⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
Robotic 3D Flower Pose Estimation for Small-Scale Urban Farms
Authors:Harsh Muriki, Hong Ray Teo, Ved Sengupta, Ai-Ping Hu
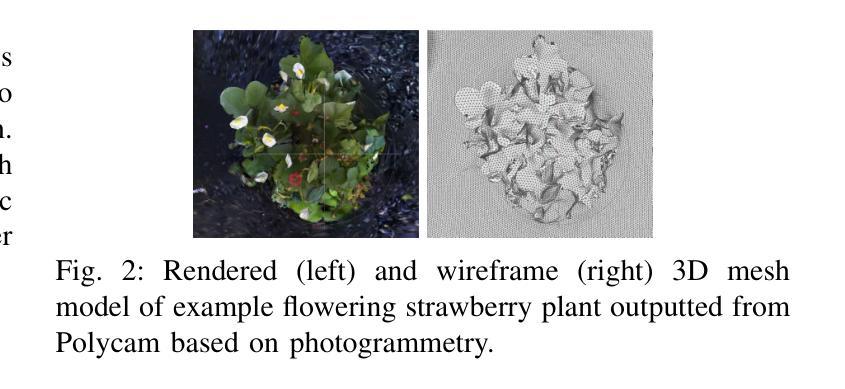
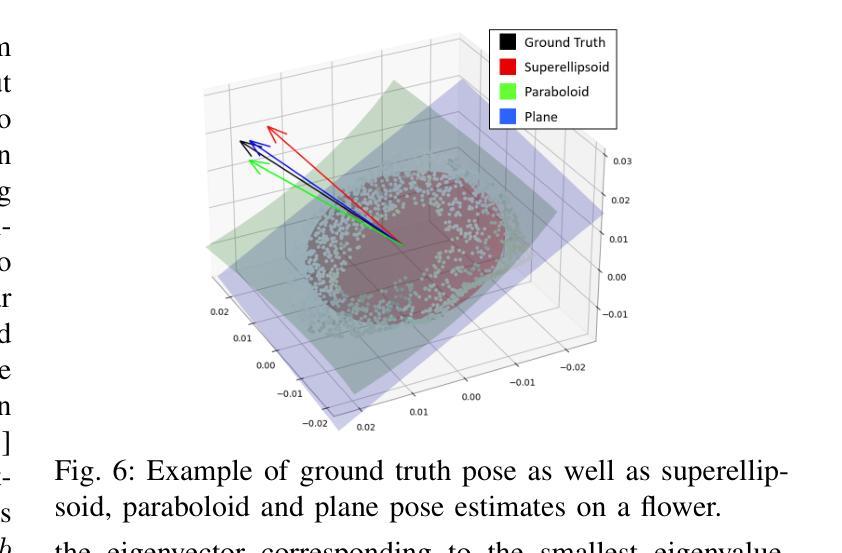
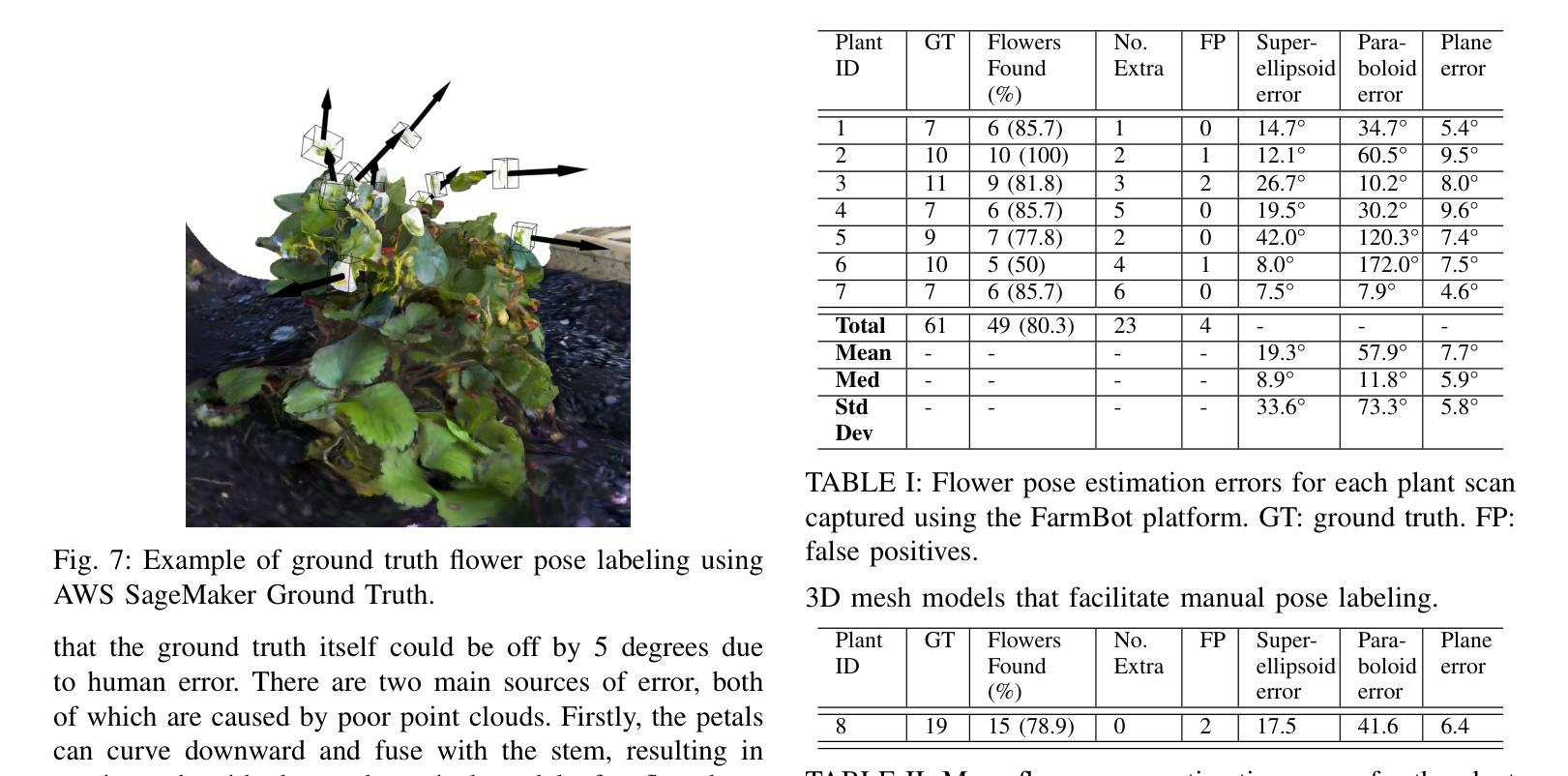
The small scale of urban farms and the commercial availability of low-cost robots (such as the FarmBot) that automate simple tending tasks enable an accessible platform for plant phenotyping. We have used a FarmBot with a custom camera end-effector to estimate strawberry plant flower pose (for robotic pollination) from acquired 3D point cloud models. We describe a novel algorithm that translates individual occupancy grids along orthogonal axes of a point cloud to obtain 2D images corresponding to the six viewpoints. For each image, 2D object detection models for flowers are used to identify 2D bounding boxes which can be converted into the 3D space to extract flower point clouds. Pose estimation is performed by fitting three shapes (superellipsoids, paraboloids and planes) to the flower point clouds and compared with manually labeled ground truth. Our method successfully finds approximately 80% of flowers scanned using our customized FarmBot platform and has a mean flower pose error of 7.7 degrees, which is sufficient for robotic pollination and rivals previous results. All code will be made available at https://github.com/harshmuriki/flowerPose.git.
城市农场的规模较小,且市面上有低成本机器人(如FarmBot)可供商业购买,这些机器人可以自动完成简单的维护任务,从而为植物表型研究提供了一个便捷的平台。我们使用了一台带有定制相机末端执行器的FarmBot,根据获取的3D点云模型来估算草莓植株的花姿态(用于机器人授粉)。我们描述了一种新型算法,该算法可将点云的正交轴上的个体占用网格转换为与六个视点相对应的2D图像。对于每张图像,我们使用针对花朵的2D目标检测模型来识别2D边界框,这些框可以转换为3D空间以提取花朵点云。姿态估计则是通过将三种形状(超椭圆、抛物面和平面)拟合到花朵点云上,并与手动标记的地面实况进行比较来完成的。我们的方法使用定制的FarmBot平台成功找到了大约80%的花朵,花朵姿态的平均误差为7.7度,这对于机器人授粉已经足够,并且与以前的结果相当。所有代码都将在https://github.com/harshmuriki/flowerPose.git上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 7 figures
Summary
城市农场的小型化和低成本机器人的商业化,如自动化简单维护任务的FarmBot,为植物表型研究提供了一个便捷的平台。研究者使用配备定制摄像头的FarmBot来估计草莓植物的花姿态(用于机器人授粉),基于获取的3D点云模型。研究团队开发了一种新算法,该算法可将点云的个别占用网格沿正交轴转换为对应的六个视角的二维图像。对于每个图像,使用二维目标检测模型识别花朵的边界框,可转换为三维空间以提取花朵的点云。通过拟合三种形状(超椭圆体、抛物面和平面)进行姿态估计,并与手动标记的真实值进行比较。研究成功找到了大约80%的花卉信息,采用定制的FarmBot平台;且其花朵姿态的平均误差为7.7度,适用于机器人授粉且有望与前人研究相提并论。相关研究代码将在 https://github.com/harshmuriki/flowerPose.git上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 城市农场小型化和低成本机器人的发展促进了植物表型研究的便捷性。
- 使用FarmBot结合定制摄像头进行草莓植物花卉姿态估计,用于机器人授粉。
- 新算法将点云占用网格转换为对应六个视角的二维图像,实现花卉的识别和分析。
- 利用二维目标检测模型识别花朵边界框,并转换为三维空间进行姿态估计。
- 通过拟合不同形状进行姿态估计,与手动标记的真实值相比,具有较低误差。
- 研究成功识别了大约80%的花卉信息,并采用定制FarmBot平台完成实验。
- 该研究在花卉姿态估计方面的平均误差为7.7度,适合机器人授粉工作。
点此查看论文截图



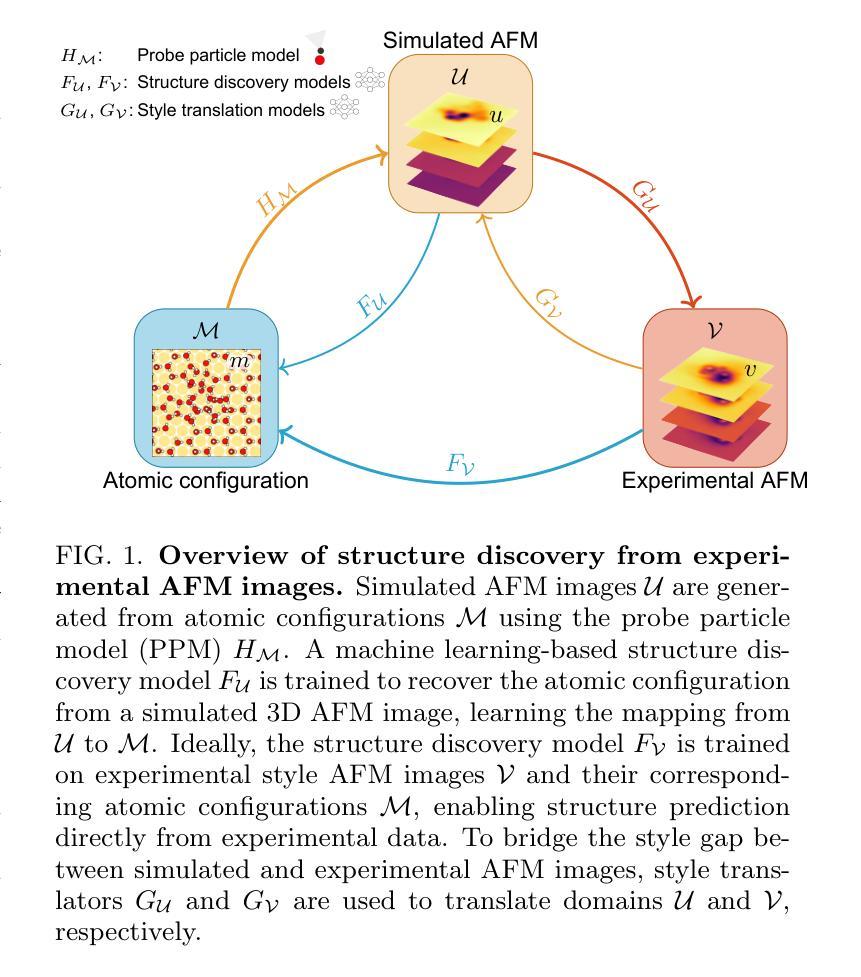
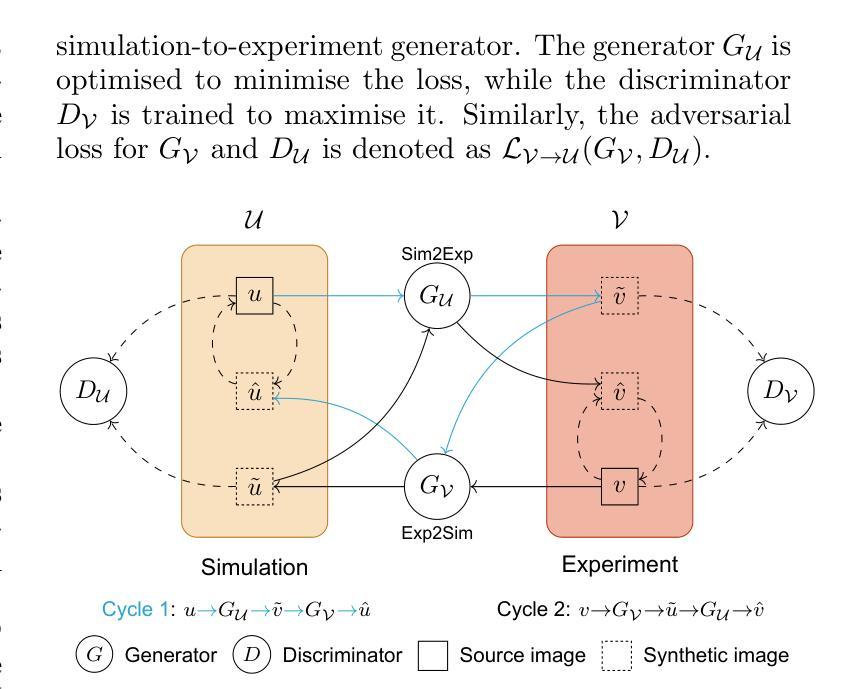
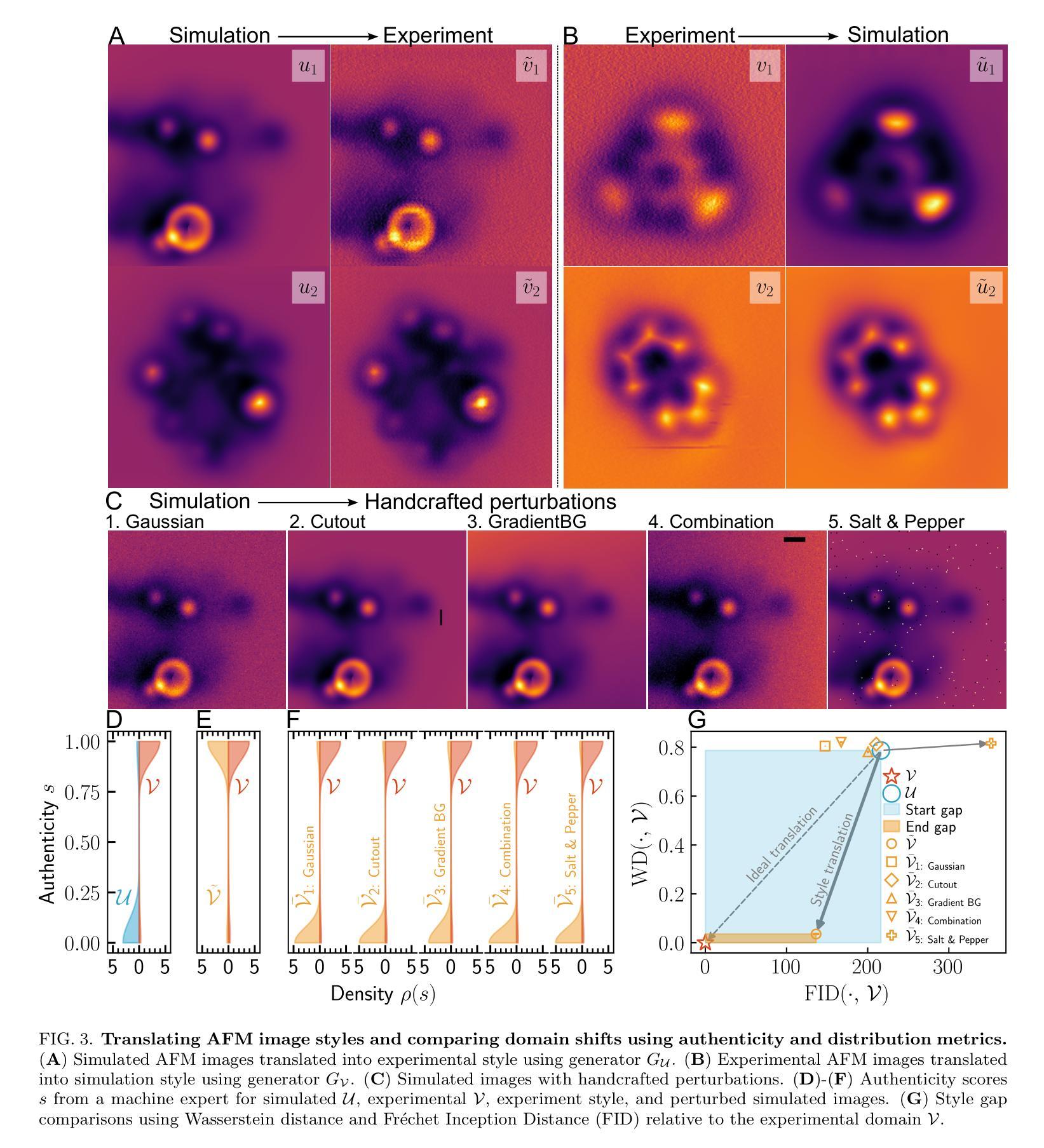
Improving atomic force microscopy structure discovery via style-translation
Authors:Jie Huang, Niko Oinonen, Fabio Priante, Filippo Federici Canova, Lauri Kurki, Chen Xu, Adam S. Foster
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a key tool for characterising nanoscale structures, with functionalised tips now offering detailed images of the atomic structure. In parallel, AFM simulations using the particle probe model provide a cost-effective approach for rapid AFM image generation. Using state-of-the-art machine learning models and substantial simulated datasets, properties such as molecular structure, electrostatic potential, and molecular graph can be predicted from AFM images. However, transferring model performance from simulated to experimental AFM images poses challenges due to the subtle variations in real experimental data compared to the seemingly flawless simulations. In this study, we explore style translation to augment simulated images and improve the predictive performance of machine learning models in surface property analysis. We reduce the style gap between simulated and experimental AFM images and demonstrate the method’s effectiveness in enhancing structure discovery models through local structural property distribution comparisons. This research presents a novel approach to improving the efficiency of machine learning models in the absence of labelled experimental data.
原子力显微镜(AFM)是表征纳米结构的关键工具,其功能化的尖端现在能够提供原子结构的详细图像。同时,使用粒子探针模型的AFM模拟为快速生成AFM图像提供了一种经济高效的方法。利用最先进的机器学习模型和大量的模拟数据集,可以从AFM图像预测分子结构、静电势和分子图等属性。然而,将从模拟到实验AFM图像的模型性能转移却面临挑战,因为与看似完美的模拟相比,实际实验数据存在细微变化。在这项研究中,我们探索风格翻译以扩充模拟图像,提高机器学习模型在分析表面属性方面的预测性能。我们缩小了模拟AFM图像与实验AFM图像之间的风格差距,通过局部结构属性分布比较,证明了该方法在提高结构发现模型方面的有效性。本研究提出了一种在缺乏标记实验数据的情况下提高机器学习模型效率的新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 7 figures
Summary
原子力显微镜(AFM)是表征纳米结构的关键工具,功能化探针尖可以提供原子结构的详细图像。同时,使用粒子探针模型的AFM模拟为快速AFM图像生成提供了经济高效的方法。借助最新机器模型模拟数据集,可以从AFM图像预测分子结构、静电势等属性。然而,将模型性能从模拟转移到实验AFM图像面临挑战,因为现实实验数据与看似完美的模拟之间存在微妙差异。本研究探讨风格翻译技术,增强模拟图像以提高机器学习模型在表面性质分析中的预测性能。我们减少了模拟和实验AFM图像之间的风格差异,通过局部结构属性分布比较,证明了该方法在提升结构发现模型中的有效性。本研究提出一种改进机器学习模型效率的新方法,即使在没有标记实验数据的情况下也能发挥作用。
Key Takeaways
- AFM是表征纳米结构的重要工具,功能化探针尖能提供原子结构的详细图像。
- AFM模拟利用粒子探针模型进行快速图像生成。
- 利用最新机器学习和模拟数据集,可以从AFM图像预测分子结构等属性。
- 将模型性能从模拟转移到实验AFM图像存在挑战,因为现实与模拟之间存在微妙差异。
- 风格翻译技术用于增强模拟图像,提高机器学习模型在表面性质分析中的预测性能。
- 方法通过减少模拟和实验AFM图像之间的风格差异来提高结构发现模型的效率。
点此查看论文截图

Draw-In-Mind: Learning Precise Image Editing via Chain-of-Thought Imagination
Authors:Ziyun Zeng, Junhao Zhang, Wei Li, Mike Zheng Shou
In recent years, integrating multimodal understanding and generation into a single unified model has emerged as a promising paradigm. While this approach achieves strong results in text-to-image (T2I) generation, it still struggles with precise image editing. We attribute this limitation to an imbalanced division of responsibilities. The understanding module primarily functions as a translator that encodes user instructions into semantic conditions, while the generation module must simultaneously act as designer and painter, inferring the original layout, identifying the target editing region, and rendering the new content. This imbalance is counterintuitive because the understanding module is typically trained with several times more data on complex reasoning tasks than the generation module. To address this issue, we introduce Draw-In-Mind (DIM), a dataset comprising two complementary subsets: (i) DIM-T2I, containing 14M long-context image-text pairs to enhance complex instruction comprehension; and (ii) DIM-Edit, consisting of 233K chain-of-thought imaginations generated by GPT-4o, serving as explicit design blueprints for image edits. We connect a frozen Qwen2.5-VL-3B with a trainable SANA1.5-1.6B via a lightweight two-layer MLP, and train it on the proposed DIM dataset, resulting in DIM-4.6B-T2I/Edit. Despite its modest parameter scale, DIM-4.6B-Edit achieves SOTA or competitive performance on the ImgEdit and GEdit-Bench benchmarks, outperforming much larger models such as UniWorld-V1 and Step1X-Edit. These findings demonstrate that explicitly assigning the design responsibility to the understanding module provides significant benefits for image editing. Our dataset and models will be available at https://github.com/showlab/DIM.
