⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
Enhancing Robustness in Post-Processing Watermarking: An Ensemble Attack Network Using CNNs and Transformers
Authors:Tzuhsuan Huang, Cheng Yu Yeo, Tsai-Ling Huang, Hong-Han Shuai, Wen-Huang Cheng, Jun-Cheng Chen
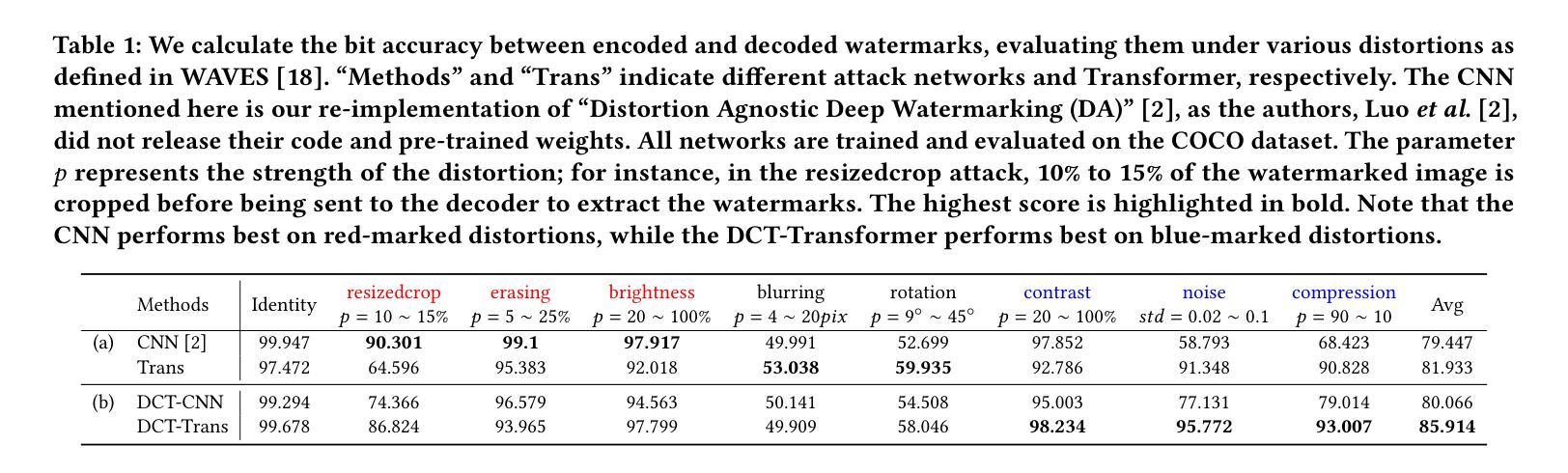
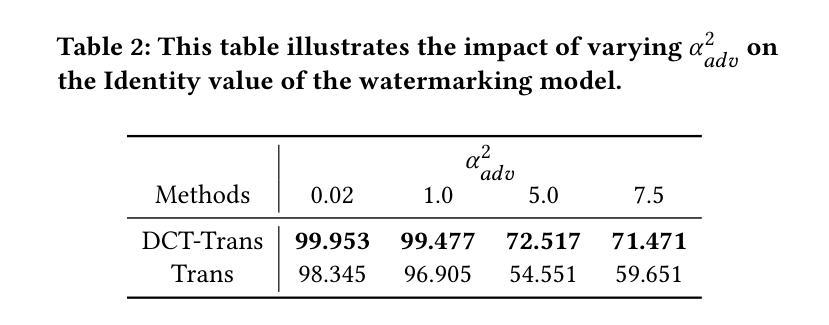
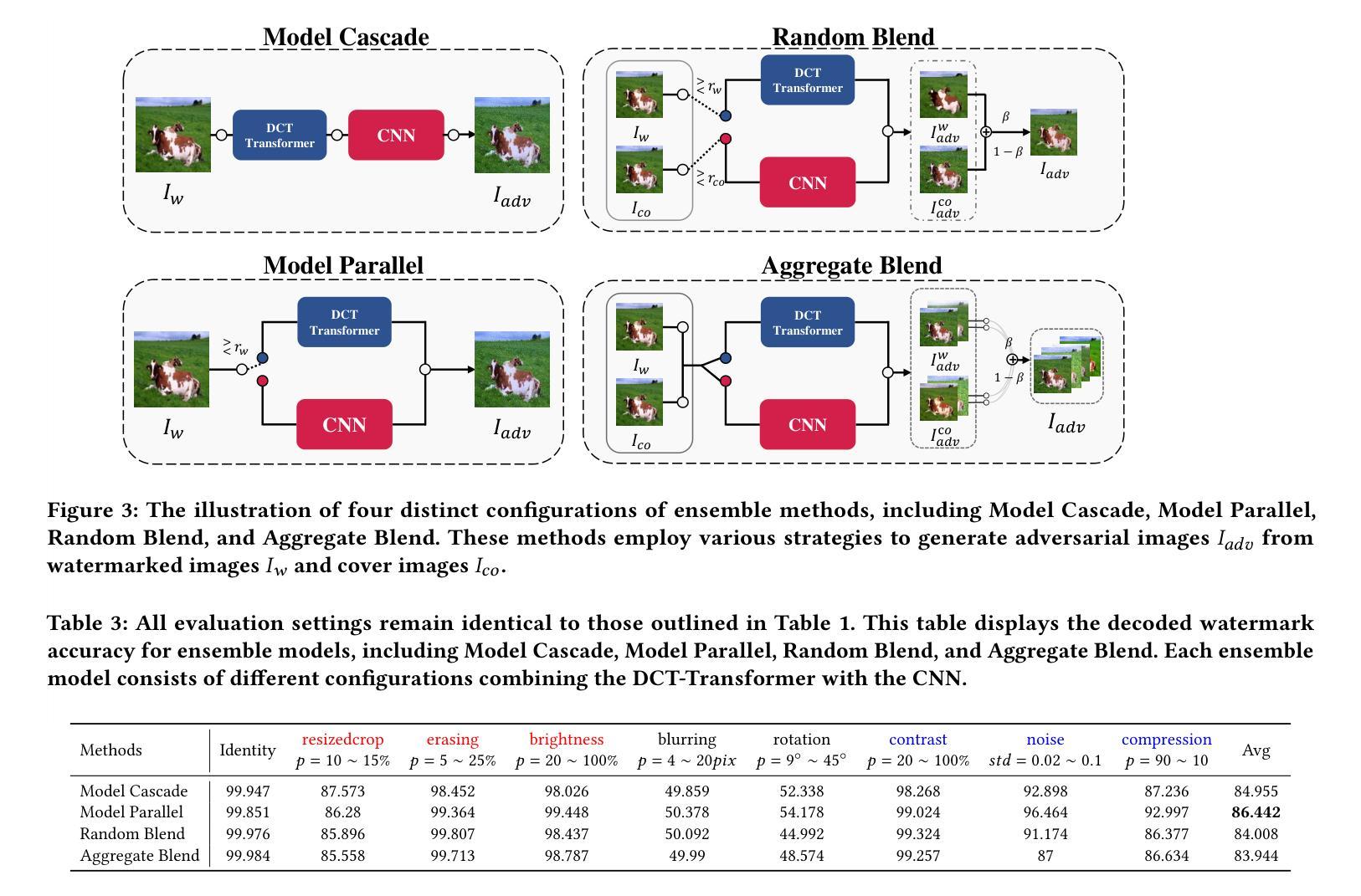
Recent studies on deep watermarking have predominantly focused on in-processing watermarking, which integrates the watermarking process into image generation. However, post-processing watermarking, which embeds watermarks after image generation, offers more flexibility. It can be applied to outputs from any generative model (e.g. GANs, diffusion models) without needing access to the model’s internal structure. It also allows users to embed unique watermarks into individual images. Therefore, this study focuses on post-processing watermarking and enhances its robustness by incorporating an ensemble attack network during training. We construct various versions of attack networks using CNN and Transformer in both spatial and frequency domains to investigate how each combination influences the robustness of the watermarking model. Our results demonstrate that combining a CNN-based attack network in the spatial domain with a Transformer-based attack network in the frequency domain yields the highest robustness in watermarking models. Extensive evaluation on the WAVES benchmark, using average bit accuracy as the metric, demonstrates that our ensemble attack network significantly enhances the robustness of baseline watermarking methods under various stress tests. In particular, for the Regeneration Attack defined in WAVES, our method improves StegaStamp by 18.743%. The code is released at:https://github.com/aiiu-lab/DeepRobustWatermark.
近期关于深度水印的研究主要集中于处理中的水印,即将水印过程集成到图像生成中。然而,后处理水印方法,即在图像生成后嵌入水印,提供了更大的灵活性。它可以应用于任何生成模型的输出(例如GANs、扩散模型),而无需访问模型的内部结构。它还允许用户将独特的水印嵌入到单独的图像中。因此,本研究专注于后处理水印,并通过在训练过程中结合集成攻击网络来提高其稳健性。我们构建了各种版本的攻击网络,使用CNN和Transformer在空间域和频域进行研究,以调查每种组合如何影响水印模型的稳健性。我们的结果表明,在空间域中使用基于CNN的攻击网络与频域中使用基于Transformer的攻击网络相结合,为水印模型提供了最高的稳健性。我们在WAVES基准测试集上进行了广泛评估,以平均位准确性作为度量标准,证明我们的集成攻击网络在各种压力测试下显著提高了基线水印方法的稳健性。特别是在WAVES中定义的再生攻击情况下,我们的方法将StegaStamp提高了18.743%。代码已发布在:https://github.com/aiiu-lab/DeepRobustWatermark。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
深度学习水印技术的新研究聚焦于在图像生成过程中的水印嵌入。然而,研究也表明,对生成图像进行后续处理的水印嵌入方法具有更大的灵活性。该方法可应用于任何生成模型的输出,无需了解模型的内部结构,并能为单幅图像嵌入独特的水印。本研究重点关注后续处理水印技术,并通过训练过程中结合集成攻击网络来提高其稳健性。研究发现结合CNN在空间和基于Transformer在频率域的攻击网络将大大提高水印模型的稳健性。在WAVES基准测试上的评估显示,集成攻击网络显著提高了基线水印方法在各种压力测试下的稳健性。特别是针对WAVES定义的再生攻击,我们的方法提高了StegaStamp的准确率高达18.743%。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 当前深度水印研究主要关注在图像生成过程中的水印嵌入方法。
- 另一种方法是采用后处理水印技术,该技术具有更大的灵活性,适用于各种生成模型的输出。
- 研究重点是通过结合集成攻击网络提高后处理水印技术的稳健性。
- 结合CNN在空间和基于Transformer在频率域的攻击网络能够显著提高水印模型的稳健性。
- 在WAVES基准测试上,集成攻击网络显著增强了基线水印方法的稳健性,尤其是在面对特定类型的攻击时。
- 相关代码已公开发布在GitHub上供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

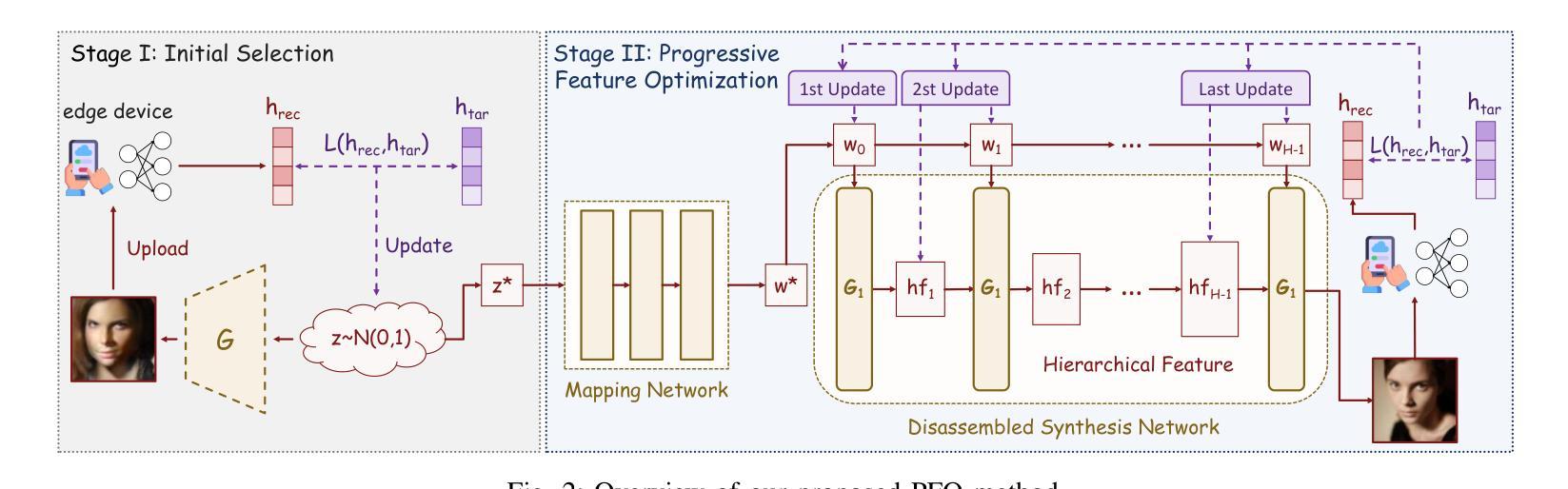
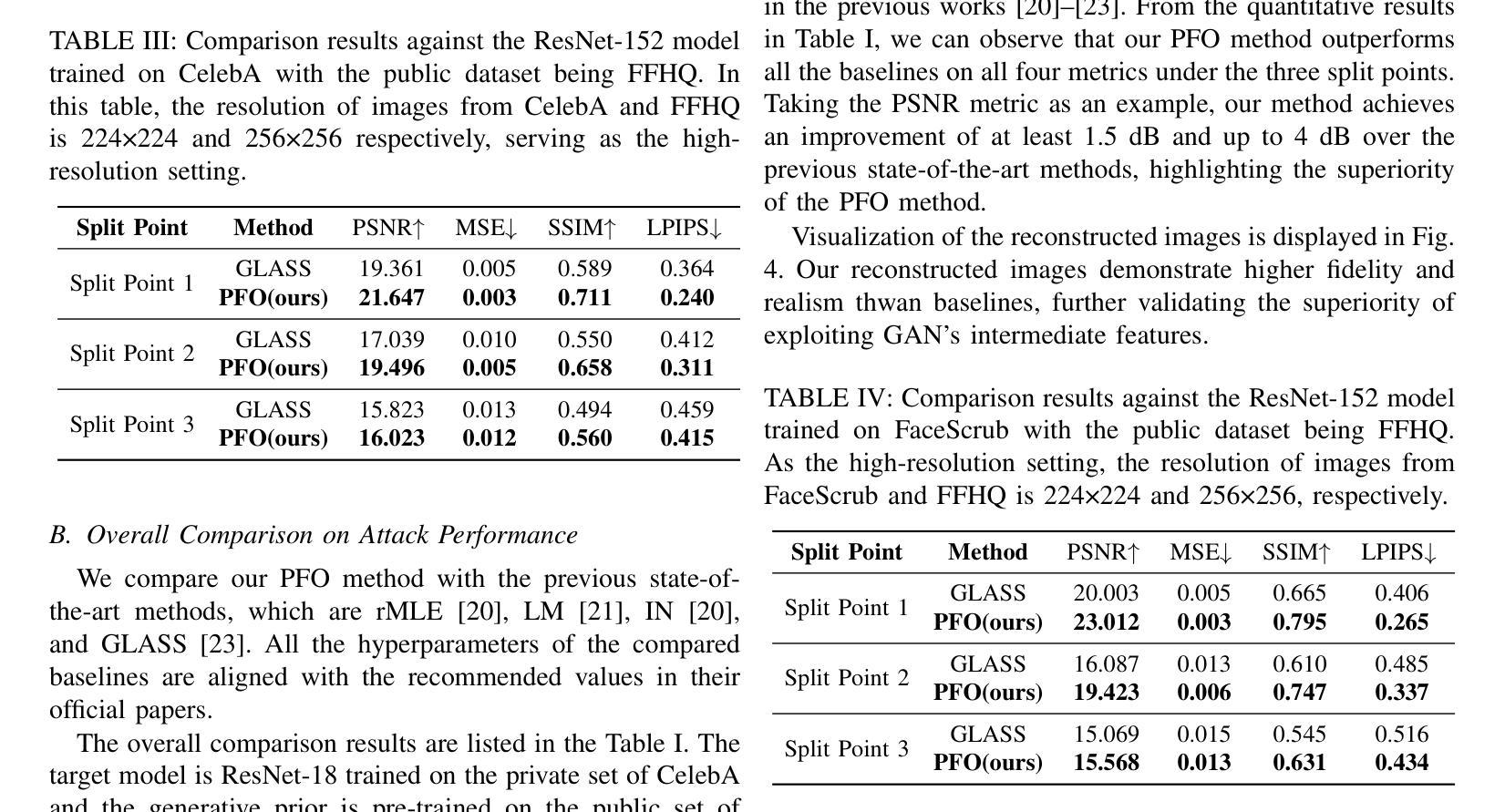
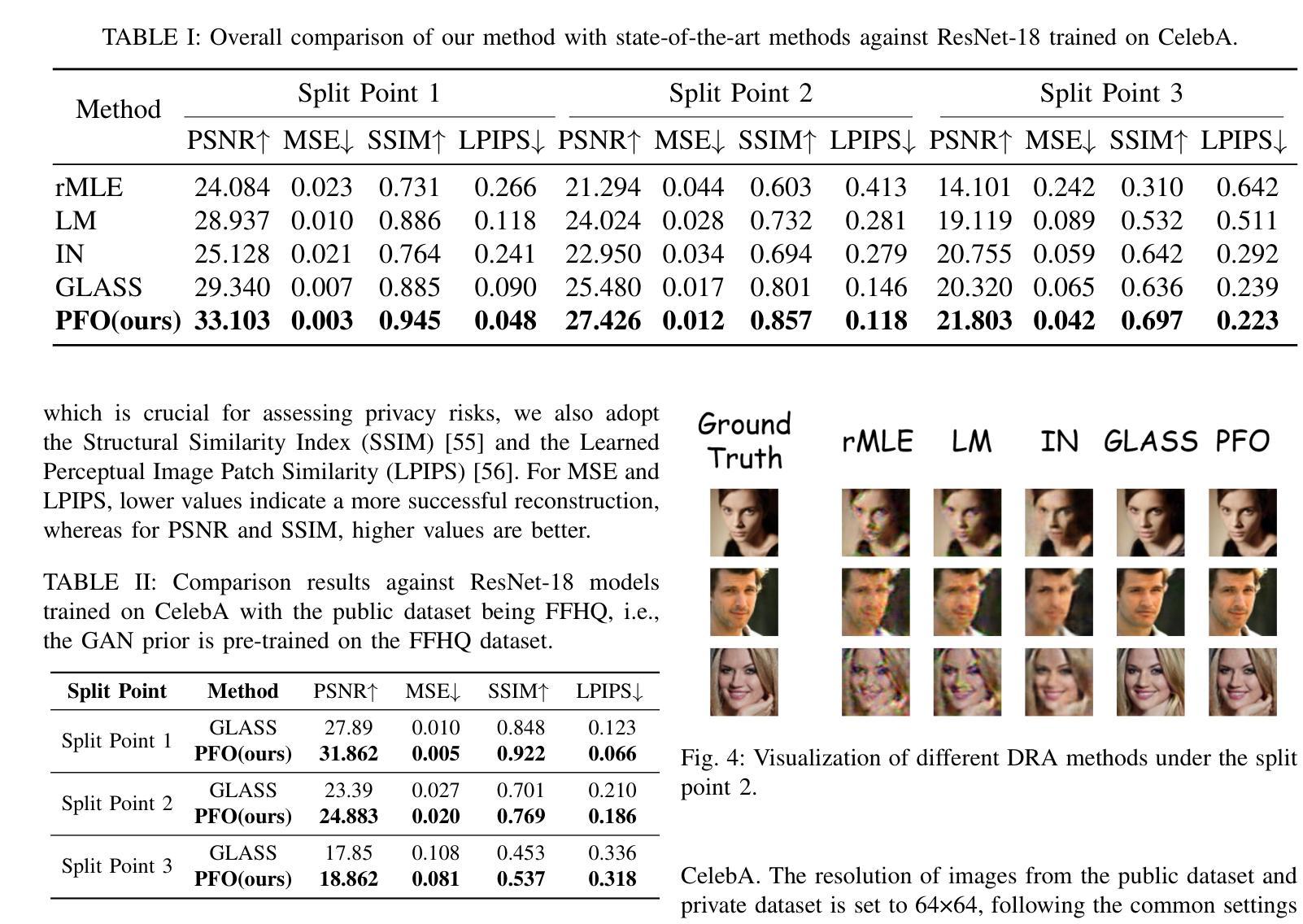
Revisiting the Privacy Risks of Split Inference: A GAN-Based Data Reconstruction Attack via Progressive Feature Optimization
Authors:Yixiang Qiu, Yanhan Liu, Hongyao Yu, Hao Fang, Bin Chen, Shu-Tao Xia, Ke Xu
