⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-09 更新
Painting the market: generative diffusion models for financial limit order book simulation and forecasting
Authors:Alfred Backhouse, Kang Li, Jakob Foerster, Anisoara Calinescu, Stefan Zohren
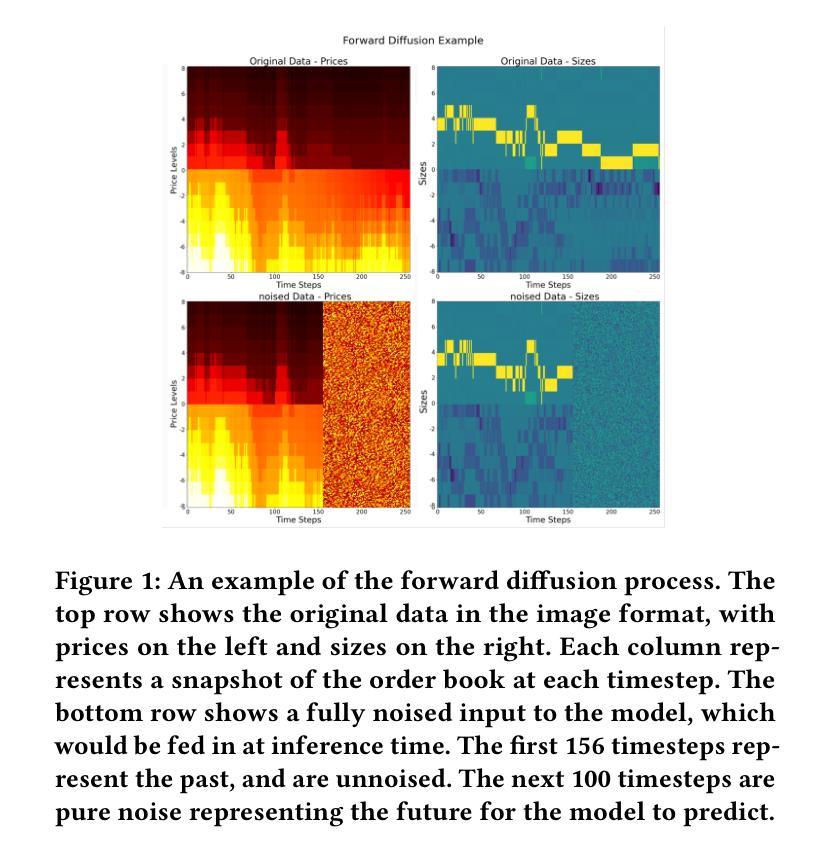
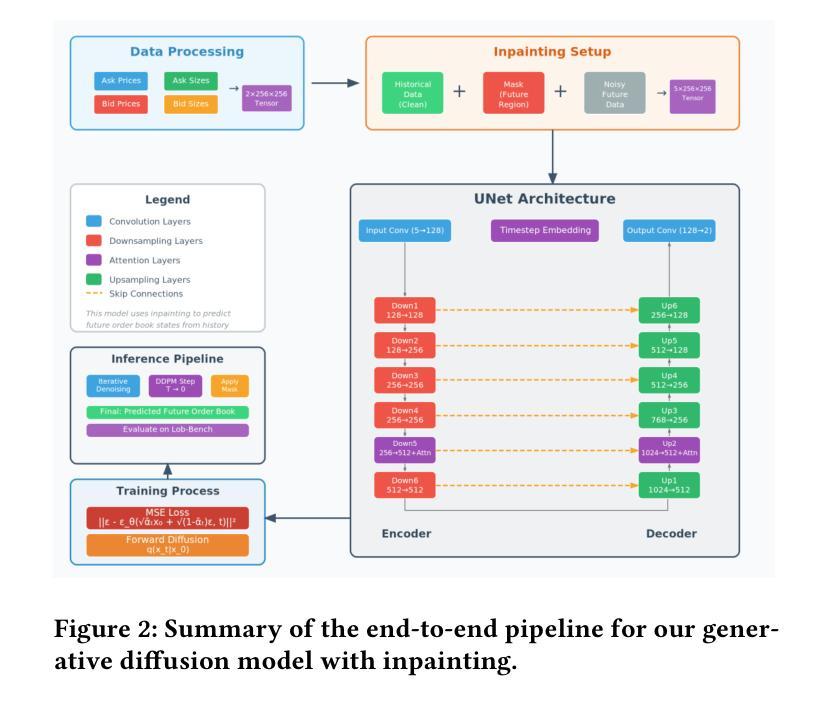
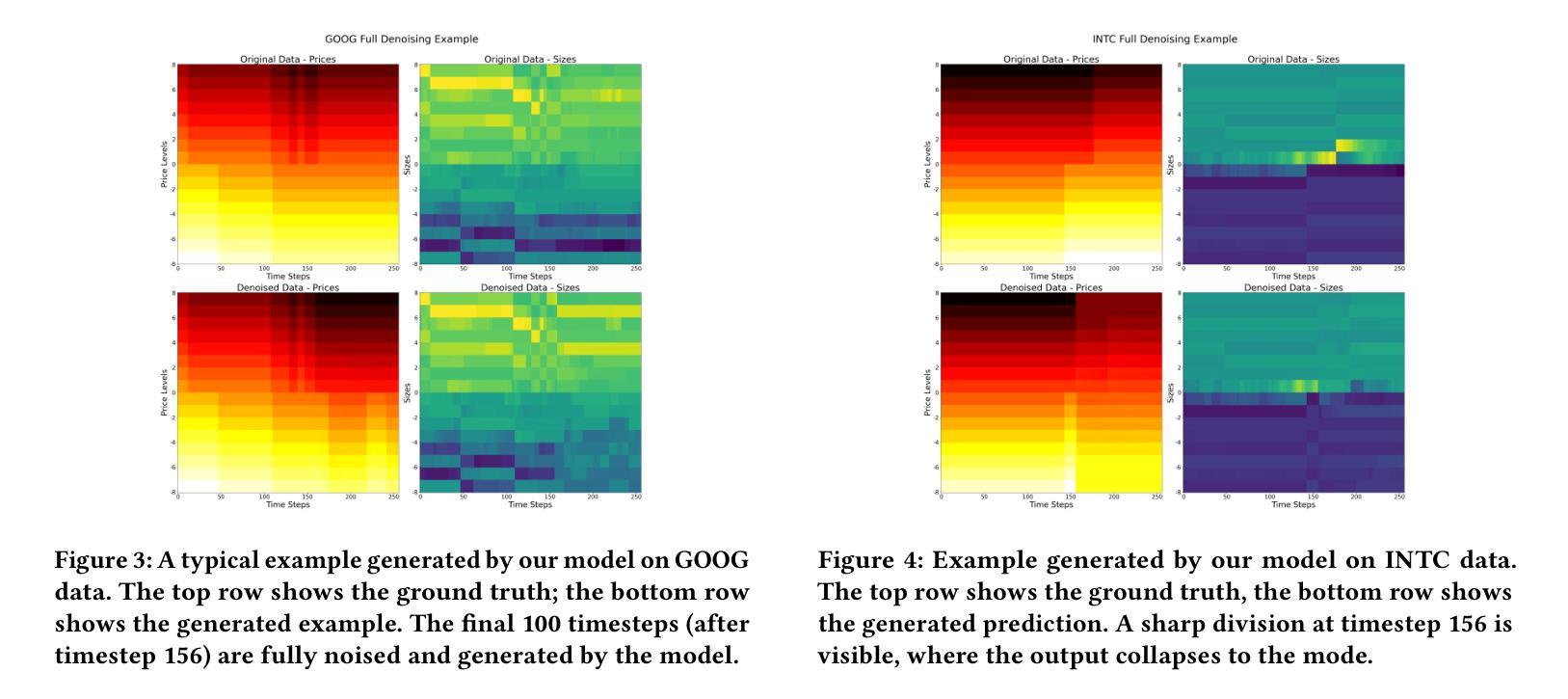
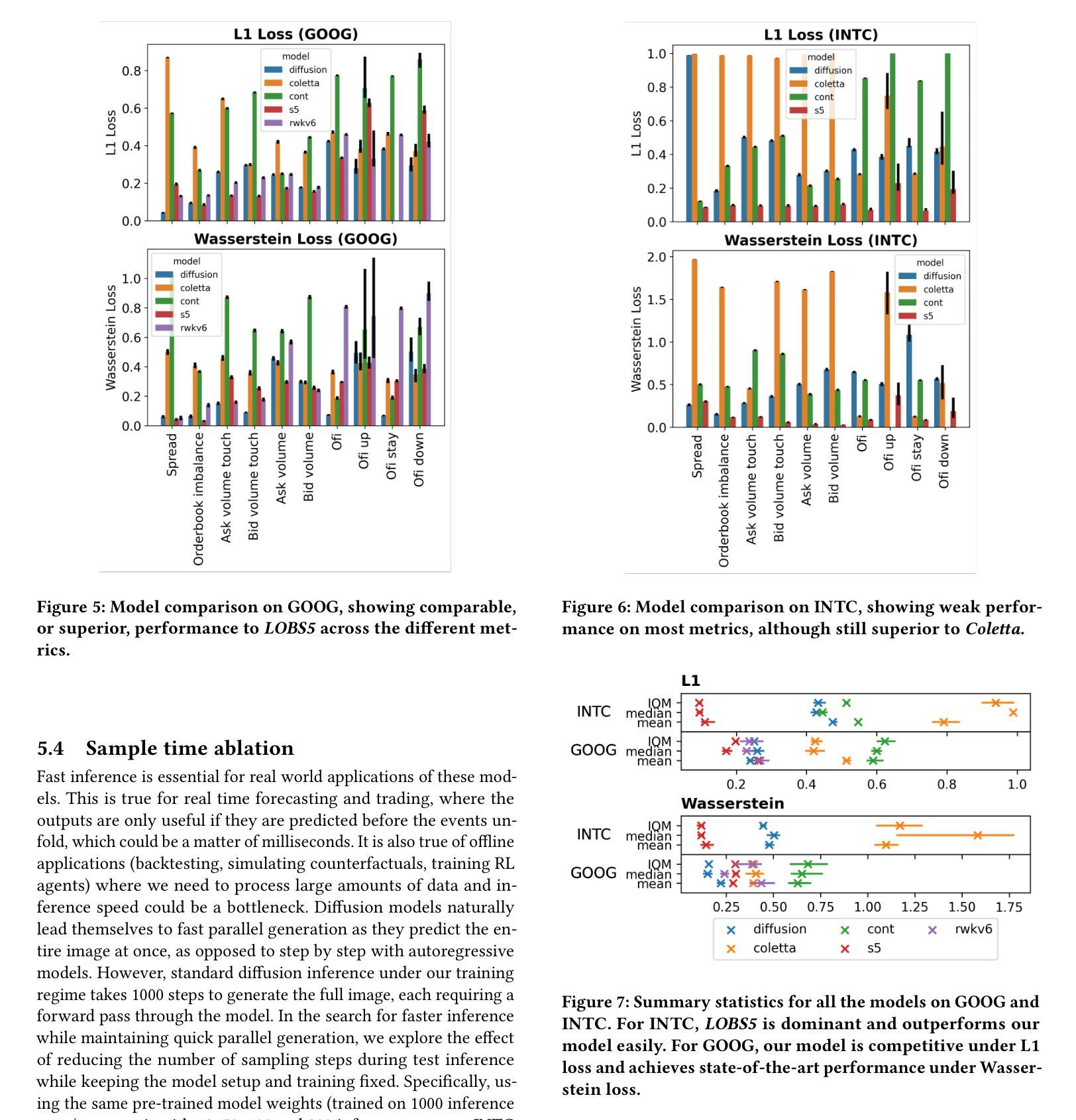
Simulating limit order books (LOBs) has important applications across forecasting and backtesting for financial market data. However, deep generative models struggle in this context due to the high noise and complexity of the data. Previous work uses autoregressive models, although these experience error accumulation over longer-time sequences. We introduce a novel approach, converting LOB data into a structured image format, and applying diffusion models with inpainting to generate future LOB states. This method leverages spatio-temporal inductive biases in the order book and enables parallel generation of long sequences overcoming issues with error accumulation. We also publicly contribute to LOB-Bench, the industry benchmark for LOB generative models, to allow fair comparison between models using Level-2 and Level-3 order book data (with or without message level data respectively). We show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on LOB-Bench, despite using lower fidelity data as input. We also show that our method prioritises coherent global structures over local, high-fidelity details, providing significant improvements over existing methods on certain metrics. Overall, our method lays a strong foundation for future research into generative diffusion approaches to LOB modelling.
模拟限价订单簿(LOBs)在金融市场的预测和回溯测试中具有重要应用。然而,由于数据的高噪声和复杂性,深度生成模型在此场景中面临挑战。之前的工作使用自回归模型,尽管这些模型在较长的时间序列上会出现误差累积。我们引入了一种新方法,将LOB数据转换为结构化图像格式,并应用带有填充的扩散模型来生成未来的LOB状态。这种方法利用订单书中的时空归纳偏见,并能够实现并行生成长序列,克服误差累积问题。我们还为LOB生成模型的行业基准LOB-Bench做出贡献,以便使用Level-2和Level-3订单簿数据(分别带有或不带消息级数据)在模型之间进行公平比较。我们显示,尽管我们的模型使用较低保真度的数据作为输入,但在LOB-Bench上实现了最新性能。我们还表明,我们的方法优先关注连贯的全局结构,而非局部的高保真细节,在某些指标上较现有方法取得了显著改进。总的来说,我们的方法为将来研究生成扩散方法在LOB建模中的应用奠定了坚实基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICAIF
Summary
模拟限价指令簿(LOBs)在金融市场的预测和回溯测试中具有重要应用。然而,由于数据的高噪声和复杂性,深度生成模型在这方面表现不佳。尽管以前的工作使用了自回归模型,但这些模型在长序列中会出现误差累积。我们提出了一种新方法,将LOB数据转换为结构化图像格式,并应用带有填充的扩散模型来生成未来的LOB状态。此方法利用订单簿中的时空归纳偏见,并能够实现并行生成长序列,克服误差累积问题。我们还为LOB生成模型的行业基准LOB-Bench做出了贡献,以便使用Level-2和Level-3订单簿数据(分别带或不带消息级数据)进行模型之间的公平比较。我们显示,即使使用较低保真度的数据作为输入,我们的模型在LOB-Bench上也能实现最先进的性能。我们还表明,我们的方法优先考虑连贯的全局结构而非局部的、高保真的细节,在某些指标上较现有方法有了显著改进。总体而言,我们的方法为将来研究生成扩散方法在LOB建模中的应用奠定了坚实基础。
Key Takeaways
- 模拟限价指令簿(LOBs)在金融市场的预测和回溯测试中具有重要应用。
- 深度生成模型在模拟LOB数据时面临高噪声和复杂性数据的挑战。
- 自回归模型在长序列中存在误差累积问题。
- 提出一种新方法,将LOB数据转换为结构化图像格式,并应用扩散模型生成未来LOB状态。
- 该方法利用订单簿的时空归纳偏见,实现并行生成长序列。
- 对LOB生成模型的行业基准LOB-Bench做出贡献,实现模型间的公平比较。
点此查看论文截图

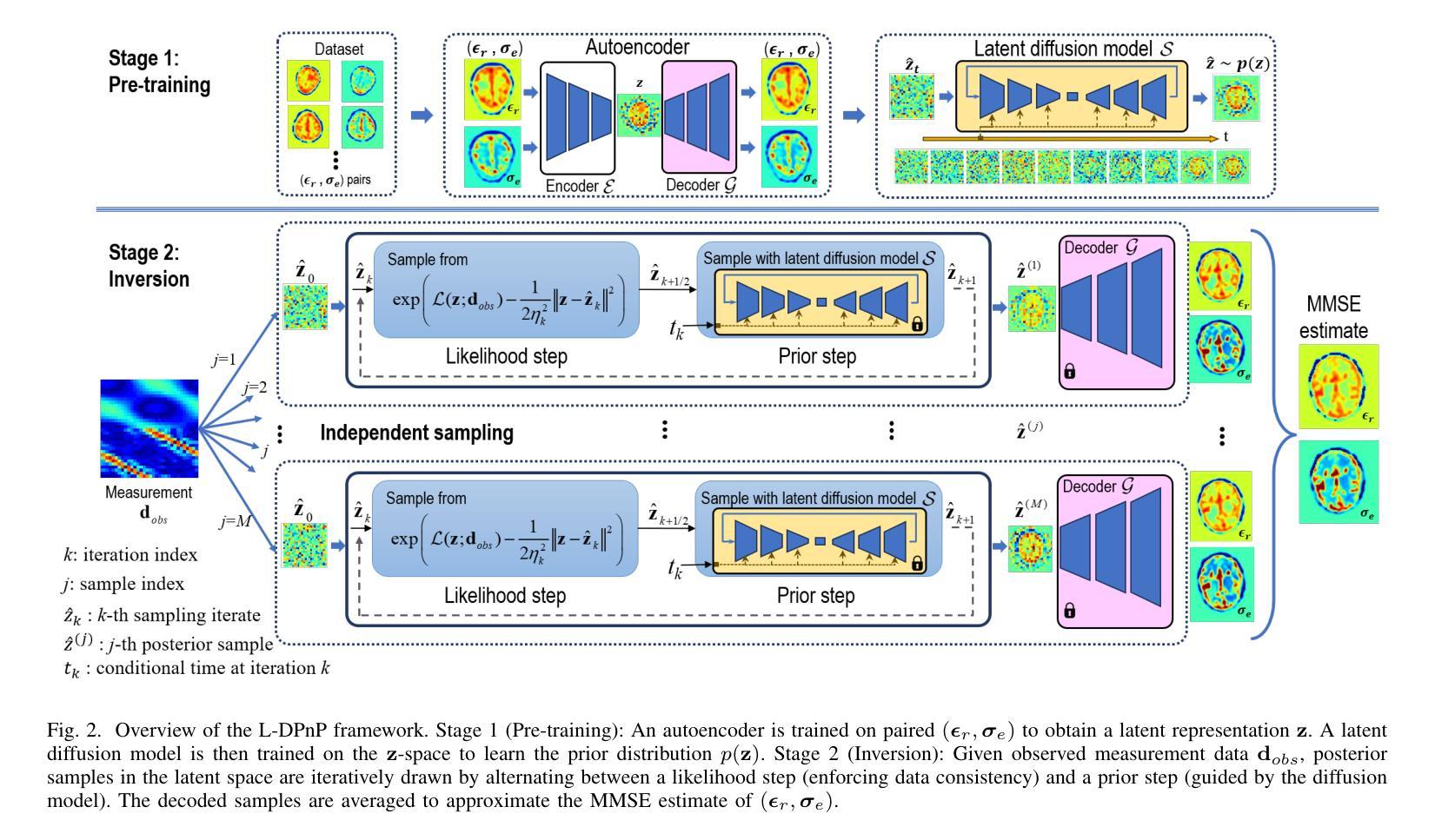
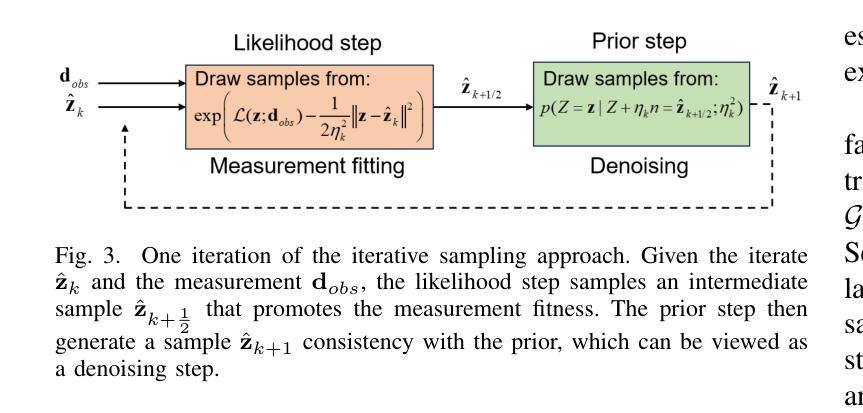
Plug-and-Play Latent Diffusion for Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering with Application to Brain Imaging
Authors:Rui Guo, Yi Zhang, Yhonatan Kvich, Tianyao Huang, Maokun Li, Yonina C. Eldar
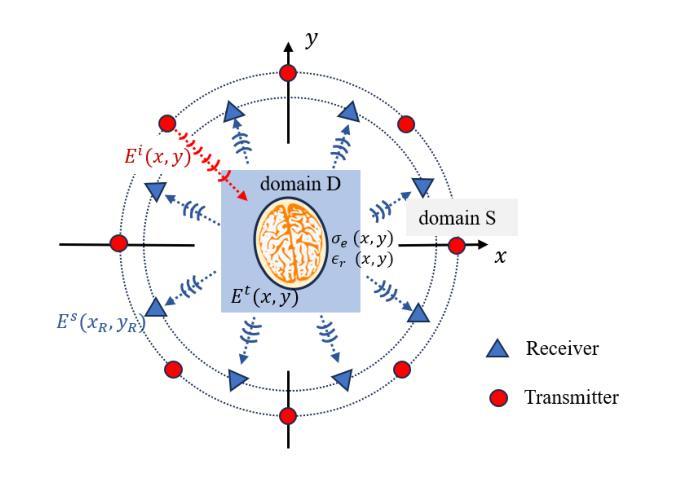
Electromagnetic (EM) imaging is an important tool for non-invasive sensing with low-cost and portable devices. One emerging application is EM stroke imaging, which enables early diagnosis and continuous monitoring of brain strokes. Quantitative imaging is achieved by solving an inverse scattering problem (ISP) that reconstructs permittivity and conductivity maps from measurements. In general, the reconstruction accuracy is limited by its inherent nonlinearity and ill-posedness. Existing methods, including learning-free and learning-based approaches, fail to either incorporate complicated prior distributions or provide theoretical guarantees, posing difficulties in balancing interpretability, distortion error, and reliability. To overcome these limitations, we propose a posterior sampling method based on latent diffusion for quantitative EM brain imaging, adapted from a generative plug-and-play (PnP) posterior sampling framework. Our