⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-10 更新
AxelSMOTE: An Agent-Based Oversampling Algorithm for Imbalanced Classification
Authors:Sukumar Kishanthan, Asela Hevapathige
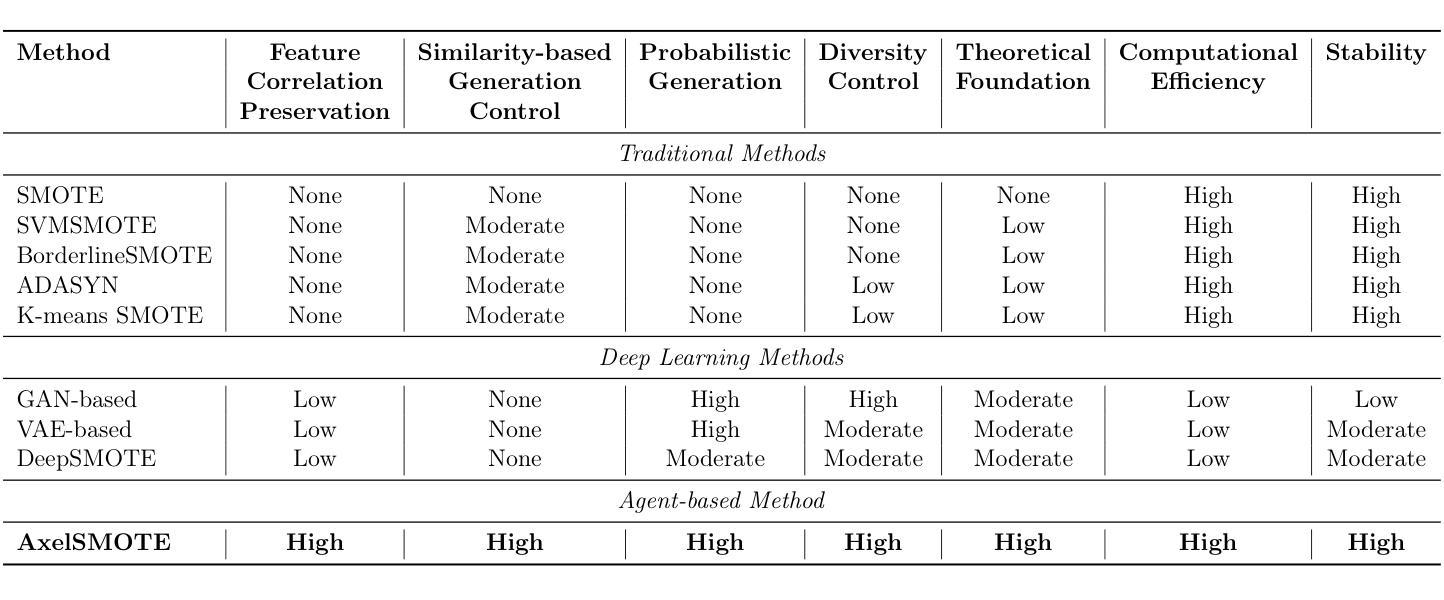
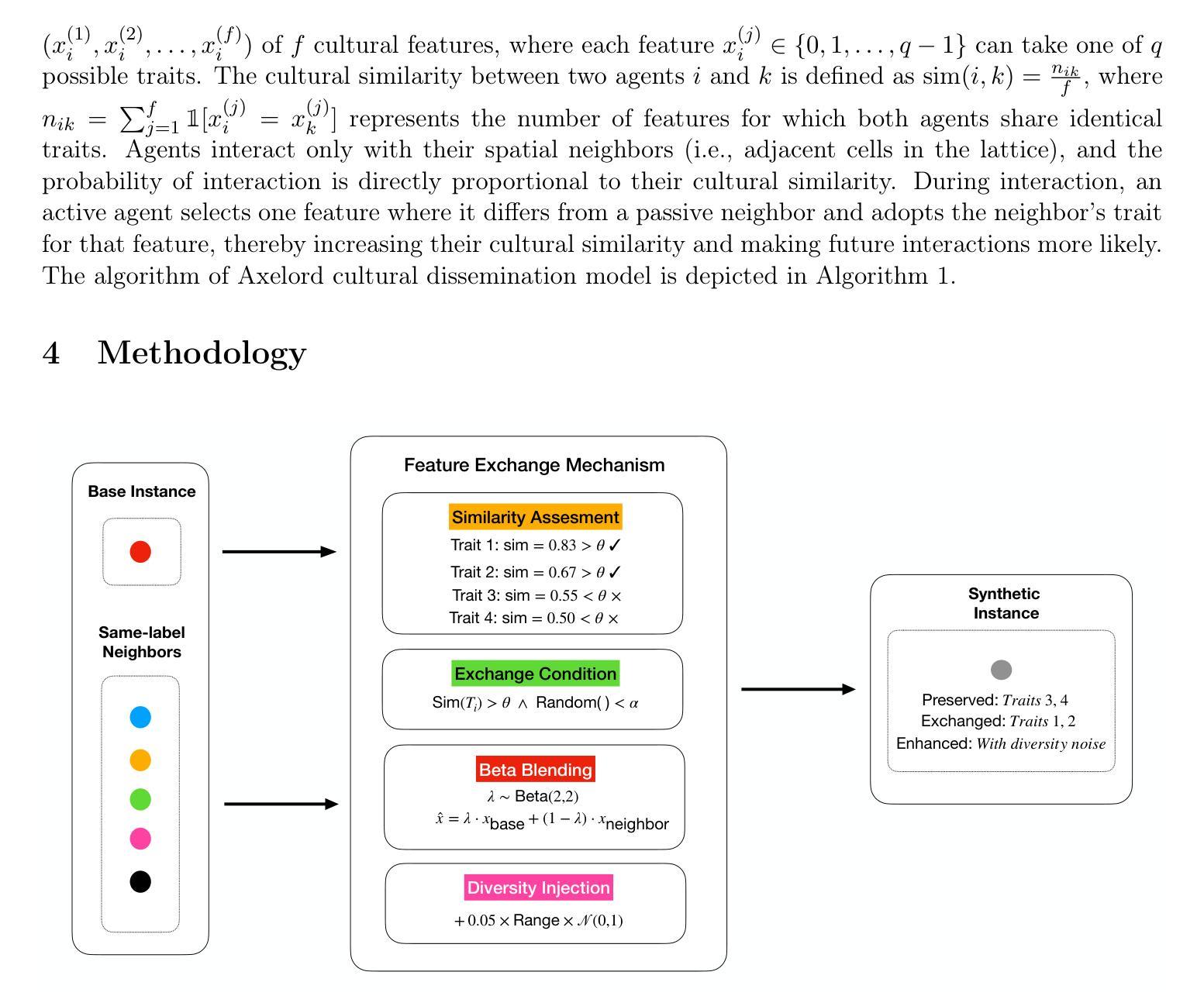
Class imbalance in machine learning poses a significant challenge, as skewed datasets often hinder performance on minority classes. Traditional oversampling techniques, which are commonly used to alleviate class imbalance, have several drawbacks: they treat features independently, lack similarity-based controls, limit sample diversity, and fail to manage synthetic variety effectively. To overcome these issues, we introduce AxelSMOTE, an innovative agent-based approach that views data instances as autonomous agents engaging in complex interactions. Based on Axelrod’s cultural dissemination model, AxelSMOTE implements four key innovations: (1) trait-based feature grouping to preserve correlations; (2) a similarity-based probabilistic exchange mechanism for meaningful interactions; (3) Beta distribution blending for realistic interpolation; and (4) controlled diversity injection to avoid overfitting. Experiments on eight imbalanced datasets demonstrate that AxelSMOTE outperforms state-of-the-art sampling methods while maintaining computational efficiency.
机器学习中的类别不平衡问题是一个重大挑战,因为数据集的偏斜往往会降低对少数类别的性能。传统的过采样技术通常用于缓解类别不平衡问题,但存在几个缺点:它们独立处理特征,缺乏基于相似性的控制,限制样本多样性,并且无法有效地管理合成多样性。为了克服这些问题,我们引入了AxelSMOTE,这是一种基于创新的代理方法,它将数据实例视为参与复杂交互的自治代理。基于Axelrod的文化传播模型,AxelSMOTE实现了四个关键创新点:(1)基于特征的分组来保留相关性;(2)基于相似性的概率交换机制以实现有意义的交互;(3)Beta分布混合以实现真实插值;(4)控制多样性注入以避免过度拟合。在八个不平衡数据集上的实验表明,AxelSMOTE在保持计算效率的同时,优于最新的采样方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:机器学习中的类别不平衡问题对模型性能产生重大影响。传统过采样技术在处理类别不平衡问题时存在诸多缺陷。为解决这些问题,引入了一种基于代理的创新方法AxelSMOTE,该方法将数据实例视为自主代理,进行复杂交互。AxelSMOTE实现了四个关键创新点,包括基于特征的分组、基于相似度的概率交换机制、Beta分布混合以及控制多样性注入。实验证明,AxelSMOTE在不平衡数据集上的性能优于其他先进的采样方法,同时保持了计算效率。
Key Takeaways:
- 类别不平衡问题在机器学习中普遍存在,对模型性能产生重大影响。
- 传统过采样技术存在诸多缺陷,如独立处理特征、缺乏相似度控制、样本多样性有限等。
- AxelSMOTE是一种基于代理的创新方法,引入复杂交互的数据处理方式。
- AxelSMOTE实现了四个关键创新点:基于特征的分组、概率交换机制、Beta分布混合以及控制多样性注入。
- AxelSMOTE在多个不平衡数据集上的实验表现优于其他先进的采样方法。
- AxelSMOTE能够保持计算效率,为处理类别不平衡问题提供有效解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

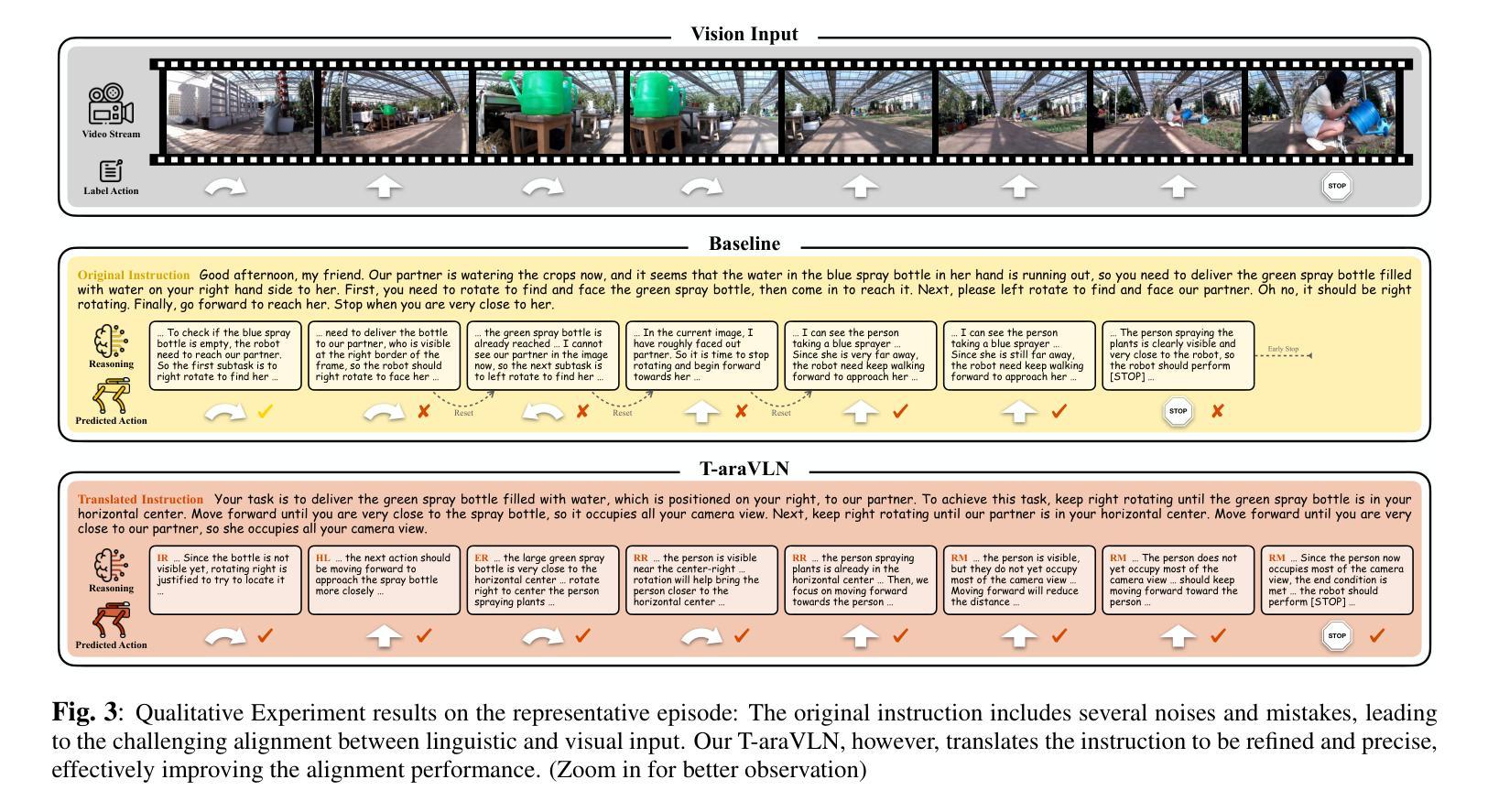
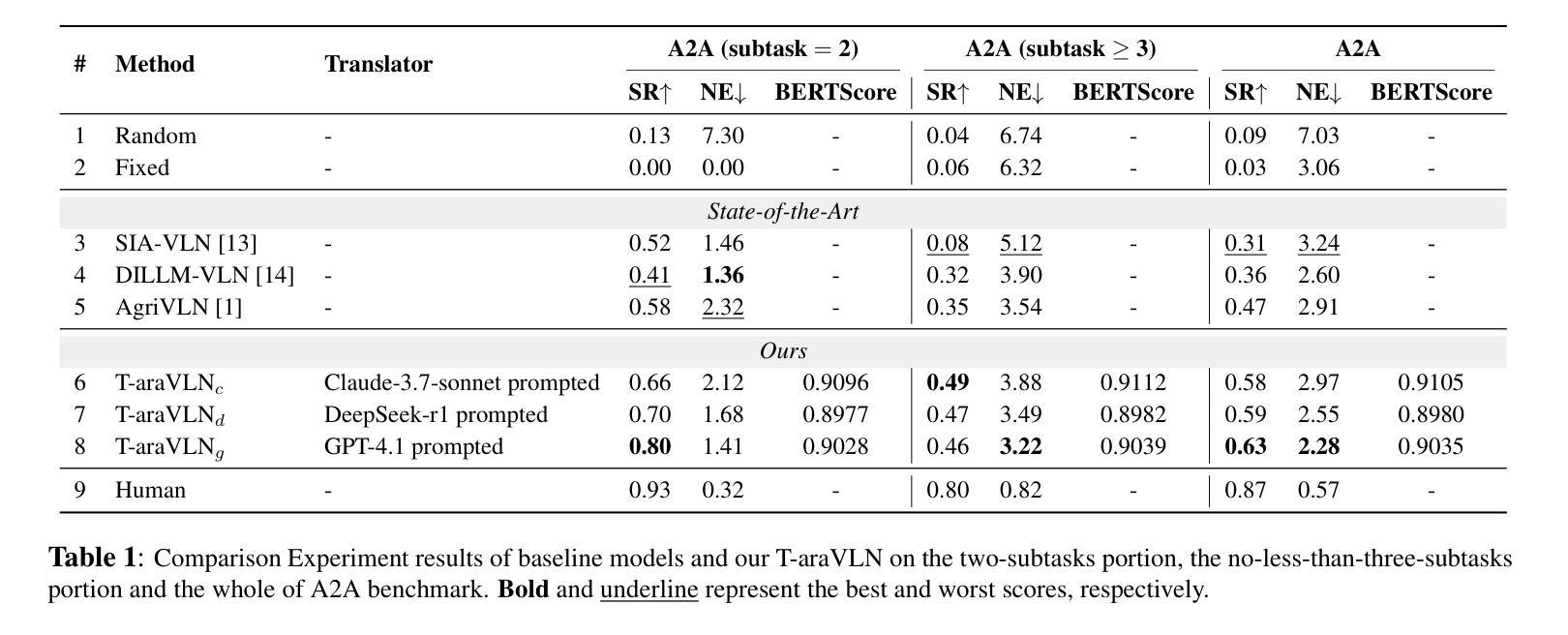
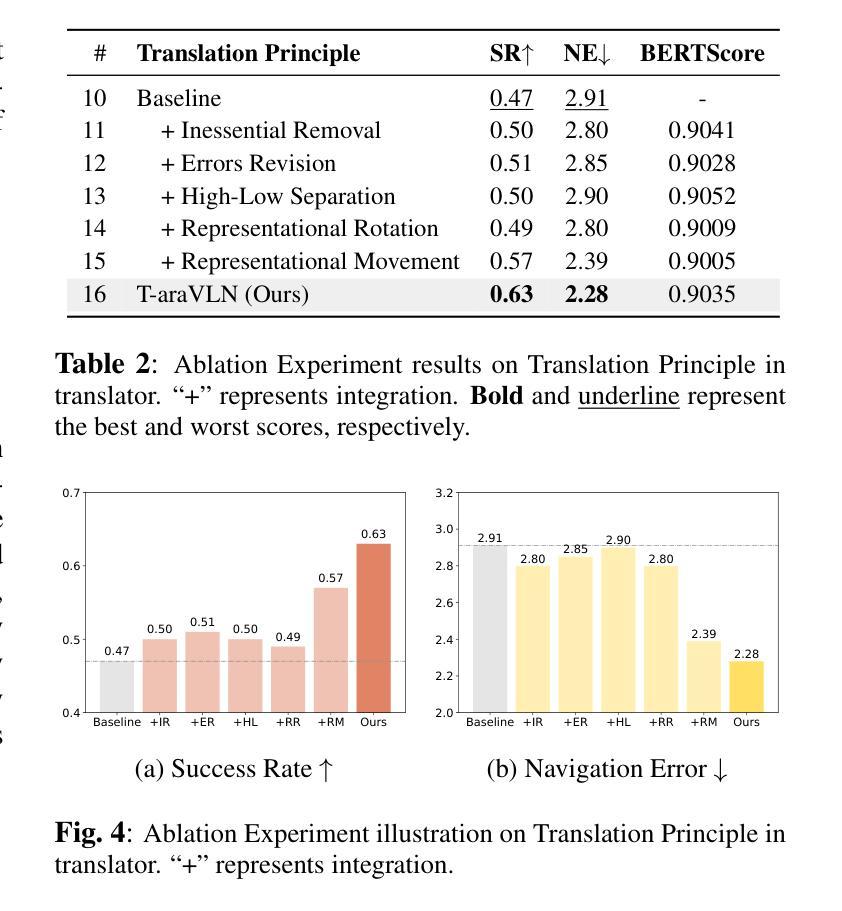
T-araVLN: Translator for Agricultural Robotic Agents on Vision-and-Language Navigation
Authors:Xiaobei Zhao, Xingqi Lyu, Xiang Li
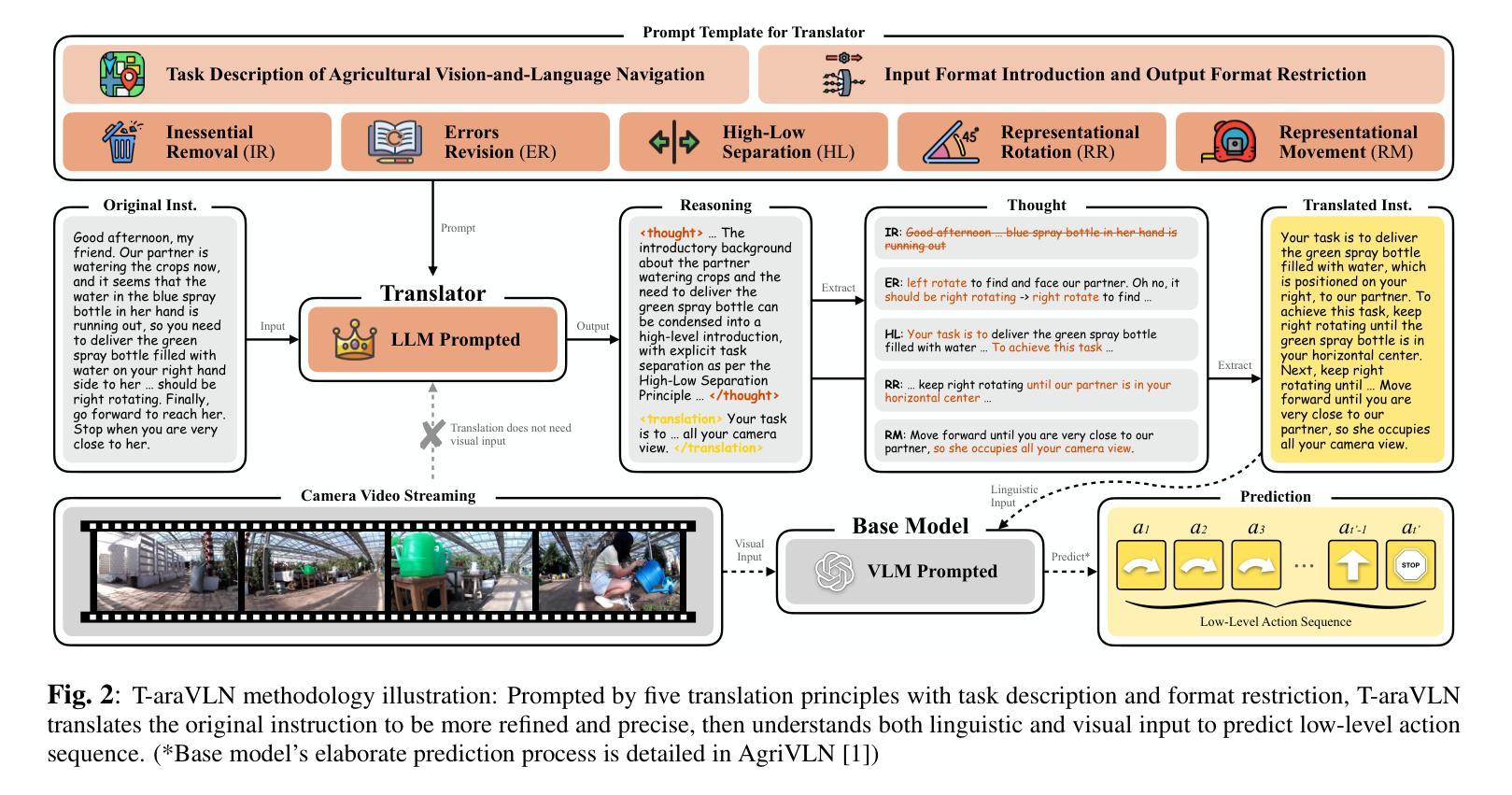
Agricultural robotic agents have been becoming powerful helpers in a wide range of agricultural tasks, nevertheless, still heavily rely on manual operation or untransportable railway for movement. The AgriVLN method and the A2A benchmark pioneeringly extend Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) to the agricultural domain, enabling agents navigate to the target position following the natural language instructions. AgriVLN effectively understands the simple instructions, however, often misunderstands the complicated instructions. To bridge this gap, we propose the method of Translator for Agricultural Robotic Agents on Vision-and-Language Navigation (T-araVLN), in which the Instruction Translator module translates the original instruction to be both refined and precise. Being evaluated on the A2A benchmark, our T-araVLN effectively improves SR from 0.47 to 0.63 and reduces NE from 2.91m to 2.28m, demonstrating the state-of-the-art performance in the agricultural domain. Code: https://github.com/AlexTraveling/T-araVLN.
农业机器人代理在广泛的农业任务中已成为强大的助手,然而仍然严重依赖于手动操作或不可移动的铁路进行移动。AgriVLN方法和A2A基准率先将视觉和语言导航(VLN)扩展到农业领域,使代理能够根据自然语言指令导航到目标位置。AgriVLN能有效地理解简单指令,但常常误解复杂指令。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了农业机器人代理视觉和语言导航翻译器方法(T-araVLN),其中的指令翻译模块将原始指令翻译为既精细又精确的指令。在A2A基准测试中评估,我们的T-araVLN方法有效地提高了成功率从0.47到0.63,并将定位误差从2.91米减少到2.28米,显示出在农业领域的最先进的性能。代码地址:https://github.com/AlexTraveling/T-araVLN。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
农业机器人已经在广泛的农业任务中成为有力的助手,但它们仍然严重依赖于手动操作或不可移动的铁路进行移动。AgriVLN方法和A2A基准率先将视觉和语言导航(VLN)扩展到农业领域,使代理能够根据自然语言指令导航到目标位置。尽管AgriVLN可以有效地理解简单指令,但经常误解复杂指令。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了面向农业机器人代理的视觉和语言导航翻译方法(T-araVLN),其中的指令翻译模块将原始指令翻译为既精确又精炼的指令。在A2A基准测试上评估,我们的T-araVLN方法有效地提高了成功率从0.47到0.63,并将导航误差从2.91米减少到2.28米,展现出农业领域的最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 农业机器人已经在各种农业任务中发挥重要作用,但在移动方面仍面临依赖手动操作或不可移动运输方式的问题。
- AgriVLN方法和A2A基准首次将视觉和语言导航技术应用于农业领域,使机器人能够根据自然语言指令进行导航。
- AgriVLN在处理复杂指令时存在误解的问题。
- 为解决上述问题,提出了T-araVLN方法,其中的指令翻译模块能够精炼和精确翻译原始指令。
- 在A2A基准测试上,T-araVLN方法显著提高了成功率和减少了导航误差。
- T-araVLN方法展示了农业领域最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

