⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-09 更新
Sticker-TTS: Learn to Utilize Historical Experience with a Sticker-driven Test-Time Scaling Framework
Authors:Jie Chen, Jinhao Jiang, Yingqian Min, Zican Dong, Shijie Wang, Wayne Xin Zhao, Ji-Rong Wen
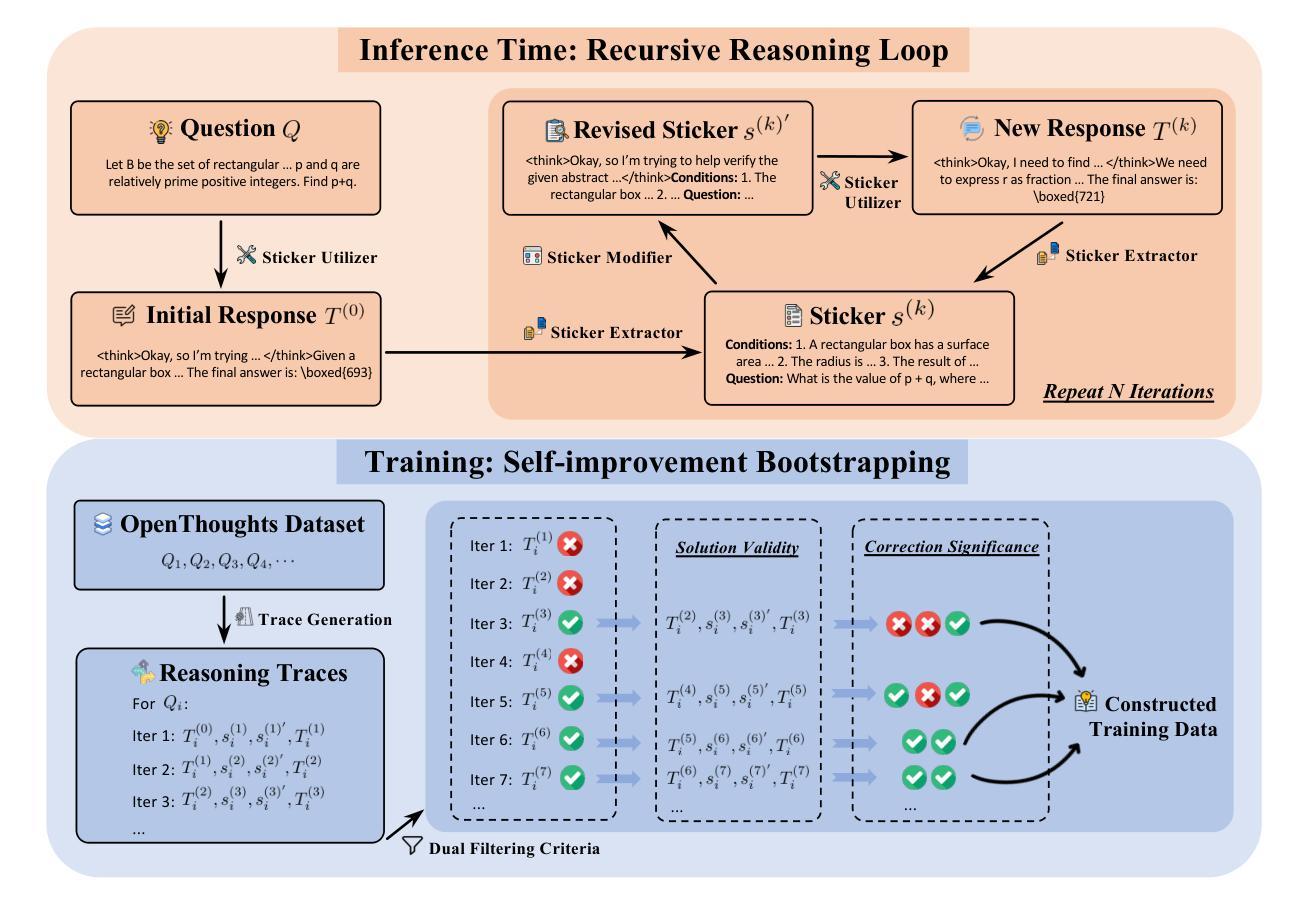
Large reasoning models (LRMs) have exhibited strong performance on complex reasoning tasks, with further gains achievable through increased computational budgets at inference. However, current test-time scaling methods predominantly rely on redundant sampling, ignoring the historical experience utilization, thereby limiting computational efficiency. To overcome this limitation, we propose Sticker-TTS, a novel test-time scaling framework that coordinates three collaborative LRMs to iteratively explore and refine solutions guided by historical attempts. At the core of our framework are distilled key conditions-termed stickers-which drive the extraction, refinement, and reuse of critical information across multiple rounds of reasoning. To further enhance the efficiency and performance of our framework, we introduce a two-stage optimization strategy that combines imitation learning with self-improvement, enabling progressive refinement. Extensive evaluations on three challenging mathematical reasoning benchmarks, including AIME-24, AIME-25, and OlymMATH, demonstrate that Sticker-TTS consistently surpasses strong baselines, including self-consistency and advanced reinforcement learning approaches, under comparable inference budgets. These results highlight the effectiveness of sticker-guided historical experience utilization. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Sticker-TTS.