approach allows to flexibly integrate prior knowledge into physics-based inversion without requiring paired measurement-label datasets. We first learn the prior distribution of targets from an unlabeled dataset, and then incorporate the learned prior into posterior sampling. In particular, we train a latent diffusion model on permittivity and conductivity maps to capture their prior distribution. Then, given measurements and the forward model describing EM wave physics, we perform posterior sampling by alternating between two samplers that respectively enforce the likelihood and prior distributions. Finally, reliable reconstruction is obtained through minimum mean squared error (MMSE) estimation based on the samples. Experimental results on brain imaging demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in reconstruction accuracy and structural similarity while maintaining high measurement fidelity.
电磁(EM)成像是一种重要的非侵入式感知工具,具有低成本和便携性。其一个新兴应用是电磁卒中成像,能够实现脑卒中的早期发现和持续监控。定量成像通过解决逆散射问题(ISP)实现,即通过对测量值进行重构来生成电容率和电导率图。一般来说,重构的准确性受到其固有非线性性和不适定性的限制。现有方法,包括无学习方法和基于学习的方法,无法融入复杂的先验分布或提供理论保证,难以在可解释性、失真误差和可靠性之间取得平衡。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于潜在扩散的贝叶斯采样方法,用于定量电磁脑成像,该方法改编自生成式即插即用(PnP)贝叶斯采样框架。我们的方法允许将先验知识灵活地融入基于物理的反演过程中,而无需配对测量标签数据集。我们首先从无标签数据集中学习目标的先验分布,然后将学到的先验融入贝叶斯采样。具体来说,我们在电容率和电导率图上训练一个潜在扩散模型,以捕捉它们的先验分布。然后,给定测量值和描述电磁波物理的正向模型,我们通过交替使用两个采样器来执行贝叶斯采样,这两个采样器分别强制执行可能性和先验分布。最后,通过基于样本的最小均方误差(MMSE)估计获得可靠的重建结果。在脑成像实验上的结果表明,我们的方法在重建精度和结构相似性方面达到了最先进的性能,同时保持了高测量保真度。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
电磁(EM)成像是非侵入式感应的重要工具,具有低成本和便携性设备。其新兴应用之一为EM卒中成像,可实现脑卒中的早期诊断和持续监测。定量成像通过解决逆散射问题(ISP)实现,从测量值重建介电常数和电导率图。然而,重建精度通常受限于问题的固有非线性和不适定性。现有方法,包括无学习和基于学习的方法,难以融入复杂的先验分布或提供理论保证,因此在解释性、失真误差和可靠性之间取得平衡存在困难。为克服这些限制,我们提出一种基于潜在扩散的后验采样方法,用于定量EM脑成像,该方法改编自生成式即插即用(PnP)后验采样框架。我们的方法允许灵活地将先验知识融入物理基础的反演中,而无需配对测量标签数据集。我们首先从无标签数据集中学习目标先验分布,然后将学到的先验融入后验采样中。具体来说,我们对介电常数和电导率图训练潜在扩散模型,以捕捉其先验分布。然后,给定测量值和描述电磁波物理的正向模型,我们通过交替使用两个采样器来执行后验采样,分别强制实施似然性和先验分布。最后,通过最小均方误差(MMSE)估计获得可靠的重建结果。在脑成像实验上的结果表明,我们的方法在实现重建精度和结构相似性方面达到最新水平,同时保持高测量保真度。
关键见解
