⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-30 更新
Orochi: Versatile Biomedical Image Processor
Authors:Gaole Dai, Chenghao Zhou, Yu Zhou, Rongyu Zhang, Yuan Zhang, Chengkai Hou, Tiejun Huang, Jianxu Chen, Shanghang Zhang
Deep learning has emerged as a pivotal tool for accelerating research in the life sciences, with the low-level processing of biomedical images (e.g., registration, fusion, restoration, super-resolution) being one of its most critical applications. Platforms such as ImageJ (Fiji) and napari have enabled the development of customized plugins for various models. However, these plugins are typically based on models that are limited to specific tasks and datasets, making them less practical for biologists. To address this challenge, we introduce Orochi, the first application-oriented, efficient, and versatile image processor designed to overcome these limitations. Orochi is pre-trained on patches/volumes extracted from the raw data of over 100 publicly available studies using our Random Multi-scale Sampling strategy. We further propose Task-related Joint-embedding Pre-Training (TJP), which employs biomedical task-related degradation for self-supervision rather than relying on Masked Image Modelling (MIM), which performs poorly in downstream tasks such as registration. To ensure computational efficiency, we leverage Mamba’s linear computational complexity and construct Multi-head Hierarchy Mamba. Additionally, we provide a three-tier fine-tuning framework (Full, Normal, and Light) and demonstrate that Orochi achieves comparable or superior performance to current state-of-the-art specialist models, even with lightweight parameter-efficient options. We hope that our study contributes to the development of an all-in-one workflow, thereby relieving biologists from the overwhelming task of selecting among numerous models.
深度学习已成为加速生命科学领域研究的关键工具之一,其在生物医学图像的底层处理(例如注册、融合、修复、超分辨率)方面的应用尤为关键。ImageJ(Fiji)和napari等平台为各种模型定制插件的开发提供了支持。然而,这些插件通常仅限于特定任务和数据集,对于生物学家来说实用性较低。为了应对这一挑战,我们推出了Orochi,这是一款面向应用、高效且通用的图像处理工具,旨在克服这些限制。Orochi采用我们的随机多尺度采样策略,对来自超过100项公开研究的原始数据提取的补丁/体积进行预训练。我们进一步提出了任务相关联合嵌入预训练(TJP),它采用生物医学任务相关退化进行自监督,而不是依赖遮挡图像建模(MIM),后者在注册等下游任务中表现不佳。为了保证计算效率,我们利用Mamba的线性计算复杂性,构建了多头层次Mamba。此外,我们提供了三层微调框架(全面、正常和轻量级),并证明Orochi即使使用轻量级参数高效选项,也能达到或超越当前先进的专业模型性能。我们希望本研究为全集成工作流程的发展做出贡献,从而减轻生物学家在选择众多模型方面的繁重任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by 39th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025) as spotlight paper
Summary
基于深度学习在生命科学领域中的重要性,特别是其在生物医学图像处理中的应用,研究团队开发了Orochi图像处理工具。Orochi通过采用多种策略如随机多尺度采样和面向任务联合嵌入预训练,提高了对多种下游任务的适应性。同时,它采用高效的计算策略以多层次的微调框架实现了出色的性能,旨在为生物学家提供一个集成的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在生命科学研究中的加速作用显著,特别是在生物医学图像处理方面。
- 当前存在的图像处理工具如ImageJ和napari虽然允许定制插件,但它们在特定任务和数据集上的局限性限制了其实用性。
- Orochi是一个针对生物医学图像处理的综合性工具,通过预训练和策略优化提高了对各种任务的适应性。
- Orochi采用随机多尺度采样策略,基于超过100项公开研究的数据进行训练。
- Task-related Joint-embedding Pre-Training(TJP)方法用于自我监督,不依赖Mask Image Modelling(MIM),后者在某些下游任务中表现不佳。
- Orochi利用高效的计算策略实现线性计算复杂度,并通过多层次微调框架实现出色的性能。
点此查看论文截图
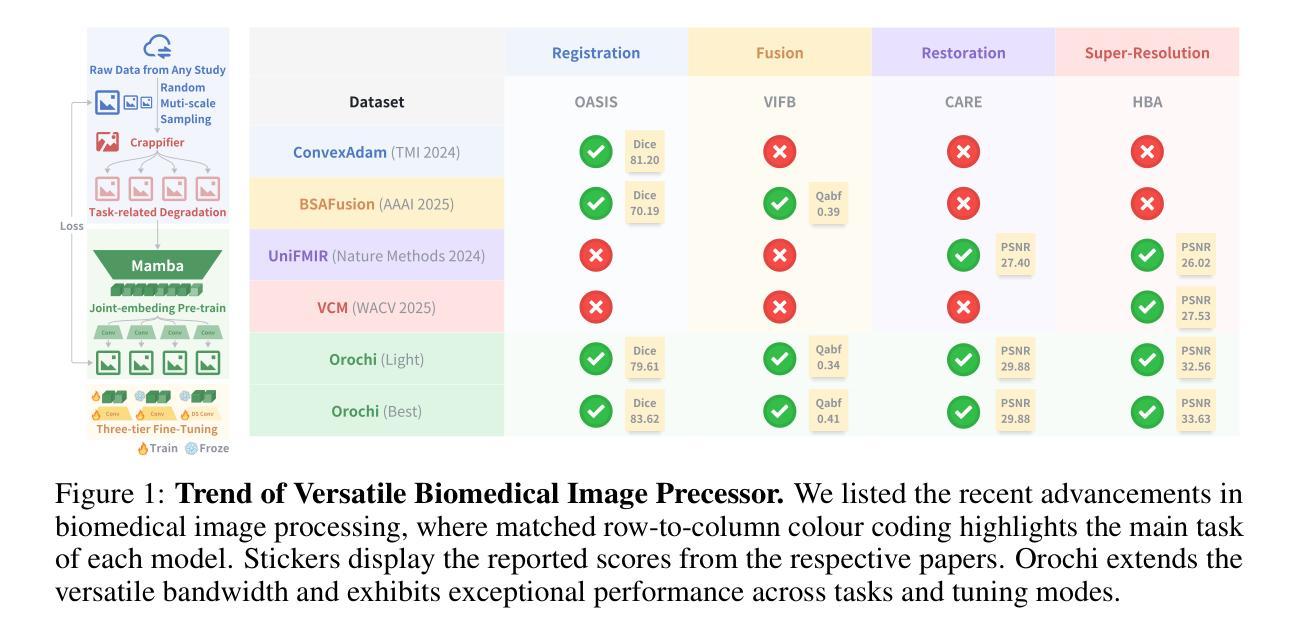
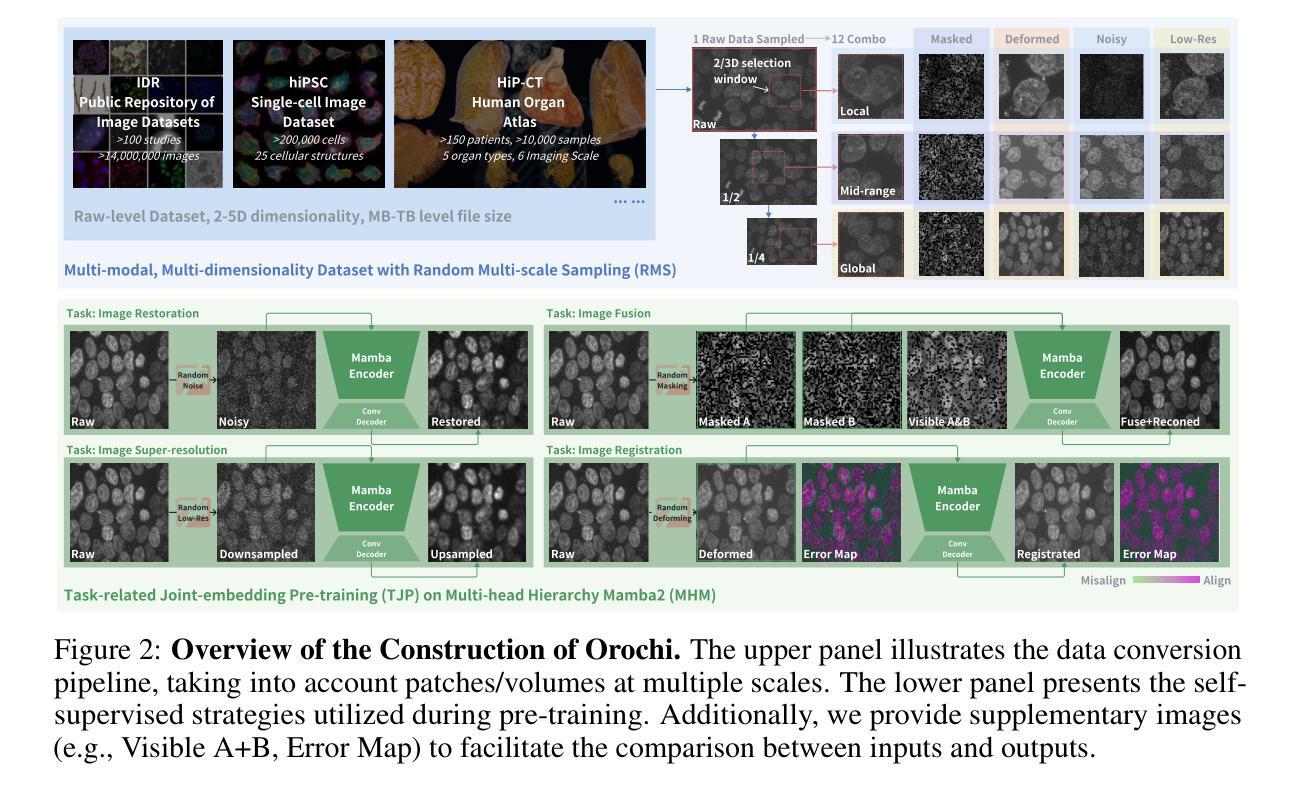
U-MAN: U-Net with Multi-scale Adaptive KAN Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Bohan Huang, Qianyun Bao, Haoyuan Ma
Medical image segmentation faces significant challenges in preserving fine-grained details and precise boundaries due to complex anatomical structures and pathological regions. These challenges primarily stem from two key limitations of conventional U-Net architectures: (1) their simple skip connections ignore the encoder-decoder semantic gap between various features, and (2) they lack the capability for multi-scale feature extraction in deep layers. To address these challenges, we propose the U-Net with Multi-scale Adaptive KAN (U-MAN), a novel architecture that enhances the emerging Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) with two specialized modules: Progressive Attention-Guided Feature Fusion (PAGF) and the Multi-scale Adaptive KAN (MAN). Our PAGF module replaces the simple skip connection, using attention to fuse features from the encoder and decoder. The MAN module enables the network to adaptively process features at multiple scales, improving its ability to segment objects of various sizes. Experiments on three public datasets (BUSI, GLAS, and CVC) show that U-MAN outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in defining accurate boundaries and preserving fine details.
