⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-30 更新
Integrating Background Knowledge in Medical Semantic Segmentation with Logic Tensor Networks
Authors:Luca Bergamin, Giovanna Maria Dimitri, Fabio Aiolli
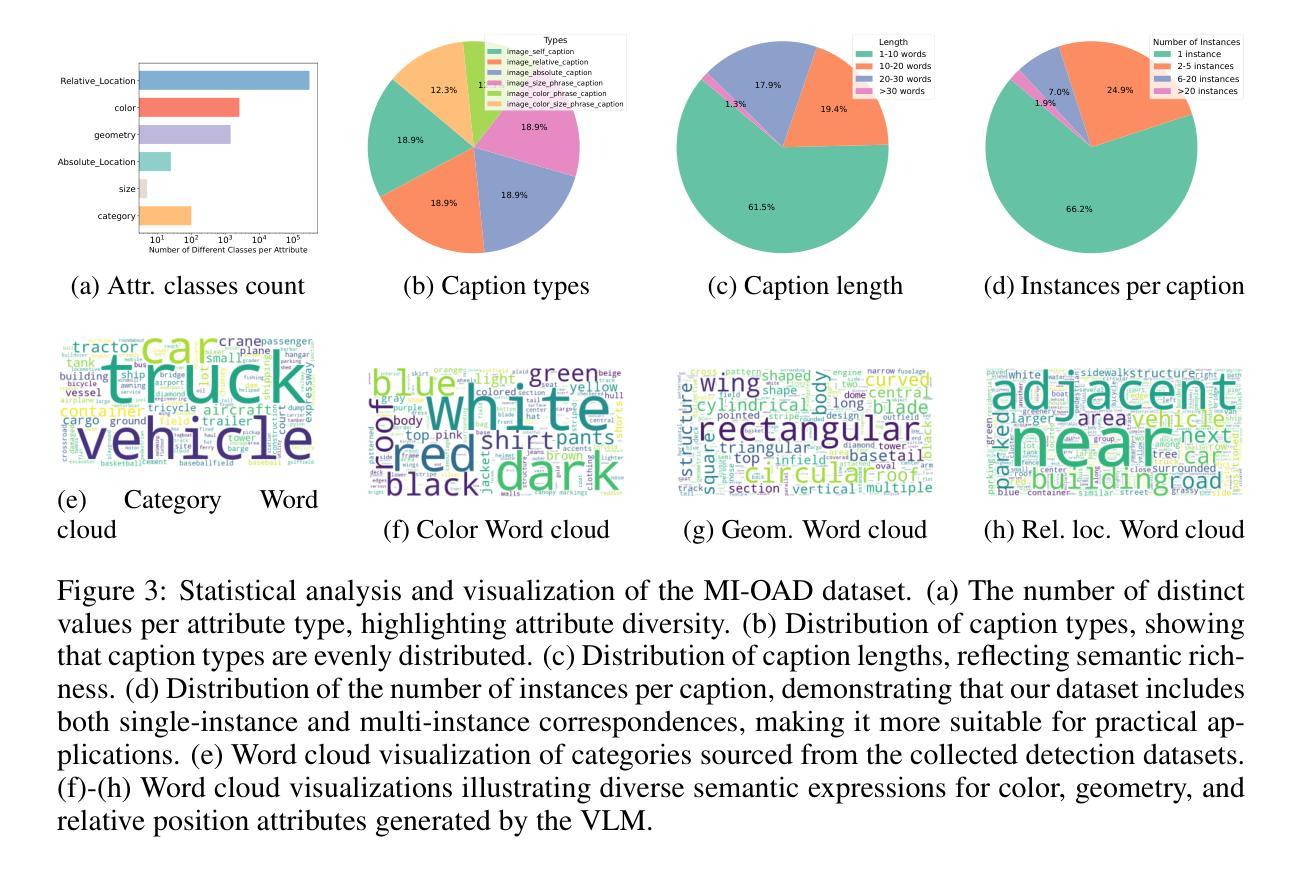
Semantic segmentation is a fundamental task in medical image analysis, aiding medical decision-making by helping radiologists distinguish objects in an image. Research in this field has been driven by deep learning applications, which have the potential to scale these systems even in the presence of noise and artifacts. However, these systems are not yet perfected. We argue that performance can be improved by incorporating common medical knowledge into the segmentation model’s loss function. To this end, we introduce Logic Tensor Networks (LTNs) to encode medical background knowledge using first-order logic (FOL) rules. The encoded rules span from constraints on the shape of the produced segmentation, to relationships between different segmented areas. We apply LTNs in an end-to-end framework with a SwinUNETR for semantic segmentation. We evaluate our method on the task of segmenting the hippocampus in brain MRI scans. Our experiments show that LTNs improve the baseline segmentation performance, especially when training data is scarce. Despite being in its preliminary stages, we argue that neurosymbolic methods are general enough to be adapted and applied to other medical semantic segmentation tasks.
