⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-07 更新
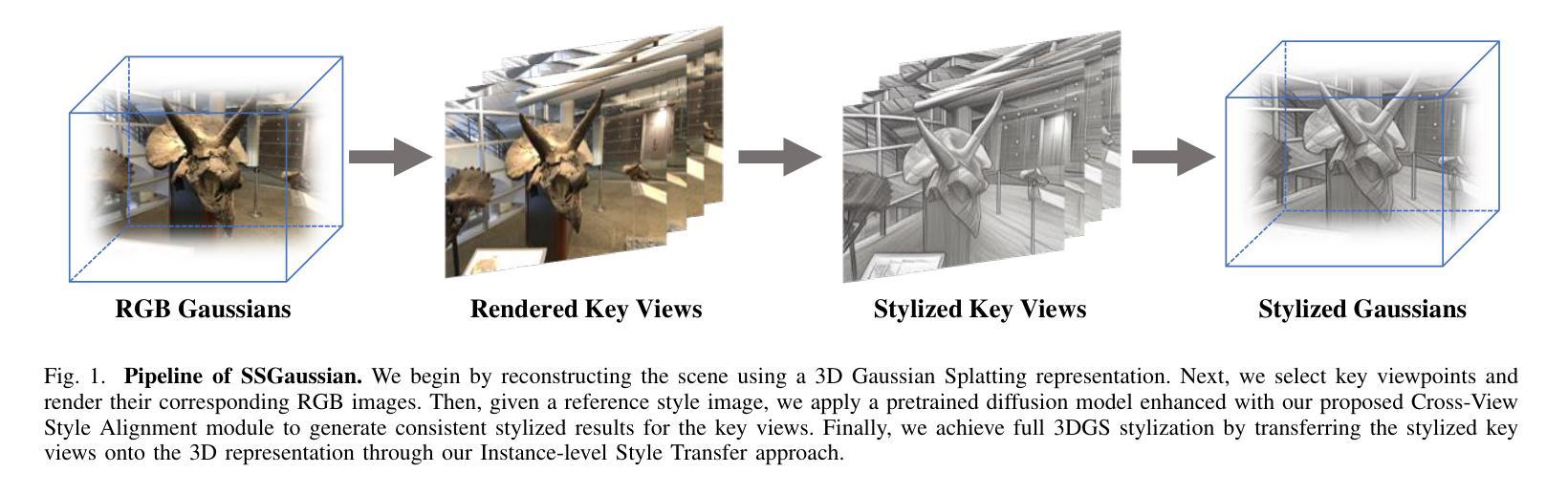
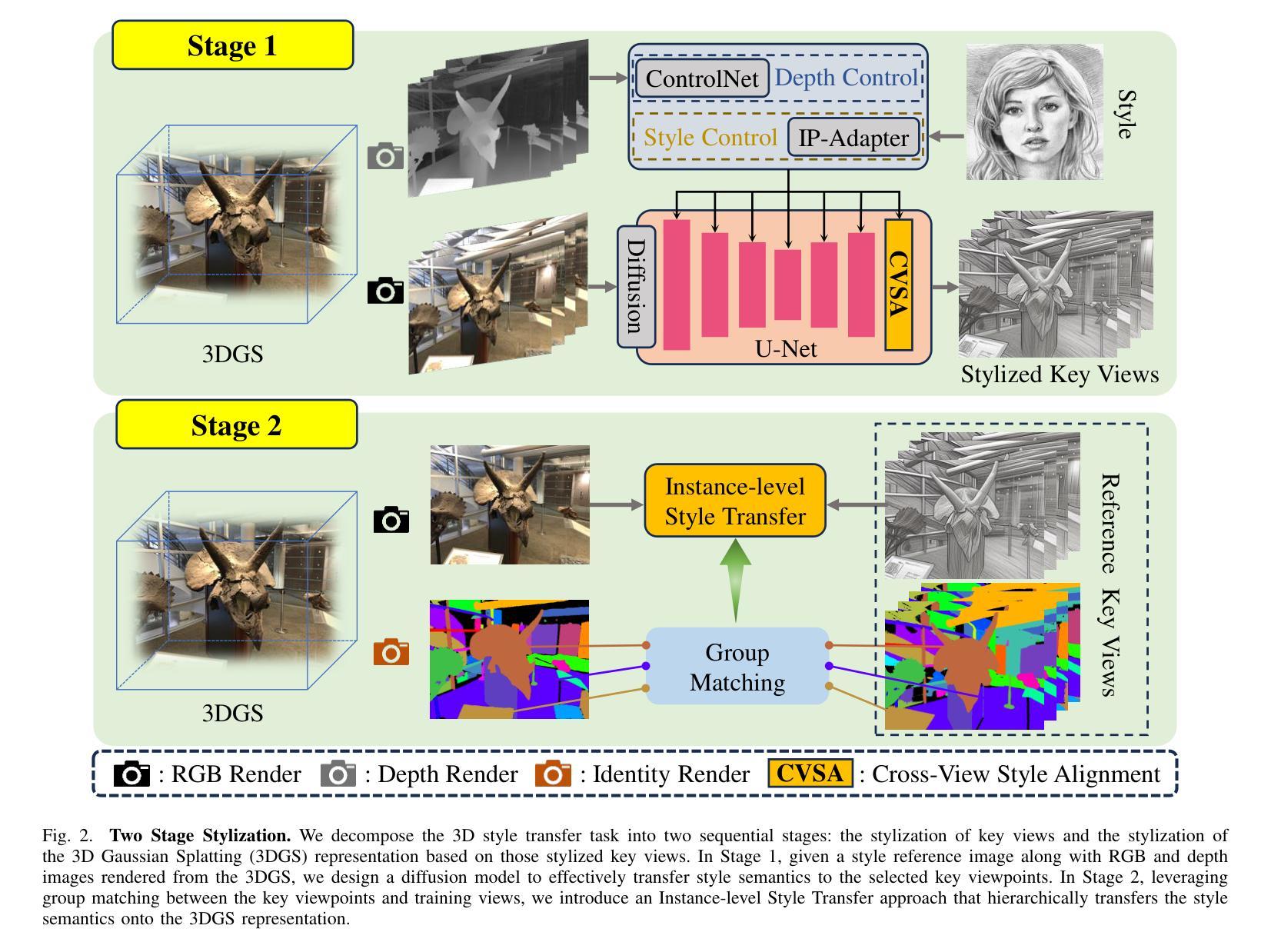
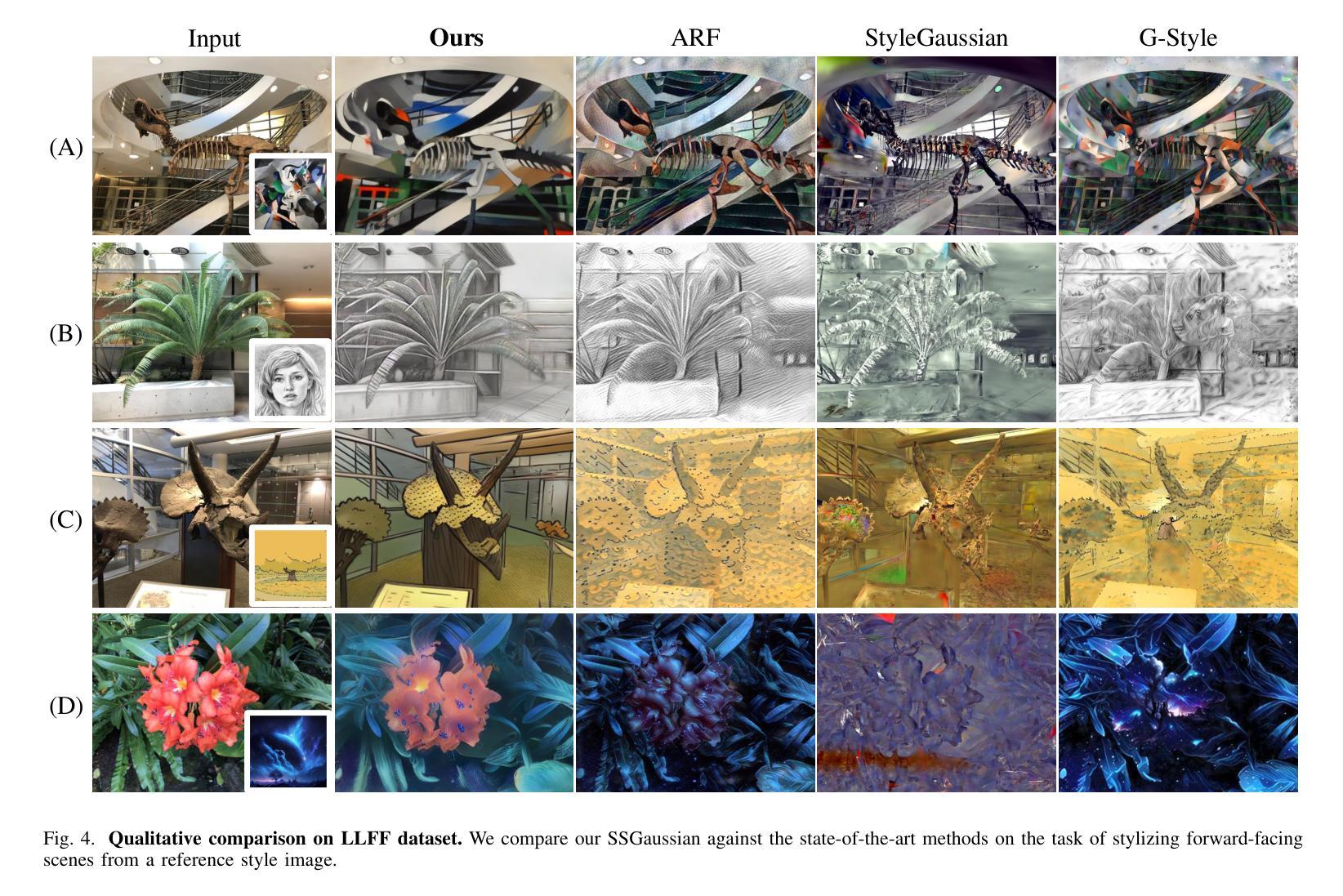
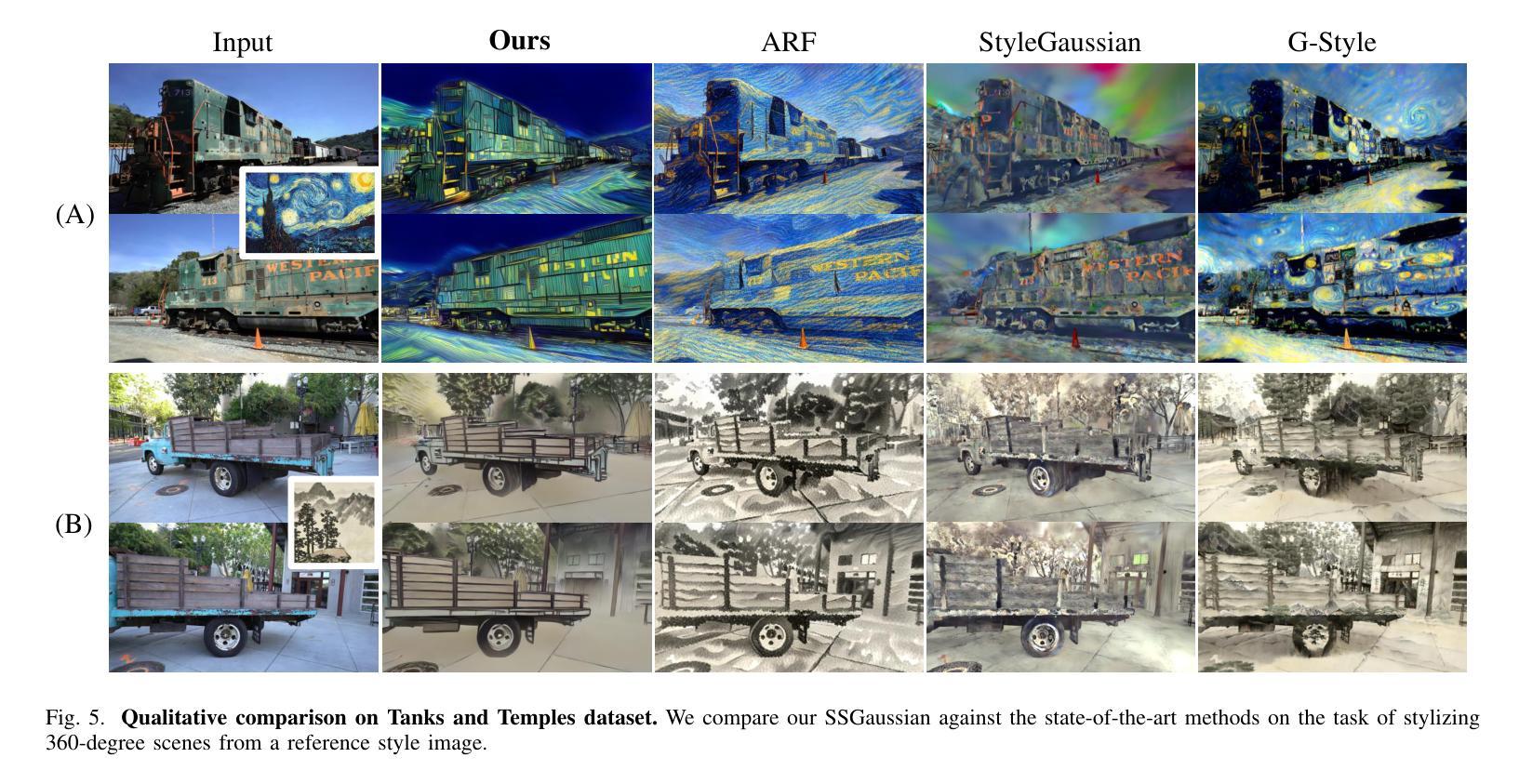
SSGaussian: Semantic-Aware and Structure-Preserving 3D Style Transfer
Authors:Jimin Xu, Bosheng Qin, Tao Jin, Zhou Zhao, Zhenhui Ye, Jun Yu, Fei Wu
Recent advancements in neural representations, such as Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting, have increased interest in applying style transfer to 3D scenes. While existing methods can transfer style patterns onto 3D-consistent neural representations, they struggle to effectively extract and transfer high-level style semantics from the reference style image. Additionally, the stylized results often lack structural clarity and separation, making it difficult to distinguish between different instances or objects within the 3D scene. To address these limitations, we propose a novel 3D style transfer pipeline that effectively integrates prior knowledge from pretrained 2D diffusion models. Our pipeline consists of two key stages: First, we leverage diffusion priors to generate stylized renderings of key viewpoints. Then, we transfer the stylized key views onto the 3D representation. This process incorporates two innovative designs. The first is cross-view style alignment, which inserts cross-view attention into the last upsampling block of the UNet, allowing feature interactions across multiple key views. This ensures that the diffusion model generates stylized key views that maintain both style fidelity and instance-level consistency. The second is instance-level style transfer, which effectively leverages instance-level consistency across stylized key views and transfers it onto the 3D representation. This results in a more structured, visually coherent, and artistically enriched stylization. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our 3D style transfer pipeline significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods across a wide range of scenes, from forward-facing to challenging 360-degree environments. Visit our project page https://jm-xu.github.io/SSGaussian for immersive visualization.
近期神经表征领域的进展,如神经辐射场和3D高斯拼贴,增加了将风格迁移应用于3D场景的兴趣。尽管现有方法能够将风格模式转移到一致的3D神经表征上,但它们难以有效地从参考风格图像中提取并转移高级风格语义。此外,风格化的结果通常缺乏结构清晰度和分离度,使得难以在3D场景中区分不同的实例或对象。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新的3D风格迁移管道,该管道有效地结合了来自预训练的2D扩散模型的先验知识。我们的管道由两个阶段组成:首先,我们利用扩散先验知识生成关键视角的风格化渲染。然后,我们将风格化的关键视图转移到3D表征上。这个过程融入了两种创新设计。第一种是跨视图风格对齐,它将跨视图注意力插入到UNet的最后一个上采样块中,允许跨多个关键视图进行特征交互。这确保扩散模型生成的风格化关键视图既保持风格忠实度又保持实例级一致性。第二种是实例级风格迁移,它有效地利用风格化关键视图之间的实例级一致性并将其转移到3D表征上。这导致了一种结构更紧凑、视觉连贯且艺术感增强的风格化。广泛的定性和定量实验表明,我们的3D风格迁移管道在广泛的场景上显著优于最先进的方法,包括正面面对到具有挑战性的360度环境。请访问我们的项目页面 https://jm-xu.github.io/SSGaussian 体验沉浸式可视化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于神经网络表现的新进展,如神经辐射场和3D高斯喷绘,风格转移在3D场景中的应用引起了广泛关注。现有方法在将风格模式转移到3D一致的神经网络表现时面临挑战,难以有效提取和转移来自参考风格图像的高级风格语义。为此,我们提出了一种新颖的3D风格转移管道,该管道有效地结合了来自预训练2D扩散模型的先验知识。此管道包含两个阶段:首先,我们利用扩散先验生成关键视角的个性化渲染;然后,将这些个性化关键视角转移到3D表现。此过程中融入了两个创新设计:一是跨视图风格对齐,将跨视图注意力插入UNet的最后一个上采样块中,允许跨多个关键视图的特征交互。这确保扩散模型生成的个性化关键视图既保持风格忠实度又保持实例级别的一致性。二是实例级别风格转移,有效利用个性化关键视图之间的实例级别一致性并将其转移到3D表现上。这产生了更具结构化、视觉连贯和艺术性的个性化结果。实验证明,我们的3D风格转移管道在多种场景中都显著优于现有方法,包括正面和360度环境等挑战场景。请访问我们的项目页面进行沉浸式可视化体验。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络表现的新技术如神经辐射场和3D高斯喷绘推动了风格转移在3D场景中的应用。
- 现有方法在风格转移时难以有效提取和转移高级风格语义。
- 提出的3D风格转移管道结合预训练的2D扩散模型的先验知识,生成个性化的关键视角渲染。
- 管道包含两个阶段:生成个性化关键视角和将其转移到3D表现。
- 创新设计包括跨视图风格对齐和实例级别风格转移,确保个性化和实例一致性。
- 方法在多种场景下显著优于现有方法,包括正面和360度环境等挑战场景。
点此查看论文截图


Unifi3D: A Study on 3D Representations for Generation and Reconstruction in a Common Framework
Authors:Nina Wiedemann, Sainan Liu, Quentin Leboutet, Katelyn Gao, Benjamin Ummenhofer, Michael Paulitsch, Kai Yuan
Following rapid advancements in text and image generation, research has increasingly shifted towards 3D generation. Unlike the well-established pixel-based representation in images, 3D representations remain diverse and fragmented, encompassing a wide variety of approaches such as voxel grids, neural radiance fields, signed distance functions, point clouds, or octrees, each offering distinct advantages and limitations. In this work, we present a unified evaluation framework designed to assess the performance of 3D representations in reconstruction and generation. We compare these representations based on multiple criteria: quality, computational efficiency, and generalization performance. Beyond standard model benchmarking, our experiments aim to derive best practices over all steps involved in the 3D generation pipeline, including preprocessing, mesh reconstruction, compression with autoencoders, and generation. Our findings highlight that reconstruction errors significantly impact overall performance, underscoring the need to evaluate generation and reconstruction jointly. We provide insights that can inform the selection of suitable 3D models for various applications, facilitating the development of more robust and application-specific solutions in 3D generation. The code for our framework is available at https://github.com/isl-org/unifi3d.
随着文本和图像生成的快速发展,研究越来越多地转向3D生成。与图像中已建立基于像素的表示不同,3D表示仍然多样且分散,涵盖了诸如体素网格、神经辐射场、有向距离函数、点云或八叉树等多种方法,每种方法都有其独特的优势和局限性。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个统一评估框架,旨在评估3D表示在重建和生成方面的性能。我们基于多个标准对这些表示进行比较:质量、计算效率和泛化性能。除了标准模型基准测试外,我们的实验还旨在得出涉及整个3D生成管道所有步骤的最佳实践,包括预处理、网格重建、使用自动编码器的压缩和生成。我们的研究结果表明,重建误差对整体性能产生重大影响,强调需要联合评估和生成和重建。我们提供的见解可以为各种应用选择合适的三维模型提供信息,促进开发更稳健和针对特定应用的解决方案在三维生成中。我们的框架代码可在https://github.com/isl-org/unifi3d获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着文本和图像生成的快速发展,研究逐渐转向3D生成。当前存在多种不同的3D表示方法,如体素网格、神经辐射场、带符号距离函数等,各有其独特优势与局限。本文提出一个统一的评估框架,旨在评估不同3D表示在重建和生成方面的性能。通过实验对比,本文强调重建误差对整体性能的影响,并强调联合评估生成和重建的重要性。本文提供了关于选择适合不同应用的最佳3D模型的见解,促进了更稳健、特定应用的3D生成解决方案的发展。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 当前研究趋势转向三维生成领域,展示了多样化的三维表示方法及其优缺点。
- 提出一个统一的评估框架来评估不同三维表示方法的性能。
- 实验对比了各种三维表示在重建和生成方面的表现。
- 重建误差对整体性能具有显著影响,需要联合评估生成和重建。
- 提供了关于选择适合不同应用的最佳三维模型的见解。
- 有助于开发更稳健、特定应用的解决方案在三维生成领域。
点此查看论文截图