医学图像分割在保留精细粒度和精确边界方面面临着重大挑战,这是由于复杂的解剖结构和病理区域所导致的。这些挑战主要源于传统U-Net架构的两个关键局限性:(1)其简单的跳跃连接忽略了各种特征之间的编码器-解码器语义鸿沟;(2)它们在深层中缺乏多尺度特征提取的能力。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了具有多尺度自适应KAN(U-MAN)的U-Net,这是一种新型架构,它通过两个专用模块增强了新兴的Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN):渐进式注意力引导特征融合(PAGF)和多尺度自适应KAN(MAN)。我们的PAGF模块使用注意力融合编码器和解码器的特征,替换了简单的跳跃连接。MAN模块使网络能够自适应地处理多尺度特征,提高了分割各种尺寸物体的能力。在BUSI、GLAS和CVC三个公共数据集上的实验表明,U-MAN优于最先进的方法,特别是在定义精确边界和保留细节方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages
Summary
本文提出了一个基于Kolmogorov-Arnold网络的改进模型U-Net Multi-scale Adaptive KAN(U-MAN),针对医学图像分割中的精细粒度细节保留和精确边界保持问题。通过引入Progressive Attention-Guided Feature Fusion(PAGF)和多尺度自适应KAN(MAN)两个模块,解决了传统U-Net架构的语义差距和多尺度特征提取不足的问题。实验结果表明,U-MAN在公开数据集上的表现优于现有方法,特别是在边界准确性和细节保留方面。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临保留精细粒度和精确边界的挑战。
- 传统U-Net架构存在语义差距和多尺度特征提取的问题。
- U-MAN模型结合了Kolmogorov-Arnold网络(KAN)与两个模块:Progressive Attention-Guided Feature Fusion(PAGF)和多尺度自适应KAN(MAN)。
- PAGF模块使用注意力机制融合编码器和解码器的特征,替代了简单的跳跃连接。
- MAN模块使网络能够自适应地处理多尺度特征,提高了分割不同大小物体的能力。
- 实验结果表明U-MAN在公开数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

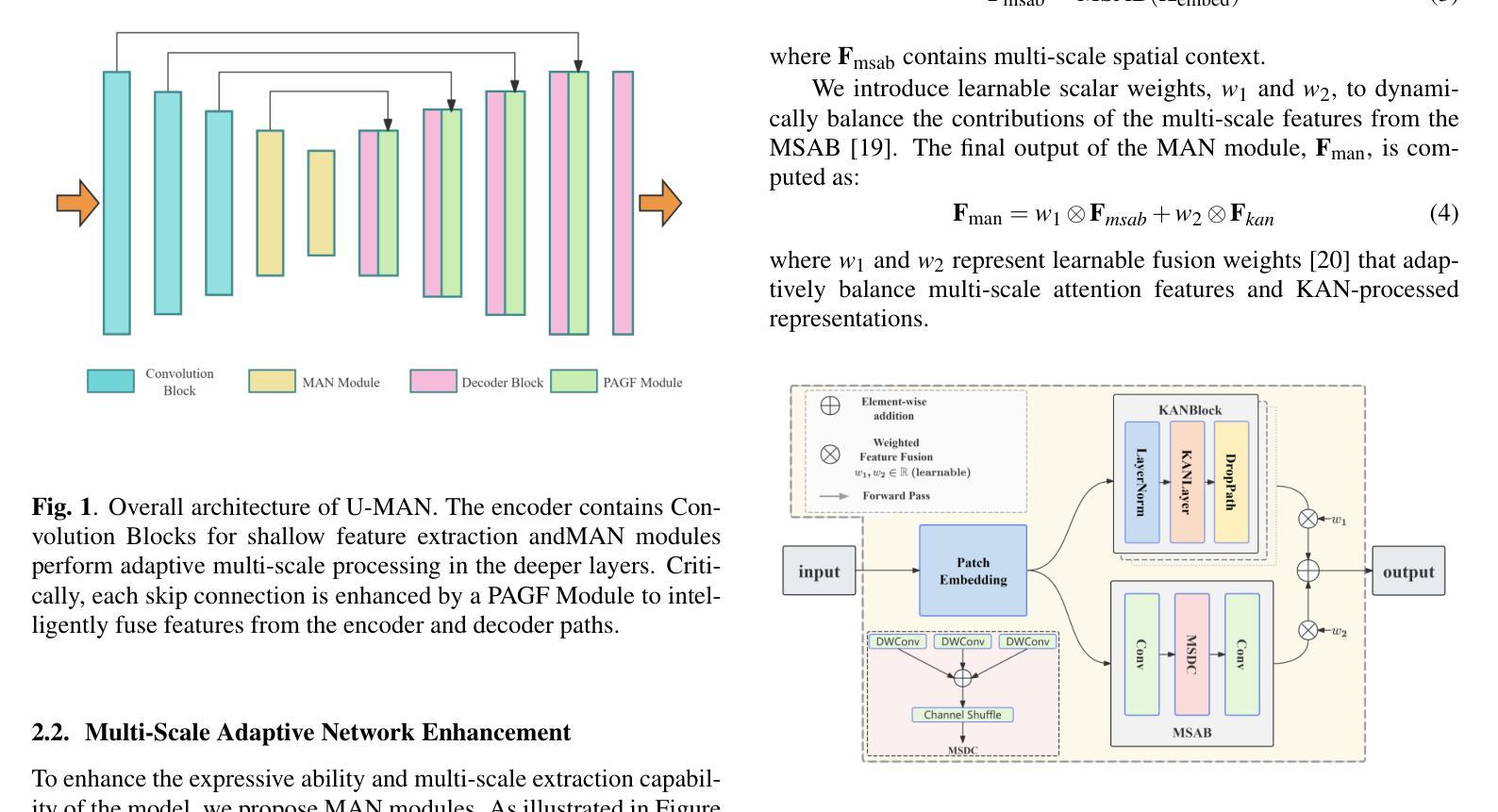
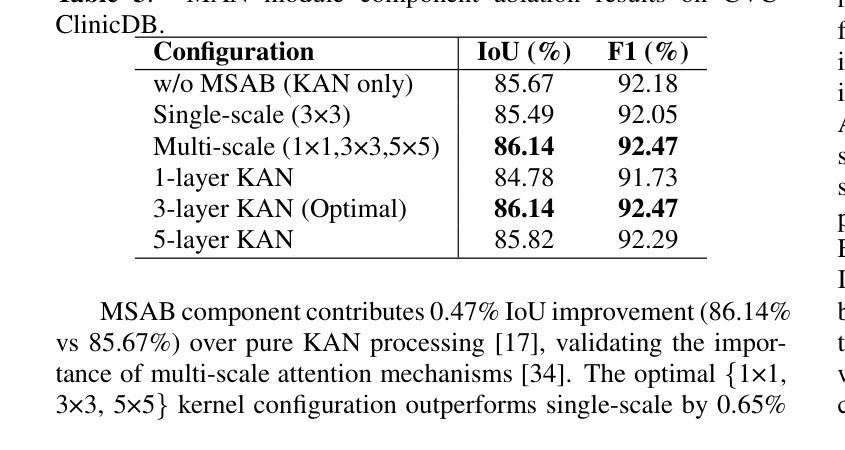
Integrating Background Knowledge in Medical Semantic Segmentation with Logic Tensor Networks
Authors:Luca Bergamin, Giovanna Maria Dimitri, Fabio Aiolli
Semantic segmentation is a fundamental task in medical image analysis, aiding medical decision-making by helping radiologists distinguish objects in an image. Research in this field has been driven by deep learning applications, which have the potential to scale these systems even in the presence of noise and artifacts. However, these systems are not yet perfected. We argue that performance can be improved by incorporating common medical knowledge into the segmentation model’s loss function. To this end, we introduce Logic Tensor Networks (LTNs) to encode medical background knowledge using first-order logic (FOL) rules. The encoded rules span from constraints on the shape of the produced segmentation, to relationships between different segmented areas. We apply LTNs in an end-to-end framework with a SwinUNETR for semantic segmentation. We evaluate our method on the task of segmenting the hippocampus in brain MRI scans. Our experiments show that LTNs improve the baseline segmentation performance, especially when training data is scarce. Despite being in its preliminary stages, we argue that neurosymbolic methods are general enough to be adapted and applied to other medical semantic segmentation tasks.
语义分割是医学图像分析中的一项基本任务,通过帮助放射科医生区分图像中的对象来辅助医疗决策。该领域的研究主要受到深度学习应用的影响,即使存在噪声和伪像,深度学习也有潜力推动这些系统的规模化应用。然而,这些系统尚未完善。我们认为可以通过将通用医学知识纳入分割模型的损失函数来提高性能。为此,我们引入了逻辑张量网络(LTNs),使用一阶逻辑(FOL)规则编码医学背景知识。编码的规则从对生成分割形状的约束扩展到不同分割区域之间的关系。我们在端到端的框架中应用了LTNs与SwinUNETR进行语义分割。我们对脑MRI扫描中海马体的分割任务进行了评估。实验表明,LTNs提高了基线分割性能,特别是在训练数据稀缺的情况下。尽管仍处于初步阶段,我们认为神经符号方法足够通用,可以适应并应用于其他医学语义分割任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at TAIM@IJCNN 2025
Summary
医学图像语义分割是医学决策支持中的基础任务之一,通过帮助放射科医生区分图像中的对象来辅助决策。本研究引入逻辑张量网络(LTNs)来编码医学背景知识,并将其应用于医学图像语义分割模型中。实验表明,LTNs能提高基线分割性能,特别是在训练数据稀缺的情况下。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在医学图像分析中是一项基础任务,有助于放射科医生区分图像中的对象,从而支持医学决策。
- 深度学习在医学图像语义分割领域的应用推动了研究发展,并具备在存在噪声和伪影的情况下扩展系统的潜力。
- 在分割模型的损失函数中融入医学常识能提高性能。
- 逻辑张量网络(LTNs)被引入以使用一阶逻辑(FOL)规则编码医学背景知识。
- LTNs可应用于端对端框架中的SwinUNETR进行语义分割。
- 在大脑MRI扫描中分割海马的实验中,LTNs改善了基线分割性能。
点此查看论文截图
Beyond Classification Accuracy: Neural-MedBench and the Need for Deeper Reasoning Benchmarks
Authors:Miao Jing, Mengting Jia, Junling Lin, Zhongxia Shen, Lijun Wang, Yuanyuan Peng, Huan Gao, Mingkun Xu, Shangyang Li
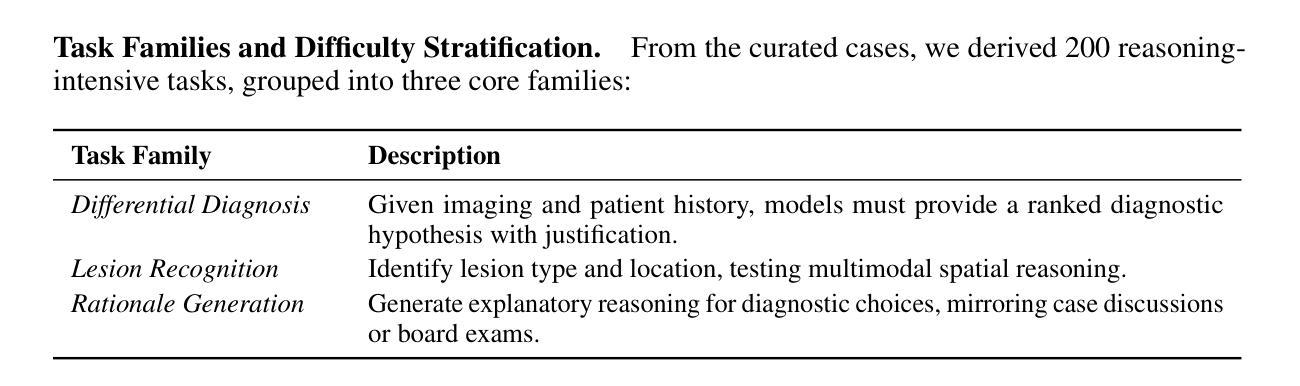
Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved remarkable performance on standard medical benchmarks, yet their true clinical reasoning ability remains unclear. Existing datasets predominantly emphasize classification accuracy, creating an evaluation illusion in which models appear proficient while still failing at high-stakes diagnostic reasoning. We introduce Neural-MedBench, a compact yet reasoning-intensive benchmark specifically designed to probe the limits of multimodal clinical reasoning in neurology. Neural-MedBench integrates multi-sequence MRI scans, structured electronic health records, and clinical notes, and encompasses three core task families: differential diagnosis, lesion recognition, and rationale generation. To ensure reliable evaluation, we develop a hybrid scoring pipeline that combines LLM-based graders, clinician validation, and semantic similarity metrics. Through systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art VLMs, including GPT-4o, Claude-4, and MedGemma, we observe a sharp performance drop compared to conventional datasets. Error analysis shows that reasoning failures, rather than perceptual errors, dominate model shortcomings. Our findings highlight the necessity of a Two-Axis Evaluation Framework: breadth-oriented large datasets for statistical generalization, and depth-oriented, compact benchmarks such as Neural-MedBench for reasoning fidelity. We release Neural-MedBench at https://neuromedbench.github.io/ as an open and extensible diagnostic testbed, which guides the expansion of future benchmarks and enables rigorous yet cost-effective assessment of clinically trustworthy AI.