近年来,将多模态理解和生成集成到一个单一统一模型中已成为一种前景看好的范式。虽然这一方法在文本到图像(T2I)生成方面取得了很好的效果,但在精确图像编辑方面仍存在困难。我们将这一局限性归因于职责划分的不平衡。理解模块主要充当将用户指令编码为语义条件的翻译器,而生成模块必须同时充当设计师和画家,推断原始布局,识别目标编辑区域,并呈现新内容。这种不平衡是令人困惑的,因为理解模块通常使用大量数据进行复杂推理任务的训练,而生成模块的可用数据相对较少。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了Draw-In-Mind(DIM)数据集,它由两个互补的子集组成:(i)DIM-T2I包含用于增强复杂指令理解的14M长上下文图像文本对;(ii)DIM-Edit由GPT-4o生成的思维链图像组成,包含233K张图像,作为图像编辑的明确设计蓝图。我们通过轻量级两层MLP将冷冻的Qwen2.5-VL-3B与可训练的SANA1.5-1.6B连接起来,并在提出的DIM数据集上进行训练,得到DIM-4.6B-T2I/Edit模型。尽管其参数规模适中,DIM-4.6B-Edit在ImgEdit和GEdit-Bench基准测试中实现了最先进的性能或具有竞争力,超过了诸如UniWorld-V1和Step1X-Edit等大型模型。这些发现表明,明确将设计责任分配给理解模块对于图像编辑具有显著优势。我们的数据集和模型将在https://github.com/showlab/DIM上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tech Report
Summary
近年,多模态理解与生成融合进单一模型成为有前景的研究范式,尽管在文本图像生成上取得良好效果,但在图像精确编辑上仍有局限。本文提出Draw-In-Mind数据集,包含两个互补子集,旨在解决理解模块与生成模块间的职责不平衡问题。训练基于DIM数据集的新模型DIM-4.6B-T2I/Edit展现出强大的图像编辑性能,达到了目前顶尖或竞争力水平。这显示明确设计责任分配对于图像编辑的显著优势。模型和数据集将在网上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态理解与生成统一模型成为研究热点,尤其在文本图像生成领域表现优异。
- 当前模型在图像精确编辑方面存在挑战,主要由于理解模块与生成模块职责不平衡。
- Draw-In-Mind数据集的引入旨在解决上述问题,包含两个互补子集,用于增强复杂指令理解和图像编辑设计蓝图。
- 基于DIM数据集的新模型DIM-4.6B-T2I/Edit展现出强大的图像编辑性能。
- 模型即便参数规模不大,也能达到顶尖或竞争力水平,显示明确分配设计责任的优势。
- 该模型在ImgEdit和GEdit-Bench基准测试中表现优异,超越了一些更大的模型。
点此查看论文截图



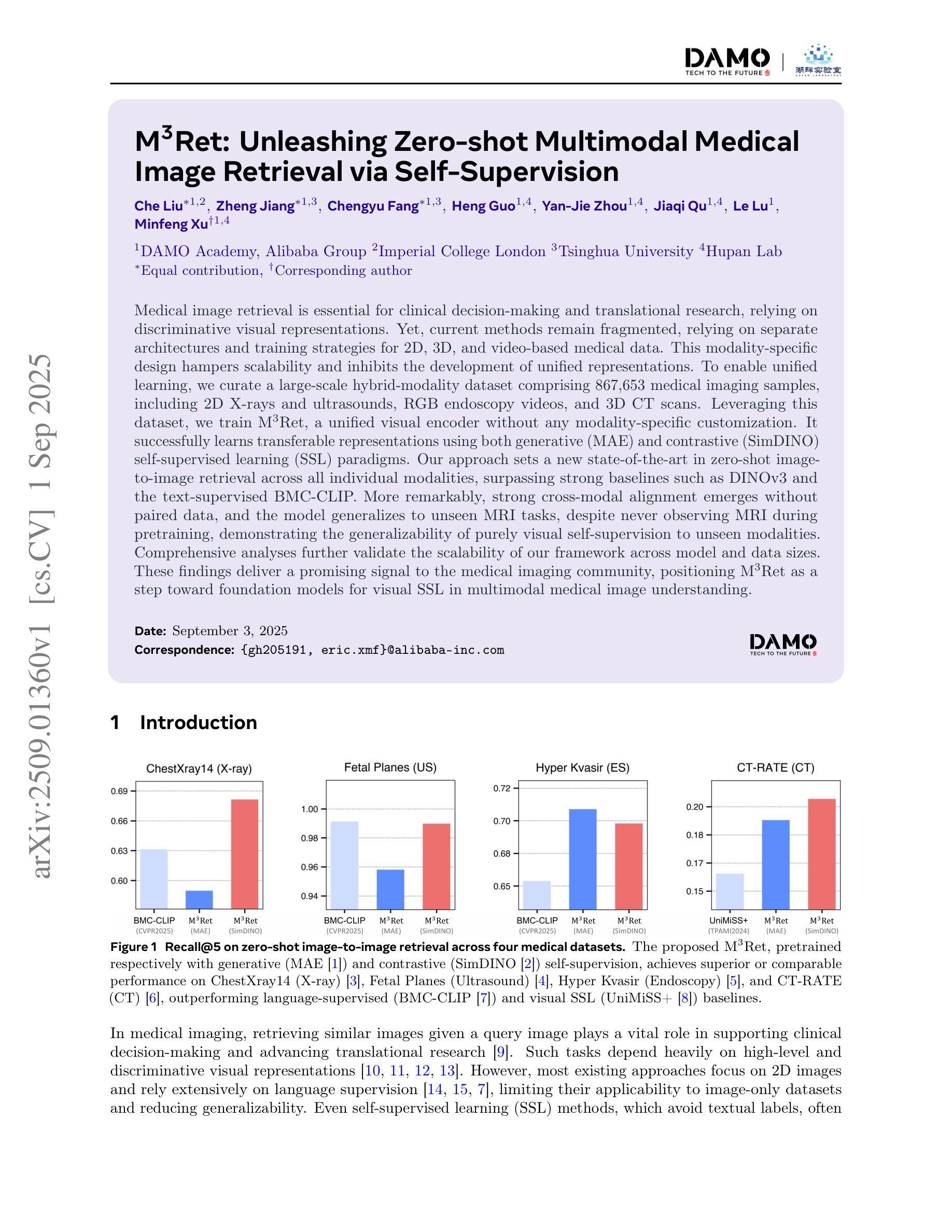
M3Ret: Unleashing Zero-shot Multimodal Medical Image Retrieval via Self-Supervision
Authors:Che Liu, Zheng Jiang, Chengyu Fang, Heng Guo, Yan-Jie Zhou, Jiaqi Qu, Le Lu, Minfeng Xu
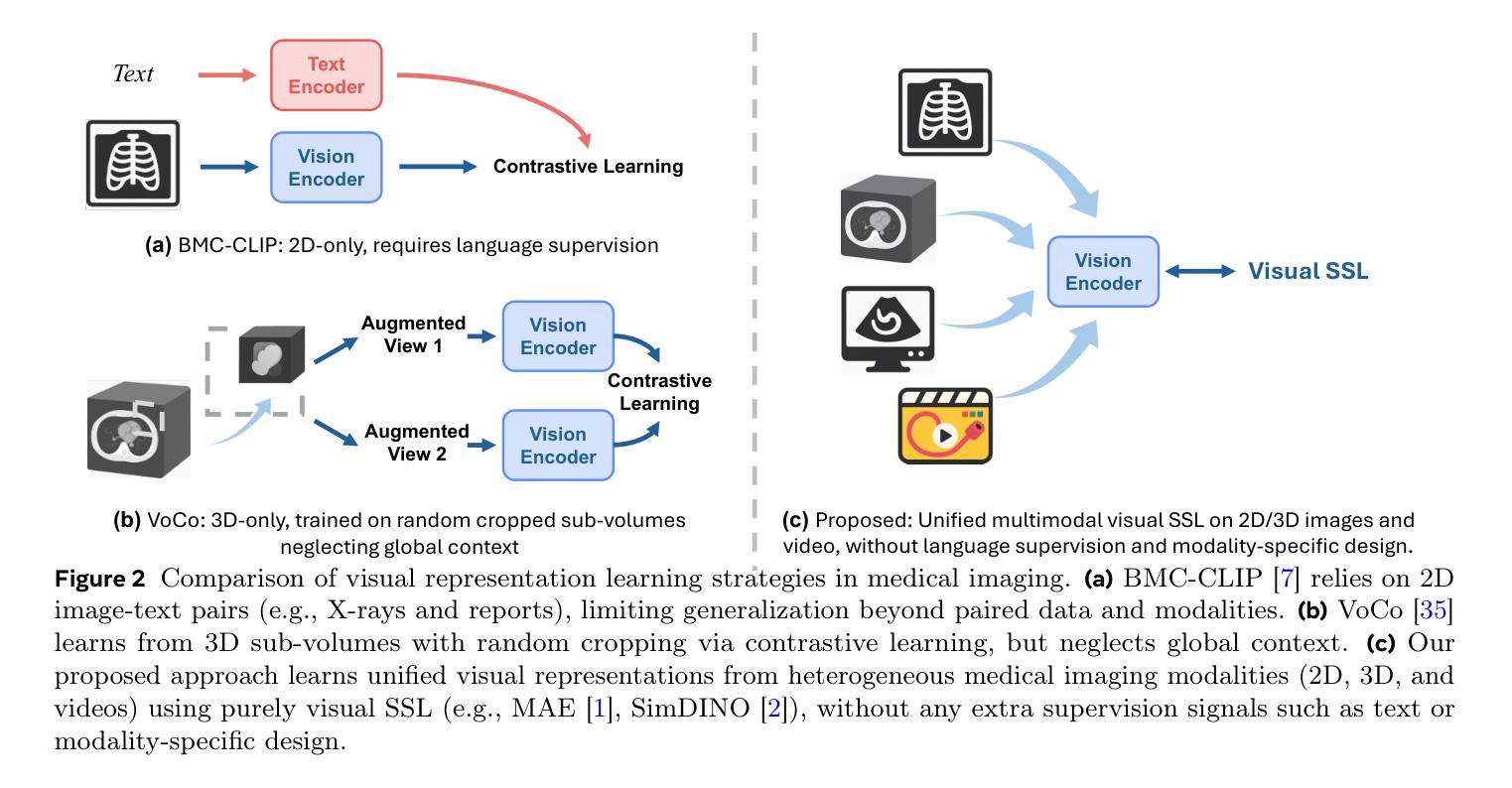
Medical image retrieval is essential for clinical decision-making and translational research, relying on discriminative visual representations. Yet, current methods remain fragmented, relying on separate architectures and training strategies for 2D, 3D, and video-based medical data. This modality-specific design hampers scalability and inhibits the development of unified representations. To enable unified learning, we curate a large-scale hybrid-modality dataset comprising 867,653 medical imaging samples, including 2D X-rays and ultrasounds, RGB endoscopy videos, and 3D CT scans. Leveraging this dataset, we train M3Ret, a unified visual encoder without any modality-specific customization. It successfully learns transferable representations using both generative (MAE) and contrastive (SimDINO) self-supervised learning (SSL) paradigms. Our approach sets a new state-of-the-art in zero-shot image-to-image retrieval across all individual modalities, surpassing strong baselines such as DINOv3 and the text-supervised BMC-CLIP. More remarkably, strong cross-modal alignment emerges without paired data, and the model generalizes to unseen MRI tasks, despite never observing MRI during pretraining, demonstrating the generalizability of purely visual self-supervision to unseen modalities. Comprehensive analyses further validate the scalability of our framework across model and data sizes. These findings deliver a promising signal to the medical imaging community, positioning M3Ret as a step toward foundation models for visual SSL in multimodal medical image understanding.
医学图像检索对于临床决策和转化研究至关重要,依赖于区分性的视觉表示。然而,当前的方法仍然支离破碎,针对2D、3D和基于视频的医疗数据,依赖不同的架构和训练策略。这种模态特定的设计阻碍了可扩展性,并抑制了统一表示的发展。为了支持统一学习,我们创建了一个大规模混合模态数据集,包含867,653个医学成像样本,包括2D X光片和超声波、RGB内窥镜视频和3D CT扫描。利用该数据集,我们训练了M3Ret,这是一种统一的视觉编码器,无需任何模态特定的定制。它成功地利用生成式(MAE)和对比式(SimDINO)自监督学习(SSL)范式学习可迁移的表示。我们的方法在零样本图像到图像检索方面为所有个体模态设定了新的最先进的性能,超越了强大的基线模型,如DINOv3和文本监督的BMC-CLIP。更值得一提的是,即使没有配对数据也出现了强大的跨模态对齐,而且该模型可以推广到未见过的MRI任务,尽管在预训练阶段从未接触过MRI数据,这证明了纯视觉自监督对未见模态的泛化能力。全面的分析进一步验证了我们的框架在不同模型和数据规模上的可扩展性。这些发现向医学成像界传递了积极的信号,并将M3Ret定位为面向多模态医学图像理解的视觉SSL基础模型的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary:
本研究针对医疗图像检索在临床决策和转化研究中的重要性,提出了一个统一视觉编码器M3Ret。该编码器无需针对特定模态进行定制,能够在大型混合模态数据集上进行训练,并成功利用生成式(MAE)和对比式(SimDINO)自监督学习范式学习可迁移表示。M3Ret在零样本图像检索方面表现出卓越性能,超越了DINOv3和文本监督的BMC-CLIP等强基线模型。此外,该模型在未见过MRI任务的情况下具有良好的泛化能力,证明了纯粹视觉自监督在未见模态中的通用性。综合分析验证了该框架在模型和数据规模方面的可扩展性。这些发现对医疗成像领域具有积极意义,为视觉自监督在多种模态医疗图像理解中的基础模型发展奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways:
- 医疗图像检索在临床决策和转化研究中具有重要意义,依赖于判别性视觉表示。
- 当前方法因针对2D、3D和视频基础医疗数据的独立架构和训练策略而显得零散,阻碍了可扩展性和统一表示的发展。
- 提出了一种大型混合模态数据集,包含867,653个医疗成像样本,用于训练统一的视觉编码器M3Ret。
- M3Ret无需特定模态定制,利用生成式和对比式自监督学习范式成功学习可迁移表示。
- M3Ret在零样本图像检索方面表现优异,超越其他强基线模型,并显示出在不同模态间的良好对齐效果。
- 模型在未见过的MRI任务中表现出良好的泛化能力,证明了纯粹视觉自监督的通用性。
点此查看论文截图
A Unified Low-level Foundation Model for Enhancing Pathology Image Quality
Authors:Ziyi Liu, Zhe Xu, Jiabo Ma, Wenqaing Li, Junlin Hou, Fuxiang Huang, Xi Wang, Ronald Cheong Kin Chan, Terence Tsz Wai Wong, Hao Chen
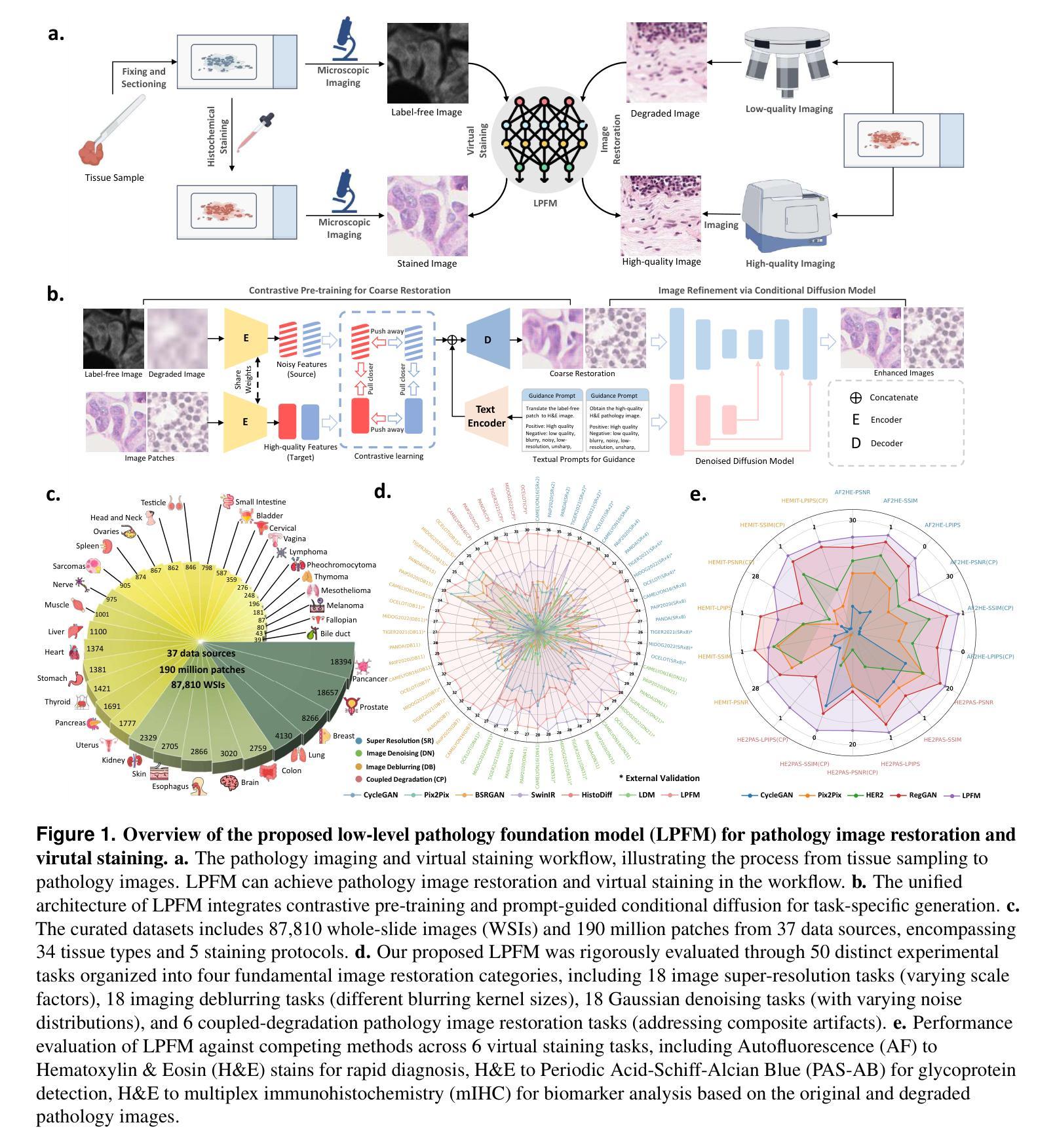
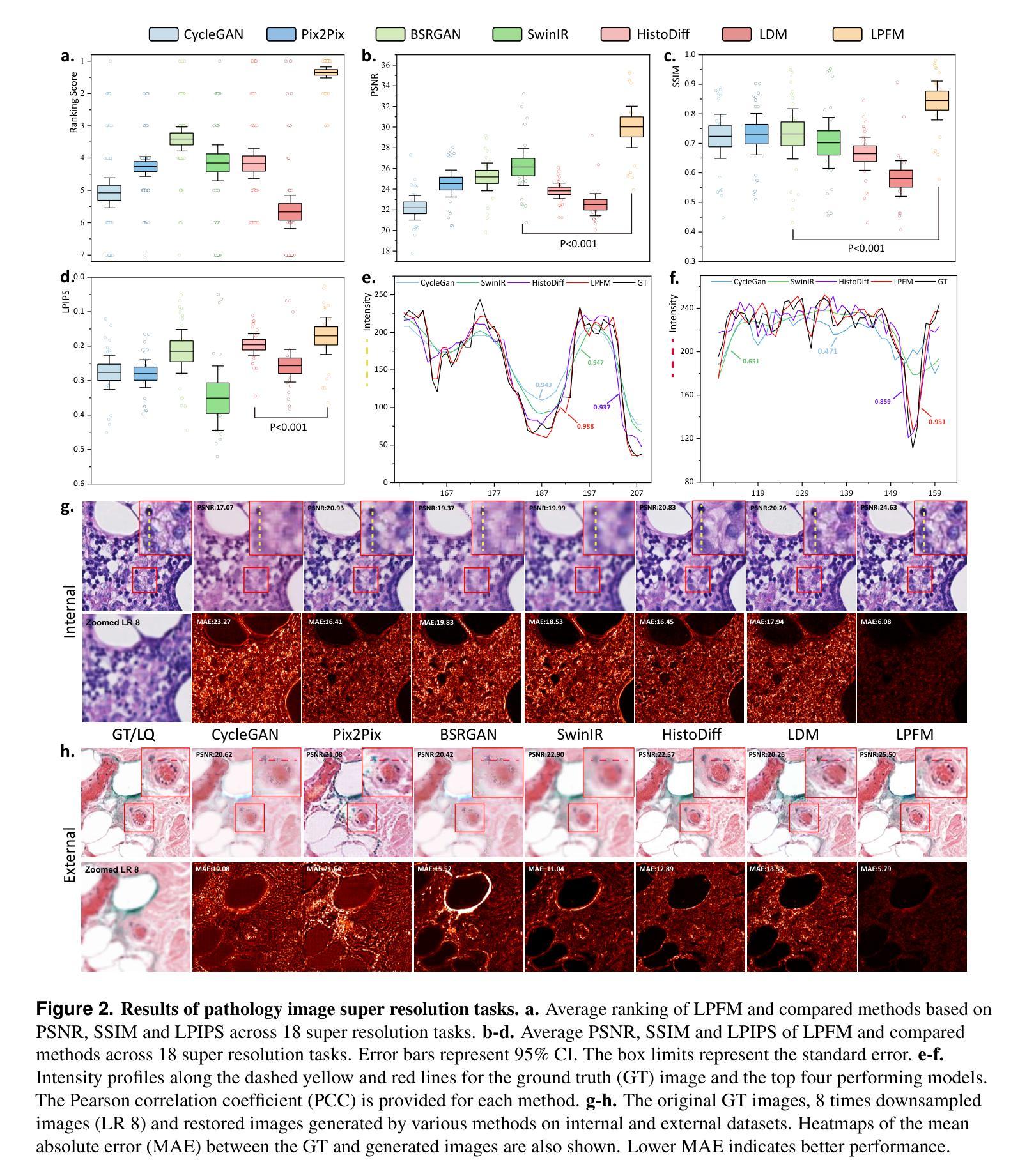
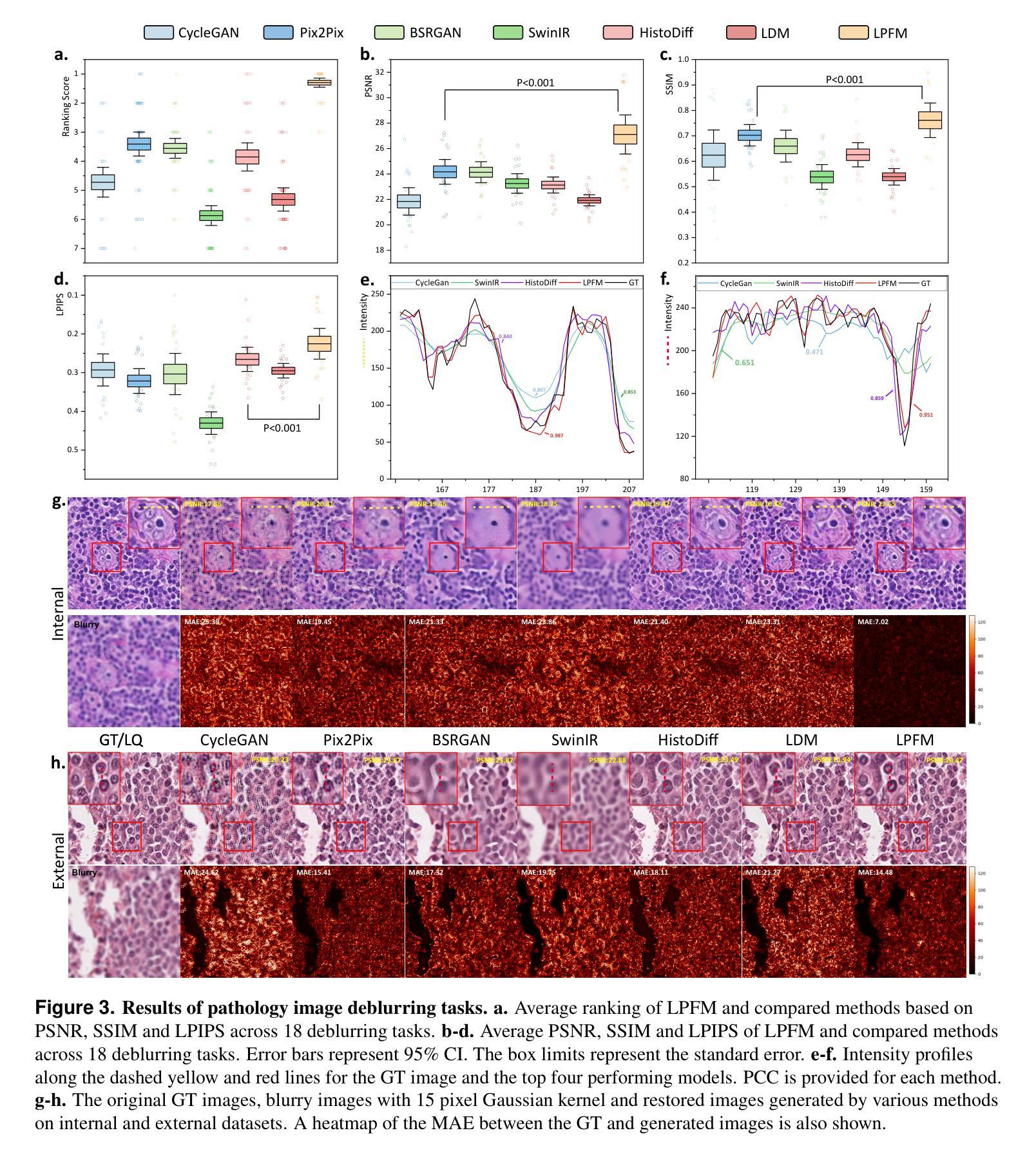
Foundation models have revolutionized computational pathology by achieving remarkable success in high-level diagnostic tasks, yet the critical challenge of low-level image enhancement remains largely unaddressed. Real-world pathology images frequently suffer from degradations such as noise, blur, and low resolution due to slide preparation artifacts, staining variability, and imaging constraints, while the reliance on physical staining introduces significant costs, delays, and inconsistency. Although existing methods target individual problems like denoising or super-resolution, their task-specific designs lack the versatility to handle the diverse low-level vision challenges encountered in practice. To bridge this gap, we propose the first unified Low-level Pathology Foundation Model (LPFM), capable of enhancing image quality in restoration tasks, including super-resolution, deblurring, and denoising, as well as facilitating image translation tasks like virtual staining (H&E and special stains), all through a single adaptable architecture. Our approach introduces a contrastive pre-trained encoder that learns transferable, stain-invariant feature representations from 190 million unlabeled pathology images, enabling robust identification of degradation patterns. A unified conditional diffusion process dynamically adapts to specific tasks via textual prompts, ensuring precise control over output quality. Trained on a curated dataset of 87,810 whole slied images (WSIs) across 34 tissue types and 5 staining protocols, LPFM demonstrates statistically significant improvements (p<0.01) over state-of-the-art methods in most tasks (56/66), achieving Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) gains of 10-15% for image restoration and Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) improvements of 12-18% for virtual staining.