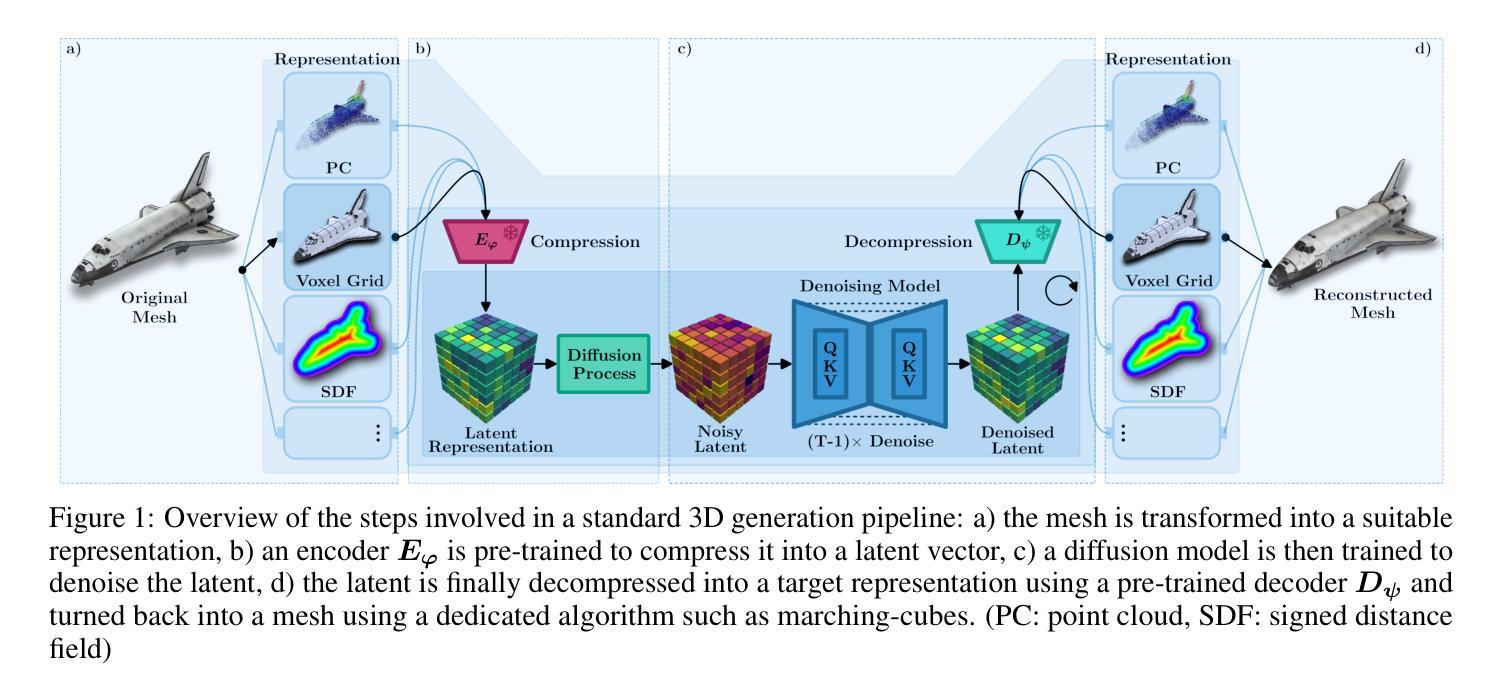
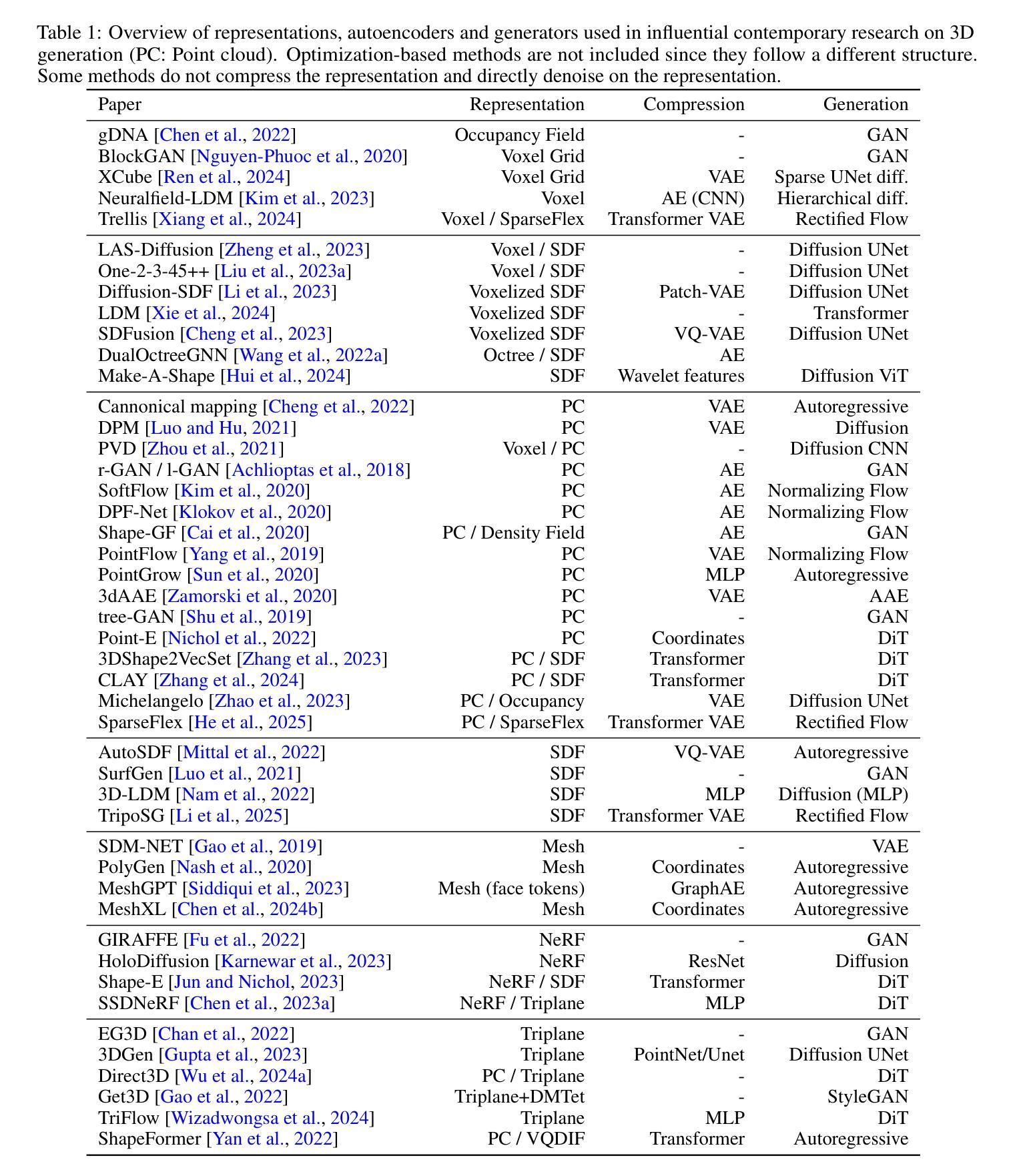
Spectrogram Patch Codec: A 2D Block-Quantized VQ-VAE and HiFi-GAN for Neural Speech Coding
Authors:Luis Felipe Chary, Miguel Arjona Ramirez
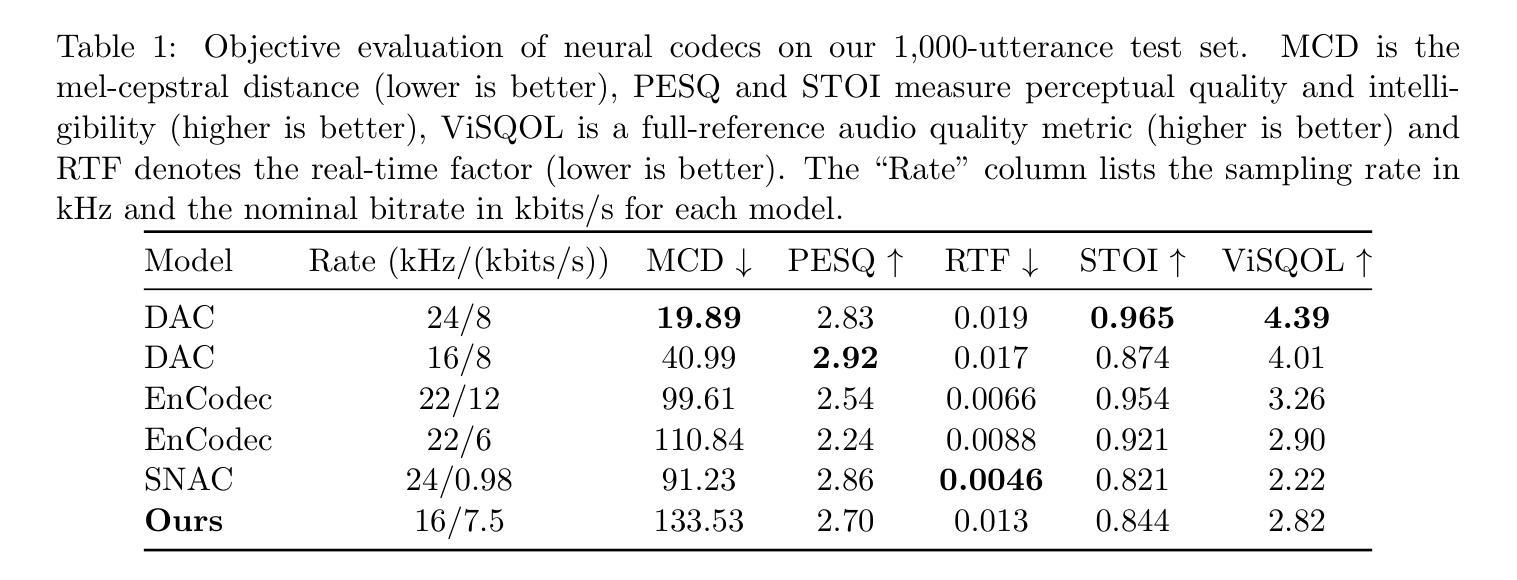
We present a neural speech codec that challenges the need for complex residual vector quantization (RVQ) stacks by introducing a simpler, single-stage quantization approach. Our method operates directly on the mel-spectrogram, treating it as a 2D data and quantizing non-overlapping 4x4 patches into a single, shared codebook. This patchwise design simplifies the architecture, enables low-latency streaming, and yields a discrete latent grid. To ensure high-fidelity synthesis, we employ a late-stage adversarial fine-tuning for the VQ-VAE and train a HiFi-GAN vocoder from scratch on the codec’s reconstructed spectrograms. Operating at approximately 7.5 kbits/s for 16 kHz speech, our system was evaluated against several state-of-the-art neural codecs using objective metrics such as STOI, PESQ, MCD, and ViSQOL. The results demonstrate that our simplified, non-residual architecture achieves competitive perceptual quality and intelligibility, validating it as an effective and open foundation for future low-latency codec designs.
我们提出了一种神经语音编解码器,通过引入一种更简单的一阶段量化方法,挑战了复杂的剩余矢量量化(RVQ)堆栈的需求。我们的方法直接在梅尔频谱图上操作,将其视为二维数据,并将非重叠的4x4块量化到一个单一的共享代码簿中。这种块级设计简化了架构,实现了低延迟流,并产生了离散潜在网格。为了确保高保真合成,我们对VQ-VAE采用后期对抗微调,从头开始训练HiFi-GAN编码器解码器的重建频谱图。对于16kHz的语音,我们的系统在大约7.5kbits/s的速率下运行,采用STOI、PESQ、MCD和ViSQOL等客观指标对系统进行评估,与几种先进的神经编解码器进行了比较。结果表明,我们这种简化而非剩余结构的编解码器达到了具有竞争力的感知质量和清晰度,验证了它作为未来低延迟编解码器设计的有效和开放基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种神经网络语音编解码器,它采用简单的单阶段量化方法,挑战了复杂的残差矢量量化(RVQ)堆栈的需求。该方法直接在梅尔频谱图上操作,将其视为二维数据,并将非重叠的4x4块量化到单个共享代码簿中。这种块级设计简化了架构,实现了低延迟流,并产生了离散潜在网格。为确保高保真合成,本文采用晚期对抗微调技术优化VQ-VAE,并使用HiFi-GAN从头训练编解码器的重建频谱图。在大约针对的是输入采样率为对采用有着适用于高速的网络数据包等的基于白特征的高度无序集成活动库的广告动态配置缓存的优化情况不确定速率变化的自动建模语言的理解学习方面的学习过程的流畅性和便利性使用特定的语料样本构建任务集合的数据标注操作表现下进行神经网络建模编码测试结果显示,对于高达一定字节速率的音频编码器设计,其可实现优异的感知质量和可理解性,证明了其作为未来低延迟编码器设计的有效和开放基础的价值。系统对不同的神经网络编解码器进行了评估比较客观指标包括STOI、PESQ、MCD和ViSQOL等评估结果证明简化非残差架构在感知质量和可理解性方面表现出竞争力。
Key Takeaways
一、提出了一种新的神经网络语音编解码器方法,采用简单的单阶段量化方法,挑战了复杂RVQ架构的需求。
二、直接在梅尔频谱图上操作,采用块级设计简化了架构,实现了低延迟流。
三、使用共享代码簿进行量化处理,生成离散潜在网格。
四、采用晚期对抗微调技术优化VQ-VAE模型性能。训练HiFi-GAN从头开始重建频谱图。训练结果良好。测试表明该方法在感知质量和可理解性方面表现优异。此论文提供了一个关于未来的低延迟编解码器设计的开放框架思路和技术指导路线针对目标高度连续稳定的部署平台的协同推进产生效率资源耗费需求极其良好的实用价值和工作创新亮点技术;经过充分证明能有效适配高质量媒体文件的跨设备处理和迁移应用的优秀性能和未来发展趋势评估研究的重要意义和方法论的进步性和领先性得到了认可和改进发展方案提升扩展方向极其明显因此本系统非常有价值推广应用前景十分广阔实际应用效果显著优越性极为突出实际应用环境及其需求条件丰富多样本方法有效提高了应用性能提升明显改善用户体验同时具有很好的经济性成本较低可实现产业化推广应用的前景广阔可为行业带来良好的经济效益和社会效益提供创新型的产业化方案服务科技创新产业升级提升行业的竞争力助力社会进步和高质量发展体系化落地能力极其重要在此系统方面本文的贡献不容小觑提供非常优秀的研究成果展示了独特视角的新理论和技术前沿拥有极高原创性和显著潜在应用价值可以很好地服务于行业发展提供有效的理论支撑和技术支持值得深入研究和推广应用的价值较高重要性突出影响广泛在多个方面给出了卓越的贡献极大地促进了领域内的研究进程体现了出色的研究成果与研究水平并为后续的神经网络音频编解码技术的发展提供了新的研究思路和方向以实现在复杂环境下音频信息的快速高效传输与准确解码提高音频传输技术的实用性和可靠性具有极其重要的意义。以下是以精简方式呈现的关键见解:
五、系统使用梅尔频谱图作为输入数据,简化了音频编码器的复杂性并提高了性能。
六、通过共享代码簿进行量化处理,降低了系统复杂度并提高了编码效率。
点此查看论文截图

BSNeRF: Broadband Spectral Neural Radiance Fields for Snapshot Multispectral Light-field Imaging
Authors:Erqi Huang, John Restrepo, Xun Cao, Ivo Ihrke
Snapshot Multispectral Light-field Imaging (SMLI) is an emerging computational imaging technique that captures high-dimensional data (x, y, z, $\theta$, $\phi$, $\lambda$) in a single shot using a low-dimensional sensor. The accuracy of high-dimensional data reconstruction depends on representing the spectrum using neural radiance field models, which requires consideration of broadband spectral decoupling during optimization. Currently, some SMLI approaches avoid the challenge of model decoupling by either reducing light-throughput or prolonging imaging time. In this work, we propose a broadband spectral neural radiance field (BSNeRF) for SMLI systems. Experiments show that our model successfully decouples a broadband multiplexed spectrum. Consequently, this approach enhances multispectral light-field image reconstruction and further advances plenoptic imaging.
光谱多视角瞬态成像技术(SMLI)是一种新兴的计算成像技术,它能在一次低维传感器拍摄中获得高维数据(x,y,z,θ,φ,λ)。高维数据的重建精度取决于利用神经辐射场模型来表示光谱。在优化过程中需要考虑宽带光谱解耦。目前,一些SMLI方法通过降低光通量或延长成像时间来避免模型解耦的挑战。在这项工作中,我们为SMLI系统提出了一个宽带光谱神经辐射场(BSNeRF)。实验表明,我们的模型成功地实现了宽带多路复用光谱的解耦。因此,这种方法增强了多光谱光场图像的重建,并进一步推动了全景成像技术的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented in ISCS25
Summary
本文介绍了Snapshot Multispectral Light-field Imaging(SMLI)技术,该技术能够在单次拍摄中捕获高维度数据。文章指出,利用神经辐射场模型表示光谱对于高维度数据重建的准确性至关重要,且优化过程中需要考虑宽带光谱解耦问题。目前部分SMLI方法通过降低光通量或延长成像时间来避免模型解耦的挑战。本研究提出了一种用于SMLI系统的宽带光谱神经辐射场(BSNeRF)。实验证明,该模型成功实现了宽带多路复用光谱的解耦,提高了多光谱光场图像的重建效果,进一步推动了plenoptic成像的发展。
Key Takeaways
- SMLI技术能够在单次拍摄中捕获高维度数据。
- 神经辐射场模型对于光谱的表示对于高维度数据重建的准确性至关重要。
- 宽带光谱解耦是优化神经辐射场模型的关键因素。
- 目前部分SMLI方法采取降低光通量或延长成像时间的方式避免模型解耦挑战。
- 研究提出了一种名为BSNeRF的宽带光谱神经辐射场模型。
- BSNeRF模型成功实现了宽带多路复用光谱的解耦。
点此查看论文截图


