⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-08 更新
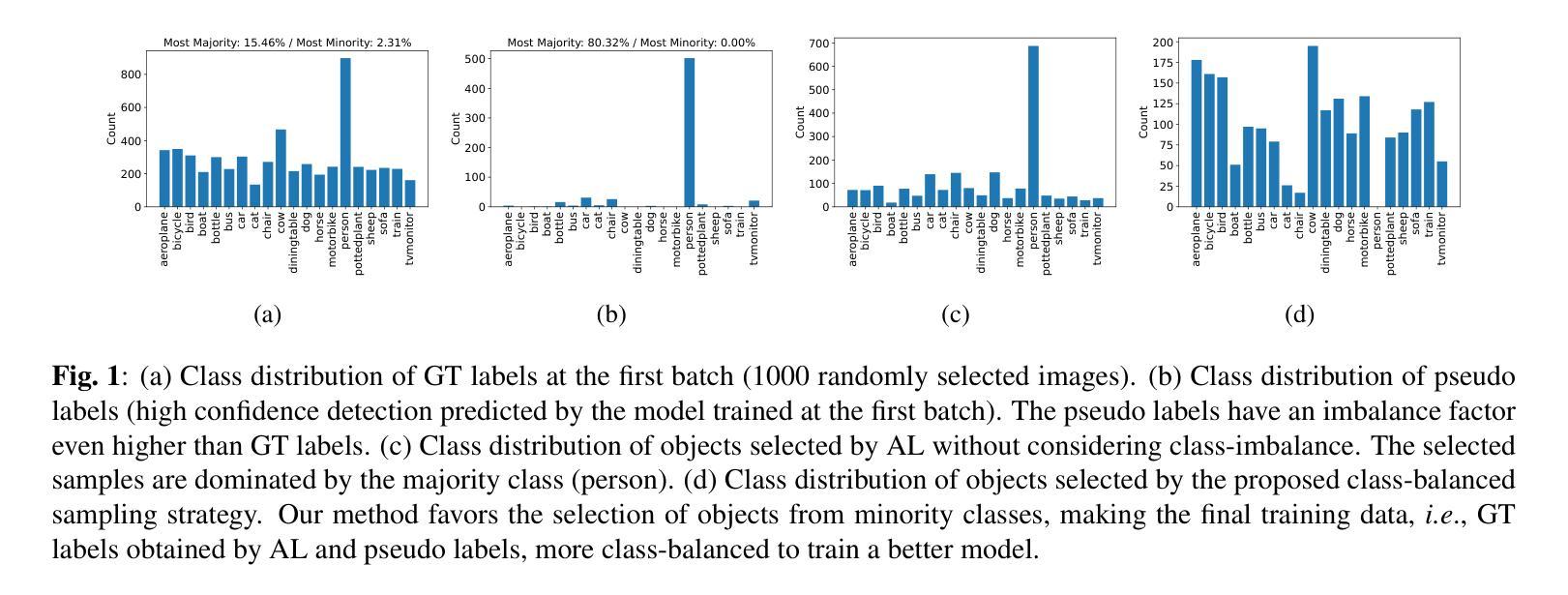
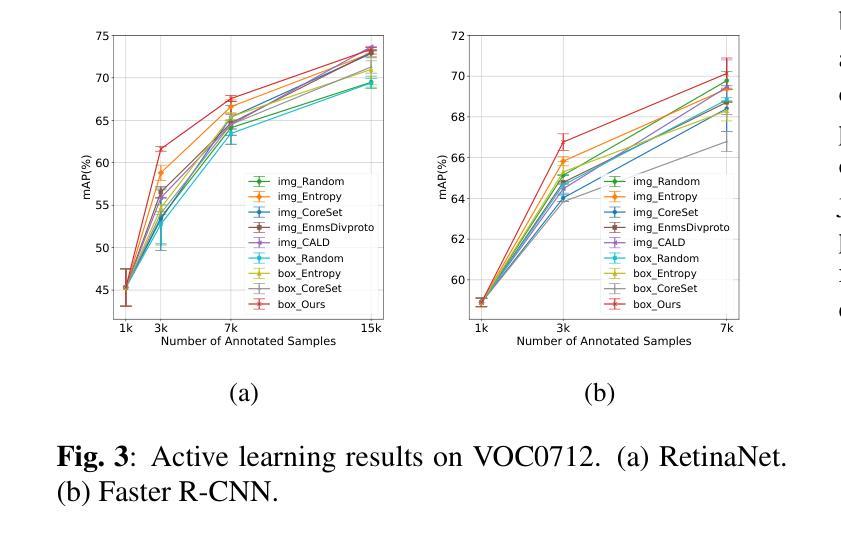
Box-Level Class-Balanced Sampling for Active Object Detection
Authors:Jingyi Liao, Xun Xu, Chuan-Sheng Foo, Lile Cai
Training deep object detectors demands expensive bounding box annotation. Active learning (AL) is a promising technique to alleviate the annotation burden. Performing AL at box-level for object detection, i.e., selecting the most informative boxes to label and supplementing the sparsely-labelled image with pseudo labels, has been shown to be more cost-effective than selecting and labelling the entire image. In box-level AL for object detection, we observe that models at early stage can only perform well on majority classes, making the pseudo labels severely class-imbalanced. We propose a class-balanced sampling strategy to select more objects from minority classes for labelling, so as to make the final training data, \ie, ground truth labels obtained by AL and pseudo labels, more class-balanced to train a better model. We also propose a task-aware soft pseudo labelling strategy to increase the accuracy of pseudo labels. We evaluate our method on public benchmarking datasets and show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
训练深度目标检测器需要大量的边界框标注。主动学习(AL)是一种有望减轻标注负担的技术。对于目标检测进行框级主动学习,即选择最具有信息量的框进行标注,并通过伪标签对稀疏标注的图像进行补充,已被证明比选择和标注整个图像更具成本效益。在目标检测的框级主动学习中,我们观察到早期的模型只能在多数类上表现良好,导致伪标签出现严重的类别不平衡。我们提出了一种类别平衡采样策略,选择更多的少数类别对象进行标注,以使最终的训练数据(即通过主动学习获得的真实标签和伪标签)在类别上更加平衡,从而训练出更好的模型。我们还提出了一种任务感知的软伪标签策略,以提高伪标签的准确性。我们在公共基准数据集上评估了我们的方法,并证明了我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICIP2024
Summary
本文探讨了基于主动学习的目标检测中的盒级采样策略。文章指出,在早期的模型训练中,模型对主要类别的表现较好,导致伪标签出现严重的类别不平衡问题。为解决这一问题,文章提出了类平衡采样策略,旨在选择更多的少数类别目标进行标注,使得最终的训练数据更为平衡。同时,文章还提出了任务感知的软伪标签策略,以提高伪标签的准确性。在公共基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法达到了业界最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习目标检测需要昂贵的边界框标注,主动学习(AL)可减轻标注负担。
- 在目标检测的盒级主动学习中,早期模型对主要类别的表现较好,导致伪标签出现类别不平衡问题。
- 提出类平衡采样策略,选择更多的少数类别目标进行标注,使训练数据更为平衡。
- 提出任务感知的软伪标签策略,提高伪标签的准确性。
- 公开数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性。
- 该方法实现了业界最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图



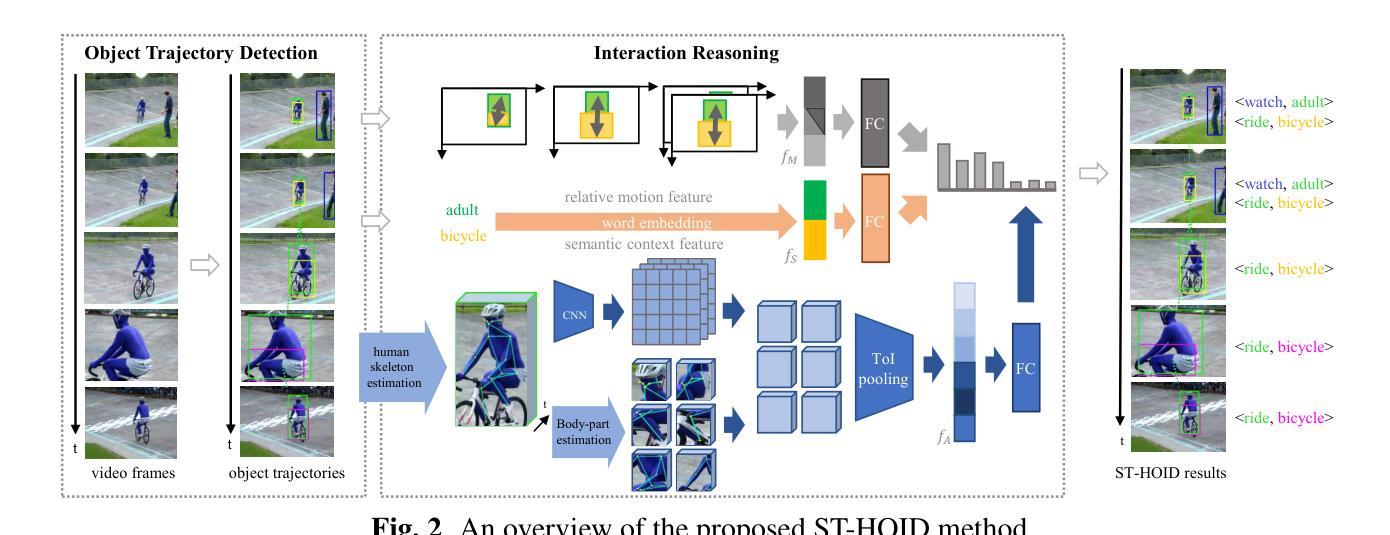
Spatial-Temporal Human-Object Interaction Detection
Authors:Xu Sun, Yunqing He, Tongwei Ren, Gangshan Wu
In this paper, we propose a new instance-level human-object interaction detection task on videos called ST-HOID, which aims to distinguish fine-grained human-object interactions (HOIs) and the trajectories of subjects and objects. It is motivated by the fact that HOI is crucial for human-centric video content understanding. To solve ST-HOID, we propose a novel method consisting of an object trajectory detection module and an interaction reasoning module. Furthermore, we construct the first dataset named VidOR-HOID for ST-HOID evaluation, which contains 10,831 spatial-temporal HOI instances. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of our method. The experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms the baselines generated by the state-of-the-art methods of image human-object interaction detection, video visual relation detection and video human-object interaction recognition.
本文提出了一种新的视频实例级人-物交互检测任务,称为ST-HOID。该任务旨在区分精细的人-物交互(HOI)以及主体和物体的轨迹。其动机在于,人-物交互对于以人类为中心的视频内容理解至关重要。为解决ST-HOID,我们提出了一种新方法,包括物体轨迹检测模块和交互推理模块。此外,我们构建了用于ST-HOID评估的第一个数据集VidOR-HOID,其中包含10831个时空人-物交互实例。我们进行了大量实验来评估我们的方法的有效性。实验结果表明,我们的方法在图像人-物交互检测、视频视觉关系检测和视频人-物交互识别等现有技术的基础上取得了优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的视频实例级人机交互检测任务——ST-HOID,旨在精细区分视频中的人机交互(HOI)以及主体和对象的轨迹。为解决ST-HOID,提出了一种由目标轨迹检测模块和交互推理模块组成的新方法。同时构建了首个用于ST-HOID评估的VidOR-HOID数据集,包含10,831个时空人机交互实例。实验证明,该方法优于图像人机交互检测、视频视觉关系检测和视频人机交互识别的最新基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的视频实例级人机交互检测任务——ST-HOID。
- ST-HOID旨在精细区分视频中的人机交互以及主体和对象的轨迹。
- 提出了一个由目标轨迹检测模块和交互推理模块组成的新方法来解决ST-HOID任务。
- 构建了首个用于ST-HOID评估的VidOR-HOID数据集。
- VidOR-HOID数据集包含大量的时空人机交互实例。
- 实验证明,该方法在性能上超越了现有的最新基线方法。
点此查看论文截图