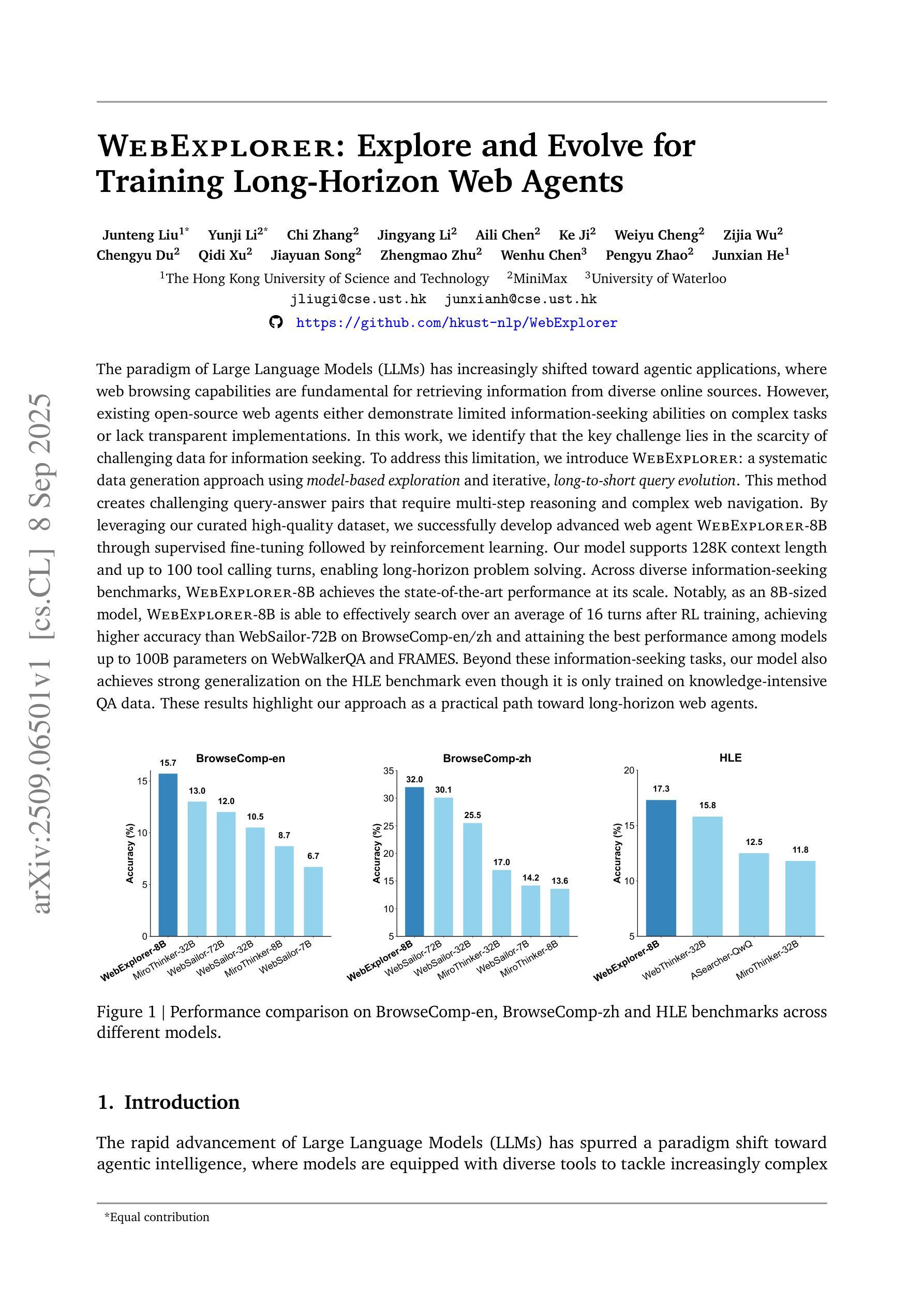
WebExplorer: Explore and Evolve for Training Long-Horizon Web Agents
Authors:Junteng Liu, Yunji Li, Chi Zhang, Jingyang Li, Aili Chen, Ke Ji, Weiyu Cheng, Zijia Wu, Chengyu Du, Qidi Xu, Jiayuan Song, Zhengmao Zhu, Wenhu Chen, Pengyu Zhao, Junxian He
The paradigm of Large Language Models (LLMs) has increasingly shifted toward agentic applications, where web browsing capabilities are fundamental for retrieving information from diverse online sources. However, existing open-source web agents either demonstrate limited information-seeking abilities on complex tasks or lack transparent implementations. In this work, we identify that the key challenge lies in the scarcity of challenging data for information seeking. To address this limitation, we introduce WebExplorer: a systematic data generation approach using model-based exploration and iterative, long-to-short query evolution. This method creates challenging query-answer pairs that require multi-step reasoning and complex web navigation. By leveraging our curated high-quality dataset, we successfully develop advanced web agent WebExplorer-8B through supervised fine-tuning followed by reinforcement learning. Our model supports 128K context length and up to 100 tool calling turns, enabling long-horizon problem solving. Across diverse information-seeking benchmarks, WebExplorer-8B achieves the state-of-the-art performance at its scale. Notably, as an 8B-sized model, WebExplorer-8B is able to effectively search over an average of 16 turns after RL training, achieving higher accuracy than WebSailor-72B on BrowseComp-en/zh and attaining the best performance among models up to 100B parameters on WebWalkerQA and FRAMES. Beyond these information-seeking tasks, our model also achieves strong generalization on the HLE benchmark even though it is only trained on knowledge-intensive QA data. These results highlight our approach as a practical path toward long-horizon web agents.
大型语言模型(LLM)的范式越来越转向代理应用,其中网页浏览能力对于从各种在线来源检索信息至关重要。然而,现有的开源网络代理要么在复杂任务上表现出有限的信息搜索能力,要么缺乏透明的实现。在这项工作中,我们发现关键挑战在于缺乏信息搜索的挑战性数据。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了WebExplorer:一种基于模型探索和数据迭代、从长到短的查询演变的有系统的数据生成方法。这种方法创建了需要多步骤推理和复杂网络导航的具有挑战性的查询答案对。通过利用我们精心制作的高质量数据集,我们成功地开发了先进的网络代理WebExplorer-8B,通过监督微调后采用强化学习。我们的模型支持最多包含高达12万字的上下文长度和长达10万次的工具调用,可实现长期问题解决。在各种信息搜索基准测试中,WebExplorer-8B在其规模上实现了最先进的性能。值得注意的是,作为规模为8亿参数的模型,WebExplorer-8B在经过强化学习训练后能够在平均超过16轮搜索中有效查找信息,在BrowseComp-en/zh上的准确性高于WebSailor-72B,并在WebWalkerQA和FRAMES上达到了迄今为止参数在百亿规模内的模型的最佳性能表现。除了这些信息搜索任务之外,即使在知识密集型问答数据上进行训练的情况下,我们的模型也在HLE基准测试上实现了强大的泛化能力。这些结果凸显了我们方法在面向长期视野的网络代理方向上的实际应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了大型语言模型(LLM)在面向代理应用时的挑战,尤其是信息检索方面的不足。针对这一问题,提出了一种名为WebExplorer的系统化数据生成方法,通过模型探索和查询的迭代演化,生成具有挑战性问答对。基于此数据集训练出的WebExplorer-8B模型,支持长语境和多次工具调用,能在多种信息搜索任务上实现最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在代理应用中面临信息检索能力的挑战。
- WebExplorer方法通过模型探索和查询迭代演化解决数据稀缺问题。
- WebExplorer-8B模型基于WebExplorer方法开发,支持长语境和多次工具调用。
- WebExplorer-8B模型在多种信息搜索任务上实现最佳性能。
- 该模型在知识密集型问答数据上表现出强大的泛化能力。
- WebExplorer-8B模型在浏览比较任务上的准确率高于WebSailor-72B。
点此查看论文截图
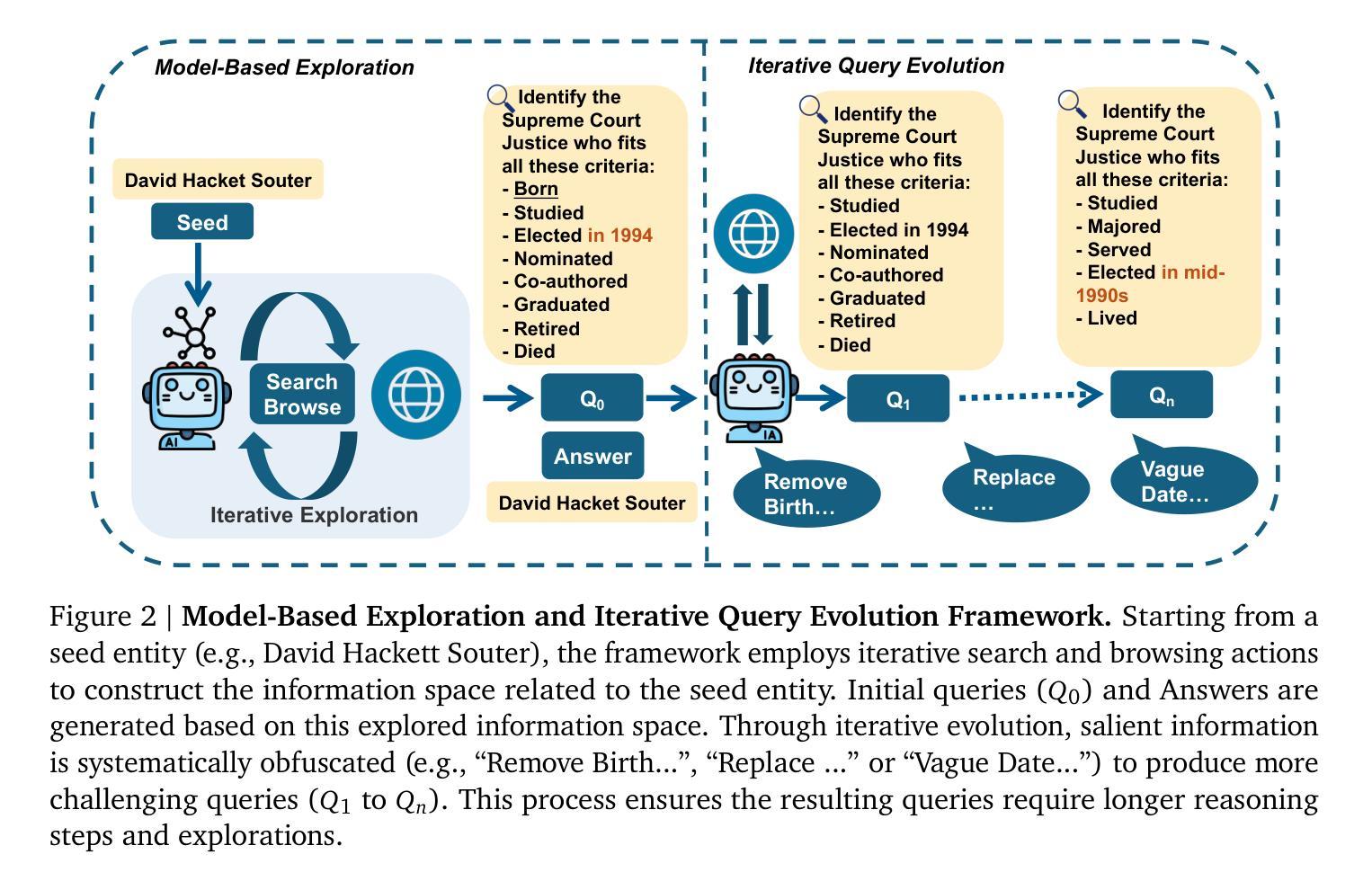
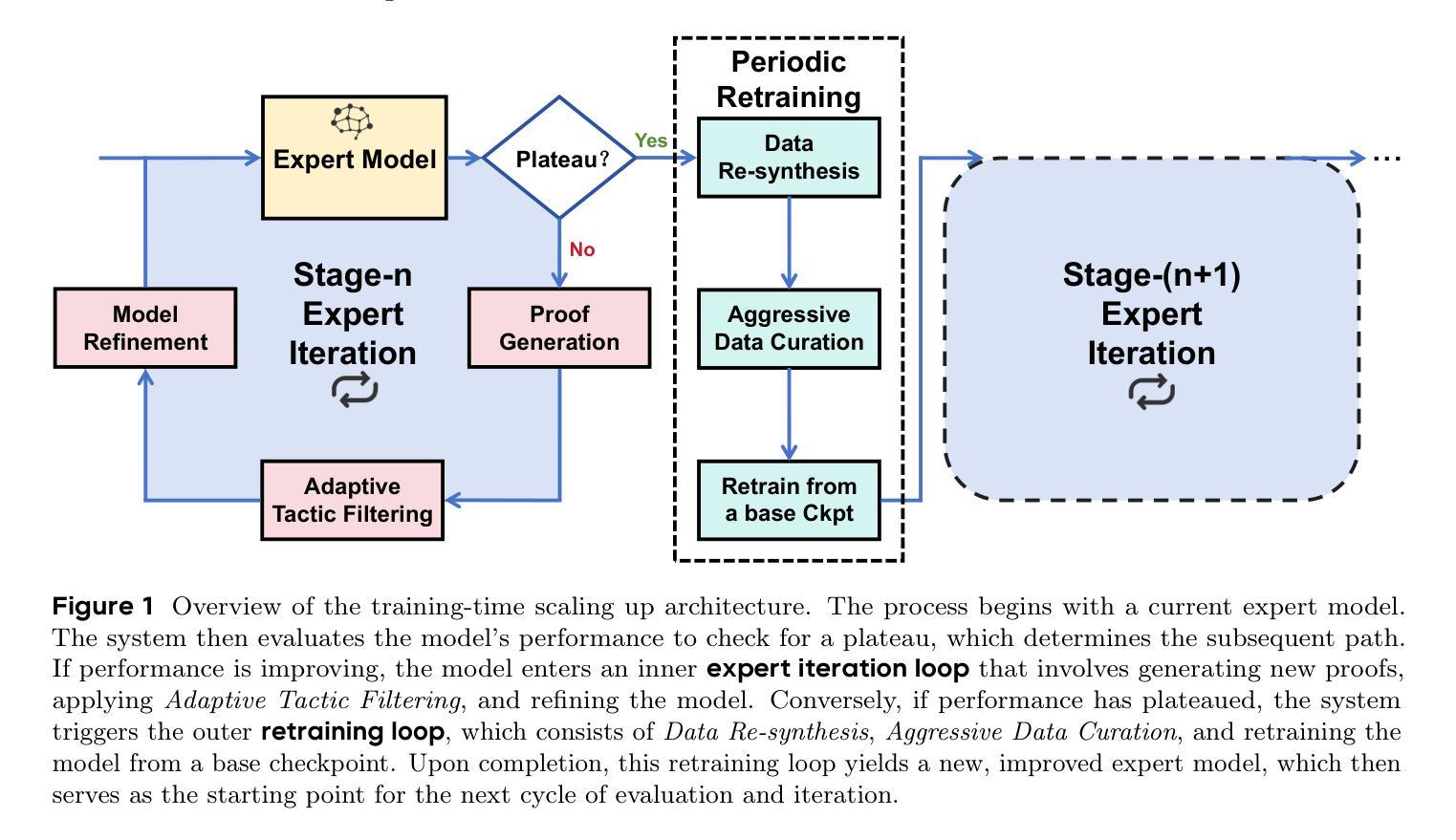
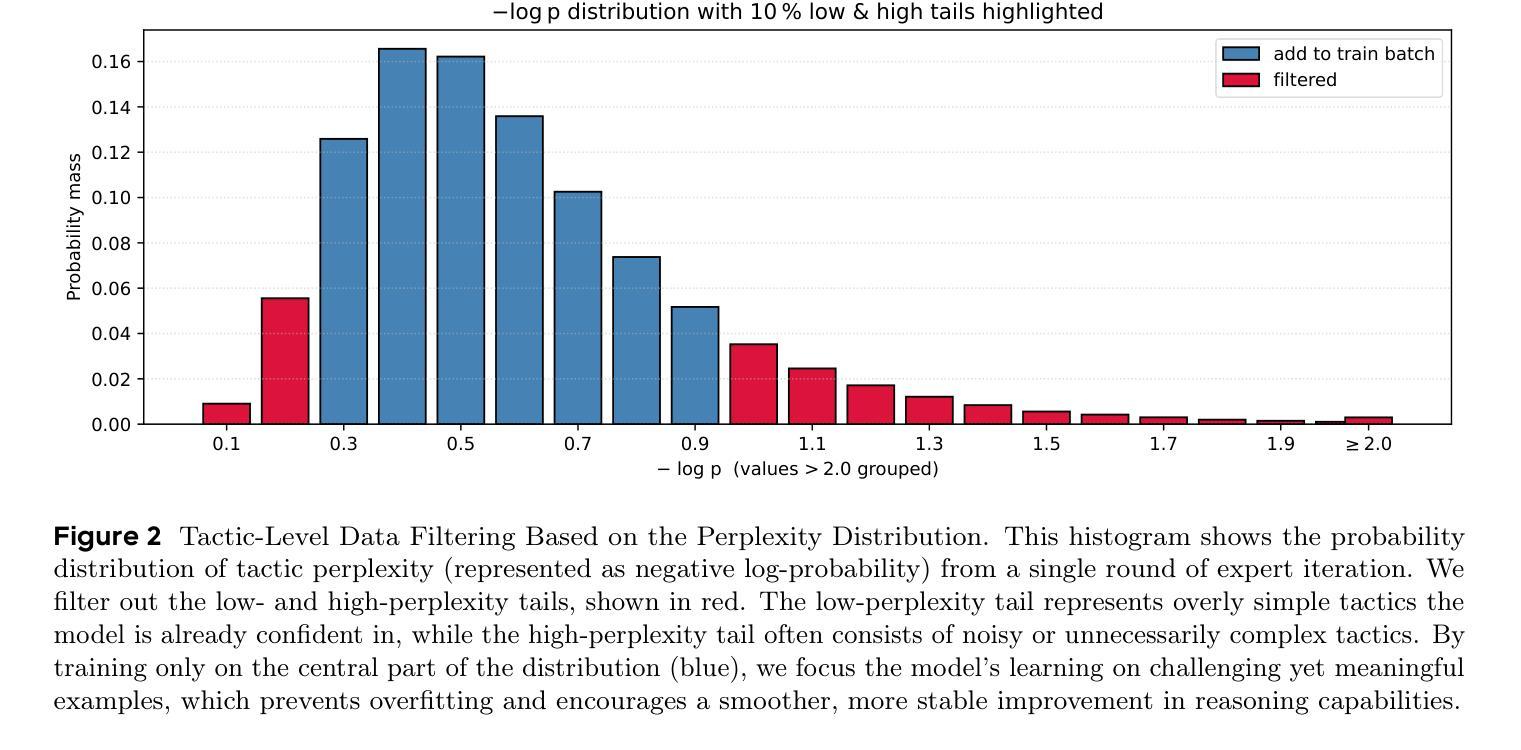
Scaling up Multi-Turn Off-Policy RL and Multi-Agent Tree Search for LLM Step-Provers
Authors:Ran Xin, Zeyu Zheng, Yanchen Nie, Kun Yuan, Xia Xiao
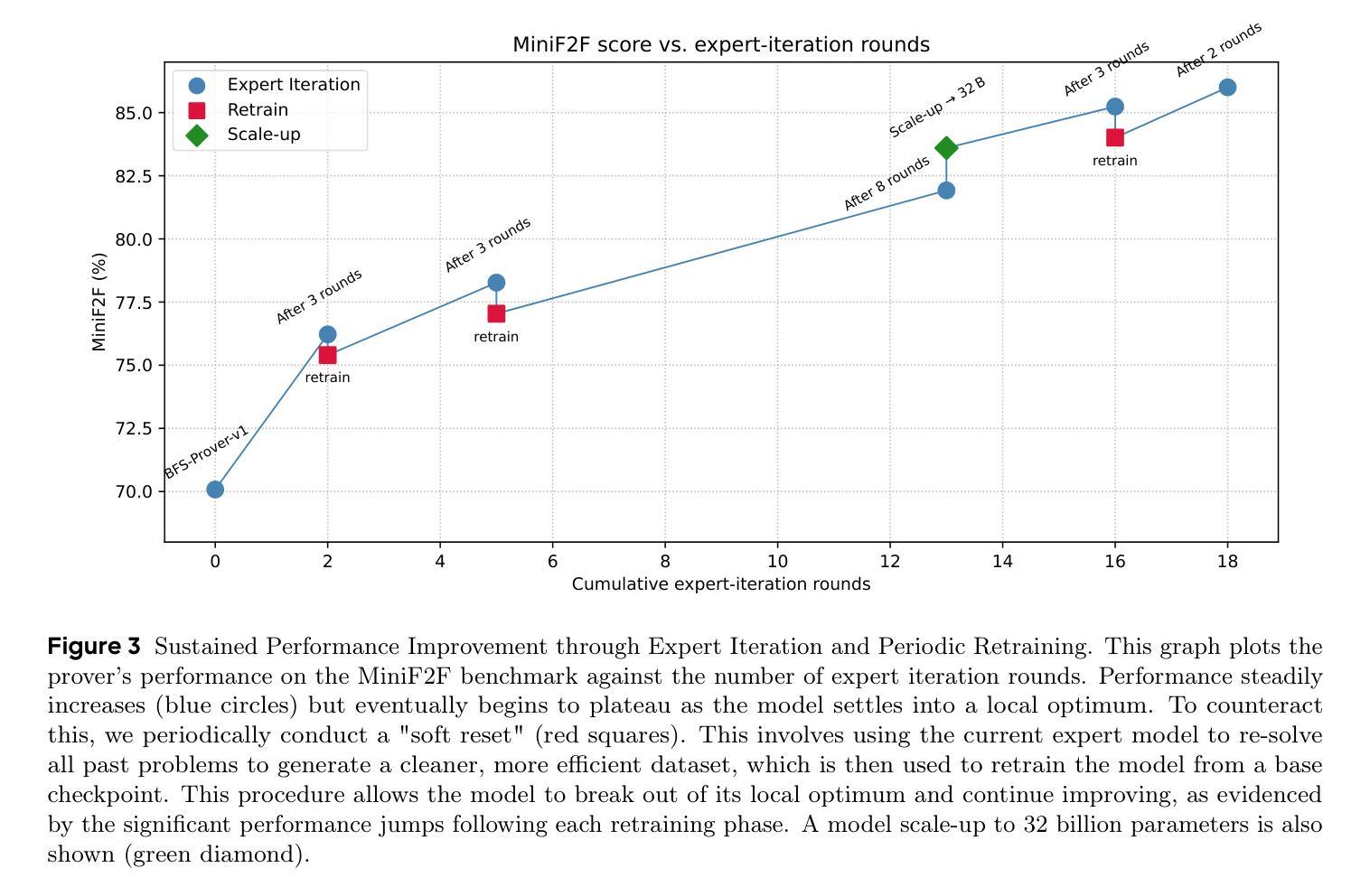
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into automated theorem proving has shown immense promise, yet is fundamentally constrained by challenges in scaling up both training-time reinforcement learning (RL) and inference-time compute. This paper introduces \texttt{BFS-Prover-V2}, a system designed to address this dual scaling problem. We present two primary innovations. The first is a novel multi-turn off-policy RL framework for continually improving the performance of LLM step-prover at training time. This framework, inspired by the principles of AlphaZero, utilizes a multi-stage expert iteration pipeline featuring adaptive tactic-level data filtering and periodic retraining to surmount the performance plateaus that typically curtail long-term RL in LLM-based agents. The second innovation is a planner-enhanced multi-agent search architecture that scales reasoning capabilities at inference time. This architecture employs a general reasoning model as a high-level planner to iteratively decompose complex theorems into a sequence of simpler subgoals. This hierarchical approach substantially reduces the search space, enabling a team of parallel prover agents to collaborate efficiently by leveraging a shared proof cache. We demonstrate that this dual approach to scaling yields state-of-the-art results on established formal mathematics benchmarks. \texttt{BFS-Prover-V2} achieves 95.08% and 41.4% on the MiniF2F and ProofNet test sets respectively. While demonstrated in the domain of formal mathematics, the RL and inference techniques presented in this work are of broader interest and may be applied to other domains requiring long-horizon multi-turn reasoning and complex search.
将大型语言模型(LLM)集成到自动化定理证明中已显示出巨大的潜力,但从根本上受到训练时强化学习(RL)和推理时计算扩展挑战的限制。本文介绍了
BFS-Prover-V2系统,该系统旨在解决这一双重扩展问题。我们提出了两个主要的创新点。第一个是新型的多轮离线策略强化学习框架,旨在不断提高训练时LLM逐步证明的性能。该框架受到AlphaZero原则的启发,采用多阶段专家迭代管道,具有自适应战术级数据过滤和定期重新训练的功能,以克服通常限制长期RL的性能平台问题。第二个创新点是一个增强规划的多智能体搜索架构,该架构在推理时间扩展了推理能力。该架构采用通用推理模型作为高级规划器,将复杂的定理迭代地分解为一系列更简单的子目标。这种分层方法大大减少了搜索空间,使一组并行证明智能体能够利用共享证明缓存进行高效协作。我们证明了这种双重扩展方法可以在建立的数学基准测试上达到最新结果。BFS-Prover-V2在MiniF2F和ProofNet测试集上分别达到了95.08%和41.4%的准确率。虽然本工作在形式数学领域得到了展示,但本工作中提出的强化学习和推理技术具有更广泛的兴趣,并可应用于其他需要长期多轮推理和复杂搜索的领域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化定理证明中的应用展现出巨大的潜力,但面临着训练时强化学习(RL)和推理时计算扩展的双重挑战。本文介绍了\texttt{BFS-Prover-V2},一个旨在解决这一双重扩展问题的系统。主要创新点包括:一是在训练时采用新型的多回合离线RL框架,持续提高LLM逐步证明的性能;二是采用规划增强的多智能体搜索架构,在推理时扩展推理能力。前者受AlphaZero原理启发,利用多阶段专家迭代管道,具有自适应战术级数据过滤和定期再训练功能,以克服性能瓶颈;后者采用通用推理模型作为高级规划器,将复杂定理分解为一系列简单子目标。这种层次方法大大减少了搜索空间,使一组并行证明智能体能够通过共享证明缓存进行有效协作。在形式数学基准测试中,这种双重扩展方法取得了最新结果。\texttt{BFS-Prover-V2}在MiniF2F和ProofNet测试集上的准确率分别达到95.08%和41.4%。虽然此工作是在形式数学领域展示的,但提出的RL和推理技术具有更广泛的应用前景,可应用于其他需要长期多回合推理和复杂搜索的领域。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化定理证明中具有巨大潜力,但仍面临训练强化学习(RL)和推理计算的双重扩展挑战。
- \texttt{BFS-Prover-V2}系统通过两项主要创新解决这些问题:一是采用新型多回合离线RL框架提高LLM性能;二是使用规划增强的多智能体搜索架构扩展推理能力。
- RL框架受AlphaZero原理启发,利用多阶段专家迭代管道和自适应战术级数据过滤及定期再训练来克服性能瓶颈。
- 推理架构采用通用推理模型作为高级规划器,将复杂定理分解为简单子目标,减少搜索空间。
- \texttt{BFS-Prover-V2}在形式数学基准测试中表现优异,在MiniF2F和ProofNet测试集上的准确率分别达95.08%和41.4%。
- 虽然案例研究集中在形式数学领域,但提出的RL和推理技术具有更广泛的应用潜力,可应用于其他需要长期多回合推理和复杂搜索的领域。
点此查看论文截图