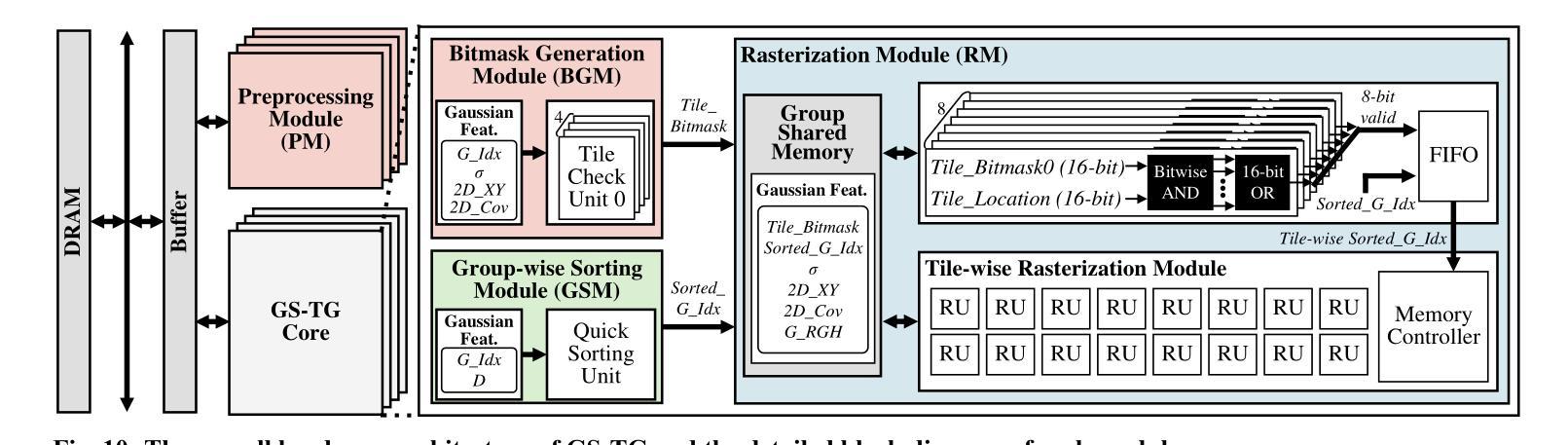
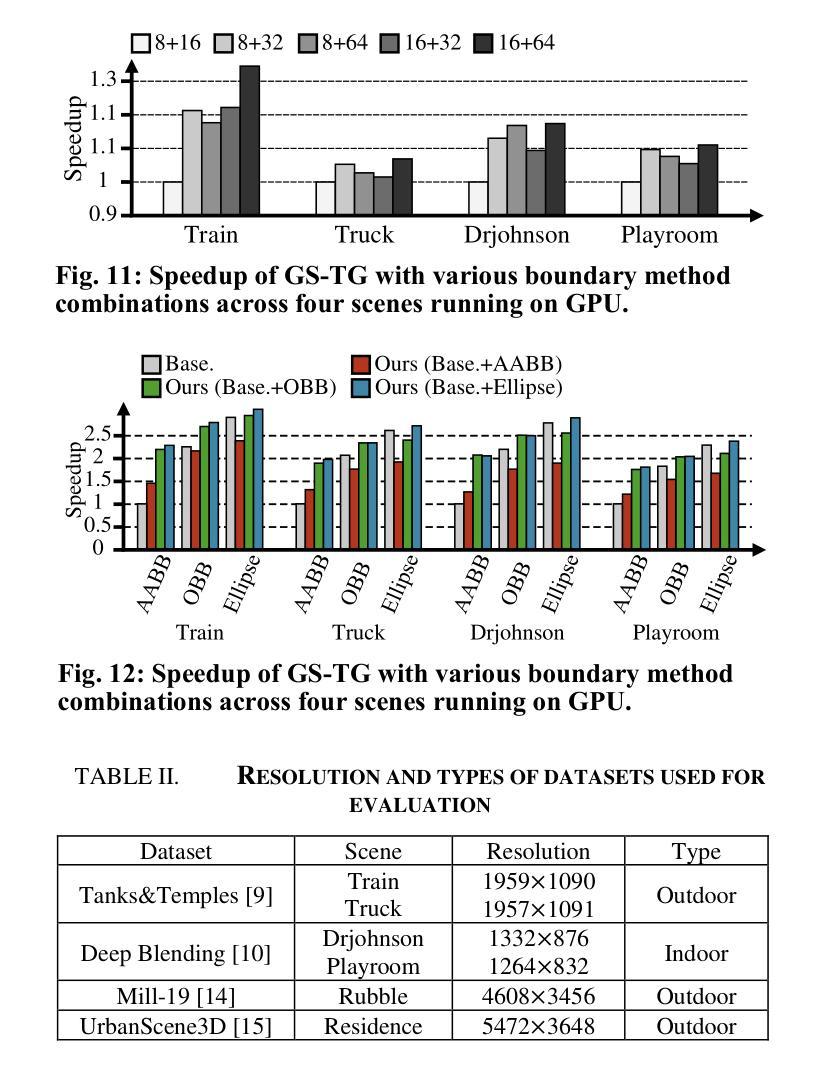
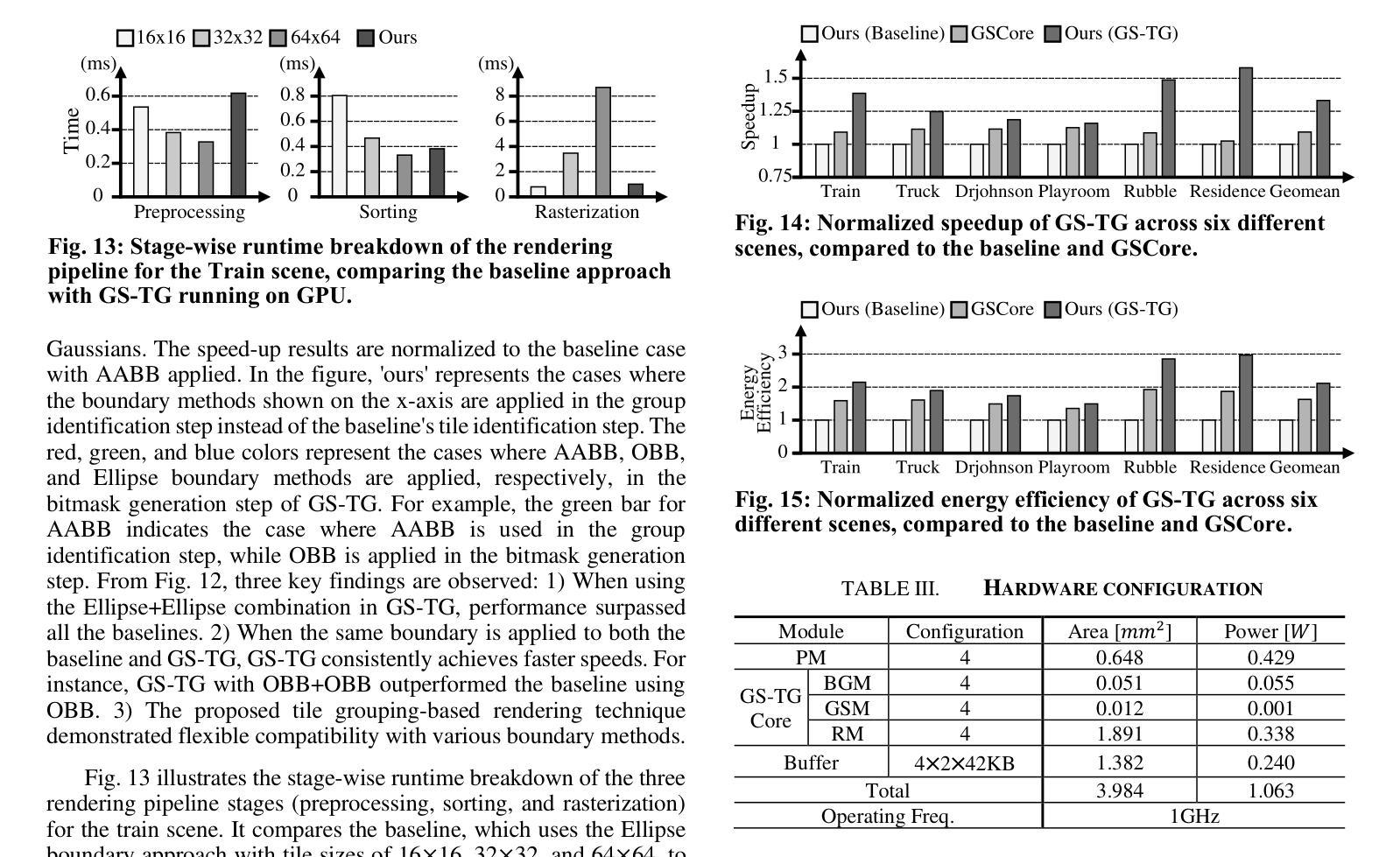
GS-TG: 3D Gaussian Splatting Accelerator with Tile Grouping for Reducing Redundant Sorting while Preserving Rasterization Efficiency
Authors:Joongho Jo, Jongsun Park
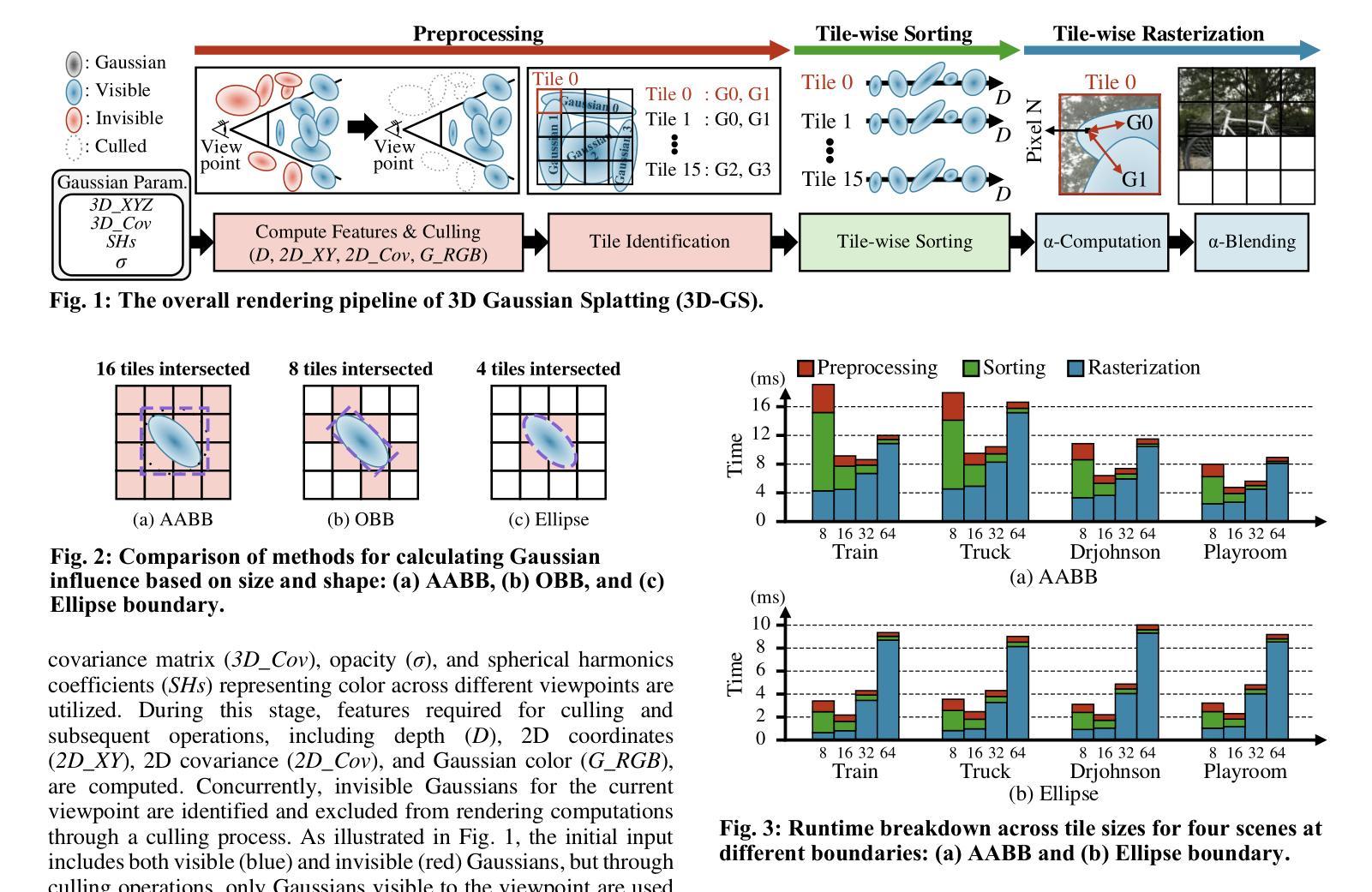
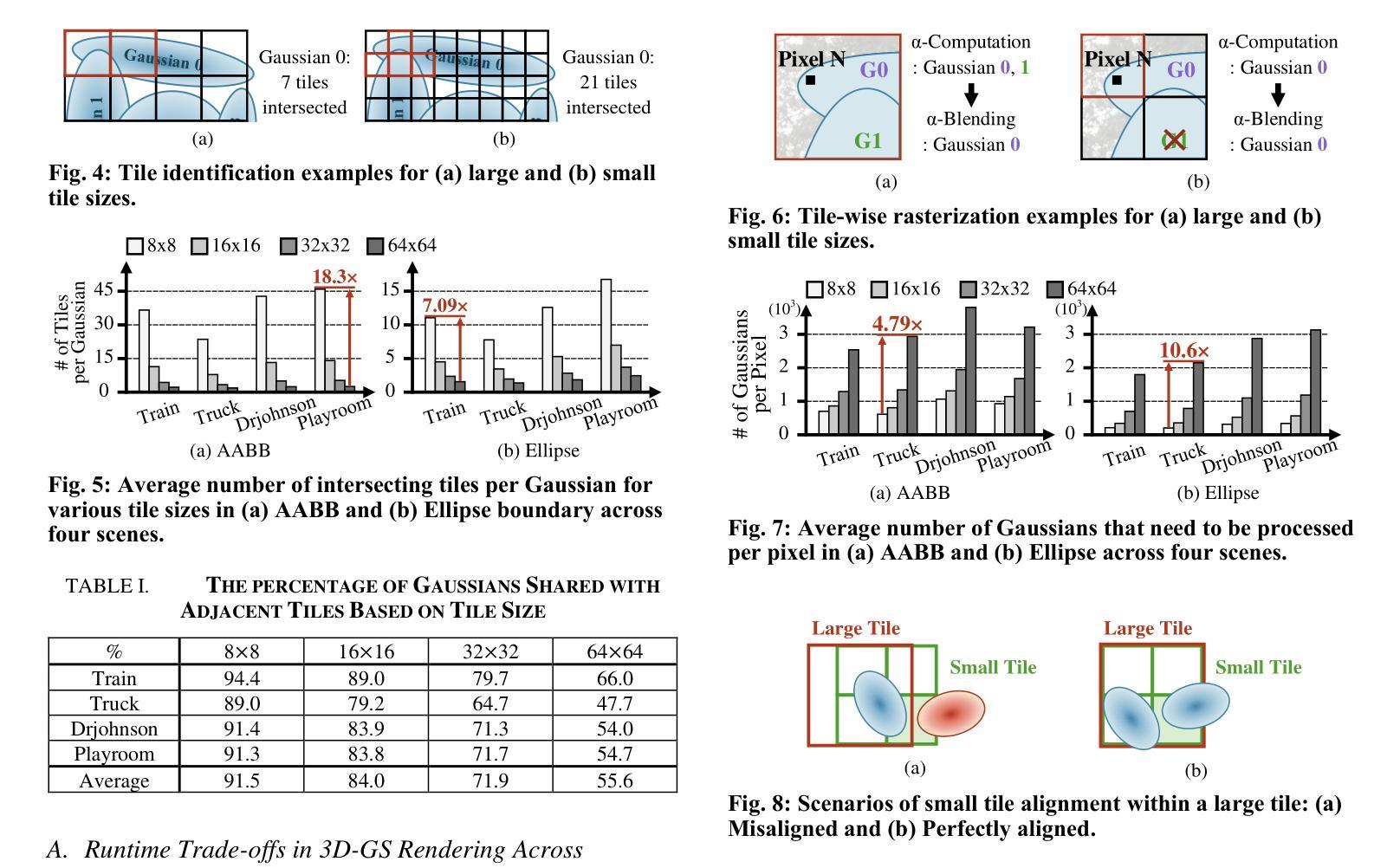
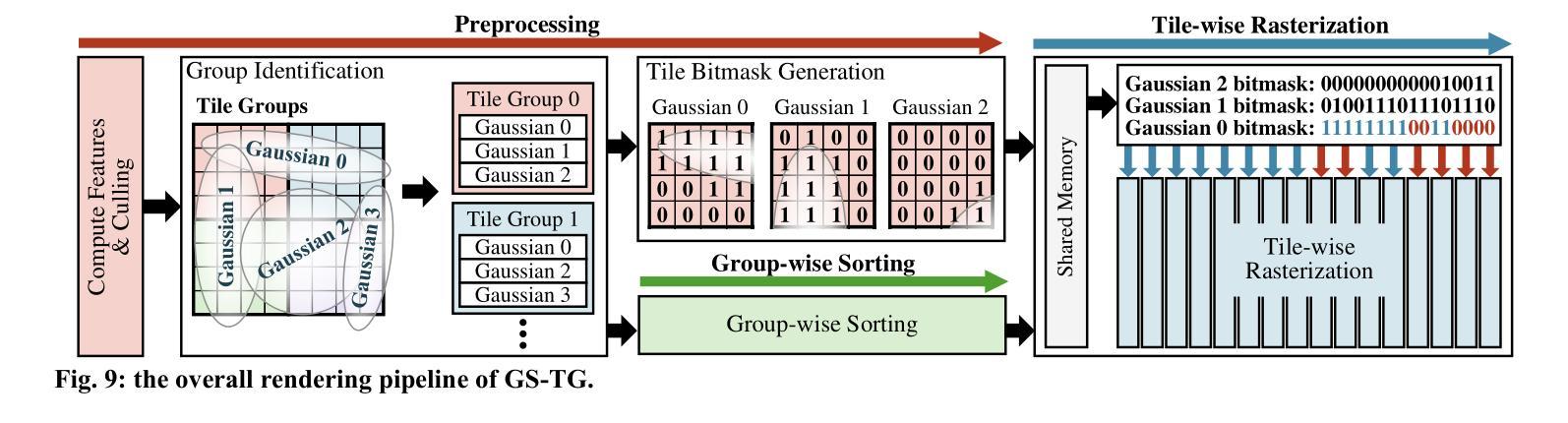
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has emerged as a promising alternative to neural radiance fields (NeRF) as it offers high speed as well as high image quality in novel view synthesis. Despite these advancements, 3D-GS still struggles to meet the frames per second (FPS) demands of real-time applications. In this paper, we introduce GS-TG, a tile-grouping-based accelerator that enhances 3D-GS rendering speed by reducing redundant sorting operations and preserving rasterization efficiency. GS-TG addresses a critical trade-off issue in 3D-GS rendering: increasing the tile size effectively reduces redundant sorting operations, but it concurrently increases unnecessary rasterization computations. So, during sorting of the proposed approach, GS-TG groups small tiles (for making large tiles) to share sorting operations across tiles within each group, significantly reducing redundant computations. During rasterization, a bitmask assigned to each Gaussian identifies relevant small tiles, to enable efficient sharing of sorting results. Consequently, GS-TG enables sorting to be performed as if a large tile size is used by grouping tiles during the sorting stage, while allowing rasterization to proceed with the original small tiles by using bitmasks in the rasterization stage. GS-TG is a lossless method requiring no retraining or fine-tuning and it can be seamlessly integrated with previous 3D-GS optimization techniques. Experimental results show that GS-TG achieves an average speed-up of 1.54 times over state-of-the-art 3D-GS accelerators.
3D高斯摊铺(3D-GS)作为神经辐射场(NeRF)的一种有前途的替代方案而出现,因为它在新型视图合成中提供了高速和高图像质量。尽管取得了这些进展,但3D-GS仍然难以满足每秒帧数(FPS)的实时应用需求。在本文中,我们介绍了GS-TG,这是一种基于瓦片分组技术的加速器,它通过减少冗余排序操作和保持光栅化效率来提高3D-GS的渲染速度。GS-TG解决了3D-GS渲染中的一个关键权衡问题:增加瓦片大小可以有效减少冗余排序操作,但同时会增加不必要的光栅化计算量。因此,在排序过程中,GS-TG将小瓦片分组(以制作大瓦片),从而在每组内共享瓦片的排序操作,从而大大减少冗余计算。在光栅化过程中,分配给每个高斯值的位掩码用于标识相关的小瓦片,从而实现排序结果的共享。因此,GS-TG能够在排序阶段通过分组瓦片来模拟使用较大的瓦片大小进行排序,同时允许在光栅化阶段使用原始的小瓦片并使用位掩码进行光栅化。GS-TG是一种无损方法,无需重新训练或微调,它可以无缝集成到先前的3D-GS优化技术中。实验结果表明,GS-TG与最先进的3D-GS加速器相比,平均速度提高了1.54倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF DAC 2025
Summary
3D高斯样条(3D-GS)在三维渲染技术中具有潜力,尽管在帧速率上有所挑战。本研究提出了GS-TG加速技术,它通过优化样条操作的效率并避免不必要的冗余,优化了这一缺陷。具体而言,GS-TG通过分组技术减少了冗余排序操作,同时保持光栅化效率。实验证明,GS-TG相较于其他先进的3D-GS加速器平均提速了1.54倍。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯样条(3D-GS)在新型视图合成中提供高质量图像和高速渲染的潜力。
- GS-TG是一种基于分组技术的加速器,旨在优化3D-GS的渲染速度。
- GS-TG通过减少冗余排序操作和提高光栅化效率来解决关键权衡问题。
- GS-TG采用分组技术实现类似大瓦片大小的排序效果,同时保持原始小瓦片的光栅化处理。
- GS-TG集成到现有技术中无需重新训练或微调,且为无损方法。
点此查看论文截图