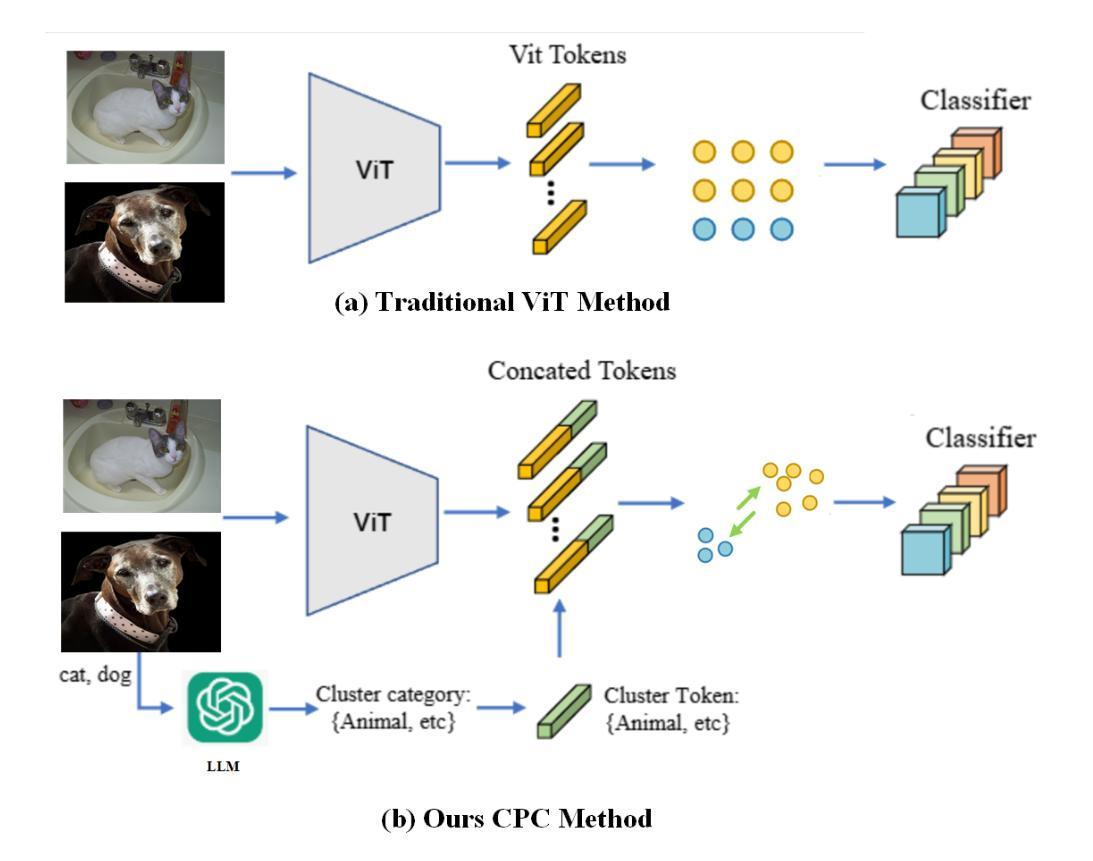
Contrastive Prompt Clustering for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowen Ma, Wenqiao Zhang, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels has gained attention for its cost-effectiveness. Most existing methods emphasize inter-class separation, often neglecting the shared semantics among related categories and lacking fine-grained discrimination. To address this, we propose Contrastive Prompt Clustering (CPC), a novel WSSS framework. CPC exploits Large Language Models (LLMs) to derive category clusters that encode intrinsic inter-class relationships, and further introduces a class-aware patch-level contrastive loss to enforce intra-class consistency and inter-class separation. This hierarchical design leverages clusters as coarse-grained semantic priors while preserving fine-grained boundaries, thereby reducing confusion among visually similar categories. Experiments on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 demonstrate that CPC surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in WSSS.
利用图像级标签进行弱监督语义分割(WSSS)因其成本效益而备受关注。大多数现有方法强调类间分离,往往忽略了相关类别之间的共享语义,且缺乏精细的粒度鉴别。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了对比提示聚类(CPC),这是一种新型的WSSS框架。CPC利用大型语言模型(LLM)来推导编码类间内在关系的类别聚类,并进一步引入了一种类感知的补丁级对比损失,以加强类内一致性和类间分离。这种层次化的设计利用聚类作为粗粒度的语义先验,同时保留精细的边界,从而减少视觉上相似类别之间的混淆。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014上的实验表明,CPC超越了现有的弱监督语义分割的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注弱监督语义分割(WSSS)问题,提出一种名为对比提示聚类(CPC)的新框架。该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)推导类别聚类,并引入类感知补丁级对比损失,以加强类内一致性和类间分离。CPC的层次设计利用聚类作为粗粒度语义先验,同时保留精细边界,减少视觉相似类别之间的混淆。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014上的实验表明,CPC在WSSS领域超越了现有先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)问题受到关注,因其在仅使用图像级标签的情况下具有成本效益。
- 现有方法往往忽视类别间的共享语义,缺乏精细粒度鉴别。
- 提出新的WSSS框架——对比提示聚类(CPC)。
- CPC利用大型语言模型(LLM)推导类别聚类,编码内在类别间关系。
- CPC引入类感知补丁级对比损失,以加强类内一致性和类间分离。
- CPC的层次设计利用聚类作为粗粒度语义先验,同时保留精细边界。
点此查看论文截图

DriveIndia: An Object Detection Dataset for Diverse Indian Traffic Scenes
Authors:Rishav Kumar, D. Santhosh Reddy, P. Rajalakshmi
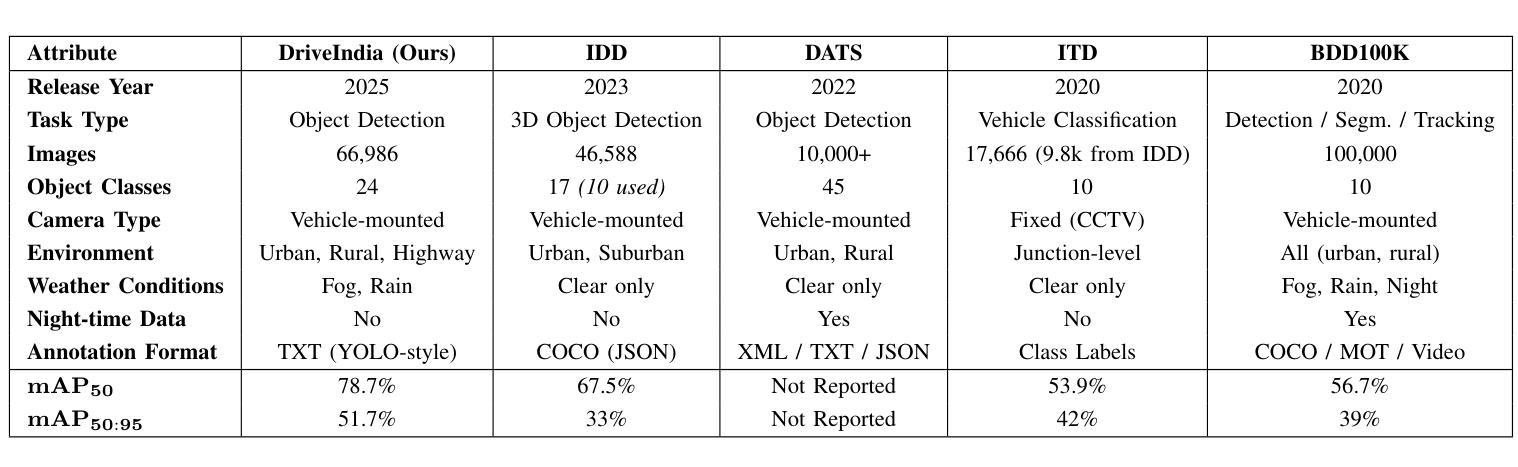
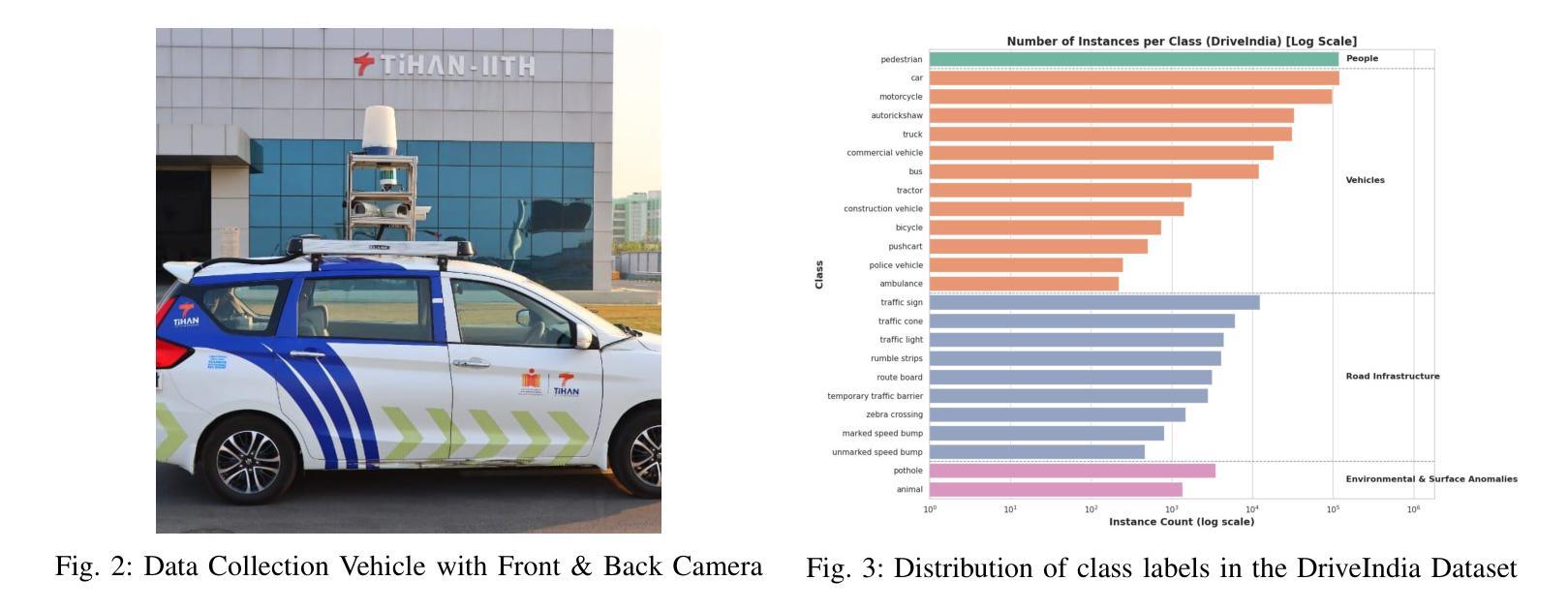
We introduce DriveIndia, a large-scale object detection dataset purpose-built to capture the complexity and unpredictability of Indian traffic environments. The dataset contains 66,986 high-resolution images annotated in YOLO format across 24 traffic-relevant object categories, encompassing diverse conditions such as varied weather (fog, rain), illumination changes, heterogeneous road infrastructure, and dense, mixed traffic patterns and collected over 120+ hours and covering 3,400+ kilometers across urban, rural, and highway routes. DriveIndia offers a comprehensive benchmark for real-world autonomous driving challenges. We provide baseline results using state-of-the-art YOLO family models, with the top-performing variant achieving a mAP50 of 78.7%. Designed to support research in robust, generalizable object detection under uncertain road conditions, DriveIndia will be publicly available via the TiHAN-IIT Hyderabad dataset repository https://tihan.iith.ac.in/TiAND.html (Terrestrial Datasets -> Camera Dataset).
我们介绍了DriveIndia,这是一个专为捕捉印度交通环境的复杂性和不可预测性而构建的大规模物体检测数据集。该数据集包含66,986张高分辨率图像,采用YOLO格式进行标注,涵盖24个与交通相关的物体类别,涉及多种条件,如多变的天气(雾、雨)、光照变化、道路基础设施的多样性以及密集、混合的交通模式,并在超过120小时的时间内,在城市、乡村和高速公路路线等超过3,400公里的距离内收集。DriveIndia为现实世界中的自动驾驶挑战提供了全面的基准测试。我们使用最先进的YOLO家族模型提供基线结果,表现最佳的变体达到50%的mAP(平均准确率)。设计用于支持不确定道路条件下的稳健、通用物体检测研究,DriveIndia将通过TiHAN-印度理工学院海得拉巴数据集存储库公开可用:https://tihan.iith.ac.in/TiAND.html(陆地数据集->相机数据集)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ITSC 2025 Conference. Updated the Table 2 of Benchmark Results
Summary:
介绍了一个名为DriveIndia的大型物体检测数据集,专为捕捉印度交通环境的复杂性和不可预测性而设计。包含6.6万余张高分辨率图像,标注了24个与交通相关的对象类别,涵盖多种条件如不同天气、光照变化、道路基础设施多样以及密集混合的交通模式。该数据集提供YOLO格式的数据基准测试成绩报告。此数据集提供了YOLO家族模型最高表现性能的模型版本实现了一个约为78.7%的mAP50指标,可满足研究复杂条件下的鲁棒通用物体检测的需要。其支持应对不确定路况的研究和一般的物体检测需求,可公开访问的数据库链接是:https://tihan.iith.ac.in/TiAND.html。这是实现自动驾驶的一大突破,值得广泛关注和深入探索。驱动印度项目的建立是一个值得借鉴的例子,为我们展示了在多样化现实环境中实现高性能自动行驶方案的关键方法和技术可能之一。其主要目的就是辅助公众深入理解物联网对于实际应用的需求变化起到了关键的引导作用。让我们对此应用更为深入的挖掘和改进其功能来满足用户的需求和市场环境的多变性问题以体现其功能稳定性不断提升的独特作用和应用价值的推广和完善现有的相关产品以达到智能化的现实生活所拥有产品服务价值的目标。这是一项开创性的工作,对自动驾驶技术的发展具有重要影响。它有助于推动自动驾驶技术在复杂环境中的落地应用,对于提高自动驾驶系统的鲁棒性和安全性具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways:
- DriveIndia是一个针对印度交通环境的大型物体检测数据集,包含超过6万张高分辨率图像,标注了多种交通相关对象类别。
- 数据集涵盖多种条件,包括不同天气、光照变化、道路基础设施多样性和密集混合的交通模式。
点此查看论文截图




