面影响。在三个公共医疗数据集上的大量实验表明,SPENet优于现有的最先进方法,实现了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by MICCAI2025
Summary
本文介绍了Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation(FSMIS)的目标是利用少量标注图像对新型医疗对象进行分割。针对基于原型的方法在生成单一全局原型时忽略类内变化的问题,提出了Self-guided Prototype Enhancement Network(SPENet)。该网络包括Multi-level Prototype Generation(MPG)模块和Query-guided Local Prototype Enhancement(QLPE)模块,分别实现多粒度测量和自适应优化支持原型。实验证明,SPENet在三个公开医疗数据集上优于现有最先进的方法,实现了优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation (FSMIS) 旨在使用少量标注图像对新型医疗对象进行分割。
- 现有基于原型的方法忽略类内变化,生成单一全局原型。
- Self-guided Prototype Enhancement Network (SPENet) 引入Multi-level Prototype Generation (MPG) 模块,实现多粒度测量,同时生成全局和局部原型。
- SPENet通过Query-guided Local Prototype Enhancement (QLPE) 模块自适应优化支持原型,减轻支持图像与查询图像之间的差异带来的负面影响。
- SPENet在三个公开医疗数据集上实现优越性能,优于现有最先进方法。
- 多粒度测量和自适应优化是SPENet的两个关键创新点。
点此查看论文截图



Advancing Minority Stress Detection with Transformers: Insights from the Social Media Datasets
Authors:Santosh Chapagain, Cory J Cascalheira, Shah Muhammad Hamdi, Soukaina Filali Boubrahimi, Jillian R. Scheer
Individuals from sexual and gender minority groups experience disproportionately high rates of poor health outcomes and mental disorders compared to their heterosexual and cisgender counterparts, largely as a consequence of minority stress as described by Meyer’s (2003) model. This study presents the first comprehensive evaluation of transformer-based architectures for detecting minority stress in online discourse. We benchmark multiple transformer models including ELECTRA, BERT, RoBERTa, and BART against traditional machine learning baselines and graph-augmented variants. We further assess zero-shot and few-shot learning paradigms to assess their applicability on underrepresented datasets. Experiments are conducted on the two largest publicly available Reddit corpora for minority stress detection, comprising 12,645 and 5,789 posts, and are repeated over five random seeds to ensure robustness. Our results demonstrate that integrating graph structure consistently improves detection performance across transformer-only models and that supervised fine-tuning with relational context outperforms zero and few-shot approaches. Theoretical analysis reveals that modeling social connectivity and conversational context via graph augmentation sharpens the models’ ability to identify key linguistic markers such as identity concealment, internalized stigma, and calls for support, suggesting that graph-enhanced transformers offer the most reliable foundation for digital health interventions and public health policy.
来自性少数和性别少数群体的个体在健康结果不良和心理健康障碍方面的比例明显高于其异性恋和顺性别群体,这很大程度上是由于Meyer(2003)提出的少数群体压力模型所描述的原因。本研究首次全面评估了基于转换器的架构在检测在线对话中的少数群体压力方面的表现。我们对包括ELECTRA、BERT、RoBERTa和BART在内的多种转换器模型进行了基准测试,并与传统的机器学习方法和图形增强变体进行了比较。我们进一步评估了零样本学习和少样本学习范式,以评估它们在代表性不足的数据集上的适用性。实验是在两个用于少数群体压力检测的最大的公开可用的Reddit语料库上进行的,包含12645个和5789个帖子,并且为了确保稳健性,实验重复了五次随机种子。结果表明,整合图形结构可以持续提高检测性能,并且监督微调与关系上下文相比零样本和少样本方法更具优势。理论分析表明,通过图形增强建模社会连通性和对话上下文可以加强模型识别关键语言标记的能力,如身份隐瞒、内在耻辱感和寻求支持等,这表明图形增强的转换器提供了最可靠的数字健康干预和公共卫生政策的基石。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in Social Network Analysis and Mining Journal (SNAM)
Summary
本文研究了基于Transformer架构的模型在检测网络言论中少数群体压力的应用,并与传统的机器学习和图形增强变体进行了比较。实验在最大的Reddit数据集上进行,结果表明整合图形结构能提高检测性能,监督微调关系上下文优于零和少镜头方法。这表明图形增强Transformer为数字健康干预和公共卫生政策提供了最可靠的基础。
Key Takeaways
- 少数群体经历更高的不良健康结果和心理健康障碍的比例。
- 此研究首次全面评估了基于Transformer的架构来检测网络言论中的少数群体压力。
- 研究对比了ELECTRA、BERT、RoBERTa和BART等多个Transformer模型。
- 实验在最大的Reddit数据集上进行,涉及12,645和5,789篇帖子,且重复了五次随机种子以确保稳健性。
- 整合图形结构能显著提高检测性能。
- 监督微调关系上下文的方法优于零样本和少样本学习方法。
点此查看论文截图


RS-OOD: A Vision-Language Augmented Framework for Out-of-Distribution Detection in Remote Sensing
Authors:Yingrui Ji, Jiansheng Chen, Jingbo Chen, Anzhi Yue, Chenhao Wang, Kai Li, Yao Zhu
Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection represents a critical challenge in remote sensing applications, where reliable identification of novel or anomalous patterns is essential for autonomous monitoring, disaster response, and environmental assessment. Despite remarkable progress in OOD detection for natural images, existing methods and benchmarks remain poorly suited to remote sensing imagery due to data scarcity, complex multi-scale scene structures, and pronounced distribution shifts. To this end, we propose RS-OOD, a novel framework that leverages remote sensing-specific vision-language modeling to enable robust few-shot OOD detection. Our approach introduces three key innovations: spatial feature enhancement that improved scene discrimination, a dual-prompt alignment mechanism that cross-verifies scene context against fine-grained semantics for spatial-semantic consistency, and a confidence-guided self-training loop that dynamically mines pseudo-labels to expand training data without manual annotation. RS-OOD consistently outperforms existing methods across multiple remote sensing benchmarks and enables efficient adaptation with minimal labeled data, demonstrating the critical value of spatial-semantic integration.
