⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-08 更新
Few-shot Human Action Anomaly Detection via a Unified Contrastive Learning Framework
Authors:Koichiro Kamide, Shunsuke Sakai, Shun Maeda, Chunzhi Gu, Chao Zhang
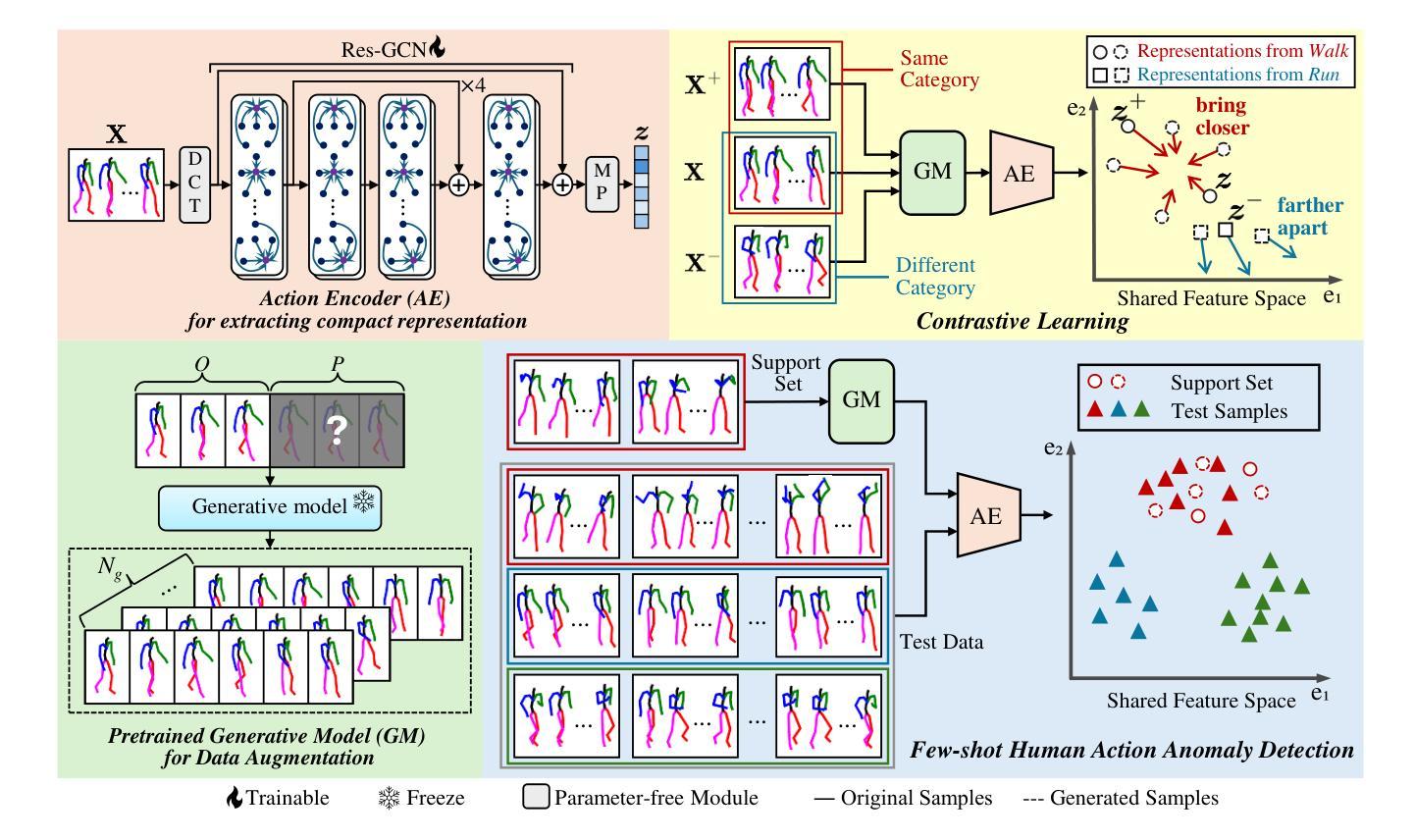
Human Action Anomaly Detection (HAAD) aims to identify anomalous actions given only normal action data during training. Existing methods typically follow a one-model-per-category paradigm, requiring separate training for each action category and a large number of normal samples. These constraints hinder scalability and limit applicability in real-world scenarios, where data is often scarce or novel categories frequently appear. To address these limitations, we propose a unified framework for HAAD that is compatible with few-shot scenarios. Our method constructs a category-agnostic representation space via contrastive learning, enabling AD by comparing test samples with a given small set of normal examples (referred to as the support set). To improve inter-category generalization and intra-category robustness, we introduce a generative motion augmentation strategy harnessing a diffusion-based foundation model for creating diverse and realistic training samples. Notably, to the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to introduce such a strategy specifically tailored to enhance contrastive learning for action AD. Extensive experiments on the HumanAct12 dataset demonstrate the state-of-the-art effectiveness of our approach under both seen and unseen category settings, regarding training efficiency and model scalability for few-shot HAAD.
人类行为异常检测(HAAD)旨在仅在训练期间给定正常行为数据的情况下识别异常行为。现有方法通常遵循一种针对每个类别的模型范式,需要为每个动作类别进行单独训练,并且需要大量正常样本。这些约束阻碍了可扩展性,并限制了其在现实世界场景中的应用,因为数据通常稀缺或经常出现新的类别。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一个统一的HAAD框架,该框架可与少数场景兼容。我们的方法通过对比学习构建了一个类别无关的表示空间,通过比较测试样本和给定的一组正常样本(称为支持集)来实现异常检测。为了提高跨类别泛化和类别内稳健性,我们引入了一种基于扩散的基础模型的生成运动增强策略,用于创建多样且逼真的训练样本。值得注意的是,据我们所知,我们的工作是首次引入这样一种专门增强动作异常检测对比学习的策略。在HumanAct12数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在可见和不可见类别设置下均达到了最先进的效果,提高了少数样本HAAD的训练效率和模型可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于对比学习的人类行为异常检测统一框架。该框架针对少样本情况下的人类行为异常检测问题,通过构建类别无关的表示空间并利用对比学习进行对比检测。此外,还引入了一种基于扩散模型的生成式运动增强策略,以提高跨类别泛化和类别内鲁棒性。在HumanAct12数据集上的实验表明,该方法在可见和不可见类别设置下均达到了最先进的性能,提高了训练效率和模型可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究旨在解决人类行为异常检测中的少样本问题,提出一个统一框架,适用于多种场景。
- 通过构建类别无关的表示空间,利用对比学习进行对比检测。
- 引入生成式运动增强策略,提高跨类别泛化和类别内鲁棒性。
- 采用扩散模型为基础模型进行训练样本的创建,生成多样且真实的样本。
- 该方法在HumanAct12数据集上进行了实验验证,表现出优异的性能。
- 该方法提高了训练效率和模型的可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图



Few-Shot Pattern Detection via Template Matching and Regression
Authors:Eunchan Jo, Dahyun Kang, Sanghyun Kim, Yunseon Choi, Minsu Cho
We address the problem of few-shot pattern detection, which aims to detect all instances of a given pattern, typically represented by a few exemplars, from an input image. Although similar problems have been studied in few-shot object counting and detection (FSCD), previous methods and their benchmarks have narrowed patterns of interest to object categories and often fail to localize non-object patterns. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective detector based on template matching and regression, dubbed TMR. While previous FSCD methods typically represent target exemplars as spatially collapsed prototypes and lose structural information, we revisit classic template matching and regression. It effectively preserves and leverages the spatial layout of exemplars through a minimalistic structure with a small number of learnable convolutional or projection layers on top of a frozen backbone We also introduce a new dataset, dubbed RPINE, which covers a wider range of patterns than existing object-centric datasets. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the three benchmarks, RPINE, FSCD-147, and FSCD-LVIS, and demonstrates strong generalization in cross-dataset evaluation.