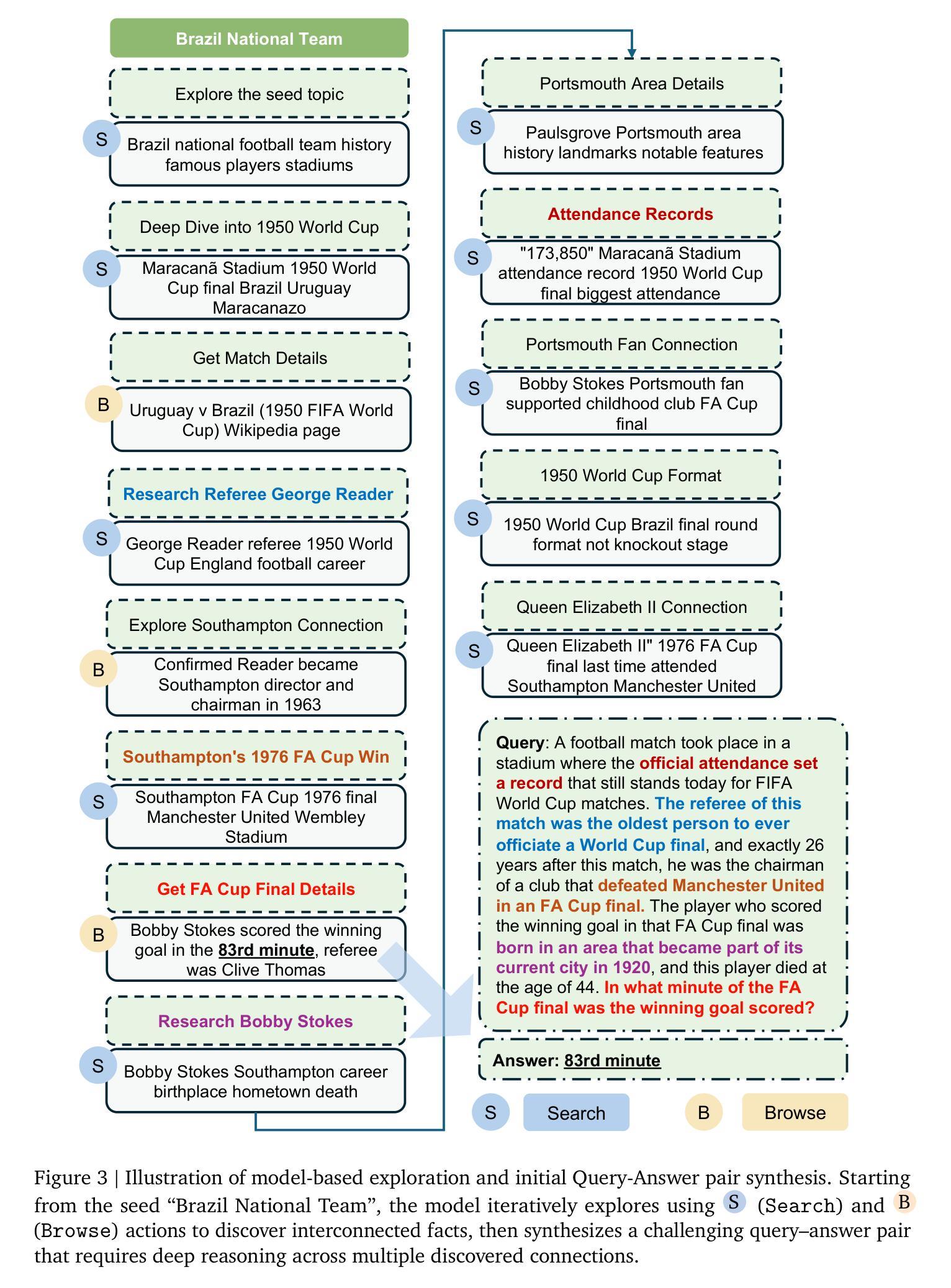
Tree of Agents: Improving Long-Context Capabilities of Large Language Models through Multi-Perspective Reasoning
Authors:Song Yu, Xiaofei Xu, Ke Deng, Li Li, Lin Tian
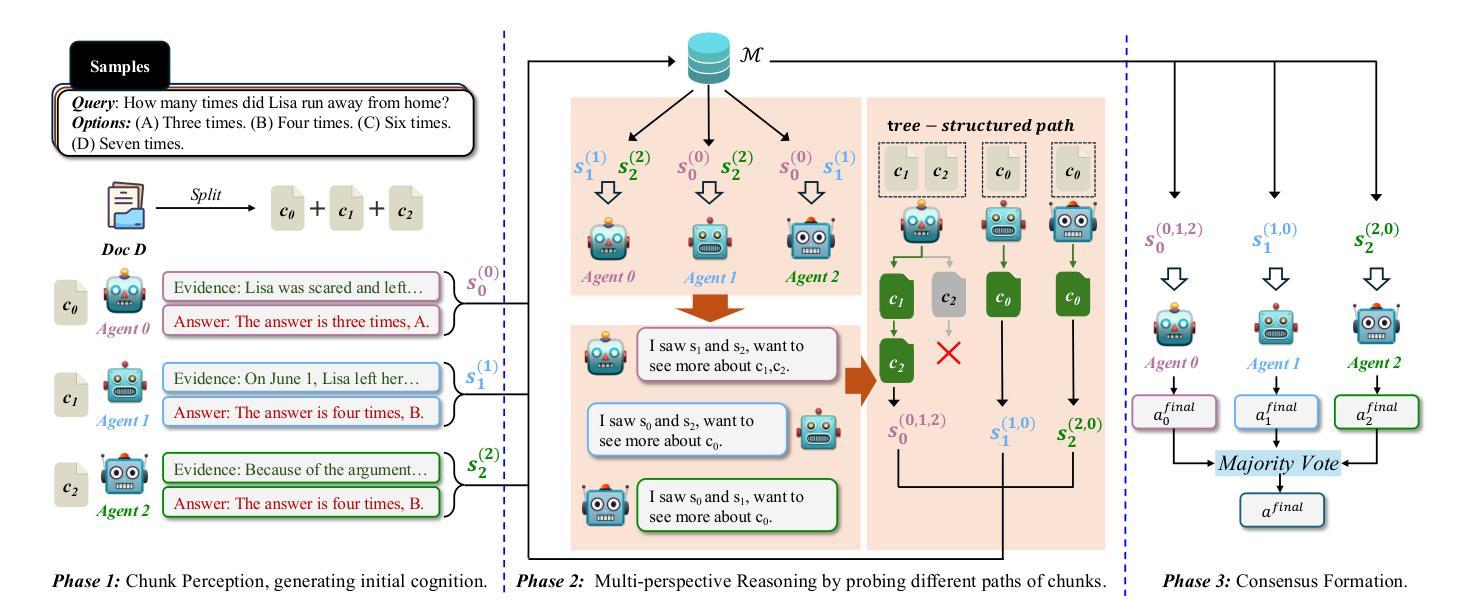
Large language models (LLMs) face persistent challenges when handling long-context tasks, most notably the lost in the middle issue, where information located in the middle of a long input tends to be underutilized. Some existing methods that reduce input have the risk of discarding key information, while others that extend context windows often lead to attention dispersion. To address these limitations, we propose Tree of Agents (TOA), a multi-agent reasoning framework that segments the input into chunks processed by independent agents. Each agent generates its local cognition, then agents dynamically exchange information for collaborative reasoning along tree-structured paths. TOA enables agents to probe different reasoning orders for multi-perspective understanding, effectively mitigating position bias and reducing hallucinations. To improve processing efficiency, we incorporate prefix-hash caching and adaptive pruning strategies, achieving significant performance improvements with comparable API overhead. Experiments show that TOA, powered by compact LLaMA3.1-8B, significantly outperforms multiple baselines and demonstrates comparable performance to the latest and much larger commercial models, such as Gemini1.5-pro, on various long-context tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/Aireduce952/Tree-of-Agents.
大规模语言模型(LLM)在处理长上下文任务时面临持续挑战,最显著的是中间信息丢失问题,即长输入中的中间信息往往得不到充分利用。一些减少输入的方法有丢弃关键信息的风险,而另一些扩展上下文窗口的方法则常常导致注意力分散。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Agent树(TOA)这一多智能体推理框架,它将输入分割成由独立智能体处理的块。每个智能体生成其局部认知,然后智能体沿着树状结构路径动态交换信息进行协同推理。TOA使智能体能够探究不同的推理顺序以实现多角度理解,有效地减轻位置偏见并减少幻觉。为了提高处理效率,我们结合了前缀哈希缓存和自适应修剪策略,在API开销相当的情况下实现了显著的性能提升。实验表明,由紧凑LLaMA3.1-8B驱动的TOA显著优于多个基线,并在各种长上下文任务上展现了与最新的更大规模商业模型(如Gemini1.5-pro)相当的性能。代码可在https://github.com/Aireduce952/Tree-of-Agents找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 5 figures
Summary
大型语言模型在处理长文本任务时面临信息丢失的问题,尤其是中间部分的信息。为解决这一问题,本文提出了多智能体推理框架——Tree of Agents(TOA)。该框架将输入分割成多个片段,由独立智能体进行处理。智能体间动态交换信息,实现协作推理。TOA通过不同的推理顺序和多角度理解,减少偏见和误判。结合前缀哈希缓存和自适应剪枝策略,提高了处理效率。实验证明,TOA在多种长文本任务上表现优异,与小型语言模型相比性能显著,与大型商业模型相比表现相当。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在处理长文本任务时存在中间信息丢失的问题。
- Tree of Agents(TOA)是一个多智能体推理框架,旨在解决这一问题。
- TOA将输入分割成片段,由独立智能体处理,并通过动态信息交换实现协作推理。
- TOA通过不同的推理顺序和多角度理解,减少偏见和误判。
- TOA结合了前缀哈希缓存和自适应剪枝策略,提高了处理效率。
- 实验证明,TOA在多种长文本任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