Transferring Styles for Reduced Texture Bias and Improved Robustness in Semantic Segmentation Networks
Authors:Ben Hamscher, Edgar Heinert, Annika Mütze, Kira Maag, Matthias Rottmann
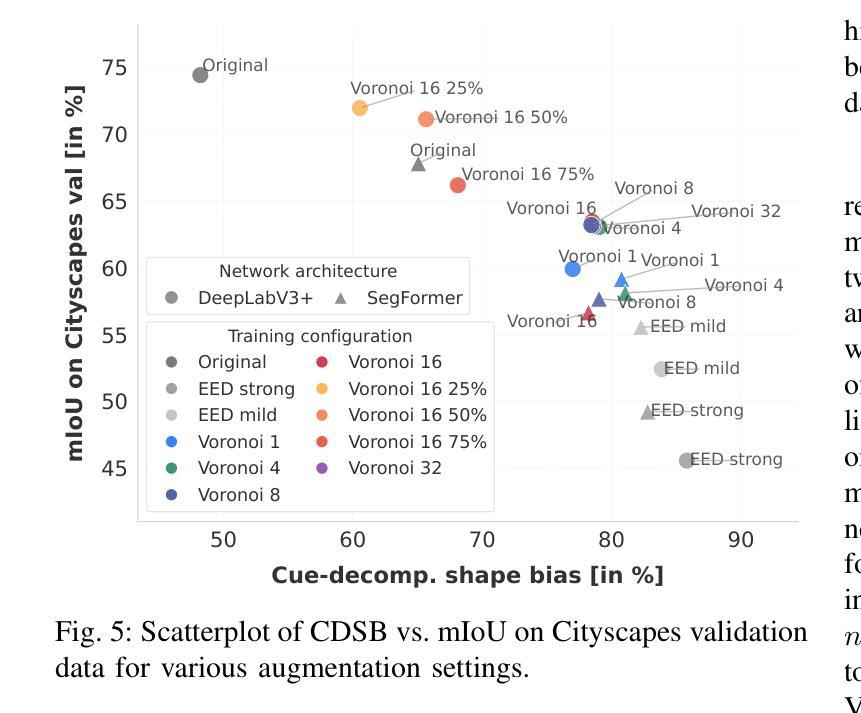
Recent research has investigated the shape and texture biases of deep neural networks (DNNs) in image classification which influence their generalization capabilities and robustness. It has been shown that, in comparison to regular DNN training, training with stylized images reduces texture biases in image classification and improves robustness with respect to image corruptions. In an effort to advance this line of research, we examine whether style transfer can likewise deliver these two effects in semantic segmentation. To this end, we perform style transfer with style varying across artificial image areas. Those random areas are formed by a chosen number of Voronoi cells. The resulting style-transferred data is then used to train semantic segmentation DNNs with the objective of reducing their dependence on texture cues while enhancing their reliance on shape-based features. In our experiments, it turns out that in semantic segmentation, style transfer augmentation reduces texture bias and strongly increases robustness with respect to common image corruptions as well as adversarial attacks. These observations hold for convolutional neural networks and transformer architectures on the Cityscapes dataset as well as on PASCAL Context, showing the generality of the proposed method.
最近的研究已经探讨了深度神经网络(DNN)在图像分类中的形状和纹理偏见,这些偏见会影响其泛化能力和稳健性。研究表明,与常规DNN训练相比,使用风格化图像进行训练减少了图像分类中的纹理偏见,并提高了对图像腐蚀的稳健性。为了推进这一研究领域,我们研究了风格转换是否也能在语义分割中产生这两种效果。为此,我们在人工图像区域之间执行风格转换。这些随机区域由选定数量的Voronoi细胞组成。然后将生成的风格转换数据用于训练语义分割DNN,目的是减少其对纹理线索的依赖,同时增强其对基于形状特征的依赖。在我们的实验中,事实证明,在语义分割中,风格转换增强减少了纹理偏见,并大大提高了对常见图像腐蚀以及对抗性攻击的稳健性。这些观察结果在城市景观数据集和PASCAL Context数据集上的卷积神经网络和转换器架构中都得到了验证,显示了所提出方法的普遍性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted at ECAI 2025
Summary
深度神经网络(DNN)在图像分类中的形状和纹理偏见影响其泛化能力和稳健性。研究表明,与常规DNN训练相比,使用风格化图像进行训练减少了图像分类中的纹理偏见,并提高了对图像腐蚀的稳健性。本研究探索了风格转移是否也能在语义分割中产生这两种效果。通过在不同的人工图像区域进行风格转移,并使用风格转移后的数据训练语义分割DNN,旨在减少其对纹理线索的依赖,同时提高其对基于形状的特征的依赖。实验结果表明,在语义分割中,风格转移增强减少了纹理偏见,并显著提高了对常见图像腐蚀以及对抗性攻击的稳健性。这些观察结果在城市景观数据集和PASCAL Context数据集上的卷积神经网络和转换器架构中都得到了验证,显示了该方法的普遍性。
Key Takeaways
- DNN在图像分类中存在形状和纹理偏见,影响泛化能力和稳健性。
- 与常规DNN训练相比,使用风格化图像训练可提高图像分类的稳健性。
- 风格转移被应用于语义分割,以减少对纹理线索的依赖并提高对形状特征的依赖。
- 风格转移增强在语义分割中减少了纹理偏见。
- 风格转移增强提高了语义分割模型对常见图像腐蚀和对抗性攻击的稳健性。
- 实验结果在城市景观数据集和PASCAL Context数据集上的卷积神经网络和转换器架构中得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图



NOCTIS: Novel Object Cyclic Threshold based Instance Segmentation
Authors:Max Gandyra, Alessandro Santonicola, Michael Beetz
Instance segmentation of novel objects instances in RGB images, given some example images for each object, is a well known problem in computer vision. Designing a model general enough to be employed for all kinds of novel objects without (re-) training has proven to be a difficult task. To handle this, we present a new training-free framework, called: Novel Object Cyclic Threshold based Instance Segmentation (NOCTIS). NOCTIS integrates two pre-trained models: Grounded-SAM 2 for object proposals with precise bounding boxes and corresponding segmentation masks; and DINOv2 for robust class and patch embeddings, due to its zero-shot capabilities. Internally, the proposal-object matching is realized by determining an object matching score based on the similarity of the class embeddings and the average maximum similarity of the patch embeddings with a new cyclic thresholding (CT) mechanism that mitigates unstable matches caused by repetitive textures or visually similar patterns. Beyond CT, NOCTIS introduces: (i) an appearance score that is unaffected by object selection bias; (ii) the usage of the average confidence of the proposals bounding box and mask as a scoring component; and (iii) an RGB-only pipeline that performs even better than RGB-D ones. We empirically show that NOCTIS, without further training/fine tuning, attains state-of-the-art results regarding the mean AP score, w.r.t. the best RGB and RGB-D methods on the seven core datasets of the BOP 2023 challenge for the “Model-based 2D segmentation of unseen objects” task.
在RGB图像中对新型物体实例进行实例分割,给定每个物体的示例图像,这是计算机视觉领域的一个知名问题。设计一种足够通用的模型,可以应用于各种新型物体而无需(重新)训练,已被证明是一项艰巨的任务。为了处理这个问题,我们提出了一种新的无需训练框架,称为:基于循环阈值的新型物体实例分割(NOCTIS)。NOCTIS集成了两个预训练模型:用于生成精确边界框和相应分割掩码的Grounded-SAM 2;以及具有零样本能力的DINOv2,用于生成稳健的类别和补丁嵌入。在内部,通过基于类别嵌入的相似性以及与补丁嵌入的平均最大相似性的对象匹配分数来实现提案对象匹配,采用新的循环阈值(CT)机制来缓解由重复纹理或视觉相似模式引起的不稳定匹配。除了CT,NOCTIS还引入了:(i)一种不受对象选择偏见影响的外观分数;(ii)使用提案边界框和掩码的平均置信度作为评分组件;(iii)仅使用RGB的管道,其性能甚至优于RGB-D管道。我们通过实验证明,NOCTIS无需进一步的训练或微调,即可在BOP 2023挑战的七个核心数据集上,针对“未见物体的基于模型的二维分割”任务,达到最先进的平均准确率(mean AP score)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures, 5 tables, ICLR 2026 preprint
Summary
本文介绍了一种无需训练的新型物体实例分割框架——NOCTIS。它通过集成Grounded-SAM 2和DINOv2两个预训练模型,利用循环阈值机制实现对象提案匹配,引入外观评分并优化评分组件,从而在仅使用RGB图像的情况下达到甚至超越了RGB-D方法的效果。在BOP 2023挑战的七个核心数据集上,NOCTIS在“未见物体的模型基础二维分割”任务中达到了最先进的平均精度(mean AP score)。
Key Takeaways
- NOCTIS是一种无需训练的新型物体实例分割框架。
- 集成Grounded-SAM 2和DINOv2两个预训练模型实现精准的对象提案匹配。
- 通过循环阈值机制(CT)处理因重复纹理或相似模式导致的不稳定匹配问题。
- 引入外观评分,不受对象选择偏见的影响。
- 使用提案的边界框和遮罩的平均置信度作为评分组件。
- NOCTIS在仅使用RGB图像的情况下表现优异,甚至超越RGB-D方法。
点此查看论文截图



Egocentric Human-Object Interaction Detection: A New Benchmark and Method
Authors:Kunyuan Deng, Yi Wang, Lap-Pui Chau
Egocentric human-object interaction (Ego-HOI) detection is crucial for intelligent agents to understand and assist human activities from a first-person perspective. However, progress has been hindered by the lack of benchmarks and methods tailored to egocentric challenges such as severe hand-object occlusion. In this paper, we introduce the real-world Ego-HOI detection task and the accompanying Ego-HOIBench, a new dataset with over 27K egocentric images and explicit, fine-grained hand-verb-object triplet annotations across 123 categories. Ego-HOIBench covers diverse daily scenarios, object types, and both single- and two-hand interactions, offering a comprehensive testbed for Ego-HOI research. Benchmarking existing third-person HOI detectors on Ego-HOIBench reveals significant performance gaps, highlighting the need for egocentric-specific solutions. To this end, we propose Hand Geometry and Interactivity Refinement (HGIR), a lightweight, plug-and-play scheme that leverages hand pose and geometric cues to enhance interaction representations. Specifically, HGIR explicitly extracts global hand geometric features from the estimated hand pose proposals, and further refines interaction features through pose-interaction attention, enabling the model to focus on subtle hand-object relationship differences even under severe occlusion. HGIR significantly improves Ego-HOI detection performance across multiple baselines, achieving new state-of-the-art results on Ego-HOIBench. Our dataset and method establish a solid foundation for future research in egocentric vision and human-object interaction understanding. Project page: https://dengkunyuan.github.io/EgoHOIBench/
以自我为中心的与物体交互(Ego-HOI)检测对于智能主体从第一人称视角理解和辅助人类活动至关重要。然而,由于缺乏针对以自我为中心挑战的基准和方法,如手部与物体的严重遮挡等,进展一直受到阻碍。在本文中,我们介绍了现实世界中的Ego-HOI检测任务以及配套使用的Ego-HOIBench数据集。Ego-HOIBench包含超过2.7万张以自我为中心的图片,包含手、动词和对象三方面的详细标注信息,涉及日常场景和多种类型的物体及交互场景。它为Ego-HOI研究提供了一个全面的测试平台。对现有第三人称HOI检测器在Ego-HOIBench上的基准测试表明存在显著的性能差距,这突显了对特定于以自我为中心解决方案的需求。为此,我们提出了手几何和交互细化(HGIR)网络框架是一种轻量级且即插即用的方案,利用手势和几何线索增强交互表示。具体来说,HGIR从估计的手部姿态提案中明确提取全局手部几何特征,并通过姿态交互注意力进一步细化交互特征,使模型即使在严重遮挡下也能关注手部与物体之间微妙的关系差异。HGIR显著提高了多个基线任务的Ego-HOI检测性能,并在Ego-HOIBench上取得了最新的最佳结果。我们的数据集和方法为未来的以自我为中心的视觉和人与物体交互理解研究奠定了坚实的基础。项目页面:https://dengkunyuan.github.io/EgoHOIBench/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了面向第一人称视角的以人为中心的人与物体交互(Ego-HOI)检测任务的重要性,并针对缺乏针对第一人称视角的挑战性数据集的问题,推出了新的数据集Ego-HOIBench。该数据集包含超过27K张以自我为中心的图像和详细的精细标注的手-动词-物体三元组注释。此外,本文还提出了一种针对Ego-HOI检测任务的新方法Hand Geometry and Interactivity Refinement(HGIR),该方法利用手势和几何线索来增强交互表示,显著提高Ego-HOI检测性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 介绍了面向第一人称视角的以人为中心的人与物体交互(Ego-HOI)检测任务的重要性。
- 缺乏针对第一人称视角挑战的基准数据集是研究的瓶颈。
- 推出了新的数据集Ego-HOIBench,包含超过27K张以自我为中心的图像和详细的精细标注。
- 现有第三人称HOI检测器在Ego-HOIBench上的性能存在显著差距,需要针对第一人称视角的特定解决方案。
- 提出了Hand Geometry and Interactivity Refinement(HGIR)方法,利用手势和几何线索增强交互表示。
- HGIR通过提取手部全局几何特征和姿势交互注意力,即使在严重遮挡下也能关注手部与物体的微妙关系差异。
- HGIR在多个基准测试上显著提高了Ego-HOI检测性能,并在Ego-HOIBench上取得了最新结果。
点此查看论文截图




