⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-10 更新
Contrastive Anatomy-Contrast Disentanglement: A Domain-General MRI Harmonization Method
Authors:Daniel Scholz, Ayhan Can Erdur, Robbie Holland, Viktoria Ehm, Jan C. Peeken, Benedikt Wiestler, Daniel Rueckert
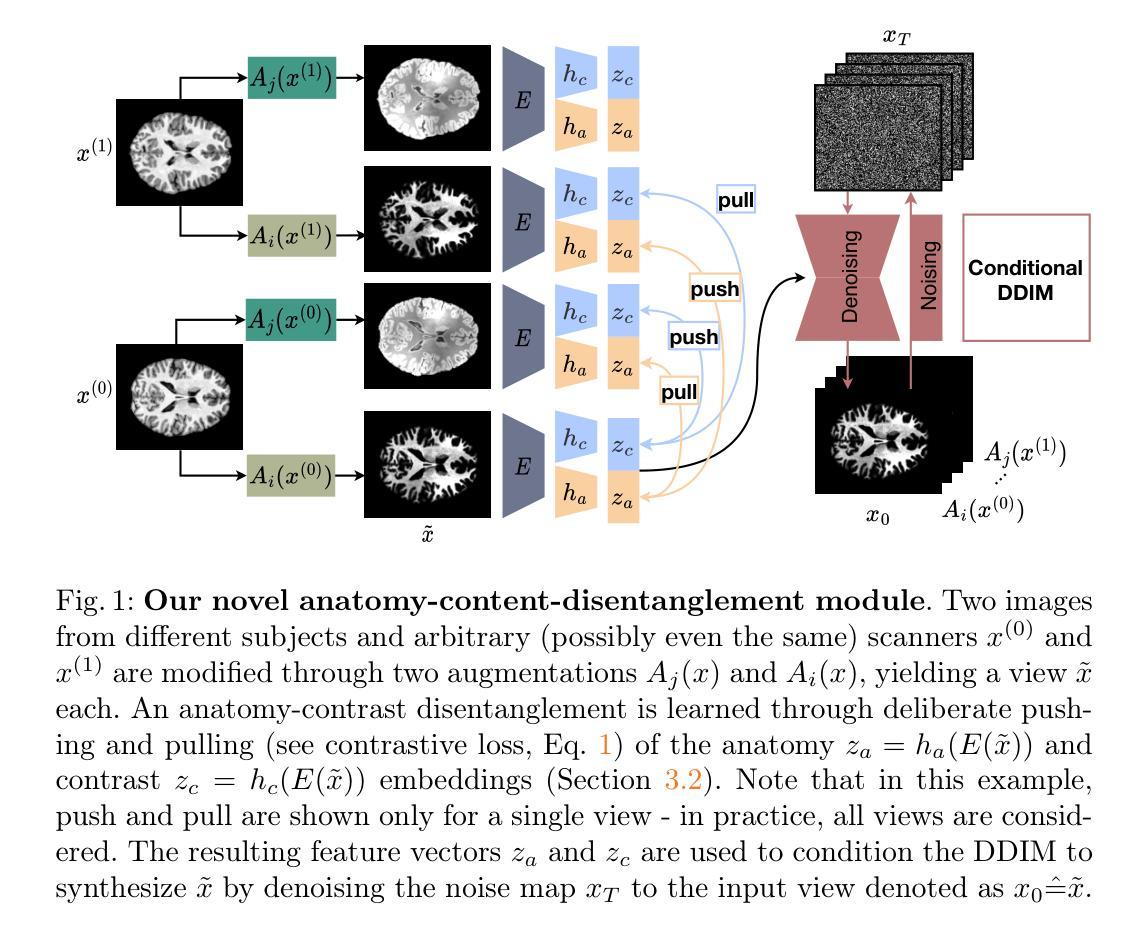
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an invaluable tool for clinical and research applications. Yet, variations in scanners and acquisition parameters cause inconsistencies in image contrast, hindering data comparability and reproducibility across datasets and clinical studies. Existing scanner harmonization methods, designed to address this challenge, face limitations, such as requiring traveling subjects or struggling to generalize to unseen domains. We propose a novel approach using a conditioned diffusion autoencoder with a contrastive loss and domain-agnostic contrast augmentation to harmonize MR images across scanners while preserving subject-specific anatomy. Our method enables brain MRI synthesis from a single reference image. It outperforms baseline techniques, achieving a +7% PSNR improvement on a traveling subjects dataset and +18% improvement on age regression in unseen. Our model provides robust, effective harmonization of brain MRIs to target scanners without requiring fine-tuning. This advancement promises to enhance comparability, reproducibility, and generalizability in multi-site and longitudinal clinical studies, ultimately contributing to improved healthcare outcomes.