最近,视觉语言模型(VLMs)在标准医疗基准测试上取得了显著的成绩,然而其真正的临床推理能力仍不明确。现有数据集主要强调分类准确性,这导致了一种评估错觉,即模型虽然表现得很好,但在高风险诊断推理方面仍然存在问题。我们推出了Neural-MedBench,这是一个紧凑而推理密集型的基准测试,专门用于探索神经学临床推理的极限。Neural-MedBench集成了多序列MRI扫描、结构化电子病历和临床笔记,包括三个核心任务家族:鉴别诊断、病灶识别和理由生成。为了确保可靠的评估,我们开发了一个混合评分管道,结合了基于大型语言模型的评分者、临床医生验证和语义相似性度量。通过对最先进的VLMs的系统评估,包括GPT-4o、Claude-4和MedGemma,我们观察到与常规数据集相比,性能急剧下降。错误分析表明,推理失败而不是感知错误主导了模型的不足。我们的研究结果表明了双向评估框架的必要性:面向广度的大型数据集用于统计泛化,以及面向深度的紧凑基准测试,如Neural-MedBench,用于推理保真度。我们在https://neuromedbench.github.io/上发布了Neural-MedBench,作为一个开放和可扩展的诊断测试平台,以指导未来基准测试的扩展,并能够实现严格而经济的临床可信人工智能评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 12 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对神经学领域中的多模态临床推理能力评估的基准测试平台Neural-MedBench。该平台集成了MRI扫描、结构化电子病历和临床笔记等核心任务,包括诊断鉴别、病灶识别和理由生成等核心任务家族。文章指出,现有的数据集主要侧重于分类准确性,无法真正评估模型的诊断推理能力。因此,作者开发了一个混合评分管道来确保评估的可靠性,并对当前先进的VLMs进行了系统评估。文章强调需要Two-Axis评估框架,包括用于统计泛化的大数据集和用于推理忠实度的紧凑基准测试平台。最后,作者发布了Neural-MedBench作为开放和可扩展的诊断测试平台。
Key Takeaways
- 现有数据集主要关注分类准确性,无法真实评估模型的诊断推理能力。
- Neural-MedBench是一个针对神经学领域的多模态临床推理基准测试平台。
- Neural-MedBench集成了MRI扫描、结构化电子病历和临床笔记等核心任务。
- 评估方法结合了LLM评分器、临床医生验证和语义相似性度量。
- 与传统数据集相比,当前先进的VLMs在Neural-MedBench上的性能显著下降。
- 错误分析显示,模型失败的主要原因是推理失败而非感知错误。
点此查看论文截图
FoodSEM: Large Language Model Specialized in Food Named-Entity Linking
Authors:Ana Gjorgjevikj, Matej Martinc, Gjorgjina Cenikj, Sašo Džeroski, Barbara Koroušić Seljak, Tome Eftimov
This paper introduces FoodSEM, a state-of-the-art fine-tuned open-source large language model (LLM) for named-entity linking (NEL) to food-related ontologies. To the best of our knowledge, food NEL is a task that cannot be accurately solved by state-of-the-art general-purpose (large) language models or custom domain-specific models/systems. Through an instruction-response (IR) scenario, FoodSEM links food-related entities mentioned in a text to several ontologies, including FoodOn, SNOMED-CT, and the Hansard taxonomy. The FoodSEM model achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to related models/systems, with F1 scores even reaching 98% on some ontologies and datasets. The presented comparative analyses against zero-shot, one-shot, and few-shot LLM prompting baselines further highlight FoodSEM’s superior performance over its non-fine-tuned version. By making FoodSEM and its related resources publicly available, the main contributions of this article include (1) publishing a food-annotated corpora into an IR format suitable for LLM fine-tuning/evaluation, (2) publishing a robust model to advance the semantic understanding of text in the food domain, and (3) providing a strong baseline on food NEL for future benchmarking.
本文介绍了FoodSEM,这是一种最新微调过的开源大型语言模型(LLM),用于命名实体链接(NEL)到与食品相关的本体。据我们所知,食品NEL是一项任务,无法由最新通用的大型语言模型或定制的领域特定模型/系统准确解决。通过指令-响应(IR)场景,FoodSEM将文本中提到的与食品相关的实体链接到多个本体,包括FoodOn、SNOMED-CT和汉萨分类法。FoodSEM模型与相关的模型/系统相比,达到了最新性能水平,在某些本体和数据集上的F1分数甚至达到98%。与零样本、单样本和少量样本的大型语言模型提示基线相比的分析进一步突出了FoodSEM在非微调版本上的卓越性能。通过将FoodSEM及其相关资源公开可用,本文的主要贡献包括:(1)将食品注释语料库发布为适合大型语言模型微调/评估的IR格式,(2)发布一个稳健的模型,以推进食品领域的文本语义理解,(3)为未来的基准测试提供食品NEL的强基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in the Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Discovery Science (DS 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了FoodSEM,这是一种针对食品相关本体命名实体链接任务的先进微调开源大型语言模型。FoodSEM在食品领域的文本语义理解上表现出卓越性能,与现有模型/系统相比具有优势,并提供了强有力的基准以供未来评估。
Key Takeaways
- FoodSEM是一个针对食品相关本体命名实体链接任务的大型语言模型。
- FoodSEM能够链接文本中的食品相关实体到多个本体,包括FoodOn、SNOMED-CT和Hansard分类法。
- FoodSEM实现了先进性能,与相关领域模型/系统相比具有优势,F1分数在某些本体和数据集上甚至达到98%。
- FoodSEM通过指令响应场景进行工作。
- FoodSEM及其相关资源已公开发布,为食品领域的文本语义理解做出了主要贡献。
- FoodSEM的发布提供了一个强大的基准,供未来在食品命名实体链接任务上进行评估。
点此查看论文截图
Unveiling Obscured Accretion in the Local Universe
Authors:Indrani Pal, Stefano Marchesi, Ross Silver, Marco Ajello, Vittoria Gianolli, Núria Torres-Albà, Isaiah Cox, Xiurui Zhao, Dhrubojyoti Sengupta, Anuvab Banerjee, Kouser Imam, Andrealuna Pizzetti
Heavily obscured Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN), especially Compton-thick sources with line-of-sight column density ($N_{\rm H,los}$) $>$ 10$^{24}$ cm$^{-2}$, are critical to understanding supermassive black hole (SMBH) growth and the origin of the Cosmic X-ray Background (CXB). However, their observed fraction remains significantly below model predictions, due to strong absorption bias, even in the hard X-ray (i.e., above 10 keV) band. We analyze a sample of 26 nearby ($z < 0.1$) AGN from the Swift-BAT 150-month catalog, selected via mid-IR to X-ray diagnostics and observed with NuSTAR and soft X-ray telescopes (Xmm-Newton, Chandra, or Swift-xrt). Using self-consistent torus models (MyTorus, Borus02, and UXCLUMPY), we aim to constrain $N_{\rm H,los}$, the average torus column density, and other geometrical parameters of the obscuring medium. A comparative analysis among the three torus models showed that while estimates of $N_{\rm{H,los}}$ were generally in agreement, Borus02 tended to classify a slightly larger number of sources as Compton-thick AGN (CT-AGN). Building on this comparison, we benchmark two prediction schemes – a mid-IR/X-ray relation and a machine-learning model – against our broadband best-fit $N_{\rm H,los}$ measurements to assess which approach more effectively bridges the gap between predicted and measured obscuration, finding that while the former works effectively in the heavily obscured region (log$\rm{N_H} \gtrsim$ 23.5 $\rm{cm^{-2}}$), the latter provides improved accuracy, particularly for Compton-thin to moderately thick regimes (log$\rm{N_H} \lesssim$ 23.5 $\rm{cm^{-2}}$).
被严重遮蔽的活跃星系核(Active Galactic Nuclei,简称AGN),特别是视线柱密度($N_{\rm H,los}$)大于10$^{24}$ cm$^{-2}$的康普顿厚源,对于理解超大质量黑洞(SMBH)的增长和宇宙X射线背景(CXB)的起源至关重要。然而,由于其强烈的吸收偏见,即使在硬X射线(即高于10 keV)波段,它们的观测比例仍显著低于模型预测。我们分析了来自Swift-BAT 150个月目录的26个近距离($z < 0.1$)的AGN样本,通过中红外到X射线的诊断方法选出来,并用NuSTAR和软X射线望远镜(Xmm-Newton、Chandra或Swift-xrt)进行观测。我们使用自洽的环模型(MyTorus、Borus02和UXCLUMPY)来限制$N_{\rm H,los}$、平均环柱密度以及遮蔽介质的其他几何参数。对三个环模型的比较分析表明,虽然对$N_{\rm{H,los}}$的估计大体上是一致的,但Borus02更倾向于将更多的源分类为康普顿厚AGN(CT-AGN)。基于这一比较,我们将两种预测方案——中红外/X射线关系和机器学习模型——与我们的宽带最佳拟合$N_{\rm H,los}$测量值进行比较,以评估哪种方法更有效地弥合了预测和测量遮蔽之间的鸿沟,发现前者在重度遮蔽区域(log$\rm{N_H} \geq 23.5 cm^{-2}$)中有效,而后者则提供了更高的准确性,特别是在康普顿薄到中等厚度范围(log$\rm{N_H} \leq 23.5 cm^{-2}$)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 13 Figures, submitted to the journal
Summary
本文研究了被严重遮蔽的活跃星系核(Active Galactic Nuclei,简称AGN),特别是线视向柱密度($N_{\rm H,los}$)大于10$^{24}$ cm$^{-2}$的康普顿厚源。文章分析了来自Swift-BAT 150个月的26个附近($z < 0.1$)的AGN样本,通过红外至X射线的诊断方法进行筛选,并用NuSTAR和软X射线望远镜(如Xmm-Newton、Chandra或Swift-xrt)观测。使用一致的环模型(MyTorus、Borus02和UXCLUMPY),文章旨在限制$N_{\rm H,los}$、平均环柱密度以及遮蔽介质的其它几何参数。比较三个环模型的估计值,发现Borus02更偏向于将更多的源分类为康普顿厚AGN(CT-AGN)。文章通过对比两个预测方案(红外/X射线关系和机器学习模型)与宽带最佳拟合的$N_{\rm H,los}$测量值,评估哪种方法更有效地弥合了预测和测量遮蔽之间的鸿沟,发现红外/X射线关系在高度遮蔽区域有效,而机器学习模型在康普顿薄至中等厚度区域提供更准确的预测。
Key Takeaways
- 重遮蔽的活跃星系核,特别是康普顿厚源,对理解超大质量黑洞增长和宇宙X射线背景起源至关重要。
- 来自Swift-BAT 150个月的26个附近AGN样本被用于分析。
- 使用自我一致的环模型来限制线视向柱密度和遮蔽介质的几何参数。
- Borus02模型更倾向于将更多源分类为康普顿厚AGN。
- 通过比较,发现机器学习模型在预测康普顿薄至中等厚度区域的遮蔽程度时更为准确。
- 中红外/X射线关系在高度遮蔽区域是有效的预测工具。
点此查看论文截图
Patch-Based Diffusion for Data-Efficient, Radiologist-Preferred MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Rohan Sanda, Asad Aali, Andrew Johnston, Eduardo Reis, Jonathan Singh, Gordon Wetzstein, Sara Fridovich-Keil
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) requires long acquisition times, raising costs, reducing accessibility, and making scans more susceptible to motion artifacts. Diffusion probabilistic models that learn data-driven priors can potentially assist in reducing acquisition time. However, they typically require large training datasets that can be prohibitively expensive to collect. Patch-based diffusion models have shown promise in learning effective data-driven priors over small real-valued datasets, but have not yet demonstrated clinical value in MRI. We extend the Patch-based Diffusion Inverse Solver (PaDIS) to complex-valued, multi-coil MRI reconstruction, and compare it against a state-of-the-art whole-image diffusion baseline (FastMRI-EDM) for 7x undersampled MRI reconstruction on the FastMRI brain dataset. We show that PaDIS-MRI models trained on small datasets of as few as 25 k-space images outperform FastMRI-EDM on image quality metrics (PSNR, SSIM, NRMSE), pixel-level uncertainty, cross-contrast generalization, and robustness to severe k-space undersampling. In a blinded study with three radiologists, PaDIS-MRI reconstructions were chosen as diagnostically superior in 91.7% of cases, compared to baselines (i) FastMRI-EDM and (ii) classical convex reconstruction with wavelet sparsity. These findings highlight the potential of patch-based diffusion priors for high-fidelity MRI reconstruction in data-scarce clinical settings where diagnostic confidence matters.
