⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-10 更新
Barlow-Swin: Toward a novel siamese-based segmentation architecture using Swin-Transformers
Authors:Morteza Kiani Haftlang, Mohammadhossein Malmir, Foroutan Parand, Umberto Michelucci, Safouane El Ghazouali
Medical image segmentation is a critical task in clinical workflows, particularly for the detection and delineation of pathological regions. While convolutional architectures like U-Net have become standard for such tasks, their limited receptive field restricts global context modeling. Recent efforts integrating transformers have addressed this, but often result in deep, computationally expensive models unsuitable for real-time use. In this work, we present a novel end-to-end lightweight architecture designed specifically for real-time binary medical image segmentation. Our model combines a Swin Transformer-like encoder with a U-Net-like decoder, connected via skip pathways to preserve spatial detail while capturing contextual information. Unlike existing designs such as Swin Transformer or U-Net, our architecture is significantly shallower and competitively efficient. To improve the encoder’s ability to learn meaningful features without relying on large amounts of labeled data, we first train it using Barlow Twins, a self-supervised learning method that helps the model focus on important patterns by reducing unnecessary repetition in the learned features. After this pretraining, we fine-tune the entire model for our specific task. Experiments on benchmark binary segmentation tasks demonstrate that our model achieves competitive accuracy with substantially reduced parameter count and faster inference, positioning it as a practical alternative for deployment in real-time and resource-limited clinical environments. The code for our method is available at Github repository: https://github.com/mkianih/Barlow-Swin.
医学图像分割是临床工作流程中的关键任务,特别是在检测和描绘病理区域方面。虽然U-Net等卷积架构已成为此类任务的标配,但其有限的感受野限制了全局上下文建模。最近将变压器集成起来的努力解决了这一问题,但往往导致深度过大、计算成本高昂的模型,不适合实时使用。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种专为实时二进制医学图像分割设计的端到端轻量化新型架构。我们的模型结合了类似Swin Transformer的编码器和类似U-Net的解码器,通过跳过路径连接,以保留空间细节并捕获上下文信息。与现有的Swin Transformer或U-Net设计不同,我们的架构显著更浅且效率更高。为了改善编码器在不依赖大量标记数据的情况下学习有意义特征的能力,我们首先使用Barlow Twins对其进行训练,这是一种自监督学习方法,通过减少学习特征中的不必要重复,帮助模型关注重要模式。在此预训练之后,我们对整个模型进行微调,以适应我们的特定任务。在基准二进制分割任务上的实验表明,我们的模型在参数计数大幅减少且推理速度更快的情况下实现了具有竞争力的准确性,这使其成为在实时和资源受限的临床环境中部署的实际可行替代方案。我们的方法的代码可在Github仓库中找到:https://github.com/mkianih/Barlow-Swin。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对实时二元医学图像分割的新型端到端轻量化架构。该模型结合Swin Transformer风格的编码器和U-Net风格的解码器,通过跳过路径连接以保留空间细节并捕获上下文信息。采用Barlow Twins自监督学习方法提高编码器学习有意义特征的能力,并在预训练后对整个模型进行微调。实验表明,该模型在减少参数数量和加快推理速度的同时,实现了具有竞争力的准确性,使其成为在实时和资源有限的临床环境中部署的实用替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在临床工作流程中至关重要,尤其用于病理区域的检测和划分。
- 虽然U-Net等卷积架构已成为此类任务的标准,但其有限的感受野限制了全局上下文建模。
- 最近将transformer集成起来的努力解决了这个问题,但往往导致模型过于复杂,不适合实时使用。
- 本文提出了一种新型端到端轻量化架构,结合Swin Transformer风格的编码器和U-Net风格的解码器,以进行实时二元医学图像分割。
- 该模型通过跳过路径连接保留空间细节并捕获上下文信息。
- 采用Barlow Twins自监督学习方法提高编码器学习特征的能力,并在预训练后进行微调。
点此查看论文截图

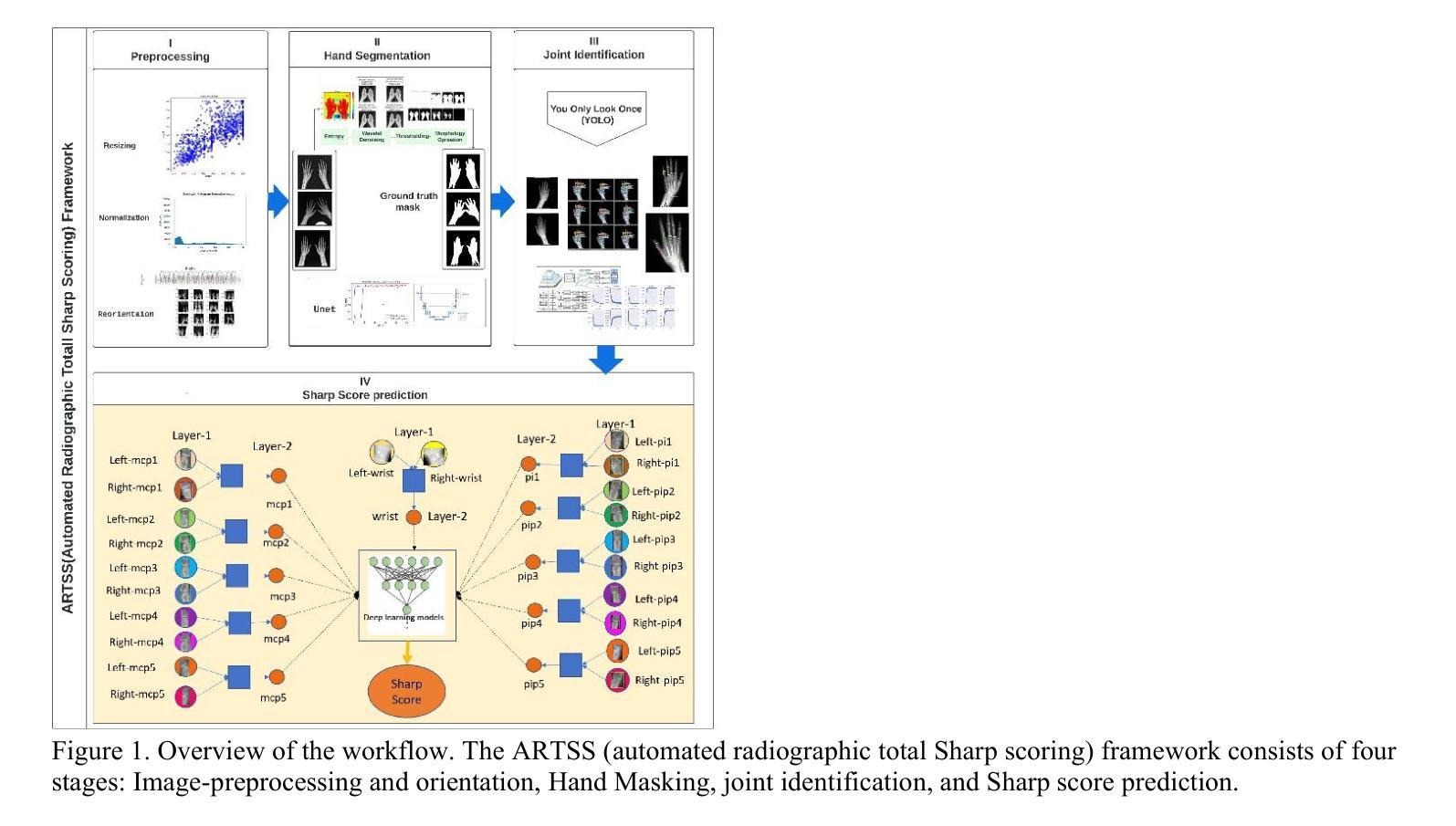
Automated Radiographic Total Sharp Score (ARTSS) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Solution to Reduce Inter-Intra Reader Variation and Enhancing Clinical Practice
Authors:Hajar Moradmand, Lei Ren
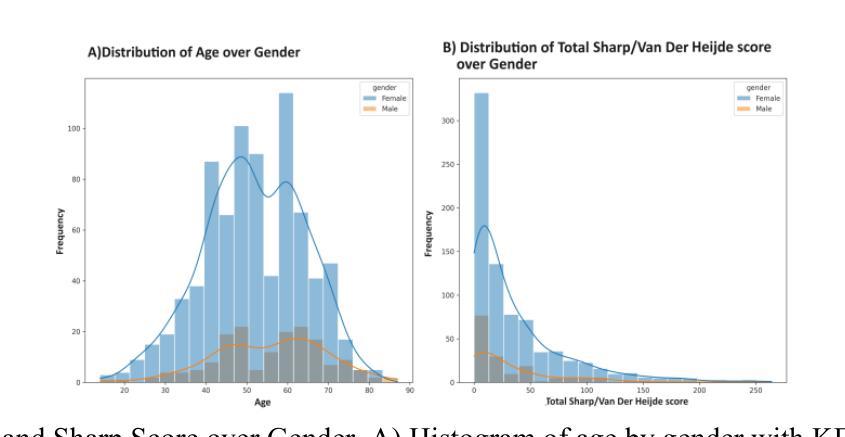
Assessing the severity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using the Total Sharp/Van Der Heijde Score (TSS) is crucial, but manual scoring is often time-consuming and subjective. This study introduces an Automated Radiographic Sharp Scoring (ARTSS) framework that leverages deep learning to analyze full-hand X-ray images, aiming to reduce inter- and intra-observer variability. The research uniquely accommodates patients with joint disappearance and variable-length image sequences. We developed ARTSS using data from 970 patients, structured into four stages: I) Image pre-processing and re-orientation using ResNet50, II) Hand segmentation using UNet.3, III) Joint identification using YOLOv7, and IV) TSS prediction using models such as VGG16, VGG19, ResNet50, DenseNet201, EfficientNetB0, and Vision Transformer (ViT). We evaluated model performance with Intersection over Union (IoU), Mean Average Precision (MAP), mean absolute error (MAE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and Huber loss. The average TSS from two radiologists was used as the ground truth. Model training employed 3-fold cross-validation, with each fold consisting of 452 training and 227 validation samples, and external testing included 291 unseen subjects. Our joint identification model achieved 99% accuracy. The best-performing model, ViT, achieved a notably low Huber loss of 0.87 for TSS prediction. Our results demonstrate the potential of deep learning to automate RA scoring, which can significantly enhance clinical practice. Our approach addresses the challenge of joint disappearance and variable joint numbers, offers timesaving benefits, reduces inter- and intra-reader variability, improves radiologist accuracy, and aids rheumatologists in making more informed decisions.
评估类风湿性关节炎(RA)的严重程度对于治疗方案的制定至关重要,通常采用Total Sharp/Van Der Heijde Score(TSS)进行评分。然而,手动评分耗时且主观性较强。本研究介绍了一种Automated Radiographic Sharp Scoring(ARTSS)框架,该框架利用深度学习技术来分析全手X射线图像,旨在减少观察者之间的差异和观察者在多次评分间的差异。这项研究独特地解决了关节消失和可变长度图像序列的患者问题。我们使用来自970名患者的数据来开发ARTSS框架,分为四个阶段:I)使用ResNet50对图像进行预处理和重新定向;II)使用UNet 3对手部进行分割;III)使用YOLOv7进行关节识别;IV)使用诸如VGG16、VGG19、ResNet50、DenseNet201、EfficientNetB0和Vision Transformer(ViT)等模型进行TSS预测。我们使用交集比(IoU)、平均精度均值(MAP)、平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE)和Huber损失来评估模型性能。以两位放射科医生平均的TSS作为真实值。模型训练采用三折交叉验证,每折包含452个训练样本和227个验证样本,外部测试包括291个未见过的受试者。我们的关节识别模型达到了99%的准确率。表现最佳的ViT模型在TSS预测方面取得了显著较低的Huber损失为0.87。我们的结果证明了深度学习在自动化RA评分中的潜力,这可能会极大地提高临床实践水平。我们的方法解决了关节消失和可变关节数量的问题,节省了时间,减少了观察者间和观察者自身多次评分间的差异,提高了放射科医生准确评估的准确性,并帮助风湿科医生做出更明智的决策。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究使用深度学习技术提出一种自动类风湿性关节炎评分(ARTSS)框架,用于分析全手X射线图像,以评估类风湿性关节炎(RA)的严重性。该框架旨在减少观察者之间的差异和观察者内部的差异,提高评估效率和准确性。研究过程中,采用了深度学习方法对图像进行预处理、手部分割、关节识别和总尖锐度预测。最佳模型为Vision Transformer(ViT),在预测总尖锐度方面取得了显著的低Huber损失值0.87。此研究展示了深度学习在自动化RA评分方面的潜力,能显著提高临床实践效率,解决关节消失和关节数量变化的问题,节省时间,提高评估准确性,帮助风湿病学家做出更明智的决策。
关键见解
- 本研究引入了一种基于深度学习的自动类风湿性关节炎评分(ARTSS)框架,用于分析全手X射线图像。
- ARTSS框架旨在减少评分过程中的主观性和时间消耗。
- 研究过程中涉及图像预处理、手部分割、关节识别和总尖锐度预测等多个阶段。
- 最佳模型为Vision Transformer(ViT),在预测总尖锐度方面取得了显著的低Huber损失值。
- 此框架能够处理关节消失和关节数量变化的情况,具有广泛的适用性。
- ARTSS框架的应用能提高评估准确性,帮助风湿病学家做出更明智的决策。
点此查看论文截图

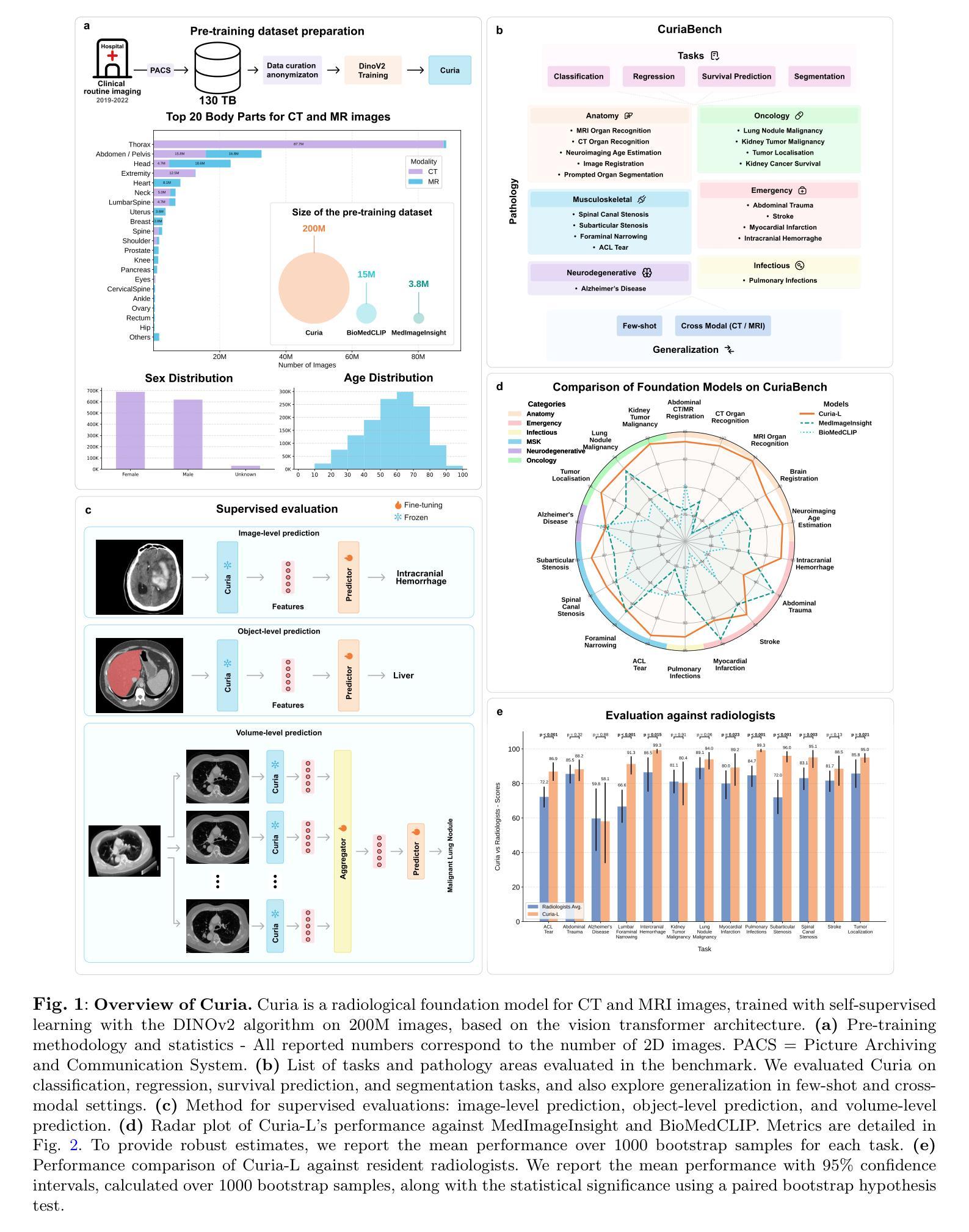
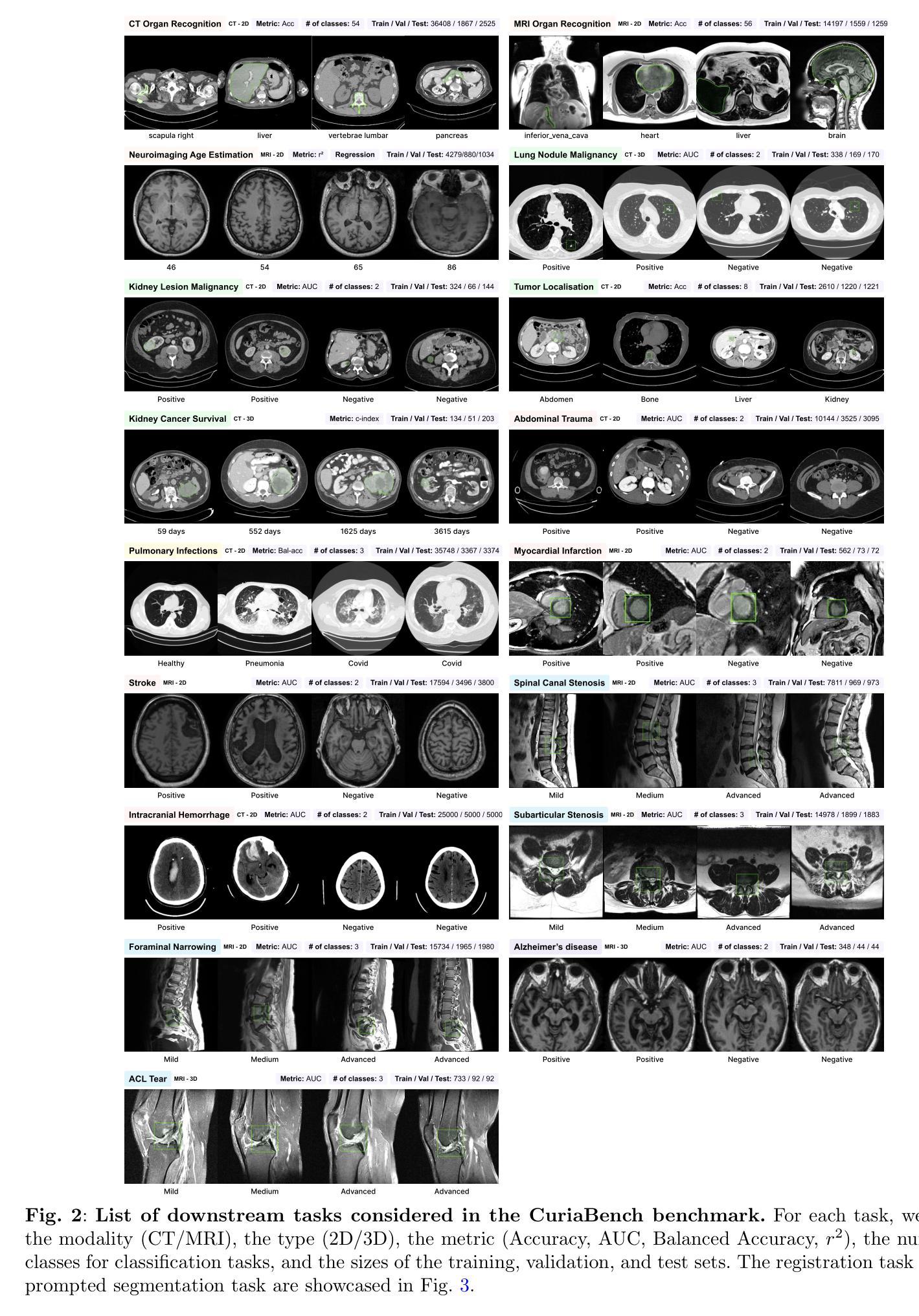
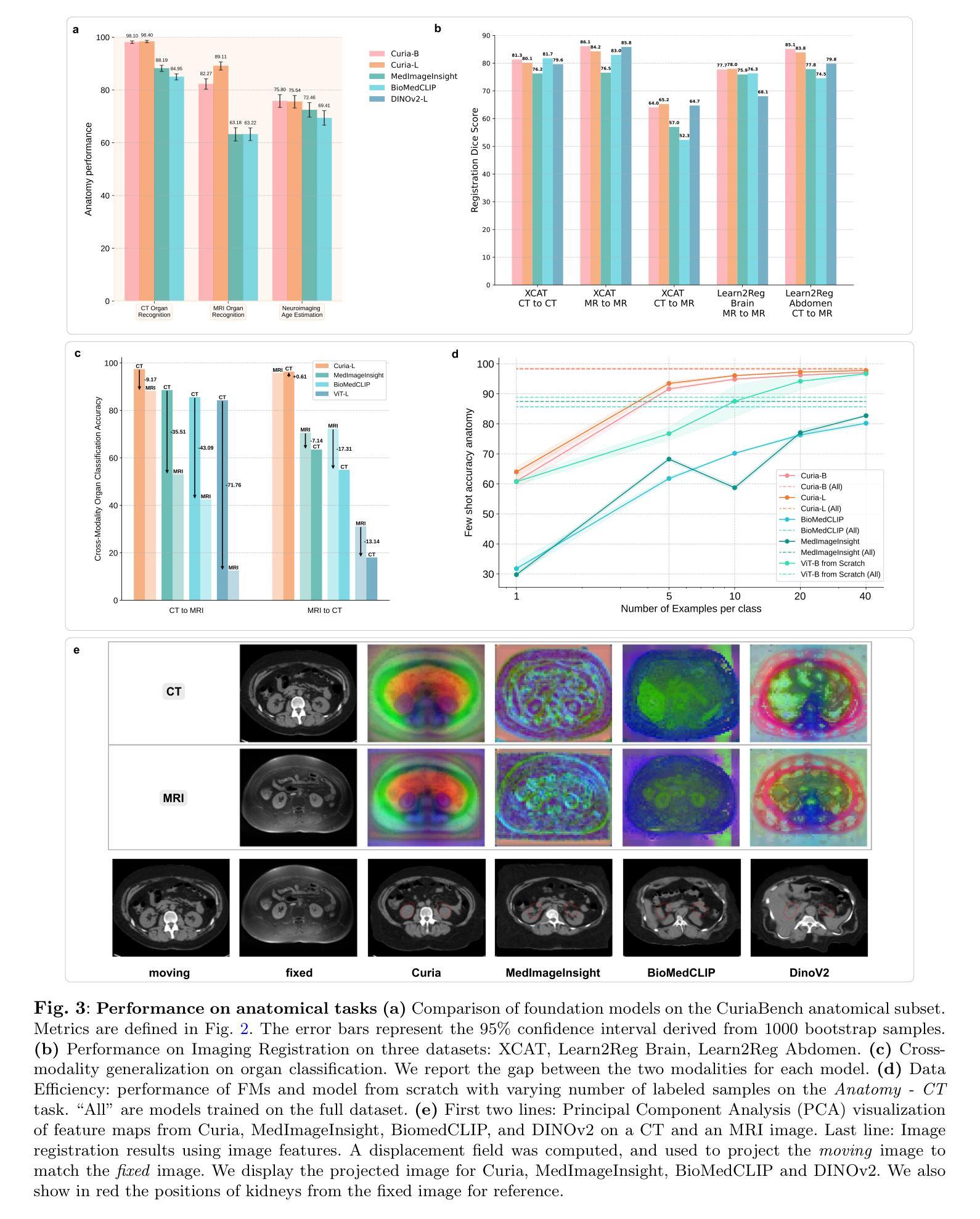
Curia: A Multi-Modal Foundation Model for Radiology
Authors:Corentin Dancette, Julien Khlaut, Antoine Saporta, Helene Philippe, Elodie Ferreres, Baptiste Callard, Théo Danielou, Léo Alberge, Léo Machado, Daniel Tordjman, Julie Dupuis, Korentin Le Floch, Jean Du Terrail, Mariam Moshiri, Laurent Dercle, Tom Boeken, Jules Gregory, Maxime Ronot, François Legou, Pascal Roux, Marc Sapoval, Pierre Manceron, Paul Hérent
AI-assisted radiological interpretation is based on predominantly narrow, single-task models. This approach is impractical for covering the vast spectrum of imaging modalities, diseases, and radiological findings. Foundation models (FMs) hold the promise of broad generalization across modalities and in low-data settings. However, this potential has remained largely unrealized in radiology. We introduce Curia, a foundation model trained on the entire cross-sectional imaging output of a major hospital over several years, which to our knowledge is the largest such corpus of real-world data-encompassing 150,000 exams (130 TB). On a newly curated 19-task external validation benchmark, Curia accurately identifies organs, detects conditions like brain hemorrhages and myocardial infarctions, and predicts outcomes in tumor staging. Curia meets or surpasses the performance of radiologists and recent foundation models, and exhibits clinically significant emergent properties in cross-modality, and low-data regimes. To accelerate progress, we release our base model’s weights at https://huggingface.co/raidium/curia.
人工智能辅助放射学解读主要基于狭窄、单一任务的模型。这种方法对于覆盖广泛的成像模式、疾病和放射学发现来说并不实用。基础模型(FMs)有望在跨模态和低数据环境中实现广泛通用化。然而,这一潜力在放射学领域一直未能得到充分发挥。我们引入了Curia,这是一个在大型医院数年的横断面成像输出上训练的基础模型,据我们所知,这是涵盖现实世界数据的最大此类语料库,包含15万份检查(130TB)。在一个新编制的包含19项任务的外部验证基准测试中,Curia能准确识别器官,检测如脑出血和心肌梗死等状况,并在肿瘤分期中预测结果。Curia达到了或超越了放射学家和最新基础模型的性能,在跨模态和低数据环境中表现出了具有临床意义的突发特性。为了加速进展,我们在https://huggingface.co/raidium/curia上发布了基础模型的权重。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于大型真实世界医学影像数据训练的放射学基础模型Curia。该模型能够跨多种成像模态和缺乏数据的环境进行广泛的推广,可识别器官、检测疾病并预测肿瘤分期等任务。其性能已经达到或超过了放射学家和最近的基础模型,展现出在临床上有重要价值的跨模态和少数据环境下的特性。
Key Takeaways
- AI在放射学解读中的应用主要基于狭窄的单任务模型,难以覆盖广泛的成像方式、疾病和放射学发现。
- 基础模型(FMs)具有在多种模态和低数据环境下进行广泛推广的潜力。
- Curia是一个在大型医院多年来的全部横断面影像数据上训练的基础模型,包含15万种检查、130TB的数据,是迄今为止最大的真实世界数据集合。
- Curia在外部验证的19项任务中表现出色,能够准确识别器官、检测疾病如脑出血和心肌梗塞,并预测肿瘤分期。
- Curia的性能已经达到或超过了放射学家和最近的其他基础模型。
- Curia展现出跨模态和少数据环境下的临床显著特性。
点此查看论文截图