大型推理模型(LRMs)在复杂的推理任务中表现出了强大的性能,通过增加推理时的计算预算,可以进一步获得收益。然而,当前的测试时间扩展方法主要依赖于冗余采样,忽略了历史经验的利用,从而限制了计算效率。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了Sticker-TTS,这是一种新型的测试时间扩展框架,它协调了三个协作式LRMs,以历史尝试为指导,迭代地探索和完善解决方案。我们的框架的核心是提炼出的关键条件——称为“贴纸”,它驱动了跨多轮推理的重要信息的提取、精炼和再利用。为了进一步提高我们框架的效率和性能,我们引入了一种两阶段优化策略,结合了模仿学习与自我改进,实现了逐步完善。在三个具有挑战性的数学推理基准测试上的广泛评估,包括AIME-24、AIME-25和奥林匹克数学,证明Sticker-TTS在可比较推理预算下,持续超越了强大的基线,包括自我一致性验证和先进的强化学习方法。这些结果突显了贴纸引导的历史经验利用的有效性。我们的代码和数据可在https://github.com/RUCAIBox/Sticker-TTS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 1 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文提出一种名为Sticker-TTS的新型测试时缩放框架,用于在复杂推理任务中提升大型推理模型(LRMs)的性能。该框架通过协调三个协同工作的LRMs,以历史尝试为指导,通过迭代探索和优化解决方案。其核心是提取、精炼和重用关键信息的贴纸,以提高效率和性能。在多个数学推理基准测试上的评估结果表明,Sticker-TTS在相似的推理预算下,始终优于包括自我一致性在内的先进强化学习等强基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- Sticker-TTS是一种新型测试时缩放框架,用于提升大型推理模型在复杂推理任务中的性能。
- 该框架通过协调三个协同工作的LRMs,利用历史尝试来指导迭代探索和优化解决方案。
- Sticker-TTS的核心是贴纸概念,用于提取、精炼和重用关键信息。
- 通过引入两阶段优化策略,结合了模仿学习与自我改进,实现了逐步优化。
- 在多个数学推理基准测试上的评估结果表明,Sticker-TTS性能优越。
