⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-09 更新
A Meta-Fusion Architecture for Few-Shot Classification of Spike Waveforms in High-Bandwidth Brain-Machine Interfacing
Authors:Tao Fang, Majid Zamani
There is a need for fast adaptation in spike sorting algorithms to implement brain-machine interface (BMIs) in different applications. Learning and adapting the functionality of the sorting process in real-time can significantly improve the performance. However, deep neural networks (DNNs) depend on large amounts of data for training models and their performance sustainability decreases when data is limited. Inspired by meta-learning, this paper proposes a few-shot spike sorting (FS-SS) framework with variable network model size that requires minimal learning training and supervision. The framework is not only compatible with few-shot adaptations, but also it uses attention mechanism and dilated convolutional neural networks. This allows scaling the network parameters to learn the important features of spike signals and to quickly generalize the learning ability to new spike waveforms in recording channels after few observations. The FS-SS was evaluated by using freely accessible datasets, also compared with the other state-of-the-art algorithms. The average classification accuracy of the proposed method is 99.28%, which shows extreme robustness to background noise and similarity of the spike waveforms. When the number of training samples is reduced by 90%, the parameter scale is reduced by 68.2%, while the accuracy only decreased by 0.55%. The paper also visualizes the model’s attention distribution under spike sorting tasks of different difficulty levels. The attention distribution results show that the proposed model has clear interpretability and high robustness.
在脑机接口(BMIs)的不同应用中,对排序算法中的快速适应有需求。实时学习和适应排序过程的功能可以显著提高性能。然而,深度神经网络(DNNs)依赖于大量的数据来训练模型,在数据量有限的情况下其性能可持续性会降低。本文受元学习的启发,提出了一种具有可变网络模型大小的少量样本排序(FS-SS)框架,该框架只需要最少的学习训练和监管。该框架不仅适用于小样例的适应,而且它还使用了注意力机制和膨胀卷积神经网络。这使得网络参数可以扩展到学习神经脉冲信号的重要特征,并在经过几次观察后迅速推广到新的脉冲波形中的记录通道的学习能力。使用可自由访问的数据集对FS-SS进行了评估,并将其与其他最先进的算法进行了比较。所提出方法的平均分类准确度为99.28%,显示出对背景噪声和脉冲波形的相似性的极高稳健性。当训练样本数量减少90%时,参数规模减少了68.2%,而准确率仅下降了0.55%。本文还可视化模型在不同难度水平的脉冲排序任务下的注意力分布结果。注意力分布结果表明所提出模型具有清晰的解释性和高鲁棒性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
