⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-08 更新
FedMVP: Federated Multimodal Visual Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Mainak Singha, Subhankar Roy, Sarthak Mehrotra, Ankit Jha, Moloud Abdar, Biplab Banerjee, Elisa Ricci
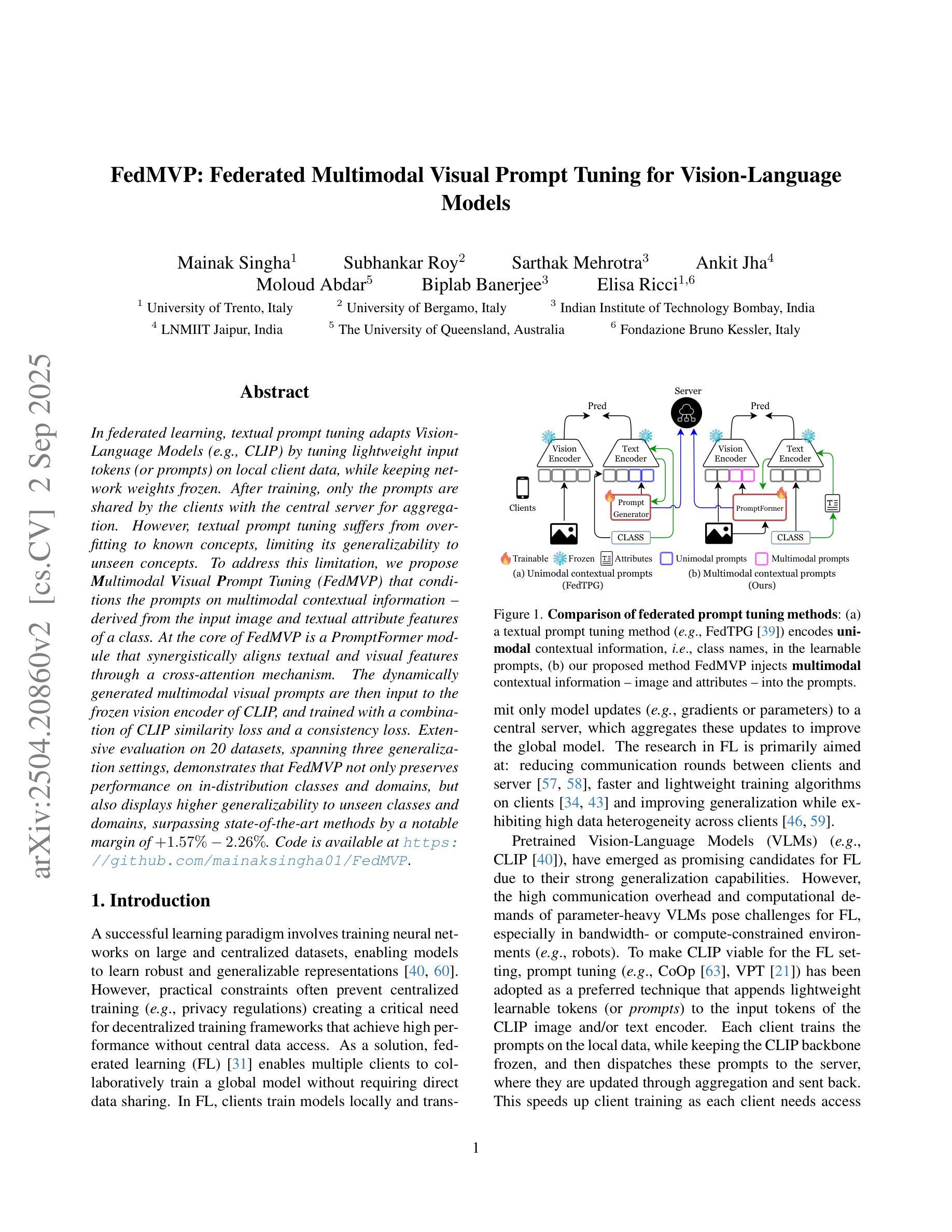
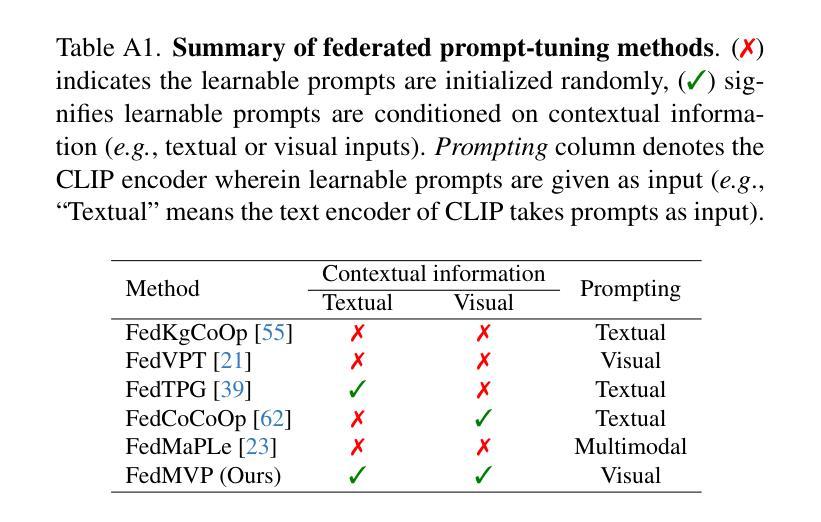
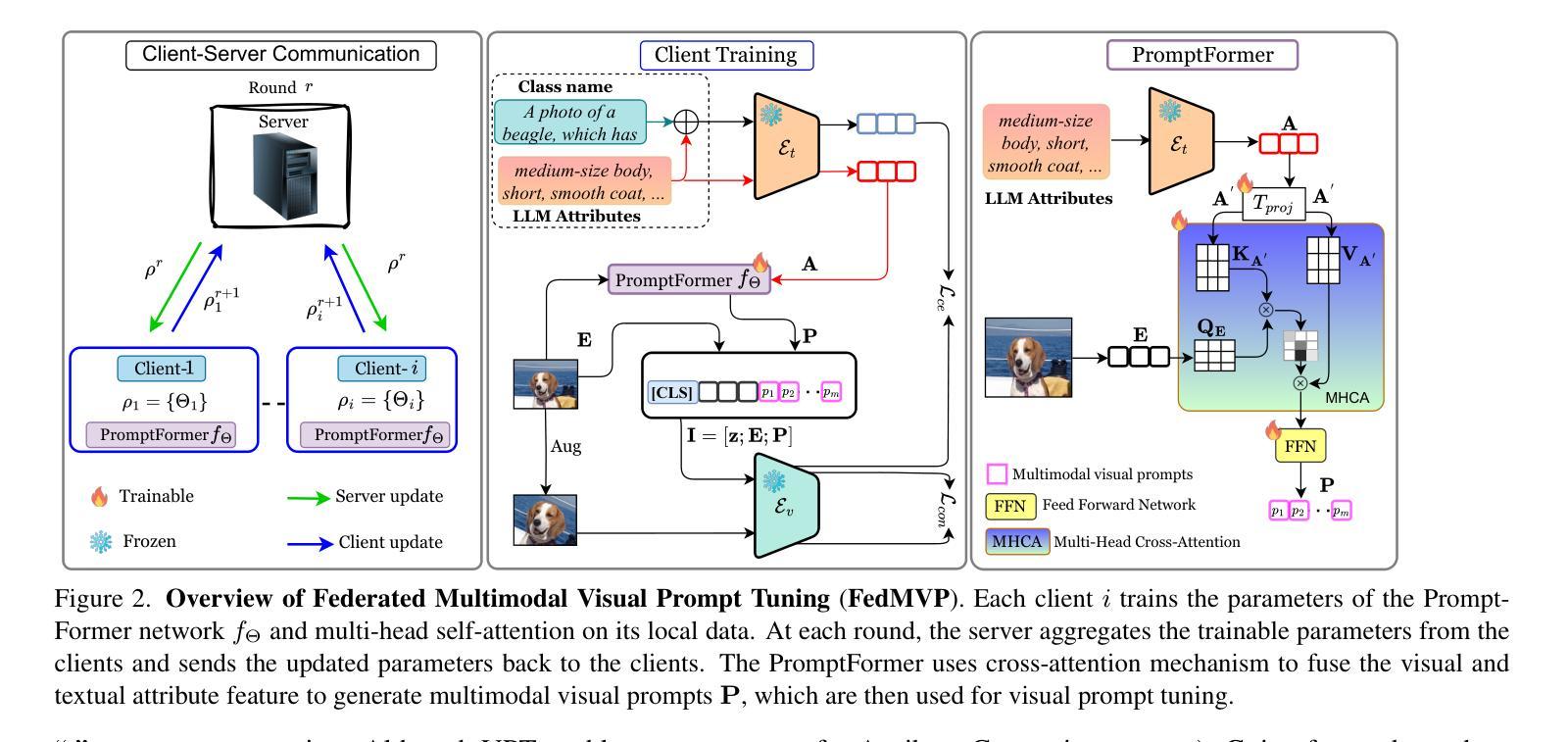
In federated learning, textual prompt tuning adapts Vision-Language Models (e.g., CLIP) by tuning lightweight input tokens (or prompts) on local client data, while keeping network weights frozen. After training, only the prompts are shared by the clients with the central server for aggregation. However, textual prompt tuning suffers from overfitting to known concepts, limiting its generalizability to unseen concepts. To address this limitation, we propose Multimodal Visual Prompt Tuning (FedMVP) that conditions the prompts on multimodal contextual information - derived from the input image and textual attribute features of a class. At the core of FedMVP is a PromptFormer module that synergistically aligns textual and visual features through a cross-attention mechanism. The dynamically generated multimodal visual prompts are then input to the frozen vision encoder of CLIP, and trained with a combination of CLIP similarity loss and a consistency loss. Extensive evaluation on 20 datasets, spanning three generalization settings, demonstrates that FedMVP not only preserves performance on in-distribution classes and domains, but also displays higher generalizability to unseen classes and domains, surpassing state-of-the-art methods by a notable margin of +1.57% - 2.26%. Code is available at https://github.com/mainaksingha01/FedMVP.