- Sticker-TTS在相似的推理预算下,优于包括自我一致性在内的先进强化学习等强基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

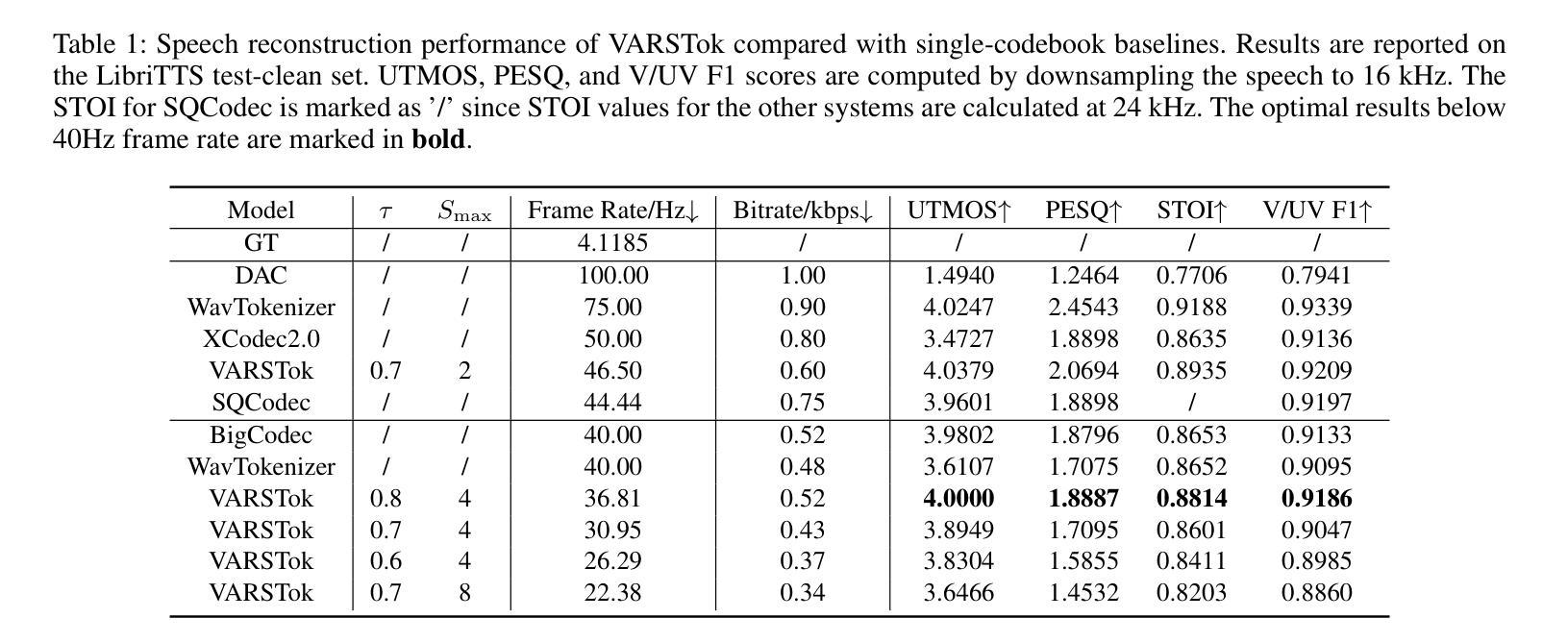
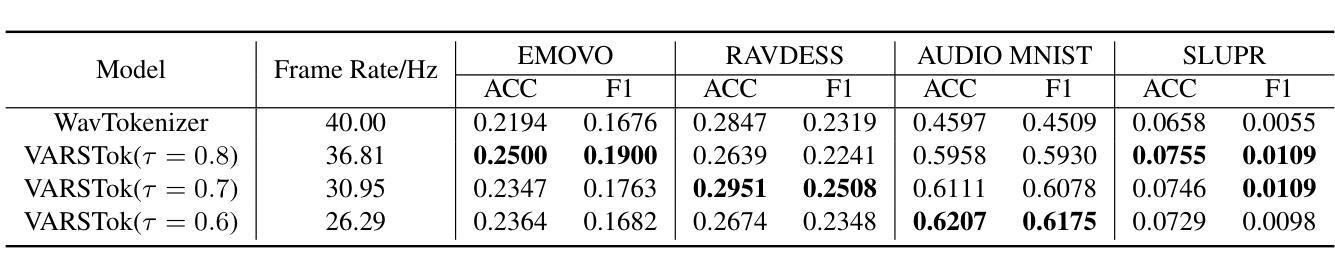
Say More with Less: Variable-Frame-Rate Speech Tokenization via Adaptive Clustering and Implicit Duration Coding
Authors:Rui-Chen Zheng, Wenrui Liu, Hui-Peng Du, Qinglin Zhang, Chong Deng, Qian Chen, Wen Wang, Yang Ai, Zhen-Hua Ling
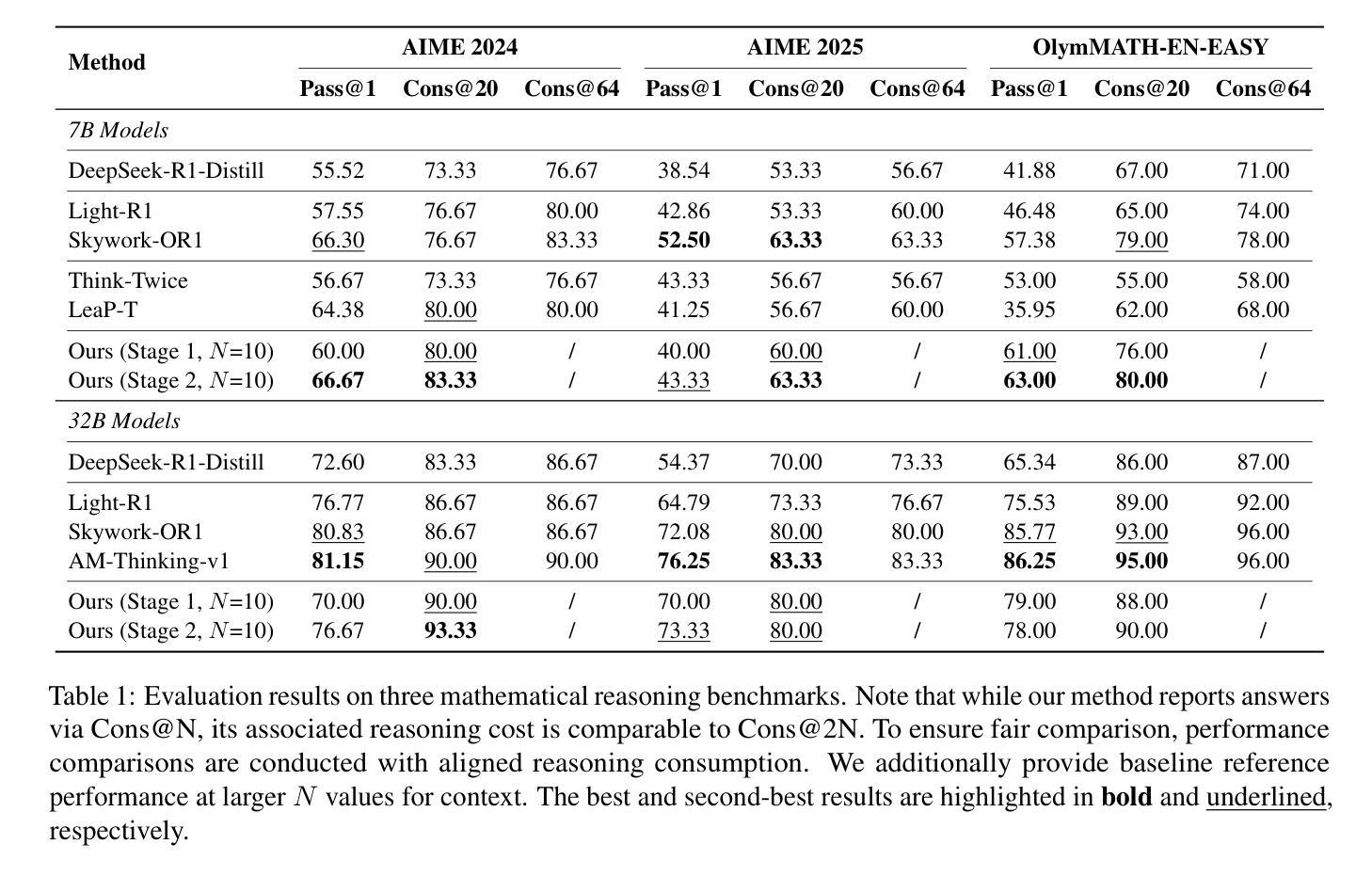
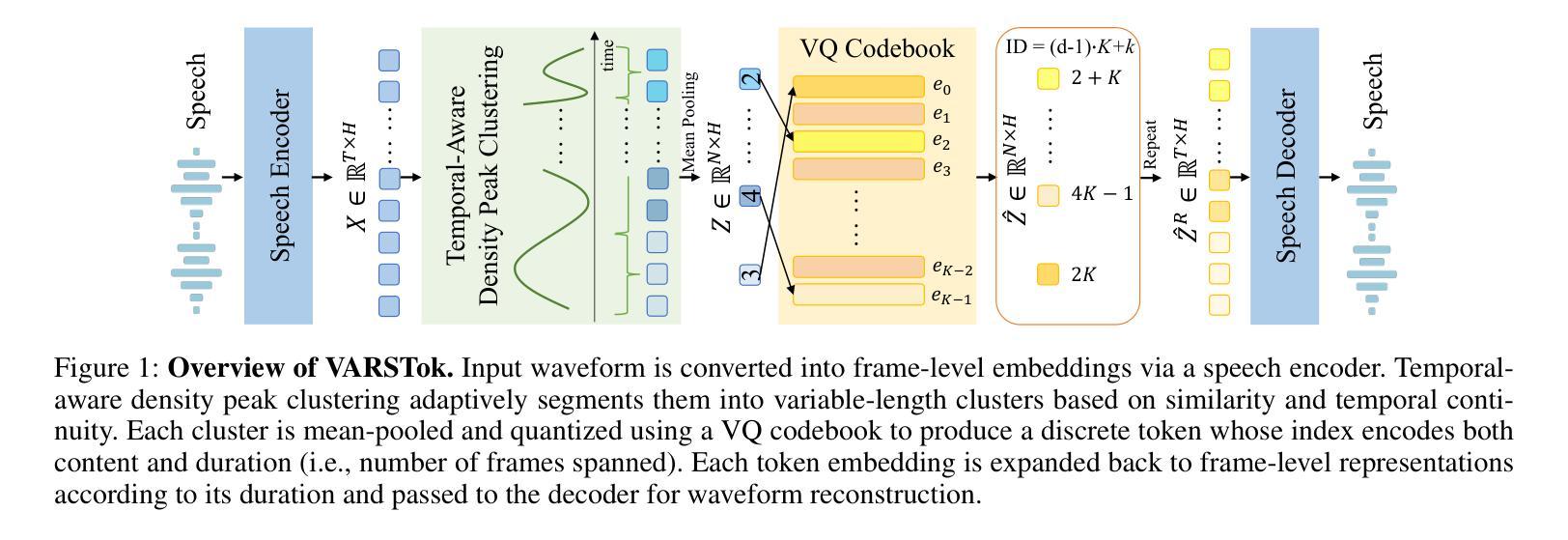
Existing speech tokenizers typically assign a fixed number of tokens per second, regardless of the varying information density or temporal fluctuations in the speech signal. This uniform token allocation mismatches the intrinsic structure of speech, where information is distributed unevenly over time. To address this, we propose VARSTok, a VAriable-frame-Rate Speech Tokenizer that adapts token allocation based on local feature similarity. VARSTok introduces two key innovations: (1) a temporal-aware density peak clustering algorithm that adaptively segments speech into