⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-10 更新
Let’s Roleplay: Examining LLM Alignment in Collaborative Dialogues
Authors:Abhijnan Nath, Carine Graff, Nikhil Krishnaswamy
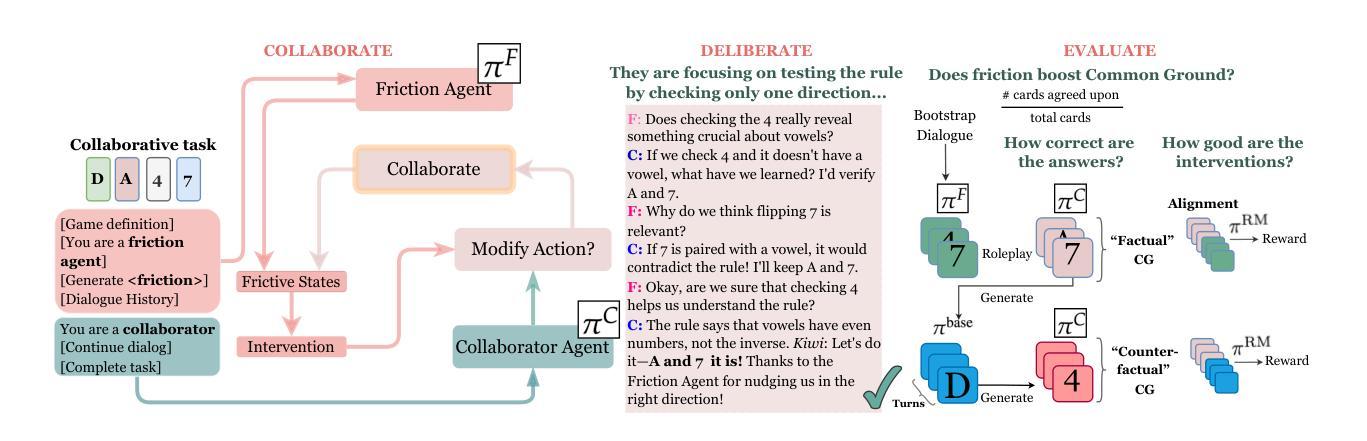
As Large Language Models (LLMs) integrate into diverse workflows, they are increasingly being considered “collaborators” with humans. If such AI collaborators are to be reliable, their behavior over multiturn interactions must be predictable, validated and verified before deployment. Common alignment techniques are typically developed under simplified single-user settings and do not account for the dynamics of long-horizon multiparty interactions. This paper examines how different alignment methods affect LLM agents’ effectiveness as partners in multiturn, multiparty collaborations. We study this question through the