The growing complexity of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) has led to the adoption of Split Inference (SI), a collaborative paradigm that partitions computation between edge devices and the cloud to reduce latency and protect user privacy. However, recent advances in Data Reconstruction Attacks (DRAs) reveal that intermediate features exchanged in SI can be exploited to recover sensitive input data, posing significant privacy risks. Existing DRAs are typically effective only on shallow models and fail to fully leverage semantic priors, limiting their reconstruction quality and generalizability across datasets and model architectures. In this paper, we propose a novel GAN-based DRA framework with Progressive Feature Optimization (PFO), which decomposes the generator into hierarchical blocks and incrementally refines intermediate representations to enhance the semantic fidelity of reconstructed images. To stabilize the optimization and improve image realism, we introduce an L1-ball constraint during reconstruction. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms prior attacks by a large margin, especially in high-resolution scenarios, out-of-distribution settings, and against deeper and more complex DNNs.
深度神经网络(DNNs)日益增长的复杂性导致采用Split Inference(SI)技术。作为一种合作型范式,它在边缘设备和云之间分配计算任务以减少延迟并保护用户隐私。然而,数据重建攻击(DRAs)的最新进展表明,中间特征交换在SI中可以用于恢复敏感输入数据,从而带来重大隐私风险。现有的DRAs通常仅在浅层模型上有效,未能充分利用语义先验信息,从而限制了其重建质量和跨数据集和模型架构的通用性。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的新型DRA框架,其中包含渐进特征优化(PFO),该框架将生成器分解为分层块并逐层优化中间表示形式,以提高重建图像语义保真度。为了稳定优化并改善图像的真实性,我们在重建过程中引入了L1球约束。大量实验表明,我们的方法大大优于先前攻击,特别是在高分辨率场景、非内部分布设置以及针对更深和更复杂的DNNs时效果更佳。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
深度神经网络(DNN)的复杂性增长推动了Split Inference(SI)的应用。但新的数据重建攻击(DRA)揭示了SI中交换的中间特征可被用来恢复敏感输入数据,带来隐私风险。现有的DRAs通常在浅层模型上有效,无法充分利用语义先验信息。本文提出一种基于GAN的DRA框架,结合渐进特征优化(PFO),分解生成器为层次块并逐步优化中间表示,提高重建图像语义保真度。引入L1球约束以优化稳定性和图像真实性。实验证明,该方法在高清场景、非分布设置和更复杂的DNNs上的攻击效果远超先前方法。
Key Takeaways
- Split Inference(SI)被应用于深度神经网络(DNN),旨在减少延迟和保护用户隐私。
- 数据重建攻击(DRA)可以利用SI中的中间特征恢复敏感输入数据,带来隐私风险。
- 现有DRAs主要适用于浅层模型,且在利用语义先验信息方面存在局限性。
- 提出一种基于GAN的DRA框架,结合渐进特征优化(PFO),提高重建图像的语义保真度。
- 引入L1球约束以优化图像的真实性和稳定性。
- 该方法在多种实验场景下的攻击效果优于先前的攻击方法。
点此查看论文截图


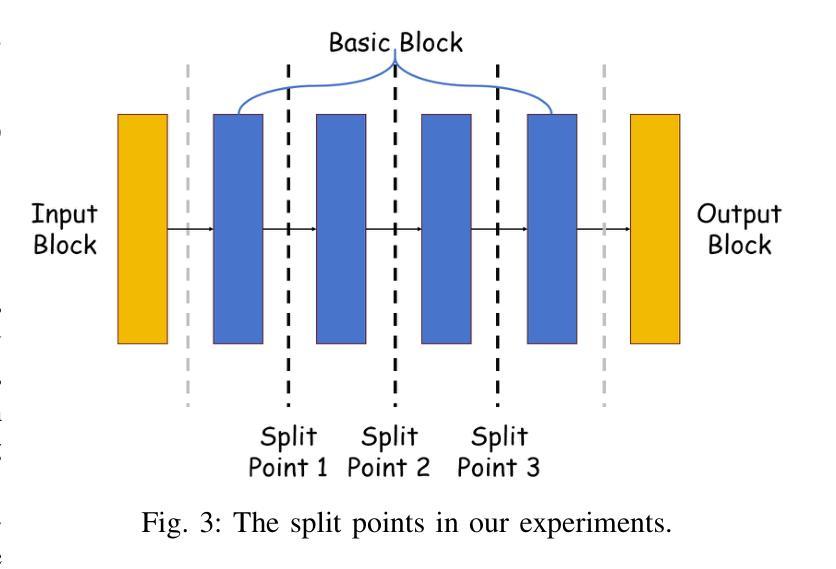
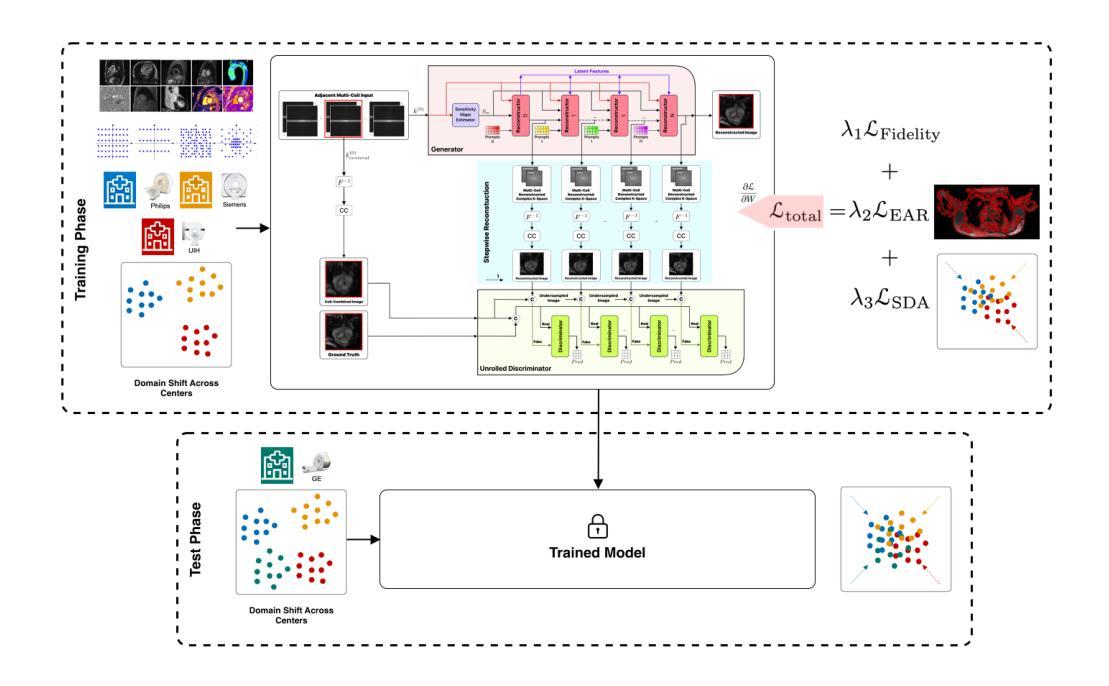
GENRE-CMR: Generalizable Deep Learning for Diverse Multi-Domain Cardiac MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Kian Anvari Hamedani, Narges Razizadeh, Shahabedin Nabavi, Mohsen Ebrahimi Moghaddam
Accelerated Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) image reconstruction remains a critical challenge due to the trade-off between scan time and image quality, particularly when generalizing across diverse acquisition settings. We propose GENRE-CMR, a generative adversarial network (GAN)-based architecture employing a residual deep unrolled reconstruction framework to enhance reconstruction fidelity and generalization. The architecture unrolls iterative optimization into a cascade of convolutional subnetworks, enriched with residual connections to enable progressive feature propagation from shallow to deeper stages. To further improve performance, we integrate two loss functions: (1) an Edge-Aware Region (EAR) loss, which guides the network to focus on structurally informative regions and helps prevent common reconstruction blurriness; and (2) a Statistical Distribution Alignment (SDA) loss, which regularizes the feature space across diverse data distributions via a symmetric KL divergence formulation. Extensive experiments confirm that GENRE-CMR surpasses state-of-the-art methods on training and unseen data, achieving 0.9552 SSIM and 38.90 dB PSNR on unseen distributions across various acceleration factors and sampling trajectories. Ablation studies confirm the contribution of each proposed component to reconstruction quality and generalization. Our framework presents a unified and robust solution for high-quality CMR reconstruction, paving the way for clinically adaptable deployment across heterogeneous acquisition protocols.
