⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-08 更新
TaleDiffusion: Multi-Character Story Generation with Dialogue Rendering
Authors:Ayan Banerjee, Josep Lladós, Umapada Pal, Anjan Dutta
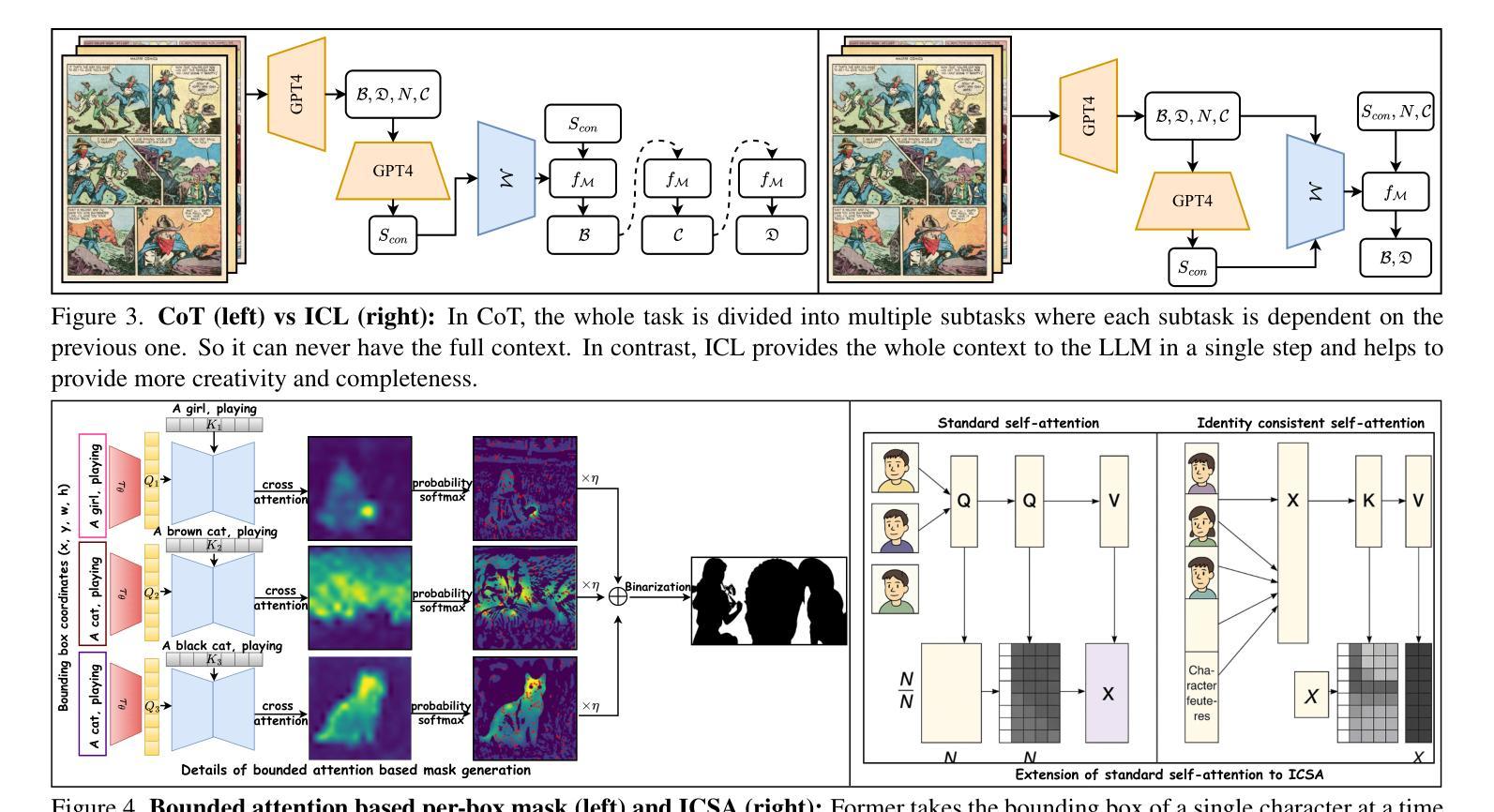
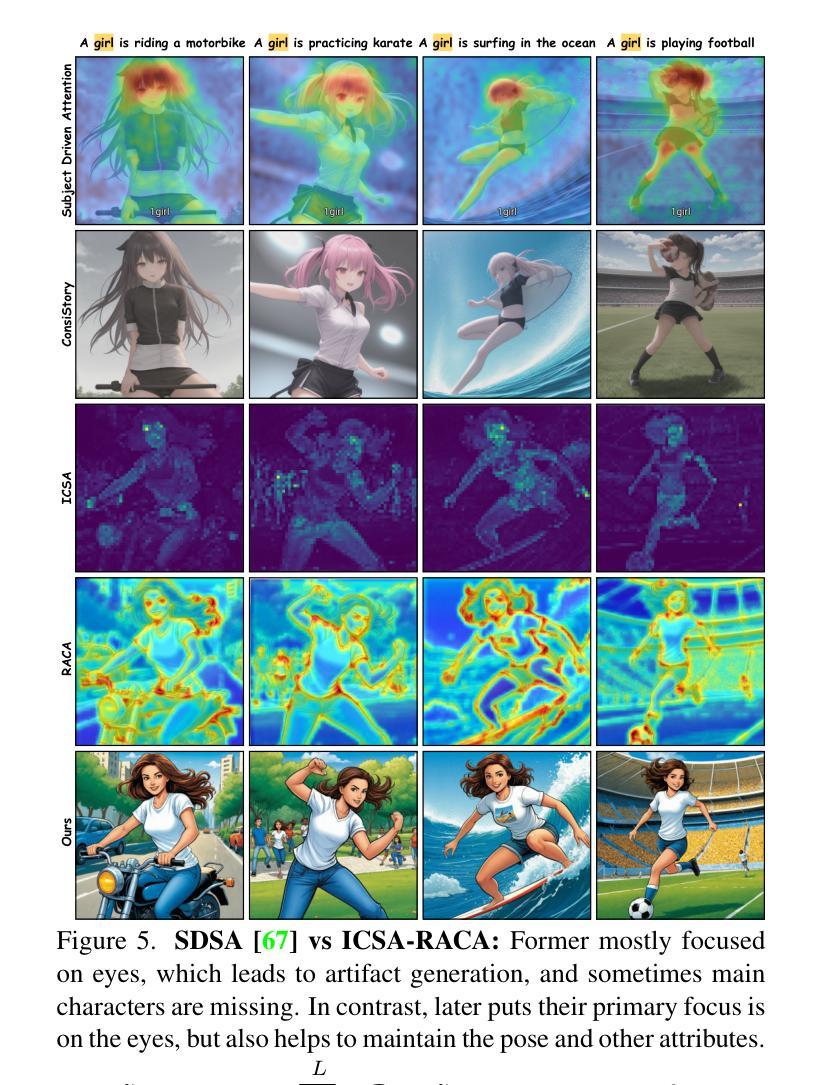
Text-to-story visualization is challenging due to the need for consistent interaction among multiple characters across frames. Existing methods struggle with character consistency, leading to artifact generation and inaccurate dialogue rendering, which results in disjointed storytelling. In response, we introduce TaleDiffusion, a novel framework for generating multi-character stories with an iterative process, maintaining character consistency, and accurate dialogue assignment via postprocessing. Given a story, we use a pre-trained LLM to generate per-frame descriptions, character details, and dialogues via in-context learning, followed by a bounded attention-based per-box mask technique to control character interactions and minimize artifacts. We then apply an identity-consistent self-attention mechanism to ensure character consistency across frames and region-aware cross-attention for precise object placement. Dialogues are also rendered as bubbles and assigned to characters via CLIPSeg. Experimental results demonstrate that TaleDiffusion outperforms existing methods in consistency, noise reduction, and dialogue rendering.