在遥感应用中,离群分布(OOD)检测是一个关键挑战。在自主监控、灾害响应和环境评估中,可靠地识别新颖或异常模式至关重要。尽管在自然图像中的离群分布检测取得了显著进展,但由于数据稀缺、复杂的多尺度场景结构和明显的分布偏移,现有方法和基准测试对于遥感图像仍不太适合。为此,我们提出了RS-OOD,这是一个利用遥感特定视觉语言建模的新框架,以实现健壮的少镜头离群分布检测。我们的方法引入了三个关键创新点:空间特征增强,提高场景鉴别能力;双提示对齐机制,通过场景上下文与精细粒度语义的交叉验证实现空间语义一致性;以及置信度引导的自训练循环,动态挖掘伪标签以扩展训练数据而无需手动注释。RS-OOD在多个遥感基准测试中始终优于现有方法,并在少量标注数据下实现了有效的适应,证明了空间语义集成的关键价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
远程遥感中异常检测是一大挑战,该论文提出了一种针对遥感影像的少样本异常检测新框架RS-OOD,该框架具有三大创新点:增强空间特征以提高场景鉴别能力,通过双提示对齐机制进行场景上下文与精细语义的空间语义一致性校验,以及通过置信度引导的自训练循环动态挖掘伪标签来扩充训练数据且无需手动标注。该框架在多遥感数据集上表现优于现有方法,在少量标签数据的情况下也有良好适应能力。
Key Takeaways
- 在遥感应用中,新型或异常模式的可靠识别是关键的挑战,对自动监控、灾害响应和环境评估至关重要。
- RS-OOD框架针对遥感影像的少样本异常检测提出了三大创新点。
- 空间特征增强提高了场景的鉴别能力。
- 双提示对齐机制实现了场景上下文与精细语义的空间语义一致性校验。
- 通过置信度引导的自训练循环可动态挖掘伪标签以扩充训练数据。
- RS-OOD在多个遥感数据集上表现出超越现有方法的性能。
点此查看论文截图


DroneSR: Rethinking Few-shot Thermal Image Super-Resolution from Drone-based Perspective
Authors:Zhipeng Weng, Xiaopeng Liu, Ce Liu, Xingyuan Guo, Yukai Shi, Liang Lin
Although large scale models achieve significant improvements in performance, the overfitting challenge still frequently undermines their generalization ability. In super resolution tasks on images, diffusion models as representatives of generative models typically adopt large scale architectures. However, few-shot drone-captured infrared training data frequently induces severe overfitting in large-scale architectures. To address this key challenge, our method proposes a new Gaussian quantization representation learning method oriented to diffusion models that alleviates overfitting and enhances robustness. At the same time, an effective monitoring mechanism tracks large scale architectures during training to detect signs of overfitting. By introducing Gaussian quantization representation learning, our method effectively reduces overfitting while maintaining architecture complexity. On this basis, we construct a multi source drone-based infrared image benchmark dataset for detection and use it to emphasize overfitting issues of large scale architectures in few sample, drone-based diverse drone-based image reconstruction scenarios. To verify the efficacy of the method in mitigating overfitting, experiments are conducted on the constructed benchmark. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing super resolution approaches and significantly mitigates overfitting of large scale architectures under complex conditions. The code and DroneSR dataset will be available at: https://github.com/wengzp1/GARLSR.
虽然大规模模型在性能上取得了显著改进,但过拟合挑战仍然经常破坏其泛化能力。在图像超分辨率任务中,以扩散模型为代表的生成模型通常采用大规模架构。然而,在无人机捕获的红外训练数据中,少量数据常常导致大规模架构出现过拟合现象。为了应对这一关键挑战,我们的方法提出了一种面向扩散模型的新型高斯量化表示学习方法,该方法可以缓解过拟合现象并增强模型的稳健性。同时,有效的监控机制可以在训练过程中跟踪大规模架构,以检测过拟合的迹象。通过引入高斯量化表示学习,我们的方法在保持架构复杂性的同时,有效地减少了过拟合现象。在此基础上,我们构建了一个基于多源无人机的红外图像基准数据集,用于检测,并强调在少量样本、基于无人机的多样化无人机图像重建场景中大规模架构的过拟合问题。为了验证该方法在缓解过拟合方面的有效性,我们在构建的基准数据集上进行了实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法优于现有的超分辨率方法,并在复杂条件下显著缓解了大规模架构的过拟合问题。代码和数据集将公布在:https://github.com/wengzp1/GARLSR。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大模型虽然在性能上取得了显著的提升,但过拟合问题仍然频繁地影响了它们的泛化能力。针对超分辨率图像任务中,大型架构在无人机捕获的红外训练数据上经常出现严重过拟合的问题,本文提出了一种面向扩散模型的高斯量化表示学习方法,以减轻过拟合并增强稳健性。同时,通过有效的监控机制在训练过程中跟踪大型架构,以检测过拟合的迹象。引入高斯量化表示学习后,本文方法在保持架构复杂性的同时,有效地减少了过拟合。基于此,我们构建了一个用于检测的多源无人机红外图像基准数据集,并强调在少数样本、基于无人机的多样化图像重建场景中大型架构的过拟合问题。实验结果表明,我们的方法在减轻过拟合方面优于现有的超分辨率方法,并在复杂条件下显著减轻了大型架构的过拟合问题。
Key Takeaways
- 大型模型在性能提升的同时面临过拟合问题,影响其泛化能力。
- 扩散模型作为生成模型的代表,在图像超分辨率任务中常采用大型架构。
- 无人机捕获的红外训练数据对大型架构经常导致严重的过拟合。
- 提出了一种新的高斯量化表示学习方法,面向扩散模型,以减轻过拟合并增强稳健性。
- 引入有效监控机制,在训练过程中跟踪大型架构,以检测过拟合迹象。
- 高斯量化表示学习方法在减少过拟合的同时保持了架构的复杂性。
点此查看论文截图





Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation via Ordinary Differential Equations over Time Intervals
Authors:Huan Ni, Qingshan Liu, Xiaonan Niu, Danfeng Hong, Lingli Zhao, Haiyan Guan
Cross-domain few-shot segmentation (CD-FSS) not only enables the segmentation of unseen categories with very limited samples, but also improves cross-domain generalization ability within the few-shot segmentation framework. Currently, existing CD-FSS studies typically design multiple independent modules to enhance the cross-domain generalization ability of feature representations. However, the independence among these modules hinders the effective flow of knowledge, making it difficult to fully leverage their collective potential. In contrast, this paper proposes an all-in-one module based on ordinary differential equations and Fourier transform, resulting in a structurally concise method–Few-Shot Segmentation over Time Intervals (FSS-TIs). FSS-TIs assumes the existence of an ODE relationship between the spectra (including amplitude and phase spectra) of domain-specific features and domain-agnostic features. This ODE formulation yields an iterative transformation process along a sequence of time intervals, while simultaneously applying affine transformations with randomized perturbations to the spectra. In doing so, the exploration of domain-agnostic feature representation spaces and the simulation of diverse potential target-domain distributions are reformulated as an optimization process over the intrinsic parameters of the ODE. Moreover, we strictly constrain the support-sample selection during target-domain fine-tuning so that it is consistent with the requirements of real-world few-shot segmentation tasks. For evaluation, we introduce five datasets from substantially different domains and define two sets of cross-domain few-shot segmentation tasks to comprehensively analyze the performance of FSS-TIs. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of FSS-TIs over existing CD-FSS methods, and in-depth ablation studies further validate the cross-domain adaptability of FSS-TIs.
跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)不仅能够在非常有限的样本下实现对未见类别的分割,而且还提高了小样本分割框架内的跨域泛化能力。目前,现有的CD-FSS研究通常设计多个独立模块来增强特征表示的跨域泛化能力。然而,这些模块的独立性阻碍了知识的有效流动,使得难以充分利用它们的集体潜力。相比之下,本文提出了一个基于常微分方程和傅里叶变换的全方位模块,从而得到了一种结构简洁的方法——基于时间间隔的小样本分割(FSS-TIs)。FSS-TIs假设特定领域的特征光谱(包括振幅和相位光谱)与领域通用的特征之间存在常微分方程关系。该常微分方程的公式化产生了一个沿时间间隔序列的迭代转换过程,同时光谱应用了带有随机扰动的仿射变换。通过这种方式,领域通用的特征表示空间的探索和各种潜在目标域分布的模拟被重新表述为常微分方程的内在参数的优化过程。此外,我们严格限制了目标域微调过程中的支持样本选择,使其符合现实世界中少量样本分割任务的要求。为了评估性能,我们从不同领域引入了五个数据集,并定义了两套跨域小样本分割任务来全面分析FSS-TIs的性能。实验结果证明了FSS-TIs相较于现有CD-FSS方法的优越性,深入的消融研究进一步验证了FSS-TIs的跨域适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了跨域小样本分割(CD-FSS)的挑战,并指出传统方法多采用多个独立模块提升跨域泛化能力,但这种方法存在知识流通不畅的问题。针对此,本文提出了一种基于常微分方程和傅里叶变换的全合一模块方法——FSS-TIs。该方法通过常微分方程(ODE)建模域特定特征与域通用特征之间的光谱关系,并沿时间序列进行迭代转换。实验证明,FSS-TIs在跨域小样本分割任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- CD-FSS面临通过有限样本进行未见类别分割以及提升跨域泛化能力的挑战。
- 传统CD-FSS研究通过设计多个独立模块增强跨域泛化能力,但存在知识流通不畅的问题。
- FSS-TIs方法基于常微分方程和傅里叶变换提出全合一模块,使方法更简洁有效。
- FSS-TIs假设域特定特征和域通用特征之间存在ODE关系,并通过迭代转换沿时间序列优化特征表示。
- 严格约束目标域微调时的支持样本选择,以符合真实世界小样本分割任务的要求。
- 在五个不同领域的数据集上进行了评估,定义了两套跨域小样本分割任务,证明了FSS-TIs的优越性。
点此查看论文截图


Analysis of Error Sources in LLM-based Hypothesis Search for Few-Shot Rule Induction
Authors:Aishni Parab, Hongjing Lu, Ying Nian Wu, Sumit Gulwani
Inductive reasoning enables humans to infer abstract rules from limited examples and apply them to novel situations. In this work, we compare an LLM-based hypothesis search framework with direct program generation approaches on few-shot rule induction tasks. Our findings show that hypothesis search achieves performance comparable to humans, while direct program generation falls notably behind. An error analysis reveals key bottlenecks in hypothesis generation and suggests directions for advancing program induction methods. Overall, this paper underscores the potential of LLM-based hypothesis search for modeling inductive reasoning and the challenges in building more efficient systems.
归纳推理使人类能够从有限的例子中推断出抽象规则,并将其应用到新情境中。在这项工作中,我们比较了基于LLM的假设搜索框架和直接程序生成方法在少量归纳推理任务上的表现。我们的研究结果表明,假设搜索的表现与人类相当,而直接程序生成的表现则明显落后。通过错误分析,我们揭示了假设生成的关键瓶颈,并为推进程序归纳方法提供了方向。总的来说,这篇论文强调了基于LLM的假设搜索在模拟归纳推理方面的潜力,以及构建更高效系统的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is the preprint version corresponding to our NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on Multimodal Algorithmic Reasoning submission
Summary
本文探讨了基于LLM的假设搜索框架与直接程序生成方法在少样本规则归纳任务中的比较。研究发现,假设搜索的性能与人类相当,而直接程序生成则明显落后。误差分析揭示了假设生成的关键瓶颈,为推进程序归纳方法提供了方向。总体而言,本文突出了LLM假设搜索在模拟归纳推理方面的潜力以及构建更高效系统所面临的挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 归纳推理能从有限例子中推断出抽象规则并应用于新情境。
- LLM-based假设搜索框架在少样本规则归纳任务中的性能与人类相当。
- 直接程序生成方法在少样本规则归纳任务中表现较差。
- 误差分析揭示了假设生成过程中的关键瓶颈。
- LLM-based假设搜索具有建模归纳推理的潜力。
- 构建更高效的系统是当前的挑战。
点此查看论文截图



Spotlighter: Revisiting Prompt Tuning from a Representative Mining View
Authors:Yutong Gao, Maoyuan Shao, Xinyang Huang, Chuang Zhu, Lijuan Sun, Yu Weng, Xuan Liu, Guoshun Nan
CLIP’s success has demonstrated that prompt tuning can achieve robust cross-modal semantic alignment for tasks ranging from open-domain recognition to fine-grained classification. However, redundant or weakly relevant feature components introduce noise and incur unnecessary computational costs. In this work, we propose Spotlighter, a lightweight token-selection framework that simultaneously enhances accuracy and efficiency in prompt tuning. Spotlighter evaluates each visual token’s activation from both sample-wise and semantic-wise perspectives and retains only the top-scoring tokens for downstream prediction. A class-specific semantic memory bank of learned prototypes refines this selection, ensuring semantic representativeness and compensating for discarded features. To further prioritize informative signals, we introduce a two-level ranking mechanism that dynamically weights token–prototype interactions. Across 11 few-shot benchmarks, Spotlighter outperforms CLIP by up to 11.19% in harmonic mean accuracy and achieves up to 0.8K additional FPS, with only 21 extra parameters. These results establish Spotlighter as an effective and scalable baseline for prompt tuning. Code for our method will be available at https://github.com/greatest-gourmet/Spotlighter.