加速心血管磁共振(CMR)图像重建仍然是一个关键挑战,因为在扫描时间和图像质量之间存在权衡,特别是在不同采集环境之间进行推广时。我们提出了GENRE-CMR,这是一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的架构,采用残差深度展开重建框架,以提高重建的保真度和通用性。该架构将迭代优化展开成卷积子网络的级联,通过残差连接丰富特征,实现从浅层到深层阶段的渐进特征传播。为了进一步提高性能,我们集成了两种损失函数:(1)边缘感知区域(EAR)损失,引导网络关注结构信息丰富的区域,有助于防止常见的重建模糊;(2)统计分布对齐(SDA)损失,通过对称KL散度公式,对特征空间进行不同数据分布的规范化。大量实验证实,GENRE-CMR在训练和未见数据上超越了最先进的方法,在不同加速因子和采样轨迹的未见分布上实现了0.9552的结构相似性度量(SSIM)和38.90分贝的峰值信噪比(PSNR)。消融研究证实了所提出组件对重建质量和通用性的贡献。我们的框架为高质量CMR重建提供了统一且稳健的解决方案,为在临床环境中适应不同采集协议部署铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的架构GENRE-CMR,采用残差深度展开重建框架,提高重建保真度和通用性。它将迭代优化展开为一系列卷积子网络,借助残差连接实现从浅层到深层阶段的特征传播。同时集成Edge-Aware Region(EAR)损失和Statistical Distribution Alignment(SDA)损失,分别引导网络关注结构信息区域并规范化不同数据分布的特征空间。实验证明,GENRE-CMR在训练和未见数据上超越现有方法,实现0.9552的SSIM和38.90 dB的PSNR。
Key Takeaways
- GENRE-CMR利用GAN架构解决心血管磁共振(CMR)图像重建的挑战。
- 采用残差深度展开重建框架,提高重建质量和通用性。
- 集成EAR损失,引导网络关注结构信息区域,减少重建模糊。
- 集成SDA损失,通过对称KL散度公式规范化不同数据分布的特征空间。
- 在各种加速因素和采样轨迹下,GENRE-CMR在未见数据上实现0.9552的SSIM和38.90 dB的PSNR,超越现有方法。
- 消融研究证实了每个提议组件对重建质量和通用性的贡献。
点此查看论文截图

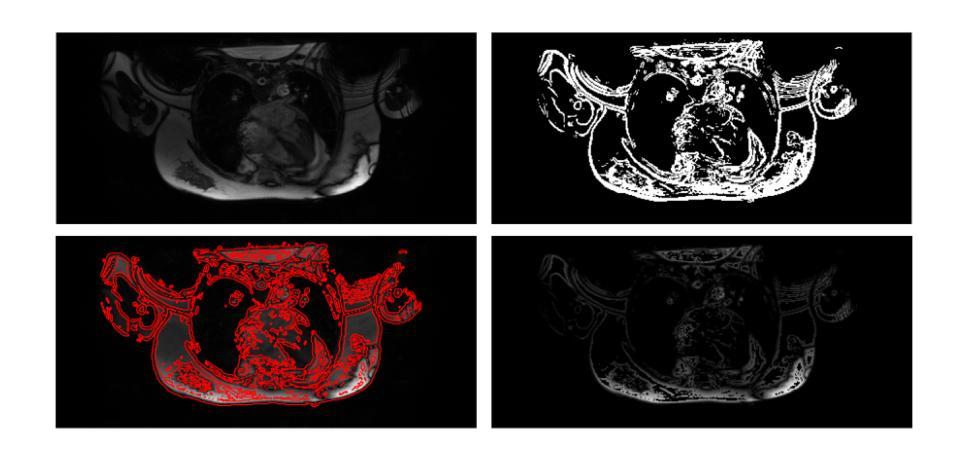
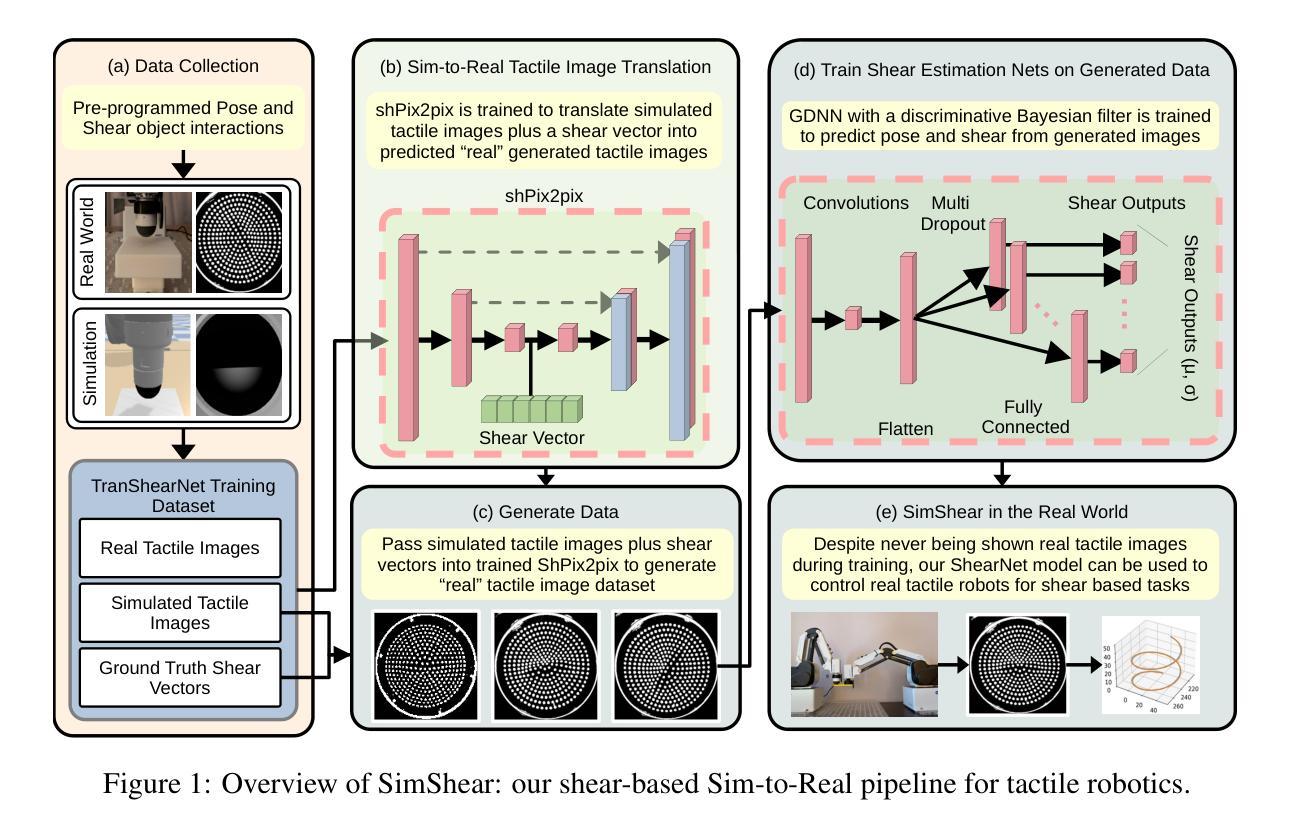
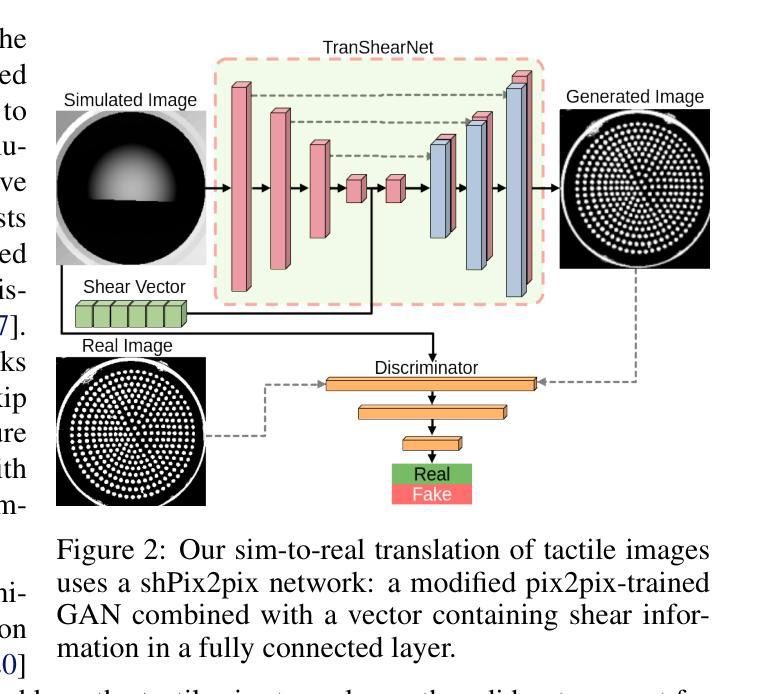
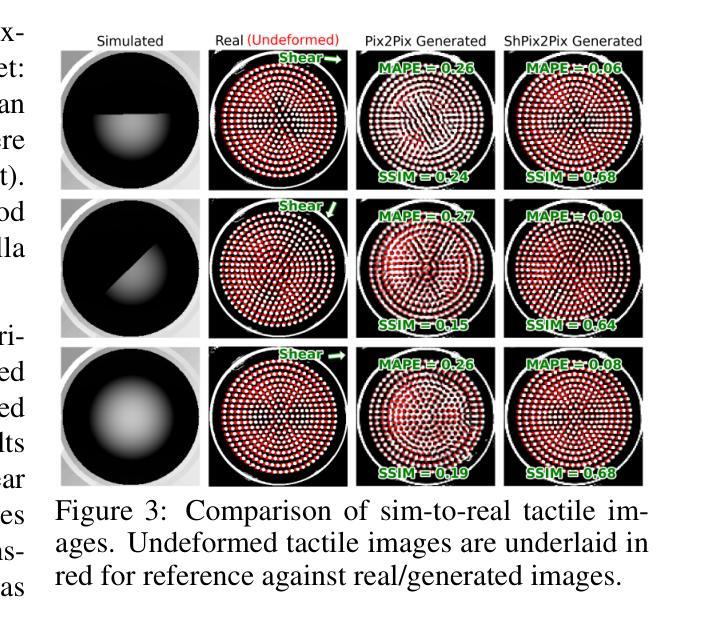
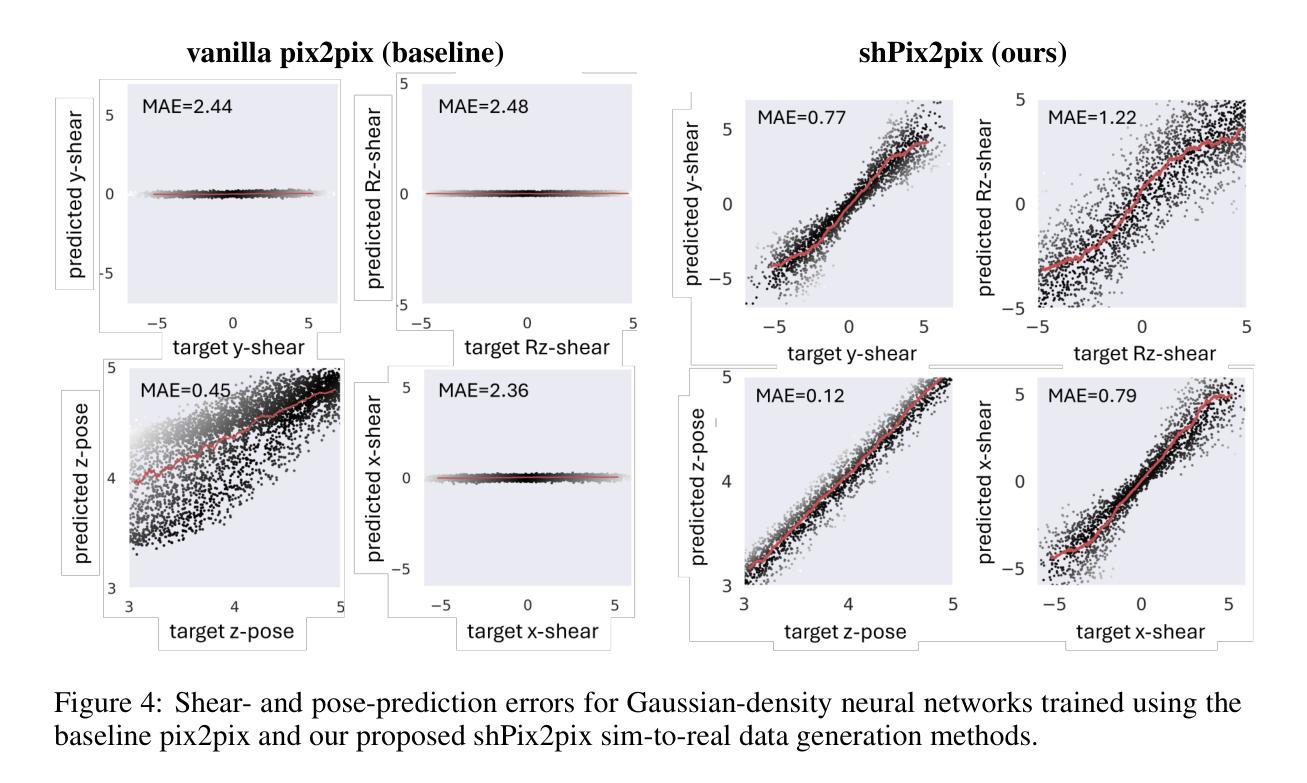
SimShear: Sim-to-Real Shear-based Tactile Servoing
Authors:Kipp McAdam Freud, Yijiong Lin, Nathan F. Lepora
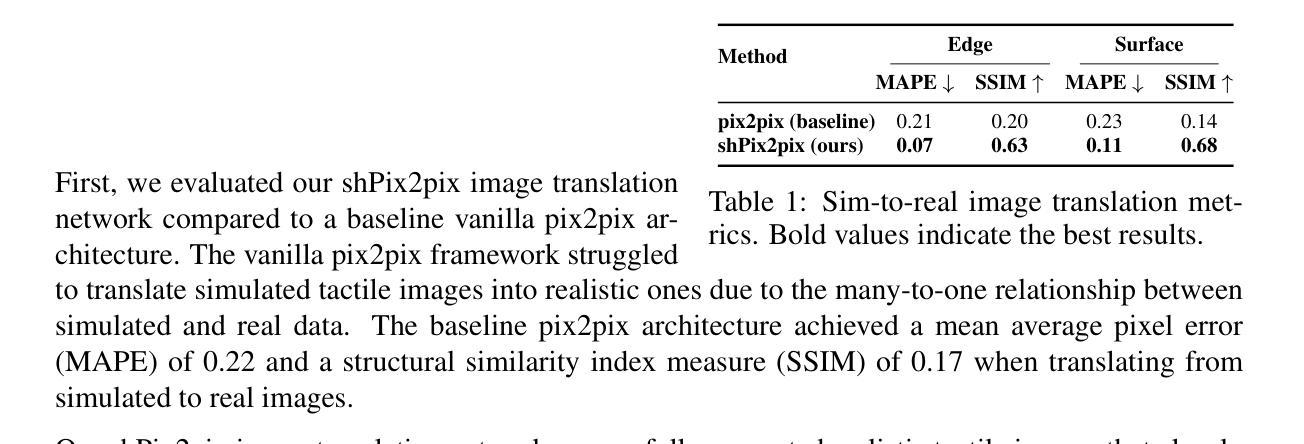
We present SimShear, a sim-to-real pipeline for tactile control that enables the use of shear information without explicitly modeling shear dynamics in simulation. Shear, arising from lateral movements across contact surfaces, is critical for tasks involving dynamic object interactions but remains challenging to simulate. To address this, we introduce shPix2pix, a shear-conditioned U-Net GAN that transforms simulated tactile images absent of shear, together with a vector encoding shear information, into realistic equivalents with shear deformations. This method outperforms baseline pix2pix approaches in simulating tactile images and in pose/shear prediction. We apply SimShear to two control tasks using a pair of low-cost desktop robotic arms equipped with a vision-based tactile sensor: (i) a tactile tracking task, where a follower arm tracks a surface moved by a leader arm, and (ii) a collaborative co-lifting task, where both arms jointly hold an object while the leader follows a prescribed trajectory. Our method maintains contact errors within 1 to 2 mm across varied trajectories where shear sensing is essential, validating the feasibility of sim-to-real shear modeling with rigid-body simulators and opening new directions for simulation in tactile robotics.