我们解决小样图案检测的问题,其目的是从输入图像中检测给定图案的所有实例,这些图案通常通过几个样本表示。尽管类似的问题已经在小样本目标计数和检测(FSCD)中进行了研究,但之前的方法及其基准测试将图案兴趣局限于目标类别,并且往往无法定位非目标图案。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于模板匹配和回归的简单有效的检测器,被称为TMR。虽然之前的FSCD方法通常将目标样本表示为空间塌陷的原型并丢失结构信息,我们重新研究了经典的模板匹配和回归。它通过极简的结构有效地保留并利用了样本的空间布局,该结构具有少量的可学习卷积层或投影层,建立在冻结的backbone之上。我们还引入了一个新的数据集,名为RPINE,它比现有的以对象为中心的数据集涵盖了更广泛的图案范围。我们的方法在RPINE、FSCD-147和FSCD-LVIS这三个基准测试上都超越了最先进的方法,并在跨数据集评估中表现出强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICCV 2025 (highlight)
Summary
本文解决了少样本模式检测的问题,旨在从输入图像中检测出给定模式的所有实例。文章提出了一种基于模板匹配和回归的检测器TMR,该检测器能有效保留和利用范例的空间布局信息,从而解决之前方法忽视非对象模式定位的问题。此外,文章还引入了一个新数据集RPINE,覆盖的模式范围更广。实验表明,TMR在RPINE、FSCD-147和FSCD-LVIS三个基准测试集上都优于现有方法,并在跨数据集评估中展现出强大的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 文章解决了少样本模式检测问题,旨在从输入图像中检测出给定模式的所有实例。
- 提出了一种基于模板匹配和回归的检测器TMR,有效保留和利用范例的空间布局信息。
- 引入了一个新的数据集RPINE,包含更广泛的模式范围。
- TMR在RPINE、FSCD-147和FSCD-LVIS三个基准测试集上的表现优于现有方法。
- 文章指出之前的方法在表示目标范例时容易丢失结构信息,而TMR通过极简结构有效解决了这一问题。
- TMR通过顶部可学习的卷积层或投影层,在冻结的骨干网上进行工作。
点此查看论文截图





ReProCon: Scalable and Resource-Efficient Few-Shot Biomedical Named Entity Recognition
Authors:Jeongkyun Yoo, Nela Riddle, Andrew Hoblitzell
Named Entity Recognition (NER) in biomedical domains faces challenges due to data scarcity and imbalanced label distributions, especially with fine-grained entity types. We propose ReProCon, a novel few-shot NER framework that combines multi-prototype modeling, cosine-contrastive learning, and Reptile meta-learning to tackle these issues. By representing each category with multiple prototypes, ReProCon captures semantic variability, such as synonyms and contextual differences, while a cosine-contrastive objective ensures strong interclass separation. Reptile meta-updates enable quick adaptation with little data. Using a lightweight fastText + BiLSTM encoder with much lower memory usage, ReProCon achieves a macro-$F_1$ score close to BERT-based baselines (around 99 percent of BERT performance). The model remains stable with a label budget of 30 percent and only drops 7.8 percent in $F_1$ when expanding from 19 to 50 categories, outperforming baselines such as SpanProto and CONTaiNER, which see 10 to 32 percent degradation in Few-NERD. Ablation studies highlight the importance of multi-prototype modeling and contrastive learning in managing class imbalance. Despite difficulties with label ambiguity, ReProCon demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in resource-limited settings, making it suitable for biomedical applications.
生物医学领域的命名实体识别(NER)由于数据稀缺和标签分布不平衡而面临挑战,尤其是在精细粒度的实体类型中。我们提出了ReProCon,这是一种新的少样本NER框架,结合了多原型建模、余弦对比学习和Reptile元学习来解决这些问题。ReProCon通过多个原型表示每个类别,从而捕捉语义变化,如同义词和上下文差异,同时余弦对比目标确保类间强分离。Reptile元更新使模型能够用少量数据进行快速适应。使用内存使用更低的轻量级fastText + BiLSTM编码器,ReProCon的宏观F1分数接近BERT基准(约99%的BERT性能)。在标签预算为30%的情况下,该模型保持稳定,在扩展从19个类别到50个类别时,F1分数仅下降7.8%,优于SpanProto和CONTaiNER等基线模型,这些模型在Few-NERD中的性能下降10%到32%。消融研究强调了多原型建模和对比学习在管理类别不平衡中的重要性。尽管存在标签模糊性的困难,ReProCon在资源有限的环境中表现出卓越的性能,使其成为生物医学应用的理想选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对生物医学领域命名实体识别(NER)任务中的小样本学习问题,提出的ReProCon框架。该框架结合了多原型建模、余弦对比学习和Reptile元学习,以应对数据稀缺和标签分布不平衡的挑战。ReProCon通过多个原型表示每个类别,捕获语义变化,如同义词和上下文差异。余弦对比目标确保类间强分离,而Reptile元更新则实现了快速适应少量数据。实验表明,ReProCon在宏观F1分数上接近BERT基准测试,且在标签预算有限和类别扩展情况下表现稳定,优于其他基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- ReProCon是一个针对生物医学领域命名实体识别的小样本学习框架,旨在解决数据稀缺和标签分布不平衡的问题。
- 该框架结合了多原型建模、余弦对比学习和Reptile元学习,以捕捉语义变化和快速适应少量数据。
- ReProCon通过多个原型表示每个类别,以捕获同义词和上下文差异。
- 余弦对比学习确保了类间的强分离。
- 使用轻量级的fastText + BiLSTM编码器,ReProCon实现了接近BERT基准的宏观F1分数,且内存使用较低。
- ReProCon在有限的标签预算和类别扩展情况下表现稳定,优于其他基线方法,如SpanProto和CONTaiNER。
- 消融研究强调了多原型建模和对比学习在应对类别不平衡中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图





Bridging Generalization and Personalization in Wearable Human Activity Recognition via On-Device Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Pixi Kang, Julian Moosmann, Mengxi Liu, Bo Zhou, Michele Magno, Paul Lukowicz, Sizhen Bian
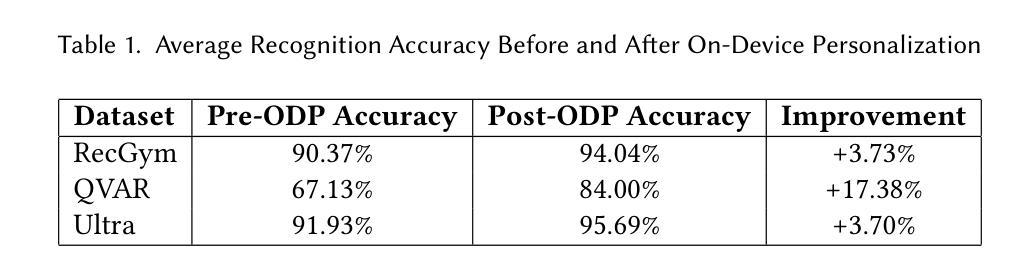
Human Activity Recognition (HAR) with wearable devices requires both strong generalization across diverse users and efficient personalization for individuals. However, conventional HAR models often fail to generalize when faced with user-specific variations, leading to degraded performance. To address this challenge, we propose a novel on-device few-shot learning framework that bridges generalization and personalization in wearable HAR. Our method first trains a generalizable representation across users and then rapidly adapts to new users with only a few labeled samples, updating lightweight classifier layers directly on resource-constrained devices. This approach achieves robust on-device learning with minimal computation and memory cost, making it practical for real-world deployment. We implement our framework on the energy-efficient RISC-V GAP9 microcontroller and evaluate it on three benchmark datasets (RecGym, QVAR-Gesture, Ultrasound-Gesture). Across these scenarios, post-deployment adaptation improves accuracy by 3.73%, 17.38%, and 3.70%, respectively. These results demonstrate that few-shot on-device learning enables scalable, user-aware, and energy-efficient wearable human activity recognition by seamlessly uniting generalization and personalization \footnote{https://github.com/kangpx/onlineTiny2023}.
