⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-10 更新
HD 143811 AB b: A Directly Imaged Planet Orbiting a Spectroscopic Binary in Sco-Cen
Authors:Nathalie K. Jones, Jason J. Wang, Eric L. Nielsen, Robert J. De Rosa, Anne E. Peck, William Roberson, Jean-Baptiste Ruffio, Jerry W. Xuan, Bruce A. Macintosh, S. Mark Ammons, Vanessa P. Bailey, Travis S. Barman, Joanna Bulger, Eugene Chiang, Jeffrey K. Chilcote, Gaspard Duchêne, Thomas M. Esposito, Michael P. Fitzgerald, Katherine B. Follette, Stephen Goodsell, James R. Graham, Alexandra Z. Greenbaum, Pascale Hibon, Patrick Ingraham, Paul Kalas, Quinn M. Konopacky, Michael C. Liu, Franck Marchis, Jérôme Maire, Christian Marois, Brenda Matthews, Dimitri Mawet, Stanimir Metchev, Maxwell A. Millar-Blanchaer, Rebecca Oppenheimer, David W. Palmer, Jenny Patience, Marshall D. Perrin, Lisa Poyneer, Laurent Pueyo, Abhijith Rajan, Julian Rameau, Fredrik T. Rantakyrö, Bin Ren, Aniket Sanghi, Dmitry Savransky, Adam C. Schneider, Anand Sivaramakrishnan, Adam J. R. W. Smith, Inseok Song, Remi Sommer, Sandrine Thomas, Kimberly Ward-Duong, Schuyler G. Wolff
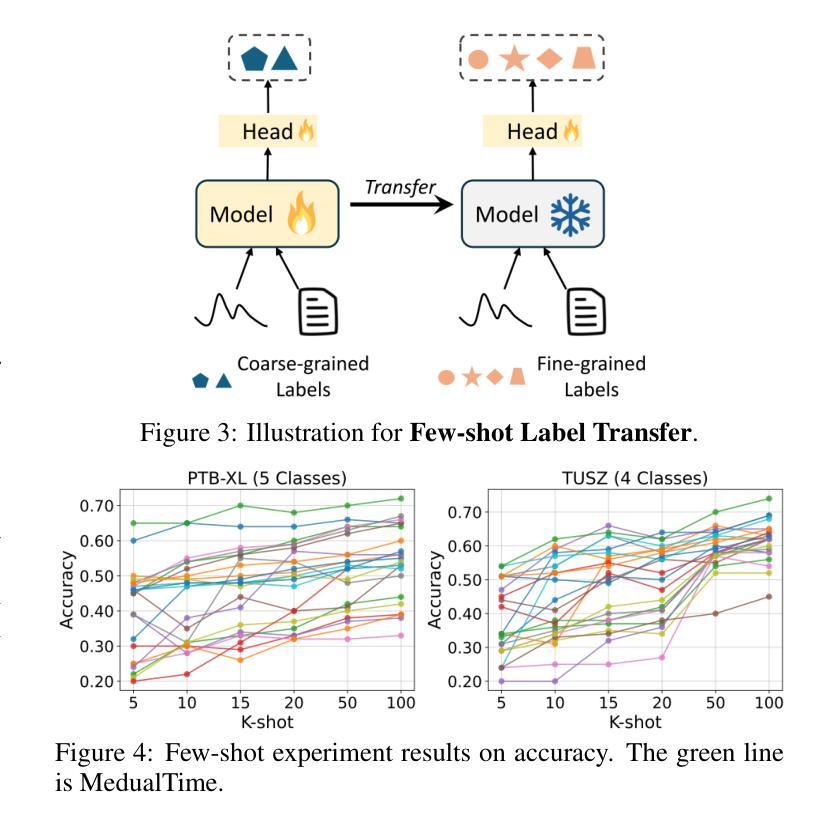
We present confirmation of HD 143811 AB b, a substellar companion to spectroscopic binary HD 143811 AB through direct imaging with the Gemini Planet Imager (GPI) and Keck NIRC2. HD 143811 AB was observed as a part of the Gemini Planet Imager Exoplanet Survey (GPIES) in 2016 and 2019 and is a member of the Sco-Cen star formation region. The companion object is detected $\sim 430$ mas from the host star by GPI. With two GPI epochs and one from Keck/NIRC2 in 2022, we confirm through common proper motion analysis that the object is bound to its host star. We derive an orbit with a semi-major axis of $64 ^{+32}{-14}$ au and eccentricity $\sim 0.23$. Spectral analysis of the GPI $H$-band spectrum and NIRC2 \textit{L’} photometry provides additional proof that this object is a substellar companion. We compare the spectrum of HD 143811 AB b to PHOENIX stellar models and Exo-REM exoplanet atmosphere models and find that Exo-REM models provide the best fits to the data. From the Exo-REM models, we derive an effective temperature of $1042^{+178}{-132}$ K for the planet and translate the derived luminosity of the planet to a mass of $5.6 \pm 1.1~M_\textrm{Jup}$ assuming hot-start evolutionary models. HD 143811 AB b is one of only a few planets to be directly imaged around a binary, and future characterization of this object will shed light on the formation of planets around binary star systems.
