⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-10 更新
Automated Radiographic Total Sharp Score (ARTSS) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Solution to Reduce Inter-Intra Reader Variation and Enhancing Clinical Practice
Authors:Hajar Moradmand, Lei Ren
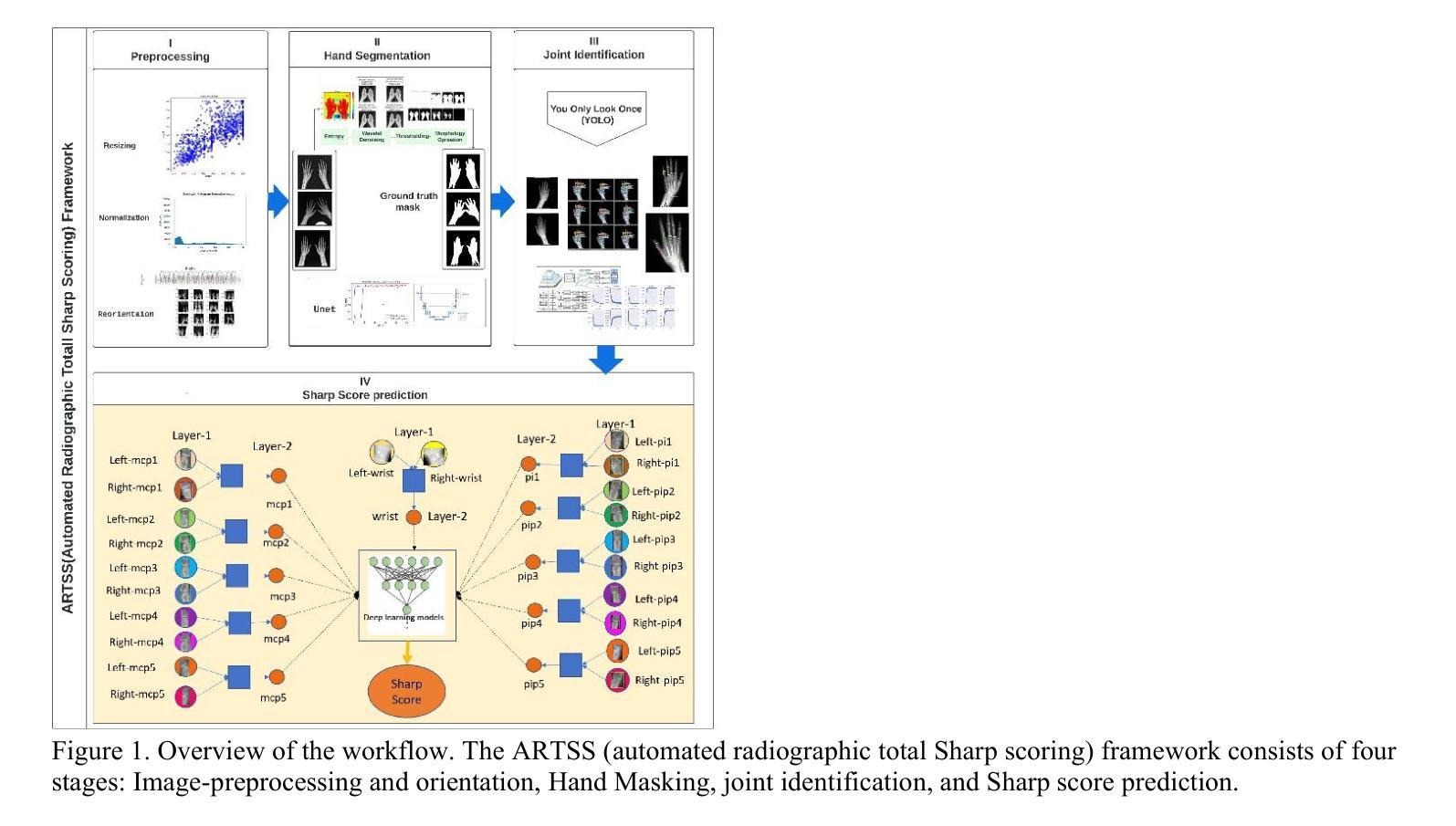
Assessing the severity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) using the Total Sharp/Van Der Heijde Score (TSS) is crucial, but manual scoring is often time-consuming and subjective. This study introduces an Automated Radiographic Sharp Scoring (ARTSS) framework that leverages deep learning to analyze full-hand X-ray images, aiming to reduce inter- and intra-observer variability. The research uniquely accommodates patients with joint disappearance and variable-length image sequences. We developed ARTSS using data from 970 patients, structured into four stages: I) Image pre-processing and re-orientation using ResNet50, II) Hand segmentation using UNet.3, III) Joint identification using YOLOv7, and IV) TSS prediction using models such as VGG16, VGG19, ResNet50, DenseNet201, EfficientNetB0, and Vision Transformer (ViT). We evaluated model performance with Intersection over Union (IoU), Mean Average Precision (MAP), mean absolute error (MAE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and Huber loss. The average TSS from two radiologists was used as the ground truth. Model training employed 3-fold cross-validation, with each fold consisting of 452 training and 227 validation samples, and external testing included 291 unseen subjects. Our joint identification model achieved 99% accuracy. The best-performing model, ViT, achieved a notably low Huber loss of 0.87 for TSS prediction. Our results demonstrate the potential of deep learning to automate RA scoring, which can significantly enhance clinical practice. Our approach addresses the challenge of joint disappearance and variable joint numbers, offers timesaving benefits, reduces inter- and intra-reader variability, improves radiologist accuracy, and aids rheumatologists in making more informed decisions.