我们提出了SimShear,这是一个用于触觉控制的模拟到现实管道,它能够在模拟过程中不使用明确的剪切动力学模型就使用剪切信息。剪切力产生于接触表面的横向运动,对于涉及动态对象交互的任务至关重要,但在模拟中仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了shPix2pix,这是一个受剪切力条件约束的U-Net GAN,它能够将模拟的触觉图像(不含剪切力)与编码剪切信息的向量相结合,转化为具有剪切变形的现实等效图像。该方法在模拟触觉图像、姿态/剪切预测方面优于基线pix2pix方法。我们将SimShear应用于两个控制任务中,使用一对配备有基于视觉的触觉传感器的低成本桌面机械臂:(i)触觉跟踪任务,其中跟随臂跟踪领导者臂移动的表面;(ii)协作协同提升任务,其中两个机械臂共同握住一个对象,领导者臂遵循预定的轨迹。我们的方法在各种轨迹上保持接触误差在1到2毫米之间,剪切感知至关重要,验证了使用刚体模拟器进行模拟到现实的剪切建模的可行性,并为触觉机器人的模拟打开了新的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 2025 Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL)
Summary
本文介绍了SimShear,这是一种用于触觉控制的模拟到现实场景的管道,它能够在模拟过程中使用剪切信息,而无需显式建模剪切动力学。SimShear通过引入shPix2pix,一个受剪切力条件约束的U-Net GAN,将模拟的触觉图像(无剪切信息)与编码剪切信息的向量相结合,转化为具有剪切变形的真实图像。该方法在模拟触觉图像和姿态/剪切预测方面优于基本的pix2pix方法。文章还展示了SimShear在两台低成本桌面机器人手臂上的两个控制任务的应用,包括触觉跟踪任务和协作协同升降任务。该方法在剪切感知至关重要的不同轨迹上保持接触误差在1至2毫米范围内,验证了使用刚体模拟器进行模拟到现实的剪切建模的可行性,为触觉机器人模拟提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- SimShear是一种模拟到现实的管道,用于处理触觉控制中的剪切信息,无需显式模拟剪切动力学。
- shPix2pix是一个受剪切条件约束的U-Net GAN,能够将模拟的触觉图像转化为具有剪切变形的真实图像。
- SimShear在模拟触觉图像和姿态/剪切预测方面的性能优于基本的pix2pix方法。
- SimShear应用于两个机器人控制任务:触觉跟踪任务和协作协同升降任务。
- SimShear在剪切感知重要的不同轨迹上保持低接触误差。
- 该方法验证了使用刚体模拟器进行模拟到现实的剪切建模的可行性。
点此查看论文截图

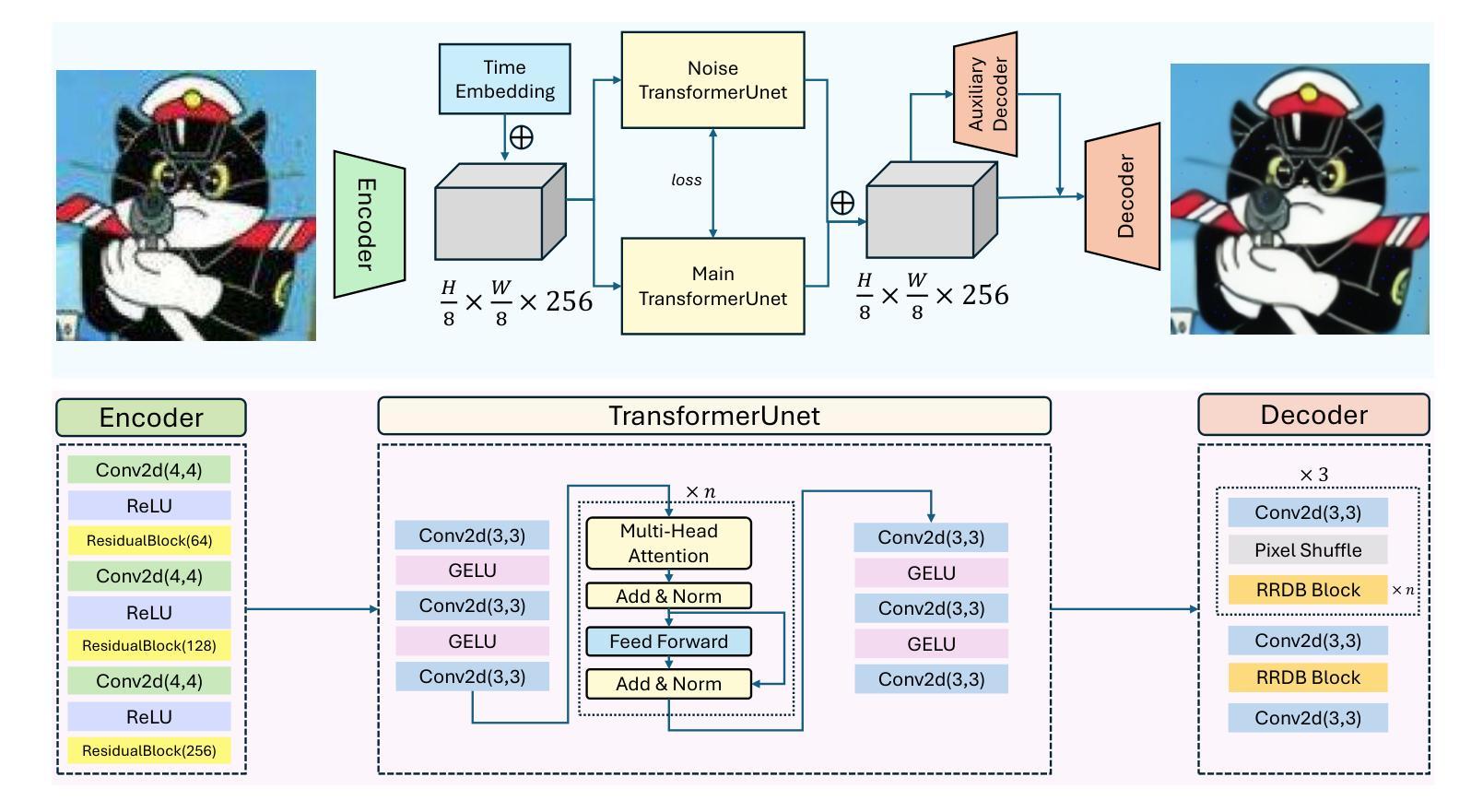
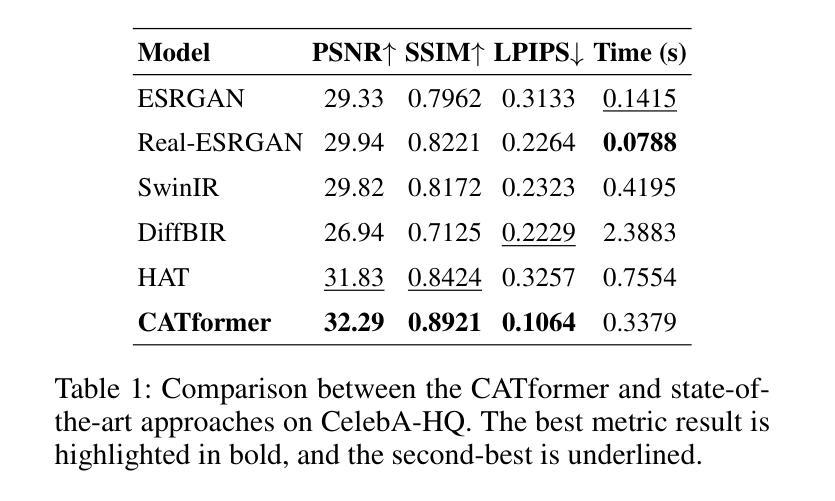
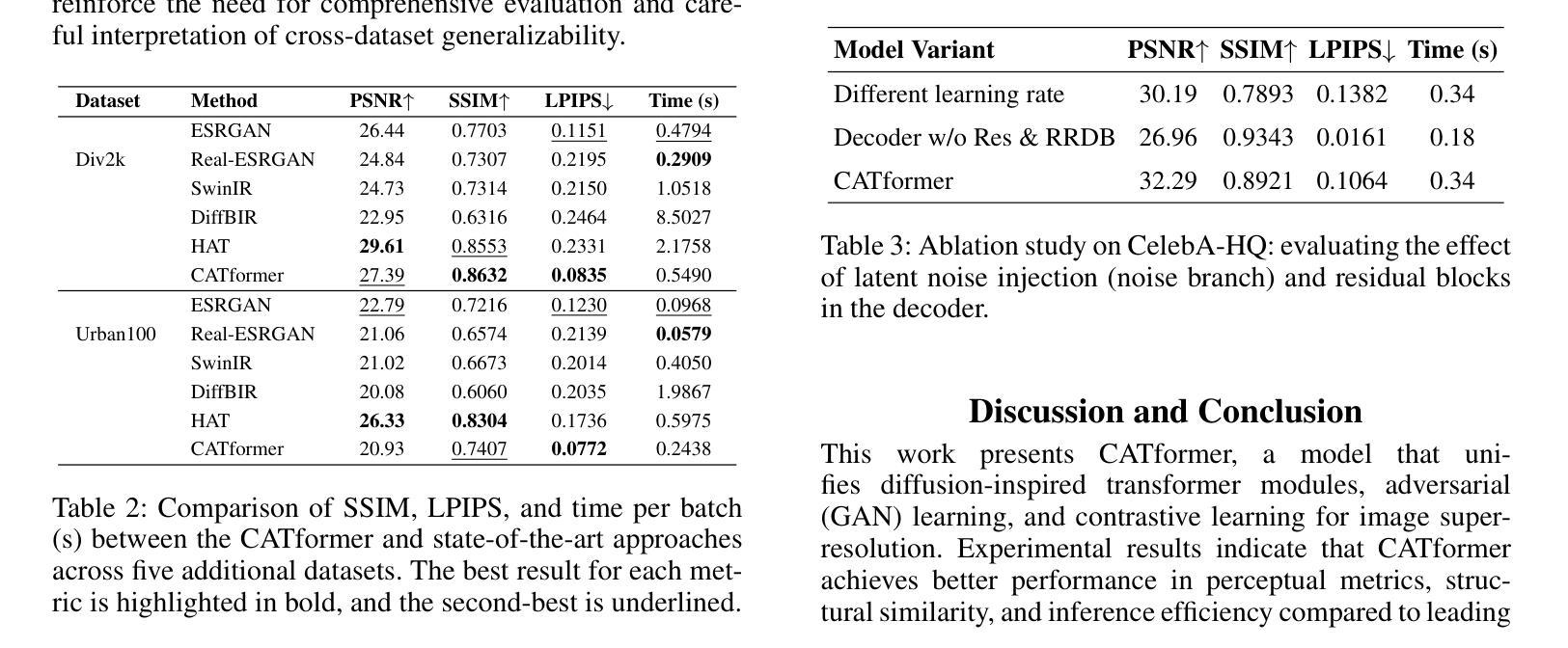
CATformer: Contrastive Adversarial Transformer for Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Qinyi Tian, Spence Cox, Laura E. Dalton
Super-resolution remains a promising technique to enhance the quality of low-resolution images. This study introduces CATformer (Contrastive Adversarial Transformer), a novel neural network integrating diffusion-inspired feature refinement with adversarial and contrastive learning. CATformer employs a dual-branch architecture combining a primary diffusion-inspired transformer, which progressively refines latent representations, with an auxiliary transformer branch designed to enhance robustness to noise through learned latent contrasts. These complementary representations are fused and decoded using deep Residual-in-Residual Dense Blocks for enhanced reconstruction quality. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that CATformer outperforms recent transformer-based and diffusion-inspired methods both in efficiency and visual image quality. This work bridges the performance gap among transformer-, diffusion-, and GAN-based methods, laying a foundation for practical applications of diffusion-inspired transformers in super-resolution.