人类活动识别(HAR)技术通过可穿戴设备实现,需要兼顾跨不同用户的强大泛化能力和针对个人的高效个性化。然而,传统的HAR模型在面对用户特定变化时往往无法泛化,导致性能下降。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新型的在设备端的小样本学习框架,它可以在可穿戴的HAR中弥泛化和个性化之间的差距。我们的方法首先训练一个跨用户的通用表示,然后仅通过少量标记样本快速适应新用户,直接在资源受限的设备上更新轻量级分类器层。这种方法实现了具有最小计算和内存成本的稳健在设备端学习,使其成为实际部署的实际选择。我们在能效高的RISC-V GAP9微控制器上实现了我们的框架,并在三个基准数据集(RecGym、QVAR-Gesture、Ultrasound-Gesture)上对其进行了评估。在这些场景中,部署后的适应分别提高了3.73%、17.38%和3.70%的准确率。这些结果表明,通过无缝结合泛化和个性化,小样本在设备端学习可实现可扩展的、用户感知的和能效高的可穿戴人类活动识别。[^https://github.com/kangpx/onlineTiny2023]。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的在设备端进行小样本学习的框架,旨在解决可穿戴设备中人类活动识别(HAR)的用户特定变化带来的泛化问题。该框架首先训练跨用户的通用表示,然后仅使用少量标记样本对新用户进行快速适应,直接在资源受限的设备上更新轻量级分类器层。这种方法实现了具有最小计算和内存成本的在设备端稳健学习,适用于现实世界部署。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种新型在设备端进行小样本学习的框架,旨在解决可穿戴设备中人类活动识别的泛化问题。
- 该框架结合了跨用户的通用表示和针对个人的快速适应,只需少量标记样本。
- 框架在资源受限的设备上更新轻量级分类器层,减少计算和内存成本。
- 方法在真实世界部署中表现出稳健性,适用于多种应用场景。
- 在三个基准数据集上进行了评估(RecGym、QVAR-Gesture、Ultrasound-Gesture)。
- 部署后的适应提高了准确性,表明小样本在设备端学习可以提高可穿戴人类活动识别的可扩展性、用户意识和能效。
点此查看论文截图


Two-Stage Quranic QA via Ensemble Retrieval and Instruction-Tuned Answer Extraction
Authors:Mohamed Basem, Islam Oshallah, Ali Hamdi, Khaled Shaban, Hozaifa Kassab
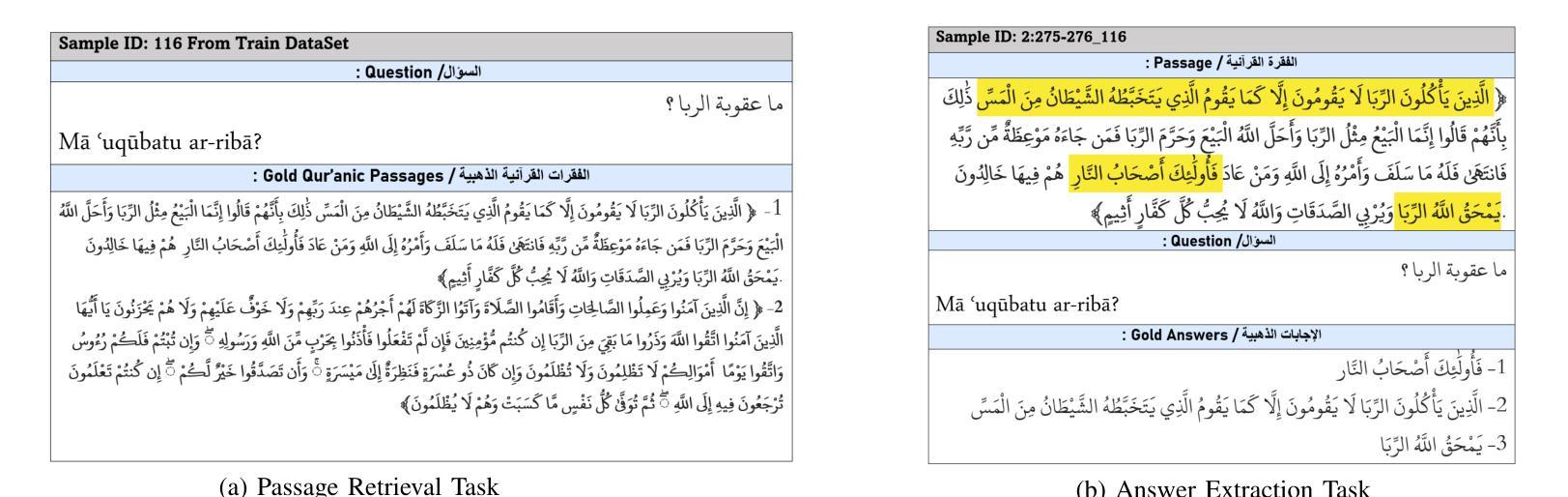
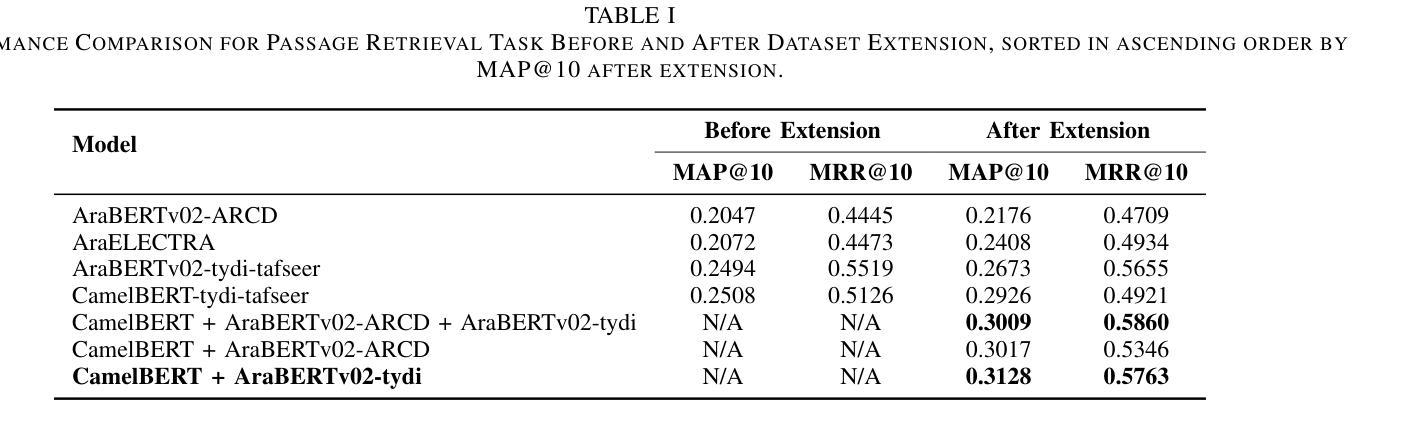
Quranic Question Answering presents unique challenges due to the linguistic complexity of Classical Arabic and the semantic richness of religious texts. In this paper, we propose a novel two-stage framework that addresses both passage retrieval and answer extraction. For passage retrieval, we ensemble fine-tuned Arabic language models to achieve superior ranking performance. For answer extraction, we employ instruction-tuned large language models with few-shot prompting to overcome the limitations of fine-tuning on small datasets. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on the Quran QA 2023 Shared Task, with a MAP@10 of 0.3128 and MRR@10 of 0.5763 for retrieval, and a pAP@10 of 0.669 for extraction, substantially outperforming previous methods. These results demonstrate that combining model ensembling and instruction-tuned language models effectively addresses the challenges of low-resource question answering in specialized domains.
古兰经问答存在独特的挑战,原因在于古典阿拉伯语的复杂性和宗教文本丰富的语义。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的两阶段框架,解决了段落检索和答案提取两个问题。对于段落检索,我们组合了经过精细调整的阿拉伯语模型,以实现出色的排名性能。对于答案提取,我们采用指令训练的大型语言模型进行小样本提示,以克服在小数据集上进行微调时的局限性。我们的方法在古兰经问答共享任务2023中取得了最新成果,检索的MAP@10为0.3128,MRR@10为0.5763,提取的pAP@10为0.669,显著优于以前的方法。这些结果表明,模型组合和指令训练的语言模型相结合有效地解决了特定领域低资源问答中的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages , 4 figures , Accepted in Aiccsa 2025 , https://conferences.sigappfr.org/aiccsa2025/
Summary
论文提出一种新颖的分为两阶段的框架,应对基于《古兰经》的问题回答中的挑战。该框架结合了精细调整的阿拉伯语语言模型,实现了出色的排名性能,并采用指令微调的大型语言模型进行答案提取。该方法在Quran QA 2023共享任务中取得了优异的结果。该研究结果证明结合模型集成和指令微调的语言模型可以有效解决低资源问答中的挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究针对《古兰经》问答中的语言复杂性和语义丰富性提出了独特的挑战。
- 采用两阶段框架,首先进行段落检索,然后进行答案提取。
- 段落检索使用了精细调整的阿拉伯语语言模型,实现了优秀的排名性能。
- 答案提取部分采用了指令微调的大型语言模型,通过少样本提示来克服在小型数据集上精细调整的局限性。
- 该方法在Quran QA 2023共享任务中取得了最佳结果,展现了其有效性。
- 结合模型集成和指令微调的语言模型是解决低资源问答中的挑战的有效方法。
点此查看论文截图


Advancing Dialectal Arabic to Modern Standard Arabic Machine Translation
Authors:Abdullah Alabdullah, Lifeng Han, Chenghua Lin
Dialectal Arabic (DA) poses a persistent challenge for natural language processing (NLP), as most everyday communication in the Arab world occurs in dialects that diverge significantly from Modern Standard Arabic (MSA). This linguistic divide impedes progress in Arabic machine translation. This paper presents two core contributions to advancing DA-MSA translation for the Levantine, Egyptian, and Gulf dialects, particularly in low-resource and computationally constrained settings: (i) a comprehensive evaluation of training-free prompting techniques, and (ii) the development of a resource-efficient fine-tuning pipeline. Our evaluation of prompting strategies across six large language models (LLMs) found that few-shot prompting consistently outperformed zero-shot, chain-of-thought, and our proposed Ara-TEaR method. Ara-TEaR is designed as a three-stage self-refinement prompting process, targeting frequent meaning-transfer and adaptation errors in DA-MSA translation. In this evaluation, GPT-4o achieved the highest performance across all prompting settings. For fine-tuning LLMs, a quantized Gemma2-9B model achieved a chrF++ score of 49.88, outperforming zero-shot GPT-4o (44.58). Joint multi-dialect trained models outperformed single-dialect counterparts by over 10% chrF++, and 4-bit quantization reduced memory usage by 60% with less than 1% performance loss. The results and insights of our experiments offer a practical blueprint for improving dialectal inclusion in Arabic NLP, showing that high-quality DA-MSA machine translation is achievable even with limited resources and paving the way for more inclusive language technologies.