我们通过对光谱双星HD 143811 AB进行直接成像,证实了其亚恒星伴星HD 143811 AB b的存在。该成像采用双子座行星成像仪(GPI)和凯克NIRC2完成。HD 143811 AB作为双子座行星成像仪外行星调查(GPIES)的一部分,于2016年和2019年观测到,是Sco-Cen星形成区域的一员。伴星物体距离主星约430 mas的位置被GPI探测到。通过两个GPI时段和凯克/NIRC2在2022年的观测数据,我们通过常见的运动特性分析确认该物体与主星有联系。我们推导出了一个轨道,其半长轴为64 ± 32 au,偏心率为约0.23。GPI H波段光谱和NIRC2 L’光度计的光谱分析提供了进一步的证据表明该物体是一个亚恒星伴星。我们将HD 143811 AB b的光谱与PHOENIX恒星模型和Exo-REM外行星大气模型进行比较,发现Exo-REM模型与数据吻合度最高。根据Exo-REM模型,我们得出该行星的有效温度为1042 ± 178 K,并根据热启动演化模型推断出该行星的亮度对应的质量为5.6 ± 1.1 MJup。HD 143811 AB b是少数围绕双星直接成像的行星之一,对该物体的未来特征研究将阐明围绕双星系统的行星形成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 7 figures
Summary
HD 143811 AB b是一颗围绕光谱双星HD 143811 AB的次恒星伴侣,通过Gemini行星成像仪(GPI)和Keck NIRC2进行直接成像得到确认。该伴侣星通过恒动分析被证实是围绕主星运行的,并推导出了其轨道的半长轴和离心率。光谱分析提供了额外的证明,表明该对象是一个次恒星伴侣。比较其光谱与PHOENIX恒星模型和Exo-REM行星大气模型,发现Exo-REM模型最适合当前数据。由此模型得出该行星的有效温度,并根据热启动进化模型推算出其质量。HD 143811 AB b是少数在双星系统中直接成像的行星之一,对其未来的特征研究将阐明双星系统行星的形成。
Key Takeaways
- HD 143811 AB b被确认为一颗围绕光谱双星HD 143811 AB的次恒星伴侣。
- 通过GPI和Keck NIRC2的直接成像以及恒动分析,证实了该伴侣星与主星的关系。
- 推导出了该伴侣星的轨道半长轴和离心率。
- 光谱分析进一步证明该对象具有次恒星特性。
- Exo-REM模型与HD 143811 AB b的光谱最为匹配,从中得出其有效温度。
- 基于热启动进化模型和Exo-REM模型,推算出该行星的质量约为木星质量的5.6倍。
点此查看论文截图
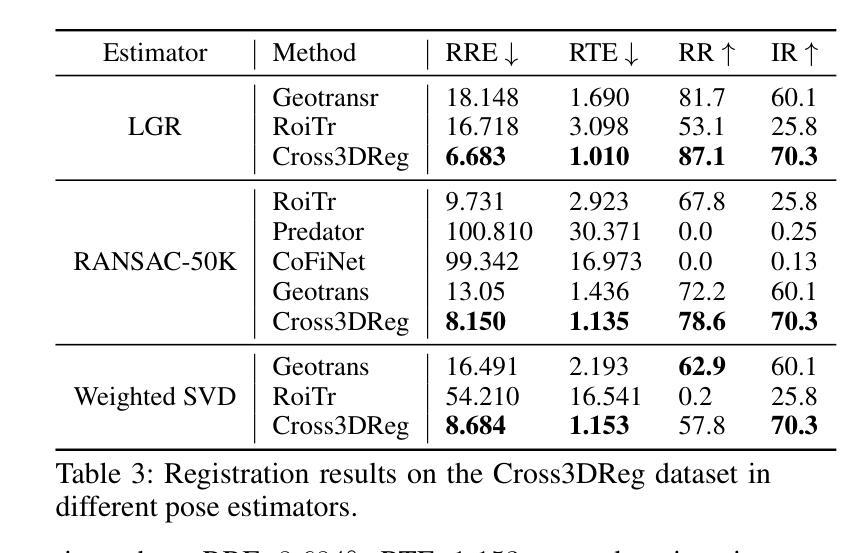
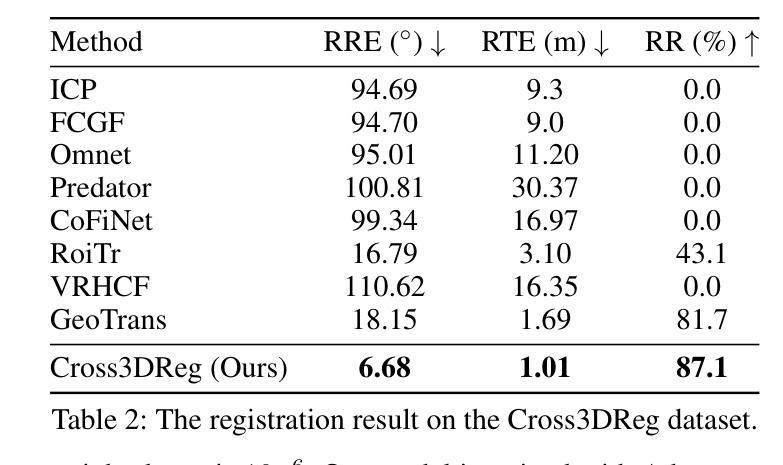
Cross3DReg: Towards a Large-scale Real-world Cross-source Point Cloud Registration Benchmark
Authors:Zongyi Xu, Zhongpeng Lang, Yilong Chen, Shanshan Zhao, Xiaoshui Huang, Yifan Zuo, Yan Zhang, Qianni Zhang, Xinbo Gao
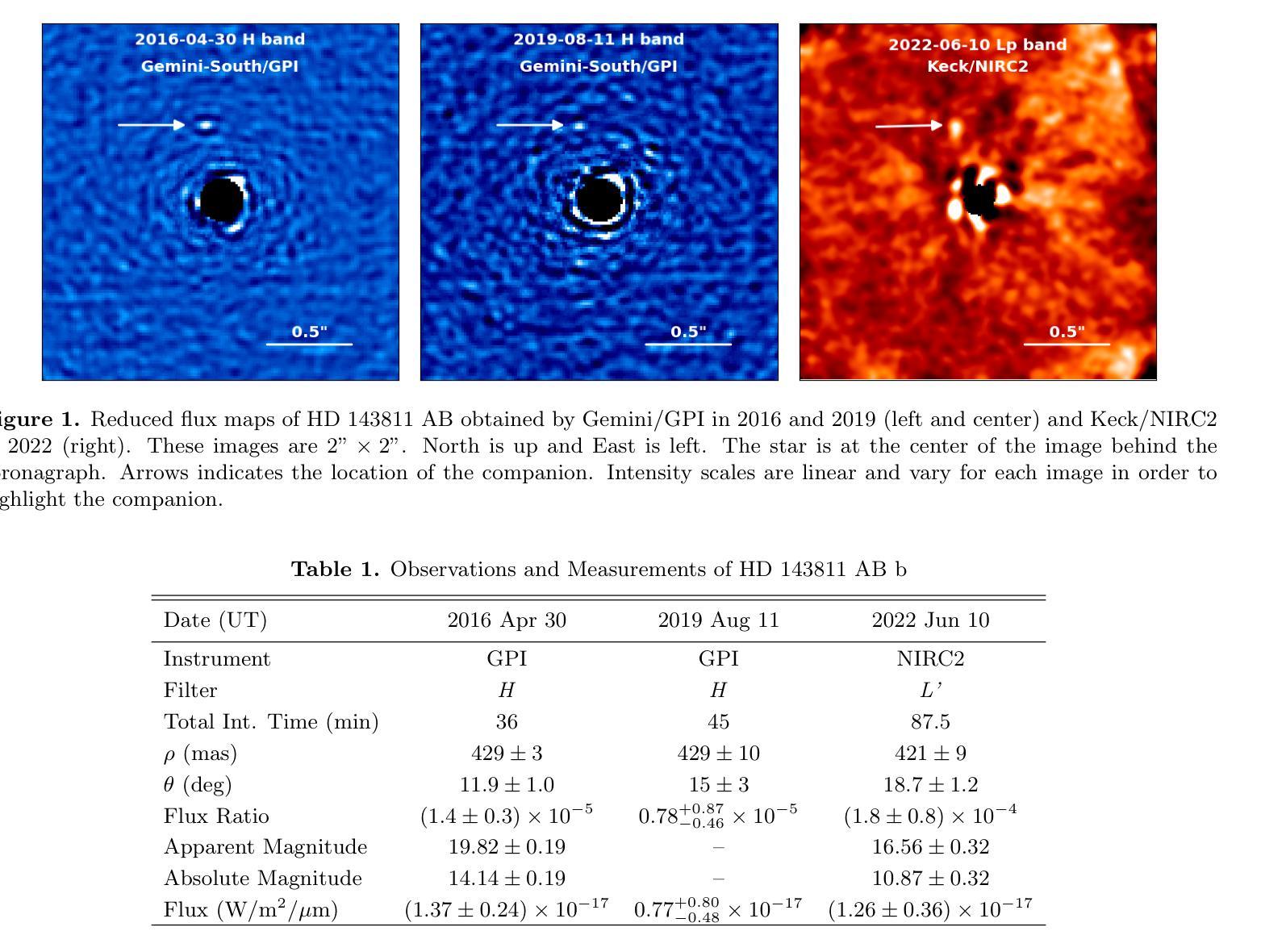