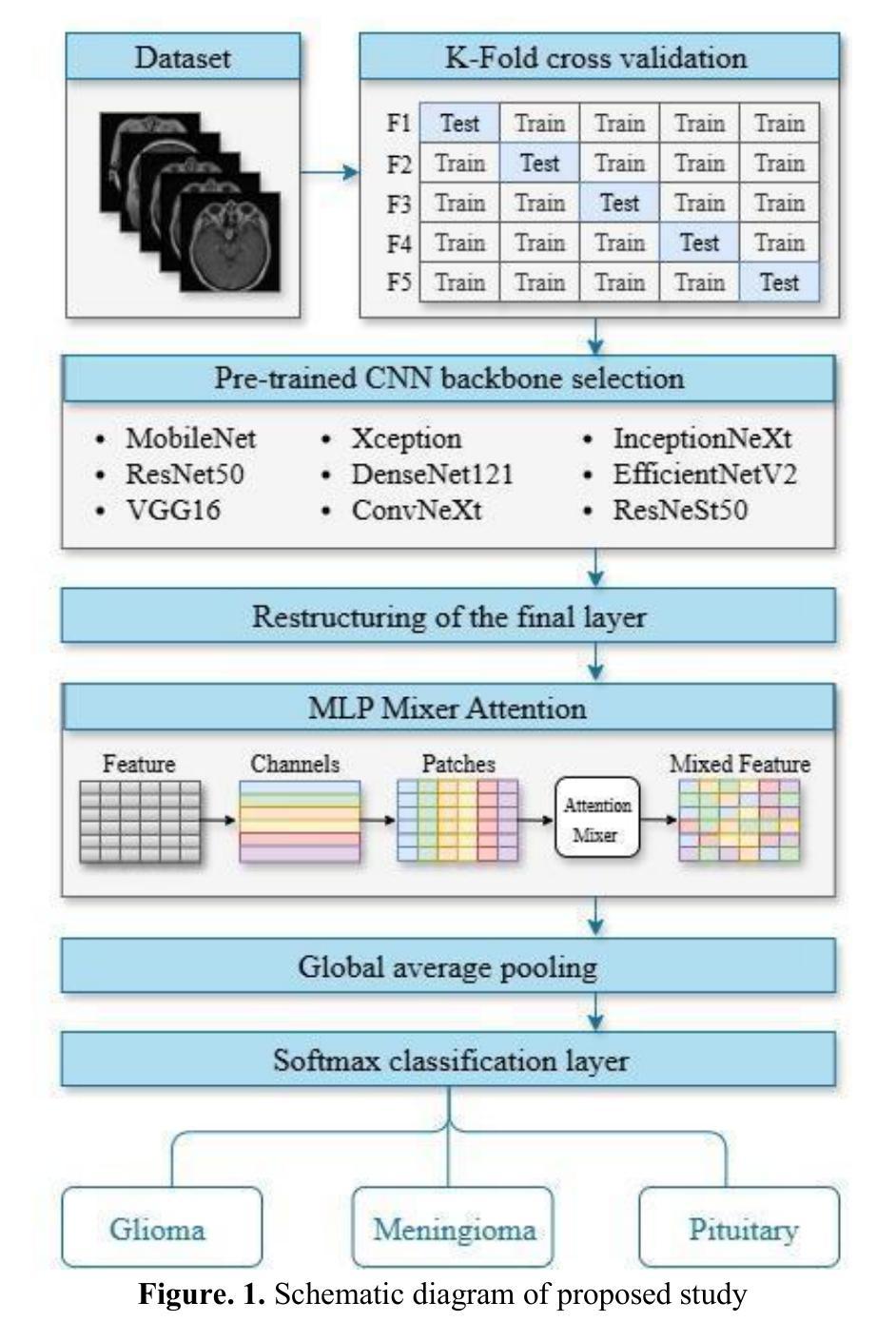
MRI-Based Brain Tumor Detection through an Explainable EfficientNetV2 and MLP-Mixer-Attention Architecture
Authors:Mustafa Yurdakul, Şakir Taşdemir
Brain tumors are serious health problems that require early diagnosis due to their high mortality rates. Diagnosing tumors by examining Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) images is a process that requires expertise and is prone to error. Therefore, the need for automated diagnosis systems is increasing day by day. In this context, a robust and explainable Deep Learning (DL) model for the classification of brain tumors is proposed. In this study, a publicly available Figshare dataset containing 3,064 T1-weighted contrast-enhanced brain MRI images of three tumor types was used. First, the classification performance of nine well-known CNN architectures was evaluated to determine the most effective backbone. Among these, EfficientNetV2 demonstrated the best performance and was selected as the backbone for further development. Subsequently, an attention-based MLP-Mixer architecture was integrated into EfficientNetV2 to enhance its classification capability. The performance of the final model was comprehensively compared with basic CNNs and the methods in the literature. Additionally, Grad-CAM visualization was used to interpret and validate the decision-making process of the proposed model. The proposed model’s performance was evaluated using the five-fold cross-validation method. The proposed model demonstrated superior performance with 99.50% accuracy, 99.47% precision, 99.52% recall and 99.49% F1 score. The results obtained show that the model outperforms the studies in the literature. Moreover, Grad-CAM visualizations demonstrate that the model effectively focuses on relevant regions of MRI images, thus improving interpretability and clinical reliability. A robust deep learning model for clinical decision support systems has been obtained by combining EfficientNetV2 and attention-based MLP-Mixer, providing high accuracy and interpretability in brain tumor classification.
脑肿瘤是严重的健康问题,由于其高死亡率,需要早期诊断。通过检查磁共振成像(MRI)图像来诊断肿瘤是一个需要专业知识且容易出错的过程。因此,对自动诊断系统的需求每天都在增加。在此背景下,提出了一种用于脑肿瘤分类的稳健且可解释的深度学习(DL)模型。本研究使用了一个公开的Figshare数据集,其中包含三种肿瘤类型的3064张T1加权增强脑MRI图像。首先,评估了九种知名CNN架构的分类性能,以确定最有效的主干网络。其中,EfficientNetV2表现最佳,被选为进一步发展的主干网络。随后,将注意力机制的MLP-Mixer架构集成到EfficientNetV2中,以增强其分类能力。将最终模型的性能与基本CNN和文献中的方法进行了全面比较。此外,使用Grad-CAM可视化来解释和验证所提出模型的决策过程。所提出模型的性能采用五倍交叉验证法进行评估。所提出模型的性能卓越,准确度为99.50%,精确度为99.47%,召回率为99.52%,F1分数为99.49%。所获得的结果表明,该模型在文献中的表现更胜一筹。此外,Grad-CAM可视化显示,该模型能够有效地关注MRI图像的相关区域,从而提高可解释性和临床可靠性。通过结合EfficientNetV2和基于注意力的MLP-Mixer,获得了一个用于临床决策支持系统的稳健深度学习模型,在脑肿瘤分类中具有高精度和可解释性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习模型结合EfficientNetV2和注意力机制MLP-Mixer,对脑肿瘤分类实现高准确度(99.5%)和高可解释性,有助临床决策支持系统的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤的高死亡率使其早期准确诊断变得至关重要。
- 深度学习模型在脑肿瘤诊断中具有潜力,尤其是自动化诊断系统。
- EfficientNetV2在多种知名CNN架构中表现最佳,被选为进一步研究的基础架构。
- 引入了注意力机制的MLP-Mixer架构以增强EfficientNetV2的分类能力。
- 该模型通过Grad-CAM可视化展现了决策过程,增强了模型的可解释性。
- 模型表现出高准确率(99.5%),优于现有文献中的其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

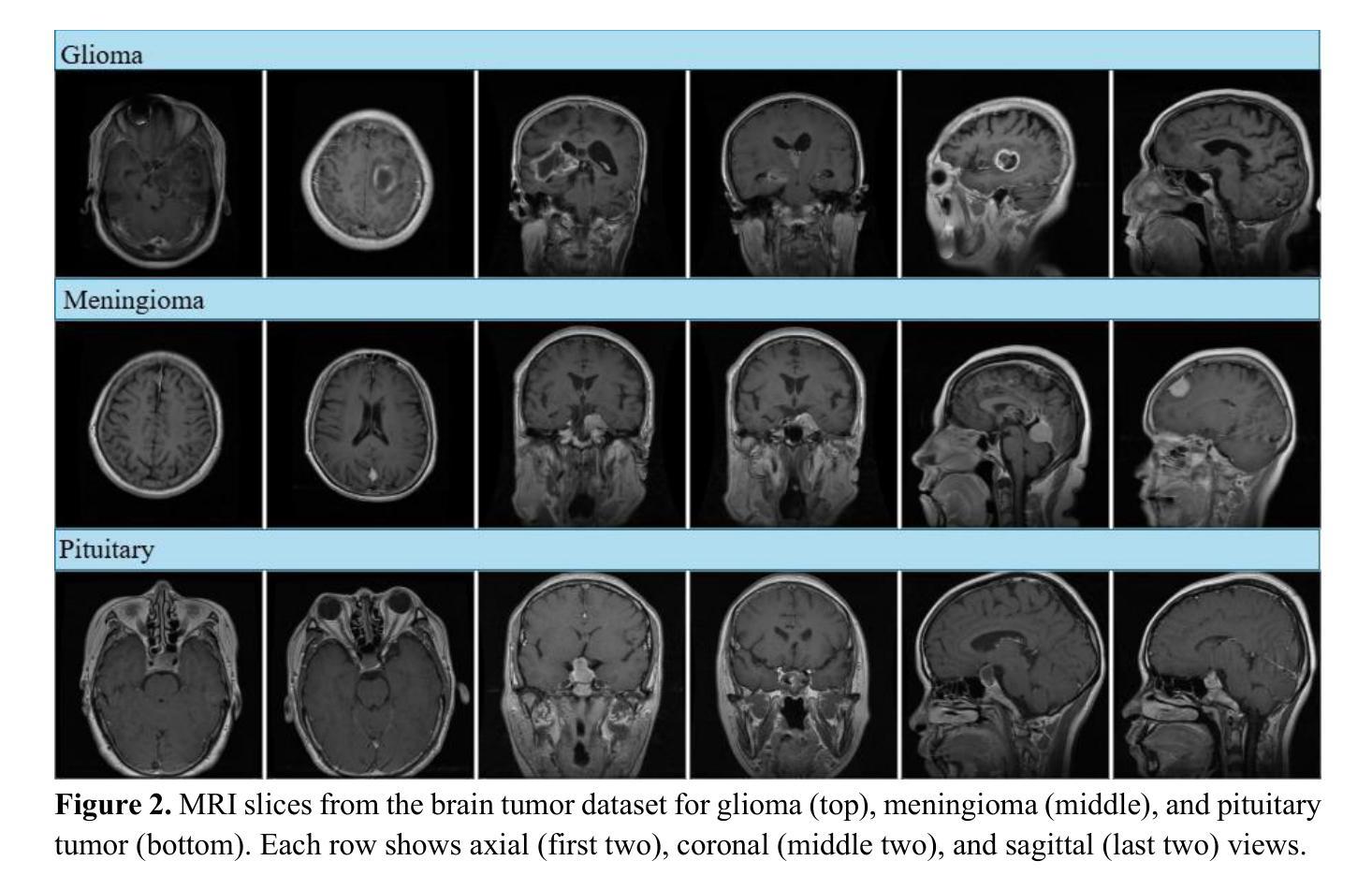
MM-DINOv2: Adapting Foundation Models for Multi-Modal Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Daniel Scholz, Ayhan Can Erdur, Viktoria Ehm, Anke Meyer-Baese, Jan C. Peeken, Daniel Rueckert, Benedikt Wiestler
Vision foundation models like DINOv2 demonstrate remarkable potential in medical imaging despite their origin in natural image domains. However, their design inherently works best for uni-modal image analysis, limiting their effectiveness for multi-modal imaging tasks that are common in many medical fields, such as neurology and oncology. While supervised models perform well in this setting, they fail to leverage unlabeled datasets and struggle with missing modalities, a frequent challenge in clinical settings. To bridge these gaps, we introduce MM-DINOv2, a novel and efficient framework that adapts the pre-trained vision foundation model DINOv2 for multi-modal medical imaging. Our approach incorporates multi-modal patch embeddings, enabling vision foundation models to effectively process multi-modal imaging data. To address missing modalities, we employ full-modality masking, which encourages the model to learn robust cross-modality relationships. Furthermore, we leverage semi-supervised learning to harness large unlabeled datasets, enhancing both the accuracy and reliability of medical predictions. Applied to glioma subtype classification from multi-sequence brain MRI, our method achieves a Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) of 0.6 on an external test set, surpassing state-of-the-art supervised approaches by +11.1%. Our work establishes a scalable and robust solution for multi-modal medical imaging tasks, leveraging powerful vision foundation models pre-trained on natural images while addressing real-world clinical challenges such as missing data and limited annotations.
DINOv2等视觉基础模型虽然在医学成像领域展现出显著潜力,尽管它们最初是在自然图像领域开发的。然而,它们的设计本质上最适合单模态图像分析,在医学领域常见的多模态成像任务中效果不佳,例如在神经学和肿瘤学中。尽管监督模型在这种环境中表现良好,但它们无法利用未标记的数据集,并且在缺失模态的情况下面临挑战,这在临床环境中是常见的。为了弥补这些差距,我们引入了MM-DINOv2,这是一个新颖且高效框架,它将预训练的视觉基础模型DINOv2适应于多模态医学成像。我们的方法结合了多模态补丁嵌入,使视觉基础模型能够有效地处理多模态成像数据。为了解决缺失模态的问题,我们采用了全模态掩蔽技术,该技术鼓励模型学习稳健的跨模态关系。此外,我们还利用半监督学习来利用大量的未标记数据集,提高医疗预测的准确性和可靠性。在通过多序列脑部MRI进行胶质瘤亚型分类的应用中,我们的方法达到了外部测试集上的Matthews相关系数(MCC)为0.6,相较于最新的监督方法提高了+11.1%。我们的工作为多模态医学成像任务建立了一个可扩展和稳健的解决方案,利用在天然图像上预先训练的强大视觉基础模型,同时解决现实世界中的临床挑战,如缺失数据和有限的注释。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
尽管起源于自然图像领域,DINOv2等视觉基础模型在医学成像中展现出显著潜力。然而,它们的设计本质上最适合单模态图像分析,在医学领域常见的多模态成像任务中效果有限,如神经学和肿瘤学等领域。虽然监督模型在这种设置下表现良好,但它们无法利用未标记数据集,并且难以应对临床环境中常见的缺失模态挑战。为了弥补这些差距,我们推出了MM-DINOv2,这是一个新颖且高效框架,将预训练的视觉基础模型DINOv2适应于多模态医学成像。我们的方法结合了多模态补丁嵌入,使视觉基础模型能够处理多模态成像数据。为解决缺失模态问题,我们采用全模态掩蔽,鼓励模型学习稳健的跨模态关系。此外,我们利用半监督学习利用大量未标记数据集,提高医疗预测的准确性和可靠性。在来自多序列脑部MRI的胶质瘤亚型分类应用中,我们的方法在外部测试集上达到0.6的Matthews相关系数(MCC),比最先进的监督方法高出+11.1%。我们的工作为多模态医学成像任务建立了一个可扩展和稳健的解决方案,利用在天然图像上预训练的强大视觉基础模型,同时解决现实世界中的临床挑战,如缺失数据和有限注释。
关键见解
- DINOv2等视觉基础模型在医学成像中具有显著潜力,尽管它们最初是为自然图像设计的。
- 这些模型在单模态图像分析方面表现最佳,但在多模态医学成像任务中的效果有限。
- 多模态成像在医学领域很常见,特别是在神经学和肿瘤学等领域。
- 监督模型难以利用未标记数据集和应对缺失模态的挑战。
- MM-DINOv2框架是第一个将预训练的视觉基础模型适应于多模态医学成像的研究。
- 通过多模态补丁嵌入和全面模态掩蔽解决多模态数据分析和缺失模态问题。
点此查看论文截图

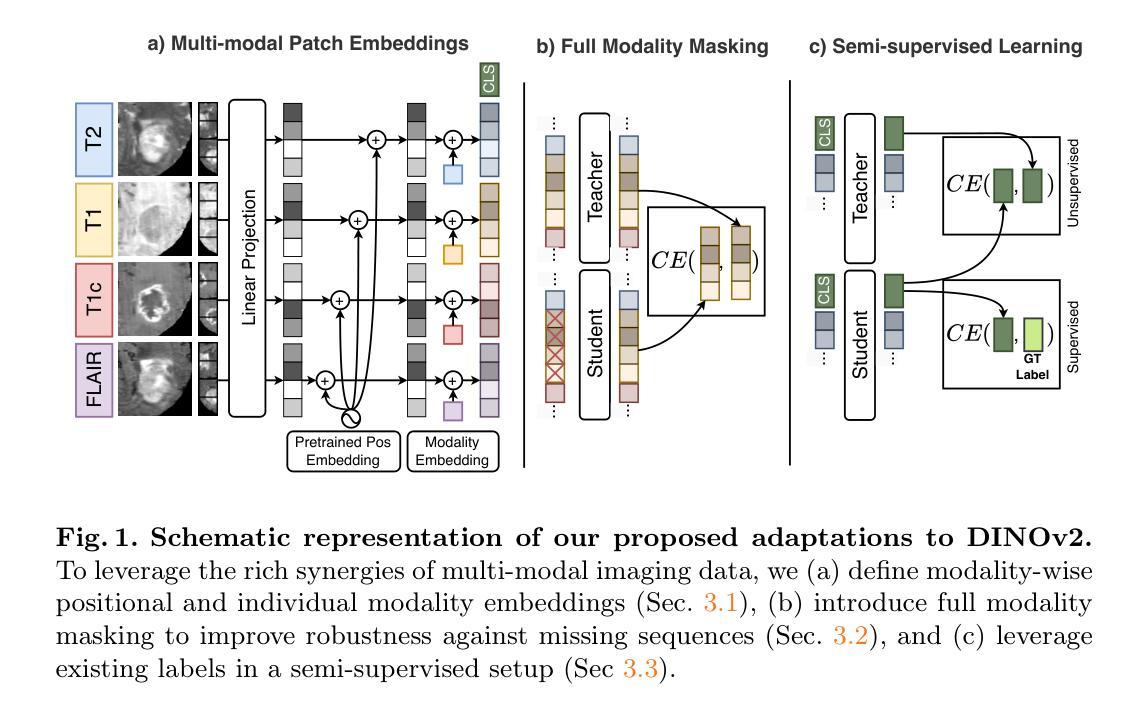
Contrastive Anatomy-Contrast Disentanglement: A Domain-General MRI Harmonization Method
Authors:Daniel Scholz, Ayhan Can Erdur, Robbie Holland, Viktoria Ehm, Jan C. Peeken, Benedikt Wiestler, Daniel Rueckert
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an invaluable tool for clinical and research applications. Yet, variations in scanners and acquisition parameters cause inconsistencies in image contrast, hindering data comparability and reproducibility across datasets and clinical studies. Existing scanner harmonization methods, designed to address this challenge, face limitations, such as requiring traveling subjects or struggling to generalize to unseen domains. We propose a novel approach using a conditioned diffusion autoencoder with a contrastive loss and domain-agnostic contrast augmentation to harmonize MR images across scanners while preserving subject-specific anatomy. Our method enables brain MRI synthesis from a single reference image. It outperforms baseline techniques, achieving a +7% PSNR improvement on a traveling subjects dataset and +18% improvement on age regression in unseen. Our model provides robust, effective harmonization of brain MRIs to target scanners without requiring fine-tuning. This advancement promises to enhance comparability, reproducibility, and generalizability in multi-site and longitudinal clinical studies, ultimately contributing to improved healthcare outcomes.
磁共振成像(MRI)在临床和研究应用中具有极高的价值。然而,扫描仪和采集参数的差异导致图像对比度的不一致性,阻碍了不同数据集和临床研究之间的数据可比性和可重复性。为解决这一挑战而设计的现有扫描仪谐调方法面临一些局限性,例如需要移动受试者或难以推广到未见领域。我们提出了一种使用条件扩散自编码器的新方法,该方法结合了对比损失和领域无关的对比增强技术,可以在保留特定主体解剖结构的同时,实现跨扫描仪的MR图像谐调。我们的方法能够实现从单个参考图像合成大脑MRI。在移动受试者数据集上,我们的方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面较基线技术提高了7%,在未见过的年龄回归测试中提高了18%。我们的模型提供了一种稳健有效的脑MRI谐调方法,无需微调即可针对目标扫描仪。这一进展有望增强多站点和纵向临床研究的可比性、可重复性和泛化性,最终为改善医疗结果做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
磁共振成像(MRI)在临床和研究应用中具有很大价值。不同扫描仪和采集参数造成的图像对比差异,给数据在不同数据集和临床研究中的可比性和可重复性带来挑战。针对这一挑战,现有扫描仪调和方法存在局限,如需要移动受试者或难以推广到未见领域。本研究提出一种使用条件扩散自编码器与对比损失和领域无关的对比增强相结合的新方法,实现对不同扫描仪下MR图像的一致化处理,同时保留个体特定解剖结构。该方法可从单一参考图像合成大脑MRI。相较于基线技术,在移动受试者数据集上实现了峰值信号噪声比(PSNR)提升7%,在未见年龄回归任务上提升18%。该方法为大脑MRI向目标扫描仪的稳健、有效调和提供了解决方案,无需微调即可实现。此进步有望增强多站点和纵向临床研究的可比性、可重复性和泛化性,最终为改善医疗结果做出贡献。
Key Takeaways
- MRI在临床和研究应用中具有重要价值,但不同扫描仪和采集参数导致图像对比差异,影响数据比较和再现性。
- 现有扫描仪调和方法存在局限性,如移动受试者需求和难以推广至未见领域。
- 研究提出了一种新的方法,使用条件扩散自编码器和对比损失,结合领域无关的对比增强,以调和不同扫描仪下的MR图像。
- 该方法能够在保留个体特定解剖结构的同时,从单一参考图像合成大脑MRI。
- 与基线技术相比,该方法在移动受试者数据集上实现了PSNR的提升,并在未见年龄回归任务上表现出显著改进。
- 该方法为大脑MRI的稳健、有效调和提供了解决方案,适用于多种扫描仪,无需微调。
点此查看论文截图