模型在高级诊断任务中取得了显著成功,为计算病理学带来了革命性的变化。然而,低层次图像增强的关键挑战仍未得到很好的解决。现实世界中的病理图像由于切片制备过程中的伪影、染色差异和成像限制等因素,经常出现噪声、模糊和低分辨率等退化现象。而依赖于物理染色会引入成本高昂、延迟和不一致性等问题。虽然现有方法针对去噪或超分辨率等单个问题进行优化,但它们具有特定的任务导向设计,缺乏处理实践中遇到的多样化低层次视觉挑战的通用性。为了弥补这一差距,我们首次提出了统一的低层次病理基础模型(LPFM),该模型能够在恢复任务中增强图像质量,包括超分辨率、去模糊和去噪等任务,并且能促进图像翻译任务,如虚拟染色(H&E染色和特殊染色),所有这些功能都通过单一的适应架构实现。我们的方法引入了一个对比预训练编码器,该编码器从1.9亿张未标记的病理图像中学习可迁移的、染色不变的特征表示,从而能够稳健地识别退化模式。一个统一的条件扩散过程通过文本提示动态适应特定任务,确保对输出质量的精确控制。在包含多种组织和染色协议的87,810张全幻灯片图像(WSI)的数据集上训练,LPFM在大多数任务上均实现了显著优于现有技术的改进(p<0.01),在图像恢复任务中峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了10-15%,虚拟染色任务的结构相似性指数(SSIM)提高了12-18%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模型已经在高级诊断任务中取得了革命性的成果,但在低级图像增强方面仍存在挑战。病理图像经常受到噪声、模糊和低分辨率等退化问题的影响,而依赖于物理染色带来的成本、延迟和不一致性也加剧了这些问题。现有方法主要解决去噪或超分辨率等单一问题,缺乏应对实践中遇到的各种低级视觉挑战的能力。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了首个统一的低级病理基础模型(LPFM),能够在恢复任务中提高图像质量,包括超分辨率、去模糊和去噪,并促进图像翻译任务,如虚拟染色(H&E和特殊染色),通过一个单一的可适应架构实现。通过对比预训练编码器学习可转移、染色不变的特征表示,并引入一个统一的条件扩散过程来动态适应特定任务,确保输出质量的精确控制。在涵盖34种组织和5种染色协议的87810张全幻灯片图像(WSIs)数据集上训练,LPFM在大多数任务中实现了显著的改进(p<0.01),图像恢复的峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了10-15%,虚拟染色的结构相似性指数(SSIM)提高了12-18%。
Key Takeaways
- 现有模型在高层次诊断任务中取得显著成功,但在低层次图像增强方面仍面临挑战。
- 病理图像面临噪声、模糊和低分辨率等问题,现有方法缺乏应对多种问题的通用性。
- 提出的低级病理基础模型(LPFM)能够统一处理图像恢复和虚拟染色任务。
- LPFM通过对比预训练编码器学习染色不变的特征表示。
- LPFM引入统一的条件扩散过程,可动态适应不同任务。
- LPFM在多个任务上实现了显著的改进,包括图像恢复的PSNR和虚拟染色的SSIM。
点此查看论文截图

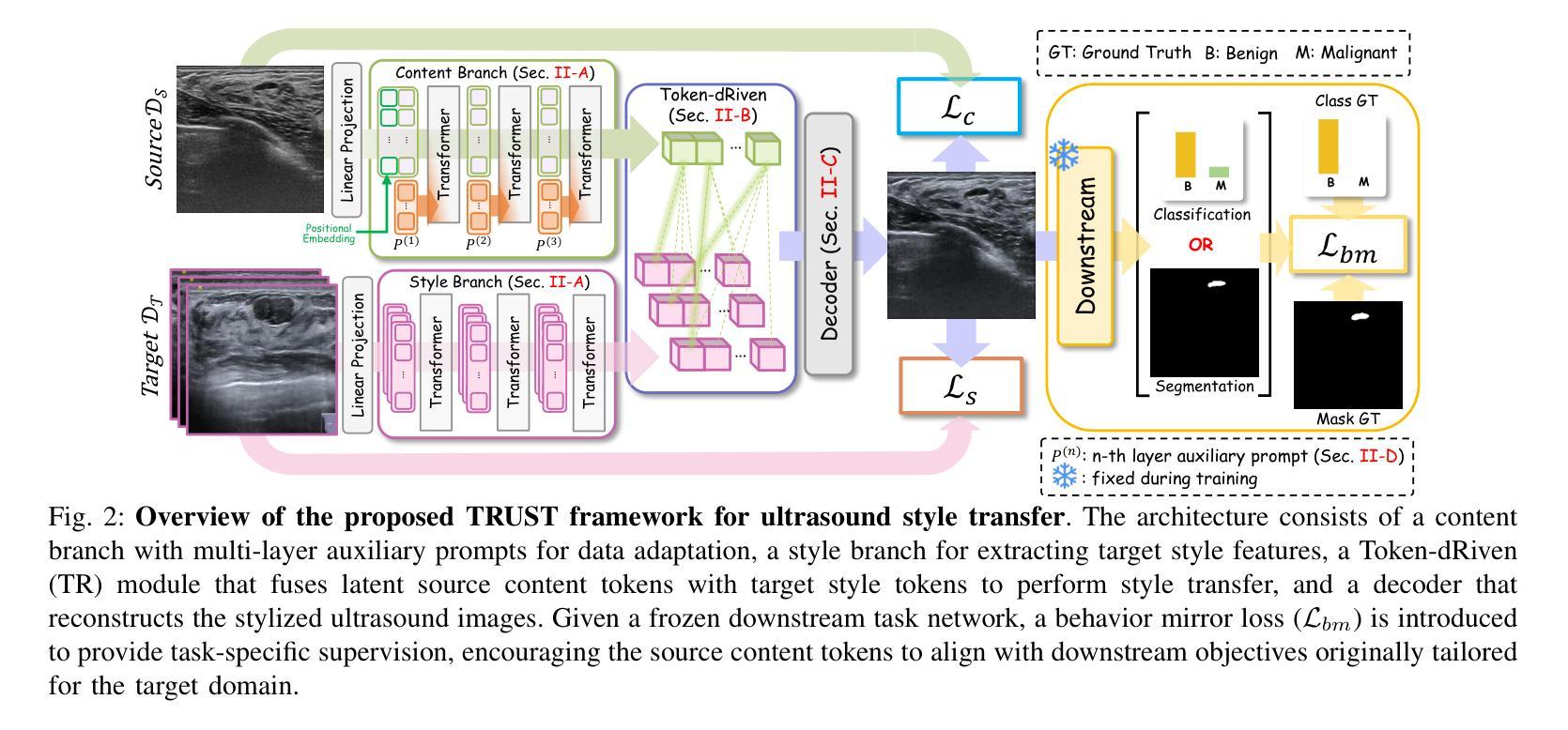
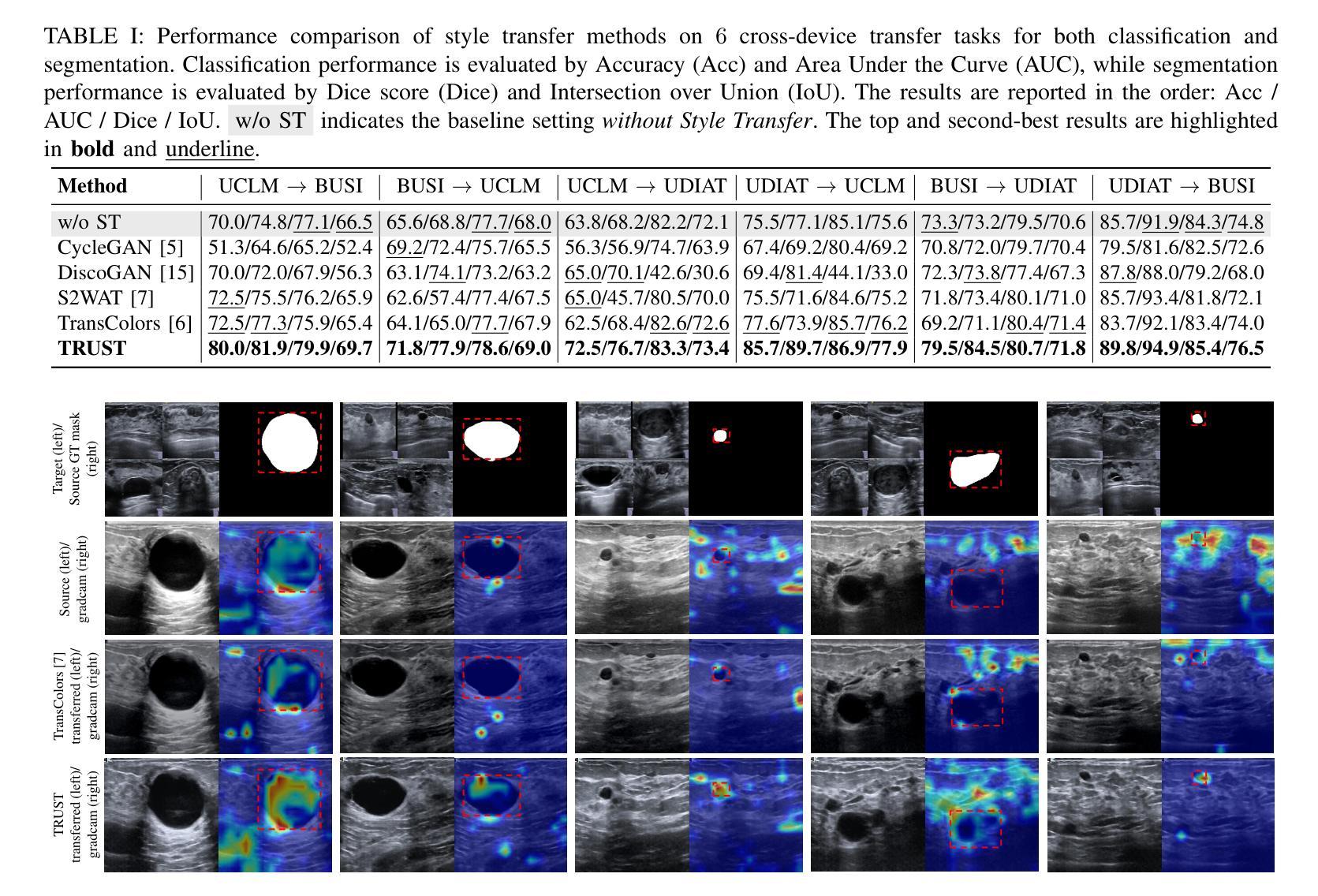
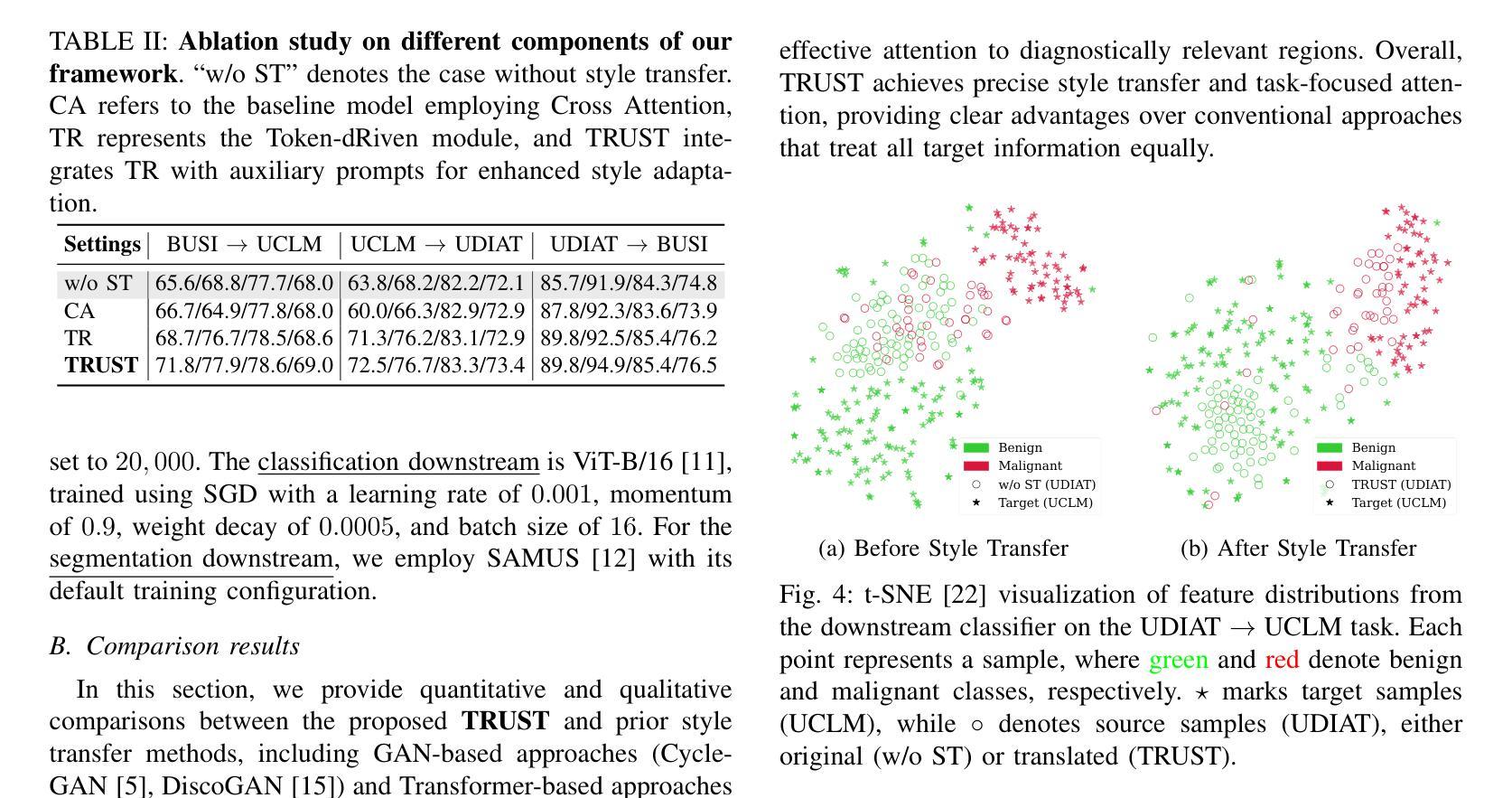
TRUST: Token-dRiven Ultrasound Style Transfer for Cross-Device Adaptation
Authors:Nhat-Tuong Do-Tran, Ngoc-Hoang-Lam Le, Ian Chiu, Po-Tsun Paul Kuo, Ching-Chun Huang
Ultrasound images acquired from different devices exhibit diverse styles, resulting in decreased performance of downstream tasks. To mitigate the style gap, unpaired image-to-image (UI2I) translation methods aim to transfer images from a source domain, corresponding to new device acquisitions, to a target domain where a frozen task model has been trained for downstream applications. However, existing UI2I methods have not explicitly considered filtering the most relevant style features, which may result in translated images misaligned with the needs of downstream tasks. In this work, we propose TRUST, a token-driven dual-stream framework that preserves source content while transferring the common style of the target domain, ensuring that content and style remain unblended. Given multiple styles in the target domain, we introduce a Token-dRiven (TR) module that operates from two perspectives: (1) a data view–selecting “suitable” target tokens corresponding to each source token, and (2) a model view–identifying ``optimal” target tokens for the downstream model, guided by a behavior mirror loss. Additionally, we inject auxiliary prompts into the source encoder to match content representation with downstream behavior. Experimental results on ultrasound datasets demonstrate that TRUST outperforms existing UI2I methods in both visual quality and downstream task performance.