磁共振成像(MRI)需要较长的采集时间,这增加了成本,降低了可及性,并使扫描更容易受到运动伪影的影响。学习数据驱动先验的扩散概率模型有助于减少采集时间。然而,它们通常需要大量的训练数据集,而这些数据的收集成本可能非常高。基于补丁的扩散模型在小型实数数据集上显示出学习有效数据驱动先验的潜力,但尚未在MRI中显示出临床价值。我们将基于补丁的扩散反演求解器(PaDIS)扩展到复数、多线圈MRI重建,并将其与FastMRI-EDM最先进的全图像扩散基线进行比较,用于FastMRI脑部数据集的7倍欠采样MRI重建。我们表明,使用仅2.5万k空间图像的小数据集训练的PaDIS-MRI模型在图像质量指标(PSNR、SSIM、NRMSE)、像素级不确定性、跨对比度泛化和严重k空间欠采样鲁棒性方面优于FastMRI-EDM。在三名放射科医生进行的盲法研究中,与基线(i)FastMRI-EDM和(ii)经典凸重构小波稀疏性相比,PaDIS-MRI重建在91.7%的情况下被选择为诊断上更优越。这些发现突出了基于补丁的扩散先验在数据稀缺的临床环境中进行高保真MRI重建的潜力,在这些环境中,诊断信心至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code is available at: https://github.com/voilalab/PaDIS-MRI
Summary
基于Patch的扩散模型(PaDIS-MRI)在复数、多线圈MRI重建中展现出优势,相较于FastMRI-EDM等先进全图扩散基线方法,其在FastMRI脑部数据集上的7倍欠采样MRI重建效果更优。PaDIS-MRI在小型数据集上训练,仅需少量k空间图像,便能于图像质量指标(PSNR、SSIM、NRMSE)、像素级不确定性、跨对比度泛化以及抗严重k空间欠采样等方面表现出色。三位放射科医生参与的双盲研究中,PaDIS-MRI重建在91.7%的情况下被选为诊断上更优。这表明在数据稀缺的临床环境中,对于需要提高诊断信心的场合,基于Patch的扩散先验具有潜在的高保真MRI重建价值。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散概率模型能减少MRI的采集时间,提高图像质量并降低运动伪影的影响。
- 基于Patch的扩散模型(PaDIS-MRI)在复数、多线圈MRI重建中有优势。
- PaDIS-MRI能在小型数据集上训练,对图像质量指标表现优异,包括PSNR、SSIM和NRMSE等。
- PaDIS-MRI具有出色的像素级不确定性处理和跨对比度泛化能力。
- PaDIS-MRI即使在严重k空间欠采样的情况下也能表现出良好的鲁棒性。
- 双盲研究结果显示,PaDIS-MRI在诊断上的表现优于其他方法,被选为最优方案的比例高达91.7%。
- 基于Patch的扩散先验在高保真MRI重建方面具有潜在价值,特别是在数据稀缺的临床环境中。
点此查看论文截图
The LongiMam model for improved breast cancer risk prediction using longitudinal mammograms
Authors:Manel Rakez, Thomas Louis, Julien Guillaumin, Foucauld Chamming’s, Pierre Fillard, Brice Amadeo, Virginie Rondeau
Risk-adapted breast cancer screening requires robust models that leverage longitudinal imaging data. Most current deep learning models use single or limited prior mammograms and lack adaptation for real-world settings marked by imbalanced outcome distribution and heterogeneous follow-up. We developed LongiMam, an end-to-end deep learning model that integrates both current and up to four prior mammograms. LongiMam combines a convolutional and a recurrent neural network to capture spatial and temporal patterns predictive of breast cancer. The model was trained and evaluated using a large, population-based screening dataset with disproportionate case-to-control ratio typical of clinical screening. Across several scenarios that varied in the number and composition of prior exams, LongiMam consistently improved prediction when prior mammograms were included. The addition of prior and current visits outperformed single-visit models, while priors alone performed less well, highlighting the importance of combining historical and recent information. Subgroup analyses confirmed the model’s efficacy across key risk groups, including women with dense breasts and those aged 55 years or older. Moreover, the model performed best in women with observed changes in mammographic density over time. These findings demonstrate that longitudinal modeling enhances breast cancer prediction and support the use of repeated mammograms to refine risk stratification in screening programs. LongiMam is publicly available as open-source software.
风险适应型乳腺癌筛查需要强大的模型,这些模型可利用纵向成像数据。当前大多数深度学习模型仅使用单次或有限的先前乳腺X光检查,并且缺乏针对结果分布不均衡和随访异质性的真实世界环境的适应性。我们开发了LongiMam,这是一种端到端的深度学习模型,可以整合当前以及最多四个先前的乳腺X光检查。LongiMam结合了卷积神经网络和循环神经网络,以捕获预测乳腺癌的空间和时间模式。该模型使用大规模基于人群筛查数据集进行训练和评估,具有典型临床筛查中的不平衡病例对照比例。在先前检查的数量和组成不同的几个场景中,包含先前乳腺X光检查时,LongiMam始终提高了预测能力。当前和先前就诊的添加表现优于单次就诊模型,而仅使用先前的信息表现较差,这突出了结合历史和最新信息的重要性。亚组分析证实了该模型在关键风险群体中的有效性,包括乳腺组织密度较大的女性和年龄55岁及以上的女性。此外,在观察到乳腺X光检查密度随时间变化的女性中,该模型的性能最佳。这些发现表明纵向建模增强了乳腺癌预测,并支持使用多次乳腺X光检查来改进筛查程序中的风险分层。LongiMam作为开源软件可供公众使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为LongiMam的深度学习模型,该模型结合了当前和最多四个先前的乳腺X线摄影图像,用于风险适应的乳腺癌筛查。它通过卷积神经网络和循环神经网络捕捉乳腺癌的空间和时间模式。模型使用大型基于人群的数据集进行训练和评估,展现出优良的性能,特别是结合了先前的检查信息后,预测性能显著提升。该模型公开可用。
Key Takeaways
- LongiMam模型结合了纵向成像数据,用于风险适应的乳腺癌筛查。
- 模型结合了卷积神经网络和循环神经网络,以捕捉乳腺癌的空间和时间模式。
- LongiMam在包含先前乳腺X线摄影图像时预测性能提升。
- 相较于仅使用单次访问信息的模型,结合历史和最新信息的模型表现更好。
- 子组分析证实该模型在关键风险群体中的有效性。
- LongiMam模型在观察到乳腺密度随时间变化的女性中表现最佳。
- 纵向建模有助于提高乳腺癌预测的准确性。
点此查看论文截图
Tracing the Origins of Hot Halo Gas in Milky Way-Type Galaxies with SMUGGLE
Authors:Zhijie Zhang, Xiaoxia Zhang, Hui Li, Taotao Fang, Yang Luo, Federico Marinacci, Laura V. Sales, Paul Torrey, Mark Vogelsberger, Qingzheng Yu, Feng Yuan
Current galaxy formation models predict the existence of X-ray-emitting gaseous halos around Milky Way (MW)-type galaxies. To investigate properties of this coronal gas in MW-like galaxies, we analyze a suite of high-resolution simulations based on the SMUGGLE framework and compare the results with X-ray observations of both the MW and external galaxies. We find that for subgrid models incorporating any form of stellar feedback, e.g., early feedback (including stellar winds and radiation) and/or supernova (SN) explosions, the total 0.5-2 keV luminosity is consistent within uncertainties with X-ray observations of the MW and with scaling relations derived for external disk galaxies. However, all models exhibit an X-ray surface brightness profile that declines too steeply beyond $\sim5$ kpc, underpredicting the extended emission seen in recent eROSITA stacking results. Across all subgrid prescriptions, the simulated surface brightness and emission measure fall below MW observations by at least 1-2 orders of magnitude, with the most severe discrepancy occurring in the no-feedback model. Our results suggest that (i) stellar feedback primarily shapes the innermost hot atmosphere (central $\sim5$ kpc), with comparable contributions from early feedback and SNe to the resulting X-ray luminosity; (ii) additional mechanisms such as gravitational heating, active galactic nuclei feedback, and/or Compton effects of GeV cosmic ray are necessary to generate the extended, volume-filling hot gaseous halo of MW-mass galaxies; (iii) the origins of hot corona in MW-like galaxies are partially distinct from those of the warm ($\sim10^5$ K) gas, by combining our previous finding that the SMUGGLE model successfully reproduces the kinematics and spatial distribution of MW O VI absorbers.