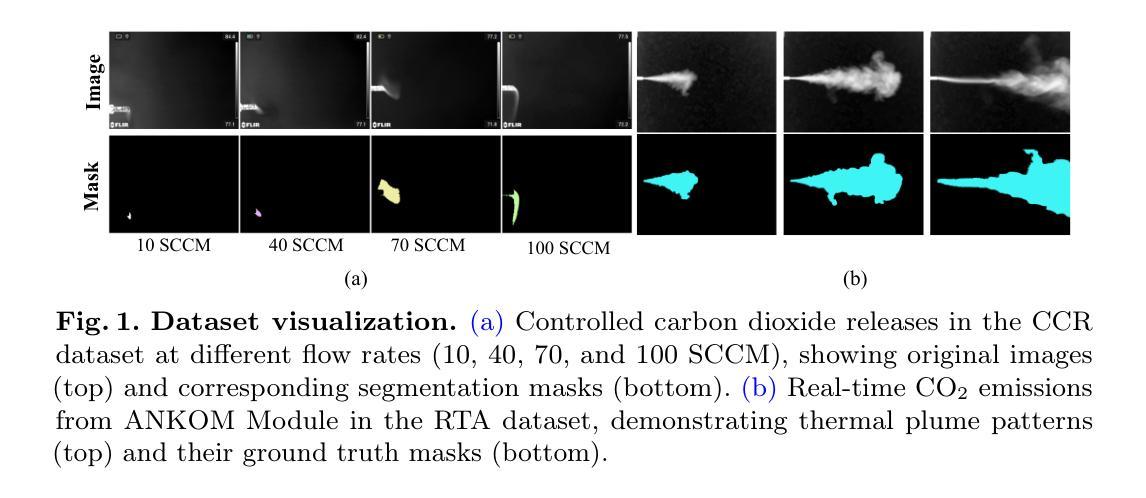
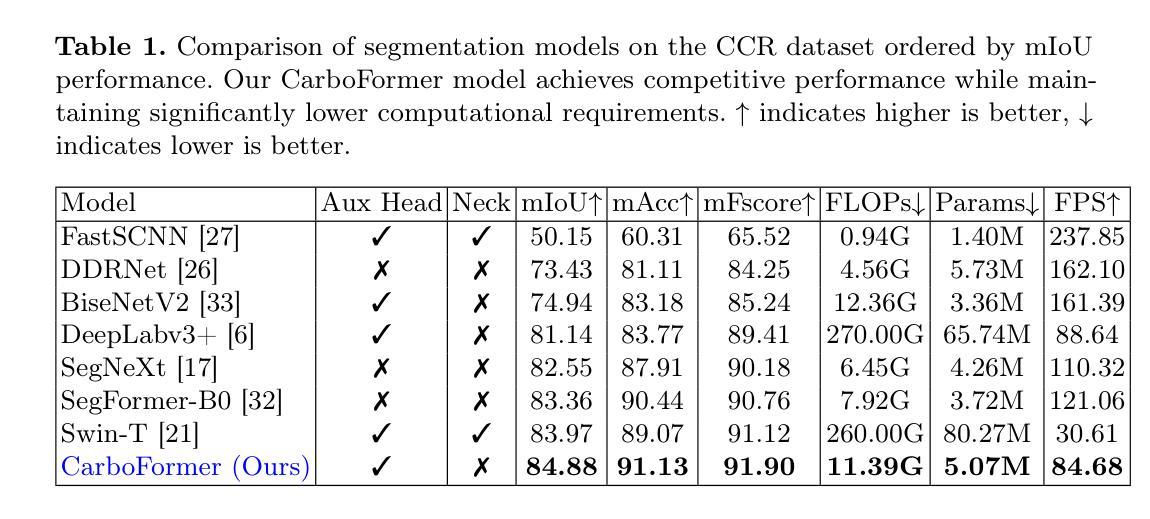
CarboFormer: A Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Architecture for Efficient Carbon Dioxide Detection Using Optical Gas Imaging
Authors:Taminul Islam, Toqi Tahamid Sarker, Mohamed G Embaby, Khaled R Ahmed, Amer AbuGhazaleh
Carbon dioxide (CO$_2$) emissions are critical indicators of both environmental impact and various industrial processes, including livestock management. We introduce CarboFormer, a lightweight semantic segmentation framework for Optical Gas Imaging (OGI), designed to detect and quantify CO$_2$ emissions across diverse applications. Our approach integrates an optimized encoder-decoder architecture with specialized multi-scale feature fusion and auxiliary supervision strategies to effectively model both local details and global relationships in gas plume imagery while achieving competitive accuracy with minimal computational overhead for resource-constrained environments. We contribute two novel datasets: (1) the Controlled Carbon Dioxide Release (CCR) dataset, which simulates gas leaks with systematically varied flow rates (10-100 SCCM), and (2) the Real Time Ankom (RTA) dataset, focusing on emissions from dairy cow rumen fluid in vitro experiments. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that CarboFormer achieves competitive performance with 84.88% mIoU on CCR and 92.98% mIoU on RTA, while maintaining computational efficiency with only 5.07M parameters and operating at 84.68 FPS. The model shows particular effectiveness in challenging low-flow scenarios and significantly outperforms other lightweight methods like SegFormer-B0 (83.36% mIoU on CCR) and SegNeXt (82.55% mIoU on CCR), making it suitable for real-time monitoring on resource-constrained platforms such as programmable drones. Our work advances both environmental sensing and precision livestock management by providing robust and efficient tools for CO$_2$ emission analysis.
二氧化碳(CO2)排放是环境影响和各种工业过程(包括牲畜管理)的关键指标。我们介绍了CarboFormer,这是一个用于光学气体成像(OGI)的轻量级语义分割框架,旨在检测并量化各种应用中CO2的排放量。我们的方法整合了优化的编码器-解码器架构,具有多尺度特征融合和辅助监督策略,以有效地对气体喷射图像中的局部细节和全局关系进行建模,同时在资源受限的环境中实现具有竞争力的准确性和最小的计算开销。我们贡献了两个新颖的数据集:(1)控制二氧化碳排放(CCR)数据集,模拟系统变化的气流率(10-100 SCCM)下的气体泄漏;(2)实时安科姆(RTA)数据集,专注于体外实验中奶牛瘤胃流体的排放。全面评估表明,CarboFormer在CCR上实现了具有竞争力的性能,达到84.88%的mIoU,在RTA上达到92.98%的mIoU,同时保持计算效率,仅有5.07M参数,运行速度为每秒84.68帧。该模型在具有挑战性的低流量场景中表现出卓越的效果,并且显著优于其他轻量级方法,如SegFormer-B0(CCR上为83.36%的mIoU)和SegNeXt(CCR上为82.55%的mIoU)。因此,它适合在资源受限的平台(如可编程无人机)上进行实时监视。我们的工作通过提供用于CO2排放分析的稳健和高效工具,推动了环境感知和精确牲畜管理的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了CarboFormer,一个为光学气体成像(OGI)设计的轻量级语义分割框架,用于检测并量化CO₂排放,适用于多种应用。该框架整合了优化后的编码器-解码器架构,采用多尺度特征融合和辅助监督策略,有效建模气体云团影像中的局部细节和全局关系,同时在资源受限环境中实现具有竞争力的精度和较低的计算开销。文章贡献了两个新数据集:控制二氧化碳释放(CCR)数据集和实时安科姆(RTA)数据集。评估表明,CarboFormer在CCR上实现了84.88%的mIoU,在RTA上实现了92.98%的mIoU,同时保持计算效率,仅有5.07M参数,运行速度为84.68 FPS。该模型在挑战性的低流量场景中表现优异,显著优于其他轻量级方法,适合在资源受限的平台(如可编程无人机)上进行实时监测。本文的工作为二氧化碳排放分析和精准畜牧业管理提供了稳健高效的工具,推动了环境感知和精准畜牧业的发展。
关键见解
- CarboFormer是一个针对光学气体成像的轻量级语义分割框架,用于检测和量化CO₂排放。
- 框架整合了优化后的编码器-解码器架构,并结合多尺度特征融合和辅助监督策略。
- 贡献了两个新数据集:CCR和RTA,分别模拟系统变化流率和奶牛体内发酵实验中的气体排放。
- CarboFormer在CCR和RTA数据集上分别实现了84.88%和92.98%的mIoU,表现出色。
- 模型在资源受限的环境中具有计算效率和实时性能,适合在可编程无人机等平台上进行实时监测。
- 模型在挑战性的低流量场景中表现优异,显著优于其他轻量级方法。
点此查看论文截图


Advancing Marine Research: UWSAM Framework and UIIS10K Dataset for Precise Underwater Instance Segmentation
Authors:Hua Li, Shijie Lian, Zhiyuan Li, Runmin Cong, Chongyi Li, Laurence T. Yang, Weidong Zhang, Sam Kwong
With recent breakthroughs in large-scale modeling, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated significant potential in a variety of visual applications. However, due to the lack of underwater domain expertise, SAM and its variants face performance limitations in end-to-end underwater instance segmentation tasks, while their higher computational requirements further hinder their application in underwater scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a large-scale underwater instance segmentation dataset, UIIS10K, which includes 10,048 images with pixel-level annotations for 10 categories. Then, we introduce UWSAM, an efficient model designed for automatic and accurate segmentation of underwater instances. UWSAM efficiently distills knowledge from the SAM ViT-Huge image encoder into the smaller ViT-Small image encoder via the Mask GAT-based Underwater Knowledge Distillation (MG-UKD) method for effective visual representation learning. Furthermore, we design an End-to-end Underwater Prompt Generator (EUPG) for UWSAM, which automatically generates underwater prompts instead of explicitly providing foreground points or boxes as prompts, thus enabling the network to locate underwater instances accurately for efficient segmentation. Comprehensive experimental results show that our model is effective, achieving significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods on multiple underwater instance datasets. Datasets and codes are available at https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K.
随着大规模建模的最新突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在各种视觉应用中表现出了巨大的潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中面临性能局限,而它们较高的计算要求进一步阻碍了在水下场景中的应用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,其中包括10,048张具有像素级注释的10类图像。接着,我们介绍了专为水下实例自动准确分割而设计的UWSAM模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器提炼知识,并将其运用到较小的ViT-Small图像编码器上,以实现有效的视觉表征学习。此外,我们为UWSAM设计了端到端的水下提示生成器(EUPG),它会自动生成水下提示,而不是显式提供前景点或框作为提示,从而使网络能够准确定位水下实例,以实现高效的分割。综合实验结果表明,我们的模型非常有效,在多个水下实例数据集上实现了对最先进方法显著的性能改进。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随着大规模建模的突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在多种视觉应用中展现出巨大潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中的性能受到限制。为此,我们提出了大规模的水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,并介绍了为水下实例自动准确分割而设计的UWSAM模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器提炼知识,用于更有效的视觉表征学习。我们还为UWSAM设计了端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG),能够自动生成水下提示,而非明确提供前景点或框,从而使网络能够准确定位水下实例,实现高效分割。
Key Takeaways:
- SAM在视觉应用中有巨大潜力,但在水下实例分割任务中因缺乏水下领域专业知识而受限。
- 提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,包含10,048张具有像素级注释的图像,涉及10个类别。
- 介绍了为水下实例分割而设计的UWSAM模型,该模型通过知识蒸馏技术提高性能。
- UWSAM使用基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,从大型图像编码器提炼知识,用于更有效的视觉表征学习。
- 引入了端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG),能够自动生成水下提示,提高网络定位水下实例的准确性。
- UWSAM在多个水下实例数据集上实现了对最新技术的显著性能改进。
点此查看论文截图