方言阿拉伯语(DA)对自然语言处理(NLP)构成了持续的挑战。阿拉伯世界的日常沟通大多发生在与现代标准阿拉伯语(MSA)存在显著差异的方言中。这种语言鸿沟阻碍了阿拉伯语机器翻译的进步。本文针对莱万托、埃及和海湾方言的DA-MSA翻译,特别是在资源有限和计算受限的环境中,提出了两项核心贡献:(i)对无训练提示技术的全面评估,(ii)资源高效微调管道的开发。我们在六个大型语言模型(LLM)上评估了提示策略,发现少提示法始终优于零提示法、思维链和我们提出的Ara-TEaR方法。Ara-TEaR被设计为一个三阶段的自我完善提示过程,旨在解决DA-MSA翻译中常见的意义转换和适应错误。在此评估中,GPT-4o在所有提示设置中表现最佳。在微调LLM方面,量化后的Gemma2-9B模型在chrF++上取得了49.88的分数,超过了零步GPT-4o(44.58)。联合多方言训练模型在chrF++上的表现超过了单方言训练模型超过10%,而4位量化减少了60%的内存使用,同时性能损失不到1%。我们的实验的结果和见解提供了一个实际的蓝图,用于改善方言在阿拉伯NLP中的包容性,表明即使在有限的资源下也能实现高质量的DA-MSA机器翻译,并为更具包容性的语言技术铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要介绍了针对阿拉伯方言(DA)与现代标准阿拉伯语(MSA)之间的翻译挑战,提出了一系列解决方案。文章详细评估了无需训练提示技术,并开发了一种资源高效的微调管道。评估结果显示,少样本提示法表现最佳,GPT-4o在所有提示设置中的性能最高。对于微调大型语言模型(LLM),量化后的Gemma2-9B模型表现出最佳性能。联合多方言训练模型比单方言模型性能高出超过10%,而4位量化减少了60%的内存使用,同时性能损失不到1%。这些结果提供了改善阿拉伯语NLP中方言包容性的实用蓝图。
Key Takeaways
- 阿拉伯方言(DA)与自然语言处理(NLP)之间的挑战:由于阿拉伯世界中的日常沟通主要发生在与现代标准阿拉伯语(MSA)差异显著的方言中,这阻碍了阿拉伯机器翻译的进步。
- 对无需训练提示技术的全面评估:文章评估了多种无需训练的提示技术,包括少样本提示、零样本和链式思维等。结果显示少样本提示法表现最佳。
- Ara-TEaR方法的引入:作为一种三阶段自我完善提示过程,该方法针对方言与现代标准阿拉伯语翻译中的常见意义转移和适应错误。
- GPT-4o在提示设置中的最佳性能:在评估中,GPT-4o在所有提示设置中的表现最佳。
- 量化模型在微调中的优势:量化后的Gemma2-9B模型在微调大型语言模型方面表现出最佳性能,且内存使用减少了60%,性能损失极小。
- 联合多方言训练模型的优势:联合多方言(如Levantine、埃及和海湾方言)训练的模型比单方言模型性能更高,超出10%。
点此查看论文截图

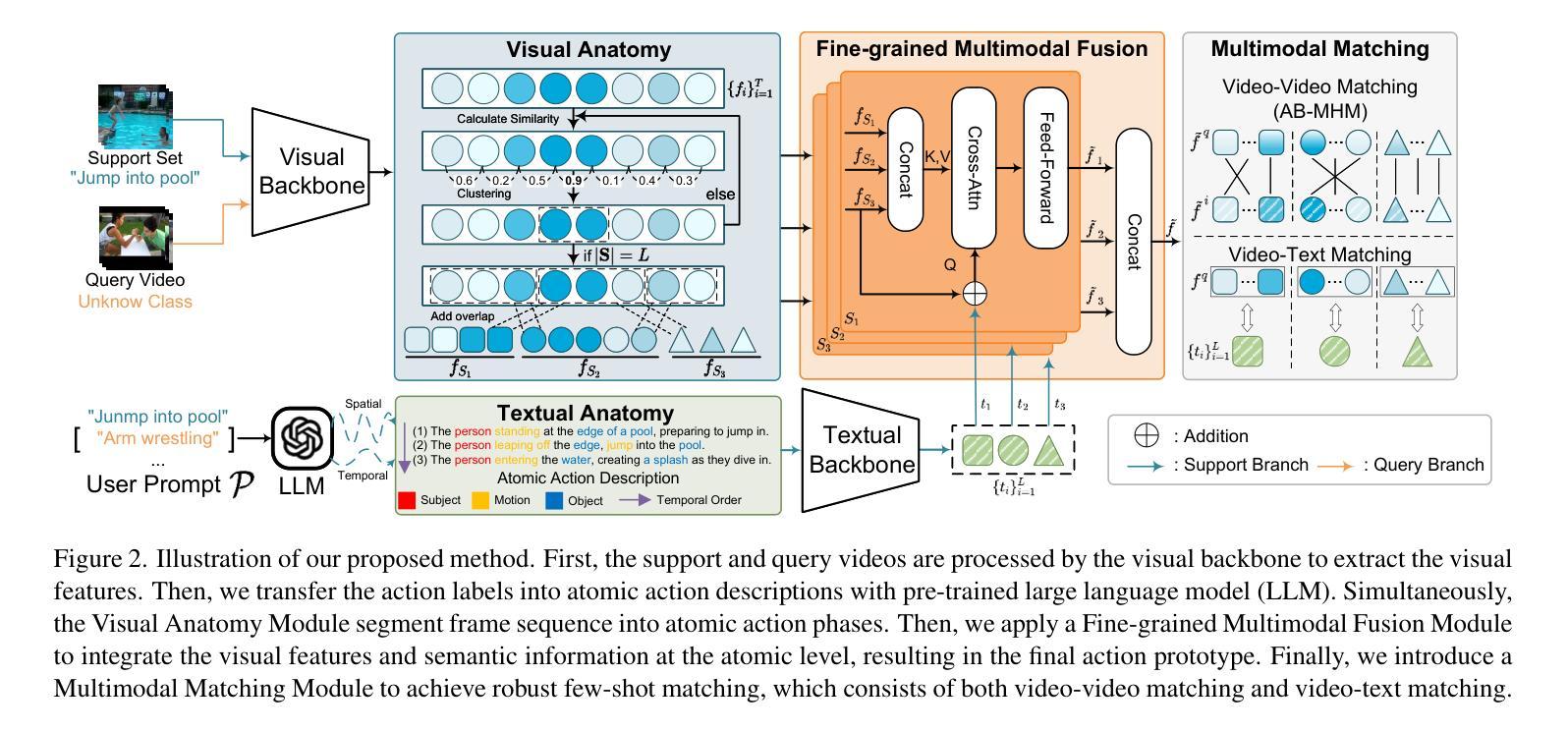
Beyond Label Semantics: Language-Guided Action Anatomy for Few-shot Action Recognition
Authors:Zefeng Qian, Xincheng Yao, Yifei Huang, Chongyang Zhang, Jiangyong Ying, Hong Sun
Few-shot action recognition (FSAR) aims to classify human actions in videos with only a small number of labeled samples per category. The scarcity of training data has driven recent efforts to incorporate additional modalities, particularly text. However, the subtle variations in human posture, motion dynamics, and the object interactions that occur during different phases, are critical inherent knowledge of actions that cannot be fully exploited by action labels alone. In this work, we propose Language-Guided Action Anatomy (LGA), a novel framework that goes beyond label semantics by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to dissect the essential representational characteristics hidden beneath action labels. Guided by the prior knowledge encoded in LLM, LGA effectively captures rich spatiotemporal cues in few-shot scenarios. Specifically, for text, we prompt an off-the-shelf LLM to anatomize labels into sequences of atomic action descriptions, focusing on the three core elements of action (subject, motion, object). For videos, a Visual Anatomy Module segments actions into atomic video phases to capture the sequential structure of actions. A fine-grained fusion strategy then integrates textual and visual features at the atomic level, resulting in more generalizable prototypes. Finally, we introduce a Multimodal Matching mechanism, comprising both video-video and video-text matching, to ensure robust few-shot classification. Experimental results demonstrate that LGA achieves state-of-the-art performance across multipe FSAR benchmarks.