文本到故事可视化是一个挑战,因为需要在多个帧之间进行持续的角色互动。现有方法在角色一致性方面存在困难,导致出现伪影和对话渲染不准确的问题,从而导致故事叙述不连贯。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了TaleDiffusion,这是一个通过迭代过程生成多角色故事的新框架,通过后期处理来保持角色一致性和准确的对话分配。给定一个故事,我们使用预训练的LLM通过上下文学习生成每帧描述、角色细节和对话,然后通过基于边界的注意力感知框掩码技术来控制角色互动并尽量减少伪影。接着,我们应用身份一致的自注意力机制以确保跨帧的角色一致性,以及区域感知的跨注意力以实现精确的对象放置。对话也被渲染为气泡,并通过CLIPSeg分配给角色。实验结果表明,在一致性、降噪和对话渲染方面,TaleDiffusion优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为TaleDiffusion的新框架,用于生成多角色故事。该框架通过迭代过程维护角色一致性,并通过后处理实现准确的对话分配。利用预训练的大型语言模型生成每帧描述、角色细节和对话,采用基于有界注意力的每框掩码技术控制角色交互并减少伪影。通过身份一致的自注意力机制确保跨帧的角色一致性,以及区域感知的跨注意力实现精确的对象放置。对话以气泡形式呈现,并通过CLIPSeg分配给角色。实验结果表明,TaleDiffusion在一致性、降噪和对话渲染方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- TaleDiffusion是一个用于生成多角色故事的全新框架。
- 该框架通过迭代过程维护角色一致性。
- 通过预训练的大型语言模型生成每帧的描述、角色细节和对话。
- 采用基于有界注意力的每框掩码技术来控制角色交互并减少伪影。
- 通过自注意力机制确保跨帧的角色一致性。
- 采用区域感知的跨注意力实现精确的对象放置。
点此查看论文截图



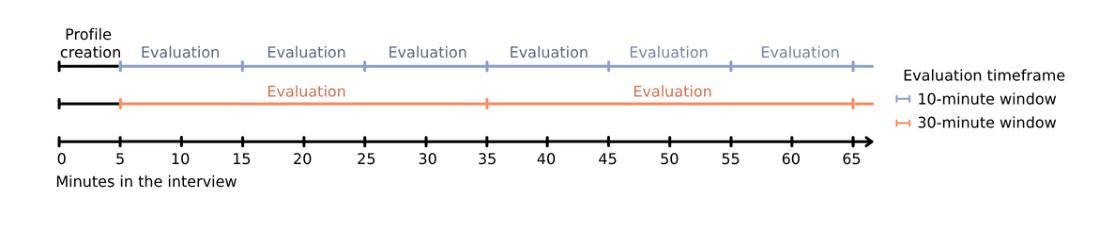
Towards Stable and Personalised Profiles for Lexical Alignment in Spoken Human-Agent Dialogue
Authors:Keara Schaaij, Roel Boumans, Tibor Bosse, Iris Hendrickx
Lexical alignment, where speakers start to use similar words across conversation, is known to contribute to successful communication. However, its implementation in conversational agents remains underexplored, particularly considering the recent advancements in large language models (LLMs). As a first step towards enabling lexical alignment in human-agent dialogue, this study draws on strategies for personalising conversational agents and investigates the construction of stable, personalised lexical profiles as a basis for lexical alignment. Specifically, we varied the amounts of transcribed spoken data used for construction as well as the number of items included in the profiles per part-of-speech (POS) category and evaluated profile performance across time using recall, coverage, and cosine similarity metrics. It was shown that smaller and more compact profiles, created after 10 min of transcribed speech containing 5 items for adjectives, 5 items for conjunctions, and 10 items for adverbs, nouns, pronouns, and verbs each, offered the best balance in both performance and data efficiency. In conclusion, this study offers practical insights into constructing stable, personalised lexical profiles, taking into account minimal data requirements, serving as a foundational step toward lexical alignment strategies in conversational agents.
词汇对齐对话过程中,说话者开始使用相似的词汇,这对于成功交流起着重要作用。然而,它在对话代理中的实现仍然鲜有研究,尤其是考虑到最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进展。作为实现人机对话词汇对齐的第一步,本研究借鉴个性化对话代理的策略,并研究构建稳定、个性化的词汇表作为词汇对齐的基础。具体来说,我们构建了不同长度的词汇表,并评估了不同词汇数量对词汇对齐的影响,使用召回率、覆盖率和余弦相似度等指标来评估词汇表随时间变化的性能。研究表明,经过包含形容词5项、连词5项以及每个包含副词、名词、代词和动词各含大约五项大约持续约十分钟内容的语音内容构建的词汇表能最佳地实现性能和数据效率的平衡。总的来说,本研究从构建稳定的个性化词汇表角度入手,深入探讨了如何尽可能降低数据量需求,作为对话代理中实现词汇对齐策略的基础步骤。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for TSD 2025
Summary
这篇论文探讨了词汇对齐在对话交流中的重要性,特别是在人与智能对话系统中的运用。研究提出个性化对话系统的策略,并构建稳定、个性化的词汇表作为词汇对齐的基础。通过调整转录语音数据的数量和词汇表中每个词类的项目数量,研究评估了词汇表的性能。结果表明,构建包含形容词5项、连词5项以及副词、名词、代词和动词各10项的简短词汇表可达到最佳的性能与数据效率平衡。这为对话系统中的词汇对齐策略提供了实践性的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 词汇对齐在对话交流中至关重要,尤其是在人与智能对话系统的交互中。
- 研究提出了个性化对话系统的策略,这是实现词汇对齐的重要一步。
- 构建稳定、个性化的词汇表是实现词汇对齐的基础。
- 调整转录语音数据的数量和词汇表中每个词类的项目数量会影响词汇表的性能。
- 简短且包含特定项目数量的词汇表在性能和数据效率之间达到了最佳平衡。
- 该研究为对话系统中词汇对齐策略的实践提供了有价值的见解。
点此查看论文截图

Chatbot Deployment Considerations for Application-Agnostic Human-Machine Dialogues
Authors:Pablo Rivas, Chelsi Chelsi, Nishit Nishit, Laharika Ravula
Automatic conversation systems based on natural language responses are becoming ubiquitous, in part, due to major advances in computational linguistics and machine learning. The easy access to robust and affordable platforms are causing companies to have an unprecedented rush to adopt chatbot technologies for customer service and support. However, this rush has caused judgment lapses when releasing chatbot technologies into production systems. This paper aims to shed light on basic, elemental, considerations that technologists must consider before deploying a chatbot. Our approach takes one particular case to draw lessons for those considering the implementation of chatbots. By looking at this case-study, we aim to call for consideration of societal values as a paramount factor before deploying a chatbot and consider the societal implications of releasing these types of systems.
基于自然语言回应的自动对话系统正变得无处不在,部分原因是计算语言学和机器学习方面的重大进展。容易获得稳健且实惠的平台正在使公司竞相采用聊天机器人技术进行客户服务和支持。然而,这种仓促推动导致在将聊天机器人技术投放生产系统时出现判断失误。本文旨在阐明在部署聊天机器人之前,技术人员必须考虑的基本要素。我们的方法以一个特定案例为例,为那些正在考虑实施聊天机器人的人提供经验教训。通过案例研究,我们呼吁在部署聊天机器人之前,首先考虑社会价值观是一个至关重要的因素,并考虑发布这些类型的系统所带来的社会影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The Third Workshop on Reasoning and Learning for Human-Machine Dialogues at the Thirty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-20)
Summary
自动对话系统基于自然语言响应的技术日益普及,得益于计算语言学和机器学习方面的重大进展。稳健且经济实惠的平台的普及,使得企业纷纷采用聊天机器人技术进行客户服务和支持。然而,这种匆忙将聊天机器人技术投入生产系统造成了判断失误。本文旨在阐述在部署聊天机器人之前,技术人员需要考虑的基本要素。通过个案研究,我们呼吁在部署聊天机器人之前考虑社会价值观这一重要因素,并考虑发布这些系统对社会的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 自动对话系统基于自然语言响应的技术日益普及,得益于计算语言学和机器学习的进展。
- 聊天机器人技术被企业广泛采用,用于客户服务和支持。
- 在部署聊天机器人技术到生产系统时,存在判断失误的情况。
- 技术人员在部署聊天机器人之前,需要考虑基本要素。
- 社会价值是一个重要的因素,需要在部署聊天机器人之前考虑。
- 发布这些系统对社会的影响需要被重视。
点此查看论文截图


Quantitative imaging of 478-keV prompt gamma rays from boron neutron capture reactions
Authors:Tetsuya Mizumoto, Shotaro Komura, Atsushi Takada, Yoshinori Sakurai, Toru Tanimori
The accurate imaging and quantitative measurement of 478-keV prompt gamma rays are critical for advancing boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), a promising cancer treatment. Although numerical simulations have indicated that such measurements are feasible, their practical application has proven challenging. This study introduces a gamma-ray imaging detector designed specifically for precise BNCT measurements. Using boron-rich phantom samples, we successfully imaged 478-keV gamma rays and established a linear correlation between gamma-ray production and boron concentration. Furthermore, applying this technique in a recognized BNCT treatment facility demonstrated the detector’s effectiveness in monitoring boron dose distribution during neutron irradiation, both in pretreatment diagnostics and throughout the treatment process.