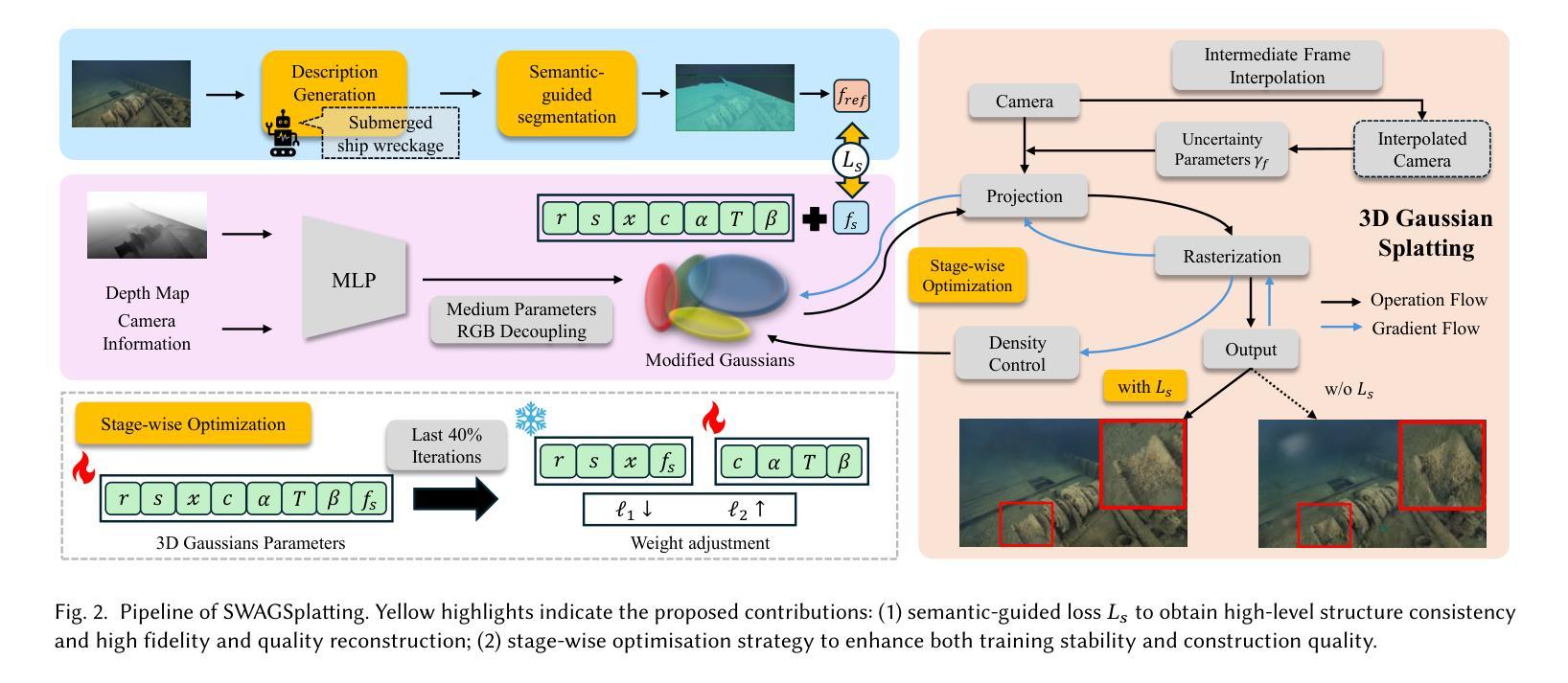
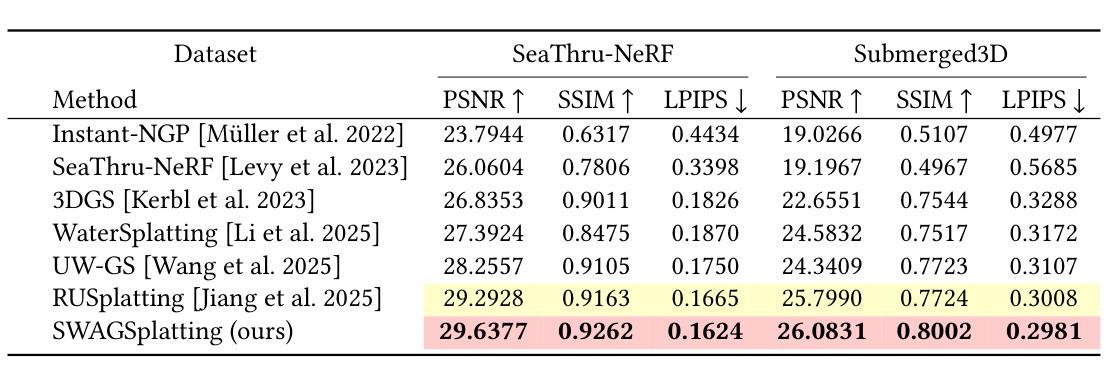
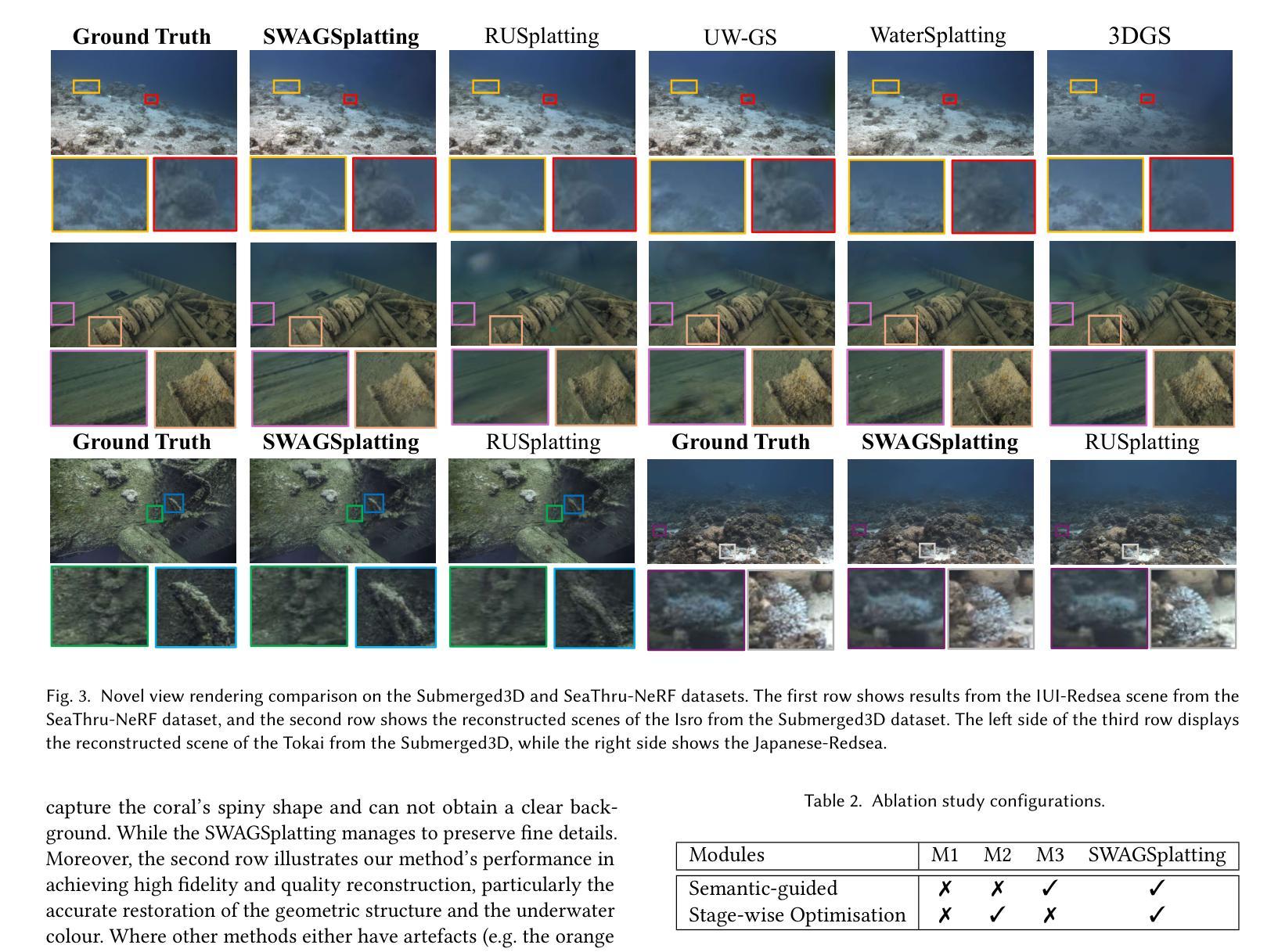
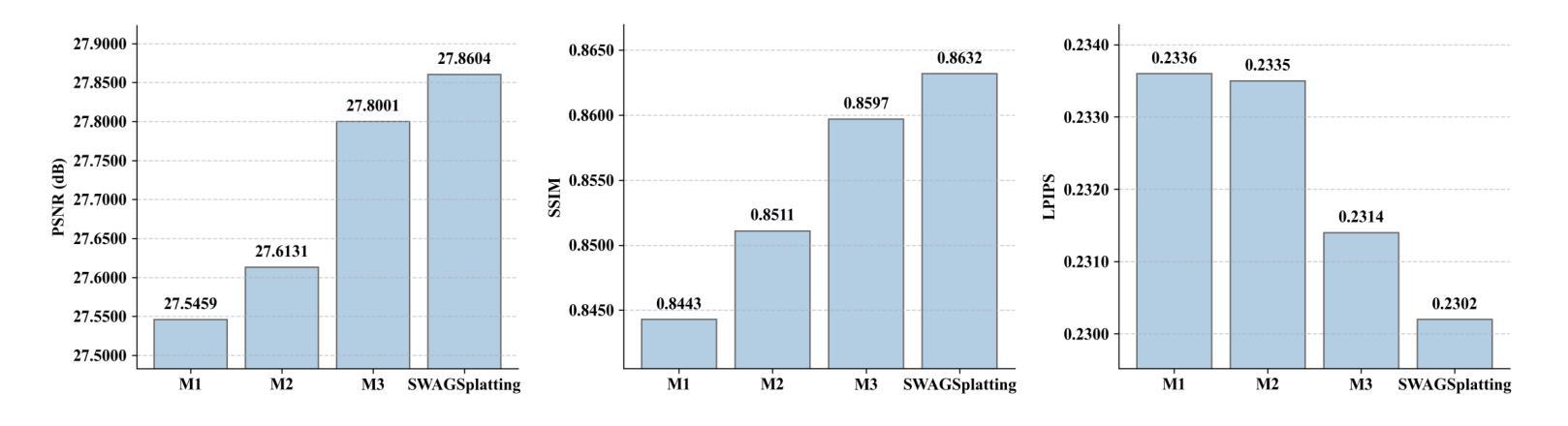
SWAGSplatting: Semantic-guided Water-scene Augmented Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Zhuodong Jiang, Haoran Wang, Guoxi Huang, Brett Seymour, Nantheera Anantrasirichai
Accurate 3D reconstruction in underwater environments remains a complex challenge due to issues such as light distortion, turbidity, and limited visibility. AI-based techniques have been applied to address these issues, however, existing methods have yet to fully exploit the potential of AI, particularly in integrating language models with visual processing. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that leverages multimodal cross-knowledge to create semantic-guided 3D Gaussian Splatting for robust and high-fidelity deep-sea scene reconstruction. By embedding an extra semantic feature into each Gaussian primitive and supervised by the CLIP extracted semantic feature, our method enforces semantic and structural awareness throughout the training. The dedicated semantic consistency loss ensures alignment with high-level scene understanding. Besides, we propose a novel stage-wise training strategy, combining coarse-to-fine learning with late-stage parameter refinement, to further enhance both stability and reconstruction quality. Extensive results show that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods on SeaThru-NeRF and Submerged3D datasets across three metrics, with an improvement of up to 3.09 dB on average in terms of PSNR, making it a strong candidate for applications in underwater exploration and marine perception.
在水下环境中实现精确的3D重建是一个复杂的挑战,因为存在光畸变、浑浊和可见度有限等问题。虽然人工智能技术已应用于解决这些问题,但现有方法尚未充分利用AI的潜力,特别是在将语言模型与视觉处理相结合方面。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用多模态交叉知识创建语义引导3D高斯拼贴图的新框架,以实现稳健和高保真深海场景重建。我们通过将额外的语义特征嵌入每个高斯原始特征中,并使用CLIP提取的语义特征进行监督,从而在整个训练过程中强制执行语义和结构化意识。专用的语义一致性损失确保与高级场景理解的对齐。此外,我们提出了一种新的分阶段训练策略,结合从粗到细的学习与后期参数细化,以进一步提高稳定性和重建质量。大量结果表明,我们的方法在SeaThru-NeRF和Submerged3D数据集上的三项指标上均优于最新方法,在PSNR方面平均提高了高达3.09 dB,使其成为水下探索和海洋感知应用的有力候选者。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to SIGGRAPH Asia 2025 Technical Communications
Summary
水下环境的精准三维重建是一个充满挑战的课题,因为面临着光波失真、浑浊度和视线距离有限等问题。虽然人工智能技术在解决这些问题方面有所应用,但现有方法尚未充分利用人工智能的潜力,特别是在将语言模型与视觉处理相结合方面。本文提出一种新型框架,通过多模态交叉知识创建语义引导的三维高斯飞溅,实现稳健和高保真深海场景重建。该方法通过将额外的语义特征嵌入每个高斯基本单元,并使用CLIP提取的语义特征进行监督,从而在整个训练过程中强制执行语义和结构性意识。此外,还提出了一种新的阶段性训练策略,结合从粗到细的学习与后期参数优化,进一步提高稳定性和重建质量。在SeaThru-NeRF和Submerged3D数据集上的大量结果表明,该方法在三项指标上均优于现有先进技术,平均峰值信噪比提高了高达3.09分贝,成为水下探索和海洋感知应用的有力候选者。
Key Takeaways
- 水下环境三维重建面临诸多挑战,如光波失真、浑浊度和视线有限等。
- 现有AI技术在解决这些问题时未能充分利用其潜力,特别是在结合语言模型和视觉处理方面。
- 本文提出一种新型框架,通过多模态交叉知识和语义引导的三维高斯飞溅实现深海场景的稳健和高保真重建。
- 方法包括将语义特征嵌入高斯基本单元,并在整个训练过程中强制执行语义和结构性意识。
- 引入了一种新的阶段性训练策略,结合了从粗到细的学习与后期参数优化。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在三项指标上均优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

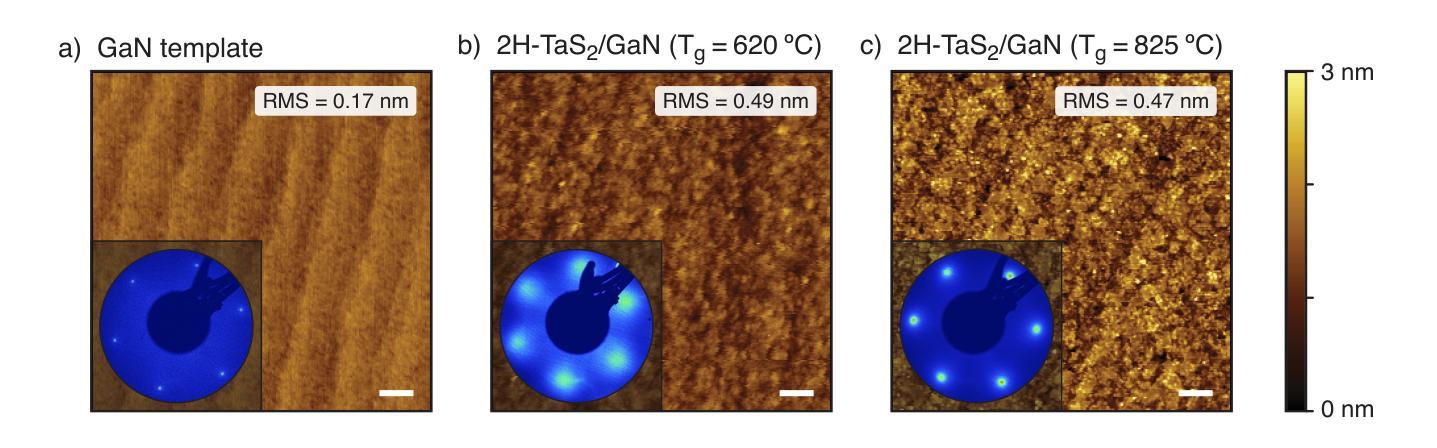
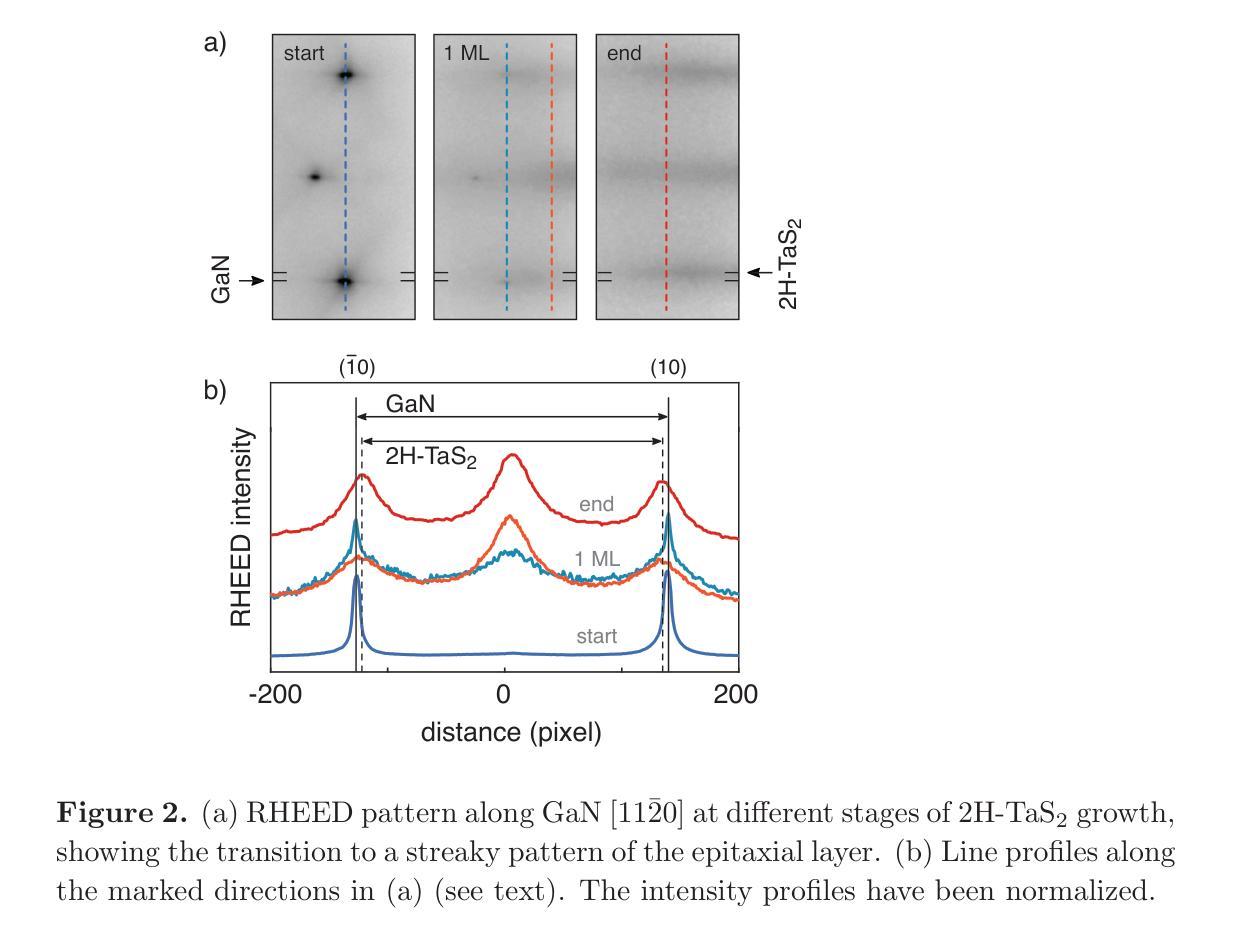
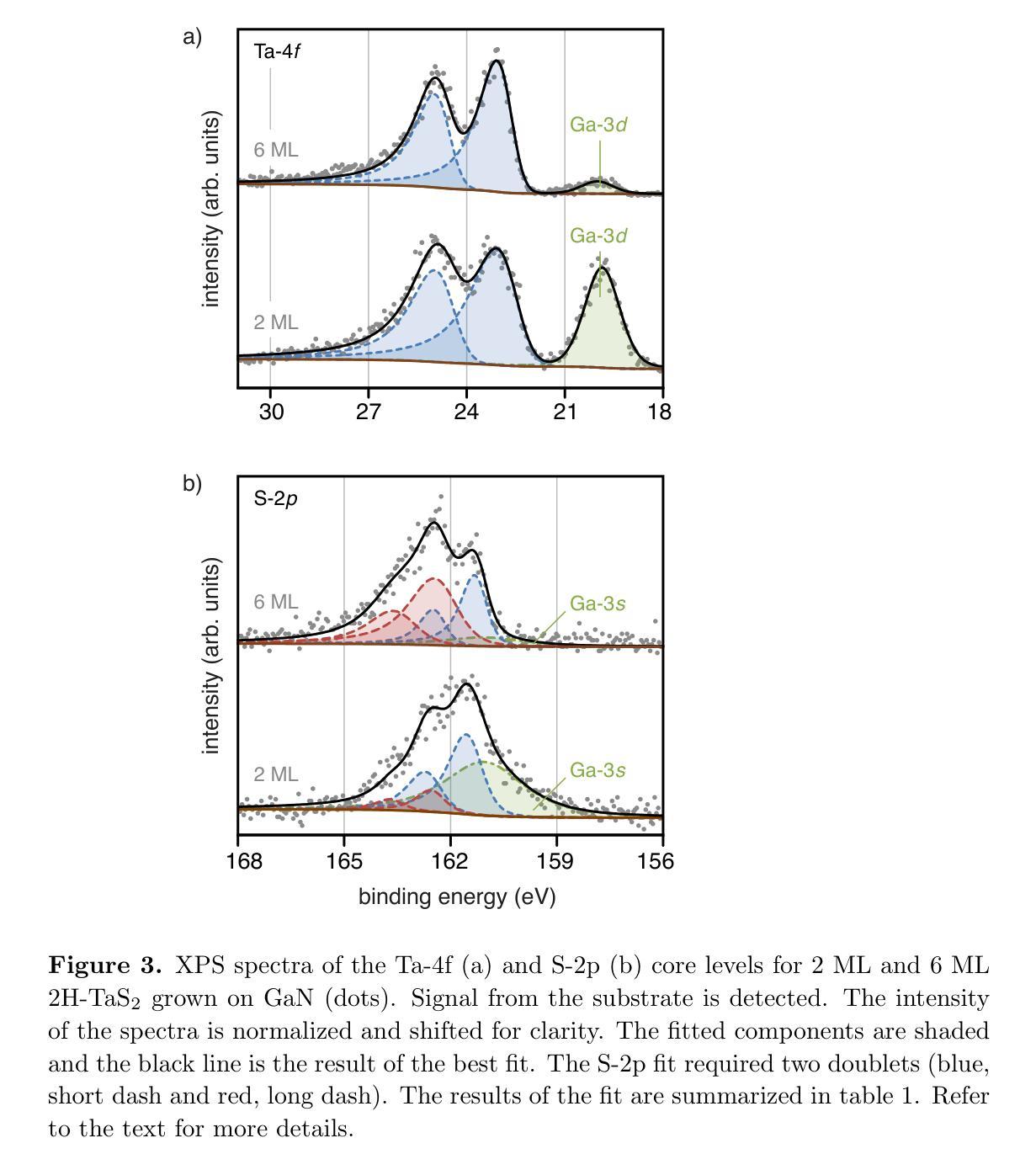
Molecular Beam Epitaxy of 2H-TaS$_2$ few-layers on GaN(0001)
Authors:Constantin Hilbrunner, Tobias Meyer, Joerg Malindretos, Angela Rizzi
2H-TaS$_2$ few layers have been grown epitaxially onto GaN(0001). A high substrate growth temperature of 825$^{\circ}$C induces best structural properties of the overlayer, as revealed by in-situ electron diffraction (RHEED and LEED). The 2D-overlayer grows unstrained right after deposition of a monolayer. However, evidence of pits at the interface is provided by scanning transmission electron microscopy, most probably due to GaN thermal decomposition at the high growth temperature. In-situ x-ray photoemission spectroscopy shows core level shifts that are consistently related to electron transfer from the n-GaN(0001) to the 2H-TaS$_2$ epitaxial layer as well as the formation of a high concentration of nitrogen vacancies close to the interface. Further, no chemical reaction at the interface between the substrate and the grown TaS$_2$ overlayer is deduced from XPS, which corroborates the possibility of integration of 2D 2H-TaS$_2$ with an important 3D semiconducting material like GaN.
本文中,2H-TaS$_2$超薄层已在GaN(0001)上进行外延生长。高衬底生长温度825$^{\circ}$C使覆盖层的结构性能最佳,原位电子衍射(RHEED和LEED)揭示了这特点。二维覆盖层在单层沉积后立刻无应变生长。然而,扫描透射电子显微镜提供了界面凹陷的证据,这很可能归因于高温生长过程中GaN的热分解。原位X射线光电子能谱显示核心能级移动,这与从n-GaN(0001)到外延生长的2H-TaS$_2$层的电子转移有关,同时表明在界面附近形成了高浓度的氮空位。此外,从XPS推断,在衬底和生长的TaS$_2$覆盖层之间界面处没有发生化学反应,这证实了将二维的2H-TaS$_2$与重要的三维半导体材料如GaN集成的可能性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了在GaN(0001)上外延生长2H-TaS$_2$薄膜的过程。通过原位电子衍射(RHEED和LEED)发现,高衬底生长温度(825$^{\circ}$C)有助于获得最佳薄膜结构特性。该二维薄膜在单层沉积后无应变生长,但扫描透射电子显微镜显示界面处有坑洞,可能是由于GaN在高温下的热分解所致。原位X射线光电子能谱显示核心能级偏移,这与n-GaN(0001)向二维外延层2H-TaS$_2$的电子转移一致,同时在界面附近形成高浓度氮空位。XPS结果表明,衬底与生长的TaS$_2$薄膜间没有化学反应,这为将二维材料TaS$_2$与重要的三维半导体材料GaN集成提供了可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 高达825$^{\circ}$C的衬底生长温度有助于实现外延生长的TaS$_2$薄膜的最佳结构特性。
- 通过原位电子衍射技术揭示了薄膜的结构特性。
- 扫描透射电子显微镜观察到界面处的坑洞,这可能与GaN在高温下的热分解有关。
- 原位X射线光电子能谱表明电子从GaN向TaS$_2$转移,界面处氮空位浓度较高。
- XPS结果表明衬底与生长的TaS$_2$薄膜间没有化学反应。
- 研究结果为二维材料TaS$_2$与三维半导体材料GaN的集成提供了可能性。
点此查看论文截图