少样本动作识别(FSAR)旨在利用每一类别仅有少量标记样本对视频中的行为进行分类。由于训练数据的稀缺,最近的研究努力融入了额外的模式,尤其是文本。然而,人类姿势、运动动态以及在各个阶段发生的对象交互的细微变化,是动作的关键固有知识,仅凭动作标签是无法完全利用的。在此工作中,我们提出了Language-Guided Action Anatomy(LGA)这一新框架,它通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)来剖析隐藏在动作标签下的关键表征特征,超越了标签语义。在LLM编码的先验知识的引导下,LGA有效地捕获了少样本场景中的丰富时空线索。具体来说,对于文本,我们提示现成的LLM将标签解剖成原子动作描述的序列,侧重于动作的三个核心元素(主体、运动、对象)。对于视频,视觉解剖模块将动作分割成原子视频阶段,以捕获动作的序列结构。一种精细的融合策略在原子层面整合了文本和视频特征,产生了更具概括性的原型。最后,我们引入了一种多模态匹配机制,包括视频-视频和视频-文本匹配,以确保可靠的少样本分类。实验结果表明,LGA在多个人体少样本动作识别基准测试中达到了最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出了一个名为Language-Guided Action Anatomy(LGA)的新框架,用于解决少样本动作识别问题。该框架借助大型语言模型(LLM)对动作标签进行解构,捕捉动作的关键代表性特征。通过视觉解剖模块和视频片段匹配机制,实现文本和视觉特征的深度融合,从而增强模型在多动作场景下的泛化能力和识别性能。实验结果表明,LGA在多个FSAR基准测试中实现了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
以下是本文的七个关键见解:
- LGA框架结合文本和视觉信息来解决少样本动作识别问题。
- LGA利用大型语言模型(LLM)解构动作标签,挖掘动作的内在知识。
- LGA通过视觉解剖模块将动作分解为原子视频阶段,捕捉动作的序列结构。
- LGA采用精细的融合策略,在原子层面整合文本和视觉特征。
- LGA引入视频片段和视频文本匹配机制,确保稳健的少样本分类。
- LGA在多个FSAR基准测试中取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图



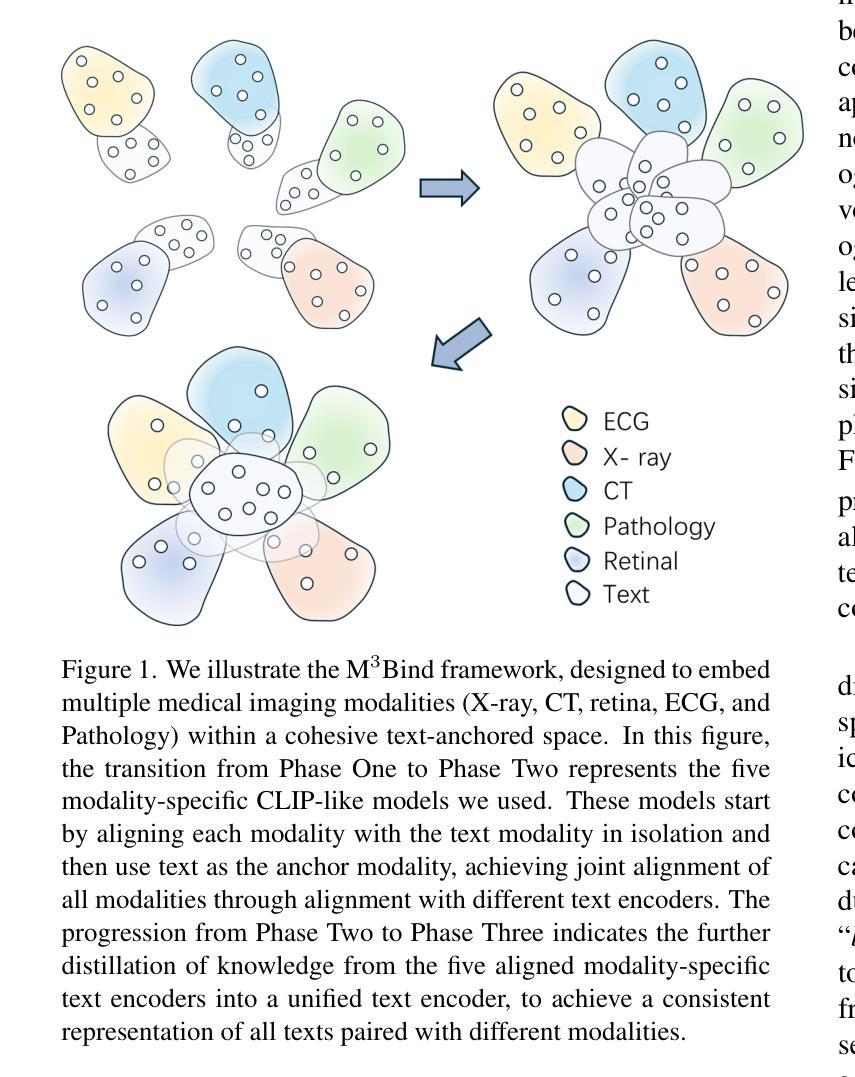
Multimodal Medical Image Binding via Shared Text Embeddings
Authors:Yunhao Liu, Suyang Xi, Shiqi Liu, Hong Ding, Chicheng Jin, Chong Zhong, Junjun He, Catherine C. Liu, Yiqing Shen
Medical image analysis increasingly relies on the integration of multiple imaging modalities to capture complementary anatomical and functional information, enabling more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Achieving aligned feature representations across these diverse modalities is therefore important for effective multimodal analysis. While contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) and its variant have enabled image-text alignments, they require explicitly paired data between arbitrary two modalities, which is difficult to acquire in medical contexts. To address the gap, we present Multimodal Medical Image Binding with Text (M\textsuperscript{3}Bind), a novel pre-training framework that enables seamless alignment of multiple medical imaging modalities through a shared text representation space without requiring explicit paired data between any two medical image modalities. Specifically, based on the insight that different images can naturally bind with text, M\textsuperscript{3}Bind first fine-tunes pre-trained CLIP-like image-text models to align their modality-specific text embedding space while preserving their original image-text alignments. Subsequently, we distill these modality-specific text encoders into a unified model, creating a shared text embedding space. Experiments on X-ray, CT, retina, ECG, and pathological images on multiple downstream tasks demonstrate that M\textsuperscript{3}Bind achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot, few-shot classification and cross-modal retrieval tasks compared to its CLIP-like counterparts. These results validate M\textsuperscript{3}Bind’s effectiveness in achieving cross-image-modal alignment for medical analysis.