对478-keV即时伽马射线的精确成像和定量测量对于发展硼中子捕获疗法(BNCT)这一前景光明的癌症治疗方法至关重要。尽管数值模拟表明这样的测量是可行的,但其实际应用却证明是有挑战性的。本研究介绍了一种专门设计用于精确BNCT测量的伽马射线成像探测器。我们使用富含硼的幻影样本成功地对478-keV伽马射线进行了成像,并建立了伽马射线产量与硼浓度之间的线性关系。此外,在公认的BNCT治疗设施中应用此技术,证明了该探测器在监测中子照射过程中的硼剂量分布方面的有效性,无论是在治疗前诊断还是在整个治疗过程中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 8 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本文介绍了针对硼中子俘获疗法(BNCT)中478-keV即时伽马射线的精确成像和定量测量的研究。该研究设计了一种专门用于精确BNCT测量的伽马射线成像探测器,通过对富硼 Phantom样本的成功成像,建立了伽马射线产量与硼浓度之间的线性关系。此外,在实际应用的BNCT治疗设施中使用该探测器,有效监测了中子照射过程中的硼剂量分布,可用于治疗前诊断以及整个治疗过程的监测。
Key Takeaways
- 硼中子俘获疗法(BNCT)是一种有前途的癌症治疗方法,需要准确成像和定量测量478-keV的即时伽马射线来促进其发展。
- 通过数值模拟证实了测量478-keV伽马射线的可行性,但实际应用具有挑战性。
- 研究开发了一种专门用于BNCT测量的伽马射线成像探测器。
- 使用富硼 Phantom样本成功成像,证明了探测器的有效性。
- 建立了伽马射线产量与硼浓度之间的线性关系。
- 探测器可用于实际应用的BNCT治疗设施中,监测中子照射过程中的硼剂量分布。
- 该技术既可用于治疗前诊断,也可在整个治疗过程中进行监测。
点此查看论文截图

Schema-Guided Response Generation using Multi-Frame Dialogue State for Motivational Interviewing Systems
Authors:Jie Zeng, Yukiko I. Nakano
The primary goal of Motivational Interviewing (MI) is to help clients build their own motivation for behavioral change. To support this in dialogue systems, it is essential to guide large language models (LLMs) to generate counselor responses aligned with MI principles. By employing a schema-guided approach, this study proposes a method for updating multi-frame dialogue states and a strategy decision mechanism that dynamically determines the response focus in a manner grounded in MI principles. The proposed method was implemented in a dialogue system and evaluated through a user study. Results showed that the proposed system successfully generated MI-favorable responses and effectively encouraged the user’s (client’s) deliberation by asking eliciting questions.
动机性访谈(MI)的主要目标是帮助客户建立自己的行为改变动机。为了在对话系统中支持这一点,引导大型语言模型(LLM)生成与MI原则一致的咨询师回应至关重要。本研究采用模式引导的方法,提出了一种更新多帧对话状态的方法和一种策略决策机制,以动态确定以MI原则为基础的反应重点。所提出的方法在一个对话系统中得到了实现,并通过用户研究进行了评估。结果表明,该系统成功生成了有利于MI的响应,并通过提出引导性问题有效地鼓励了用户(客户)的思考。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28pages, 15 figures, 10 tables
Summary
本文介绍了如何通过采用模式引导的方法,在对话系统中应用动机性访谈(MI)的原则,以帮助用户(即客户)建立改变行为的动力。通过更新多帧对话状态和策略决策机制,该系统能够生成符合MI原则的回答,并通过提出问题鼓励用户深思。经过用户研究评估,该系统成功生成了有利于MI的回应。
Key Takeaways
- 动机性访谈(MI)的核心目标是帮助客户建立改变行为的动力。
- 在对话系统中应用MI原则时,需要引导大型语言模型(LLMs)生成符合MI原则的回答。
- 采用模式引导的方法可以更新多帧对话状态,使系统能够更灵活地与用户交流。
- 策略决策机制能够动态确定回应的重点,确保对话符合MI原则。
- 通过用户研究评估,该系统成功生成了有利于MI的回应。
- 该系统通过提出问题鼓励用户深思,有助于增强用户的动机和自我反思。
点此查看论文截图



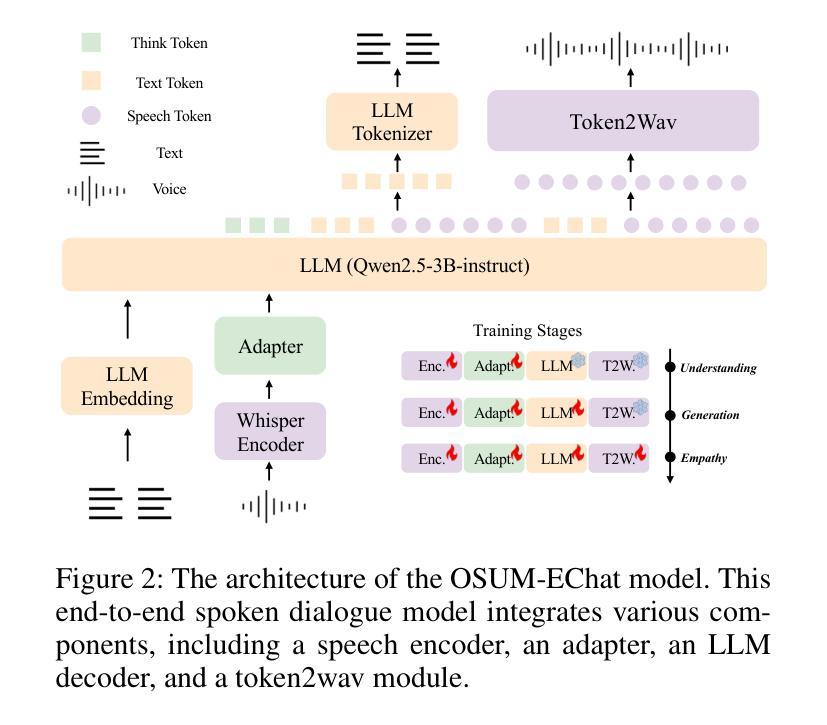
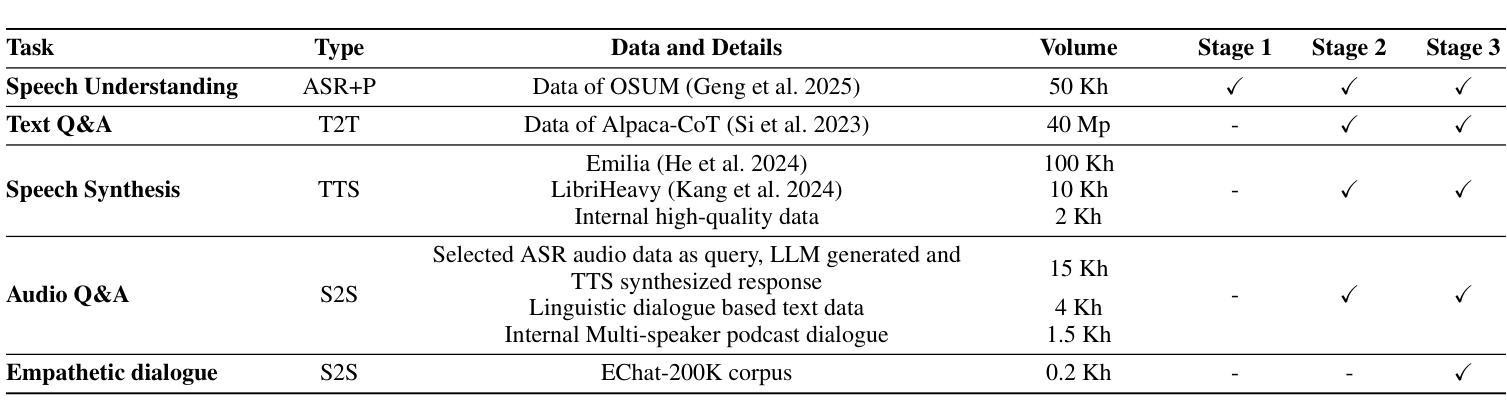
OSUM-EChat: Enhancing End-to-End Empathetic Spoken Chatbot via Understanding-Driven Spoken Dialogue
Authors:Xuelong Geng, Qijie Shao, Hongfei Xue, Shuiyuan Wang, Hanke Xie, Zhao Guo, Yi Zhao, Guojian Li, Wenjie Tian, Chengyou Wang, Zhixian Zhao, Kangxiang Xia, Ziyu Zhang, Zhennan Lin, Tianlun Zuo, Mingchen Shao, Yuang Cao, Guobin Ma, Longhao Li, Yuhang Dai, Dehui Gao, Dake Guo, Lei Xie
Empathy is crucial in enabling natural interactions within spoken dialogue systems, allowing machines to recognize and respond appropriately to paralinguistic cues such as age, gender, and emotion. Recent advancements in end-to-end speech language models, which unify speech understanding and generation, provide promising solutions. However, several challenges persist, including an over-reliance on large-scale dialogue datasets, insufficient extraction of paralinguistic cues vital for conveying empathy, and the lack of empathy-specific datasets and evaluation frameworks. To address these issues, we introduce OSUM-EChat, an open-source, end-to-end spoken dialogue system designed to enhance empathetic interactions, particularly in resource-limited settings. OSUM-EChat introduces two key innovations: (1) a three-stage understanding-driven spoken dialogue training strategy that extends the capabilities of a large speech understanding model to spoken dialogue tasks, and (2) a linguistic-paralinguistic dual thinking mechanism that integrates paralinguistic understanding through a chain of thought with dialogue generation, enabling the system to produce more empathetic responses. This approach reduces reliance on large-scale dialogue datasets while maintaining high-quality empathetic interactions. Additionally, we introduce the EChat-200K dataset, a rich corpus of empathetic speech-to-speech dialogues, and the EChat-eval benchmark, a comprehensive framework for evaluating the empathetic capabilities of dialogue systems. Experimental results demonstrate that OSUM-EChat outperforms end-to-end spoken dialogue models regarding empathetic responsiveness, validating its effectiveness.
