⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-08 更新
Towards Inclusive Communication: A Unified LLM-Based Framework for Sign Language, Lip Movements, and Audio Understanding
Authors:Jeong Hun Yeo, Hyeongseop Rha, Sungjune Park, Junil Won, Yong Man Ro
Audio is the primary modality for human communication and has driven the success of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) technologies. However, such systems remain inherently inaccessible to individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing. Visual alternatives such as sign language and lip reading offer effective substitutes, and recent advances in Sign Language Translation (SLT) and Visual Speech Recognition (VSR) have improved audio-less communication. Yet, these modalities have largely been studied in isolation, and their integration within a unified framework remains underexplored. In this paper, we introduce the first unified framework capable of handling diverse combinations of sign language, lip movements, and audio for spoken-language text generation. We focus on three main objectives: (i) designing a unified, modality-agnostic architecture capable of effectively processing heterogeneous inputs; (ii) exploring the underexamined synergy among modalities, particularly the role of lip movements as non-manual cues in sign language comprehension; and (iii) achieving performance on par with or superior to state-of-the-art models specialized for individual tasks. Building on this framework, we achieve performance on par with or better than task-specific state-of-the-art models across SLT, VSR, ASR, and AVSR. Furthermore, our analysis reveals that explicitly modeling lip movements as a separate modality significantly improves SLT performance.
音频是人类沟通的主要方式,并推动了自动语音识别(ASR)技术的成功。然而,这些系统对于聋哑人士来说仍然天生无法访问。手语和唇读等视觉替代方案提供了有效的替代方法,最近在手语翻译(SLT)和视觉语音识别(VSR)方面的进展提高了无声沟通的效率。然而,这些模式大多被孤立研究,它们在统一框架中的整合仍然未被充分探索。在本文中,我们介绍了第一个能够处理手语、唇动和音频等多种组合的统一框架,用于生成口语文本。我们重点关注三个主要目标:(i)设计一种统一、与模态无关的架构,能够有效处理异构输入;(ii)探索未被充分研究的模态之间的协同作用,特别是唇动作为非手动线索在手语理解中的作用;(iii)达到或超过针对单个任务专业化的最新模型的性能。基于该框架,我们在SLT、VSR、ASR和AVSR方面的性能达到或优于特定任务的最先进模型。此外,我们的分析表明,将唇动明确建模为单独的模式可以显著提高SLT性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at: https://github.com/JeongHun0716/UniSLA
Summary
本文介绍了一个统一框架,该框架能够处理包括手语、嘴唇动作和音频在内的多种组合,用于生成口语文本。研究重点包括设计一种统一、模式无关的结构,以有效处理异构输入;探索各模式间尤其是嘴唇动作在非手动提示手语理解中的角色;以及实现与或优于针对个别任务的最新模型的性能。通过这一框架,研究者在手语翻译、视觉语音识别、语音识别和视听语音识别方面达到了与最新模型相当或更好的性能。此外,分析显示,将嘴唇动作作为独立模式进行建模可以显著提高手语翻译性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出了首个能够处理手语、嘴唇动作和音频等多种模式的统一框架,用于生成口语文本。
- 研究重点包括设计一种有效的统一架构,探索各模式间的协同作用,并达到或超越针对个别任务的最新模型性能。
- 分析发现,将嘴唇动作作为独立模式进行建模可以显著提高手语翻译性能。
- 该框架在手语翻译、视觉语音识别、语音识别和视听语音识别方面取得了显著成果。