HECATE: An ECS-based Framework for Teaching and Developing Multi-Agent Systems
Authors:Arthur Casals, Anarosa A. F. Brandão
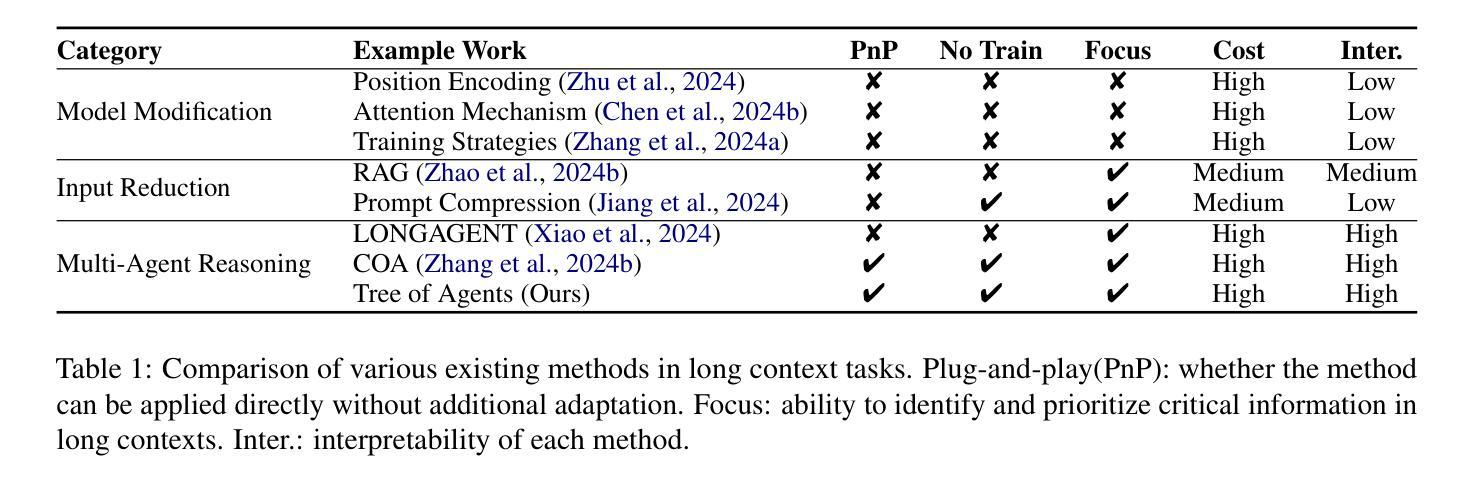
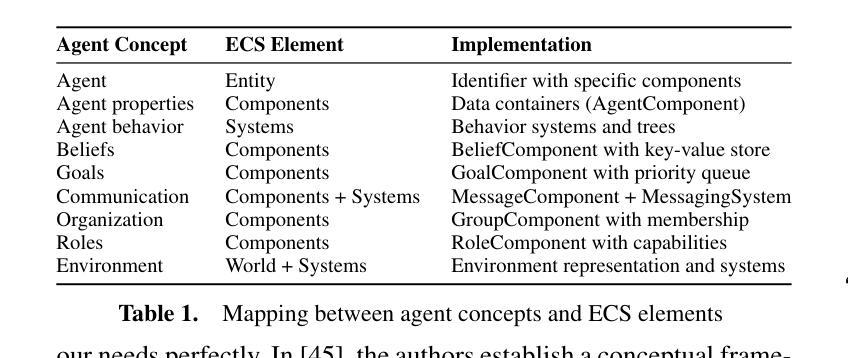
This paper introduces HECATE, a novel framework based on the Entity-Component-System (ECS) architectural pattern that bridges the gap between distributed systems engineering and MAS development. HECATE is built using the Entity-Component-System architectural pattern, leveraging data-oriented design to implement multiagent systems. This approach involves engineering multiagent systems (MAS) from a distributed systems (DS) perspective, integrating agent concepts directly into the DS domain. This approach simplifies MAS development by (i) reducing the need for specialized agent knowledge and (ii) leveraging familiar DS patterns and standards to minimize the agent-specific knowledge required for engineering MAS. We present the framework’s architecture, core components, and implementation approach, demonstrating how it supports different agent models.
本文介绍了HECATE,这是一个基于实体组件系统(ECS)架构模式的新型框架,旨在缩小分布式系统工程和MAS开发之间的差距。HECATE采用实体组件系统架构模式构建,利用面向数据的设计来实现多智能体系统。该方法从分布式系统(DS)的角度来构建多智能体系统(MAS),直接将智能体概念集成到DS领域。这种方法通过(i)减少特殊智能体知识的需求以及(ii)利用熟悉的DS模式和标准来减少工程MAS所需的特定智能体知识,从而简化了MAS的开发。我们介绍了该框架的架构、核心组件和实现方法,展示了它如何支持不同的智能体模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ECAI-2025
Summary
HECATE是一个基于实体组件系统(ECS)架构模式的新型框架,旨在缩小分布式系统工程和MAS开发之间的差距。该框架利用数据导向设计来实现多智能体系统,通过整合智能体概念到DS领域来简化MAS开发,减少了对专业智能体知识的需求,并借助熟悉的DS模式和标准来最小化工程MAS所需的特定知识。
Key Takeaways
- HECATE是一个基于实体组件系统(ECS)架构模式的框架。
- 它旨在缩小分布式系统工程和MAS开发之间的差距。
- HECATE利用数据导向设计来实现多智能体系统。
- 通过整合智能体概念到DS领域来简化MAS开发。
- 该框架减少了对专业智能体知识的需求。
- HECATE借助熟悉的DS模式和标准来简化MAS开发。
点此查看论文截图

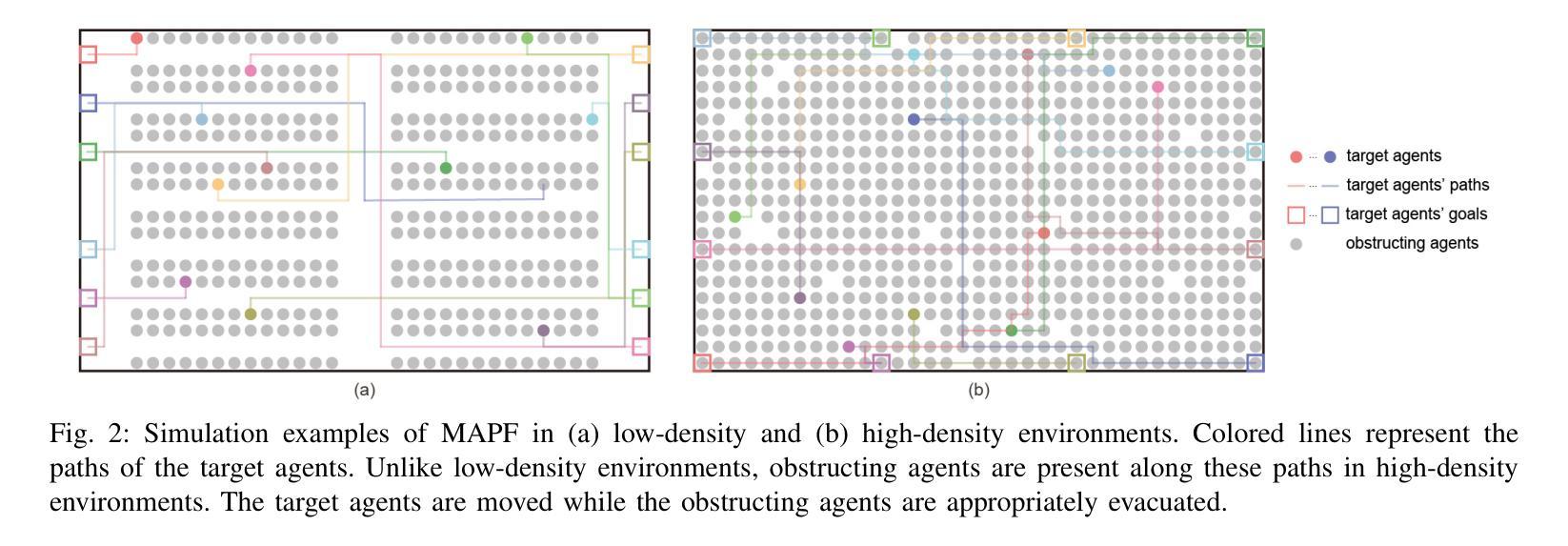
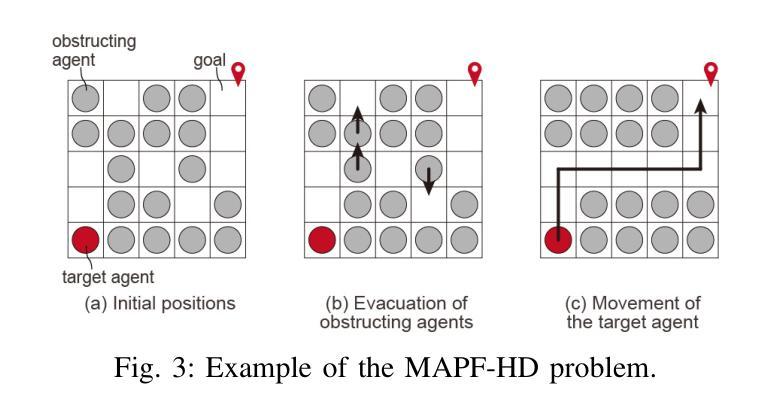
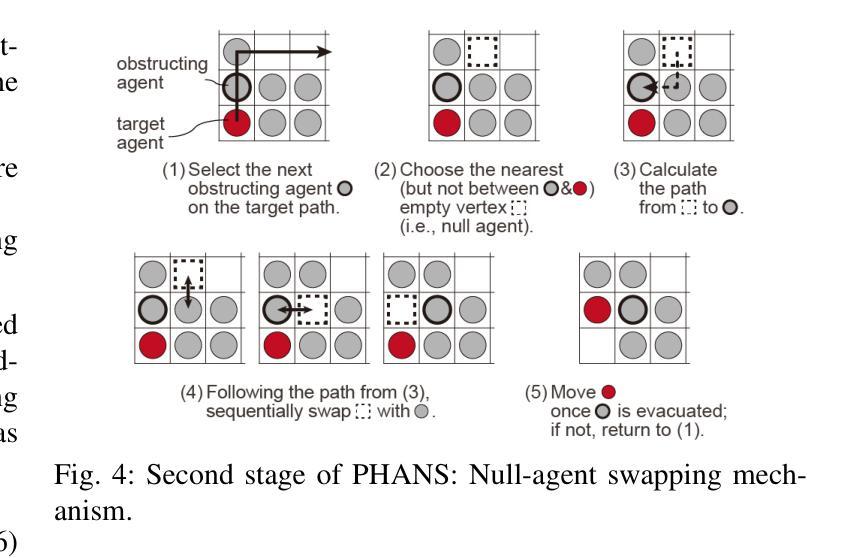
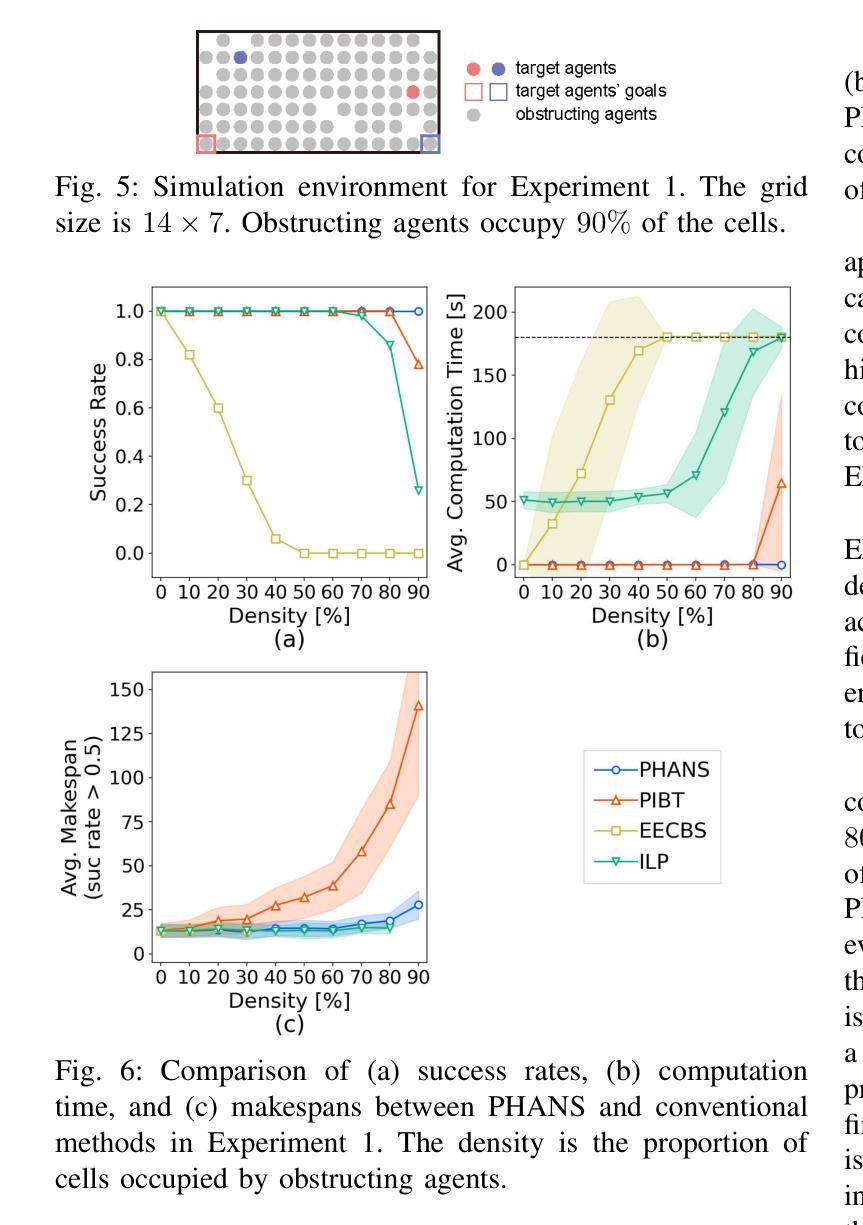
MAPF-HD: Multi-Agent Path Finding in High-Density Environments
Authors:Hiroya Makino, Seigo Ito
Multi-agent path finding (MAPF) involves planning efficient paths for multiple agents to move simultaneously while avoiding collisions. In typical warehouse environments, agents are often sparsely distributed along aisles. However, increasing the agent density can improve space efficiency. When the agent density is high, we must optimize the paths not only for goal-assigned agents but also for those obstructing them. This study proposes a novel MAPF framework for high-density environments (MAPF-HD). Several studies have explored MAPF in similar settings using integer linear programming (ILP). However, ILP-based methods require substantial computation time to optimize all agent paths simultaneously. Even in small grid-based environments with fewer than $100$ cells, these computations can incur tens to hundreds of seconds. These high computational costs render these methods impractical for large-scale applications such as automated warehouses and valet parking. To address these limitations, we introduce the phased null-agent swapping (PHANS) method. PHANS employs a heuristic approach to incrementally swap positions between agents and empty vertices. This method solves the MAPF-HD problem within seconds to tens of seconds, even in large environments containing more than $700$ cells. The proposed method can potentially improve efficiency in various real-world applications such as warehouse logistics, traffic management, or crowd control. Code is available at https://github.com/ToyotaCRDL/MAPF-in-High-Density-Envs.
多智能体路径规划(MAPF)涉及为多个智能体规划高效路径,使其可以同时移动并避免碰撞。在典型的仓库环境中,智能体通常沿通道稀疏分布。然而,增加智能体的密度可以提高空间效率。当智能体密度较高时,我们必须为已分配目标的智能体以及阻碍他们的智能体优化路径。本研究针对高密度环境提出了一种新的MAPF框架(MAPF-HD)。已有一些研究在类似环境中使用整数线性规划(ILP)探索了MAPF。然而,基于ILP的方法需要大量的计算时间来同时优化所有智能体的路径。即使在拥有少于100个单元的小型网格环境中,这些计算也需要花费数十至数百秒的时间。这些高昂的计算成本使得这些方法对于大规模应用(如自动化仓库和代客泊车)来说不切实际。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了分阶段空智能体交换(PHANS)方法。PHANS采用启发式方法逐步交换智能体与空顶点之间的位置。即使在包含超过700个单元的大型环境中,该方法也可以在几秒到几十秒内解决MAPF-HD问题。所提出的方法有可能提高仓库物流、交通管理或人群控制等各种现实应用中的效率。代码可通过https://github.com/ToyotaCRDL/MAPF-in-High-Density-Envs获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 12 figures
Summary
在仓库等大规模应用场景中,多智能体路径规划(MAPF)对于提高空间效率至关重要。面对高密度智能体环境,现有的基于整数线性规划(ILP)的方法计算成本高昂,难以实现快速优化。本研究提出了一种针对高密度环境的MAPF新框架(MAPF-HD),并引入了分阶段空智能体交换(PHANS)方法。PHANS采用启发式方法逐步交换智能体与空位置,能在几秒到几十秒内解决大型环境中的MAPF-HD问题,有望提高仓库物流、交通管理或人群控制等应用的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体路径规划(MAPF)在高密度智能体环境中尤为重要,需优化所有智能体的路径。
- 现有基于整数线性规划(ILP)的方法计算成本高昂,不适用于大规模应用场景。
- 提出了针对高密度环境的MAPF新框架(MAPF-HD)。
- 引入了分阶段空智能体交换(PHANS)方法,采用启发式方法逐步优化智能体路径。
- PHANS方法能在几秒到几十秒内解决大型环境中的MAPF-HD问题。
- PHANS方法具有实际应用价值,可应用于仓库物流、交通管理、人群控制等领域。
点此查看论文截图


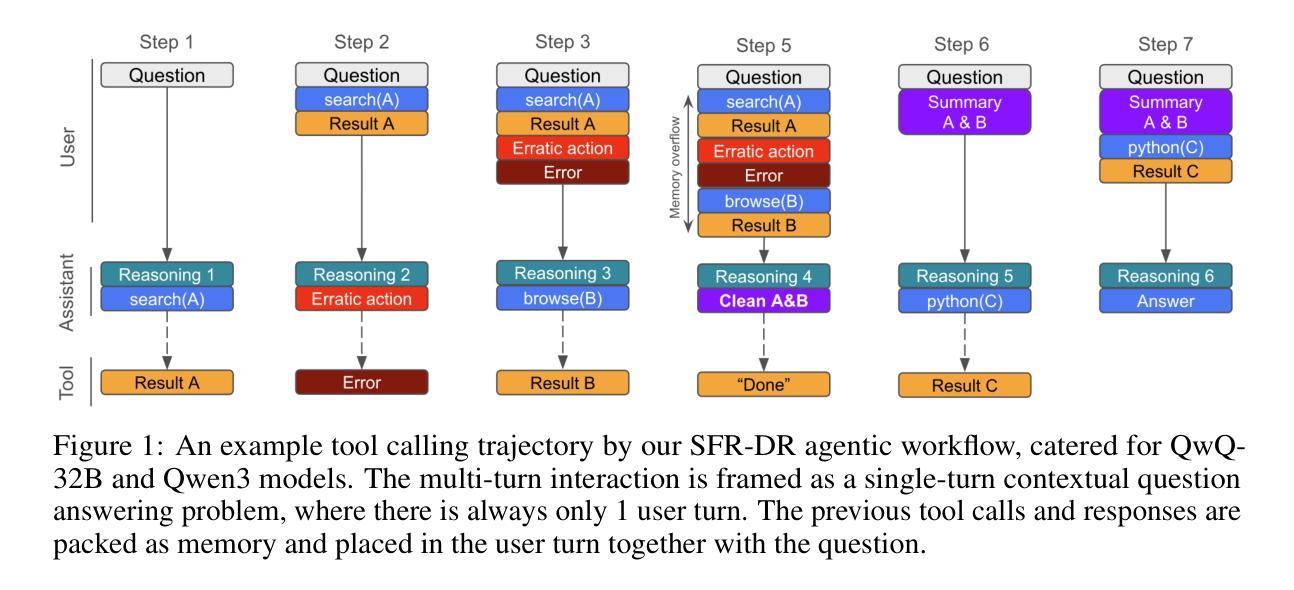
SFR-DeepResearch: Towards Effective Reinforcement Learning for Autonomously Reasoning Single Agents
Authors:Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shrey Pandit, Revanth Gangi Reddy, Austin Xu, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong, Shafiq Joty
Equipping large language models (LLMs) with complex, interleaved reasoning and tool-use capabilities has become a key focus in agentic AI research, especially with recent advances in reasoning-oriented (``thinking’’) models. Such capabilities are key to unlocking a number of important applications. One such application is Deep Research (DR), which requires extensive search and reasoning over many sources. Our work in this paper focuses on the development of native Autonomous Single-Agent models for DR featuring minimal web crawling and Python tool integration. Unlike multi-agent systems, where agents take up pre-defined roles and are told what to do at each step in a static workflow, an autonomous single-agent determines its next action dynamically based on context, without manual directive. While prior work has proposed training recipes for base or instruction-tuned LLMs, we focus on continual reinforcement learning (RL) of reasoning-optimized models to further enhance agentic skills while preserving reasoning ability. Towards this end, we propose a simple RL recipe with entirely synthetic data, which we apply to various open-source LLMs. Our best variant SFR-DR-20B achieves up to 28.7% on Humanity’s Last Exam benchmark. In addition, we conduct key analysis experiments to provide more insights into our methodologies.
赋予大型语言模型(LLM)复杂、交织的推理和工具使用能力已成为代理人工智能研究的关键焦点,尤其是随着面向推理的(“思考”)模型的最新进展。这些能力是解锁许多重要应用的关键。其中一个应用是深度研究(DR),它需要在多个来源之间进行广泛搜索和推理。本文的工作重点是为DR开发本地自主单代理模型,具有最小的网络爬虫和Python工具集成。与多代理系统不同,多代理系统中的代理扮演预先定义的角色,并在静态工作流中的每个步骤中被告知要做什么,而自主单代理则根据上下文动态地确定其下一个行动,无需手动指令。虽然先前的工作已经提出了针对基础或指令微调LLM的训练配方,但我们专注于对推理优化模型的持续强化学习(RL),以进一步增强代理技能,同时保留推理能力。为此,我们提出了一种简单的RL配方,使用完全合成数据,并应用于各种开源LLM。我们最好的变体SFR-DR-20B在“人类最后的考试”基准测试中达到了28.7%的准确率。此外,我们还进行了关键的分析实验,以提供更多关于我们方法论的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在融合复杂交织的推理和工具使用能力方面成为人工智能研究的重点,特别是随着面向推理的“思考”模型的最新发展。本文专注于为深度研究(DR)开发自主的单一代理模型,该模型具有最小的网络爬虫和Python工具集成。不同于多代理系统,自主单一代理能基于上下文动态确定其下一步行动,无需手动指导。本文聚焦于持续强化学习(RL)的推理优化模型,以提高代理技能并保留推理能力。我们提出了一个简单的全合成数据的RL配方,并应用于各种开源LLM。最佳变体SFR-DR-20B在人类最后考试基准测试中达到了28.7%的准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)正在研究如何集成复杂的推理和工具使用能力,这是面向应用的重要方向。
- 自主单一代理模型被开发用于深度研究(DR),能最小程度地使用网络爬虫和Python工具集成。
- 与多代理系统不同,自主单一代理能基于上下文动态决策,无需手动指导。
- 通过对推理优化模型进行持续强化学习(RL),提高了代理技能并保留了推理能力。
- 提出一个简单的全合成数据的强化学习配方,适用于各种开源LLM。
- 最佳模型SFR-DR-20B在人类最后考试基准测试中的准确率为28.7%。
点此查看论文截图