当前星系形成模型预测在类似银河系(MW)的星系周围存在发射X射线的气体晕。为了研究MW型星系中这种冕状气体的属性,我们基于SMUGGLE框架分析了一套高分辨率模拟,并将结果与MW和外部星系的X射线观测结果进行比较。我们发现,对于任何形式的恒星反馈(如早期反馈(包括恒星风和辐射)和/或超新星(SN)爆炸)的亚网格模型,其总0.5-2千电子伏的亮度在不确定性与MW的X射线观测结果和外部星系的缩放关系派生结果之间是一致的。然而,所有模型的X射线表面亮度分布曲线在距离约5千秒差距之外下降得太陡峭,低于最近的eROSITA堆叠结果所观察到的扩展发射。在所有亚网格规定中,模拟的表面亮度和发射量至少低于MW观测值一个到两个数量级,无反馈模型中出现最严重的差异。我们的结果表明:(i)恒星反馈主要塑造了最内部的热大气(中心约5千秒差距),早期反馈和超新星对最终的X射线亮度有相当的贡献;(ii)为了产生类似银河系质量的扩展、体积填充热气体晕,需要额外的机制,如引力加热、活动星系核反馈和/或GeV宇宙射线的康普顿效应;(iii)结合我们之前发现SMUGGLE模型成功再现了MW O VI吸收体的运动学和空间分布,MW型星系中热冕的起源与约10万度(暖)气体的起源部分不同。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 7 figures, 1 table;
Summary
该文本研究了基于SMUGGLE框架的高分辨率模拟下,类似于银河系(MW)的星系中的X射线发射气体特性。研究发现,考虑恒星反馈(如早期反馈和/或超新星爆发)的模型与银河系和外星系的X射线观测结果相符。然而,所有模型在约5kpc以外的区域X射线表面亮度分布下降得太快,低于最近的eROSITA叠加结果所观察到的扩展发射。这表明仅依靠恒星反馈无法完全解释观察到的现象,可能需要其他机制如引力加热、活动星系核反馈和/或相对论宇宙射线效应等生成延展性、体积填充热气体晕。因此,银河系类似星系的热冕的起源可能与较温暖(约10万度)气体的起源部分不同。
Key Takeaways
- 基于SMUGGLE框架的高分辨率模拟显示,对于考虑恒星反馈的模型,其与银河系及外星系的X射线观测结果一致。
- 所有的模拟模型在约5kpc以外的区域展现出X射线表面亮度分布下降过快的现象。
- 模拟结果与最近的eROSITA叠加结果相比,模拟的表面亮度和发射度量低于实际观测结果,差距达到至少1-2个数量级。
- 无反馈的模型出现了最严重的差异。
- 恒星反馈主要塑造了最内部的热大气(中心约5kpc),早期反馈和超新星对X射线光度有相当的贡献。
- 生成延展性、体积填充热气体晕可能需要额外的机制,如引力加热、活动星系核反馈和相对论宇宙射线效应等。
点此查看论文截图
Intercept Cancer: Cancer Pre-Screening with Large Scale Healthcare Foundation Models
Authors:Liwen Sun, Hao-Ren Yao, Gary Gao, Ophir Frieder, Chenyan Xiong
Cancer screening, leading to early detection, saves lives. Unfortunately, existing screening techniques require expensive and intrusive medical procedures, not globally available, resulting in too many lost would-be-saved lives. We present CATCH-FM, CATch Cancer early with Healthcare Foundation Models, a cancer pre-screening methodology that identifies high-risk patients for further screening solely based on their historical medical records. With millions of electronic healthcare records (EHR), we establish the scaling law of EHR foundation models pretrained on medical code sequences, pretrain compute-optimal foundation models of up to 2.4 billion parameters, and finetune them on clinician-curated cancer risk prediction cohorts. In our retrospective evaluation comprising of thirty thousand patients, CATCH-FM achieves strong efficacy, with 50% sensitivity in predicting first cancer risks at 99% specificity cutoff, and outperforming feature-based tree models and both general and medical LLMs by up to 20% AUPRC. Despite significant demographic, healthcare system, and EHR coding differences, CATCH-FM achieves state-of-the-art pancreatic cancer risk prediction on the EHRSHOT few-shot leaderboard, outperforming EHR foundation models pretrained using on-site patient data. Our analysis demonstrates the robustness of CATCH-FM in various patient distributions, the benefits of operating in the ICD code space, and its ability to capture non-trivial cancer risk factors. Our code will be open-sourced.
癌症筛查能够导致早期发现,从而拯救生命。然而,现有的筛查技术需要昂贵且侵入性的医疗程序,并非全球通用,导致许多本可挽救的生命丧失。我们提出CATCH-FM(CATCH Cancer early with Healthcare Foundation Models,即CATCH早期癌症与医疗基础模型),这是一种癌症预筛查方法,仅基于患者的历史医疗记录来确定高危患者,以供进一步筛查。我们利用数百万份电子健康记录(EHR),建立基于医疗编码序列的EHR基础模型的可扩展性法则,预训练了优化计算的最多高达2.4亿参数的基础模型,并通过医生精心策划的癌症风险预测队列进行微调。在我们的涵盖三万名患者的回顾性评估中,CATCH-FM表现出强大的有效性,在99%的特异性截断点预测首次癌症风险的敏感性达到50%,并且相较于基于特征树模型和一般与医疗LLM模型,其提高了高达20%的AUPRC。尽管存在显著的人口统计特征、医疗保健系统和EHR编码差异,CATCH-FM仍在EHRSHOT的少样本领导者名单上实现了最先进的胰腺癌风险预测水平,并超越了使用现场患者数据预训练的EHR基础模型。我们的分析展示了CATCH-FM在各种患者分布中的稳健性,以及在ICD代码空间中操作的好处以及其捕捉非重要癌症风险因素的能力。我们的代码将开源共享。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于历史医疗记录的癌症预筛查方法CATCH-FM,能够仅通过患者的历史医疗记录识别出高风险患者,为进一步的筛查提供依据,从而有助于癌症的早期发现。该方法通过对电子健康记录(EHR)进行规模化建模,训练出参数达数十亿的优化基础模型,并在临床医生策划的癌症风险预测队列中进行微调。在包含三万名患者的回顾性评估中,CATCH-FM表现出强大的效能,在预测首次癌症风险方面具有较高的灵敏度和特异性,且相较于基于特征的树模型和一般及医疗大型语言模型,具有更高的AUPRC值。尽管存在人口统计学、医疗系统和EHR编码差异,CATCH-FM在EHRSHOT少样本排行榜上仍实现了最先进的胰腺癌风险预测性能。分析表明,CATCH-FM在各种患者分布中表现稳健,在ICD代码空间中操作具有优势,并能捕捉非平凡的癌症风险因素。
关键见解
- CATCH-FM是一种基于历史医疗记录的癌症预筛查方法,可识别出高风险患者。
- 通过电子健康记录(EHR)建立规模化模型,训练出大型基础模型。
- CATCH-FM在预测首次癌症风险方面表现出高灵敏度和特异性。
- 与其他模型相比,CATCH-FM具有更高的AUPRC值。
- CATCH-FM在不同人口统计学、医疗系统和EHR编码背景下表现出稳健性。
- CATCH-FM在胰腺癌风险预测方面达到了最新技术水平。
- CATCH-FM能够捕捉非平凡的癌症风险因素。
点此查看论文截图
PathGene: Benchmarking Driver Gene Mutations and Exon Prediction Using Multicenter Lung Cancer Histopathology Image Dataset
Authors:Liangrui Pan, Qingchun Liang, Shen Zhao, Songqing Fan, Shaoliang Peng
Accurately predicting gene mutations, mutation subtypes and their exons in lung cancer is critical for personalized treatment planning and prognostic assessment. Faced with regional disparities in medical resources and the high cost of genomic assays, using artificial intelligence to infer these mutations and exon variants from routine histopathology images could greatly facilitate precision therapy. Although some prior studies have shown that deep learning can accelerate the prediction of key gene mutations from lung cancer pathology slides, their performance remains suboptimal and has so far been limited mainly to early screening tasks. To address these limitations, we have assembled PathGene, which comprises histopathology images paired with next-generation sequencing reports from 1,576 patients at the Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, and 448 TCGA-LUAD patients. This multi-center dataset links whole-slide images to driver gene mutation status, mutation subtypes, exon, and tumor mutational burden (TMB) status, with the goal of leveraging pathology images to predict mutations, subtypes, exon locations, and TMB for early genetic screening and to advance precision oncology. Unlike existing datasets, we provide molecular-level information related to histopathology images in PathGene to facilitate the development of biomarker prediction models. We benchmarked 11 multiple-instance learning methods on PathGene for mutation, subtype, exon, and TMB prediction tasks. These experimental methods provide valuable alternatives for early genetic screening of lung cancer patients and assisting clinicians to quickly develop personalized precision targeted treatment plans for patients. Code and data are available at https://github.com/panliangrui/NIPS2025/.
准确地预测肺癌中的基因突变、突变亚型及其外显子对于个性化治疗计划和预后评估至关重要。面对医疗资源的地域差异和高昂的基因组检测成本,利用人工智能从常规病理图像推断这些突变和外显子变异可以极大地促进精准治疗。虽然一些早期的研究已经表明深度学习可以加速从肺癌病理切片中预测关键基因突变,但其性能仍然不够理想,迄今为止主要局限于早期筛查任务。为了解决这些局限性,我们汇集了PathGene,它包括来自中南大学附属第二湘雅医院的1576名患者的病理图像和下一代测序报告,以及448名TCGA-LUAD患者。这个多中心数据集将全幻灯片图像与驱动基因突变状态、突变亚型、外显子和肿瘤突变负荷(TMB)状态相关联,旨在利用病理图像预测突变、亚型、外显子位置和TMB,用于早期基因筛查,并推动精准肿瘤学的发展。与现有数据集不同,PathGene提供了与病理图像相关的分子水平信息,有助于开发生物标志物预测模型。我们在PathGene上对突变、亚型、外显子和TMB预测任务进行了11种多实例学习方法基准测试。这些实验方法为肺癌患者的早期基因筛查提供了有价值的替代方案,帮助临床医生快速为患者制定个性化的精准靶向治疗方案。代码和数据可在https://github.com/panliangrui/NIPS2025/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This submission is being withdrawn because we identified issues in the analysis that may affect the results. A corrected version will be submitted in the future. The manuscript is withdrawn as it requires substantial revision. An improved version will be submitted in the future
Summary
本文介绍了利用人工智能从常规病理图像推断肺癌基因突变和基因外显子变异的重要性,以解决医疗资源分配不均和基因组检测成本高昂的问题。通过构建包含多中心数据的PathGene数据集,结合深度学习技术,旨在实现对肺癌基因突变、亚型、基因外显子位置和肿瘤突变负荷的预测,以推进精准肿瘤学的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 准确预测肺癌基因突变、亚型及外显子对个性化治疗计划和预后评估至关重要。
- 利用人工智能从常规病理图像推断基因突变有助于促进精准治疗。
- PathGene数据集结合多中心数据,包括病理图像和基因测序报告,旨在预测肺癌的多种遗传特征。
- PathGene数据集提供分子水平信息,有助于开发生物标志物预测模型。
- 多种实例学习方法被应用于PathGene数据集上进行突变、亚型、外显子和肿瘤突变负荷的预测任务。
- 这些方法对于早期肺癌患者的遗传筛查具有宝贵价值。
- 这些技术有助于临床医生快速为肺癌患者制定个性化的精准靶向治疗方案。
点此查看论文截图
cadrille: Multi-modal CAD Reconstruction with Online Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Maksim Kolodiazhnyi, Denis Tarasov, Dmitrii Zhemchuzhnikov, Alexander Nikulin, Ilya Zisman, Anna Vorontsova, Anton Konushin, Vladislav Kurenkov, Danila Rukhovich
