⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-10 更新
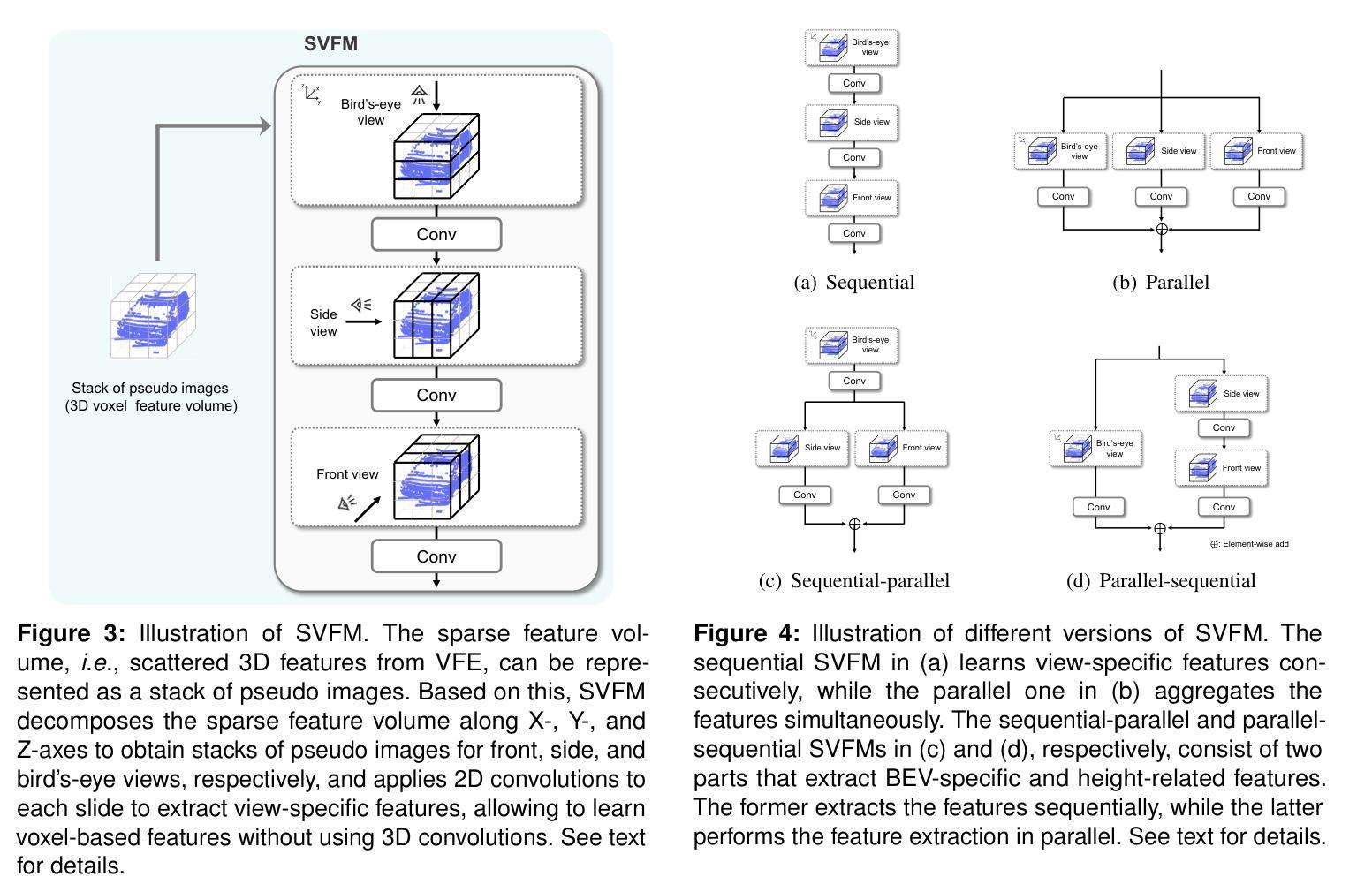
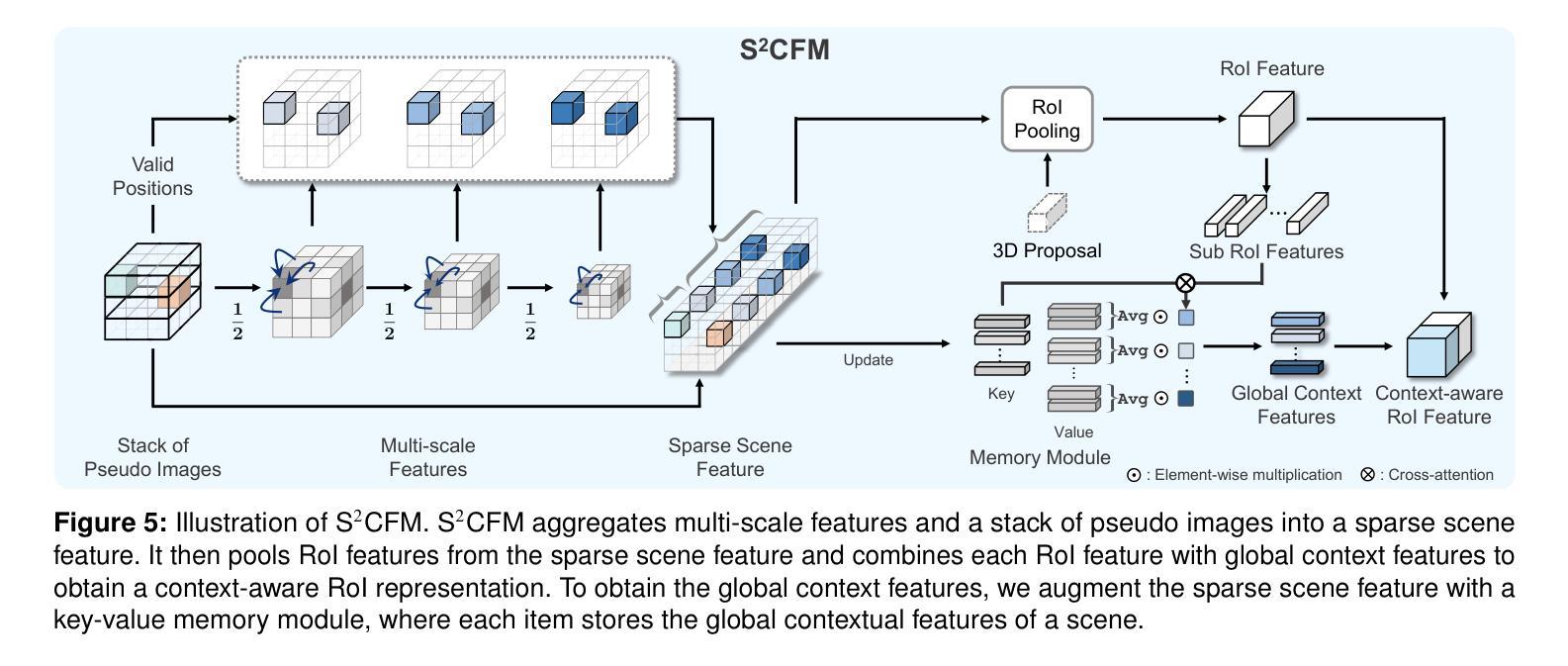
3DPillars: Pillar-based two-stage 3D object detection
Authors:Jongyoun Noh, Junghyup Lee, Hyekang Park, Bumsub Ham
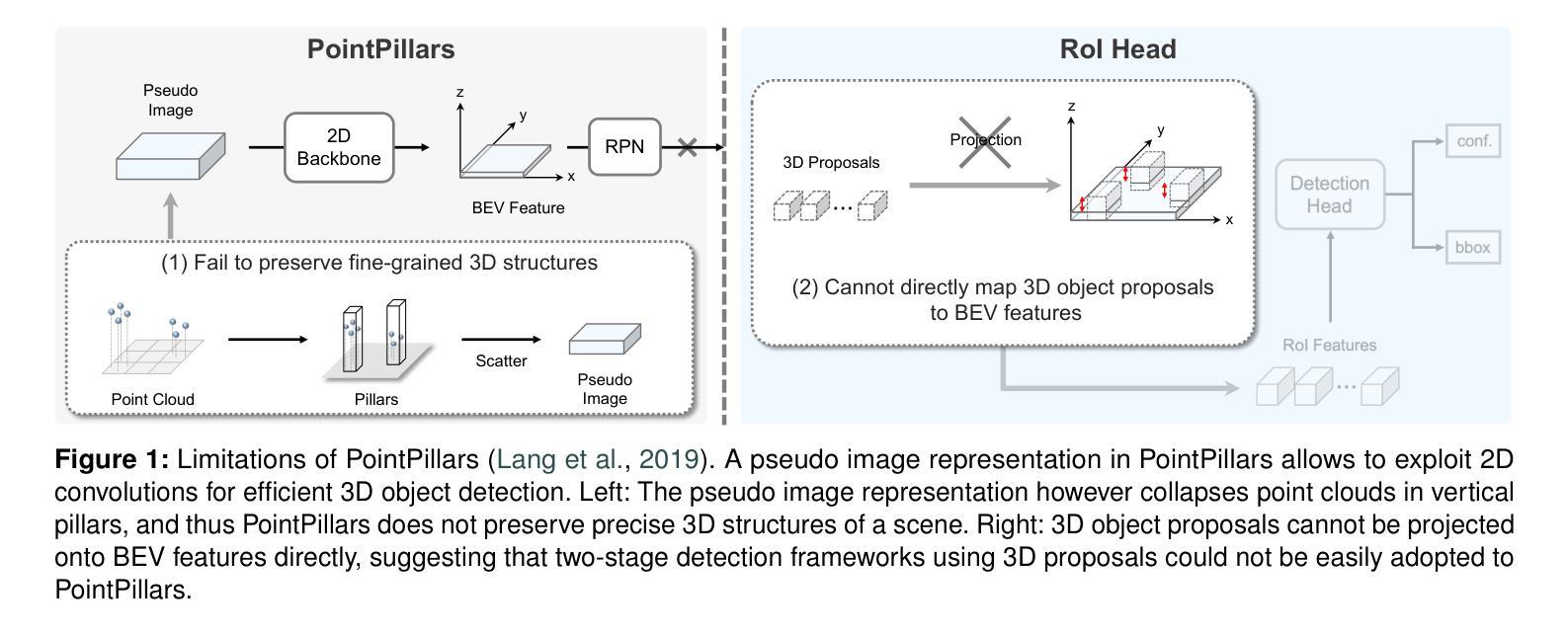
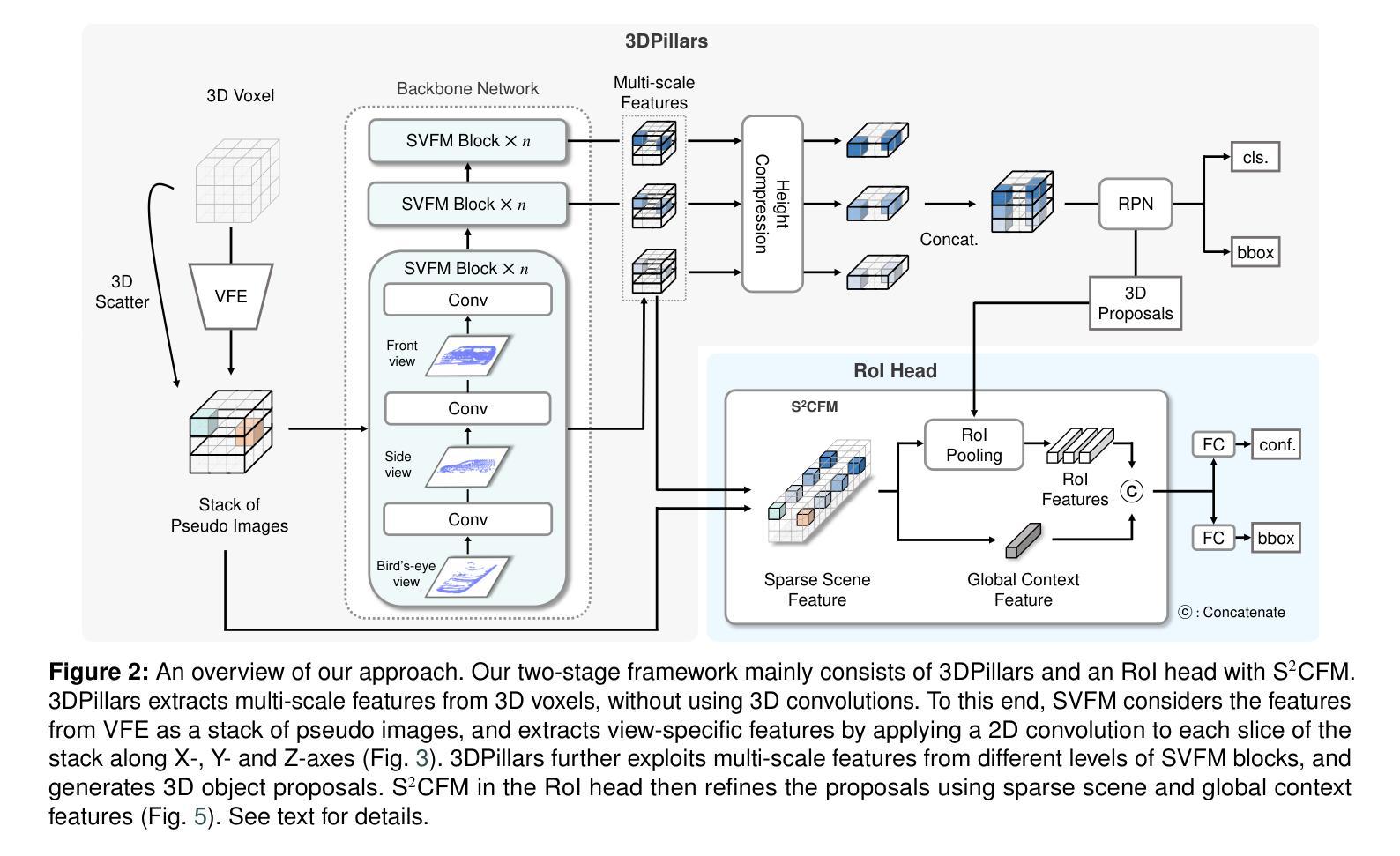
PointPillars is the fastest 3D object detector that exploits pseudo image representations to encode features for 3D objects in a scene. Albeit efficient, PointPillars is typically outperformed by state-of-the-art 3D detection methods due to the following limitations: 1) The pseudo image representations fail to preserve precise 3D structures, and 2) they make it difficult to adopt a two-stage detection pipeline using 3D object proposals that typically shows better performance than a single-stage approach. We introduce in this paper the first two-stage 3D detection framework exploiting pseudo image representations, narrowing the performance gaps between PointPillars and state-of-the-art methods, while retaining its efficiency. Our framework consists of two novel components that overcome the aforementioned limitations of PointPillars: First, we introduce a new CNN architecture, dubbed 3DPillars, that enables learning 3D voxel-based features from the pseudo image representation efficiently using 2D convolutions. The basic idea behind 3DPillars is that 3D features from voxels can be viewed as a stack of pseudo images. To implement this idea, we propose a separable voxel feature module that extracts voxel-based features without using 3D convolutions. Second, we introduce an RoI head with a sparse scene context feature module that aggregates multi-scale features from 3DPillars to obtain a sparse scene feature. This enables adopting a two-stage pipeline effectively, and fully leveraging contextual information of a scene to refine 3D object proposals. Experimental results on the KITTI and Waymo Open datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our approach, achieving a good compromise in terms of speed and accuracy.