- 该研究强调了视觉信息(如手语和嘴唇动作)在音频无法访问或缺失情况下的重要性。
- 此研究为整合不同沟通模式提供了一个有效的平台,增强了沟通障碍人士的沟通能力。
点此查看论文截图



Unifying Diarization, Separation, and ASR with Multi-Speaker Encoder
Authors:Muhammad Shakeel, Yui Sudo, Yifan Peng, Chyi-Jiunn Lin, Shinji Watanabe
This paper presents a unified multi-speaker encoder (UME), a novel architecture that jointly learns representations for speaker diarization (SD), speech separation (SS), and multi-speaker automatic speech recognition (ASR) tasks using a shared speech foundational encoder. We leverage the hidden representations from multiple layers of UME as a residual weighted-sum encoding (RWSE) to effectively use information from different semantic levels, contributing to bottom-up alignment between tasks. This joint training approach captures the inherent interdependencies among the tasks, enhancing overall performance on overlapping speech data. Our evaluations demonstrate that UME substantially improves over the single-task baselines dedicated to SD, SS, and multi-speaker ASR on LibriMix evaluation sets. Notably, for SD, UME outperforms the previous studies, achieving diarization error rates of 1.37% and 2.29% on Libri2Mix and Libri3Mix evaluation sets, respectively.
本文提出了一种统一的多说话人编码器(UME)的新架构,该架构通过共享的基础语音编码器联合学习说话人分图(SD)、语音分离(SS)和多说话人自动语音识别(ASR)任务的表示。我们利用UME多层隐藏表示作为残差加权和编码(RWSE),有效利用来自不同语义级别的信息,促进任务之间的自下而上的对齐。这种联合训练方法捕获任务之间的内在相互依赖性,提高了重叠语音数据上的整体性能。我们的评估表明,在LibriMix评估集上,与专门用于SD、SS和多说话人ASR的单任务基线相比,UME有显著改善。值得注意的是,对于SD,UME的表现优于之前的研究,在Libri2Mix和Libri3Mix评估集上分别达到了分图错误率为1.37%和2.29%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE ASRU 2025
总结
本文提出了一种统一的多说话人编码器(UME)的新架构,该架构可以联合学习说话人分段(SD)、语音分离(SS)和多说话人自动语音识别(ASR)任务的表示。通过利用UME多层隐藏表示作为残差加权和编码(RWSE),有效使用不同语义层次的信息,实现任务之间的自下而上的对齐。联合训练方式捕捉任务之间的内在相互依赖性,提高重叠语音数据的整体性能。在LibriMix评估集上的评估结果表明,UME在SD、SS和多说话人ASR的单任务基准测试上有了显著改进。特别是在SD方面,UME的表现优于之前的研究,在Libri2Mix和Libri3Mix评估集上的分段错误率分别为1.37%和2.29%。
关键见解
- 提出了统一的多说话人编码器(UME)新架构,可联合学习多种语音任务。
- 使用残差加权和编码(RWSE)融合多层隐藏表示,以提高不同语义层次的信息利用。
- 通过自下而上的对齐方式实现任务间的对齐。
- 联合训练方式捕捉任务间的内在相互依赖性。
- UME在LibriMix评估集上的表现优于单任务基准测试。
- 在说话人分段(SD)任务上,UME表现尤为出色,错误率低至1.37%和2.29%。
- UME有助于提高处理重叠语音数据的整体性能。
点此查看论文截图



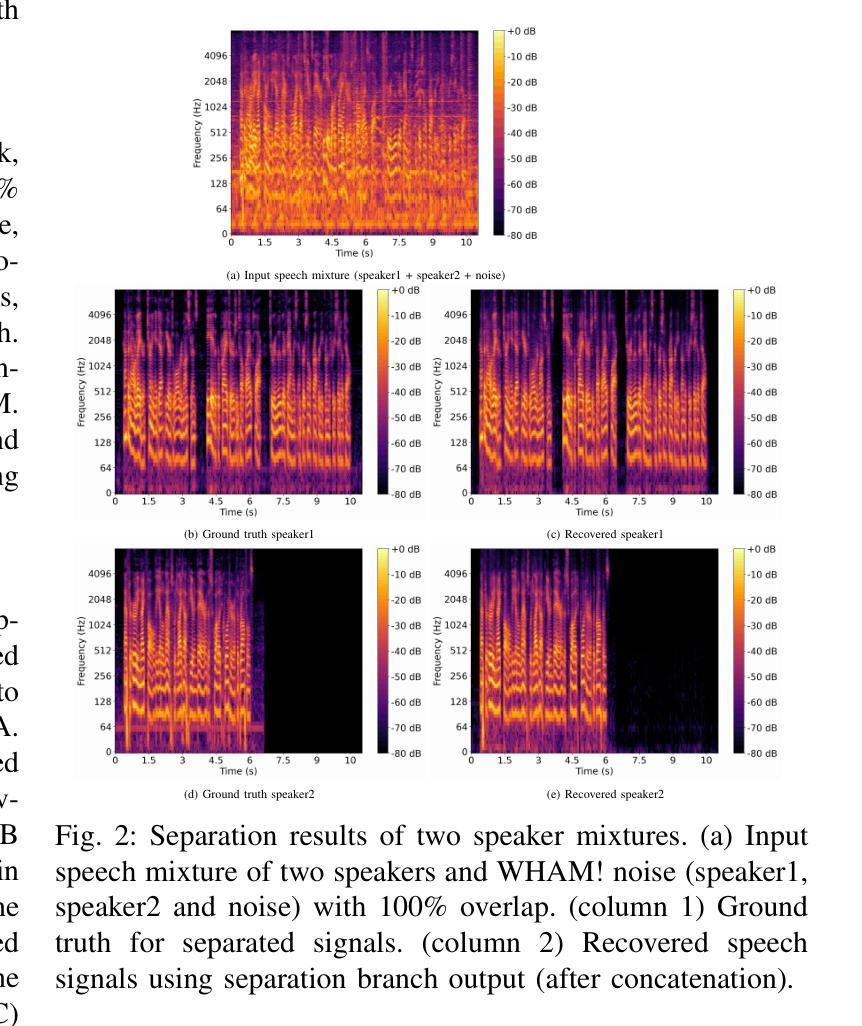

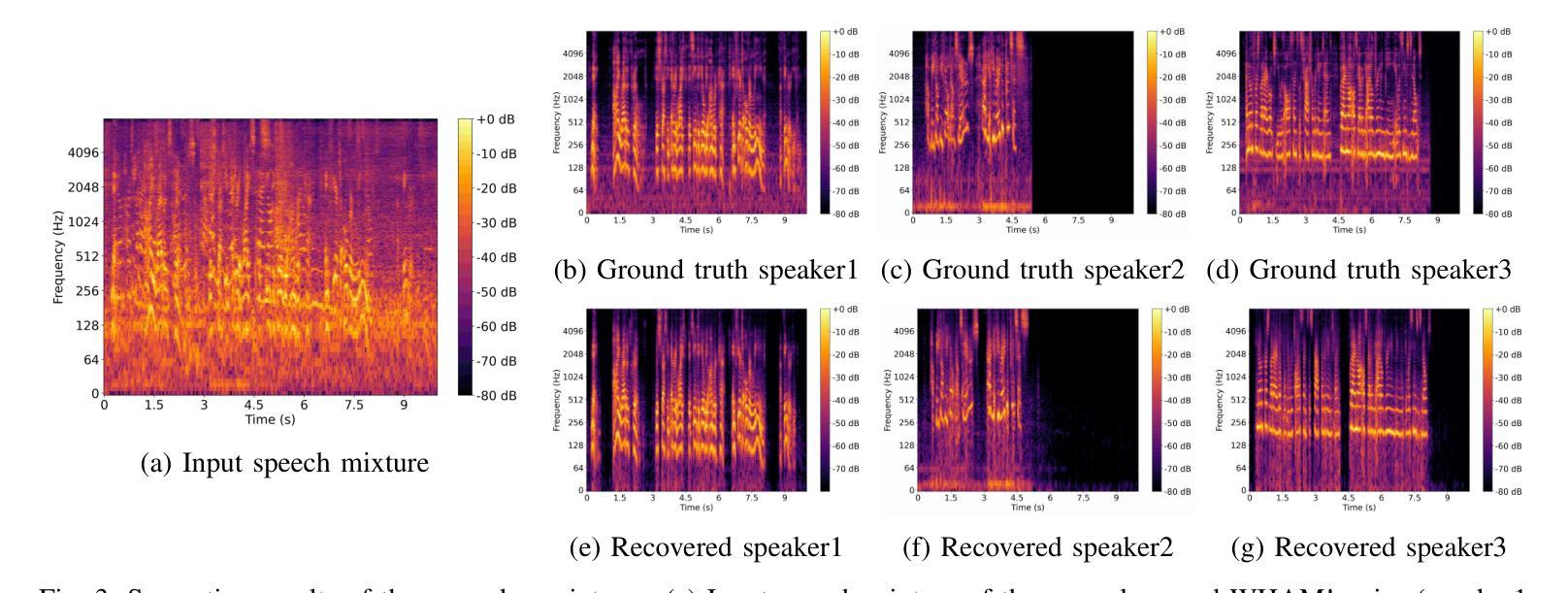

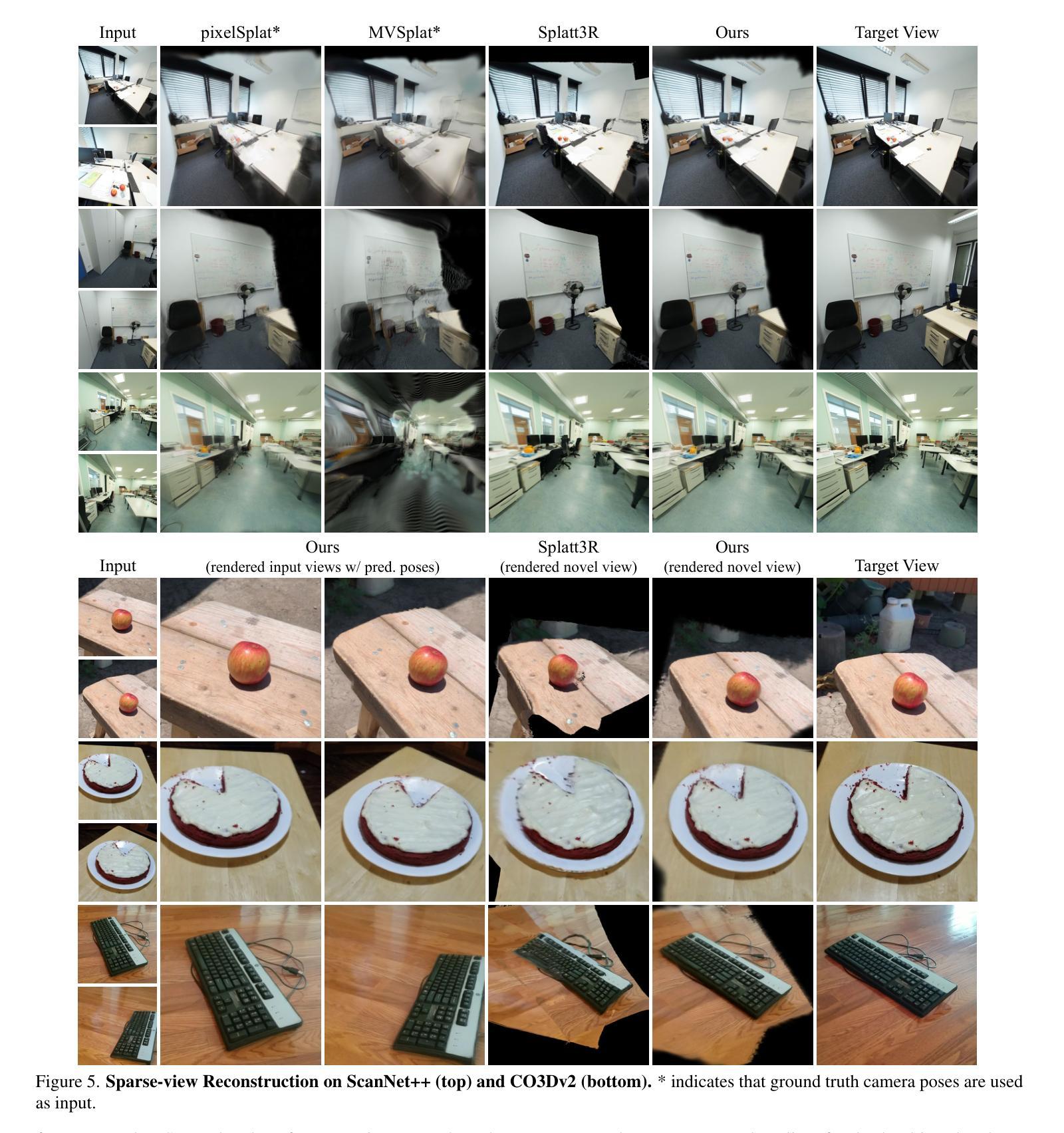
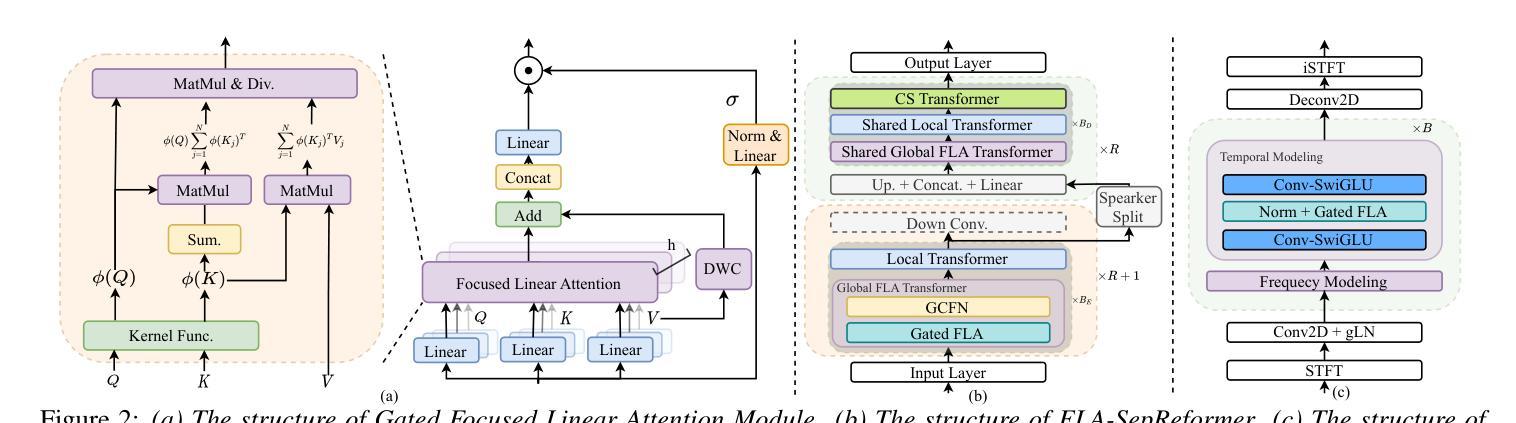
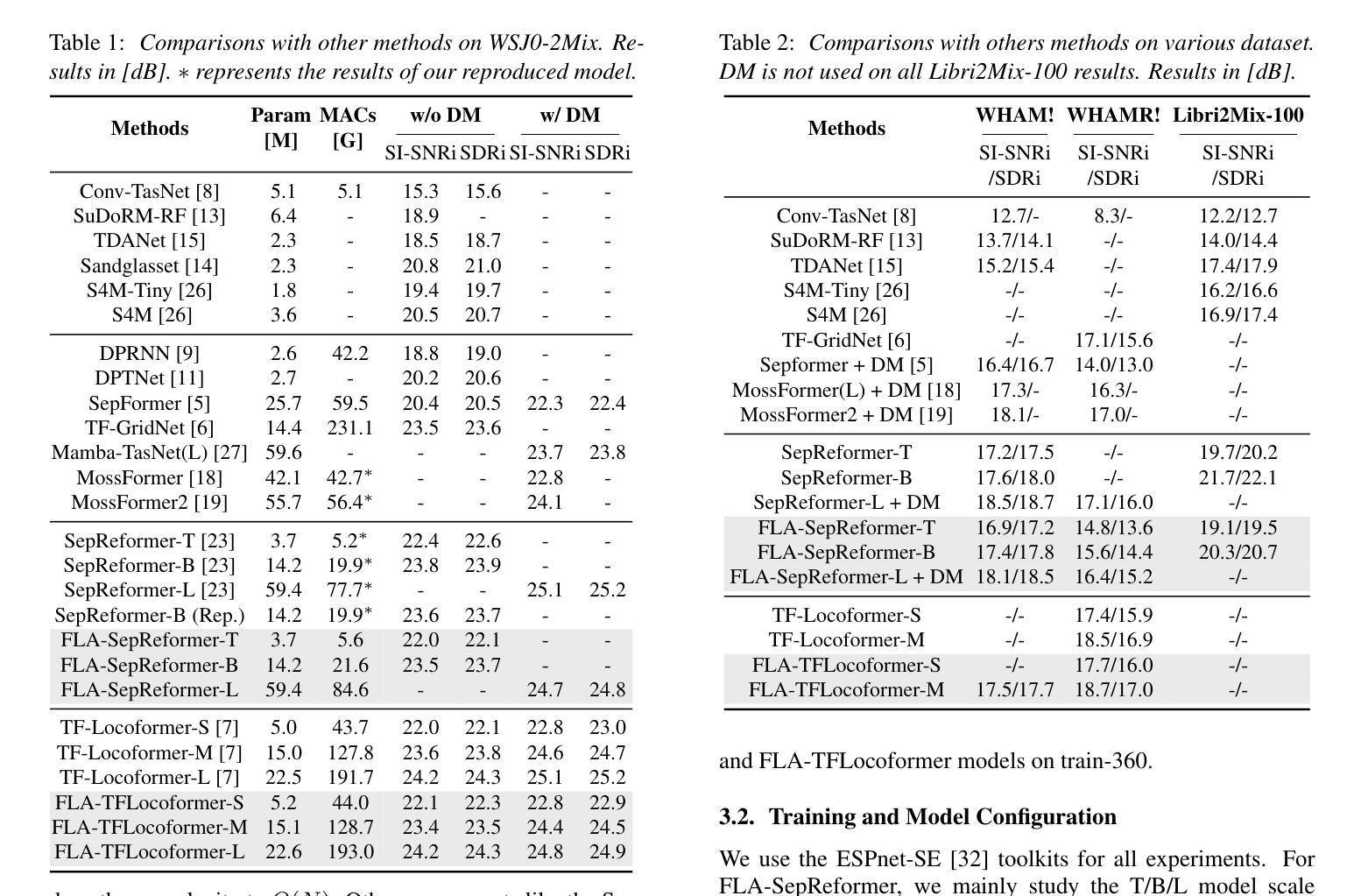
FLASepformer: Efficient Speech Separation with Gated Focused Linear Attention Transformer
Authors:Haoxu Wang, Yiheng Jiang, Gang Qiao, Pengteng Shi, Biao Tian