Cross-source point cloud registration, which aims to align point cloud data from different sensors, is a fundamental task in 3D vision. However, compared to the same-source point cloud registration, cross-source registration faces two core challenges: the lack of publicly available large-scale real-world datasets for training the deep registration models, and the inherent differences in point clouds captured by multiple sensors. The diverse patterns induced by the sensors pose great challenges in robust and accurate point cloud feature extraction and matching, which negatively influence the registration accuracy. To advance research in this field, we construct Cross3DReg, the currently largest and real-world multi-modal cross-source point cloud registration dataset, which is collected by a rotating mechanical lidar and a hybrid semi-solid-state lidar, respectively. Moreover, we design an overlap-based cross-source registration framework, which utilizes unaligned images to predict the overlapping region between source and target point clouds, effectively filtering out redundant points in the irrelevant regions and significantly mitigating the interference caused by noise in non-overlapping areas. Then, a visual-geometric attention guided matching module is proposed to enhance the consistency of cross-source point cloud features by fusing image and geometric information to establish reliable correspondences and ultimately achieve accurate and robust registration. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art registration performance. Our framework reduces the relative rotation error (RRE) and relative translation error (RTE) by $63.2%$ and $40.2%$, respectively, and improves the registration recall (RR) by $5.4%$, which validates its effectiveness in achieving accurate cross-source registration.