从不同设备获取的超声图像呈现出各种风格,导致下游任务性能下降。为了缩小风格差距,无配对图像到图像(UI2I)转换方法旨在将图像从源域(对应新设备采集)转移到目标域,其中冻结的任务模型已针对下游应用进行训练。然而,现有的UI2I方法没有明确考虑过滤最相关的风格特征,这可能导致翻译后的图像与下游任务的需求不匹配。在这项工作中,我们提出了TRUST,这是一个基于标记的双向流框架,能够在保持源内容的同时转移目标域的共同风格,确保内容和风格保持统一。对于目标域中的多种风格,我们引入了Token-dRiven(TR)模块,该模块从两个角度进行操作:(1)数据视图–选择每个源标记对应的“合适”目标标记;(2)模型视图–由行为镜像损失引导,为下游模型识别“最佳”目标标记。此外,我们向源编码器注入辅助提示,以匹配内容表示和下游行为。在超声数据集上的实验结果表明,TRUST在视觉质量和下游任务性能方面都优于现有的UI2I方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to APSIPA ASC 2025
Summary
本文介绍了超声图像在不同设备采集时产生的风格差异对下游任务性能的影响。为解决这一问题,提出了基于令牌驱动的双流框架TRUST,该框架在迁移图像风格时能够保留源内容,并确保内容和风格不混淆。通过引入Token-dRiven(TR)模块,从数据视角和模型视角选择适合的令牌,提高下游任务性能。同时,通过注入辅助提示匹配内容表示与下游行为。在超声数据集上的实验表明,TRUST在视觉质量和下游任务性能上均优于现有UI2I方法。
Key Takeaways
- 超声图像在不同设备采集时存在风格差异,影响下游任务性能。
- 现行的UI2I方法没有明确地考虑过滤最相关的风格特征,可能导致翻译图像与下游任务需求不匹配。
- 提出基于令牌驱动的双流框架TRUST,该框架旨在解决UI2I中的风格转换问题。
- TRUST能够保留源内容并迁移目标域的共同风格,确保内容和风格的分离。
- 引入Token-dRiven(TR)模块,从数据视角和模型视角选择适合的令牌,提高下游任务性能。
- 通过注入辅助提示匹配内容表示与下游行为,提高模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

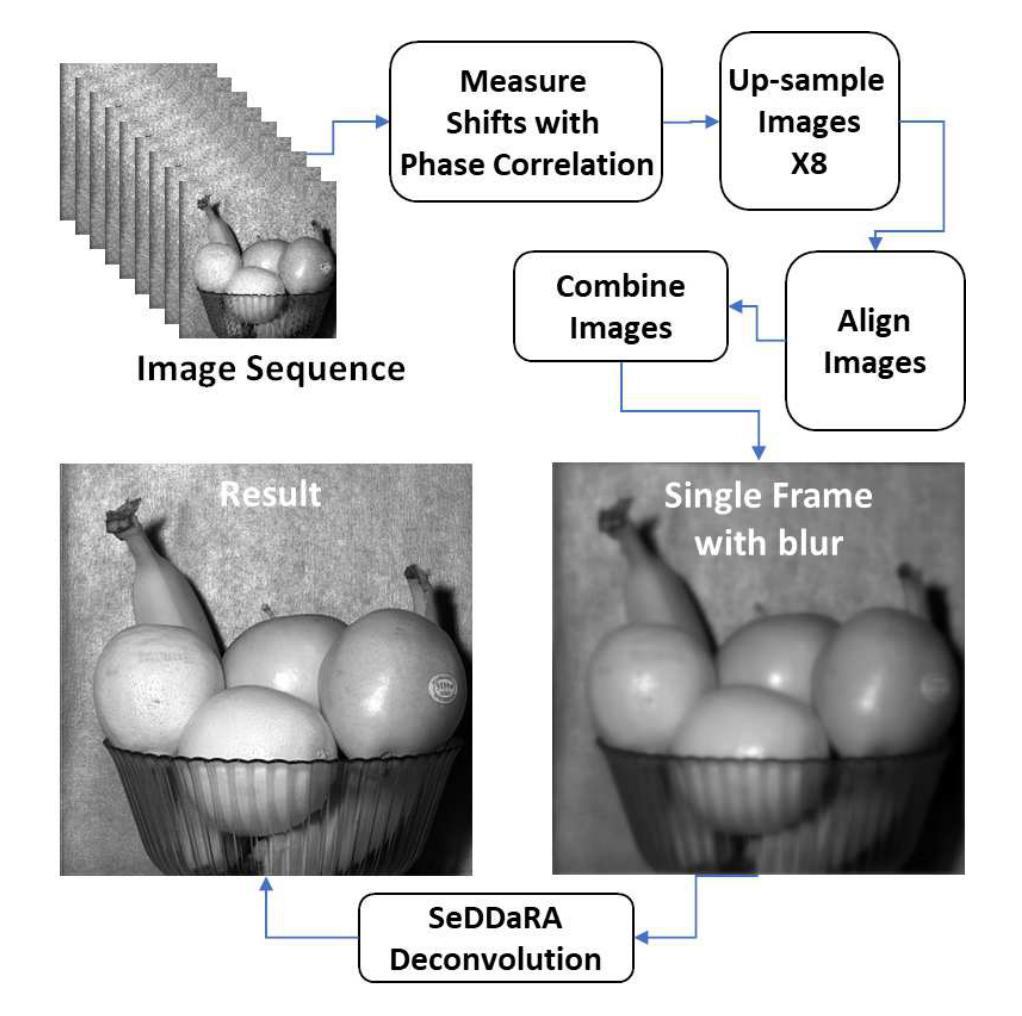
Application of Super-Sampling to Microscopy Images Produces Image Resolution below Optical Diffraction Limit
Authors:James N. Caron
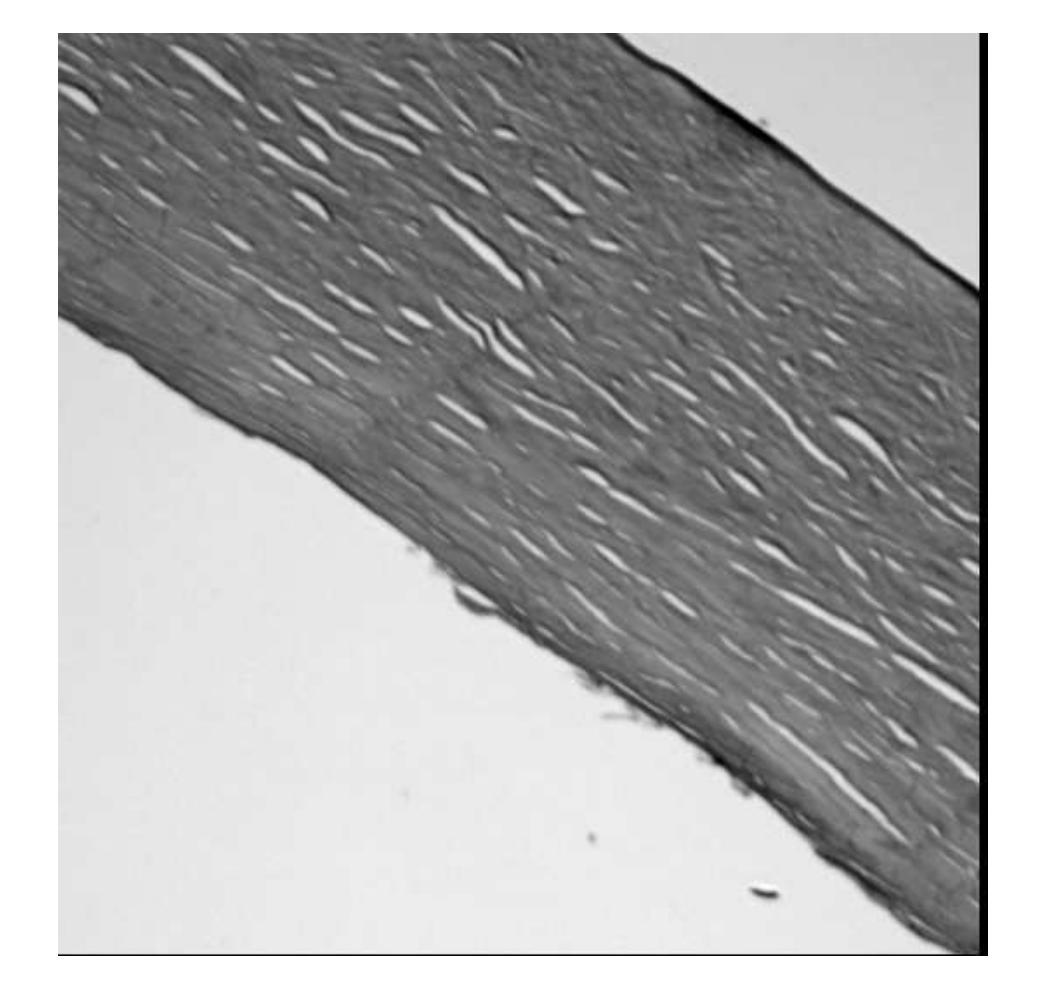
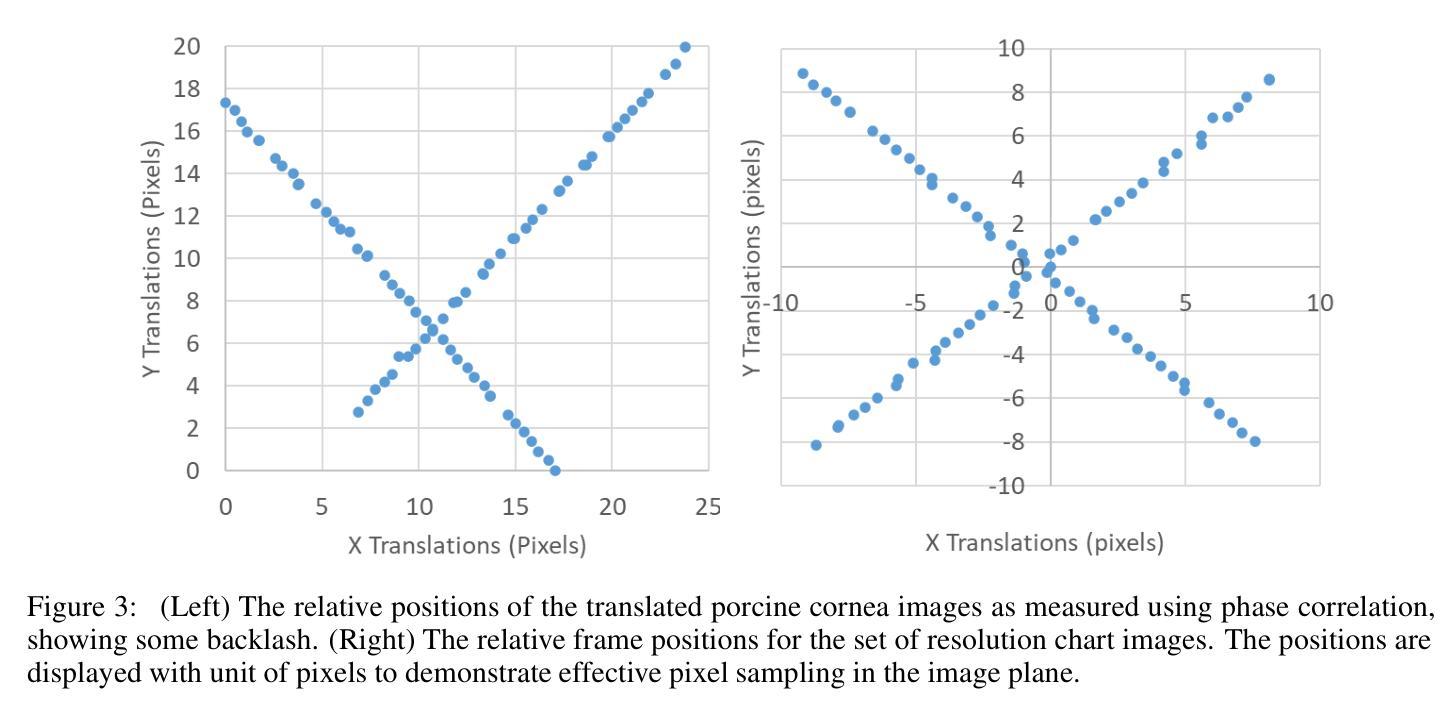
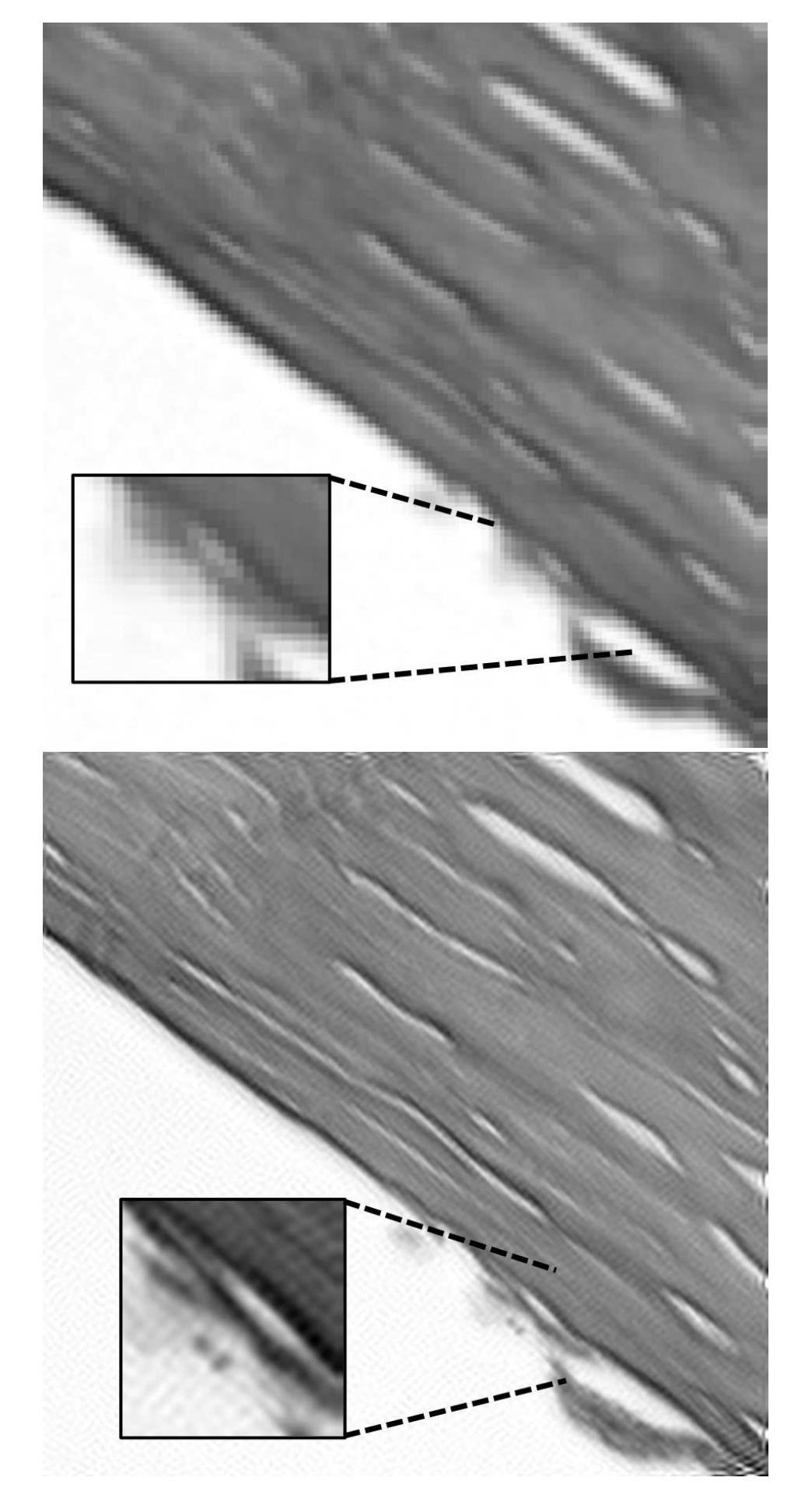
Image Phase Alignment Super-Sampling (ImPASS) is a computational imaging algorithm for converting a sequence of displaced low-resolution images into a single high-resolution image. The method consists of a unique combination of Phase Correlation image registration and SeDDaRA blind deconvolution. The method has previously been validated in simulations and applied successfully to images captured in a laboratory setting. As discussed here, the performance of ImPASS surpasses similar methods that provide quantitative results. ImPASS is applied for the first time to images taken by a widefield microscope, requiring no customization other than a translation stage, to determine if this approach can subceed the diffraction limit for this application. The 80-frame image sets had as targets a slide with a slice of Porcine Cornea, and a standard US Air Force resolution chart, providing quantitative and quantitative assessments. The sets were up-sampled by a factor of eight, aligned, combined, and processed. The measurement revealed that image resolution improved by a factor of 2.68 and subceeded the diffraction limit by a factor of 1.79.