PointPillars是最快的3D目标检测器,它利用伪图像表示来编码场景中3D对象的功能。尽管效率很高,但由于以下限制,PointPillars通常被最新的3D检测方法所超越:1)伪图像表示无法保留精确的三维结构;2)这使得难以采用使用三维对象提议的两阶段检测流程,通常单阶段方法表现出更好的性能。我们在本文中介绍了利用伪图像表示的首个两阶段3D检测框架,在保持PointPillars效率的同时,缩小了与最新方法之间的性能差距。我们的框架由两个新颖组件组成,克服了PointPillars的上述限制:首先,我们引入了一种新的CNN架构,称为3DPillars,它能够有效地利用二维卷积从伪图像表示中学习基于三维体素的特征。3DPillars的基本思想是将三维体素特征视为伪图像的堆叠。为了实现这一想法,我们提出了一个可分离的体素特征模块,该模块可以提取体素特征而无需使用三维卷积。其次,我们引入了一个带有稀疏场景上下文特征模块的RoI头,该模块从3DPillars聚合多尺度特征以获得稀疏场景特征。这使得可以有效地采用两阶段管道,并充分利用场景的上下文信息来优化三维对象提议。在KITTI和Waymo Open数据集上的实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性和效率,在速度和准确性方面达到了良好的折衷。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 11 figures
Summary
点云伪图像表示方法的改进框架被提出,其中包括一个高效的两阶段三维检测器。通过引入名为3DPillars的新CNN架构,结合可分离的体素特征模块,解决了点云伪图像表示难以保存精确三维结构和难以采用两阶段检测管道的问题。此外,还引入了具有稀疏场景上下文特征模块的RoI头,以有效地采用两阶段管道并充分利用场景的上下文信息对三维对象提议进行改进。实验结果证明,该框架具有有效性和效率,并在速度和准确性方面达到了良好的平衡。此方法实现了高效的三维目标检测器的突破性改进,针对复杂环境更具可靠性。对于未来三维目标检测技术的发展具有启示意义。
Key Takeaways
- PointPillars是快速的三维物体检测器,它通过伪图像表示编码场景中的三维物体特征。然而,它通常被最新技术超越。
- 引入了一种新的两阶段三维检测框架,利用伪图像表示法缩小了性能差距,同时保持了效率。
- 新框架包含两个新组件:一个名为3DPillars的CNN架构和带有稀疏场景上下文特征模块的RoI头。
点此查看论文截图

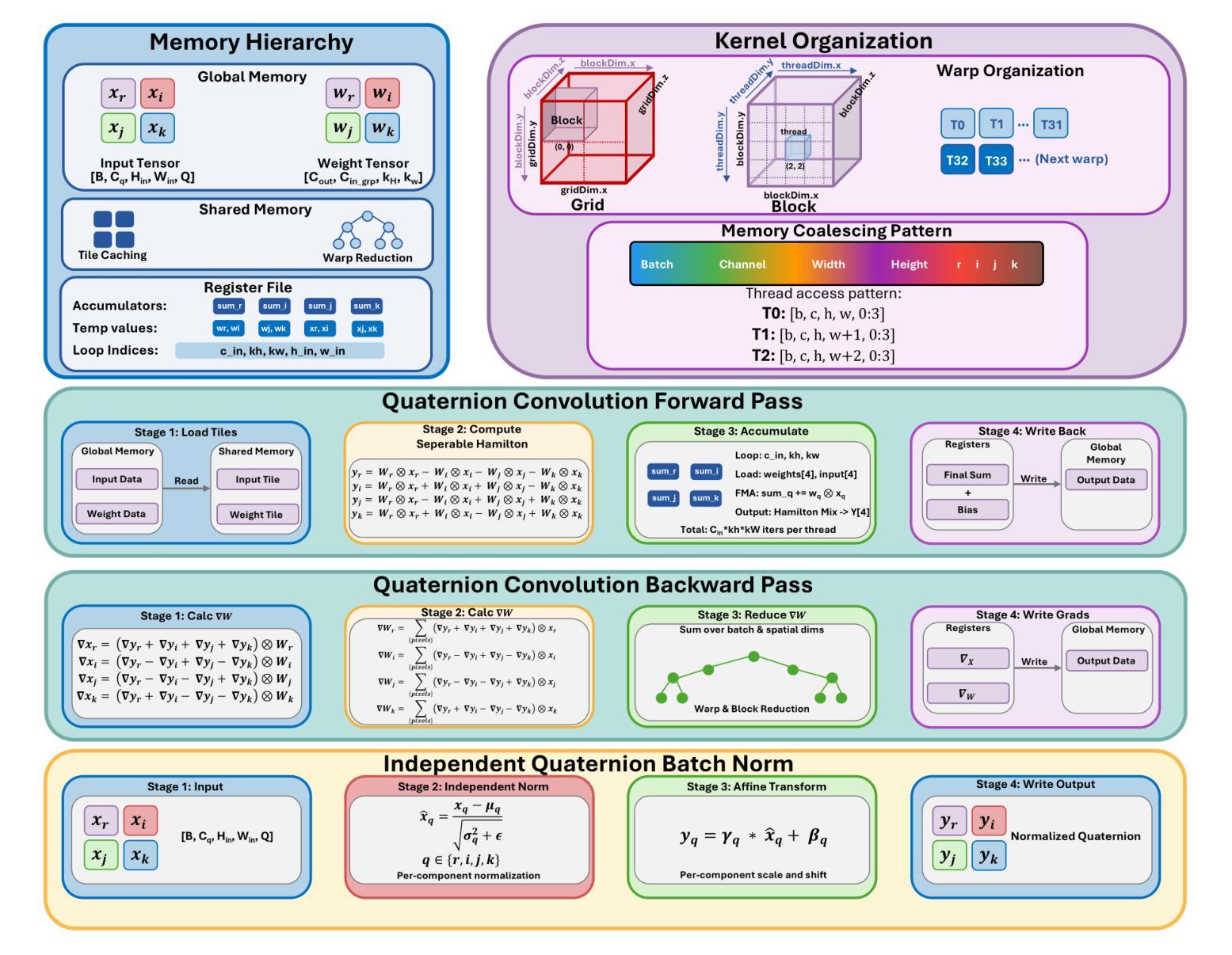
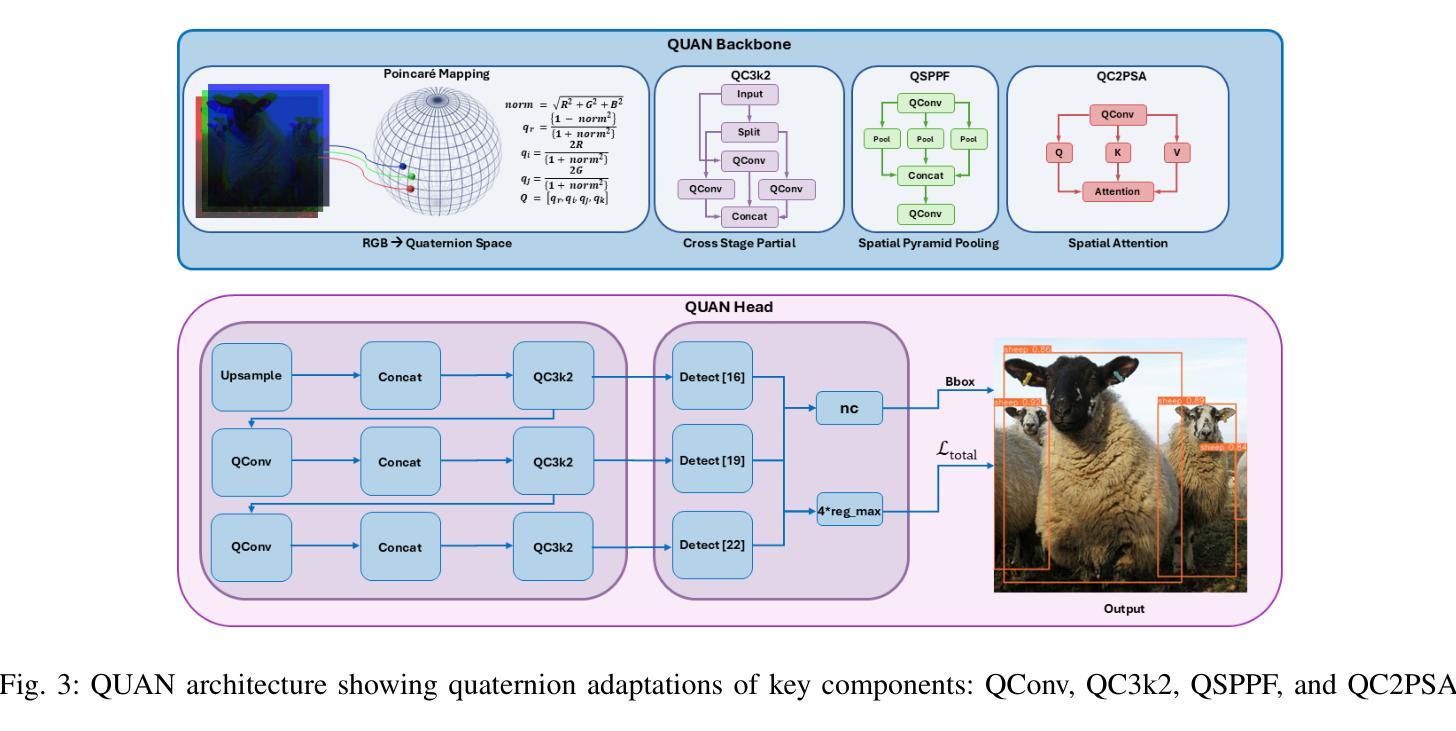
Quaternion Approximation Networks for Enhanced Image Classification and Oriented Object Detection
Authors:Bryce Grant, Peng Wang
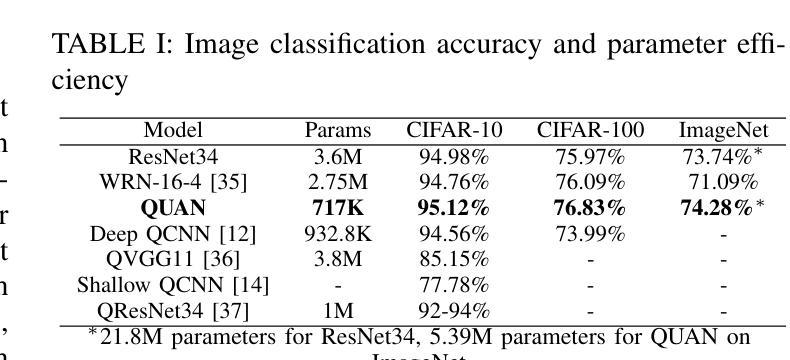
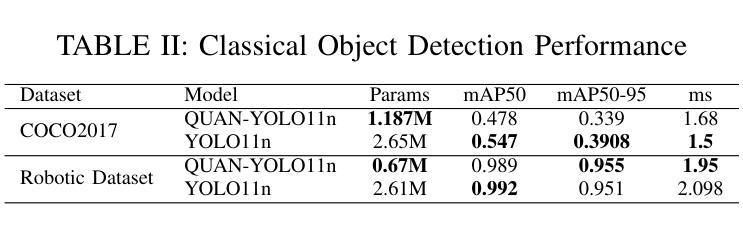
This paper introduces Quaternion Approximate Networks (QUAN), a novel deep learning framework that leverages quaternion algebra for rotation equivariant image classification and object detection. Unlike conventional quaternion neural networks attempting to operate entirely in the quaternion domain, QUAN approximates quaternion convolution through Hamilton product decomposition using real-valued operations. This approach preserves geometric properties while enabling efficient implementation with custom CUDA kernels. We introduce Independent Quaternion Batch Normalization (IQBN) for training stability and extend quaternion operations to spatial attention mechanisms. QUAN is evaluated on image classification (CIFAR-10/100, ImageNet), object detection (COCO, DOTA), and robotic perception tasks. In classification tasks, QUAN achieves higher accuracy with fewer parameters and faster convergence compared to existing convolution and quaternion-based models. For objection detection, QUAN demonstrates improved parameter efficiency and rotation handling over standard Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) while establishing the SOTA for quaternion CNNs in this downstream task. These results highlight its potential for deployment in resource-constrained robotic systems requiring rotation-aware perception and application in other domains.
本文介绍了Quaternion Approximate Networks(QUAN)这一新型深度学习框架,它利用四元数代数进行旋转等变图像分类和对象检测。不同于常规的四元数神经网络试图在四元数域内完全运行,QUAN通过利用实值操作的Hamilton产品分解来近似四元数卷积。这种方法在保留几何属性的同时,能够使用自定义的CUDA内核实现高效实现。我们引入了独立四元数批量归一化(IQBN)以实现训练稳定性,并将四元数操作扩展到空间注意力机制。QUAN在图像分类(CIFAR-10/100、ImageNet)、对象检测(COCO、DOTA)和机器人感知任务中进行了评估。在分类任务中,与现有的卷积和四元数模型相比,QUAN具有更高的精度、更少的参数和更快的收敛速度。在对象检测方面,QUAN在标准卷积神经网络(CNN)上展示了更高的参数效率和旋转处理能力,同时在此下游任务中为四元数CNN建立了最新技术。这些结果突显了其在需要旋转感知的资源受限机器人系统中的部署潜力,以及其他领域的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IROS 2025
Summary
本文介绍了Quaternion Approximate Networks(QUAN)这一新型深度学习框架,它利用四元数代数实现旋转等价图像分类和对象检测。QUAN通过汉密尔顿产品分解近似四元数卷积,利用实值操作进行实现,保留了几何属性且能高效执行。此外,还介绍了独立四元数批量归一化(IQBN)以提高训练稳定性,并将四元数操作扩展到空间注意机制。QUAN在图像分类、对象检测和机器人感知任务上的表现优异,具有较高准确性和参数效率,尤其在资源受限的需要旋转感知的机器人系统中具有部署潜力。
Key Takeaways
- QUAN是一种基于四元数代数的深度学习框架,用于旋转等价的图像分类和对象检测。
- QUAN通过汉密尔顿产品分解近似四元数卷积,使用实值操作实现,保留了几何属性且提高了效率。
- QUAN引入了独立四元数批量归一化(IQBN)以提高训练稳定性。
- QUAN将四元数操作扩展到空间注意机制。
- QUAN在图像分类、对象检测任务上表现优秀,相比现有卷积和四元数模型,具有更高的准确性和更快的收敛速度。
- QUAN在对象检测方面,相较于标准卷积神经网络(CNNs)具有更好的参数效率和旋转处理能力。
点此查看论文截图

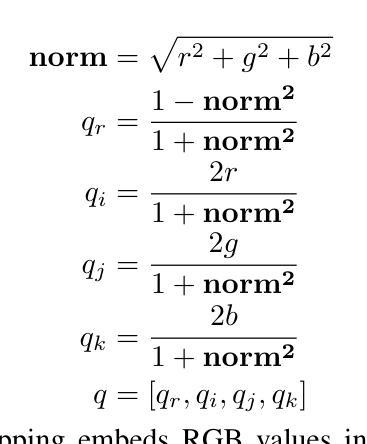
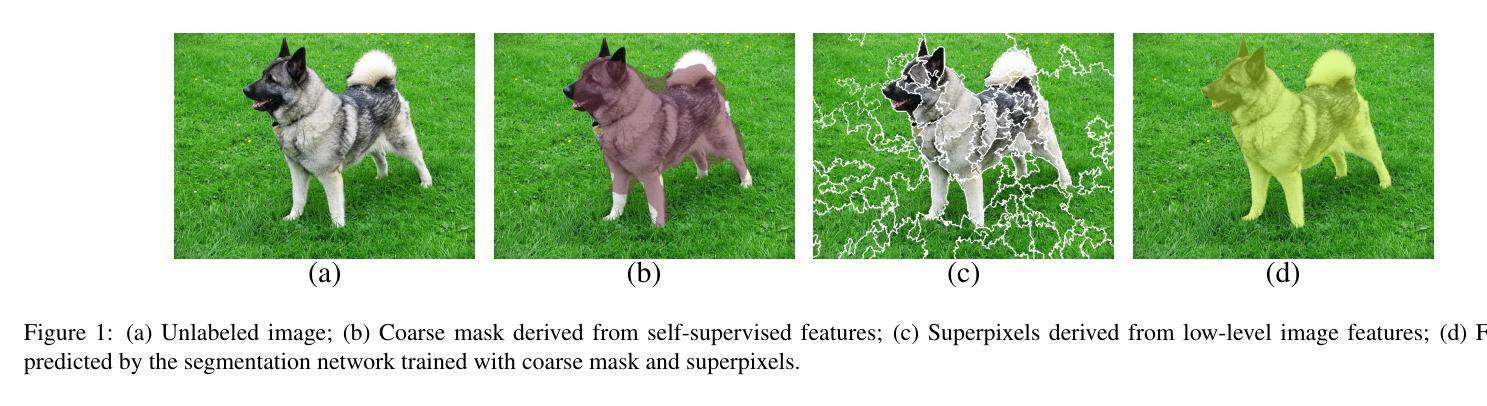
Unsupervised Instance Segmentation with Superpixels
Authors:Cuong Manh Hoang