共情在口语对话系统内的自然交互中至关重要,它让机器能够识别和适当回应诸如年龄、性别和情绪等副语言线索。端到端的语言模型最近的进步,这些模型统一了语音理解和生成,提供了很有前景的解决方案。然而,仍存在一些挑战,包括过度依赖大规模的对话数据集,对传递共情至关重要的副语言线索提取不足,以及缺乏专门针对共情的数据集和评估框架。为了解决这些问题,我们推出了OSUM-EChat,这是一个开源的端到端口语对话系统,旨在增强共情交互,特别是在资源有限的环境中。OSUM-EChat引入了两项关键创新:一是以理解为主导的三阶段口语对话训练策略,它扩展了大型语音理解模型在口语对话任务上的能力;二是语言-副语言双重思考机制,它将副语言理解融入思维链进行对话生成,使系统能够产生更具共情的回应。这种方法减少了大规模对话数据集的依赖,同时保持了高质量的共情交互。此外,我们还推出了EChat-200K数据集,这是一份丰富的共情语音对话语料库,以及EChat-eval基准测试,这是一个全面评估对话系统共情能力的框架。实验结果表明,OSUM-EChat在共情响应方面优于端到端的口语对话模型,验证了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
共情在口语对话系统中实现自然交互至关重要,它让机器能够识别和回应年龄、性别和情感等副语言线索。尽管端到端的自然语言模型在统一语音理解和生成方面取得了进展,但仍存在依赖大规模对话数据集、未能充分提取对表达共情至关重要的副语言线索以及缺乏针对共情的特定数据集和评估框架等挑战。为解决这些问题,我们推出了OSUM-EChat这一开源的端到端口语对话系统,旨在加强共情交互,特别是在资源有限的环境中。OSUM-EChat引入了两个关键创新点:一是以理解为核心的三阶段口语对话训练策略,扩展了大规模语音理解模型在口语对话任务上的能力;二是语言-副语言双重思考机制,通过一系列思考将副语言理解与对话生成相结合,使系统能够产生更共情的回应。这种方法减少了大规模对话数据集的依赖,同时保持了高质量的共情交互。此外,我们还推出了EChat-200K数据集,这是一份丰富的共情性语音对话语料库,以及EChat-eval基准测试,这是一个全面评估对话系统共情能力的框架。实验结果表明,OSUM-EChat在共情响应方面优于端到端的口语对话模型,验证了其有效性。
关键见解
- 共情在口语对话系统中对于实现自然交互至关重要,允许机器识别并适当回应副语言线索。
- 端到端的自然语言模型在统一语音理解和生成方面取得进展,但仍存在挑战。
- OSUM-EChat是一个旨在增强共情交互的开源端到端口语对话系统。
- OSUM-EChat引入了三阶段口语对话训练策略和语言-副语言双重思考机制。
- 该系统通过减少大规模对话数据集的依赖,维持了高质量的共情交互。
- 推出了EChat-200K数据集,包含丰富的共情性语音对话内容。
点此查看论文截图




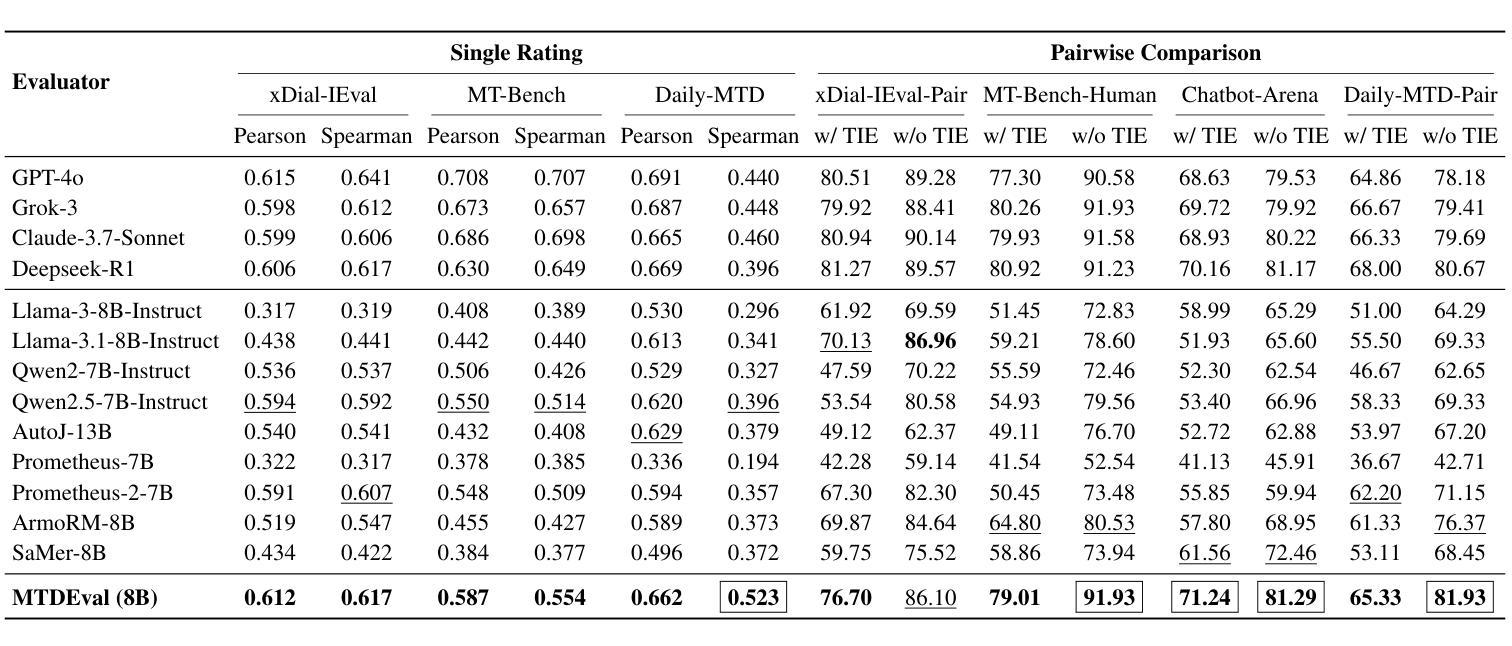
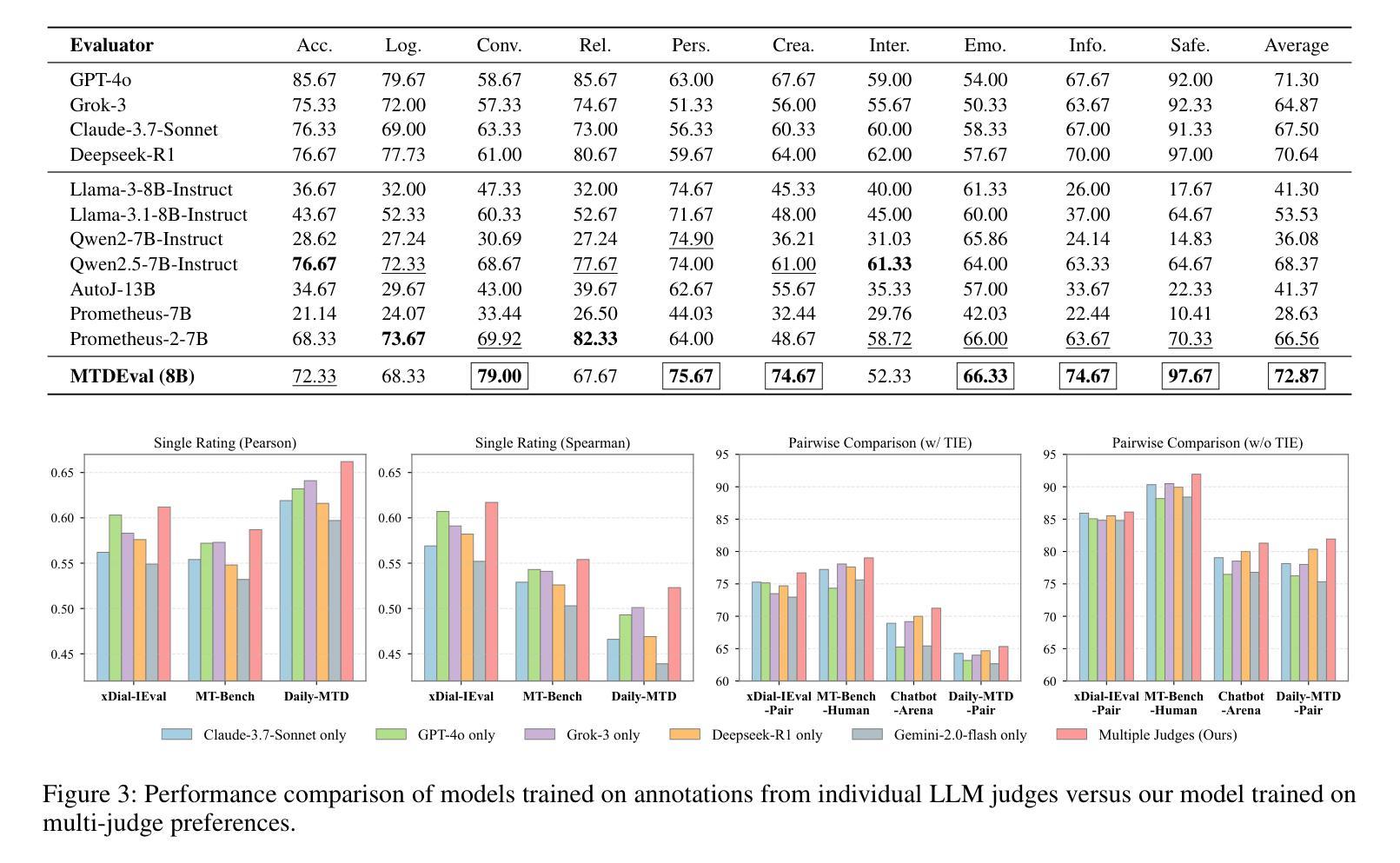
Learning an Efficient Multi-Turn Dialogue Evaluator from Multiple Judges
Authors:Yuqi Tang, Kehua Feng, Yunfeng Wang, Zhiwen Chen, Chengfei Lv, Gang Yu, Qiang Zhang, Keyan Ding
Evaluating the conversational abilities of large language models (LLMs) remains a challenging task. Current mainstream approaches primarily rely on the “LLM-as-a-judge” paradigm, where an LLM is prompted to serve as an evaluator to assess dialogue quality. However, such methods often suffer from various biases, which undermine the reliability and consistency of the evaluation results. To mitigate these biases, recent methods employ multiple LLMs as judges and aggregate their judgments to select the optimal assessment. Although effective, this multi-judge approach incurs significant computational overhead during inference. In this paper, we propose an efficient multi-turn dialogue evaluator that captures the collective wisdom of multiple LLM judges by aggregating their preference knowledge into a single model. Our approach preserves the advantages of diverse multi-judge feedback while drastically reducing the evaluation cost, enabling fast and flexible dialogue quality assessment. Extensive experiments on seven single rating and pairwise comparison dialogue evaluation benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing baselines across diverse scenarios, showcasing its efficiency and robustness.
评估大型语言模型(LLM)的对话能力仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。当前的主流方法主要依赖于“LLM作为评判员”的模式,即提示LLM充当评估员,以评估对话质量。然而,这些方法常常会受到各种偏见的影响,从而破坏了评估结果的可靠性和一致性。为了减少这些偏见,最近的方法采用多个LLM作为评判员,并将他们的判断汇总起来以选择最佳评估结果。尽管这种方法有效,但在推理过程中却产生了巨大的计算开销。在本文中,我们提出了一种高效的多轮对话评估器,它通过将一个模型汇总多个LLM评判员的偏好知识来捕捉集体智慧。我们的方法保留了多种多评判员反馈的优势,同时大大降低了评估成本,实现了快速灵活的对话质量评估。在七个单一评分和配对比较对话评估基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在多种场景下都优于现有基线,展现了其高效性和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 2 pages, under review
Summary
大语言模型的对话能力评估仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。当前主流方法主要依赖于“LLM作为评判者”的模式,但这种方法存在偏见问题,影响评估结果的可靠性和一致性。为缓解这一问题,近期方法采用多个LLM作为评判者并汇聚判断以选择最佳评估。尽管有效,但多评判者方法在推理过程中会产生巨大的计算开销。本文提出一种高效的多轮对话评估器,通过汇聚多个LLM评判者的偏好知识到一个单一模型中,捕捉集体智慧。该方法在保留多样化多评判者反馈优势的同时,大幅降低了评估成本,实现了快速灵活的对话质量评估。
Key Takeaways
- 对话能力评估对于大语言模型(LLM)仍具挑战性。
- 当前主流评估方法依赖于LLM作为评判者,但存在偏见问题。
- 多评判者方法能有效缓解偏见,但计算开销大。
- 本文提出一种新型对话评估器,融合多个LLM的判断。
- 该方法提高了评估效率并降低了成本。
- 实验证明该方法在多种对话评估基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图



Binaural Target Speaker Extraction using HRTFs
Authors:Yoav Ellinson, Sharon Gannot
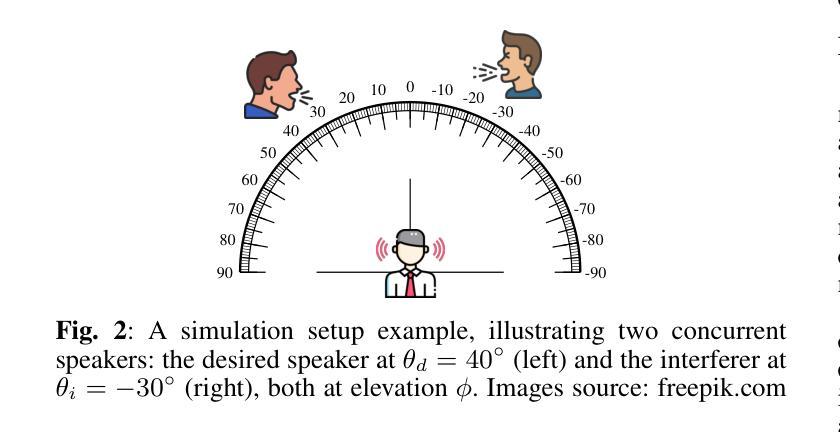