医学影像分析越来越依赖于多种成像模式的融合,以捕捉互补的解剖和功能性信息,从而实现更准确的诊断和制定治疗方案。因此,在这些不同的模式之间实现对齐的特征表示对于有效的多模态分析至关重要。虽然对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)及其变体已经实现了图像文本的对齐,但它们需要在任意两个模态之间明确配对的数据,这在医学环境中很难获取。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了基于文本的多模态医学图像绑定(M\textsuperscript{3}Bind),这是一种新的预训练框架,它能够通过共享文本表示空间无缝对齐多个医学成像模式,而无需在任意两个医学图像模式之间要求明确的配对数据。具体来说,基于不同图像可以自然绑定文本的看法,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind首先微调预训练的CLIP类图像文本模型,以对齐其特定于模态的文本嵌入空间,同时保留其原始的图像文本对齐。然后,我们将这些特定于模态的文本编码器蒸馏到一个统一模型中,创建一个共享的文本嵌入空间。在X射线、CT、视网膜、心电图和病理图像等多种下游任务上的实验表明,与CLIP类模型相比,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本、少样本分类和跨模态检索任务上实现了最先进的性能。这些结果验证了M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在实现医学分析中的跨图像模态对齐方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 figures
Summary
该文介绍了医疗图像分析中对多种成像模式集成的重要性,并指出为实现跨不同模式的对齐特征表示所面临的挑战。为解决这一问题,提出了一种新的预训练框架——多模态医学图像与文本绑定(M\textsuperscript{3}Bind),该框架能够在无需任意两种医学图像模式之间明确配对数据的情况下,通过共享文本表示空间实现多医学成像模式的无缝对齐。实验结果表明,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本、少样本分类和跨模态检索任务上的性能达到最新水平,验证了其在医学分析中实现跨图像模态对齐的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分析受益于多成像模式的集成,以获取互补的解剖和功能性信息,促进更准确诊断和治疗计划。
- 跨不同医学成像模式实现对齐特征表示是有效多模态分析的关键。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind是一种新的预训练框架,可在无需任意两种医学图像模式之间明确配对数据的情况下,实现无缝对齐。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind基于不同图像自然绑定文本的观念,首先微调预训练的CLIP类图像-文本模型,以对齐模态特定的文本嵌入空间,同时保留其原始图像-文本对齐。
- M\textsuperscript{3}Bind通过蒸馏模态特定文本编码器到统一模型,创建共享文本嵌入空间。
- 实验结果表明,M\textsuperscript{3}Bind在零样本、少样本分类和跨模态检索任务上的性能达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图


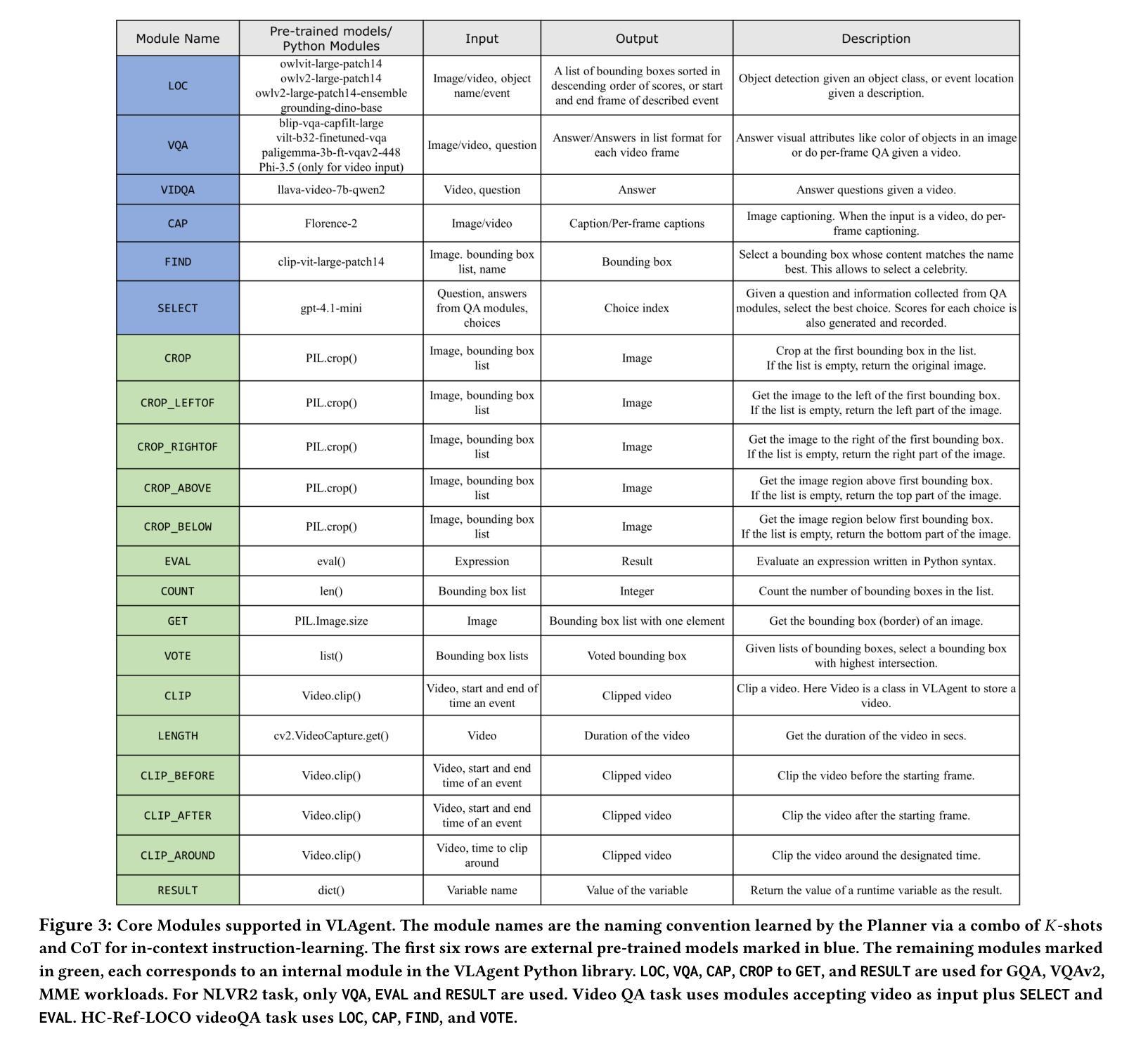
A Vision-Language Agent System for Compositional Reasoning with VLM-assisted Script and Executable Generation
Authors:Yichang Xu, Gaowen Liu, Ramana Rao Kompella, Sihao Hu, Tiansheng Huang, Fatih Ilhan, Selim Furkan Tekin, Zachary Yahn, Ling Liu
The advancement in large language models (LLMs) and large vision models has fueled the rapid progress in multi-modal vision-text reasoning capabilities. However, existing vision-language models (VLMs) to date offer poor performance for compositional reasoning. This paper presents VLAgent, a vision-language agent system for vision-text compositional reasoning with three novel features. First, VLAgent leverages a pre-trained LLM with few-shot context learning to generate the planning script for each compositional reasoning task and provides a backend engine to generate and perform executable runtime, which maps the planning script into executable code using the VLAgent library for VLAgent executor. Second, VLAgent introduces the SS-parser, which identifies and corrects logic errors embedded in the LLM-generated planning script, to further enhance the quality of script-executable mapping. Third, VLAgent introduces the compositional reasoning output verifier, which validates and refines the output of complex compositional reasoning steps, by leveraging complementary reasoning techniques, e.g., ensemble learning and caption analysis. Extensive experiments are conducted on six visual benchmarks and compared to a dozen of the SoTA visual reasoning models. The results show that VLAgent outperforms existing representative approaches for compositional text-visual reasoning. Our code and datasets with outputs will be made available upon acceptance.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)和大型视觉模型的进步,多模态视觉文本推理能力的快速发展得到了推动。然而,迄今为止的现有视觉语言模型(VLM)在组合推理方面的表现较差。本文提出了VLAgent,一个用于视觉文本组合推理的视觉语言代理系统,具有三个新颖的特点。首先,VLAgent利用预训练的大型语言模型进行少量上下文学习,为每项组合推理任务生成规划脚本,并提供后端引擎来生成并执行运行时脚本,使用VLAgent库将规划脚本映射为可执行代码以供VLAgent执行器使用。其次,VLAgent引入了SS解析器,用于识别和纠正大型语言模型生成的规划脚本中的逻辑错误,以进一步提高脚本可执行映射的质量。第三,VLAgent引入了组合推理输出验证器,它通过利用互补推理技术(如集成学习和字幕分析)来验证和优化复杂组合推理步骤的输出。在六个视觉基准测试上进行了广泛实验,并与一系列最先进的视觉推理模型进行了比较。结果表明,VLAgent在组合文本视觉推理方面优于现有代表性方法。我们的代码和包含输出的数据集将在接受后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)和大型视觉模型的进步推动了多模态视觉文本推理能力的快速发展。然而,现有的视觉语言模型(VLM)在组合推理方面的表现不佳。本文提出了VLAgent,一个具有三个新特性的视觉语言代理系统,用于视觉文本组合推理。VLAgent利用预训练的大型语言模型进行少量上下文学习,为每项组合推理任务生成规划脚本,并提供后端引擎来生成并执行运行时脚本。此外,VLAgent还引入了SS解析器,用于识别和纠正大型语言模型生成的规划脚本中的逻辑错误。最后,VLAgent引入了组合推理输出验证器,通过利用互补推理技术(如集成学习和字幕分析)来验证和细化复杂组合推理步骤的输出。在六个视觉基准测试上的大量实验表明,VLAgent在组合文本视觉推理方面优于现有代表性方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型和视觉模型的进步推动了多模态视觉文本推理的发展。
- 现有视觉语言模型在组合推理方面的表现不佳。
- VLAgent系统具有三个新特性,包括利用预训练的大型语言模型进行少量上下文学习,生成规划脚本并映射为可执行代码。
- VLAgent引入了SS解析器来识别和纠正规划脚本中的逻辑错误。
- VLAgent包含组合推理输出验证器,用于验证和细化复杂组合推理步骤的输出。
- VLAgent在六个视觉基准测试上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图





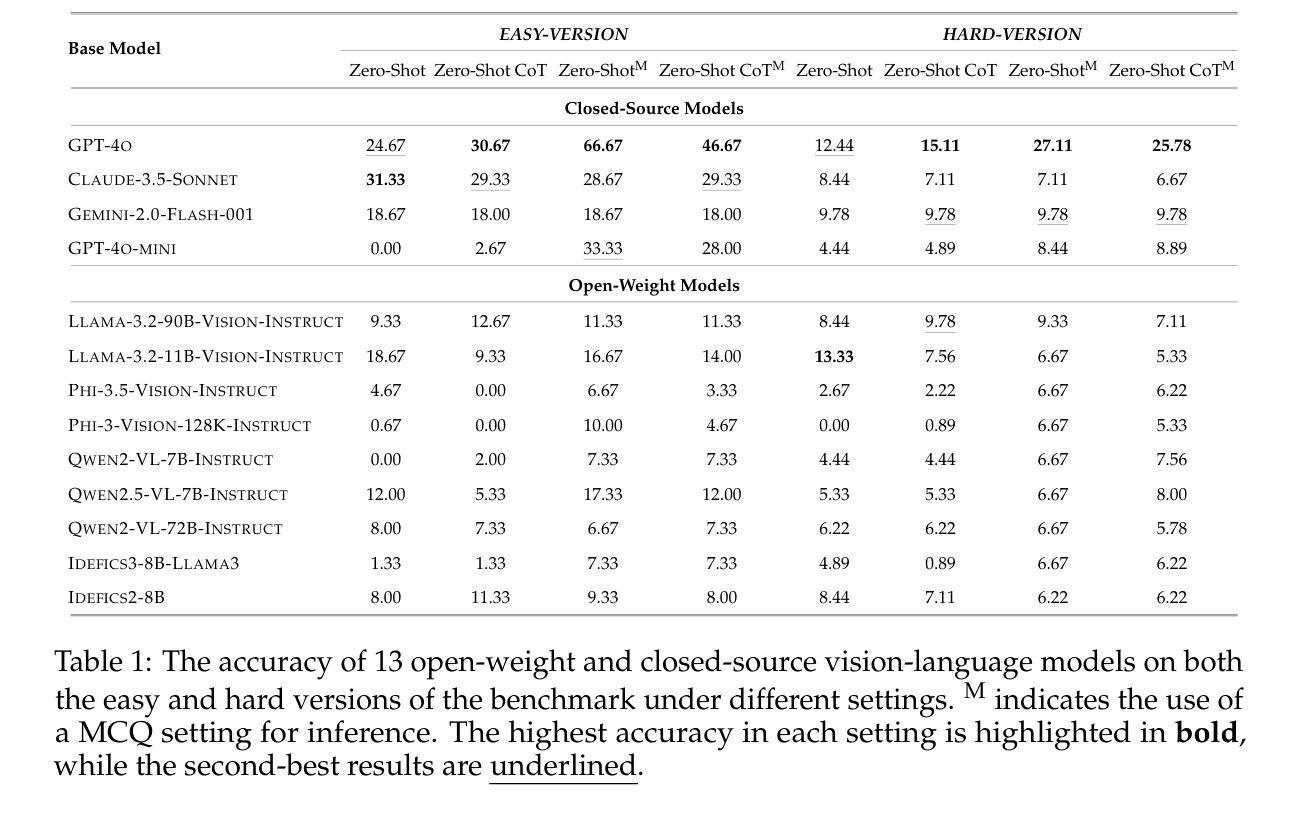
Texture or Semantics? Vision-Language Models Get Lost in Font Recognition
Authors:Zhecheng Li, Guoxian Song, Yujun Cai, Zhen Xiong, Junsong Yuan, Yiwei Wang
Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit remarkable visual and linguistic capabilities, achieving impressive performance in various tasks such as image recognition and object localization. However, their effectiveness in fine-grained tasks remains an open question. In everyday scenarios, individuals encountering design materials, such as magazines, typography tutorials, research papers, or branding content, may wish to identify aesthetically pleasing fonts used in the text. Given their multimodal capabilities and free accessibility, many VLMs are often considered potential tools for font recognition. This raises a fundamental question: Do VLMs truly possess the capability to recognize fonts? To investigate this, we introduce the Font Recognition Benchmark (FRB), a compact and well-structured dataset comprising 15 commonly used fonts. FRB includes two versions: (i) an easy version, where 10 sentences are rendered in different fonts, and (ii) a hard version, where each text sample consists of the names of the 15 fonts themselves, introducing a stroop effect that challenges model perception. Through extensive evaluation of various VLMs on font recognition tasks, we arrive at the following key findings: (i) Current VLMs exhibit limited font recognition capabilities, with many state-of-the-art models failing to achieve satisfactory performance and being easily affected by the stroop effect introduced by textual information. (ii) Few-shot learning and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting provide minimal benefits in improving font recognition accuracy across different VLMs. (iii) Attention analysis sheds light on the inherent limitations of VLMs in capturing semantic features.
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)展现出令人瞩目的视觉和语言能力,在各种任务中取得了令人印象深刻的表现,如图像识别和对象定位。然而,它们在精细任务中的有效性仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在日常场景中,人们遇到设计材料,如杂志、字体教程、研究论文或品牌内容,可能会希望识别文本中美观的字体。考虑到它们的多模式能力和自由可访问性,许多VLMs通常被认为是字体识别的潜在工具。这引发了一个根本性的问题:VLMs是否真的具备字体识别的能力?为了调查这个问题,我们引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB),这是一个包含15种常用字体的紧凑且结构良好的数据集。FRB包括两个版本:(i)一个简单版本,其中10个句子以不同的字体呈现;(ii)一个困难版本,其中每个文本样本由这15种字体的名称组成,引入一种斯特鲁普效应,挑战模型的感知能力。通过对各种VLM在字体识别任务上的广泛评估,我们得出了以下关键发现:(i)当前VLM在字体识别方面的能力有限,许多最先进的模型无法达到满意的性能,并且容易受到文本信息引入的斯特鲁普效应的影响。(ii)小样本学习和思维链(CoT)提示在不同VLM中提供最小的改善字体识别准确性的好处。(iii)注意力分析揭示了VLM在捕获语义特征方面的内在局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to COLM 2025
摘要
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像识别、物体定位等方面表现出卓越的视觉和语言能力。然而,其在精细任务中的效果仍然有待探索。对于日常场景中遇到的字体识别问题,例如杂志、排版教程、研究论文或品牌内容中的字体,人们希望模型能够识别出文本中使用的美观字体。考虑到VLMs的多模态能力和开放性访问性,其被视为潜在字体识别工具。然而,我们的研究引入了字体识别基准测试集(FRB),包含15种常用字体和两个版本:一个简单版本,其中10句话用不同的字体呈现;一个困难版本,其中每个文本样本由这15种字体的名称组成,引入斯特鲁普效应挑战模型的感知能力。通过对各种VLMs在字体识别任务上的广泛评估,我们发现当前VLMs在字体识别方面能力有限,许多先进模型无法达到令人满意的性能,且容易受到斯特鲁普效应的影响。此外,小样学习法和Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示对改进不同VLMs的字体识别准确度仅提供有限帮助。注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕获语义特征方面的内在局限性。
关键见解
- 当前视觉语言模型(VLMs)在字体识别方面的能力有限。
- 许多先进模型在字体识别任务上的表现并不理想,容易受到斯特鲁普效应的影响。
- 小样学习法和Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示对改进字体识别准确度的作用有限。
- 注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕获语义特征方面的内在局限性。
- FRB测试集为评估VLMs在字体识别方面的性能提供了有效工具。
- VLMs在日常场景中的实际应用能力仍需进一步研究和优化。
点此查看论文截图



Legacy Learning Strategy Based on Few-Shot Font Generation Models for Automatic Text Design in Metaverse Content
Authors:Younghwi Kim, Dohee Kim, Seok Chan Jeong, Sunghyun Sim
The metaverse consists of hardware, software, and content, among which text design plays a critical role in enhancing user immersion and usability as a content element. However, in languages such as Korean and Chinese that require thousands of unique glyphs, creating new text designs involves high costs and complexity. To address this, this study proposes a training strategy called Legacy Learning, which recombines and transforms structures based on existing text design models. This approach enables the generation of new text designs and improves quality without manual design processes. To evaluate Legacy Learning, it was applied to Korean and Chinese text designs. Additionally, we compared results before and after on seven state of the art text generation models. As a result, text designs generated using Legacy Learning showed over a 30% difference in Frechet Inception Distance (FID) and Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) metrics compared to the originals, and also exhibited meaningful style variations in visual comparisons. Furthermore, the repeated learning process improved the structural consistency of the generated characters, and an OCR based evaluation showed increasing recognition accuracy across iterations, indicating improved legibility of the generated glyphs. In addition, a System Usability Scale (SUS) survey was conducted to evaluate usability among metaverse content designers and general users. The expert group recorded a score of 95.78 (“Best Imaginable”), while the non expert group scored 76.42 (“Excellent”), indicating an overall high level of usability. These results suggest that Legacy Learning can significantly improve both the production efficiency and quality of text design in the metaverse environment.