跨源点云注册旨在对齐不同传感器的点云数据,是3D视觉中的一项基本任务。然而,与同源点云注册相比,跨源注册面临两大挑战:缺乏可用于训练深度注册模型的大型现实世界数据集,以及多个传感器捕获的点云之间的固有差异。传感器引起的不同模式给稳健和精确的点云特征提取和匹配带来了巨大挑战,从而影响了注册的准确性。为了推动该领域的研究,我们构建了Cross3DReg,这是当前最大的现实世界多模态跨源点云注册数据集,分别由旋转机械激光雷达和混合固态激光雷达收集。此外,我们设计了一个基于重叠的跨源注册框架,该框架利用未对齐的图像来预测源点云和目标点云之间的重叠区域,有效地过滤掉无关区域的冗余点,并显著减轻非重叠区域中噪声引起的干扰。然后,提出了一种视觉几何注意力引导匹配模块,通过融合图像和几何信息,增强跨源点云特征的一致性,建立可靠的对应关系,最终实现准确稳健的注册。大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的注册性能。我们的框架降低了相对旋转误差(RRE)和相对平移误差(RTE)分别为63.2%和40.2%,提高了注册召回率(RR)5.4%,验证了其在实现跨源注册准确性方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
跨源点云注册是对来自不同传感器的点云数据进行对齐的基础任务。然而,与同源点云注册相比,跨源注册面临两大挑战:缺乏用于训练深度注册模型的大型真实世界数据集,以及由多个传感器捕获的点云之间的固有差异。传感器的多样模式对稳健和精确的点云特征提取和匹配造成了极大的挑战,从而影响注册精度。为了推动该领域的研究,我们构建了Cross3DReg,这是当前最大且真实的跨源点云注册数据集,由旋转机械激光雷达和混合固态激光雷达收集。我们设计了一个基于重叠的跨源注册框架,它利用未对齐的图像来预测源和目标点云之间的重叠区域,有效地过滤掉无关区域的冗余点,并显著减轻非重叠区域中噪声引起的干扰。然后,提出了一个视觉几何注意力引导匹配模块,通过融合图像和几何信息,增强跨源点云特征的一致性,建立可靠的对应关系,最终实现准确稳健的注册。实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的注册性能,相对旋转误差(RRE)和相对平移误差(RTE)分别降低了63.2%和4.0%,注册召回率(RR)提高了5.4%,验证了其在跨源注册中的有效性。
关键见解
- 跨源点云注册面临缺乏大型真实世界数据集和传感器多样性带来的挑战。
- 构建了Cross3DReg数据集,由旋转机械激光雷达和混合固态激光雷达收集而成,是目前最大且真实的跨源点云注册数据集。
- 设计了基于重叠的跨源注册框架,通过预测源和目标点云之间的重叠区域来过滤冗余点并减轻噪声干扰。
- 引入视觉几何注意力引导匹配模块,融合图像和几何信息,增强跨源点云特征的一致性。
- 提出的方法实现了先进的注册性能,相对旋转误差和相对平移误差显著降低,同时提高了注册召回率。
- 方法验证了其在跨源注册中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

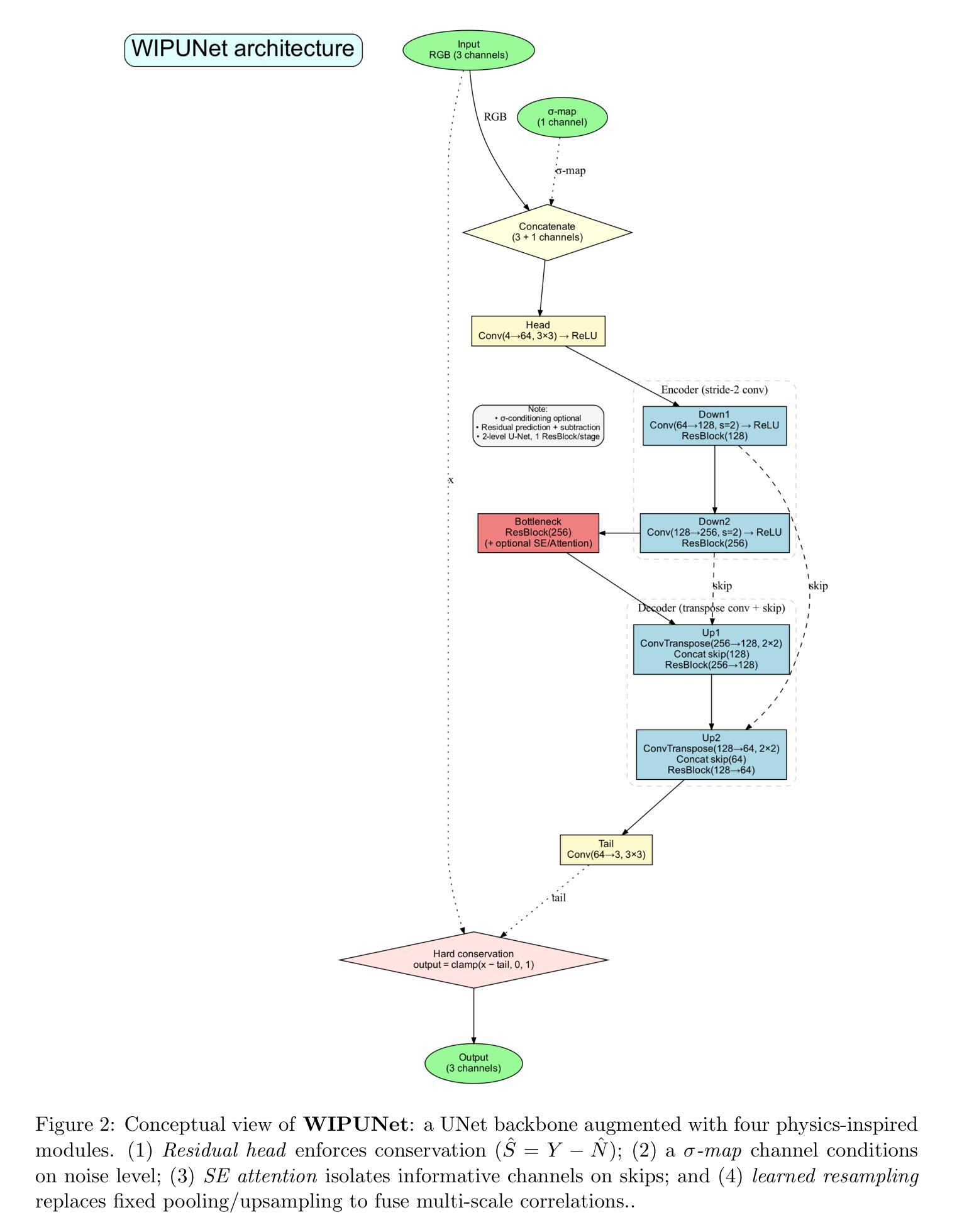
WIPUNet: A Physics-inspired Network with Weighted Inductive Biases for Image Denoising
Authors:Wasikul Islam
In high-energy particle physics, collider measurements are contaminated by “pileup”, overlapping soft interactions that obscure the hard-scatter signal of interest. Dedicated subtraction strategies exploit physical priors such as conservation, locality, and isolation. Inspired by