磁共振成像(MRI)是临床和研究应用中不可或缺的工具。然而,扫描仪和采集参数的变化会导致图像对比度的不一致,这阻碍了跨数据集和临床研究的数据可比性和可重复性。现有的扫描仪统一方法旨在解决这一挑战,但面临一些局限性,例如需要移动受试者或难以推广到未见领域。我们提出了一种使用条件扩散自编码器和对比损失以及领域无关的对比增强来协调跨扫描仪的MR图像的新方法,同时保留特定于主体的解剖学结构。我们的方法能够实现从单个参考图像合成大脑MRI。它在移动受试者数据集上实现了比基线技术高出+7%的峰值信噪比(PSNR),并在未见年龄回归方面提高了+18%。我们的模型提供了对大脑MRI的稳健有效的统一处理,可针对目标扫描仪进行协调,而无需进行微调。这一进展有望增强多站点和纵向临床研究的可比性、可重复性和泛化性,最终为改善医疗保健结果做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用条件扩散自编码器与对比损失和域无关对比增强技术来统一磁共振图像的方法。该方法能够在不同扫描仪之间实现图像和谐统一,同时保留主体特定的解剖结构。该方法可实现从单个参考图像合成大脑MRI,并在旅行受试者数据集上实现了比基线技术高出+7%的PSNR改进,在未见年龄回归任务上实现了+18%的改进。该模型为针对目标扫描仪的稳健有效的脑部MRI和谐化提供了解决方案,无需微调即可实现。此技术有望增强多站点和纵向临床研究的可比性、重复性和泛化性,最终为改善医疗保健结果做出贡献。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)在临床和研究应用中的价值。
- 扫描仪和采集参数的变化导致图像对比度的不一致性,影响数据集和临床研究之间的数据可比性和可重复性。
- 现有扫描仪和谐化方法存在挑战,如需要移动受试者或难以推广到未见领域。
- 提出了一种新型方法,使用条件扩散自编码器与对比损失和域无关对比增强来和谐化MR图像。
- 方法能够在不同扫描仪间实现图像和谐统一,同时保留主体特定解剖结构。
- 方法实现了从单个参考图像合成大脑MRI,并在旅行受试者数据集和未见年龄回归任务上取得了显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

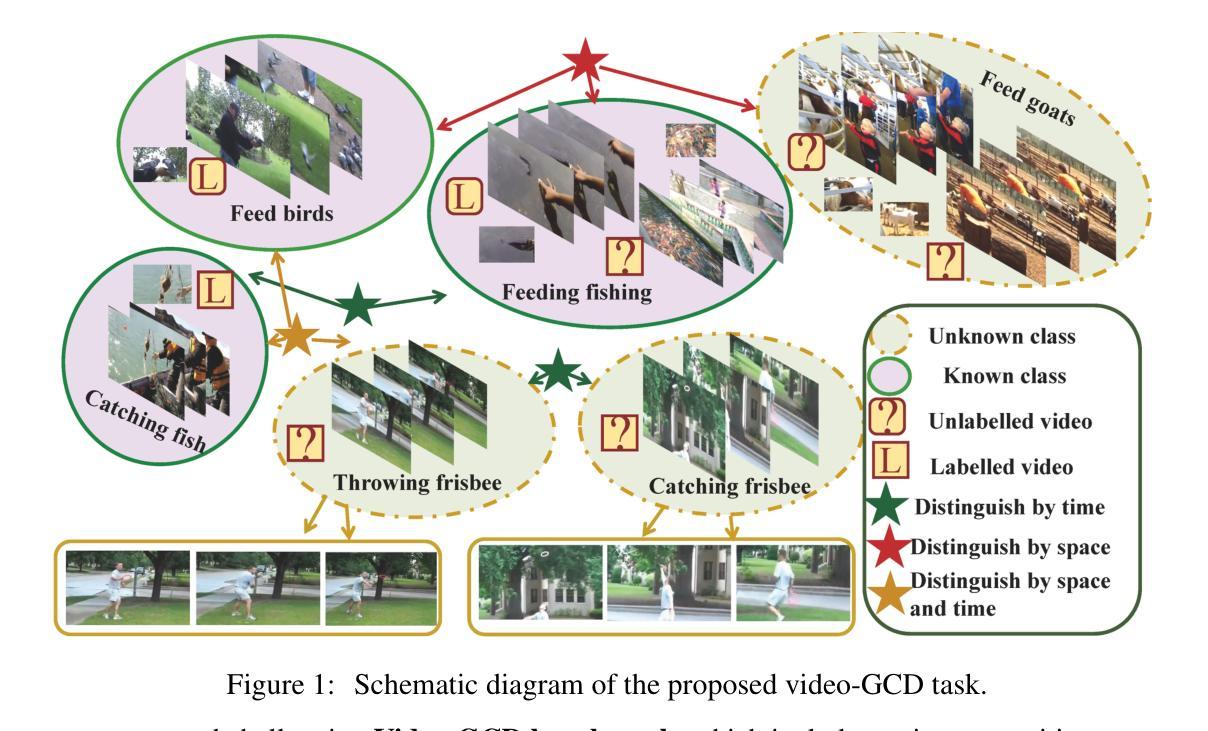
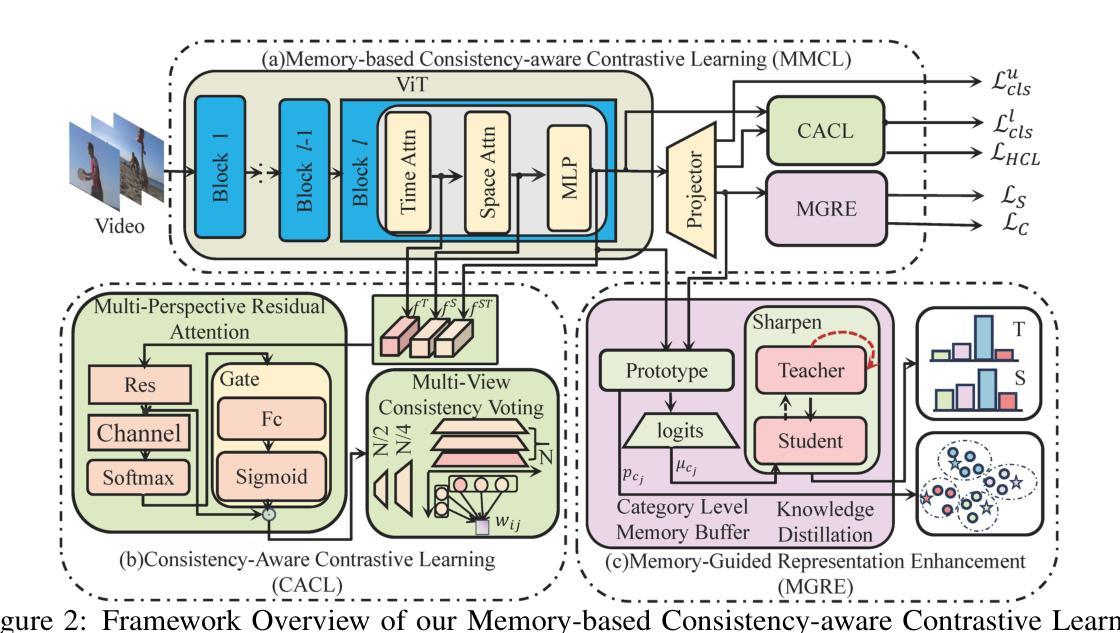
Video-based Generalized Category Discovery via Memory-Guided Consistency-Aware Contrastive Learning
Authors:Zhang Jing, Pu Nan, Xie Yu Xiang, Guo Yanming, Lu Qianqi, Zou Shiwei, Yan Jie, Chen Yan
Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) is an emerging and challenging open-world problem that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. Most existing GCD methods focus on discovering categories in static images. However, relying solely on static visual content is often insufficient to reliably discover novel categories. To bridge this gap, we extend the GCD problem to the video domain and introduce a new setting, termed Video-GCD. Thus, effectively integrating multi-perspective information across time is crucial for accurate Video-GCD. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel Memory-guided Consistency-aware Contrastive Learning (MCCL) framework, which explicitly captures temporal-spatial cues and incorporates them into contrastive learning through a consistency-guided voting mechanism. MCCL consists of two core components: Consistency-Aware Contrastive Learning(CACL) and Memory-Guided Representation Enhancement (MGRE). CACL exploits multiperspective temporal features to estimate consistency scores between unlabeled instances, which are then used to weight the contrastive loss accordingly. MGRE introduces a dual-level memory buffer that maintains both feature-level and logit-level representations, providing global context to enhance intra-class compactness and inter-class separability. This in turn refines the consistency estimation in CACL, forming a mutually reinforcing feedback loop between representation learning and consistency modeling. To facilitate a comprehensive evaluation, we construct a new and challenging Video-GCD benchmark, which includes action recognition and bird classification video datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms competitive GCD approaches adapted from image-based settings, highlighting the importance of temporal information for discovering novel categories in videos. The code will be publicly available.