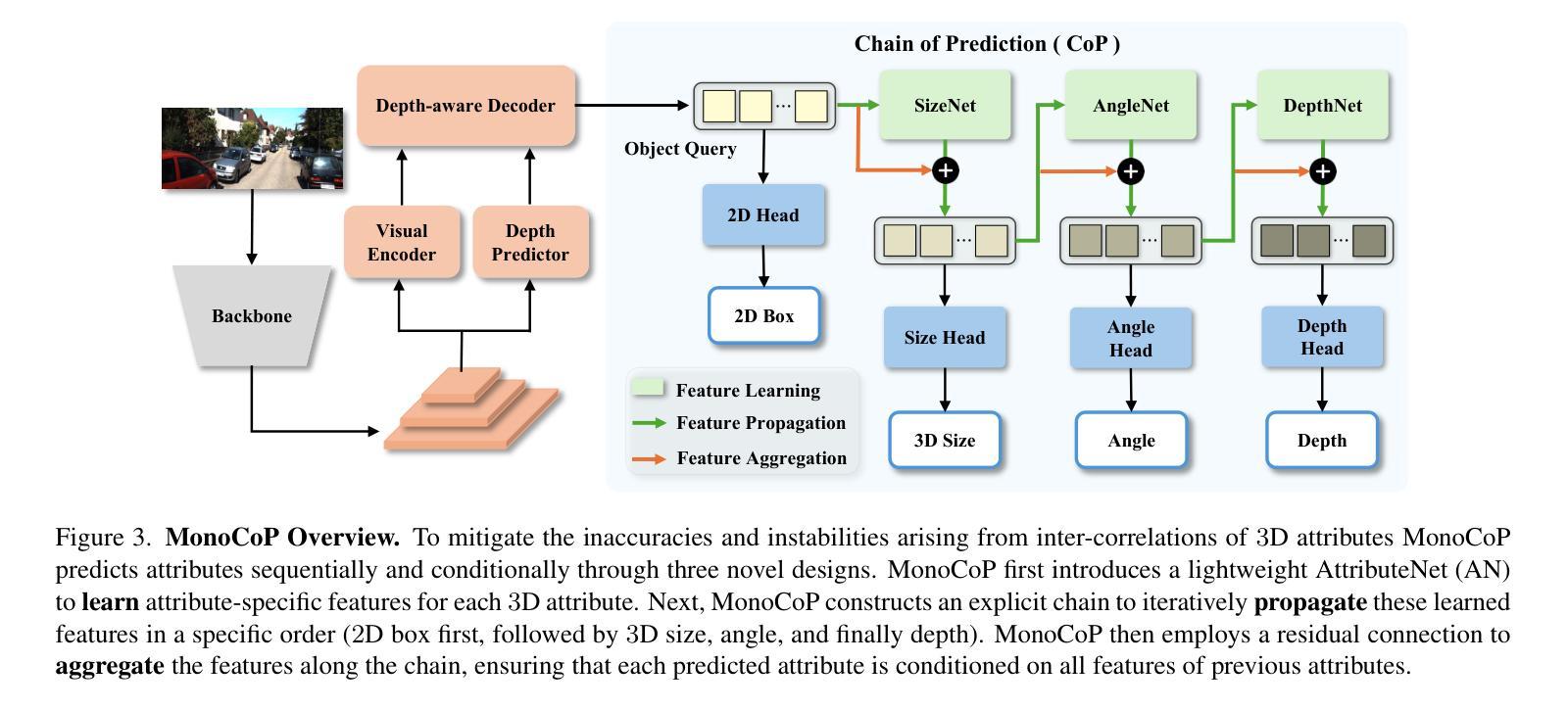
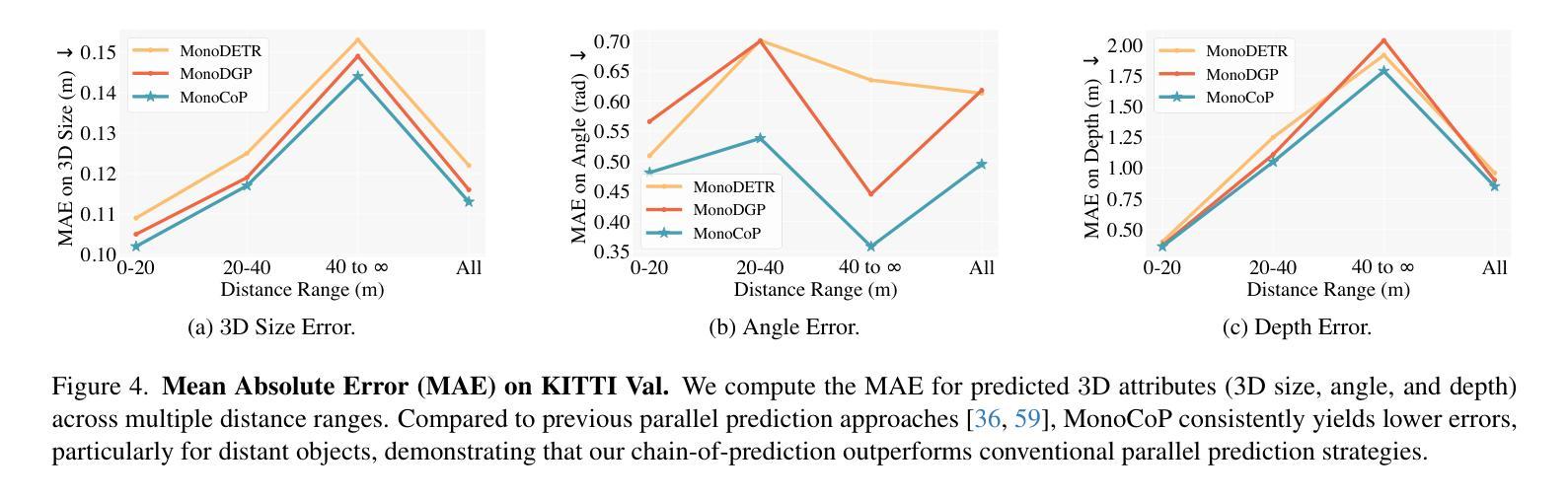
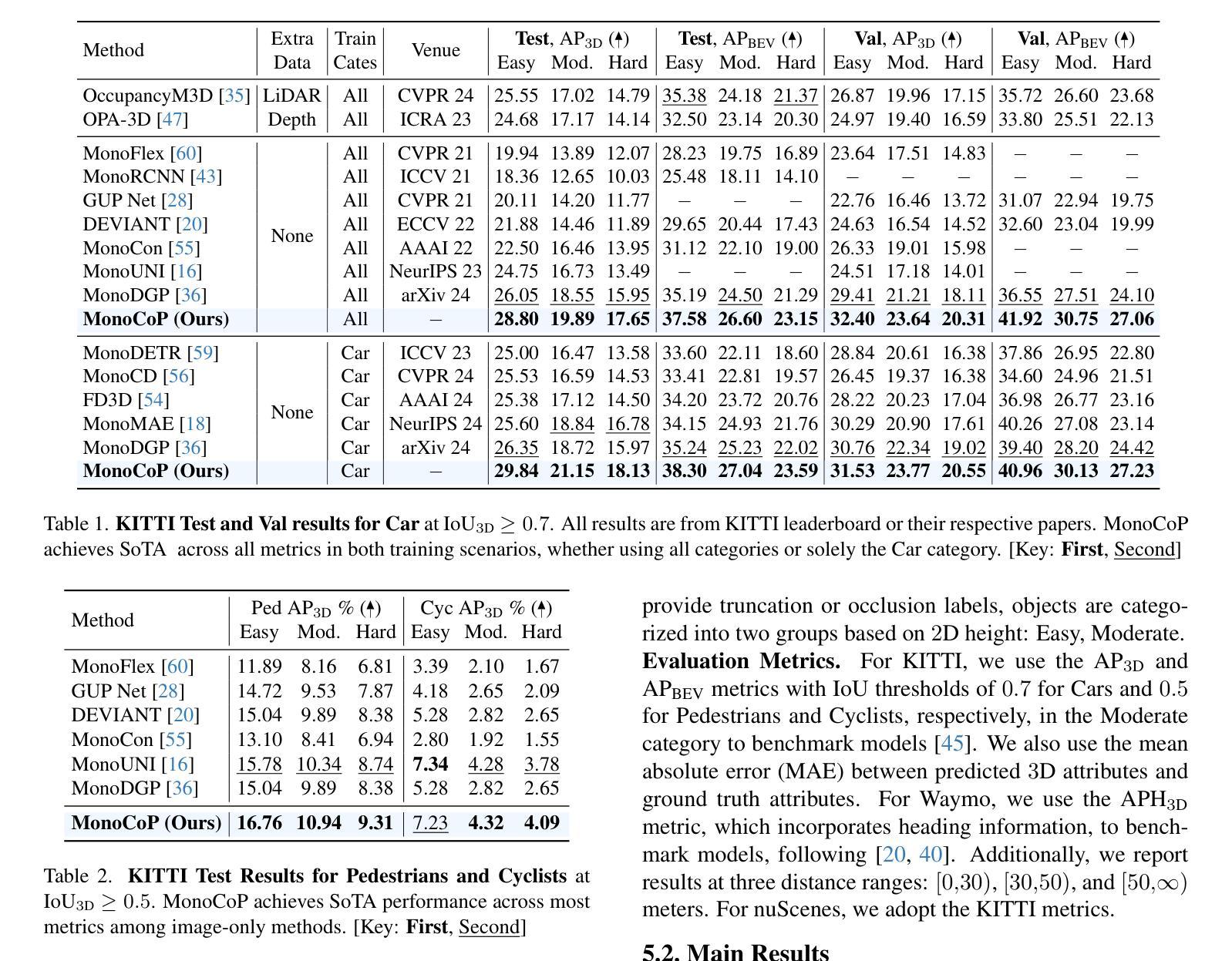
MonoCoP: Chain-of-Prediction for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Authors:Zhihao Zhang, Abhinav Kumar, Girish Chandar Ganesan, Xiaoming Liu
Accurately predicting 3D attributes is crucial for monocular 3D object detection (Mono3D), with depth estimation posing the greatest challenge due to the inherent ambiguity in mapping 2D images to 3D space. While existing methods leverage multiple depth cues (e.g., estimating depth uncertainty, modeling depth error) to improve depth accuracy, they overlook that accurate depth prediction requires conditioning on other 3D attributes, as these attributes are intrinsically inter-correlated through the 3D to 2D projection, which ultimately limits overall accuracy and stability. Inspired by Chain-of-Thought (CoT) in large language models (LLMs), this paper proposes MonoCoP, which leverages a Chain-of-Prediction (CoP) to predict attributes sequentially and conditionally via three key designs. First, it employs a lightweight AttributeNet (AN) for each 3D attribute to learn attribute-specific features. Next, MonoCoP constructs an explicit chain to propagate these learned features from one attribute to the next. Finally, MonoCoP uses a residual connection to aggregate features for each attribute along the chain, ensuring that later attribute predictions are conditioned on all previously processed attributes without forgetting the features of earlier ones. Experimental results show that our MonoCoP achieves state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance on the KITTI leaderboard without requiring additional data and further surpasses existing methods on the Waymo and nuScenes frontal datasets.
准确预测3D属性对于单目3D对象检测(Mono3D)至关重要,深度估计则是最大的挑战,因为将2D图像映射到3D空间存在固有的不确定性。虽然现有方法利用多种深度线索(例如估计深度不确定性、建模深度误差)来提高深度准确性,但它们忽略了准确的深度预测需要依赖于其他3D属性,因为这些属性通过3D到2D的投影固有地相互关联,这最终限制了总体准确性和稳定性。本文受到大型语言模型(LLMs)中的思维链(CoT)的启发,提出了MonoCoP方法,它利用预测链(CoP)来按顺序和有条件地预测属性,主要通过三个关键设计实现。首先,它为每个3D属性采用轻量级的AttributeNet(AN)来学习特定于属性的特征。接下来,MonoCoP构建了一个明确的链条来传播从一个属性学习到的特征到下一个属性。最后,MonoCoP使用残差连接来沿链条聚合每个属性的特征,确保后续属性预测依赖于所有先前处理的属性,同时不会忘记早期属性的特征。实验结果表明,我们的MonoCoP在KITTI排行榜上达到了最新技术水平,并且无需额外数据,在Waymo和nuScenes正面数据集上超过了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF I plan to re-format and re-write this paper
Summary
本文提出一种基于Chain-of-Prediction(CoP)的单眼三维物体检测(Mono3D)方法。它通过对多个三维属性进行序列预测和条件预测,提高了深度估计的准确性。通过构建显式链传播特定特征,并利用残差连接确保后续属性预测基于所有先前处理过的属性,提高了整体准确性和稳定性。在KITTI、Waymo和nuScenes数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- MonoCoP方法利用Chain-of-Prediction(CoP)进行三维属性预测,以提高深度估计的准确性。
- 通过构建显式链传播特定特征,每个三维属性都有对应的AttributeNet(AN)来学习属性特定特征。
- MonoCoP通过残差连接确保后续属性预测基于所有先前处理过的属性,从而提高整体准确性。
- 与现有方法相比,MonoCoP在KITTI、Waymo和nuScenes数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
- 该方法不依赖额外数据,具有广泛的应用前景。
- MonoCoP强调了三维属性之间的内在联系,通过条件预测提高了深度估计的准确性。
点此查看论文截图


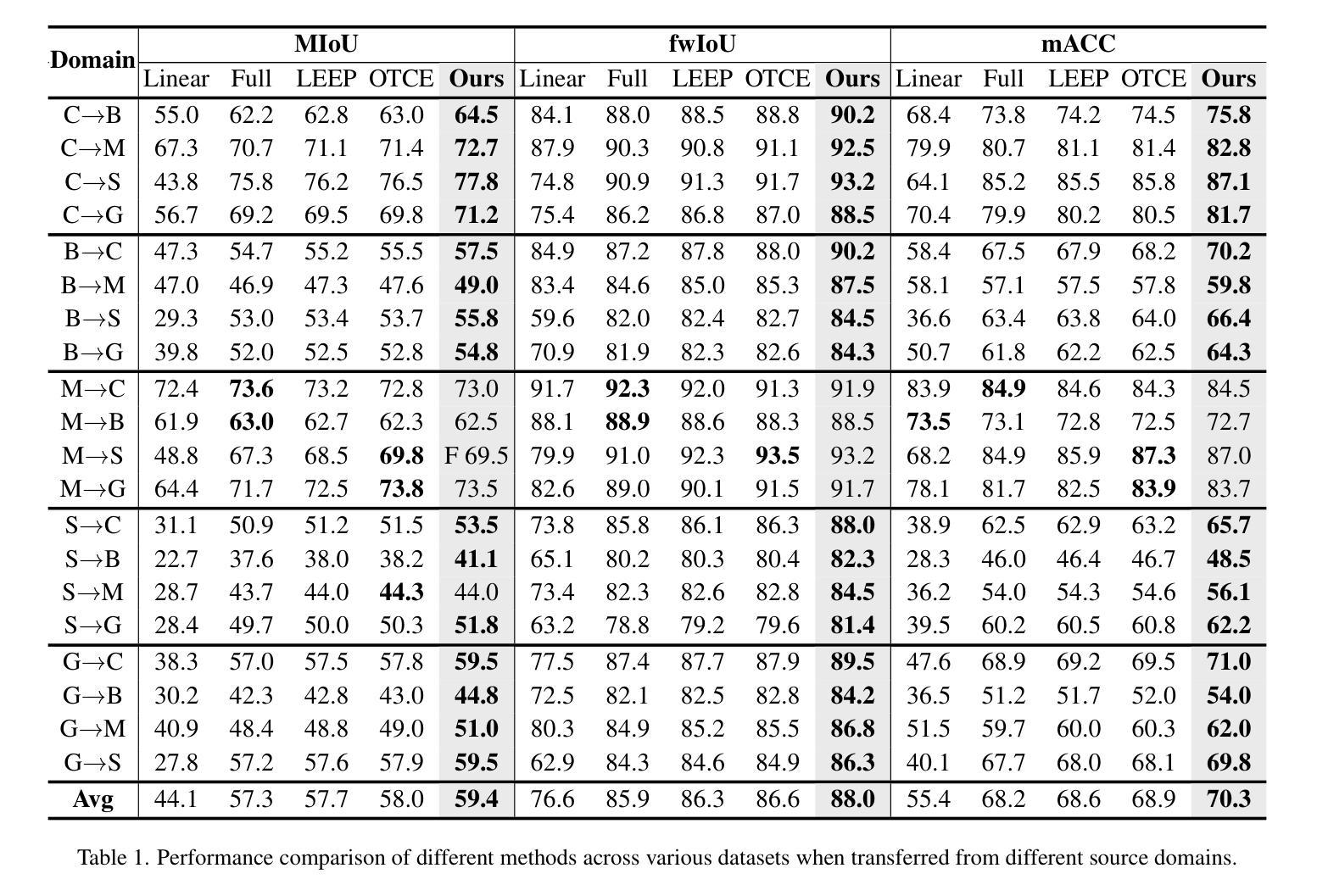
Transferable Mask Transformer: Cross-domain Semantic Segmentation with Region-adaptive Transferability Estimation
Authors:Jianhua Liu, Zhengyu Li, Yanru Wu, Jingge Wang, Yang Tan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guan Wang, Yang Li
Recent advances in Vision Transformers (ViTs) have set new benchmarks in semantic segmentation. However, when adapting pretrained ViTs to new target domains, significant performance degradation often occurs due to distribution shifts, resulting in suboptimal global attention. Since self-attention mechanisms are inherently data-driven, they may fail to effectively attend to key objects when source and target domains exhibit differences in texture, scale, or object co-occurrence patterns. While global and patch-level domain adaptation methods provide partial solutions, region-level adaptation with dynamically shaped regions is crucial due to spatial heterogeneity in transferability across different image areas. We present Transferable Mask Transformer (TMT), a novel region-level adaptation framework for semantic segmentation that aligns cross-domain representations through spatial transferability analysis. TMT consists of two key components: (1) An Adaptive Cluster-based Transferability Estimator (ACTE) that dynamically segments images into structurally and semantically coherent regions for localized transferability assessment, and (2) A Transferable Masked Attention (TMA) module that integrates region-specific transferability maps into ViTs’ attention mechanisms, prioritizing adaptation in regions with low transferability and high semantic uncertainty. Comprehensive evaluations across 20 cross-domain pairs demonstrate TMT’s superiority, achieving an average 2% MIoU improvement over vanilla fine-tuning and a 1.28% increase compared to state-of-the-art baselines. The source code will be publicly available.
关于Vision Transformers(ViTs)的最新进展已经在语义分割领域设定了新的基准。然而,当将预训练的ViTs适应到新目标域时,由于分布转移,往往会出现性能上的显著下降,导致全局注意力不佳。由于自注意力机制本质上是数据驱动的,当源域和目标域在纹理、尺度或对象共现模式上存在差异时,它们可能无法有效地关注关键对象。虽然全局和补丁级别的域适应方法提供了部分解决方案,但由于不同图像区域在转移能力上的空间异质性,动态形状区域的区域级适应至关重要。我们提出了Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT),这是一种用于语义分割的新型区域级适应框架,它通过空间转移能力分析来对齐跨域表示。TMT由两个关键组件构成:(1)基于自适应聚类的转移能力估计器(ACTE),它动态地将图像分割成结构和语义上连贯的区域,以进行局部化的转移能力评估;(2)可转移的掩模注意力(TMA)模块,该模块将区域特定的转移能力图集成到ViTs的注意力机制中,优先适应低转移能力和高语义不确定性的区域。在20个跨域对的综合评估中,TMT的表现卓越,与简单的微调相比,平均提高了2%的MIoU,与最新的基线相比增加了1.28%。源代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对语义分割任务的新型区域级自适应框架——Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT)。该框架通过空间可转移性分析实现对跨域表示的匹配。TMT包含两个关键组件:自适应聚类转移评估器(ACTE)和可转移掩膜注意力模块(TMA)。ACTE动态地将图像分割为结构化和语义连贯的区域,进行局部转移评估;而TMA模块则将区域特定的转移能力图融入ViT的注意力机制中,优先适应低转移能力和高语义不确定性的区域。通过广泛的跨域对比实验验证,TMT相较于基准方法实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs)在语义分割上取得了新的突破,但在目标域适应时面临性能下降问题。
- 自注意力机制在跨域情况下可能无法有效关注关键对象,特别是当源域和目标域在纹理、尺度或对象共现模式上存在差异时。
- 当前的全局和补丁级域适应方法虽然提供了部分解决方案,但区域级适应更为重要。
- Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT)是一个新型区域级适应框架,通过空间可转移性分析实现跨域表示的匹配。
- TMT包含两个关键组件:ACTE和TMA,分别用于动态区域分割和融入ViT的注意力机制中。
点此查看论文截图