this analogy, we investigate how such principles can inform image denoising by embedding physics-guided inductive biases into neural architectures. This paper is a proof of concept: rather than targeting state-of-the-art (SOTA) benchmarks, we ask whether physics-inspired priors improve robustness under strong corruption. We introduce a hierarchy of PU-inspired denoisers: a residual CNN with conservation constraints, its Gaussian-noise variants, and the Weighted Inductive Pileup-physics-inspired U-Network for Denoising (WIPUNet), which integrates these ideas into a UNet backbone. On CIFAR-10 with Gaussian noise at $\sigma\in{15,25,50,75,100}$, PU-inspired CNNs are competitive with standard baselines, while WIPUNet shows a \emph{widening margin} at higher noise. Complementary BSD500 experiments show the same trend, suggesting physics-inspired priors provide stability where purely data-driven models degrade. Our contributions are: (i) translating pileup-mitigation principles into modular inductive biases; (ii) integrating them into UNet; and (iii) demonstrating robustness gains at high noise without relying on heavy SOTA machinery.
在高能粒子物理学中,对撞机测量受到“堆积”的干扰,即重叠的软相互作用掩盖了感兴趣的硬散射信号。专用的减法策略利用物理先验知识,如守恒、局部性和隔离性。受此启发,我们调查了如何将这些原则通过嵌入物理引导归纳偏见到神经网络架构中来指导图像去噪。本文是一个概念验证:我们并不追求针对最新前沿技术的基准测试,而是询问物理启发先验知识是否能在强干扰下提高稳健性。我们介绍了一系列PU启发的去噪器:具有守恒约束的残差CNN、其高斯噪声变体以及加权归纳堆积物理启发U网络(WIPUNet),它将这些想法集成到UNet主干中。在带有高斯噪声的CIFAR-10上,σ∈{15,25,50,75,100},PU启发CNN与标准基线具有竞争力,而WIPUNet在较高噪声下显示出越来越宽的边际。补充的BSD500实验显示同样的趋势,表明物理启发先验在纯数据驱动模型退化时提供了稳定性。我们的贡献在于:(i)将堆积缓解原则转化为模块化归纳偏见;(ii)将其集成到UNet中;(iii)在不依赖重型最新技术机器的情况下,展示了在高噪声下的稳健性提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 4 figures
摘要
基于高能物理实验中的粒子堆积(pileup)现象研究启示,该文探讨如何利用物理学先验知识指导图像去噪。文章介绍了一系列受pileup启发的去噪器,包括具有守恒约束的残差CNN、高斯噪声变体以及集成了这些思想的加权诱导堆积物理启发去噪U网络(WIPUNet)。实验表明,在噪声环境下,这些去噪器表现稳健,尤其在较高噪声水平下表现更优。研究贡献在于将pileup缓解原则转化为模块化归纳偏见,将其集成到UNet中,并展示了在高噪声环境下的稳健性提升,无需依赖复杂的最新技术。