针对脑机接口中不同应用的快速适应需求,需对棘波排序算法进行改进。本文提出一种基于元学习的小样本棘波排序框架,具有可变网络模型大小,需要最小的学习训练和监管。该框架不仅兼容小样本适应,还使用注意力机制和膨胀卷积神经网络,可快速泛化新棘波波形的学习能力。实验证明其分类准确率极高,对背景噪声和波形相似性具有极强的稳健性。当训练样本数量减少时,其参数规模和准确率下降幅度较小。同时,该模型在不同难度的棘波排序任务下表现出清晰的解释性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 棘波排序算法需要快速适应不同的脑机接口应用以提高性能。
- 本文提出的框架利用小样本棘波排序技术适应了这一需求,实现最小化学习训练和监管的要求。
- 通过使用注意力机制和膨胀卷积神经网络,该框架能够快速泛化新棘波波形的学习能力。
- 实验结果表明该框架的分类准确率极高,且对背景噪声和波形相似性具有很强的稳健性。
- 当训练样本数量减少时,该框架表现出优秀的灵活性和稳定性。即使减少了90%的训练样本,其参数规模仅减少了约三分之一,同时准确率仅下降了不到半个百分点。
- 该模型的可视化展示显示出其在不同难度的棘波排序任务下的解释性和稳健性。这种展示进一步增强了人们对模型的认知和信任。
点此查看论文截图

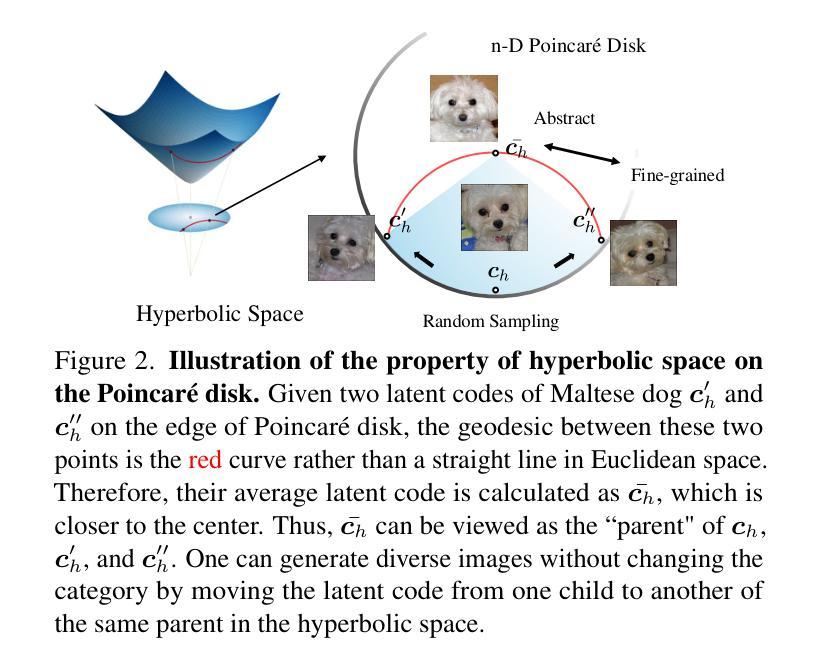
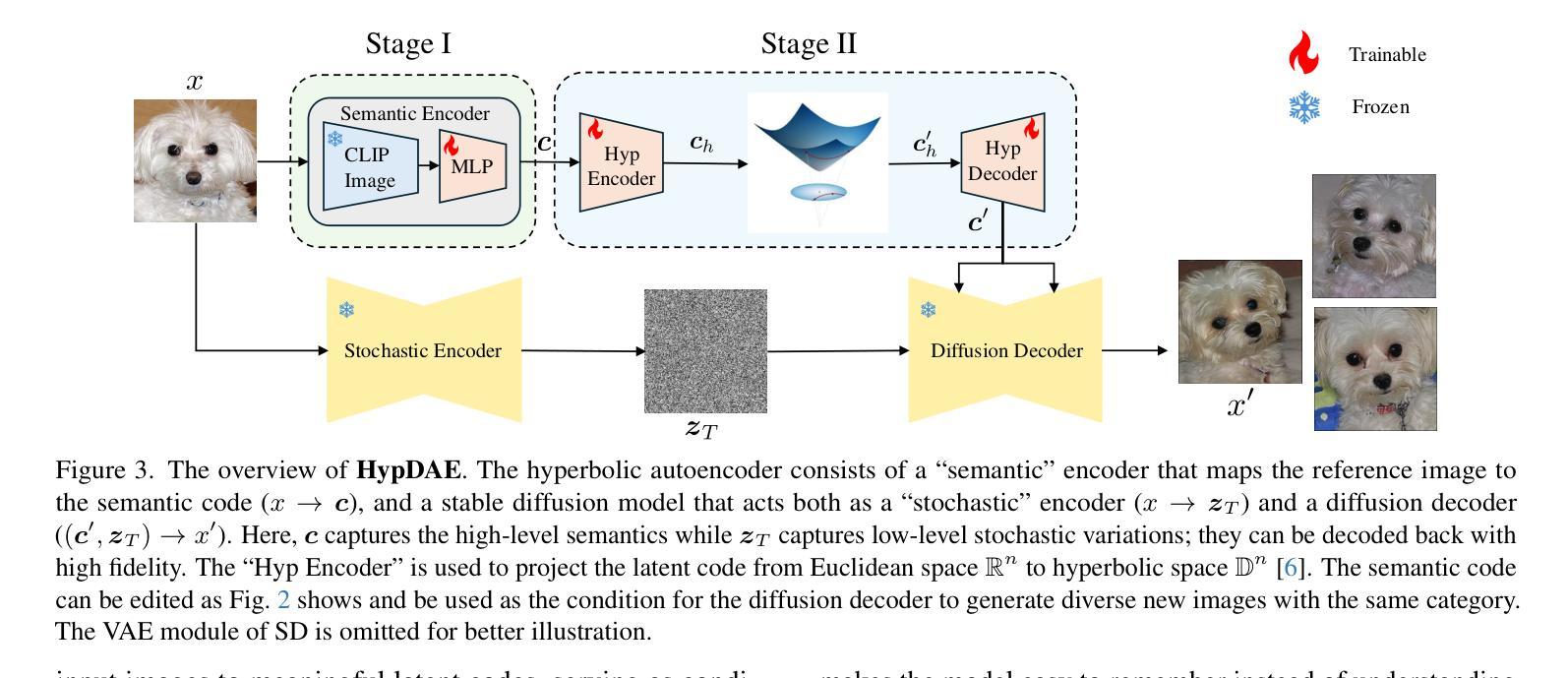
HypDAE: Hyperbolic Diffusion Autoencoders for Hierarchical Few-shot Image Generation
Authors:Lingxiao Li, Kaixuan Fan, Boqing Gong, Xiangyu Yue
Few-shot image generation aims to generate diverse and high-quality images for an unseen class given only a few examples in that class. A key challenge in this task is balancing category consistency and image diversity, which often compete with each other. Moreover, existing methods offer limited control over the attributes of newly generated images. In this work, we propose Hyperbolic Diffusion Autoencoders (HypDAE), a novel