超分辨率技术依然是一种能够提升低分辨率图像质量的具有前景的技术。本研究介绍了CATformer(对比对抗性转换器),这是一种新型神经网络,融合了扩散启发特征细化、对抗性学习和对比学习。CATformer采用双分支架构,结合主要扩散启发转换器,逐步优化潜在表示,以及一个辅助转换器分支,通过学习潜在对比增强对噪声的鲁棒性。这些互补的表示融合并使用深度Residual-in-Residual Dense块进行解码,以提高重建质量。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,CATformer在效率和视觉图像质量上均优于最新的基于转换器和扩散的方法。这项工作缩小了基于转换器、扩散和GAN的方法之间的性能差距,为扩散启发转换器的实际应用在超分辨率领域奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为CATformer的新型神经网络,它结合了扩散启发特征细化、对抗性学习与对比学习。CATformer采用双分支架构,主分支为扩散启发变压器,用于逐步优化潜在表示,辅助分支为增强噪声鲁棒性的对比学习变压器。两者融合并使用深度Residual-in-Residual Dense Blocks进行解码,以提高重建质量。在基准数据集上的实验表明,CATformer在效率和视觉图像质量上均优于最近的基于变压器和扩散的方法。该研究缩小了基于变压器、扩散和GAN的方法之间的性能差距,为扩散启发变压器在超分辨率中的实际应用奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- CATformer是一种结合扩散启发特征细化、对抗性学习和对比学习的新型神经网络。
- CATformer采用双分支架构,主分支用于逐步优化潜在表示,辅助分支增强噪声鲁棒性。
- 通过对比学习,CATformer能够学习潜在对比,提高模型的性能。
- CATformer使用深度Residual-in-Residual Dense Blocks进行解码,以提高图像重建质量。
- 在基准数据集上的实验表明,CATformer在效率和视觉质量上均表现优异。
- CATformer的研究缩小了不同方法之间的性能差距,为扩散启发变压器在超分辨率中的应用奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图


A Novel Local Focusing Mechanism for Deepfake Detection Generalization
Authors:Mingliang Li, Lin Yuanbo Wu, Changhong Liu, Hanxi Li
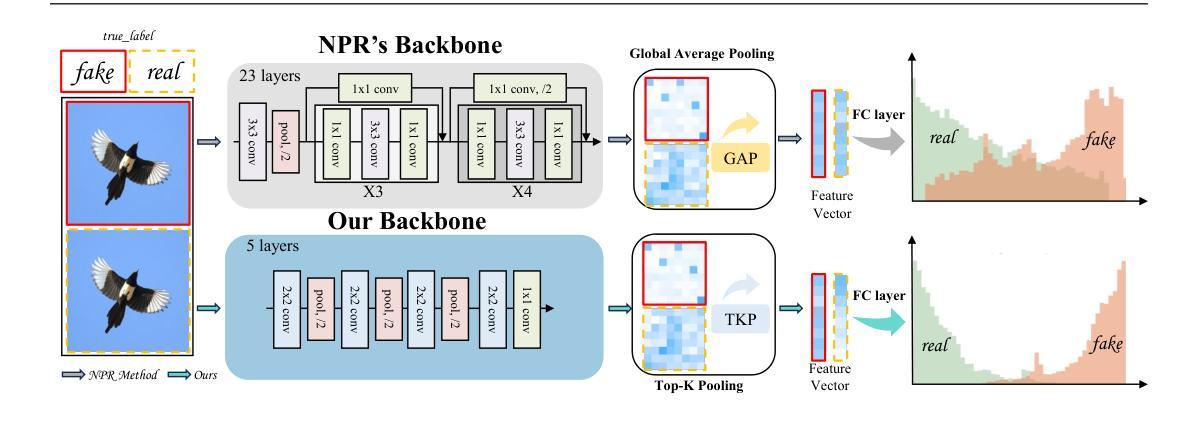
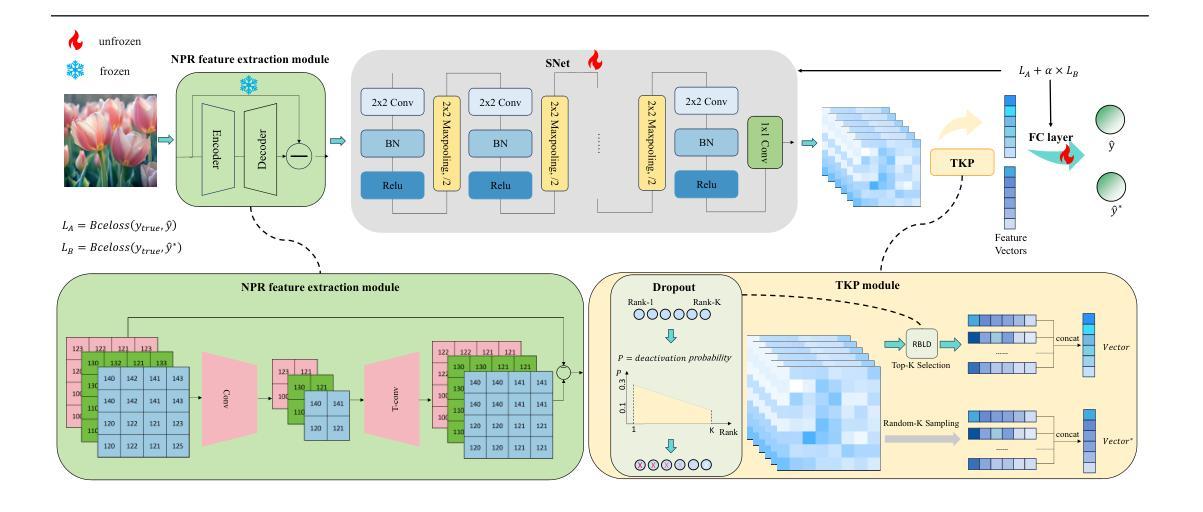
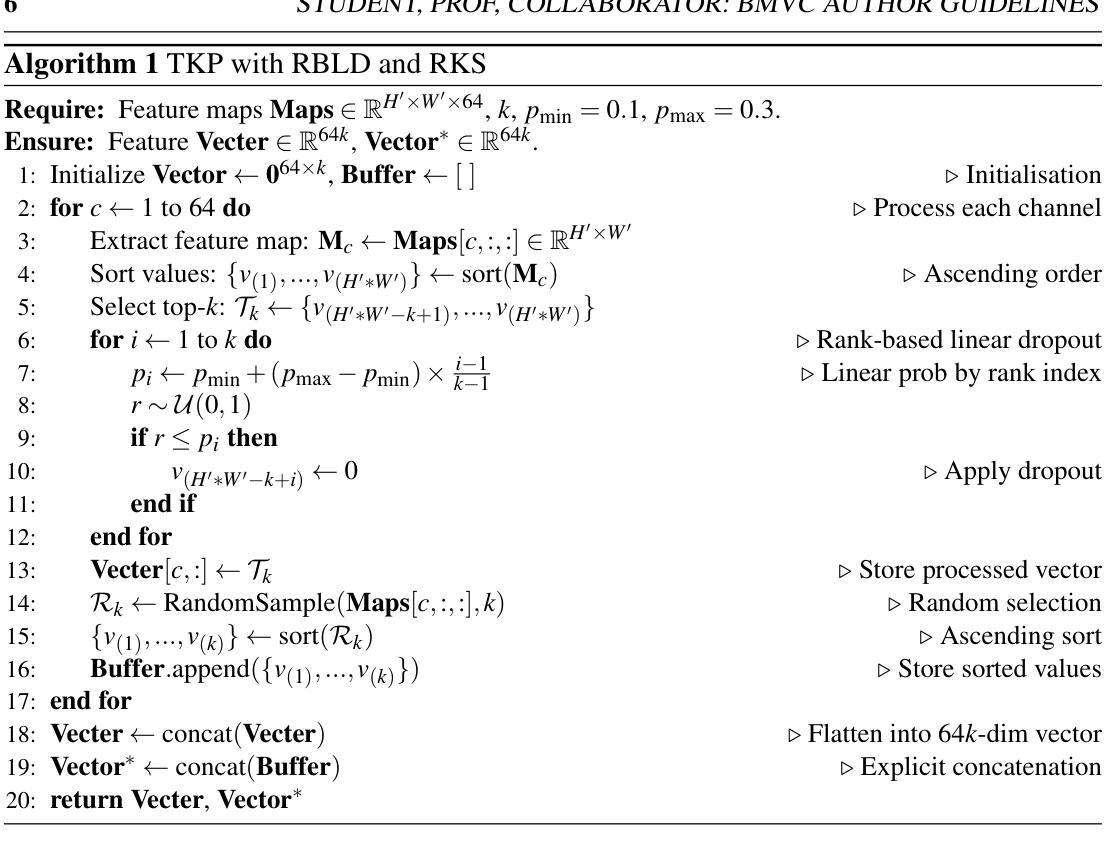
The rapid advancement of deepfake generation techniques has intensified the need for robust and generalizable detection methods. Existing approaches based on reconstruction learning typically leverage deep convolutional networks to extract differential features. However, these methods show poor generalization across object categories (e.g., from faces to cars) and generation domains (e.g., from GANs to Stable Diffusion), due to intrinsic limitations of deep CNNs. First, models trained on a specific category tend to overfit to semantic feature distributions, making them less transferable to other categories, especially as network depth increases. Second, Global Average Pooling (GAP) compresses critical local forgery cues into a single vector, thus discarding discriminative patterns vital for real-fake classification. To address these issues, we propose a novel Local Focus Mechanism (LFM) that explicitly attends to discriminative local features for differentiating fake from real images. LFM integrates a Salience Network (SNet) with a task-specific Top-K Pooling (TKP) module to select the K most informative local patterns. To mitigate potential overfitting introduced by Top-K pooling, we introduce two regularization techniques: Rank-Based Linear Dropout (RBLD) and Random-K Sampling (RKS), which enhance the model’s robustness. LFM achieves a 3.7 improvement in accuracy and a 2.8 increase in average precision over the state-of-the-art Neighboring Pixel Relationships (NPR) method, while maintaining exceptional efficiency at 1789 FPS on a single NVIDIA A6000 GPU. Our approach sets a new benchmark for cross-domain deepfake detection. The source code are available in https://github.com/lmlpy/LFM.git
