⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-09 更新
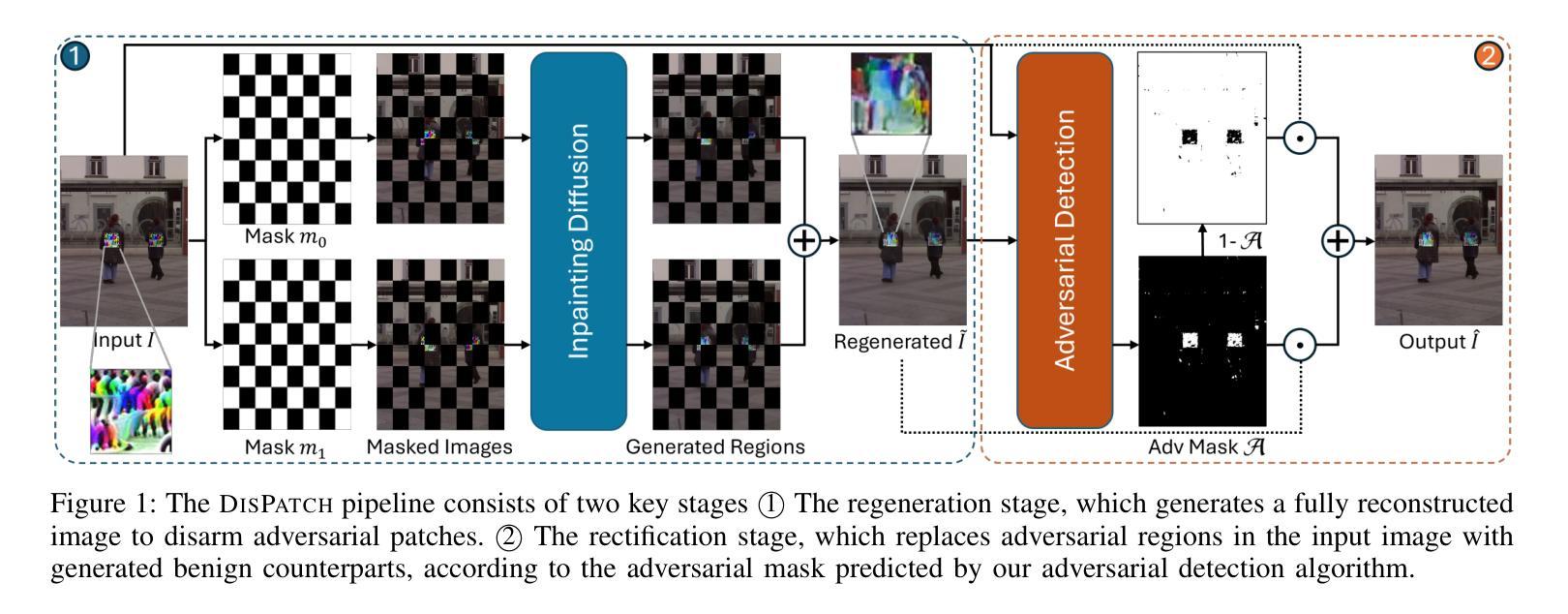
DisPatch: Disarming Adversarial Patches in Object Detection with Diffusion Models
Authors:Jin Ma, Mohammed Aldeen, Christopher Salas, Feng Luo, Mashrur Chowdhury, Mert Pesé, Long Cheng
Object detection is fundamental to various real-world applications, such as security monitoring and surveillance video analysis. Despite their advancements, state-of-theart object detectors are still vulnerable to adversarial patch attacks, which can be easily applied to real-world objects to either conceal actual items or create non-existent ones, leading to severe consequences. Given the current diversity of adversarial patch attacks and potential unknown threats, an ideal defense method should be effective, generalizable, and robust against adaptive attacks. In this work, we introduce DISPATCH, the first diffusion-based defense framework for object detection. Unlike previous works that aim to “detect and remove” adversarial patches, DISPATCH adopts a “regenerate and rectify” strategy, leveraging generative models to disarm attack effects while preserving the integrity of the input image. Specifically, we utilize the in-distribution generative power of diffusion models to regenerate the entire image, aligning it with benign data. A rectification process is then employed to identify and replace adversarial regions with their regenerated benign counterparts. DISPATCH is attack-agnostic and requires no prior knowledge of the existing patches. Extensive experiments across multiple detectors and attacks demonstrate that DISPATCH consistently outperforms state-of-the-art defenses on both hiding attacks and creating attacks, achieving the best overall mAP.5 score of 89.3% on hiding attacks, and lowering the attack success rate to 24.8% on untargeted creating attacks. Moreover, it maintains strong robustness against adaptive attacks, making it a practical and reliable defense for object detection systems.