图像相位对准超采样(ImPASS)是一种计算成像算法,可将一系列位移的低分辨率图像转换为单一的高分辨率图像。该方法由相位相关图像配准和SeDDaRA盲解卷积的独特组合构成。该方法已在模拟中得到验证,并成功应用于实验室捕获的图像。正如这里讨论的,ImPASS的性能超过了提供定量结果的其他类似方法。ImPASS首次应用于宽场显微镜拍摄的图像,除平移台外,无需其他定制,以确定此方法是否可以超越此应用程序的衍射极限。80帧图像集的目标是一块带有猪角膜切片和标准的美国空军分辨率图的载玻片,提供了定量和定性评估。这些图像集以八倍的上采样率进行处理,对齐、组合和加工。测量结果显示,图像分辨率提高了2.68倍,超越了衍射极限的1.79倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures. Extended version first presented at Optica Biophotonics Congress: Optics in the Life Sciences, 2025
Summary
本文介绍了图像相位对齐超采样(ImPASS)算法,该算法通过一系列位移的低分辨率图像生成单一的高分辨率图像。结合相位相关图像配准和盲去卷积技术,该方法成功应用于实验室设置的图像中,并且在仿真和定量结果上均验证了其性能优势。此外,本文首次将ImPASS应用于宽场显微镜拍摄的图像,不需要定制化,只需通过平移阶段即可应用。通过对比试验,证明了该方法提高了图像分辨率并超越了衍射极限。
Key Takeaways
- ImPASS算法可以将一系列位移的低分辨率图像转化为单一高分辨率图像。
- 该算法结合了相位相关图像配准和盲去卷积技术。
- ImPASS在仿真和实验室设置中都得到了验证,并且在定量结果上表现出优势。
- ImPASS首次应用于宽场显微镜拍摄的图像。
- 应用ImPASS后,图像分辨率提高了2.68倍。
- ImPASS超越了衍射极限,提高了成像质量。
点此查看论文截图

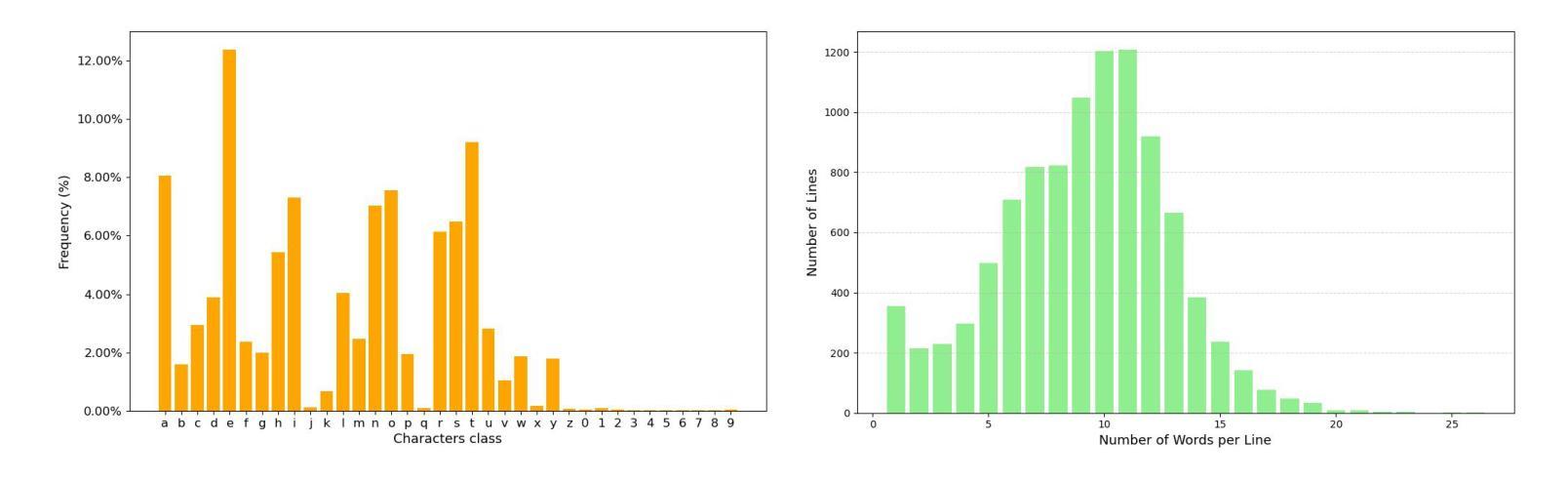
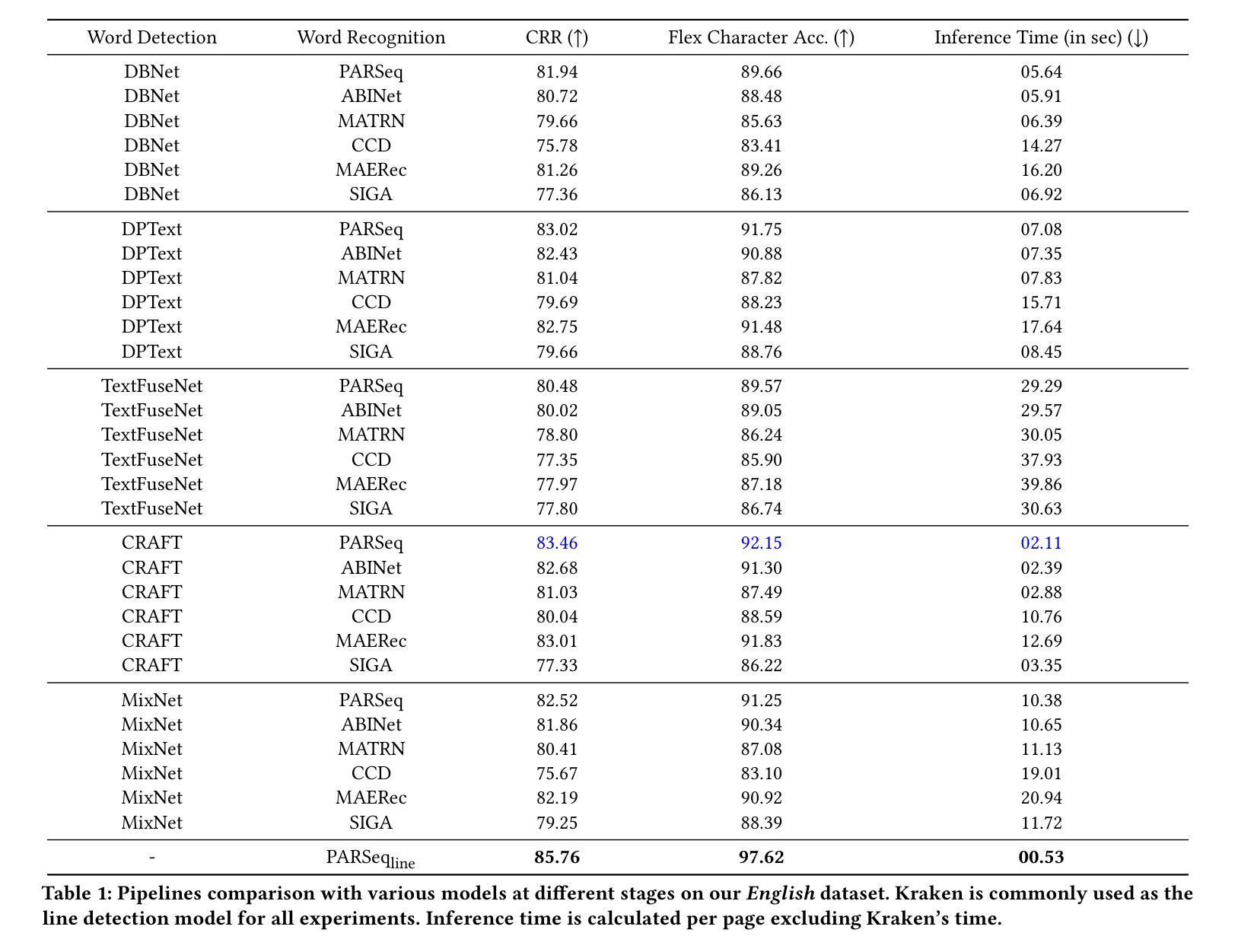
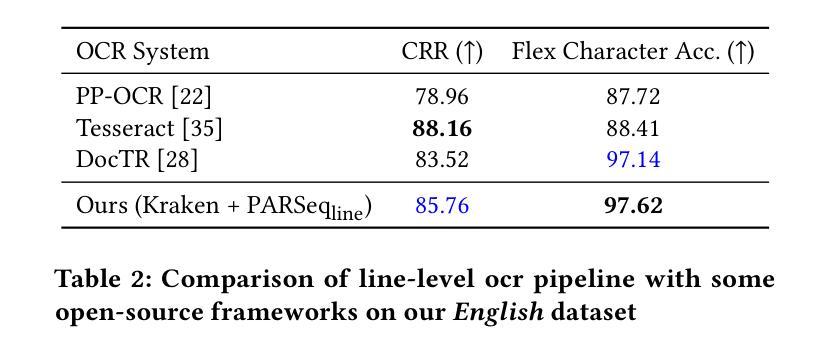
Why Stop at Words? Unveiling the Bigger Picture through Line-Level OCR
Authors:Shashank Vempati, Nishit Anand, Gaurav Talebailkar, Arpan Garai, Chetan Arora
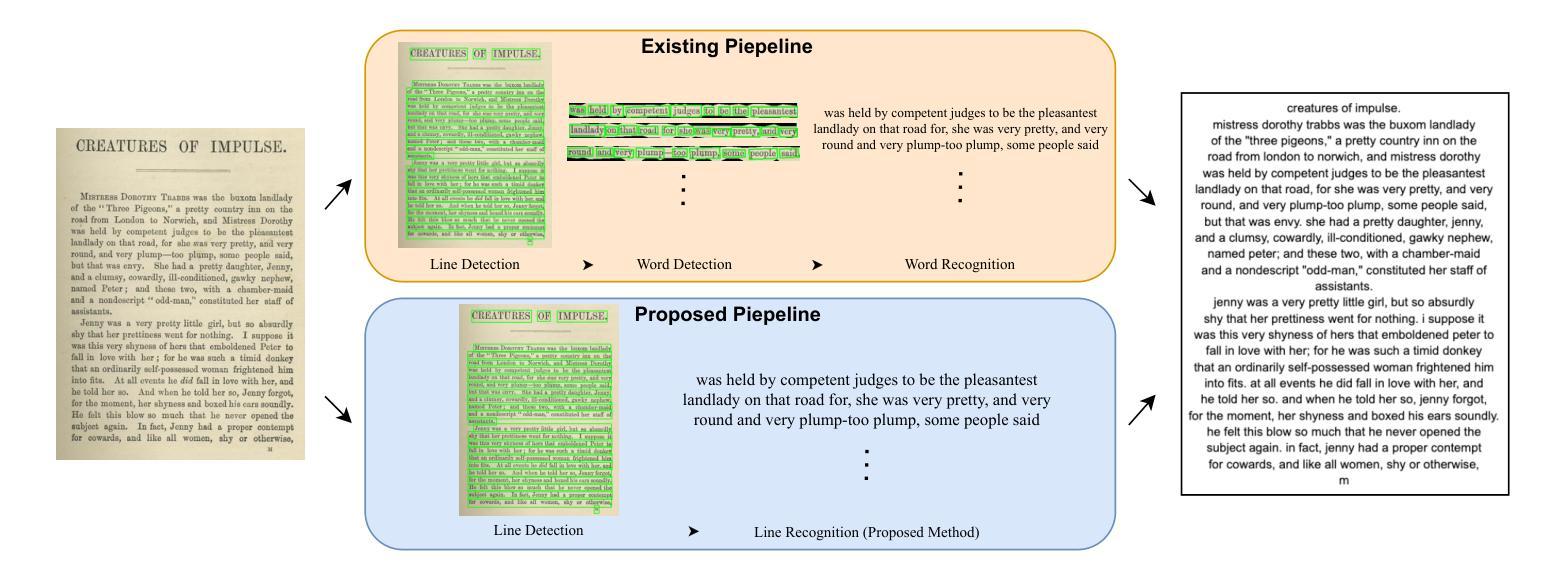
Conventional optical character recognition (OCR) techniques segmented each character and then recognized. This made them prone to error in character segmentation, and devoid of context to exploit language models. Advances in sequence to sequence translation in last decade led to modern techniques first detecting words and then inputting one word at a time to a model to directly output full words as sequence of characters. This allowed better utilization of language models and bypass error-prone character segmentation step. We observe that the above transition in style has moved the bottleneck in accuracy to word segmentation. Hence, in this paper, we propose a natural and logical progression from word level OCR to line-level OCR. The proposal allows to bypass errors in word detection, and provides larger sentence context for better utilization of language models. We show that the proposed technique not only improves the accuracy but also efficiency of OCR. Despite our thorough literature survey, we did not find any public dataset to train and benchmark such shift from word to line-level OCR. Hence, we also contribute a meticulously curated dataset of 251 English page images with line-level annotations. Our experimentation revealed a notable end-to-end accuracy improvement of 5.4%, underscoring the potential benefits of transitioning towards line-level OCR, especially for document images. We also report a 4 times improvement in efficiency compared to word-based pipelines. With continuous improvements in large language models, our methodology also holds potential to exploit such advances. Project Website: https://nishitanand.github.io/line-level-ocr-website
传统的光学字符识别(OCR)技术通过对每个字符进行分割然后再进行识别。这使得它们在字符分割时容易出错,并且无法利用上下文来利用语言模型。过去十年中序列到序列翻译的进展导致了现代技术首先检测单词,然后一次输入一个单词到模型中,直接输出由字符序列组成的完整单词。这允许更好地利用语言模型,并绕过容易出现错误的字符分割步骤。我们观察到上述风格的变化已将准确性的瓶颈转移到单词分割上。因此,在本文中,我们提出了从单词级OCR到行级OCR的自然且逻辑性的进步。该提议允许绕过单词检测中的错误,并为更好地利用语言模型提供了更大的句子上下文。我们表明,所提出的技术不仅提高了OCR的准确性,还提高了其效率。尽管我们进行了彻底的文献调查,但没有找到任何公共数据集来训练和评估从单词到行级OCR的这种转变。因此,我们还精心制作了一个包含251个英语页面图像的行级注释数据集。我们的实验显示端到端准确率提高了5.4%,这突显了转向行级OCR的潜在效益,尤其是对于文档图像。我们还报告了与基于单词的管道相比,效率提高了4倍。随着大型语言模型的不断改进,我们的方法也具有利用这些进展的潜力。项目网站:https://nishitanand.github.io/line-level-ocr-website
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages. Project Website: https://nishitanand.github.io/line-level-ocr-website
Summary
本文主要介绍了传统光学字符识别(OCR)技术的局限,包括字符分割易出错和缺乏语境利用语言模型的问题。随着序列到序列翻译技术的进步,现代OCR技术开始直接检测单词并输入模型进行识别,从而提高了语言模型的利用率并避免了易错的字符分割步骤。本文观察到这一转变提高了识别准确性,并将瓶颈转移到单词级别的分割上。因此,本文提出了从单词级别OCR到行级别OCR的自然逻辑发展,通过绕过单词检测中的错误并提供更大的句子语境来更好地利用语言模型。实验表明,该方法不仅提高了准确性,还提高了OCR的效率。同时,由于没有找到相应的公共数据集来训练和评估这种从单词到行级别的OCR转变,本文还贡献了一个精心策划的包含251页英文图像的行级别注释数据集。实验结果显示,端到端的准确率提高了5.4%,体现了向行级别OCR过渡的潜在优势,特别是在文档图像方面。
Key Takeaways
- 传统OCR技术通过字符分割进行识别,存在易错和缺乏语境的问题。
- 现代OCR技术通过检测单词进行识别,提高了语言模型的利用率并避免了字符分割的错误。
- OCR技术的瓶颈已从字符级别转移到单词级别分割。
- 本文提出从单词级别OCR到行级别OCR的自然过渡,以提高准确性和效率。
- 行级别OCR能够绕过单词检测中的错误,并提供更大的句子语境以更好地利用语言模型。
- 缺乏公共数据集用于训练和评估这种从单词到行级别的OCR转变。
- 本文贡献了一个精心策划的行级别注释数据集,并报告了显著的端到端准确率和效率改进。
点此查看论文截图




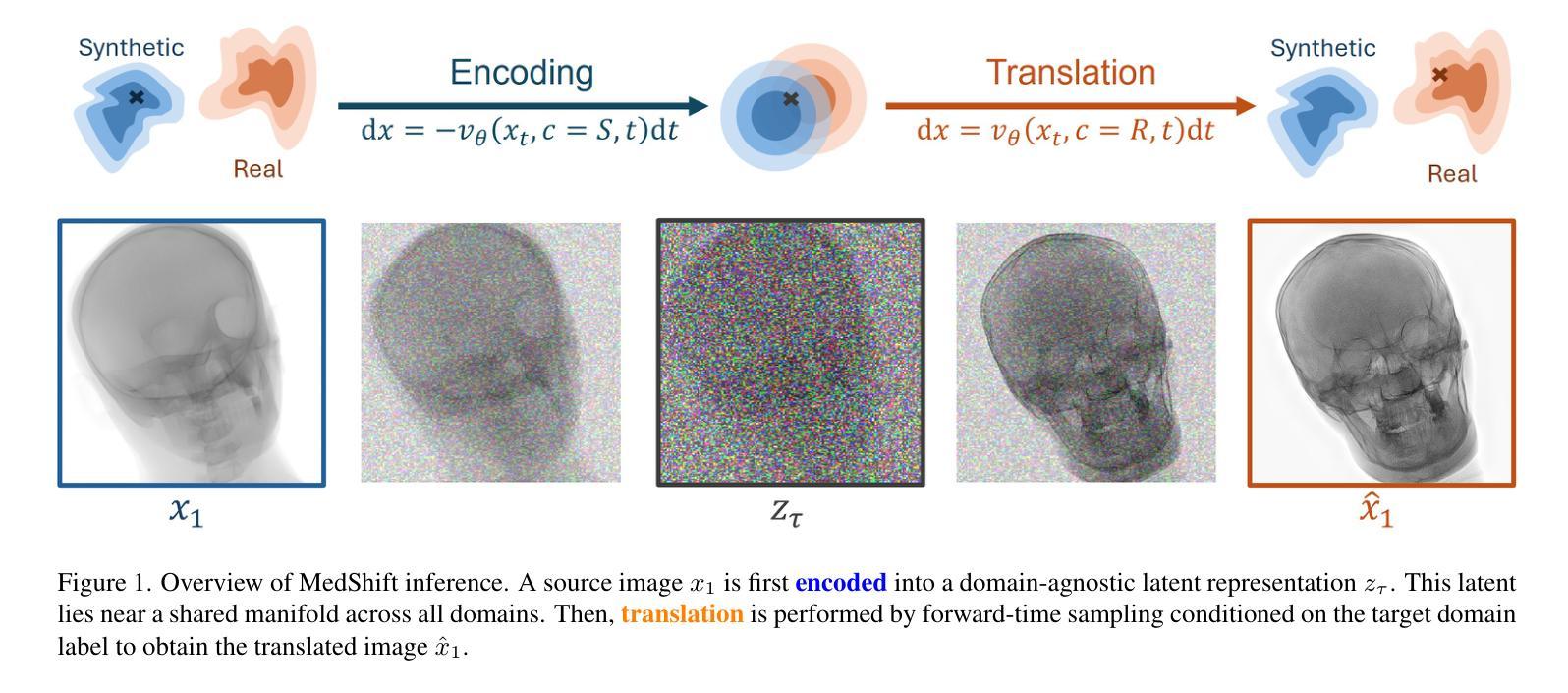
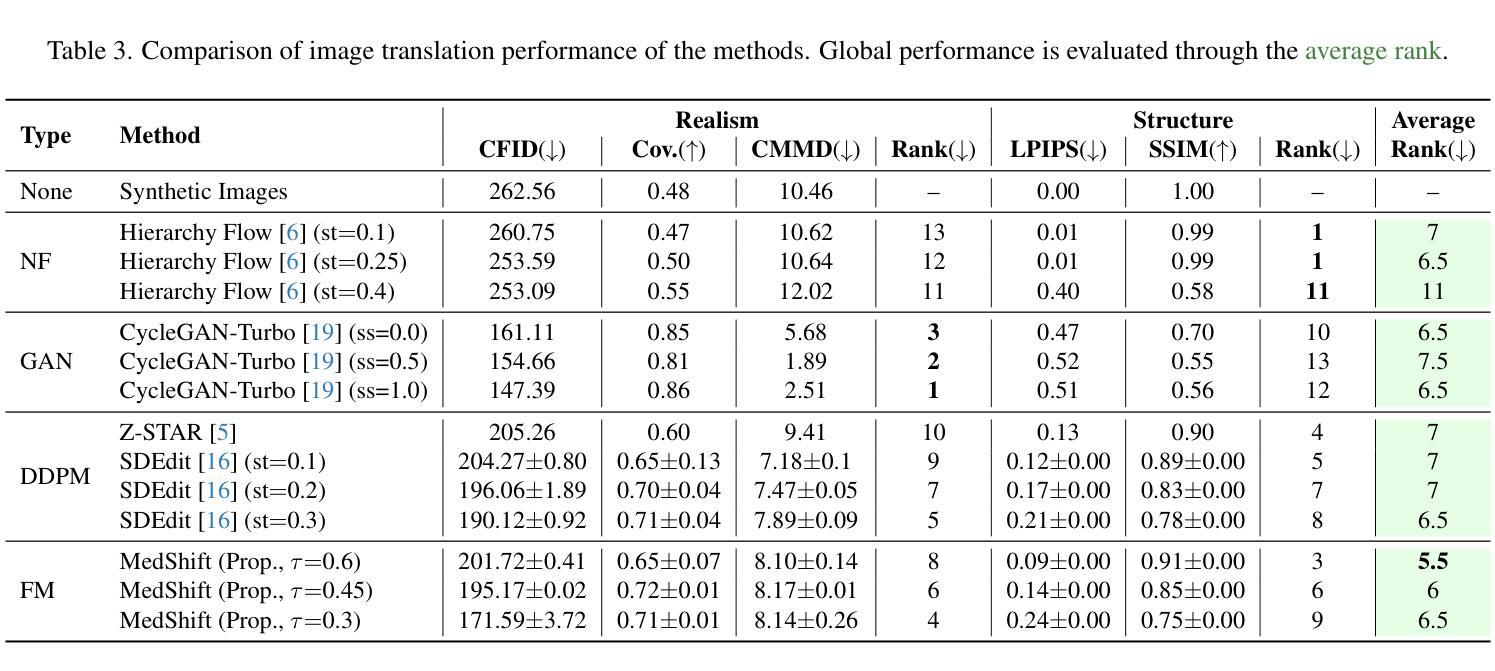
MedShift: Implicit Conditional Transport for X-Ray Domain Adaptation
Authors:Francisco Caetano, Christiaan Viviers, Peter H. H. de With, Fons van der Sommen
Synthetic medical data offers a scalable solution for training robust models, but significant domain gaps limit its generalizability to real-world clinical settings. This paper addresses the challenge of cross-domain translation between synthetic and real X-ray images of the head, focusing on bridging discrepancies in attenuation behavior, noise characteristics, and soft tissue representation. We propose MedShift, a unified class-conditional generative model based on Flow Matching and Schrodinger Bridges, which enables high-fidelity, unpaired image translation across multiple domains. Unlike prior approaches that require domain-specific training or rely on paired data, MedShift learns a shared domain-agnostic latent space and supports seamless translation between any pair of domains seen during training. We introduce X-DigiSkull, a new dataset comprising aligned synthetic and real skull X-rays under varying radiation doses, to benchmark domain translation models. Experimental results demonstrate that, despite its smaller model size compared to diffusion-based approaches, MedShift offers strong performance and remains flexible at inference time, as it can be tuned to prioritize either perceptual fidelity or structural consistency, making it a scalable and generalizable solution for domain adaptation in medical imaging. The code and dataset are available at https://caetas.github.io/medshift.html
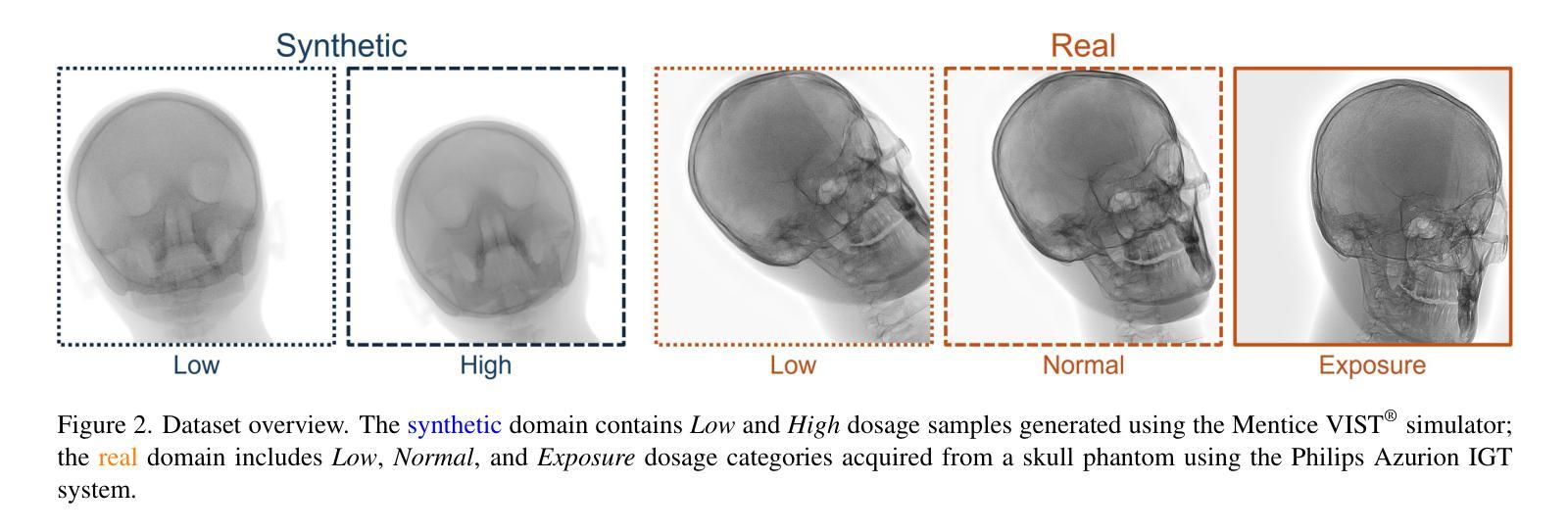
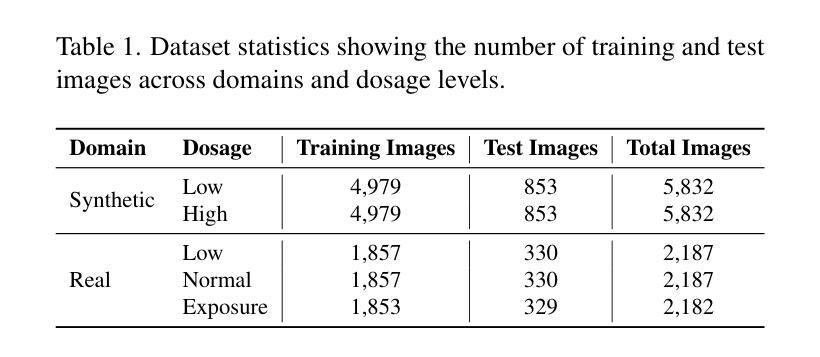
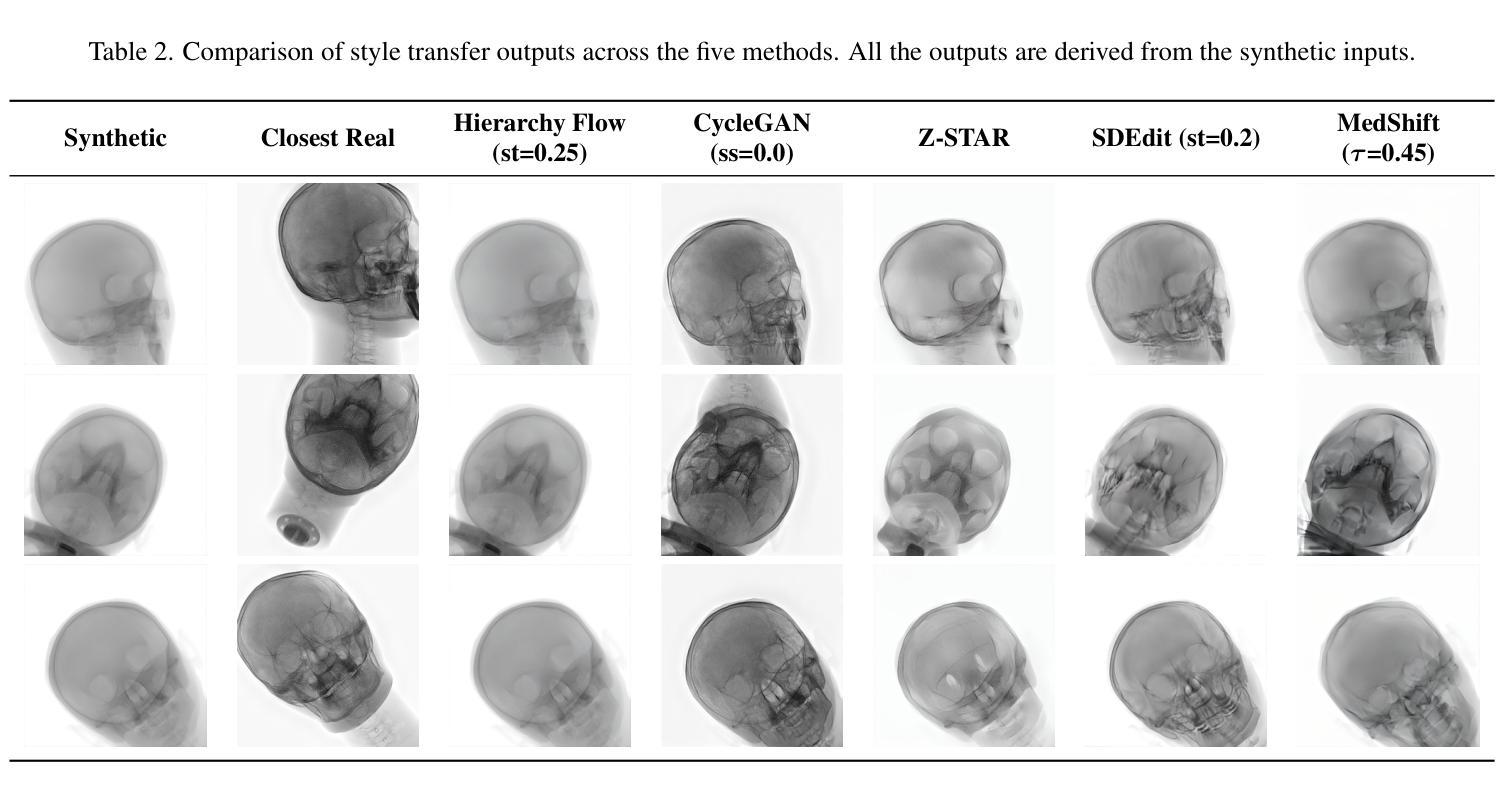