在联邦学习中,文本提示调整方法通过调整轻量级输入令牌(或提示)来适应视觉语言模型(例如CLIP),同时保持网络权重冻结,在本地客户端数据上应用。训练后,只有提示被客户端与中央服务器共享以进行聚合。然而,文本提示调整面临对已知概念的过度拟合问题,这限制了其在未见概念上的泛化能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了多模态视觉提示调整(FedMVP),它通过多模态上下文信息来设置提示,这些上下文信息来源于输入图像和文本属性特征的类别。FedMVP的核心是PromptFormer模块,它通过交叉注意机制协同对齐文本和视觉特征。然后,动态生成的多模态视觉提示被输入到CLIP的冻结视觉编码器,并用CLIP相似性损失和一致性损失的组合进行训练。在跨越三种泛化设置的20个数据集上的广泛评估表明,FedMVP不仅在内部分布类别和领域上保持性能,而且在未见类别和领域上表现出更高的泛化能力,超出最新方法一个明显的幅度(提高+ 1.57%至+ 2.26%)。代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/mainaksingha01/FedMVP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ICCV 2025
Summary
联邦学习中,文本提示调整适应视觉语言模型(如CLIP),通过调整轻量级输入令牌(或提示)在本地客户端数据上,同时保持网络权重冻结。训练后,只有提示被客户端与中央服务器共享以进行聚合。然而,文本提示调整会过度拟合已知概念,限制了其对未见概念的泛化能力。为解决此局限性,我们提出多模式视觉提示调整(FedMVP),该调整基于输入图像和类别文本属性特征的多模式上下文信息来生成提示。FedMVP的核心是PromptFormer模块,它通过交叉注意机制协同对齐文本和视觉特征。然后,将动态生成的多模式视觉提示输入到CLIP的冻结视觉编码器,并用CLIP相似性损失和一致性损失的组合进行训练。在跨越三种泛化设置的20个数据集上的广泛评估表明,FedMVP不仅保持了同类和域内的性能,而且在未见类别和域内表现出更高的泛化能力,超出最新方法显著的优势为+1.57% - 2.26%。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习中,文本提示调整是适应Vision-Language模型(如CLIP)的一种策略,通过调整本地数据上的轻量级输入令牌(或提示),同时保持网络权重不变。
- 文本提示调整面临过度拟合已知概念的挑战,限制了其在未见概念上的泛化能力。
- 为了解决这一局限性,提出了多模式视觉提示调整(FedMVP),该策略基于输入图像和文本属性特征的多模式上下文信息来生成提示。
- FedMVP的核心是PromptFormer模块,它通过交叉注意机制协同文本和视觉特征的对齐。
- FedMVP在广泛的数据集上进行了评估,显示出对未见类别和域的高泛化能力,并超越了现有方法的性能。
- FedMVP结合了CLIP相似性损失和一致性损失进行训练。
点此查看论文截图
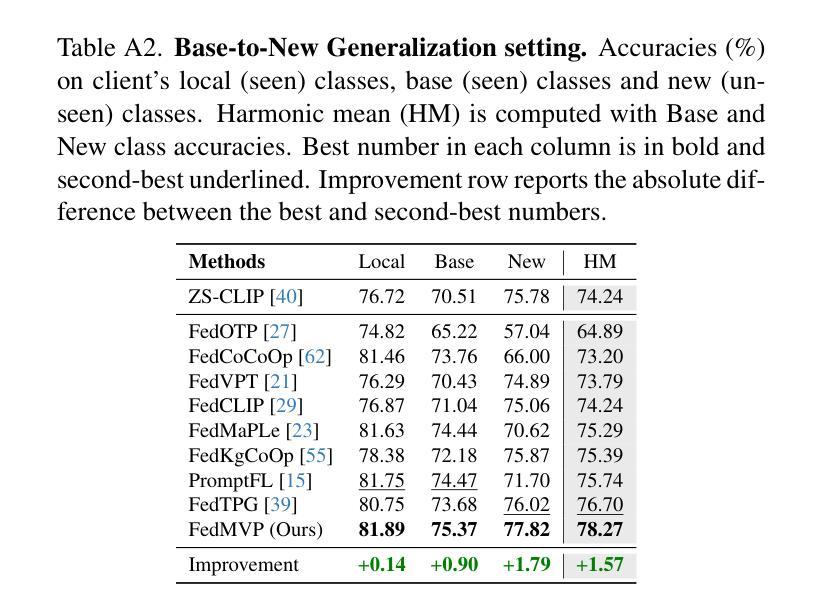