Speech separation always faces the challenge of handling prolonged time sequences. Past methods try to reduce sequence lengths and use the Transformer to capture global information. However, due to the quadratic time complexity of the attention module, memory usage and inference time still increase significantly with longer segments. To tackle this, we introduce Focused Linear Attention and build FLASepformer with linear complexity for efficient speech separation. Inspired by SepReformer and TF-Locoformer, we have two variants: FLA-SepReformer and FLA-TFLocoformer. We also add a new Gated module to improve performance further. Experimental results on various datasets show that FLASepformer matches state-of-the-art performance with less memory consumption and faster inference. FLA-SepReformer-T/B/L increases speed by 2.29x, 1.91x, and 1.49x, with 15.8%, 20.9%, and 31.9% GPU memory usage, proving our model’s effectiveness.
语音分离始终面临处理长时间序列的挑战。过去的方法试图减少序列长度并使用Transformer捕捉全局信息。然而,由于注意力模块的二次时间复杂度,随着段落的增长,内存使用和推理时间仍然显著增加。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了聚焦线性注意力,并构建了具有线性复杂度的FLASepformer,以实现高效的语音分离。受SepReformer和TF-Locoformer的启发,我们有两种变体:FLA-SepReformer和FLA-TFLocoformer。我们还添加了一个新的门控模块来进一步提高性能。在各种数据集上的实验结果表明,FLASepformer具有较小的内存消耗和更快的推理速度,达到了最先进的技术性能。FLA-SepReformer-T/B/L的速度提高了2.29倍、1.91倍和1.49倍,GPU内存使用率分别降低了15.8%、20.9%和31.9%,证明了我们的模型的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Interspeech 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对语音分离中长期序列处理难题的解决方案。通过引入聚焦线性注意力机制,构建具有线性复杂度的FLASepformer模型,提高语音分离效率。模型有两种变体:FLA-SepReformer和FLA-TFLocoformer,并添加新的Gated模块进一步提升性能。实验结果表明,FLASepformer达到最新性能水平,同时降低内存消耗并提高推理速度。
Key Takeaways
- 语音分离面临处理长期序列的挑战。
- 过去的方法试图通过减少序列长度和使用Transformer捕捉全局信息来解决这个问题。
- 由于注意力模块的二次时间复杂性,内存使用量和推理时间仍然会随着序列长度的增加而显著增加。
- 引入聚焦线性注意力机制,构建具有线性复杂度的FLASepformer模型,以提高语音分离效率。
- 有两种模型变体:FLA-SepReformer和FLA-TFLocoformer。
- 添加新的Gated模块进一步提升性能。
点此查看论文截图


WildSpoof Challenge Evaluation Plan
Authors:Yihan Wu, Jee-weon Jung, Hye-jin Shim, Xin Cheng, Xin Wang
The WildSpoof Challenge aims to advance the use of in-the-wild data in two intertwined speech processing tasks. It consists of two parallel tracks: (1) Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis for generating spoofed speech, and (2) Spoofing-robust Automatic Speaker Verification (SASV) for detecting spoofed speech. While the organizers coordinate both tracks and define the data protocols, participants treat them as separate and independent tasks. The primary objectives of the challenge are: (i) to promote the use of in-the-wild data for both TTS and SASV, moving beyond conventional clean and controlled datasets and considering real-world scenarios; and (ii) to encourage interdisciplinary collaboration between the spoofing generation (TTS) and spoofing detection (SASV) communities, thereby fostering the development of more integrated, robust, and realistic systems.