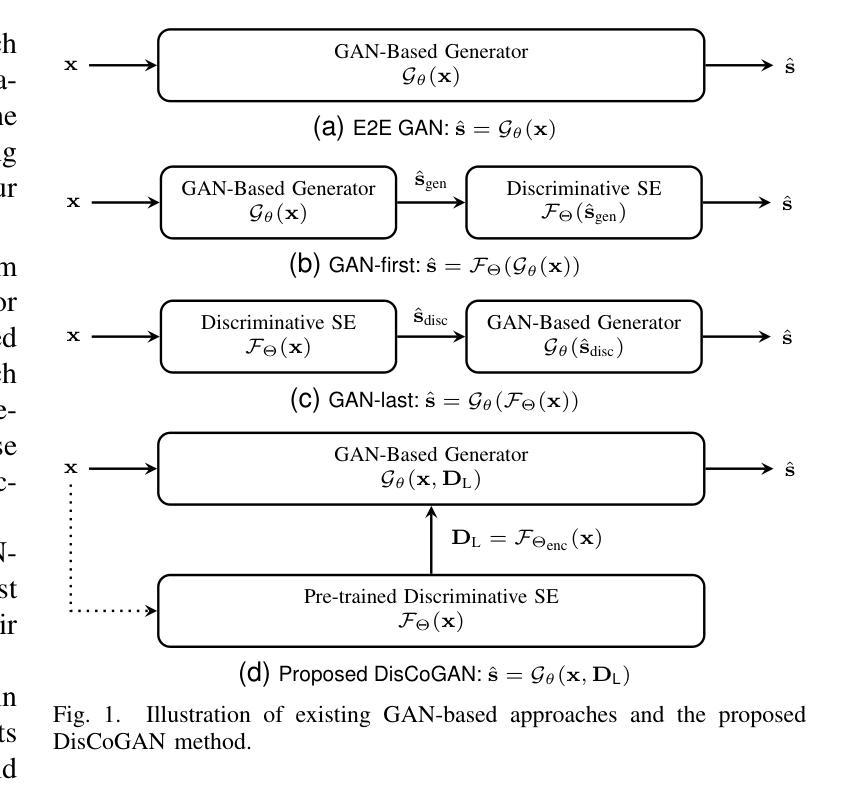
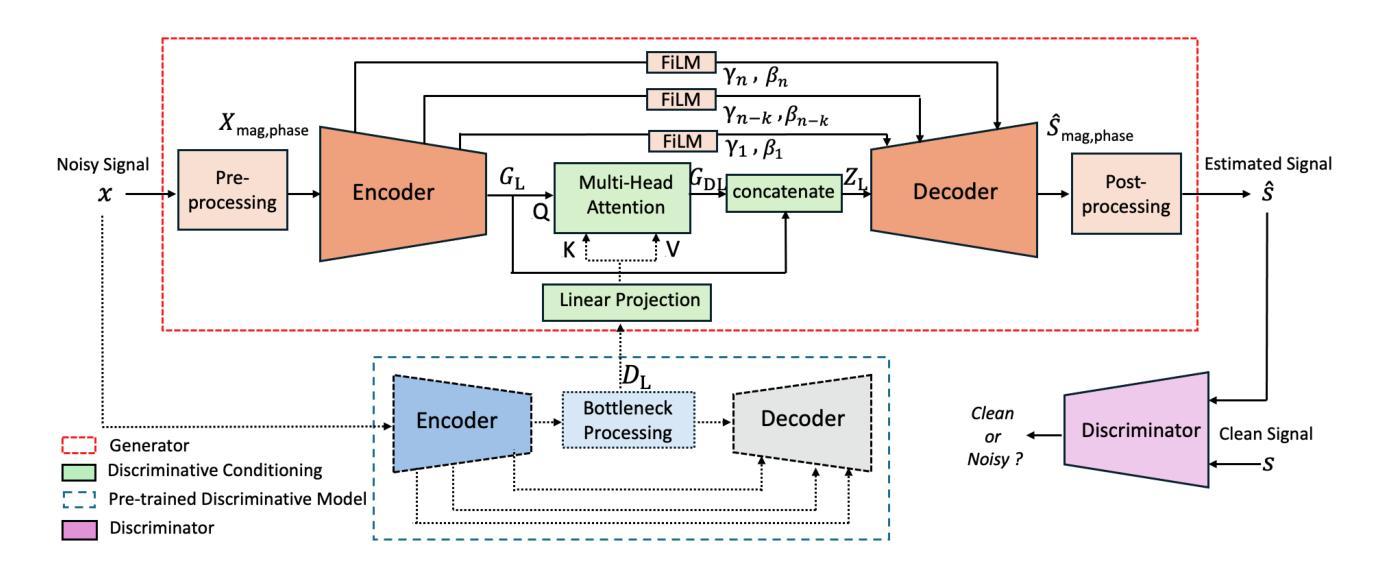
Leveraging Discriminative Latent Representations for Conditioning GAN-Based Speech Enhancement
Authors:Shrishti Saha Shetu, Emanuël A. P. Habets, Andreas Brendel
Generative speech enhancement methods based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models have shown promising results in various speech enhancement tasks. However, their performance in very low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) scenarios remains under-explored and limited, as these conditions pose significant challenges to both discriminative and generative state-of-the-art methods. To address this, we propose a method that leverages latent features extracted from discriminative speech enhancement models as generic conditioning features to improve GAN-based speech enhancement. The proposed method, referred to as DisCoGAN, demonstrates performance improvements over baseline models, particularly in low-SNR scenarios, while also maintaining competitive or superior performance in high-SNR conditions and on real-world recordings. We also conduct a comprehensive evaluation of conventional GAN-based architectures, including GANs trained end-to-end, GANs as a first processing stage, and post-filtering GANs, as well as discriminative models under low-SNR conditions. We show that DisCoGAN consistently outperforms existing methods. Finally, we present an ablation study that investigates the contributions of individual components within DisCoGAN and analyzes the impact of the discriminative conditioning method on overall performance.
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的生成性语音增强方法在各种语音增强任务中已显示出有前景的结果。然而,它们在极低信噪比(SNR)场景下的性能仍然未被充分探索和限制,因为这些条件对最先进的判别和生成方法都构成了重大挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种方法,该方法利用从判别式语音增强模型中提取的潜在特征作为通用条件特征,以改进基于GAN的语音增强。所提出的方法被称为DisCoGAN,与基线模型相比,它在低SNR场景下的性能有所提升,同时在高SNR条件和真实世界记录中保持竞争力或更出色的表现。我们还对传统的基于GAN的架构进行了全面评估,包括端到端训练的GANs、作为第一个处理阶段的GANs、后滤波GANs,以及低SNR条件下的判别模型。我们证明DisCoGAN始终优于现有方法。最后,我们进行了一项消融研究,研究了DisCoGAN中单个组件的贡献,并分析了判别条件方法对整体性能的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This manuscript has been submitted to IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing
Summary
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的生成式语音增强方法在多种语音增强任务中展现出良好的性能,但在低信噪比(SNR)场景下性能受限且尚未得到充分探索。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种利用判别式语音增强模型提取的特征作为通用条件特征来改善基于GAN的语音增强方法,称之为DisCoGAN。该方法在低SNR场景下相较于基准模型有明显性能提升,同时在高SNR条件和真实世界录音中保持竞争力或更出色的表现。我们还对常规GAN架构和判别模型进行了全面评估,证明了DisCoGAN的优越性。最后,我们进行了消融研究,探讨了DisCoGAN内部组件的贡献和判别条件方法对整体性能的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型在语音增强任务中表现出良好性能。
- 在低信噪比(SNR)场景下,现有方法性能受限。
- 提出了一种新的方法DisCoGAN,利用判别模型的特征来提升GAN在语音增强中的性能。
- DisCoGAN在低SNR场景下相较于基准模型有明显性能提升。
- DisCoGAN在高SNR条件和真实世界录音中表现竞争力或更出色。
- 对常规GAN架构和判别模型进行了全面评估,验证了DisCoGAN的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

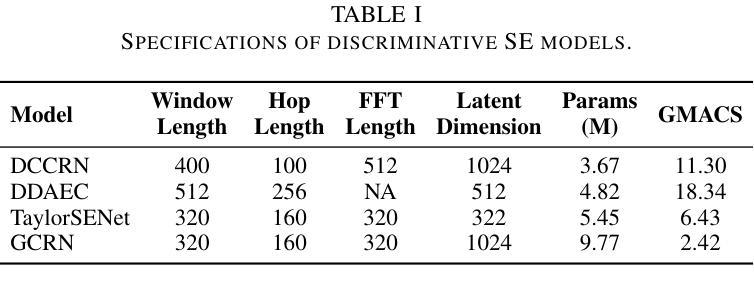
Revisiting the Privacy Risks of Split Inference: A GAN-Based Data Reconstruction Attack via Progressive Feature Optimization
Authors:Yixiang Qiu, Yanhan Liu, Hongyao Yu, Hao Fang, Bin Chen, Shu-Tao Xia, Ke Xu
The growing complexity of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) has led to the adoption of Split Inference (SI), a collaborative paradigm that partitions computation between edge devices and the cloud to reduce latency and protect user privacy. However, recent advances in Data Reconstruction Attacks (DRAs) reveal that intermediate features exchanged in SI can be exploited to recover sensitive input data, posing significant privacy risks. Existing DRAs are typically effective only on shallow models and fail to fully leverage semantic priors, limiting their reconstruction quality and generalizability across datasets and model architectures. In this paper, we propose a novel GAN-based DRA framework with Progressive Feature Optimization (PFO), which decomposes the generator into hierarchical blocks and incrementally refines intermediate representations to enhance the semantic fidelity of reconstructed images. To stabilize the optimization and improve image realism, we introduce an L1-ball constraint during reconstruction. Extensive experiments show that our method outperforms prior attacks by a large margin, especially in high-resolution scenarios, out-of-distribution settings, and against deeper and more complex DNNs.
深度神经网络(DNNs)的复杂性增长导致采用了分裂推理(SI)这种协作范式,该范式在边缘设备和云之间分配计算任务,以减少延迟并保护用户隐私。然而,数据重建攻击(DRAs)的最新进展表明,SI中交换的中间特征可能被利用来恢复敏感输入数据,从而带来重大的隐私风险。现有的DRAs通常只在浅层模型上有效,未能充分利用语义先验知识,从而限制了其重建质量和在数据集和模型架构上的通用性。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的新型DRA框架,该框架具有渐进特征优化(PFO)功能,将生成器分解为分层块并增量优化中间表示,以提高重建图像语义保真度。为了稳定优化并提高图像的真实性,我们在重建过程中引入了L1球约束。大量实验表明,我们的方法在大多数攻击面前表现出明显优势,特别是在高分辨率场景、超出分布设置以及对抗更深、更复杂的DNNs时。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
Summary
深度学习网络的复杂性增长促进了分割推理(Split Inference,SI)这一协作范式的应用,该范式将计算任务在边缘设备和云端之间进行分区,以降低延迟并保护用户隐私。然而,数据重建攻击(Data Reconstruction Attacks,DRAs)显示,SI中交换的中间特征可能被用来恢复敏感输入数据,带来重大隐私风险。针对此问题,本文提出一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的DRA框架,并引入渐进特征优化(Progressive Feature Optimization,PFO),以改善重建图像的质量并提高其语义保真度。实验表明,该方法在高清场景、非分布设置以及对抗更深更复杂深度神经网络的情况下,均显著优于现有攻击方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度神经网络(DNNs)的复杂性增长推动了Split Inference(SI)的应用,以优化计算并保护隐私。
- 数据重建攻击(DRAs)揭示了中间特征可能被用于恢复敏感输入数据的风险。
- 现有DRAs通常仅在浅层模型上有效,且未能充分利用语义先验信息。
- 本文提出一种基于GAN的DRA框架,引入渐进特征优化(PFO)提高重建图像的质量和语义保真度。
- 该方法通过分解生成器为层次块并增量优化中间表示来实现。
- L1-ball约束被引入以优化稳定性和提高图像逼真度。
点此查看论文截图

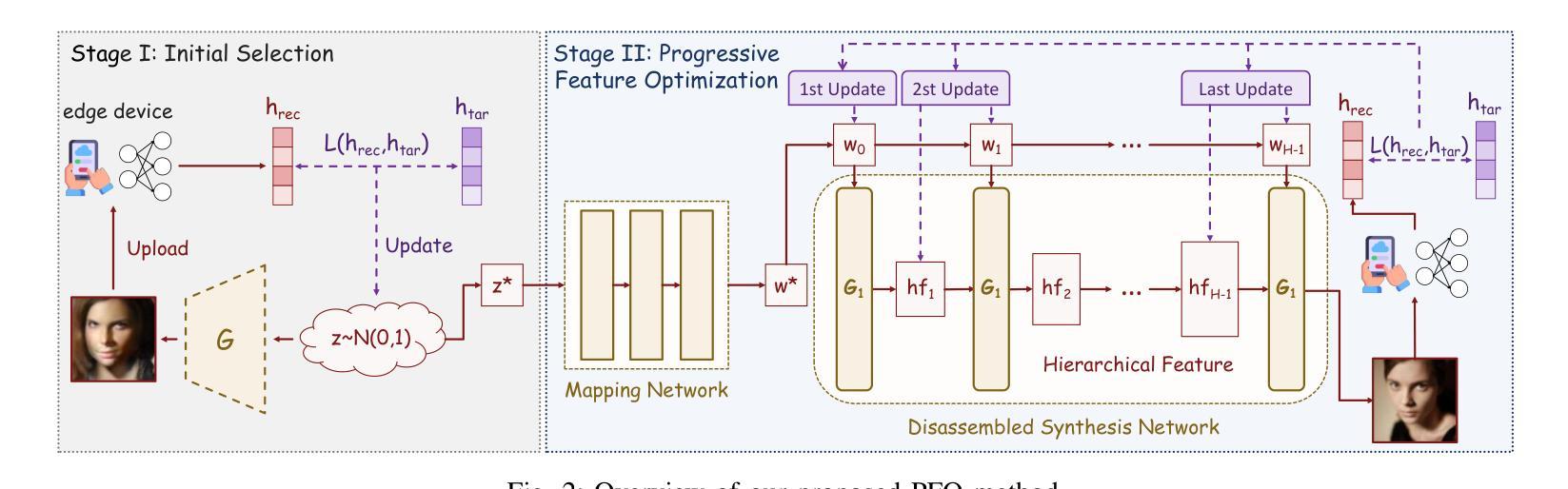

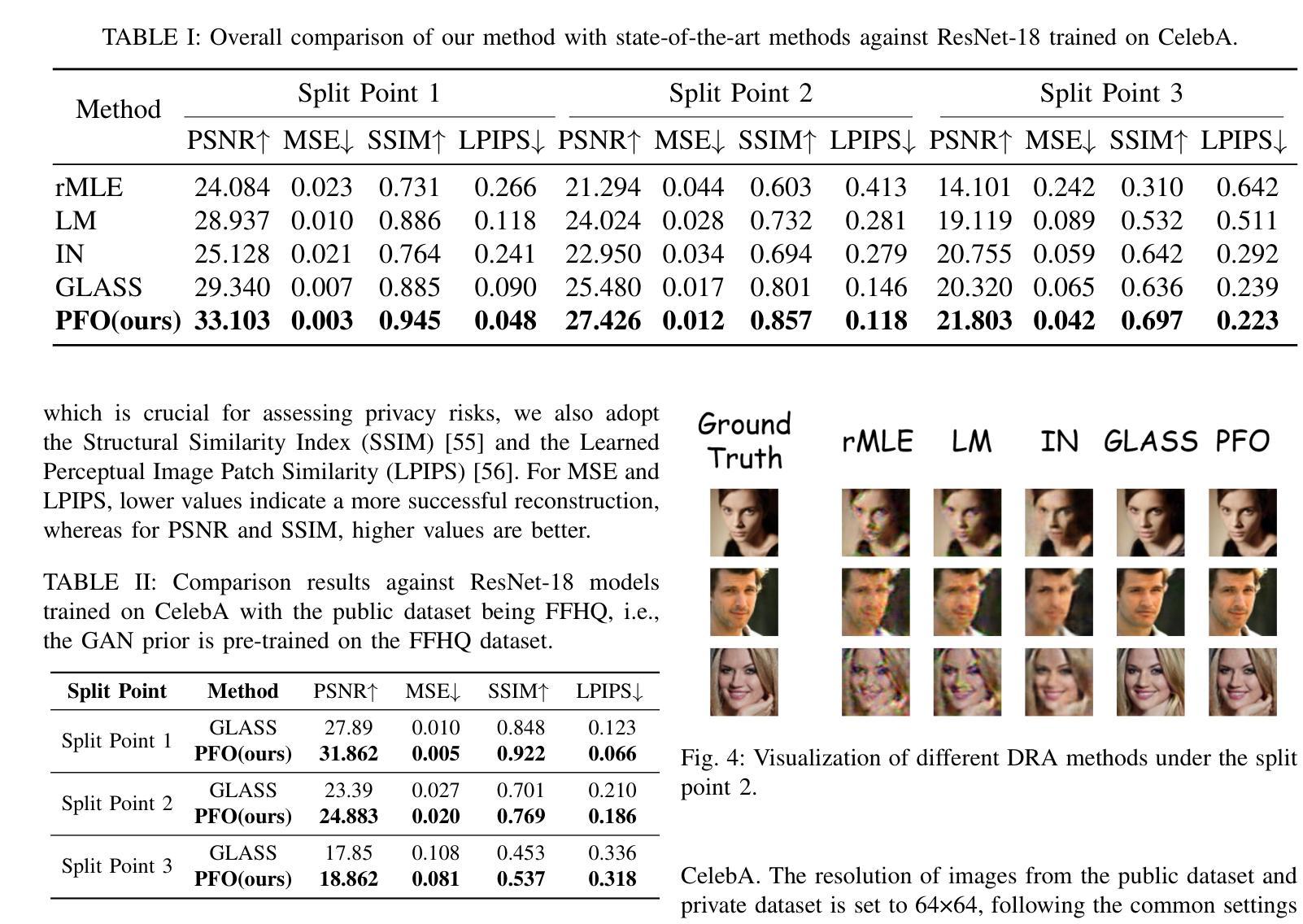
Can we make NeRF-based visual localization privacy-preserving?
Authors:Maxime Pietrantoni, Martin Humenberger, Torsten Sattler, Gabriela Csurka
Visual localization (VL) is the task of estimating the camera pose in a known scene. VL methods, a.o., can be distinguished based on how they represent the scene, e.g., explicitly through a (sparse) point cloud or a collection of images or implicitly through the weights of a neural network. Recently, NeRF-based methods have become popular for VL. While NeRFs offer high-quality novel view synthesis, they inadvertently encode fine scene details, raising privacy concerns when deployed in cloud-based localization services as sensitive information could be recovered. In this paper, we tackle this challenge on two ends. We first propose a new protocol to assess privacy-preservation of NeRF-based representations. We show that NeRFs trained with photometric losses store fine-grained details in their geometry representations, making them vulnerable to privacy attacks, even if the head that predicts colors is removed. Second, we propose ppNeSF (Privacy-Preserving Neural Segmentation Field), a NeRF variant trained with segmentation supervision instead of RGB images. These segmentation labels are learned in a self-supervised manner, ensuring they are coarse enough to obscure identifiable scene details while remaining discriminativeness in 3D. The segmentation space of ppNeSF can be used for accurate visual localization, yielding state-of-the-art results.
视觉定位(VL)是估计已知场景中的相机姿态的任务。VL方法,可以基于它们如何表示场景来区分,例如,通过(稀疏)点云或图像集合进行显式表示,或通过神经网络的权重进行隐式表示。最近,基于NeRF的方法在VL中变得流行。虽然NeRF提供了高质量的新视角合成,但它们无意中编码了场景的细节信息,当部署在云端的定位服务中时引发了隐私担忧,因为可能恢复出敏感信息。在本文中,我们从两个方面解决了这一挑战。首先,我们提出了一种新的协议来评估基于NeRF表示的隐私保护。我们展示,用光度损失训练的NeRF在其几何表示中存储了详细的细节信息,使其容易受到隐私攻击,即使移除了预测颜色的头部也是如此。其次,我们提出了ppNeSF(隐私保护神经网络分割场),这是一种用分割监督而不是RGB图像训练的NeRF变体。这些分割标签以自我监督的方式学习,确保它们足够粗略以掩盖可识别的场景细节,同时在3D中保持辨别力。ppNeSF的分割空间可用于精确视觉定位,达到最新技术水平的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视觉定位(VL)是估计已知场景中相机姿态的任务。VL方法可根据如何表示场景来区分,例如通过(稀疏)点云或图像集合显式表示,或通过神经网络权重隐式表示。最近,基于NeRF的方法在VL中变得流行。虽然NeRF提供了高质量的新视图合成,但它们无意中编码了场景的精细细节,当部署在云端的定位服务中时会引发隐私担忧,因为可能恢复敏感信息。本文解决这一挑战的两端。首先,我们提出了一种新协议来评估NeRF表示的隐私保护能力。我们证明,使用光度损失训练的NeRF在其几何表示中存储了精细的细节,即使移除预测颜色的头部,也容易受到隐私攻击。其次,我们提出了ppNeSF(隐私保护神经分割场),这是一种使用分割监督而不是RGB图像训练的NeRF变体。这些分割标签以自我监督的方式学习,确保它们足够粗糙以掩盖场景的可识别细节,同时在3D中保持辨别力。ppNeSF的分割空间可用于准确视觉定位,取得最新结果。
要点总结
- 基于NeRF的方法已成为视觉定位的主流方法,并具有较高的定位准确性。
- NeRF因其对场景的精细细节编码而在云端定位服务中引发隐私担忧。
- 提出了一种新的协议来评估NeRF在隐私保护方面的表现,结果显示基于光度损失训练的NeRF易受隐私攻击。
- 提出了一种新的NeRF变体ppNeSF,通过分割监督训练,能在保护隐私的同时保持对场景的精细表示和定位准确性。
- ppNeSF的分割空间可以用于准确视觉定位,并取得了业界最佳效果。
- 提出了以自我监督方式学习分割标签的方法,确保了隐私保护和定位准确性的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