- 电磁成像对于非侵入式感应是一个重要工具,其低成本和便携性使其具有广泛的应用前景。
- 定量电磁卒中成像可实现早期和持续的脑卒中诊断与监测。
- 现有电磁成像方法在重建精度上受到限制,面临非线性及不适定性问题。
- 提出一种基于潜在扩散的后验采样方法用于定量电磁脑成像,该方法结合了物理基础的反演与灵活的先验知识融入。
- 方法通过训练潜在扩散模型捕捉介电常数和电导率图的先验分布,进而提升重建精度。
- 结合测量值和电磁波物理的正向模型进行后验采样,通过交替采样器实现似然性和先验性的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

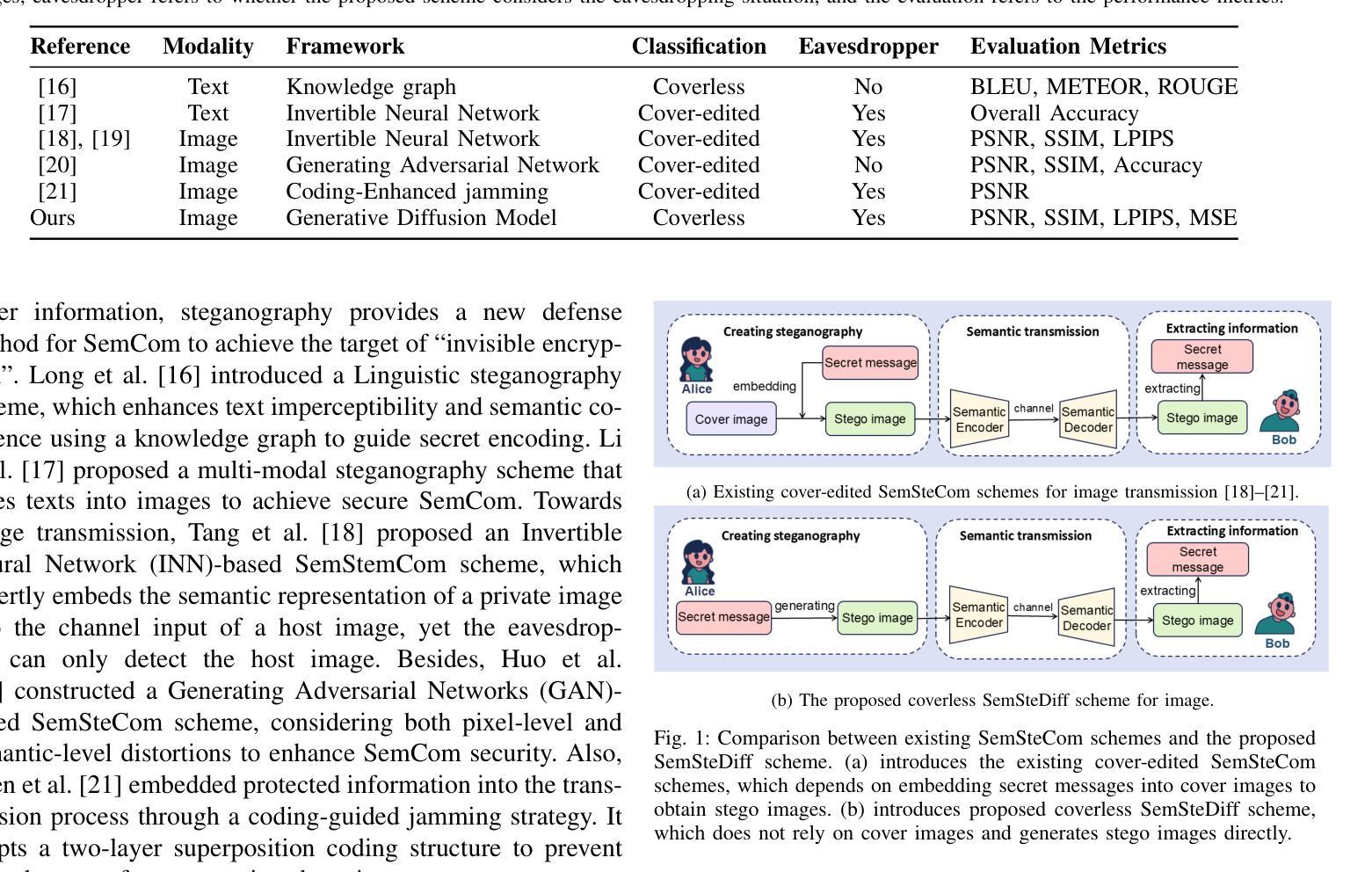
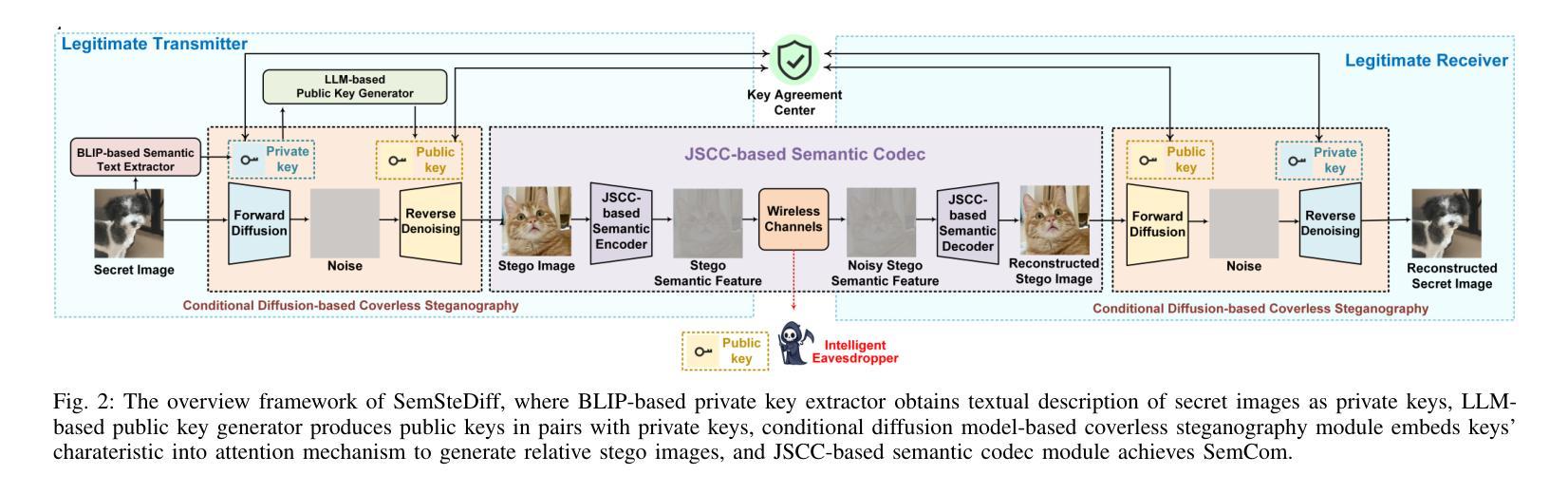
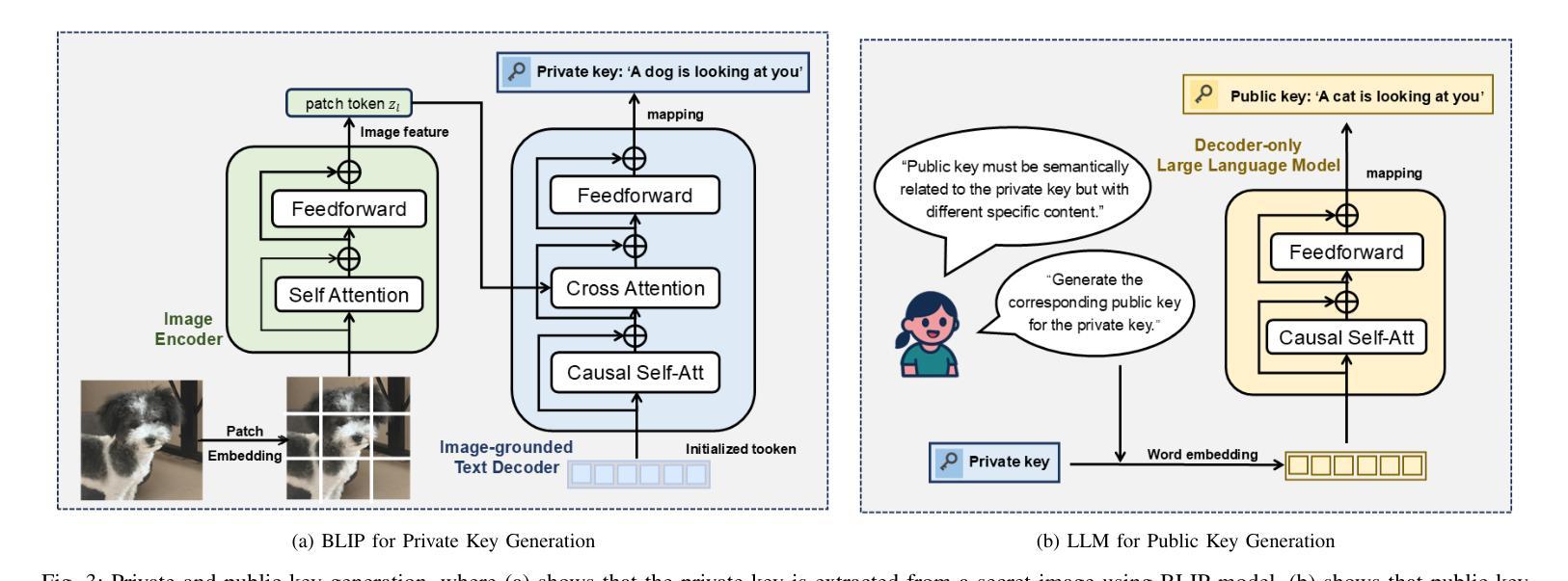
SemSteDiff: Generative Diffusion Model-based Coverless Semantic Steganography Communication
Authors:Song Gao, Rui Meng, Xiaodong Xu, Haixiao Gao, Yiming Liu, Chenyuan Feng, Ping Zhang, Tony Q. S. Quek, Dusit Niyato
Semantic communication (SemCom), as a novel paradigm for future communication systems, has recently attracted much attention due to its superiority in communication efficiency. However, similar to traditional communication, it also suffers from eavesdropping threats. Intelligent eavesdroppers could launch advanced semantic analysis techniques to infer secret semantic information. Therefore, some researchers have designed Semantic Steganography Communication (SemSteCom) scheme to confuse semantic eavesdroppers. However, the state-of-the-art SemSteCom schemes for image transmission rely on the pre-selected cover image, which limits the universality. To address this issue, we propose a Generative Diffusion Model-based Coverless Semantic Steganography Communication (SemSteDiff) scheme to hide secret images into generated stego images. The semantic related private and public keys enable legitimate receiver to decode secret images correctly while the eavesdropper without completely true key-pairs fail to obtain them. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the plug-and-play design in different Joint Source-Channel Coding (JSCC) frameworks. The comparison results under different eavesdroppers’ threats show that, when Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) = 0 dB, the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of the legitimate receiver is 4.14 dB higher than that of the eavesdropper.