variable-length units, and (2) a novel implicit duration coding scheme that embeds both content and temporal span into a single token index, eliminating the need for auxiliary duration predictors. Extensive experiments show that VARSTok significantly outperforms strong fixed-rate baselines. Notably, it achieves superior reconstruction naturalness while using up to 23% fewer tokens than a 40 Hz fixed-frame-rate baseline. VARSTok further yields lower word error rates and improved naturalness in zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to demonstrate that a fully dynamic, variable-frame-rate acoustic speech tokenizer can be seamlessly integrated into downstream speech language models. Speech samples are available at https://zhengrachel.github.io/VARSTok.
现有的语音分词器通常每秒分配固定数量的令牌,无论语音信号中信息密度或时间波动的变化如何。这种统一的令牌分配与语音的内在结构不匹配,语音中的信息在时间上分布不均。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了VARSTok,这是一种基于局部特征相似性的可变帧率语音分词器,它可以根据局部特征相似性来适应令牌分配。VARSTok引入了两个关键创新点:(1)一种时间感知密度峰值聚类算法,可以自适应地将语音分割成可变长度的单元;(2)一种新的隐式时长编码方案,将内容和时长嵌入单个令牌索引中,无需辅助时长预测器。大量实验表明,VARSTok显著优于强大的固定速率基线。