In this work, we aim to imitate the human ability to selectively attend to a single speaker, even in the presence of multiple simultaneous talkers. To achieve this, we propose a novel approach for binaural target speaker extraction that leverages the listener’s Head-Related Transfer Function (HRTF) to isolate the desired speaker. Notably, our method does not rely on speaker embeddings, making it speaker-independent and enabling strong generalization across multiple speech datasets and languages. We employ a fully complex-valued neural network that operates directly on the complex-valued Short-Time Fourier transform (STFT) of the mixed audio signals, and compare it to a Real-Imaginary (RI)-based neural network, demonstrating the advantages of the former. We first evaluate the method in an anechoic, noise-free scenario, achieving excellent extraction performance while preserving the binaural cues of the target signal. We then extend the evaluation to reverberant conditions. Our method proves robust, maintaining speech clarity and source directionality while simultaneously reducing reverberation. A comparative analysis with existing binaural Target Speaker Extraction (TSE) methods demonstrates that our approach attains performance on par with competing techniques in terms of noise reduction and perceptual quality, while offering a clear advantage in preserving binaural cues.Demo-page: https://bi-ctse-hrtf.github.io
在这项工作中,我们的目标是模仿人类有选择地关注单一说话者的能力,即使在有多个同时说话的情境中也能如此。为了实现这一目标,我们提出了一种新型的利用双耳目标说话者提取的方法,该方法利用听众的头部相关传输函数(HRTF)来分离目标说话者的声音。值得注意的是,我们的方法不依赖于说话者嵌入,使其成为独立于说话者的方法,并在多个语音数据集和语言之间实现了强大的泛化能力。我们采用一个全复数神经网络,直接在混合音频信号的复数短时傅里叶变换(STFT)上操作,并将其与基于实虚(RI)的神经网络进行比较,展示了前者的优势。我们首先在无混响、无噪声的场景下评估该方法,在保持目标信号的双耳线索的同时实现了出色的提取性能。然后我们将评估扩展到混响条件。我们的方法证明是稳健的,在保持语音清晰度和源方向性的同时减少了混响。与现有的双耳目标说话者提取(TSE)方法的比较分析表明,我们的方法在降噪和感知质量方面的性能与竞争技术相当,同时在保留双耳线索方面具有明显的优势。演示页面:https://bi-ctse-hrtf.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用人类听觉系统选择性注意单一说话者的能力,实现双耳目标说话者提取的新方法。利用听者头部相关传输函数(HRTF)隔离目标说话者的声音。此方法无需依赖说话者嵌入,具有良好的泛化能力,可跨越多个语音数据集和语言使用。研究采用了完全复数神经网络直接处理混合音频信号的复数短时傅里叶变换(STFT),并与基于实虚数(RI)的神经网络进行了比较,显示了前者的优势。在无声学回声和噪声的情境中评估此方法,表现出优异的提取性能且保留了目标信号的双耳线索。此外,在具有回声的条件下进行评估时,该方法保持了良好的表现,证明其在维持语音清晰度和来源方向性的同时减少回声的能力。与现有的双耳目标说话者提取方法相比,本文方法在降噪和感知质量方面表现相当,但在保留双耳线索方面具有明显优势。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种模仿人类选择性注意单一说话者的能力进行双耳目标说话者提取的新方法。
- 利用听者头部相关传输函数(HRTF)来隔离目标说话者的声音,无需依赖说话者嵌入,具有良好的泛化能力。
- 采用完全复数神经网络处理混合音频信号的复数短时傅里叶变换(STFT),显示出较高的性能。
- 在无声学回声和噪声的环境中评估此方法时,表现出良好的提取性能并保留了目标信号的双耳线索。
- 在具有回声的条件下评估时,该方法能维持语音清晰度和来源方向性,同时减少回声。
- 与现有双耳目标说话者提取方法相比,在降噪和感知质量方面表现相当。
点此查看论文截图



SPIN-ODE: Stiff Physics-Informed Neural ODE for Chemical Reaction Rate Estimation
Authors:Wenqing Peng, Zhi-Song Liu, Michael Boy
Estimating rate coefficients from complex chemical reactions is essential for advancing detailed chemistry. However, the stiffness inherent in real-world atmospheric chemistry systems poses severe challenges, leading to training instability and poor convergence, which hinder effective rate coefficient estimation using learning-based approaches. To address this, we propose a Stiff Physics-Informed Neural ODE framework (SPIN-ODE) for chemical reaction modelling. Our method introduces a three-stage optimisation process: first, a black-box neural ODE is trained to fit concentration trajectories; second, a Chemical Reaction Neural Network (CRNN) is pre-trained to learn the mapping between concentrations and their time derivatives; and third, the rate coefficients are fine-tuned by integrating with the pre-trained CRNN. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and newly proposed real-world datasets validate the effectiveness and robustness of our approach. As the first work addressing stiff neural ODE for chemical rate coefficient discovery, our study opens promising directions for integrating neural networks with detailed chemistry.