随着深度伪造生成技术的快速发展,对稳健且通用的检测方法的需求愈发迫切。现有的基于重建学习的方法通常利用深度卷积网络来提取差异特征。然而,由于深度CNN的内在局限性,这些方法在对象类别(例如从人脸到汽车)和生成领域(例如从GAN到Stable Diffusion)之间的泛化能力较差。首先,针对特定类别训练的模型往往会对语义特征分布产生过度拟合,使其难以转移到其他类别,尤其是随着网络深度的增加。其次,全局平均池化(GAP)将关键的局部伪造线索压缩成一个单一的向量,从而丢弃了对于真实和伪造分类至关重要的判别模式。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新颖的局部焦点机制(LFM),它专注于区分真实和伪造图像的判别局部特征。LFM将显著性网络(SNet)与特定任务的Top-K池化(TKP)模块相结合,选择K个最具信息量的局部模式。为了缓解Top-K池化可能引入的过度拟合问题,我们引入了两种正则化技术:基于排名的线性dropout(RBLD)和随机K采样(RKS),提高了模型的稳健性。与最先进的邻近像素关系(NPR)方法相比,LFM在准确性上提高了3.7%,平均精度提高了2.8%,同时在单个NVIDIA A6000 GPU上保持了出色的效率。我们的方法为跨域深度伪造检测设定了新的基准。源代码可在https://github.com/lmlpy/LFM.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型本地焦点机制(LFM),解决了深度伪造图像检测中跨对象类别和生成域泛化性能差的问题。该机制通过显著性网络(SNet)和任务特定Top-K池化模块(TKP)的结合,关注鉴别局部特征,以提高模型对真实和伪造图像的区分能力。通过引入两种正则化技术:基于排名的线性丢弃(RBLD)和随机K采样(RKS),增强了模型的稳健性。LFM在准确率和平均精度上取得了显著改进,相比现有方法有明显提升,同时在单一NVIDIA A6000 GPU上保持了高效率。
Key Takeaways
- 深度伪造生成技术的快速发展加剧了需要寻找稳健且可泛化的检测办法。
- 当前基于重建学习的方法主要利用深度卷积网络提取特征,但在跨对象类别和生成域方面的泛化性能不佳。
- 本地焦点机制(LFM)通过关注鉴别局部特征来提高模型性能。
- LFM结合显著性网络(SNet)和任务特定Top-K池化模块(TKP)进行选择性的特征提取。
- 引入两种正则化技术以增强模型的稳健性:基于排名的线性丢弃(RBLD)和随机K采样(RKS)。
- LFM在准确率和平均精度上实现了显著改进,相比现有方法表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

Foundations and Models in Modern Computer Vision: Key Building Blocks in Landmark Architectures
Authors:Radu-Andrei Bourceanu, Neil De La Fuente, Jan Grimm, Andrei Jardan, Andriy Manucharyan, Cornelius Weiss, Daniel Cremers, Roman Pflugfelder
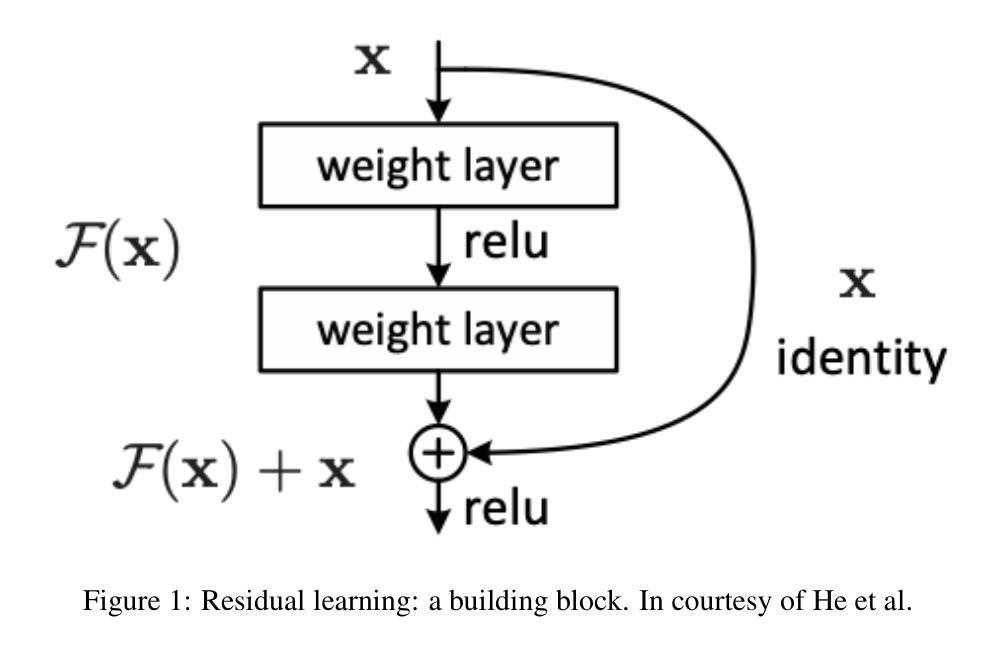
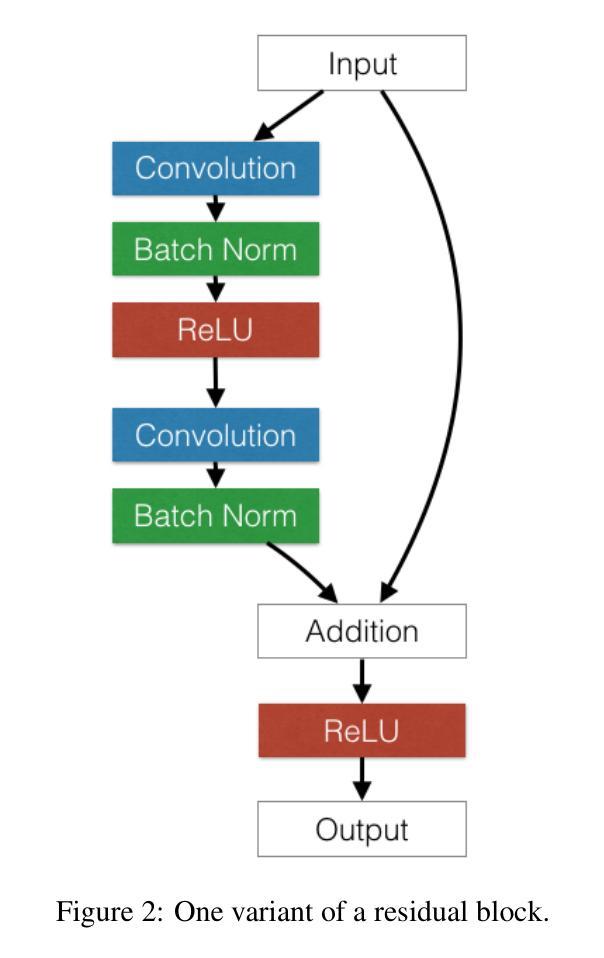
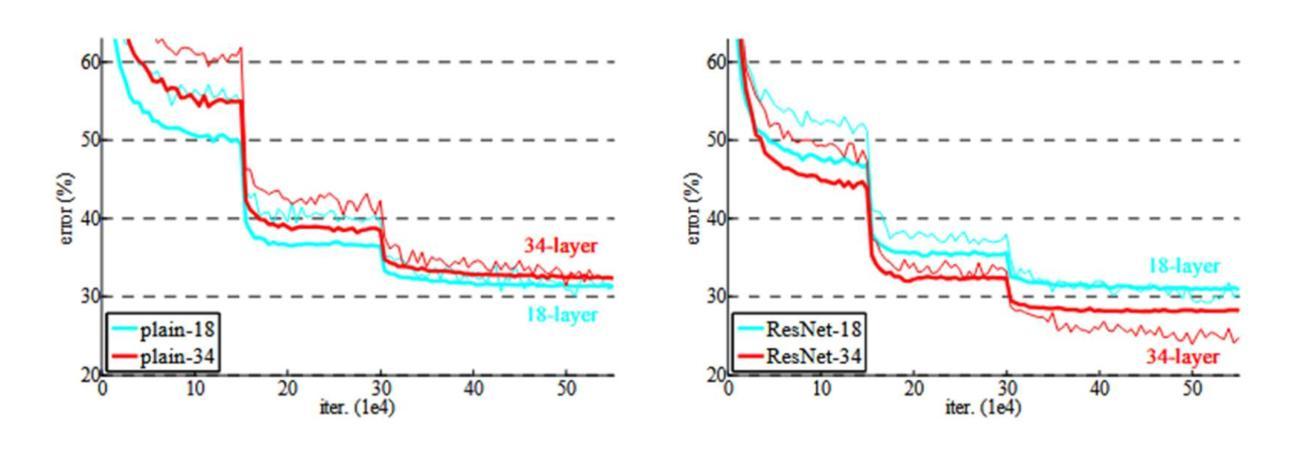
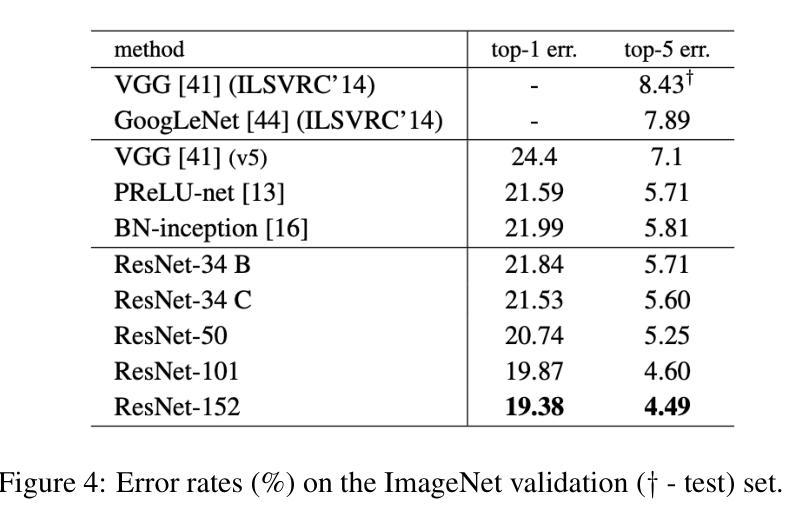
This report analyzes the evolution of key design patterns in computer vision by examining six influential papers. The analysis begins with foundational architectures for image recognition. We review ResNet, which introduced residual connections to overcome the vanishing gradient problem and enable effective training of significantly deeper convolutional networks. Subsequently, we examine the Vision Transformer (ViT), which established a new paradigm by applying the Transformer architecture to sequences of image patches, demonstrating the efficacy of attention-based models for large-scale image recognition. Building on these visual representation backbones, we investigate generative models. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are analyzed for their novel adversarial training process, which challenges a generator against a discriminator to learn complex data distributions. Then, Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) are covered, which improve upon prior generative methods by performing a sequential denoising process in a perceptually compressed latent space. LDMs achieve high-fidelity synthesis with greater computational efficiency, representing the current state-of-the-art for image generation. Finally, we explore self-supervised learning techniques that reduce dependency on labeled data. DINO is a self-distillation framework in which a student network learns to match the output of a momentum-updated teacher, yielding features with strong k-NN classification performance. We conclude with Masked Autoencoders (MAE), which utilize an asymmetric encoder-decoder design to reconstruct heavily masked inputs, providing a highly scalable and effective method for pre-training large-scale vision models.