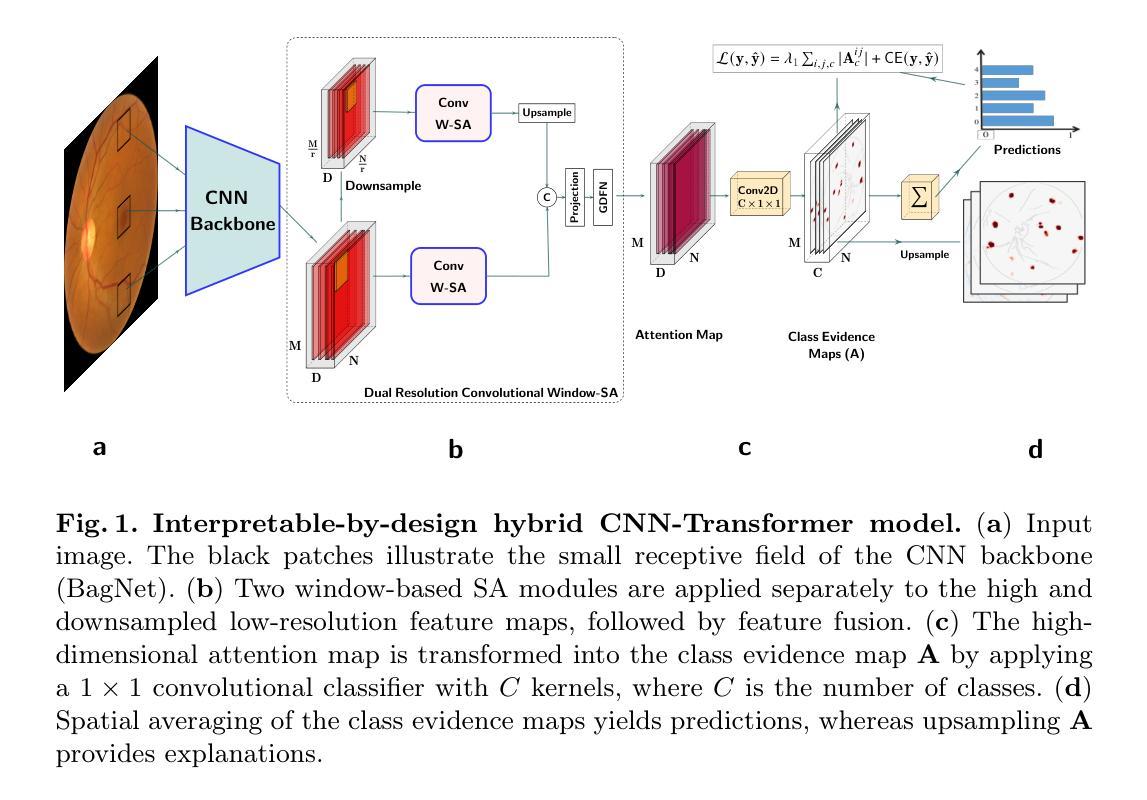
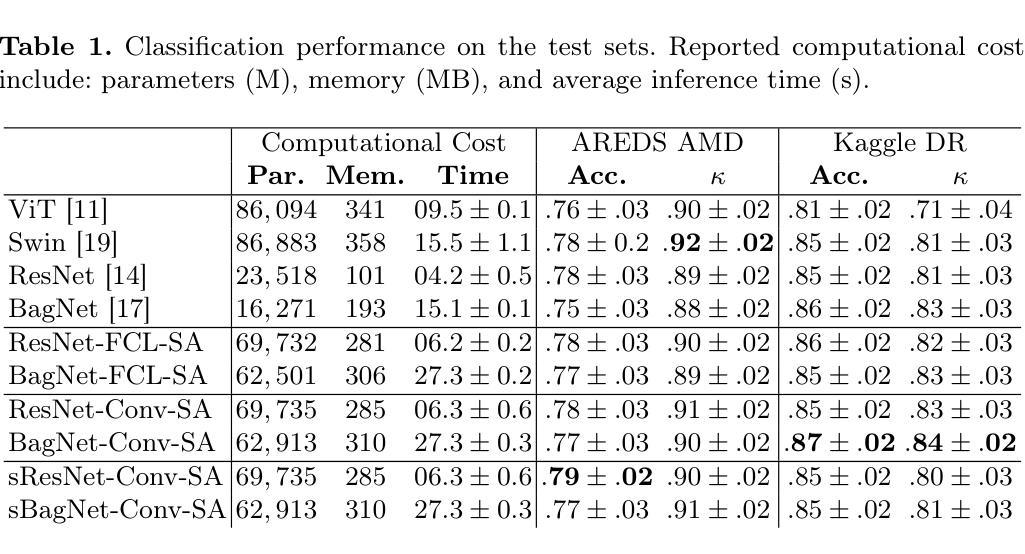
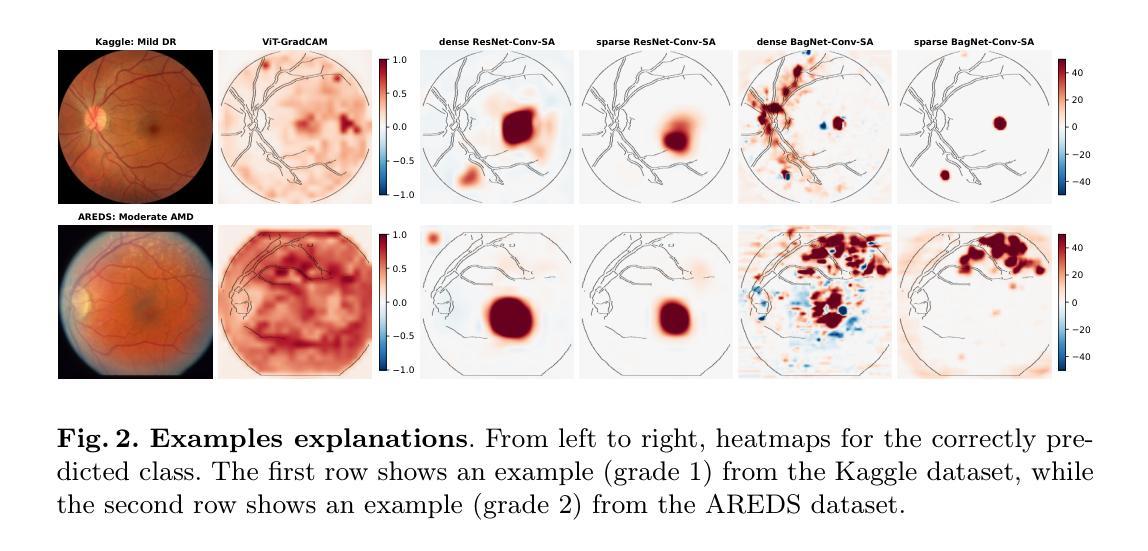
A Hybrid Fully Convolutional CNN-Transformer Model for Inherently Interpretable Disease Detection from Retinal Fundus Images
Authors:Kerol Djoumessi, Samuel Ofosu Mensah, Philipp Berens
In many medical imaging tasks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) efficiently extract local features hierarchically. More recently, vision transformers (ViTs) have gained popularity, using self-attention mechanisms to capture global dependencies, but lacking the inherent spatial localization of convolutions. Therefore, hybrid models combining CNNs and ViTs have been developed to combine the strengths of both architectures. However, such hybrid models are difficult to interpret, which hinders their application in medical imaging. In this work, we introduce an interpretable-by-design hybrid fully convolutional CNN-Transformer architecture for retinal disease detection. Unlike widely used post-hoc saliency methods for ViTs, our approach generates faithful and localized evidence maps that directly reflect the mode’s decision process. We evaluated our method on two medical tasks focused on disease detection using color fundus images. Our model achieves state-of-the-art predictive performance compared to black-box and interpretable models and provides class-specific sparse evidence maps in a single forward pass. The code is available at: https://github.com/kdjoumessi/Self-Explainable-CNN-Transformer.