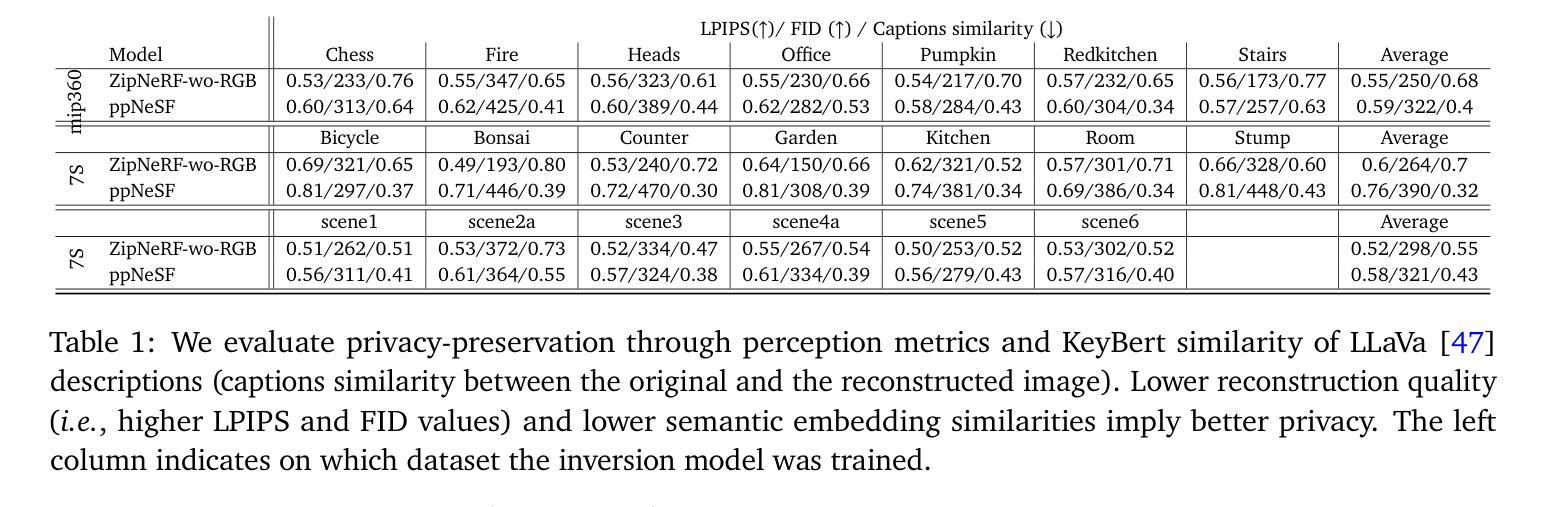

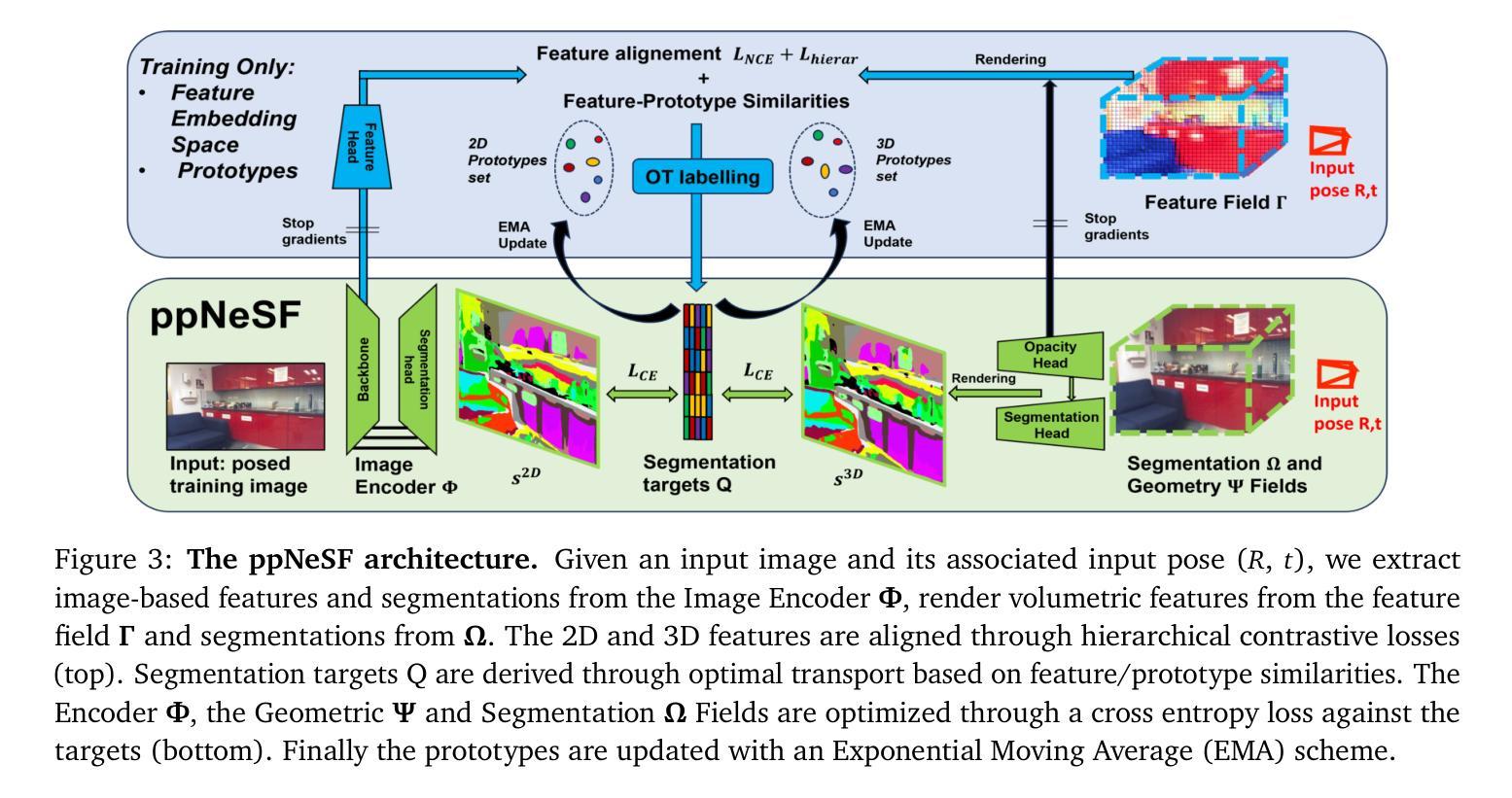

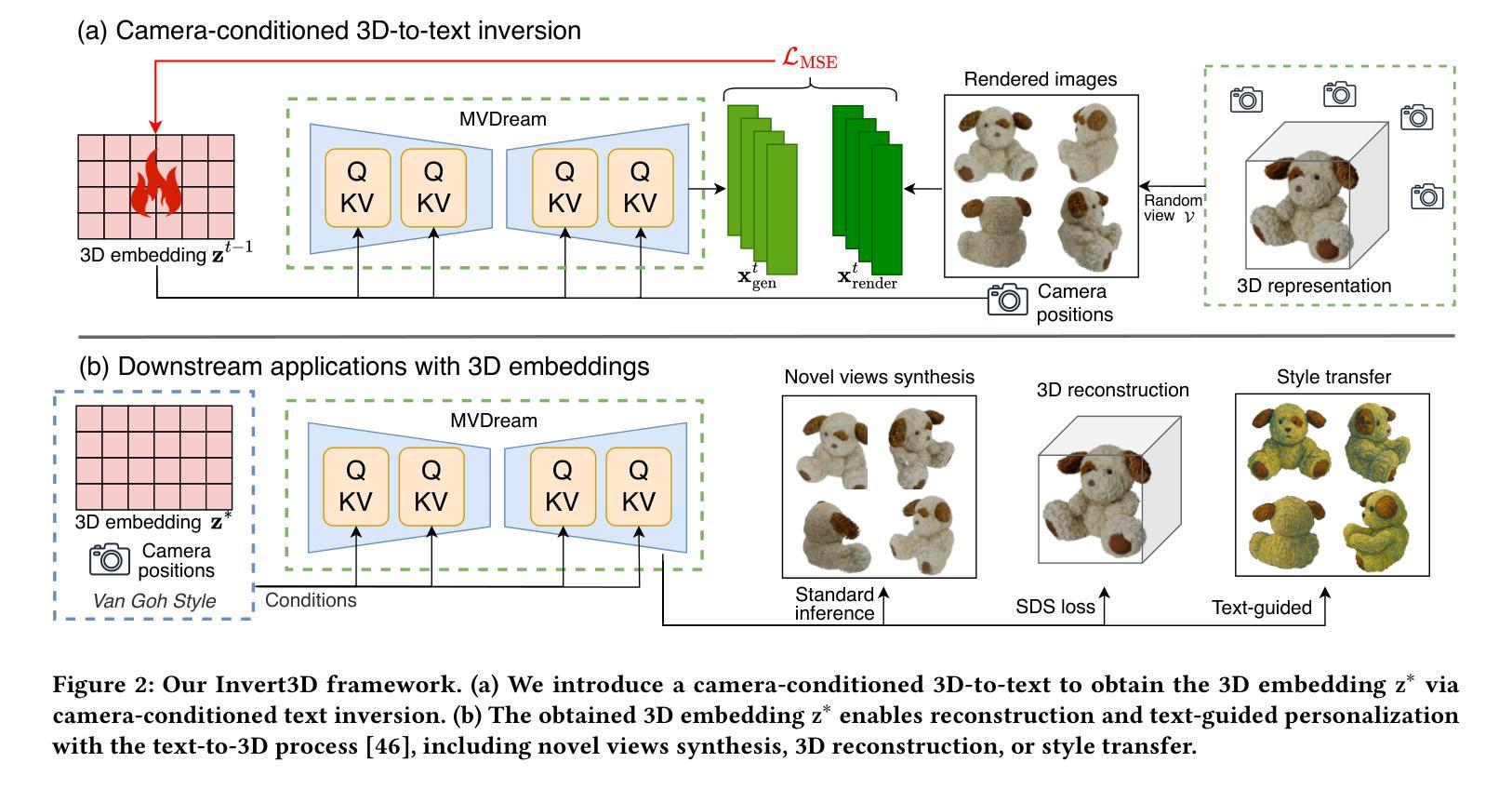
Align 3D Representation and Text Embedding for 3D Content Personalization
Authors:Qi Song, Ziyuan Luo, Ka Chun Cheung, Simon See, Renjie Wan
Recent advances in NeRF and 3DGS have significantly enhanced the efficiency and quality of 3D content synthesis. However, efficient personalization of generated 3D content remains a critical challenge. Current 3D personalization approaches predominantly rely on knowledge distillation-based methods, which require computationally expensive retraining procedures. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{Invert3D}, a novel framework for convenient 3D content personalization. Nowadays, vision-language models such as CLIP enable direct image personalization through aligned vision-text embedding spaces. However, the inherent structural differences between 3D content and 2D images preclude direct application of these techniques to 3D personalization. Our approach bridges this gap by establishing alignment between 3D representations and text embedding spaces. Specifically, we develop a camera-conditioned 3D-to-text inverse mechanism that projects 3D contents into a 3D embedding aligned with text embeddings. This alignment enables efficient manipulation and personalization of 3D content through natural language prompts, eliminating the need for computationally retraining procedures. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Invert3D achieves effective personalization of 3D content. Our work is available at: https://github.com/qsong2001/Invert3D.
最近,NeRF和3DGS的进步大大提高了3D内容合成的效率和质量。然而,生成3D内容的个性化仍然是一个巨大的挑战。当前的3D个性化方法主要依赖于基于知识蒸馏的方法,这需要计算昂贵的再训练过程。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了“Invert3D”,一个便于3D内容个性化的新型框架。如今,诸如CLIP之类的视觉语言模型可以通过对齐的视觉文本嵌入空间实现直接图像个性化。然而,3D内容与2D图像之间的内在结构差异使得这些技术无法直接应用于3D个性化。我们的方法通过建立3D表示与文本嵌入空间之间的对齐来弥补这一差距。具体来说,我们开发了一种受相机条件限制的3D到文本的逆向机制,该机制将3D内容投影到与文本嵌入对齐的3D嵌入中。这种对齐可以通过自然语言提示实现3D内容的高效操作和个性化,而无需进行计算机再训练过程。大量实验证明,Invert3D能够实现有效的3D内容个性化。我们的工作在:https://github.com/qsong2001/Invert3D 可供查阅。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
NeRF和3DGS的最新进展大大提高了3D内容合成的效率和质量,但生成内容的个性化仍然是一个关键问题。当前方法主要依赖基于知识蒸馏的方法,这需要昂贵的重新训练过程。为此,提出了Invert3D框架,通过建立3D表示与文本嵌入空间的对齐,实现便捷的3D内容个性化。该框架通过相机条件的3D到文本的逆向机制,将3D内容投影到与文本嵌入对齐的3D嵌入空间,从而实现通过自然语言提示高效操作和个性化3D内容,无需重新训练。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF和3DGS技术提高了3D内容合成的效率和质量。
- 3D内容个性化仍是关键挑战,现有方法主要依赖知识蒸馏,需昂贵重新训练过程。
- Invert3D框架旨在解决此挑战,实现便捷的3D内容个性化。
- 该框架通过建立3D表示与文本嵌入空间的对齐来工作。
- 通过相机条件的3D到文本的逆向机制,将3D内容投影到与文本嵌入对齐的3D嵌入空间。
- 该框架使得通过自然语言提示高效操作和个性化3D内容成为可能。
点此查看论文截图


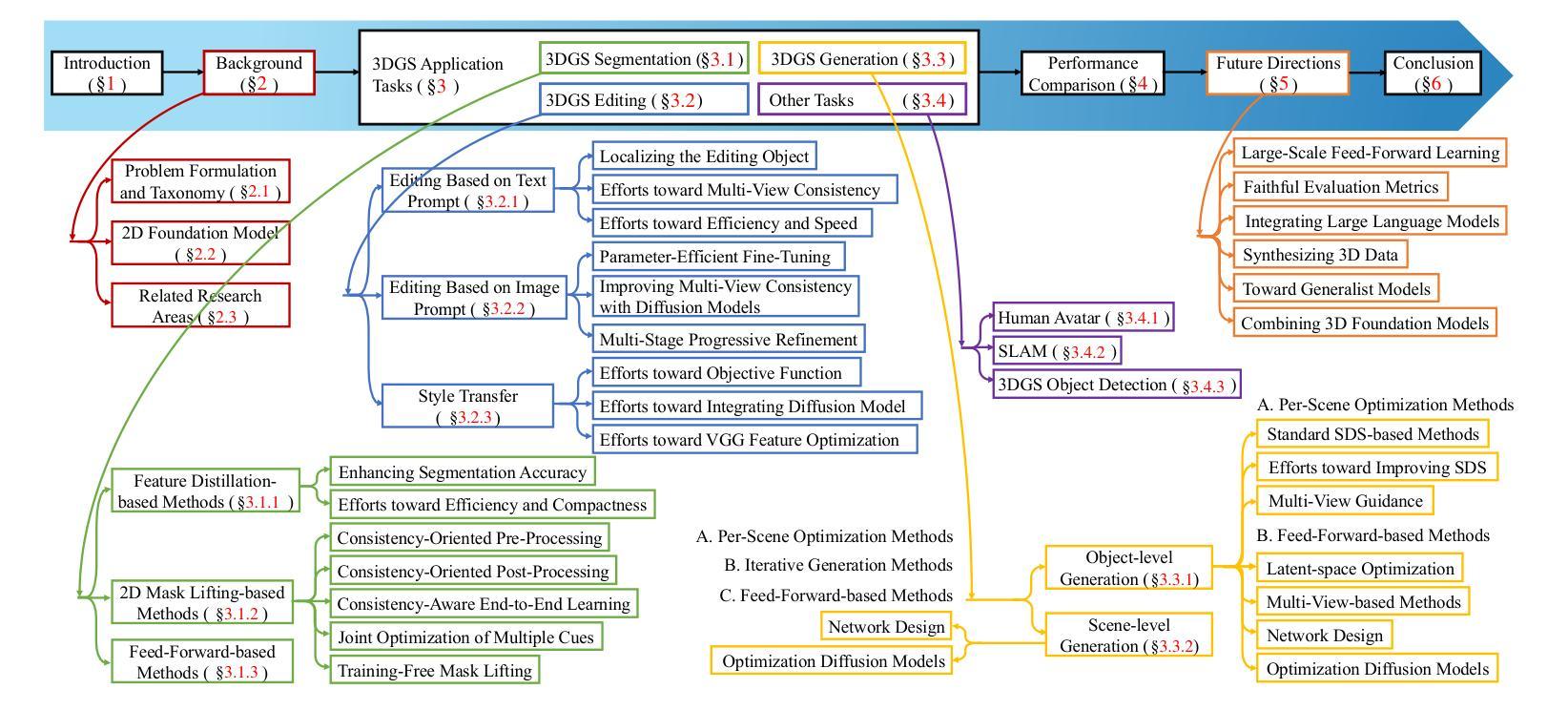
A Survey on 3D Gaussian Splatting Applications: Segmentation, Editing, and Generation
Authors:Shuting He, Peilin Ji, Yitong Yang, Changshuo Wang, Jiayi Ji, Yinglin Wang, Henghui Ding
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently emerged as a powerful alternative to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) for 3D scene representation, offering high-fidelity photorealistic rendering with real-time performance. Beyond novel view synthesis, the explicit and compact nature of 3DGS enables a wide range of downstream applications that require geometric and semantic understanding. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of recent progress in 3DGS applications. It first introduces 2D foundation models that support semantic understanding and control in 3DGS applications, followed by a review of NeRF-based methods that inform their 3DGS counterparts. We then categorize 3DGS applications into segmentation, editing, generation, and other functional tasks. For each, we summarize representative methods, supervision strategies, and learning paradigms, highlighting shared design principles and emerging trends. Commonly used datasets and evaluation protocols are also summarized, along with comparative analyses of recent methods across public benchmarks. To support ongoing research and development, a continually updated repository of papers, code, and resources is maintained at https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications.
3D高斯延展(3DGS)作为一种强大的技术,近期已经成为神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在三维场景表示方面的有力替代品,它以真实性能表现提供高保真照片级渲染。除了新视角合成之外,3DGS的明确和紧凑特性还使得它在需要几何和语义理解的下游应用方面具有广泛应用。这篇综述全面概述了3DGS应用的最新进展。它首先介绍了支持3DGS应用中的语义理解和控制的二维基础模型,然后回顾了基于NeRF的方法,以为其3DGS对应物提供信息。接着我们将3DGS应用分类为分割、编辑、生成和其他功能任务。对于每一项任务,我们总结了代表性方法、监督策略和学习范式,并强调了共享设计原则和新兴趋势。此外,还总结了常用数据集和评估协议,以及在公共基准测试上对近期方法进行对比分析。为了支持持续的研究和开发,论文、代码和资源的持续更新仓库可访问https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF GitHub Repo: https://github.com/heshuting555/Awesome-3DGS-Applications
Summary
基于三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术的最新进展,本文全面概述了其在三维场景表示方面的应用。文章介绍了支持三维高斯拼贴应用的二维基础模型,回顾了基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的方法以启发其对应的3DGS技术。文章将3DGS应用分为分割、编辑、生成和其他功能任务,并对每个任务的代表性方法、监督策略和学范式进行了总结,同时强调了共享的设计原则和新兴趋势。此外,文章还概述了常用数据集和评估协议,并在公共基准测试上对近期方法进行对比分析。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) 作为Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) 的有力替代方案,可实现高质量的三维场景表示。
- 3DGS 具有高保真度照片级渲染和实时性能。
- 3DGS 支持广泛的下游应用,包括分割、编辑、生成和其他功能任务,这些任务需要几何和语义理解。
- 文章回顾了NeRF方法,为理解其对应的3DGS技术提供了基础。
- 文章提供了数据集和评估协议的概述,并进行近期方法的对比分析。
点此查看论文截图