本报告通过分析六篇有影响力的论文,分析了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变。分析从图像识别的基本架构开始。我们回顾了ResNet,它引入了残差连接,克服了梯度消失问题,使得训练更深层次的卷积网络变得有效。之后,我们研究了将Transformer架构应用于图像补丁序列的Vision Transformer(ViT),这奠定了新的范式,并证明了基于注意力的模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。在这些视觉表示主干的基础上,我们研究了生成模型。分析了生成对抗网络(GANs)的新型对抗训练过程,该过程挑战生成器与鉴别器学习复杂的数据分布。然后介绍了潜在扩散模型(LDMs),通过对先前生成方法的改进,在感知压缩的潜在空间中执行序贯去噪过程,实现了高保真合成和更高的计算效率,代表了当前图像生成的最新技术。最后,我们探索了减少对比标签数据依赖性的自监督学习技术。DINO是一种自蒸馏框架,学生网络学习匹配动量更新后的教师输出,产生具有强大k-NN分类性能的特征。最后以Masked Autoencoders(MAE)为例,它采用对称的编码器-解码器设计来重建高度遮罩的输入,提供了一种可伸缩性高、有效的预训练大规模视觉模型的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇报告分析了计算机视觉中关键设计模式的演变,通过考察六篇有影响力的论文,从基础的图像识别架构到生成模型、自监督学习技术进行了深入探讨。报告强调了残差连接、Transformer架构、生成对抗网络(GANs)、潜在扩散模型(LDMs)以及自蒸馏框架(DINO)和掩码自动编码器(MAE)等关键技术和方法的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 报告分析了计算机视觉领域关键设计模式的演进,从图像识别的基础架构开始。
- 介绍了ResNet如何引入残差连接解决梯度消失问题,并有效训练更深的卷积网络。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)首次将Transformer架构应用于图像补丁序列,展示了基于注意力的模型在大规模图像识别中的有效性。
- 报告探讨了生成模型,特别是生成对抗网络(GANs)的对抗性训练过程,以及潜在扩散模型(LDMs)在生成方法上的改进。
- 自监督学习技术减少了对面标签数据的依赖,其中DINO自蒸馏框架和Masked Autoencoders(MAE)是代表方法。
- LDMs通过感知压缩的潜在空间中的连续去噪过程提高了生成图像的质量和计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

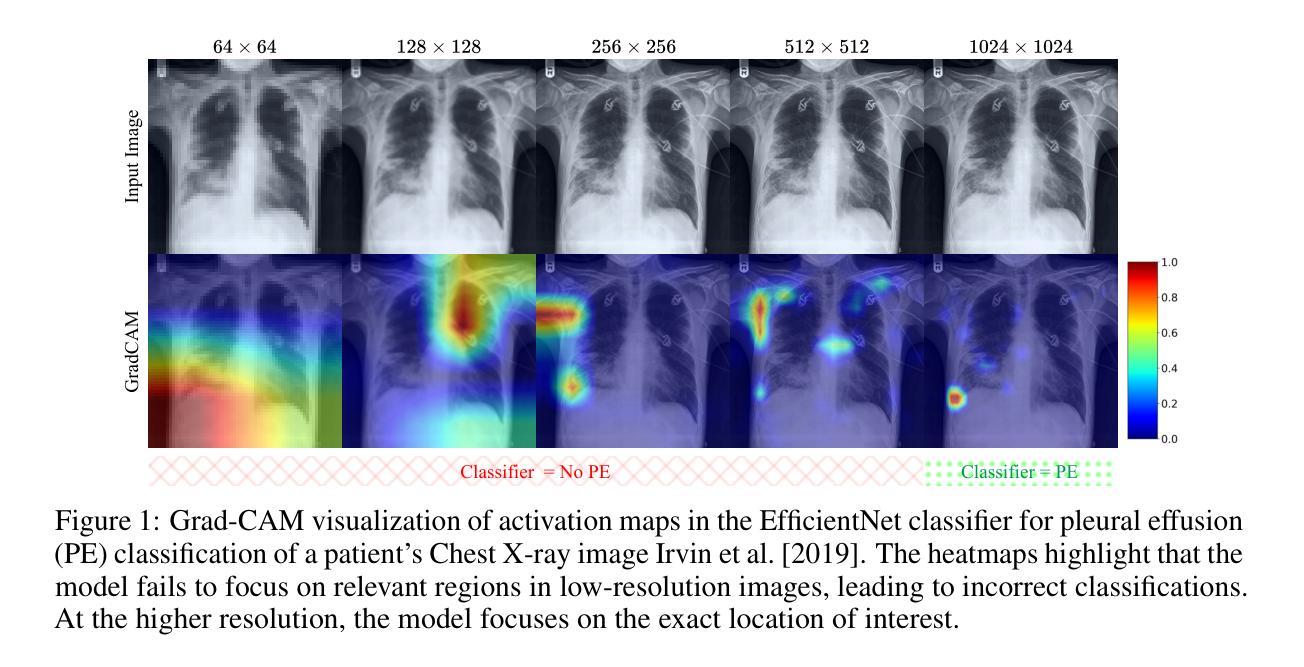
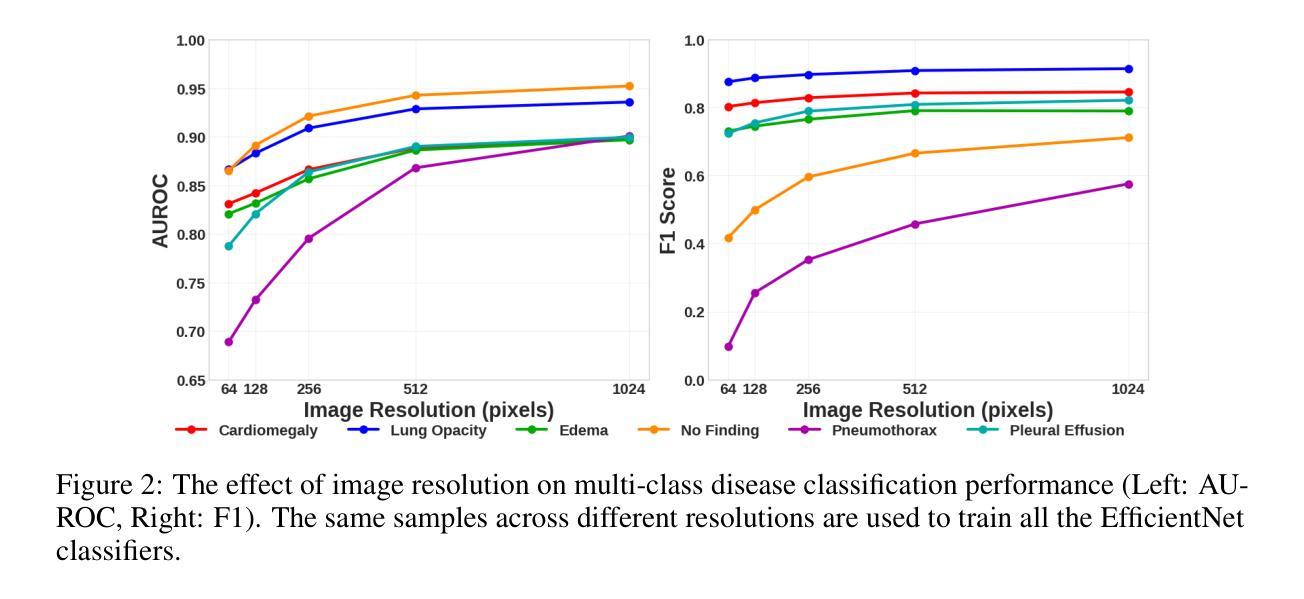
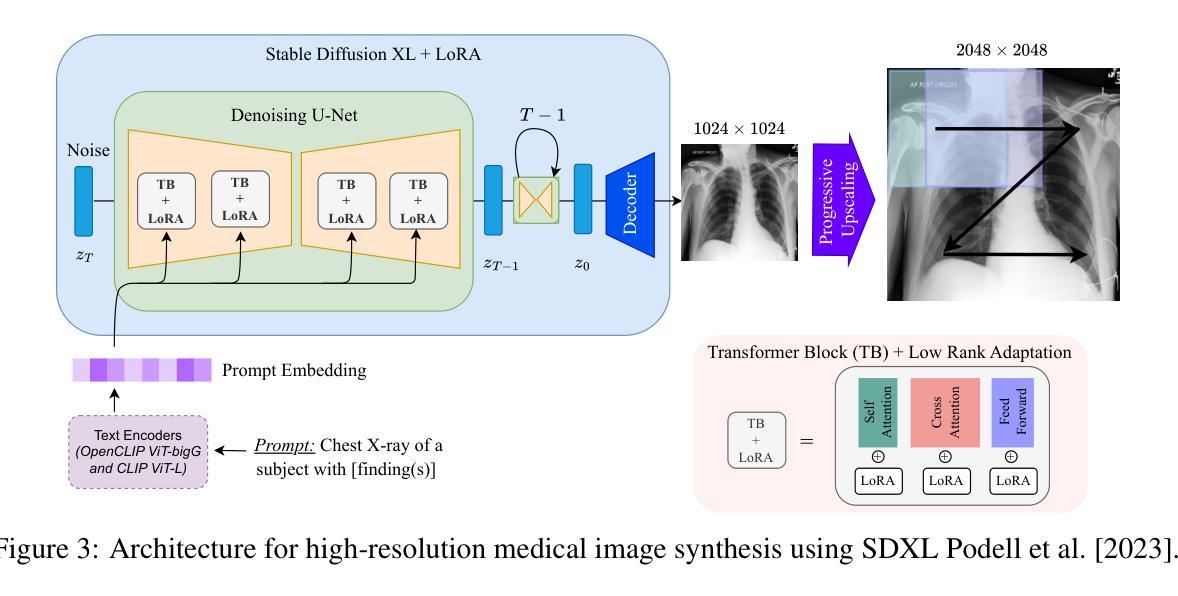
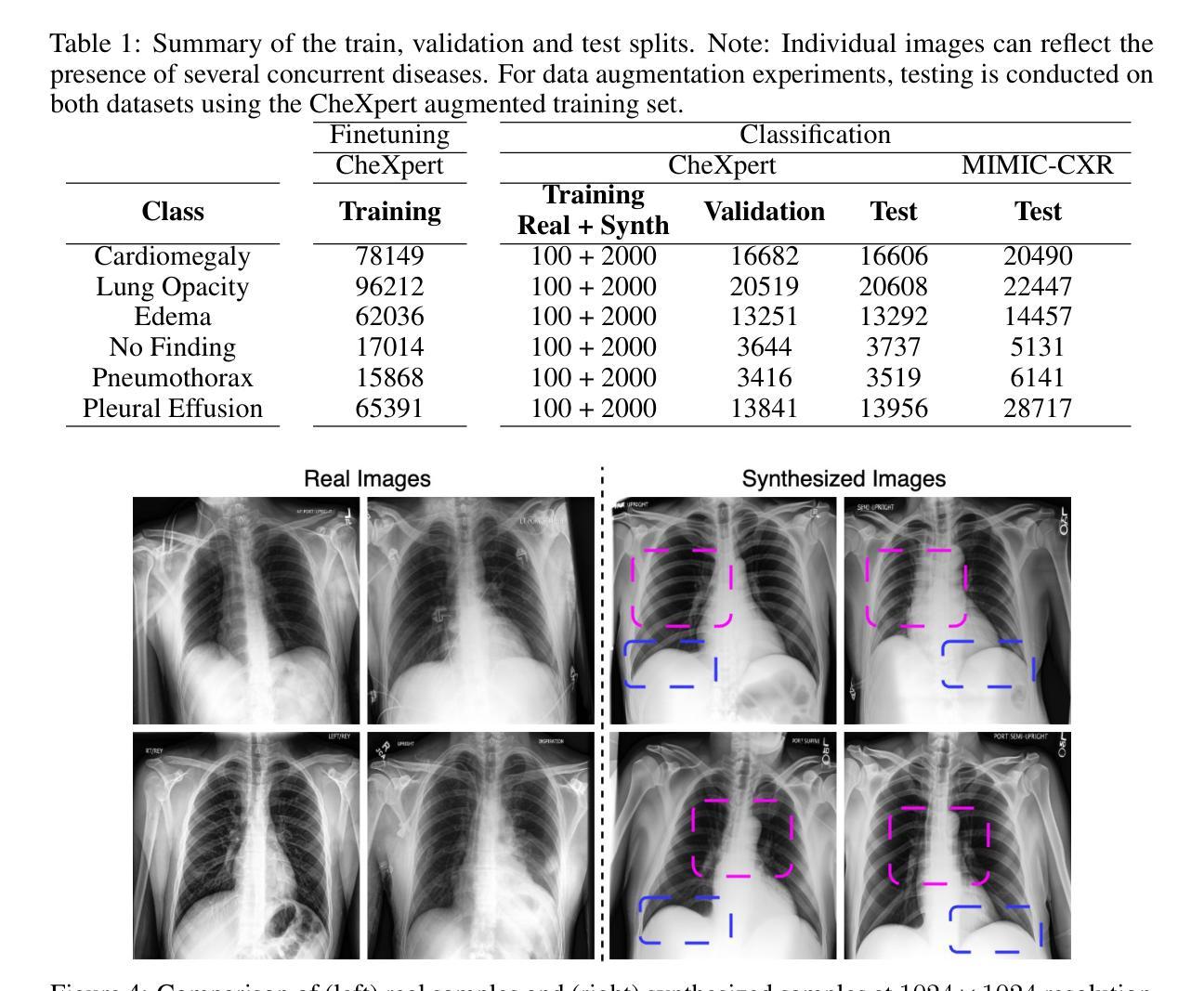
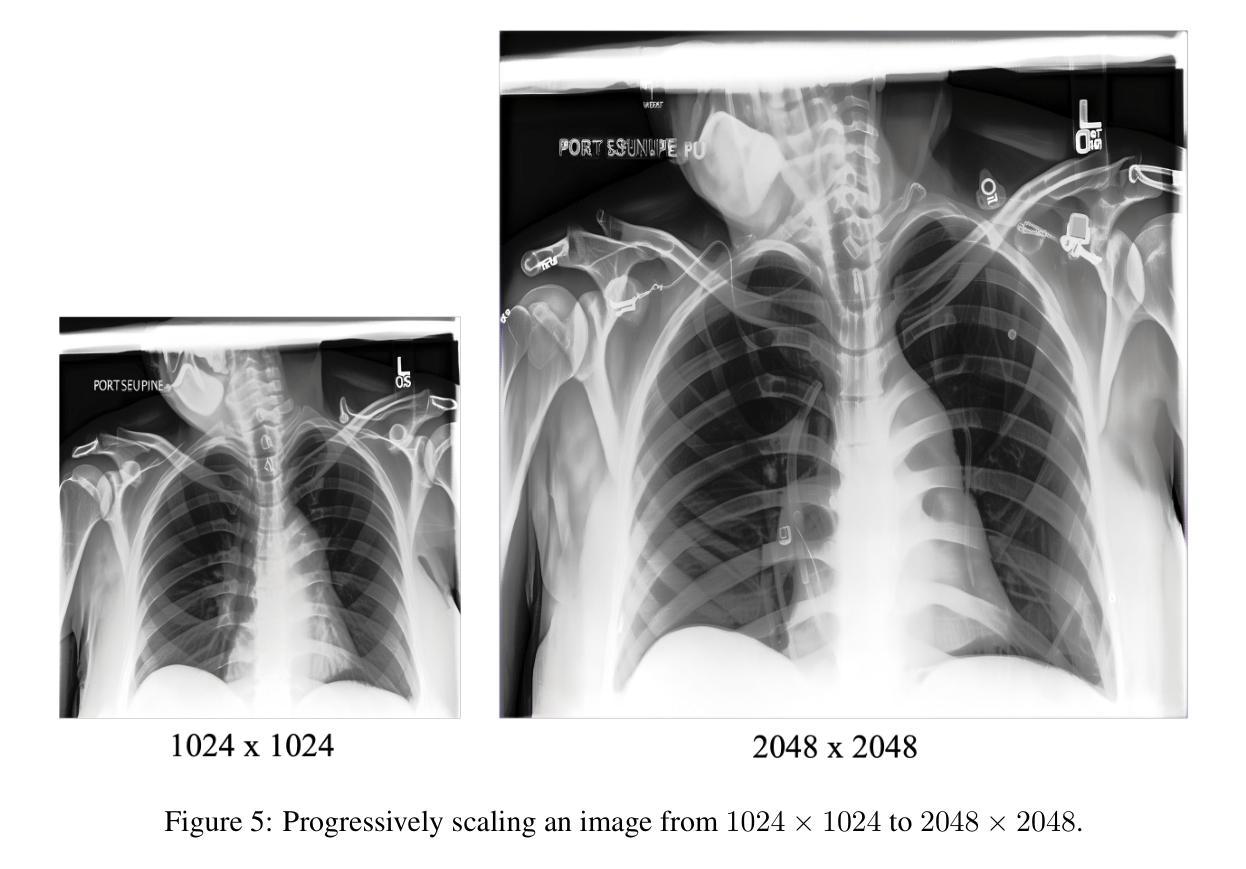
Pixel Perfect MegaMed: A Megapixel-Scale Vision-Language Foundation Model for Generating High Resolution Medical Images
Authors:Zahra TehraniNasab, Hujun Ni, Amar Kumar, Tal Arbel
Medical image synthesis presents unique challenges due to the inherent complexity and high-resolution details required in clinical contexts. Traditional generative architectures such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational Auto Encoder (VAEs) have shown great promise for high-resolution image generation but struggle with preserving fine-grained details that are key for accurate diagnosis. To address this issue, we introduce Pixel Perfect MegaMed, the first vision-language foundation model to synthesize images at resolutions of 1024x1024. Our method deploys a multi-scale transformer architecture designed specifically for ultra-high resolution medical image generation, enabling the preservation of both global anatomical context and local image-level details. By leveraging vision-language alignment techniques tailored to medical terminology and imaging modalities, Pixel Perfect MegaMed bridges the gap between textual descriptions and visual representations at unprecedented resolution levels. We apply our model to the CheXpert dataset and demonstrate its ability to generate clinically faithful chest X-rays from text prompts. Beyond visual quality, these high-resolution synthetic images prove valuable for downstream tasks such as classification, showing measurable performance gains when used for data augmentation, particularly in low-data regimes. Our code is accessible through the project website - https://tehraninasab.github.io/pixelperfect-megamed.