CLIP的成功表明,提示调整可以实现从开放域识别到精细分类任务的稳健跨模态语义对齐。然而,冗余或弱相关的特征成分会引入噪声并产生不必要的计算成本。在这项工作中,我们提出了Spotlighter,这是一个轻量级的令牌选择框架,可以同时提高准确性和效率。Spotlighter从样本和语义两个角度评估每个视觉令牌的激活,仅保留得分最高的令牌进行下游预测。一个特定类别的语义记忆库中的学习原型可以优化此选择,确保语义代表性并补偿丢弃的特征。为了进一步优化信息信号,我们引入了一个两级排名机制,该机制可以动态地权衡令牌与原型之间的交互。在11个少样本基准测试中,Spotlighter的调和平均准确率比CLIP高出高达11.19%,并且实现了高达0.8K的额外FPS,仅有额外的21个参数。这些结果证明了Spotlighter在提示调整方面的有效性和可扩展性。我们的方法的相关代码将发布在:https://github.com/greatest-gourmet/Spotlighter上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as EMNLP 2025 Findings
Summary
本文介绍了CLIP在跨模态语义对齐任务中的成功应用,但也指出了冗余和弱相关特征所带来的问题。为解决这些问题,作者提出了Spotlighter框架,它通过选择关键的视觉令牌进行微调来提高准确性和效率。Spotlighter结合了样本和语义两个角度对视觉令牌进行评估,并保留得分最高的令牌用于下游预测。此外,通过引入类特定的语义记忆库和学习原型来完善令牌选择,以确保语义代表性和弥补丢失的特征。实验结果表明,Spotlighter在多个少样本基准测试上的表现优于CLIP,且具有良好的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP的成功证明了提示调整在跨模态语义对齐任务中的有效性。
- 冗余和弱相关特征可能导致噪声和不必要的计算成本。
- Spotlighter框架旨在提高准确性和效率,通过选择关键的视觉令牌进行微调。
- Spotlighter结合样本和语义角度评估视觉令牌,并保留得分最高的令牌。
- 类特定的语义记忆库和学习原型用于完善令牌选择,确保语义代表性。
- Spotlighter在多个少样本基准测试上的表现优于CLIP。
点此查看论文截图


Language-Aware Information Maximization for Transductive Few-Shot CLIP
Authors:Ghassen Baklouti, Maxime Zanella, Ismail Ben Ayed
Transductive few-shot learning has triggered an abundant literature focusing on vision-only models, but is still at a nascent stage within the recent context of foundational vision-language models (VLMs). Only a few recent methods addressed the problem, pointing to the potential of tranduction in VLMs and to the need for VLM-tailored methods. Building on this momentum, we leverage information-theoretic concepts and recent progress in parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), developing a highly competitive transductive few-shot CLIP method. Specifically, we introduce a novel Language-aware Information MaximizatiOn (LIMO) loss integrating three complementary terms: (i) the mutual information between the vision inputs and the textual class descriptions; (ii) a Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence penalizing deviation of the network’s probabilistic outputs from the text-driven zero-shot predictions; and (iii) a standard cross-entropy loss based on the labeled shots. Furthermore, we challenge the commonly followed fine-tuning practices in the context of transductive few-shot learning, and explore PEFT strategies, completely overlooked in this context. Surprisingly, we observe substantial boosts in performances, which points to the potential of adapting a subset of the model’s parameters in the transductive few-shot setting. We report comprehensive evaluations, which show that LIMO outperforms the very recent transductive few-shot CLIP methods by a large margin and yields significant gains over the best-performing inductive methods. Our code is publicly available at:[ \href{https://github.com/ghassenbaklouti/LIMO}{\text{here}} ]
转导式小样本学习已经引发了大量关于仅视觉模型的文献,但在基础视觉语言模型(VLMs)的最近背景下,它仍处于起步阶段。只有少数近期方法解决了这个问题,指出了VLMs中的翻译潜力以及针对VLM量身定制的方法的需求。在此基础上,我们利用信息论的概念和参数效率微调(PEFT)的最新进展,开发了一种极具竞争力的转导式小样本CLIP方法。具体来说,我们引入了一种新的语言感知信息最大化(LIMO)损失,融合了三项互补的条款:(i)视觉输入和文本类别描述之间的互信息;(ii)Kullback-Leibler(KL)散度惩罚网络概率输出与文本驱动零样本预测之间的偏差;(iii)基于有标签样本的标准交叉熵损失。此外,我们质疑转导式小样本学习背景下通常采用的微调实践,并探索在此背景下完全被忽视的PEFT策略。令人惊讶的是,我们观察到性能的大幅提升,这表明在转导式小样本设置中适应模型的部分参数具有潜力。我们报告了全面的评估,表明LIMO在最近的转导式小样本CLIP方法上具有很大优势,并且在最佳性能的归纳方法上也取得了显著收益。我们的代码可在[\url{https://github.com/ghassenbaklouti/LIMO}{此处}]公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了基于信息理论概念的转换少样本学习方法的研究。该研究针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的转换少样本学习问题,提出了一种新的语言感知信息最大化(LIMO)损失函数,并挑战了现有的微调实践。该研究观察到,通过调整部分模型参数进行转换少样本设置时,性能会显著提升。该研究公开的代码可供访问。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的转换少样本学习进行了深入研究。
- 提出了一种新的语言感知信息最大化(LIMO)损失函数,结合了三种互补的术语。
- 挑战了现有的微调实践,探索了参数效率微调(PEFT)策略在转换少样本学习中的应用。
- 通过调整模型的部分参数,观察到性能显著提升。
- LIMO损失函数在最近的转换少样本CLIP方法上取得了显著的优势。
- 与表现最佳的非转换方法相比,LIMO也取得了显著的收益。
点此查看论文截图


Summarize-Exemplify-Reflect: Data-driven Insight Distillation Empowers LLMs for Few-shot Tabular Classification
Authors:Yifei Yuan, Jiatong Li, Weijia Zhang, Mohammad Aliannejadi, Evangelos Kanoulas, Renjun Hu
Recent studies show the promise of large language models (LLMs) for few-shot tabular classification but highlight challenges due to the variability in structured data. To address this, we propose distilling data into actionable insights to enable robust and effective classification by LLMs. Drawing inspiration from human learning processes, we introduce InsightTab, an insight distillation framework guided by principles of divide-and-conquer, easy-first, and reflective learning. Our approach integrates rule summarization, strategic exemplification, and insight reflection through deep collaboration between LLMs and data modeling techniques. The obtained insights enable LLMs to better align their general knowledge and capabilities with the particular requirements of specific tabular tasks. We extensively evaluate InsightTab on nine datasets. The results demonstrate consistent improvement over state-of-the-art methods. Ablation studies further validate the principle-guided distillation process, while analyses emphasize InsightTab’s effectiveness in leveraging labeled data and managing bias.