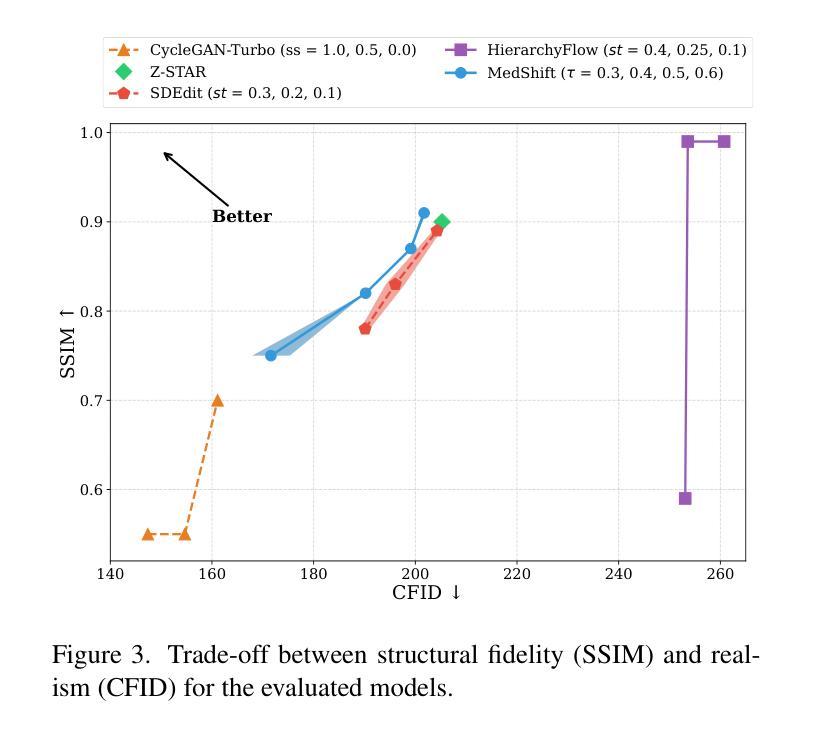
合成医疗数据为训练稳健模型提供了可扩展的解决方案,但由于领域差距较大,其在真实世界临床环境中的通用性受到限制。本文针对合成和真实头部X射线图像跨域翻译的挑战,专注于解决衰减行为、噪声特征和软组织表示方面的差异。我们提出了MedShift,这是一种基于流匹配和薛定谔桥的统一的类条件生成模型,能够实现多个领域之间的高保真、无配对图像翻译。与需要特定领域训练或依赖配对数据的先前方法不同,MedShift学习共享的领域无关潜在空间,并支持在训练期间看到的任何一对领域之间进行无缝翻译。我们引入了X-DigiSkull,这是一个新的数据集,包含不同辐射剂量下的合成和真实颅骨X射线的对齐图像,以评估领域翻译模型。实验结果表明,尽管与基于扩散的方法相比,MedShift的模型规模较小,但在推理时间却表现出强大的性能和灵活性,因为它可以调整以优先注重感知保真度或结构一致性,使其成为医学影像领域自适应的可扩展和通用解决方案。代码和数据集可在https://caetas.github.io/medshift.html找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the ICCV 2025 AIM Workshop
Summary
本文探讨了合成医疗数据在训练稳健模型中的应用,但由于领域差距较大,其在真实临床环境中的通用性受到限制。针对头部合成X射线图像与真实X射线图像之间的跨域翻译问题,本文提出了一种基于流匹配和薛定谔桥的通用类别条件生成模型MedShift。该模型能够在多个领域之间实现高保真、无配对的图像翻译。相较于需要特定领域训练或依赖配对数据的传统方法,MedShift学习了一个通用的领域无关潜在空间,并支持在训练期间看到的任意两个领域间的无缝翻译。为评估领域翻译模型,本文引入了包含不同辐射剂量下的合成与真实颅骨X射线对齐数据的新数据集X-DigiSkull。实验结果表明,虽然MedShift的模型尺寸小于基于扩散的方法,但其性能强大且推理灵活,可调整以优先保证感知保真度或结构一致性,成为医学成像领域自适应的可扩展和通用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 合成医疗数据为训练稳健模型提供了可扩展的解决方案,但其在真实临床环境中的通用性受限。
- 论文聚焦于头部合成X射线图像和真实X射线图像之间的跨域翻译挑战。
- 提出了基于流匹配和薛定谔桥的MedShift模型,实现高保真、无配对的跨领域图像翻译。
- MedShift学习通用的领域无关潜在空间,支持任意两个领域间的无缝翻译。
- 引入X-DigiSkull数据集,用于评估合成与真实颅骨X射线的领域翻译模型性能。
- 实验结果表明,MedShift虽小但性能强大,并能在推理时灵活调整以平衡感知保真度和结构一致性。
点此查看论文截图

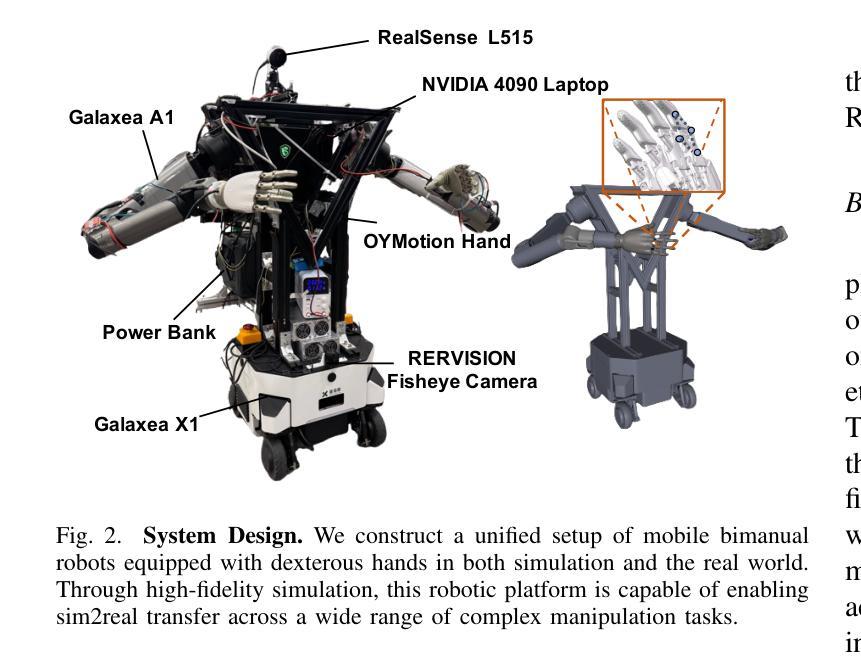
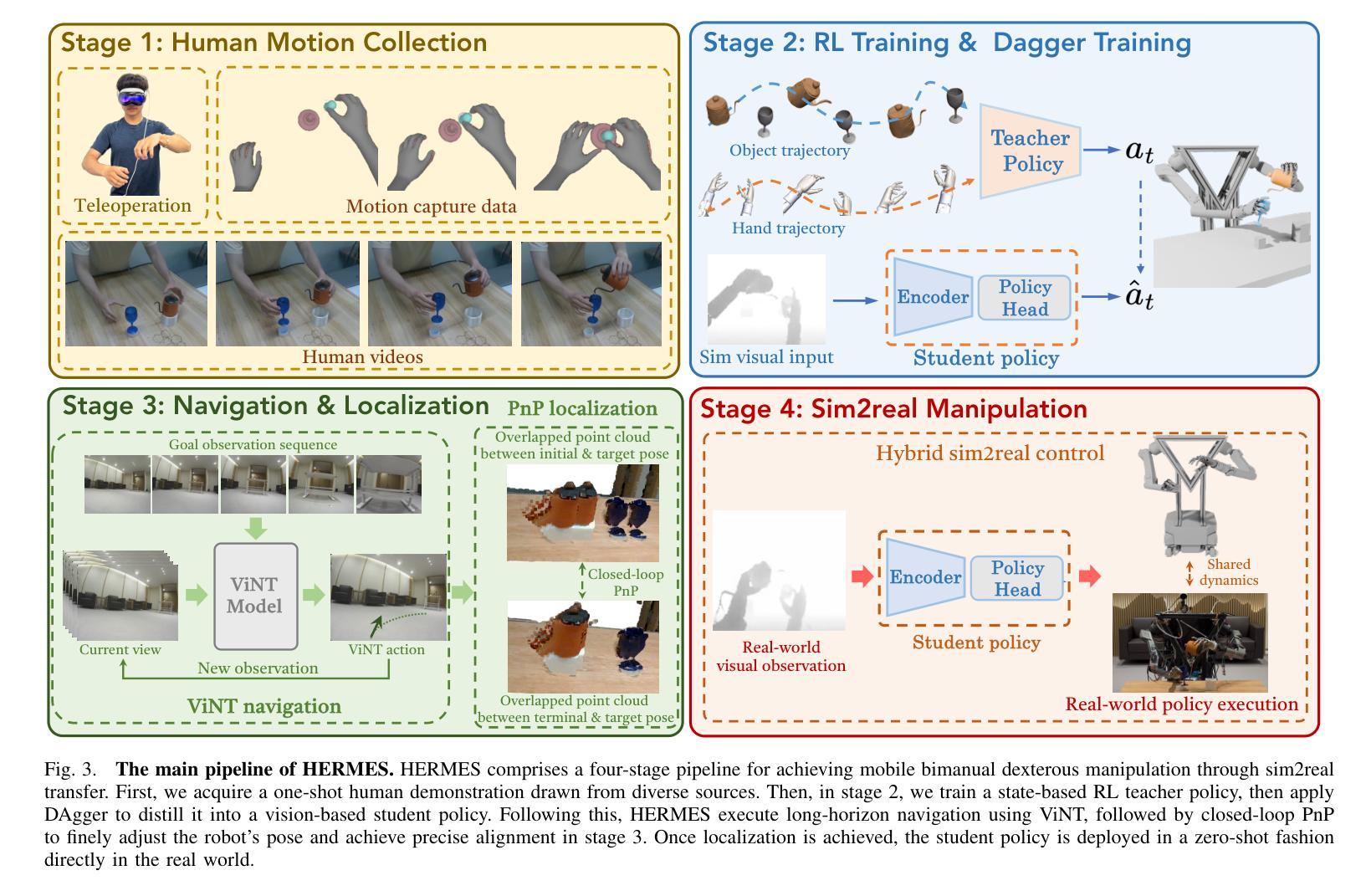
HERMES: Human-to-Robot Embodied Learning from Multi-Source Motion Data for Mobile Dexterous Manipulation
Authors:Zhecheng Yuan, Tianming Wei, Langzhe Gu, Pu Hua, Tianhai Liang, Yuanpei Chen, Huazhe Xu
Leveraging human motion data to impart robots with versatile manipulation skills has emerged as a promising paradigm in robotic manipulation. Nevertheless, translating multi-source human hand motions into feasible robot behaviors remains challenging, particularly for robots equipped with multi-fingered dexterous hands characterized by complex, high-dimensional action spaces. Moreover, existing approaches often struggle to produce policies capable of adapting to diverse environmental conditions. In this paper, we introduce HERMES, a human-to-robot learning framework for mobile bimanual dexterous manipulation. First, HERMES formulates a unified reinforcement learning approach capable of seamlessly transforming heterogeneous human hand motions from multiple sources into physically plausible robotic behaviors. Subsequently, to mitigate the sim2real gap, we devise an end-to-end, depth image-based sim2real transfer method for improved generalization to real-world scenarios. Furthermore, to enable autonomous operation in varied and unstructured environments, we augment the navigation foundation model with a closed-loop Perspective-n-Point (PnP) localization mechanism, ensuring precise alignment of visual goals and effectively bridging autonomous navigation and dexterous manipulation. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that HERMES consistently exhibits generalizable behaviors across diverse, in-the-wild scenarios, successfully performing numerous complex mobile bimanual dexterous manipulation tasks. Project Page:https://gemcollector.github.io/HERMES/.
利用人类运动数据赋予机器人多种操作技能已成为机器人操作中的一项有前途的范式。然而,将多源人类手势动作转化为可行的机器人行为仍然是一个挑战,特别是对于配备多指灵巧手且动作空间复杂、高维度的机器人。此外,现有方法往往难以产生能够适应多种环境条件的策略。在本文中,我们介绍了HERMES,这是一种人类到机器人的学习框架,用于移动双手动作灵巧操作。首先,HERMES制定了一种统一的强化学习方法,能够无缝地将来自多个源头的不同人类手势动作转化为物理上可行的机器人行为。其次,为了缓解模拟到现实的差距,我们设计了一种基于深度图像的端到端模拟到现实的转移方法,以提高对真实场景的总括能力。此外,为了在多变和非结构化的环境中实现自主操作,我们增加了基于闭环透视n点(PnP)定位机制的导航基础模型,确保视觉目标的精确对齐,有效桥接自主导航和灵巧操作。广泛的实验结果表明,HERMES在多种野外场景中表现出持续的总括能力,成功完成众多复杂的移动双手灵巧操作任务。项目页面:https://gemcollector.github.io/HERMES/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人类动作数据赋予机器人通用操控技能已成为机器人操控领域的一种有前途的范式。然而,将多源人类手部动作转化为可行的机器人行为仍然具有挑战性,特别是对于配备复杂、高维度动作空间的灵巧多指机器人。本文介绍HERMES,一种用于移动灵巧双手动作操控的人类到机器人学习框架。它使用统一强化学习方法无缝转化来自多个来源的异质人类手部动作为物理合理的机器人行为。同时,采用端到端的深度图像sim2real转移方法减少模拟到现实的差距,增强在现实世界的泛化能力。此外,为在多变和非结构化环境中实现自主操作,我们整合导航基础模型与闭环Perspective-n-Point(PnP)定位机制,确保视觉目标的精确对齐,有效桥接自主导航与灵巧操控。实验结果证明HERMES在不同场景的通用行为表现优异,成功执行多种复杂移动灵巧操控任务。
Key Takeaways
- 利用人类动作数据赋予机器人通用操控技能已成为一种有前途的范式。
- 将多源人类手部动作转化为机器人行为具有挑战性,尤其是高维度动作空间的复杂机器人。
- HERMES框架使用统一强化学习方法转化人类手部动作为机器人行为。
- HERMES采用深度图像sim2real转移方法减少模拟与现实的差距。
- 结合导航模型与闭环PnP定位机制,提升机器人在多变环境中的自主操作能力。
- HERMES在多种复杂移动灵巧操控任务中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图



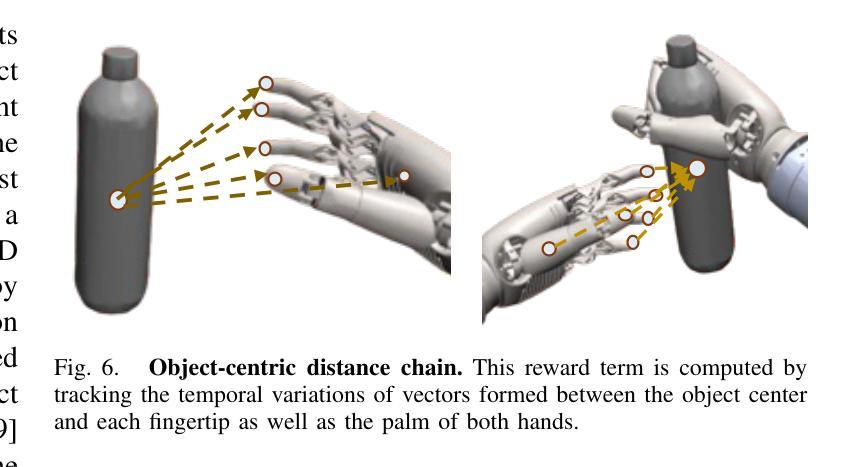
Is Uncertainty Quantification a Viable Alternative to Learned Deferral?
Authors:Anna M. Wundram, Christian F. Baumgartner
Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds the potential to dramatically improve patient care. However, it is not infallible, necessitating human-AI-collaboration to ensure safe implementation. One aspect of AI safety is the models’ ability to defer decisions to a human expert when they are likely to misclassify autonomously. Recent research has focused on methods that learn to defer by optimising a surrogate loss function that finds the optimal trade-off between predicting a class label or deferring. However, during clinical translation, models often face challenges such as data shift. Uncertainty quantification methods aim to estimate a model’s confidence in its predictions. However, they may also be used as a deferral strategy which does not rely on learning from specific training distribution. We hypothesise that models developed to quantify uncertainty are more robust to out-of-distribution (OOD) input than learned deferral models that have been trained in a supervised fashion. To investigate this hypothesis, we constructed an extensive evaluation study on a large ophthalmology dataset, examining both learned deferral models and established uncertainty quantification methods, assessing their performance in- and out-of-distribution. Specifically, we evaluate their ability to accurately classify glaucoma from fundus images while deferring cases with a high likelihood of error. We find that uncertainty quantification methods may be a promising choice for AI deferral.