评估类风湿性关节炎(RA)的严重程度对于使用总Sharp/Van Der Heijde评分(TSS)来说非常关键,但手动评分通常既耗时又带有主观性。本研究介绍了一个自动化放射性Sharp评分(ARTSS)框架,该框架利用深度学习分析全手X光片图像,旨在减少观察者之间的差异和观察者内部差异。该研究独特地适应了关节消失和可变长度图像序列的患者。我们使用来自970名患者的数据开发ARTSS,分为四个阶段:I)使用ResNet50进行图像预处理和重新定位,II)使用UNet.3进行手部分割,III)使用YOLOv7进行关节识别,以及IV)使用诸如VGG16、VGG19、ResNet50、DenseNet201、EfficientNetB0和Vision Transformer(ViT)等模型进行TSS预测。我们使用交并比(IoU)、平均精度均值(MAP)、平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE)和Huber损失来评估模型性能。两名放射科医生的平均TSS被用作真实值。模型训练采用3倍交叉验证,每一折包含452个训练样本和227个验证样本,外部测试包括291个未见过的受试者。我们的关节识别模型达到了99%的准确率。表现最佳的模型ViT在TSS预测方面取得了显著较低的Huber损失,为0.87。我们的结果展示了深度学习在自动化RA评分中的潜力,这可能会显著增强临床实践。我们的方法解决了关节消失和可变关节数量的问题,带来了省时的好处,减少了不同医生间的差异以及医生内部差异,提高了放射科医生的准确性,并帮助风湿科医生做出更明智的决策。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用深度学习技术,开发了一种名为ARTSS的自动化类风湿性关节炎评分框架,用于分析全手X光图像,旨在减少评分的主观性和耗时。研究通过四个步骤进行,包括图像预处理、手部分割、关节识别和TSS预测。最佳模型为Vision Transformer(ViT),在TSS预测中表现优异。此框架有助于解决关节消失和关节数量变化的问题,提高评分准确性,为类风湿性关节炎的临床实践带来显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究引入了ARTSS框架,利用深度学习技术自动化评估类风湿性关节炎的严重性。
- ARTSS框架通过图像预处理、手部分割、关节识别和TSS预测四个步骤进行。
- 最佳模型为Vision Transformer(ViT),在TSS预测中表现优异,Huber损失较低。
- 此框架有助于解决关节消失和关节数量变化的问题。
- 自动化评分可节省时间,减少评分的主观性,提高评分准确性。
- 自动化评分可提高医生的准确性,有助于类风湿病患者做出更明智的决策。
点此查看论文截图

Investigating Location-Regularised Self-Supervised Feature Learning for Seafloor Visual Imagery
Authors:Cailei Liang, Adrian Bodenmann, Emma J Curtis, Samuel Simmons, Kazunori Nagano, Stan Brown, Adam Riese, Blair Thornton
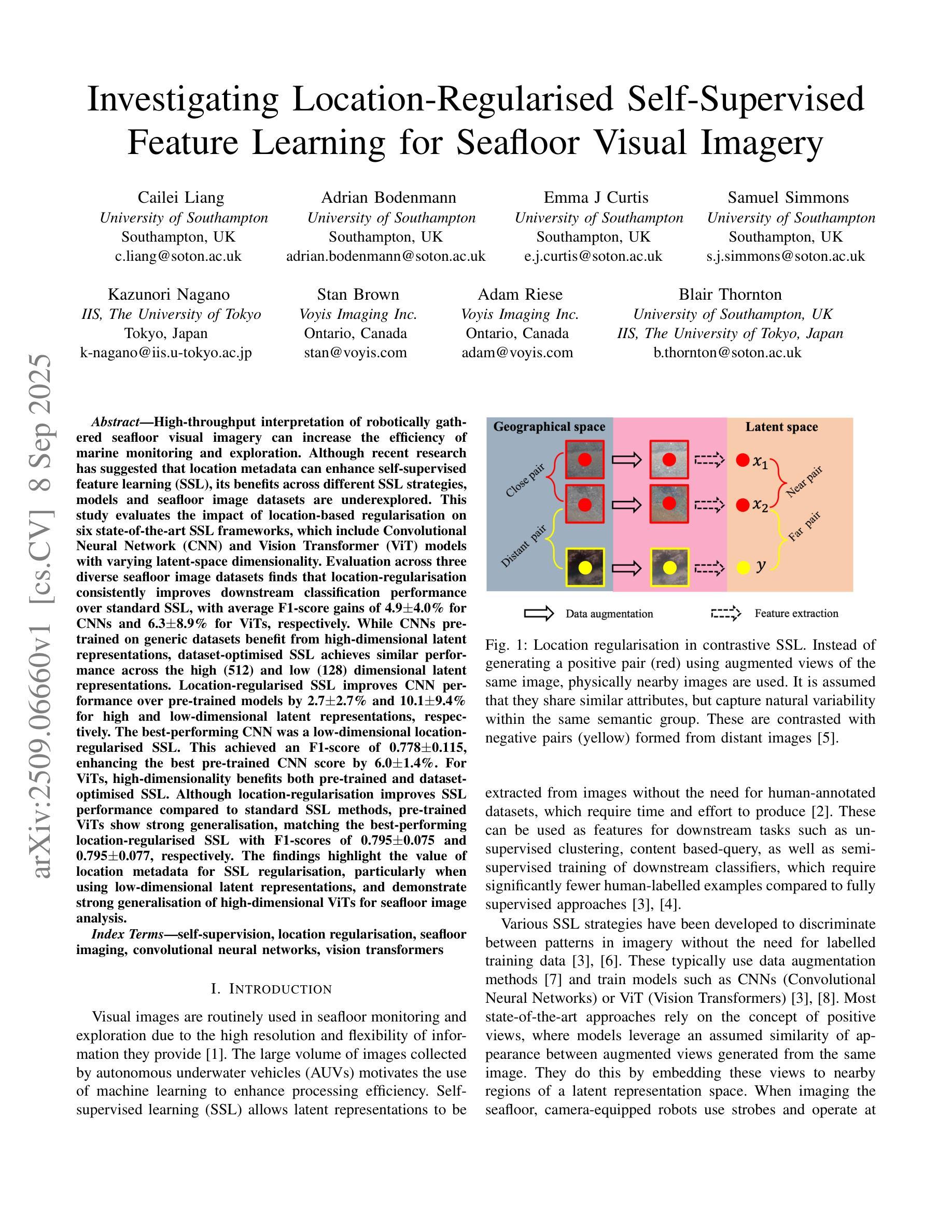
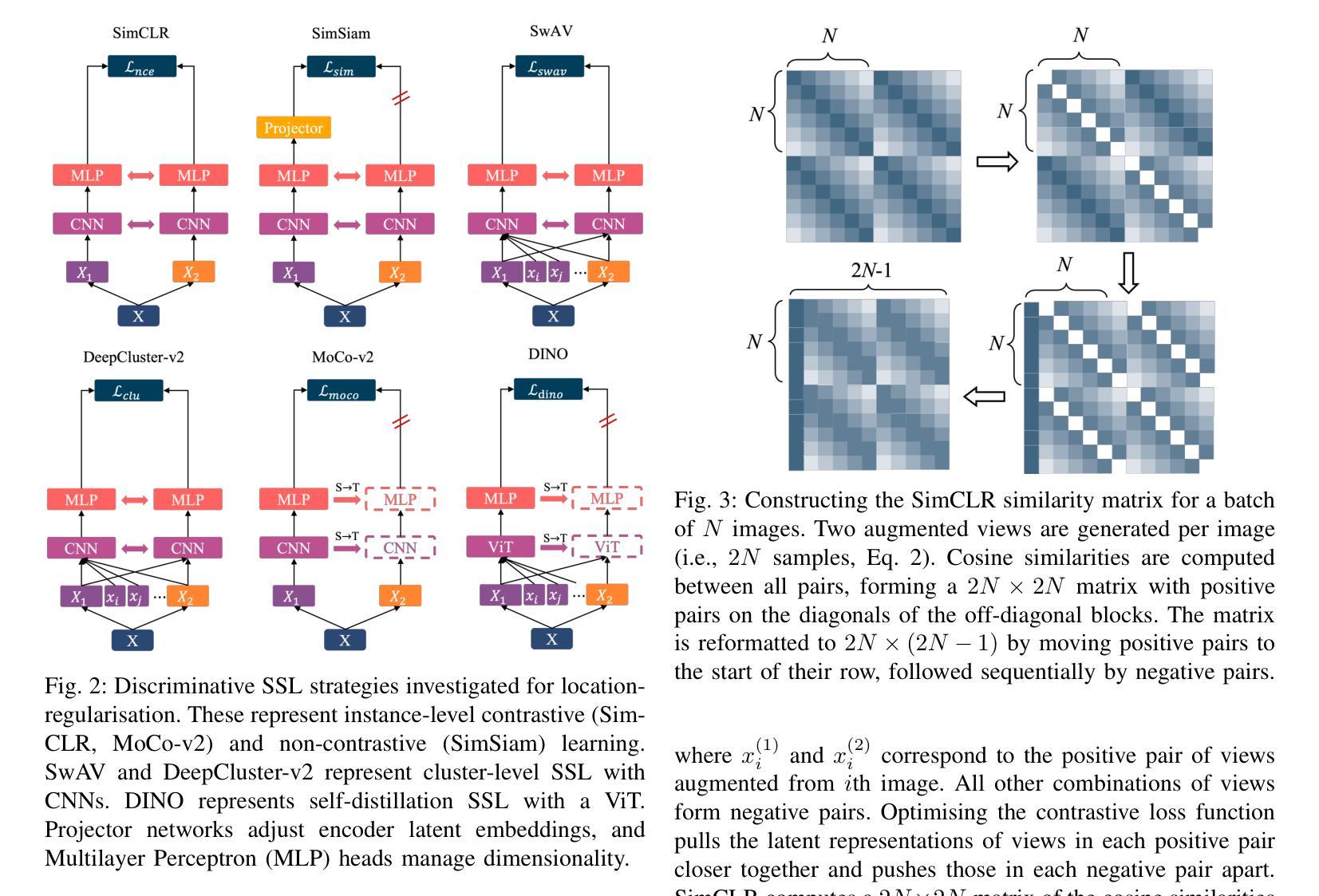
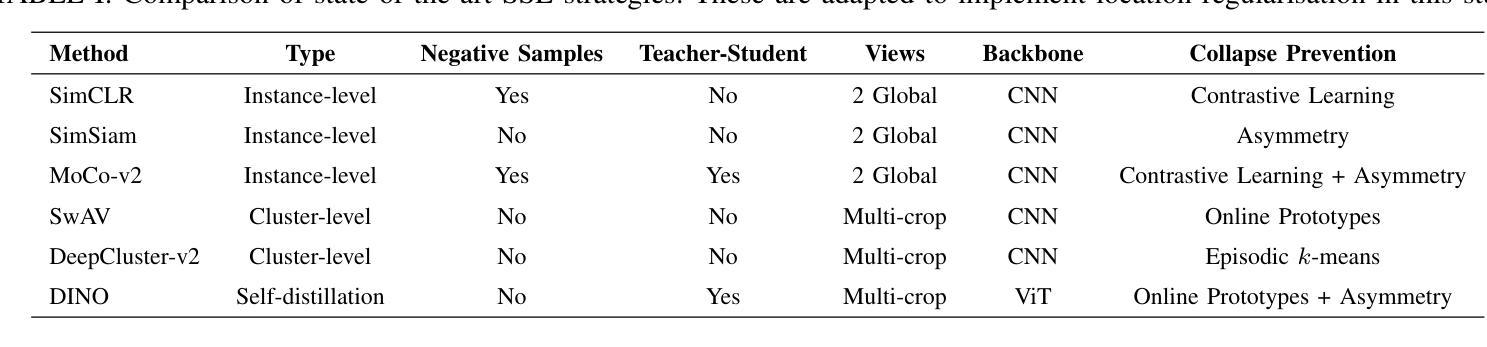