语义通信(SemCom)作为未来通信系统的全新范式,因其通信效率上的优越性而近期备受关注。然而,与传统通信类似,它也面临着窃听威胁。智能窃听者可以发动先进的语义分析技术来推断秘密语义信息。因此,一些研究人员设计了语义隐身通信(SemSteCom)方案来迷惑语义窃听者。然而,当前用于图像传输的SemSteCom方案依赖于预先选择的载体图像,这限制了其通用性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于生成扩散模型的无需载体语义隐身通信(SemSteDiff)方案,将秘密图像隐藏在生成的隐写图像中。语义相关的私有和公钥使合法接收者能够正确解码秘密图像,而完全没有完全正确密钥对的窃听者则无法获取它们。仿真结果表明,在不同联合源信道编码(JSCC)框架下,即插即用设计的有效性。在不同窃听者威胁下的比较结果表明,当信噪比(SNR)= 0 dB时,合法接收者的峰值信噪比(PSNR)比窃听者高4.14 dB。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 11 figures
Summary
语义通信(SemCom)作为未来通信系统的全新范式,因其在通信效率方面的优越性而备受关注。但同样面临窃听威胁。智能窃听者可能利用高级语义分析技术推断秘密语义信息。为应对这一问题,研究人员设计了语义隐写通信(SemSteCom)方案以迷惑语义窃听者。针对当前图像传输的SemSteCom方案依赖于预选的载体图像,限制了其通用性。我们提出了基于生成扩散模型的无需载体语义隐写通信(SemSteDiff)方案,将秘密图像隐藏在生成的隐写图像中。语义相关的私钥和公钥使合法接收者能够正确解码秘密图像,而窃听者若没有完整的密钥对则无法获取。模拟结果表明,该即插即用设计在不同联合源信道编码(JSCC)框架中的有效性。在不同窃听威胁下的对比结果表明,在信噪比(SNR)= 0 dB时,合法接收者的峰值信噪比(PSNR)比窃听者高4.14 dB。
Key Takeaways
- 语义通信(SemCom)能提高通信效率,但面临智能窃听者的威胁。
- 现有图像传输的SemSteCom方案受限于预选的载体图像,缺乏通用性。
- 提出基于生成扩散模型的无需载体语义隐写通信(SemSteDiff)方案。
- 该方案利用语义相关的私钥和公钥,确保合法接收者能正确解码秘密图像。
- 模拟和对比实验表明,SemSteDiff方案在多种情境下均有效对抗窃听者威胁。
- 在信噪比(SNR)= 0 dB时,合法接收者的PSNR显著高于窃听者。
点此查看论文截图

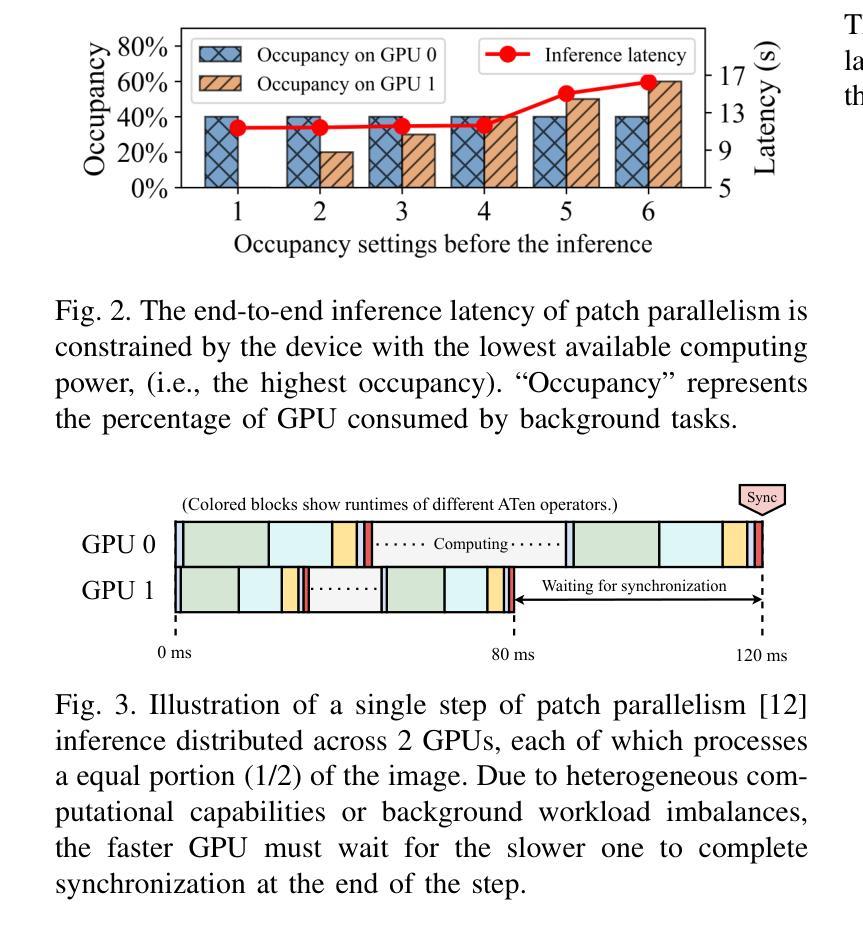
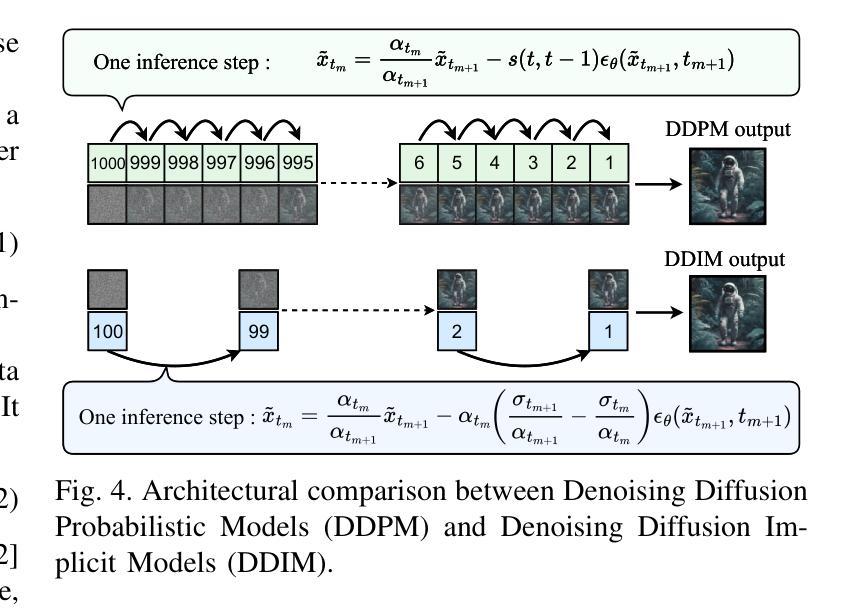
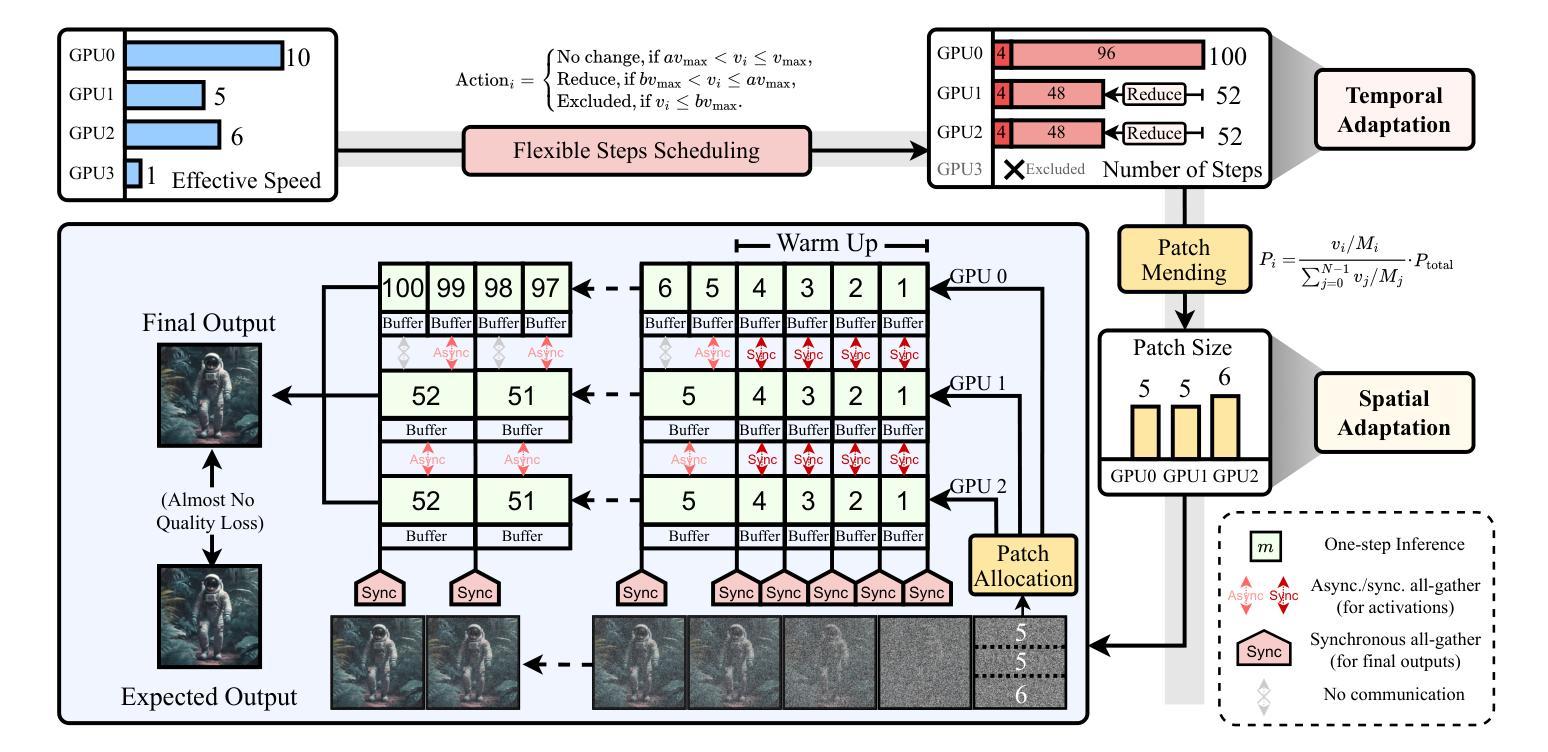
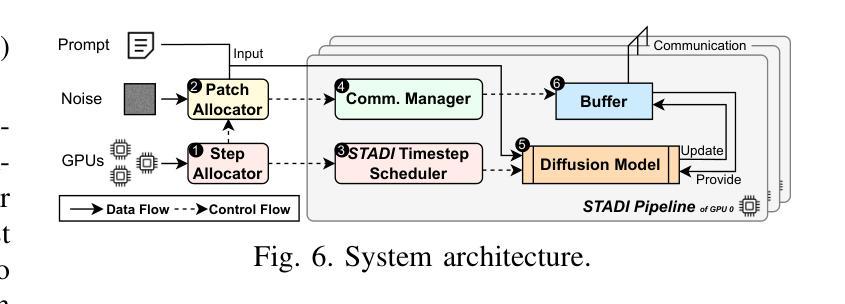
STADI: Fine-Grained Step-Patch Diffusion Parallelism for Heterogeneous GPUs
Authors:Han Liang, Jiahui Zhou, Zicheng Zhou, Xiaoxi Zhang, Xu Chen
The escalating adoption of diffusion models for applications such as image generation demands efficient parallel inference techniques to manage their substantial computational cost. However, existing diffusion parallelism inference schemes often underutilize resources in heterogeneous multi-GPU environments, where varying hardware capabilities or background tasks cause workload imbalance. This paper introduces Spatio-Temporal Adaptive Diffusion Inference (STADI), a novel framework to accelerate diffusion model inference in such settings. At its core is a hybrid scheduler that orchestrates fine-grained parallelism across both temporal and spatial dimensions. Temporally, STADI introduces a novel computation-aware step allocator applied after warmup phases, using a least-common-multiple-minimizing quantization technique to reduce denoising steps on slower GPUs and execution synchronization. To further minimize GPU idle periods, STADI executes an elastic patch parallelism mechanism that allocates variably sized image patches to GPUs according to their computational capability, ensuring balanced workload distribution through a complementary spatial mechanism. Extensive experiments on both load-imbalanced and heterogeneous multi-GPU clusters validate STADI’s efficacy, demonstrating improved load balancing and mitigation of performance bottlenecks. Compared to patch parallelism, a state-of-the-art diffusion inference framework, our method significantly reduces end-to-end inference latency by up to 45% and significantly improves resource utilization on heterogeneous GPUs.