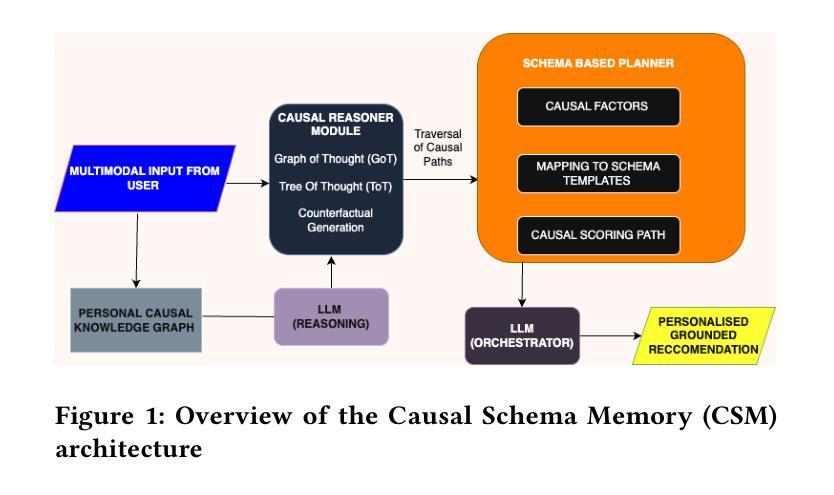
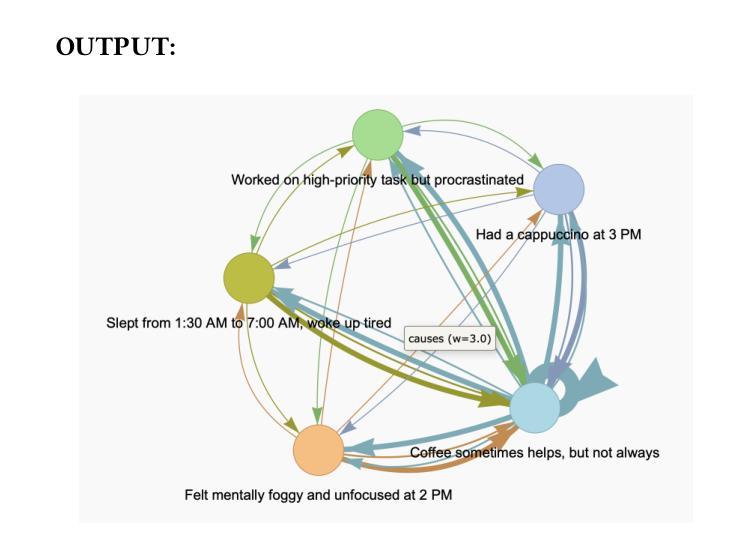
REMI: A Novel Causal Schema Memory Architecture for Personalized Lifestyle Recommendation Agents
Authors:Vishal Raman, Vijai Aravindh R, Abhijith Ragav
Personalized AI assistants often struggle to incorporate complex personal data and causal knowledge, leading to generic advice that lacks explanatory power. We propose REMI, a Causal Schema Memory architecture for a multimodal lifestyle agent that integrates a personal causal knowledge graph, a causal reasoning engine, and a schema based planning module. The idea is to deliver explainable, personalized recommendations in domains like fashion, personal wellness, and lifestyle planning. Our architecture uses a personal causal graph of the user’s life events and habits, performs goal directed causal traversals enriched with external knowledge and hypothetical reasoning, and retrieves adaptable plan schemas to generate tailored action plans. A Large Language Model orchestrates these components, producing answers with transparent causal explanations. We outline the CSM system design and introduce new evaluation metrics for personalization and explainability, including Personalization Salience Score and Causal Reasoning Accuracy, to rigorously assess its performance. Results indicate that CSM based agents can provide more context aware, user aligned recommendations compared to baseline LLM agents. This work demonstrates a novel approach to memory augmented, causal reasoning in personalized agents, advancing the development of transparent and trustworthy AI lifestyle assistants.
个性化人工智能助理在融入复杂的个人数据和因果知识时经常遇到困难,导致提供缺乏解释力的通用建议。我们提出了REMI,这是一种针对多模式生活方式代理的因果模式记忆架构,它集成了个人因果知识图谱、因果推理引擎和基于模式的规划模块。我们的理念是在时尚、个人健康和生活规划等领域提供可解释的、个性化的建议。我们的架构使用了用户的生平事件和习惯的因果图,执行以目标为导向的因果遍历,并丰富外部知识和假设推理,检索可适应的模式图以生成定制的行动计划。大型语言模型协调这些组件,产生具有透明因果解释的答案。我们概述了CSM系统设计的要点,并为个性化和可解释性引入了新的评估指标,包括个性化显著性得分和因果推理准确性,以严格评估其性能。结果表明,基于CSM的代理可以提供比基于LLM的代理更贴近上下文和用户需求的建议。这项工作展示了在个性化代理中增强记忆和因果推理的新方法,推动了透明和可靠的人工智能生活助理的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 2 figures, Accepted at the OARS Workshop, KDD 2025, Paper link: https://oars-workshop.github.io/papers/Raman2025.pdf
Summary
本文探讨个性化AI助理在面对复杂个人数据和因果知识时的挑战,提出REMI的因果模式记忆架构,用于多模式生活方式代理。该架构结合个人因果知识图谱、因果推理引擎和基于模式的规划模块,旨在提供时尚、个人健康和生活规划等领域的可解释、个性化建议。使用用户的生命事件和习惯的因果图,结合外部知识和假设推理进行目标导向的因果遍历,检索适应性的计划模式生成个性化的行动计划。大型语言模型协调这些组件,产生具有透明因果解释的答案。本文介绍CSM系统设计,并引入新的评估指标以评估个性化程度和解释性,包括个性化显著分数和因果推理准确性。结果表明,基于CSM的代理可以提供更基于上下文和用户对齐的建议,相较于基础的大型语言模型代理表现更优。本研究展示了在个性化代理中实现增强记忆和因果推理的新方法,推动透明度和可信赖的AI生活助理的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 现有AI助理在整合复杂个人数据和因果知识方面存在挑战,导致建议缺乏解释力。
- REMI架构结合了个人因果知识图谱、因果推理引擎和基于模式的规划模块来解决这一问题。
- 该架构旨在在时尚、个人健康和生活规划等领域提供可解释、个性化的建议。
- 使用用户的生命事件和习惯的因果图进行目标导向的因果遍历。
- 大型语言模型用于协调各个组件,产生具有透明因果解释的答案。
- 引入新的评估指标包括个性化显著分数和因果推理准确性以评估系统的性能。
点此查看论文截图


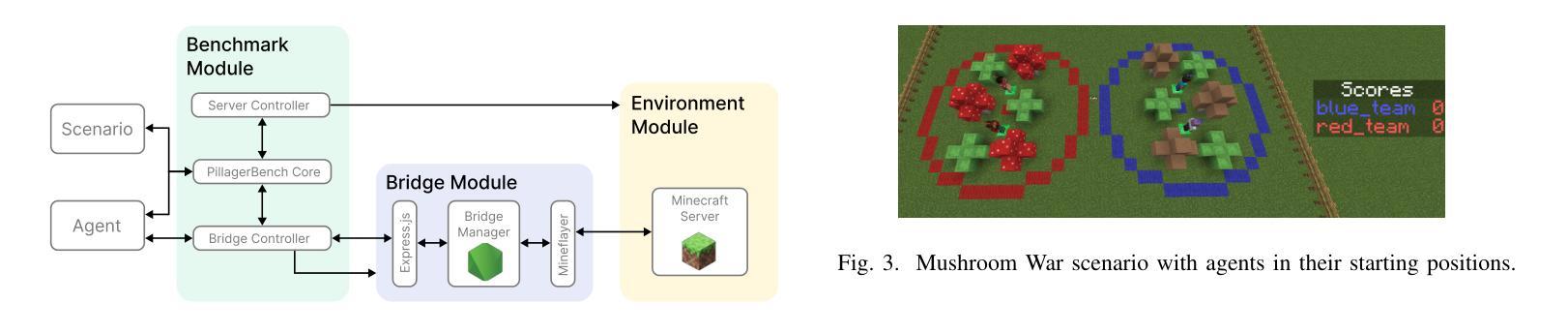
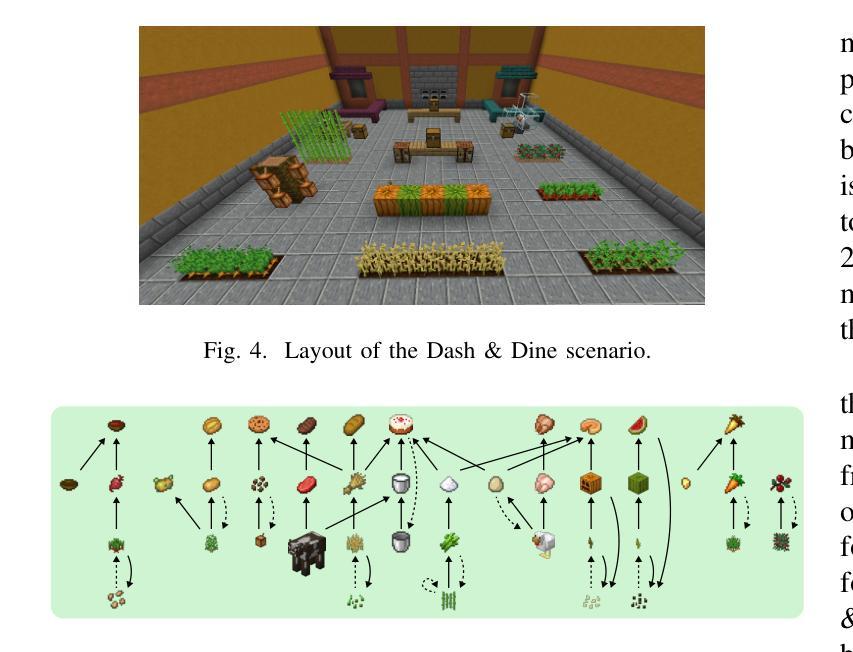
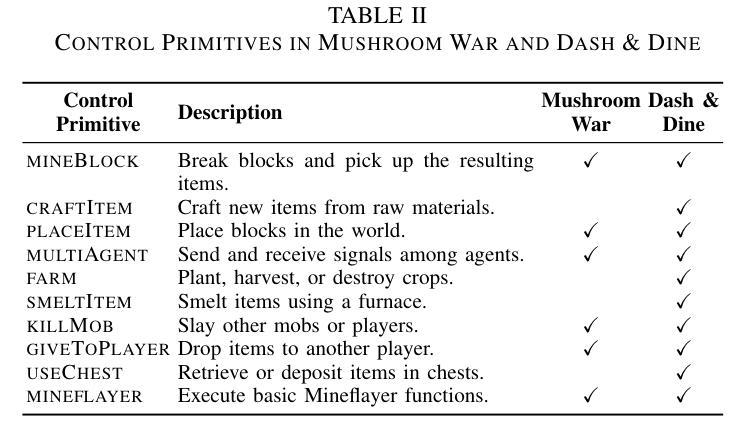
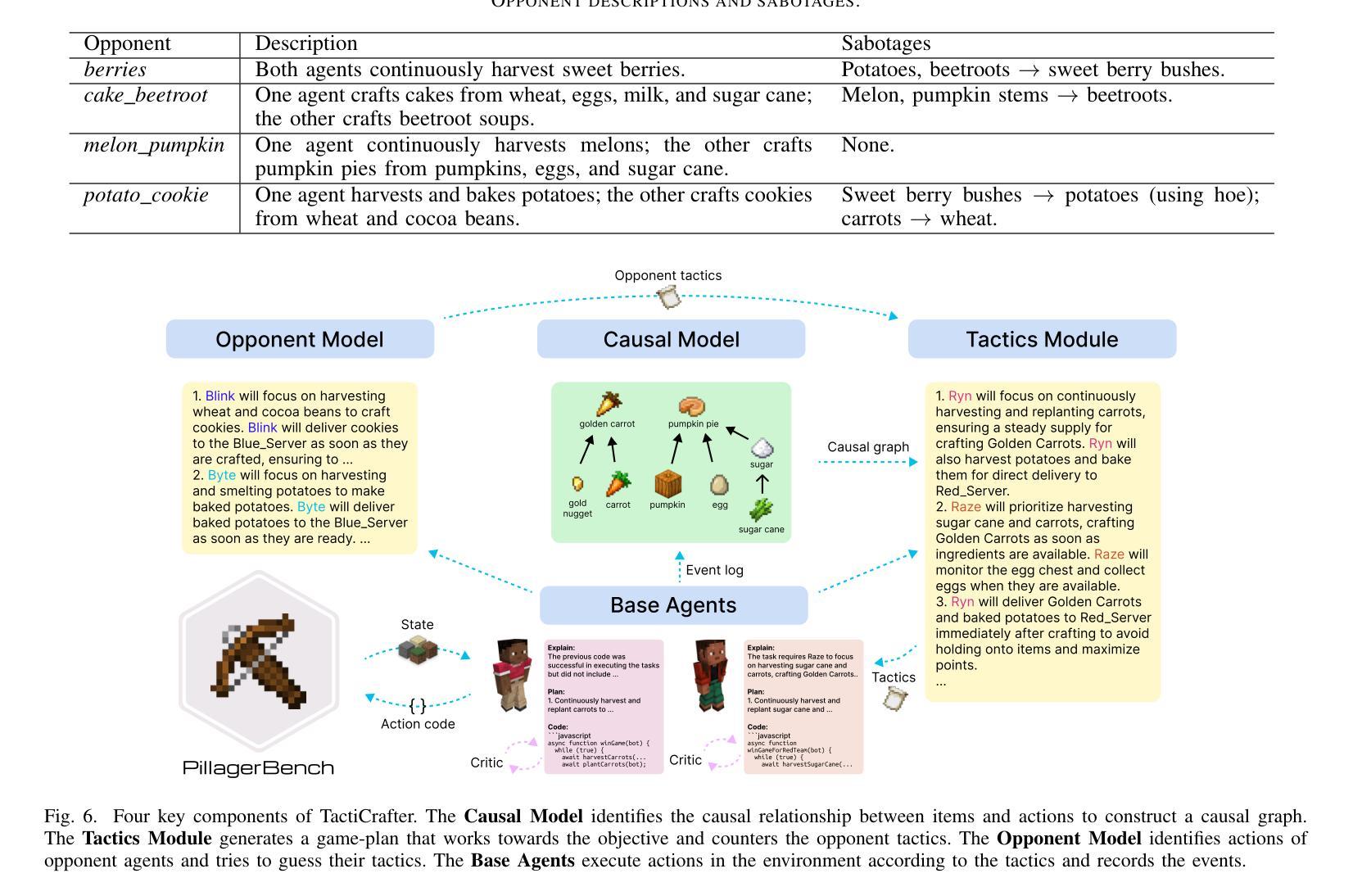
PillagerBench: Benchmarking LLM-Based Agents in Competitive Minecraft Team Environments
Authors:Olivier Schipper, Yudi Zhang, Yali Du, Mykola Pechenizkiy, Meng Fang
LLM-based agents have shown promise in various cooperative and strategic reasoning tasks, but their effectiveness in competitive multi-agent environments remains underexplored. To address this gap, we introduce PillagerBench, a novel framework for evaluating multi-agent systems in real-time competitive team-vs-team scenarios in Minecraft. It provides an extensible API, multi-round testing, and rule-based built-in opponents for fair, reproducible comparisons. We also propose TactiCrafter, an LLM-based multi-agent system that facilitates teamwork through human-readable tactics, learns causal dependencies, and adapts to opponent strategies. Our evaluation demonstrates that TactiCrafter outperforms baseline approaches and showcases adaptive learning through self-play. Additionally, we analyze its learning process and strategic evolution over multiple game episodes. To encourage further research, we have open-sourced PillagerBench, fostering advancements in multi-agent AI for competitive environments.
基于LLM的代理在各种合作和策略推理任务中显示出潜力,但在竞争性的多代理环境中,其有效性仍被探索得不够深入。为了解决这一差距,我们推出了PillagerBench,这是一个用于在Minecraft中实时竞技团队对抗团队场景中评估多代理系统的新型框架。它提供了一个可扩展的API、多轮测试以及基于规则的内置对手,以实现公平、可重复的比较。我们还提出了TactiCrafter,这是一个基于LLM的多代理系统,它通过人类可读的战术促进团队合作,学习因果依赖关系,并适应对手的策略。我们的评估表明,TactiCrafter优于基准方法,并通过自我游戏展示自适应学习。此外,我们分析了其在多个游戏片段中的学习过程以及策略演变。为了鼓励进一步研究,我们已开源PillagerBench,促进竞争环境中多智能体人工智能的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF for the source code, see https://github.com/aialt/PillagerBench
Summary
LLM-based代理在多种合作和策略推理任务中展现出潜力,但在竞争多代理环境中的有效性尚未得到充分探索。为弥补这一不足,研究者推出PillagerBench框架,用于评估在Minecraft中实时竞争团队对抗场景的多代理系统。该框架提供可扩展API、多轮测试,以及基于规则的内置对手,以实现公平、可重复的比较。同时,提出TactiCrafter系统,该系统基于LLM,通过人类可阅读战术促进团队合作,学习因果关系,并适应对手策略。评估显示,TactiCrafter优于基准方法,展示通过自我博弈的适应性学习。此外,分析其在多个游戏集中的学习过程及策略演变。为鼓励进一步研究,已开源PillagerBench,促进竞争环境中多代理人工智能的发展。
Key Takeaways
- LLM-based代理在合作和策略推理任务中表现出潜力。
- 在竞争多代理环境中的有效性需要更多探索。
- PillagerBench框架用于评估实时竞争团队对抗场景中的多代理系统。
- PillagerBench提供可扩展API、多轮测试及内置对手。
- TactiCrafter是基于LLM的多代理系统,能促进团队合作,学习因果关系并适应对手策略。
- TactiCrafter优于其他方法,展现适应性学习并通过自我博弈不断进步。
点此查看论文截图


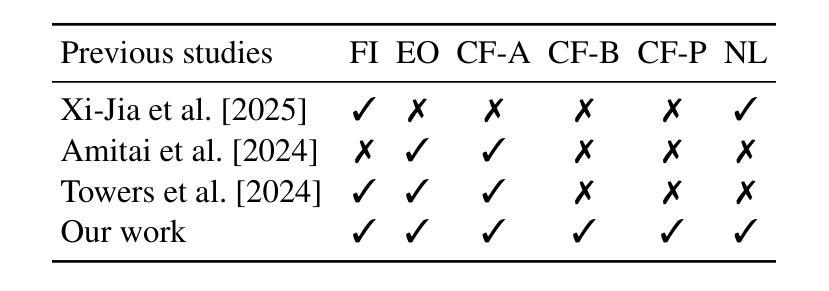
TalkToAgent: A Human-centric Explanation of Reinforcement Learning Agents with Large Language Models
Authors:Haechang Kim, Hao Chen, Can Li, Jong Min Lee
Explainable Reinforcement Learning (XRL) has emerged as a promising approach in improving the transparency of Reinforcement Learning (RL) agents. However, there remains a gap between complex RL policies and domain experts, due to the limited comprehensibility of XRL results and isolated coverage of current XRL approaches that leave users uncertain about which tools to employ. To address these challenges, we introduce TalkToAgent, a multi-agent Large Language Models (LLM) framework that delivers interactive, natural language explanations for RL policies. The architecture with five specialized LLM agents (Coordinator, Explainer, Coder, Evaluator, and Debugger) enables TalkToAgent to automatically map user queries to relevant XRL tools and clarify an agent’s actions in terms of either key state variables, expected outcomes, or counterfactual explanations. Moreover, our approach extends previous counterfactual explanations by deriving alternative scenarios from qualitative behavioral descriptions, or even new rule-based policies. We validated TalkToAgent on quadruple-tank process control problem, a well-known nonlinear control benchmark. Results demonstrated that TalkToAgent successfully mapped user queries into XRL tasks with high accuracy, and coder-debugger interactions minimized failures in counterfactual generation. Furthermore, qualitative evaluation confirmed that TalkToAgent effectively interpreted agent’s actions and contextualized their meaning within the problem domain.
可解释性强化学习(XRL)作为一种有前景的方法,在提升强化学习(RL)代理的透明度方面展现出了巨大潜力。然而,由于XRL结果的有限可理解性和当前XRL方法的孤立覆盖,使得复杂RL策略与领域专家之间存在差距,使用户对使用哪些工具感到不确定。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了TalkToAgent,这是一个多代理的大型语言模型(LLM)框架,为RL策略提供交互式自然语言解释。该架构包含五个专业LLM代理(协调器、解释器、编码员、评估器和调试器),使TalkToAgent能够自动将用户查询映射到相关的XRL工具,并根据关键状态变量、预期结果或反事实解释澄清代理的行动。此外,我们的方法通过从定性行为描述或甚至新的基于规则的策略中推导出替代场景,扩展了之前的反事实解释。我们在著名的非线性控制基准——四罐过程控制问题上验证了TalkToAgent。结果表明,TalkToAgent能够成功地将用户查询映射到XRL任务,且具有较高的准确性,编码器和调试器之间的交互最小化了反事实生成中的故障。此外,定性评估证实,TalkToAgent有效地解释了代理的行动,并在问题域内对其意义进行了语境化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 31 pages total
Summary:出现了一种有前景的方法,即通过Explainable Reinforcement Learning(XRL)提高强化学习(RL)代理的透明度。为解决当前XRL结果理解有限和现有XRL方法孤立的问题,我们引入了TalkToAgent,这是一个多代理的大型语言模型(LLM)框架,可为RL策略提供交互式自然语言解释。该架构包含五个专业LLM代理,可自动将用户查询映射到相关的XRL工具,并澄清代理关于关键状态变量、预期结果或反事实解释的举动。我们验证了TalkToAgent在处理四重水箱过程控制问题上的有效性,结果表明TalkToAgent能够准确地将用户查询映射到XRL任务,且编码器和调试器之间的互动减少了反事实生成中的失败。此外,定性评估证实TalkToAgent有效地解释了代理的行动并将其置于问题域中。
Key Takeaways:
- XRL提高了RL代理的透明度。
- TalkToAgent是一个多代理LLM框架,为RL策略提供交互式自然语言解释。
- TalkToAgent包含五个专业LLM代理,可自动映射用户查询到相关XRL工具。
- 该框架能澄清代理关于关键状态变量、预期结果或反事实解释的行为。
- 在四重水箱过程控制问题上的验证表明,TalkToAgent能准确映射用户查询到XRL任务。
- 编码器和调试器之间的互动减少了反事实生成中的失败。
点此查看论文截图