WildSpoof挑战旨在推进野外数据在两个相互关联的语音识别任务中的应用。它包含两个并行轨道:(1)用于生成欺骗语音的文本到语音(TTS)合成,(2)用于检测欺骗语音的欺骗稳健自动语音识别(SASV)。虽然组织者协调这两个轨道并定义数据协议,但参与者将其视为独立且独立的任务。该挑战的主要目标是:(i)促进野外数据在TTS和SASV两者中的应用,超越传统的干净且受控的数据集,并考虑真实场景;(ii)鼓励欺骗生成(TTS)和欺骗检测(SASV)社区之间的跨学科合作,从而促进开发更集成、更稳健和更现实的系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICASSP 2026 challenge
Summary
该文本介绍了“WildSpoof挑战”的目标和构成,旨在推进野外数据在两项交织的语音处理任务中的应用。该挑战包括两个并行轨道:(1)文本到语音(TTS)合成生成伪造语音;(2)检测伪造语音的防伪造自动语音识别(SASV)。挑战的主要目标是推动野外数据在TTS和SASV中的应用,并鼓励欺骗生成(TTS)和欺骗检测(SASV)社区之间的跨学科合作,从而促进开发更加集成、稳健和现实的系统。
Key Takeaways
- WildSpoof Challenge旨在推进野外数据在两项交织的语音处理任务的应用。
- 挑战包括两个并行轨道:文本到语音合成以及检测伪造语音的自动语音识别。
- 该挑战的主要目标是推动野外数据在语音合成和语音识别领域的使用,并鼓励跨学科合作。
- 通过使用野外数据,该挑战希望推动更加集成、稳健和现实的系统开发。
- 该挑战旨在考虑真实场景中的数据协议应用,而非仅仅依赖于传统的清洁和控制数据集。
- 在这个挑战中,尽管有两个不同的轨道,但组织者在协调和定义数据协议方面是发挥核心作用的。参与者则将这两个轨道视为独立的任务来处理。
点此查看论文截图


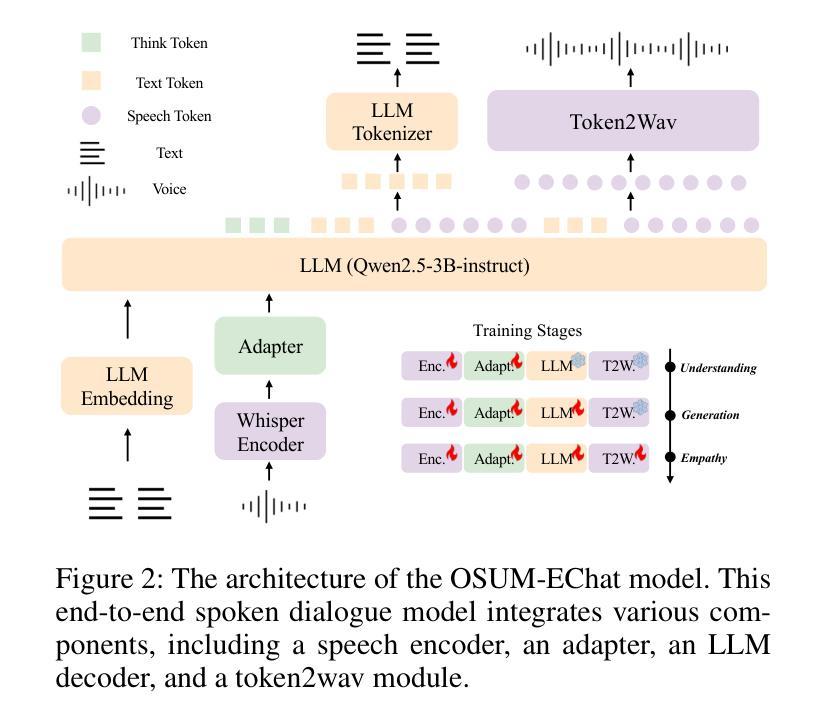
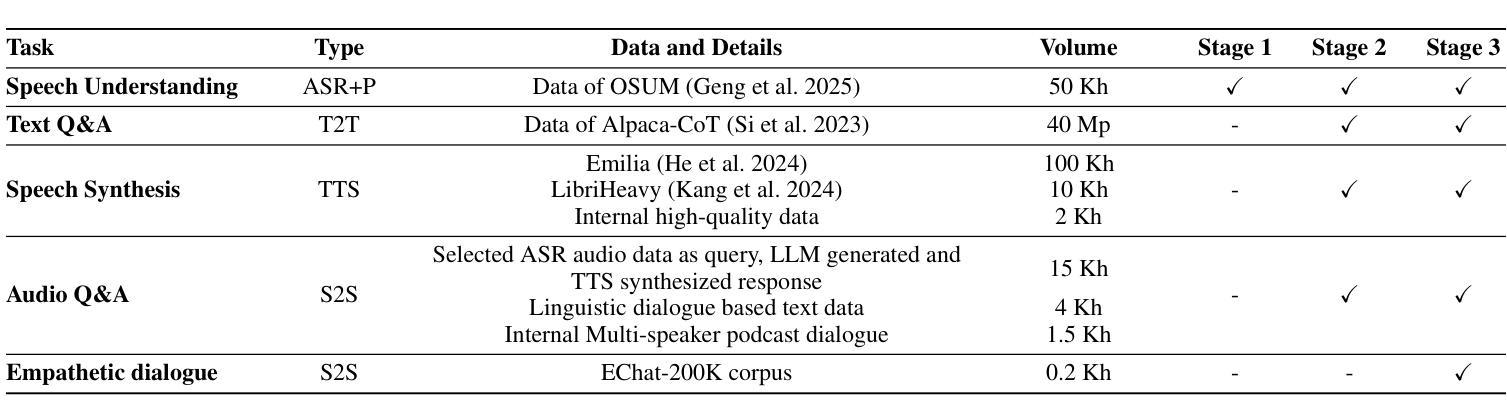
OSUM-EChat: Enhancing End-to-End Empathetic Spoken Chatbot via Understanding-Driven Spoken Dialogue
Authors:Xuelong Geng, Qijie Shao, Hongfei Xue, Shuiyuan Wang, Hanke Xie, Zhao Guo, Yi Zhao, Guojian Li, Wenjie Tian, Chengyou Wang, Zhixian Zhao, Kangxiang Xia, Ziyu Zhang, Zhennan Lin, Tianlun Zuo, Mingchen Shao, Yuang Cao, Guobin Ma, Longhao Li, Yuhang Dai, Dehui Gao, Dake Guo, Lei Xie
Empathy is crucial in enabling natural interactions within spoken dialogue systems, allowing machines to recognize and respond appropriately to paralinguistic cues such as age, gender, and emotion. Recent advancements in end-to-end speech language models, which unify speech understanding and generation, provide promising solutions. However, several challenges persist, including an over-reliance on large-scale dialogue datasets, insufficient extraction of paralinguistic cues vital for conveying empathy, and the lack of empathy-specific datasets and evaluation frameworks. To address these issues, we introduce OSUM-EChat, an open-source, end-to-end spoken dialogue system designed to enhance empathetic interactions, particularly in resource-limited settings. OSUM-EChat introduces two key innovations: (1) a three-stage understanding-driven spoken dialogue training strategy that extends the capabilities of a large speech understanding model to spoken dialogue tasks, and (2) a linguistic-paralinguistic dual thinking mechanism that integrates paralinguistic understanding through a chain of thought with dialogue generation, enabling the system to produce more empathetic responses. This approach reduces reliance on large-scale dialogue datasets while maintaining high-quality empathetic interactions. Additionally, we introduce the EChat-200K dataset, a rich corpus of empathetic speech-to-speech dialogues, and the EChat-eval benchmark, a comprehensive framework for evaluating the empathetic capabilities of dialogue systems. Experimental results demonstrate that OSUM-EChat outperforms end-to-end spoken dialogue models regarding empathetic responsiveness, validating its effectiveness.