Exponentially Weighted Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling for Long-Tailed Object Detection Model Training in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Surveillance Scenarios
Authors:Taufiq Ahmed, Abhishek Kumar, Constantino Álvarez Casado, Anlan Zhang, Tuomo Hänninen, Lauri Loven, Miguel Bordallo López, Sasu Tarkoma
Object detection models often struggle with class imbalance, where rare categories appear significantly less frequently than common ones. Existing sampling-based rebalancing strategies, such as Repeat Factor Sampling (RFS) and Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling (IRFS), mitigate this issue by adjusting sample frequencies based on image and instance counts. However, these methods are based on linear adjustments, which limit their effectiveness in long-tailed distributions. This work introduces Exponentially Weighted Instance-Aware Repeat Factor Sampling (E-IRFS), an extension of IRFS that applies exponential scaling to better differentiate between rare and frequent classes. E-IRFS adjusts sampling probabilities using an exponential function applied to the geometric mean of image and instance frequencies, ensuring a more adaptive rebalancing strategy. We evaluate E-IRFS on a dataset derived from the Fireman-UAV-RGBT Dataset and four additional public datasets, using YOLOv11 object detection models to identify fire, smoke, people and lakes in emergency scenarios. The results show that E-IRFS improves detection performance by 22% over the baseline and outperforms RFS and IRFS, particularly for rare categories. The analysis also highlights that E-IRFS has a stronger effect on lightweight models with limited capacity, as these models rely more on data sampling strategies to address class imbalance. The findings demonstrate that E-IRFS improves rare object detection in resource-constrained environments, making it a suitable solution for real-time applications such as UAV-based emergency monitoring. The code is available at: https://github.com/futurians/E-IRFS.
对象检测模型经常面临类别不平衡的问题,其中稀有类别的出现频率显著低於常见类别。现有的基于采样的再平衡策略,如重复因子采样(RFS)和实例感知重复因子采样(IRFS),通过根据图像和实例计数调整样本频率来缓解这个问题。然而,这些方法基于线性调整,在长尾分布中限制了其有效性。本研究引入了加权实例感知重复因子采样(E-IRFS),它是IRFS的扩展,应用指数缩放来更好地区分稀有类别和常见类别。E-IRFS通过使用应用于图像和实例频率几何均值的指数函数来调整采样概率,确保更自适应的再平衡策略。我们在从Fireman-UAV-RGBT数据集派生的数据集和另外四个公开数据集上评估了E-IRFS,使用YOLOv11对象检测模型来识别紧急场景中的火灾、烟雾、人员和湖泊。结果表明,与基线相比,E-IRFS提高了22%的检测性能,并且优于RFS和IRFS,特别是在稀有类别方面。分析还强调,E-IRFS对容量有限的轻量级模型影响更大,因为这些模型更依赖数据采样策略来解决类别不平衡问题。研究结果表明,E-IRFS在资源受限的环境中提高了稀有对象检测能力,使其成为适用于实时应用(如基于无人机的紧急监测)的合适解决方案。代码可用在:https://github.com/futurians/E-IRFS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures, 9 tables, 6 formulas, conference paper, code available
Summary:
针对目标检测模型中常见的类别不平衡问题,文章提出了一种新的采样策略——基于指数权重的实例感知重复因子采样(E-IRFS)。E-IRFS对图像和实例频率的几何均值应用指数函数来调整采样概率,更有效地平衡了稀有和常见类别。实验结果表明,在应急场景下的数据集上,E-IRFS能提高目标检测性能,特别是在识别稀有类别时表现更佳。此外,对于容量有限的轻量级模型,E-IRFS的影响更为显著。它为资源受限环境中的稀有目标检测提供了有效解决方案,适合用于无人机应急监测等实时应用。
Key Takeaways:
- 目标检测模型面临类别不平衡问题,稀有类别出现频率远低于常见类别。
- 现有采样策略如RFS和IRFS通过调整样本频率来平衡此类问题,但效果有限。
- 引入E-IRFS策略,通过对图像和实例频率的几何均值应用指数函数来调整采样概率。
- E-IRFS在多个数据集上的实验结果表明其能有效提高目标检测性能,特别是在识别稀有类别方面。
- E-IRFS对轻量级模型的影响更为显著,这些模型更依赖于数据采样策略来解决类别不平衡问题。
- E-IRFS适用于资源受限环境中的稀有目标检测,为实时应用如无人机应急监测提供了有效解决方案。
点此查看论文截图




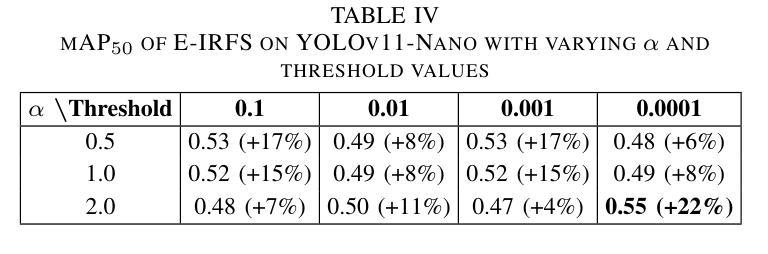

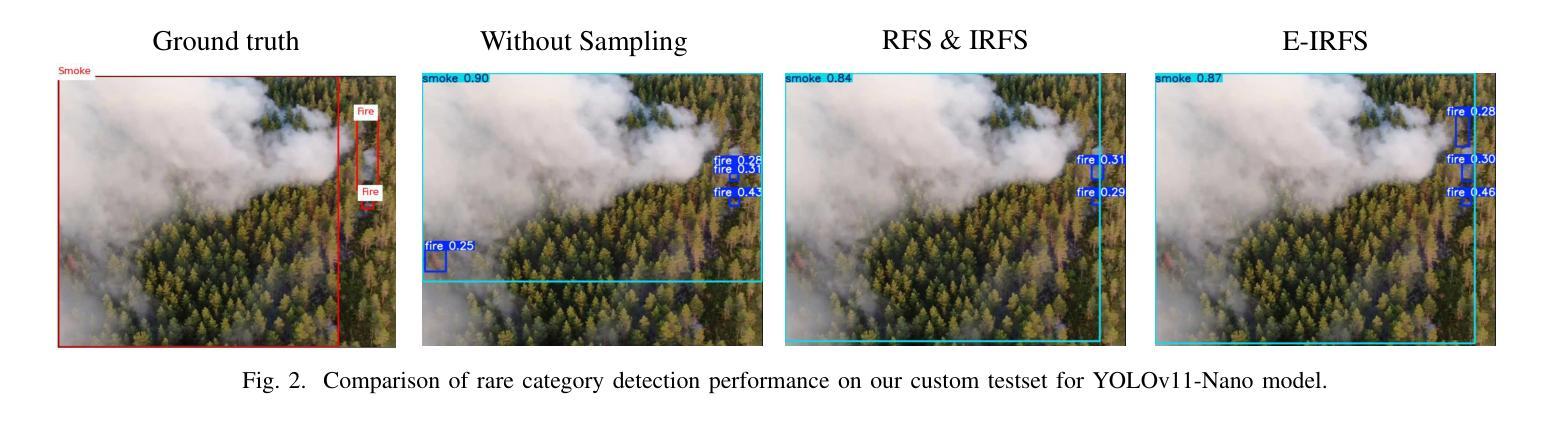
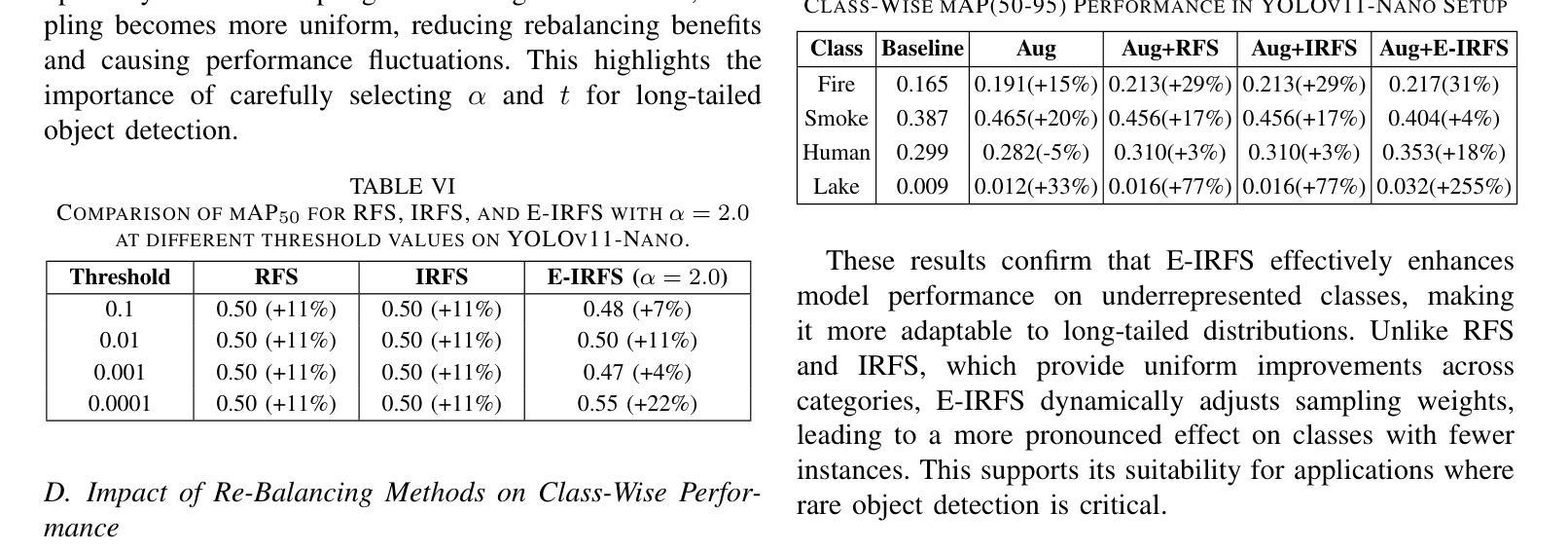
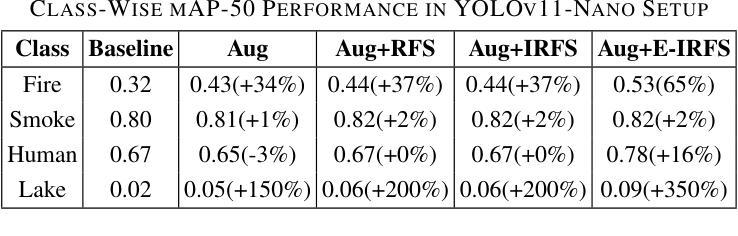
Image Augmentation Agent for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) has achieved remarkable progress using only image-level labels. However, most existing WSSS methods focus on designing new network structures and loss functions to generate more accurate dense labels, overlooking the limitations imposed by fixed datasets, which can constrain performance improvements. We argue that more diverse trainable images provides WSSS richer information and help model understand more comprehensive semantic pattern. Therefore in this paper, we introduce a novel approach called Image Augmentation Agent (IAA) which shows that it is possible to enhance WSSS from data generation perspective. IAA mainly design an augmentation agent that leverages large language models (LLMs) and diffusion models to automatically generate additional images for WSSS. In practice, to address the instability in prompt generation by LLMs, we develop a prompt self-refinement mechanism. It allow LLMs to re-evaluate the rationality of generated prompts to produce more coherent prompts. Additionally, we insert an online filter into diffusion generation process to dynamically ensure the quality and balance of generated images. Experimental results show that our method significantly surpasses state-of-the-art WSSS approaches on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 datasets.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)仅使用图像级标签取得了显著的进步。然而,大多数现有的WSSS方法主要集中在设计新的网络结构和损失函数来生成更准确的密集标签,而忽视了固定数据集带来的限制,这些限制可能会限制性能的提升。我们认为,提供更多可训练图像可以为WSSS提供更丰富的信息,并帮助模型理解更全面的语义模式。因此,在本文中,我们介绍了一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的新方法,表明从数据生成的角度增强WSSS是可能的。IAA主要设计了一个增强代理,利用大型语言模型(LLM)和扩散模型自动为WSSS生成额外的图像。在实践中,为了解决LLM生成提示的不稳定性,我们开发了一种提示自我完善机制。它允许LLM重新评估生成的提示的合理性,以产生更连贯的提示。此外,我们在扩散生成过程中插入了一个在线过滤器,以动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了最先进的WSSS方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Neurocomputing 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Image Augmentation Agent(IAA)的方法,从数据生成的角度提升弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的性能。该方法利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和扩散模型自动生成额外的图像,并设计了提示自我优化机制和在线过滤器,以提高生成图像的质量和平衡性。在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS方法主要关注设计新的网络结构和损失函数以生成更准确的密集标签,但固定数据集的局限性限制了性能的提升。
- 本文从数据生成的角度提出一种名为IAA的新方法,以提高WSSS的性能。
- IAA利用大型语言模型和扩散模型自动生成额外的图像,为WSSS提供更多元化的信息。
- 为了解决LLMs在提示生成中的不稳定问题,开发了一种提示自我优化机制,使LLMs能够重新评估生成的提示的合理性,产生更连贯的提示。
- 在扩散生成过程中插入在线过滤器,以动态确保生成图像的质量和平衡。
- 实验结果表明,IAA方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上显著超越了现有的WSSS方法。
点此查看论文截图