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) plays a central role in engineering and manufacturing, making it possible to create precise and editable 3D models. Using a variety of sensor or user-provided data as inputs for CAD reconstruction can democratize access to design applications. However, existing methods typically focus on a single input modality, such as point clouds, images, or text, which limits their generalizability and robustness. Leveraging recent advances in vision-language models (VLM), we propose a multi-modal CAD reconstruction model that simultaneously processes all three input modalities. Inspired by large language model (LLM) training paradigms, we adopt a two-stage pipeline: supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on large-scale procedurally generated data, followed by reinforcement learning (RL) fine-tuning using online feedback, obtained programatically. Furthermore, we are the first to explore RL fine-tuning of LLMs for CAD tasks demonstrating that online RL algorithms such as Group Relative Preference Optimization (GRPO) outperform offline alternatives. In the DeepCAD benchmark, our SFT model outperforms existing single-modal approaches in all three input modalities simultaneously. More importantly, after RL fine-tuning, cadrille sets new state-of-the-art on three challenging datasets, including a real-world one.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造业中扮演着核心角色,使得创建精确且可编辑的3D模型成为可能。使用各种传感器或用户提供的数据作为CAD重建的输入,可以使设计应用程序的访问更加普及。然而,现有方法通常专注于单一输入模式,如点云、图像或文本,这限制了其通用性和稳健性。我们利用最近的视觉语言模型(VLM)进展,提出了一种多模态CAD重建模型,该模型可以同时处理三种输入模式。受到大型语言模型(LLM)训练范式的启发,我们采用了两阶段流程:首先在大量程序生成数据上进行有监督微调(SFT),然后采用在线反馈进行强化学习(RL)微调,这些反馈是通过程序获得的。此外,我们是首次探索RL微调LLM用于CAD任务的研究团队,表明在线RL算法(如集团相对偏好优化(GRPO))优于离线替代方案。在DeepCAD基准测试中,我们的SFT模型在所有三种输入模式上均优于现有的单模态方法。更重要的是,经过RL微调后,“cadrille”在三个具有挑战性的数据集上均达到了最新水平,包括一个真实世界的数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造业中的核心作用,研究提出一种多模态CAD重建模型,可同时处理点云、图像和文本三种输入模态。该模型采用大型语言模型(LLM)的训练范式,通过监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)两个阶段进行训练。在DeepCAD基准测试中,该模型在三种输入模态上的性能均优于现有的单模态方法。经过RL微调后,该模型在三个具有挑战性的数据集上创造了新的技术水准,包括一个真实世界的数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机辅助设计(CAD)在工程和制造业中扮演着核心角色,能够创建精确且可编辑的3D模型。
- 现有的CAD重建方法主要关注单一的输入模态,如点云、图像或文本,这限制了其通用性和稳健性。
- 研究提出了一种多模态CAD重建模型,能够同时处理三种输入模态,提高了模型的泛化能力和稳健性。
- 该模型采用大型语言模型的训练范式,通过监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)两个阶段进行训练。
- 研究首次探索了用于CAD任务的LLM的RL微调,并发现在线RL算法如Group Relative Preference Optimization(GRPO)优于离线替代方案。
- 在DeepCAD基准测试中,该模型性能优于现有的单模态方法,同时处理所有三种输入模态。
点此查看论文截图
Towards Scalable Language-Image Pre-training for 3D Medical Imaging
Authors:Chenhui Zhao, Yiwei Lyu, Asadur Chowdury, Edward Harake, Akhil Kondepudi, Akshay Rao, Xinhai Hou, Honglak Lee, Todd Hollon
The scalability of current language-image pre-training for 3D medical imaging, such as CT and MRI, is constrained by the need for radiologists to manually curate raw clinical studies. In this work, we pioneer pre-training directly on uncurated studies, which both aligns more closely with the radiologist’s workflow and provides a natural path to scalability. However, the unique structure of such data presents new challenges for existing model architectures, which were originally designed for 2D slices or single 3D scans. To address this, we introduce a novel hierarchical attention mechanism inspired by the intrinsic hierarchy of radiology data: slice, scan, and study. We denote our framework as Hierarchical attention for Language-Image Pre-training (HLIP). Trained on 220K studies with 3.13 million scans for brain MRI and 240K studies with 1.44 million scans for head CT, HLIP achieves state-of-the-art performance, e.g., +10.5% balanced ACC on the proposed publicly available brain MRI benchmark Pub-Brain-5; +8.3% and +1.7% macro AUC on head CT benchmarks CQ500 and RSNA, respectively. HLIP also exhibits strong generalizability on existing 3D medical language-image pre-training benchmarks, e.g., +4.3% macro AUC on the Rad-ChestCT benchmark when pre-trained on CT-RATE. These results demonstrate that, with HLIP, directly pre-training on uncurated clinical datasets is a scalable and effective direction for language-image pre-training in 3D medical imaging. The code is available at https://github.com/Zch0414/hlip.
当前针对如CT和MRI等3D医学影像的语言图像预训练的可扩展性受限于放射科医生需要手动整理原始临床研究的需求。在这项工作中,我们率先对未整理的研究进行直接预训练,这更符合放射科医生的工作流程,并为实现可扩展性提供了自然路径。然而,此类数据的独特结构给现有模型架构带来了新挑战,这些模型最初是为2D切片或单个3D扫描而设计的。为了解决这一问题,我们受放射数据内在层次结构的启发,引入了一种新型层次注意机制:切片、扫描和研究。我们将我们的框架称为用于语言图像预训练的分层注意力(HLIP)。在24万项研究、涉及包含144万扫描的大脑MRI上以及涉及超过数百万切片的大型真实头部CT数据上进行训练后,HLIP取得了最先进的性能,例如在提出的公开可用的大脑MRI基准测试Pub-Brain-5上提高了+10.5%的平衡准确度;在头部CT基准测试CQ500和RSNA上分别提高了+8.3%和+1.7%的宏AUC。HLIP在现有的三维医学语言图像预训练基准测试中表现出强大的泛化能力,例如在CT-RATE上预训练后在Rad-ChestCT基准测试上提高了+4.3%的宏AUC。这些结果表明,使用HLIP对未整理的临床数据集进行直接预训练是医学影像领域语言图像预训练的可扩展和有效方向。代码可在https://github.com/Zch0414/hlip访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
当前语言图像在医学领域的预训练受限于放射科医生手动筛选原始临床研究的需要。本研究率先尝试直接在未筛选的研究上进行预训练,更符合放射科医生的工作流程,并为扩大规模提供了自然路径。针对此类数据的独特结构带来的挑战,本研究引入了一种新颖的层次注意力机制,借鉴放射数据的内在层次结构:切片、扫描和研究。我们称之为用于语言图像预训练的层次注意力框架(HLIP)。在公开可用的脑MRI基准测试Pub-Brain-5上,HLIP取得了领先水平,如平衡准确率提高10.5%;在头部CT基准测试CQ500和RSNA上,宏观AUC分别提高8.3%和1.7%。HLIP在现有的医学三维语言图像预训练基准测试中展现出强大的泛化能力。此方法的代码已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 当前医学图像预训练受限于手动筛选临床研究的繁琐过程。
- 研究首次尝试在未筛选的研究数据上直接进行预训练,更贴近放射科医生的工作流程并实现规模化。
- 为解决数据独特结构带来的挑战,引入了新颖的层次注意力机制,包括切片、扫描和研究三个层次。
- HLIP框架在多个基准测试中表现优异,如Pub-Brain-5上的平衡准确率提高10.5%。
- HLIP展现出强大的泛化能力,适用于多种医学三维语言图像预训练场景。
点此查看论文截图
DescriptorMedSAM: Language-Image Fusion with Multi-Aspect Text Guidance for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Wenjie Zhang, Liming Luo, Mengnan He, Jiarui Hai, Jiancheng Ye
Accurate organ segmentation is essential for clinical tasks such as radiotherapy planning and disease monitoring. Recent foundation models like MedSAM achieve strong results using point or bounding-box prompts but still require manual interaction. We propose DescriptorMedSAM, a lightweight extension of MedSAM that incorporates structured text prompts, ranging from simple organ names to combined shape and location descriptors to enable click-free segmentation. DescriptorMedSAM employs a CLIP text encoder to convert radiology-style descriptors into dense embeddings, which are fused with visual tokens via a cross-attention block and a multi-scale feature extractor. We designed four descriptor types: Name (N), Name + Shape (NS), Name + Location (NL), and Name + Shape + Location (NSL), and evaluated them on the FLARE 2022 dataset under zero-shot and few-shot settings, where organs unseen during training must be segmented with minimal additional data. NSL prompts achieved the highest performance, with a Dice score of 0.9405 under full supervision, a 76.31% zero-shot retention ratio, and a 97.02% retention ratio after fine-tuning with only 50 labeled slices per unseen organ. Adding shape and location cues consistently improved segmentation accuracy, especially for small or morphologically complex structures. We demonstrate that structured language prompts can effectively replace spatial interactions, delivering strong zero-shot performance and rapid few-shot adaptation. By quantifying the role of descriptor, this work lays the groundwork for scalable, prompt-aware segmentation models that generalize across diverse anatomical targets with minimal annotation effort.
精确器官分割对于临床任务(如放疗计划和疾病监测)至关重要。最近的MedSAM等基础模型通过使用点或边界框提示取得了强大的结果,但仍需要手动交互。我们提出了DescriptorMedSAM,它是MedSAM的轻量级扩展,结合了结构化的文本提示,从简单的器官名称到结合形状和位置描述符,以实现无需点击的分割。DescriptorMedSAM采用CLIP文本编码器将放射学风格的描述符转换为密集嵌入,通过跨注意力块和多尺度特征提取器与视觉令牌融合。我们设计了四种描述符类型:名称(N)、名称+形状(NS)、名称+位置(NL)和名称+形状+位置(NSL),并在FLARE 2022数据集上进行了零样本和少样本设置下的评估,其中在训练期间未见的器官必须在没有额外数据的情况下进行分割。NSL提示在全监督下获得了最高性能,Dice分数为0.9405,零样本保留率为76.31%,仅在看不见的器官上有50个标签切片后进行微调时保留率为97.02%。添加形状和位置线索可以持续改善分割精度,尤其是对于小型或形态复杂的结构。我们证明了结构化语言提示可以有效地替代空间交互,提供强大的零样本性能,并快速适应少数样本。通过对描述符的作用进行量化,这项工作奠定了可扩展、提示感知分割模型的基础,这些模型可以在多种解剖目标之间进行泛化,并减少注释工作量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了DescriptorMedSAM模型,它是MedSAM的轻量级扩展。该模型采用结构化文本提示,结合点或边界框提示,实现了无需点击的分割。通过融合放射学描述符号与视觉标记,DescriptorMedSAM在FLARE 2022数据集上取得了优异的性能,特别是结合形状和位置提示时表现更佳。此模型为可扩展、提示感知的分割模型奠定了基础,能够跨多种解剖目标进行泛化,并减少标注工作量。
Key Takeaways
- DescriptorMedSAM是MedSAM的轻量级扩展,用于实现无需点击的器官分割。
- 该模型采用结构化文本提示,包括器官名称、形状和位置描述等。
- DescriptorMedSAM在FLARE 2022数据集上进行了零样本和少样本设置下的评估,显示出很高的性能。
- 结合形状和位置提示显著提高分割精度,特别是在小或形态复杂的结构上。
- 该模型可有效替代空间交互,实现强大的零样本性能和快速的少样本适应。
- DescripterMedSAM为可扩展、提示感知的分割模型奠定了基础,能够泛化到不同的解剖目标。
点此查看论文截图
LLaVA-RadZ: Can Multimodal Large Language Models Effectively Tackle Zero-shot Radiology Recognition?