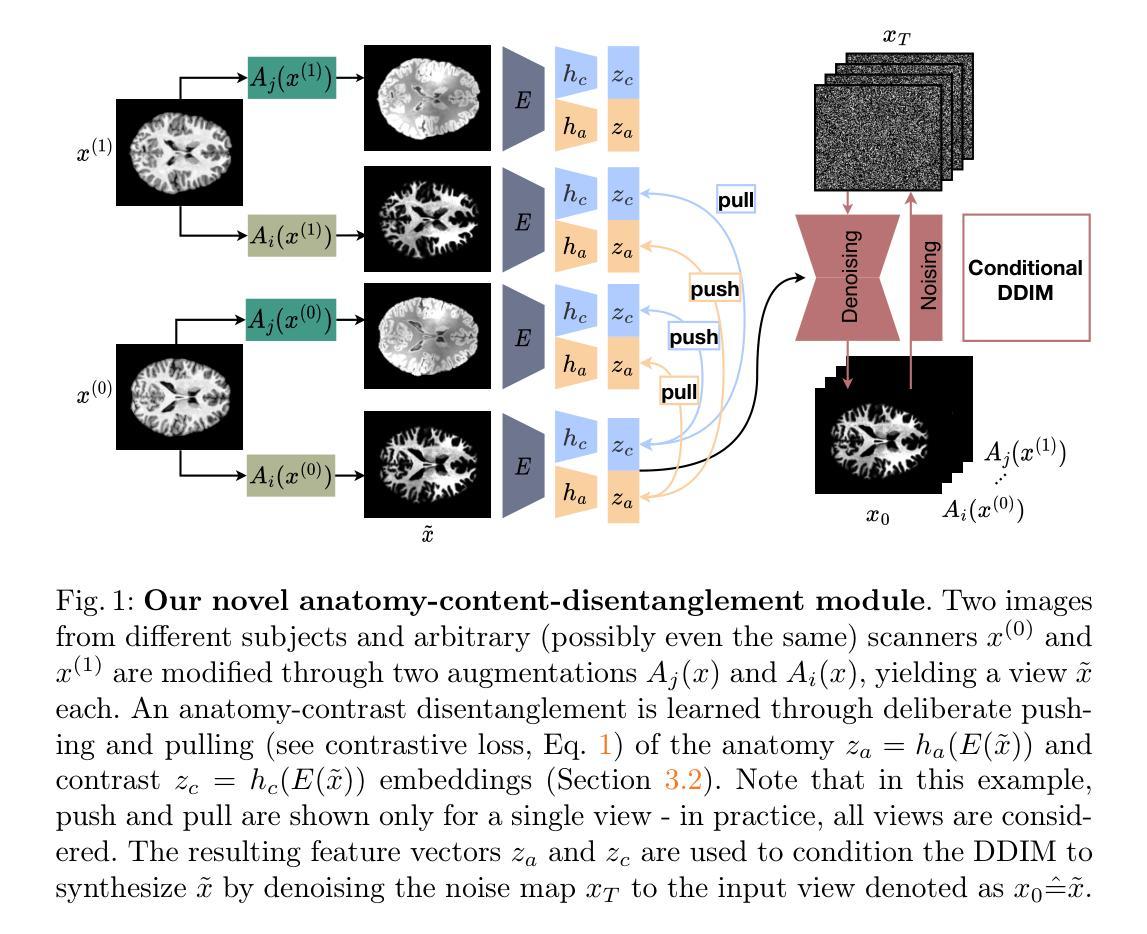
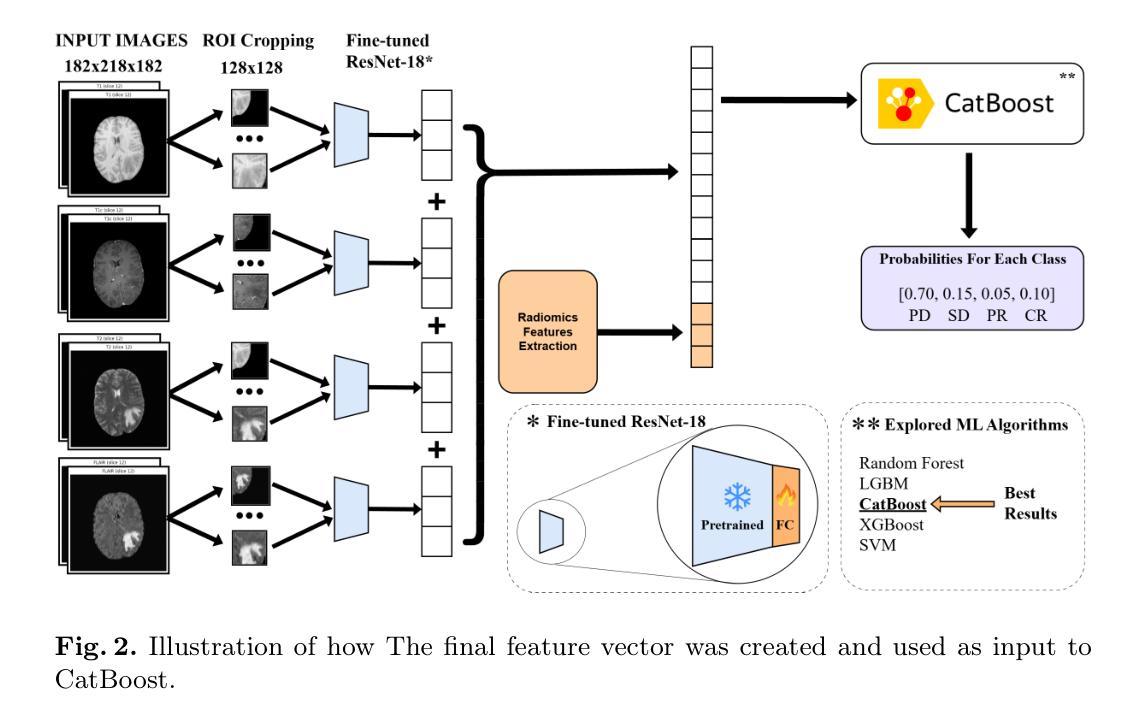
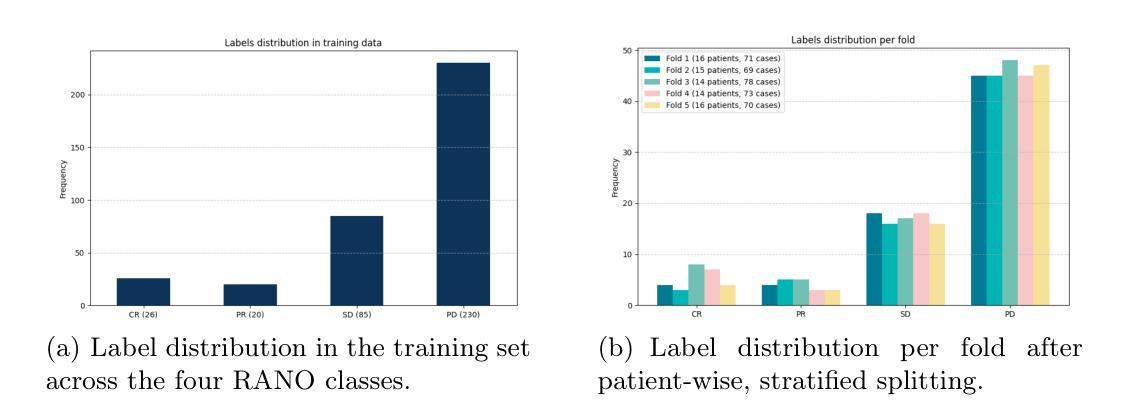
Predicting Brain Tumor Response to Therapy using a Hybrid Deep Learning and Radiomics Approach
Authors:Daniil Tikhonov, Matheus Scatolin, Mohor Banerjee, Qiankun Ji, Ahmed Jaheen, Mostafa Salem, Abdelrahman Elsayed, Hu Wang, Sarim Hashmi, Mohammad Yaqub
Accurate evaluation of the response of glioblastoma to therapy is crucial for clinical decision-making and patient management. The Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria provide a standardized framework to assess patients’ clinical response, but their application can be complex and subject to observer variability. This paper presents an automated method for classifying the intervention response from longitudinal MRI scans, developed to predict tumor response during therapy as part of the BraTS 2025 challenge. We propose a novel hybrid framework that combines deep learning derived feature extraction and an extensive set of radiomics and clinically chosen features. Our approach utilizes a fine-tuned ResNet-18 model to extract features from 2D regions of interest across four MRI modalities. These deep features are then fused with a rich set of more than 4800 radiomic and clinically driven features, including 3D radiomics of tumor growth and shrinkage masks, volumetric changes relative to the nadir, and tumor centroid shift. Using the fused feature set, a CatBoost classifier achieves a mean ROC AUC of 0.81 and a Macro F1 score of 0.50 in the 4-class response prediction task (Complete Response, Partial Response, Stable Disease, Progressive Disease). Our results highlight that synergizing learned image representations with domain-targeted radiomic features provides a robust and effective solution for automated treatment response assessment in neuro-oncology.
对胶质母细胞瘤治疗反应的准确评估对于临床决策和患者管理至关重要。神经肿瘤学反应评估(RANO)标准提供了一个标准化的框架来评估患者的临床反应,但其在应用过程中可能较为复杂且存在观察者间的差异。本文介绍了一种自动分类干预反应的方法,该方法基于纵向MRI扫描开发,旨在作为BraTS 2025挑战赛的一部分来预测治疗过程中的肿瘤反应。我们提出了一种新型混合框架,结合了深度学习特征提取和一组丰富的放射学及临床选择特征。我们的方法利用经过微调后的ResNet-18模型来从四种MRI模式的2D感兴趣区域中提取特征。这些深度特征然后与超过4800个放射学及临床驱动特征集融合,包括肿瘤的3D放射学增长和萎缩掩模、相对于最低点的体积变化以及肿瘤质心位移。使用融合特征集,CatBoost分类器在4类反应预测任务中实现了平均ROC AUC为0.81和宏观F1分数为0.50(完全反应、部分反应、稳定性疾病、进展性疾病)。我们的结果强调,将学习到的图像表示与针对特定领域的放射学特征相结合,为神经肿瘤学中自动治疗反应评估提供了稳健有效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the BraTS-Lighthouse 2025 Challenge (MICCAI 2025)
Summary
本研究提出了一种结合深度学习特征提取和大量放射学及临床特征的混合框架,用于自动分类胶质母细胞瘤对治疗的反应。该研究利用精细调整的ResNet-18模型从MRI的四种模态中提取特征,并与超过4800个放射学及临床特征融合。融合特征集通过CatBoost分类器实现平均ROC AUC为0.81和宏观F1分数为0.50的4类反应预测任务。研究结果表明,将学习到的图像表示与针对领域的放射学特征相结合,为神经肿瘤学中的自动治疗反应评估提供了稳健有效的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 临床决策和患者管理中,准确评估胶质母细胞瘤对治疗的反应至关重要。
- RANO标准提供了一个评估患者临床反应的标准化框架,但其应用复杂且存在观察者差异。
- 研究提出了一种混合框架,结合深度学习特征提取和大量放射学及临床特征进行自动分类。
- 利用ResNet-18模型从MRI的四种模态中提取特征。
- 特征集融合了超过4800个放射学及临床特征,包括肿瘤生长和萎缩掩模的3D放射学特征、相对于最低点的体积变化和肿瘤质心偏移等。
- CatBoost分类器在4类反应预测任务中取得了良好的性能,平均ROC AUC为0.81,宏观F1分数为0.50。
点此查看论文截图

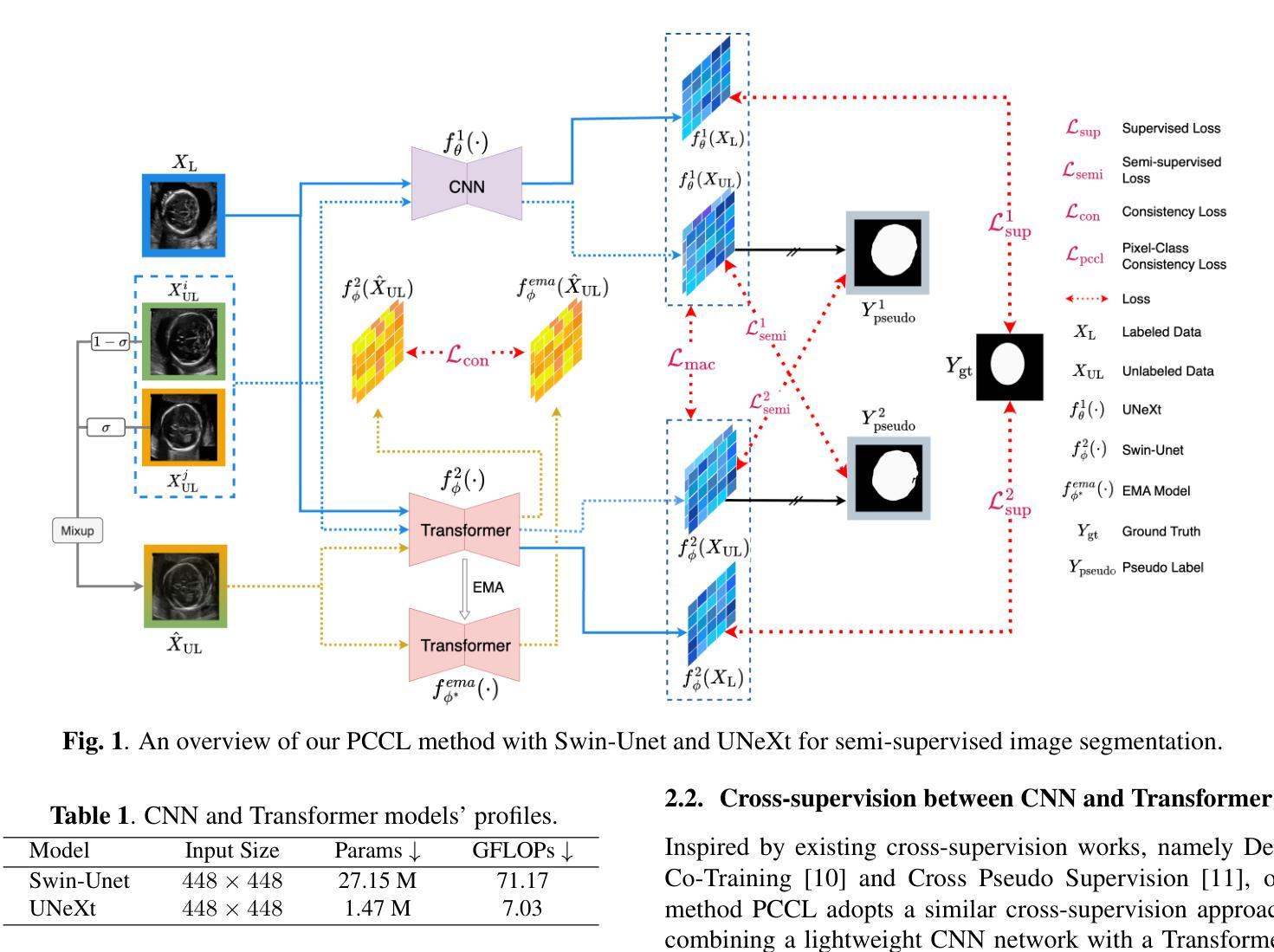
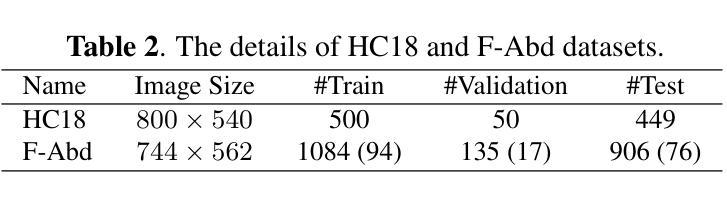
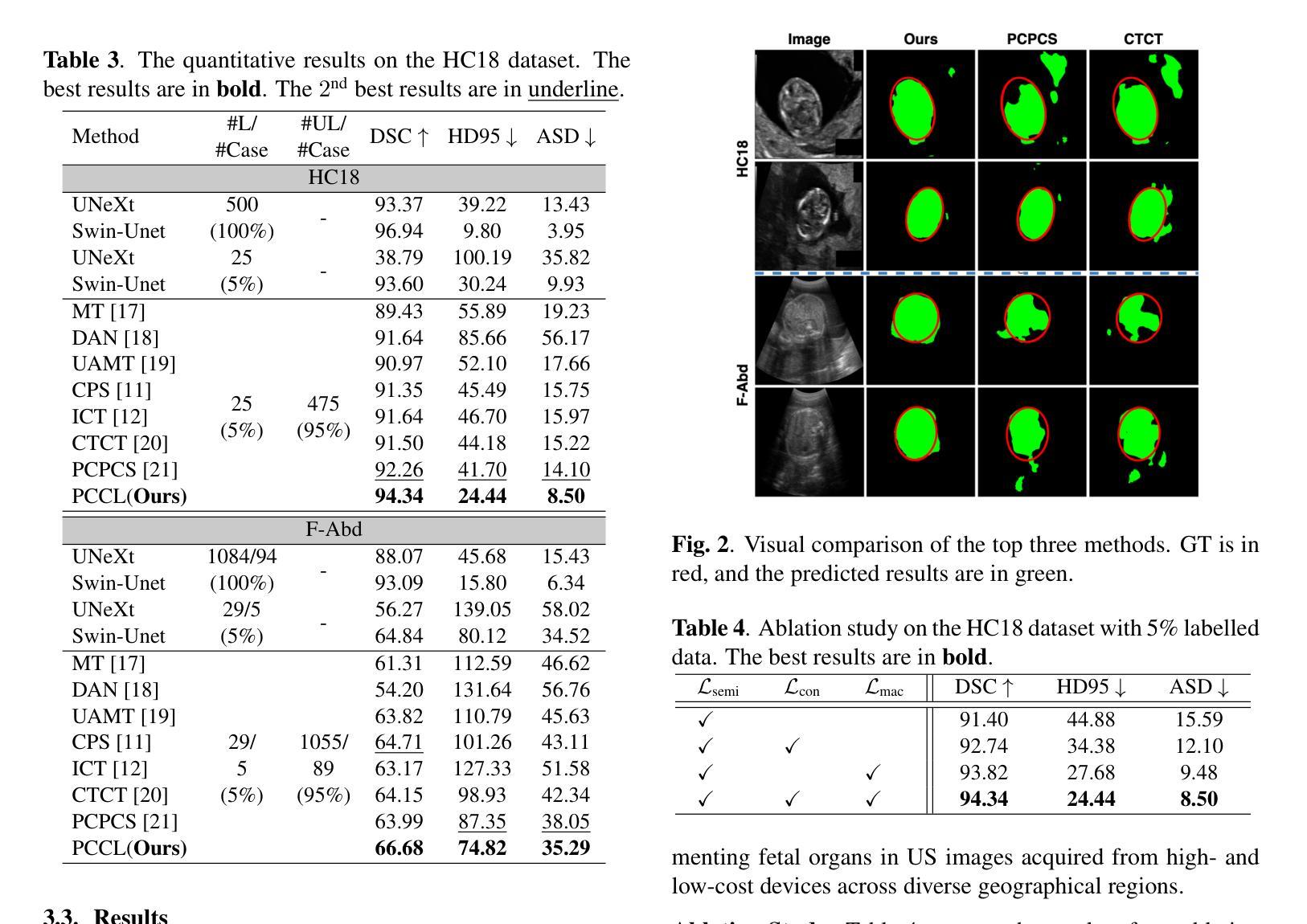
Leveraging Information Divergence for Robust Semi-Supervised Fetal Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Authors:Fangyijie Wang, Guénolé Silvestre, Kathleen M. Curran
Maternal-fetal Ultrasound is the primary modality for monitoring fetal development, yet automated segmentation remains challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality annotations. To address this limitation, we propose a semi-supervised learning framework that leverages information divergence for robust fetal ultrasound segmentation. Our method employs a lightweight convolutional network (1.47M parameters) and a Transformer-based network, trained jointly with labelled data through standard supervision and with unlabelled data via cross-supervision. To encourage consistent and confident predictions, we introduce an information divergence loss that combines per-pixel Kullback-Leibler divergence and Mutual Information Gap, effectively reducing prediction disagreement between the two models. In addition, we apply mixup on unlabelled samples to further enhance robustness. Experiments on two fetal ultrasound datasets demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms seven state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods. When only 5% of training data is labelled, our framework improves the Dice score by 2.39%, reduces the 95% Hausdorff distance by 14.90, and decreases the Average Surface Distance by 4.18. These results highlight the effectiveness of leveraging information divergence for annotation-efficient and robust medical image segmentation. Our code is publicly available on GitHub.
母体胎儿超声波是监测胎儿发育的主要方式,但由于高质量标注的缺乏,自动化分割仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种利用信息散度进行稳健的胎儿超声分割的半监督学习框架。我们的方法采用了一个轻量级的卷积网络(147万个参数)和一个基于Transformer的网络,通过标准监督与标记数据联合训练,并通过互监督的方式与未标记数据训练。为了鼓励一致和自信的预测,我们引入了一种信息散度损失,它将像素级的Kullback-Leibler散度和互信息差距相结合,有效地减少了两个模型之间的预测分歧。此外,我们对未标记样本应用了mixup,以进一步增强稳健性。在两个胎儿超声数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法一直优于七种最先进的半监督方法。当只有5%的训练数据被标记时,我们的框架提高了Dice得分2.39%,将95%的Hausdorff距离减少了14.90%,并降低了平均表面距离4.18%。这些结果突出了利用信息散度进行标注有效和稳健医学图像分割的有效性。我们的代码已在GitHub上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本提出了一种基于信息散度的半监督学习框架,用于稳健的胎儿超声分割。该方法结合了轻量级卷积网络和基于Transformer的网络,通过标准监督训练标签数据,并通过交叉监督训练未标记数据。引入信息散度损失鼓励一致和可靠的预测,并有效减少模型之间的预测分歧。在胎儿超声数据集上的实验表明,该方法在仅使用5%的训练数据标注时,相较于其他七种先进的半监督方法表现出优越性能。此框架提高了Dice得分,减少了Hausdorff距离和平均表面距离,证明了其在医学图像分割中的标注效率和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种半监督学习框架,用于胎儿超声图像的自动化分割。
- 结合轻量级卷积网络和基于Transformer的网络进行训练。
- 通过标准监督和交叉监督方式训练数据和未标记数据。
- 引入信息散度损失以减少模型间的预测分歧。
- 在胎儿超声数据集上进行了实验验证,显示优越性能。
- 在仅使用少量标注数据时,该方法依然表现出良好效果。
- 公开代码并已在GitHub上提供。
点此查看论文截图