最近的研究显示大型语言模型(LLM)在少量表格分类方面的潜力,但同时也强调了由于结构化数据变化多样所带来的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出将数据提炼成可操作的见解,以实现LLM的稳健和有效的分类。我们借鉴人类学习过程,引入了InsightTab,这是一个以分而治之、先易后难和反思学习原则为指导的见解提炼框架。我们的方法通过LLM和数据建模技术之间的深度合作,整合规则总结、战略例证和见解反思。所获得的见解使LLM能够更好地将其一般知识和能力与特定表格任务的具体要求相匹配。我们在九个数据集上广泛评估了InsightTab。结果表明,与最新技术相比,它表现出了一致的优势。消融研究进一步验证了原则指导的提炼过程的有效性,而分析则强调了InsightTab在利用标记数据和偏误管理方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 25 Findings
Summary:针对大型语言模型(LLM)在少样本表格分类中面临的挑战,如结构化数据的变化性问题,我们提出通过提炼数据为可操作性的见解来应对。通过借鉴人类学习过程的原则,我们推出InsightTab,一个由分而治之、易先行和反思学习原则引导的见解提炼框架。该框架通过规则总结、战略实例化和深度洞察反思,实现LLM与数据建模技术的深度合作。在九个数据集上的评估结果表明,InsightTab较最新方法具有持续的改进效果。消融研究进一步验证了原则指导的提炼过程的有效性,同时分析强调了InsightTab在利用标记数据和偏见管理方面的优势。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM在少样本表格分类任务面临结构化数据变化性的挑战。
- 提出InsightTab框架,整合规则总结、战略实例化和深度洞察反思。
- InsightTab框架借鉴了人类学习的原则,如分而治之、易先行和反思学习。
- InsightTab通过与数据建模技术的深度合作,使LLM更好地适应特定表格任务的要求。
- 在九个数据集上的评估显示,InsightTab较现有方法表现更优。
- 消融研究验证了原则指导的见解提炼过程的有效性。
点此查看论文截图






Few-Shot Neuro-Symbolic Imitation Learning for Long-Horizon Planning and Acting
Authors:Pierrick Lorang, Hong Lu, Johannes Huemer, Patrik Zips, Matthias Scheutz
Imitation learning enables intelligent systems to acquire complex behaviors with minimal supervision. However, existing methods often focus on short-horizon skills, require large datasets, and struggle to solve long-horizon tasks or generalize across task variations and distribution shifts. We propose a novel neuro-symbolic framework that jointly learns continuous control policies and symbolic domain abstractions from a few skill demonstrations. Our method abstracts high-level task structures into a graph, discovers symbolic rules via an Answer Set Programming solver, and trains low-level controllers using diffusion policy imitation learning. A high-level oracle filters task-relevant information to focus each controller on a minimal observation and action space. Our graph-based neuro-symbolic framework enables capturing complex state transitions, including non-spatial and temporal relations, that data-driven learning or clustering techniques often fail to discover in limited demonstration datasets. We validate our approach in six domains that involve four robotic arms, Stacking, Kitchen, Assembly, and Towers of Hanoi environments, and a distinct Automated Forklift domain with two environments. The results demonstrate high data efficiency with as few as five skill demonstrations, strong zero- and few-shot generalizations, and interpretable decision making.