在口语对话系统中实现自然交互,共情至关重要。它允许机器识别并适当回应诸如年龄、性别和情感等副语言线索。端到端的最近进展为语言模型将语音理解和生成统一起来,提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,仍存在一些挑战,包括过于依赖大规模的对话数据集、未能充分提取对于传达共情至关重要的副语言线索,以及缺乏针对共情的特定数据集和评估框架。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了OSUM-EChat,这是一个开源的端到端口语对话系统,旨在增强共情互动,特别是在资源有限的环境中。OSUM-EChat有两个关键的创新点:(1)一个三阶段的理解驱动式对话训练策略,它扩展了大型语音理解模型在口语对话任务方面的能力;(2)一种语言副语言双重思考机制,它将副语言理解融入一系列思维与对话生成之中,使系统能够产生更具共情的回应。这种方法降低了对大规模对话数据集的依赖,同时保持了高质量的共情互动。此外,我们还引入了EChat-200K数据集,这是一个丰富的共情语音对话语料库,以及EChat-eval基准测试,一个全面评估对话系统共情能力的框架。实验结果表明,OSUM-EChat在共情响应方面优于端到端的口语对话模型,验证了其有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文强调了共情在口语对话系统中实现自然交互的重要性,并指出机器通过识别年龄、性别和情感等副语言线索来作出恰当回应的能力。近期端到端的语音语言模型的进步为统一语音理解和生成提供了解决方案。然而,仍存在一些挑战,如过于依赖大规模对话数据集、未能充分提取对表达共情至关重要的副语言线索以及缺乏针对共情的特定数据集和评估框架。为解决这些问题,本文介绍了OSUM-EChat这一开源的端到端口语对话系统,旨在增强共情互动,特别是在资源有限的环境中。OSUM-EChat引入了两个关键创新点:一是以理解为主导的口语对话三阶段训练策略,该策略扩展了大规模语音理解模型在口语对话任务中的应用能力;二是语言-副语言双重思考机制,该机制将副语言理解与思维链相结合,推动对话生成,使系统能够产生更具共情的回应。这种方法减少了大规模对话数据集的依赖,同时保持了高质量的共情互动。此外,本文还介绍了EChat-200K数据集,这是一个丰富的共情性语音对话语料库,以及EChat-eval基准测试,一个全面评估对话系统共情能力的框架。实验结果表明,OSUM-EChat在共情响应方面优于端到端的口语对话模型,验证了其有效性。
关键见解
- 共情在口语对话系统中实现自然交互至关重要,机器需要识别并响应副语言线索如年龄、性别和情感。
- 端到端的语音语言模型为统一语音理解和生成提供了前景。
- 当前面临的挑战包括依赖大规模对话数据集、未能充分提取副语言线索以及缺乏针对共情的特定数据集和评估框架。
- OSUM-EChat是一个旨在增强共情互动的开源端到端口语对话系统。
- OSUM-EChat引入了三阶段训练策略和双重思考机制,以提高共情互动的质量和减少对数据集的依赖。
- EChat-200K数据集是一个丰富的共情性语音对话语料库。
点此查看论文截图




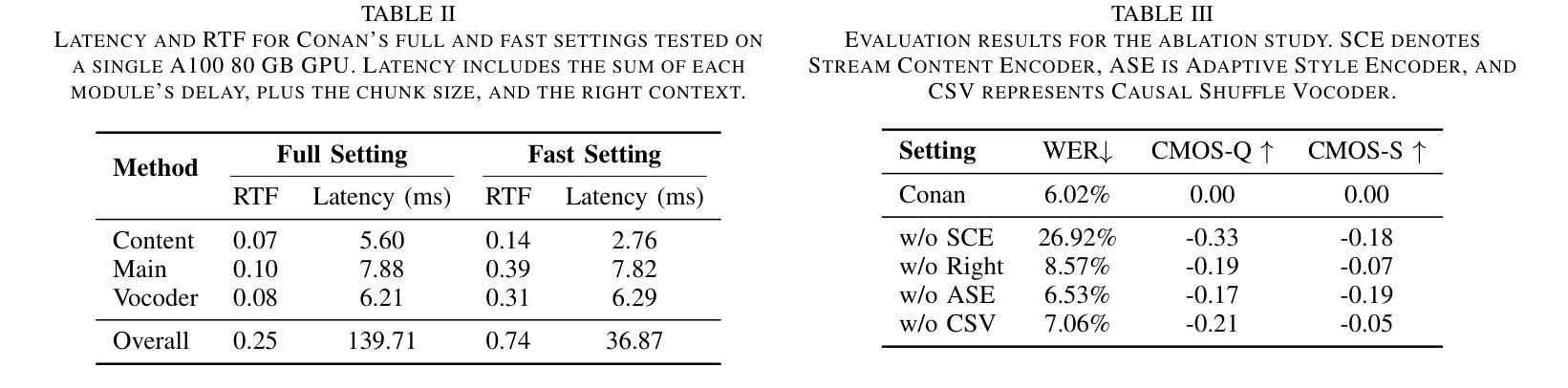
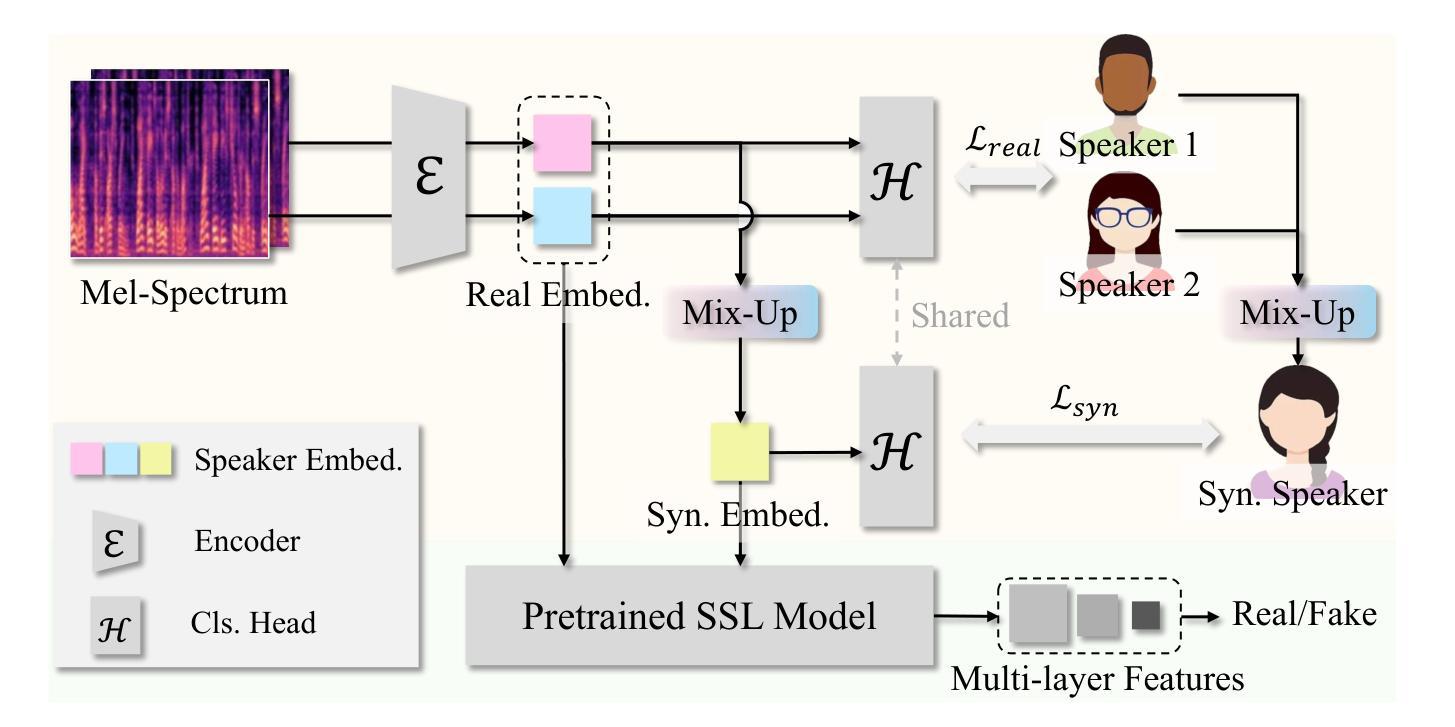
Conan: A Chunkwise Online Network for Zero-Shot Adaptive Voice Conversion
Authors:Yu Zhang, Baotong Tian, Zhiyao Duan
Zero-shot online voice conversion (VC) holds significant promise for real-time communications and entertainment. However, current VC models struggle to preserve semantic fidelity under real-time constraints, deliver natural-sounding conversions, and adapt effectively to unseen speaker characteristics. To address these challenges, we introduce Conan, a chunkwise online zero-shot voice conversion model that preserves the content of the source while matching the voice timbre and styles of reference speech. Conan comprises three core components: 1) a Stream Content Extractor that leverages Emformer for low-latency streaming content encoding; 2) an Adaptive Style Encoder that extracts fine-grained stylistic features from reference speech for enhanced style adaptation; 3) a Causal Shuffle Vocoder that implements a fully causal HiFiGAN using a pixel-shuffle mechanism. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that Conan outperforms baseline models in subjective and objective metrics. Audio samples can be found at https://aaronz345.github.io/ConanDemo.