High-throughput interpretation of robotically gathered seafloor visual imagery can increase the efficiency of marine monitoring and exploration. Although recent research has suggested that location metadata can enhance self-supervised feature learning (SSL), its benefits across different SSL strategies, models and seafloor image datasets are underexplored. This study evaluates the impact of location-based regularisation on six state-of-the-art SSL frameworks, which include Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Vision Transformer (ViT) models with varying latent-space dimensionality. Evaluation across three diverse seafloor image datasets finds that location-regularisation consistently improves downstream classification performance over standard SSL, with average F1-score gains of $4.9 \pm 4.0%$ for CNNs and $6.3 \pm 8.9%$ for ViTs, respectively. While CNNs pretrained on generic datasets benefit from high-dimensional latent representations, dataset-optimised SSL achieves similar performance across the high (512) and low (128) dimensional latent representations. Location-regularised SSL improves CNN performance over pre-trained models by $2.7 \pm 2.7%$ and $10.1 \pm 9.4%$ for high and low-dimensional latent representations, respectively. For ViTs, high-dimensionality benefits both pre-trained and dataset-optimised SSL. Although location-regularisation improves SSL performance compared to standard SSL methods, pre-trained ViTs show strong generalisation, matching the best-performing location-regularised SSL with F1-scores of $0.795 \pm 0.075$ and $0.795 \pm 0.077$, respectively. The findings highlight the value of location metadata for SSL regularisation, particularly when using low-dimensional latent representations, and demonstrate strong generalisation of high-dimensional ViTs for seafloor image analysis.