approach that operates in hyperbolic space to capture hierarchical relationships among images from seen categories. By leveraging pre-trained foundation models, HypDAE generates diverse new images for unseen categories with exceptional quality by varying stochastic subcodes or semantic codes. Most importantly, the hyperbolic representation introduces an additional degree of control over semantic diversity through the adjustment of radii within the hyperbolic disk. Extensive experiments and visualizations demonstrate that HypDAE significantly outperforms prior methods by achieving a better balance between preserving category-relevant features and promoting image diversity with limited data. Furthermore, HypDAE offers a highly controllable and interpretable generation process.
少样本图像生成旨在针对某一未见类别仅通过少量样本生成多样化和高质量图像。该任务的关键挑战在于平衡类别一致性和图像多样性,这两者通常相互竞争。此外,现有方法对新生成图像的属性控制有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了Hyperbolic Diffusion Autoencoders(HypDAE),这是一种新型方法,在双曲空间中操作以捕获已见类别图像之间的层次关系。通过利用预训练的基模型,HypDAE通过改变随机子代码或语义代码生成具有卓越质量的新类别多样图像。最重要的是,双曲表示通过调整双曲圆盘内的半径,在语义多样性上提供了额外的控制程度。大量实验和可视化结果表明,HypDAE通过在保留类别相关特征和促进图像多样性之间取得更好的平衡,显著优于先前的方法,并且在有限数据下表现优异。此外,HypDAE提供了高度可控和可解释的生成过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025, Code is available at: https://github.com/lingxiao-li/HypDAE