零样本在线语音转换(VC)在实时通信和娱乐方面有着巨大的潜力。然而,当前的VC模型在实时约束下很难保持语义保真,实现自然转换的语音,并有效地适应未见过的说话人特征。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了Conan,一种分块的在线零样本语音转换模型,它能保持源内容的同时匹配参考语音的音色和风格。Conan包含三个核心组件:1)流内容提取器,它利用Emformer进行低延迟流内容编码;2)自适应风格编码器,从参考语音中提取精细的风格特征,以增强风格适应;3)因果混洗vocoder,它使用像素混洗机制实现了全因果HiFiGAN。实验评估表明,Conan在主观和客观指标上都优于基线模型。音频样本可在https://aaronz345.github.io/ConanDemo找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ASRU 2025
Summary
零样本在线语音转换技术(VC)在实时通信和娱乐领域具有巨大潜力。然而,当前VC模型难以在实时约束下保持语义保真、实现自然的声音转换以及有效适应未见过的说话人特征。为解决这些挑战,我们推出Conan模型,一种分块在线零样本语音转换模型,能够在保留源内容的同时匹配参考语音的音色和风格。Conan包括三个核心组件:1) 流内容提取器,利用Emformer进行低延迟流内容编码;2) 适应性风格编码器,从参考语音中提取精细的风格特征以增强风格适应;3) 因果洗牌Vocoder,采用像素洗牌机制实现全因果HiFiGAN。实验评估显示,Conan在主观和客观指标上均优于基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- 零样本在线语音转换技术在实时通信和娱乐中有广泛应用前景。
- 当前VC模型面临保持语义保真、自然声音转换和适应未见说话人特征的挑战。
- Conan模型是一种分块在线零样本语音转换模型,能保留源内容并匹配参考语音的音色和风格。
- Conan包括流内容提取器、适应性风格编码器和因果洗牌Vocoder三个核心组件。
- 流内容提取器利用Emformer进行低延迟流内容编码。
- 适应性风格编码器从参考语音中提取精细风格特征,增强风格适应。
- 因果洗牌Vocoder采用像素洗牌机制实现全因果HiFiGAN。
点此查看论文截图





IndexTTS2: A Breakthrough in Emotionally Expressive and Duration-Controlled Auto-Regressive Zero-Shot Text-to-Speech
Authors:Siyi Zhou, Yiquan Zhou, Yi He, Xun Zhou, Jinchao Wang, Wei Deng, Jingchen Shu
Existing autoregressive large-scale text-to-speech (TTS) models have advantages in speech naturalness, but their token-by-token generation mechanism makes it difficult to precisely control the duration of synthesized speech. This becomes a significant limitation in applications requiring strict audio-visual synchronization, such as video dubbing. This paper introduces IndexTTS2, which proposes a novel, general, and autoregressive model-friendly method for speech duration control. The method supports two generation modes: one explicitly specifies the number of generated tokens to precisely control speech duration; the other freely generates speech in an autoregressive manner without specifying the number of tokens, while faithfully reproducing the prosodic features of the input prompt. Furthermore, IndexTTS2 achieves disentanglement between emotional expression and speaker identity, enabling independent control over timbre and emotion. In the zero-shot setting, the model can accurately reconstruct the target timbre (from the timbre prompt) while perfectly reproducing the specified emotional tone (from the style prompt). To enhance speech clarity in highly emotional expressions, we incorporate GPT latent representations and design a novel three-stage training paradigm to improve the stability of the generated speech. Additionally, to lower the barrier for emotional control, we designed a soft instruction mechanism based on text descriptions by fine-tuning Qwen3, effectively guiding the generation of speech with the desired emotional orientation. Finally, experimental results on multiple datasets show that IndexTTS2 outperforms state-of-the-art zero-shot TTS models in terms of word error rate, speaker similarity, and emotional fidelity. Audio samples are available at: https://index-tts.github.io/index-tts2.github.io/
现有的自回归大规模文本到语音(TTS)模型在语音自然度方面具优势,但其逐令牌生成机制使得难以精确控制合成语音的持续时间。这在需要严格音视频同步的应用中成为一大局限,例如视频配音。本文介绍了IndexTTS2,它提出了一种新颖、通用、适用于自回归模型的语音持续时间控制方法。该方法支持两种生成模式:一种明确指定生成的令牌数量以精确控制语音持续时间;另一种以自回归的方式自由生成语音,无需指定令牌数量,同时忠实再现输入提示的韵律特征。此外,IndexTTS2实现了情感表达和说话人身份的解耦,实现对音色和情感的独立控制。在零样本设置下,模型可以准确重建目标音色(来自音色提示),同时完美再现指定的情感基调(来自风格提示)。为提高高度情感表达中的语音清晰度,我们融入了GPT潜在表征,并设计了一种新型三阶段训练范式,以提高生成语音的稳定性。此外,为了降低情感控制的障碍,我们基于文本描述设计了柔和的指令机制,通过微调Qwen3,有效地引导语音朝着期望的情感方向生成。最后,多个数据集上的实验结果表明,IndexTTS2在词错误率、说话人相似度和情感保真度方面优于零样本TTS模型。音频样本可在:[https://index-tts.github.io/index-tts2.github.io/]查看。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种新型文本转语音(TTS)模型IndexTTS2,该模型具有对语音时长的精确控制能力,适用于需要严格音视频同步的应用场景,如视频配音。IndexTTS2支持两种生成模式:一种是通过指定生成的令牌数量来精确控制语音时长;另一种是以自回归的方式自由生成语音,同时忠实保留输入提示的韵律特征。此外,IndexTTS2实现了情感表达和说话人身份的解耦,能够独立控制音色和情感。通过融入GPT潜在表征并采用三阶段训练范式,提高了在高度情感表达时的语音清晰度。同时,设计了一种基于文本描述的软指令机制,通过微调Qwen3,有效引导生成具有所需情感倾向的语音。实验结果表明,IndexTTS2在词错误率、说话人相似度和情感保真度等方面优于现有零样本TTS模型。
关键见解
- IndexTTS2模型引入了一种新的文本转语音(TTS)方法,能够精确控制合成语音的时长。
- 模型支持两种生成模式,一种可指定生成的令牌数量来控制语音时长,另一种则以自回归方式生成语音,同时保留输入提示的韵律特征。
- IndexTTS2实现了情感表达和说话人身份的解耦,允许独立控制音色和情感。
- 通过融入GPT潜在表征和三阶段训练范式提高语音清晰度。
- 采用基于文本描述的软指令机制,通过微调Qwen3有效引导生成具有所需情感倾向的语音。
- 实验结果表明,IndexTTS2在词错误率、说话人相似度和情感保真度等方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图





CAARMA: Class Augmentation with Adversarial Mixup Regularization
Authors:Massa Baali, Xiang Li, Hao Chen, Syed Abdul Hannan, Rita Singh, Bhiksha Raj