目标检测在各种实际应用中扮演着重要角色,如安全监控和监控视频分析等。尽管已经取得了进展,但最新的目标检测器仍然容易受到对抗补丁攻击的影响,这些攻击可以很容易地应用于真实世界的物体上,以掩盖实际物品或制造不存在的物品,从而带来严重后果。考虑到当前对抗补丁攻击的多样性和潜在未知威胁,理想的防御方法应该是有效、通用和针对适应性攻击的稳健。在这项工作中,我们介绍了DISPATCH,这是第一个基于扩散的目标检测防御框架。与以往旨在“检测和移除”对抗补丁的工作不同,DISPATCH采用“再生和纠正”策略,利用生成模型来消除攻击效果,同时保持输入图像的完整性。具体来说,我们利用扩散模型的内部分布生成能力来再生整个图像,使其与良性数据对齐。然后采用校正过程来识别和替换对抗区域,并用其再生的良性对应物进行替换。DISPATCH对攻击持中立态度,无需事先了解现有补丁。在多个检测器和攻击上的广泛实验表明,无论是在隐藏攻击还是创建攻击方面,DISPATCH都优于最新的防御手段,在隐藏攻击方面取得了最佳的整体mAP 5分数为89.3%,在无目标创建攻击方面将攻击成功率降低到24.8%。此外,它对适应性攻击具有很强的稳健性,成为目标检测系统实用可靠的防御手段。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对对象检测中的对抗性补丁攻击的新防御框架DISPATCH。不同于传统的检测和移除策略,DISPATCH采用“再生和修正”策略,利用生成模型消除攻击效果,同时保持输入图像的完整性。实验表明,DISPATCH在隐藏攻击和创建攻击上均表现出优异的性能,实现对未知攻击的零先验知识防御。它在隐藏攻击方面达到了最佳总体mAP得分89.3%,在不受控制的创建攻击中将攻击成功率降低到24.8%,并在对抗性攻击中保持了强大的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- DISPATCH是首个针对对象检测的扩散模型防御框架。
- 不同于传统的“检测和移除”策略,DISPATCH采用“再生和修正”策略来处理对抗性补丁攻击。
- DISPATCH利用生成模型消除攻击效果,同时保持输入图像的完整性。
- DISPATCH对所有已知和未知的对抗性补丁攻击都具有防护作用,无需任何先验知识。
- 实验表明,DISPATCH在隐藏攻击和创建攻击上的性能均优于现有防御手段。