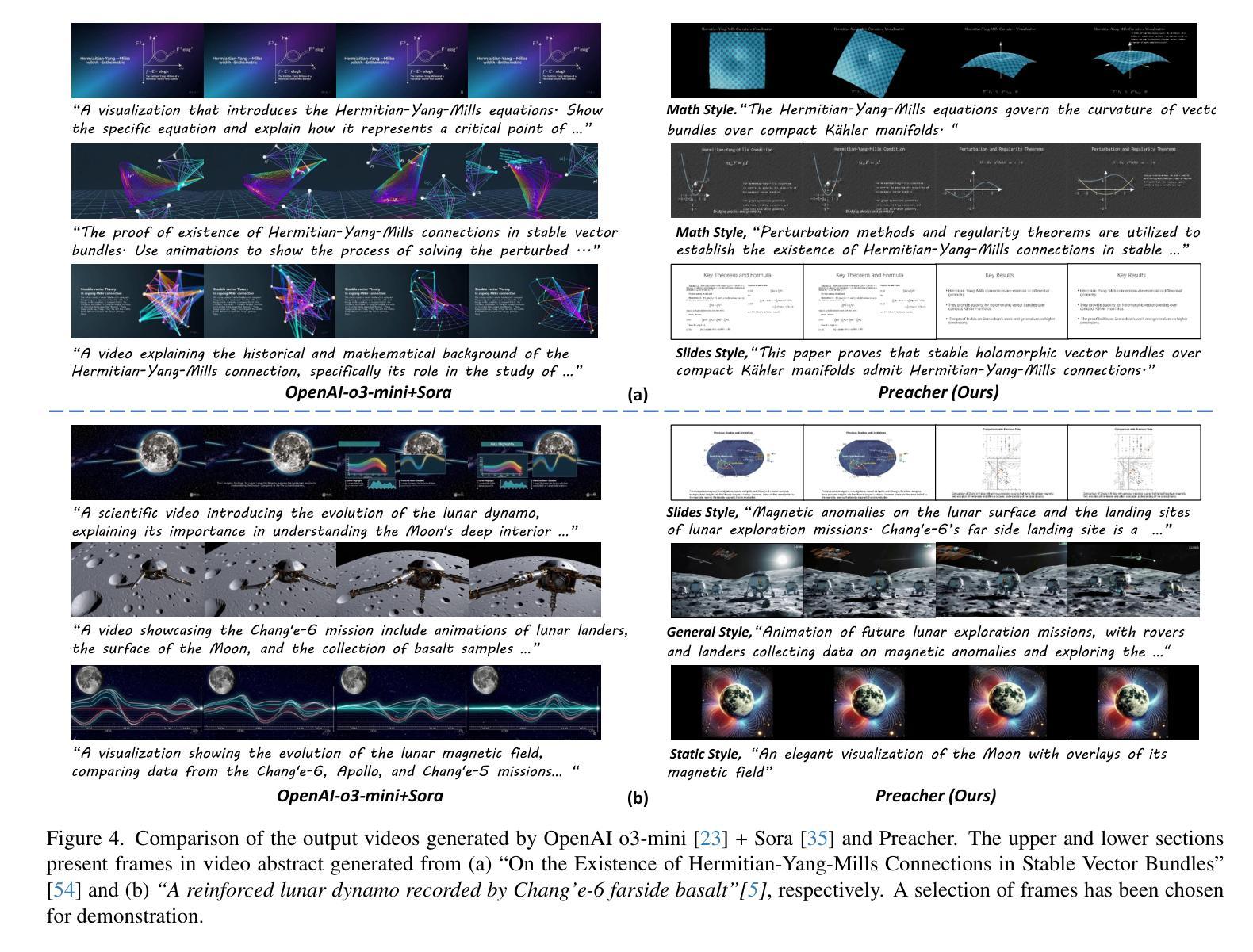
Preacher: Paper-to-Video Agentic System
Authors:Jingwei Liu, Ling Yang, Hao Luo, Fan Wang, Hongyan Li, Mengdi Wang
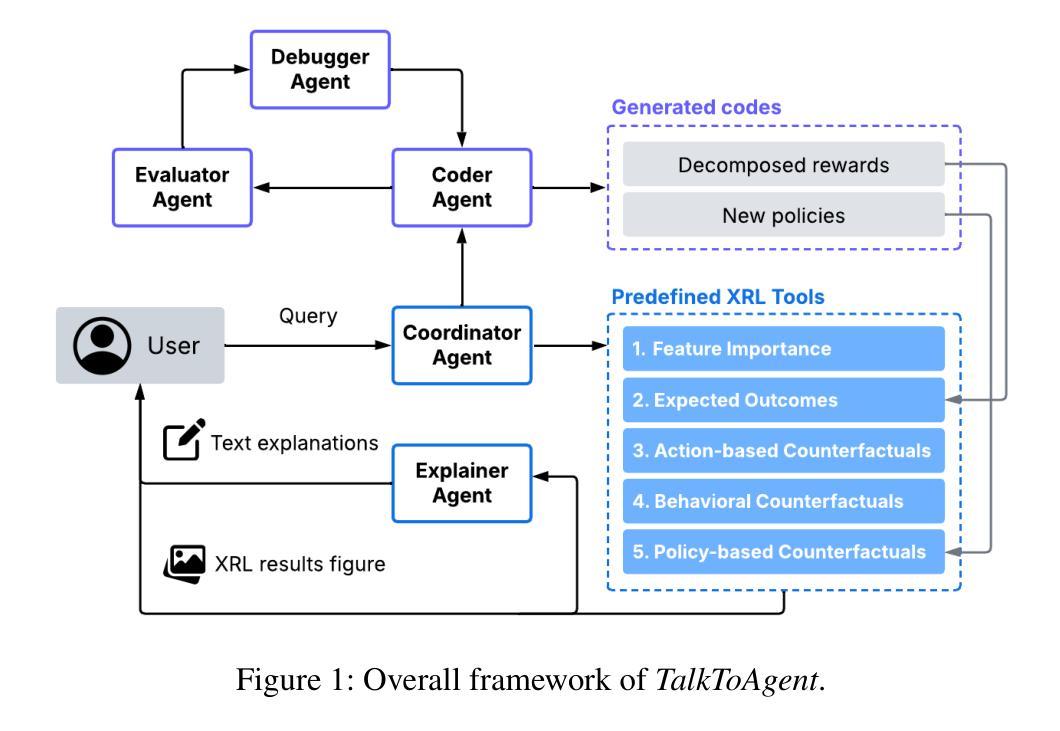
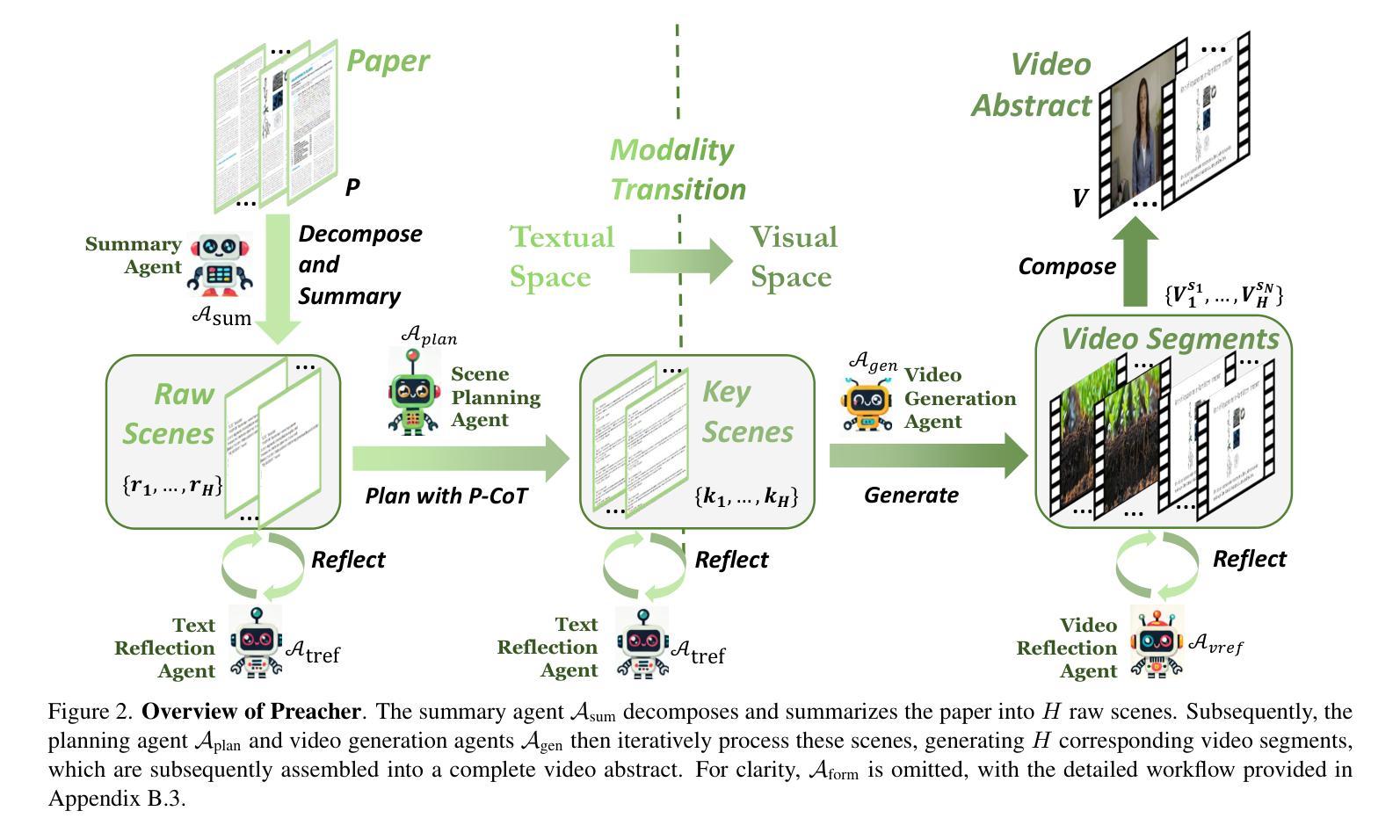
The paper-to-video task converts a research paper into a structured video abstract, distilling key concepts, methods, and conclusions into an accessible, well-organized format. While state-of-the-art video generation models demonstrate potential, they are constrained by limited context windows, rigid video duration constraints, limited stylistic diversity, and an inability to represent domain-specific knowledge. To address these limitations, we introduce Preacher, the first paper-to-video agentic system. Preacher employs a topdown approach to decompose, summarize, and reformulate the paper, followed by bottom-up video generation, synthesizing diverse video segments into a coherent abstract. To align cross-modal representations, we define key scenes and introduce a Progressive Chain of Thought (P-CoT) for granular, iterative planning. Preacher successfully generates high-quality video abstracts across five research fields, demonstrating expertise beyond current video generation models. Code will be released at: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/Paper2Video
这篇论文将研究论文转化为结构化的视频摘要,将关键概念、方法和结论转化为易于访问、组织良好的格式。尽管最新的视频生成模型展现出潜力,但它们受限于有限的上下文窗口、固定的视频时长约束、有限的风格多样性以及无法表示特定领域知识。为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了Preacher,这是第一个论文到视频的智能系统。Preacher采用自上而下的方法分解、总结和重构论文,然后进行自下而上的视频生成,将各种视频片段合成一个连贯的摘要。为了对齐跨模态表示,我们定义了关键场景并引入了渐进式思维链(P-CoT)进行精细、迭代的规划。Preacher成功地在五个研究领域生成了高质量的视频摘要,展现出超越当前视频生成模型的专长。代码将在https://github.com/Gen-Verse/Paper2Video发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025. Code: https://github.com/Gen-Verse/Paper2Video
Summary
论文转视频任务是将研究论文转化为结构化视频摘要,将关键概念、方法和结论转化为可访问、组织良好的格式。为解决当前视频生成模型的局限性,如有限上下文窗口、视频持续时间限制、风格单一以及无法表达领域特定知识等,我们引入了Preacher系统。该系统采用自上而下的方式分解、总结和重构论文,然后通过自下而上的视频生成方式,将多样化的视频片段合成一个连贯的摘要。为实现跨模态表示的对齐,我们定义了关键场景并引入了渐进思维链(P-CoT)进行精细的迭代规划。Preacher成功生成了五个研究领域的高质量视频摘要,展现了超越现有视频生成模型的专业能力。
Key Takeaways
- 论文转视频任务旨在将研究论文转化为结构化视频摘要,提高信息的可访问性和组织性。
- 当前视频生成模型存在多种局限性,如上下文窗口有限、视频时长约束、风格单一以及无法表达领域特定知识等。
- Preacher是首个论文转视频的智能系统,采用自上而下的方法处理论文,并辅以自下而上的视频生成。
- Preacher通过分解、总结和重构论文,有效提炼关键信息。
- 为实现跨模态表示的对齐,Preacher定义了关键场景并引入了渐进思维链(P-CoT)进行精细的迭代规划。
- Preacher系统成功生成了五个研究领域的高质量视频摘要。
点此查看论文截图

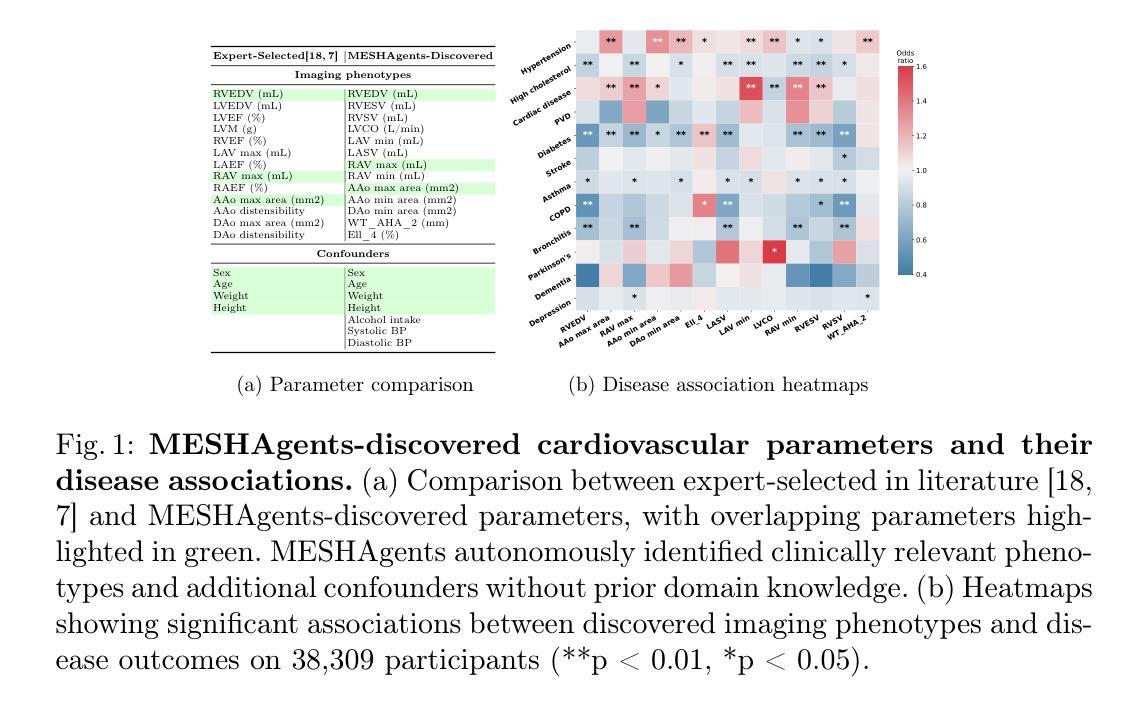
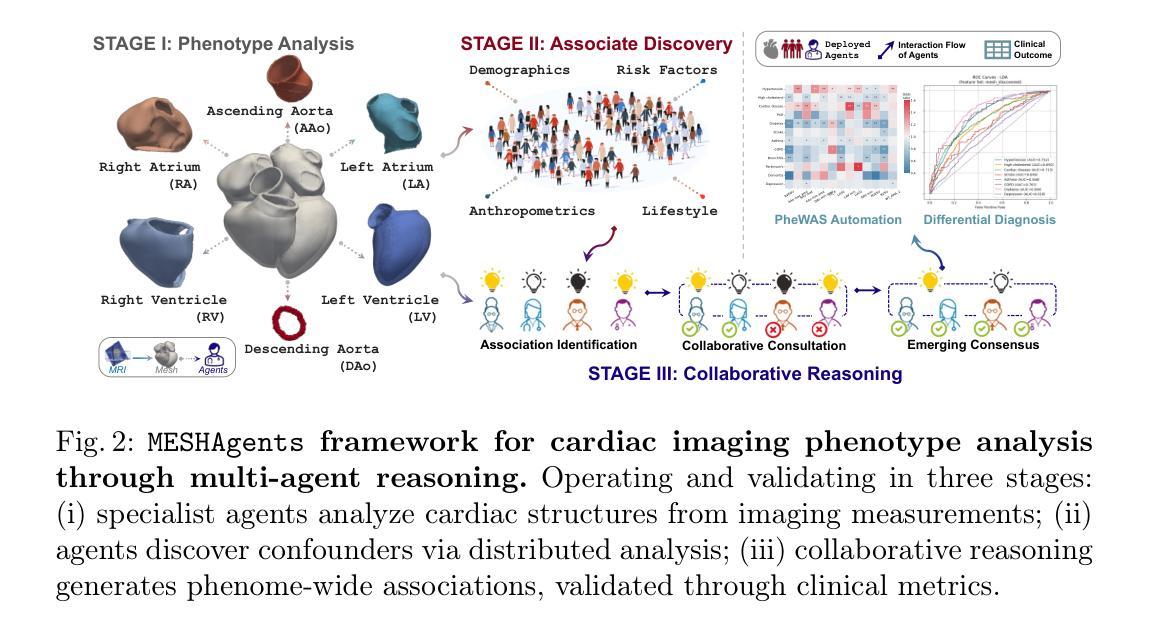
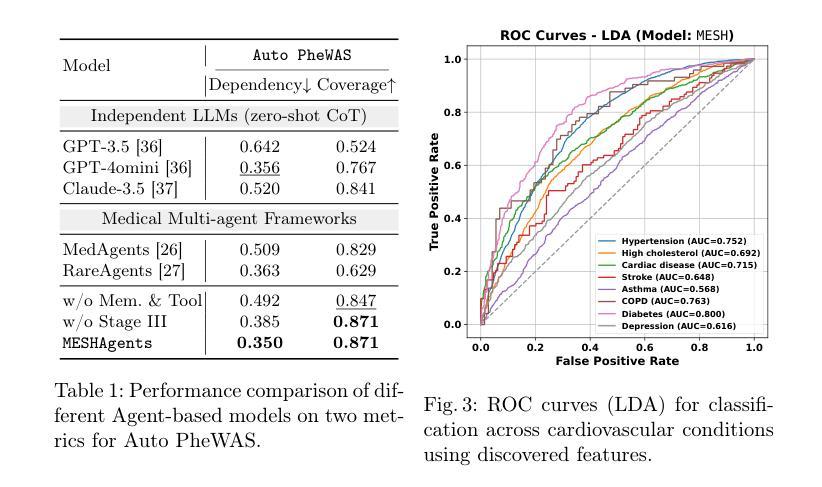
Multi-Agent Reasoning for Cardiovascular Imaging Phenotype Analysis
Authors:Weitong Zhang, Mengyun Qiao, Chengqi Zang, Steven Niederer, Paul M Matthews, Wenjia Bai, Bernhard Kainz
Identifying associations between imaging phenotypes, disease risk factors, and clinical outcomes is essential for understanding disease mechanisms. However, traditional approaches rely on human-driven hypothesis testing and selection of association factors, often overlooking complex, non-linear dependencies among imaging phenotypes and other multi-modal data. To address this, we introduce Multi-agent Exploratory Synergy for the Heart (MESHAgents): a framework that leverages large language models as agents to dynamically elicit, surface, and decide confounders and phenotypes in association studies. Specifically, we orchestrate a multi-disciplinary team of AI agents, which spontaneously generate and converge on insights through iterative, self-organizing reasoning. The framework dynamically synthesizes statistical correlations with multi-expert consensus, providing an automated pipeline for phenome-wide association studies (PheWAS). We demonstrate the system’s capabilities through a population-based study of imaging phenotypes of the heart and aorta. MESHAgents autonomously uncovered correlations between imaging phenotypes and a wide range of non-imaging factors, identifying additional confounder variables beyond standard demographic factors. Validation on diagnosis tasks reveals that MESHAgents-discovered phenotypes achieve performance comparable to expert-selected phenotypes, with mean AUC differences as small as $-0.004_{\pm0.010}$ on disease classification tasks. Notably, the recall score improves for 6 out of 9 disease types. Our framework provides clinically relevant imaging phenotypes with transparent reasoning, offering a scalable alternative to expert-driven methods.
识别成像表型、疾病风险因素和临床结果之间的关联对于理解疾病机制至关重要。然而,传统方法依赖于人为驱动的假设检验和关联因素的选择,往往忽略了成像表型和其他多模式数据之间复杂、非线性的依赖关系。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了心脏多智能体探索协同(MESHAgents):一个利用大型语言模型作为智能体来动态提取、显示和决定关联研究中的混杂因素和表型的框架。具体来说,我们协调了一个跨学科的AI智能体团队,这些智能体能自发地生成见解并通过迭代、自我组织推理达成共该智能体团队能够自发产生见解,并通过迭代和自我组织推理达成共通过对混杂因素的研究和多领域专家的共识,框架动态合成统计相关性,为全现象关联研究(PheWAS)提供自动化管道。我们通过一项基于人群的心脏和大动脉成像表型研究来展示系统的能力。MESHAgents自主地发现了成像表型与一系列非成像因素之间的关联,除了标准的人口学因素外,还确定了额外的混杂变量。在诊断任务上的验证表明,MESHAgents发现的表型在疾病分类任务上的表现与专家选择的表型相当,平均AUC差异仅为±0.01范围内,有9种疾病中有六种疾病的召回率有所提高。我们的框架提供了具有透明推理的临床相关成像表型,为专家驱动的方法提供了可替代的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by MICCAI 2025
Summary
基于成像表型、疾病风险因素与临床结果之间的关联,对于理解疾病机制至关重要。然而,传统方法依赖于人为驱动的假设检验和关联因素的选择,往往忽略了成像表型之间以及其他多模式数据之间复杂的非线性依赖关系。为此,我们引入Multi-agent Exploratory Synergy for the Heart(MESHAgents):一个利用大型语言模型作为代理的框架,能够动态地引发、显现并决定关联研究中的混淆因素和表型。通过人口基础的心和主动脉成像表型研究,MESHAgents自主地揭示了成像表型与一系列非成像因素之间的联系,确定了超出标准人口统计因素的额外混淆变量。在诊断任务上的验证表明,MESHAgents发现的表型在疾病分类任务上的性能与专家选择的表型相当,平均AUC差异仅为$-0.004_{\pm0.010}$,且9种疾病中有6种的召回率有所提高。我们的框架提供了具有透明推理的临床相关成像表型,为专家驱动的方法提供了可伸缩的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 传统方法在关联研究中忽略了成像表型与其他数据间的复杂非线性关系。
- MESHAgents框架利用大型语言模型作为代理,能动态确定关联研究中的混淆因素和表型。
- 通过人口基础研究,MESHAgents发现了成像表型与非成像因素之间的联系。
- MESHAgents确定的表型在疾病分类任务上的性能与专家选择的表型相当。
- MESHAgents能提高诊断任务的召回率,特别是在某些疾病类型上。
- 该框架提供的成像表型具有透明推理,为专家驱动的方法提供了可伸缩的替代方案。
点此查看论文截图