对机器人收集的深海视觉图像进行高效解读,可以提高海洋监测和勘探的效率。尽管最近有研究表明,位置元数据可以增强自监督特征学习(SSL)的效果,但其在不同的SSL策略、模型和海底图像数据集上的益处尚未得到充分探索。本研究评估了基于位置的常规化对六种最先进的SSL框架的影响,这些框架包括具有不同潜在空间维度的卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)模型。在三个不同的海底图像数据集上的评估发现,与标准SSL相比,位置常规化持续提高了下游分类性能,CNN的平均F1分数提高了4.9±4.0%,而ViT提高了6.3±8.9%。虽然预训练在通用数据集上的CNN受益于高维潜在表示,但针对数据集的SSL在高(512)和低(128)维潜在表示上实现了相似的性能。位置正则化的SSL提高了CNN在高维和低维潜在表示上的性能,分别提高了2.7±2.7%和提高了10.1±9.4%。对于ViT而言,高维表示对预训练和针对数据集的SSL都有益。尽管位置常规化提高了与标准SSL方法相比的SSL性能,但预训练的ViT表现出强大的泛化能力,与最佳性能的位置常规化SSL相匹配,F1分数分别为0.795±0.075和0.795±0.077。这些发现强调了位置元数据对SSL正则化的价值,特别是在使用低维潜在表示时,并证明了高维ViT在海底图像分析中的强大泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
机器人采集的海底视觉图像的高通量解释能提高海洋监测与探索的效率。本研究评估了基于位置的常规化对六种最先进的自监督特征学习框架的影响,这些框架包括卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)模型,具有不同的潜在空间维度。在三个不同的海底图像数据集上的评估发现,与标准SSL相比,位置常规化能持续提高下游分类性能,CNN的平均F1得分提高了$4.9 \pm 4.0%$,而ViT提高了$6.3 \pm 8.9%$。尽管在通用数据集上预训练的CNN受益于高维潜在表示,但针对数据集的SSL在高维(512)和低维(128)潜在表示方面实现了相似性能。位置常规化的SSL改进了CNN在预训练模型上的性能,在高维和低维潜在表示上分别提高了$2.7 \pm 2.7%$和$10.1 \pm 9.4%$。对于ViT,高维表示有利于预训练和针对数据集的SSL。虽然位置常规化提高了SSL性能,但预训练的ViT表现出强大的泛化能力,与位置常规化的SSL的最佳性能相匹配,F1得分分别为$0.795 \pm 0.075$和$0.795 \pm 0.077$。研究强调了位置元数据在SSL正则化中的价值,特别是使用低维潜在表示时,并展示了高维ViT在海底图像分析中的强大泛化能力。
要点
- 高通量解释机器人采集的海底视觉图像能提高海洋监测和探索的效率。
- 位置元数据对自监督特征学习(SSL)的效益显著,尤其是在低维潜在表示方面。
- 基于位置的常规化能提高下游分类性能,CNN和ViT模型均受益。
- 预训练的CNN模型在通用数据集上表现良好,而针对数据集的SSL在不同维度上具有相似的性能表现。
- 位置常规化的SSL改进了CNN预训练模型的表现。
- 对于ViT模型,高维表示无论对于预训练还是针对数据集的SSL都有益。
点此查看论文截图
Does DINOv3 Set a New Medical Vision Standard?
Authors:Che Liu, Yinda Chen, Haoyuan Shi, Jinpeng Lu, Bailiang Jian, Jiazhen Pan, Linghan Cai, Jiayi Wang, Yundi Zhang, Jun Li, Cosmin I. Bercea, Cheng Ouyang, Chen Chen, Zhiwei Xiong, Benedikt Wiestler, Christian Wachinger, Daniel Rueckert, Wenjia Bai, Rossella Arcucci
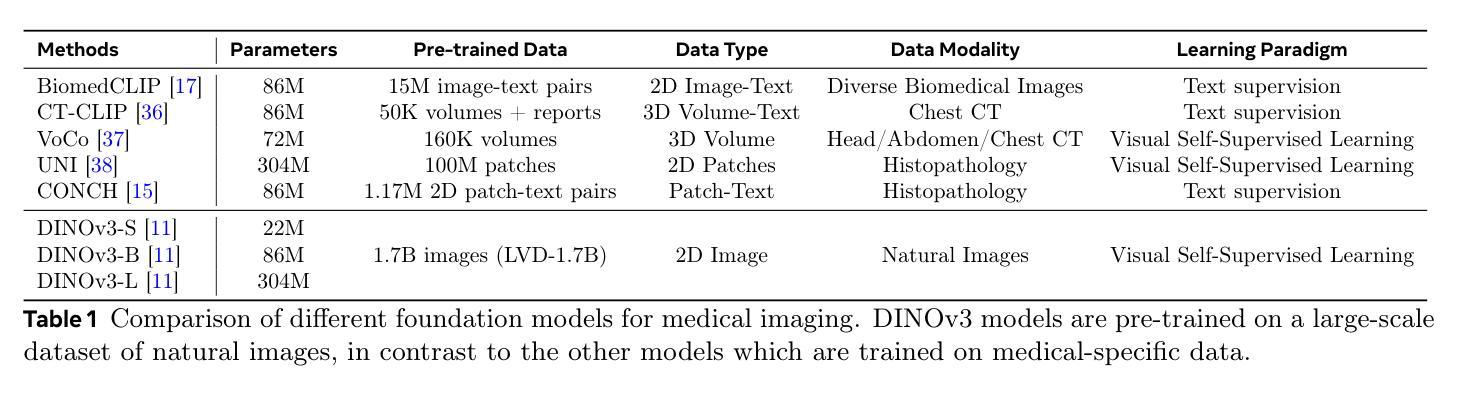
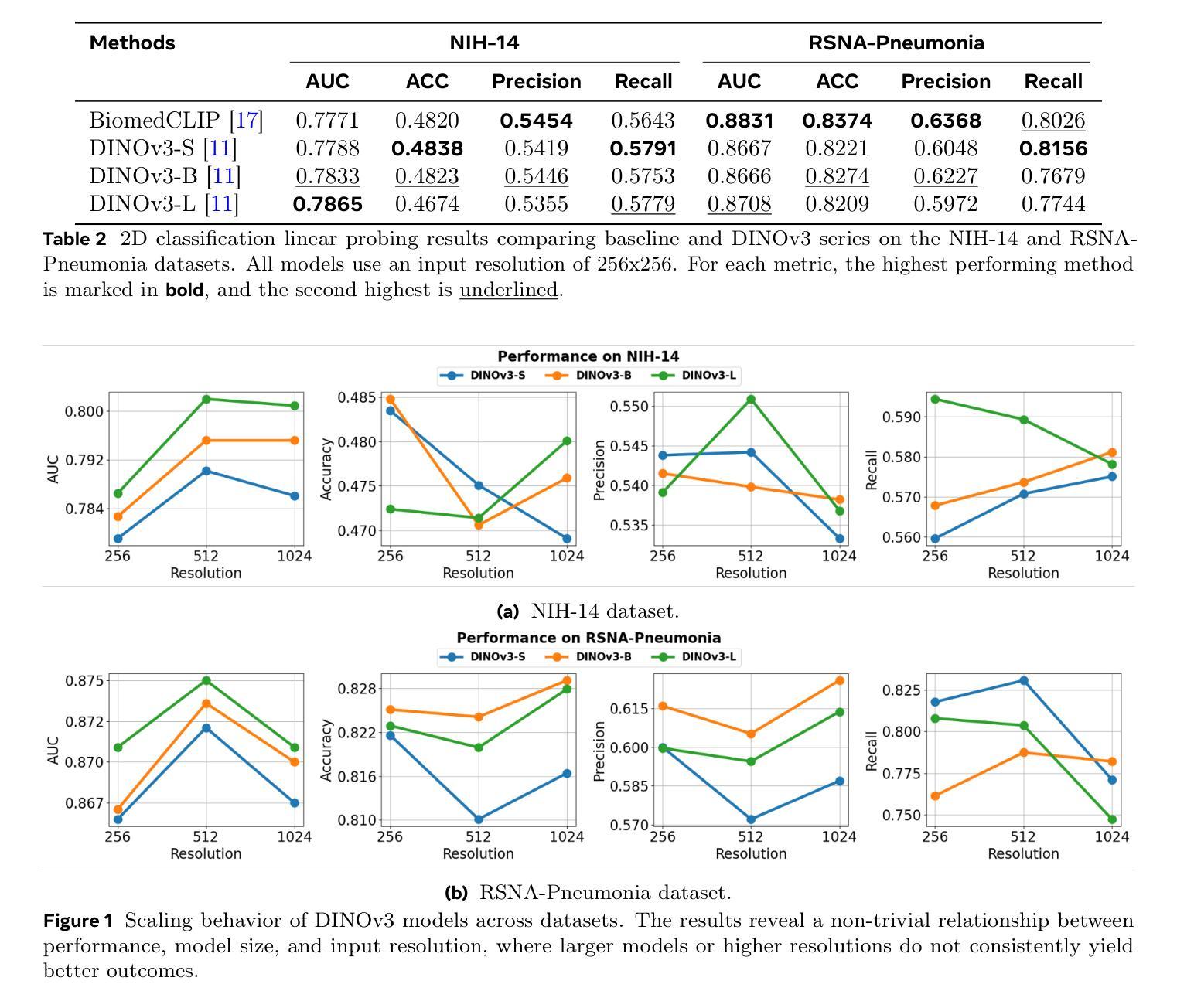