- 在隐藏攻击方面,DISPATCH达到了最佳总体mAP得分89.3%。
- 在不受控制的创建攻击中,DISPATCH将攻击成功率降低到24.8%。
点此查看论文截图


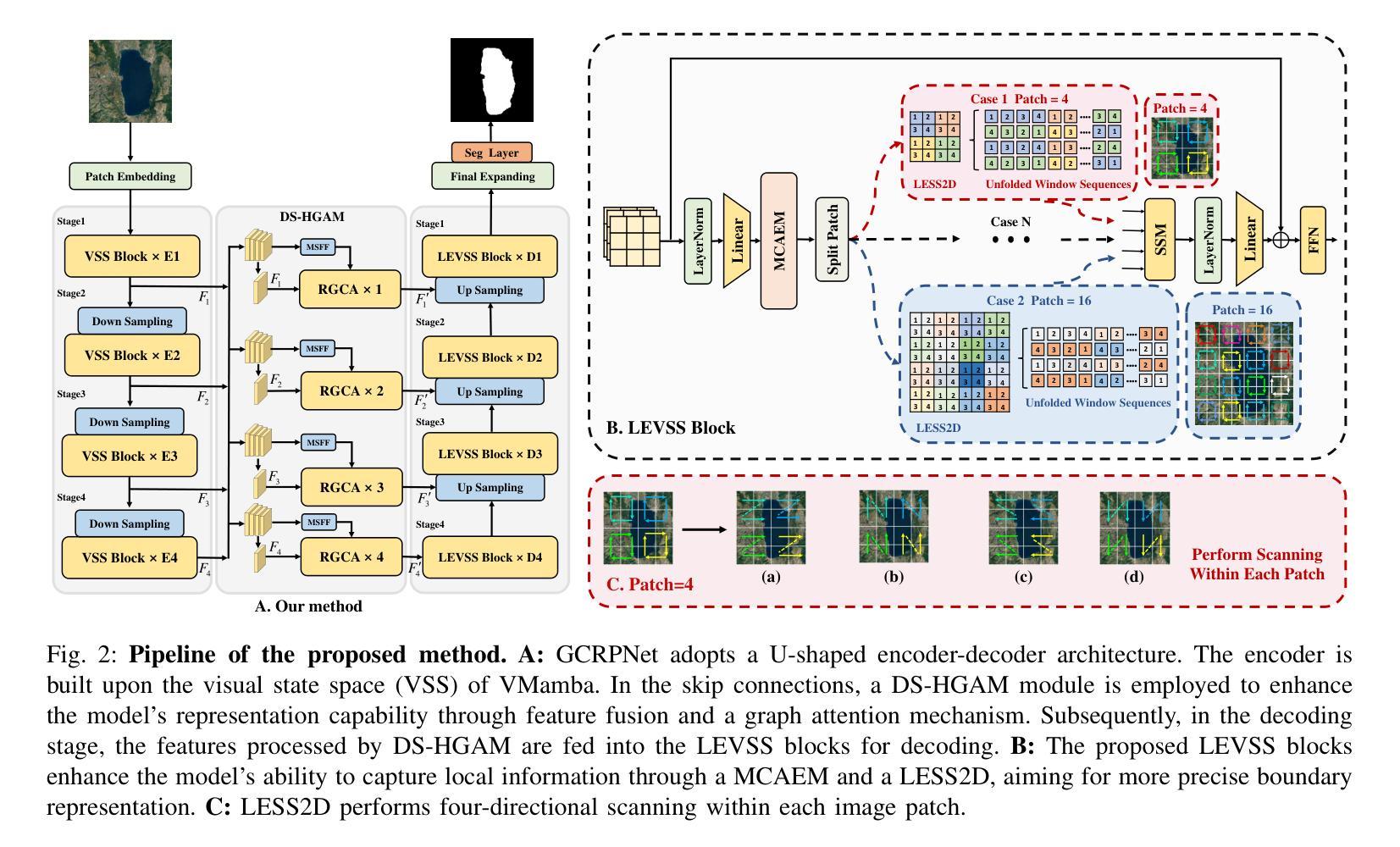
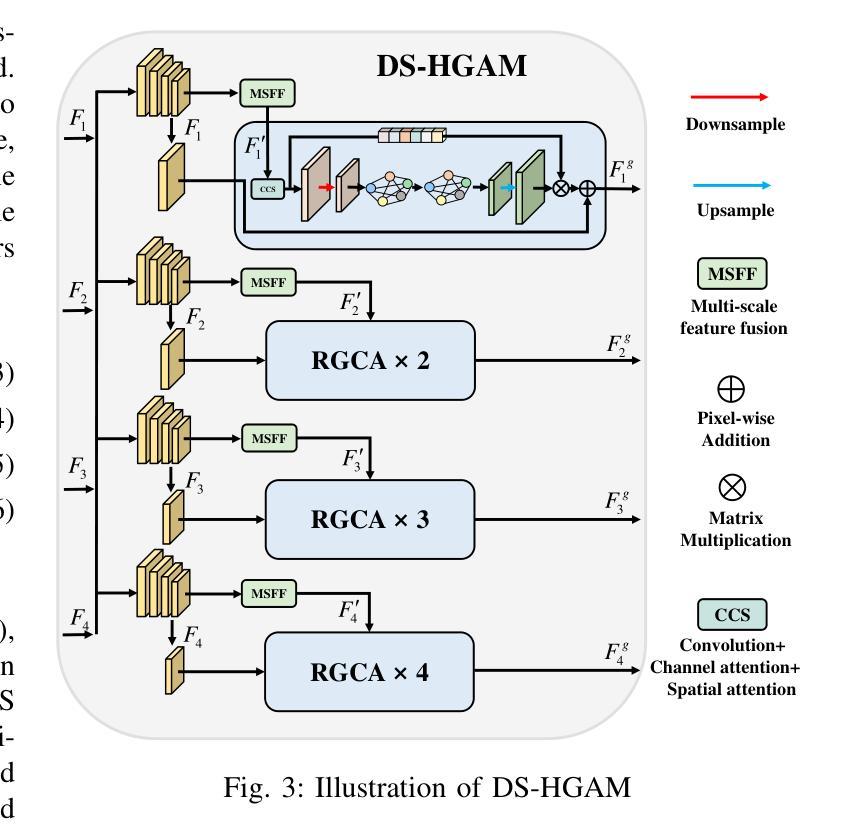
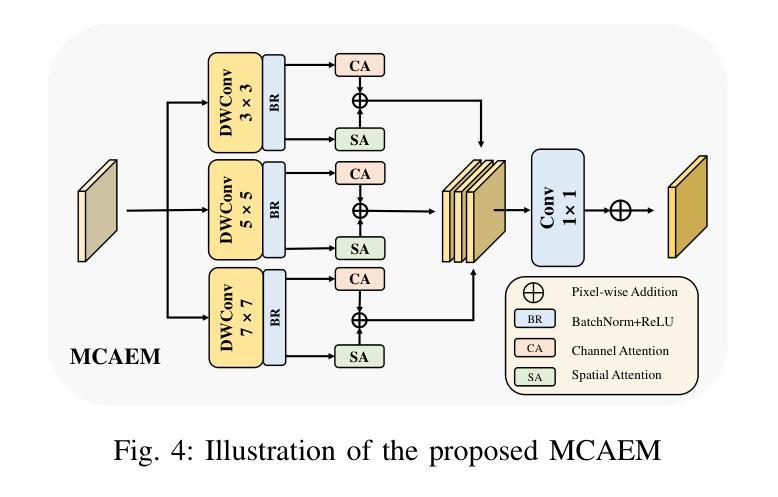
GCRPNet: Graph-Enhanced Contextual and Regional Perception Network For Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images
Authors:Mengyu Ren, Yutong Li, Hua Li, Runmin Cong, Sam Kwong
Salient object detection (SOD) in optical remote sensing images (ORSIs) faces numerous challenges, including significant variations in target scales and low contrast between targets and the background. Existing methods based on vision transformers (ViTs) and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) architectures aim to leverage both global and local features, but the difficulty in effectively integrating these heterogeneous features limits their overall performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose a graph-enhanced contextual and regional perception network (GCRPNet), which builds upon the Mamba architecture to simultaneously capture long-range dependencies and enhance regional feature representation. Specifically, we employ the visual state space (VSS) encoder to extract multi-scale features. To further achieve deep guidance and enhancement of these features, we first design a difference-similarity guided hierarchical graph attention module (DS-HGAM). This module strengthens cross-layer interaction capabilities between features of different scales while enhancing the model’s structural perception,allowing it to distinguish between foreground and background more effectively. Then, we design the LEVSS block as the decoder of GCRPNet. This module integrates our proposed adaptive scanning strategy and multi-granularity collaborative attention enhancement module (MCAEM). It performs adaptive patch scanning on feature maps processed via multi-scale convolutions, thereby capturing rich local region information and enhancing Mamba’s local modeling capability. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance, validating its effectiveness and superiority.