关键见解
- 高能物理实验中的堆积现象对图像去噪具有启示作用,可借助物理先验信息提高图像去噪的稳健性。
- 文章介绍了一系列受堆积现象启发的图像去噪器,包括残差CNN、高斯噪声变体以及WIPUNet。
- 在噪声环境下,这些受启发的去噪器表现稳健,特别是在较高噪声水平下相比传统方法更具优势。
- 研究成功将pileup缓解原则转化为模块化归纳偏见,并将其集成到UNet中。
- 该研究重视提高去噪器在恶劣环境下的稳健性,而不是单纯追求最佳性能基准。
- 文章通过实验验证了物理启发先验信息在提高模型稳定性方面的作用,尤其是在纯数据驱动模型退化的情况下。
点此查看论文截图


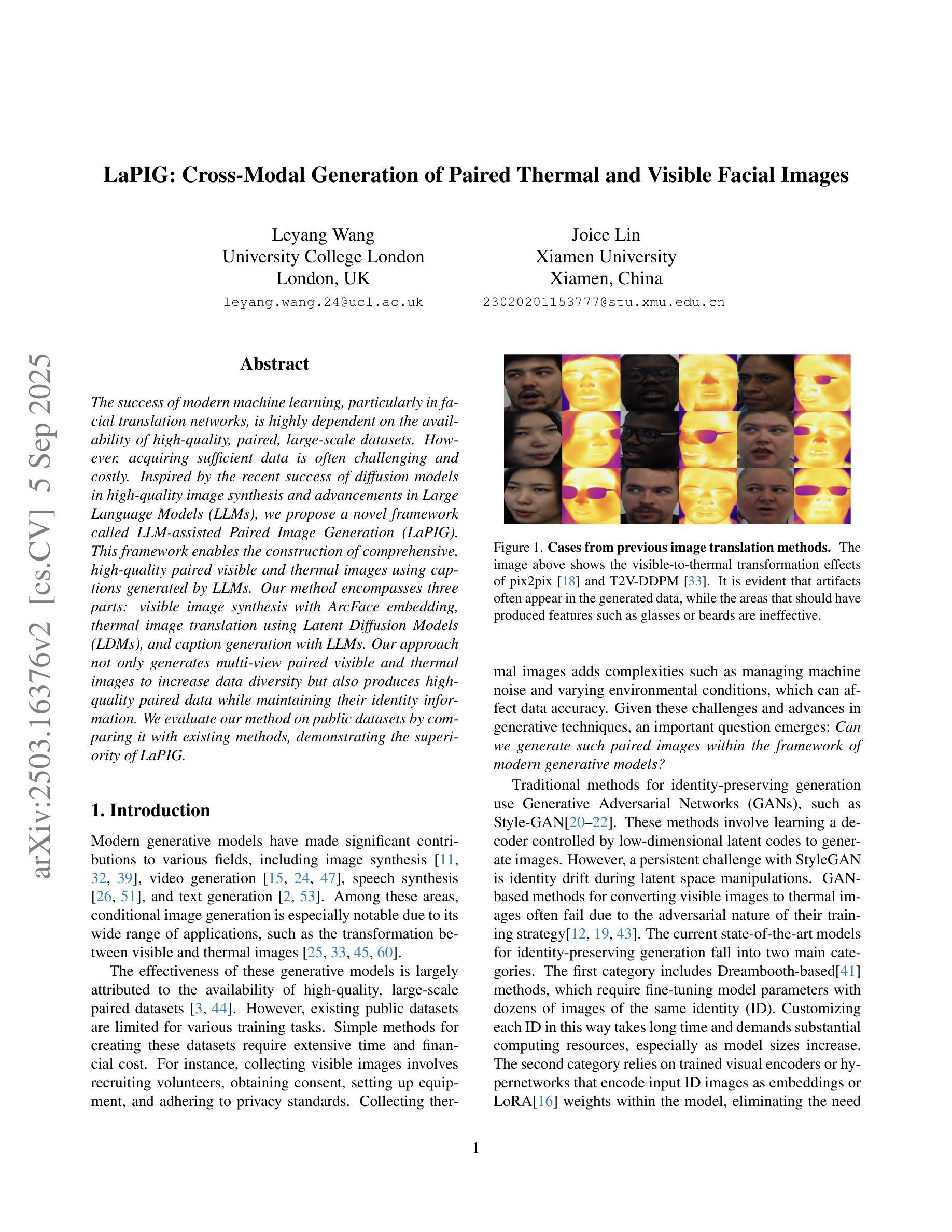
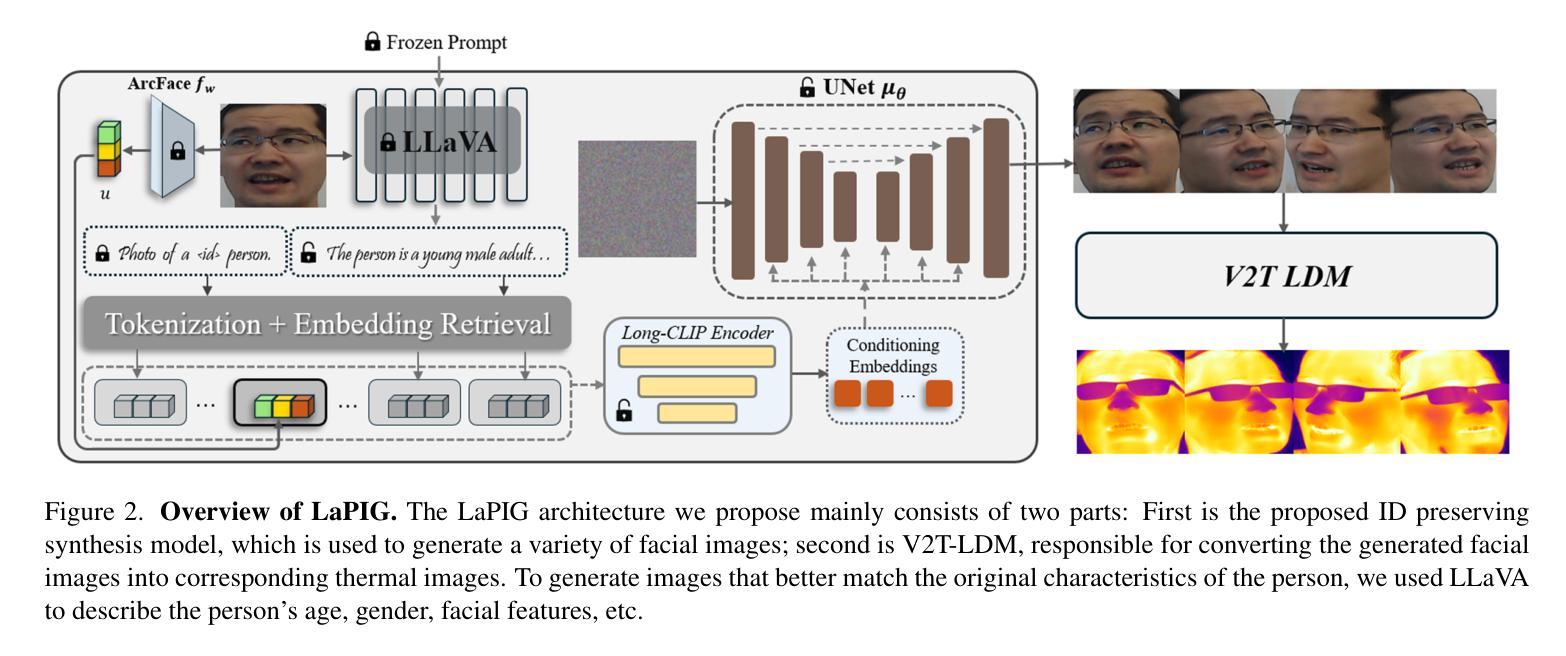
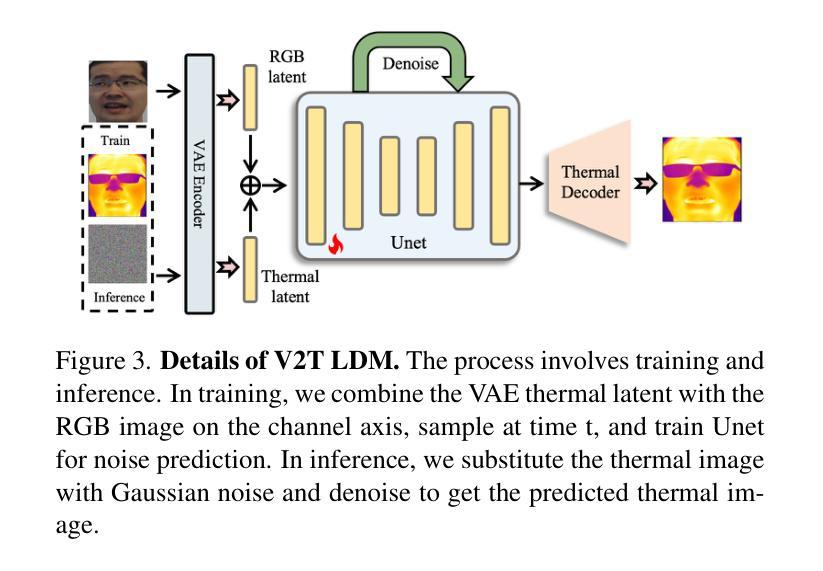
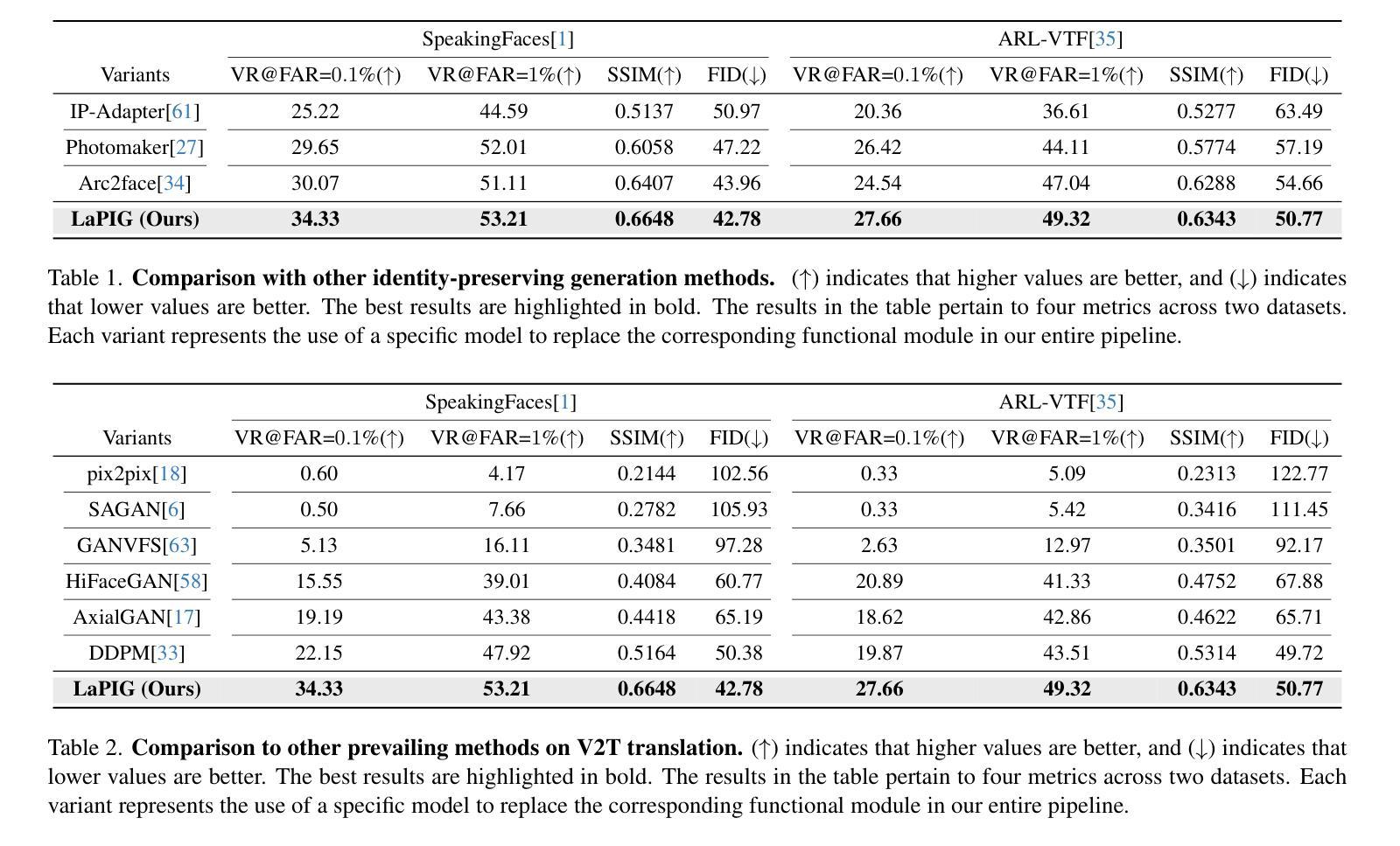
LaPIG: Cross-Modal Generation of Paired Thermal and Visible Facial Images
Authors:Leyang Wang, Joice Lin
The success of modern machine learning, particularly in facial translation networks, is highly dependent on the availability of high-quality, paired, large-scale datasets. However, acquiring sufficient data is often challenging and costly. Inspired by the recent success of diffusion models in high-quality image synthesis and advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), we propose a novel framework called LLM-assisted Paired Image Generation (LaPIG). This framework enables the construction of comprehensive, high-quality paired visible and thermal images using captions generated by LLMs. Our method encompasses three parts: visible image synthesis with ArcFace embedding, thermal image translation using Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs), and caption generation with LLMs. Our approach not only generates multi-view paired visible and thermal images to increase data diversity but also produces high-quality paired data while maintaining their identity information. We evaluate our method on public datasets by comparing it with existing methods, demonstrating the superiority of LaPIG.