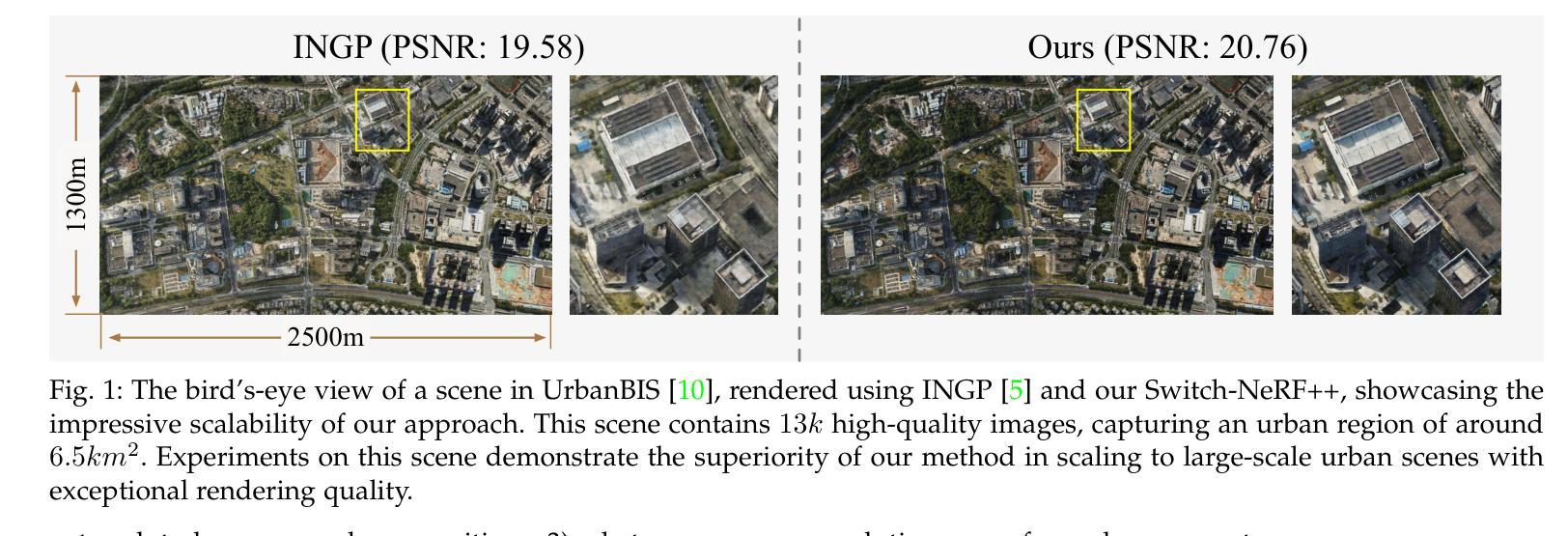
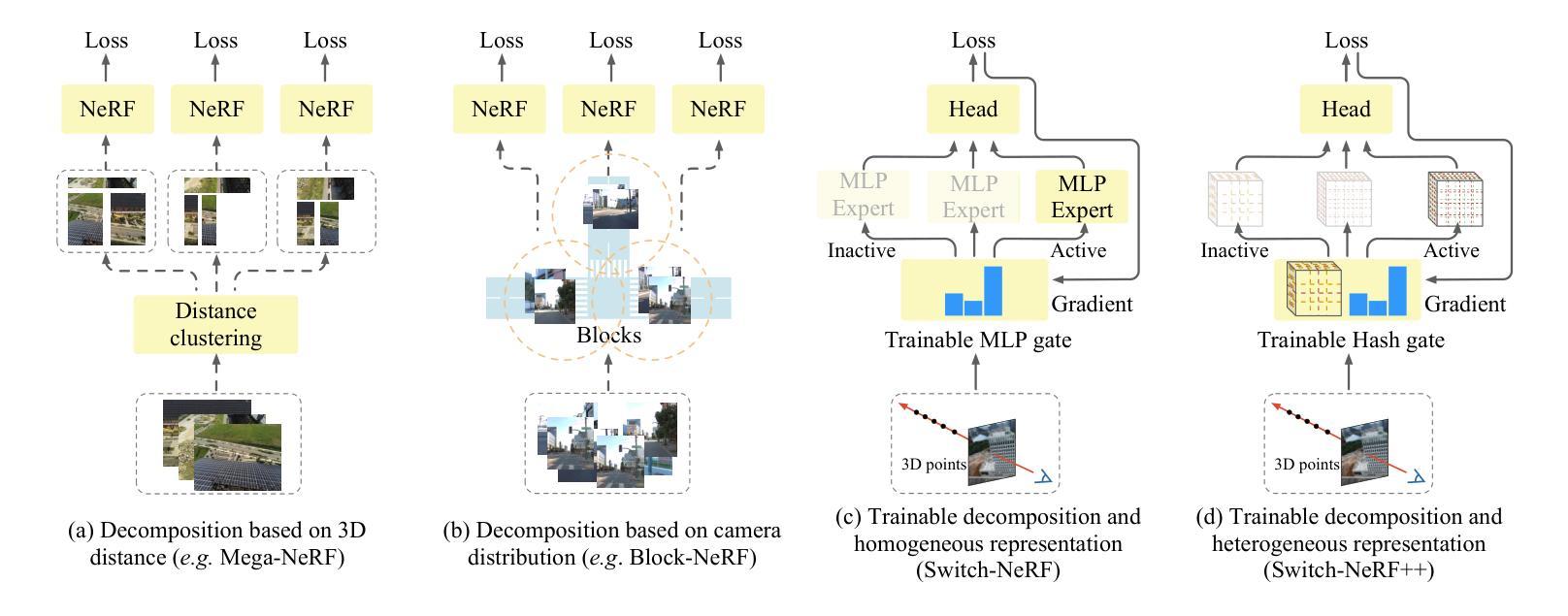
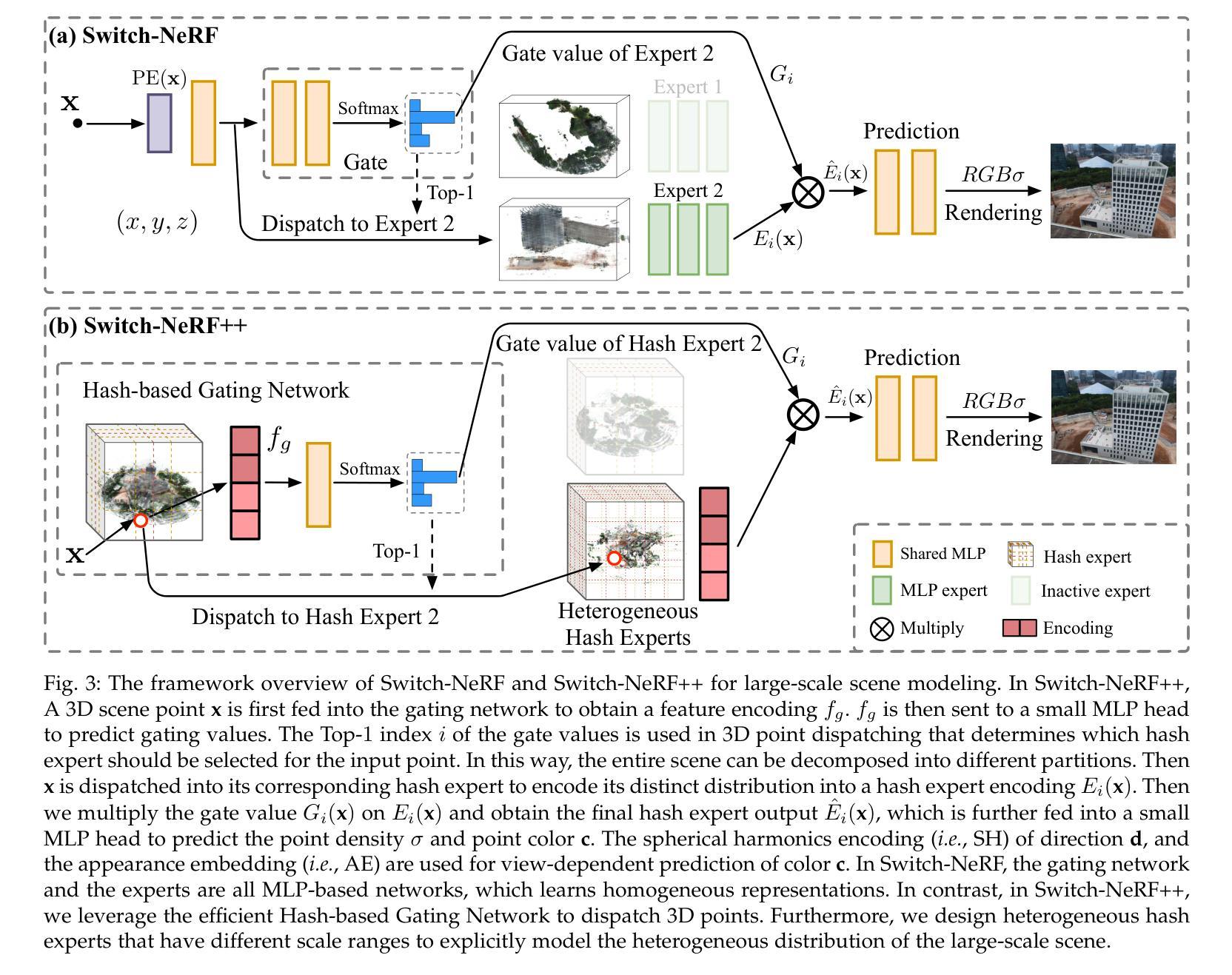
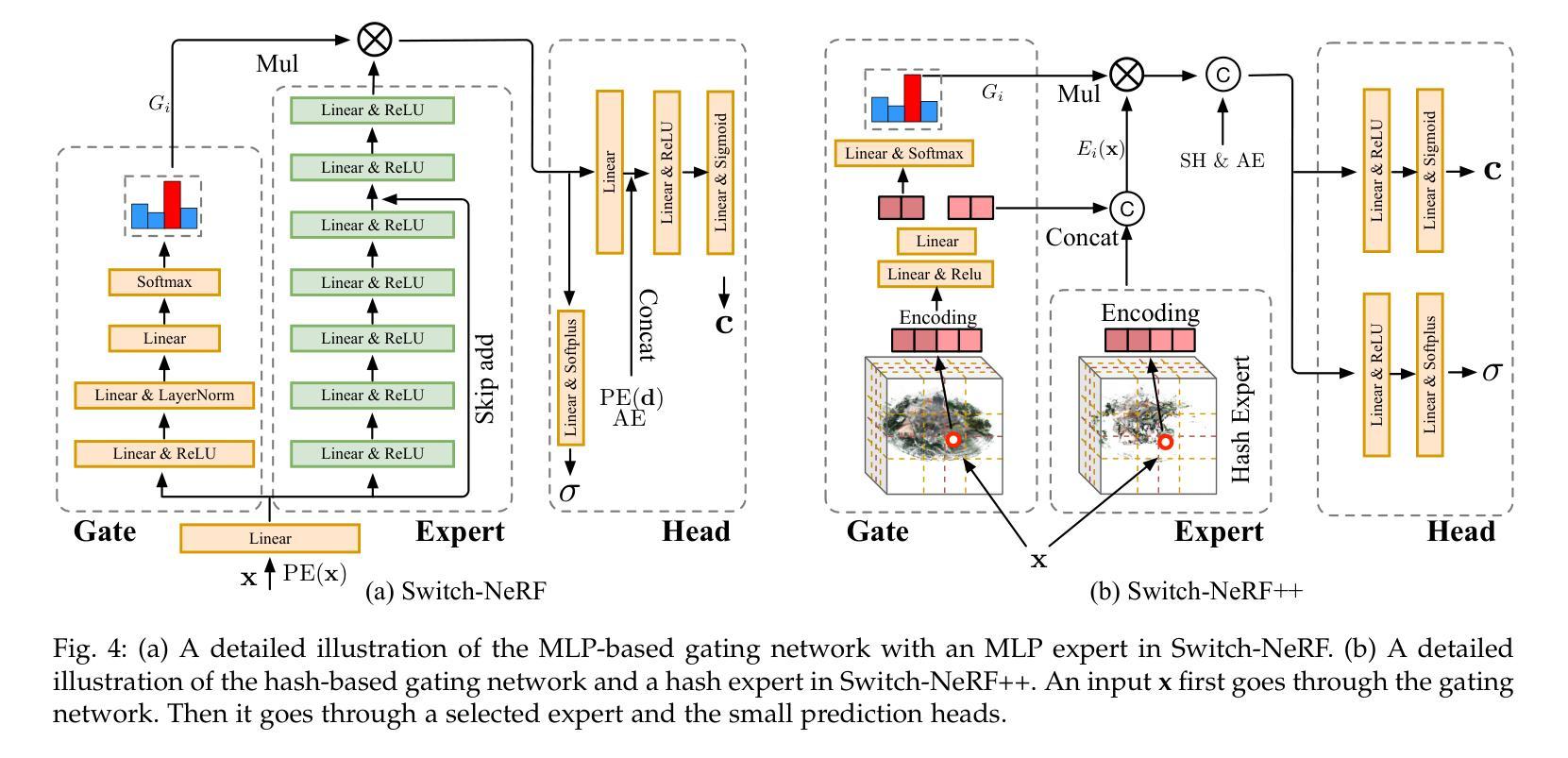
Learning Heterogeneous Mixture of Scene Experts for Large-scale Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Zhenxing Mi, Ping Yin, Xue Xiao, Dan Xu
Recent NeRF methods on large-scale scenes have underlined the importance of scene decomposition for scalable NeRFs. Although achieving reasonable scalability, there are several critical problems remaining unexplored, i.e., learnable decomposition, modeling scene heterogeneity, and modeling efficiency. In this paper, we introduce Switch-NeRF++, a Heterogeneous Mixture of Hash Experts (HMoHE) network that addresses these challenges within a unified framework. It is a highly scalable NeRF that learns heterogeneous decomposition and heterogeneous NeRFs efficiently for large-scale scenes in an end-to-end manner. In our framework, a gating network learns to decompose scenes and allocates 3D points to specialized NeRF experts. This gating network is co-optimized with the experts by our proposed Sparsely Gated Mixture of Experts (MoE) NeRF framework. We incorporate a hash-based gating network and distinct heterogeneous hash experts. The hash-based gating efficiently learns the decomposition of the large-scale scene. The distinct heterogeneous hash experts consist of hash grids of different resolution ranges, enabling effective learning of the heterogeneous representation of different scene parts. These design choices make our framework an end-to-end and highly scalable NeRF solution for real-world large-scale scene modeling to achieve both quality and efficiency. We evaluate our accuracy and scalability on existing large-scale NeRF datasets and a new dataset with very large-scale scenes ($>6.5km^2$) from UrbanBIS. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach can be easily scaled to various large-scale scenes and achieve state-of-the-art scene rendering accuracy. Furthermore, our method exhibits significant efficiency, with an 8x acceleration in training and a 16x acceleration in rendering compared to Switch-NeRF. Codes will be released at https://github.com/MiZhenxing/Switch-NeRF.
近期的NeRF在大规模场景应用的方法强调了场景分解对于可扩展NeRF的重要性。尽管已经实现了合理的可扩展性,但仍存在几个关键问题尚未探索,即可学习的分解、场景异质性的建模和建模效率。在本文中,我们介绍了Switch-NeRF++,这是一个异质混合哈希专家(HMoHE)网络,它在一个统一框架内解决了这些挑战。这是一种高度可扩展的NeRF,能够以端到端的方式有效地对大规模场景进行异质分解和异质NeRF建模。在我们的框架中,门控网络学习分解场景并将3D点分配给专门的NeRF专家。门控网络通过我们提出的稀疏门控混合专家(MoE)NeRF框架与专家共同优化。我们采用了基于哈希的门控网络和不同的异质哈希专家。基于哈希的门控网络有效地学习了大规模场景的分解。不同的异质哈希专家由不同分辨率范围的哈希网格组成,能够实现不同场景部分异质表示的有效学习。这些设计选择使我们的框架成为用于现实世界大规模场景建模的端到端和高度可扩展的NeRF解决方案,以实现质量和效率。我们在现有的大规模NeRF数据集和来自UrbanBIS的新的大规模场景(> 6.5km^2)数据集上评估了我们的准确性和可扩展性。大量实验表明,我们的方法可以轻松地扩展到各种大规模场景,并实现最先进的场景渲染精度。此外,我们的方法在训练和渲染方面与Switch-NeRF相比分别实现了8倍和1 结点的加速。代码将在https://github.com/MiZhenxing/Switch-NeRF发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TPAMI
Summary
本文介绍了Switch-NeRF++,一种基于Heterogeneous Mixture of Hash Experts (HMoHE)网络的端到端高效NeRF模型。该模型解决了大规模场景NeRF中的几个关键问题,包括场景分解、场景异质性的建模和建模效率。Switch-NeRF++通过引入基于哈希的门控网络和不同的异质哈希专家来实现大规模场景的异质分解和高效建模。该方法实现了高质量的渲染效果和显著的计算效率提升。
Key Takeaways
- Switch-NeRF++是一个可扩展的NeRF模型,用于处理大规模场景。
- 模型引入了Heterogeneous Mixture of Hash Experts (HMoHE)网络来解决场景分解和场景异质性的建模问题。
- 模型通过一个门控网络学习场景分解,并将3D点分配给特定的NeRF专家。
- 模型采用基于哈希的门控网络和不同的异质哈希专家来实现高效的场景分解。
- 通过使用不同分辨率范围的哈希网格,模型可以有效地学习场景的异质表示。
- Switch-NeRF++在大型场景渲染中实现了高质量和高效性,相比Switch-NeRF有8倍的训练加速和16倍的渲染加速。
点此查看论文截图