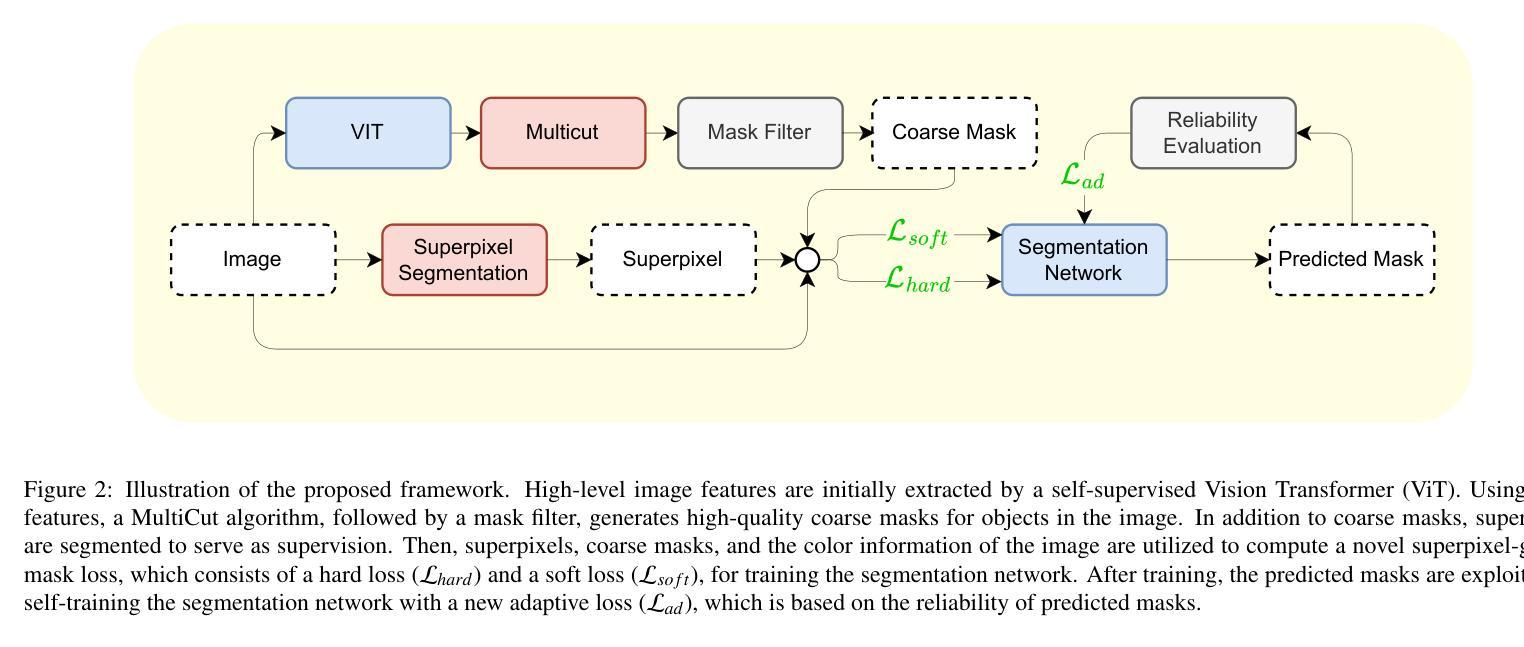
Instance segmentation is essential for numerous computer vision applications, including robotics, human-computer interaction, and autonomous driving. Currently, popular models bring impressive performance in instance segmentation by training with a large number of human annotations, which are costly to collect. For this reason, we present a new framework that efficiently and effectively segments objects without the need for human annotations. Firstly, a MultiCut algorithm is applied to self-supervised features for coarse mask segmentation. Then, a mask filter is employed to obtain high-quality coarse masks. To train the segmentation network, we compute a novel superpixel-guided mask loss, comprising hard loss and soft loss, with high-quality coarse masks and superpixels segmented from low-level image features. Lastly, a self-training process with a new adaptive loss is proposed to improve the quality of predicted masks. We conduct experiments on public datasets in instance segmentation and object detection to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework. The results show that the proposed framework outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods.
实例分割在机器人、人机交互和自动驾驶等许多计算机视觉应用中至关重要。目前,流行的模型通过大量的人工注释进行训练,在实例分割方面取得了令人印象深刻的性能,但这些注释的收集成本高昂。因此,我们提出了一种新的框架,该框架能够高效且有效地对对象进行分割,而无需人工注释。首先,应用MultiCut算法对自监督特征进行粗略的掩膜分割。然后,使用掩膜过滤器获得高质量的粗略掩膜。为了训练分割网络,我们计算了一种新型的超像素引导掩膜损失,该损失包括硬损失和软损失,由高质量的粗略掩膜和从低级图像特征中分割出来的超像素组成。最后,提出了一种新的自适应损失的自训练过程,以提高预测掩膜的质量。我们在实例分割和对象检测的公共数据集上进行了实验,以证明所提框架的有效性。结果表明,所提框架优于以前的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文主要研究无需人工标注的情况下的实例分割问题。通过使用MultiCut算法对自监督特征进行粗分割,并使用掩膜滤波器获得高质量粗分割掩膜。为了训练分割网络,利用超像素引导设计了一种新的掩膜损失函数,包括硬损失和软损失,结合高质量粗分割掩膜和从低层次图像特征中提取的超像素。最后,通过自我训练过程及新的自适应损失函数进一步提高预测掩膜的质量。在公共数据集上的实验表明,本文提出的框架在实例分割和对象检测方面优于以前的最先进方法。
关键见解
- 实例分割在计算机视觉的多个应用中至关重要,如机器人技术、人机交互和自动驾驶。
- 当前流行模型需要大量人工标注数据来进行训练,这增加了成本。
- 提出了一种新的框架,无需人工标注即可有效地进行对象分割。
- 使用MultiCut算法进行粗分割,并通过掩膜滤波器提高分割质量。