在许多医学成像任务中,卷积神经网络(CNN)能够高效地分层提取局部特征。最近,使用自注意力机制捕捉全局依赖性的视觉变压器(ViT)越来越受欢迎,但在卷积所固有的空间定位方面仍存在不足。因此,为了结合两种架构的优点,已经开发出了结合CNN和ViT的混合模型。然而,这种混合模型难以解释,阻碍了它们在医学成像中的应用。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种可解释设计的混合全卷积CNN-Transformer架构,用于视网膜疾病检测。与广泛用于ViT的后验显著性方法不同,我们的方法生成忠实且定位的证据图,直接反映模型的决策过程。我们在两个以疾病检测为重点的医学任务上评估了我们的方法,使用的是彩色眼底图像。我们的模型与黑箱和可解释模型相比,达到了最先进的预测性能,并在单次前向传递中提供了特定类别的稀疏证据图。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/kdjoumessi/Self-Explainable-CNN-Transformer 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the Workshop on Interpretability of Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Computing (IMIMIC) at MICCAI 2025 for oral presentation
Summary
本文介绍了一种为视网膜疾病检测而设计的可解释的混合全卷积CNN-Transformer架构。该架构结合了CNN和ViT的优点,生成忠实且定位的证据图,直接反映模型的决策过程。在颜色眼底图像的疾病检测任务上,该模型实现了与黑箱和可解释模型相比的先进预测性能,并提供单前向传递的类特定稀疏证据图。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种混合CNN-Transformer架构,旨在实现视网膜疾病检测的模型设计。
- 该架构结合了CNN和ViT的优点,旨在提高模型的性能和可解释性。
- 该模型生成忠实且定位的证据图,直接反映模型的决策过程。
- 模型在颜色眼底图像的疾病检测任务上实现了先进预测性能。
- 模型相比黑箱和可解释模型表现出更高的性能。
- 模型提供单前向传递的类特定稀疏证据图,有助于提高模型的可解释性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

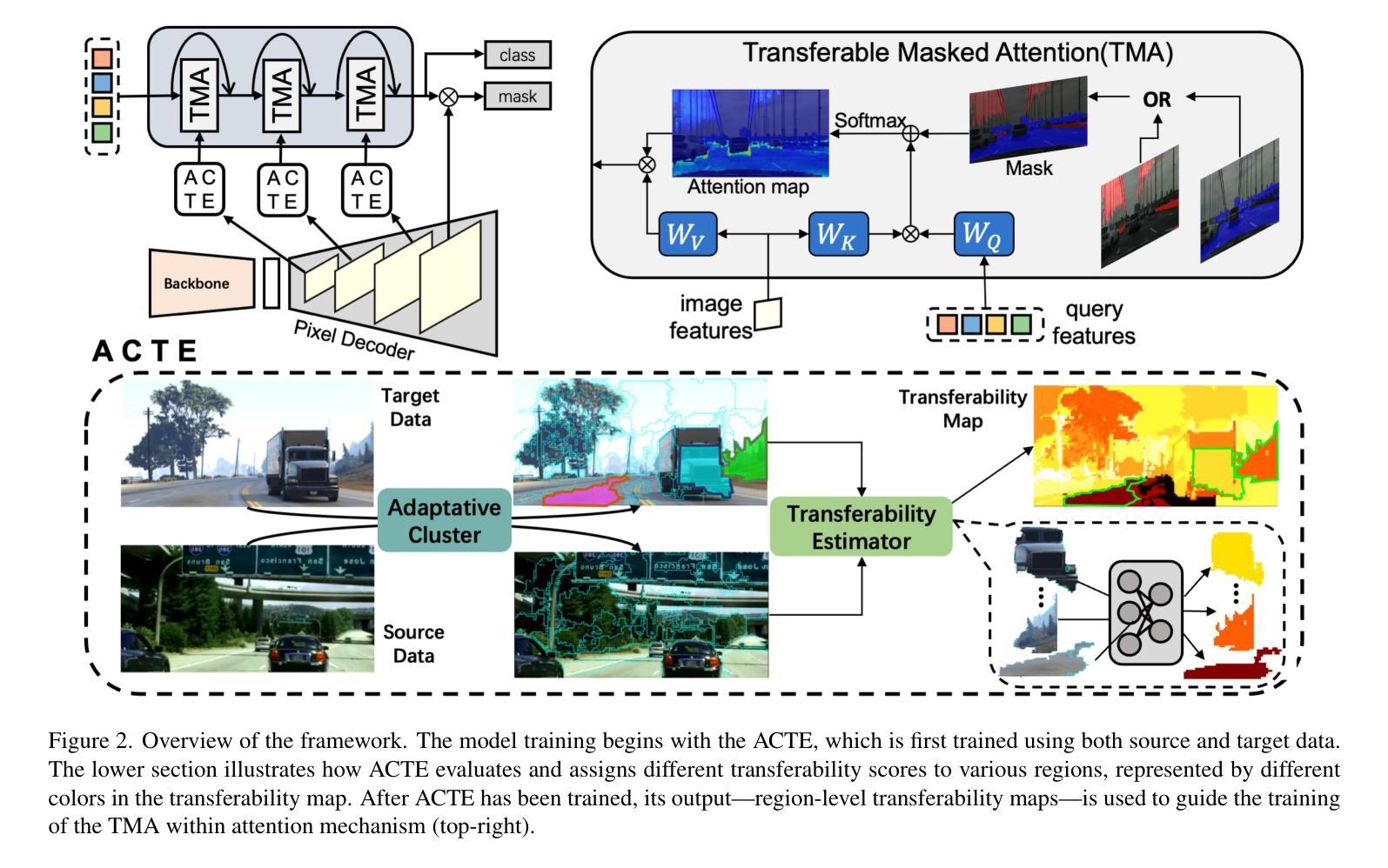
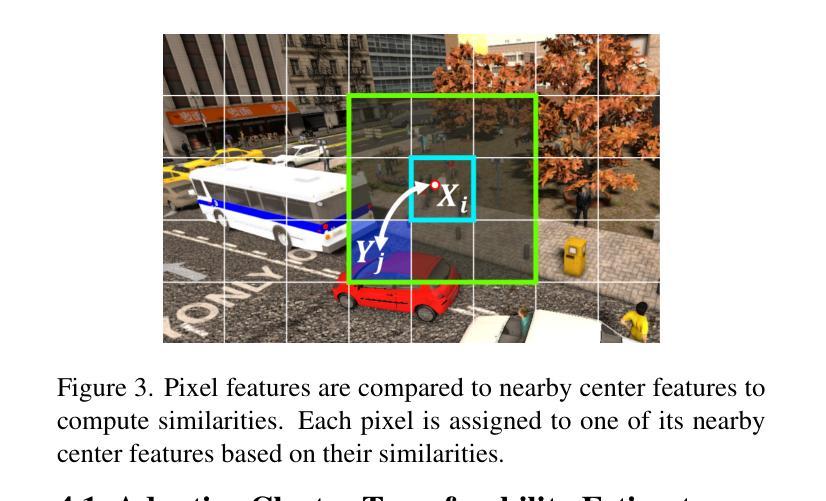
Transferable Mask Transformer: Cross-domain Semantic Segmentation with Region-adaptive Transferability Estimation
Authors:Jianhua Liu, Zhengyu Li, Yanru Wu, Jingge Wang, Yang Tan, Ruizhe Zhao, Guan Wang, Yang Li
Recent advances in Vision Transformers (ViTs) have set new benchmarks in semantic segmentation. However, when adapting pretrained ViTs to new target domains, significant performance degradation often occurs due to distribution shifts, resulting in suboptimal global attention. Since self-attention mechanisms are inherently data-driven, they may fail to effectively attend to key objects when source and target domains exhibit differences in texture, scale, or object co-occurrence patterns. While global and patch-level domain adaptation methods provide partial solutions, region-level adaptation with dynamically shaped regions is crucial due to spatial heterogeneity in transferability across different image areas. We present Transferable Mask Transformer (TMT), a novel region-level adaptation framework for semantic segmentation that aligns cross-domain representations through spatial transferability analysis. TMT consists of two key components: (1) An Adaptive Cluster-based Transferability Estimator (ACTE) that dynamically segments images into structurally and semantically coherent regions for localized transferability assessment, and (2) A Transferable Masked Attention (TMA) module that integrates region-specific transferability maps into ViTs’ attention mechanisms, prioritizing adaptation in regions with low transferability and high semantic uncertainty. Comprehensive evaluations across 20 cross-domain pairs demonstrate TMT’s superiority, achieving an average 2% MIoU improvement over vanilla fine-tuning and a 1.28% increase compared to state-of-the-art baselines. The source code will be publicly available.