值得注意的是,它在使用令牌方面比40Hz的固定帧率基线少达23%的情况下,实现了更优越的重建自然度。VARSTok还进一步降低了单词错误率,并在零样本文本到语音的合成中提高了自然度。据我们所知,这是第一项工作,展示了可以无缝集成到下游语音语言模型中的完全动态、可变帧率的声学语音分词器。语音样本可通过https://zhengrachel.github.io/VARSTok获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
语音信号中的信息分布是不均匀的,传统的固定帧率语音令牌化方法无法匹配这种结构。因此,我们提出了VARSTok——一种基于局部特征相似性的可变帧率语音令牌化方法。它通过引入基于自适应的分割方法和新型的隐性时长编码方案实现了较高的性能和优越性。这项技术是第一个将动态的可变帧率音频令牌无缝集成到下游语音识别模型中的研究。同时减少了令牌的使用量并提高零射速文本到语音合成的自然度。更多信息请访问我们的网站获取。
Key Takeaways
传统语音令牌化方法存在固定帧率的问题,导致语音信息分配的不匹配。这是因为语音信息的分布是随时间不均匀变化的。VARSTok针对这个问题引入了基于局部特征相似性的自适应令牌分配策略。这一创新有助于解决固定帧率的问题。这意味着每个令牌能够更有效地捕捉语音中的信息,从而提高了语音识别的准确性。
VARSTok提出了一个基于时间感知的密度峰值聚类算法。这种算法自适应地将语音分成不同长度的单位,并改善了语音的分割效果。这种算法的创新之处在于它能够根据语音信号的实时变化来动态调整令牌的分配,从而使得令牌化的过程更加贴近实际的语音信息分布。它不仅能够捕捉到每个词的边界,还可以准确地识别出不同句子的语速变化以及短暂的停顿。这在语音处理过程中是至关重要的一个环节,能够帮助语音识别模型更好地理解语言的实际表达方式和情感色彩。在理论上讲,它大大提高了模型的适应性和准确性。这也意味着在未来应用中可以实现更为精确的语音识别和自然度更高的语音合成效果。这项创新意味着我们能够更有效地处理各种音频文件中的数据和信息从而帮助改进语音交互和识别的效果并推动相关技术的发展和应用范围。
点此查看论文截图


WenetSpeech-Yue: A Large-scale Cantonese Speech Corpus with Multi-dimensional Annotation