模仿学习使得智能系统能够在最小监督下获得复杂的行为。然而,现有方法通常关注短期技能,需要大量数据集,并且在解决长期任务或在任务变化和分布转移中泛化时遇到困难。我们提出了一种新型的神经符号框架,该框架可以从少数技能演示中联合学习连续控制政策和符号域抽象。我们的方法将高级任务结构抽象为图形,通过回答集编程求解器发现符号规则,并使用扩散政策模仿学习训练低级控制器。高级查询器过滤出任务相关信息,使每个控制器专注于最小的观察空间和动作空间。我们的基于图形的神经符号框架能够捕获复杂的状态转换,包括非空间和时间关系,这些状态转换在有限演示数据集中往往无法被数据驱动学习或聚类技术发现。我们在涉及四个机械臂、堆叠、厨房、装配和汉诺塔环境的六个领域以及具有两个环境的独特自动化叉车领域验证了我们的方法。结果表明,在仅五个技能演示的情况下具有较高的数据效率,具有强大的零次和少次泛化能力,以及可解释的决策制定。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at CoRL 2025; to appear in PMLR
Summary
神经符号框架联合学习连续控制策略和符号域抽象,通过少量技能演示实现高效模仿学习。该方法抽象出高级任务结构为图,通过答案集编程求解器发现符号规则,并使用扩散策略模仿学习训练低级控制器。高级别过滤器会过滤出任务相关信息,使每个控制器专注于最小的观测和动作空间。该方法能捕捉复杂的状态转换,包括非空间和时间关系,在有限演示数据集上优于数据驱动学习或聚类技术。验证结果表明,该方法在多个领域具有高效的数据利用率、强大的零次和少次泛化能力,以及可解释性的决策制定。
Key Takeaways
- 神经符号框架结合了连续控制策略和符号域抽象的联合学习。
- 通过少量技能演示实现模仿学习。
- 方法包括任务结构的图抽象、符号规则的发现以及低级控制器的训练。
- 高级别过滤器有助于专注于最小的观测和动作空间。
- 该方法可以捕捉复杂的状态转换,包括非空间和时间关系。
- 验证结果展示了其高效数据利用率、强大的泛化能力。
- 该方法提供可解释的决策制定。
点此查看论文截图



WEBEYETRACK: Scalable Eye-Tracking for the Browser via On-Device Few-Shot Personalization
Authors:Eduardo Davalos, Yike Zhang, Namrata Srivastava, Yashvitha Thatigotla, Jorge A. Salas, Sara McFadden, Sun-Joo Cho, Amanda Goodwin, Ashwin TS, Gautam Biswas
With advancements in AI, new gaze estimation methods are exceeding state-of-the-art (SOTA) benchmarks, but their real-world application reveals a gap with commercial eye-tracking solutions. Factors like model size, inference time, and privacy often go unaddressed. Meanwhile, webcam-based eye-tracking methods lack sufficient accuracy, in particular due to head movement. To tackle these issues, we introduce We bEyeTrack, a framework that integrates lightweight SOTA gaze estimation models directly in the browser. It incorporates model-based head pose estimation and on-device few-shot learning with as few as nine calibration samples (k < 9). WebEyeTrack adapts to new users, achieving SOTA performance with an error margin of 2.32 cm on GazeCapture and real-time inference speeds of 2.4 milliseconds on an iPhone 14. Our open-source code is available at https://github.com/RedForestAi/WebEyeTrack.
随着人工智能的进步,新的眼动追踪方法已经超越了最先进的基准测试,但它们在现实世界的应用中却显示出与商业眼动追踪解决方案之间的差距。模型大小、推理时间和隐私等因素往往被忽视。同时,基于网络摄像头的眼动追踪方法由于缺乏足够的准确性,尤其是由于头部移动导致的。为了解决这些问题,我们推出了WebEyeTrack框架,它直接在浏览器中集成了轻量级的最新眼动追踪模型。它结合了基于模型的头部姿态估计和在设备上的小样本学习,只需极少数的校准样本(k < 9)。WebEyeTrack能够适应新用户,在GazeCapture上的误差范围为2.32厘米,具有实时推理速度,在iPhone 14上为2.4毫秒。我们的开源代码可在https://github.com/RedForestAi/WebEyeTrack找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures, 1 table
Summary
随着AI技术的发展,新的眼动追踪方法超越了现有技术基准,但其实际应用与商业眼动追踪解决方案之间存在差距。为解决模型大小、推理时间、隐私等问题,我们推出了WebEyeTrack框架,直接在浏览器中集成轻量级眼动追踪模型。它采用基于模型的头部姿态估计和少量样本(少于9个)的在线few-shot学习技术。WebEyeTrack能够适应新用户,在GazeCapture上实现误差范围仅为2.32厘米的高性能表现,并在iPhone 14上实现实时推理速度2.4毫秒。我们的开源代码可通过网址获取:https://github.com/RedForestAi/WebEyeTrack。
Key Takeaways
- 新眼动追踪方法超越现有技术基准,但实际应用与商业解决方案存在差距。
- WebEyeTrack框架旨在解决模型大小、推理时间、隐私等问题。
- WebEyeTrack直接在浏览器中集成轻量级眼动追踪模型。
- 框架采用基于模型的头部姿态估计和少量样本的在线few-shot学习技术。
- WebEyeTrack能够适应新用户,实现误差范围小和实时推理速度快的性能表现。
- WebEyeTrack在GazeCapture上的误差范围为2.32厘米。
点此查看论文截图





Bridging Language Gaps: Enhancing Few-Shot Language Adaptation
Authors:Philipp Borchert, Jochen De Weerdt, Marie-Francine Moens
The disparity in language resources poses a challenge in multilingual NLP, with high-resource languages benefiting from extensive data, while low-resource languages lack sufficient data for effective training. Our Contrastive Language Alignment with Prompting (CoLAP) method addresses this gap by integrating contrastive learning with cross-lingual representations, facilitating task-specific knowledge transfer from high-resource to lower-resource languages. The primary advantage of our approach is its data efficiency, enabling rapid adaptation to new languages and reducing the need for large labeled datasets. We conduct experiments with multilingual encoder-only and decoder-only language models on natural language understanding tasks, including natural language inference and relation extraction, evaluating performance across both high- and low-resource languages. Our results demonstrate that CoLAP outperforms few-shot cross-lingual transfer baselines and in-context learning, even with limited available data. This effectively narrows the cross-lingual performance gap, contributing to the development of more efficient multilingual NLP techniques.