lens of friction agents that intervene in group dialogues to encourage the collaborative group to slow down and reflect upon their reasoning for deliberative decision-making. Using a roleplay methodology, we evaluate interventions from differently-trained friction agents in collaborative task conversations. We propose a novel counterfactual evaluation framework that quantifies how friction interventions change the trajectory of group collaboration and belief alignment. Our results show that a friction-aware approach significantly outperforms common alignment baselines in helping both convergence to a common ground, or agreed-upon task-relevant propositions, and correctness of task outcomes.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)融入到各种工作流程中,它们越来越多地被视为人类的“合作伙伴”。如果要这种AI合作伙伴可靠,它们在多轮交互中的行为必须在部署前是可预测、经过验证和核实的。常见的对齐技术通常是在简化的单用户设置下开发的,并没有考虑到长期多方的交互动态。本文研究了不同的对齐方法如何影响LLM代理在多轮多方协作中的合作有效性。我们通过干预群体对话的摩擦剂来审视这个问题,鼓励协作群体放慢速度,反思他们在深思熟虑的决策推理。我们采用角色扮演的方法,评估不同训练的摩擦剂在协作任务对话中的干预效果。我们提出了一个新的反事实评估框架,量化摩擦干预如何改变群体协作和信念对齐的轨迹。我们的结果表明,与常见的对齐基线相比,摩擦感知的方法在帮助达成共同点和任务相关命题的共识以及任务结果的正确性方面表现出显著的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)作为人类协作伙伴的可靠性至关重要,其在多轮多方互动中的行为需可预测、验证和确认。本文研究了不同对齐方法如何影响LLM代理作为多方协作伙伴的有效性。通过介入集团对话的摩擦剂,鼓励协作集团放慢速度,反思其推理,以实现审慎决策。研究表明,摩擦感知的方法在帮助达成共识和正确任务结果方面显著优于常规对齐基线。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多轮多方互动中的行为预测、验证和确认非常重要。
- 传统对齐技术未考虑到长期多方互动的动力学。
- 摩擦剂能够介入集团对话,鼓励协作集团进行反思,实现审慎决策。
- 角色扮演方法被用来评估不同训练的摩擦剂在协作任务对话中的干预效果。
- 新型的反事实评估框架可以量化摩擦干预对集团协作轨迹和信念对齐的影响。
- 摩擦感知的方法在帮助达成共识方面显著优于常规对齐方法。
点此查看论文截图

StreamMind: Unlocking Full Frame Rate Streaming Video Dialogue through Event-Gated Cognition
Authors:Xin Ding, Hao Wu, Yifan Yang, Shiqi Jiang, Donglin Bai, Zhibo Chen, Ting Cao