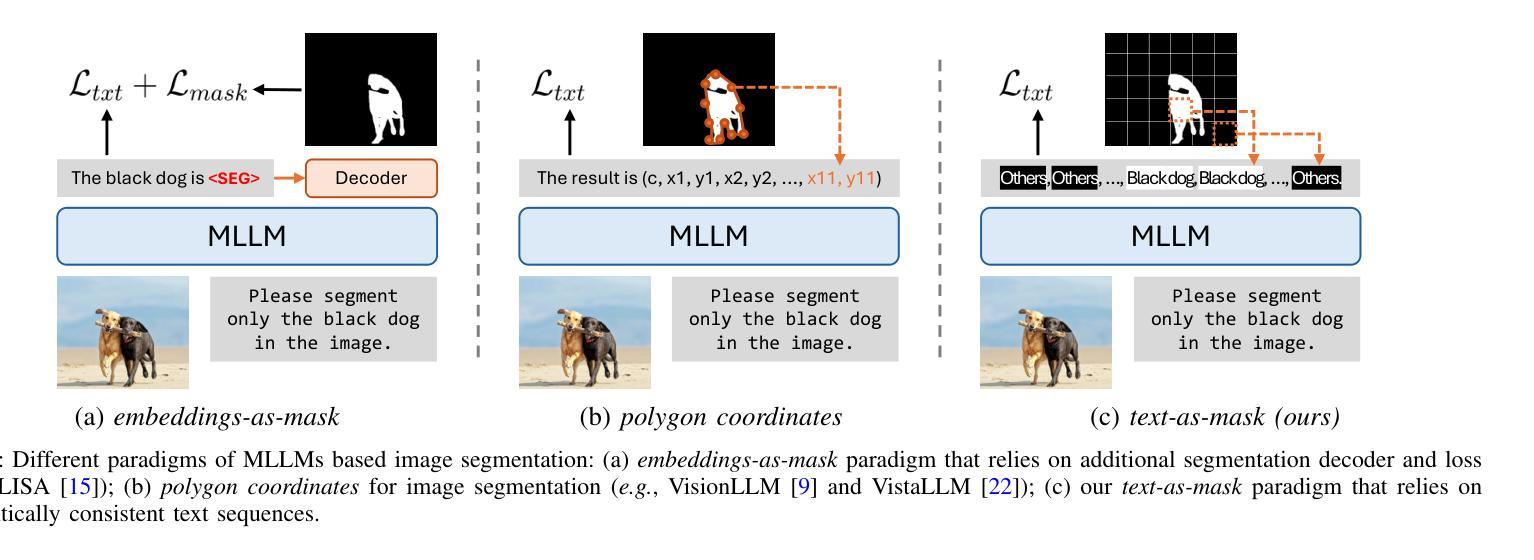
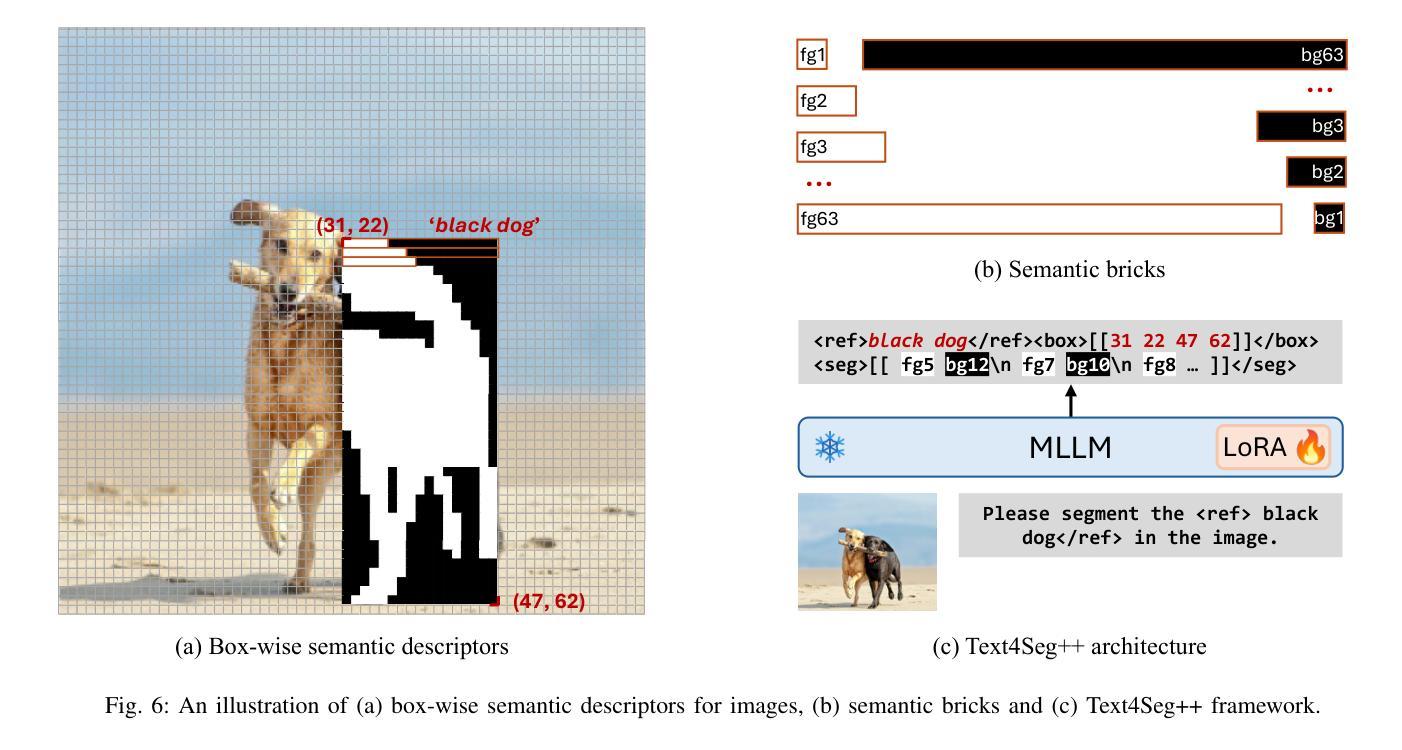
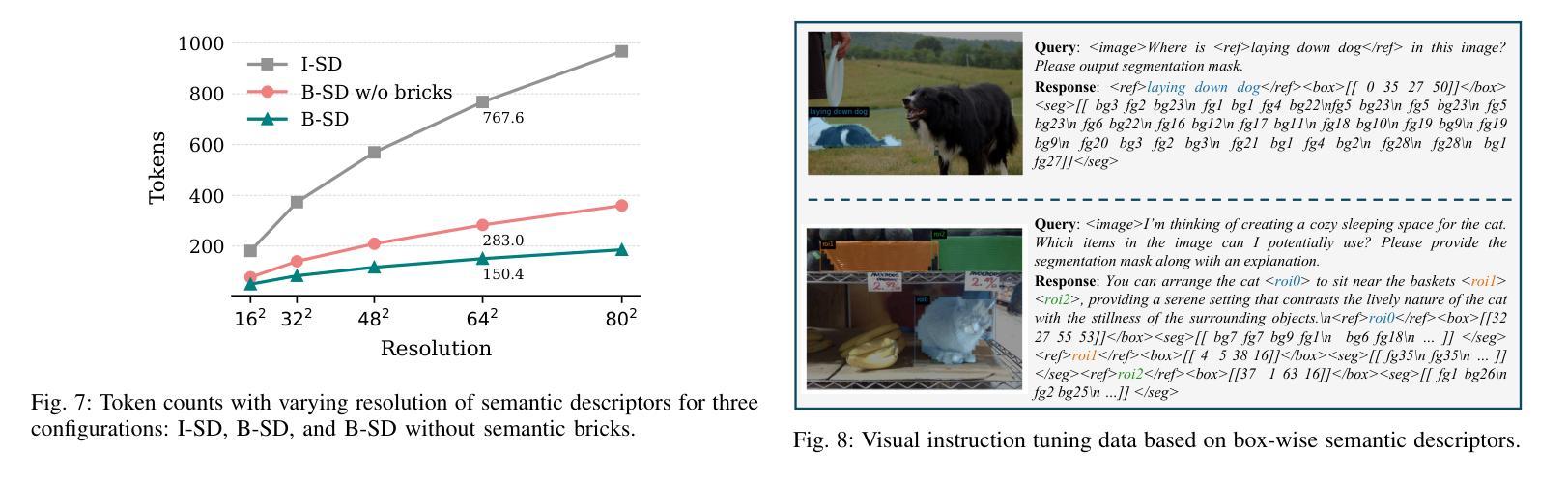
Text4Seg++: Advancing Image Segmentation via Generative Language Modeling
Authors:Mengcheng Lan, Chaofeng Chen, Jiaxing Xu, Zongrui Li, Yiping Ke, Xudong Jiang, Yingchen Yu, Yunqing Zhao, Song Bai
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown exceptional capabilities in vision-language tasks. However, effectively integrating image segmentation into these models remains a significant challenge. In this work, we propose a novel text-as-mask paradigm that casts image segmentation as a text generation problem, eliminating the need for additional decoders and significantly simplifying the segmentation process. Our key innovation is semantic descriptors, a new textual representation of segmentation masks where each image patch is mapped to its corresponding text label. We first introduce image-wise semantic descriptors, a patch-aligned textual representation of segmentation masks that integrates naturally into the language modeling pipeline. To enhance efficiency, we introduce the Row-wise Run-Length Encoding (R-RLE), which compresses redundant text sequences, reducing the length of semantic descriptors by 74% and accelerating inference by $3\times$, without compromising performance. Building upon this, our initial framework Text4Seg achieves strong segmentation performance across a wide range of vision tasks. To further improve granularity and compactness, we propose box-wise semantic descriptors, which localizes regions of interest using bounding boxes and represents region masks via structured mask tokens called semantic bricks. This leads to our refined model, Text4Seg++, which formulates segmentation as a next-brick prediction task, combining precision, scalability, and generative efficiency. Comprehensive experiments on natural and remote sensing datasets show that Text4Seg++ consistently outperforms state-of-the-art models across diverse benchmarks without any task-specific fine-tuning, while remaining compatible with existing MLLM backbones. Our work highlights the effectiveness, scalability, and generalizability of text-driven image segmentation within the MLLM framework.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉语言任务中表现出了卓越的能力。然而,有效地将图像分割集成到这些模型中仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的文本遮罩范式,将图像分割视为文本生成问题,无需额外的解码器,并显著简化了分割过程。我们的关键创新之处在于语义描述符,这是分割遮罩的一种新文本表示,其中每个图像块都映射到其相应的文本标签。我们首先引入图像级语义描述符,这是分割遮罩的块对齐文本表示,自然地融入语言建模流程。为了提高效率,我们引入了行运行长度编码(R-RLE),它压缩了冗余的文本序列,在不影响性能的情况下,将语义描述符的长度减少了74%,并将推理速度提高了3倍。在此基础上,我们最初的框架Text4Seg在广泛的视觉任务中实现了强大的分割性能。为了进一步提高颗粒度和紧凑性,我们提出了框级语义描述符,其使用边界框定位感兴趣区域,并通过称为语义砖的结构化遮罩令牌表示区域遮罩。这导致了我们改进后的模型Text4Seg++,它将分割制定为下一个砖块预测任务,结合了精度、可扩展性和生成效率。在天然和遥感数据集上的综合实验表明,Text4Seg++在多种基准测试中始终优于最新模型,且无需任何特定任务的微调,同时与现有的MLLM骨干网兼容。我们的工作突出了MLLM框架内文本驱动图像分割的有效性和可扩展性以及普遍性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Extended version of our conference paper arXiv:2410.09855
Summary
本文提出了一种新的文本驱动图像分割方法,将图像分割转化为文本生成问题,通过语义描述符实现文本与图像的映射。引入图像级语义描述符和行级运行长度编码(R-RLE)提高效率,构建初始框架Text4Seg。为进一步提高精度和效率,提出盒级语义描述符,实现区域掩膜的表示和结构化掩码的令牌化。改进后的模型Text4Seg++在多种视觉任务上表现优异,无需特定任务的微调,并在自然和遥感数据集上优于最新模型。该研究展示了文本驱动图像分割在大型多模态语言模型(MLLM)框架中的有效性、可扩展性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的文本驱动图像分割方法,将图像分割转化为文本生成问题。
- 引入了语义描述符,实现了文本与图像的映射。
- 通过图像级语义描述符和行级运行长度编码(R-RLE)提高了效率。
- 初始框架Text4Seg在多种视觉任务上表现优异。
- 为进一步提高精度和效率,提出了盒级语义描述符和语义砖的概念。
- 改进后的模型Text4Seg++在多种数据集上表现优于最新模型,无需特定任务微调。
点此查看论文截图


Reasoning Language Model for Personalized Lung Cancer Screening
Authors:Chuang Niu, Ge Wang
Accurate risk assessment in lung cancer screening is critical for enabling early cancer detection and minimizing unnecessary invasive procedures. The Lung CT Screening Reporting and Data System (Lung-RADS) has been widely used as the standard framework for patient management and follow-up. Nevertheless, Lung-RADS faces trade-offs between sensitivity and specificity, as it stratifies risk solely based on lung nodule characteristics without incorporating various risk factors. Here we propose a reasoning language model (RLM) to integrate radiology findings with longitudinal medical records for individualized lung cancer risk assessment. Through a systematic study including dataset construction and distillation, supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning, and comprehensive evaluation, our model makes significant improvements in risk prediction performance on datasets in the national lung screening trial. Notably, RLM can decompose the risk evaluation task into sub-components, analyze the contributions of diverse risk factors, and synthesize them into a final risk score computed using our data-driven system equation. Our approach improves both predictive accuracy and monitorability through the chain of thought reasoning process, thereby facilitating clinical translation into lung cancer screening.
在肺癌筛查中进行准确的风险评估对于实现早期癌症检测并尽量减少不必要的侵入性程序至关重要。肺部CT筛查报告和数据系统(Lung-RADS)已广泛应用于患者管理和随访的标准框架。然而,Lung-RADS在灵敏度和特异度之间存在权衡,因为它仅仅基于肺结节特征进行风险分层,而没有纳入各种风险因素。在这里,我们提出了一种推理语言模型(RLM),以整合放射学检查结果与纵向医疗记录,进行个性化的肺癌风险评估。通过包括数据集构建和蒸馏、监督微调、强化学习和综合评估的系统研究,我们的模型在国家肺部筛查试验的数据集上风险预测性能得到了显著提高。值得注意的是,RLM可以将风险评估任务分解为子组件,分析各种风险因素的贡献,并使用我们的数据驱动系统方程将其合并成最终风险分数。我们的方法通过思维推理过程提高了预测精度和可监控性,从而促进了临床应用于肺癌筛查的转化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
肺癌筛查中准确的风险评估对于实现早期癌症检测并最小化不必要的侵入性程序至关重要。本文提出一种融合放射学检查结果与纵向医疗记录的推理语言模型(RLM),用于个性化肺癌风险评估。该模型通过数据集构建、蒸馏、监督微调、强化学习和综合评价的系统性研究,在国家级肺癌筛查试验数据集上显著提高风险预测性能。RLM能分解风险评估任务,分析各种风险因素的贡献,并通过数据驱动的系统方程合成最终风险分数,提高预测精度和监控能力,有助于临床应用于肺癌筛查。
Key Takeaways
- 肺癌筛查中的风险评估对于早期癌症检测和减少不必要的侵入性程序至关重要。
- Lung-RADS作为患者管理和随访的标准框架,但在风险评估方面存在灵敏度和特异度的权衡。
- 提出了融合放射学检查结果与纵向医疗记录的推理语言模型(RLM)进行个性化肺癌风险评估。
- RLM通过分解风险评估任务,分析多种风险因素,并通过数据驱动的系统方程合成最终风险分数。
- RLM在国家级肺癌筛查试验数据集上显著提高风险预测性能。
- RLM能提高预测精度和监控能力,有助于临床应用于肺癌筛查。
点此查看论文截图

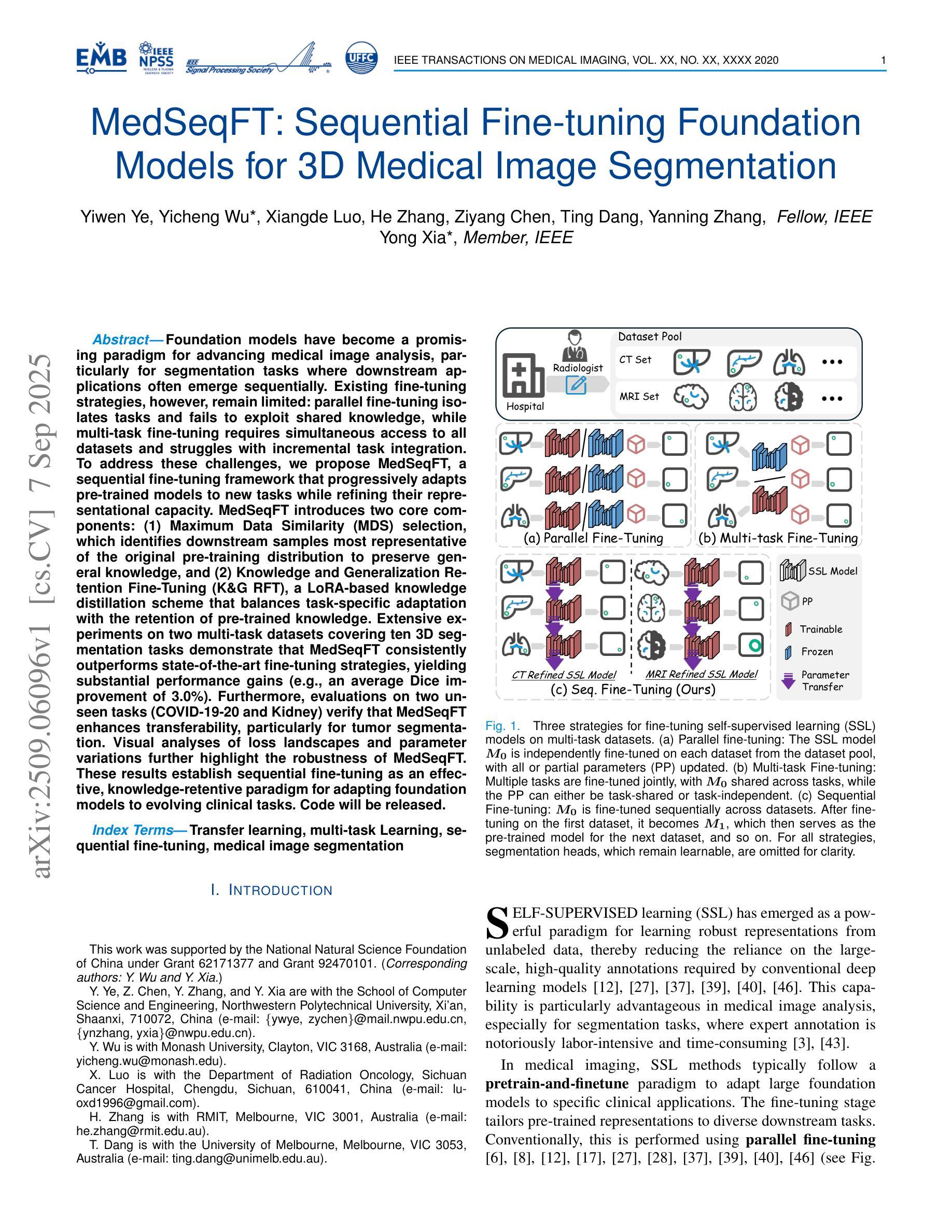
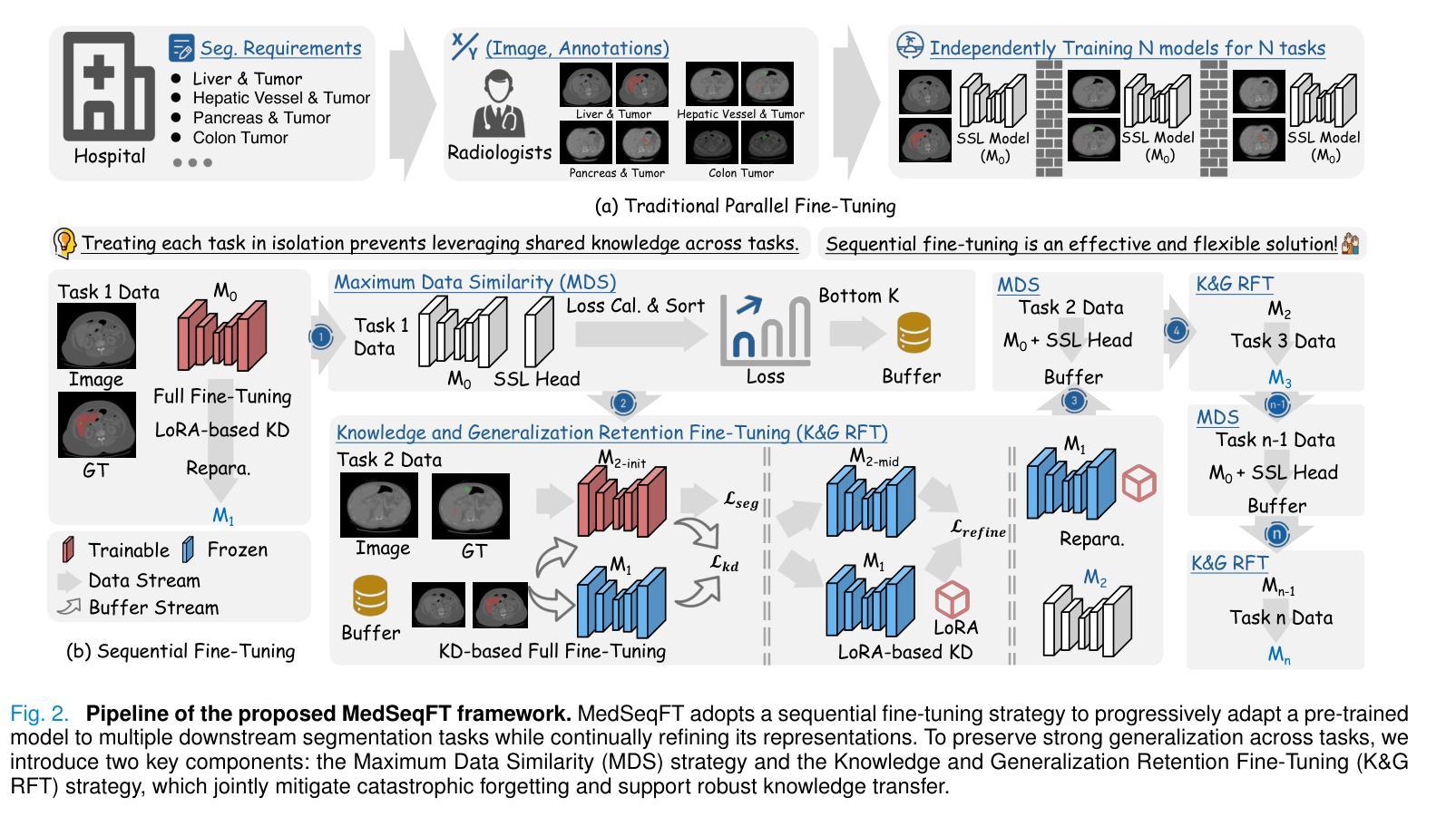
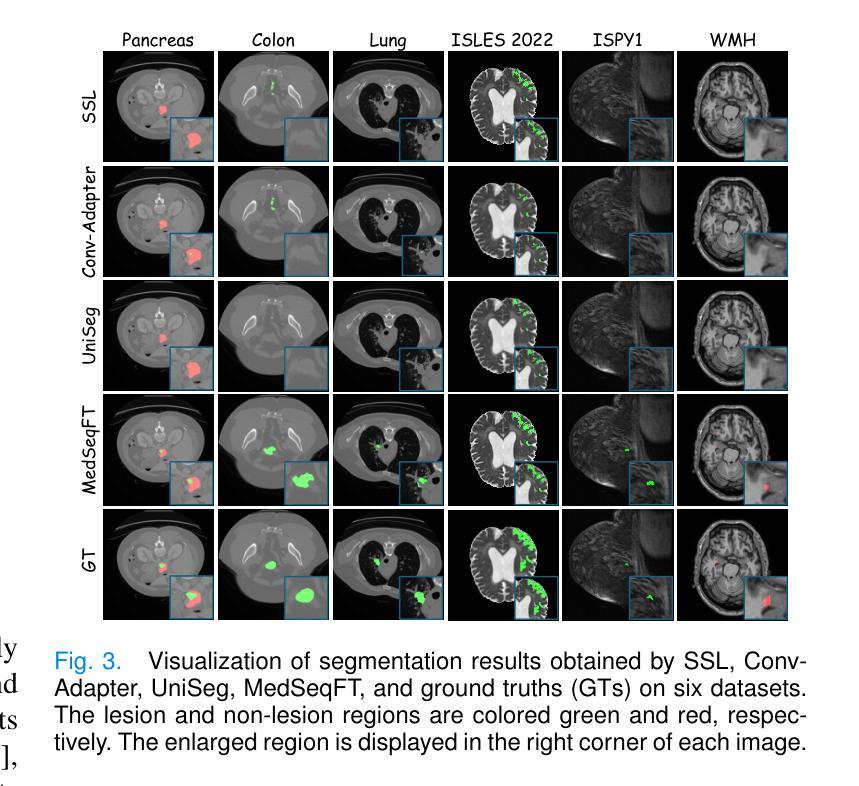
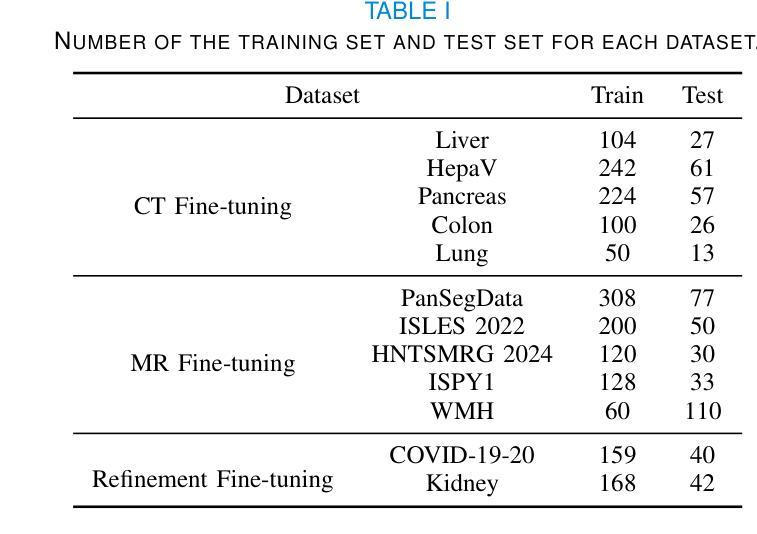
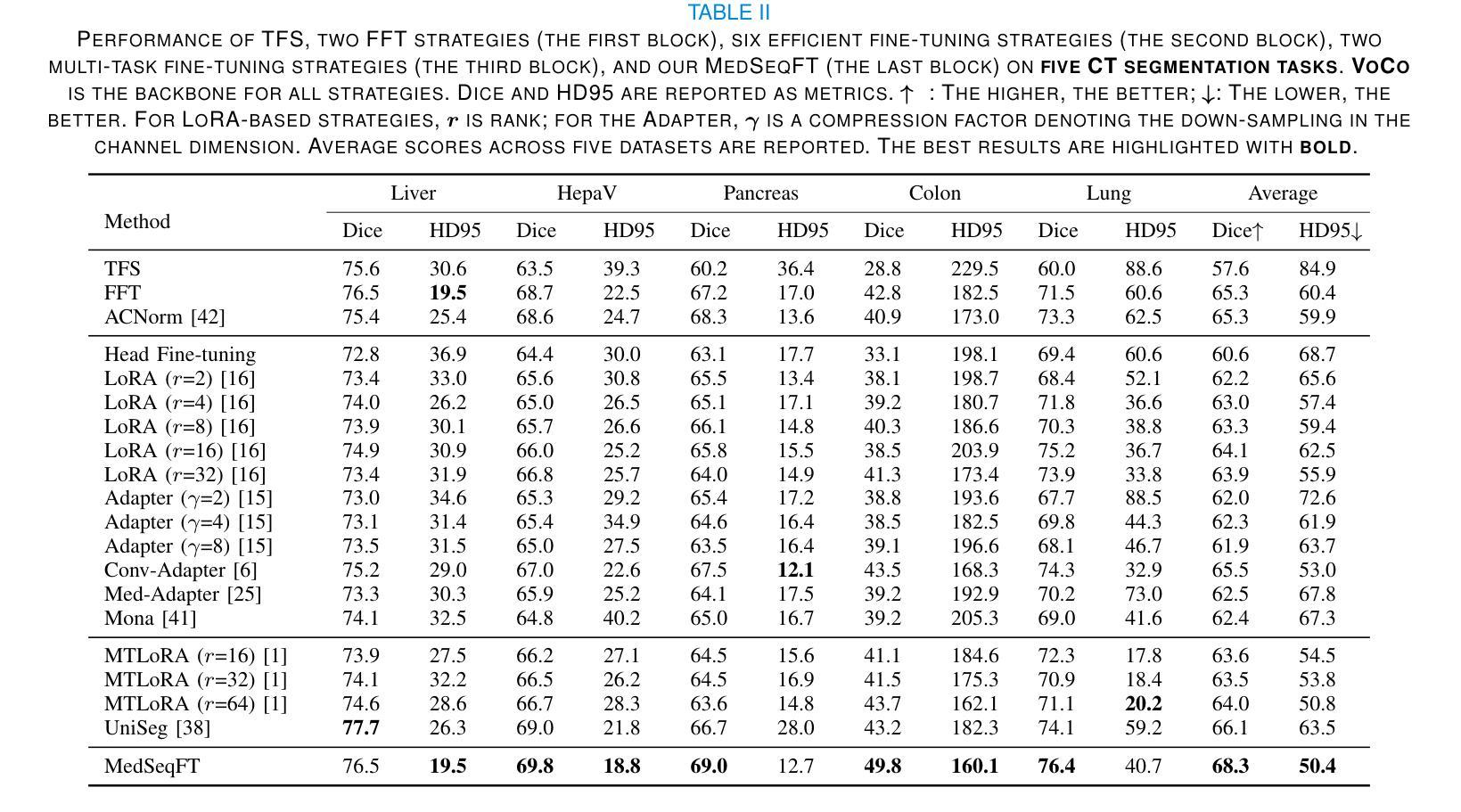
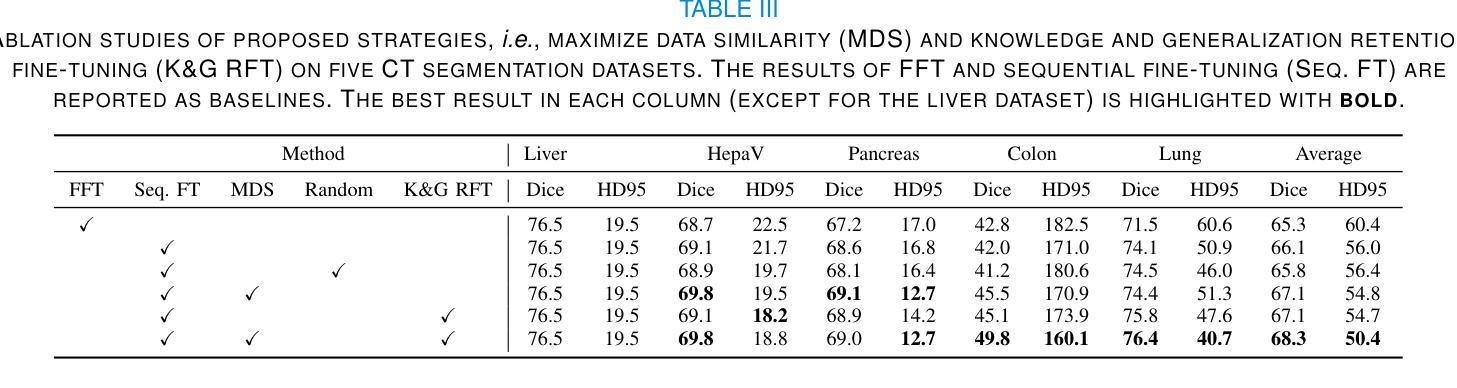
MedSeqFT: Sequential Fine-tuning Foundation Models for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yiwen Ye, Yicheng Wu, Xiangde Luo, He Zhang, Ziyang Chen, Ting Dang, Yanning Zhang, Yong Xia
Foundation models have become a promising paradigm for advancing medical image analysis, particularly for segmentation tasks where downstream applications often emerge sequentially. Existing fine-tuning strategies, however, remain limited: parallel fine-tuning isolates tasks and fails to exploit shared knowledge, while multi-task fine-tuning requires simultaneous access to all datasets and struggles with incremental task integration. To address these challenges, we propose MedSeqFT, a sequential fine-tuning framework that progressively adapts pre-trained models to new tasks while refining their representational capacity. MedSeqFT introduces two core components: (1) Maximum Data Similarity (MDS) selection, which identifies downstream samples most representative of the original pre-training distribution to preserve general knowledge, and (2) Knowledge and Generalization Retention Fine-Tuning (K&G RFT), a LoRA-based knowledge distillation scheme that balances task-specific adaptation with the retention of pre-trained knowledge. Extensive experiments on two multi-task datasets covering ten 3D segmentation tasks demonstrate that MedSeqFT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art fine-tuning strategies, yielding substantial performance gains (e.g., an average Dice improvement of 3.0%). Furthermore, evaluations on two unseen tasks (COVID-19-20 and Kidney) verify that MedSeqFT enhances transferability, particularly for tumor segmentation. Visual analyses of loss landscapes and parameter variations further highlight the robustness of MedSeqFT. These results establish sequential fine-tuning as an effective, knowledge-retentive paradigm for adapting foundation models to evolving clinical tasks. Code will be released.
医学图像分析中的基础模型已经成为一个前景光明的模式,特别是对于经常依次出现下游应用的分割任务。然而,现有的微调策略仍然存在局限性:并行微调隔离任务并且无法利用共享知识,而多任务微调需要同时访问所有数据集并且难以进行增量任务集成。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了MedSeqFT,这是一个顺序微调框架,可以逐步适应预训练模型以应对新任务,同时提高其代表性能力。MedSeqFT引入了两个核心组件:(1)最大数据相似性(MDS)选择,它确定了最能代表原始预训练分布的下游样本,以保留一般知识;(2)知识与泛化保留微调(K&G RFT),这是一种基于LoRA的知识蒸馏方案,平衡了针对任务的适应性和保留预训练知识。在两个多任务数据集上的广泛实验涵盖了十个3D分割任务,证明MedSeqFT始终优于最先进的微调策略,产生了实质性的性能提升(例如,平均Dice系数提高了3.0%)。此外,在两个未见任务(COVID-19-20和肾脏)上的评估证实,MedSeqFT提高了可迁移性,特别是对于肿瘤分割。损失景观和参数变化的视觉分析进一步突出了MedSeqFT的稳健性。这些结果证明了顺序微调是一种有效且知识保留性强的模式,适用于将基础模型适应于不断发展的临床任务。代码将发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures
摘要
医学图像分析领域,采用基础模型(foundation models)进行研究的现状及其面临的挑战。针对现有微调策略(fine-tuning)的局限性,提出MedSeqFT框架。该框架包含两大核心组件:最大数据相似性(MDS)选择和知识及泛化能力保留微调(K&G RFT)。MedSeqFT可实现基础模型的渐进适应,并保持预训练知识的一般性。通过实验证明其有效性。MedSeqFT相对于当前主流的微调策略具有明显的优势,实现了巨大的性能提升(例如平均Dice系数提高3.0%)。对两个未见任务(COVID-19-20和肾脏分割)的评估也验证了其强大的迁移能力。代码即将发布。该摘要简明扼要地总结了文本的核心内容。
关键见解
- 基础模型已成为推动医学图像分析进步的有望范式,特别是在分割任务中,下游应用常常陆续出现。
- 现有微调策略存在局限性:平行微调孤立任务且未能充分利用共享知识,多任务微调则需要同时访问所有数据集并在集成新增任务时面临困难。
- MedSeqFT框架旨在解决这些挑战,通过渐进适应新任务并完善其表征能力来优化预训练模型。框架包含两大核心组件:最大数据相似性选择和知识及泛化能力保留微调。
- 实验证明MedSeqFT在多任务数据集上的表现优于现有微调策略,实现显著性能提升(如平均Dice系数提高3.0%)。
点此查看论文截图
High-Quality Tomographic Image Reconstruction Integrating Neural Networks and Mathematical Optimization
Authors:Anuraag Mishra, Andrea Gilch, Benjamin Apeleo Zubiri, Jan Rolfes, Frauke Liers
In this work, we develop a novel technique for reconstructing images from projection-based nano- and microtomography. Our contribution focuses on enhancing reconstruction quality, particularly for specimen composed of homogeneous material phases connected by sharp edges. This is accomplished by training a neural network to identify edges within subpictures. The trained network is then integrated into a mathematical optimization model, to reduce artifacts from previous reconstructions. To this end, the optimization approach favors solutions according to the learned predictions, however may also determine alternative solutions if these are strongly supported by the raw data. Hence, our technique successfully incorporates knowledge about the homogeneity and presence of sharp edges in the sample and thereby eliminates blurriness. Our results on experimental datasets show significant enhancements in interface sharpness and material homogeneity compared to benchmark algorithms. Thus, our technique produces high-quality reconstructions, showcasing its potential for advancing tomographic imaging techniques.
在这项工作中,我们开发了一种基于投影纳米和显微层析成像重建图像的新技术。我们的贡献主要集中在提高重建质量,特别是对于由锐利边缘连接而成的均匀材料相组成的样本。这是通过训练神经网络来识别子图像中的边缘来实现的。然后,将训练好的网络集成到数学优化模型中,以减少先前重建产生的伪影。为此,优化方法会根据学习到的预测来选择解决方案,但如果这些预测得到原始数据的强烈支持,也可能会确定其他解决方案。因此,我们的技术成功地将样本中的均匀性和锐利边缘的知识纳入其中,从而消除了模糊性。我们在实验数据集上的结果显示,与基准算法相比,界面清晰度和材料均匀性有了显著的提高。因此,我们的技术产生了高质量的重建图像,展示了其在推进层析成像技术方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36 pages, 17 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于投影纳米和微层析成像技术的新型图像重建技术。该技术旨在提高重建质量,特别是对于由均匀材料相通过锐边连接组成的样本。通过训练神经网络来识别子图像中的边缘,并将其集成到数学优化模型中,以减少先前重建中的伪影。优化方法根据学习预测选择解决方案,但如果原始数据强烈支持,也可能会确定其他解决方案。因此,该技术成功结合了样本的均质性和锐边存在知识,消除了模糊性。对实验数据集的结果显示,与基准算法相比,界面清晰度和材料均质性有了显著提高。因此,该技术产生高质量的重建图像,展示了其在推进层析成像技术方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 开发了基于投影纳米和微层析成像的新型图像重建技术。
- 技术重点在于提高重建质量,特别是针对由均匀材料相和锐边组成的样本。
- 通过训练神经网络识别子图像中的边缘,集成到数学优化模型中。
- 优化模型能减少伪影,并根据学习预测选择解决方案。
- 技术结合了样本的均质性和锐边存在的知识,消除了图像模糊。
- 实验数据集结果显示,与基准算法相比,界面清晰度和材料均质性有显著改善。
点此查看论文截图