从复杂的化学反应中估计速率系数对于推进详细的化学研究至关重要。然而,真实世界大气化学系统固有的刚性问题带来了严重的挑战,导致训练不稳定和收敛性差,阻碍了基于学习的速率系数估计的有效进行。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一个用于化学反应建模的刚物理信息神经网络常微分方程(SPIN-ODE)框架。我们的方法引入了一个三阶段的优化过程:首先,训练一个黑箱神经网络常微分方程来拟合浓度轨迹;其次,预训练一个化学反应神经网络(CRNN)来学习浓度及其时间导数之间的映射关系;最后,通过与预训练的CRNN集成来微调速率系数。在合成数据和新提出的真实世界数据集上的大量实验验证了我们的方法的有效性和稳健性。作为解决针对化学速率系数发现的刚性神经常微分方程的第一项工作,我们的研究为神经网络与详细化学的融合开辟了充满希望的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI) 2025
Summary
神经网络常微分方程(Neural ODE)结合化学动力学建模的方法被提出,用于解决真实大气化学系统刚度带来的训练不稳定和收敛性差的问题。该方法包括三个阶段:训练神经网络常微分方程以拟合浓度轨迹,预训练化学反应神经网络(CRNN)学习浓度及其时间导数的映射关系,以及通过整合预训练的CRNN对速率系数进行微调。实验证明该方法在合成和新提出真实数据集上的有效性和稳健性,为神经网络与详细化学的结合打开了新的研究路径。
Key Takeaways
- 真实大气化学系统的刚度给基于学习的速率系数估计带来了挑战,导致训练不稳定和收敛性差。
- 提出了一种名为SPIN-ODE的刚物理信息神经网络常微分方程框架,用于解决化学反应建模中的问题。
- SPIN-ODE包括三个阶段的优化过程:训练神经网络常微分方程、预训练化学反应神经网络,以及微调速率系数。
- 方法通过整合预训练的CRNN对速率系数进行微调,实现更有效的学习。
- 广泛实验证明该方法在合成和真实数据集上的有效性和稳健性。
- 作为首次解决化学速率系数发现的刚神经ODE问题的研究,该研究具有开创性。
点此查看论文截图





Dial-In LLM: Human-Aligned LLM-in-the-loop Intent Clustering for Customer Service Dialogues
Authors:Mengze Hong, Wailing Ng, Chen Jason Zhang, Yuanfeng Song, Di Jiang
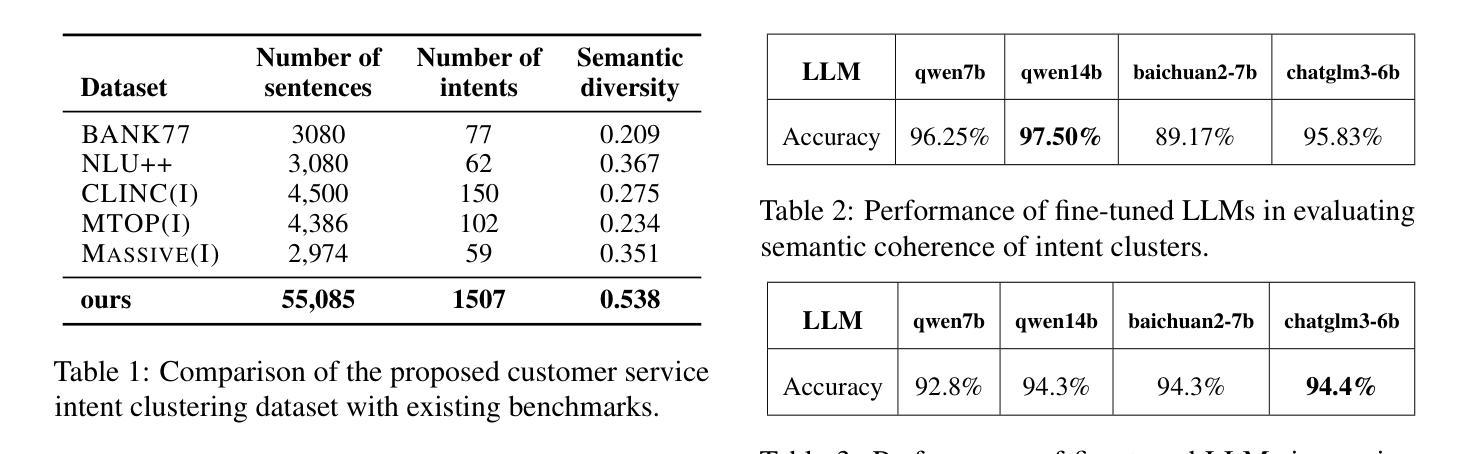
Discovering customer intentions is crucial for automated service agents, yet existing intent clustering methods often fall short due to their reliance on embedding distance metrics and neglect of underlying semantic structures. To address these limitations, we propose an LLM-in-the-loop (LLM-ITL) intent clustering framework, integrating the language understanding capabilities of LLMs into conventional clustering algorithms. Specifically, this paper (1) examines the effectiveness of fine-tuned LLMs in semantic coherence evaluation and intent cluster naming, achieving over 95% accuracy aligned with human judgments; (2) designs an LLM-ITL framework that facilitates the iterative discovery of coherent intent clusters and the optimal number of clusters; and (3) introduces context-aware techniques tailored for customer service dialogue. Since existing English benchmarks lack sufficient semantic diversity and intent coverage, we further present a comprehensive Chinese dialogue intent dataset comprising over 100k real customer service calls with 1,507 human-annotated clusters. The proposed approaches significantly outperform LLM-guided baselines, achieving notable improvements in clustering quality, cost efficiency, and downstream applications. Combined with several best practices, our findings highlight the prominence of LLM-in-the-loop techniques for scalable dialogue data mining.