Summary
本文介绍了基于Hyperbolic Diffusion Autoencoders(HypDAE)的少量图像生成技术。该技术通过操作超球面空间来捕捉已见类别图像间的层次关系,为未见类别生成多样且高质量的图像。HypDAE通过调整超球面盘内的半径来控制语义多样性,且能在少量数据下实现类别相关特征的保留和图像多样性的平衡。此外,HypDAE的生成过程高度可控且可解释性强。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot image generation旨在针对未见类别仅通过少量样本生成多样且高质量的图像。
- 平衡类别一致性和图像多样性是该任务的关键挑战。
- 现有方法对新生成图像的属性控制有限。
- Hyperbolic Diffusion Autoencoders (HypDAE) 在超球面空间内操作,以捕捉已见类别图像间的层次关系。
- 通过使用预训练的基准模型,HypDAE能够通过改变随机子码或语义码生成多样且质量上乘的新图像。
- 超球面表示法提供了通过调整盘内半径来控制语义多样性的额外手段。
点此查看论文截图



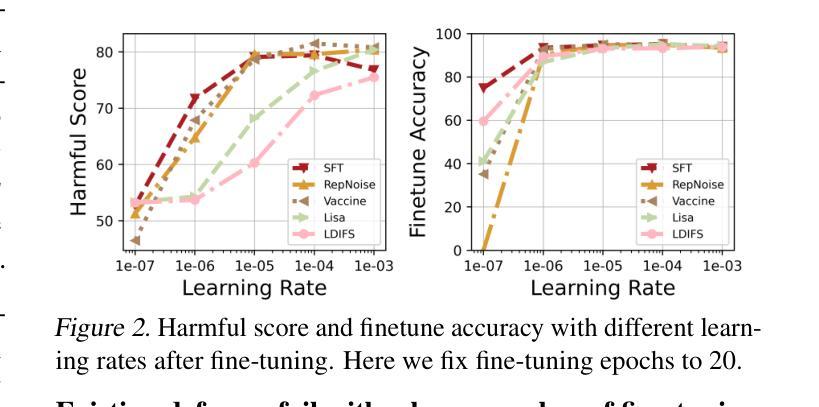
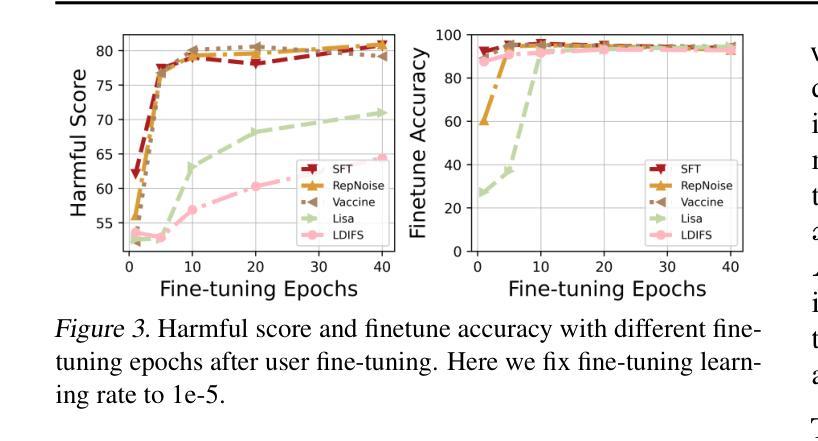
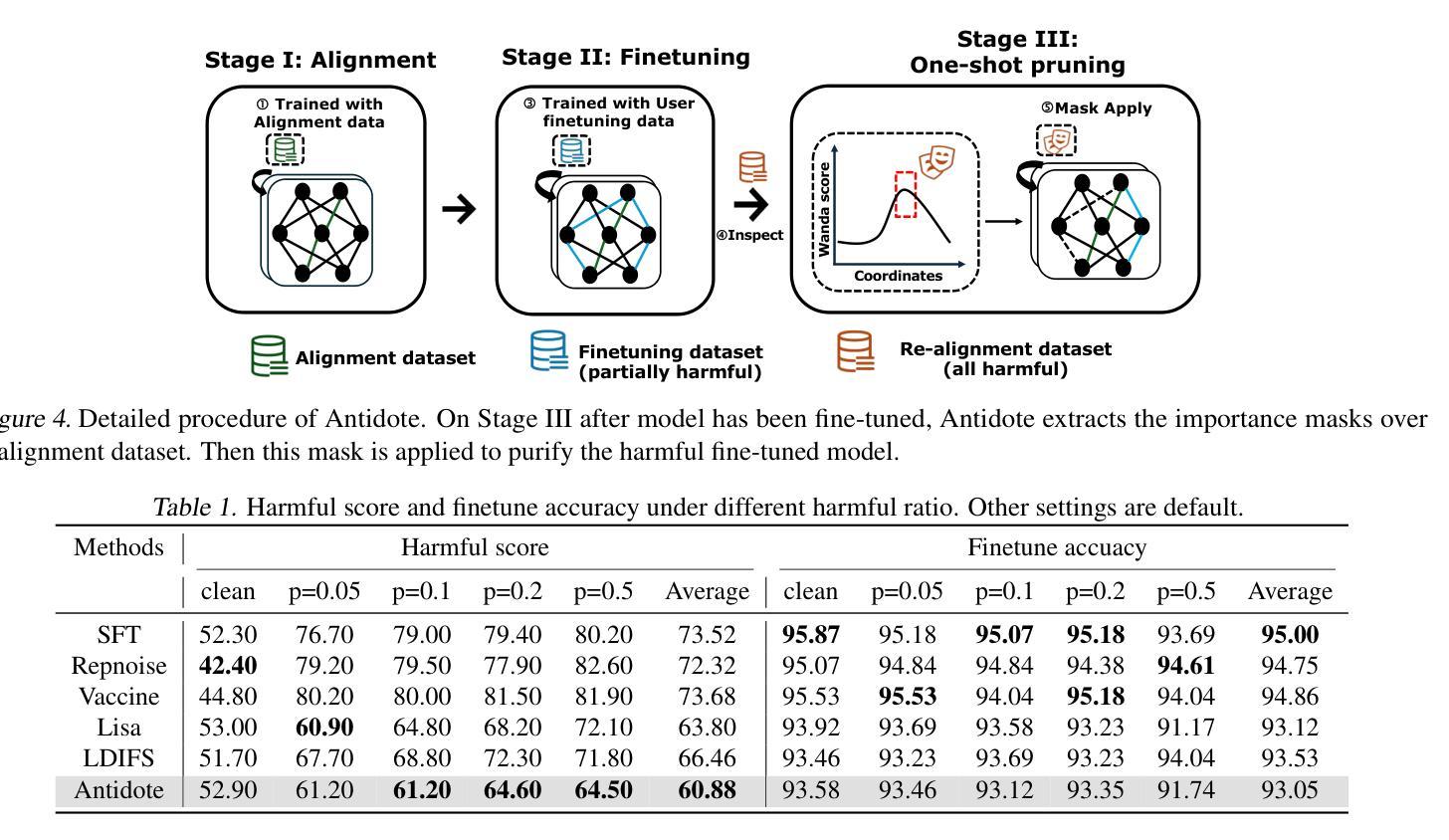
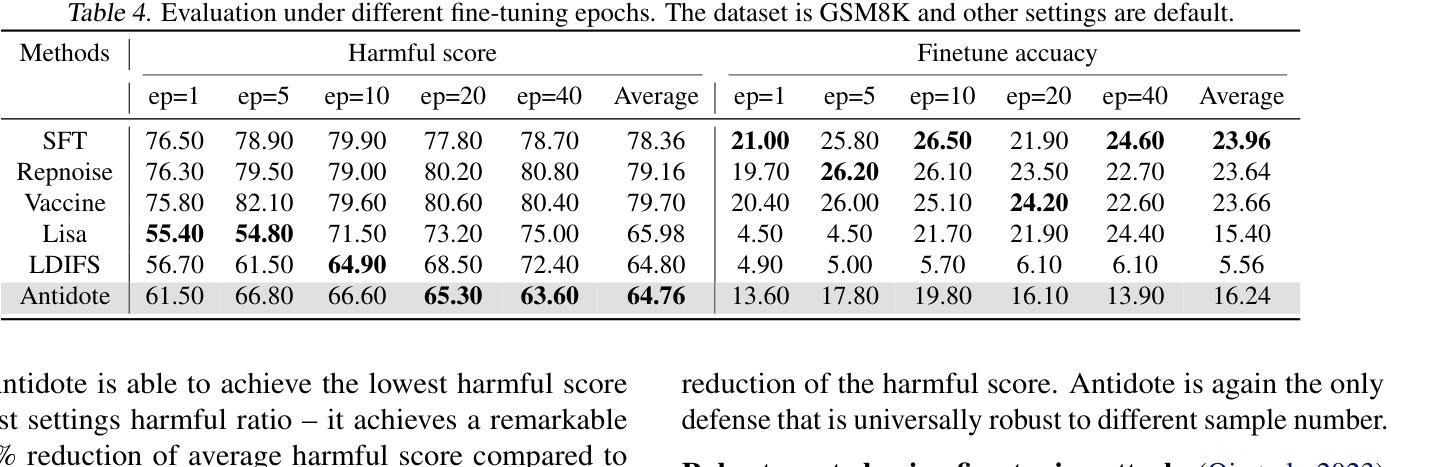
Antidote: Post-fine-tuning Safety Alignment for Large Language Models against Harmful Fine-tuning
Authors:Tiansheng Huang, Gautam Bhattacharya, Pratik Joshi, Josh Kimball, Ling Liu
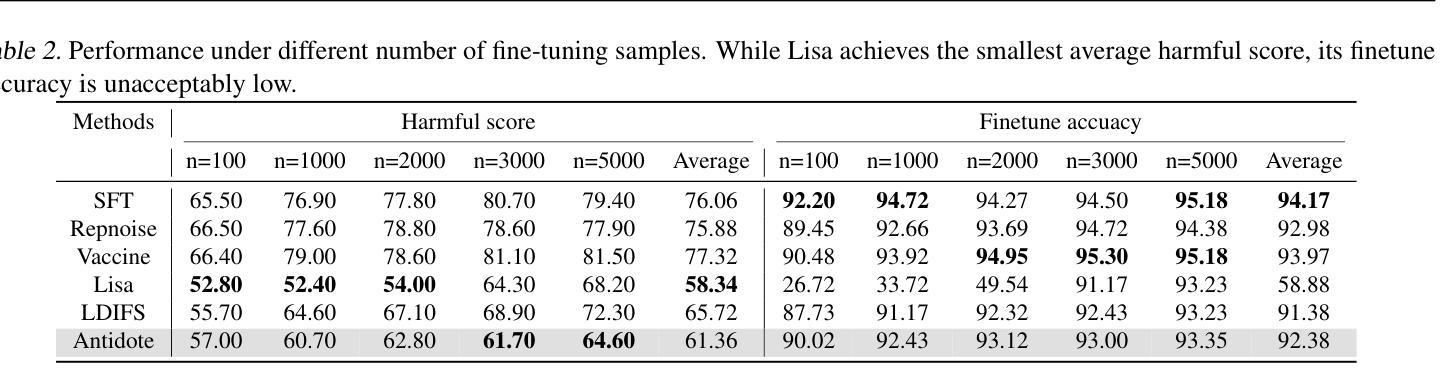
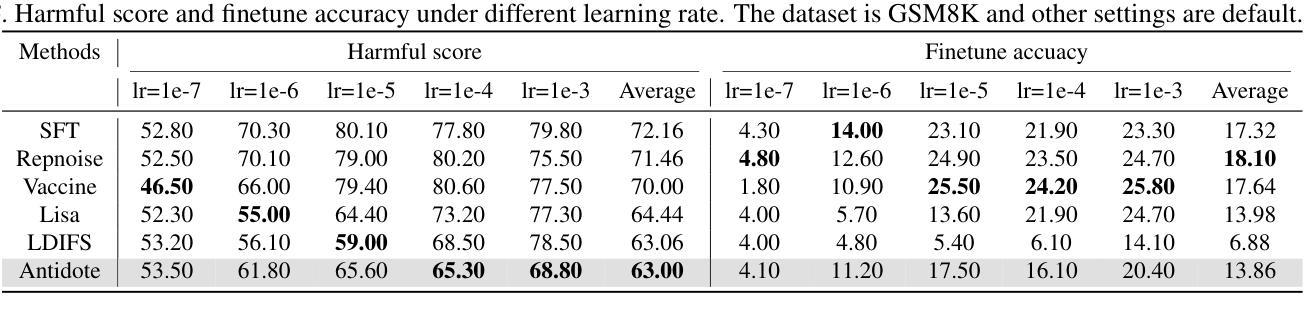
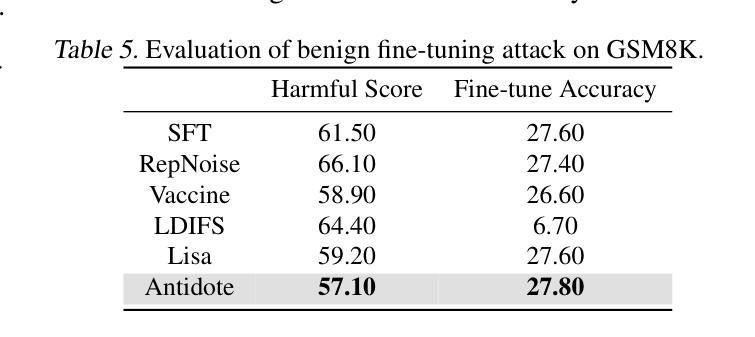