- 设计了一种新的超像素引导掩膜损失函数,结合了硬损失和软损失。
- 利用低层次图像特征中的超像素来提高分割网络的质量。
点此查看论文截图

Depthwise-Dilated Convolutional Adapters for Medical Object Tracking and Segmentation Using the Segment Anything Model 2
Authors:Guoping Xu, Christopher Kabat, You Zhang
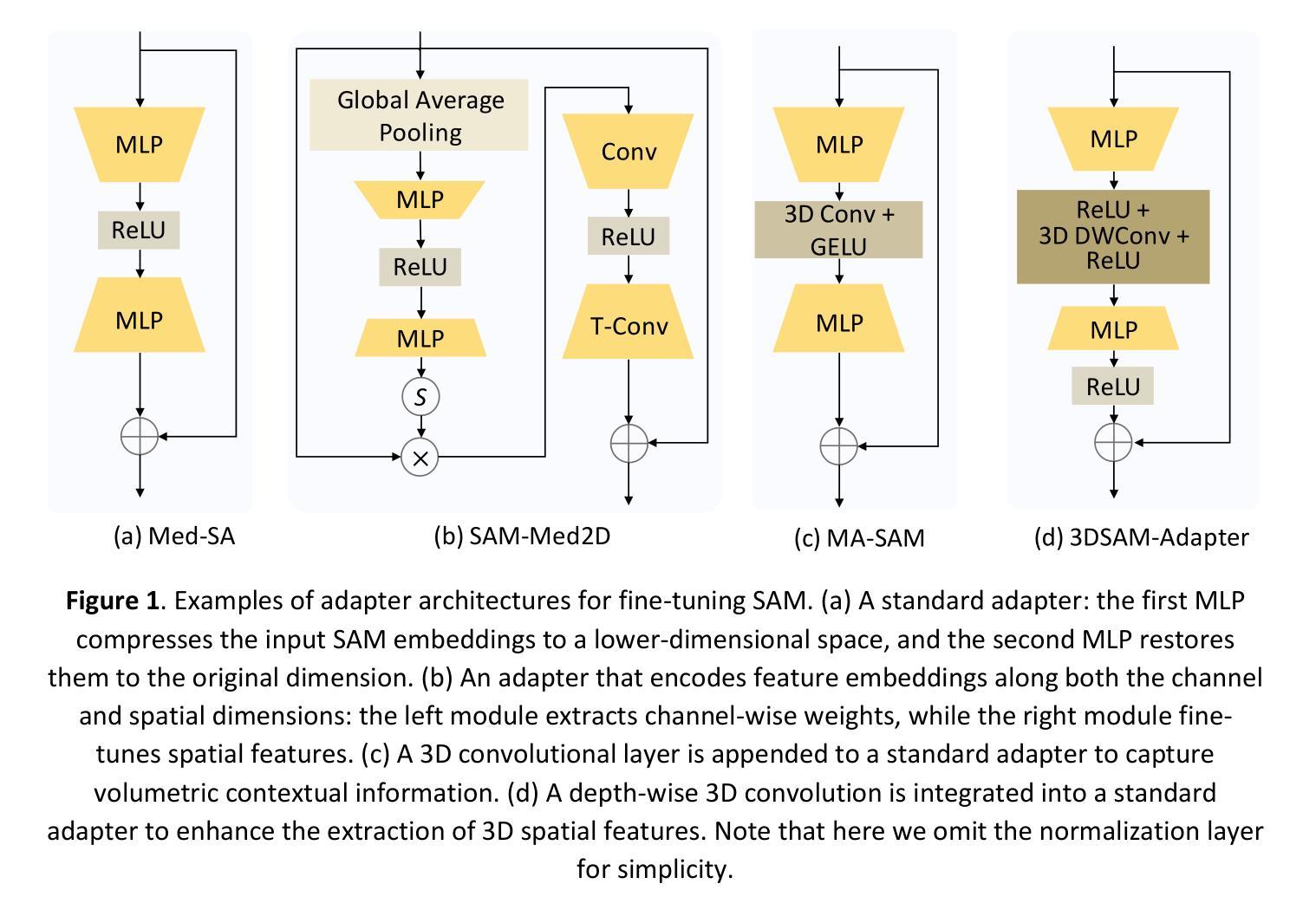
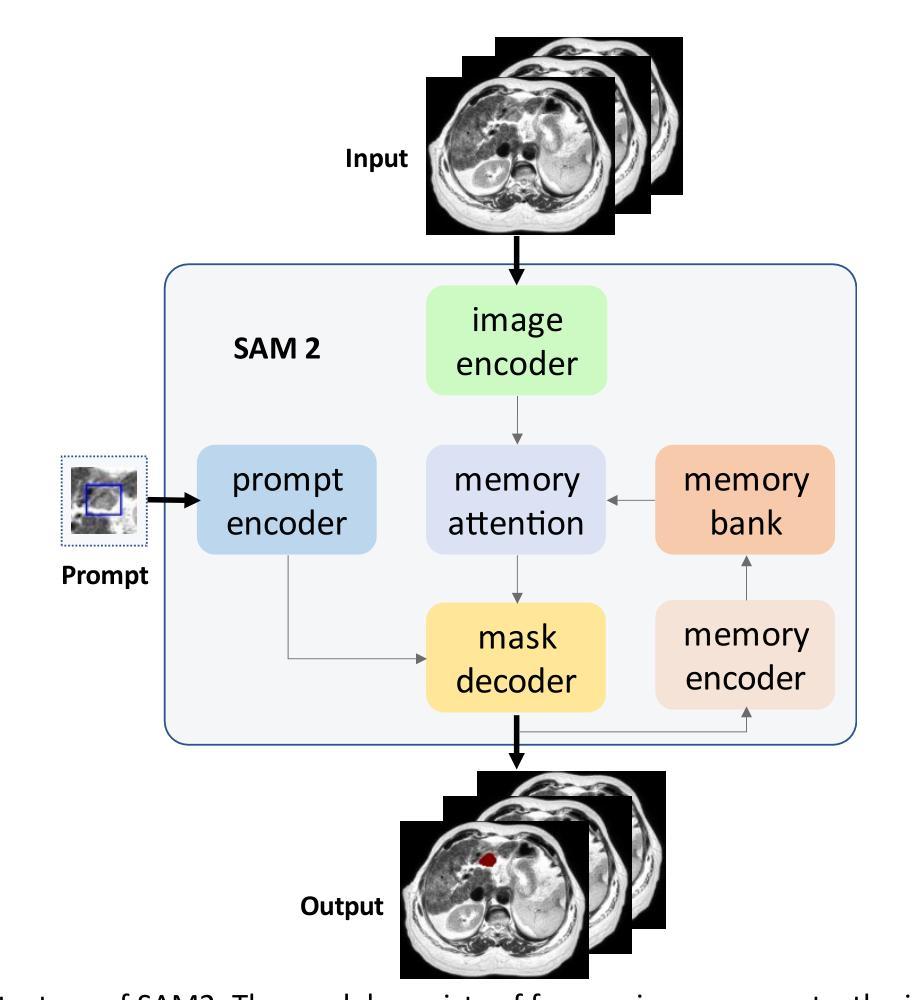
Recent advances in medical image segmentation have been driven by deep learning; however, most existing methods remain limited by modality-specific designs and exhibit poor adaptability to dynamic medical imaging scenarios. The Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) and its related variants, which introduce a streaming memory mechanism for real-time video segmentation, present new opportunities for prompt-based, generalizable solutions. Nevertheless, adapting these models to medical video scenarios typically requires large-scale datasets for retraining or transfer learning, leading to high computational costs and the risk of catastrophic forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose DD-SAM2, an efficient adaptation framework for SAM2 that incorporates a Depthwise-Dilated Adapter (DD-Adapter) to enhance multi-scale feature extraction with minimal parameter overhead. This design enables effective fine-tuning of SAM2 on medical videos with limited training data. Unlike existing adapter-based methods focused solely on static images, DD-SAM2 fully exploits SAM2’s streaming memory for medical video object tracking and segmentation. Comprehensive evaluations on TrackRad2025 (tumor segmentation) and EchoNet-Dynamic (left ventricle tracking) datasets demonstrate superior performance, achieving Dice scores of 0.93 and 0.97, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this work provides an initial attempt at systematically exploring adapter-based SAM2 fine-tuning for medical video segmentation and tracking. Code, datasets, and models will be publicly available at https://github.com/apple1986/DD-SAM2.