显著性目标检测(SOD)在光学遥感图像(ORSIs)中面临诸多挑战,包括目标尺度的显著变化和目标与背景之间的对比度低。现有的基于视觉变压器(ViTs)和卷积神经网络(CNNs)架构的方法旨在利用全局和局部特征,但有效整合这些异质特征的困难限制了它们的总体性能。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了图增强上下文和区域感知网络(GCRPNet),它基于Mamba架构,同时捕捉长程依赖关系并增强区域特征表示。具体来说,我们采用视觉状态空间(VSS)编码器提取多尺度特征。为了进一步实现这些特征的深度引导和增强,我们首先设计了一个差异相似性引导分层图注意力模块(DS-HGAM)。该模块增强了不同尺度特征之间的跨层交互能力,提高了模型的结构感知能力,使其更有效地区分前景和背景。然后,我们设计了LEVSS块作为GCRPNet的解码器。该模块结合了我们的自适应扫描策略和多粒度协同注意力增强模块(MCAEM)。它对通过多尺度卷积处理的特征图进行自适应斑块扫描,从而捕获丰富的局部区域信息,增强Mamba的局部建模能力。大量的实验结果证明了该模型达到了最先进的性能,验证了其有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于光学遥感图像,显著性目标检测面临诸多挑战,如目标尺度变化大、目标与背景对比度低。现有方法虽利用全局和局部特征,但整合这些特征的困难限制了性能。我们提出一种图增强上下文与区域感知网络(GCRPNet),结合Mamba架构捕捉远程依赖关系并增强区域特征表示。采用视觉状态空间(VSS)编码器提取多尺度特征,设计差异相似度引导层次图注意力模块(DS-HGAM)实现特征深度引导和增强,区分前景和背景。此外,设计LEVSS块作为解码器,结合自适应扫描策略和多重粒度协同注意力增强模块(MCAEM),捕捉丰富局部区域信息,增强局部建模能力。实验证实该模型性能优越。
Key Takeaways
- 显著性目标检测在光学遥感图像中面临挑战,包括目标尺度变化和低对比度。
- 现有方法基于ViTs和CNNs,旨在利用全局和局部特征,但整合困难。
- 提出GCRPNet模型,结合Mamba架构,同时捕捉远程依赖关系和增强区域特征表示。
- 采用视觉状态空间编码器提取多尺度特征。
- DS-HGAM模块加强不同尺度特征间的跨层互动,提高模型的结构感知能力。
- LEVSS块结合自适应扫描策略和MCAEM模块,捕捉局部区域信息,增强局部建模能力。
- 实验结果证实该模型性能优越。
点此查看论文截图

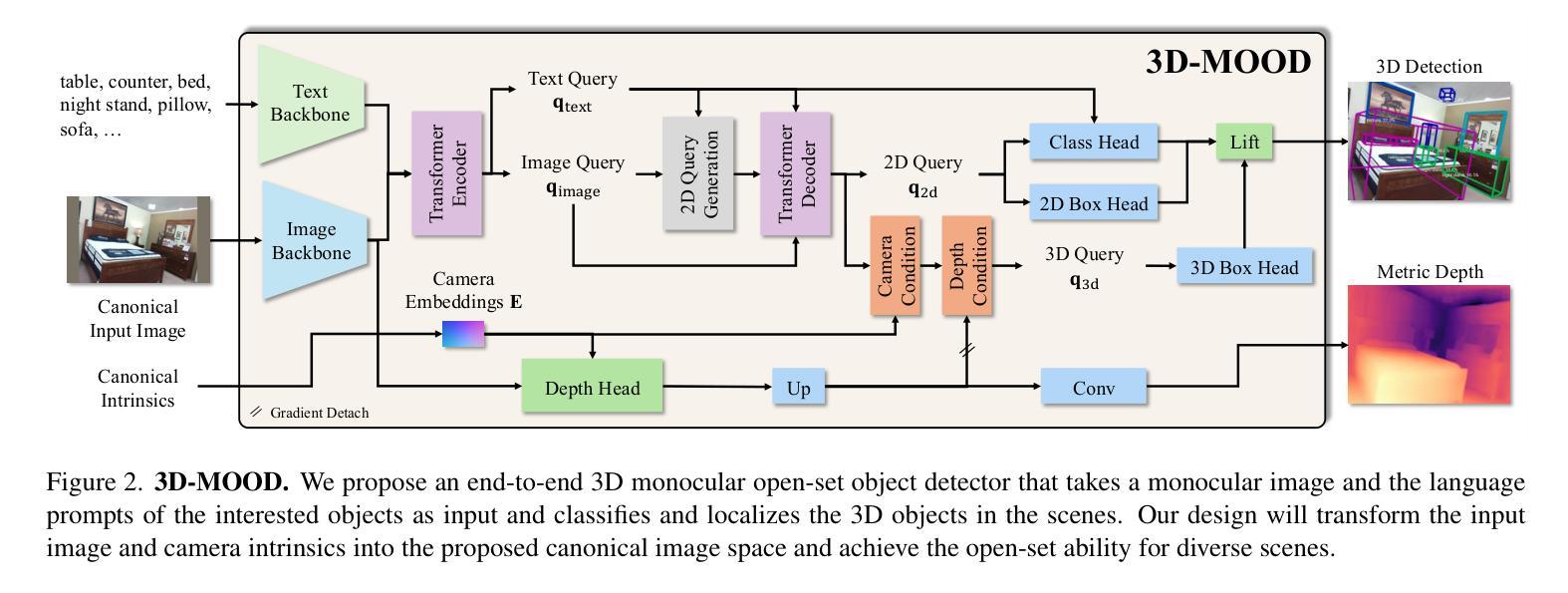