Vision Transformer(ViT)的最新进展为语义分割设定了新的基准。然而,在将预训练的ViT适应到新的目标域时,由于分布转移,性能往往会出现显著下降,导致全局注意力不佳。由于自注意力机制本质上是数据驱动的,因此当源域和目标域在纹理、尺度或对象共现模式上存在差异时,它们可能无法有效地关注关键对象。虽然全局和补丁级别的域适应方法提供了部分解决方案,但由于不同图像区域在转移性上的空间异质性,动态形状区域的区域级适应至关重要。我们提出了Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT),这是一种用于语义分割的新型区域级适应框架,它通过空间转移性分析来对齐跨域表示。TMT由两个关键组件构成:(1)基于自适应聚类的转移性估计器(ACTE),它动态地将图像分割成结构和语义上连贯的区域,以进行局部化的转移性评估;(2)可转移的掩模注意力(TMA)模块,该模块将区域特定的转移图集成到ViT的注意力机制中,优先适应低转移性和高语义不确定性的区域。在20个跨域对上的综合评估证明了TMT的优越性,与微调相比,平均MIoU提高了2%,与最新基线相比提高了1.28%。源代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对视觉Transformer在语义分割中的跨域适应性挑战,提出Transferable Mask Transformer(TMT)框架,包含Adaptive Cluster-based Transferability Estimator(ACTE)和Transferable Masked Attention(TMA)模块。ACTE动态分割图像区域以评估局部迁移性,而TMA则将区域特定的迁移性地图整合到ViTs的注意力机制中,优先适应低迁移性和高语义不确定性的区域。在20个跨域对上的综合评估显示TMT具有优势,平均与常规微调相比提高了2%的MIoU,并且比最先进的基线提高了1.28%。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在语义分割方面取得了最新进展,但在跨域适应时面临性能下降问题。
- 自注意力机制在源域和目标域存在纹理、尺度或对象共现模式差异时,可能无法有效关注关键对象。
- 当前全球和补丁级别的域适应方法提供部分解决方案,但区域级别的适应很重要,因为不同图像区域的转移能力存在空间异质性。
- 引入Transferable Mask Transformer (TMT)框架,包括Adaptive Cluster-based Transferability Estimator (ACTE) 和 Transferable Masked Attention (TMA) 模块。
- ACTE能够动态分割图像以评估局部迁移性。
- TMA整合了区域特定的迁移性地图到ViTs的注意力机制中,优先适应低迁移性和高语义不确定性的区域。
点此查看论文截图


Texture or Semantics? Vision-Language Models Get Lost in Font Recognition
Authors:Zhecheng Li, Guoxian Song, Yujun Cai, Zhen Xiong, Junsong Yuan, Yiwei Wang
Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit remarkable visual and linguistic capabilities, achieving impressive performance in various tasks such as image recognition and object localization. However, their effectiveness in fine-grained tasks remains an open question. In everyday scenarios, individuals encountering design materials, such as magazines, typography tutorials, research papers, or branding content, may wish to identify aesthetically pleasing fonts used in the text. Given their multimodal capabilities and free accessibility, many VLMs are often considered potential tools for font recognition. This raises a fundamental question: Do VLMs truly possess the capability to recognize fonts? To investigate this, we introduce the Font Recognition Benchmark (FRB), a compact and well-structured dataset comprising 15 commonly used fonts. FRB includes two versions: (i) an easy version, where 10 sentences are rendered in different fonts, and (ii) a hard version, where each text sample consists of the names of the 15 fonts themselves, introducing a stroop effect that challenges model perception. Through extensive evaluation of various VLMs on font recognition tasks, we arrive at the following key findings: (i) Current VLMs exhibit limited font recognition capabilities, with many state-of-the-art models failing to achieve satisfactory performance and being easily affected by the stroop effect introduced by textual information. (ii) Few-shot learning and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting provide minimal benefits in improving font recognition accuracy across different VLMs. (iii) Attention analysis sheds light on the inherent limitations of VLMs in capturing semantic features.
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)表现出显著的视频和语言能力,在各种任务(如图像识别和对象定位)中取得了令人印象深刻的性能。然而,它们在精细任务中的有效性仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在日常场景中,个人在遇到设计材料(如杂志、排版教程、研究论文或品牌内容)时,可能希望识别文本中视觉上美观的字体。考虑到它们的多模式能力和免费访问性,许多VLMs通常被认为是字体识别的潜在工具。这引发了一个基本问题:VLMs是否真的具备识别字体的能力?为了调查这一点,我们引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB),这是一个包含15种常用字体的紧凑且结构良好的数据集。FRB包括两个版本:(i)简易版本,其中10个句子以不同的字体呈现;(ii)困难版本,其中每个文本样本由上述的15种字体的名称组成,引入一种斯特鲁普效应,挑战模型的感知能力。通过对各种VLMs在字体识别任务上的广泛评估,我们得出以下关键发现:(i)当前VLMs在字体识别方面的能力有限,许多最先进的模型未能取得令人满意的性能,并且很容易受到文本信息引入的斯特鲁普效应的影响。(ii)在改善不同VLM的字迹识别准确性方面,小样本学习和思维链提示(CoT)提供的帮助微乎其微。(iii)注意力分析揭示了VLM在捕获语义特征方面的内在局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to COLM 2025
摘要
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像识别、物体定位等方面表现出强大的视觉和语言能力,但在精细任务上的效果仍有待探索。对于日常生活中的设计材料,如杂志、排版教程等,人们希望识别文本中的美观字体。考虑到VLMs的多模态能力和开放性访问特性,其被视为字体识别的潜在工具。然而,我们的研究发现,当前VLMs在字体识别方面的能力有限,许多顶尖模型未能取得满意表现,且易受文本信息的干扰。此外,少量学习和Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示对提升不同VLMs的字体识别准确度效果有限。注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕捉语义特征方面的内在局限。
要点
- 现代视觉语言模型在字体识别等精细任务上的表现有限,顶尖模型难以达到满意的效果。
- 少量学习和Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示在改善字体识别方面的作用有限。
- VLMs容易受到文本信息的干扰,这在研究中表现为一种“斯特鲁普效应”。
- 注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕捉语义特征方面的内在局限。
- Font Recognition Benchmark(FRB)的引入为评估VLMs在字体识别任务上的性能提供了有效工具。
- FRB包括两个版本,分别侧重于不同难度级别的字体识别任务。
点此查看论文截图





Inspiring the Next Generation of Segment Anything Models: Comprehensively Evaluate SAM and SAM 2 with Diverse Prompts Towards Context-Dependent Concepts under Different Scenes
Authors:Xiaoqi Zhao, Youwei Pang, Shijie Chang, Yuan Zhao, Lihe Zhang, Chenyang Yu, Hanqi Liu, Jiaming Zuo, Jinsong Ouyang, Weisi Lin, Georges El Fakhri, Huchuan Lu, Xiaofeng Liu
As large-scale foundation models trained on billions of image–mask pairs covering a vast diversity of scenes, objects, and contexts, SAM and its upgraded version, SAM2, have significantly influenced multiple fields within computer vision. Leveraging such unprecedented data diversity, they exhibit strong open-world segmentation capabilities, with SAM2 further enhancing these capabilities to support high-quality video segmentation. While SAMs (SAM and SAM2) have demonstrated excellent performance in segmenting context-independent concepts like people, cars, and roads, they overlook more challenging context-dependent (CD) concepts, such as visual saliency, camouflage, industrial defects, and medical lesions. CD concepts rely heavily on global and local contextual information, making them susceptible to shifts in different contexts, which requires strong discriminative capabilities from the model. The lack of comprehensive evaluation of SAMs limits understanding of their performance boundaries, which may hinder the design of future models. In this paper, we conduct a thorough evaluation of SAMs on 11 CD concepts across 2D and 3D images and videos in various visual modalities within natural, medical, and industrial scenes. We develop a unified evaluation framework for SAM and SAM2 that supports manual, automatic, and intermediate self-prompting, aided by our specific prompt generation and interaction strategies. We further explore the potential of SAM~2 for in-context learning and introduce prompt robustness testing to simulate real-world imperfect prompts. Finally, we analyze the benefits and limitations of SAMs in understanding CD concepts and discuss their future development in segmentation tasks.