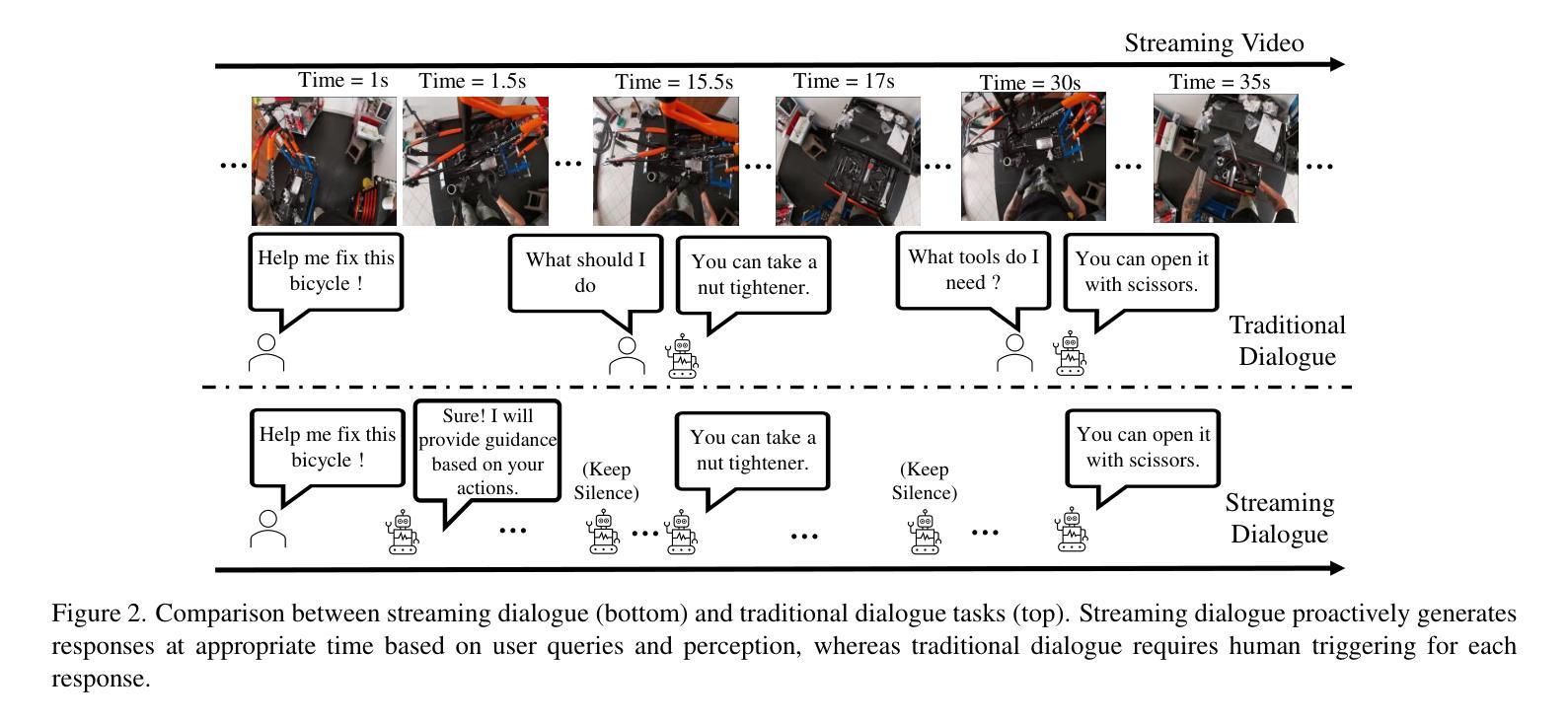
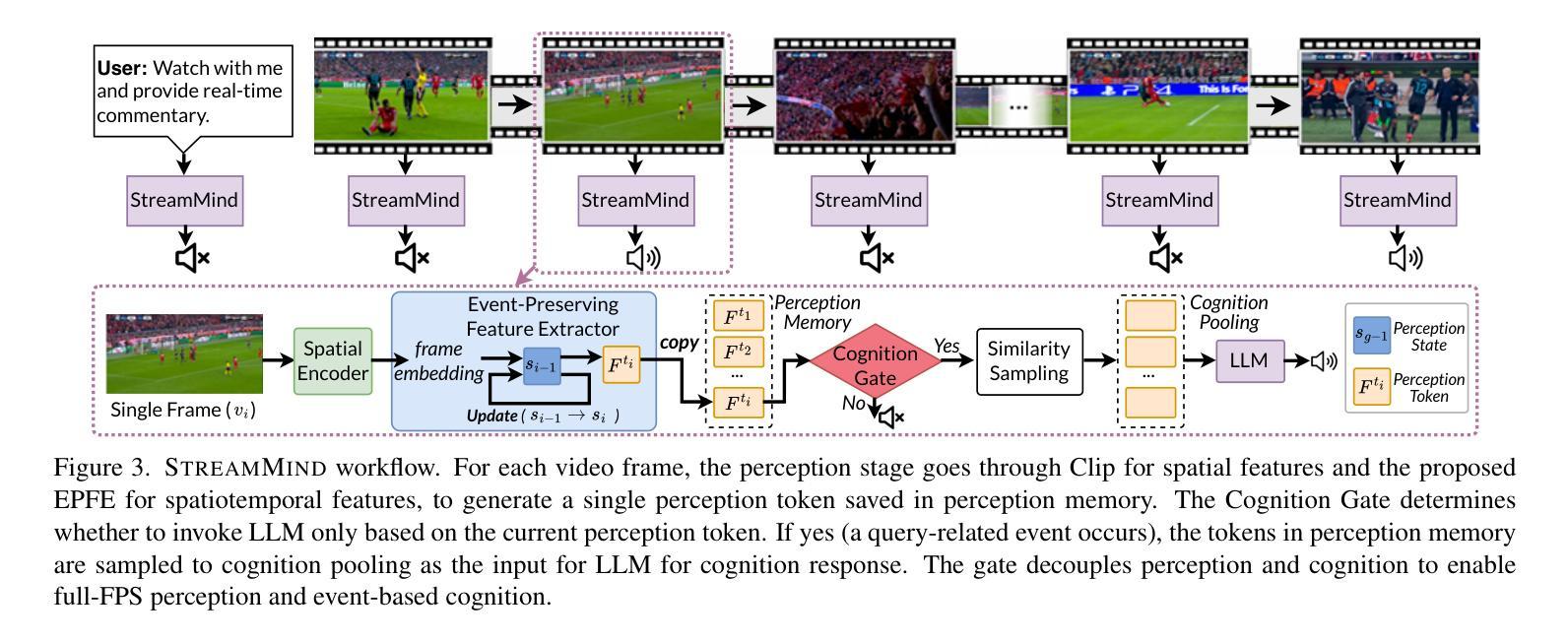
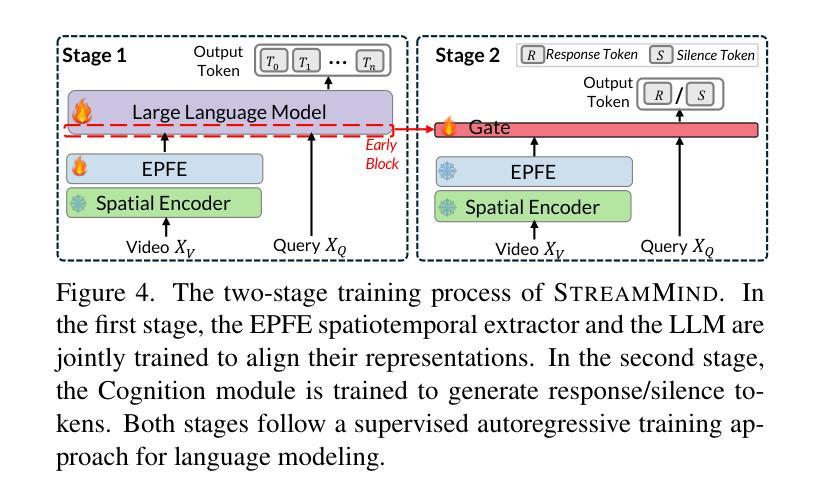
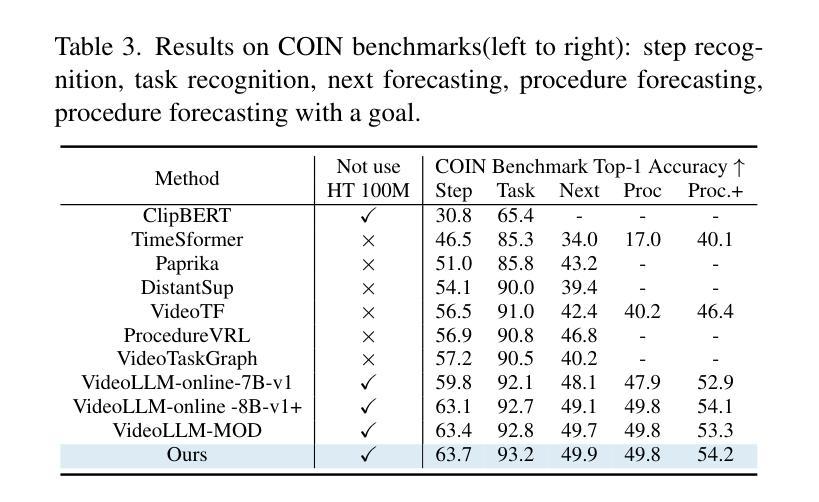
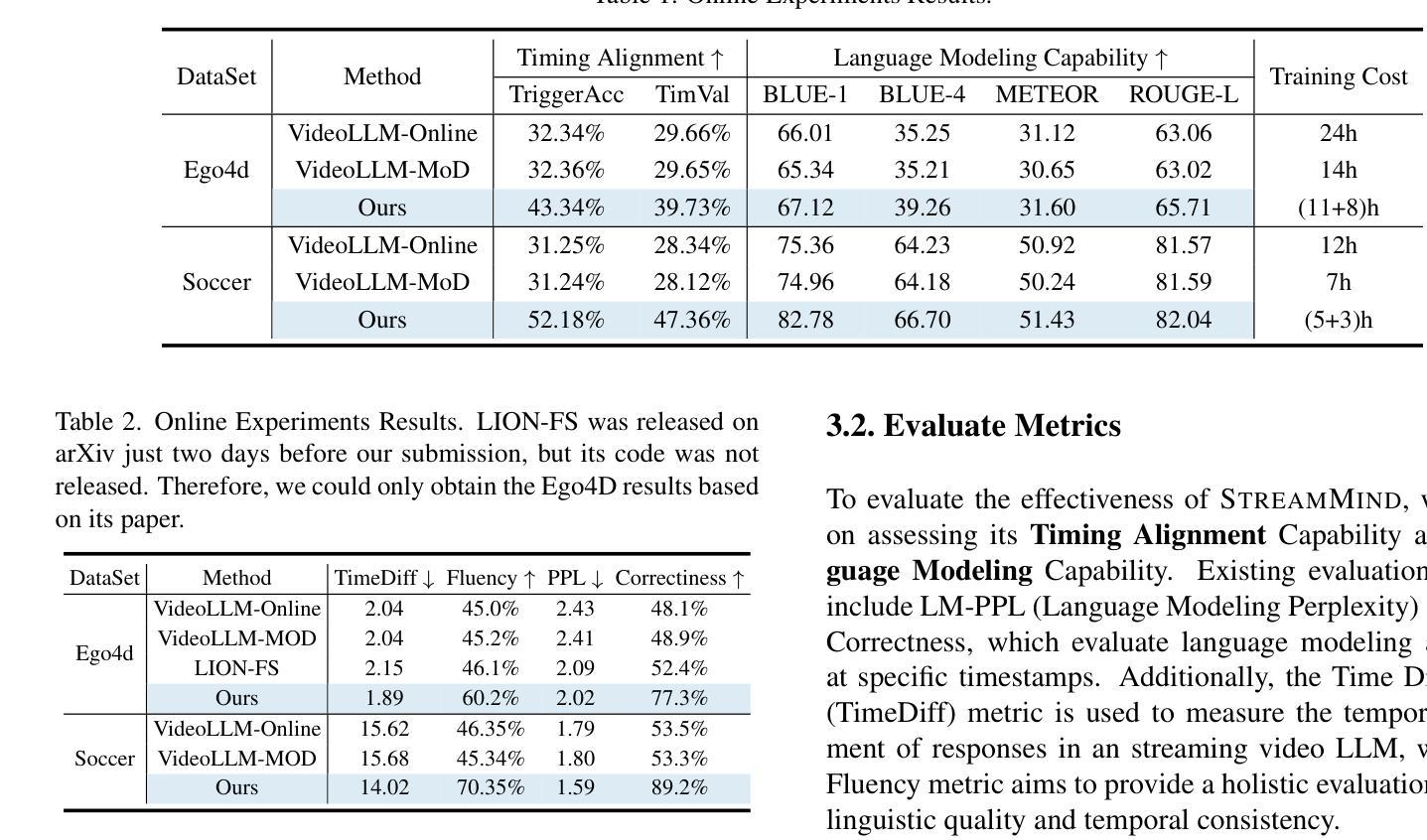
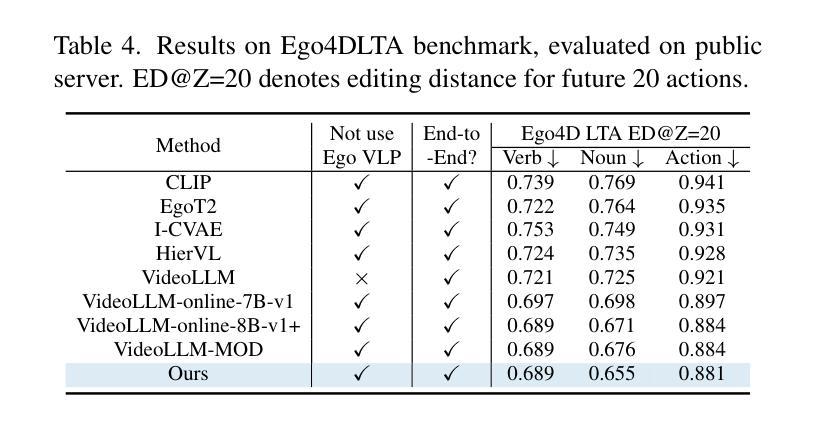
With the rise of real-world human-AI interaction applications, such as AI assistants, the need for Streaming Video Dialogue is critical. To address this need, we introduce StreamMind, a video LLM framework that achieves ultra-FPS streaming video processing (100 fps on a single A100) and enables proactive, always-on responses in real time, without explicit user intervention. To solve the key challenge of the contradiction between linear video streaming speed and quadratic transformer computation cost, we propose a novel perception-cognition interleaving paradigm named ‘’event-gated LLM invocation’’, in contrast to the existing per-time-step LLM invocation. By introducing a Cognition Gate network between the video encoder and the LLM, LLM is only invoked when relevant events occur. To realize the event feature extraction with constant cost, we propose Event-Preserving Feature Extractor (EPFE) based on state-space method, generating a single perception token for spatiotemporal features. These techniques enable the video LLM with full-FPS perception and real-time cognition response. Experiments on Ego4D and SoccerNet streaming tasks, as well as standard offline benchmarks, demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in both model capability and real-time efficiency, paving the way for ultra-high-FPS applications, such as Game AI and interactive media. The code and data is available at https://aka.ms/StreamMind.