Authors:Bangyan Li, Wenxuan Huang, Zhenkun Gao, Yeqiang Wang, Yunhang Shen, Jingzhong Lin, Ling You, Yuxiang Shen, Shaohui Lin, Wanli Ouyang, Yuling Sun
Recently, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in visual understanding and reasoning across various vision-language tasks. However, we found that MLLMs cannot process effectively from fine-grained medical image data in the traditional Visual Question Answering (VQA) pipeline, as they do not exploit the captured features and available medical knowledge fully, results in MLLMs usually performing poorly in zero-shot medical disease recognition. Fortunately, this limitation does not indicate that MLLMs are fundamentally incapable of addressing fine-grained recognition tasks. From a feature representation perspective, MLLMs demonstrate considerable potential for tackling such challenging problems. Thus, to address this challenge, we propose LLaVA-RadZ, a simple yet effective framework for zero-shot medical disease recognition via utilizing the existing MLLM features. Specifically, we design an end-to-end training strategy, termed Decoding-Side Feature Alignment Training (DFAT) to take advantage of the characteristics of the MLLM decoder architecture and incorporate modality-specific tokens tailored for different modalities. Additionally, we introduce a Domain Knowledge Anchoring Module (DKAM) to exploit the intrinsic medical knowledge of large models, which mitigates the category semantic gap in image-text alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our LLaVA-RadZ significantly outperforms traditional MLLMs in zero-shot disease recognition, achieving the comparable performance to the well-established and highly-optimized CLIP-based approaches.
最近,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在各种视觉语言任务中表现出了出色的视觉理解和推理能力。然而,我们发现MLLMs在传统的视觉问答(VQA)管道中无法有效地处理精细的医学图像数据,因为它们没有充分利用捕获的特征和可用的医学知识,导致MLLMs通常在零样本医疗疾病识别中表现不佳。幸运的是,这一局限性并不意味着MLLMs从根本上无法解决精细识别任务。从特征表示的角度来看,MLLMs在解决此类挑战性问题方面显示出巨大的潜力。因此,为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了LLaVA-RadZ框架,这是一个利用现有MLLM特征进行零样本医疗疾病识别的简单有效的框架。具体来说,我们设计了一种端到端的训练策略,称为解码侧特征对齐训练(DFAT),以利用MLLM解码器的特点,并融入针对不同模态的特定标记。此外,我们引入了领域知识锚定模块(DKAM),以利用大型模型的内在医学知识,这减轻了图像文本对齐中的类别语义差距。大量实验表明,我们的LLaVA-RadZ在零样本疾病识别方面显著优于传统MLLMs,其性能与经过良好验证和优化过的CLIP方法相当。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态大型语言模型在处理细粒度医学图像数据时存在局限性,无法有效地进行视觉理解和推理。针对这一问题,提出了LLaVA-RadZ框架,利用现有MLLM特性进行零样本医学疾病识别。通过设计解码侧特征对齐训练策略(DFAT)和领域知识锚定模块(DKAM),该框架显著提高了零样本疾病识别的性能,达到与经过良好优化和高度优化的CLIP方法相当的水平。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型在医学图像领域的细粒度识别任务中存在局限性。
- LLaVA-RadZ框架旨在解决这一问题,并提高了零样本医学疾病识别的性能。
- LLaVA-RadZ利用多模态大型语言模型的特性,通过设计解码侧特征对齐训练策略(DFAT)优化模型性能。
- 引入领域知识锚定模块(DKAM)以利用大型模型的内在医学知识。
- LLaVA-RadZ在零样本疾病识别方面表现出卓越性能,与经过高度优化的CLIP方法相当。
- 该框架简单有效,适用于医学图像领域的细粒度识别任务。
点此查看论文截图
Rethinking domain generalization in medical image segmentation: One image as one domain
Authors:Jin Hong, Bo Liu, Qiankun Zuo, Guoli Long, Siyue Li, Yudong Zhang, Shuihua Wang, Junxin Chen
Domain shifts in medical image segmentation, particularly when data comes from different centers, pose significant challenges. Intra-center variability, such as differences in scanner models or imaging protocols, can cause domain shifts as large as, or even larger than, those between centers. To address this, we propose the “one image as one domain” (OIOD) hypothesis, which treats each image as a unique domain, enabling flexible and robust domain generalization. Based on this hypothesis, we develop a unified disentanglement-based domain generalization (UniDDG) framework, which simultaneously handles both multi-source and single-source domain generalization without requiring explicit domain labels. This approach simplifies training with a fixed architecture, independent of the number of source domains, reducing complexity and enhancing scalability. We decouple each input image into content representation and style code, then exchange and combine these within the batch for segmentation, reconstruction, and further disentanglement. By maintaining distinct style codes for each image, our model ensures thorough decoupling of content representations and style codes, improving domain invariance of the content representations. Additionally, we enhance generalization with expansion mask attention (EMA) for boundary preservation and style augmentation (SA) to simulate diverse image styles, improving robustness to domain shifts. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves Dice scores of 84.43% and 88.91% for multi-source to single-center and single-center generalization in optic disc and optic cup segmentation, respectively, and 86.96% and 88.56% for prostate segmentation, outperforming current state-of-the-art domain generalization methods, offering superior performance and adaptability across clinical settings.
医学图像分割中的领域漂移,特别是当数据来自不同中心时,带来了重大挑战。来自同一中心的内部差异(如扫描仪型号或成像协议的不同)可能产生与不同中心之间的差异一样大的领域漂移,甚至更大。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了“一图一个领域”(OIOD)假设,将每一张图像视为一个独特的领域,以实现灵活和稳健的领域泛化。基于这一假设,我们开发了一个统一的基于分离的领域泛化(UniDDG)框架,可以同时处理多源和单源领域泛化,无需明确的领域标签。这种方法简化了使用固定架构的训练过程,无论源领域数量如何,都降低了复杂性并增强了可扩展性。我们将每个输入图像解耦为内容表示和风格代码,然后在批次内交换并结合这些代码进行分割、重建和进一步的解耦。通过保持每个图像独特的风格代码,我们的模型确保了内容表示和风格代码的彻底解耦,提高了内容表示的领域不变性。此外,我们利用扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)进行边界保留和风格增强(SA)来模拟多种图像风格,提高模型对领域漂移的稳健性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视盘和视杯分割的多源到单中心以及单中心泛化中分别实现了84.43%和88.91%的Dice得分,前列腺分割中分别实现了86.96%和88.56%的Dice得分。该方法在医学图像分割领域超越了现有的最先进的领域泛化方法,在各种临床环境中表现出了卓越的性能和适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对医学图像分割中的跨中心数据引起的领域漂移问题,提出“一幅图像作为一个领域”(OIOD)假设和基于统一解纠缠的领域泛化(UniDDG)框架。该方法无需明确的领域标签即可同时处理多源和单源领域泛化问题。通过将输入图像解耦为内容表示和风格代码,并在批次内进行交换和组合,以实现分割、重建和进一步的解纠缠。通过为每个图像维护独特的风格代码,确保了内容表示和风格代码的完全解耦,提高了内容表示的领域不变性。在光学圆盘、光学杯状物的分割以及前列腺分割的实验中,该方法实现了出色的性能,超越了现有的领域泛化方法,为临床环境中的不同设置提供了优越的性能和适应性。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割中的跨中心和跨模型数据导致领域漂移的挑战。
- 提出“一幅图像作为一个领域”(OIOD)假设,将每幅图像视为独特领域,实现灵活和稳健的领域泛化。
- 发展基于统一解纠缠的领域泛化(UniDDG)框架,无需明确的领域标签即可处理多源和单源领域泛化问题。
- 通过解耦输入图像为内容表示和风格代码,简化训练并增强领域泛化能力。
- 通过维护每个图像独特的风格代码,确保内容表示和风格代码的完全解耦。
- 使用扩展掩膜注意力(EMA)和风格增强(SA)进一步提高领域泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图
CADSpotting: Robust Panoptic Symbol Spotting on Large-Scale CAD Drawings
Authors:Fuyi Yang, Jiazuo Mu, Yanshun Zhang, Mingqian Zhang, Junxiong Zhang, Yongjian Luo, Lan Xu, Jingyi Yu, Yujiao Shi, Yingliang Zhang
We introduce CADSpotting, an effective method for panoptic symbol spotting in large-scale architectural CAD drawings. Existing approaches often struggle with symbol diversity, scale variations, and overlapping elements in CAD designs, and typically rely on additional features (e.g., primitive types or graphical layers) to improve performance. CADSpotting overcomes these challenges by representing primitives through densely sampled points with only coordinate attributes, using a unified 3D point cloud model for robust feature learning. To enable accurate segmentation in large drawings, we further propose a novel Sliding Window Aggregation (SWA) technique that combines weighted voting and Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Moreover, we introduce LS-CAD, a new large-scale dataset comprising 45 finely annotated floorplans, each covering approximately 1,000 $m^2$, significantly larger than prior benchmarks. LS-CAD will be publicly released to support future research. Experiments on FloorPlanCAD and LS-CAD demonstrate that CADSpotting significantly outperforms existing methods. We also showcase its practical value by enabling automated parametric 3D interior reconstruction directly from raw CAD inputs.
我们介绍了CADSpotting,这是一种在大型建筑CAD图纸中进行全景符号识别的高效方法。现有方法通常面临符号多样性、尺度变化和CAD设计中的重叠元素等挑战,并且通常依赖额外的特征(例如基本类型或图形层)来提高性能。CADSpotting通过仅具有坐标属性的密集采样点来表示基本元素,使用统一的3D点云模型进行稳健的特征学习,从而克服了这些挑战。为了在大图中实现精确分割,我们进一步提出了一种新型的滑动窗口聚合(SWA)技术,该技术结合了加权投票和非极大值抑制(NMS)。此外,我们引入了LS-CAD,这是一个新的大规模数据集,包含45个精细标注的平面图,每个平面图覆盖约1000平方米,显著大于先前的基准测试。LS-CAD将公开发布,以支持未来的研究。在FloorPlanCAD和LS-CAD上的实验表明,CADSpotting显著优于现有方法。我们还通过直接从原始CAD输入进行自动化的参数化3D室内重建,展示了其实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16pages, 14 figures, Project web-page: https://dgeneai.github.io/cadspotting-pages/
Summary
CADSpotting方法能有效解决大规模建筑CAD绘图中的全景符号识别问题。现有方法常面临符号多样性、尺度变化和元素重叠等挑战,并通常依赖额外特征(如原始类型或图形层)来提高性能。CADSpotting通过密集采样点并用统一的三维点云模型进行稳健特征学习来克服这些挑战。此外,提出了新颖的滑动窗口聚合(SWA)技术,结合加权投票和非极大值抑制(NMS)实现准确的大图分割。并引入了新型大规模数据集LS-CAD,包含45个精细标注的平面图,每个平面图约覆盖1000平方米,显著超过先前基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- CADSpotting是一种有效的全景符号识别方法,适用于大规模建筑CAD绘图。
- 现有方法面临符号多样性、尺度变化和元素重叠的挑战。
- CADSpotting通过密集采样点和统一的三维点云模型进行稳健特征学习。
- 提出了滑动窗口聚合(SWA)技术,结合加权投票和非极大值抑制(NMS)实现准确的大图分割。
- 引入了新型大规模数据集LS-CAD,用于支持未来研究。
- CADSpotting在FloorPlanCAD和LS-CAD上的实验结果表明其显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
Development and Validation of a Large Language Model for Generating Fully-Structured Radiology Reports
Authors:Chuang Niu, Md Sayed Tanveer, Md Zabirul Islam, Parisa Kaviani, Qing Lyu, Mannudeep K. Kalra, Christopher T. Whitlow, Ge Wang
Current LLMs for creating fully-structured reports face the challenges of formatting errors, content hallucinations, and privacy leakage issues when uploading data to external servers.We aim to develop an open-source, accurate LLM for creating fully-structured and standardized LCS reports from varying free-text reports across institutions and demonstrate its utility in automatic statistical analysis and individual lung nodule retrieval. With IRB approvals, our retrospective study included 5,442 de-identified LDCT LCS radiology reports from two institutions. We constructed two evaluation datasets by labeling 500 pairs of free-text and fully-structured radiology reports and one large-scale consecutive dataset from January 2021 to December 2023. Two radiologists created a standardized template for recording 27 lung nodule features on LCS. We designed a dynamic-template-constrained decoding method to enhance existing LLMs for creating fully-structured reports from free-text radiology reports. Using consecutive structured reports, we automated descriptive statistical analyses and a nodule retrieval prototype. Our best LLM for creating fully-structured reports achieved high performance on cross-institutional datasets with an F1 score of about 97%, with neither formatting errors nor content hallucinations. Our method consistently improved the best open-source LLMs by up to 10.42%, and outperformed GPT-4o by 17.19%. The automatically derived statistical distributions were consistent with prior findings regarding attenuation, location, size, stability, and Lung-RADS. The retrieval system with structured reports allowed flexible nodule-level search and complex statistical analysis. Our developed software is publicly available for local deployment and further research.