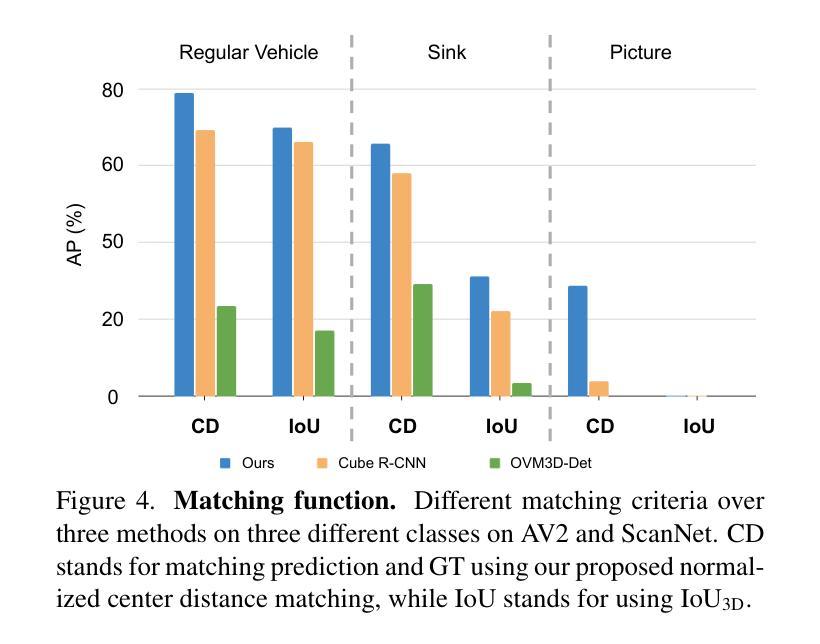
3D-MOOD: Lifting 2D to 3D for Monocular Open-Set Object Detection
Authors:Yung-Hsu Yang, Luigi Piccinelli, Mattia Segu, Siyuan Li, Rui Huang, Yuqian Fu, Marc Pollefeys, Hermann Blum, Zuria Bauer
Monocular 3D object detection is valuable for various applications such as robotics and AR/VR. Existing methods are confined to closed-set settings, where the training and testing sets consist of the same scenes and/or object categories. However, real-world applications often introduce new environments and novel object categories, posing a challenge to these methods. In this paper, we address monocular 3D object detection in an open-set setting and introduce the first end-to-end 3D Monocular Open-set Object Detector (3D-MOOD). We propose to lift the open-set 2D detection into 3D space through our designed 3D bounding box head, enabling end-to-end joint training for both 2D and 3D tasks to yield better overall performance. We condition the object queries with geometry prior and overcome the generalization for 3D estimation across diverse scenes. To further improve performance, we design the