随着扩散模型在图像生成等应用中的不断采用,需要高效的并行推理技术来管理其巨大的计算成本。然而,现有的扩散并行推理方案在异构多GPU环境中往往不能充分利用资源,其中硬件能力的差异或后台任务会导致工作量不平衡。本文介绍了时空自适应扩散推理(STADI),这是一个加速此类环境中扩散模型推理的新型框架。其核心是一个混合调度器,该调度器在时间和空间维度上协调精细粒度的并行性。在时间上,STADI在预热阶段后引入了一种新型的计算感知步骤分配器,使用最小公倍数最小化量化技术来减少较慢GPU上的降噪步骤和执行同步。为了进一步减少GPU空闲时间,STADI执行弹性补丁并行机制,根据GPU的计算能力分配不同大小的图像补丁,通过互补的空间机制确保工作量平衡分布。在负载不平衡和异构多GPU集群上的广泛实验验证了STADI的有效性,显示出改进了负载均衡并缓解了性能瓶颈。与补丁并行性相比,这是一种先进的扩散推理框架,我们的方法显著减少了端到端推理延迟,最多可达45%,并显著提高了异构GPU上的资源利用率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像生成等领域的应用日益广泛,但其计算成本高昂,需要高效的并行推理技术来应对。然而,现有的扩散并行推理方案在异构多GPU环境中未能充分利用资源,存在工作负载不平衡的问题。本文提出Spatio-Temporal Adaptive Diffusion Inference(STADI)框架,通过时空自适应调度加速扩散模型推理。该框架引入了一种计算感知的步骤分配器,使用最小公倍数最小化量化技术减少慢速GPU上的去噪步骤,并执行弹性补丁并行机制,根据GPU的计算能力分配不同大小的图像补丁,确保工作负载平衡。实验证明,STADI能有效改善负载平衡,缓解性能瓶颈,相比现有扩散推理框架,能显著降低端到端推理延迟并提高资源利用率。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成等领域应用广泛,但需要高效并行推理技术应对计算成本问题。
- 现有扩散并行推理方案在异构多GPU环境下存在资源利用不足和工作负载不平衡问题。
- STADI框架通过时空自适应调度加速扩散模型推理,引入计算感知的步骤分配器和弹性补丁并行机制。
- STADI能减少慢速GPU上的去噪步骤,并根据GPU计算能力分配图像补丁,确保工作负载平衡。
- 实验证明STADI能有效改善负载平衡,缓解性能瓶颈。
- 与现有扩散推理框架相比,STADI能显著降低端到端推理延迟。
点此查看论文截图


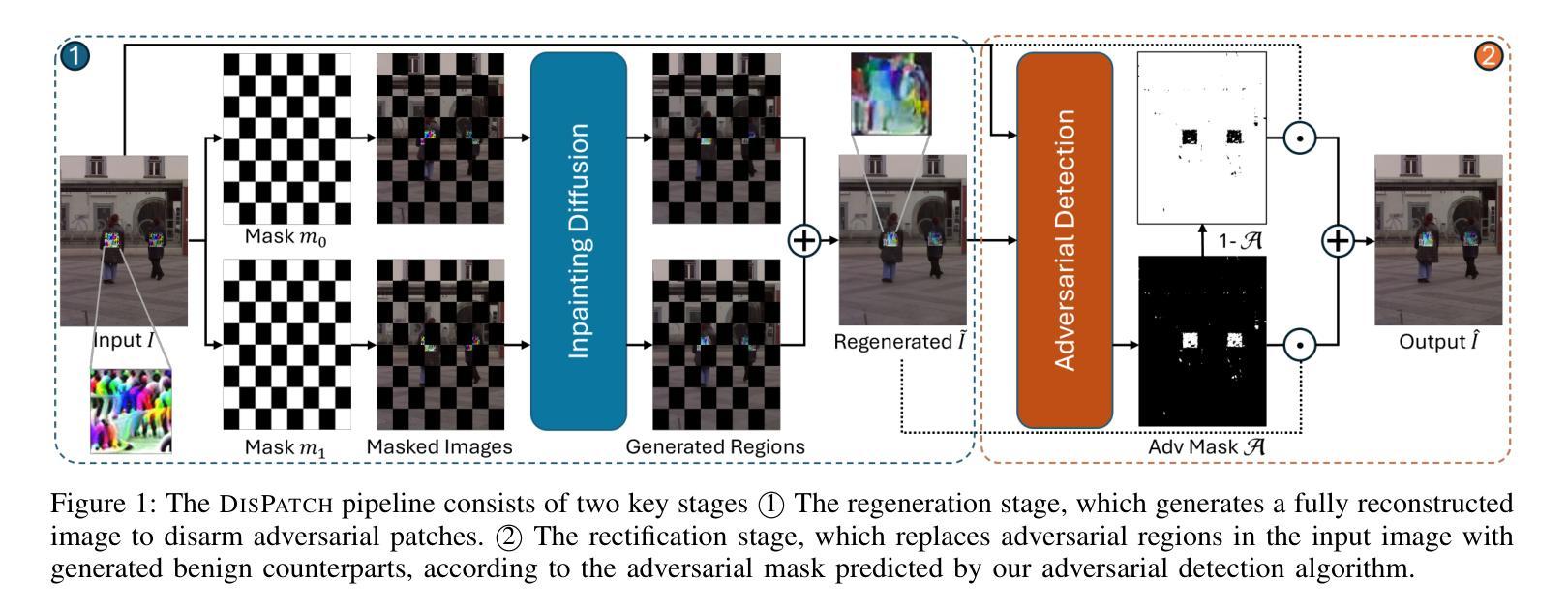
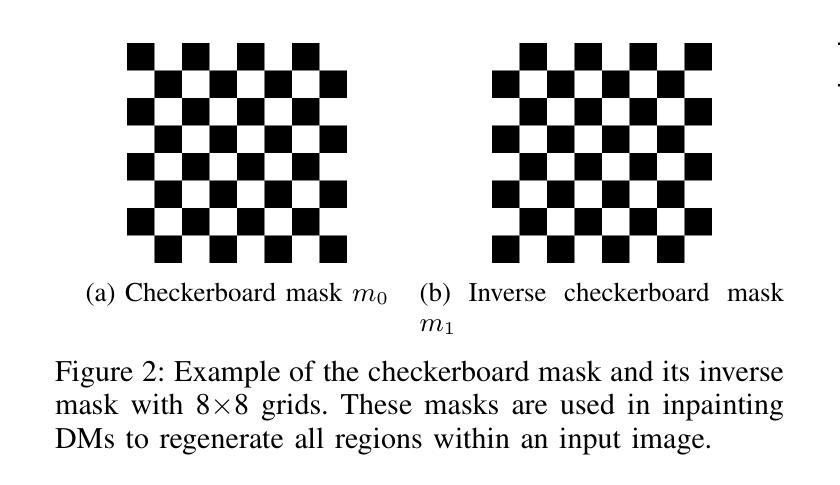
DisPatch: Disarming Adversarial Patches in Object Detection with Diffusion Models
Authors:Jin Ma, Mohammed Aldeen, Christopher Salas, Feng Luo, Mashrur Chowdhury, Mert Pesé, Long Cheng
Object detection is fundamental to various real-world applications, such as security monitoring and surveillance video analysis. Despite their advancements, state-of-theart object detectors are still vulnerable to adversarial patch attacks, which can be easily applied to real-world objects to either conceal actual items or create non-existent ones, leading to severe consequences. Given the current diversity of adversarial patch attacks and potential unknown threats, an ideal defense method should be effective, generalizable, and robust against adaptive attacks. In this work, we introduce DISPATCH, the first diffusion-based defense framework for object detection. Unlike previous works that aim to “detect and remove” adversarial patches, DISPATCH adopts a “regenerate and rectify” strategy, leveraging generative models to disarm attack effects while preserving the integrity of the input image. Specifically, we utilize the in-distribution generative power of diffusion models to regenerate the entire image, aligning it with benign data. A rectification process is then employed to identify and replace adversarial regions with their regenerated benign counterparts. DISPATCH is attack-agnostic and requires no prior knowledge of the existing patches. Extensive experiments across multiple detectors and attacks demonstrate that DISPATCH consistently outperforms state-of-the-art defenses on both hiding attacks and creating attacks, achieving the best overall mAP.5 score of 89.3% on hiding attacks, and lowering the attack success rate to 24.8% on untargeted creating attacks. Moreover, it maintains strong robustness against adaptive attacks, making it a practical and reliable defense for object detection systems.