发现客户意图对于自动服务代理至关重要,但现有的意图聚类方法往往因依赖嵌入距离度量而忽视潜在语义结构而表现不足。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种LLM-in-the-loop(LLM-ITL)意图聚类框架,将大型语言模型的语言理解能力集成到传统的聚类算法中。具体来说,本文(1)研究了微调后的LLMs在语义连贯性评估和意图聚类命名中的有效性,其准确率与人类判断对齐超过95%;(2)设计了一个LLM-ITL框架,便于发现连贯的意图簇和最优簇数;(3)引入了面向客户服务对话的上下文感知技术。由于现有的英语基准测试缺乏足够的语义多样性和意图覆盖,我们进一步提供了一个全面的中文对话意图数据集,包含超过10万条真实的客户服务呼叫记录,包含1507个人工标注的簇。所提出的方法显著优于LLM引导的基础线方法,在聚类质量、成本效率和下游应用方面取得了显著的改进。结合若干最佳实践,我们的研究凸显了LLM-in-the-loop技术在可扩展对话数据挖掘中的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by EMNLP 2025 Main Conference
Summary
基于现有的意图聚类方法在语义理解上的不足,本文提出了一种结合了大型语言模型(LLM)的意图聚类框架——LLM-in-the-loop(LLM-ITL)。该框架不仅利用LLM的语言理解能力来提升传统聚类算法的效果,还针对客户服务对话引入了语境感知技术。此外,为了弥补现有英语基准测试在语义多样性和意图覆盖上的不足,本研究还推出了一份包含10万条以上真实客户服务通话和1507个人工标注聚类的中文对话意图数据集。研究表明,LLM-ITL方法在聚类质量、成本效益和下游应用方面均显著优于LLM引导的基础方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-ITL框架结合了LLM的语言理解能力,提升了传统意图聚类算法的效果。
- LLM-ITL框架能够迭代发现连贯的意图簇和最佳簇数量。
- 针对客户服务对话,引入了语境感知技术。
- 现有的英语基准测试在语义多样性和意图覆盖方面存在不足。
- 推出了一份包含超过10万条真实客户服务通话的中文对话意图数据集。
- LLM-ITL方法在聚类质量、成本效益和下游应用方面表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图



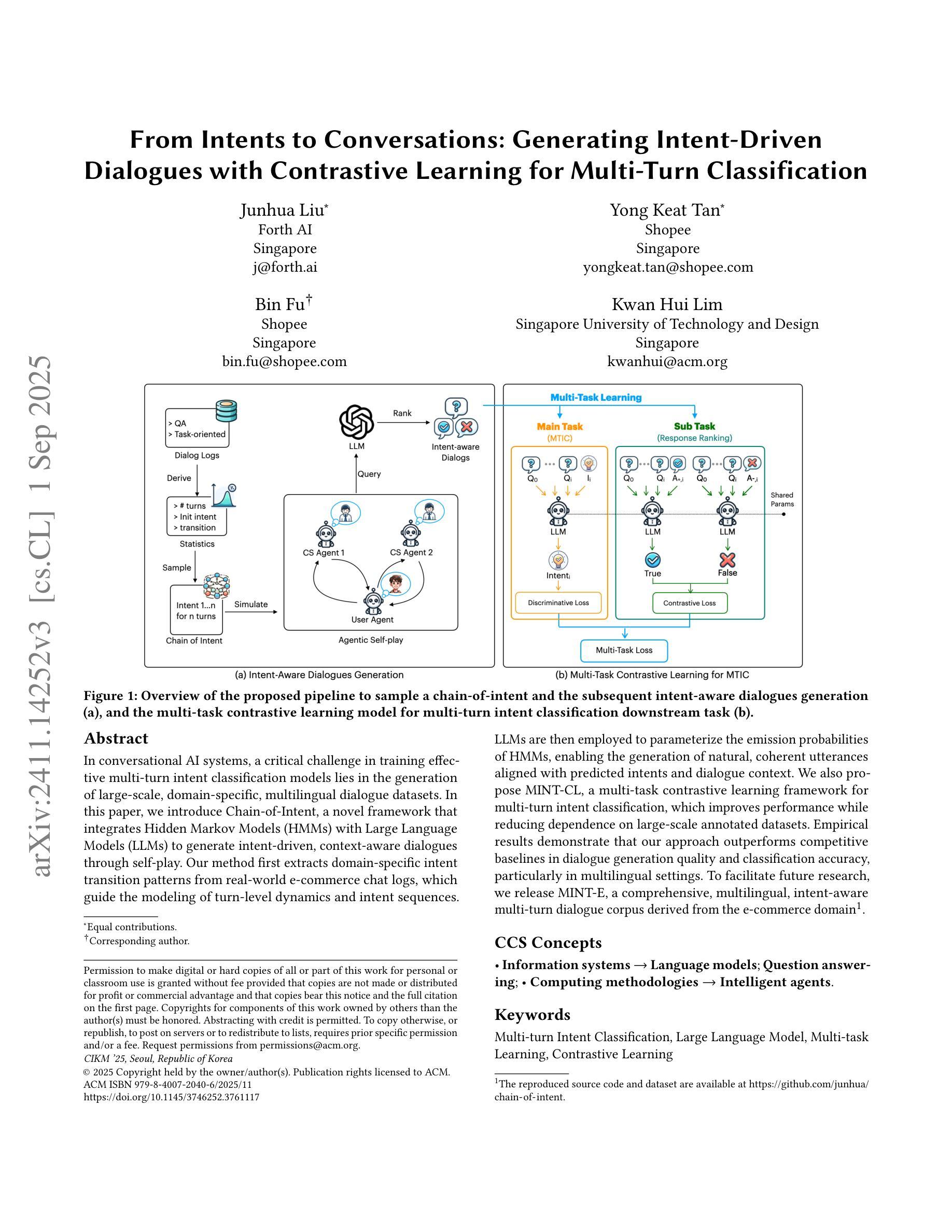
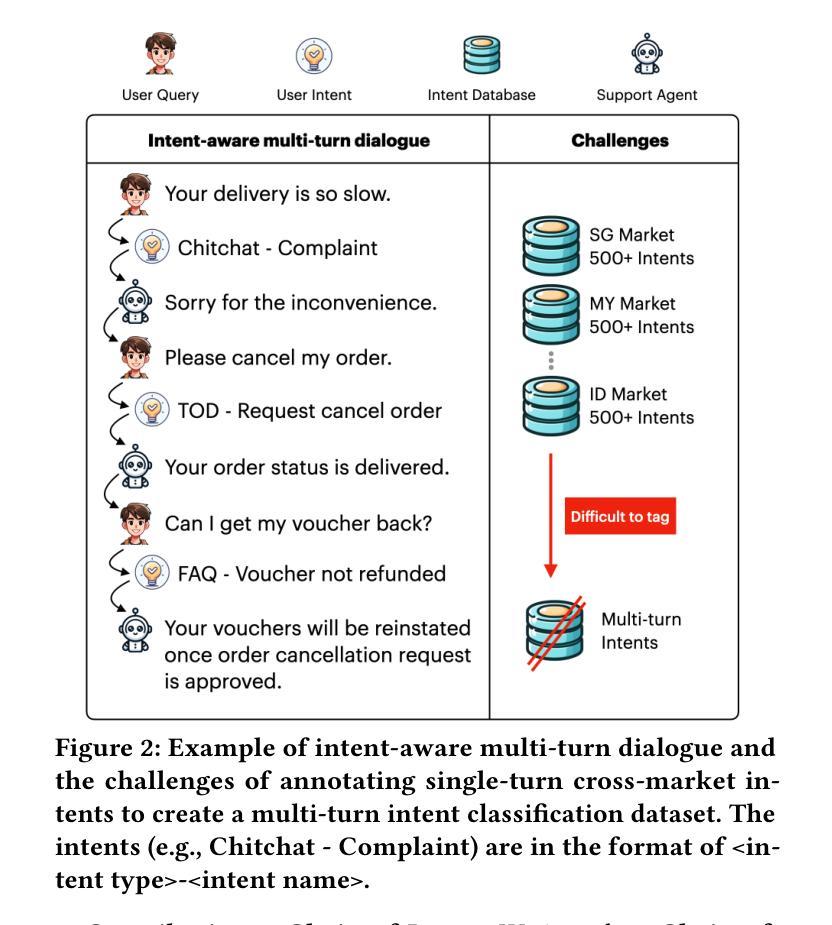
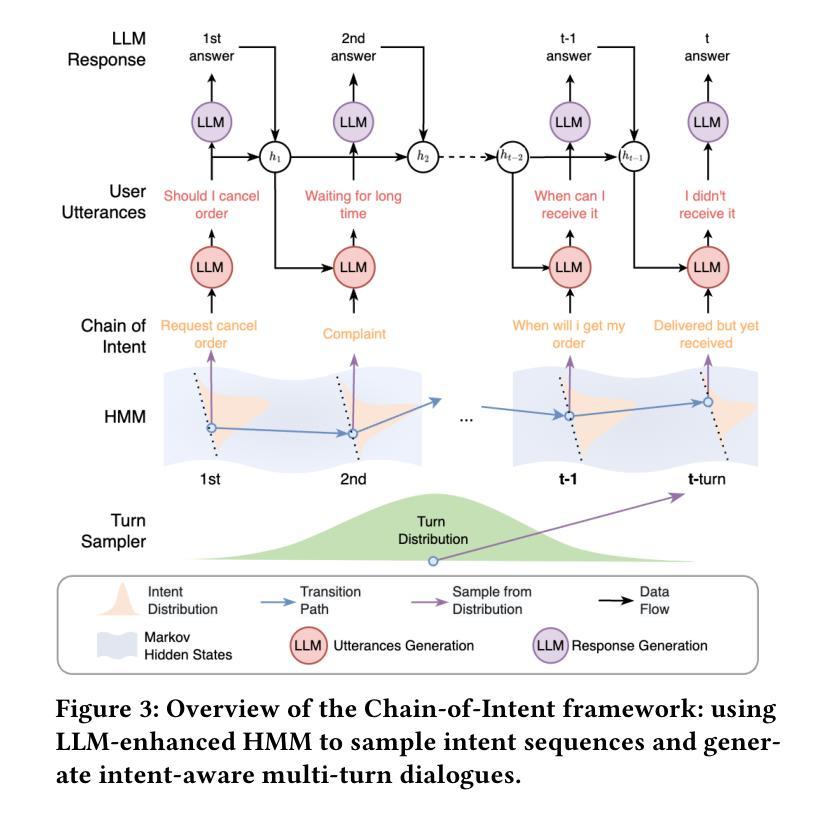
From Intents to Conversations: Generating Intent-Driven Dialogues with Contrastive Learning for Multi-Turn Classification
Authors:Junhua Liu, Yong Keat Tan, Bin Fu, Kwan Hui Lim
In conversational AI systems, a critical challenge in training effective multi-turn intent classification models lies in the generation of large-scale, domain-specific, multilingual dialogue datasets. In this paper, we introduce Chain-of-Intent, a novel framework that integrates Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) with Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate intent-driven, context-aware dialogues through self-play. Our method first extracts domain-specific intent transition patterns from real-world e-commerce chat logs, which guide the modeling of turn-level dynamics and intent sequences. LLMs are then employed to parameterize the emission probabilities of HMMs, enabling the generation of natural, coherent utterances aligned with predicted intents and dialogue context. We also propose MINT-CL, a multi-task contrastive learning framework for multi-turn intent classification, which improves performance while reducing dependence on large-scale annotated datasets. Empirical results demonstrate that our approach outperforms competitive baselines in dialogue generation quality and classification accuracy, particularly in multilingual settings. To facilitate future research, we release MINT-E, a comprehensive, multilingual, intent-aware multi-turn dialogue corpus derived from the e-commerce domain\footnote{The reproduced source code and dataset are available at https://github.com/junhua/chain-of-intent.
在对话式AI系统中,训练有效的多轮意图分类模型的关键挑战在于生成大规模、特定领域的多语言对话数据集。在本文中,我们介绍了Intent链,这是一个新型框架,它将隐马尔可夫模型(HMMs)与大型语言模型(LLMs)相结合,通过自我对抗生成意图驱动、意识形态的对话。我们的方法首先从现实世界中的电子商务聊天日志中提取特定领域的意图转换模式,这些模式引导轮级动态和意图序列的建模。然后,我们采用大型语言模型对隐马尔可夫模型的发射概率进行参数化,使生成的对话符合预期的意图和对话背景的自然连贯性。我们还提出了MINT-CL,一个用于多轮意图分类的多任务对比学习框架,它在提高性能的同时减少了大规模标注数据集的依赖。经验结果表明,我们的方法在对话生成质量和分类准确性方面优于竞争对手的基线方法,特别是在多语言环境中。为了促进未来的研究,我们发布了MINT-E,一个全面的、多语言的、意图感知的多轮对话语料库,该语料库来源于电子商务领域。(注:复现源代码和数据集可在https://github.com/junhua/chain-of-intent找到。)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Proceedings of CIKM’25