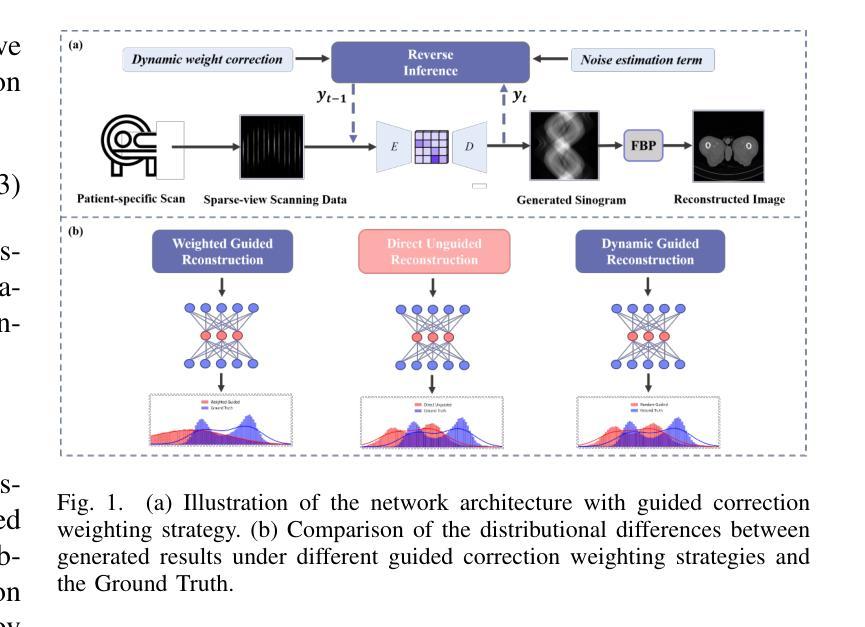
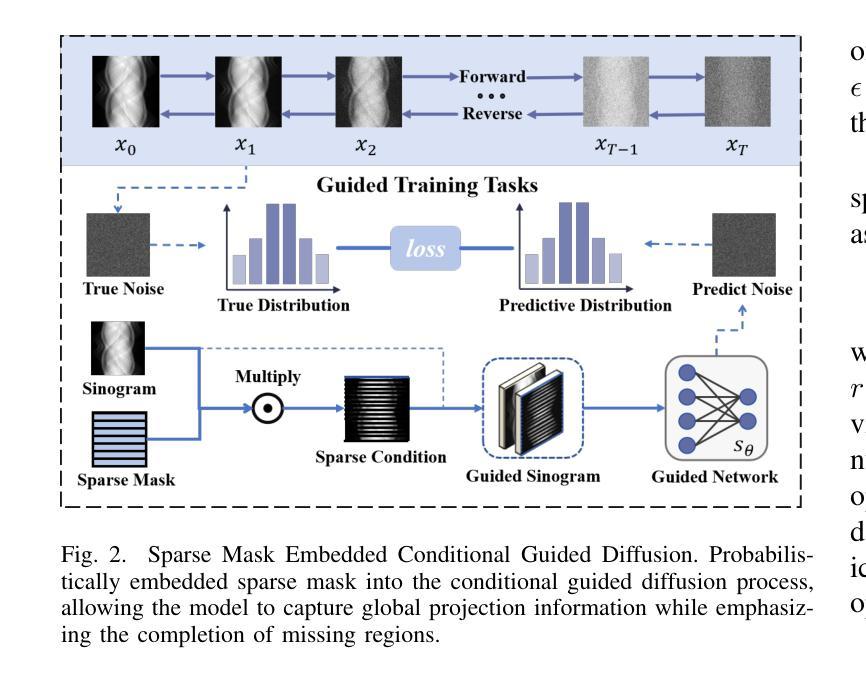
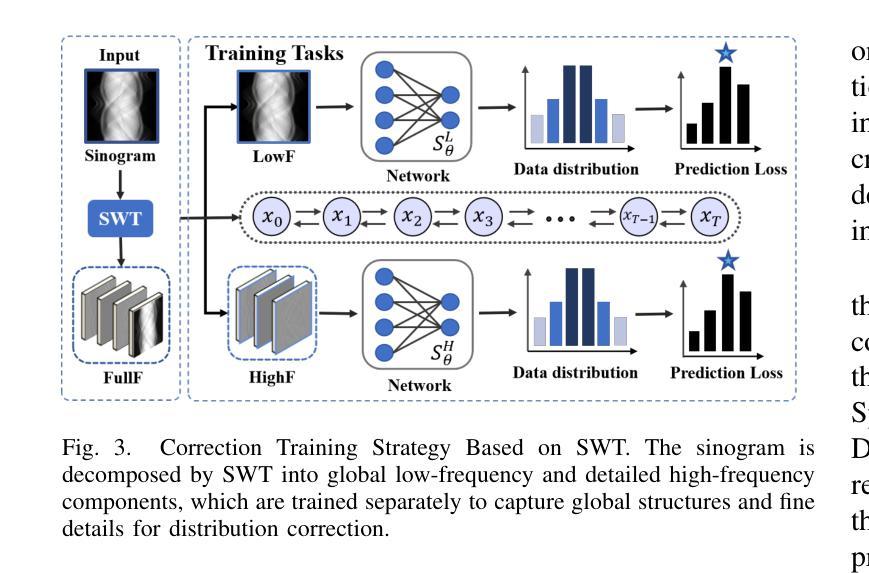
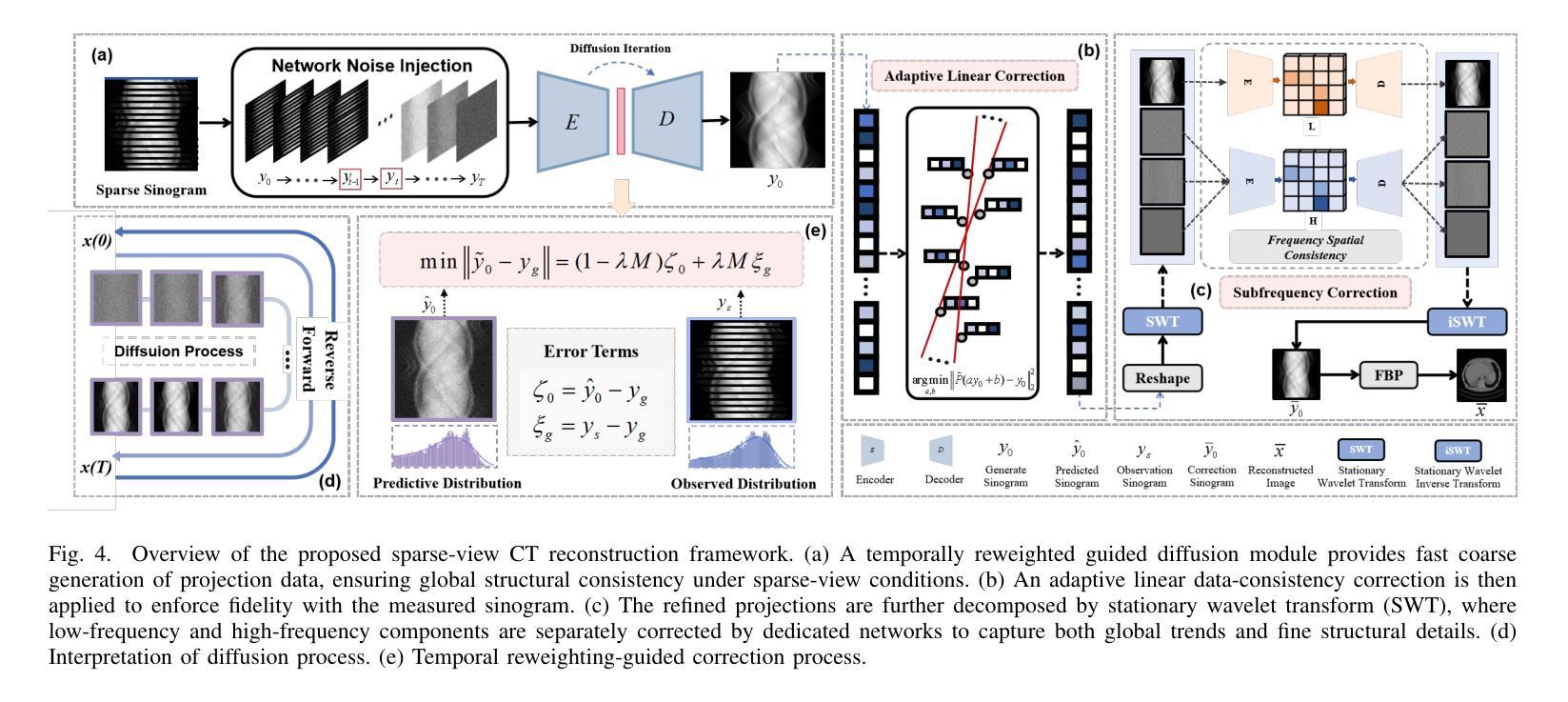
Multi-Strategy Guided Diffusion via Sparse Masking Temporal Reweighting Distribution Correction
Authors:Zekun Zhou, Yanru Gong, Liu Shi, Qiegen Liu
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable generative capabilities in image processing tasks. We propose a Sparse condition Temporal Rewighted Integrated Distribution Estimation guided diffusion model (STRIDE) for sparse-view CT reconstruction. Specifically, we design a joint training mechanism guided by sparse conditional probabilities to facilitate the model effective learning of missing projection view completion and global information modeling. Based on systematic theoretical analysis, we propose a temporally varying sparse condition reweighting guidance strategy to dynamically adjusts weights during the progressive denoising process from pure noise to the real image, enabling the model to progressively perceive sparse-view information. The linear regression is employed to correct distributional shifts between known and generated data, mitigating inconsistencies arising during the guidance process. Furthermore, we construct a dual-network parallel architecture to perform global correction and optimization across multiple sub-frequency components, thereby effectively improving the model capability in both detail restoration and structural preservation, ultimately achieving high-quality image reconstruction. Experimental results on both public and real datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves the best improvement of 2.58 dB in PSNR, increase of 2.37% in SSIM, and reduction of 0.236 in MSE compared to the best-performing baseline methods. The reconstructed images exhibit excellent generalization and robustness in terms of structural consistency, detail restoration, and artifact suppression.
扩散模型在图像处理任务中显示出显著的生成能力。我们提出了一种用于稀疏视图CT重建的稀疏条件时间加权积分分布估计引导扩散模型(STRIDE)。具体来说,我们设计了一种由稀疏条件概率引导的联合训练机制,以促进模型有效地学习缺失投影视图补全和全局信息建模。基于系统的理论分析,我们提出了一种时间变化的稀疏条件重加权指导策略,在从纯噪声到真实图像的渐进去噪过程中动态调整权重,使模型能够逐步感知稀疏视图信息。采用线性回归来校正已知数据和生成数据之间的分布偏移,减轻指导过程中产生的不一致性。此外,我们构建了一个双网络并行架构,以在多个子频率分量上执行全局校正和优化,从而有效地提高了模型在细节恢复和结构保持方面的能力,最终实现了高质量图像重建。在公共和真实数据集上的实验结果都表明,所提方法较最佳基线方法在PSNR上提高了2.58分贝,SSIM提高了2.37%,MSE降低了0.236。重建的图像在结构一致性、细节恢复和伪影抑制方面表现出良好的泛化和鲁棒性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于稀疏条件时序加权集成分布估计引导的扩散模型(STRIDE),用于稀疏视图CT重建。该模型通过联合训练机制学习缺失投影视图的补全和全局信息建模,并引入时序变化的稀疏条件重加权指导策略,在渐进去噪过程中动态调整权重。同时,采用线性回归校正已知和生成数据之间的分布偏移,构建双网络并行架构进行全局校正和优化,提高模型在细节恢复和结构保持方面的能力,实现高质量图像重建。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于稀疏条件时序重加权的扩散模型(STRIDE)用于稀疏视图CT重建。
- 通过联合训练机制学习缺失投影视图的补全和全局信息建模。
- 引入时序变化的稀疏条件重加权指导策略,在渐进去噪过程中动态调整权重。
- 采用线性回归校正分布偏移,提高模型指导过程的准确性。
- 构建双网络并行架构,进行全局校正和优化,提高细节恢复和结构保持能力。
- 实验结果在公共和真实数据集上均显示出所提方法的有效性,与最佳基线方法相比,PSNR提高2.58 dB,SSIM增加2.37%,MSE降低0.236。
点此查看论文截图