对象检测在各类现实应用场景(如安全监控和监控视频分析)中具有重要作用。尽管已有诸多进展,当前顶尖的对象检测器仍然容易受到对抗补丁攻击的影响,这些攻击可以轻易应用于现实对象,用于隐藏实际物品或制造不存在的物品,从而造成严重后果。考虑到当前对抗补丁攻击的多样性和潜在未知威胁,理想的防御方法应该是有效、通用和对抗适应性攻击保持稳健。在这项工作中,我们引入了基于扩散的首个对象检测防御框架——DISPATCH。不同于以往旨在“检测和移除”对抗补丁的方法,DISPATCH采用“再生和纠正”策略,利用生成模型消除攻击效果,同时保持输入图像的完整性。具体来说,我们利用扩散模型的内部分布生成能力,对整个图像进行再生,使其与良性数据对齐。然后采用纠正过程来识别和替换对抗区域,用其再生的良性对应物进行替换。DISPATCH对攻击持中立态度,无需事先了解现有补丁情况。在多个检测器和攻击上的广泛实验表明,无论是在隐藏攻击还是创建攻击方面,DISPATCH都始终优于最先进的防御手段,在隐藏攻击方面取得了最高的mAP分数(89.3%),并将无目标创建攻击的成功率降低到24.8%。此外,它在对抗性攻击面前保持了强大的稳健性,成为对象检测系统实用可靠的防御手段。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了针对对象检测的新防御框架——DISPATCH。该框架采用基于扩散的策略,旨在抵御对抗性补丁攻击,同时保持输入图像的完整性。不同于以往的“检测和移除”策略,DISPATCH采用“再生和纠正”策略,利用生成模型削弱攻击效果。通过利用扩散模型的内部分布生成能力来再生整个图像,使其与良性数据对齐。随后采用纠正过程识别并替换对抗性区域,以良性区域进行替代。DISATCH对各种攻击具有无差别应对的能力,无需预先了解现有的补丁信息。实验表明,与现有的防御方法相比,DISPATCH在隐藏攻击和创建攻击方面表现更优秀,隐藏攻击的mAP得分达到最高89.3%,无目标创建攻击的成功率降低到24.8%,并在自适应攻击面前保持强大的稳健性,成为对象检测系统实用可靠的防御手段。
关键见解
- 对象检测在现实世界应用中的重要性,特别是在安全监控和监控视频分析中。
- 尽管取得了进展,最先进的对象检测器仍然容易受到对抗性补丁攻击的影响。这些攻击可能导致实际物品被隐藏或创建不存在的物品,带来严重后果。
- 当前缺乏一种有效、通用且能抵御自适应攻击的防御方法。
- DISPATCH是首个针对对象检测的基于扩散的防御框架。它采用“再生和纠正”策略来削弱攻击效果并保持图像完整性。
- DISPATCH利用扩散模型的内部分布生成能力来再生整个图像,使其与良性数据对齐。
- 实验证明,DISPATCH在隐藏攻击和创建攻击方面表现优异,隐藏攻击的mAP得分达到最高89.3%,无目标创建攻击的成功率降低到24.8%。
点此查看论文截图


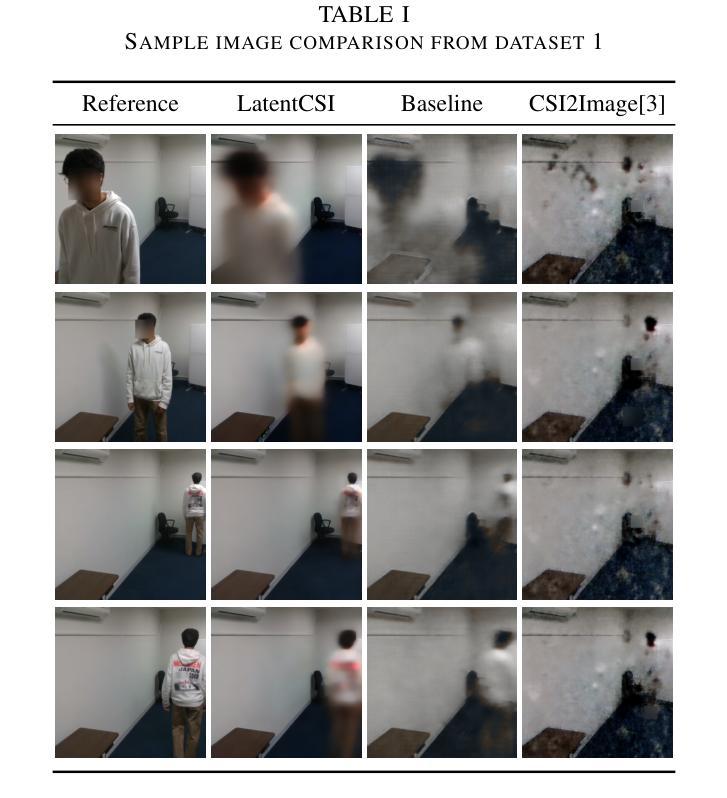
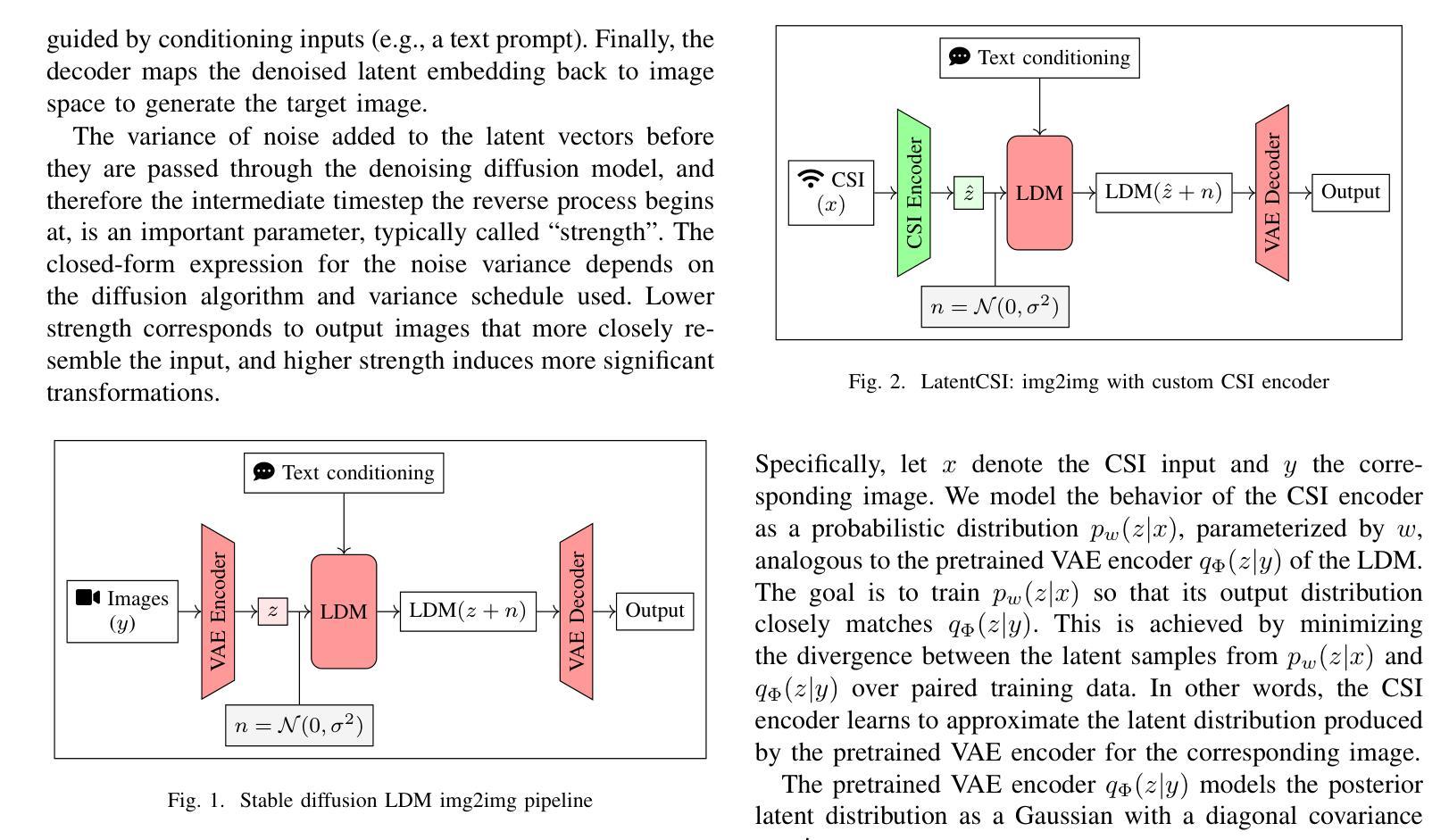
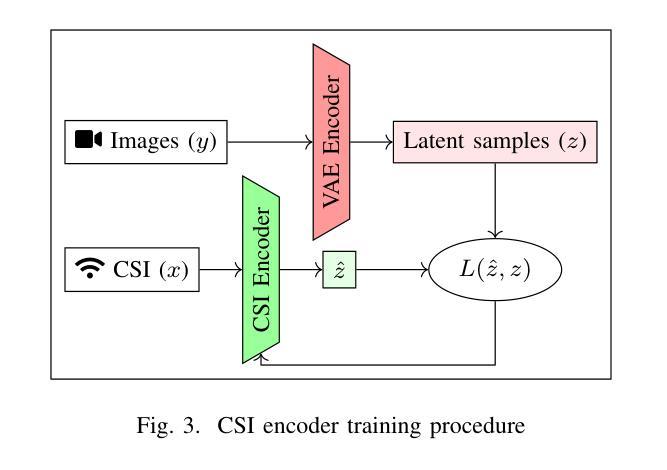
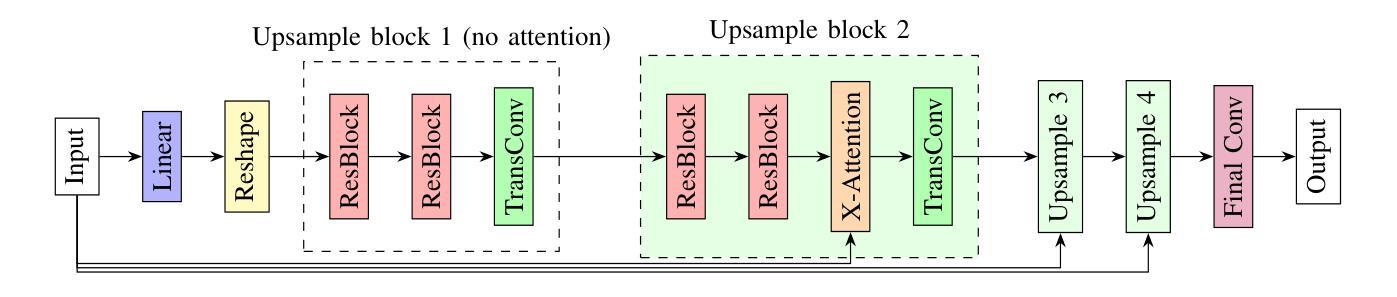
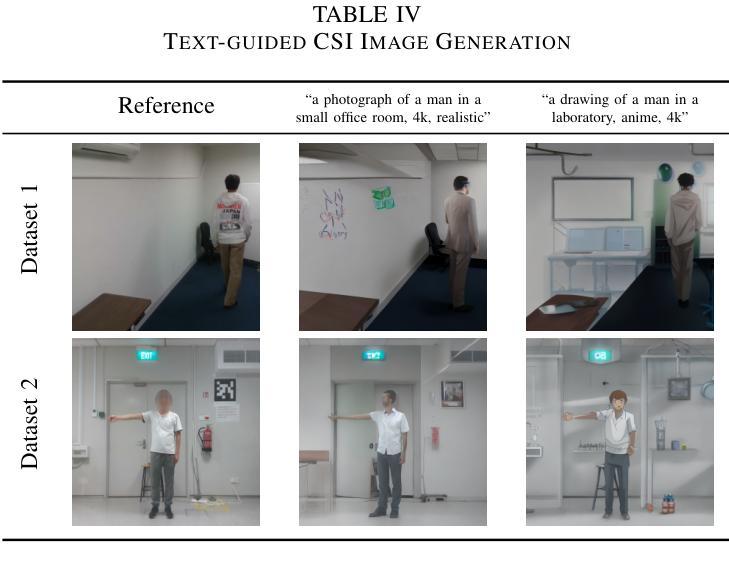
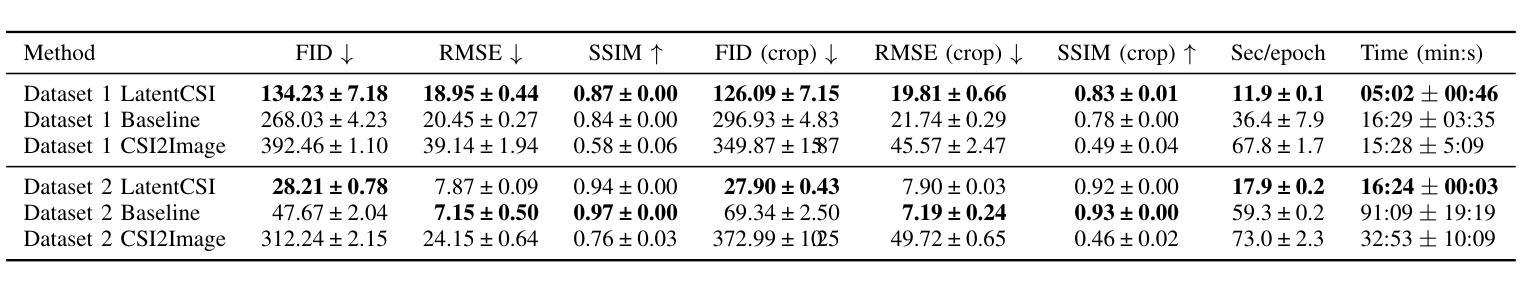
High-resolution efficient image generation from WiFi CSI using a pretrained latent diffusion model
Authors:Eshan Ramesh, Takayuki Nishio
We present LatentCSI, a novel method for generating images of the physical environment from WiFi CSI measurements that leverages a pretrained latent diffusion model (LDM). Unlike prior approaches that rely on complex and computationally intensive techniques such as GANs, our method employs a lightweight neural network to map CSI amplitudes directly