随着人工智能助手等现实世界中人机交互应用的兴起,对流式视频对话的需求变得至关重要。为了解决这一需求,我们推出了StreamMind,这是一款视频LLM框架,可实现超FPS流式视频处理(单A100上可达100fps),并可在无需用户明确干预的情况下,实时主动响应。为了解决线性视频流速度与传播式计算成本之间的关键矛盾,我们提出了一种名为“事件门控LLM调用”的新型感知认知交替范式,这与现有的按时间步长调用LLM的方法形成对比。通过在视频编码器和LLM之间引入认知门网络,只有在相关事件发生时才调用LLM。为了实现具有恒定成本的事件特征提取,我们提出了基于状态空间方法的Event-Preserving Feature Extractor(EPFE),为时空特征生成单个感知令牌。这些技术使视频LLM具备全FPS感知和实时认知响应能力。在Ego4D和SoccerNet流媒体任务以及标准离线基准测试上的实验证明了其在模型能力和实时效率方面的卓越性能,为超高FPS应用(如游戏AI和交互式媒体)铺平了道路。代码和数据可在https://aka.ms/StreamMind上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着人工智能助手等现实世界中人机交互应用的兴起,流式视频对话的需求变得至关重要。为应对这一需求,我们推出了StreamMind,这是一款视频大型语言模型框架,可实现超帧同步流式视频处理(在单个A100上达到100帧/秒),并能在无需用户明确干预的情况下实现实时主动响应。为解决线性视频流速度与二次方转换器计算成本之间的主要矛盾,我们提出了一种名为“事件门控大型语言模型调用”的新型感知认知交错范式,这与现有的按时间步长调用大型语言模型的方法形成对比。通过引入位于视频编码器和大型语言模型之间的认知门网络,仅当发生相关事件时才调用大型语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- StreamMind是一个视频大型语言模型框架,支持超帧同步流式视频处理,实现在单A100上达到100帧的处理速度。
- StreamMind能在无需用户干预的情况下实现实时主动响应。
- 为解决视频流速度与计算成本之间的矛盾,StreamMind提出了事件门控大型语言模型调用的感知认知交错范式。