作为训练在覆盖广泛场景、物体和上下文的数十亿图像-掩膜对上的大规模基础模型,SAM及其升级版SAM
2已经对计算机视觉的多个领域产生了显著影响。它们利用前所未有的数据多样性,展现出强大的开放世界分割能力,而SAM2则进一步增强了这些能力,以支持高质量的视频分割。虽然SAM(包括SAM和SAM2)在分割上下文独立概念(如人、汽车和道路)方面表现出卓越的性能,但它们忽略了更具挑战性的上下文相关(CD)概念,如视觉显著性、伪装、工业缺陷和医学病灶。CD概念严重依赖于全局和局部上下文信息,因此它们在不同上下文中的变化很大,这要求模型具备强大的辨别能力。缺乏对SAM的全面评估限制了对其性能边界的理解,这可能会阻碍未来模型的设计。在本文中,我们对SAM在涵盖自然、医学和工业场景的2D和3D图像以及视频中的各种视觉模态的11个CD概念进行了全面评估。我们为SAM和SAM2开发了一个统一的评估框架,该框架支持手动、自动和中间自我提示,辅以我们特定的提示生成和交互策略。我们进一步探索了SAM~2在上下文学习中的潜力,并引入提示稳健性测试来模拟现实世界中不完美的提示。最后,我们分析了SAM在理解CD概念方面的优点和局限性,并讨论了它们在分割任务的未来发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under submission to International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV)
摘要
SAM及其升级版SAM2模型,通过训练在涵盖广泛场景、物体和上下文的大量图像-掩膜对上,已对计算机视觉的多个领域产生了显著影响。它们利用前所未有的数据多样性,展现出强大的开放世界分割能力,而SAM2则进一步支持高质量视频分割,增强了这些能力。SAM系列模型在分割上下文独立概念(如人、车和道路)方面表现出卓越性能,但在更具挑战性的上下文依赖(CD)概念上有所忽视,如视觉显著性、伪装、工业缺陷和医疗病变。CD概念严重依赖于全局和局部上下文信息,因此在不同上下文中容易发生变化,要求模型具备强大的辨别能力。本文中,我们对SAM系列模型在跨越自然、医疗和工业场景的11个CD概念上的二维和三维图像及视频进行了全面评估。我们为SAM和SAM2开发了一个统一的评估框架,支持手动、自动和中间自提示,辅以我们的特定提示生成和交互策略。我们进一步探索了SAM2在上下文学习中的潜力,并引入提示稳健性测试来模拟现实世界中不完美的提示。最后,我们分析了SAM系列模型在理解CD概念方面的优势和局限性,并讨论了它们在分割任务中的未来发展。
关键见解
- SAM和SAM~2模型通过训练在广泛的图像-掩膜对数据上,已对计算机视觉的多个领域产生了影响。
- SAM~2支持高质量视频分割,展现了强大的开放世界分割能力。
- SAM系列模型在上下文独立概念的分割上表现出优秀性能,但在上下文依赖(CD)概念上有所不足。
- CD概念依赖于全局和局部上下文信息,这对模型的辨别能力提出了高要求。
- 本文对SAM系列模型进行了全面的CD概念评估,涉及自然、医疗和工业场景的二维和三维图像及视频。
- 统一的评估框架支持手动、自动和中间自提示,有助于更全面地评估模型性能。
点此查看论文截图



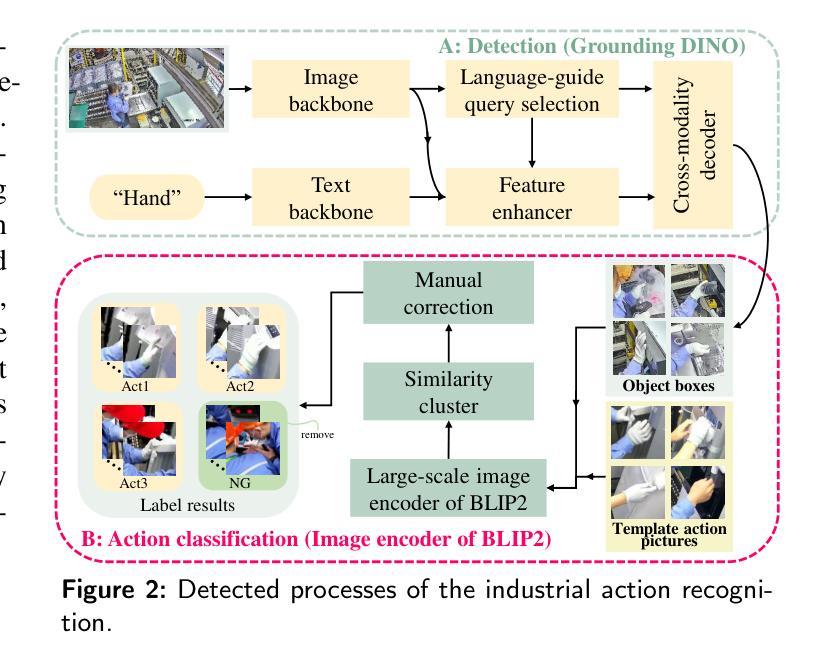
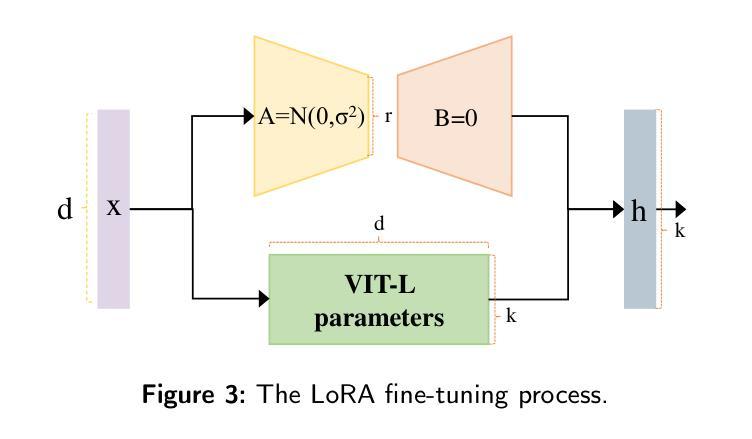