元宇宙由硬件、软件和内容组成,其中文本设计作为内容元素,在增强用户沉浸感和易用性方面扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,在诸如韩语和中文等需要数千个独特字符的语言中,创建新的文本设计涉及高昂的成本和复杂性。为了解决这一问题,本研究提出了一种名为Legacy Learning的训练策略,该策略基于现有的文本设计模型进行重组和转换。这种方法能够生成新的文本设计,并在无需手动设计流程的情况下提高质量。为了评估Legacy Learning,我们将其应用于韩语和中文的文本设计,并在七个最先进的文本生成模型上进行了应用前后的比较。结果显示,使用Legacy Learning生成的文本设计在Frechet Inception Distance(FID)和Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity(LPIPS)指标上与原始设计相比有超过30%的差异,同时在视觉比较中也表现出有意义的风格变化。此外,重复学习过程提高了生成字符的结构一致性,OCR(光学字符识别)评估显示识别准确率随着迭代而提高,表明生成的字符可识别性有所提高。此外,还进行了系统可用性量表(SUS)调查,以评估元宇宙内容设计师和一般用户的可用性。专家组得分为95.78(最高分),非专家组得分为76.42(优秀),显示出整体较高的可用性。这些结果表明,Legacy Learning可以显著提高元宇宙环境中文本设计的生产效率和质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要介绍了在元宇宙环境中,文本设计对于增强用户沉浸感和可用性的重要性。针对如韩语和中文等需要独特字符的语言,提出了Legacy Learning训练策略,该策略基于现有文本设计模型进行重组和转换,以生成新的文本设计并提高质量,无需手动设计过程。实验结果显示,Legacy Learning在FID和LPIPS指标上相较于原始设计有显著改善,生成的字符结构更加一致,识别准确率也有所提高。同时,通过系统可用性量表评估,该策略在元宇宙内容设计师和普通用户中的可用性均表现优秀。总之,Legacy Learning可显著提高文本设计的生产效率和质量。
Key Takeaways
- 文本设计在元宇宙环境中对增强用户沉浸感和可用性至关重要。
- Legacy Learning是一种基于现有文本设计模型的训练策略,能够生成新的文本设计并提高其质量。
- Legacy Learning策略在韩语和中文的文本设计中得到了应用。
- 通过FID和LPIPS指标评估,Legacy Learning在生成文本设计上表现出显著的性能提升。
- Legacy Learning能够改善生成的字符结构一致性,提高字符识别准确率。
- 系统可用性量表评估显示,Legacy Learning在元宇宙内容设计师和普通用户中的可用性均表现优秀。
点此查看论文截图


When predict can also explain: few-shot prediction to select better neural latents
Authors:Kabir Dabholkar, Omri Barak
Latent variable models serve as powerful tools to infer underlying dynamics from observed neural activity. Ideally, the inferred dynamics should align with true ones. However, due to the absence of ground truth data, prediction benchmarks are often employed as proxies. One widely-used method, $\textit{co-smoothing}$, involves jointly estimating latent variables and predicting observations along held-out channels to assess model performance. In this study, we reveal the limitations of the co-smoothing prediction framework and propose a remedy. Using a student-teacher setup, we demonstrate that models with high co-smoothing can have arbitrary extraneous dynamics in their latent representations. To address this, we introduce a secondary metric – $\textit{few-shot co-smoothing}$, performing regression from the latent variables to held-out neurons in the data using fewer trials. Our results indicate that among models with near-optimal co-smoothing, those with extraneous dynamics underperform in the few-shot co-smoothing compared to `minimal’ models that are devoid of such dynamics. We provide analytical insights into the origin of this phenomenon and further validate our findings on four standard neural datasets using a state-of-the-art method: STNDT. In the absence of ground truth, we suggest a novel measure to validate our approach. By cross-decoding the latent variables of all model pairs with high co-smoothing, we identify models with minimal extraneous dynamics. We find a correlation between few-shot co-smoothing performance and this new measure. In summary, we present a novel prediction metric designed to yield latent variables that more accurately reflect the ground truth, offering a significant improvement for latent dynamics inference.
潜在变量模型是推断观察到的神经活动潜在动态的强大工具。理想情况下,推断出的动态应与真实情况相符。然而,由于缺乏真实数据,通常使用预测基准作为代理。一种广泛使用的方法,即“协同平滑法”,涉及联合估计潜在变量并预测保留通道的观察结果,以评估模型性能。在这项研究中,我们揭示了协同平滑预测框架的局限性,并提出了一种补救措施。我们使用学生-教师设置,证明了具有高协同平滑的模型在其潜在表示中可能存在任意的额外动态。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了次要指标——“小样本协同平滑”,使用较少的试验次数从潜在变量回归数据中的保留神经元。我们的结果表明,在接近最佳协同平滑的模型中,存在额外动态的模型在少量样本协同平滑方面的表现较差,与没有此类动态的“最小”模型相比。我们对这种现象的起源进行了深入的分析洞察,并使用最先进的STNDT方法进一步验证了我们在四个标准神经数据集上的发现。在没有真实数据的情况下,我们提出了一种新的措施来验证我们的方法。通过交叉解码所有高协同平滑模型对的潜在变量,我们确定了具有最少额外动态的模型。我们发现少量样本协同平滑表现与此新度量之间存在相关性。总之,我们提出了一种新型预测指标,旨在产生更准确地反映真实情况的潜在变量,为潜在动态推断提供了重大改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文揭示了现有预测框架——协同平滑的局限性,并提出了改进方案。研究通过学生-教师设置揭示了即使具有较高协同平滑性能的模型也可能在潜在表示中存在任意额外动力学。为解决这一问题,研究引入了次要指标——少镜头协同平滑,通过较少的试验次数从潜在变量回归数据中的未观测神经元。结果表明,在接近最佳协同平滑的模型中,存在额外动力学的模型在少镜头协同平滑方面表现较差。研究提供了对此现象的解析洞察,并在四个标准神经数据集上使用最新方法验证了发现。针对缺乏真实数据的情况,研究提出了一种验证新方法的有效性衡量标准——通过交叉解码所有高协同平滑模型对的潜在变量来识别具有最少额外动力学的模型。发现少镜头协同平滑性能与新衡量标准之间存在相关性。总之,研究提出了一种新的预测指标,旨在产生更准确地反映真实情况的潜在变量,为潜在动力学推断提供了重大改进。
Key Takeaways
- 现有预测框架协同平滑存在局限性,无法准确反映模型的潜在动力学。
- 提出了一种新的预测指标——少镜头协同平滑,通过较少的试验次数评估模型性能。
- 研究发现存在额外动力学的模型在少镜头协同平滑方面表现较差。
- 提供了对这种现象的解析洞察,揭示了额外动力学对模型性能的影响。
- 在四个标准神经数据集上验证了研究的发现和新方法的有效性。
- 提出了一种新的衡量标准来验证模型是否具有最少额外动力学的方法。
点此查看论文截图