The advent of large-scale vision foundation models, pre-trained on diverse natural images, has marked a paradigm shift in computer vision. However, how the frontier vision foundation models’ efficacies transfer to specialized domains remains such as medical imaging remains an open question. This report investigates whether DINOv3, a state-of-the-art self-supervised vision transformer (ViT) that features strong capability in dense prediction tasks, can directly serve as a powerful, unified encoder for medical vision tasks without domain-specific pre-training. To answer this, we benchmark DINOv3 across common medical vision tasks, including 2D/3D classification and segmentation on a wide range of medical imaging modalities. We systematically analyze its scalability by varying model sizes and input image resolutions. Our findings reveal that DINOv3 shows impressive performance and establishes a formidable new baseline. Remarkably, it can even outperform medical-specific foundation models like BiomedCLIP and CT-Net on several tasks, despite being trained solely on natural images. However, we identify clear limitations: The model’s features degrade in scenarios requiring deep domain specialization, such as in Whole-Slide Pathological Images (WSIs), Electron Microscopy (EM), and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Furthermore, we observe that DINOv3 does not consistently obey scaling law in the medical domain; performance does not reliably increase with larger models or finer feature resolutions, showing diverse scaling behaviors across tasks. Ultimately, our work establishes DINOv3 as a strong baseline, whose powerful visual features can serve as a robust prior for multiple complex medical tasks. This opens promising future directions, such as leveraging its features to enforce multiview consistency in 3D reconstruction.