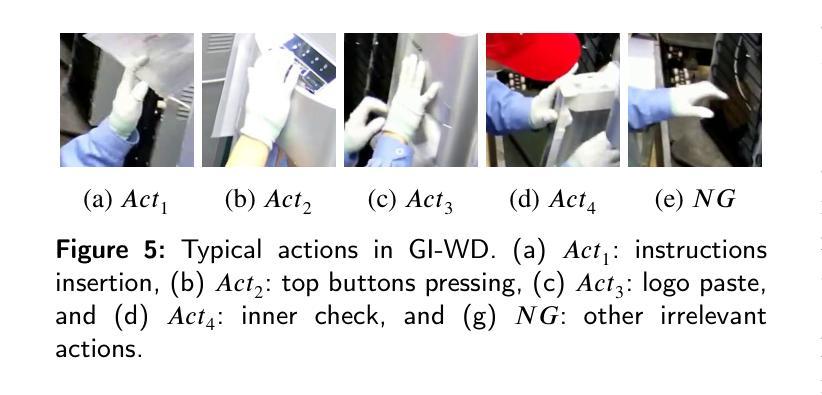
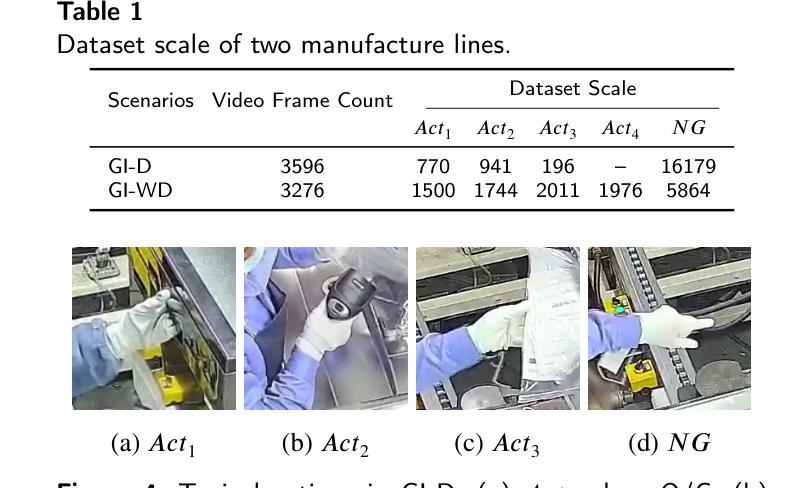
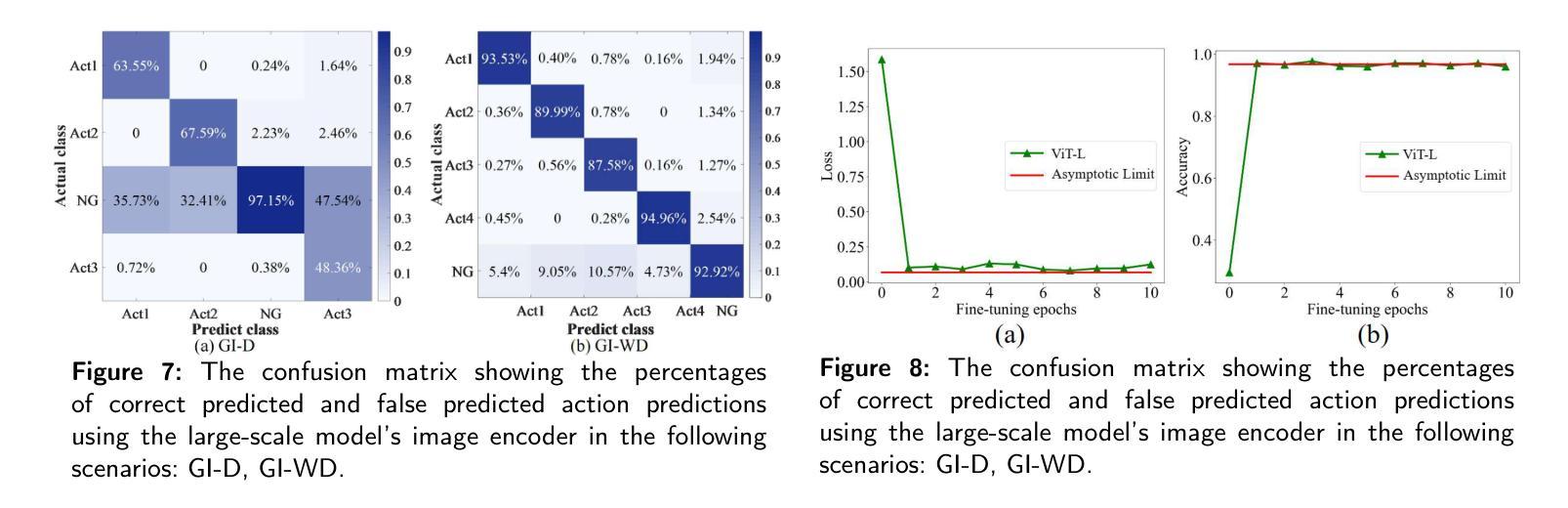
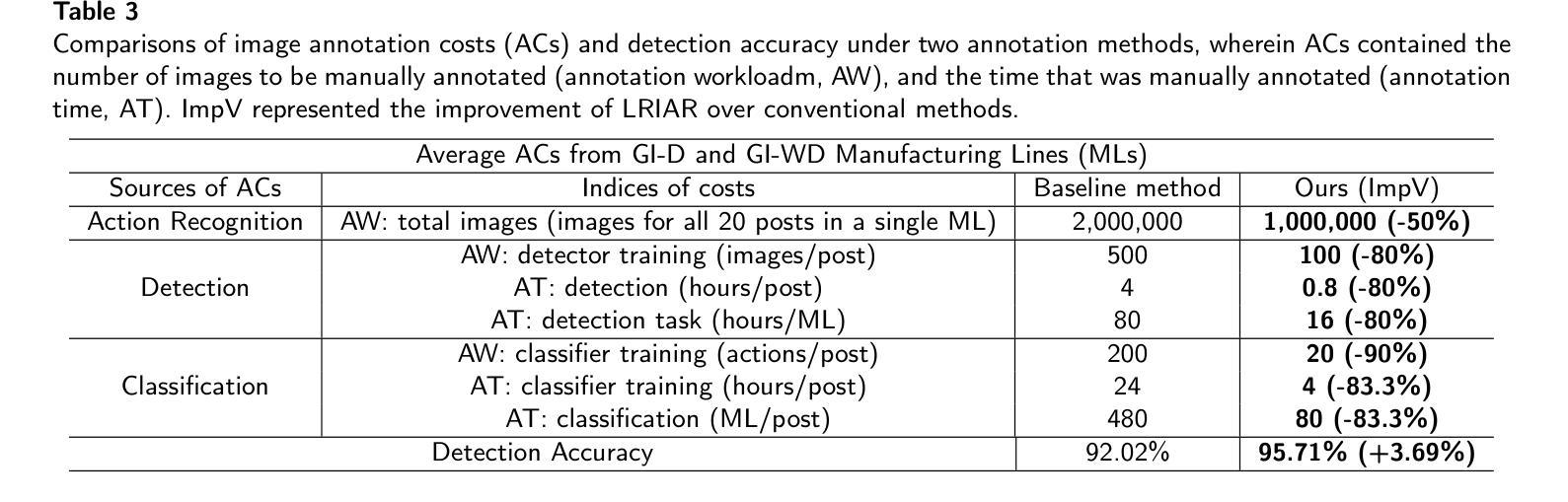
ALow-Cost Real-Time Framework for Industrial Action Recognition Using Foundation Models
Authors:Zhicheng Wang, Wensheng Liang, Ruiyan Zhuang, Shuai Li, Jianwei Tan, Xiaoguang Ma
Action recognition (AR) in industrial environments – particularly for identifying actions and operational gestures – faces persistent challenges due to high deployment costs, poor cross-scenario generalization, and limited real-time performance. To address these issues, we propose a low-cost real-time framework for industrial action recognition using foundation models, denoted as LRIAR, to enhance recognition accuracy and transferability while minimizing human annotation and computational overhead. The proposed framework constructs an automatically labeled dataset by coupling Grounding DINO with the pretrained BLIP-2 image encoder, enabling efficient and scalable action labeling. Leveraging the constructed dataset, we train YOLOv5 for real-time action detection, and a Vision Transformer (ViT) classifier is deceloped via LoRA-based fine-tuning for action classification. Extensive experiments conducted in real-world industrial settings validate the effectiveness of LRIAR, demonstrating consistent improvements over state-of-the-art methods in recognition accuracy, scenario generalization, and deployment efficiency.