语言资源的差异给多语言自然语言处理(NLP)带来了挑战,高资源语言受益于大量数据,而低资源语言则缺乏有效训练所需的数据。我们的对比语言对齐提示(CoLAP)方法通过结合对比学习与跨语言表示来解决这一问题,促进了从高资源语言到低资源语言的特定任务知识迁移。我们的方法的主要优势是数据效率高,能够快速适应新语言,减少了对大量标记数据集的需求。我们在自然语言理解任务上进行了实验,包括自然语言推理和关系抽取,评估了高资源和低资源语言的表现。实验结果表明,即使在有限的数据可用的情况下,CoLAP也优于少镜头跨语言迁移基线和内上下文学习。这有效地缩小了跨语言性能差距,为开发更有效的多语言NLP技术做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages
Summary
对比语言对齐提示方法(CoLAP)通过结合对比学习与跨语言表示,解决了多语种自然语言处理(NLP)中资源分布不均的问题。该方法优势在于数据效率高,能快速适应新语言并减少大量标注数据集的需求。实验证明,在包括自然语言推断和关系抽取等自然语言理解任务上,CoLAP在高低资源语言上的表现均优于少镜头跨语言转移基准线和上下文学习,即使数据有限。此方法有效缩小了跨语言性能差距,为开发更高效的多语种NLP技术做出贡献。
Key Takeaways
- 多语种NLP面临语言资源分布不均的挑战,高资源语言受益于大量数据,而低资源语言缺乏有效训练数据。
- CoLAP方法通过结合对比学习与跨语言表示,解决这一挑战。
- CoLAP方法的主要优势在于其数据高效性,能快速适应新语言并减少大量标注数据集的需求。
- CoLAP在多种自然语言理解任务上的表现均优于其他方法,包括自然语言推断和关系抽取。
- CoLAP在高低资源语言上的表现均很出色,缩小了跨语言性能差距。
- 实验证明了CoLAP方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图




Heterogeneous LLM Methods for Ontology Learning (Few-Shot Prompting, Ensemble Typing, and Attention-Based Taxonomies)
Authors:Aleksandra Beliaeva, Temurbek Rahmatullaev
We present a comprehensive system for addressing Tasks A, B, and C of the LLMs4OL 2025 challenge, which together span the full ontology construction pipeline: term extraction, typing, and taxonomy discovery. Our approach combines retrieval-augmented prompting, zero-shot classification, and attention-based graph modeling – each tailored to the demands of the respective task. For Task A, we jointly extract domain-specific terms and their ontological types using a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline. Training data was reformulated into a document to terms and types correspondence, while test-time inference leverages semantically similar training examples. This single-pass method requires no model finetuning and improves overall performance through lexical augmentation Task B, which involves assigning types to given terms, is handled via a dual strategy. In the few-shot setting (for domains with labeled training data), we reuse the RAG scheme with few-shot prompting. In the zero-shot setting (for previously unseen domains), we use a zero-shot classifier that combines cosine similarity scores from multiple embedding models using confidence-based weighting. In Task C, we model taxonomy discovery as graph inference. Using embeddings of type labels, we train a lightweight cross-attention layer to predict is-a relations by approximating a soft adjacency matrix. These modular, task-specific solutions enabled us to achieve top-ranking results in the official leaderboard across all three tasks. Taken together these strategies showcase the scalability, adaptability, and robustness of LLM-based architectures for ontology learning across heterogeneous domains. Code is available at: https://github.com/BelyaevaAlex/LLMs4OL-Challenge-Alexbek
我们针对LLMs4OL 2025挑战的A、B、C三项任务,构建了一个全面的系统,涵盖了整个本体构建流程:术语提取、类型划分和分类体系发现。我们的方法结合了检索增强提示、零样本分类和基于注意力的图形建模——每一项都是针对各自任务的需求量身定制的。针对A任务,我们使用检索增强生成(RAG)流程联合提取特定领域的术语及其本体类型。我们将训练数据重新格式化为文档与术语和类型之间的对应关系,而测试时的推理则利用语义相似的训练示例。这种单通道方法无需对模型进行微调,并通过词汇增强提高整体性能。B任务是为给定的术语分配类型,通过双重策略进行处理。在有限样本设置(对于有标签训练数据的领域)中,我们重复使用带有有限提示的RAG方案。在零样本设置(对于以前未见过的领域)中,我们使用一个零样本分类器,它结合了多个嵌入模型的余弦相似度得分,并使用基于置信度的加权方式。在C任务中,我们将分类体系发现建模为图形推理。我们使用类型标签的嵌入,训练一个轻量级的跨注意力层来预测“是-关系”(is-a relations),通过近似软邻接矩阵来实现。这些模块化、任务特定的解决方案使我们能够在所有三个任务中取得官方排行榜的顶尖成绩。这些策略相结合展示了LLM架构在不同领域进行本体学习的可扩展性、适应性和稳健性。相关代码可在:https://github.com/BelyaevaAlex/LLMs4OL-Challenge-Alexbek获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个全面的系统,针对LLMs4OL 2025挑战中的任务A、B和C,涵盖了整个本体构建流程:术语提取、类型标注和分类体系发现。该方法结合了检索增强提示、零样本分类和基于注意力的图形建模,每个任务都针对特定需求进行了定制。通过改革训练数据,利用语义相似训练示例,实现了无需模型微调的一次性通过方法,提高了整体性能。对于任务B的类型分配,采用双重策略,在少量样本场景下使用RAG方案,在零样本场景下使用结合多种嵌入模型的零样本分类器。任务C中的分类体系发现被建模为图形推断,使用类型标签的嵌入训练轻量级交叉注意力层,通过预测is-a关系进行建模。这些模块化的任务特定解决方案,使得我们在官方排行榜上实现了所有三个任务的首位排名。展示了LLM架构在大规模、适应性和稳健性方面的优势,适用于跨异构领域的本体学习。
Key Takeaways
- 系统全面应对LLMs4OL 2025挑战中的任务A、B和C,涵盖本体构建全流程。
- 结合检索增强提示、零样本分类和基于注意力的图形建模方法,针对各任务需求定制。
- 任务A采用基于检索增强生成(RAG)的管道联合提取领域特定术语及其本体类型。
- 任务B对类型分配采用双重策略,分别处理有标签和无标签领域的少量样本和零样本场景。
- 任务C将分类体系发现建模为图形推断,使用嵌入的交叉注意力层预测is-a关系。
- 实现所有任务在官方排行榜上的首位排名,证明了LLM架构在大规模、适应性和稳健性方面的优势。
点此查看论文截图



Few-Shot Connectivity-Aware Text Line Segmentation in Historical Documents
Authors:Rafael Sterzinger, Tingyu Lin, Robert Sablatnig
A foundational task for the digital analysis of documents is text line segmentation. However, automating this process with deep learning models is challenging because it requires large, annotated datasets that are often unavailable for historical documents. Additionally, the annotation process is a labor- and cost-intensive task that requires expert knowledge, which makes few-shot learning a promising direction for reducing data requirements. In this work, we demonstrate that small and simple architectures, coupled with a topology-aware loss function, are more accurate and data-efficient than more complex alternatives. We pair a lightweight UNet++ with a connectivity-aware loss, initially developed for neuron morphology, which explicitly penalizes structural errors like line fragmentation and unintended line merges. To increase our limited data, we train on small patches extracted from a mere three annotated pages per manuscript. Our methodology significantly improves upon the current state-of-the-art on the U-DIADS-TL dataset, with a 200% increase in Recognition Accuracy and a 75% increase in Line Intersection over Union. Our method also achieves an F-Measure score on par with or even exceeding that of the competition winner of the DIVA-HisDB baseline detection task, all while requiring only three annotated pages, exemplifying the efficacy of our approach. Our implementation is publicly available at: https://github.com/RafaelSterzinger/acpr_few_shot_hist.