大规模视觉基础模型的出现,这些模型在多样化的自然图像上进行预训练,标志着计算机视觉的范式转变。然而,前沿的视觉基础模型如何将其效能转移到专业领域,如在医学影像领域,仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。本报告旨在调查DINOv3这一先进的自监督视觉转换器(ViT)在密集预测任务中表现出的强大能力,是否可以不进行领域特定预训练,直接作为医学视觉任务的强大统一编码器。为了回答这个问题,我们在常见的医学视觉任务上评估了DINOv3的性能,包括多种医学影像模态的2D/3D分类和分割。我们通过改变模型大小和输入图像分辨率来系统地分析其可扩展性。我们的研究发现,DINOv3表现出令人印象深刻的性能,并建立了强大的新基准。值得注意的是,尽管它只经过自然图像的训练,但它甚至可以在一些任务上超越特定的医学基础模型,如BioMedCLIP和CT-Net。然而,我们也发现了明显的局限性:在需要深度领域专业化的场景中,如全幻灯片病理图像(WSIs)、电子显微镜(EM)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET),该模型的特征会有所退化。此外,我们观察到DINOv3在医学领域中并不总是遵循规模定律;性能并不一定会随着模型更大或特征分辨率更高而可靠地提高,不同任务之间表现出多样的扩展行为。最终,我们的工作确立了DINOv3作为一个强大的基准线,其强大的视觉特征可以作为多个复杂医学任务的稳健先验。这为未来方向打开了令人鼓舞的前景,例如利用其特性来执行三维重建中的多视图一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
本文探讨了基于大规模自然图像预训练的先进视觉基础模型(如DINOv3)在医疗影像领域的表现。通过对比一系列医学视觉任务(如2D/3D分类和分割)发现,DINOv3表现出色,甚至在部分任务上超越了特定医疗模型(如BiomedCLIP和CT-Net)。但模型在某些深度专业领域存在局限,如在全幻灯片病理图像(WSIs)、电子显微镜(EM)和正电子发射断层扫描(PET)等领域性能下降。此外,DINOv3在医学领域的扩展性并不稳定,模型大小增加或特征分辨率提高并不一定带来性能提升。尽管如此,DINOv3仍是强有力的基线模型,为复杂医学任务提供了稳健的先验知识。
Key Takeaways
- DINOv3作为先进的自监督视觉Transformer(ViT),在自然图像密集预测任务中表现出强大的能力。
- 在医学视觉任务中,DINOv3无需特定领域预训练即可作为强大统一的编码器使用。
- 在常见的医学视觉任务(如2D/3D分类和分割)上,DINOv3表现出令人印象深刻的性能,并建立了强大的新基准。
- DINOv3在某些任务上超越了特定的医疗模型,如BiomedCLIP和CT-Net。
- 在深度专业领域(如WSIs、EM和PET)中,DINOv3的特征存在局限性。
- DINOv3在医学领域的可扩展性不稳定:模型大小增加或特征分辨率提高并不一定带来性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

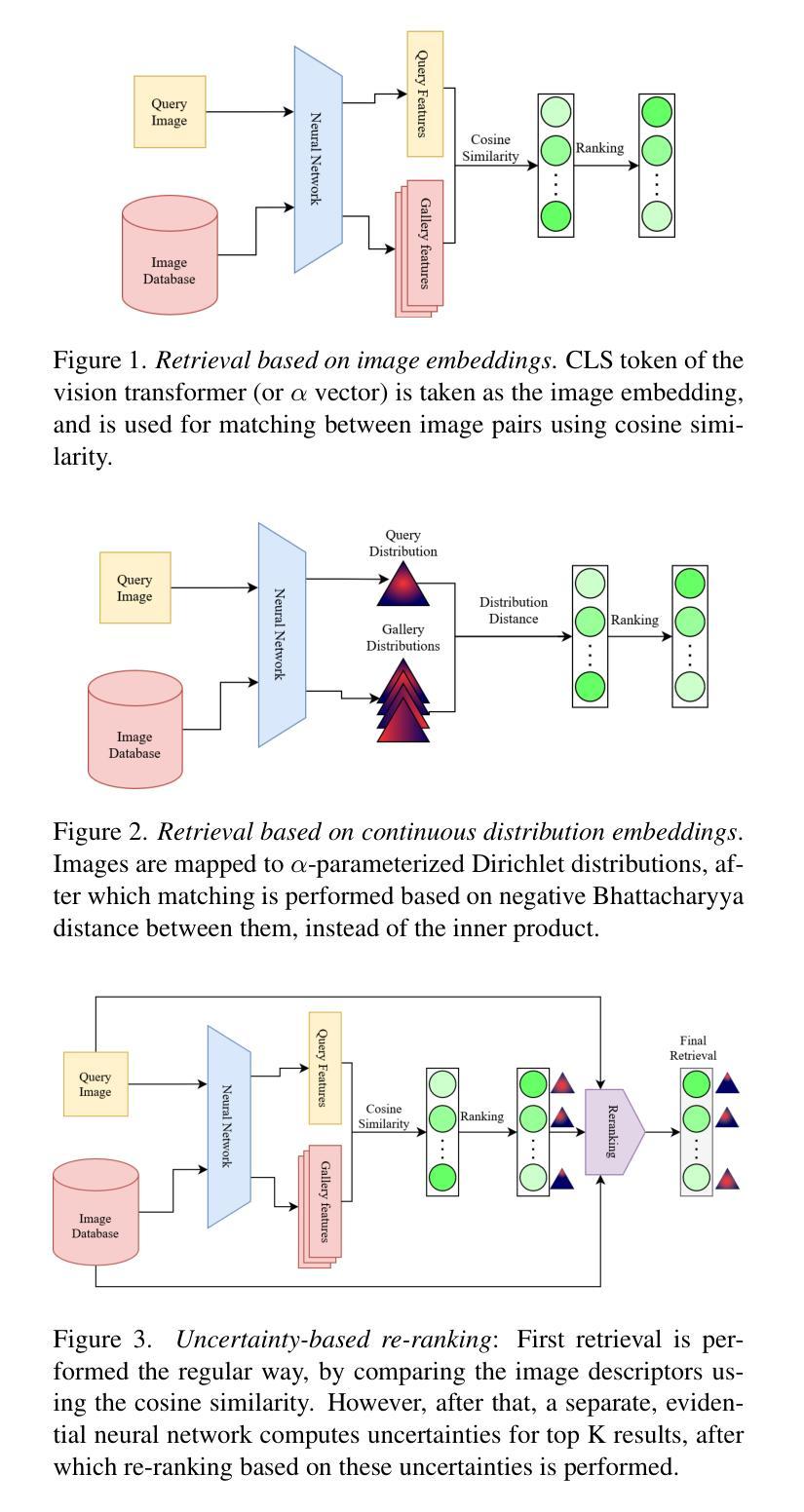
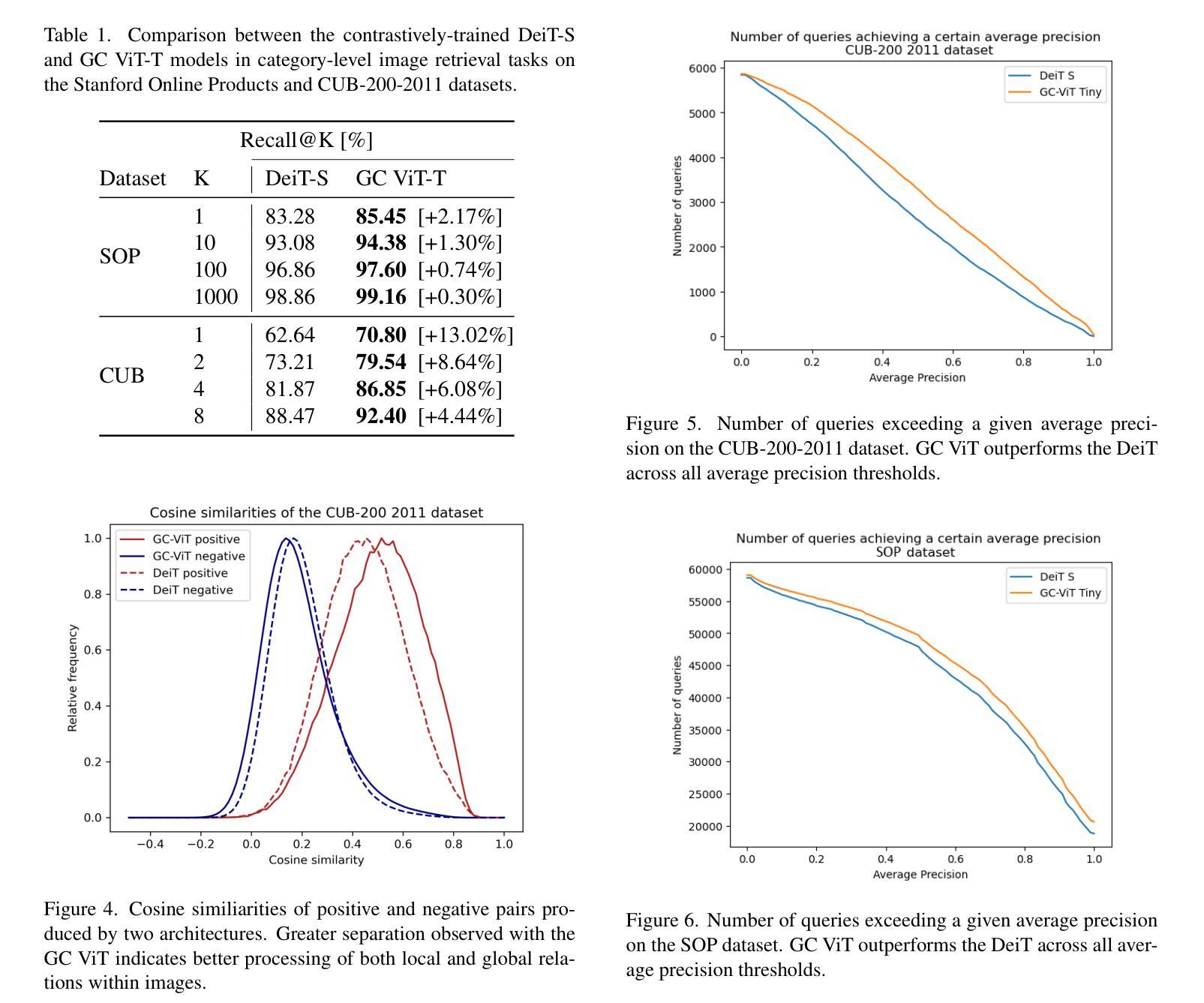
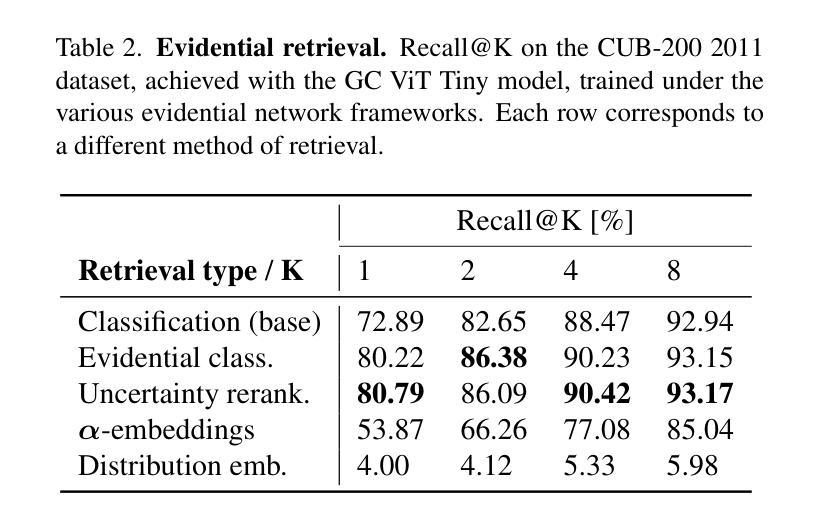
Evidential Transformers for Improved Image Retrieval
Authors:Danilo Dordevic, Suryansh Kumar
We introduce the Evidential Transformer, an uncertainty-driven transformer model for improved and robust image retrieval. In this paper, we make several contributions to content-based image retrieval (CBIR). We incorporate probabilistic methods into image retrieval, achieving robust and reliable results, with evidential classification surpassing traditional training based on multiclass classification as a baseline for deep metric learning. Furthermore, we improve the state-of-the-art retrieval results on several datasets by leveraging the Global Context Vision Transformer (GC ViT) architecture. Our experimental results consistently demonstrate the reliability of our approach, setting a new benchmark in CBIR in all test settings on the Stanford Online Products (SOP) and CUB-200-2011 datasets.