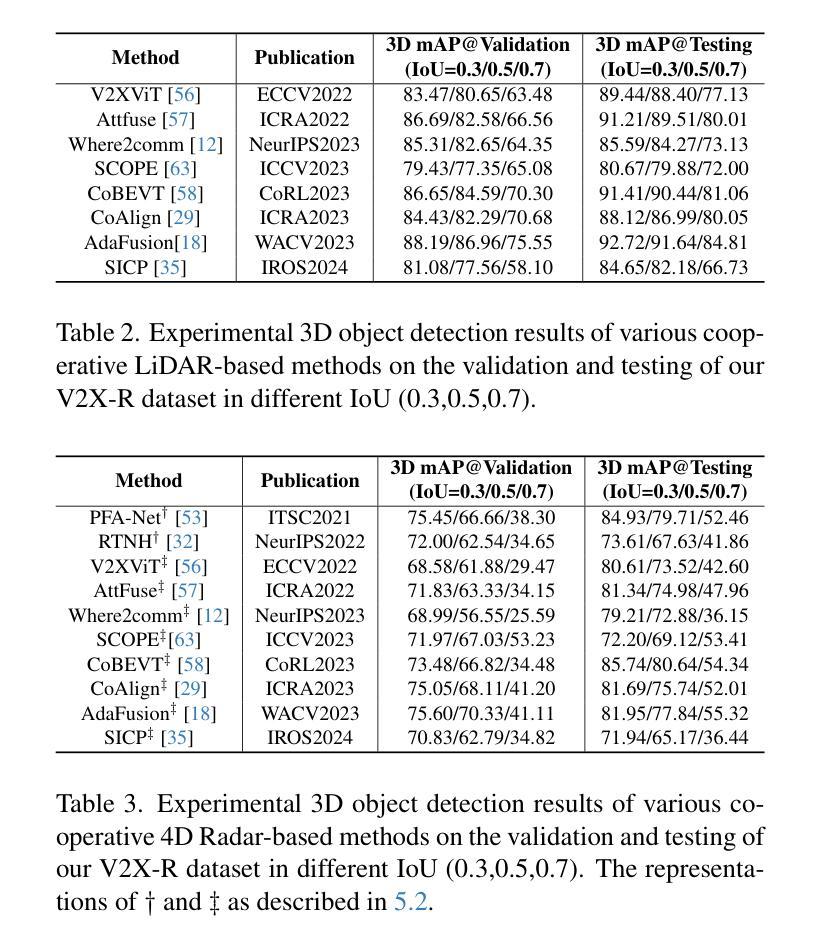
V2X-R: Cooperative LiDAR-4D Radar Fusion with Denoising Diffusion for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Xun Huang, Jinlong Wang, Qiming Xia, Siheng Chen, Bisheng Yang, Xin Li, Cheng Wang, Chenglu Wen
Current Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) systems have significantly enhanced 3D object detection using LiDAR and camera data. However, these methods suffer from performance degradation in adverse weather conditions. The weather-robust 4D radar provides Doppler and additional geometric information, raising the possibility of addressing this challenge. To this end, we present V2X-R, the first simulated V2X dataset incorporating LiDAR, camera, and 4D radar. V2X-R contains 12,079 scenarios with 37,727 frames of LiDAR and 4D radar point clouds, 150,908 images, and 170,859 annotated 3D vehicle bounding boxes. Subsequently, we propose a novel cooperative LiDAR-4D radar fusion pipeline for 3D object detection and implement it with various fusion strategies. To achieve weather-robust detection, we additionally propose a Multi-modal Denoising Diffusion (MDD) module in our fusion pipeline. MDD utilizes weather-robust 4D radar feature as a condition to prompt the diffusion model to denoise noisy LiDAR features. Experiments show that our LiDAR-4D radar fusion pipeline demonstrates superior performance in the V2X-R dataset. Over and above this, our MDD module further improved the performance of basic fusion model by up to 5.73%/6.70% in foggy/snowy conditions with barely disrupting normal performance. The dataset and code will be publicly available at: https://github.com/ylwhxht/V2X-R.
当前的车对外界(V2X)系统已经通过激光雷达和相机数据显著增强了3D对象检测功能。然而,这些方法在恶劣天气条件下会出现性能下降。天气稳定的4D雷达提供了多普勒和额外的几何信息,为解决这一挑战提供了可能性。为此,我们推出了V2X-R,这是第一个结合了激光雷达、相机和4D雷达的模拟V2X数据集。V2X-R包含12,079个场景,其中包括激光雷达和4D雷达点云37,727帧,图像150,908张,以及标注的3D车辆边界框170,859个。随后,我们提出了一种用于3D对象检测的新型合作式激光雷达-4D雷达融合管道,并采用了多种融合策略来实现它。为了实现天气稳定的检测,我们还在融合管道中提出了多模式去噪扩散(MDD)模块。MDD利用天气稳定的4D雷达特征作为条件,提示扩散模型对嘈杂的激光雷达特征进行去噪。实验表明,我们的激光雷达-4D雷达融合管道在V2X-R数据集上表现出卓越的性能。除此之外,我们的MDD模块进一步改进了基本融合模型在雾天和雪天的性能,分别提高了5.73%和6.70%,同时几乎不影响正常性能。数据集和代码将在https://github.com/ylwhxht/V2X-R公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR2025
Summary:
当前车辆到万物(V2X)系统已经通过激光雷达和摄像头数据显著提高了三维物体检测能力。然而,这些方法在恶劣天气条件下会出现性能下降的问题。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了V2X-R数据集,该数据集融合了激光雷达、摄像头和四维雷达数据。V2X-R包含了丰富的数据场景和标注框,并首次提出了一种新型的雷达与激光雷达融合管道,实现了三维物体检测。此外,本文还提出了一种多模态去噪扩散模块(MDD),以提高恶劣天气下的检测性能。实验结果表明,该方法在V2X-R数据集上表现优异,并在雾天和雪天条件下进一步提高了基本融合模型的性能。数据集和代码将在公开平台上发布。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前V2X系统在恶劣天气下三维物体检测性能下降的问题仍然存在。
- 提出了一种新的V2X-R数据集,融合了激光雷达、摄像头和四维雷达数据。
- 介绍了一种新型的雷达与激光雷达融合管道,实现了三维物体检测。
- 提出了一种多模态去噪扩散模块(MDD),提高恶劣天气下的检测性能。
- 实验表明,该方法在V2X-R数据集上表现优异。
- 在雾天和雪天条件下,MDD模块能进一步提高基本融合模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图





Enhanced Generative Data Augmentation for Semantic Segmentation via Stronger Guidance
Authors:Quang-Huy Che, Duc-Tri Le, Bich-Nga Pham, Duc-Khai Lam, Vinh-Tiep Nguyen
Data augmentation is crucial for pixel-wise annotation tasks like semantic segmentation, where labeling requires significant effort and intensive labor. Traditional methods, involving simple transformations such as rotations and flips, create new images but often lack diversity along key semantic dimensions and fail to alter high-level semantic properties. To address this issue, generative models have emerged as an effective solution for augmenting data by generating synthetic images. Controllable Generative models offer data augmentation methods for semantic segmentation tasks by using prompts and visual references from the original image. However, these models face challenges in generating synthetic images that accurately reflect the content and structure of the original image due to difficulties in creating effective prompts and visual references. In this work, we introduce an effective data augmentation pipeline for semantic segmentation using Controllable Diffusion model. Our proposed method includes efficient prompt generation using Class-Prompt Appending and Visual Prior Blending to enhance attention to labeled classes in real images, allowing the pipeline to generate a precise number of augmented images while preserving the structure of segmentation-labeled classes. In addition, we implement a class balancing algorithm to ensure a balanced training dataset when merging the synthetic and original images. Evaluation on PASCAL VOC datasets, our pipeline demonstrates its effectiveness in generating high-quality synthetic images for semantic segmentation. Our code is available at https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance.
数据增强对于像素级标注任务(如语义分割)至关重要,这些任务需要大量标注工作。传统方法,涉及旋转、翻转等简单变换,能够生成新图像,但往往缺乏关键语义维度的多样性,并且无法改变高级语义属性。为解决这一问题,生成模型作为数据增强的有效解决方案已经出现,通过生成合成图像来增强数据。可控生成模型通过使用原始图像的提示和视觉参考,为语义分割任务提供数据增强方法。然而,这些模型在生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像时面临挑战,因为创建有效的提示和视觉参考具有难度。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种使用可控扩散模型的有效数据增强管道,用于语义分割。我们提出的方法包括使用类提示追加和视觉先验混合的有效提示生成,以提高对真实图像中标记类的关注,使管道能够在保持分割标记类结构的同时,生成精确数量的增强图像。此外,我们实现了一种类平衡算法,以确保在合并合成图像和原始图像时获得平衡的训练数据集。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估表明,我们的管道在生成高质量合成图像进行语义分割方面非常有效。我们的代码可在https://github.com/chequanghuy/Enhanced-Generative-Data-Augmentation-for-Semantic-Segmentation-via-Stronger-Guidance上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in ICPRAM 2025, ISBN 978-989-758-730-6, ISSN 2184-4313
Summary
数据增强对于像素级标注任务如语义分割至关重要。传统方法简单,缺乏多样性。生成模型通过生成合成图像进行数据增强。可控生成模型通过提示和原始图像视觉参考为语义分割任务提供数据增强方法,但生成准确反映原始图像内容和结构的合成图像具有挑战性。本文引入使用可控扩散模型的语义分割有效数据增强管道,通过高效提示生成和视觉先验融合,在真实图像中增强对标记类的注意力,生成精确数量的增强图像,同时保持分割标记类的结构。此外,实现类别平衡算法,确保合成和原始图像合并时的训练数据集平衡。在PASCAL VOC数据集上的评估证明了管道生成高质量合成图像的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强在像素级标注任务中非常重要,尤其是语义分割。
- 传统数据增强方法简单但缺乏多样性。
- 生成模型可以有效解决数据增强问题,尤其是可控生成模型。
- 可控生成模型使用提示和原始图像视觉参考进行语义分割的数据增强。
- 生成合成图像时面临的主要挑战是准确反映原始图像的内容和结构。
- 引入使用可控扩散模型的有效数据增强管道,包括高效提示生成和视觉先验融合。
点此查看论文截图