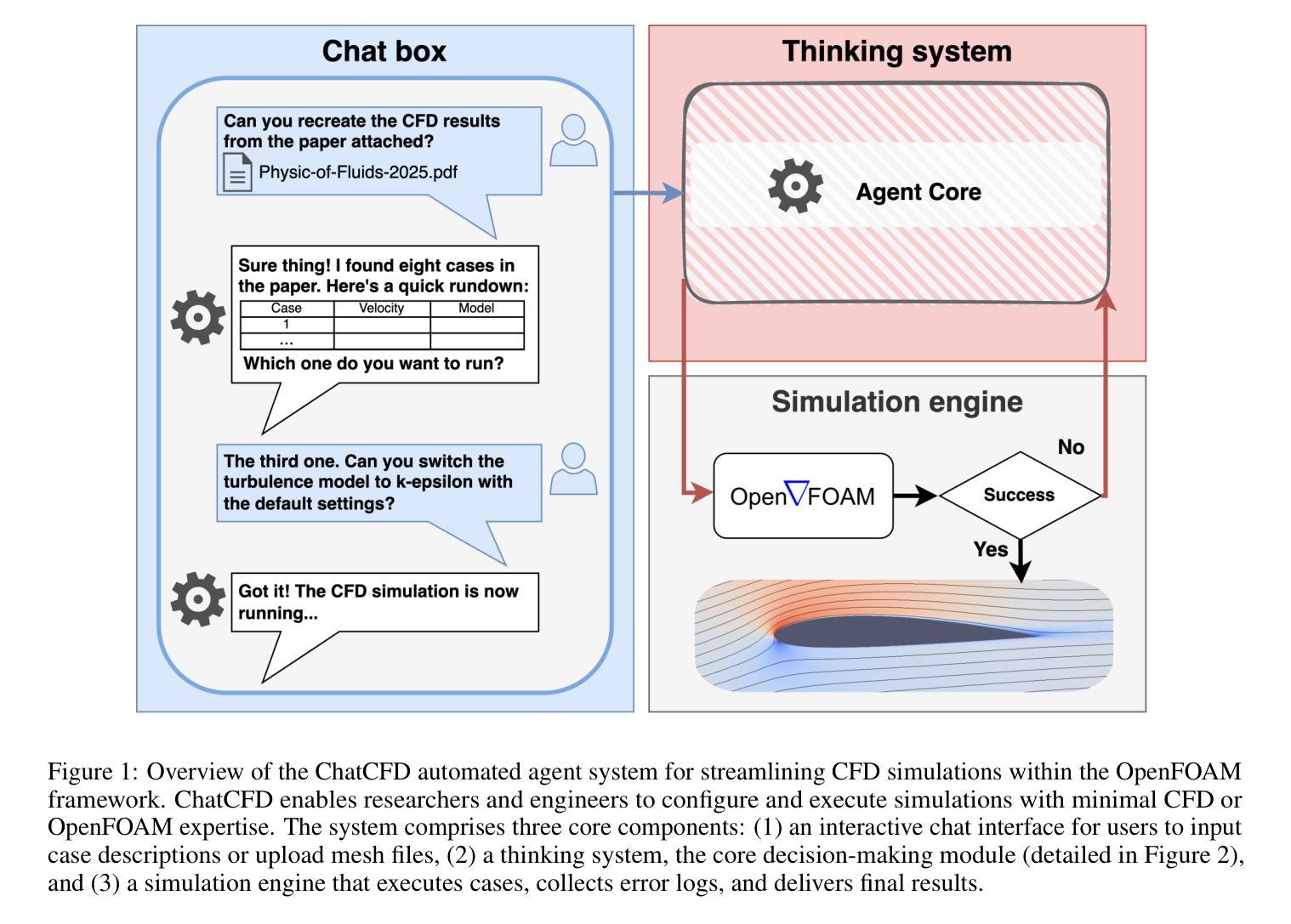
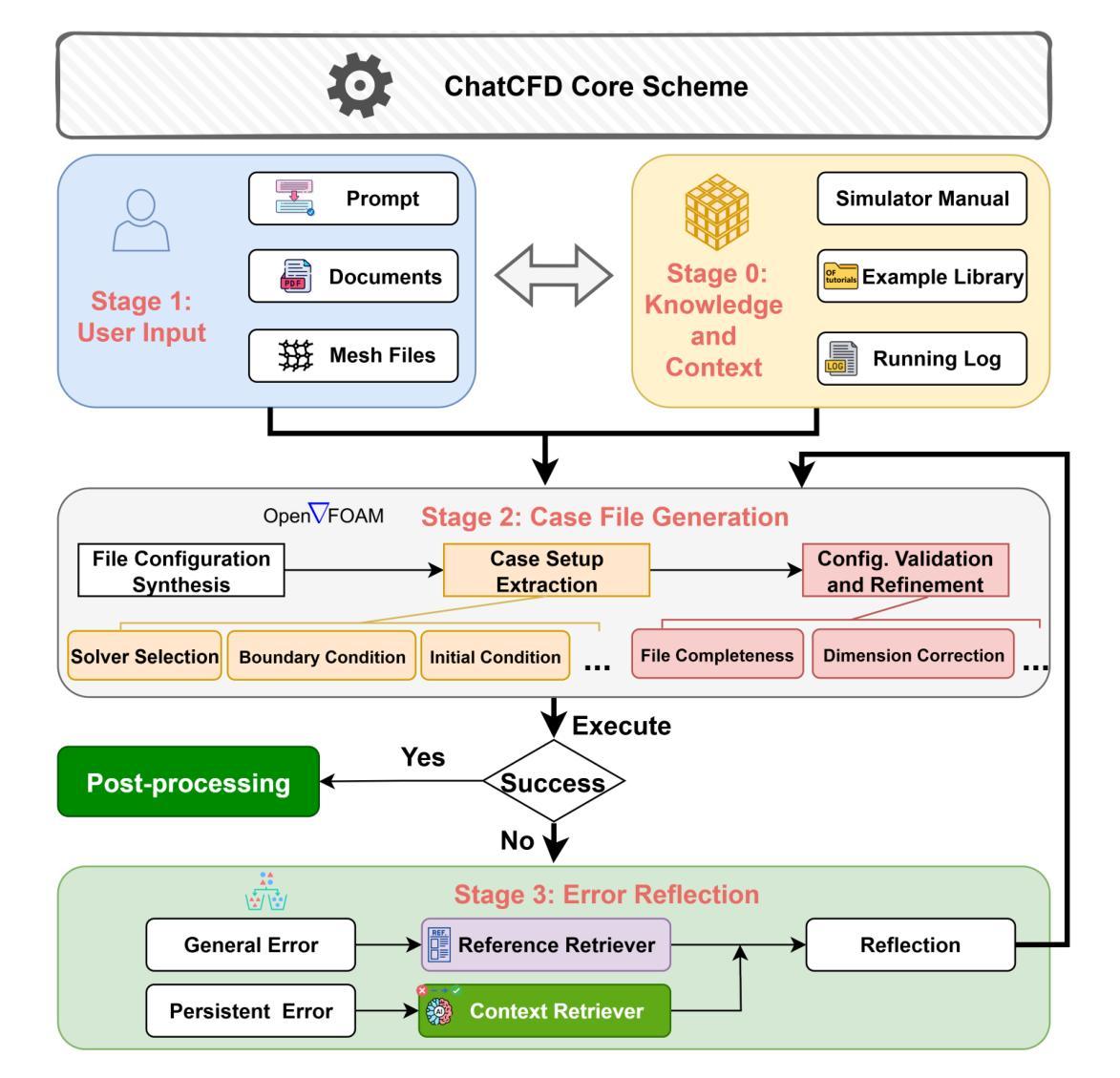
ChatCFD: An LLM-Driven Agent for End-to-End CFD Automation with Domain-Specific Structured Reasoning
Authors:E Fan, Kang Hu, Zhuowen Wu, Jiangyang Ge, Jiawei Miao, Yuzhi Zhang, He Sun, Weizong Wang, Tianhan Zhang
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is essential for advancing scientific and engineering fields but is hindered by operational complexity, high expertise requirements, and limited accessibility. This paper introduces ChatCFD, an automated agent system for OpenFOAM simulations that processes multi-modal inputs (e.g., research papers, meshes) via an interactive interface, leveraging DeepSeek-R1 and DeepSeek-V3 large language models, a multi-agent architecture, and OpenFOAM knowledge. Its four-stage pipeline (Knowledge Base Construction, User Input Processing, Case File Generation, and Execution and Error Reflection) enables iterative trial-reflection-refinement for intricate setups, supporting diverse physical models and external meshes. Validation on 205 benchmark tutorial cases, 110 perturbed variants, and 2 literature-derived cases shows ChatCFD’s 82.1 percent operational success rate on basic cases, outperforming MetaOpenFOAM (6.2 percent) and Foam-Agent (42.3 percent), and 60-80 percent on literature-derived complex cases. Turbulence model studies show a 40 percent success rate for common models versus 10 percent for rare ones like RNG k-epsilon. Physics coupling analyses reveal higher resource demands for multi-physics-coupled cases, while LLM bias toward simpler setups introduces persistent errors, such as dimensional inconsistency. Ablation studies highlight the efficacy of RAG-based modules and reflection mechanisms. By automating hypothesis testing and parameter exploration, ChatCFD accelerates scientific discovery in fluid mechanics and engineering, addressing LLM limitations through structured design and showing strong potential as a modular component in MCP-based agent networks for collaborative multi-agent systems, paving the way for scalable AI-driven CFD innovation. The code for ChatCFD is available at https://github.com/ConMoo/ChatCFD.
计算流体动力学(CFD)对于推动科学和工程领域的发展至关重要,但受到操作复杂、专业要求高、可访问性有限的阻碍。本文介绍了ChatCFD,这是一个用于OpenFOAM模拟的自动化代理系统,它通过交互式接口处理多模式输入(例如研究论文、网格),利用DeepSeek-R1和DeepSeek-V3大型语言模型、多代理架构和OpenFOAM知识。其四阶段管道(知识库构建、用户输入处理、案例文件生成、执行和错误反馈)为复杂设置提供了迭代试验-反思-改进的支持,支持多种物理模型和外部网格。对205个基准教程案例、110个扰动变体以及2个文献衍生案例的验证显示,ChatCFD在基本案例上的操作成功率为82.1%,超过了MetaOpenFOAM(6.2%)和Foam-Agent(42.3%),在文献衍生复杂案例上的成功率为60-80%。湍流模型研究表明,常见模型的成功率为40%,而稀有模型如RNG k-epsilon的成功率为10%。物理耦合分析表明,多物理耦合案例的资源需求更高,而大型语言模型对更简单设置的偏好会导致持久性错误,如尺寸不一致。消融研究突出了基于RAG的模块和反馈机制的有效性。通过自动化假设检验和参数探索,ChatCFD加速了流体力学和工程中的科学发现,通过结构化设计解决了大型语言模型的局限性,并显示出作为模块化组件在基于MCP的多代理网络中的强大潜力,为可扩展的AI驱动CFD创新奠定了基础。ChatCFD的代码可在https://github.com/ConMoo/ChatCFD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 8 figures
Summary
CFD(计算流体动力学)在科学与工程领域具有关键作用,但受到操作复杂、专业要求高和可访问性有限的限制。本文介绍了ChatCFD系统,它通过多模态输入(如研究论文、网格)和多智能体架构来自动化OpenFOAM模拟过程。该系统的管道分为四个阶段,能够实现复杂设置的迭代试验、反思和改进。验证结果表明,ChatCFD在基本案例上的操作成功率为82.1%,优于MetaOpenFOAM(6.2%)和Foam-Agent(42.3%),在复杂文献案例上的成功率为60-80%。然而,对于复杂的物理模型和多种物理现象的耦合分析需求较高资源,同时大型语言模型对于复杂设置下的错误可能偏向简化,但仍展示了在模块化智能体网络和可扩展的AI驱动的CFD创新方面的巨大潜力。如需了解更多详情,可访问我们的GitHub代码仓库:https://github.com/ConMoo/ChatCFD。
Key Takeaways
- ChatCFD是一个基于OpenFOAM的自动化代理系统,用于处理多模态输入并简化计算流体动力学的模拟过程。
- ChatCFD通过四个阶段的管道实现复杂设置的迭代试验、反思和改进。
- ChatCFD在基本案例上的操作成功率较高,优于其他系统。
- 在处理复杂物理模型和多种物理现象的耦合分析时,ChatCFD展现了其高效性但也有所受限。
- 大型语言模型在处理复杂设置时可能出现偏差,需要结构化设计来减少误差。
点此查看论文截图

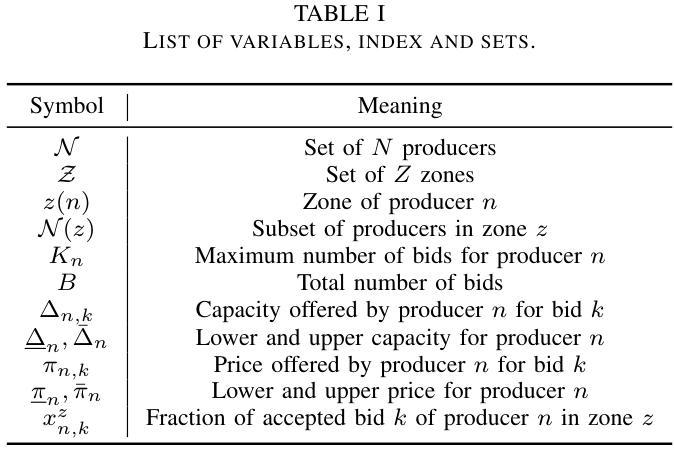
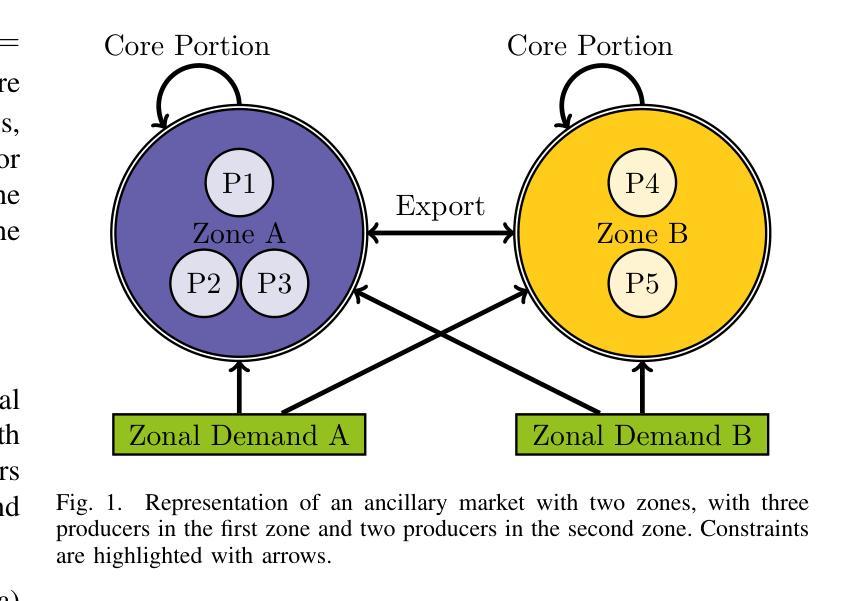
Game Theory and Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Zonal Ancillary Markets
Authors:Francesco Morri, Hélène Le Cadre, Pierre Gruet, Luce Brotcorne
We characterize zonal ancillary market coupling relying on noncooperative game theory. To that purpose, we formulate the ancillary market as a multi-leader single follower bilevel problem, that we subsequently cast as a generalized Nash game with side constraints and nonconvex feasibility sets. We determine conditions for equilibrium existence and show that the game has a generalized potential game structure. To compute market equilibrium, we rely on two exact approaches: an integrated optimization approach and Gauss-Seidel best-response, that we compare against multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. On real data from Germany and Austria, simulations indicate that multi-agent deep reinforcement learning achieves the smallest convergence rate but requires pretraining, while best-response is the slowest. On the economics side, multi-agent deep reinforcement learning results in smaller market costs compared to the exact methods, but at the cost of higher variability in the profit allocation among stakeholders. Further, stronger coupling between zones tends to reduce costs for larger zones.
我们采用非合作博弈理论来刻画区域辅助市场耦合。为此,我们将辅助市场制定为一个多领导者单一跟随者的双层问题,随后将其转化为带有侧约束和非凸可行集的广义纳什博弈。我们确定了均衡存在的条件,并证明该游戏是广义潜在博弈结构。为了计算市场均衡,我们依赖两种精确方法:一种整体优化方法和Gauss-Seidel最佳反应法,我们将它们与多智能体深度强化学习进行比较。在来自德国和奥地利的真实数据进行的模拟表明,多智能体深度强化学习具有最小的收敛速率,但需要预先训练,而最佳反应法是最慢的。在经济方面,与精确方法相比,多智能体深度强化学习导致较小的市场成本,但成本较高的利益相关者利润分配变动性更大。此外,区域之间的更强耦合往往降低了较大区域的成本。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用非合作博弈理论研究了区域辅助市场耦合的特性。文章将辅助市场建模为一个多领导单跟随者的双层问题,并进一步转化为带有侧约束和非凸可行集的广义纳什游戏。文章确定了均衡存在的条件,并展示了该游戏的广义势能游戏结构。为了计算市场均衡,文章采用了两种精确方法:一体化优化方法和高斯-赛德尔最佳反应方法,并与多智能体深度强化学习进行了比较。基于德国和奥地利实际数据的模拟结果表明,多智能体深度强化学习虽然训练成本高且收益分配存在较高不确定性,但收敛速度最快且市场成本较低。此外,区域间更强的耦合趋势有助于降低大型区域的市场成本。
Key Takeaways
- 本文利用非合作博弈理论研究了区域辅助市场耦合问题,建立了基于多层博弈的市场模型。
- 通过对市场的广义纳什游戏结构分析,确定了均衡存在的条件。
- 文章采用了两种精确方法来计算市场均衡:一体化优化方法和高斯-赛德尔最佳反应方法。
- 多智能体深度强化学习在模拟中展现出最快的收敛速度,但训练成本高且收益分配存在不确定性。
- 与精确方法相比,多智能体深度强化学习在市场成本方面表现更优。
- 区域间更强的耦合趋势有助于降低大型区域的市场成本。
点此查看论文截图