canonical image space for more efficient cross-dataset training. We evaluate 3D-MOOD on both closed-set settings (Omni3D) and open-set settings (Omni3D to Argoverse 2, ScanNet), and achieve new state-of-the-art results. Code and models are available at royyang0714.github.io/3D-MOOD.
单目3D对象检测对于各种应用(如机器人和AR/VR)具有价值。现有方法仅限于封闭集设置,其中训练和测试集由相同的场景和/或对象类别组成。然而,现实世界的应用经常会引入新的环境和新型对象类别,给这些方法带来了挑战。在本文中,我们解决了开放集设置下的单目3D对象检测问题,并引入了首个端到端的3D单目开放集对象检测器(3D-MOOD)。我们提出通过设计的3D边界框头将开放集2D检测提升到3D空间,实现对2D和3D任务的端到端联合训练,以获得更好的整体性能。我们以几何优先条件对对象查询进行条件处理,并克服了在各种场景中进行3D估计的泛化问题。为了进一步提高性能,我们设计了规范图像空间,以便进行更有效的跨数据集训练。我们在封闭集设置(Omni3D)和开放集设置(Omni3D到Argoverse 2,ScanNet)上评估了3D-MOOD,并实现了最新的最佳结果。代码和模型可在royyang0714.github.io/3D-MOOD上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
本文研究了单目3D对象检测在开放集场景下的挑战,并介绍了首个端到端的3D单目开放集对象检测器(3D-MOOD)。通过设计的3D边界框头,将开放集2D检测提升到3D空间,实现2D和3D任务的端到端联合训练,提高整体性能。此外,通过几何先验条件化对象查询,并设计标准图像空间,以提高跨数据集训练的效率和性能。在封闭集和开放集环境下对3D-MOOD进行了评估,取得了新的先进成果。
Key Takeaways
- 现有单目3D对象检测方法主要局限于封闭集场景,难以满足开放集场景下的需求。
- 论文提出了首个端到端的3D单目开放集对象检测器(3D-MOOD)。
- 通过设计的3D边界框头,将开放集2D检测提升到3D空间,实现端到端联合训练,提升整体性能。
- 结合几何先验条件化对象查询,增强了模型的泛化能力。
- 设计了标准图像空间,提高了跨数据集训练的效率和性能。
点此查看论文截图