在工业环境中进行动作识别(AR)——特别是识别动作和操作手势——由于部署成本高、跨场景泛化能力差以及实时性能有限,一直面临着持续挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种利用基础模型的工业动作识别实时低成本框架,称为LRIAR,以提高识别精度和可迁移性,同时最小化人工标注和计算开销。所提出的框架通过结合Grounding DINO和预训练的BLIP-2图像编码器,构建自动标注数据集,实现高效且可扩展的动作标注。利用构建的数据集,我们训练YOLOv5进行实时动作检测,并通过LoRA微调开发Vision Transformer(ViT)分类器进行动作分类。在真实工业环境中的广泛实验验证了LRIAR的有效性,在识别精度、场景泛化和部署效率方面均表现出优于现有最新方法的持续性改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于工业环境中动作识别面临的挑战,如高部署成本、跨场景泛化能力差和实时性能有限等问题,我们提出了一种利用基础模型的低成本实时工业动作识别框架,称为LRIAR。该框架通过结合Grounding DINO和预训练的BLIP-2图像编码器,构建自动标注数据集,实现高效可伸缩的动作标注。利用构建的数据集,我们训练YOLOv5进行实时动作检测,并通过LoRA微调技术开发Vision Transformer(ViT)分类器进行动作分类。在真实工业环境中的广泛实验验证了LRIAR的有效性,在识别精度、场景泛化和部署效率方面均表现出优于现有技术的改进。
Key Takeaways
- LRIAR框架旨在解决工业环境中动作识别的高部署成本、泛化能力差和实时性能不足的问题。
- 利用Grounding DINO和BLIP-2图像编码器构建自动标注数据集,提高标注效率和数据质量。
- 采用YOLOv5进行实时动作检测,确保动作的准确捕捉。
- 利用Vision Transformer(ViT)分类器进行动作分类,通过LoRA微调技术提高分类精度。
- LRIAR框架具有良好的泛化能力,能在不同工业场景中进行有效识别。
- 实验结果证明了LRIAR在识别精度、场景泛化能力和部署效率方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图



A Mixture of Exemplars Approach for Efficient Out-of-Distribution Detection with Foundation Models
Authors:Evelyn Mannix, Howard Bondell
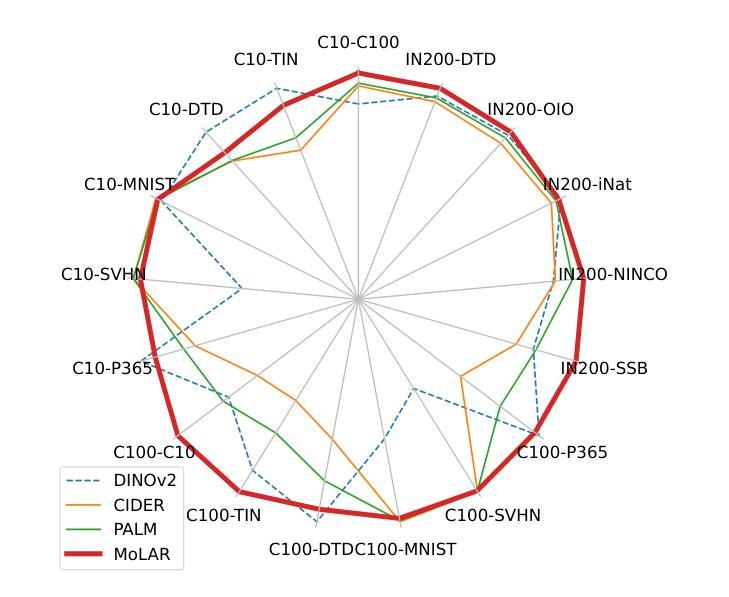
One of the early weaknesses identified in deep neural networks trained for image classification tasks was their inability to provide low confidence predictions on out-of-distribution (OOD) data that was significantly different from the in-distribution (ID) data used to train them. Representation learning, where neural networks are trained in specific ways that improve their ability to detect OOD examples, has emerged as a promising solution. However, these approaches require long training times and can add additional overhead to detect OOD examples. Recent developments in Vision Transformer (ViT) foundation models$\unicode{x2013}$large networks trained on large and diverse datasets with self-supervised approaches$\unicode{x2013}$also show strong performance in OOD detection, and could address these challenges. This paper presents Mixture of Exemplars (MoLAR), an efficient approach to tackling OOD detection challenges that is designed to maximise the benefit of training a classifier with a high quality, frozen, pretrained foundation model backbone. MoLAR provides strong OOD detection performance when only comparing the similarity of OOD examples to the exemplars, a small set of images chosen to be representative of the dataset, leading to significantly reduced overhead for OOD detection inference over other methods that provide best performance when the full ID dataset is used. Extensive experiments demonstrate the improved OOD detection performance of MoLAR in comparison to comparable approaches in both supervised and semi-supervised settings, and code is available at github.com/emannix/molar-mixture-of-exemplars.
早期在图像分类任务中训练深度神经网络时,发现的一个弱点是它们无法在对远离训练所用的内部数据分布(ID)且截然不同的外部数据分布(OOD)数据上提供低置信度预测。表现学习(representation learning)应运而生为一种颇具前景的解决方案,通过特定的训练神经网络方式提高其检测OOD样本的能力。然而,这些方法需要长时间的训练并且会额外增加检测OOD样本的开销。近期,视觉转换器(Vision Transformer,简称ViT)基础模型的研发展示了在OOD检测中的强劲性能。这些基础模型通过在大型、多样化的数据集上使用自监督方式进行大规模训练。本文提出了一个名为Mixture of Exemplars (MoLAR)的方法,旨在有效利用预训练的基础模型的优势进行高效的OOD检测挑战。MoLAR设计之初就旨在通过相似性对比来判断是否为OOD样本,只对比一小部分具有代表性的图像样本集即可实现出色的OOD检测性能。相较于使用全ID数据集表现最佳的其他方法而言,这无疑大大减少了OOD检测推理的开销。广泛的实验证明了MoLAR相较于其他可比方法在无监督及半监督设置下的出色OOD检测性能。代码可通过github.com/emannix/molar-mixture-of-exemplars访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了深度学习模型在处理图像分类任务时的一个早期弱点,即它们无法对与训练数据分布差异较大的数据进行低置信度预测。为此,研究者提出了使用表示学习方法来训练神经网络以检测异常数据的方法。最近,Vision Transformer(ViT)基础模型的出现为解决这一问题提供了有力支持。本文提出了一种名为Mixture of Exemplars(MoLAR)的有效方法,旨在最大化使用高质量、冻结的预训练基础模型训练分类器的优势。MoLAR通过比较异常数据与样本的相似性进行OOD检测,这些样本是从具有代表性的图像集中选择的少量图像。实验表明,MoLAR在监督学习和半监督学习环境中与其他类似方法的比较中表现出更强的异常检测性能。同时提供了对应的代码库地址。
Key Takeaways
以下是提取的七个关键见解:
- 深度学习模型在处理图像分类任务时面临的一个挑战是,它们难以对与训练数据分布不同的数据进行低置信度预测。
- 表示学习方法能够训练神经网络以检测异常数据分布(OOD)。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)基础模型为解决OOD检测问题提供了有效支持。
- Mixture of Exemplars(MoLAR)是一种设计用来最大化使用预训练基础模型训练分类器优势的方法。
- MoLAR通过比较异常数据与样本的相似性进行OOD检测,这种方法显著减少了异常检测的推理开销。
- 实验表明MoLAR在监督学习和半监督学习环境中与其他方法相比具有更好的OOD检测性能。
点此查看论文截图