Speaker verification is a typical zero-shot learning task, where inference of unseen classes is performed by comparing embeddings of test instances to known examples. The models performing inference must hence naturally generate embeddings that cluster same-class instances compactly, while maintaining separation across classes. In order to learn to do so, they are typically trained on a large number of classes (speakers), often using specialized losses. However real-world speaker datasets often lack the class diversity needed to effectively learn this in a generalizable manner. We introduce CAARMA, a class augmentation framework that addresses this problem by generating synthetic classes through data mixing in the embedding space, expanding the number of training classes. To ensure the authenticity of the synthetic classes we adopt a novel adversarial refinement mechanism that minimizes categorical distinctions between synthetic and real classes. We evaluate CAARMA on multiple speaker verification tasks, as well as other representative zero-shot comparison-based speech analysis tasks and obtain consistent improvements: our framework demonstrates a significant improvement of 8% over all baseline models. The code is available at: https://github.com/massabaali7/CAARMA/
说话人验证是一个典型的零样本学习任务,通过比较测试实例的嵌入和已知样本的嵌入来推断未见过的类别。因此,执行推断的模型必须自然地生成嵌入,这些嵌入能够紧密地聚类同类实例,同时保持不同类别之间的分离。为了学习如何做到这一点,它们通常会在大量类别(说话人)上进行训练,经常使用专门的损失函数。然而,现实世界的说话人数据集通常缺乏以可泛化的方式有效学习所需的类别多样性。我们引入了CAARMA,这是一个类增强框架,通过嵌入空间中的数据混合生成合成类来解决这个问题,从而扩大训练类别的数量。为了确保合成类的真实性,我们采用了一种新型的对抗细化机制,最小化合成类和真实类之间的类别差异。我们在多个说话人验证任务以及其他具有代表性的基于零样本比较的语音分析任务上评估了CAARMA,并获得了持续性的改进:我们的框架在所有基线模型上实现了8%的显著改进。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/massabaali7/CAARMA/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to EMNLP 2025 Findings
Summary:
文本介绍了一种名为CAARMA的类增强框架,用于解决现实说话人数据集中类多样性不足的问题。该框架通过嵌入空间中的数据混合生成合成类,扩大训练类的数量,并采用新的对抗细化机制确保合成类的真实性,从而最小化合成类和真实类之间的类别差异。在多个说话人验证任务以及其他基于零样本比较的语音分析任务上,CAARMA框架表现出了一致的改进,相较于所有基线模型,其改进幅度达到了显著的8%。
Key Takeaways:
- 文本介绍了CAARMA框架,旨在解决现实说话人数据集中类多样性不足的问题。
- CAARMA框架通过嵌入空间中的数据混合生成合成类,扩大训练类的数量。
- 采用新的对抗细化机制确保合成类的真实性。
- 该框架能最小化合成类和真实类之间的类别差异。
- 在多个说话人验证任务上,CAARMA框架表现优异,相较于基线模型有8%的显著改进。
- CAARMA框架也适用于其他基于零样本比较的语音分析任务。
点此查看论文截图


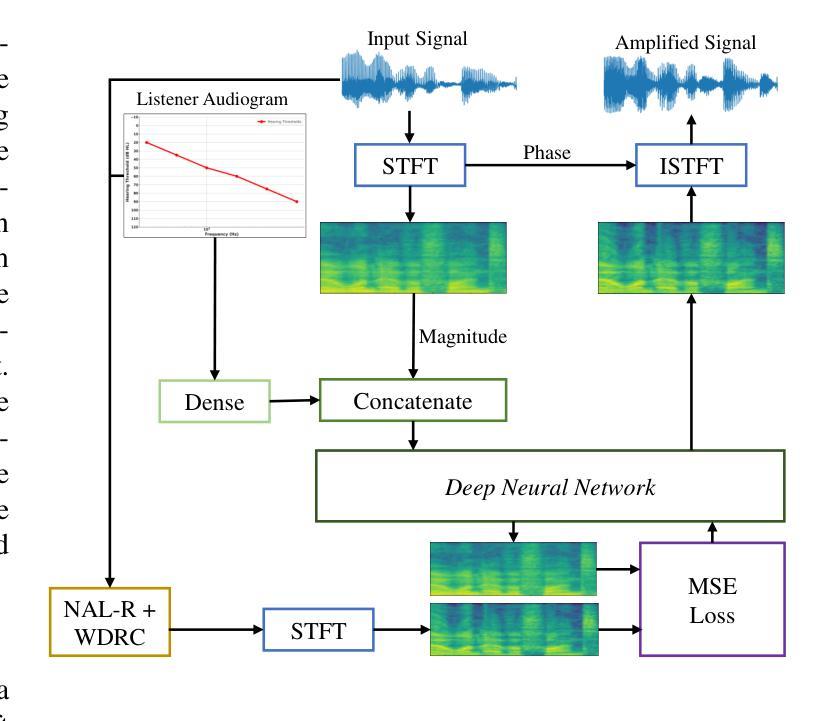
NeuroAMP: A Novel End-to-end General Purpose Deep Neural Amplifier for Personalized Hearing Aids
Authors:Shafique Ahmed, Ryandhimas E. Zezario, Hui-Guan Yuan, Amir Hussain, Hsin-Min Wang, Wei-Ho Chung, Yu Tsao
The prevalence of hearing aids is increasing. However, optimizing the amplification processes of hearing aids remains challenging due to the complexity of integrating multiple modular components in traditional methods. To address this challenge, we present NeuroAMP, a novel deep neural network designed for end-to-end, personalized amplification in hearing aids. NeuroAMP leverages both spectral features and the listener’s audiogram as inputs, and we investigate four architectures: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (CRNN), and Transformer. We also introduce Denoising NeuroAMP, an extension that integrates noise reduction along with amplification capabilities for improved performance in real-world scenarios. To enhance generalization, a comprehensive data augmentation strategy was employed during training on diverse speech (TIMIT and TMHINT) and music (Cadenza Challenge MUSIC) datasets. Evaluation using the Hearing Aid Speech Perception Index (HASPI), Hearing Aid Speech Quality Index (HASQI), and Hearing Aid Audio Quality Index (HAAQI) demonstrates that the Transformer architecture within NeuroAMP achieves the best performance, with SRCC scores of 0.9927 (HASQI) and 0.9905 (HASPI) on TIMIT, and 0.9738 (HAAQI) on the Cadenza Challenge MUSIC dataset. Notably, our data augmentation strategy maintains high performance on unseen datasets (e.g., VCTK, MUSDB18-HQ). Furthermore, Denoising NeuroAMP outperforms both the conventional NAL-R+WDRC approach and a two-stage baseline on the VoiceBank+DEMAND dataset, achieving a 10% improvement in both HASPI (0.90) and HASQI (0.59) scores. These results highlight the potential of NeuroAMP and Denoising NeuroAMP to deliver notable improvements in personalized hearing aid amplification.
助听器的普及率正在不断提高。然而,由于传统方法中整合多个模块化组件的复杂性,优化助听器的放大过程仍然是一个挑战。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了NeuroAMP,这是一种专为助听器端到端个性化放大而设计的新型深度神经网络。NeuroAMP利用频谱特征和听者的听力图作为输入,我们研究了四种架构:卷积神经网络(CNN)、长短期记忆网络(LSTM)、卷积循环神经网络(CRNN)和Transformer。我们还介绍了Denoising NeuroAMP,它是NeuroAMP的扩展,集成了降噪功能,以提高现实场景中的性能。为了增强泛化能力,我们在训练期间采用了全面的数据增强策略,训练数据集包括各种语音(TIMIT和TMHINT)和音乐(Cadenza Challenge MUSIC)数据集。通过听力辅助设备语音感知指数(HASPI)、听力辅助设备语音质量指数(HASQI)和听力辅助设备音频质量指数(HAAQI)的评估表明,NeuroAMP中的Transformer架构表现最佳,TIMIT上的HASQI和HASPI的SRCC分数分别为0.9927和0.9905,Cadenza Challenge MUSIC数据集上的HAAQI分数为0.9738。值得注意的是,我们的数据增强策略在未见过的数据集上(例如VCTK、MUSDB18-HQ)也保持了高性能。此外,Denoising NeuroAMP在VoiceBank+DEMAND数据集上的表现优于传统的NAL-R+WDRC方法和两阶段基线方法,HASPI和HASQI得分均提高了10%。这些结果突出了NeuroAMP和Denoising NeuroAMP在个性化助听器放大方面的潜力,有望带来显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence
Summary
随着助听器普及率的提高,优化其放大过程面临挑战。为此,研究团队提出了NeuroAMP这一新型的深度神经网络,用于实现端到端的个性化助听器放大。NeuroAMP结合了频谱特征和听者的听力图作为输入,并研究了四种架构。此外,还推出了集成降噪功能的Denoising NeuroAMP,以提高真实场景下的性能。通过数据增强策略及多种数据集的训练,评估结果表明Transformer架构的NeuroAMP表现最佳。Denoising NeuroAMP相较于传统方法也有显著优势,展现出个性化助听器放大的巨大潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 助听器普及率提高,优化放大过程成为关键挑战。
- NeuroAMP是一种新型的深度神经网络,用于个性化助听器放大。
- NeuroAMP结合了频谱特征和听者的听力图作为输入,研究了CNN、LSTM、CRNN和Transformer四种架构。
- Denoising NeuroAMP集成了降噪功能,提高了真实场景下的性能。
- 数据增强策略增强了模型的泛化能力。