人工智能(AI)有潜力大幅改善患者护理的质量。然而,它并非无所不能,因此需要人类-AI协作以确保安全实施。人工智能安全的一个方面是,当它们有可能自主误分类时,模型能够将决策权转交给人类专家。最近的研究集中在通过优化代理损失函数来学习推迟决策的方法,该损失函数旨在找到预测类别标签或推迟之间的最佳权衡。然而,在临床翻译过程中,模型经常面临数据迁移等挑战。不确定性量化方法旨在估计模型对其预测的信心。但它们也可以作为一种不依赖于从特定训练分布中学习的推迟策略。我们假设,与经过监督训练的学习推迟模型相比,开发用于量化不确定性的模型对超出分布(OOD)的输入更具鲁棒性。为了验证这一假设,我们在大型眼科数据集上进行了一项全面的评估研究,研究了学习推迟模型和已建立的不确定性量化方法的表现,评估其在内部和外部的分布中的表现。具体来说,我们评估了它们从眼底图像中准确分类青光眼的能力,同时推迟可能出现错误的情况。我们发现不确定性量化方法可能是AI推迟决策的一个有前途的选择。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as an oral presentation at MICCAI UNSURE 2025
Summary
人工智能(AI)有潜力大幅改善患者护理水平,但其并非万能,需要人类-AI协作以确保安全实施。AI模型在自主决策时,如预料会误判,需具备转向人类专家决策的能力。最新研究聚焦于通过优化替代损失函数来学习转向的方法,以找到预测类别或转向之间的最佳平衡。但在临床翻译中,模型常面临数据迁移等挑战。研究假设,开发用于量化不确定性的模型,相较于在监督模式下训练得到的学会转向模型,更能稳健应对离群输入。为验证此假设,我们在大型眼科数据集上进行了一项全面评估研究,对比学会转向模型和已建立的不确定性量化方法,评估其在内部和外部数据集中的表现。特别是在从眼底图像准确分类青光眼时,我们发现不确定性量化方法可能成为AI转向的一个有前途的选择。
Key Takeaways
- AI在改善病人护理方面具有巨大潜力,但需要人类-AI协作以确保安全实施。
- AI模型应具备在预测错误时转向人类专家决策的能力。
- 最新研究通过优化替代损失函数来学习模型何时应转向人类决策。
- 在临床翻译中,模型面临数据迁移等挑战。
- 量化不确定性的模型可能更稳健地应对离群输入,相较于学会转向模型。
- 在眼科数据集上的评估研究显示,不确定性量化方法在AI决策时具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

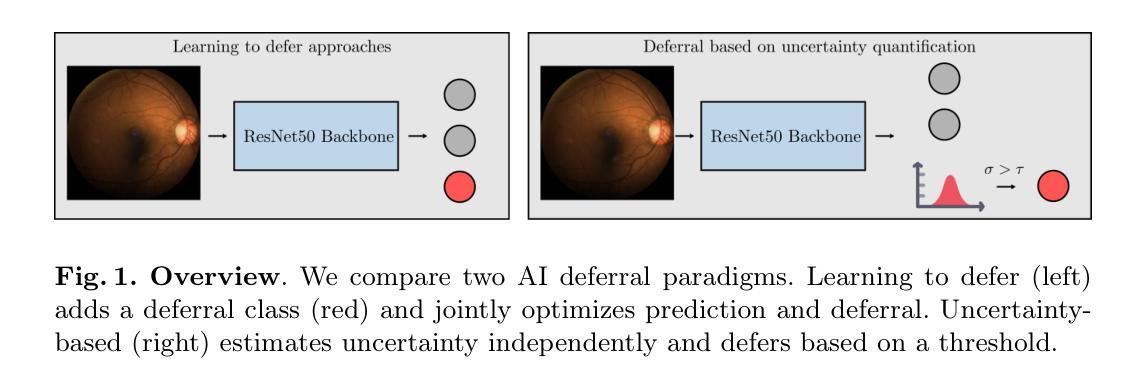
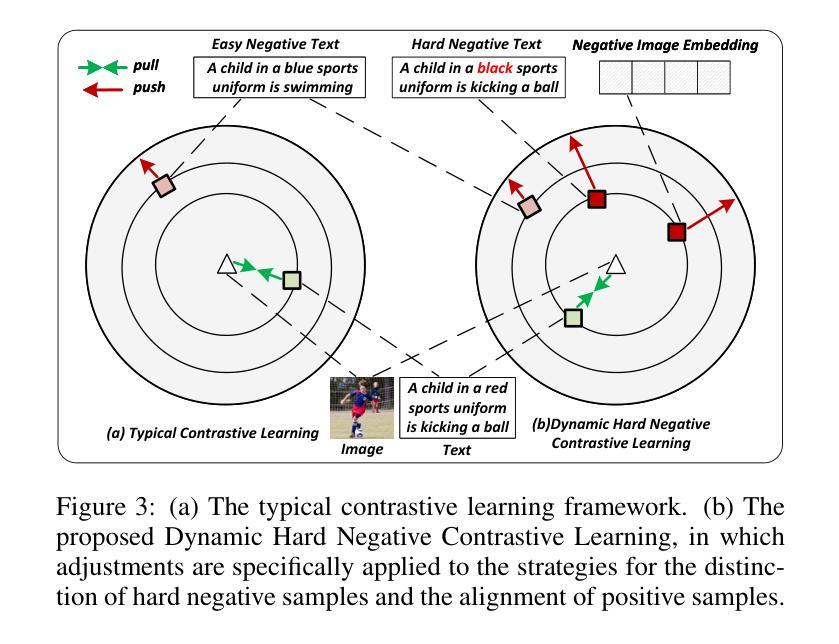
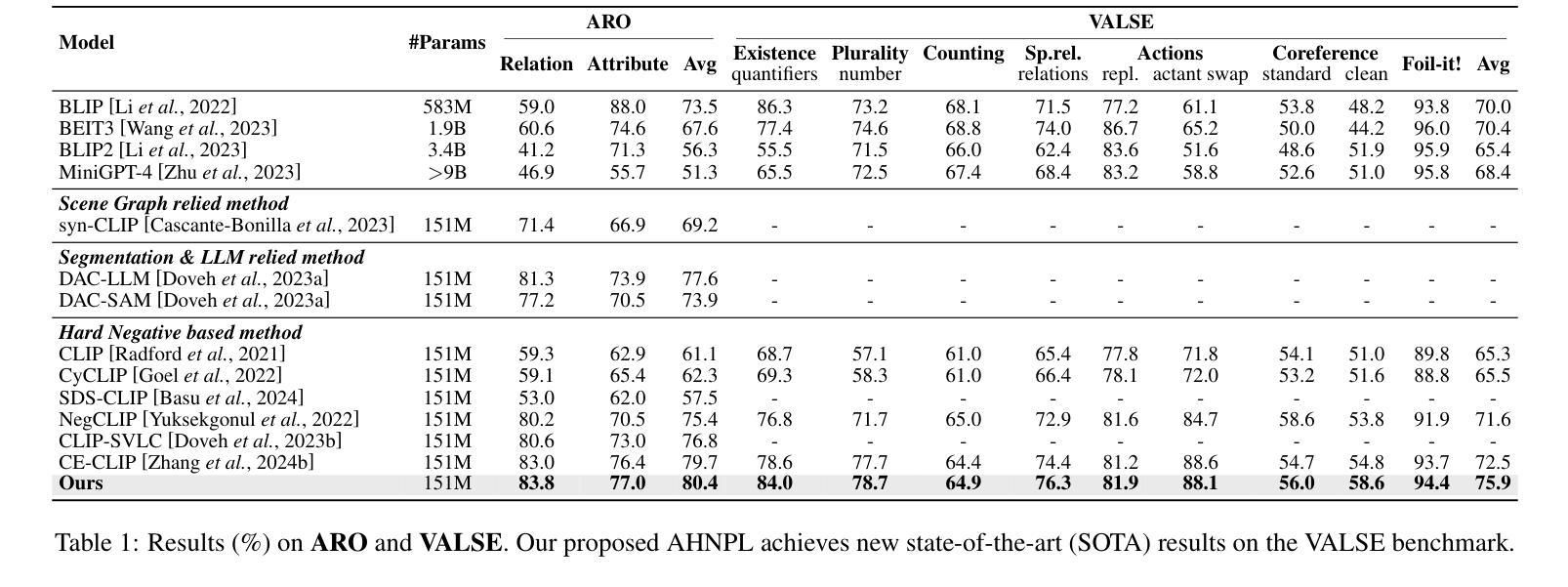
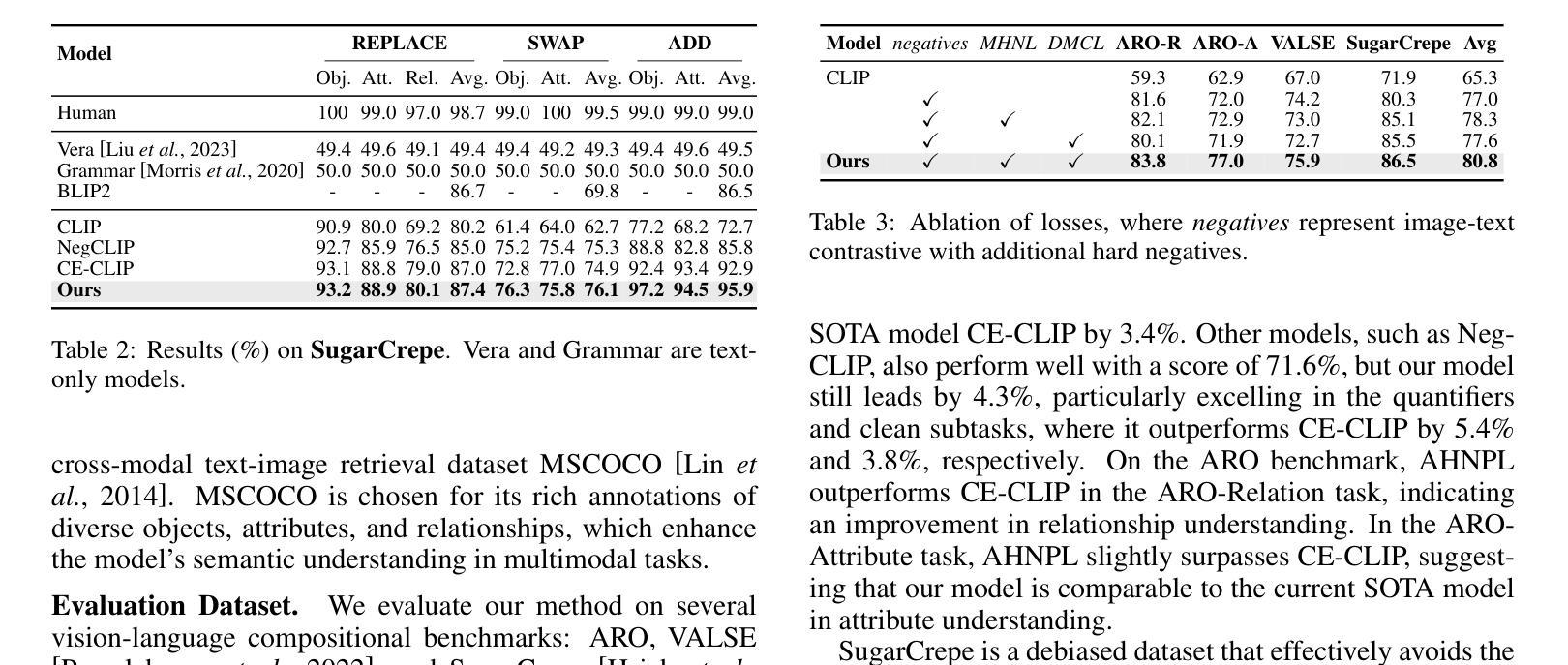
Visual Perturbation and Adaptive Hard Negative Contrastive Learning for Compositional Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Xin Huang, Ruibin Li, Tong Jia, Wei Zheng, Ya Wang
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are essential for multimodal tasks, especially compositional reasoning (CR) tasks, which require distinguishing fine-grained semantic differences between visual and textual embeddings. However, existing methods primarily fine-tune the model by generating text-based hard negative samples, neglecting the importance of image-based negative samples, which results in insufficient training of the visual encoder and ultimately impacts the overall performance of the model. Moreover, negative samples are typically treated uniformly, without considering their difficulty levels, and the alignment of positive samples is insufficient, which leads to challenges in aligning difficult sample pairs. To address these issues, we propose Adaptive Hard Negative Perturbation Learning (AHNPL). AHNPL translates text-based hard negatives into the visual domain to generate semantically disturbed image-based negatives for training the model, thereby enhancing its overall performance. AHNPL also introduces a contrastive learning approach using a multimodal hard negative loss to improve the model’s discrimination of hard negatives within each modality and a dynamic margin loss that adjusts the contrastive margin according to sample difficulty to enhance the distinction of challenging sample pairs. Experiments on three public datasets demonstrate that our method effectively boosts VLMs’ performance on complex CR tasks. The source code is available at https://github.com/nynu-BDAI/AHNPL.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)对于多模态任务,特别是需要区分视觉和文本嵌入之间细微语义差异的组合推理(CR)任务至关重要。然而,现有方法主要通过生成基于文本的硬负样本对模型进行微调,忽略了基于图像的负样本的重要性,导致视觉编码器训练不足,最终影响模型的总体性能。此外,负样本通常被一视同仁,没有考虑其难度水平,正样本的对齐也不足,这导致难以对齐困难样本对。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了自适应硬负扰动学习(AHNPL)。AHNPL将基于文本的硬负样本转换为视觉域,以生成用于训练模型的在语义上受到干扰的基于图像的负样本,从而提高模型的总体性能。AHNPL还引入了一种对比学习方法,使用多模态硬负损失来提高模型在每个模态内对硬负样本的辨别能力,以及动态边界损失会根据样本难度调整对比边界,提高具有挑战性的样本对的区分度。在三个公开数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法有效地提高了VLMs在复杂的CR任务上的性能。源代码可在https://github.com/nynu-BDAI/AHNPL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2025)
Summary
本文指出在视觉语言模型(VLMs)中,现有方法主要侧重于基于文本生成硬负样本进行微调,忽略了基于图像的负样本的重要性,导致视觉编码器训练不足,影响模型整体性能。针对这些问题,本文提出了自适应硬负扰动学习(AHNPL)方法。AHNPL将文本硬负样本转换为图像领域,生成语义干扰的图像负样本进行训练,提高了模型的性能。同时,AHNPL引入了多模态硬负损失和动态边距损失机制来提升模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在进行多模态任务,特别是组合推理任务时面临挑战,需要识别视觉和文本嵌入之间的细微语义差异。
- 现有方法主要侧重于通过生成基于文本的硬负样本来微调模型,忽略了基于图像的负样本的重要性。
- AHNPL通过将文本硬负样本转换为图像领域生成语义干扰的图像负样本,从而增强模型的性能。
- AHNPL引入了多模态硬负损失机制,提高了模型对每种模态内硬负样本的辨别能力。
- AHNPL还使用动态边距损失机制,根据样本难度调整对比边距,以提高对困难样本对的区分能力。
- 在三个公共数据集上的实验表明,AHNPL方法能有效提升VLMs在复杂推理任务上的性能。
点此查看论文截图

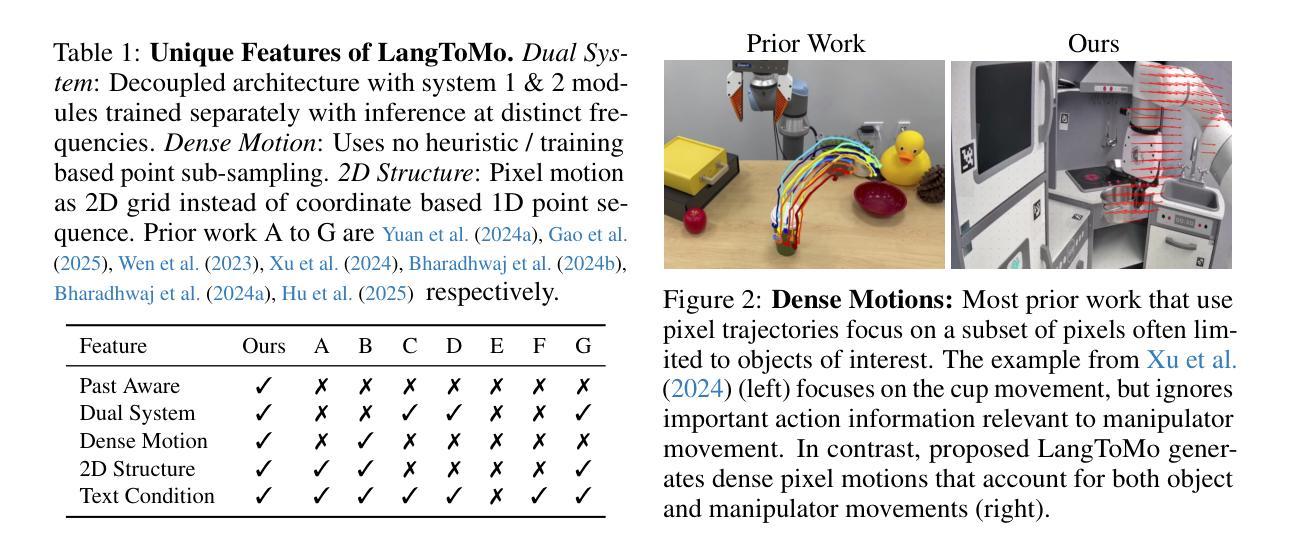
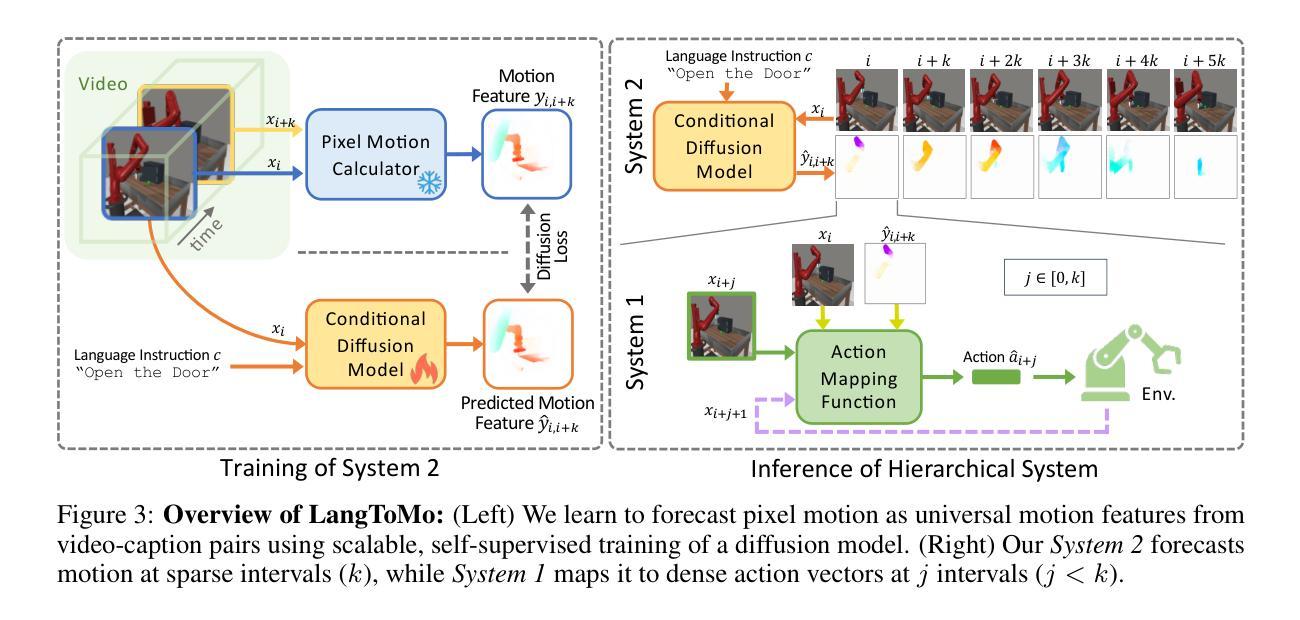
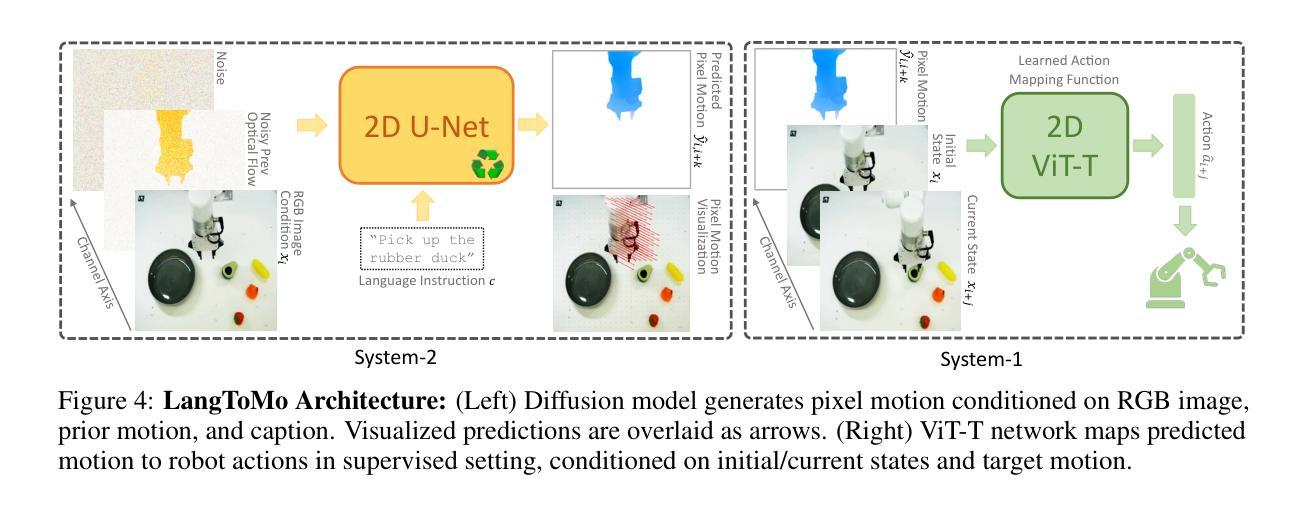
Pixel Motion as Universal Representation for Robot Control
Authors:Kanchana Ranasinghe, Xiang Li, E-Ro Nguyen, Cristina Mata, Jongwoo Park, Michael S Ryoo
We present LangToMo, a vision-language-action framework structured as a dual-system architecture that uses pixel motion forecasts as intermediate representations. Our high-level System 2, an image diffusion model, generates text-conditioned pixel motion sequences from a single frame to guide robot control. Pixel motion-a universal, interpretable, and motion-centric representation-can be extracted from videos in a weakly-supervised manner, enabling diffusion model training on any video-caption data. Treating generated pixel motion as learned universal representations, our low level System 1 module translates these into robot actions via motion-to-action mapping functions, which can be either hand-crafted or learned with minimal supervision. System 2 operates as a high-level policy applied at sparse temporal intervals, while System 1 acts as a low-level policy at dense temporal intervals. This hierarchical decoupling enables flexible, scalable, and generalizable robot control under both unsupervised and supervised settings, bridging the gap between language, motion, and action. Checkout https://kahnchana.github.io/LangToMo
我们推出了LangToMo,这是一个视觉语言行动框架,采用双重系统架构,以像素运动预测作为中间表示。我们的高级系统2是一个图像扩散模型,它能够从单帧生成文本控制的像素运动序列,从而引导机器人控制。像素运动是一种通用、可解释、以运动为中心的表示,可以以一种弱监督的方式从视频中提取,从而实现在任何视频字幕数据上进行扩散模型训练。将生成的像素运动视为学习的通用表示,我们的低级系统1模块通过运动到动作的映射函数将这些表示转换为机器人动作,这些映射函数可以是手工制作的,也可以在最少的监督下学习。系统2作为高级策略,在稀疏的时间间隔内运行,而系统1则在密集的时间间隔内作为低级策略运行。这种分层解耦实现了灵活的、可扩展的和通用的机器人控制,无论在没有监督还是有监督的环境下都能很好地工作,从而缩小了语言、运动和动作之间的差距。请访问 https://kahnchana.github.io/LangToMo 以了解更多信息。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
LangToMo是一个视觉-语言-动作框架,采用双系统架构,以像素运动预测作为中间表示。该系统的高层次模块(System 2)是一个图像扩散模型,通过单帧生成文本条件下的像素运动序列,指导机器人控制。像素运动是一种通用、可解释、以运动为中心的表现形式,可从视频中以弱监督方式提取,使扩散模型能够在任何视频字幕数据上进行训练。将生成的像素运动视为学习的通用表示,系统的低层次模块(System 1)将这些表示转化为机器人动作,通过手动或最小监督学习实现运动到动作的映射功能。System 2在稀疏时间间隔内作为高级策略应用,而System 1在密集时间间隔内作为低级策略执行。这种层次化的解耦实现了灵活的、可扩展的、通用的机器人控制,无论在无监督还是监督设置下都能很好地工作,缩小了语言、运动和动作之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- LangToMo是一个视觉-语言-动作框架,具有双系统架构。