我们介绍了证据Transformer,这是一种面向不确定性的Transformer模型,用于改进和增强图像检索功能。在本文中,我们对基于内容的图像检索(CBIR)做出了几项贡献。我们将概率方法纳入图像检索中,实现了稳健可靠的结果,其中证据分类超越了基于多类分类的传统训练,成为深度度量学习的基线。此外,我们借助全局上下文视觉Transformer(GC ViT)架构,在几个数据集上改进了最新的检索结果。我们的实验结果在所有测试环境中均证明了我们的方法可靠性,在斯坦福在线产品(SOP)和CUB-200-2011数据集上的CBIR中树立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 6 figures, presented at the 3rd Workshop on Uncertainty Quantification for Computer Vision, at the ECCV 2024 conference in Milan, Italy
Summary
本文介绍了Evidential Transformer,这是一种用于改进和稳健图像检索的不确定性驱动变压器模型。文章对基于内容的图像检索(CBIR)做出了多项贡献,通过将概率方法融入图像检索,实现了稳健可靠的结果。此外,通过利用全局上下文视觉变压器(GC ViT)架构,改进了最新检索结果。实验结果表明,该方法在Stanford Online Products(SOP)和CUB-200-2011数据集上所有测试环境中均表现可靠,为CBIR领域树立了新基准。
Key Takeaways
- Evidential Transformer是一个不确定性驱动的模型,用于改进和稳健图像检索。
- 融合了概率方法,实现了稳健可靠的图像检索结果。
- Evidential分类超越了基于多类分类的传统训练,为深度度量学习提供了新的基准。
- 利用全局上下文视觉变压器(GC ViT)架构改进了最新的检索结果。
- 在Stanford Online Products(SOP)和CUB-200-2011数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在所有测试环境中均表现可靠。
- 该方法为提高CBIR的性能树立了新的基准。
点此查看论文截图

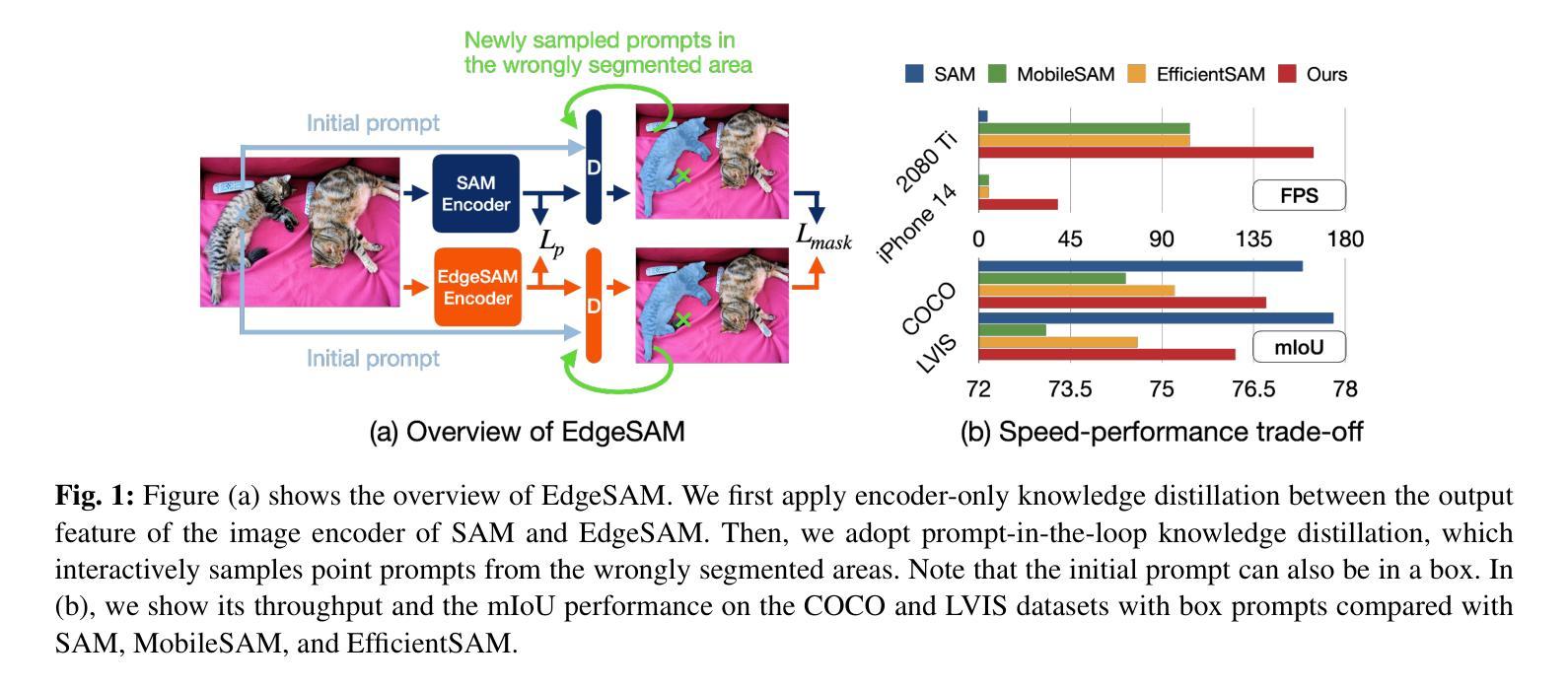
EdgeSAM: Prompt-In-the-Loop Distillation for SAM
Authors:Chong Zhou, Xiangtai Li, Chen Change Loy, Bo Dai
This paper presents EdgeSAM, an accelerated variant of the Segment Anything Model (SAM), optimized for efficient execution on edge devices with minimal compromise in performance. Our approach involves distilling the original ViT-based SAM image encoder into a purely CNN-based architecture, better suited for edge devices. We carefully benchmark various distillation strategies and demonstrate that task-agnostic encoder distillation fails to capture the full knowledge embodied in SAM. To overcome this bottleneck, we include both the prompt encoder and mask decoder in the distillation process, with box and point prompts in the loop, so that the