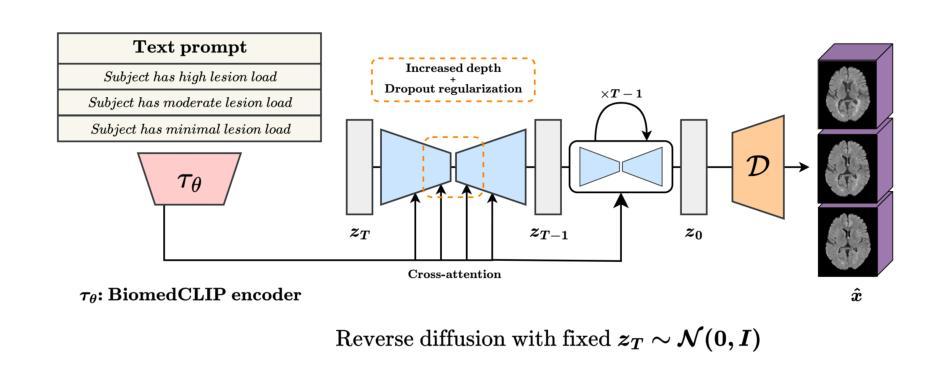
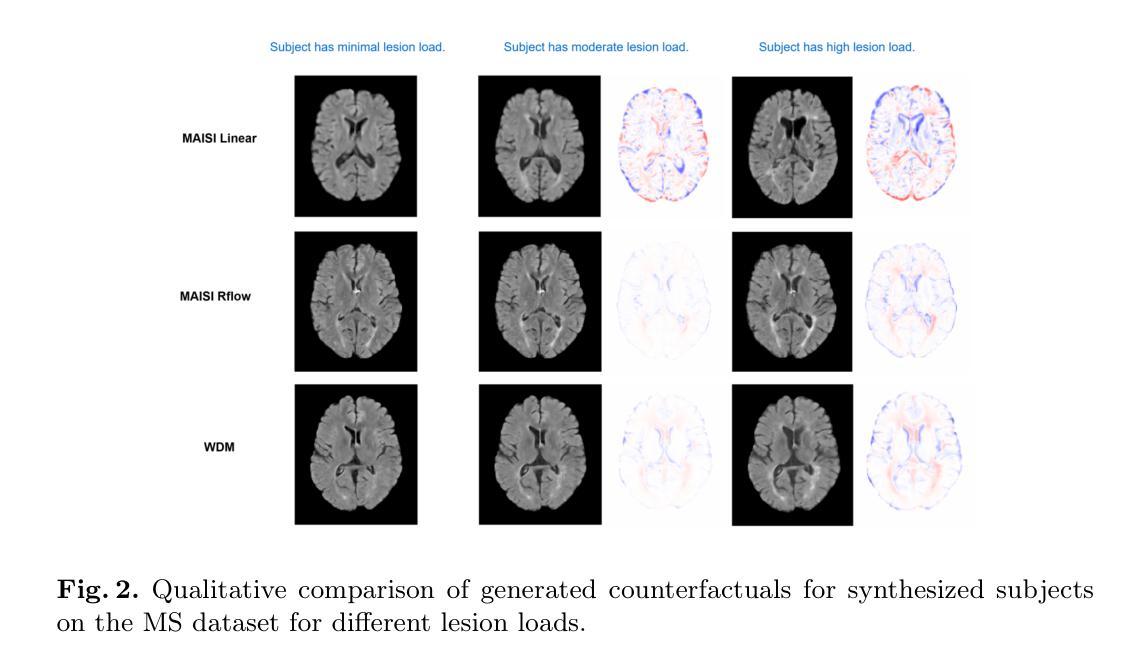
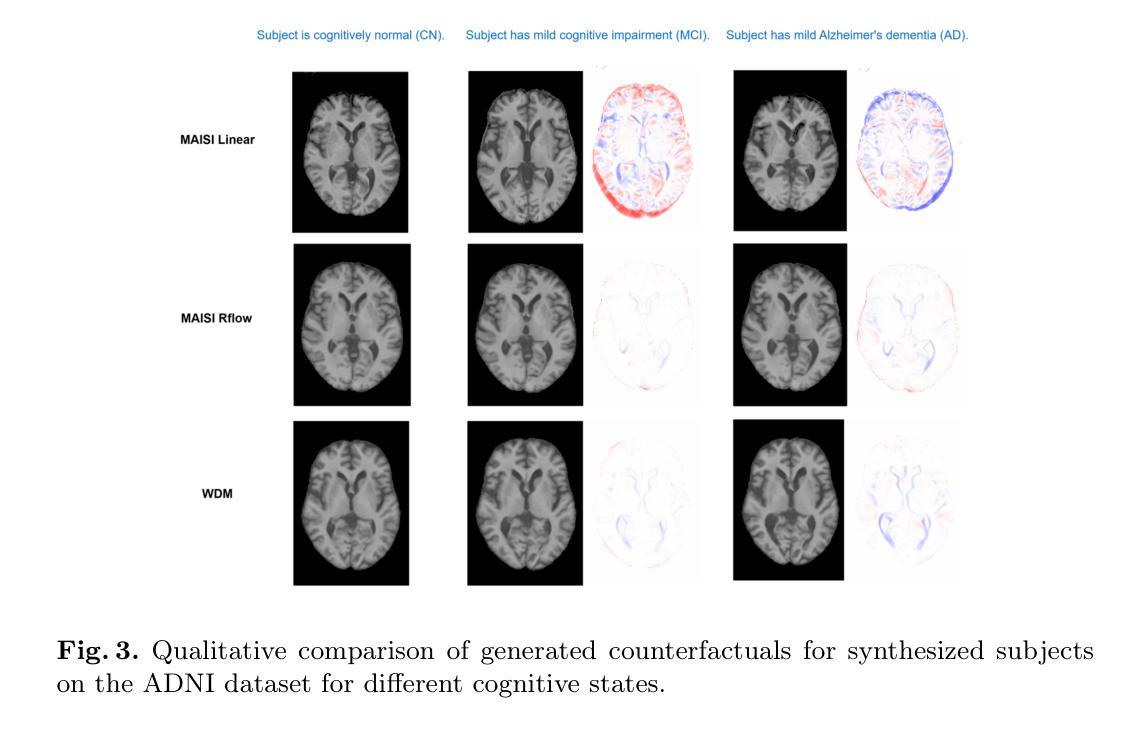
Imagining Alternatives: Towards High-Resolution 3D Counterfactual Medical Image Generation via Language Guidance
Authors:Mohamed Mohamed, Brennan Nichyporuk, Douglas L. Arnold, Tal Arbel
Vision-language models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in generating 2D images under various conditions; however the impressive performance of these models in 2D is largely enabled by extensive, readily available pretrained foundation models. Critically, comparable pretrained foundation models do not exist for 3D, significantly limiting progress in this domain. As a result, the potential of vision-language models to produce high-resolution 3D counterfactual medical images conditioned solely on natural language descriptions remains completely unexplored. Addressing this gap would enable powerful clinical and research applications, such as personalized counterfactual explanations, simulation of disease progression scenarios, and enhanced medical training by visualizing hypothetical medical conditions in realistic detail. Our work takes a meaningful step toward addressing this challenge by introducing a framework capable of generating high-resolution 3D counterfactual medical images of synthesized patients guided by free-form language prompts. We adapt state-of-the-art 3D diffusion models with enhancements from Simple Diffusion and incorporate augmented conditioning to improve text alignment and image quality. To our knowledge, this represents the first demonstration of a language-guided native-3D diffusion model applied specifically to neurological imaging data, where faithful three-dimensional modeling is essential to represent the brain’s three-dimensional structure. Through results on two distinct neurological MRI datasets, our framework successfully simulates varying counterfactual lesion loads in Multiple Sclerosis (MS), and cognitive states in Alzheimer’s disease, generating high-quality images while preserving subject fidelity in synthetically generated medical images. Our results lay the groundwork for prompt-driven disease progression analysis within 3D medical imaging.
视觉语言模型在各种条件下生成2D图像的能力令人印象深刻;然而,这些模型在2D中的出色表现很大程度上是由于大量可轻松获取的预训练基础模型的支撑。关键的是,3D领域的预训练基础模型并不存在,这极大地限制了该领域的进展。因此,视觉语言模型生成仅基于自然语言描述的高分辨率3D反事实医学图像的潜力尚未被探索。解决这一差距将能够推动强大的临床和研究应用,如个性化反事实解释、模拟疾病进展情景以及通过详细可视化假设医学状况增强医学培训。我们的工作通过引入一个框架,该框架能够生成由自由形式语言提示引导的高分辨率3D反事实医学图像,朝着解决这一挑战迈出了有意义的一步。我们改进了最先进的3D扩散模型并融入了简单扩散增强条件,以提高文本对齐和图像质量。据我们所知,这是首次将语言引导的原生3D扩散模型专门应用于神经成像数据,忠实的三维建模对于表示大脑的的三维结构至关重要。通过两个不同的神经MRI数据集的结果,我们的框架成功模拟了多发性硬化症(MS)的各种反事实病灶负荷以及阿尔茨海默病中的认知状态,生成高质量图像的同时,保持合成医学图像中主体的保真度。我们的研究为3D医学成像中的提示驱动疾病进展分析奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了视觉语言模型在生成二维图像方面的出色表现,强调了缺乏相应的三维预训练基础模型对三维领域的限制。研究提出了一种框架,能够基于自然语言描述生成高分辨率的三维虚构医疗图像,是朝着解决这一挑战的重要一步。该研究适应了先进的三维扩散模型,并进行了改进,首次展示了应用于神经成像数据的语言引导原生三维扩散模型。该研究成功模拟了多发性硬化症和阿尔茨海默病的虚构病变负荷和认知状态,为三维医学影像的病情进展分析奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型在生成二维图像方面表现出色,但缺乏相应的三维预训练基础模型限制了其在三维领域的发展。
- 研究提出了一种框架,能够基于自然语言描述生成高分辨率的三维虚构医疗图像。
- 研究适应了先进的三维扩散模型,并进行了改进,以提高图像质量和文本对齐。
- 这是首次将语言引导的原生三维扩散模型应用于神经成像数据。
- 该框架成功模拟了多发性硬化症和阿尔茨海默病的虚构病变负荷和认知状态。
- 生成的三维医疗图像质量高,且保持了个体特征。
点此查看论文截图

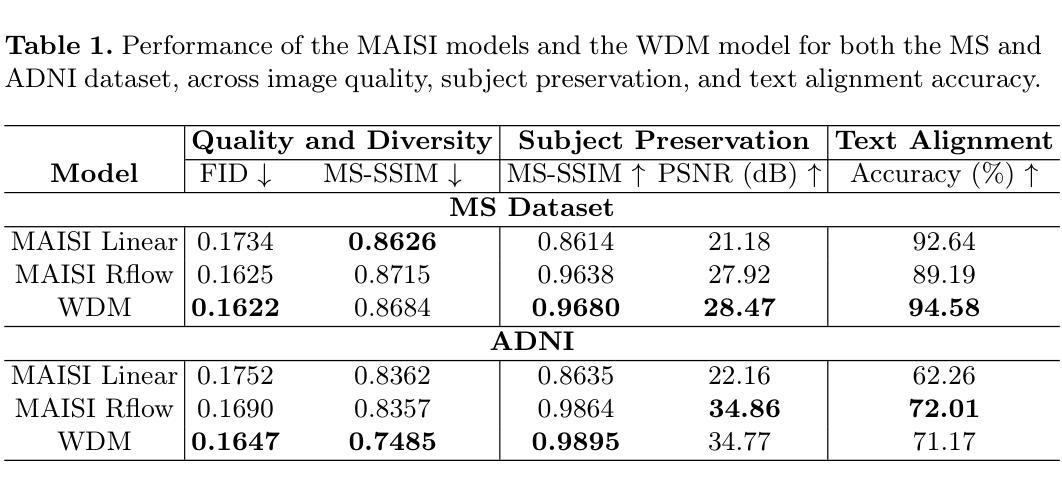
Dual Interaction Network with Cross-Image Attention for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jeonghyun Noh, Wangsu Jeon, Jinsun Park
Medical image segmentation is a crucial method for assisting professionals in diagnosing various diseases through medical imaging. However, various factors such as noise, blurriness, and low contrast often hinder the accurate diagnosis of diseases. While numerous image enhancement techniques can mitigate these issues, they may also alter crucial information needed for accurate diagnosis in the original image. Conventional image fusion strategies, such as feature concatenation can address this challenge. However, they struggle to fully leverage the advantages of both original and enhanced images while suppressing the side effects of the enhancements. To overcome the problem, we propose a dual interactive fusion module (DIFM) that effectively exploits mutual complementary information from the original and enhanced images. DIFM employs cross-attention bidirectionally to simultaneously attend to corresponding spatial information across different images, subsequently refining the complementary features via global spatial attention. This interaction leverages low- to high-level features implicitly associated with diverse structural attributes like edges, blobs, and object shapes, resulting in enhanced features that embody important spatial characteristics. In addition, we introduce a multi-scale boundary loss based on gradient extraction to improve segmentation accuracy at object boundaries. Experimental results on the ACDC and Synapse datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method quantitatively and qualitatively. Code available at: https://github.com/JJeong-Gari/DIN
医学图像分割是通过医学影像辅助专业人士诊断各种疾病的重要方法。然而,噪声、模糊和低对比度等因素经常阻碍疾病的准确诊断。虽然有许多图像增强技术可以缓解这些问题,但它们也可能会改变原始图像中用于准确诊断的关键信息。传统的图像融合策略,如特征串联,可以解决这一挑战。然而,它们在充分利用原始图像和增强图像的优势时遇到了困难,同时也抑制了增强的副作用。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种双重交互融合模块(DIFM),它能有效地利用原始图像和增强图像之间的互补信息。DIFM采用双向交叉注意力机制,可以同时关注不同图像中相应的空间信息,然后通过全局空间注意力对互补特征进行细化。这种交互利用与边缘、斑块和对象形状等多样结构属性相关的低至高层次的特征,产生包含重要空间特征的增强特征。此外,我们引入了一种基于梯度提取的多尺度边界损失,以提高对象边界的分割精度。在ACDC和Synapse数据集上的实验结果从定量和定性两个方面证明了所提方法的优越性。代码可用在:https://github.com/JJeong-Gari/DIN
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16pages
Summary
医学图像分割是协助专业人员进行疾病诊断的重要方法,但噪声、模糊和低对比度等因素会影响诊断的准确性。为改善这一问题,研究者提出一种双重交互融合模块(DIFM),该模块能有效利用原始图像和增强图像中的互补信息,通过跨双向注意力机制,同时关注不同图像中对应的空间信息,并经由全局空间注意力对互补特征进行精炼。此外,还引入基于梯度提取的多尺度边界损失,以提高对象边界的分割精度。实验结果表明,该方法在ACDC和Synapse数据集上表现出优异的定量和定性效果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在疾病诊断中起重要作用,但噪声、模糊和低对比度会影响诊断准确性。
- 双重交互融合模块(DIFM)能有效利用原始和增强图像的互补信息。
- DIFM通过跨双向注意力机制关注不同图像中对应的空间信息。
- DIFM通过全局空间注意力对互补特征进行精炼。
- 引入多尺度边界损失以提高对象边界的分割精度。
- 实验结果在ACDC和Synapse数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

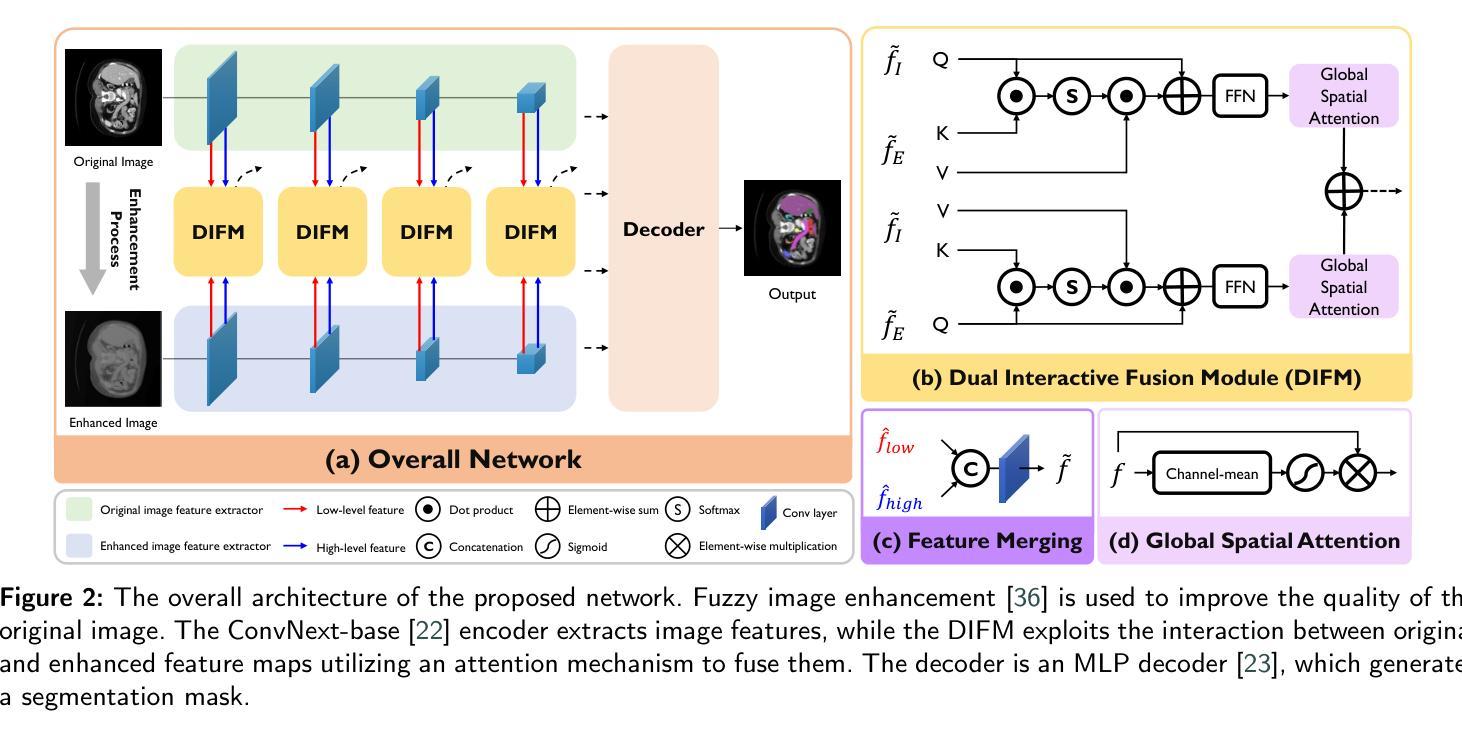
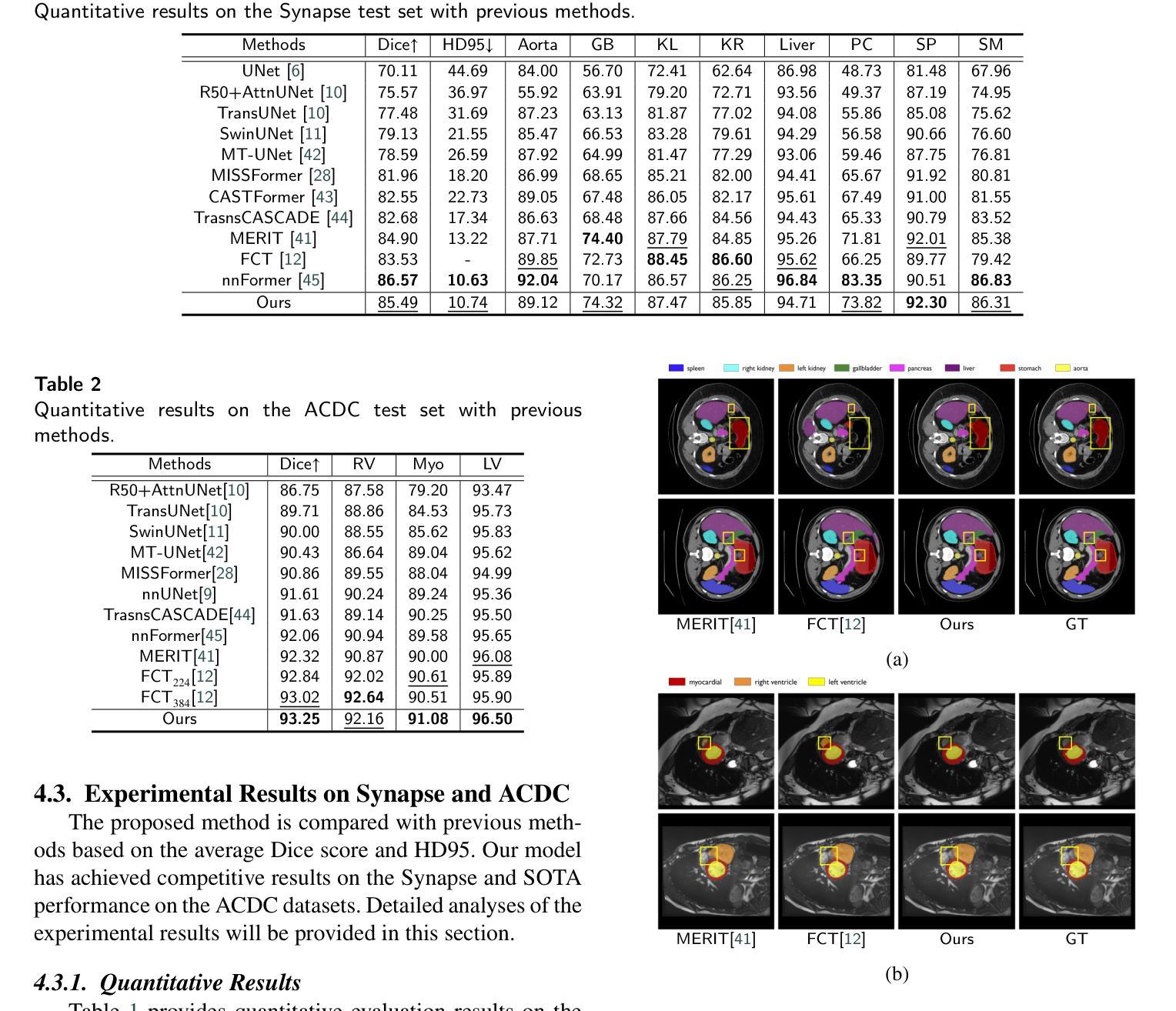
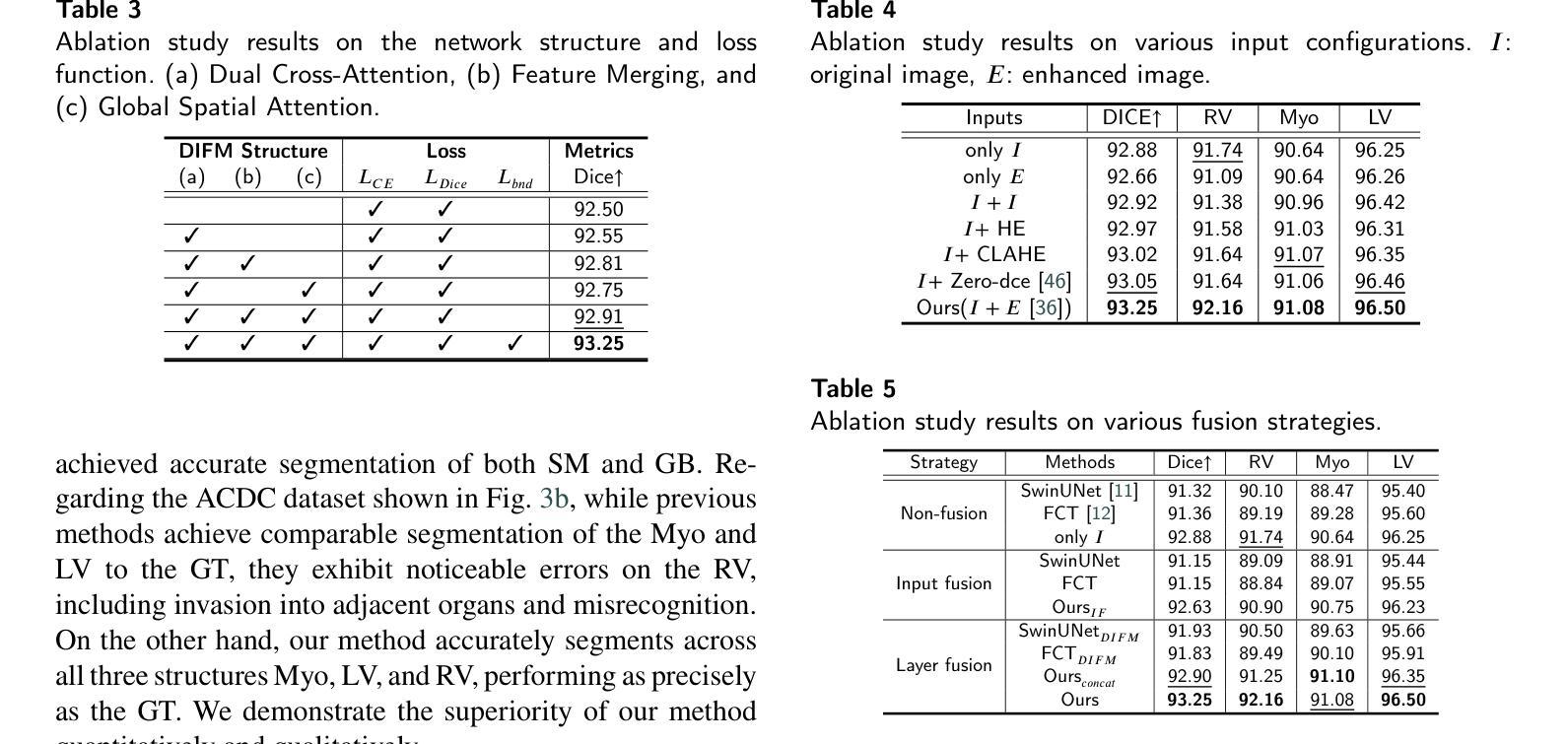
Brain Tumor Detection Through Diverse CNN Architectures in IoT Healthcare Industries: Fast R-CNN, U-Net, Transfer Learning-Based CNN, and Fully Connected CNN
Authors:Mohsen Asghari Ilani, Yaser M. Banad
Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered deep learning has advanced brain tumor diagnosis in Internet of Things (IoT)-healthcare systems, achieving high accuracy with large datasets. Brain health is critical to human life, and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides key data for brain tumor detection, serving as a major source of big data for AI-driven image classification. In this study, we classified glioma, meningioma, and pituitary tumors from MRI images using Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN) and UNet architectures. We also applied Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and CNN-based transfer learning models such as Inception-V3, EfficientNetB4, and VGG19. Model performance was assessed using F-score, recall, precision, and accuracy. The Fast R-CNN achieved the best results with 99% accuracy, 98.5% F-score, 99.5% Area Under the Curve (AUC), 99.4% recall, and 98.5% precision. Combining R-CNN, UNet, and transfer learning enables earlier diagnosis and more effective treatment in IoT-healthcare systems, improving patient outcomes. IoT devices such as wearable monitors and smart imaging systems continuously collect real-time data, which AI algorithms analyze to provide immediate insights for timely interventions and personalized care. For external cohort cross-dataset validation, EfficientNetB2 achieved the strongest performance among fine-tuned EfficientNet models, with 92.11% precision, 92.11% recall/sensitivity, 95.96% specificity, 92.02% F1-score, and 92.23% accuracy. These findings underscore the robustness and reliability of AI models in handling diverse datasets, reinforcing their potential to enhance brain tumor classification and patient care in IoT healthcare environments.
人工智能(AI)深度学习在物联网(IoT)医疗系统中推动了脑肿瘤诊断的进步,通过大规模数据集实现了高准确性。大脑健康对人类的生命至关重要,而准确的诊断则是有效治疗的关键。磁共振成像(MRI)为脑肿瘤的检测提供了关键数据,成为人工智能驱动图像分类的大数据来源之一。在这项研究中,我们使用基于区域的卷积神经网络(R-CNN)和UNet架构对胶质瘤、脑膜瘤和垂体瘤进行MRI图像分类。我们还应用了卷积神经网络(CNN)和基于CNN的迁移学习模型,如Inception-V3、EfficientNetB4和VGG19。使用F分数、召回率、精确度和准确度来评估模型性能。Fast R-CNN取得了最佳结果,准确率达到了99%,F分数为98.5%,曲线下面积(AUC)为99.5%,召回率为99.4%,精确度为98.5%。结合R-CNN、UNet和迁移学习能够在物联网医疗系统中实现早期诊断和治疗,提高患者治疗效果。物联网设备如可穿戴监测仪和智能成像系统不断收集实时数据,人工智能算法分析这些数据以提供即时见解,为及时干预和个性化护理提供指导。对于外部队列跨数据集验证,经过微调后的EfficientNetB2模型表现最佳,其精确度达到了92.11%,召回率/灵敏度为92.11%,特异性为95.96%,F1分数为92.02%,准确率为92.23%。这些发现强调了人工智能模型在处理不同数据集方面的稳健性和可靠性,进一步证明了其在物联网医疗环境中提高脑肿瘤分类和患者护理方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于人工智能深度学习的物联网医疗系统中脑肿瘤诊断技术已取得显著进展,通过大规模数据集实现高准确率。本研究利用区域卷积神经网络(R-CNN)和UNet架构对胶质瘤、脑膜瘤和垂体瘤进行MRI图像分类,同时应用卷积神经网络(CNN)和基于CNN的迁移学习模型如Inception-V3、EfficientNetB4和VGG19。其中Fast R-CNN表现最佳,准确率为99%,结合R-CNN、UNet和迁移学习能在物联网医疗系统中实现早期诊断和有效治疗,改善患者预后。此外,物联网设备如可穿戴监护仪和智能成像系统可实时收集数据,人工智能算法分析这些数据,为及时干预和个性化护理提供即时见解。研究结果显示EfficientNetB2模型在外部队列跨数据集验证中表现最佳,突显人工智能模型在处理多样数据集方面的稳健性和可靠性,具有在物联网医疗环境中提升脑肿瘤分类和患者护理的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能深度学习在物联网医疗系统的脑肿瘤诊断中取得高准确率。
- 研究使用R-CNN和UNet进行MRI图像分类,区分胶质瘤、脑膜瘤和垂体瘤。
- Fast R-CNN表现最佳,准确率高达99%。
- 迁移学习模型如Inception-V3、EfficientNetB4和VGG19也应用于研究。
- 物联网设备实时收集数据,人工智能算法提供即时分析。
- EfficientNetB2模型在跨数据集验证中表现最佳,显示人工智能模型处理多样数据集的稳健性。
- 这些技术结合有助于早期诊断和有效治疗,改善患者预后。
点此查看论文截图