Authors:Longhao Li, Zhao Guo, Hongjie Chen, Yuhang Dai, Ziyu Zhang, Hongfei Xue, Tianlun Zuo, Chengyou Wang, Shuiyuan Wang, Jie Li, Jian Kang, Xin Xu, Hui Bu, Binbin Zhang, Ruibin Yuan, Ziya Zhou, Wei Xue, Lei Xie
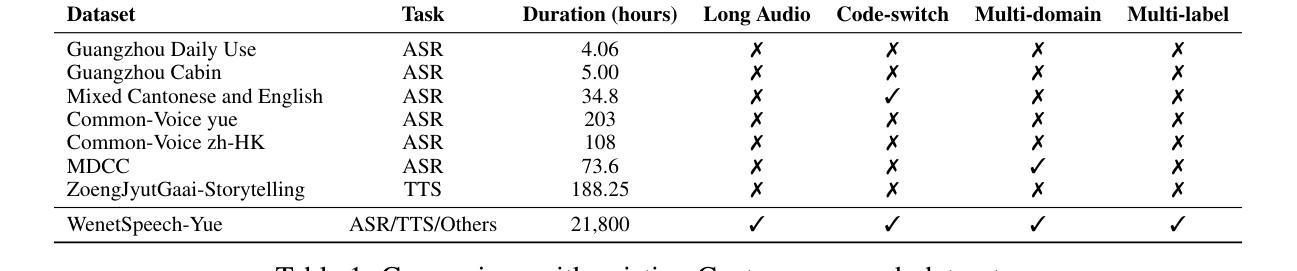
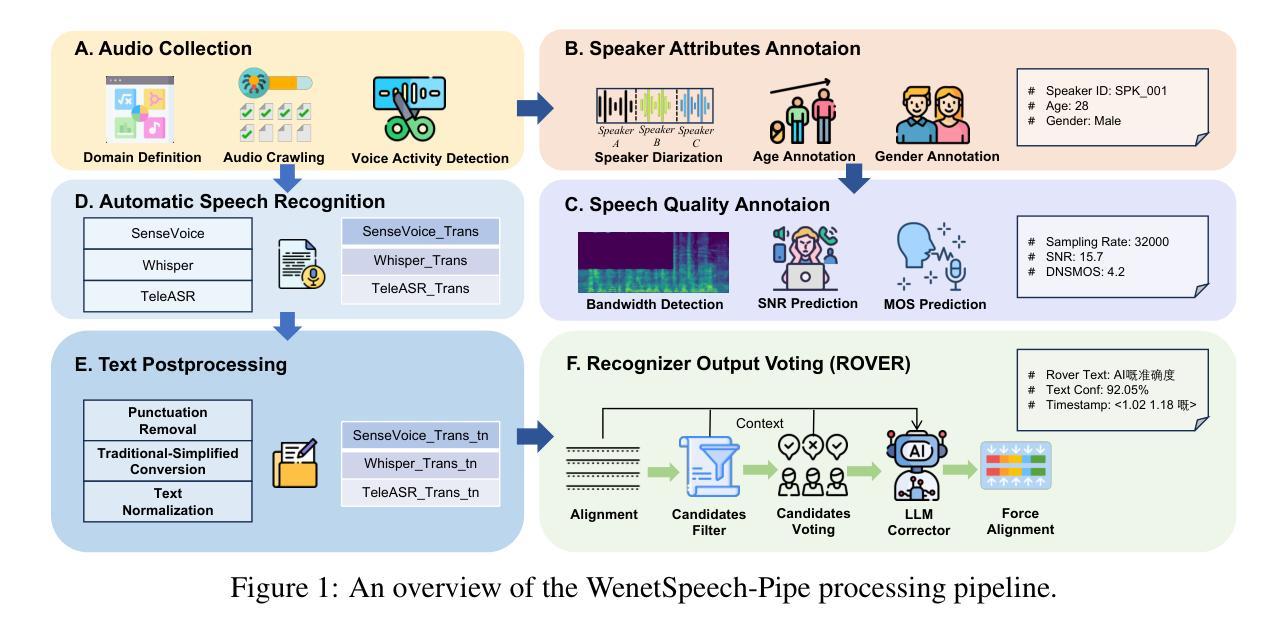
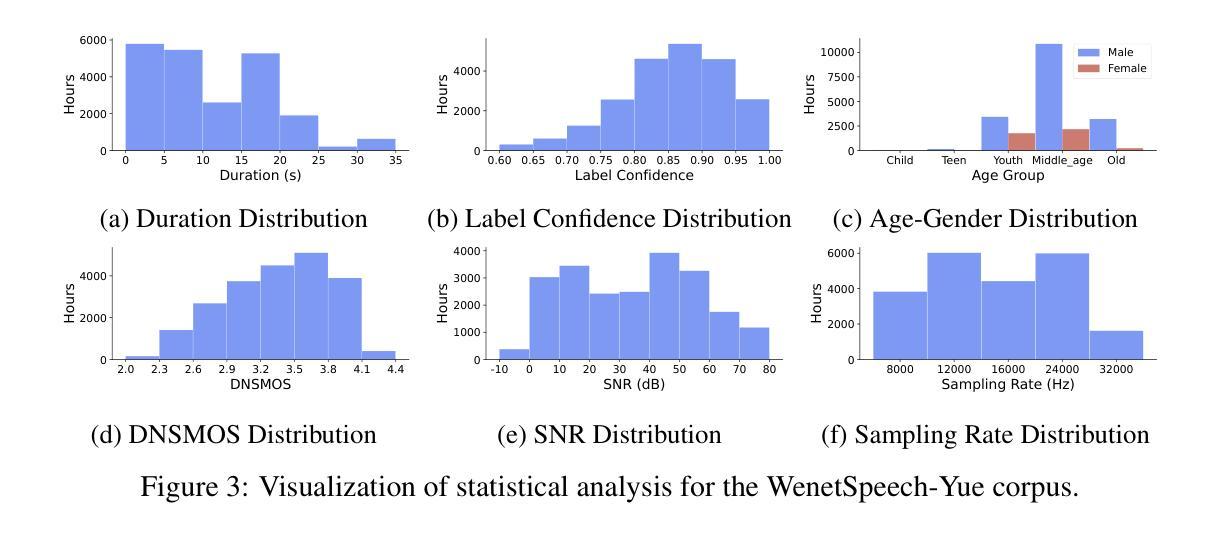
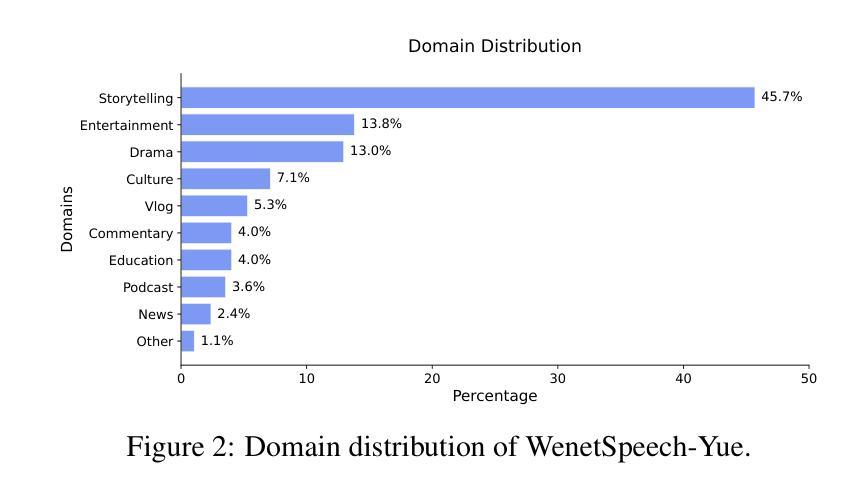
The development of speech understanding and generation has been significantly accelerated by the availability of large-scale, high-quality speech datasets. Among these, ASR and TTS are regarded as the most established and fundamental tasks. However, for Cantonese (Yue Chinese), spoken by approximately 84.9 million native speakers worldwide, limited annotated resources have hindered progress and resulted in suboptimal ASR and TTS performance. To address this challenge, we propose WenetSpeech-Pipe, an integrated pipeline for building large-scale speech corpus with multi-dimensional annotation tailored for speech understanding and generation. It comprises six modules: Audio Collection, Speaker Attributes Annotation, Speech Quality Annotation, Automatic Speech Recognition, Text Postprocessing and Recognizer Output Voting, enabling rich and high-quality annotations. Based on this pipeline, we release WenetSpeech-Yue, the first large-scale Cantonese speech corpus with multi-dimensional annotation for ASR and TTS, covering 21,800 hours across 10 domains with annotations including ASR transcription, text confidence, speaker identity, age, gender, speech quality scores, among other annotations. We also release WSYue-eval, a comprehensive Cantonese benchmark with two components: WSYue-ASR-eval, a manually annotated set for evaluating ASR on short and long utterances, code-switching, and diverse acoustic conditions, and WSYue-TTS-eval, with base and coverage subsets for standard and generalization testing. Experimental results show that models trained on WenetSpeech-Yue achieve competitive results against state-of-the-art (SOTA) Cantonese ASR and TTS systems, including commercial and LLM-based models, highlighting the value of our dataset and pipeline.