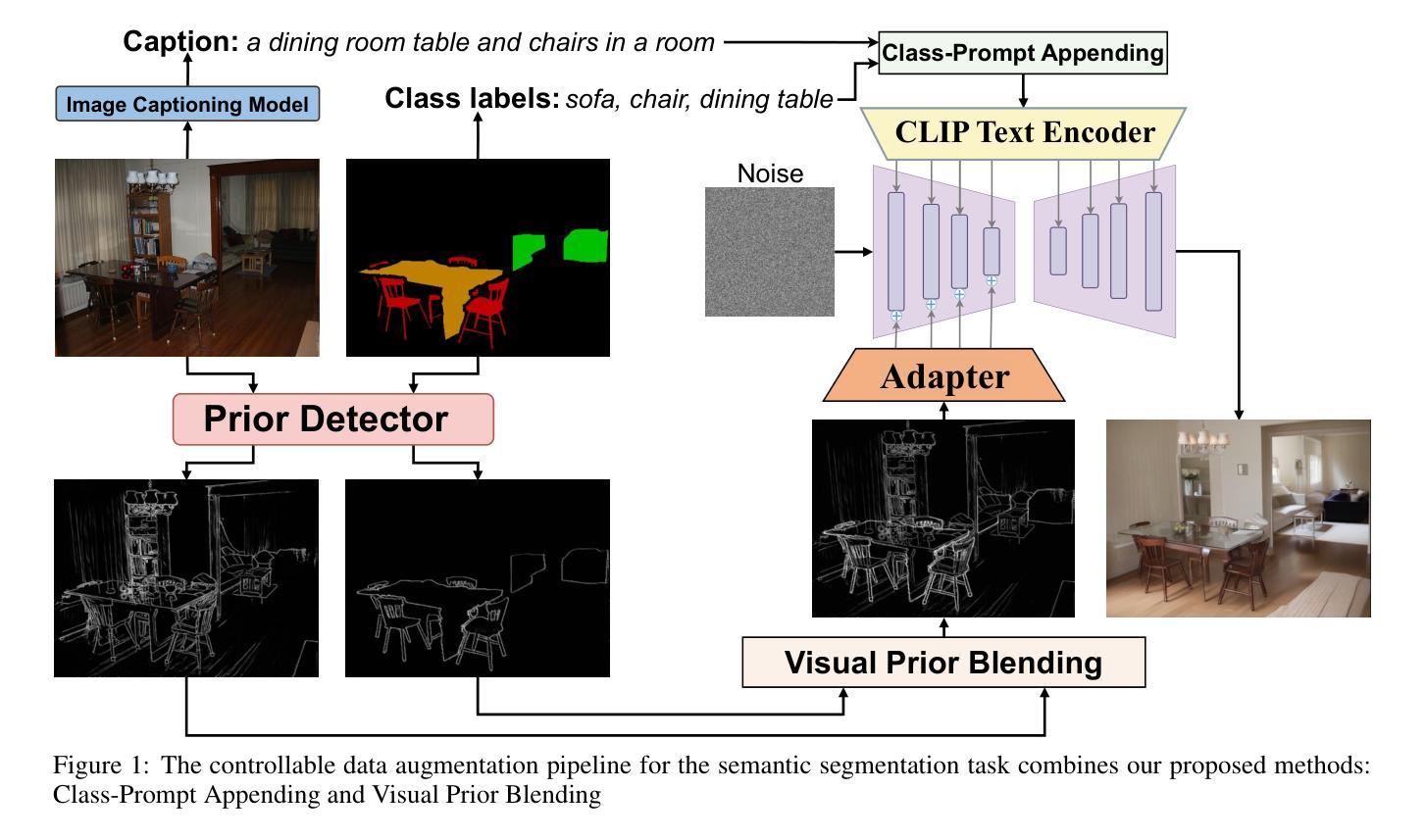




ReCLIP++: Learn to Rectify the Bias of CLIP for Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jingyun Wang, Guoliang Kang
Recent works utilize CLIP to perform the challenging unsupervised semantic segmentation task where only images without annotations are available. However, we observe that when adopting CLIP to such a pixel-level understanding task, unexpected bias (including class-preference bias and space-preference bias) occurs. Previous works don’t explicitly model the bias, which largely constrains the segmentation performance. In this paper, we propose to explicitly model and rectify the bias existing in CLIP to facilitate the unsupervised semantic segmentation task. Specifically, we design a learnable “Reference” prompt to encode class-preference bias and a projection of the positional embedding in the vision transformer to encode space-preference bias respectively. To avoid interference, two kinds of biases are firstly independently encoded into different features, i.e., the Reference feature and the positional feature. Via a matrix multiplication between the Reference feature and the positional feature, a bias logit map is generated to explicitly represent two kinds of biases. Then we rectify the logits of CLIP via a simple element-wise subtraction. To make the rectified results smoother and more contextual, we design a mask decoder which takes the feature of CLIP and the rectified logits as input and outputs a rectified segmentation mask with the help of Gumbel-Softmax operation. A contrastive loss based on the masked visual features and the text features of different classes is imposed, which makes the bias modeling and rectification process meaningful and effective. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks including PASCAL VOC, PASCAL Context, ADE20K, Cityscapes, and COCO Stuff demonstrate that our method performs favorably against previous state-of-the-arts. The implementation is available at: https://github.com/dogehhh/ReCLIP.
近期工作利用CLIP来执行具有挑战性的无监督语义分割任务,该任务仅提供没有注释的图像。然而,我们观察到,在将CLIP应用于这种像素级的理解任务时,会出现意想不到的偏见(包括类别偏好偏见和空间偏好偏见)。以前的工作没有显式地对偏见进行建模,这极大地限制了分割性能。在本文中,我们提出对CLIP中存在的偏见进行显式建模和纠正,以促进无监督语义分割任务。具体来说,我们设计了一个可学习的“参考”提示来编码类别偏好偏见,并利用视觉变压器中的位置嵌入的投影来编码空间偏好偏见。为了避免干扰,两种偏见首先被独立编码为不同的特征,即参考特征和位置特征。通过参考特征与位置特征之间的矩阵乘法,生成一个偏见逻辑图,显式表示两种偏见。然后我们通过简单的元素级减法来纠正CLIP的逻辑值。为了使校正结果更平滑、更具上下文性,我们设计了一个掩膜解码器,它接受CLIP的特征和校正后的逻辑值作为输入,借助Gumbel-Softmax操作输出一个校正后的分割掩膜。基于掩码视觉特征和不同类别文本特征的对比损失,使得偏见建模和纠正过程有意义且有效。在包括PASCAL VOC、PASCAL Context、ADE20K、Cityscapes和COCO Stuff等多个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法与之前的最新技术相比表现良好。实现详情可访问:https://github.com/dogehhh/ReCLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Extended version of our CVPR 24 paper
Summary
基于CLIP的无监督语义分割任务中,存在包括类别偏好偏见和空间偏好偏见在内的意外偏见。本文提出显式建模并纠正CLIP中存在的偏见,以提高分割性能。通过设计可学习的“参考”提示来编码类别偏好偏见,并通过视觉变压器中的位置嵌入投影来编码空间偏好偏见。独立编码两种偏见,生成偏差逻辑图以显式表示两种偏见,并通过简单元素减法纠正CLIP的逻辑。设计了一个掩膜解码器,将CLIP的特征和纠正后的逻辑图作为输入,输出纠正后的分割掩膜。实验证明,该方法在多个基准测试上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP被用于执行无监督语义分割任务。
- 执行像素级别理解任务时存在意外偏见。这些偏见包括类别偏好偏见和空间偏好偏见。
- 之前的工作没有显式建模这种偏见,这限制了分割性能。本文首次提出对CLIP中的偏见进行建模和纠正的方法。
- 通过设计可学习的“参考”提示和位置嵌入投影来分别编码类别偏好偏见和空间偏好偏见。
- 通过矩阵乘法生成偏差逻辑图来显式表示这两种偏见,并通过元素减法纠正CLIP的逻辑。
- 设计掩膜解码器输出纠正后的分割掩膜,采用Gumbel-Softmax操作帮助生成结果。
- 通过基于对比损失的掩盖视觉特征和不同类别文本特征的对比损失方法来实现偏差建模和纠正过程的意义和有效性。
点此查看论文截图

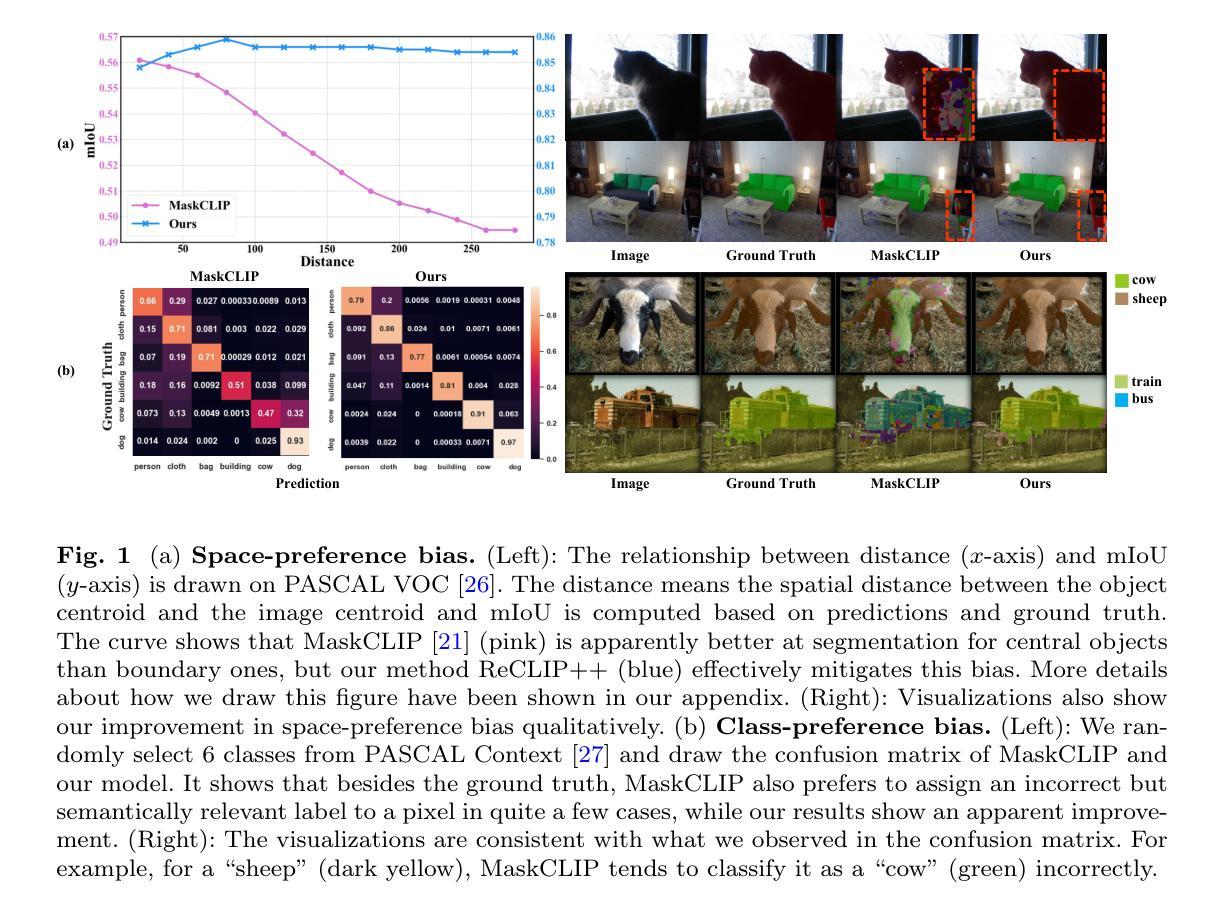
Multiple Object Detection and Tracking in Panoramic Videos for Cycling Safety Analysis
Authors:Jingwei Guo, Yitai Cheng, Meihui Wang, Ilya Ilyankou, Natchapon Jongwiriyanurak, Xiaowei Gao, Nicola Christie, James Haworth
Cyclists face a disproportionate risk of injury, yet conventional crash records are too limited to reconstruct the circumstances of incidents or to diagnose risk at the finer spatial and temporal detail needed for targeted interventions. Recently, naturalistic studies have gained traction as a way to capture the complex behavioural and infrastructural factors that contribute to crashes. These approaches typically involve the collection and analysis of video data. A video promising format is panoramic video, which can record 360-degree views around a rider. However, its use is limited by severe distortions, large numbers of small objects and boundary continuity. This study addresses these challenges by proposing a novel three-step framework: (1) enhancing object detection accuracy on panoramic imagery by segmenting and projecting the original 360-degree images into four perspective sub-images, thus reducing distortion; (2) modifying multi-object tracking models to incorporate boundary continuity and object category information for improved tracking consistency; and (3) validating the proposed approach through a real-world application focused on detecting overtaking manoeuvres by vehicles around cyclists. The methodology is evaluated using panoramic videos recorded by cyclists on London’s roadways under diverse conditions. Experimental results demonstrate notable improvements over baseline methods, achieving higher average precision across varying image resolutions. Moreover, the enhanced tracking approach yields a 3.0% increase in multi-object tracking accuracy and a 4.6% improvement in identification F-score. The overtaking detection task achieves a high F-score of 0.81, illustrating the practical effectiveness of the proposed method in real-world cycling safety scenarios. The code is available on GitHub (https://github.com/SpaceTimeLab/360_object_tracking) to ensure reproducibility.
骑自行车的人面临着不成比例的伤害风险,然而,传统的碰撞记录过于局限,无法重建事件情况或针对需要进行精细时空细节的风险诊断以实施有针对性的干预措施。最近,自然主义研究作为一种捕捉导致碰撞的复杂行为和环境因素的方法开始受到关注。这些方法通常涉及视频数据的收集和分析。一种有前景的视频格式是全景视频,它可以记录骑行者周围的360度视图。然而,其使用受到严重失真、大量小物体和边界连续性问题的限制。本研究通过提出一个新型的三步框架来解决这些挑战:(1)通过将原始360度图像分割并投影到四个透视子图像中,提高全景图像的目标检测精度,从而减少失真;(2)修改多目标跟踪模型,以纳入边界连续性和目标类别信息,以提高跟踪的一致性;(3)通过关注检测自行车周围车辆超车动作的现实应用来验证所提出的方法。该方法使用骑行者在伦敦道路上在各种条件下录制的全景视频进行评估。实验结果表明,与基准方法相比,该方法在多种图像分辨率上取得了显著的改进,平均精度更高。此外,改进后的跟踪方法使多目标跟踪精度提高了3.0%,识别F分数提高了4.6%。超车检测任务取得了高达0.81的F分数,证明了该方法在现实骑行安全场景中的实际有效性。代码已在GitHub上公开(https://github.com/SpaceTimeLab/360_object_tracking),以确保可重复性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
循环骑行者在事故中面临不成比例的伤害风险,传统的事故记录方法过于局限,无法详细重建事故情况或针对更精细的空间和时间细节进行风险评估。本研究提出了一种新型的三步框架,通过增强全景影像的目标检测精度、修改多目标跟踪模型以融入边界连续性和目标类别信息,并验证在检测骑行者周围车辆超车动作方面的实用性。该研究方法在伦敦道路骑行者的全景视频上进行了评估,实现了显著的改进。研究成果的代码已在GitHub上公开,以确保可重复性。
Key Takeaways:
- 循环骑行者面临的事故伤害风险不成比例,传统的事故记录方法存在局限性。
- 自然主义研究是了解事故复杂因素的有效方法,特别是通过视频数据的收集和分析。
- 全景视频在记录骑行者周围360度情况方面具有潜力,但存在严重的失真、小目标数量过多和边界连续性问题。
- 本研究提出了一个三步框架,包括增强全景影像的目标检测精度、改进多目标跟踪模型,并验证其在实际检测超车动作方面的应用。
- 研究在伦敦道路骑行者的全景视频上进行了评估,实现了显著改进,包括平均精度、多目标跟踪准确性和识别F分数的提高。
- 过道检测任务的高F分数证明了该方法在实际骑行安全场景中的实用性。
点此查看论文截图



Repurposing SAM for User-Defined Semantics Aware Segmentation
Authors:Rohit Kundu, Sudipta Paul, Arindam Dutta, Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury
The Segment Anything Model (SAM) excels at generating precise object masks from input prompts but lacks semantic awareness, failing to associate its generated masks with specific object categories. To address this limitation, we propose U-SAM, a novel framework that imbibes semantic awareness into SAM, enabling it to generate targeted masks for user-specified object categories. Given only object class names as input from the user, U-SAM provides pixel-level semantic annotations for images without requiring any labeled/unlabeled samples from the test data distribution. Our approach leverages synthetically generated or web crawled images to accumulate semantic information about the desired object classes. We then learn a mapping function between SAM’s mask embeddings and object class labels, effectively enhancing SAM with granularity-specific semantic recognition capabilities. As a result, users can obtain meaningful and targeted segmentation masks for specific objects they request, rather than generic and unlabeled masks. We evaluate U-SAM on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MSCOCO-80, achieving significant mIoU improvements of +17.95% and +5.20%, respectively, over state-of-the-art methods. By transforming SAM into a semantically aware segmentation model, U-SAM offers a practical and flexible solution for pixel-level annotation across diverse and unseen domains in a resource-constrained environment.
Segment Anything Model(SAM)在根据输入提示生成精确对象掩膜方面表现出色,但缺乏语义意识,无法将其生成的掩膜与特定对象类别相关联。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了U-SAM,这是一个将语义意识融入SAM的新型框架,使其能够针对用户指定的对象类别生成定向掩膜。U-SAM仅接收用户提供的对象类别名称作为输入,为图像提供像素级语义注释,而无需测试数据分布中的任何有标签或无标签样本。我们的方法利用合成生成或网络爬虫图像来积累有关所需对象类别的语义信息。然后,我们学习SAM的掩膜嵌入和对象类别标签之间的映射函数,有效地增强SAM的粒度特定语义识别能力。因此,用户可以获取他们请求的具体对象的有意义和定向分割掩膜,而不是通用和无标签的掩膜。我们在PASCAL VOC 2012和MSCOCO-80上评估了U-SAM,与最先进的方法相比,mIoU分别提高了+17.95%和+5.20%。通过将SAM转变为语义感知分割模型,U-SAM为资源受限环境中的跨不同和未见领域的像素级注释提供了实用且灵活的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
U-SAM框架解决了SAM模型在生成精确对象掩膜时缺乏语义意识的问题。通过输入用户指定的对象类别名称,U-SAM为图像提供像素级语义注释,无需测试数据分布的任何标记/未标记样本。该方法利用合成图像或网络爬虫累积所需对象类别的语义信息,学习SAM的掩膜嵌入和对象类别标签之间的映射函数,从而提高SAM对特定粒度语义的识别能力。评估结果显示,U-SAM在PASCAL VOC 2012和MSCOCO-80上分别实现了显著的mIoU改进+17.95%和+5.2%。U-SAM将SAM转化为具有语义意识的分割模型,为资源受限环境中跨不同和未见领域的像素级注释提供了实用且灵活的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- U-SAM解决了SAM模型缺乏语义意识的问题。
- U-SAM可以通过输入用户指定的对象类别名称,生成针对特定对象的像素级语义注释。
- U-SAM利用合成图像或网络爬虫数据来累积语义信息。
- U-SAM通过映射函数提高了对特定粒度语义的识别能力。
- U-SAM在PASCAL VOC 2012和MSCOCO-80数据集上实现了显著的mIoU改进。
- U-SAM将SAM转化为具有语义意识的分割模型。
点此查看论文截图