广义类别发现(GCD)是一个新兴的开放世界问题,近年来引起了越来越多的关注。现有的大多数GCD方法主要集中在静态图像中的类别发现。然而,仅依赖静态视觉内容通常不足以可靠地发现新类别。为了弥补这一差距,我们将GCD问题扩展到视频领域,并引入了一种新的设置,称为Video-GCD。因此,有效地整合跨时间的多视角信息对于准确的Video-GCD至关重要。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新颖的Memory-guided Consistency-aware Contrastive Learning(MCCL)框架,该框架能够显式捕获时空线索,并通过一致性引导投票机制将其纳入对比学习。MCCL包含两个核心组件:一致性感知对比学习(CACL)和记忆引导表示增强(MGRE)。CACL利用多视角时间特征来估计无标签实例之间的一致性分数,然后根据这些分数来加权对比损失。MGRE引入了一个双级内存缓冲区,该缓冲区同时维护特征级和逻辑级表示,提供全局上下文以增强类内紧凑性和类间可分性。这反过来又改进了CACL中的一致性估计,在表示学习和一致性建模之间形成了相互加强的反馈循环。为了进行全面的评估,我们构建了一个新的具有挑战性的Video-GCD基准测试,其中包括动作识别和鸟类分类视频数据集。大量实验表明,我们的方法显著优于来自图像基设置的竞争性GCD方法,强调了时间信息在视频中发现新类别的重要性。代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了广义类别发现(GCD)在视频领域的新挑战及解决方案。针对现有方法主要关注静态图像的问题,提出了视频广义类别发现(Video-GCD)的新设定。为应对这一挑战,文章提出了Memory-guided Consistency-aware Contrastive Learning(MCCL)框架,该框架通过一致性指导投票机制将时空线索融入对比学习。MCCL包含两个核心组件:一致性感知对比学习(CACL)和记忆引导表示增强(MGRE)。