现代机器学习,特别是在面部翻译网络方面的成功,很大程度上依赖于高质量、配对、大规模的数据集的可获得性。然而,获取足够的数据通常具有挑战性和成本高昂。受最近高质量图像合成中的扩散模型成功以及大型语言模型(LLM)进展的启发,我们提出了一种名为LLM辅助配对图像生成(LaPIG)的新型框架。该框架能够利用LLM生成的描述来构建全面、高质量的配对可见光和热红外图像。我们的方法包括三个部分:使用ArcFace嵌入的可见图像合成、使用潜在扩散模型(LDM)的热红外图像翻译,以及使用LLM的描述生成。我们的方法不仅生成多视角配对可见光和热红外图像以增加数据多样性,而且生成高质量配对数据的同时保持其身份信息的完整性。我们在公共数据集上评估了我们的方法,通过与现有方法的比较,证明了LaPIG的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代机器学习,特别是在面部翻译网络方面的成功,高度依赖于高质量、配对、大规模的数据集的可获得性。然而,获取足够的数据往往具有挑战性和成本高昂。受扩散模型在高质量图像合成和大型语言模型(LLM)进步的启发,我们提出了一种名为LLM辅助配对图像生成(LaPIG)的新型框架。该框架能够利用LLM生成的标题构建全面、高质量配对可见和红外图像。我们的方法包括三部分:使用ArcFace嵌入的可见图像合成、使用潜在扩散模型(LDM)的红外图像翻译、以及使用LLM的标题生成。我们的方法不仅生成多视角配对可见和红外图像以增加数据多样性,而且在保持身份信息的同时产生高质量配对数据。我们在公共数据集上评估了我们的方法,通过与现有方法的比较,证明了LaPIG的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 现代机器学习的成功高度依赖于高质量、配对、大规模数据集。
- 获取足够的数据具有挑战性和成本高昂。
- LLM辅助配对图像生成(LaPIG)框架结合扩散模型、ArcFace嵌入和LLM标题生成。
- LaPIG能够构建全面、高质量的配对可见和红外图像。
- 方法包括可见图像合成、红外图像翻译和标题生成三部分。
- LaPIG生成多视角配对图像以增加数据多样性。
点此查看论文截图
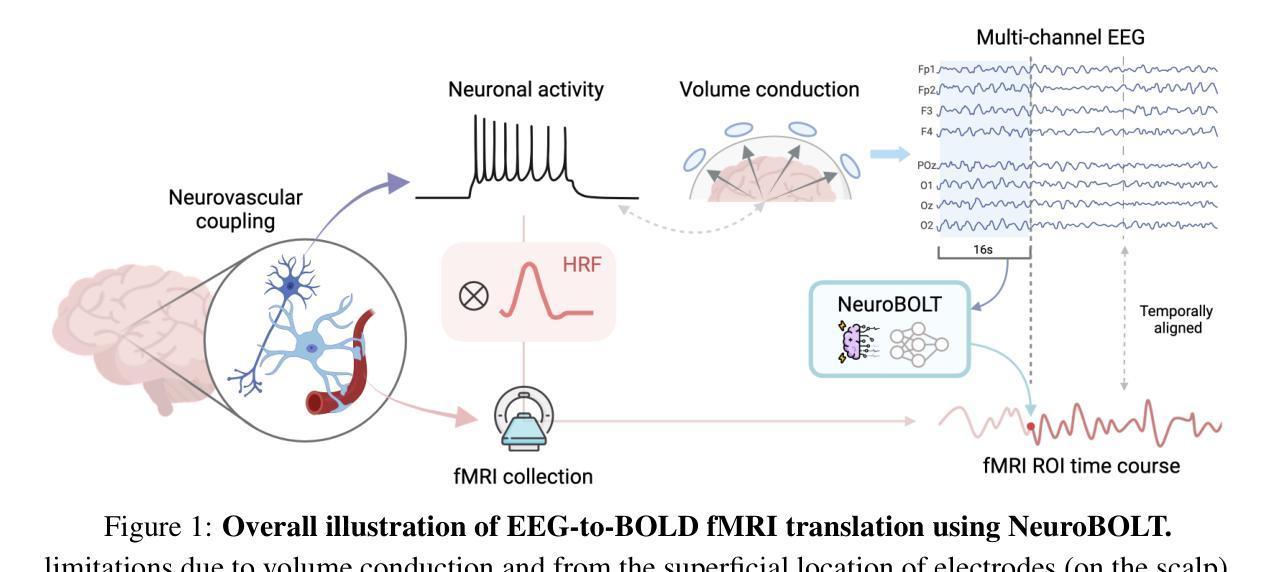
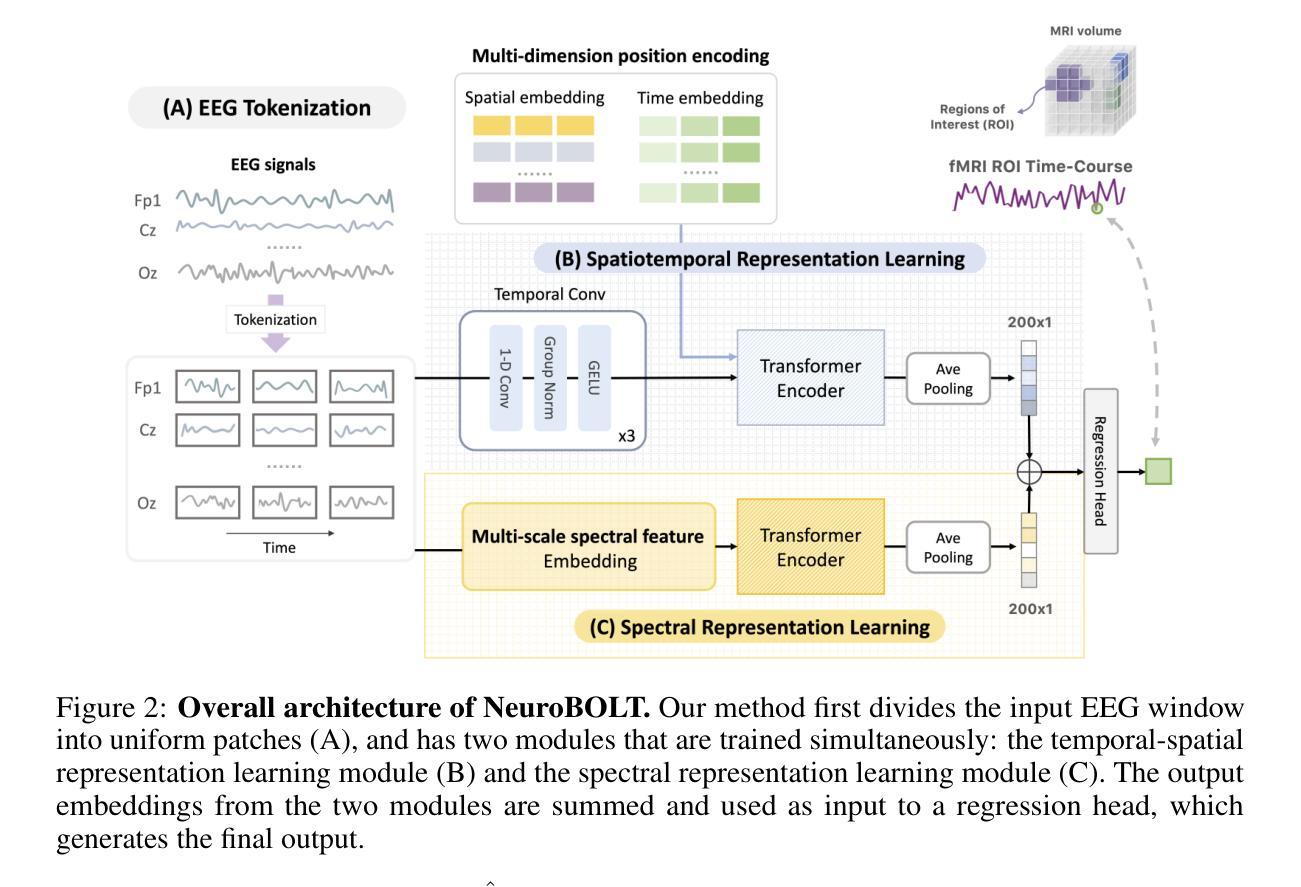
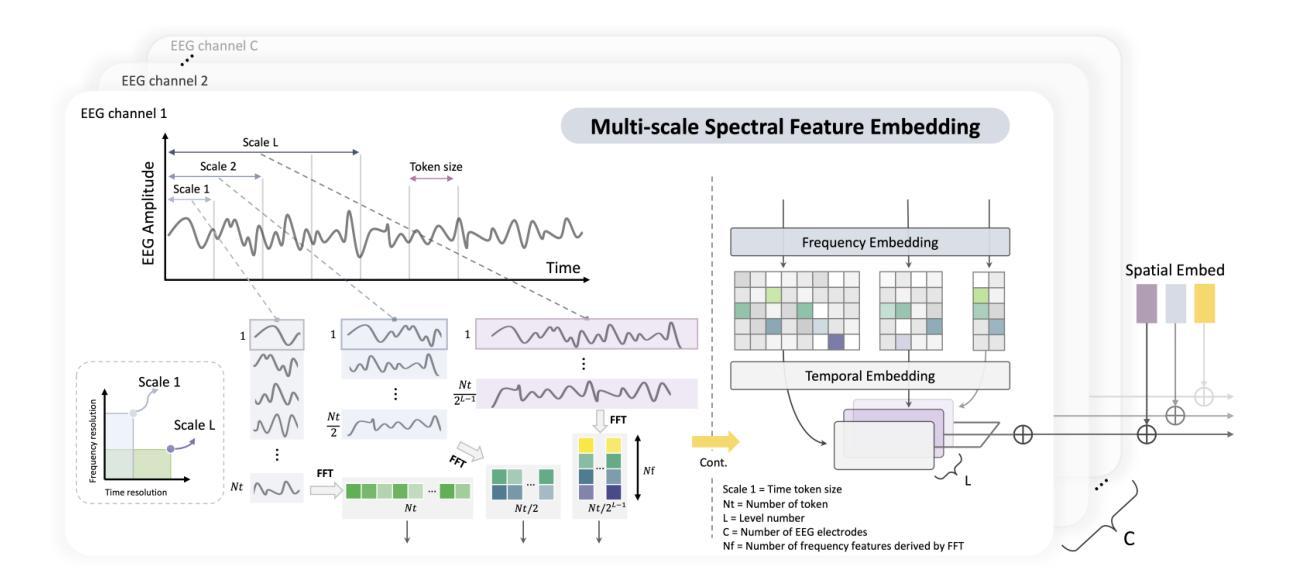
NeuroBOLT: Resting-state EEG-to-fMRI Synthesis with Multi-dimensional Feature Mapping
Authors:Yamin Li, Ange Lou, Ziyuan Xu, Shengchao Zhang, Shiyu Wang, Dario J. Englot, Soheil Kolouri, Daniel Moyer, Roza G. Bayrak, Catie Chang
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is an indispensable tool in modern neuroscience, providing a non-invasive window into whole-brain dynamics at millimeter-scale spatial resolution. However, fMRI is constrained by issues such as high operation costs and immobility. With the rapid advancements in cross-modality synthesis and brain decoding, the use of deep neural networks has emerged as a promising solution for inferring whole-brain, high-resolution fMRI features directly from electroencephalography (EEG), a more widely accessible and portable neuroimaging modality. Nonetheless, the complex projection from neural activity to fMRI hemodynamic responses and the spatial ambiguity of EEG pose substantial challenges both in modeling and interpretability. Relatively few studies to date have developed approaches for EEG-fMRI translation, and although they have made significant strides, the inference of fMRI signals in a given study has been limited to a small set of brain areas and to a single condition (i.e., either resting-state or a specific task). The capability to predict fMRI signals in other brain areas, as well as to generalize across conditions, remain critical gaps in the field. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a novel and generalizable framework: NeuroBOLT, i.e., Neuro-to-BOLD Transformer, which leverages multi-dimensional representation learning from temporal, spatial, and spectral domains to translate raw EEG data to the corresponding fMRI activity signals across the brain. Our experiments demonstrate that NeuroBOLT effectively reconstructs unseen resting-state fMRI signals from primary sensory, high-level cognitive areas, and deep subcortical brain regions, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy with the potential to generalize across varying conditions and sites, which significantly advances the integration of these two modalities.
功能磁共振成像(fMRI)是现代神经科学中不可或缺的工具,提供了以毫米级空间分辨率观察全脑动态的非侵入性窗口。然而,fMRI受到操作成本高和移动性差的限制。随着跨模态合成和大脑解码的迅速发展,深度神经网络的出现显示出一种有希望的解决方案,可以从脑电图(EEG)直接推断全脑高分辨率的fMRI特征,EEG是一种更广泛可用和便携的神经成像模式。然而,从神经活动到fMRI血流动力学反应的复杂投影以及EEG的空间模糊性,给建模和解释性都带来了巨大挑战。迄今为止,相对较少的研究开发了EEG-fMRI转换方法,尽管他们取得了重大进展,但在给定研究中推断的fMRI信号仅限于少数几个大脑区域和单一条件(即静息状态或特定任务)。预测其他脑区的fMRI信号以及在各种条件下的推广能力仍然是该领域的关键差距。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了一种新型且可推广的框架:NeuroBOLT,即神经到BOLD转换器,它利用时间、空间和光谱域的多维表示学习,将原始EEG数据转换为相应的大脑fMRI活动信号。我们的实验表明,NeuroBOLT可以有效地重建未见过的静息状态fMRI信号,包括主要的感觉、高级认知区域和深层皮质下脑区,达到了最先进的准确性,并有可能在不同条件和地点进行推广,这极大地促进了这两种模态的整合。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This preprint has been accepted to NeurIPS 2024
Summary
功能磁共振成像(fMRI)是现代神经科学中的重要工具,能够非侵入性地观察毫米级空间分辨率的全脑动态。然而,fMRI存在操作成本高和不能移动等限制。随着跨模态合成和脑解码的迅速发展,使用深度神经网络从脑电图(EEG)推断全脑高分辨率fMRI特征成为一种有前景的解决方案。然而,从神经活动到fMRI血流动力学反应的复杂投影以及EEG的空间模糊性给建模和解释性带来了挑战。研究EEG-fMRI转换的方法相对较少,虽然已经取得重要进展,但在给定研究中推断fMRI信号仅限于少数脑区和单一条件(如静息状态或特定任务)。预测其他脑区的fMRI信号以及跨条件推广仍是该领域的关键空白。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种新型、可推广的框架:NeuroBOLT(神经到BOLD转换器),它利用时间、空间和光谱域的多维表示学习,将原始EEG数据转换为相应的fMRI活动信号,涉及整个大脑。实验表明,NeuroBOLT有效地重建了未见过的静息状态fMRI信号,涉及初级感官、高级认知区域和深层皮质下脑区,具有跨条件和多地点推广的潜力,大大促进了这两种模态的整合。
Key Takeaways
- fMRI是神经科学中的关键工具,能提供全脑动态的非侵入性观察。
- 由于高成本和不能移动的限制,需要寻找替代方案以扩大fMRI的应用范围。
- EEG作为一种更广泛可访问和便携的神经成像模态,具有潜力通过深度神经网络推断fMRI特征。
- 从神经活动到fMRI信号的转换存在挑战,包括复杂的投影和EEG的空间模糊性。
- 目前的研究在EEG-fMRI转换方面取得了进展,但仍面临预测其他脑区fMRI信号及跨条件推广的挑战。
- 引入的NeuroBOLT框架能利用多维表示学习,将EEG数据转换为相应的fMRI信号,覆盖整个大脑。
点此查看论文截图