- 像素运动预测作为中间表示在该框架中起到关键作用。
- System 2是一个图像扩散模型,可从单帧生成文本条件下的像素运动序列,指导机器人控制。
- 像素运动是一种通用、可解释、以运动为中心的表现形式。
- System 1将像素运动转化为机器人动作,实现运动到动作的映射。
- 该框架实现了层次化的解耦,使机器人控制更加灵活、可扩展和通用。
- LangToMo缩小了语言、运动和动作之间的差距,无论是在无监督还是监督设置下都能很好地工作。
点此查看论文截图

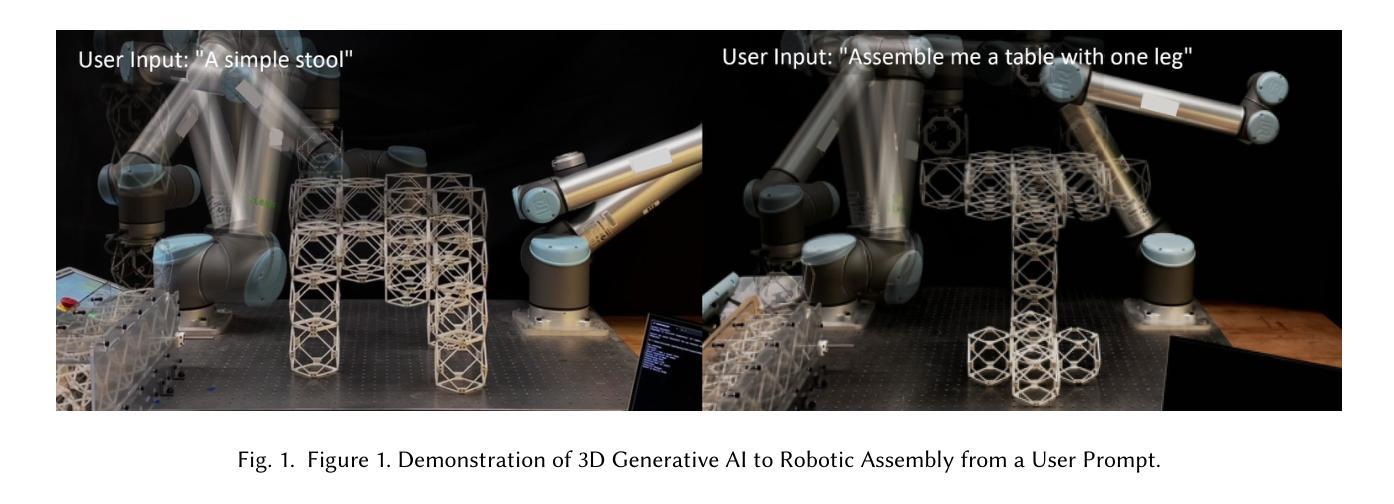
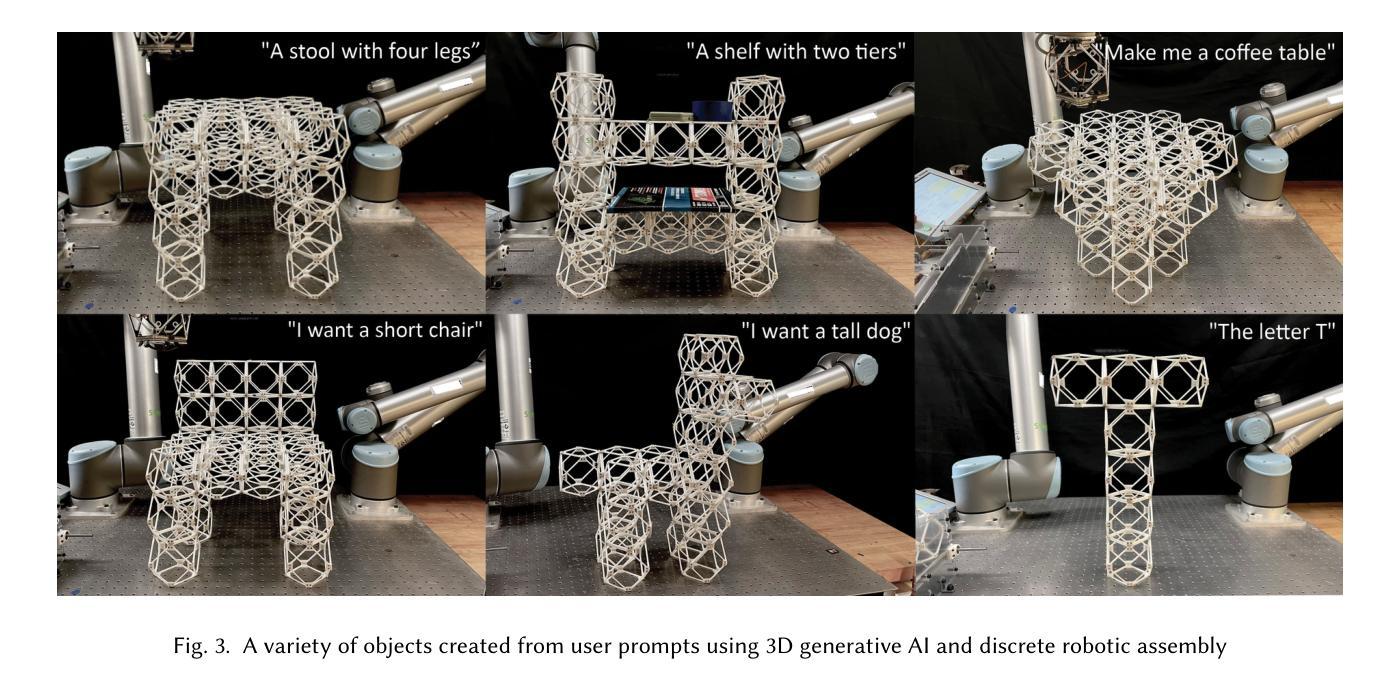
Making Physical Objects with Generative AI and Robotic Assembly: Considering Fabrication Constraints, Sustainability, Time, Functionality, and Accessibility
Authors:Alexander Htet Kyaw, Se Hwan Jeon, Miana Smith, Neil Gershenfeld
3D generative AI enables rapid and accessible creation of 3D models from text or image inputs. However, translating these outputs into physical objects remains a challenge due to the constraints in the physical world. Recent studies have focused on improving the capabilities of 3D generative AI to produce fabricable outputs, with 3D printing as the main fabrication method. However, this workshop paper calls for a broader perspective by considering how fabrication methods align with the capabilities of 3D generative AI. As a case study, we present a novel system using discrete robotic assembly and 3D generative AI to make physical objects. Through this work, we identified five key aspects to consider in a physical making process based on the capabilities of 3D generative AI. 1) Fabrication Constraints: Current text-to-3D models can generate a wide range of 3D designs, requiring fabrication methods that can adapt to the variability of generative AI outputs. 2) Time: While generative AI can generate 3D models in seconds, fabricating physical objects can take hours or even days. Faster production could enable a closer iterative design loop between humans and AI in the making process. 3) Sustainability: Although text-to-3D models can generate thousands of models in the digital world, extending this capability to the real world would be resource-intensive, unsustainable and irresponsible. 4) Functionality: Unlike digital outputs from 3D generative AI models, the fabrication method plays a crucial role in the usability of physical objects. 5) Accessibility: While generative AI simplifies 3D model creation, the need for fabrication equipment can limit participation, making AI-assisted creation less inclusive. These five key aspects provide a framework for assessing how well a physical making process aligns with the capabilities of 3D generative AI and values in the world.
3D生成式AI能够通过文本或图像输入快速且便捷地创建3D模型。然而,由于物理世界的限制,将这些输出物转化为实体仍然是一个挑战。近期的研究主要集中在提高3D生成式AI产生可制作输出的能力,而3D打印是主要制作方法。然而,本研讨会论文呼吁从更广泛的视角考虑制作方法如何与3D生成式AI的能力相匹配。作为案例研究,我们展示了一个使用离散机器人装配和3D生成式AI制作实体物体的新型系统。通过这项工作,我们确定了基于3D生成式AI的能力的物理制造过程中需要考虑的五个关键因素。
- 制作约束:目前的文本到3D模型可以生成各种3D设计,需要能够适应生成式AI输出多变性的制作方法。
- 时间:虽然生成式AI可以在几秒内生成3D模型,但制作实体物体可能需要数小时甚至数天。更快的生产速度可以让人工智能和人类在制造过程中有更紧密的迭代设计循环。
- 可持续性:虽然文本到3D模型可以在数字世界中生成数千个模型,但将这种能力扩展到现实世界将是资源密集型的,不可持续且不负责任。
- 功能:与来自3D生成式AI模型的数字输出不同,制作方法对于实体物体的实用性起着至关重要的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2025), Workshop on Generative AI and Human-Computer Interaction, Yokohama, Japan, April 26 to May 1, 2025
Summary
本文讨论了基于文本或图像输入的3D生成AI技术的快速发展及其在创建3D模型方面的潜力。尽管它能够快速生成模型,但在将这些输出转化为实际物体时仍面临挑战。本文强调了考虑制造方法与3D生成AI能力相结合的重要性,并提出一个结合离散机器人组装和3D生成AI的创新系统作为案例研究。作者指出了在基于物理制造过程中考虑五个关键方面的重要性:制造约束、时间、可持续性、功能性和可访问性。此研究有助于评估制造过程与3D生成AI的能力之间的契合度。
Key Takeaways
- 3D生成AI可从文本或图像输入中快速创建多样化的3D模型。
- 制造将这些模型转化为物理对象仍面临挑战,需要适应AI输出的多变性和满足物理世界的约束。
- 离散机器人组装技术被用作案例研究,展示了与3D生成AI结合制造物体的潜力。
- 在物理制造过程中需要考虑五个关键方面:制造约束、时间效率、可持续性、物体功能性和可访问性。
- 应评估制造过程与3D生成AI的能力是否契合,以确保有效和负责任地利用资源。
- 实现快速迭代设计和生产中人类与AI之间的紧密合作至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

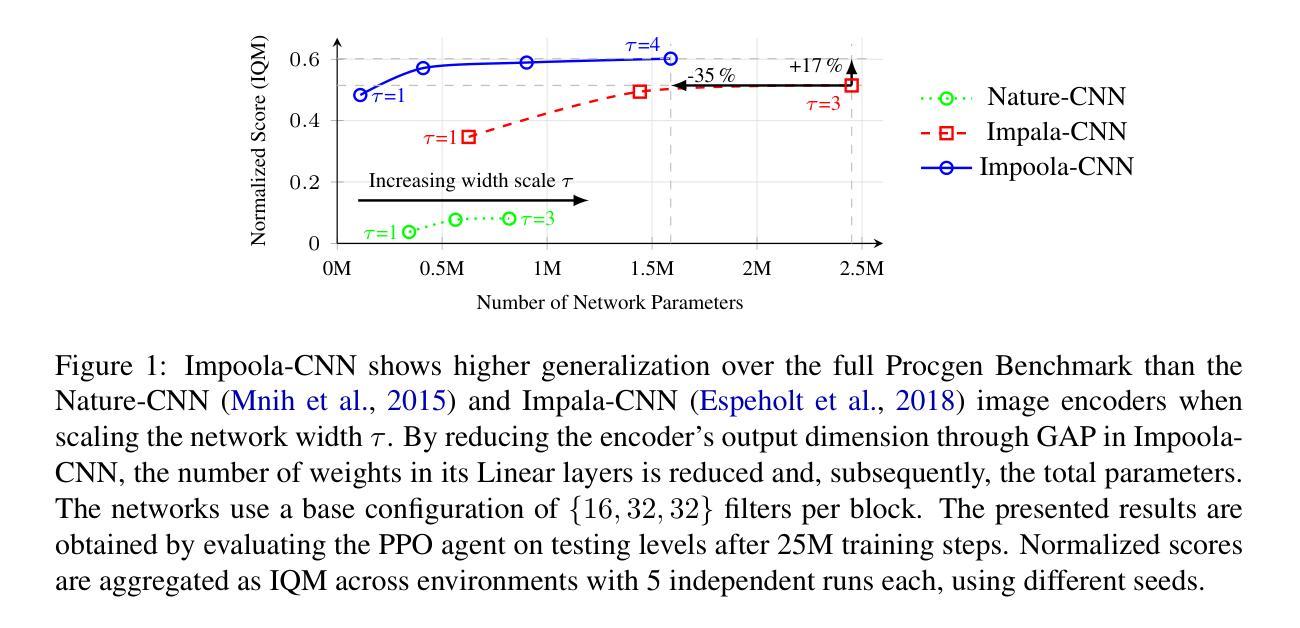
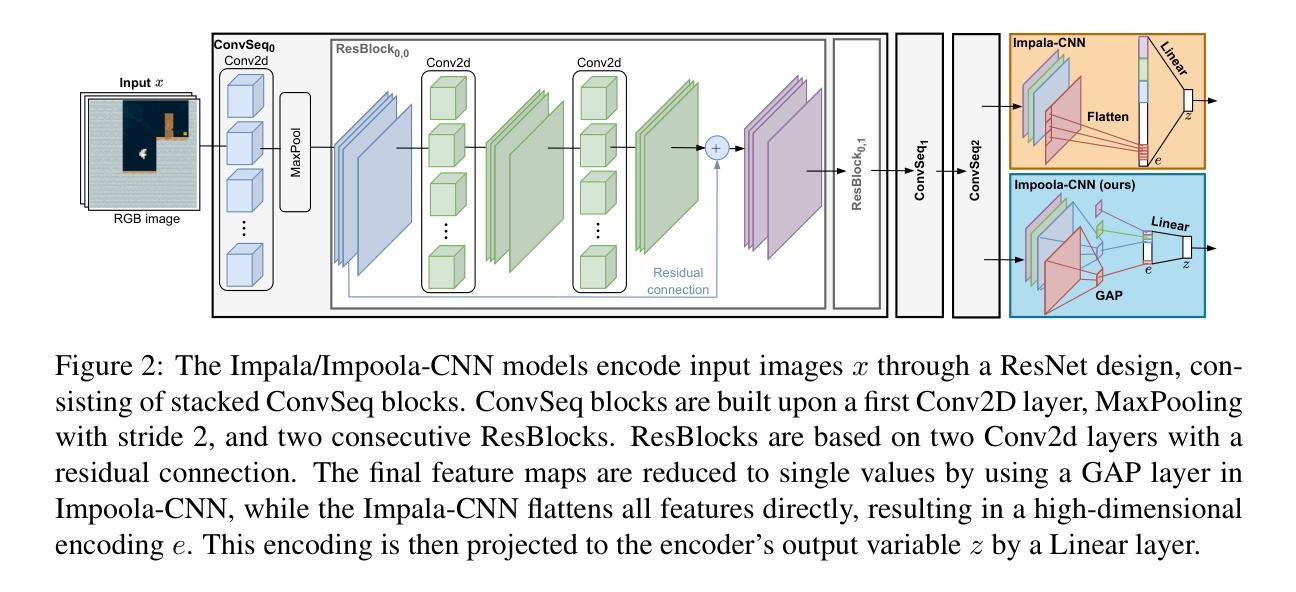
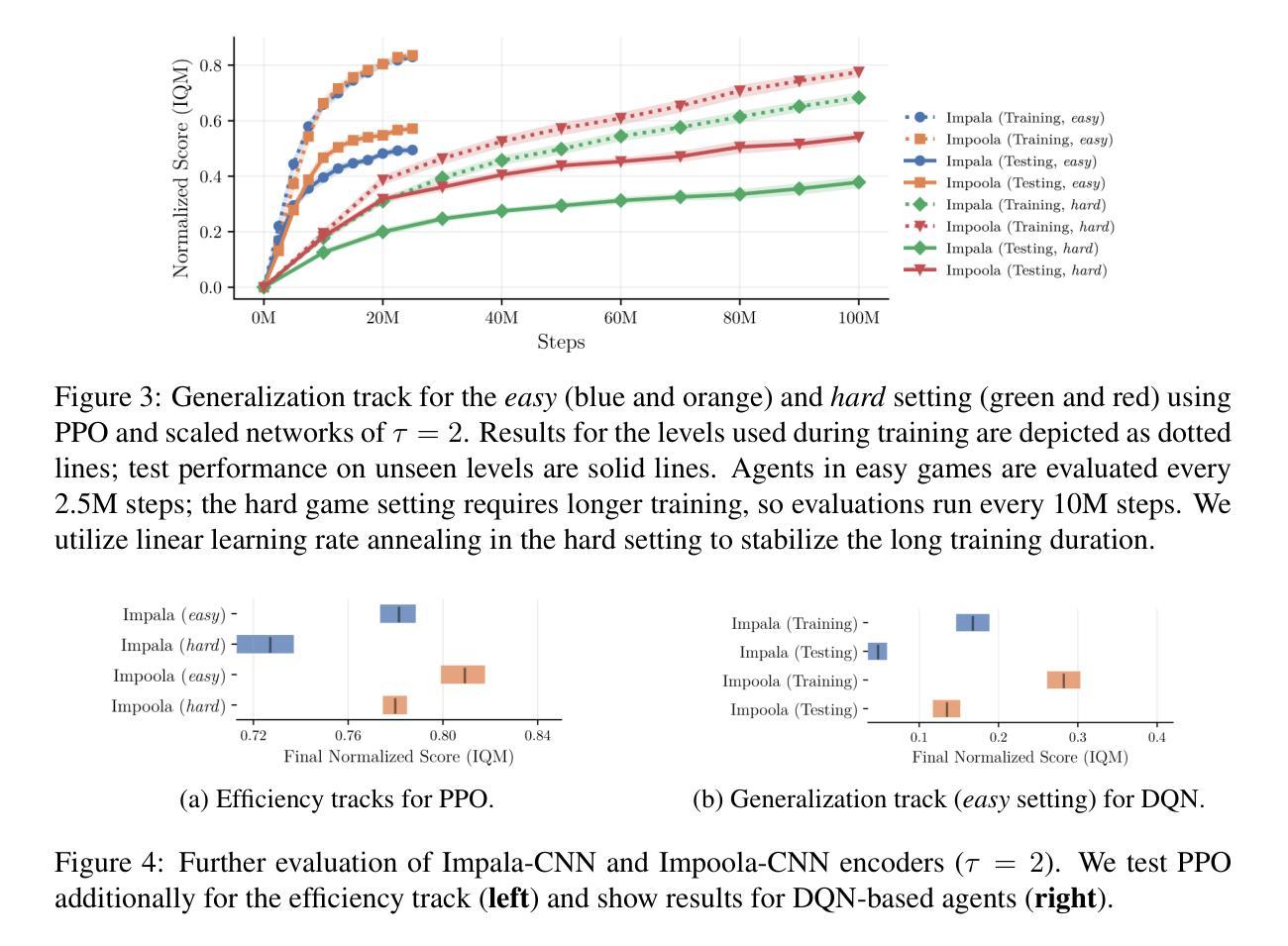
Impoola: The Power of Average Pooling for Image-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Raphael Trumpp, Ansgar Schäfftlein, Mirco Theile, Marco Caccamo
As image-based deep reinforcement learning tackles more challenging tasks, increasing model size has become an important factor in improving performance. Recent studies achieved this by focusing on the parameter efficiency of scaled networks, typically using Impala-CNN, a 15-layer ResNet-inspired network, as the image encoder. However, while Impala-CNN evidently outperforms older CNN architectures, potential advancements in network design for deep reinforcement learning-specific image encoders remain largely unexplored. We find that replacing the flattening of output feature maps in Impala-CNN with global average pooling leads to a notable performance improvement. This approach outperforms larger and more complex models in the Procgen Benchmark, particularly in terms of generalization. We call our proposed encoder model Impoola-CNN. A decrease in the network’s translation sensitivity may be central to this improvement, as we observe the most significant gains in games without agent-centered observations. Our results demonstrate that network scaling is not just about increasing model size - efficient network design is also an essential factor. We make our code available at https://github.com/raphajaner/impoola.
随着基于图像的深度强化学习处理更具挑战性的任务,模型规模的增加已成为提高性能的重要因素。近期的研究通过关注扩展网络的参数效率来实现这一点,通常使用受ResNet启发的15层Impala-CNN作为图像编码器。然而,虽然Impala-CNN明显优于较旧的CNN架构,但针对深度强化学习特定图像编码器的网络设计潜在进展却鲜有探索。我们发现,用全局平均池化代替Impala-CNN中输出特征图的平铺,会导致性能显著提高。这种方法在Procgen Benchmark上的表现优于更大、更复杂的模型,特别是在泛化方面。我们将我们提出的编码器模型称为Impoola-CNN。这种改进的核心可能是网络翻译敏感度的降低,因为我们在非以代理为中心的游戏中观察到最大的收益。我们的结果表明,网络扩展不仅仅关乎增加模型规模——高效的网络设计也是一个关键因素。我们在https://github.com/raphajaner/impoola提供我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Reinforcement Learning Conference 2025
Summary
图像深度强化学习在处理更具挑战性的任务时,模型规模的增加已成为提高性能的重要因素。最新研究通过关注扩展网络的参数效率来实现这一点,通常使用Impala-CNN作为图像编码器。然而,尽管Impala-CNN明显优于旧CNN架构,但在深度强化学习专用图像编码器的网络设计方面仍存在潜在的进步空间。研究发现,用全局平均池化替换Impala-CNN中的输出特征映射平展,能显著提高性能。在Procgen Benchmark中,这种方法优于更大、更复杂的模型,特别是在通用化方面。所提出的编码器模型被称为Impoola-CNN。网络翻译灵敏度的降低可能是这一改进的核心,因为在没有以代理为中心的观察的游戏中,我们观察到最大的收益。结果表明,网络规模扩展不仅仅是关于增加模型大小的问题——高效的网络设计也是一个关键因素。
Key Takeaways
- 模型规模增加是深度强化学习处理复杂任务时提高性能的重要因素。
- 最新研究关注扩展网络的参数效率,通常使用Impala-CNN作为图像编码器。
- Impala-CNN性能显著优于旧CNN架构,但仍存在网络设计方面的潜在进步空间。
- 通过全局平均池化替换Impala-CNN中的特征映射平展,可以进一步提高性能。
- Impoola-CNN在Procgen Benchmark中的表现优于更大、更复杂的模型,尤其在通用化方面。
- 网络翻译灵敏度的降低可能是这一改进的核心,特别是在没有以代理为中心的观察的游戏中。
点此查看论文截图