实验表明,该方法显著优于从图像基础设置中改编的GCD方法,突显了视频中的时间信息在发现新类别中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 广义类别发现(GCD)正成为开放世界问题的新兴挑战,受到越来越多的关注。
- 将GCD问题扩展到视频领域,引入新的设定——视频广义类别发现(Video-GCD)。
- 提出Memory-guided Consistency-aware Contrastive Learning(MCCL)框架,整合时空线索到对比学习中。
- MCCL包含两个核心组件:CACL和MGRE,分别用于估计一致性分数和增强表示能力。
- 建立了新的、有挑战性的Video-GCD基准测试集,包括动作识别和鸟类分类视频数据集。
- 实验表明,MCCL在发现新类别方面显著优于基于图像的GCD方法。
点此查看论文截图

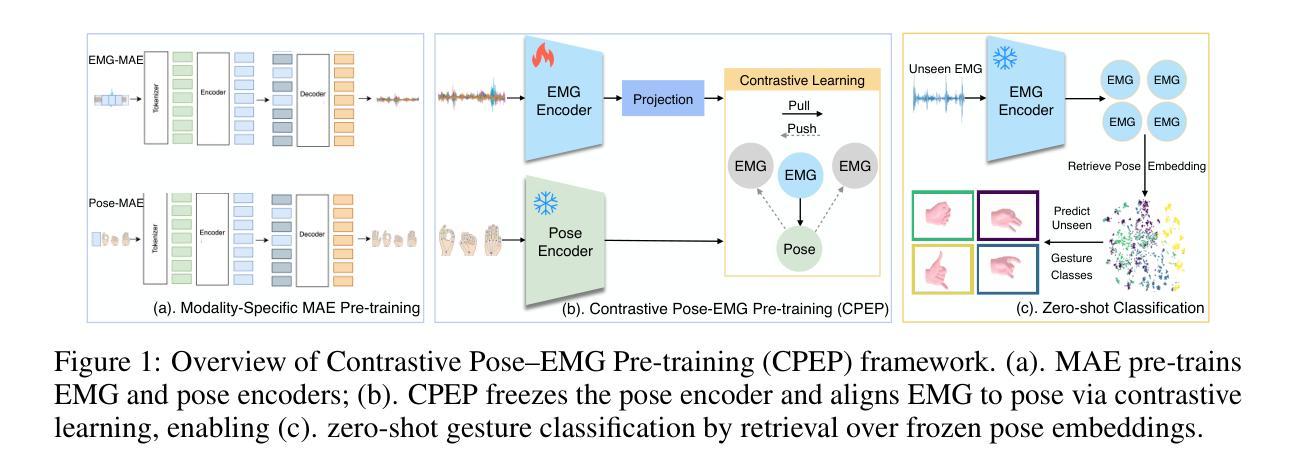
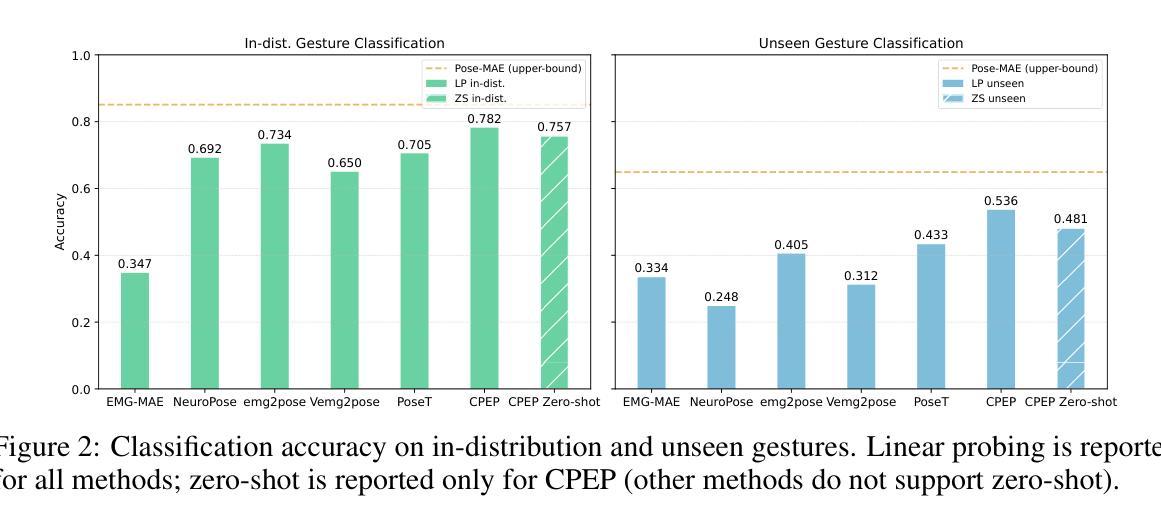
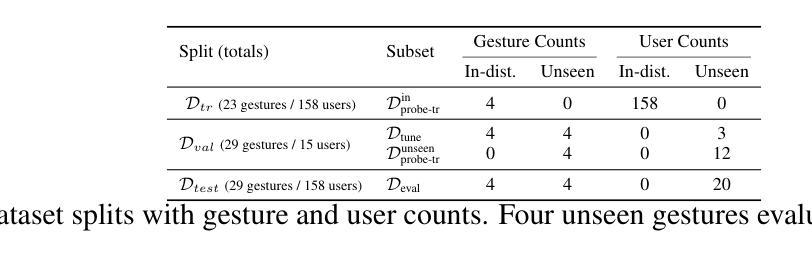
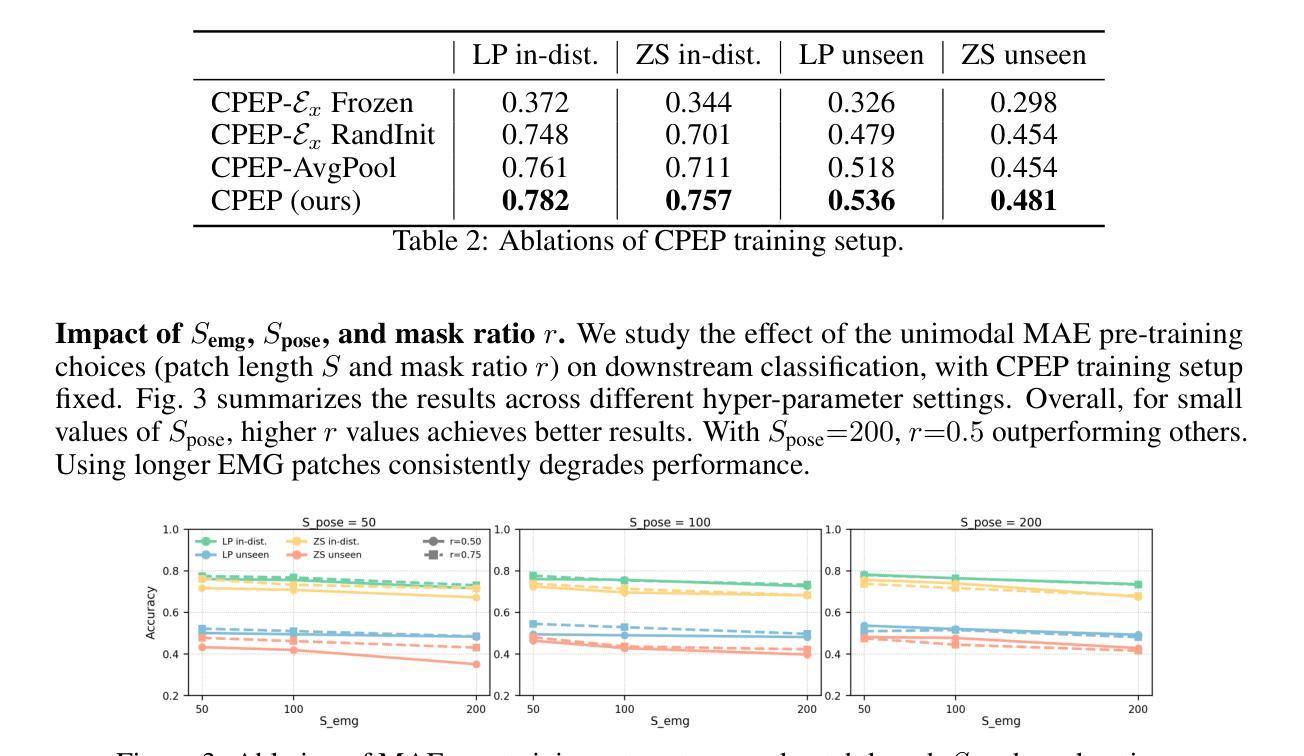
CPEP: Contrastive Pose-EMG Pre-training Enhances Gesture Generalization on EMG Signals
Authors:Wenhui Cui, Christopher Sandino, Hadi Pouransari, Ran Liu, Juri Minxha, Ellen Zippi, Aman Verma, Anna Sedlackova, Erdrin Azemi, Behrooz Mahasseni
Hand gesture classification using high-quality structured data such as videos, images, and hand skeletons is a well-explored problem in computer vision. Leveraging low-power, cost-effective biosignals, e.g. surface electromyography (sEMG), allows for continuous gesture prediction on wearables. In this paper, we demonstrate that learning representations from weak-modality data that are aligned with those from structured, high-quality data can improve representation quality and enables zero-shot classification. Specifically, we propose a Contrastive Pose-EMG Pre-training (CPEP) framework to align EMG and pose representations, where we learn an EMG encoder that produces high-quality and pose-informative representations. We assess the gesture classification performance of our model through linear probing and zero-shot setups. Our model outperforms emg2pose benchmark models by up to 21% on in-distribution gesture classification and 72% on unseen (out-of-distribution) gesture classification.