- 认知门网络的引入使得仅当发生相关事件时才调用大型语言模型。
- Event-Preserving Feature Extractor(EPFE)基于状态空间方法,实现时空特征的事件特征提取,保证提取成本恒定。
- StreamMind在Ego4D和SoccerNet流媒体任务以及标准离线基准测试上表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图


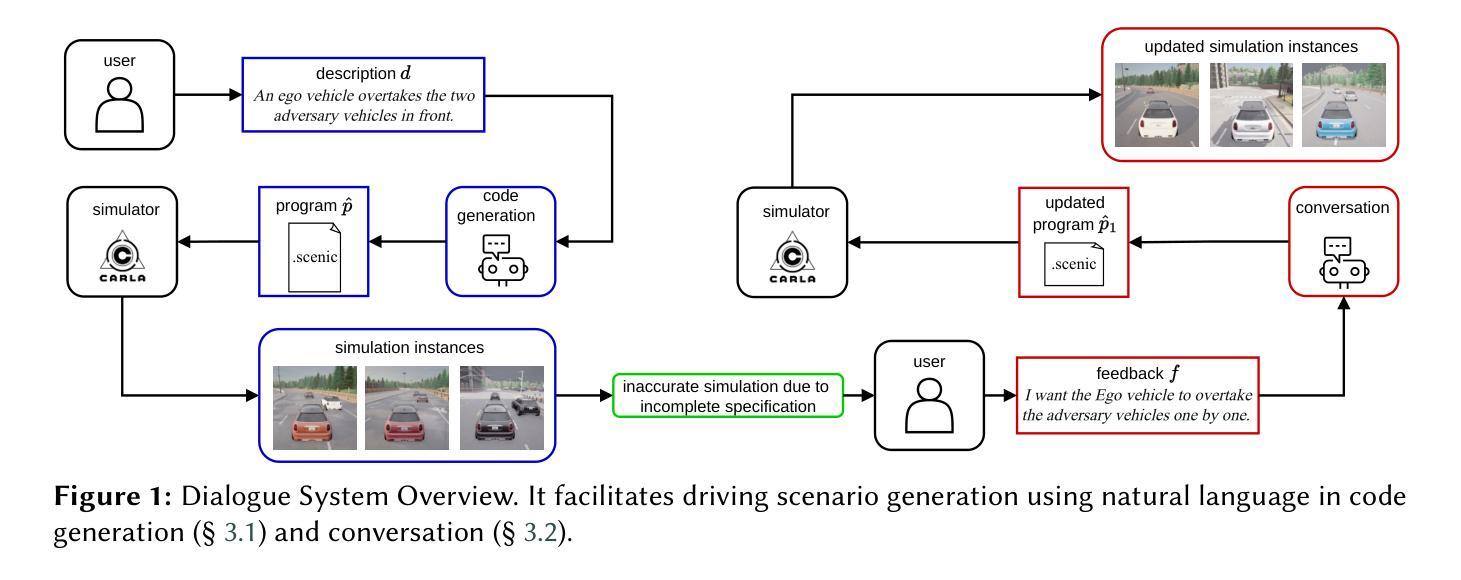
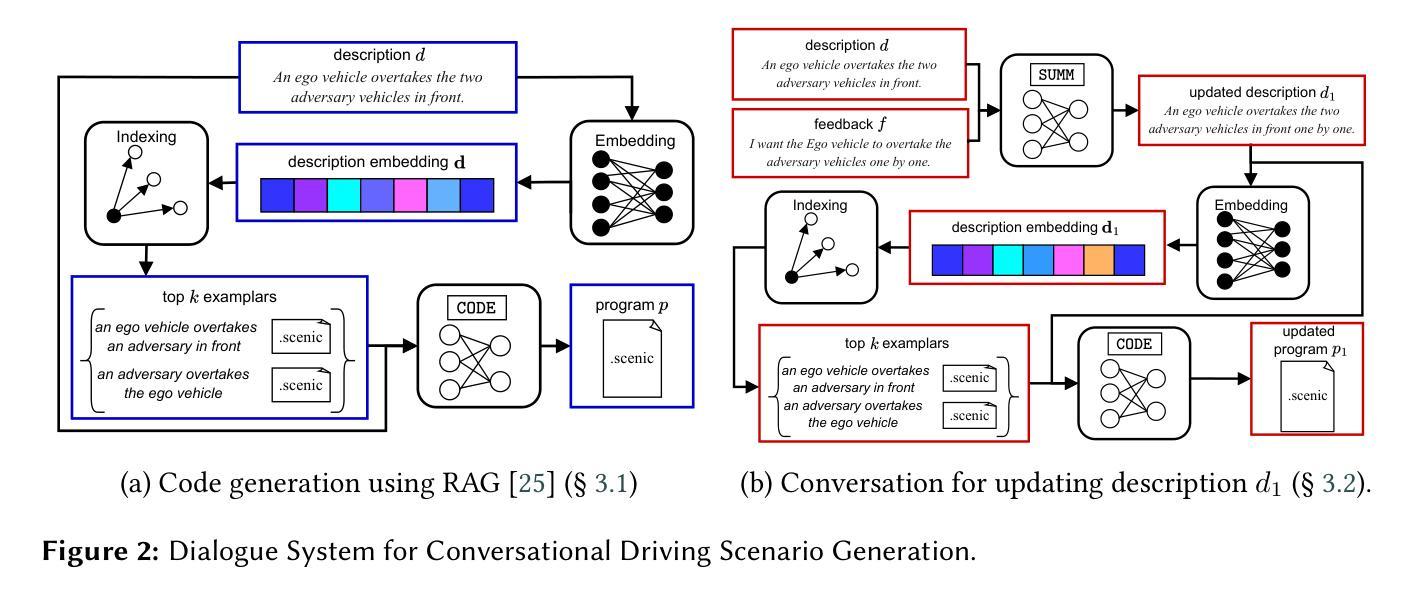
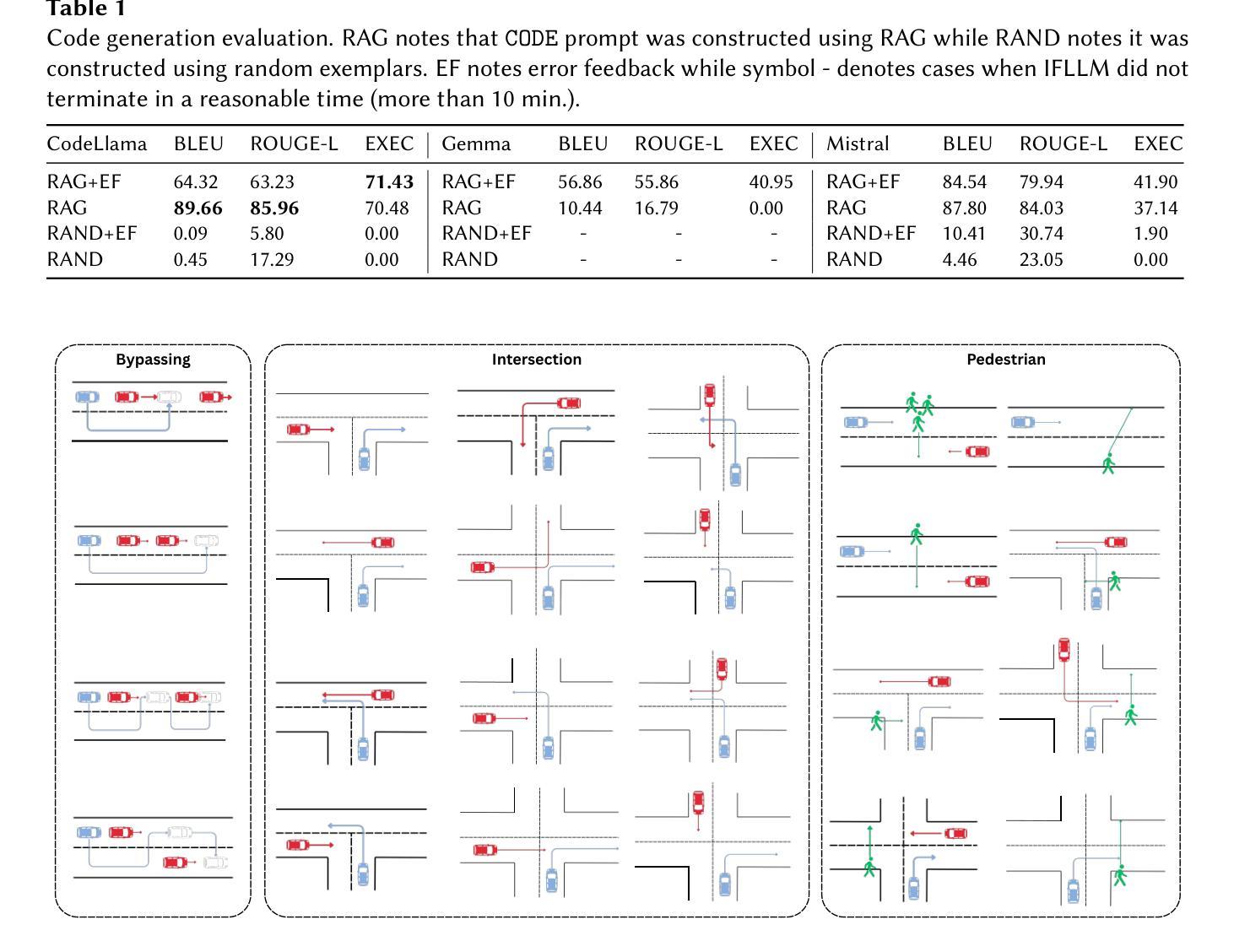
Conversational Code Generation: a Case Study of Designing a Dialogue System for Generating Driving Scenarios for Testing Autonomous Vehicles
Authors:Rimvydas Rubavicius, Antonio Valerio Miceli-Barone, Alex Lascarides, Subramanian Ramamoorthy
Cyber-physical systems like autonomous vehicles are tested in simulation before deployment, using domain-specific programs for scenario specification. To aid the testing of autonomous vehicles in simulation, we design a natural language interface, using an instruction-following large language model, to assist a non-coding domain expert in synthesising the desired scenarios and vehicle behaviours. We