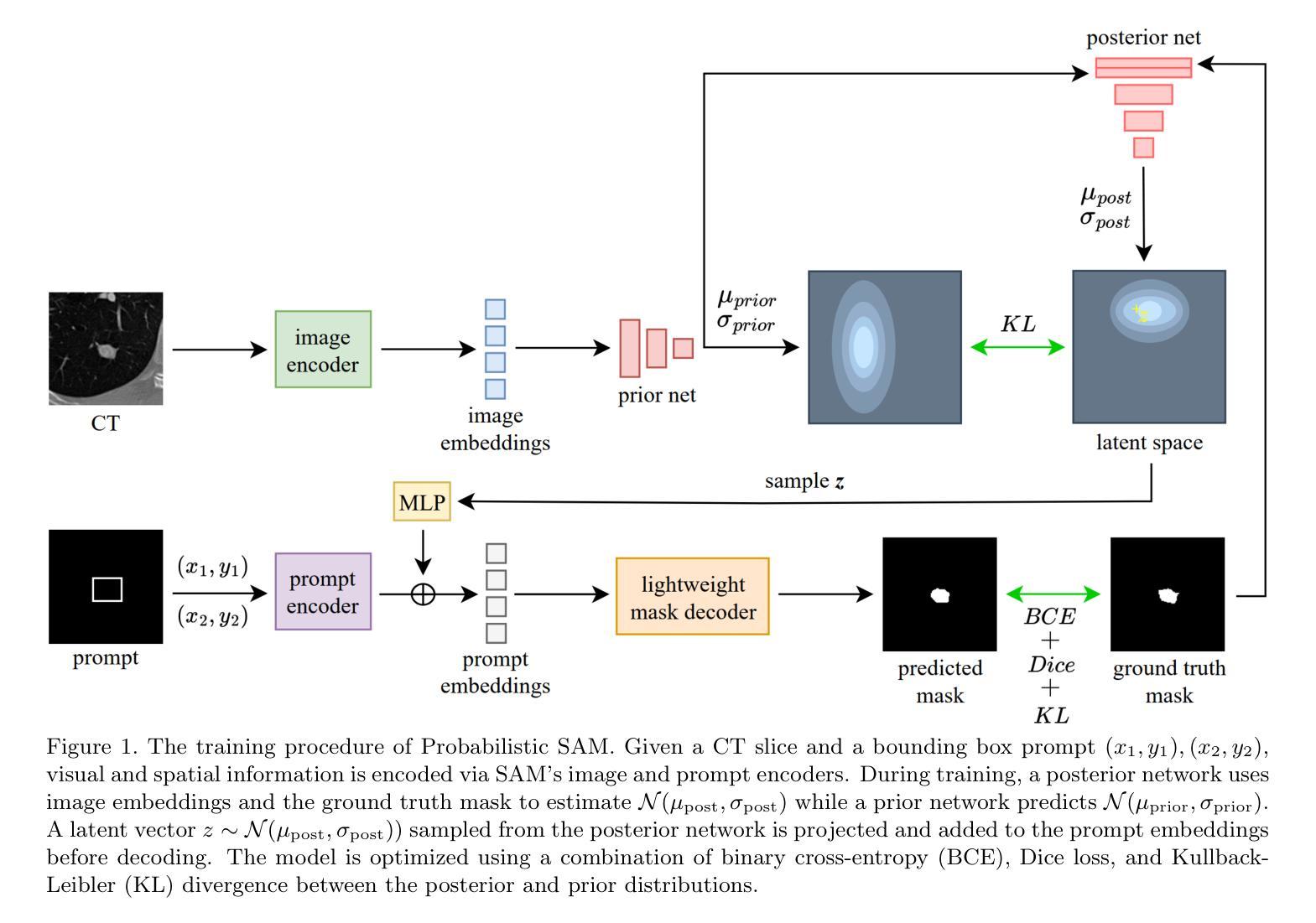
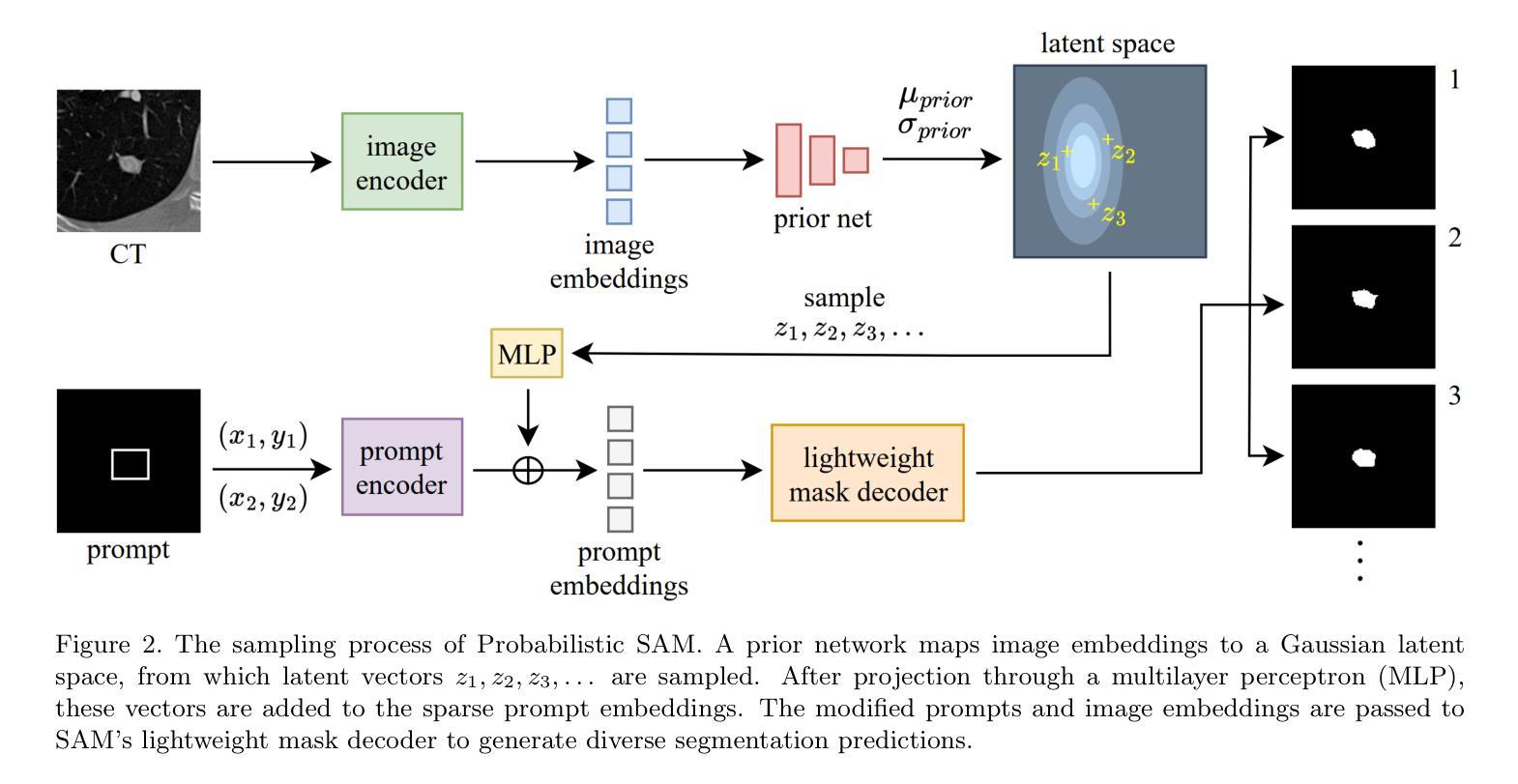
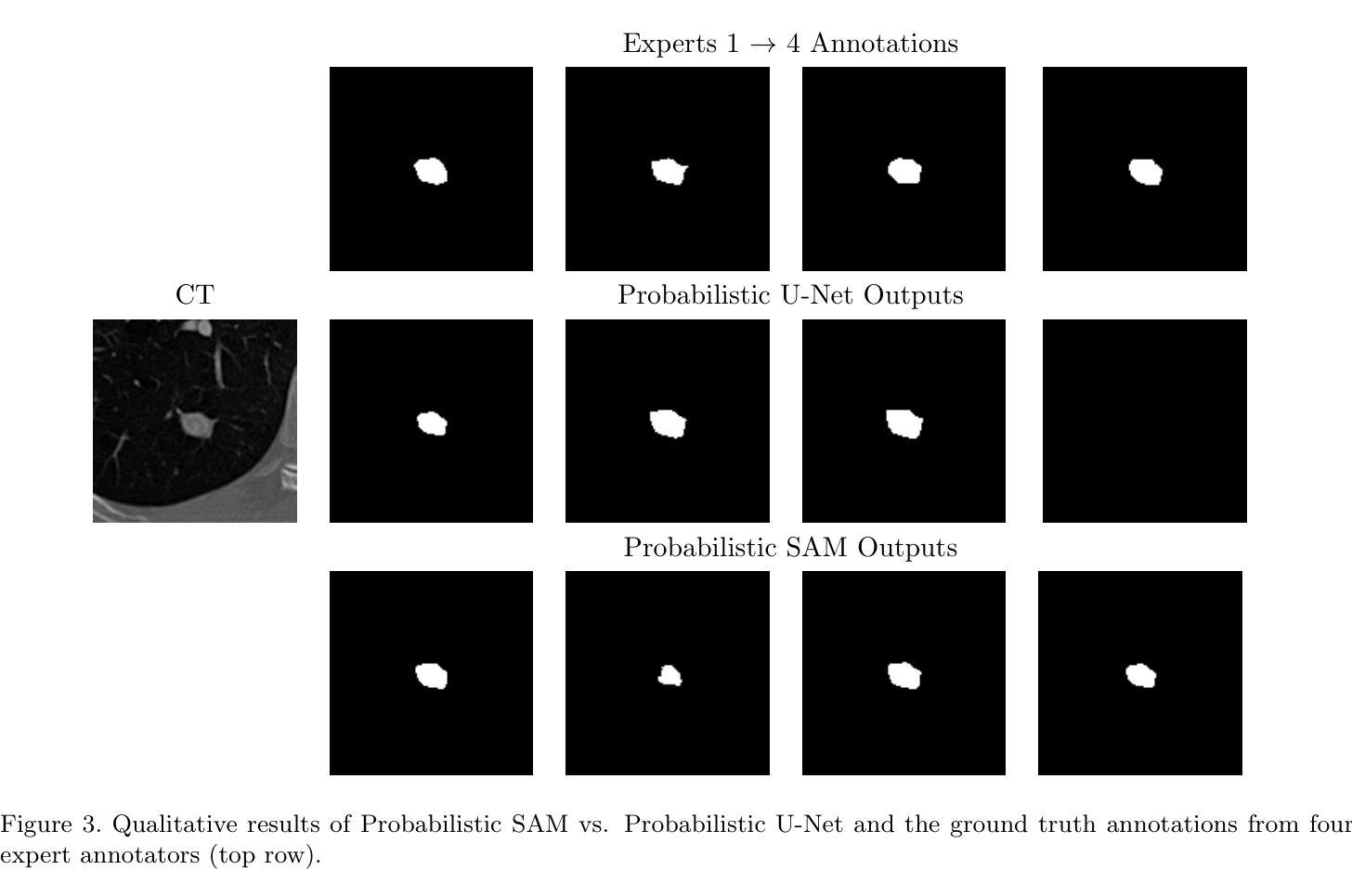
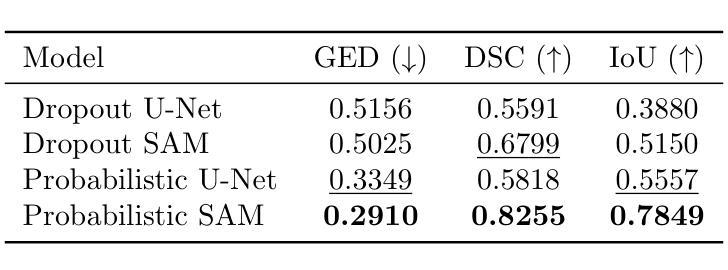
A Probabilistic Segment Anything Model for Ambiguity-Aware Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Tyler Ward, Abdullah Imran
Recent advances in promptable segmentation, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), have enabled flexible, high-quality mask generation across a wide range of visual domains. However, SAM and similar models remain fundamentally deterministic, producing a single segmentation per object per prompt, and fail to capture the inherent ambiguity present in many real-world tasks. This limitation is particularly troublesome in medical imaging, where multiple plausible segmentations may exist due to annotation uncertainty or inter-expert variability. In this paper, we introduce Probabilistic SAM, a probabilistic extension of SAM that models a distribution over segmentations conditioned on both the input image and prompt. By incorporating a latent variable space and training with a variational objective, our model learns to generate diverse and plausible segmentation masks reflecting the variability in human annotations. The architecture integrates a prior and posterior network into the SAM framework, allowing latent codes to modulate the prompt embeddings during inference. The latent space allows for efficient sampling during inference, enabling uncertainty-aware outputs with minimal overhead. We evaluate Probabilistic SAM on the public LIDC-IDRI lung nodule dataset and demonstrate its ability to produce diverse outputs that align with expert disagreement, outperforming existing probabilistic baselines on uncertainty-aware metrics. Our code is available at: https://github.com/tbwa233/Probabilistic-SAM/.
最近,提示分割领域的进展,如“任意分割模型”(SAM),已经能够在广泛的视觉领域实现灵活、高质量的面具生成。然而,SAM和类似模型仍然本质上是确定性的,每次提示只对一个对象产生一个分割结果,无法捕捉许多现实任务中存在的固有模糊性。这一局限性在医学影像中尤其麻烦,由于注释的不确定性或专家之间的差异,可能存在多个合理的分割。在本文中,我们引入了概率SAM,这是SAM的概率扩展,它对输入图像和提示建立分割分布的条件模型。通过引入潜在变量空间并使用变分目标进行训练,我们的模型学会了生成反映人类注释变异性的多样化和合理分割面具。该架构将先验网络和后验网络集成到SAM框架中,允许潜在代码在推理过程中调制提示嵌入。潜在空间允许在推理过程中进行有效采样,以最低的开销实现具有不确定性的输出。我们在公共LIDC-IDRI肺结节数据集上评估了概率SAM,证明了其产生与专家分歧相符的多样输出的能力,在不确定性感知指标上优于现有的概率基线。我们的代码位于:[https://github.com/tbwa233/Probabilistic-SAM/。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
一种新的医学图像分割模型——概率性SAM(Probabilistic Segment Anything Model)被提出。该模型克服了传统模型的确定性问题,能对同一对象的多个可能分割结果建模,适应了医学图像分割中因标注不确定性或专家间差异产生的固有模糊性。它通过引入潜在变量空间和变分目标进行训练,生成反映人类标注差异的多样化和合理分割掩膜。模型架构将先验网络和后验网络融入SAM框架,允许在推理过程中使用潜在代码调制提示嵌入。潜在空间提高了推理阶段的采样效率,实现了具有最小开销的不确定性感知输出。在公共LIDC-IDRI肺结节数据集上的评估表明,概率性SAM能够产生与专家分歧一致的多样化输出,并在不确定性感知指标上优于现有概率基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 概率性SAM模型解决了传统医学图像分割模型的确定性问题。
- 该模型能够对同一对象的多个可能分割结果建模,以适应医学图像中的标注不确定性和专家间差异。
- 通过引入潜在变量空间和变分目标训练,模型能生成反映人类标注差异的多样化且合理的分割掩膜。
- 模型架构结合了先验网络和后验网络,允许在推理过程中使用潜在代码调制提示嵌入,提高了灵活性。
- 潜在空间提高了采样效率,实现了具有最小开销的不确定性感知输出。
- 在公共数据集上的评估表明,概率性SAM在不确定性感知指标上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