大规模高质量语音数据集的可用性极大地推动了语音识别和生成技术的发展。其中,语音识别和文本转语音被认为是最为成熟和基础的任务。然而,对于全世界约有8490万本地使用者的广东话(粤语文),标注资源有限,阻碍了进展,导致语音识别和文本转语音的性能不尽如人意。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了WenetSpeech-Pipe,这是一个为语音理解和生成量身定制的大规模语音语料库构建的综合管道,具有多维度注释。它包含六个模块:音频收集、说话人属性标注、语音质量标注、自动语音识别、文本后处理和识别器输出投票,能够实现丰富且高质量的标注。基于此管道,我们发布了WenetSpeech-Yue,这是首个具有多维度注释的粤语语音识别和文本转语音的大规模语音语料库,涵盖10个领域的21800小时,注释包括语音识别转录、文本置信度、说话人身份、年龄、性别、语音质量评分等。我们还发布了WSYue-eval,这是一个全面的粤语基准测试,包含两个组成部分:WSYue-ASR-eval,用于评估短句和长句、语言切换和各种声音条件下的语音识别;以及WSYue-TTS-eval,包含基本和覆盖子集,用于标准和通用测试。实验结果表明,在WenetSpeech-Yue上训练的模型与最新的粤语语音识别和文本转语音系统相比具有竞争力,包括商业和基于大型语言模型的系统,这凸显了我们数据集和管道的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模、高质量的语音数据集极大地推动了语音识别和生成技术的发展。针对粤语(全球约8490万母语者使用的语言),由于标注资源有限,语音识别和文本转语音的性能并不理想。为此,我们提出了WenetSpeech-Pipe,这是一个为语音理解和生成量身定制的大规模语音语料库多维标注的集成管道,包含六个模块:音频收集、说话人属性标注、语音质量标注、自动语音识别、文本后处理和识别器输出投票。基于该管道,我们发布了WenetSpeech-Yue,这是首个带有多维标注的粤语语音识别和文本转语音大规模语音语料库,涵盖10个领域的21800小时,包括语音识别转录、文本置信度、说话人身份、年龄、性别、语音质量分数等标注。我们还发布了WSYue-eval,这是一个全面的粤语基准测试,包括用于评估短句和长句语音识别、代码切换和不同声学条件的WSYue-ASR-eval手动标注集以及用于标准测试和泛化测试的WSYue-TTS-eval基准和覆盖范围子集。实验结果表明,在WenetSpeech-Yue上训练的模型与最新的粤语语音识别和文本转语音系统的结果具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- WenetSpeech-Pipe:一个为粤语量身定制的大规模语音语料库多维标注的集成管道,包含音频收集、说话人属性标注等多个模块。
- WenetSpeech-Yue:首个带有多维标注的粤语语音识别和文本转语音大规模语音语料库,涵盖多个领域,提供丰富的标注信息。
- WSYue-eval:一个全面的粤语基准测试,包括用于评估短句和长句语音识别、代码切换等的WSYue-ASR-eval手动标注集以及用于标准测试和泛化测试的WSYue-TTS-eval基准集。
- WenetSpeech-Yue语料库对粤语语音识别和文本转语音性能的提升起到了关键作用。
- 该研究为粤语语言处理和人工智能领域的发展提供了重要支持。
- 集成管道和大规模语料库的应用有助于推动语音识别和生成技术的进步。
点此查看论文截图