利用高质量的结构化数据(如视频、图像和手骨架)进行手势分类是计算机视觉领域的一个研究热点。利用低功耗、成本效益高的生物信号(如表面肌电图(sEMG))可在可穿戴设备上实现连续手势预测。本文展示了从弱模态数据学习表示,并与结构化高质量数据对齐,可以提高表示质量并实现零样本分类。具体来说,我们提出了对比姿态肌电图预训练(CPEP)框架,以对齐肌电图和姿态表示,其中我们学习一种肌电图编码器,该编码器能够产生高质量和姿态信息丰富的表示。我们通过线性探查和零样本设置评估模型的手势分类性能。与emg2pose基准模型相比,我们的模型在内部手势分类上的性能提高了高达21%,在未见过的(超出分布范围)手势分类上的性能提高了72%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了利用表面肌电图(sEMG)等生物信号进行手势识别的问题。研究提出一种对比姿态肌电预训练(CPEP)框架,通过对肌电和姿态表征进行对齐,提高表征质量,实现零样本分类。模型在姿势估计和手势分类任务上表现出优异的性能,特别是在未见过的(离分布)手势分类任务上,相较于基准模型有所提升。
Key Takeaways
- 论文探讨利用表面肌电图(sEMG)等生物信号进行手势分类的问题。
- 提出一种对比姿态肌电预训练(CPEP)框架,旨在提高表征质量和实现零样本分类。
- CPEP框架通过对肌电和姿态表征进行对齐来学习高质量和姿态信息的表征。
- 模型在姿势估计和手势分类任务上具有出色性能。
- 模型在基准模型上有所提升,特别是在未见过的(离分布)手势分类任务上表现更为显著。
- 该研究展示了利用低功率、成本效益高的生物信号进行连续手势预测的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

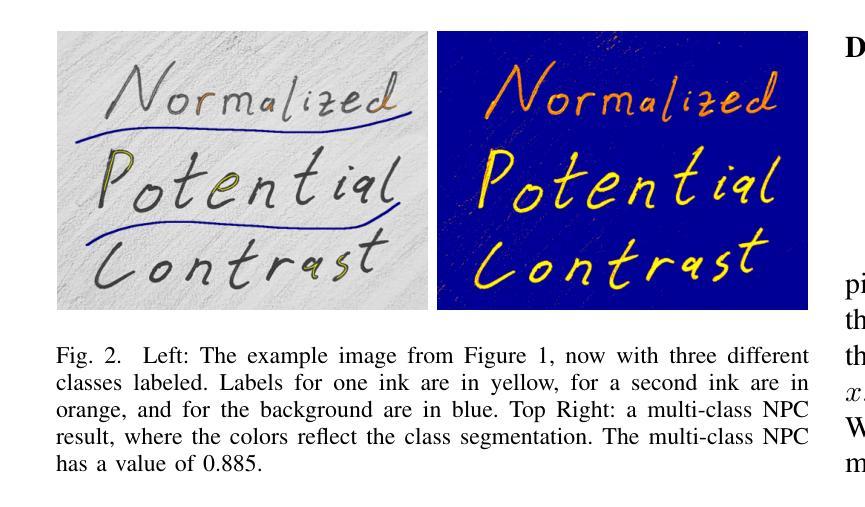
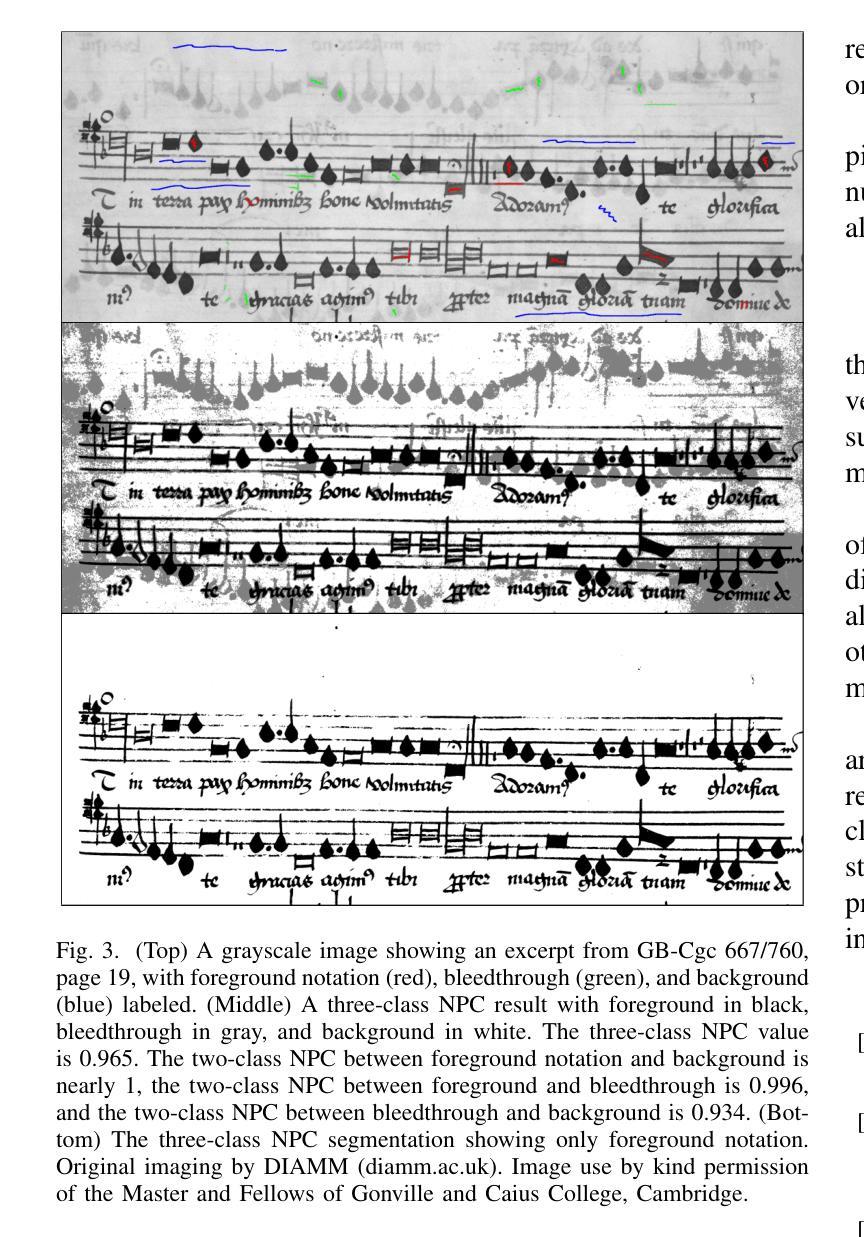
Potential Contrast: Properties, Equivalences, and Generalization to Multiple Classes
Authors:Wallace Peaslee, Anna Breger, Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb
Potential contrast is typically used as an image quality measure and quantifies the maximal possible contrast between samples from two classes of pixels in an image after an arbitrary grayscale transformation. It has been applied in cultural heritage to evaluate multispectral images using a small number of labeled pixels. In this work, we