distilled model can accurately capture the intricate dynamics between user input and mask generation. To mitigate dataset bias issues stemming from point prompt distillation, we incorporate a lightweight module within the encoder. As a result, EdgeSAM achieves a 37-fold speed increase compared to the original SAM, and it also outperforms MobileSAM/EfficientSAM, being over 7 times as fast when deployed on edge devices while enhancing the mIoUs on COCO and LVIS by 2.3/1.5 and 3.1/1.6, respectively. It is also the first SAM variant that can run at over 30 FPS on an iPhone 14. Code and demo are available at https://www.mmlab-ntu.com/project/edgesam.
本文介绍了EdgeSAM,这是Segment Anything Model(SAM)的加速版本,经过优化,可在边缘设备上高效执行,同时性能损失最小化。我们的方法是将原始的基于ViT的SAM图像编码器蒸馏到纯粹的CNN架构中,更适合边缘设备。我们仔细基准测试了多种蒸馏策略,并证明任务无关的编码器蒸馏无法捕获SAM中的全部知识。为了克服这一瓶颈,我们在蒸馏过程中包含了提示编码器和掩码解码器,以及框和点提示循环,以便蒸馏模型能够准确捕捉用户输入和掩码生成之间的复杂动态。为了解决由点提示蒸馏引起的数据集偏见问题,我们在编码器中加入了一个轻量级模块。因此,EdgeSAM与原始SAM相比实现了37倍的速度提升,并且优于MobileSAM/EfficientSAM,在边缘设备上部署时,其速度超过7倍,同时提高了COCO和LVIS的mIoUs分别为2.3/1.5和3.1/1.6。此外,它还是首个能在iPhone 14上实现超过30帧每秒运行速度的SAM变体。相关代码和演示可在https://www.mmlab-ntu.com/project/edgesam找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IJCV 2025. Project page: https://www.mmlab-ntu.com/project/edgesam
Summary
本文提出了EdgeSAM,这是Segment Anything Model(SAM)的一种加速变体,针对边缘设备的有效执行进行了优化,性能几乎没有妥协。该研究通过蒸馏原始的基于ViT的SAM图像编码器,将其转化为纯CNN架构,更适合在边缘设备上运行。经过对各种蒸馏策略的仔细评估,发现任务无关的编码器蒸馏无法捕获SAM的全部知识。为克服这一瓶颈,研究在蒸馏过程中纳入了提示编码器和掩膜解码器,并引入了框和点提示,使蒸馏模型能够准确捕捉用户输入和掩膜生成之间的复杂动态。为解决点提示蒸馏引起的数据集偏差问题,研究在编码器中加入了一个轻量级模块。EdgeSAM相比原始SAM实现了37倍的加速,并且超越了MobileSAM/EfficientSAM,在边缘设备上部署时速度提高了7倍以上,同时提高了COCO和LVIS的mIoUs分别为2.3/1.5和3.1/1.6。此外,EdgeSAM还是首个能在iPhone 14上实现超过30帧每秒运行的SAM变体。相关代码和演示可在https://www.mmlab-ntu.com/project/edgesam上找到。
Key Takeaways
- EdgeSAM是Segment Anything Model(SAM)的加速版本,针对边缘设备优化。
- 通过蒸馏技术将原始的ViT-based SAM图像编码器转化为CNN架构。
- 纳入提示编码器和掩膜解码器进行蒸馏,以捕捉用户输入与掩膜生成的复杂动态。
- 引入框和点提示解决任务无关编码器蒸馏的瓶颈。
- 融入轻量级模块以应对点提示蒸馏引发的数据集偏差问题。
- EdgeSAM相较于原始SAM有显著的加速效果,速度提高37倍。
点此查看论文截图