- Transformer架构的NeuroAMP在多种评估中表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图




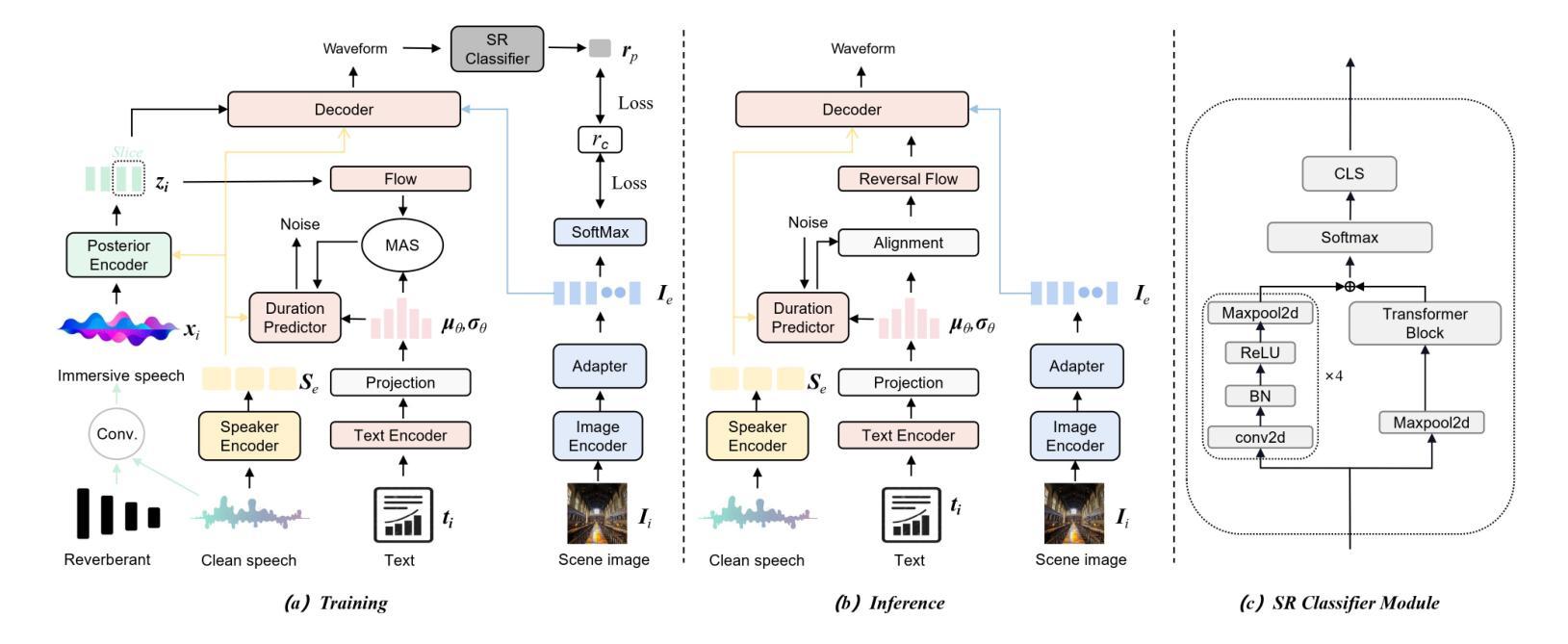
I2TTS: Image-indicated Immersive Text-to-speech Synthesis with Spatial Perception
Authors:Jiawei Zhang, Tian-Hao Zhang, Jun Wang, Jiaran Gao, Xinyuan Qian, Xu-Cheng Yin
Controlling the style and characteristics of speech synthesis is crucial for adapting the output to specific contexts and user requirements. Previous Text-to-speech (TTS) works have focused primarily on the technical aspects of producing natural-sounding speech, such as intonation, rhythm, and clarity. However, they overlook the fact that there is a growing emphasis on spatial perception of synthesized speech, which may provide immersive experience in gaming and virtual reality. To solve this issue, in this paper, we present a novel multi-modal TTS approach, namely Image-indicated Immersive Text-to-speech Synthesis (I2TTS). Specifically, we introduce a scene prompt encoder that integrates visual scene prompts directly into the synthesis pipeline to control the speech generation process. Additionally, we propose a reverberation classification and refinement technique that adjusts the synthesized mel-spectrogram to enhance the immersive experience, ensuring that the involved reverberation condition matches the scene accurately. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves high-quality scene and spatial matching without compromising speech naturalness, marking a significant advancement in the field of context-aware speech synthesis. Project demo page: https://spatialTTS.github.io/ Index Terms-Speech synthesis, scene prompt, spatial perception
控制语音合成的风格和特性对于适应特定的上下文和用户要求至关重要。之前的文本到语音(TTS)的研究主要集中在产生自然语音的技术方面,如语调、节奏和清晰度。然而,他们忽略了这样一个事实,即对合成语音的空间感知的重视程度日益增加,这可能为游戏和虚拟现实提供沉浸式体验。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种新型的多模式TTS方法,即图像指示沉浸式文本到语音合成(I2TTS)。具体来说,我们引入了一个场景提示编码器,它将视觉场景提示直接集成到合成管道中,以控制语音生成过程。此外,我们提出了一种混响分类和细化技术,该技术可以调整合成的梅尔频谱图,以增强沉浸式体验,确保所涉及的混响条件与场景准确匹配。实验结果表明,我们的模型在不影响语音自然性的情况下实现了高质量的场景和空间匹配,标志着上下文感知语音合成领域取得了重大进展。项目演示页面:https://spatialTTS.github.io/ 索引术语-语音合成,场景提示,空间感知。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by APSIPA ASC2025
Summary
本文提出一种新型的多模态文本转语音合成方法——图像指示沉浸式文本转语音合成(I2TTS)。该方法通过引入场景提示编码器,将视觉场景提示直接融入合成管道,控制语音生成过程。同时提出一种混响分类与精炼技术,调整合成频谱图,增强沉浸式体验,确保涉及的混响条件与场景准确匹配。实验结果表明,该模型实现了高质量场景和空间匹配,且不影响语音的自然性,标志着语境感知语音合成领域的重要进展。
Key Takeaways
- 文本转语音(TTS)合成的风格与特性控制对于适应特定语境和用户要求至关重要。
- 传统的TTS技术主要关注语音的技术性方面,如语调、节奏和清晰度,但忽视了合成语音的空间感知。
- 文中提出了一种新型的多模态TTS方法——图像指示沉浸式文本转语音合成(I2TTS)。
- I2TTS通过引入场景提示编码器,将视觉场景提示融入语音合成过程,实现更精准的语境感知。
- I2TTS提出的混响分类与精炼技术能调整合成频谱图,增强语音的沉浸式体验。
- 实验结果显示,I2TTS模型能在不损失语音自然性的情况下实现高质量场景和空间匹配。
点此查看论文截图


A Neural Speech Codec for Noise Robust Speech Coding
Authors:Jiayi Huang, Zeyu Yan, Wenbin Jiang, He Wang, Fei Wen
This paper considers the joint compression and enhancement problem for speech signal in the presence of noise. Recently, the SoundStream codec, which relies on end-to-end joint training of an encoder-decoder pair and a residual vector quantizer by a combination of adversarial and reconstruction losses,has shown very promising performance, especially in subjective perception quality. In this work, we provide a theoretical result to show that, to simultaneously achieve low distortion and high perception in the presence of noise, there exist an optimal two-stage optimization procedure for the joint compression and enhancement problem. This procedure firstly optimizes an encoder-decoder pair using only distortion loss and then fixes the encoder to optimize a perceptual decoder using perception loss. Based on this result, we construct a two-stage training framework for joint compression and enhancement of noisy speech signal. Unlike existing training methods which are heuristic, the proposed two-stage training method has a theoretical foundation. Finally, experimental results for various noise and bit-rate conditions are provided. The results demonstrate that a codec trained by the proposed framework can outperform SoundStream and other representative codecs in terms of both objective and subjective evaluation metrics. Code is available at \textit{https://github.com/jscscloris/SEStream}.
本文研究了噪声存在下的语音信号的联合压缩与增强问题。最近,SoundStream编解码器凭借其端到端的联合训练方式,包括编码器-解码器对和残差矢量量化器的结合,以及对抗和重建损失的组合,表现出了非常有前景的性能,特别是在主观感知质量方面。在这项工作中,我们从理论上证明,为了在噪声存在的同时实现低失真和高感知,针对联合压缩和增强问题,存在一个最优的两阶段优化程序。该程序首先仅使用失真损失优化编码器-解码器对,然后固定编码器,使用感知损失优化感知解码器。基于这一结果,我们构建了用于噪声语音信号的联合压缩和增强的两阶段训练框架。与现有的启发式训练方法不同,所提出的两阶段训练方法具有理论基础。最后,提供了各种噪声和比特率条件下的实验结果。结果表明,通过所提框架训练的编解码器在客观和主观评价指标上均优于SoundStream和其他代表性编解码器。代码可在https://github.com/jscscloris/SEStream中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了噪声环境下的语音信号联合压缩与增强问题。通过理论分析和实验验证,提出了一种基于两阶段训练框架的联合压缩与增强方法,旨在实现低失真和高感知质量。首先优化编码器-解码器对,仅使用失真损失,然后固定编码器以优化感知解码器,从而提高感知质量。实验结果表明,该框架训练的编码器在客观和主观评价指标上均优于SoundStream等其他代表性编码器。
Key Takeaways
- 论文研究噪声环境下的语音信号联合压缩与增强问题。
- SoundStream编码器在主观感知质量方面表现出良好性能。
- 论文提出了一种两阶段训练框架,旨在实现低失真和高感知质量的语音信号联合压缩与增强。
- 第一阶段优化编码器-解码器对,仅使用失真损失。
- 第二阶段固定编码器,优化感知解码器,提高感知质量。
- 实验结果表明,该框架训练的编码器在客观和主观评价指标上优于其他编码器。
点此查看论文截图