introduce a normalized version of potential contrast that removes dependence on image format and also prove equalities that enable generalization to more than two classes and to continuous settings. Finally, we exemplify the utility of multi-class normalized potential contrast through an application to a medieval music manuscript with visible bleedthrough from the back of the page. We share our implementations, based on both original algorithms and our new equalities, including generalization to multiple classes, at https://github.com/wallacepeaslee/Multiple-Class-Normalized-Potential-Contrast.
潜在对比度通常被用作图像质量的一种度量标准,它量化了在任意灰度变换后,图像中两个类别的像素样本之间可能存在的最大对比度。它已经被应用于文化遗产领域,用于评估使用少量标记像素的多光谱图像。在这项工作中,我们介绍了潜在对比度的归一化版本,它消除了对图像格式的依赖,并证明了等式,使它们能够推广到多于两个类别和连续设置的情况。最后,我们通过中世纪音乐手稿的一个应用示例,展示了多类归一化潜在对比度在可见页面背面透印情况下的实用性。我们在https://github.com/wallacepeaslee/Multiple-Class-Normalized-Potential-Contrast分享了我们的实现,这些实现基于原始算法和我们新的等式,包括推广到多个类别的内容。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了潜在对比度的归一化版本,该版本消除了对图像格式的依赖,并推广至多类及连续设置。文章还通过中世纪音乐手稿的实例,展示了多类归一化潜在对比度的实用性,可用于评估多光谱图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 潜在对比度通常用于评估图像质量,衡量两个类别像素样本之间在任意灰度变换后的最大可能对比度。
- 文章提出了潜在对比度的归一化版本,消除了其对图像格式的依赖。
- 该研究推广了潜在对比度的应用,使其适用于多类分类和连续设置。
- 通过中世纪音乐手稿的实例,展示了多类归一化潜在对比度在评估含有背景透印现象的文档图像质量方面的实用性。
- 文章分享了基于原始算法和新等式的实现,包括推广至多类分类的在线资源。
- 归一化潜在对比度的引入有助于更准确地评估图像质量,特别是在处理包含多个类别或连续色调的图像时。
点此查看论文截图