Safety aligned Large Language Models (LLMs) are vulnerable to harmful fine-tuning attacks – a few harmful data mixed in the fine-tuning dataset can break the LLMs’s safety alignment. While several defenses have been proposed, our evaluation shows that existing defenses fail \textit{when some specific training hyper-parameters are chosen} – a large learning rate or a large number of training epochs in the fine-tuning stage can easily invalidate the defense. To this end, we propose Antidote, a post-fine-tuning stage solution, which remains \textbf{\textit{agnostic to the training hyper-parameters in the fine-tuning stage}}. Antidote relies on the philosophy that by removing the harmful parameters, the harmful model can be recovered from the harmful behaviors, regardless of how those harmful parameters are formed in the fine-tuning stage. With this philosophy, we introduce a one-shot pruning stage after harmful fine-tuning to remove the harmful weights that are responsible for the generation of harmful content. Despite its embarrassing simplicity, empirical results show that Antidote can reduce harmful score while maintaining accuracy on downstream tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/git-disl/Antidote.
与安全对齐的大型语言模型(LLMs)容易受到有害微调攻击的影响——微调数据集中混入的一些有害数据会破坏LLMs的安全对齐。虽然已提出多种防御措施,但我们的评估显示,当选择某些特定的训练超参数时,现有防御措施会失效——微调阶段中较大的学习率或较多的训练周期很容易使防御失效。为此,我们提出了Antidote,这是一种后微调阶段解决方案,对微调阶段的训练超参数保持中立。Antidote的理念是通过移除有害参数,可以从有害行为中恢复有害模型,无论这些有害参数在微调阶段是如何形成的。基于这一理念,我们在有害微调之后引入了一次性修剪阶段,以去除负责生成有害内容的权重。尽管其简单得令人尴尬,但经验结果表明,Antidote可以在保持下游任务准确性的同时减少有害得分。相关代码可在 https://github.com/git-disl/Antidote 中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Rejected by AAAI25-AIA. Accepted by ICML25. Authors are thankful to the anonymous reviewers from both AAAI25-AIA and ICML25
摘要
安全对齐的大型语言模型(LLM)容易受到有害微调攻击的影响——微调数据集中混入少量有害数据会破坏LLM的安全对齐。虽然已有多种防御手段,但我们的评估显示,当选择某些特定的训练超参数(如较大的学习率或较多的训练周期)时,现有防御手段会失效。为此,我们提出一种名为Antidote的后微调阶段解决方案,它对微调阶段的训练超参数保持不可知。Antidote的理念是通过移除有害参数,可以从有害行为中恢复有害模型,无论这些有害参数在微调阶段是如何形成的。基于此理念,我们在有害微调后引入一次性修剪阶段,移除负责生成有害内容的权重。尽管方法简单,但经验结果表明,Antidote在保持下游任务准确性的同时,可以减少有害得分。相关代码可在https://github.com/git-disl/Antidote获取。
关键见解
- 安全对齐的大型语言模型(LLMs)在微调阶段易受攻击,少数有害数据点可破坏其安全对齐。
- 现有防御手段在特定训练超参数(如学习率和训练周期)选择下会失效。
- Antidote是一种后微调阶段解决方案,对训练超参数保持不可知,可抵抗有害微调攻击。
- Antidote的理念是通过移除有害参数来恢复模型,无论这些参数如何形成。
- Antidote通过一次性修剪阶段移除产生有害内容的权重。
- 尽管方法简单,但Antidote能减少有害得分并保持下游任务的准确性。
- 相关研究代码已在指定GitHub仓库中公开。
点此查看论文截图