最近,医学图像分割领域的进展得益于深度学习的发展。然而,大多数现有方法仍然受到特定模态设计的限制,对动态医学影像场景适应性较差。Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)及其相关变体引入了实时视频分割的流式内存机制,为基于提示的、可推广的解决方案提供了新的机会。然而,将这些模型适应到医疗视频场景通常需要大规模数据集进行重新训练或迁移学习,这导致了高计算成本以及灾难性遗忘的风险。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了DD-SAM2,这是一个SAM2的有效适应框架,它结合了Depthwise-Dilated Adapter(DD-Adapter)以增强多尺度特征提取,同时最小化参数开销。这种设计能够在有限的训练数据上实现对医疗视频的SAM2有效微调。与现有仅专注于静态图像的适配器方法不同,DD-SAM2充分利用SAM2的流式内存进行医疗视频目标跟踪和分割。在TrackRad2025(肿瘤分割)和EchoNet-Dynamic(左心室跟踪)数据集上的综合评估表明,其性能卓越,分别实现了Dice系数为0.93和0.97。据我们所知,这项工作初步尝试系统地探索基于适配器的SAM2微调在医疗视频分割和跟踪中的应用。代码、数据集和模型将在https://github.com/apple1986/DD-SAM2上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 6 figures
Summary
基于深度学习的医学图像分割技术近年来取得了进展,但现有方法受限于特定模态设计和动态医学影像场景适应性差的问题。Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)及其变体通过实时视频分割引入流式内存机制,为基于提示的通用解决方案提供了新的机会。然而,将这些模型适应到医学视频场景通常需要大规模数据集进行再训练或迁移学习,导致高计算成本和灾难性遗忘风险。为此,我们提出DD-SAM2,一个高效的SAM2适应框架,通过深度可分离适配器(DD-Adapter)增强多尺度特征提取,用最小的参数开销实现了在有限训练数据上的医学视频精细调整。与现有专注于静态图像的适配器方法不同,DD-SAM2充分利用SAM2的流式内存进行医学视频目标跟踪和分割。在TrackRad2025(肿瘤分割)和EchoNet-Dynamic(左心室跟踪)数据集上的全面评估显示,其Dice得分分别为0.93和0.97,表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割领域虽然有所进展,但仍面临特定模态设计和动态医学影像场景适应性问题。
- SAM2模型及其变体通过引入流式内存机制为视频分割提供了新的解决方案。
- 适应医学视频场景通常需要大规模数据集,导致高计算成本和灾难性遗忘风险。
- DD-SAM2是一个高效的SAM2适应框架,通过深度可分离适配器增强多尺度特征提取。
- DD-SAM2可在有限训练数据上进行医学视频的精细调整。
- DD-SAM2在医学视频目标跟踪和分割上表现出卓越性能。
- 在TrackRad2025和EchoNet-Dynamic数据集上的评估结果显示Dice得分高。
点此查看论文截图

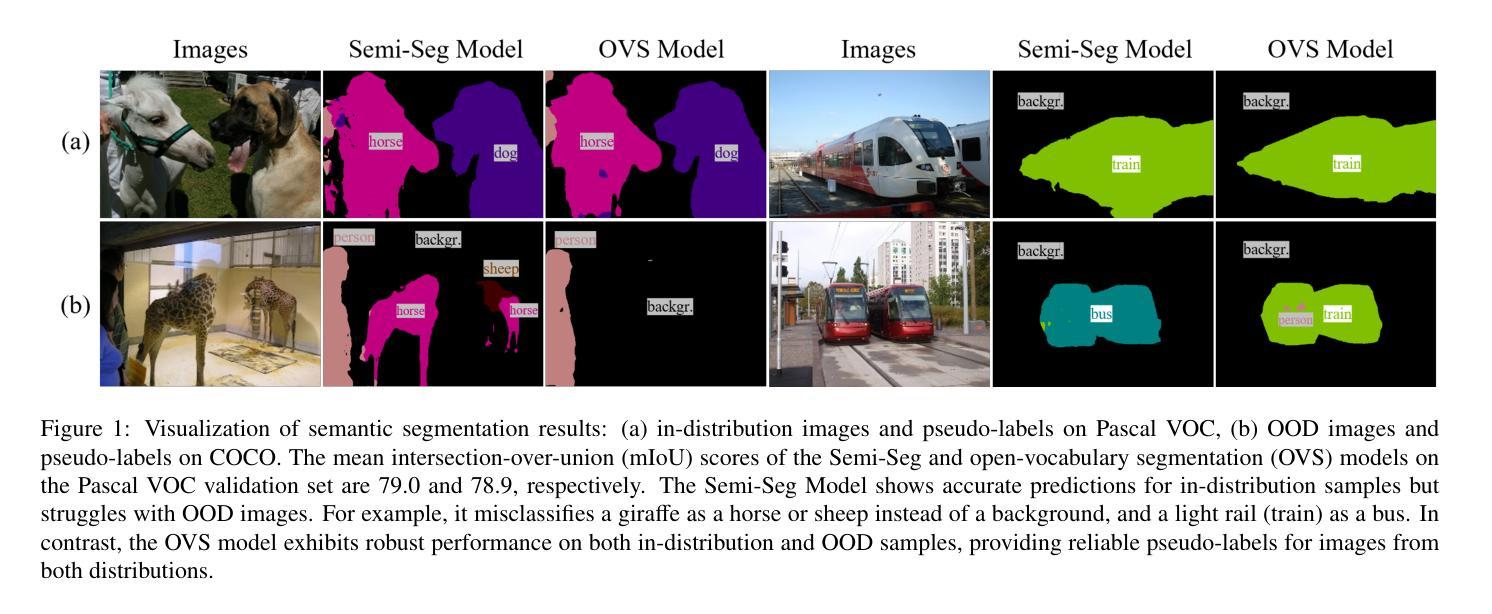
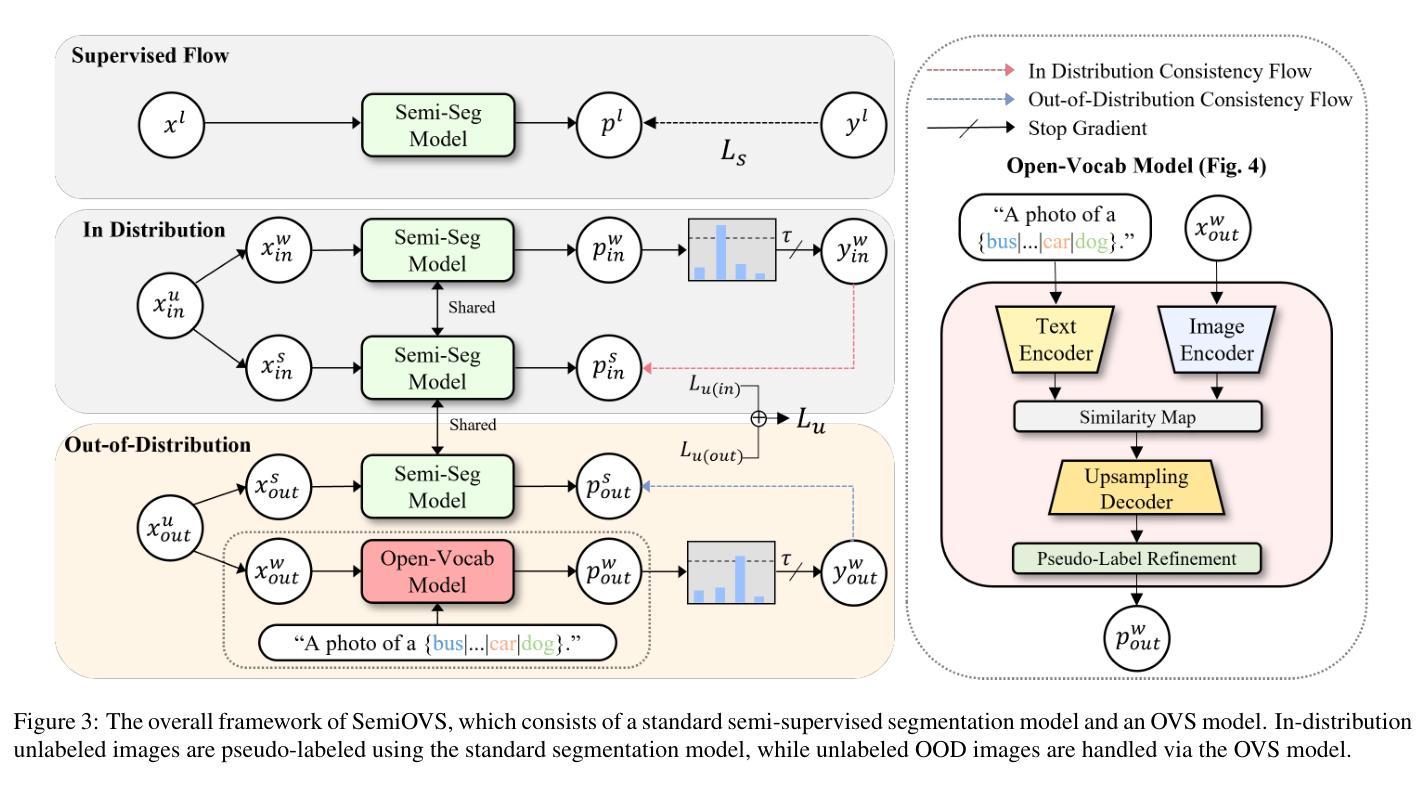
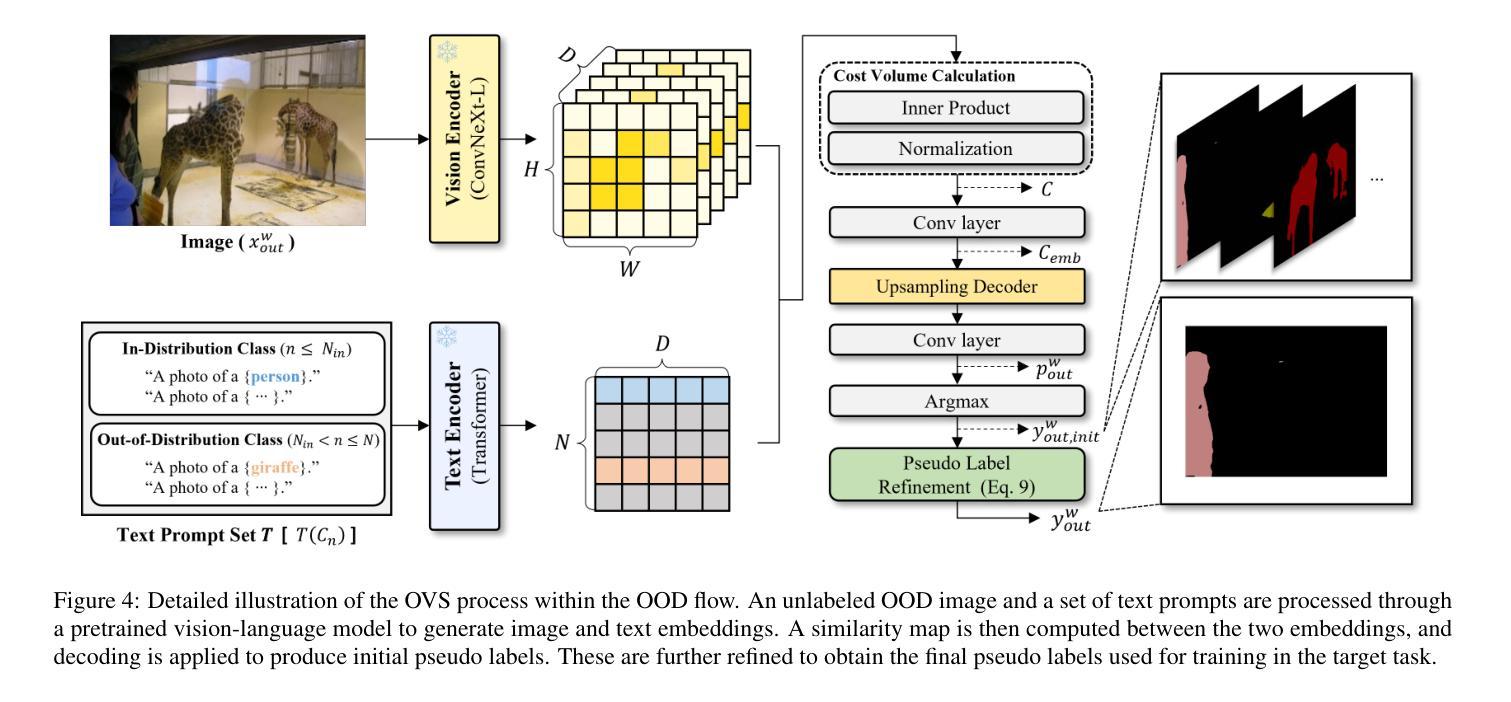
Leveraging Out-of-Distribution Unlabeled Images: Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation with an Open-Vocabulary Model
Authors:Wooseok Shin, Jisu Kang, Hyeonki Jeong, Jin Sob Kim, Sung Won Han
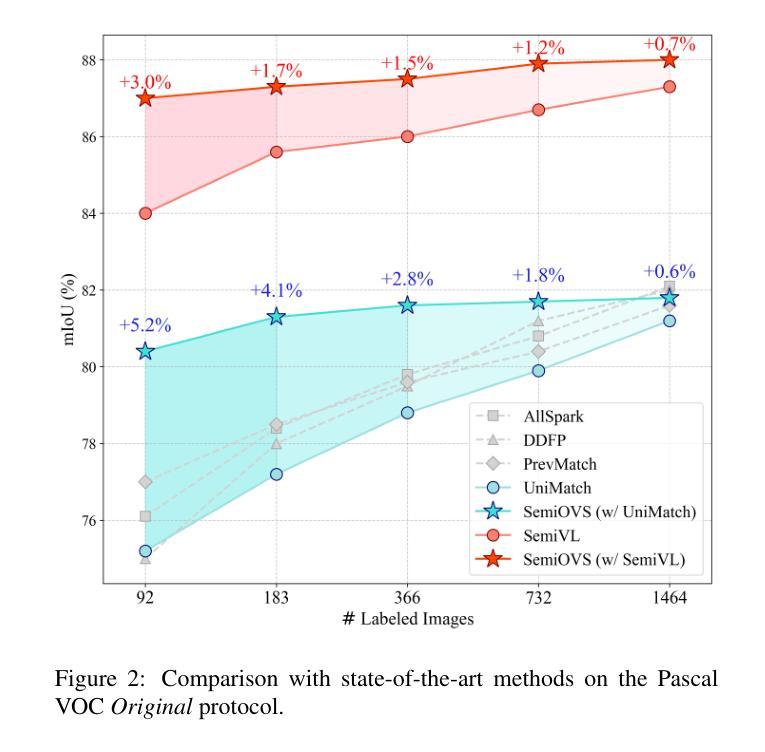