Summary
本文提出了一个名为Chain-of-Intent的新框架,该框架结合了隐马尔可夫模型(HMMs)与大型语言模型(LLMs),通过自我博弈生成意图驱动、语境感知的对话。此外,还提出了MINT-CL,一个多任务对比学习框架,用于多轮意图分类,可提高性能并减少对大规模标注数据集的依赖。实验结果表明,该方法在对话生成质量和分类准确性方面优于竞争对手,特别是在多语种环境中。
Key Takeaways
- Chain-of-Intent框架结合了隐马尔可夫模型(HMMs)与大型语言模型(LLMs),以生成与语境相关的对话。
- 提出MINT-CL框架,用于多轮意图分类,提高性能并减少对大规模标注数据集的依赖。
- 使用真实电商聊天日志中的意图转换模式来指导轮次级别动态和意图序列的建模。
- LLMs被用来参数化HMMs的发射概率,以生成与预测意图和对话语境相符的自然、连贯的语句。
- 框架在对话生成质量和分类准确性方面表现出优异的性能,特别是在多语种环境中。
- 释放了MINT-E数据集,这是一个从电商领域衍生的综合、多语种、意图感知的多轮对话语料库。
点此查看论文截图


Talk, Listen, Connect: How Humans and AI Evaluate Empathy in Responses to Emotionally Charged Narratives
Authors:Mahnaz Roshanaei, Rezvaneh Rezapour, Magy Seif El-Nasr
Social interactions promote well-being, yet barriers like geographic distance, time limitations, and mental health conditions can limit face-to-face interactions. Emotionally responsive AI systems, such as chatbots, offer new opportunities for social and emotional support, but raise critical questions about how empathy is perceived and experienced in human-AI interactions. This study examines how empathy is evaluated in AI-generated versus human responses. Using personal narratives, we explored how persona attributes (e.g., gender, empathic traits, shared experiences) and story qualities affect empathy ratings. We compared responses from standard and fine-tuned AI models with human judgments. Results show that while humans are highly sensitive to emotional vividness and shared experience, AI-responses are less influenced by these cues, often lack nuance in empathic expression. These findings highlight challenges in designing emotionally intelligent systems that respond meaningfully across diverse users and contexts, and informs the design of ethically aware tools to support social connection and well-being.
社会互动有助于提升福祉,然而地理距离、时间限制和心理健康状况等障碍可能会限制面对面的互动。情绪反应型的人工智能系统,如聊天机器人,提供了新的社交和情感支持的机会,但由此引发了关于人机交互中同情如何被感知和体验的重要问题。本研究旨在调查人工智能生成的反应与人类反应中的同情评价如何。通过个人叙事的方式,我们探讨了人格属性(如性别、移情特质、共享经验)和故事质量如何影响移情评分。我们将标准的人工智能模型和经过微调的人工智能模型的反应与人类的判断进行了比较。结果表明,虽然人类对情绪生动性和共享经验的敏感性很高,但人工智能的反应受到这些线索的影响较小,往往缺乏微妙的移情表达。这些发现突显了在设计和开发有意义的情绪智能系统方面所面临的挑战,这些系统能够在多样化的用户和情境背景下作出反应,并提示我们设计出有道德意识的工具来支持社交联系和福祉。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 4 figures, 6 tables. Title updated from “Talk, Listen, Connect: Navigating Empathy in Human-AI Interactions” to “Talk, Listen, Connect: How Humans and AI Evaluate Empathy in Responses to Emotionally Charged Narratives” in this version. This is version 2 (v2) of the paper. All previous citations of arXiv:2409.15550 with the old title still refer to the same paper
Summary
社交互动有助于提升幸福感,但地理距离、时间限制和心理健康状况等障碍限制了面对面的交流。情感响应的AI系统如聊天机器人提供了新的社交和情感支持的机会,但也引发了关于人类与AI互动中如何感知和体验同情心的关键问题。本研究探讨了AI生成响应与人类响应中的同情心如何评估。通过个人叙事,我们探讨了人格属性(如性别、同情特质、共同经历)和故事品质对同情心评价的影响。我们将标准AI模型和经过微调后的AI模型的反应与人类的判断进行了比较。结果表明,虽然人类对情感生动性和共同经历的敏感性很高,但AI的反应受这些线索的影响较小,往往缺乏微妙的同理心表达。这些发现突出了在设计能够适应不同用户和上下文环境的智能系统方面面临的挑战,也为支持社会联系和幸福感的道德意识工具的设计提供了信息。
Key Takeaways
- 社交互动对提升幸福感至关重要,但存在地理、时间等障碍限制面对面的交流。
- 情感响应的AI系统如聊天机器人可为社交和情感支持提供新机会。
- 本研究探讨了AI生成响应与人类响应中同情心评估的差异。
- 人格属性和故事品质影响同情心评价。
- AI对于情感生动性和共同经历的敏感性较低,缺乏微妙的同理心表达。
- 在设计智能系统时,需要考虑到适应不同用户和上下文环境的挑战。
点此查看论文截图