show that using it to convert utterances to the symbolic program is feasible, despite the very small training dataset. Human experiments show that dialogue is critical to successful simulation generation, leading to a 4.5 times higher success rate than a generation without engaging in extended conversation.
自主车辆等网络物理系统都在部署前在仿真环境中进行测试,使用针对场景指定的特定领域的程序。为了辅助在仿真环境中测试自主车辆,我们设计了一个自然语言接口,该接口利用指令遵循的大型语言模型,以协助非编码领域的专家合成所需的场景和车辆行为。实验表明,即使在非常小的训练数据集下,使用它将言语转化为符号程序也是可行的。人类实验表明,对话对于成功生成仿真至关重要,与使用不展开对话的生成相比,其成功率提高了4.5倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In Proceedings of GeCoIn 2025: Generative Code Intelligence Workshop, co-located with ECAI-2025
Summary
基于自主车辆测试需求,设计了一种自然语言接口,利用大型语言模型实现指令跟随,帮助非编码领域的专家在仿真环境中合成所需场景和车辆行为。通过对话方式生成仿真场景成功率高出4.5倍。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注自主车辆在仿真环境中的测试问题。
- 研究者设计了一种自然语言接口用于帮助非编码领域的专家在仿真环境中构建自主车辆测试场景。该接口采用大型语言模型实现指令跟随功能。
- 该接口通过一种小训练数据集就可以实现从人类自然语言指令到仿真模拟程序的可信转换。这种设计能够帮助在研发过程中测试和验证自主车辆的场景感知、决策规划以及控制系统。
点此查看论文截图