医学影像合成面临独特的挑战,这是由于在临床环境中需要固有的复杂性和高分辨率细节。传统的生成架构,如生成对抗网络(GANs)或变分自动编码器(VAEs)在高分辨率图像生成方面显示出巨大潜力,但在保留对于准确诊断至关重要的精细细节方面却遇到困难。为解决这一问题,我们推出了Pixel Perfect MegaMed,这是第一个以视觉语言为基础、能够在1024x1024分辨率下合成图像的模型。我们的方法采用专门设计用于超高分辨率医学影像生成的多尺度变压器架构,能够同时保留全局解剖背景和局部图像级细节。通过利用针对医学术语和成像模式的视觉语言对齐技术,Pixel Perfect MegaMed能够在前所未有的高分辨率水平上弥合了文本描述和视觉表示之间的鸿沟。我们将其模型应用于CheXpert数据集,展示了根据文本提示生成临床真实的胸部X光片的能力。除了视觉质量外,这些高分辨率的合成图像对于下游任务(如分类)具有证明价值,在数据增强方面使用时表现出可衡量的性能提升,特别是在数据稀缺的情况下。我们的代码可通过项目网站访问:https://tehraninasab.github.io/pixelperfect-megamed。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医疗图像合成面临独特的挑战,因为临床环境中需要复杂的固有性和高解析度细节。传统生成架构如生成对抗网络(GANs)或变分自动编码器(VAEs)在高解析度图像生成方面展现出巨大潜力,但在保持精细粒度细节方面存在困难,这对于准确诊断至关重要。为解决这一问题,我们推出Pixel Perfect MegaMed,首个用于合成1024x1024分辨率图像的视觉语言基础模型。该方法采用专为超高分辨率医疗图像生成设计的多尺度变压器架构,能够同时保留全局解剖背景和局部图像级细节。通过利用针对医疗术语和成像模式的视觉语言对齐技术,Pixel Perfect MegaMed在前所未有的高分辨率水平上搭建了文本描述和视觉表示之间的桥梁。我们在CheXpert数据集上应用该模型,并展示了从文本提示生成临床真实胸部X射线图像的能力。除了视觉质量外,这些高分辨率合成图像对于下游任务如分类也证明其价值,特别是在数据增强方面表现出可衡量的性能提升,尤其在低数据情况下更是如此。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像合成面临固有复杂性和高解析度细节的挑战。
- 传统生成架构如GANs和VAEs在高分辨率图像生成上表现出潜力,但难以保留精细细节。
- Pixel Perfect MegaMed是首个用于超高分辨率医疗图像生成的视觉语言基础模型。
- 该模型采用多尺度变压器架构,能同时保留全局解剖背景和局部图像级细节。
- Pixel Perfect MegaMed利用针对医疗术语和成像模式的视觉语言对齐技术。
- 该模型能在前所未有的高分辨率水平上生成临床真实的胸部X射线图像。
点此查看论文截图

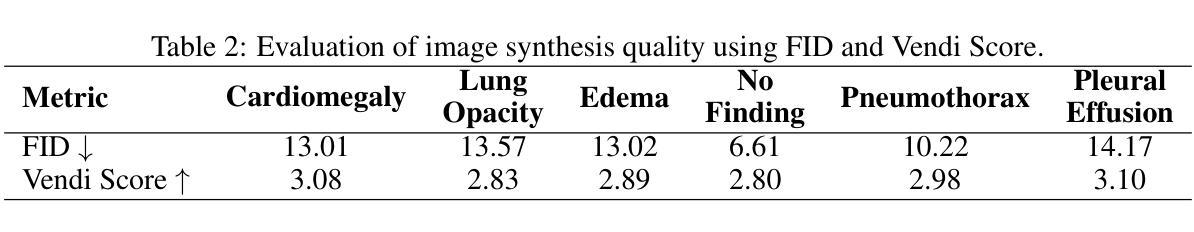
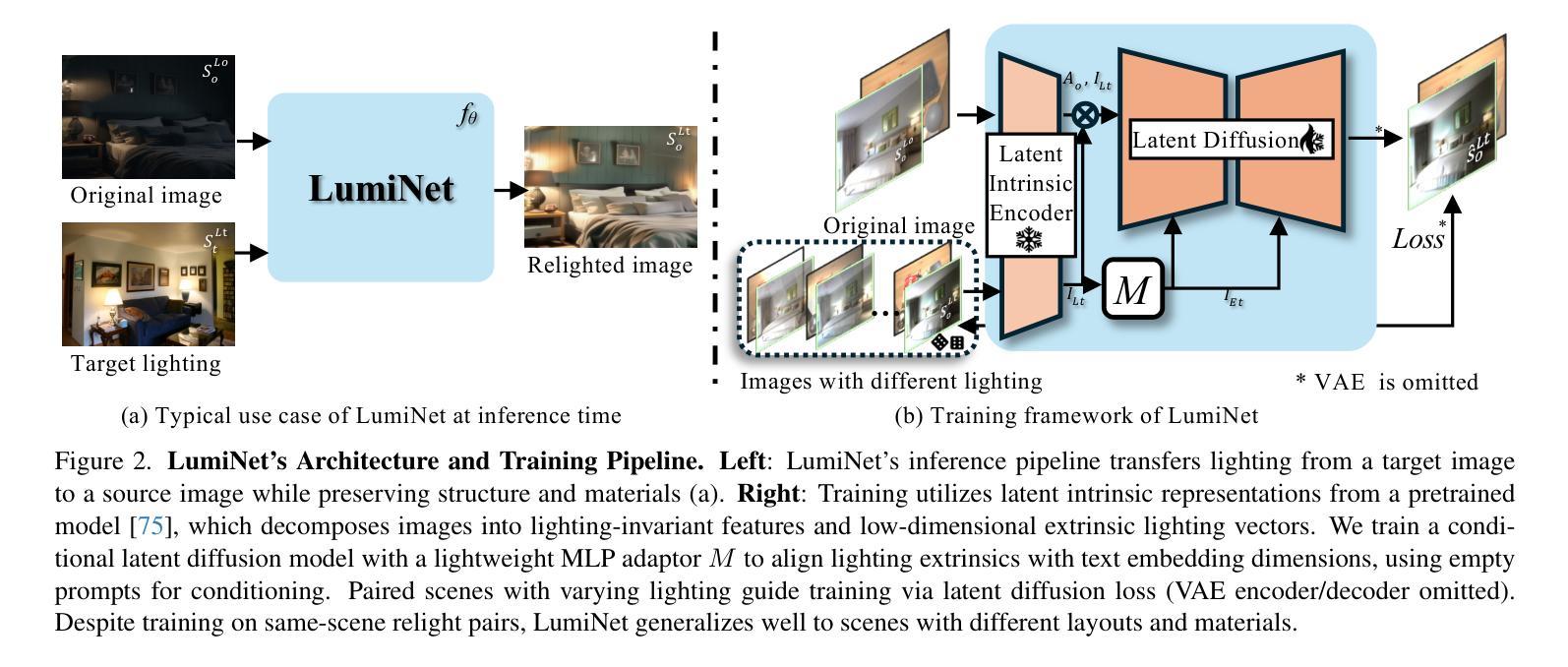
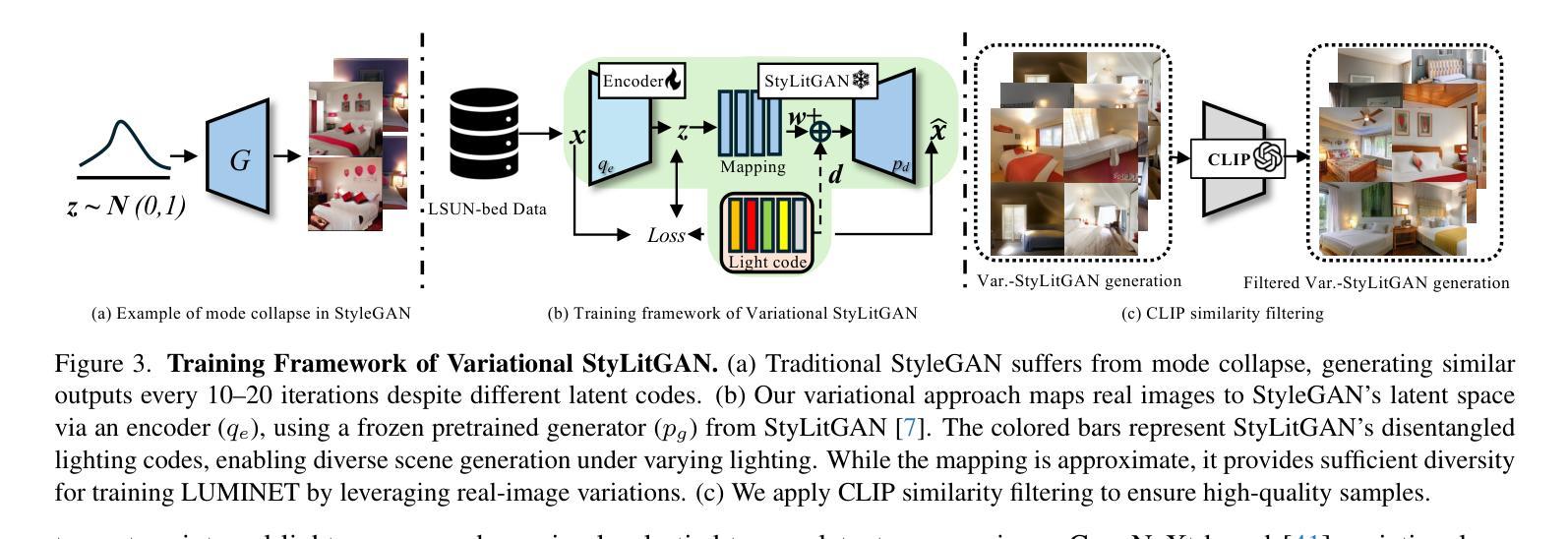
LumiNet: Latent Intrinsics Meets Diffusion Models for Indoor Scene Relighting
Authors:Xiaoyan Xing, Konrad Groh, Sezer Karaoglu, Theo Gevers, Anand Bhattad
We introduce LumiNet, a novel architecture that leverages generative models and latent intrinsic representations for effective lighting transfer. Given a source image and a target lighting image, LumiNet synthesizes a relit version of the source scene that captures the target’s lighting. Our approach makes two key contributions: a data curation strategy from the StyleGAN-based relighting model for our training, and a modified diffusion-based ControlNet that processes both latent intrinsic properties from the source image and latent extrinsic properties from the target image. We further improve lighting transfer through a learned adaptor (MLP) that injects the target’s latent extrinsic properties via cross-attention and fine-tuning. Unlike traditional ControlNet, which generates images with conditional maps from a single scene, LumiNet processes latent representations from two different images - preserving geometry and albedo from the source while transferring lighting characteristics from the target. Experiments demonstrate that our method successfully transfers complex lighting phenomena including specular highlights and indirect illumination across scenes with varying spatial layouts and materials, outperforming existing approaches on challenging indoor scenes using only images as input.
我们介绍了LumiNet,这是一种新型架构,它利用生成模型和潜在内在表示来进行有效的光照转移。给定源图像和目标光照图像,LumiNet合成源场景的重照版本,该版本捕捉目标的光照。我们的方法做出了两个主要贡献:一是基于StyleGAN的重照模型的数据整理策略,用于我们的训练;二是对基于扩散的ControlNet进行修改,该网络处理来自源图像的潜在内在属性和来自目标图像潜在外在属性。我们进一步通过学到的适配器(MLP)改进光照转移,该适配器通过跨注意力和微调注入目标潜在外在属性。与传统的ControlNet不同,后者根据单个场景生成带有条件映射的图像,LumiNet处理来自两个不同图像的潜在表示——保留源场景的几何形状和反射率,同时转移目标场景的光照特性。实验表明,我们的方法在场景空间布局和材料变化的情况下成功转移复杂的照明现象,包括高光和间接照明,并且在仅使用图像作为输入的情况下,在室内场景的复杂挑战上表现优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Corrects an evaluation bug in Table 1 due to a data normalization error. Thanks to the Sony PlayStation team for discovering and reporting the issue. The paper’s core contributions, qualitative results, and user study are unaffected. We also include a minor update to the method to further improve result quality. Project page: https://luminet-relight.github.io/
Summary
LumiNet是一个新型架构,利用生成模型和潜在内在表示进行高效的光线转移。给定源图像和目标光照图像,LumiNet合成源场景的重新照明版本,捕捉目标的光照。我们的方法做出了两个关键贡献:一是从StyleGAN的重新照明模型中为我们的训练进行数据整理策略,二是改进基于扩散的ControlNet,处理来自源图像的潜在内在属性和来自目标图像的外在潜在属性。我们进一步通过学习的适配器和交叉注意力及微调技术改进光线转移。不同于传统的ControlNet,LumiNet处理来自两个不同图像的潜在表示,保留源场景的几何和颜色信息,同时转移目标场景的光照特性。实验表明,我们的方法在复杂的照明现象转移方面表现出色,包括高光和间接照明,适用于不同空间布局和材料的不同室内场景,仅使用图像作为输入就超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- LumiNet是一个新型架构,利用生成模型和潜在表示进行光线转移。
- LumiNet可以从源图像获取潜在内在属性,并从目标图像获取潜在外在属性。
- 通过数据整理策略、改进的ControlNet和学习的适配器改进光线转移。
- LumiNet通过交叉注意力和微调技术实现目标的光照特性转移。
- LumiNet不同于传统的ControlNet,因为它处理来自两个不同图像的潜在表示。
- LumiNet保留了源场景的几何和颜色信息。
点此查看论文截图


Conditional Wasserstein Distances with Applications in Bayesian OT Flow Matching
Authors:Jannis Chemseddine, Paul Hagemann, Gabriele Steidl, Christian Wald
In inverse problems, many conditional generative models approximate the posterior measure by minimizing a distance between the joint measure and its learned approximation. While this approach also controls the distance between the posterior measures in the case of the Kullback–Leibler divergence, this is in general not hold true for the Wasserstein distance. In this paper, we introduce a conditional Wasserstein distance via a set of restricted couplings that equals the expected Wasserstein distance of the posteriors. Interestingly, the dual formulation of the conditional Wasserstein-1 flow resembles losses in the conditional Wasserstein GAN literature in a quite natural way. We derive theoretical properties of the conditional Wasserstein distance, characterize the corresponding geodesics and velocity fields as well as the flow ODEs. Subsequently, we propose to approximate the velocity fields by relaxing the conditional Wasserstein distance. Based on this, we propose an extension of OT Flow Matching for solving Bayesian inverse problems and demonstrate its numerical advantages on an inverse problem and class-conditional image generation.
在逆向问题中,许多条件生成模型通过最小化联合分布与其学习近似分布之间的距离来近似后验分布。虽然这种方法在Kullback-Leibler散度的情况下也控制了后验分布之间的距离,但对于Wasserstein距离来说,通常并不适用。在本文中,我们通过一组限制耦合引入条件Wasserstein距离,该距离等于后验的期望Wasserstein距离。有趣的是,条件Wasserstein-1流的双重形式与条件Wasserstein GAN文献中的损失非常自然地相似。我们推导出条件Wasserstein距离的理论性质,并描述了相应的测地线、速度场以及流ODEs的特性。随后,我们提出了通过放松条件Wasserstein距离来近似速度场的方法。基于此,我们提出了扩展的OT流匹配来解决贝叶斯逆向问题,并在一个逆向问题和类别条件图像生成上展示了其数值优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper supersedes arXiv:2310.13433, accepted at JMLR
Summary
本文介绍了基于条件Wasserstein距离的逆问题解决方案。文章引入了通过限制耦合集定义的条件Wasserstein距离,该距离等于后验分布的期望Wasserstein距离。此外,文章探讨了条件Wasserstein-1流的双重表述,它与条件Wasserstein GAN文献中的损失函数有自然联系。文章还推导了条件Wasserstein距离的理论属性,并展示了其解决贝叶斯逆问题的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 条件生成模型通过最小化联合分布与其学习近似之间的距离来逼近后验分布。
- Wasserstein距离下的条件生成模型并不等同于在Kullback-Leibler散度下的模型。
- 本文引入了条件Wasserstein距离,该距离是通过一组限制耦合定义的,等于后验的期望Wasserstein距离。
- 条件Wasserstein-1流的双重表述与条件Wasserstein GAN文献中的损失函数有自然联系。
- 文章推导了条件Wasserstein距离的理论属性,包括对应的测地线、速度场和流动常微分方程。
- 提出通过放松条件Wasserstein距离来近似速度场的方法。
点此查看论文截图