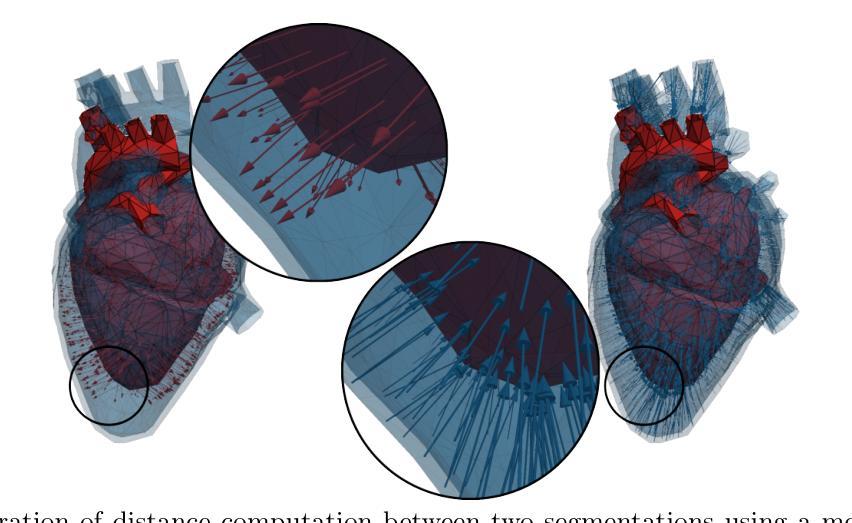
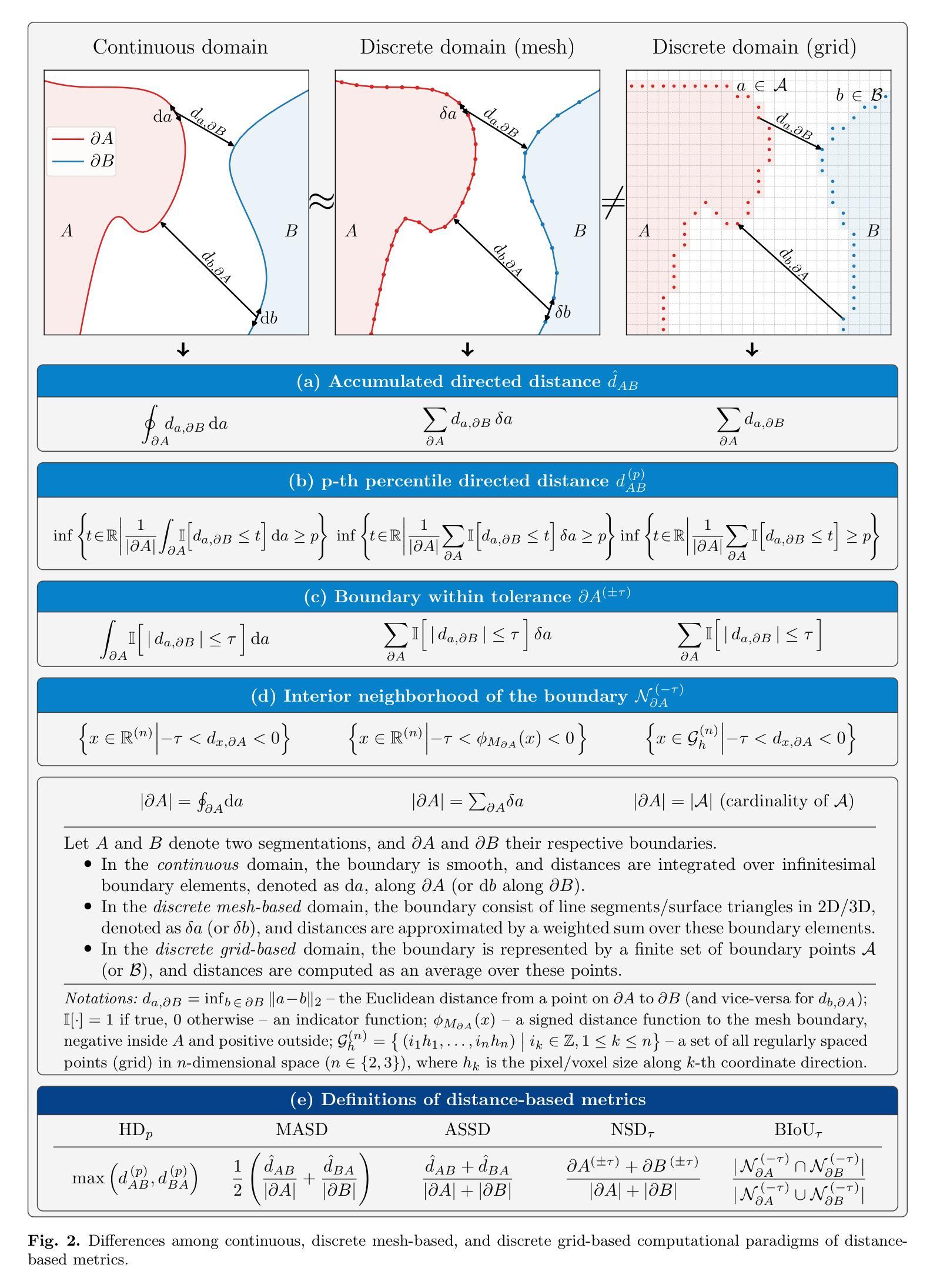
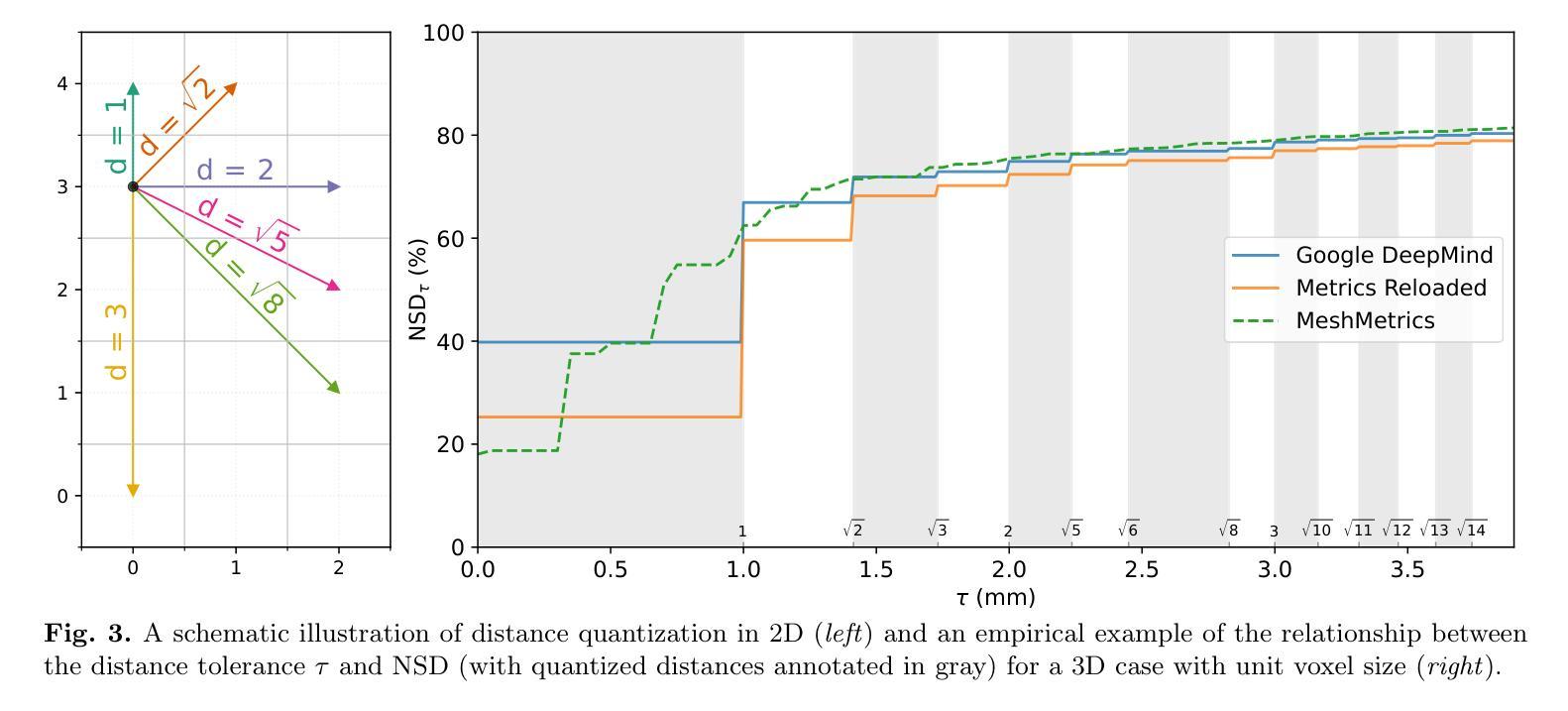
MeshMetrics: A Precise Implementation of Distance-Based Image Segmentation Metrics
Authors:Gašper Podobnik, Tomaž Vrtovec
The surge of research in image segmentation has yielded remarkable performance gains but also exposed a reproducibility crisis. A major contributor is performance evaluation, where both selection and implementation of metrics play critical roles. While recent efforts have improved the former, the reliability of metric implementation has received far less attention. Pitfalls in distance-based metric implementation can lead to considerable discrepancies between common open-source tools, for instance, exceeding 100 mm for the Hausdorff distance and 30%pt for the normalized surface distance for the same pair of segmentations. To address these pitfalls, we introduce MeshMetrics, a mesh-based framework that provides a more precise computation of distance-based metrics than conventional grid-based approaches. Through theoretical analysis and empirical validation, we demonstrate that MeshMetrics achieves higher accuracy and precision than established tools, and is substantially less affected by discretization artifacts, such as distance quantization. We release MeshMetrics as an open-source Python package, available at https://github.com/gasperpodobnik/MeshMetrics.
图像分割研究的热潮带来了显著的性能提升,但也暴露出了可重复性的危机。其中主要的贡献来自于性能评估,其中指标的选择和实施都扮演着至关重要的角色。虽然最近的努力改进了前者,但指标实施的可靠性却被忽视了。基于距离的指标实施中的陷阱会导致常见开源工具之间出现巨大差异,例如对于同一对分割,豪斯多夫距离超过100毫米,归一化表面距离超过30%。为了解决这些陷阱,我们引入了MeshMetrics,这是一个基于网格的框架,它为基于距离的指标提供了比传统的基于网格的方法更精确的计算。通过理论分析和实证验证,我们证明了MeshMetrics的准确性和精度高于现有工具,并且受到离散化伪影的影响较小,例如距离量化。我们将MeshMetrics作为一个开源Python包发布,可在https://github.com/gasperpodobnik/MeshMetrics获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了图像分割领域研究中出现的可重复性问题,主要源于性能评估中的指标选择和实现。尽管选择方面的改进已经取得了一定成果,但指标实现的可靠性却被忽视。文中指出距离度量实现中的陷阱可能导致常见开源工具间存在显著差异。为解决这些问题,文章提出了MeshMetrics框架,这是一种基于网格的方法,可以比传统的基于网格的方法更精确地计算距离度量。通过理论分析和实证验证,证明MeshMetrics的准确性和精度高于现有工具,并且受到离散化伪影的影响较小。最后,MeshMetrics作为开源Python包发布。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割领域存在可重复性问题,性能评估中的指标选择和实现是关键因素。
- 距离度量实现中的陷阱可能导致常见开源工具间存在显著差异。
- MeshMetrics框架基于网格,能更精确地计算距离度量。
- MeshMetrics的准确性和精度高于现有工具。
- MeshMetrics受到离散化伪影的影响较小。
- MeshMetrics作为开源Python包发布,便于研究人员使用。
点此查看论文截图


Segmentation and Tracking of Eruptive Solar Phenomena with Convolutional Neural Networks
Authors:Oleg Stepanyuk, Kamen Kozarev
Solar eruptive events are complex phenomena, which most often include coronal mass ejections (CME), CME-driven compressive and shock waves, flares, and filament eruptions. CMEs are large eruptions of magnetized plasma from the Sun’s outer atmosphere or corona, that propagate outward into the interplanetary space. Over the last several decades a large amount of remote solar eruption observational data has become available from ground-based and space-borne instruments. This has recently required the development of software approaches for automated characterisation of eruptive features. Most solar feature detection and tracking algorithms currently in use have restricted applicability and complicated processing chains, while complexity in engineering machine learning (ML) training sets limit the use of data-driven approaches for tracking or solar eruptive related phenomena. Recently, we introduced Wavetrack - a general algorithmic method for smart characterization and tracking of solar eruptive features. The method, based on a-trous wavelet decomposition, intensity rankings and a set of filtering techniques, allows to simplify and automate image processing and feature tracking. Previously, we applied the method successfully to several types of remote solar observations. Here we present the natural evolution of this approach. We discuss various aspects of applying Machine Learning (ML) techniques towards segmentation of high-dynamic range heliophysics observations. We trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) image segmentation models using feature masks obtained from the Wavetrack code. We present results from pre-trained models for segmentation of solar eruptive features and demonstrate their performance on a set of CME events based on SDO/AIA instrument data.
太阳爆发事件是复杂的现象,通常包括日冕物质抛射(CME)、CME驱动的压缩波和冲击波、耀斑和丝状体爆发。日冕物质抛射是太阳外层大气或日冕中的大型磁化等离子体喷发,向外传播到行星际空间。过去几十年,从地面和太空仪器获得了大量太阳爆发的远程观测数据。这最近要求开发用于自动表征爆发特征的软件方法。目前使用的大多数太阳特征检测和跟踪算法的应用范围有限且处理链复杂,而工程机器学习(ML)训练集的复杂性限制了数据驱动方法在跟踪或太阳爆发相关现象中的应用。最近,我们引入了Wavetrack——一种用于智能表征和跟踪太阳爆发特征的通用算法方法。该方法基于a-trous小波分解、强度排名和一系列滤波技术,可以简化和自动化图像处理和特征跟踪。以前,我们已经成功地将该方法应用于多种类型的远程太阳观测。这里我们介绍该方法的自然演变。我们讨论了将机器学习(ML)技术应用于高动态范围太阳物理学观测分割的各个方面。我们使用Wavetrack代码获得的特征掩膜训练了卷积神经网络(CNN)图像分割模型。我们展示了预训练模型对太阳爆发特征进行分割的结果,并基于SDO/AIA仪器数据演示了它们在CME事件集上的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to JGR: Machine Learning and Computation
Summary
本文介绍了太阳爆发事件,包括日冕物质抛射、驱动压缩波和冲击波、耀斑和丝状体爆发等。随着远程太阳爆发观测数据的增加,需要开发软件方法自动表征爆发特征。引入了一种基于小波分解、强度排名和一系列过滤技术的通用算法方法Wavetrack,用于智能表征和跟踪太阳爆发特征。此外,还讨论了应用机器学习技术分割高动态范围太阳物理观测的各个方面,并使用Wavetrack代码获得的特征掩膜训练了卷积神经网络图像分割模型。
Key Takeaways
- 太阳爆发事件包括日冕物质抛射、压缩波和冲击波、耀斑和丝状体爆发等。
- 大量远程太阳爆发观测数据需要开发软件方法进行自动表征。
- Wavetrack是一种基于小波分解的通用算法方法,用于智能表征和跟踪太阳爆发特征。
- Wavetrack已成功应用于多种远程太阳观测类型。
- 机器学习方法可用于分割高动态范围太阳物理观测数据。
- 使用Wavetrack代码获得的特征掩膜训练了卷积神经网络图像分割模型。
点此查看论文截图

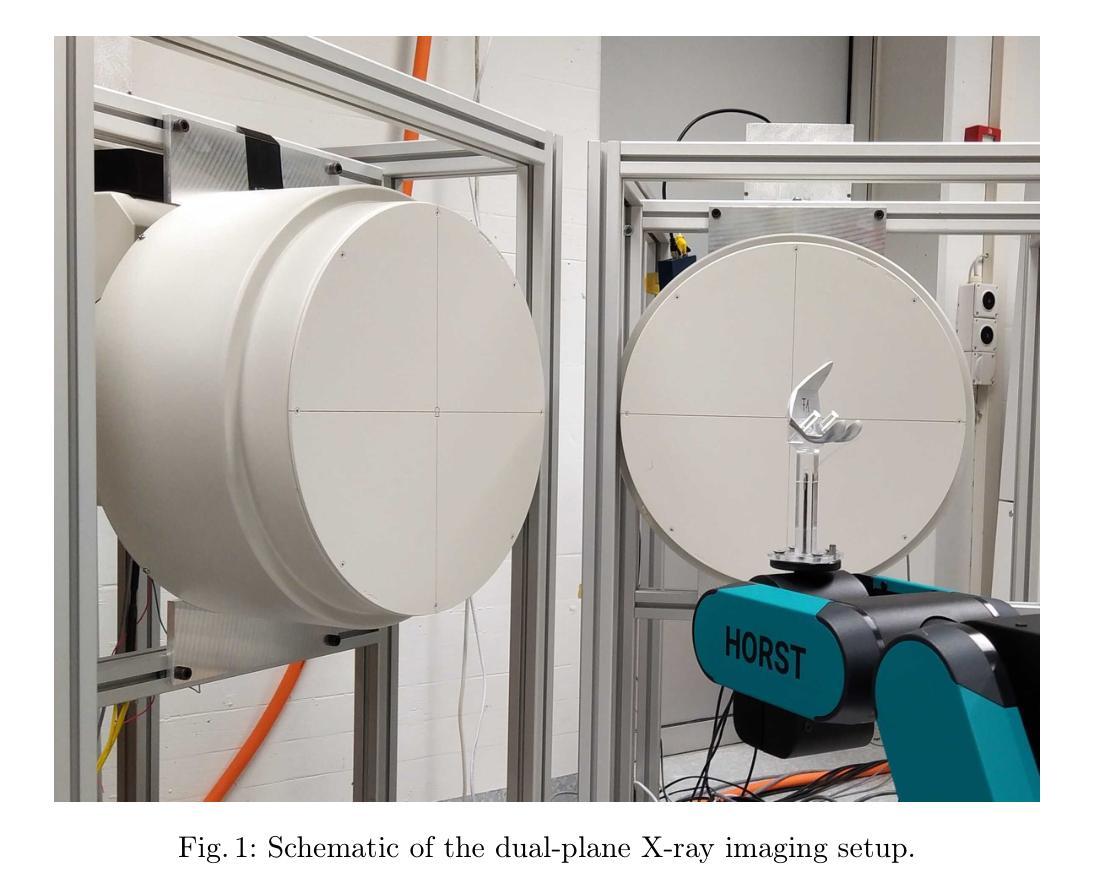
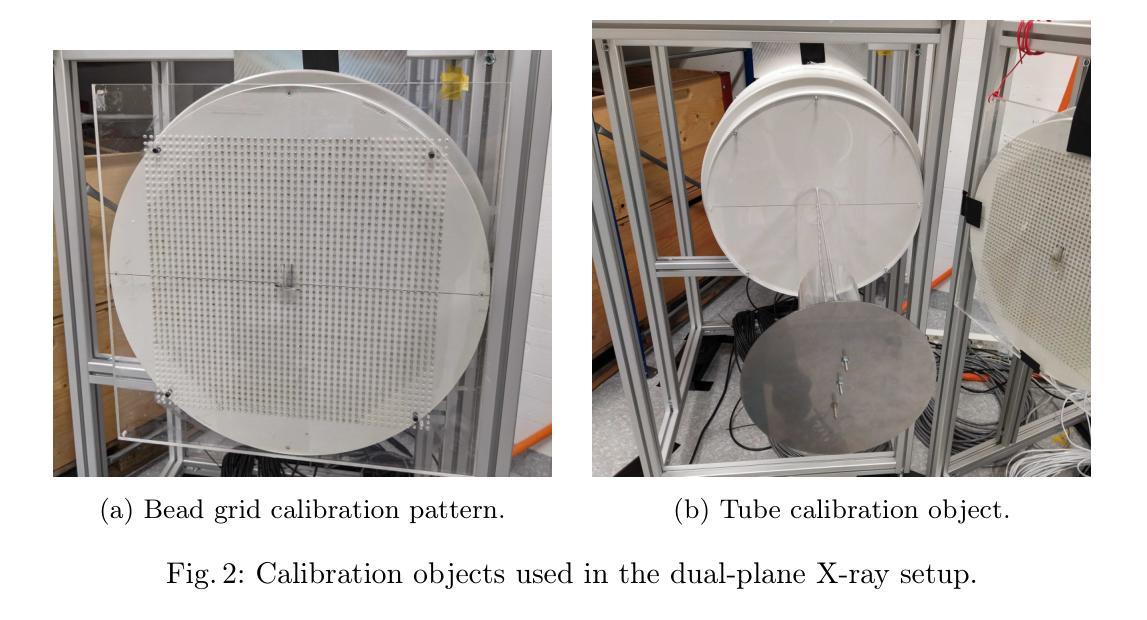
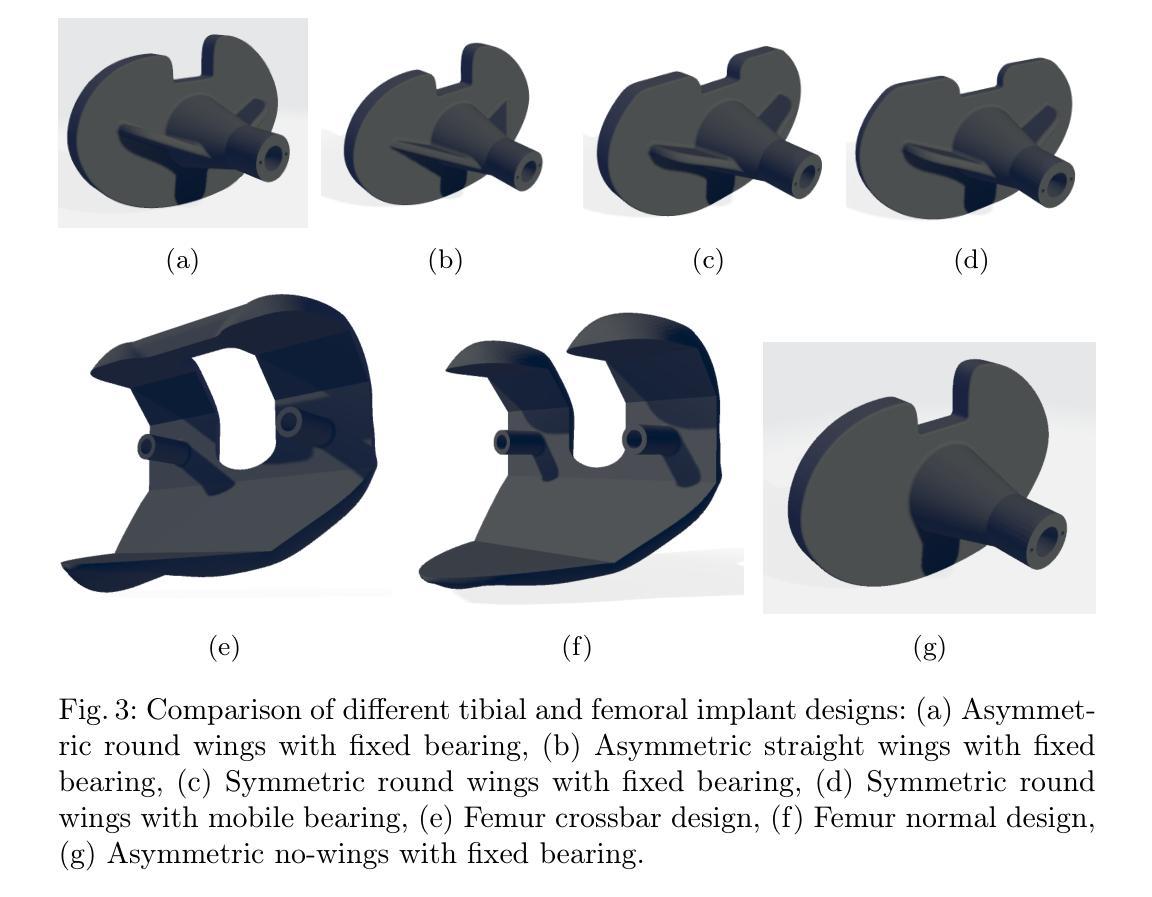
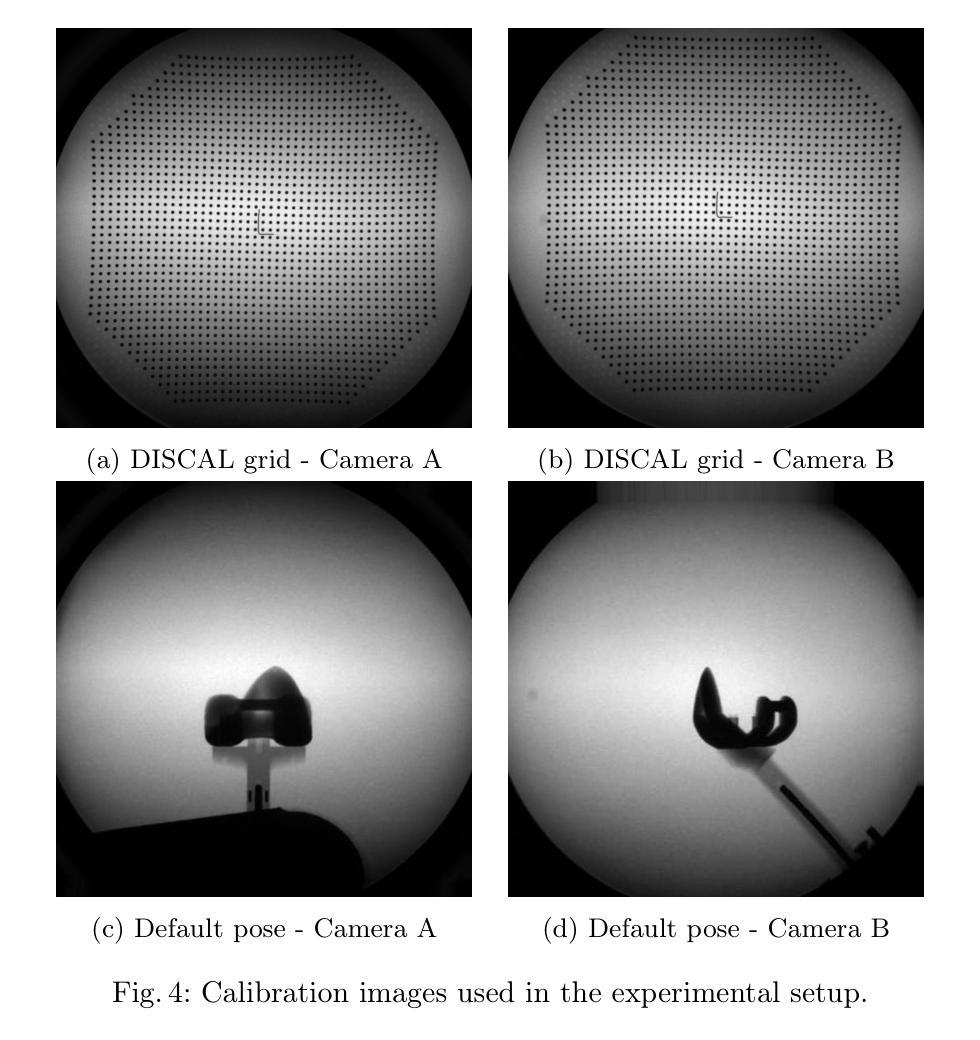
Veriserum: A dual-plane fluoroscopic dataset with knee implant phantoms for deep learning in medical imaging
Authors:Jinhao Wang, Florian Vogl, Pascal Schütz, Saša Ćuković, William R. Taylor
Veriserum is an open-source dataset designed to support the training of deep learning registration for dual-plane fluoroscopic analysis. It comprises approximately 110,000 X-ray images of 10 knee implant pair combinations (2 femur and 5 tibia implants) captured during 1,600 trials, incorporating poses associated with daily activities such as level gait and ramp descent. Each image is annotated with an automatically registered ground-truth pose, while 200 images include manually registered poses for benchmarking. Key features of Veriserum include dual-plane images and calibration tools. The dataset aims to support the development of applications such as 2D/3D image registration, image segmentation, X-ray distortion correction, and 3D reconstruction. Freely accessible, Veriserum aims to advance computer vision and medical imaging research by providing a reproducible benchmark for algorithm development and evaluation. The Veriserum dataset used in this study is publicly available via https://movement.ethz.ch/data-repository/veriserum.html, with the data stored at ETH Z"urich Research Collections: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-b-000701146.
Veriserum是一个开源数据集,旨在支持双平面透视分析深度学习注册的训练。它包含了大约11万张X光图像,图像中有10种膝关节植入物组合(2种股骨植入物和5种胫骨植入物),这些图像是在1600次试验过程中捕获的,并融入了与日常活动相关的姿势,如水平步态和斜坡下降。每张图像都标注了自动注册的地面真实姿势,而200张图像则包括手动注册的姿势,以供基准测试。Veriserum的关键特征包括双平面图像和校准工具。该数据集旨在支持应用程序的开发,例如2D/3D图像注册、图像分割、X射线失真校正和3D重建。Veriserum可自由访问,旨在通过为算法开发和评估提供可重复的基准测试,推动计算机视觉和医学成像研究的发展。本研究中使用的Veriserum数据集可通过https://movement.ethz.ch/data-repository/veriserum.html公开获取,数据存储在ETH苏黎世研究收藏中:https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-b-000701146。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been accepted at MICCAI 2025
Summary
Veriserum是一款开源数据集,包含约11万张X光图像,用于支持深度学习注册用于双平面透视分析的培训。该数据集包含每日活动姿态(如水平步态和斜坡下降)的1,600次试验期间捕获的10种膝关节植入物组合(2种股骨和5种胫骨植入物)的影像。每一张图像都带有自动注册的地面真实姿态注释,其中200张图像还包括手动注册的姿态以供基准测试。Veriserum数据集旨在支持诸如2D/3D图像注册、图像分割、X光失真校正和3D重建等应用程序的开发,并旨在通过提供可重复的基准测试来促进计算机视觉和医学成像研究的发展。该数据集已公开发布,可通过https://movement.ethz.ch/data-repository/veriserum.html访问。
Key Takeaways
- Veriserum是一个开源数据集,包含大量用于深度学习注册的X光图像。
- 数据集包含多种膝关节植入物的组合图像,模拟日常活动姿态。
- 图像带有自动注册的地面真实姿态注释,部分图像还带有手动注册的姿态用于基准测试。
- Veriserum支持多种医学成像应用,如2D/3D图像注册、图像分割、X光失真校正和3D重建。
- 数据集旨在推动计算机视觉和医学成像研究的发展。
- Veriserum数据集可通过特定链接公开访问。
点此查看论文截图