文档数字分析的基础任务是文本行分割。然而,使用深度学习模型自动化此过程具有挑战性,因为它需要大量标注数据集,而对于历史文档,这些数据集通常不可用。此外,标注过程是一项劳动密集且成本高昂的任务,需要专业知识,这使得小样本学习成为减少数据需求的颇具前景的方向。在这项工作中,我们证明简单的小规模架构与拓扑感知损失函数相结合,比更复杂的替代方案更准确且更节省数据。我们将轻量级的UNet++与专为神经元形态开发的连通性感知损失相结合,该损失显式惩罚线状分裂和意外合并之类的结构错误。为了增加我们有限的数据量,我们在仅来自每份手稿的三页标注数据中提取的小块区域上进行训练。我们的方法在U-DIADS-TL数据集上大幅改进了当前最新技术,识别准确度提高了200%,线交集提高了75%。我们的方法还实现了与DIVA-HisDB基线检测任务竞赛获奖者相当的F-Measure分数,甚至有所超越,而这一切仅需要三页标注数据即可实现,这充分证明了我们的方法的有效性。我们的实现可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/RafaelSterzinger/acpr_few_shot_hist。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, accepted at ACPR2025
Summary
文本主要介绍了针对历史文档的数字分析中的文本行分割任务。文章指出深度学习模型自动化处理该任务的挑战在于缺乏大规模标注数据集,且标注过程需要专业知识和大量人力成本。该研究通过简单架构与拓扑感知损失函数来解决这一问题,实现了高准确性和数据效率。该研究使用轻量级UNet++与专为神经元形态开发的连接感知损失来惩罚结构错误,如线条断裂和意外合并。通过训练来自仅三页手稿的小块数据,该研究的方法在U-DIADS-TL数据集上显著提高了识别准确率,实现了线交并的75%增长。该研究的方法在DIVA-HisDB基线检测任务的比赛中与冠军表现相当,仅需三页标注数据便展现出方法的有效性。相关实现已公开于[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways
- 文本行分割是数字分析文档的基础任务。
- 深度学习模型自动化处理文本行分割面临缺乏大规模标注数据集和标注过程复杂的问题。
- 研究采用简单架构与拓扑感知损失函数来解决这一问题,表现出高准确性和数据效率。
- 研究使用轻量级UNet++与连接感知损失来处理神经元形态的结构错误。
- 通过训练仅来自三页手稿的小块数据,该研究的方法在U-DIADS-TL数据集上显著提高识别准确率。
- 该研究的方法在DIVA-HisDB基线检测任务中表现优秀,与冠军表现相当,且仅需少量标注数据。
点此查看论文截图



Few-shot Unknown Class Discovery of Hyperspectral Images with Prototype Learning and Clustering
Authors:Chun Liu, Chen Zhang, Zhuo Li, Zheng Li, Wei Yang
Open-set few-shot hyperspectral image (HSI) classification aims to classify image pixels by using few labeled pixels per class, where the pixels to be classified may be not all from the classes that have been seen. To address the open-set HSI classification challenge, current methods focus mainly on distinguishing the unknown class samples from the known class samples and rejecting them to increase the accuracy of identifying known class samples. They fails to further identify or discovery the unknow classes among the samples. This paper proposes a prototype learning and clustering method for discoverying unknown classes in HSIs under the few-shot environment. Using few labeled samples, it strives to develop the ability of infering the prototypes of unknown classes while distinguishing unknown classes from known classes. Once the unknown class samples are rejected by the learned known class classifier, the proposed method can further cluster the unknown class samples into different classes according to their distance to the inferred unknown class prototypes. Compared to existing state-of-the-art methods, extensive experiments on four benchmark HSI datasets demonstrate that our proposed method exhibits competitive performance in open-set few-shot HSI classification tasks. All the codes are available at \href{https://github.com/KOBEN-ff/OpenFUCD-main} {https://github.com/KOBEN-ff/OpenFUCD-main}
开放集小样本高光谱图像(HSI)分类的目标是使用每类少量的标记像素对图像像素进行分类,其中待分类的像素可能并不都是来自已见过的类别。为了解决开放集HSI分类的挑战,当前的方法主要关注从已知类别样本中区分未知类别样本并拒绝它们,以提高识别已知类别样本的准确性。然而,它们无法在样本中进一步识别或发现未知类别。本文针对小样本环境下高光谱图像中未知类别的发现,提出了一种基于原型学习和聚类的方法。该方法利用少量标记样本,努力开发推断未知类别原型的能力,同时从已知类别中区分未知类别。当未知类别样本被学习到的已知类别分类器拒绝后,所提出的方法可以根据其与推断出的未知类别原型的距离,进一步将未知类别样本聚类到不同的类别中。与现有最先进的方法相比,在四个基准HSI数据集上的大量实验表明,我们提出的方法在开放集小样本HSI分类任务中表现出具有竞争力的性能。所有代码都可在https://github.com/KOBEN-ff/OpenFUCD-main上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对开放集超光谱图像(HSI)分类任务中样本类别未知的问题,本文提出了一种基于原型学习和聚类的方法。该方法能够在少数标注样本的情况下,推断出未知类别的原型,同时将未知类别与已知类别区分开。实验表明,该方法在开放集少样本HSI分类任务上表现出竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 开放集HSI分类面临挑战,需要区分已知和未知类别样本。
- 当前方法主要侧重于拒绝未知类别样本以提高识别准确率,但缺乏对未知类别的进一步识别或发现。
- 本文提出了一种基于原型学习和聚类的方法,用于在少样本环境下发现HSI中的未知类别。
- 该方法能够通过少量标注样本推断未知类别的原型,同时区分未知类别与已知类别。
- 通过对四个基准HSI数据集进行的广泛实验,证明该方法在开放集少样本HSI分类任务上具有竞争力。
- 所有代码均可在指定的GitHub仓库中找到。
点此查看论文截图