Sat-DN: Implicit Surface Reconstruction from Multi-View Satellite Images with Depth and Normal Supervision
Authors:Tianle Liu, Shuangming Zhao, Wanshou Jiang, Bingxuan Guo
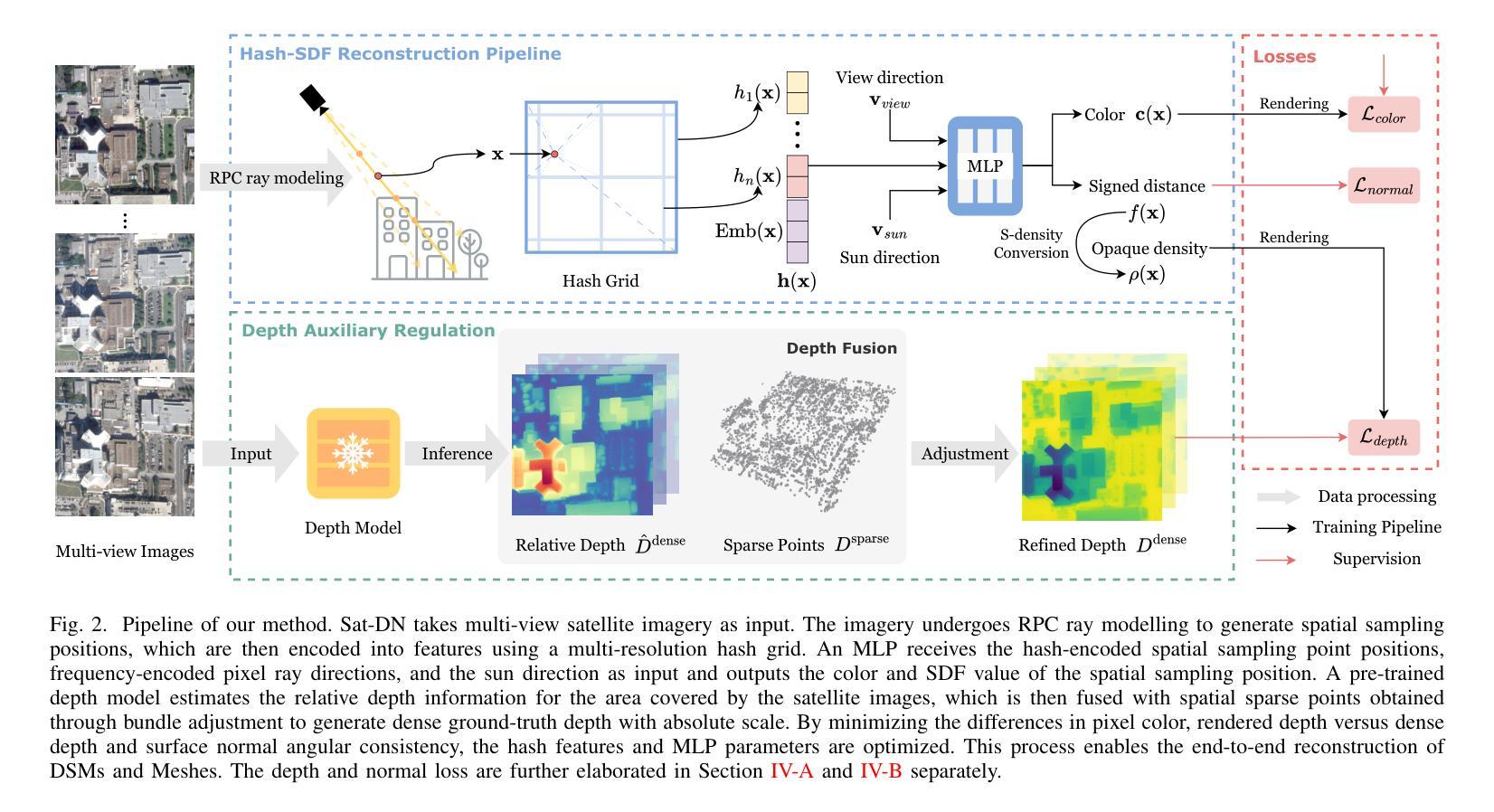
With advancements in satellite imaging technology, acquiring high-resolution multi-view satellite imagery has become increasingly accessible, enabling rapid and location-independent ground model reconstruction. However, traditional stereo matching methods struggle to capture fine details, and while neural radiance fields (NeRFs) achieve high-quality reconstructions, their training time is prohibitively long. Moreover, challenges such as low visibility of building facades, illumination and style differences between pixels, and weakly textured regions in satellite imagery further make it hard to reconstruct reasonable terrain geometry and detailed building facades. To address these issues, we propose Sat-DN, a novel framework leveraging a progressively trained multi-resolution hash grid reconstruction architecture with explicit depth guidance and surface normal consistency constraints to enhance reconstruction quality. The multi-resolution hash grid accelerates training, while the progressive strategy incrementally increases the learning frequency, using coarse low-frequency geometry to guide the reconstruction of fine high-frequency details. The depth and normal constraints ensure a clear building outline and correct planar distribution. Extensive experiments on the DFC2019 dataset demonstrate that Sat-DN outperforms existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. The code is available at https://github.com/costune/SatDN.
随着卫星成像技术的进步,获取高分辨率的多视角卫星图像变得越来越容易,能够实现快速且独立于位置的地面模型重建。然而,传统的立体匹配方法难以捕捉精细细节,虽然神经辐射场(NeRF)可以实现高质量的重建,但其训练时间非常长。此外,卫星图像中的挑战,如建筑物墙面的低可见性、像素之间的光照和风格差异以及卫星图像中纹理较弱的区域,进一步加大了合理地形几何和详细建筑物墙面重建的难度。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了Sat-DN,这是一个利用逐步训练的多分辨率哈希网格重建架构的新型框架,具有明确的深度指导和表面法线一致性约束,以提高重建质量。多分辨率哈希网格可以加速训练,而逐步策略可以逐步提高学习频率,使用粗糙的低频几何来指导精细高频细节的重建。深度和法线约束确保了清晰的建筑轮廓和正确的平面分布。在DFC2019数据集上的大量实验表明,Sat-DN优于现有方法,在定性和定量评估中都达到了最新水平。代码可在https://github.com/costune/SatDN获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着卫星成像技术的进步,获取高分辨率的多视角卫星图像越来越容易,推动了地面模型的快速重建。然而,传统立体匹配方法难以捕捉精细细节,而神经辐射场(NeRF)虽然能进行高质量重建,但训练时间过长。针对卫星图像重建中的地形几何和建筑立面重建难题,我们提出了Sat-DN框架,采用渐进式训练的多分辨率哈希网格重建架构,具有明确的深度指导和表面法线一致性约束,以提高重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- 卫星成像技术进步使得获取高分辨率多视角图像变得容易,推动了地面模型重建。
- 传统立体匹配方法难以捕捉精细细节,而NeRF训练时间过长。
- Sat-DN框架利用多分辨率哈希网格重建架构,加速训练过程。
- 渐进式训练策略能逐步提高学习频率,利用粗低频几何引导精细高频细节的重建。
- 深度约束和法线约束确保清晰的建筑轮廓和正确的平面分布。
- 在DFC2019数据集上的实验表明,Sat-DN框架在定性和定量评估中都实现了最佳结果。
点此查看论文截图
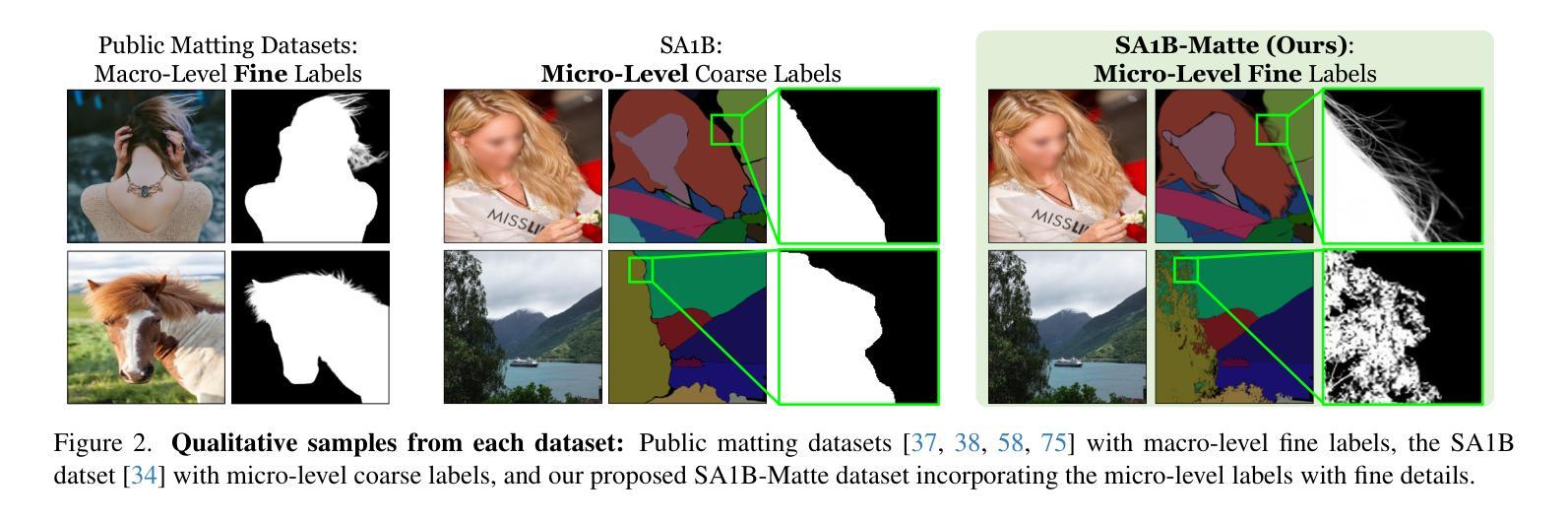
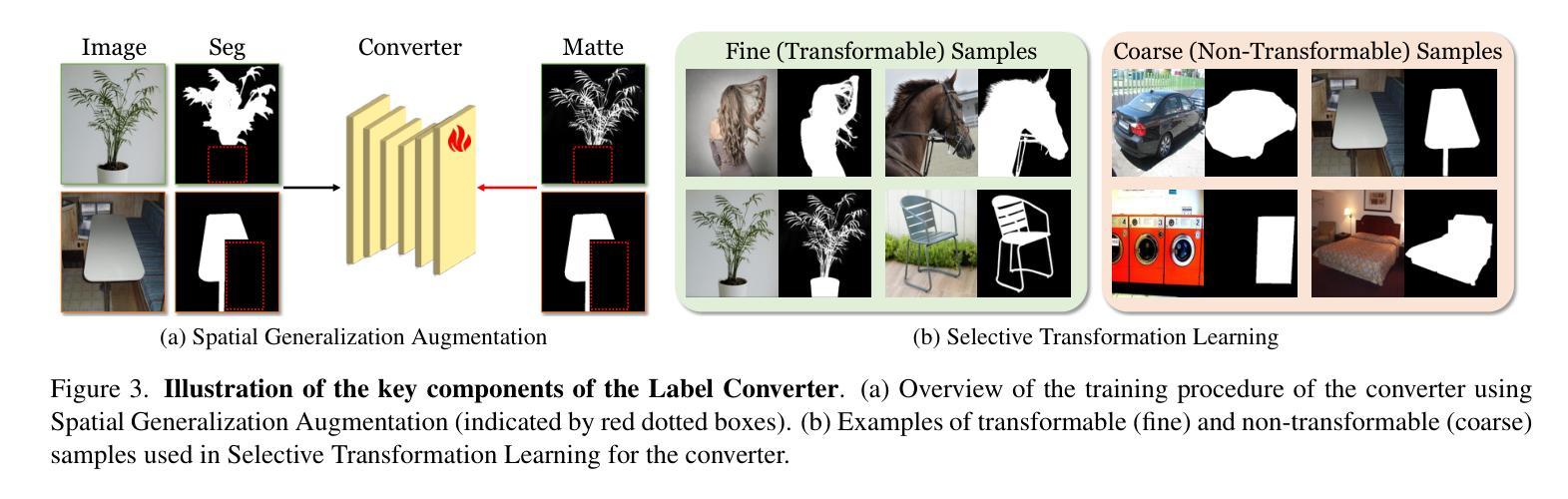
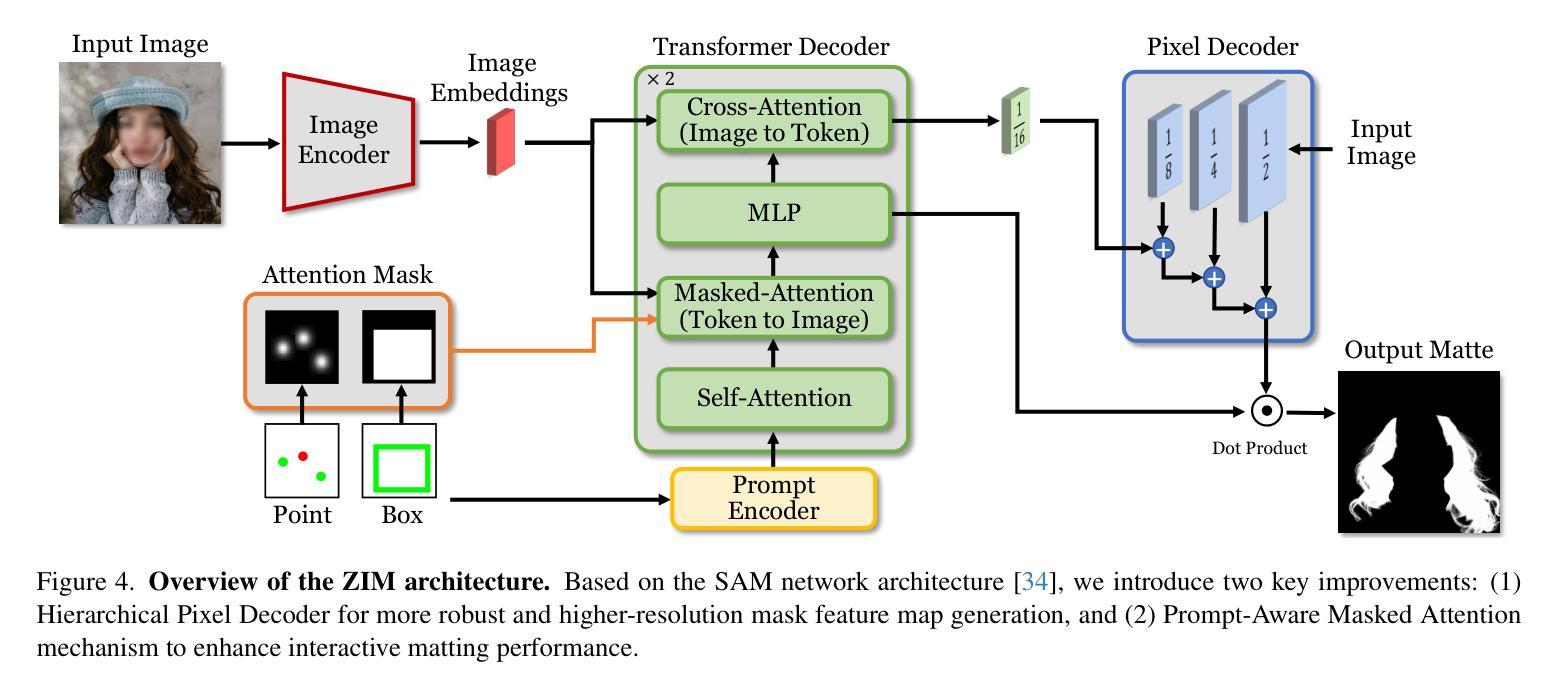
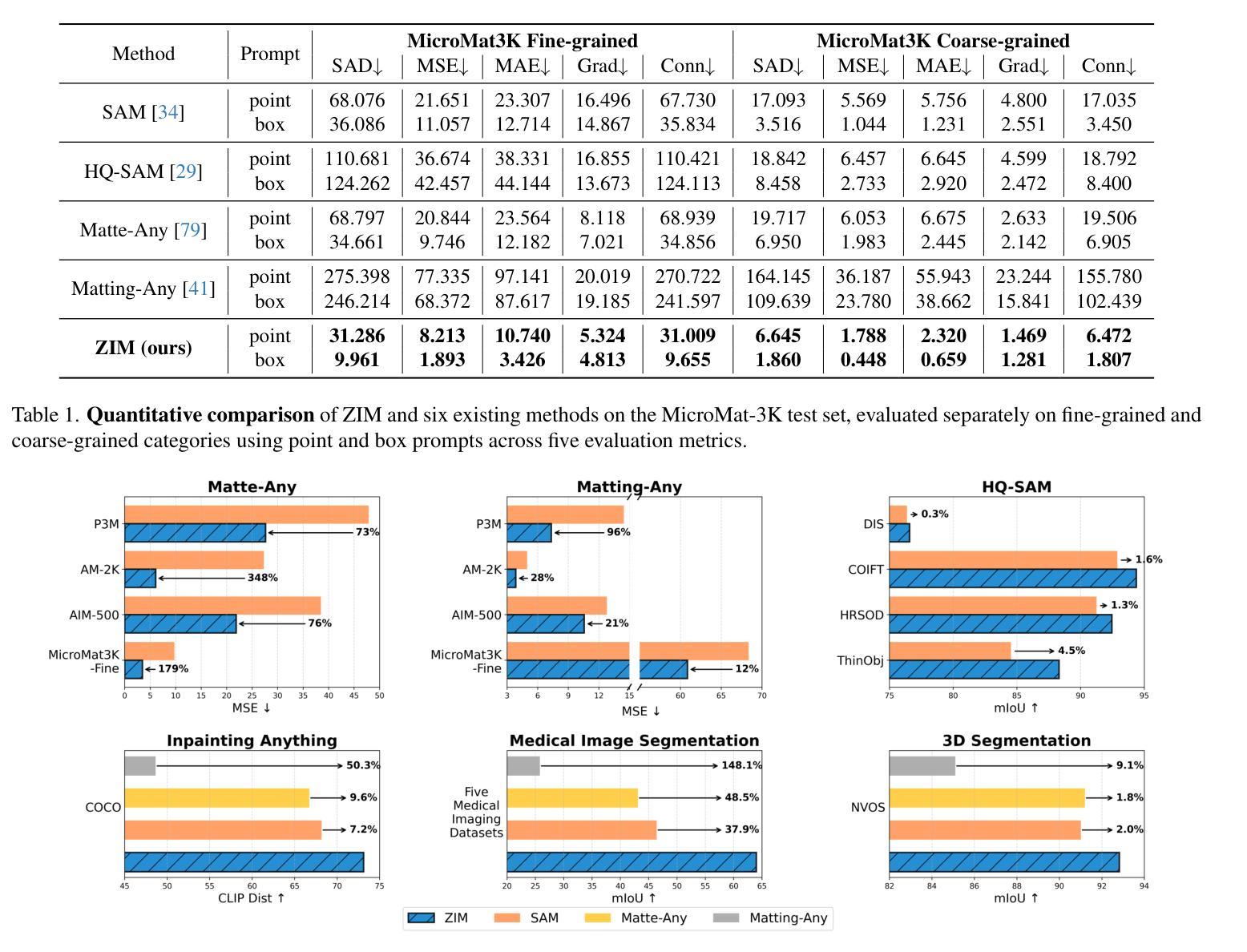
ZIM: Zero-Shot Image Matting for Anything
Authors:Beomyoung Kim, Chanyong Shin, Joonhyun Jeong, Hyungsik Jung, Se-Yun Lee, Sewhan Chun, Dong-Hyun Hwang, Joonsang Yu
The recent segmentation foundation model, Segment Anything Model (SAM), exhibits strong zero-shot segmentation capabilities, but it falls short in generating fine-grained precise masks. To address this limitation, we propose a novel zero-shot image matting model, called ZIM, with two key contributions: First, we develop a label converter that transforms segmentation labels into detailed matte labels, constructing the new SA1B-Matte dataset without costly manual annotations. Training SAM with this dataset enables it to generate precise matte masks while maintaining its zero-shot capability. Second, we design the zero-shot matting model equipped with a hierarchical pixel decoder to enhance mask representation, along with a prompt-aware masked attention mechanism to improve performance by enabling the model to focus on regions specified by visual prompts. We evaluate ZIM using the newly introduced MicroMat-3K test set, which contains high-quality micro-level matte labels. Experimental results show that ZIM outperforms existing methods in fine-grained mask generation and zero-shot generalization. Furthermore, we demonstrate the versatility of ZIM in various downstream tasks requiring precise masks, such as image inpainting and 3D NeRF. Our contributions provide a robust foundation for advancing zero-shot matting and its downstream applications across a wide range of computer vision tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/naver-ai/ZIM.
最近的分割基础模型Segment Anything Model(SAM)展现出强大的零样本分割能力,但在生成精细粒度精确蒙版方面存在不足。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种新型零样本图像抠图模型ZIM,其主要贡献有两点:首先,我们开发了一种标签转换器,能够将分割标签转换为详细的蒙版标签,从而构建无需昂贵手动注释的新SA1B-Matte数据集。使用该数据集对SAM进行训练,可以在保持其零样本能力的同时,生成精确的蒙版。其次,我们设计了一个配备分层像素解码器的零样本抠图模型,以增强蒙版表示,同时设计了一种提示感知的掩码注意机制,通过使模型关注视觉提示指定的区域来提高性能。我们使用新引入的MicroMat-3K测试集对ZIM进行了评估,该测试集包含高质量的微观级别蒙版标签。实验结果表明,ZIM在精细粒度蒙版生成和零样本泛化方面优于现有方法。此外,我们展示了ZIM在各种需要精确蒙版的下游任务中的通用性,如图像补全和3D NeRF。我们的贡献为推进零样本抠图及其在各种计算机视觉任务中的下游应用提供了坚实的基础。代码可访问https://github.com/naver-ai/ZIM。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 (Highlight)
Summary
一种新型的零样本图像抠图模型ZIM被提出,解决了现有模型在精细粒度遮罩生成上的不足。它通过标签转换器和层次化像素解码器等技术,提升了遮罩的生成精度和零样本泛化能力。ZIM模型在MicroMat-3K测试集上的表现优于现有方法,并展示了在图像修复和3D NeRF等需要精细遮罩的下游任务中的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- ZIM模型解决了SAM在精细粒度遮罩生成上的不足。
- 提出了一种新的标签转换器,将分割标签转换为详细的遮罩标签,构建了SA1B-Matte数据集,无需昂贵的人工注释。
- 通过层次化像素解码器增强遮罩表示,提高生成精细遮罩的能力。
- 引入提示感知的掩码注意机制,根据视觉提示提高模型性能。
- 在MicroMat-3K测试集上表现优于其他方法,展示在多种需要精细遮罩的下游任务中的通用性。
- ZIM模型提升了零样本抠图技术的水平,为计算机视觉任务的广泛应用提供了坚实的基础。
点此查看论文截图