In semi-supervised semantic segmentation, existing studies have shown promising results in academic settings with controlled splits of benchmark datasets. However, the potential benefits of leveraging significantly larger sets of unlabeled images remain unexplored. In real-world scenarios, abundant unlabeled images are often available from online sources (web-scraped images) or large-scale datasets. However, these images may have different distributions from those of the target dataset, a situation known as out-of-distribution (OOD). Using these images as unlabeled data in semi-supervised learning can lead to inaccurate pseudo-labels, potentially misguiding network training. In this paper, we propose a new semi-supervised semantic segmentation framework with an open-vocabulary segmentation model (SemiOVS) to effectively utilize unlabeled OOD images. Extensive experiments on Pascal VOC and Context datasets demonstrate two key findings: (1) using additional unlabeled images improves the performance of semi-supervised learners in scenarios with few labels, and (2) using the open-vocabulary segmentation (OVS) model to pseudo-label OOD images leads to substantial performance gains. In particular, SemiOVS outperforms existing PrevMatch and SemiVL methods by +3.5 and +3.0 mIoU, respectively, on Pascal VOC with a 92-label setting, achieving state-of-the-art performance. These findings demonstrate that our approach effectively utilizes abundant unlabeled OOD images for semantic segmentation tasks. We hope this work can inspire future research and real-world applications. The code is available at https://github.com/wooseok-shin/SemiOVS
在半监督语义分割领域,现有研究在基准数据集的受控分割方面已显示出有前途的结果。然而,利用大量未标记图像的潜在优势仍未被探索。在真实世界场景中,通常可以从在线来源(网络抓取图像)或大规模数据集中获得大量未标记的图像。然而,这些图像的分布可能与目标数据集的分布不同,这种情况被称为超出分布(OOD)。将这些图像作为半监督学习中的未标记数据可能导致不准确的伪标签,从而可能误导网络训练。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Knowledge-Based Systems
Summary
本文提出了一种新的半监督语义分割框架,利用开放词汇分割模型(SemiOVS)有效使用未标记的OOD图像。实验表明,使用额外的未标记图像可以提高少标签场景下半监督学习者的性能,使用开放词汇分割模型对OOD图像进行伪标记可以带来显著的性能提升。该方法在Pascal VOC等数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出了一种新的半监督语义分割框架,旨在利用大量的未标记图像以提高性能。
- 研究发现,使用额外的未标记图像在少标签场景下半监督学习的性能有所提升。
- 开放词汇分割(OVS)模型被用于对OOD图像进行伪标记,取得了显著的性能提升。
- SemiOVS框架在Pascal VOC数据集上实现了最先进的性能,相比PrevMatch和SemiVL方法分别有+3.5和+3.0 mIoU的提升。
- 该方法能够有效地利用在线来源或大规模数据集中丰富的未标记图像。
- 该研究的成果对于未来的研究和实际应用具有启发意义。
点此查看论文截图