ResearchArena: Benchmarking Large Language Models’ Ability to Collect and Organize Information as Research Agents
Authors:Hao Kang, Chenyan Xiong
Large language models (LLMs) excel across many natural language processing tasks but face challenges in domain-specific, analytical tasks such as conducting research surveys. This study introduces ResearchArena, a benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs’ capabilities in conducting academic surveys – a foundational step in academic research. ResearchArena models the process in three stages: (1) information discovery, identifying relevant literature; (2) information selection, evaluating papers’ relevance and impact; and (3) information organization, structuring knowledge into hierarchical frameworks such as mind-maps. Notably, mind-map construction is treated as a bonus task, reflecting its supplementary role in survey-writing. To support these evaluations, we construct an offline environment of 12M full-text academic papers and 7.9K survey papers. To ensure ethical compliance, we do not redistribute copyrighted materials; instead, we provide code to construct the environment from the Semantic Scholar Open Research Corpus (S2ORC). Preliminary evaluations reveal that LLM-based approaches underperform compared to simpler keyword-based retrieval methods, though recent reasoning models such as DeepSeek-R1 show slightly better zero-shot performance. These results underscore significant opportunities for advancing LLMs in autonomous research. We open-source the code to construct the ResearchArena benchmark at https://github.com/cxcscmu/ResearchArena.
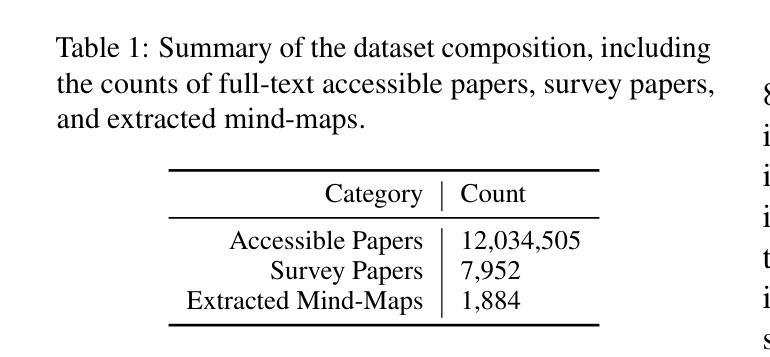
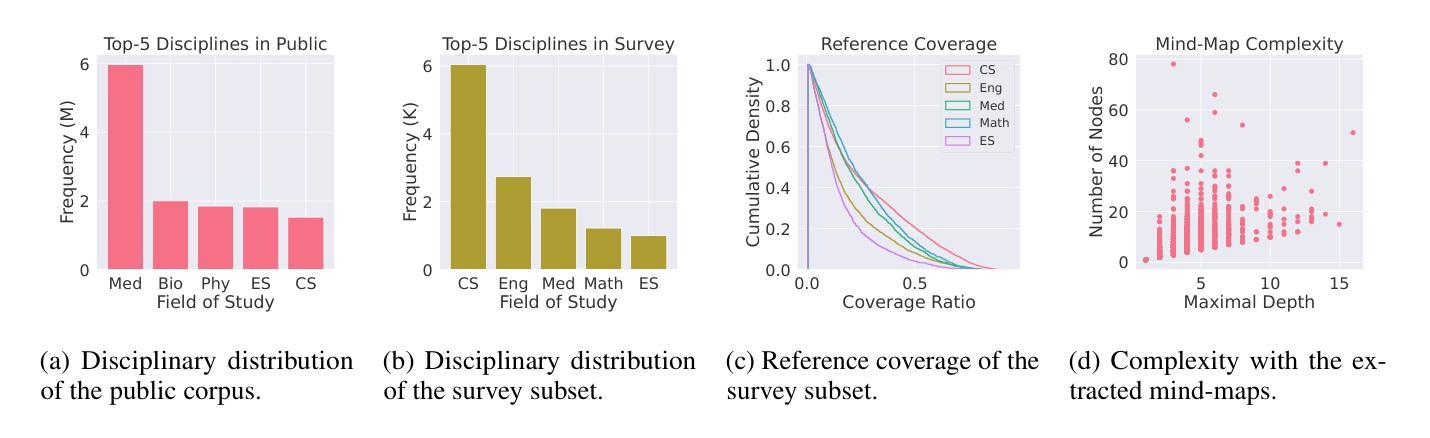
大型语言模型(LLM)在许多自然语言处理任务上表现出色,但在特定领域的分析任务,如开展研究调查方面面临挑战。本研究介绍了ResearchArena,这是一个旨在评估LLM进行学术调查能力的基准测试——学术研究中的基础步骤。ResearchArena将过程模拟为三个阶段:(1)信息发现,识别相关文献;(2)信息选择,评估论文的相关性和影响力;(3)信息组织,将知识构建成层次框架,如思维导图。值得注意的是,思维导图构建被视为附加任务,反映了其在调查报告中的辅助作用。为了支持这些评估,我们构建了包含1.2亿篇全文学术论文和7900篇调查报告的离线环境。为确保遵守伦理规定,我们不重新分发受版权保护的材料;相反,我们提供代码以从语义学者开放研究语料库(S2ORC)构建环境。初步评估表明,基于LLM的方法相比于简单的关键词检索方法表现较差,尽管最近的推理模型如DeepSeek-R1显示出略好的零样本性能。这些结果突显了推进LLM在自主研究方面的巨大机会。我们公开了构建ResearchArena基准测试的代码如下:https://github.com/cxcscmu/ResearchArena。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
研究介绍了一种名为ResearchArena的基准测试平台,旨在评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在进行学术调查方面的能力。该平台模拟了学术调查的三个阶段:信息发现、信息筛选和信息组织。初步评估显示,LLM方法相较于简单的关键词检索方法表现不佳,但最新推理模型如DeepSeek-R1在零样本任务中表现稍好。这为LLMs在自主研究方面的进步提供了重要机会。
Key Takeaways
- ResearchArena是一个评估大型语言模型(LLMs)在学术调查方面能力的基准测试平台。
- LLMs在学术调查的多个阶段表现出挑战,包括信息发现、筛选和组织。
- 信息组织阶段中的思维导图构建被视为附加任务,反映其在调查报告写作中的辅助作用。
- 为支持评估,构建了包含1.2亿篇全文学术论文和7900篇调查报告的离线环境。
- LLM方法相较于简单的关键词检索方法表现不佳,但最新推理模型如DeepSeek-R1在某些情况下表现更好。
- LLMs在自主研究方面有巨大进步空间。
点此查看论文截图


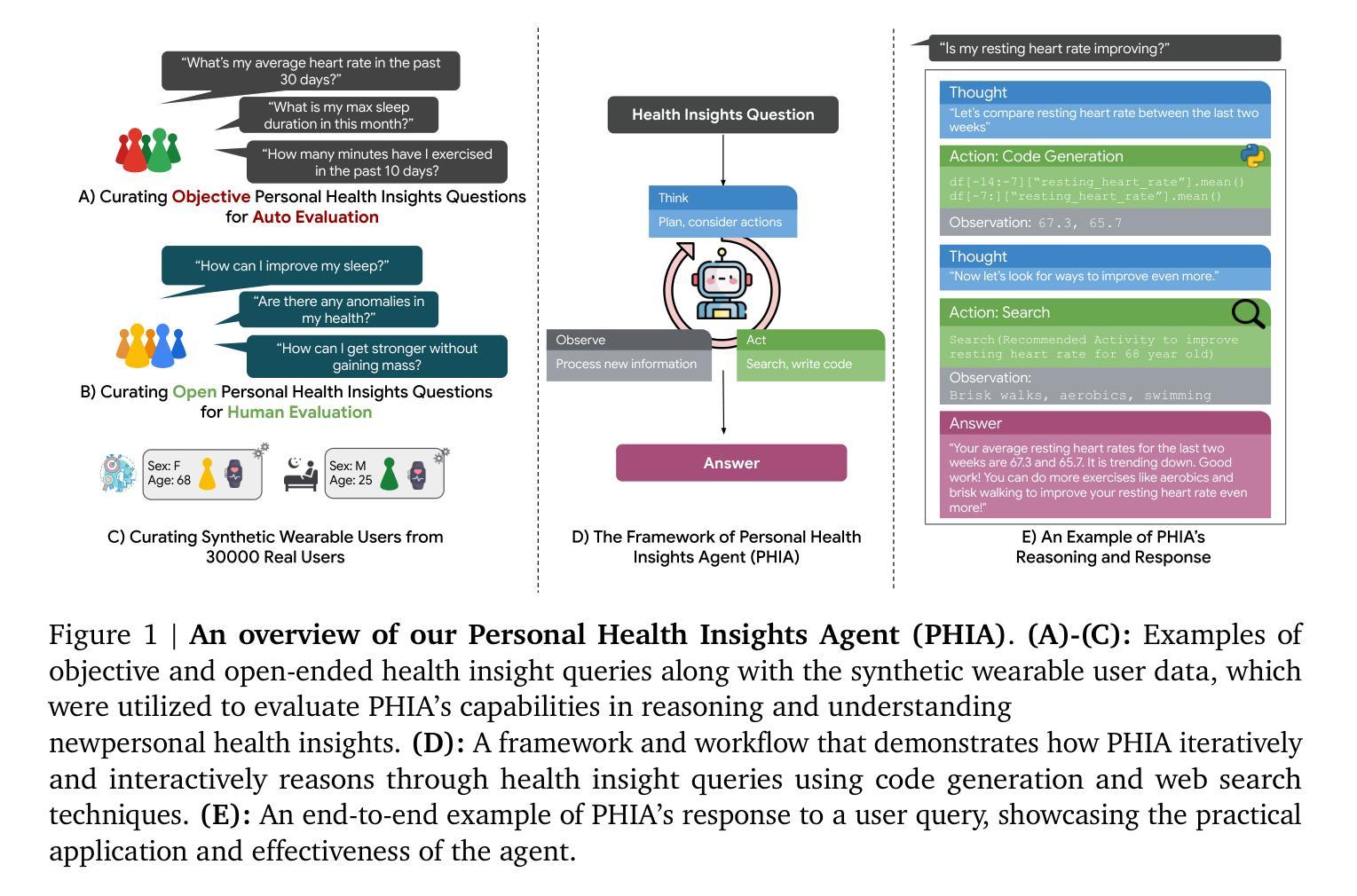
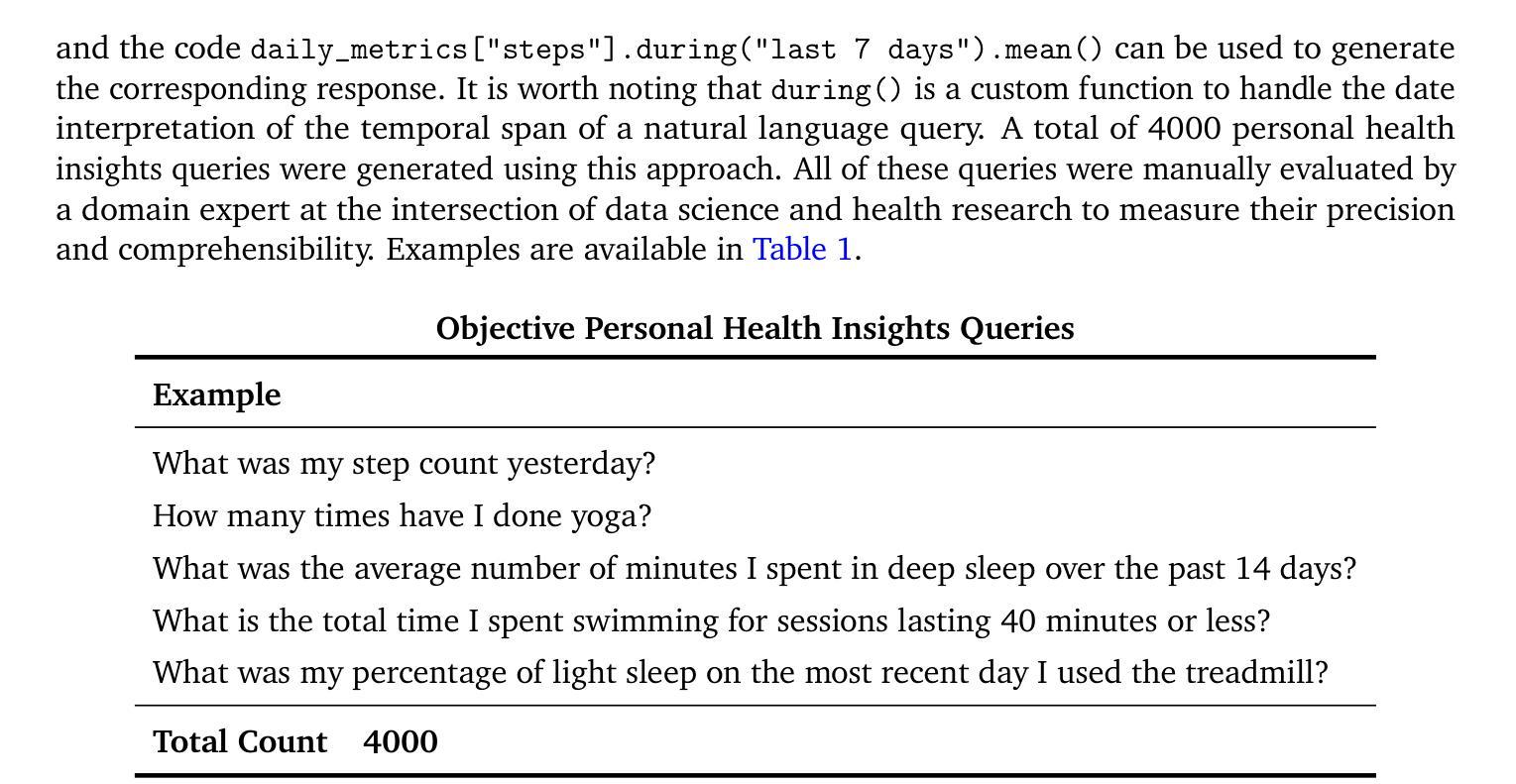
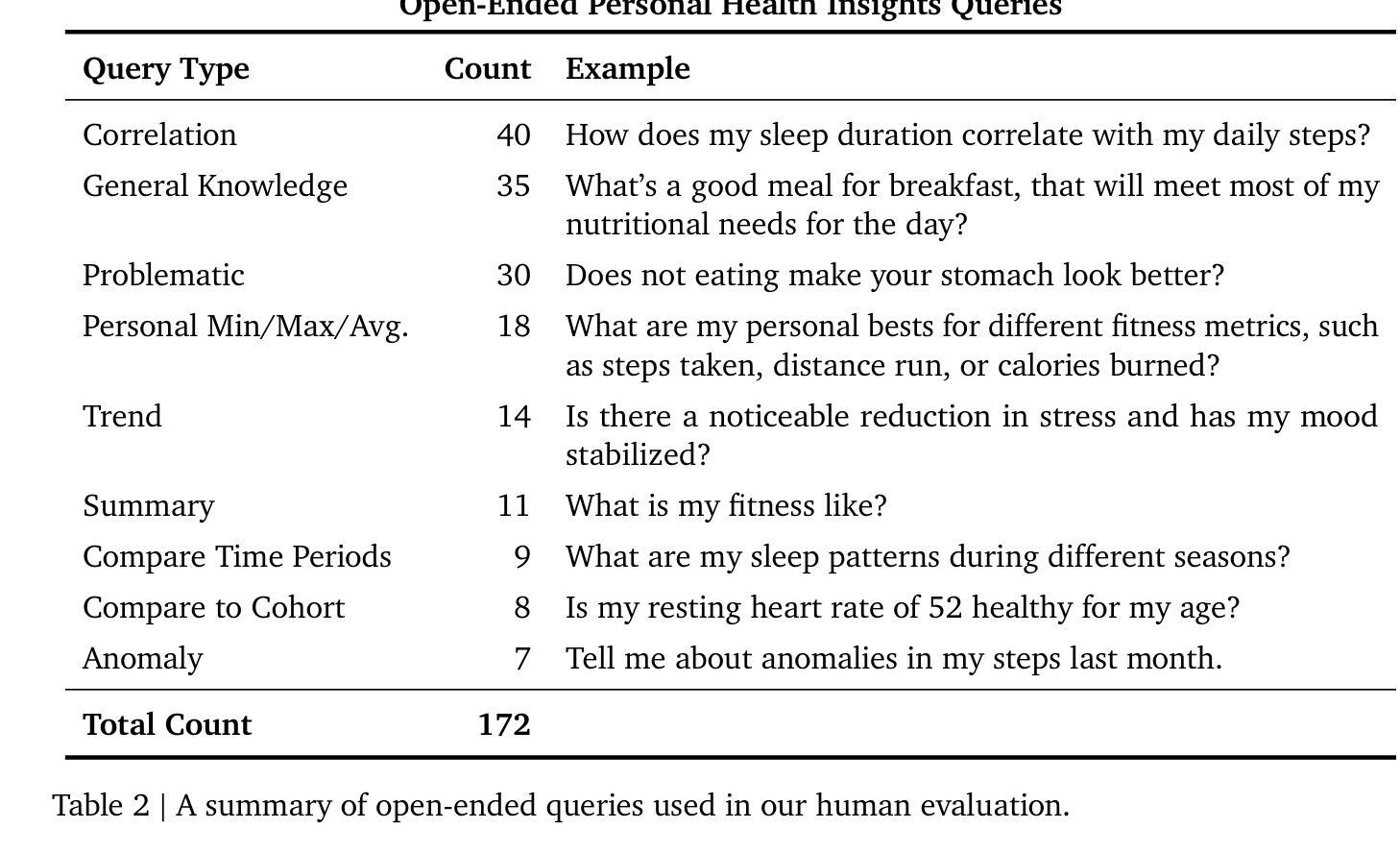
Transforming Wearable Data into Personal Health Insights using Large Language Model Agents
Authors:Mike A. Merrill, Akshay Paruchuri, Naghmeh Rezaei, Geza Kovacs, Javier Perez, Yun Liu, Erik Schenck, Nova Hammerquist, Jake Sunshine, Shyam Tailor, Kumar Ayush, Hao-Wei Su, Qian He, Cory Y. McLean, Mark Malhotra, Shwetak Patel, Jiening Zhan, Tim Althoff, Daniel McDuff, Xin Liu
Deriving personalized insights from popular wearable trackers requires complex numerical reasoning that challenges standard LLMs, necessitating tool-based approaches like code generation. Large language model (LLM) agents present a promising yet largely untapped solution for this analysis at scale. We introduce the Personal Health Insights Agent (PHIA), a system leveraging multistep reasoning with code generation and information retrieval to analyze and interpret behavioral health data. To test its capabilities, we create and share two benchmark datasets with over 4000 health insights questions. A 650-hour human expert evaluation shows that PHIA significantly outperforms a strong code generation baseline, achieving 84% accuracy on objective, numerical questions and, for open-ended ones, earning 83% favorable ratings while being twice as likely to achieve the highest quality rating. This work can advance behavioral health by empowering individuals to understand their data, enabling a new era of accessible, personalized, and data-driven wellness for the wider population.
从流行的可穿戴跟踪器中获取个性化洞察需要复杂的数值推理,这挑战了标准的大型语言模型,需要基于工具的方法,如代码生成。大型语言模型(LLM)代理人为这种大规模分析提供了前景广阔但尚未开发的解决方案。我们介绍了个人健康洞察代理(PHIA),这是一个利用多步骤推理、代码生成和信息检索来分析解读行为健康数据的系统。为了测试其能力,我们创建并分享了包含超过4000个健康洞察问题数据集。为期650小时的人类专家评估显示,PHIA在客观数值问题上的准确率显著超过强大的代码生成基线,达到了84%,对于开放式问题,获得了83%的好评,同时获得最高质量评级的可能性是原来的两倍。这项工作可以通过帮助个人理解他们的数据来推动行为健康的发展,为更广泛的人群开启一个易于访问、个性化和数据驱动的健康新时代。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 53 pages, 7 main figures, 2 main tables, accepted to Nature Communications
Summary
穿戴式追踪器所搜集的个人健康数据,需要复杂的数值分析才能转化为个人化的洞见,这挑战了传统的大型语言模型(LLM)。为此,我们引入个人健康洞见代理(PHIA),该系统采用多步骤推理与代码生成及信息检索技术来分析并解读行为健康数据。测试显示,PHIA在客观数值问题和开放性问题上的准确率分别达到了84%和获得83%的好评,且其达到最高质量评级的可能性是基线模型的两倍。此研究将推动行为健康领域的发展,使个人能够更深入地理解自身数据,为更广泛的人群带来可访问的、个性化的、数据驱动的福祉新时代。
Key Takeaways
- 穿戴式追踪器的数据需要复杂的数值分析以转化为个人洞见。
- 传统的大型语言模型(LLM)在处理这些数据时面临挑战。
- 引入个人健康洞见代理(PHIA),利用多步骤推理、代码生成和信息检索技术进行分析。
- PHIA在客观数值问题和开放性问题的测试中表现出卓越性能。
- PHIA相较于基线模型,获得更高的用户好评,且更有可能获得最高质量评级。
- 此研究有助于推动行为健康领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图