into the latent space of an LDM. We then apply the LDM’s denoising diffusion model to the latent representation with text-based guidance before decoding using the LDM’s pretrained decoder to obtain a high-resolution image. This design bypasses the challenges of pixel-space image generation and avoids the explicit image encoding stage typically required in conventional image-to-image pipelines, enabling efficient and high-quality image synthesis. We validate our approach on two datasets: a wide-band CSI dataset we collected with off-the-shelf WiFi devices and cameras; and a subset of the publicly available MM-Fi dataset. The results demonstrate that LatentCSI outperforms baselines of comparable complexity trained directly on ground-truth images in both computational efficiency and perceptual quality, while additionally providing practical advantages through its unique capacity for text-guided controllability.
我们提出了LatentCSI,这是一种利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)从WiFi CSI测量生成物理环境图像的新型方法。不同于依赖复杂且计算密集的技术(如GANs)的先前方法,我们的方法采用轻量级神经网络直接将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间。然后,我们对潜在表示应用LDM的去噪扩散模型,并使用文本指导,然后使用LDM的预训练解码器进行解码,以获得高分辨率图像。这种设计绕过了像素空间图像生成的挑战,避免了传统图像到图像管道通常需要显式图像编码阶段,从而实现高效且高质量的图像合成。我们在两个数据集上验证了我们的方法:我们使用现成的WiFi设备和相机收集的宽带CSI数据集以及公共可用的MM-Fi数据集的子集。结果表明,LatentCSI在计算效率和感知质量方面都优于直接在真实图像上训练的相似复杂度的基线,同时还可以通过其独特的文本指导可控性提供实际优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures
Summary
LatentCSI是一种基于WiFi CSI测量生成物理环境图像的新方法,它利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)。不同于依赖复杂且计算密集的技术(如GANs)的先前方法,我们的方法采用轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅直接映射到LDM的潜在空间。然后,我们对潜在表示应用LDM的去噪扩散模型,并使用文本指导,最后使用LDM的预训练解码器进行解码以获得高分辨率图像。这种方法克服了像素空间图像生成的挑战,避免了传统图像到图像管道中通常需要的显式图像编码阶段,实现了高效的高质量图像合成。
Key Takeaways
- LatentCSI利用WiFi CSI测量生成物理环境图像。
- 该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM)。
- 通过轻量级神经网络将CSI振幅映射到LDM的潜在空间。
- 应用LDM的去噪扩散模型于潜在表示。
- 使用文本指导生成图像。
- 方法绕过像素空间图像生成的挑战,实现高效高质量图像合成。
点此查看论文截图