当前的大型语言模型在创建全结构化报告时面临着格式错误、内容幻觉和隐私泄露的挑战,尤其是在将数据上传到外部服务器时。我们的目标是开发一种开源、精确的大型语言模型,用于从不同机构的自由文本报告创建全结构化、标准化的LCS报告,并展示其在自动统计分析和个人肺结节检索中的实用性。经过伦理审查委员会批准,我们的回顾性研究纳入了来自两个机构的5442份去标识化的LDCT LCS放射学报告。我们通过标记500对自由文本和全结构化放射学报告构建了两个评估数据集,以及一个从2021年1月至2023年12月的大规模连续数据集。两位放射科医生为LCS上记录27个肺结节特征创建了一个标准化模板。我们设计了一种动态模板约束解码方法,以增强现有大型语言模型从自由文本放射学报告中生成全结构化报告的能力。使用连续的结构化报告,我们自动化了描述性统计分析和一个结节检索原型。我们创建全结构化报告的最佳大型语言模型在跨机构数据集上实现了高达约97%的F1分数,没有出现格式错误或内容幻觉。我们的方法不断改进了最佳开源大型语言模型,提高了最多达10.42%,并且比GPT-4o提高了17.19%。自动得出的统计分布与关于衰减、位置、大小、稳定性和Lung-RADS的先前发现一致。使用结构化报告的检索系统可以进行灵活的结节级搜索和复杂的统计分析。我们开发的软件可公开用于本地部署和进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(LLM)在创建结构化报告时面临的挑战,如格式错误、内容幻觉和隐私泄露问题。研究团队开发了一个开源、准确的LLM,能够从不同机构的自由文本报告创建标准化结构化肺癌筛查(LCS)报告,并展示了其在自动统计分析及个性化肺结节检索中的应用。通过回顾性研究,验证了模型的高性能,并公开了开发的软件供进一步研究使用。
Key Takeaways
- 当前LLM在创建结构化报告时存在格式错误、内容幻觉和隐私泄露的问题。
- 研究团队开发了一个开源的LLM,能够创建标准化的结构化LCS报告。
- 该LLM可以从不同机构的自由文本报告中生成结构化报告。
- 通过回顾性研究验证了LLM的高性能。
- 该LLM在自动统计分析和肺结节检索方面表现出实用性。
- 最佳LLM的F1分数达到约97%,且在跨机构数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
A Unified Deep Learning Framework for Motion Correction in Medical Imaging
Authors:Jian Wang, Razieh Faghihpirayesh, Danny Joca, Polina Golland, Ali Gholipour
Deep learning has shown significant value in image registration, however, current techniques are either limited by the type and range of motion they can handle, or require iterative inference and/or retraining for new imaging data. To address these limitations, we introduce UniMo, a Unified Motion Correction framework that leverages deep neural networks to correct diverse motion in medical imaging. UniMo employs an alternating optimization scheme for a unified loss function to train an integrated model of 1) an equivariant neural network for global rigid motion correction and 2) an encoder-decoder network for local deformations. It features a geometric deformation augmenter that 1) enhances the robustness of global correction by addressing local deformations from non-rigid motion or geometric distortions, and 2) generates augmented data to improve training. UniMo is a hybrid model that uses both image intensities and shapes to achieve robust performance amid appearance variations, and therefore generalizes to multiple imaging modalities without retraining. We trained and tested UniMo to track motion in fetal magnetic resonance imaging, a challenging application due to 1) both large rigid and non-rigid motion, and 2) wide variations in image appearance. We then evaluated the trained model, without retraining, on MedMNIST, lung CT, and BraTS datasets. Results show that UniMo surpassed existing motion correction methods in accuracy, and notably enabled one-time training on a single modality while maintaining high stability and adaptability across unseen datasets. By offering a unified solution to motion correction, UniMo marks a significant advance in medical imaging, especially in applications with combined bulk and local motion. The code is available at: https://github.com/IntelligentImaging/UNIMO
深度学习在图像配准中显示出显著的价值,然而,当前的技术要么受限于它们能够处理的类型和范围的运动,要么需要对新的成像数据进行迭代推理和(或)重新训练。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了UniMo,这是一个利用深度神经网络校正医学影像中各种运动的统一运动校正框架。UniMo采用交替优化方案,为统一的损失函数训练一个集成模型,该模型包括1)用于全局刚体运动校正的等价神经网络和2)用于局部变形的编码器-解码器网络。它包含一个几何变形增强器,该增强器1)通过解决非刚体运动或几何失真引起的局部变形,增强了全局校正的稳健性,2)生成增强数据以改进训练。UniMo是一个混合模型,它使用图像强度和形状来实现稳健性能,因此能够在外观变化中保持通用性,并推广应用于多种成像模式而无需重新训练。我们训练和测试了UniMo以跟踪胎儿磁共振成像中的运动,这是一个具有挑战性的应用,因为既存在大量的刚性和非刚性运动,而且图像外观也存在很大的变化。然后我们在MedMNIST、肺部CT和BraTS数据集上评估了训练好的模型(无需重新训练)。结果表明,UniMo在准确性上超越了现有的运动校正方法,特别是在单一模态的一次性训练上表现出色,同时在跨未见数据集时保持了高度的稳定性和适应性。通过为运动校正提供统一的解决方案,UniMo在医学影像中取得了重大进展,尤其是在具有整体和局部运动的组合应用中。代码可访问于:https://github.com/IntelligentImaging/UNIMO
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures
摘要
深度学习在图像配准中展现出显著价值,但当前技术存在处理类型和范围受限的问题,或是需要针对新的成像数据进行迭代推断和再训练。为解决这些限制,我们推出了UniMo——一个统一运动校正框架,利用深度神经网络校正医学成像中的多样运动。UniMo采用交替优化方案来为一个统一的损失函数训练一个集成模型,该模型包括用于全局刚体运动校正的等价神经网络和用于局部变形的编码器-解码器网络。它拥有一个几何变形增强器,旨在通过解决非刚性运动或几何失真引起的局部变形问题,增强全局校正的稳健性,并生成扩充数据以改进训练。UniMo是一个混合模型,同时使用图像强度和形状来实现稳健性能,因此在外观变化中表现出色,并能推广到多种成像模式而无需重新训练。我们对胎儿磁共振成像这一具有挑战性的应用进行了训练和测试,该应用存在大量刚性和非刚性运动以及广泛的图像外观变化。然后我们在MedMNIST、肺部CT和BraTS数据集上评估了训练好的模型。结果表明,UniMo在准确性上超越了现有的运动校正方法,并且能够在单一模态上一次训练后,维持高稳定性和适应性处理未见数据集。UniMo的统一运动校正解决方案标志着医学成像领域的重大进展,尤其是在存在整体和局部运动的应用中。相关代码可通过https://github.com/IntelligentImaging/UNIMO获取。
关键见解
- UniMo是一个统一运动校正框架,用于医学成像中的多样运动校正。
- 该框架结合深度神经网络进行全局和局部运动校正。
- UniMo采用交替优化方案和几何变形增强器提高模型性能。
- UniMo能够处理多种成像模式,而无需针对新数据重新训练模型。
- 在具有挑战性的胎儿磁共振成像应用中,UniMo表现出卓越的性能。
- UniMo在多个数据集上的表现优于现有的运动校正方法。
点此查看论文截图
Img2CAD: Reverse Engineering 3D CAD Models from Images through VLM-Assisted Conditional Factorization
Authors:Yang You, Mikaela Angelina Uy, Jiaqi Han, Rahul Thomas, Haotong Zhang, Yi Du, Hansheng Chen, Francis Engelmann, Suya You, Leonidas Guibas
Reverse engineering 3D computer-aided design (CAD) models from images is an important task for many downstream applications including interactive editing, manufacturing, architecture, robotics, etc. The difficulty of the task lies in vast representational disparities between the CAD output and the image input. CAD models are precise, programmatic constructs that involve sequential operations combining discrete command structure with continuous attributes, making it challenging to learn and optimize in an end-to-end fashion. Concurrently, input images introduce inherent challenges such as photometric variability and sensor noise, complicating the reverse engineering process. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that conditionally factorizes the task into two sub-problems. First, we leverage vision-language foundation models (VLMs), a finetuned Llama3.2, to predict the global discrete base structure with semantic information. Second, we propose TrAssembler that, conditioned on the discrete structure with semantics, predicts the continuous attribute values. To support the training of our TrAssembler, we further constructed an annotated CAD dataset of common objects from ShapeNet. Putting all together, our approach and data demonstrate significant first steps towards CAD-ifying images in the wild. Code and data can be found in https://github.com/qq456cvb/Img2CAD.
从图像中逆向工程3D计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型是许多下游应用的重要任务,包括交互式编辑、制造、建筑、机器人等。该任务的难度在于CAD输出与图像输入之间存在的巨大代表性差异。CAD模型是精确的程序构建,涉及将离散命令结构与连续属性相结合进行顺序操作,以端到端的方式学习和优化具有挑战性。同时,输入图像带来了固有的挑战,例如光度变化和传感器噪声,使逆向工程过程复杂化。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型方法,该方法有条件地将任务分解为两个子问题。首先,我们利用视觉语言基础模型(VLMs)和经过微调后的Llama3.2来预测带有语义信息的全局离散基础结构。其次,我们提出了TrAssembler,它在给定带有语义的离散结构条件下,预测连续属性值。为了支持TrAssembler的训练,我们还构建了来自ShapeNet的常见对象注释CAD数据集。综上所述,我们的方法和数据为在野外实现图像的CAD化迈出了重要的一步。代码和数据可在https://github.com/qq456cvb/Img2CAD中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to SIGGRAPH Asia 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种从图像中逆向工程3D计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型的新方法,该方法将任务分为两个子问题。首先,利用视觉语言基础模型(VLMs)预测带有语义信息的全局离散基础结构;其次,提出TrAssembler,根据离散结构和语义预测连续属性值。为支持TrAssembler的训练,还构建了一个来自ShapeNet的常见物体CAD数据集。此方法实现了从自然图像到CAD模型的转化。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了从图像中逆向工程3D CAD模型的重要性及其在多个领域的应用价值。
- 任务难度体现在CAD输出与图像输入之间的巨大代表性差异。
- CAD模型涉及离散命令结构与连续属性的组合,使得端到端的优化学习更具挑战性。
- 图像输入存在固有的挑战,如光度变化和传感器噪声,增加了逆向工程的复杂性。
- 提出了一种新的方法,将任务分为两个子问题:预测全局离散基础结构并带有语义信息,以及根据离散结构和语义预测连续属性值。
- 为了支持TrAssembler的训练,构建了一个来自ShapeNet的常见物体CAD数据集。