语义分割是医学图像分析中的一项基本任务,通过帮助放射科医生区分图像中的对象来辅助医疗决策。该领域的研究主要受到深度学习应用驱动,深度学习具有在存在噪声和伪影的情况下也能扩展这些系统的潜力。然而,这些系统尚未完善。我们认为,通过将通用医学知识融入分割模型的损失函数,可以提高性能。为此,我们引入了逻辑张量网络(LTNs),使用一阶逻辑(FOL)规则编码医学背景知识。编码的规则从产生的分割形状的约束,到不同分割区域之间的关系都有涵盖。我们在端到端的框架中应用了LTNs和SwinUNETR进行语义分割。我们在脑MRI扫描中对海马体分割任务评估了我们的方法。实验表明,LTNs提高了基线分割性能,特别是在训练数据稀缺的情况下。尽管还处于初步阶段,我们认为神经符号方法足够通用,可以适应并应用于其他医学语义分割任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at TAIM@IJCNN 2025
Summary
本文探讨语义分割在医学图像分析中的重要作用,通过引入逻辑张量网络(LTNs)将医学背景知识编码进分割模型的损失函数中,以提高分割性能。实验表明,在训练数据稀缺的情况下,LTNs能够改善基线分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在医学图像分析中起重要作用,帮助放射科医生区分图像中的对象,辅助医疗决策。
- 深度学习在医学图像分割中有广泛应用潜力,但现有系统尚待完善。
- 引入逻辑张量网络(LTNs)将医学背景知识编码进分割模型的损失函数,能改善分割性能。
- LTNs通过一阶逻辑规则编码医学背景知识,包括产生的分割形状的约束以及不同分割区域之间的关系。
- 在脑MRI扫描中分割海马体的任务上评估了所提出的方法,实验结果表明LTNs能提高基线分割性能。
- 神经符号方法具有足够的通用性,可适应并应用于其他医学语义分割任务。
点此查看论文截图
Neptune-X: Active X-to-Maritime Generation for Universal Maritime Object Detection
Authors:Yu Guo, Shengfeng He, Yuxu Lu, Haonan An, Yihang Tao, Huilin Zhu, Jingxian Liu, Yuguang Fang
Maritime object detection is essential for navigation safety, surveillance, and autonomous operations, yet constrained by two key challenges: the scarcity of annotated maritime data and poor generalization across various maritime attributes (e.g., object category, viewpoint, location, and imaging environment). To address these challenges, we propose Neptune-X, a data-centric generative-selection framework that enhances training effectiveness by leveraging synthetic data generation with task-aware sample selection. From the generation perspective, we develop X-to-Maritime, a multi-modality-conditioned generative model that synthesizes diverse and realistic maritime scenes. A key component is the Bidirectional Object-Water Attention module, which captures boundary interactions between objects and their aquatic surroundings to improve visual fidelity. To further improve downstream tasking performance, we propose Attribute-correlated Active Sampling, which dynamically selects synthetic samples based on their task relevance. To support robust benchmarking, we construct the Maritime Generation Dataset, the first dataset tailored for generative maritime learning, encompassing a wide range of semantic conditions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach sets a new benchmark in maritime scene synthesis, significantly improving detection accuracy, particularly in challenging and previously underrepresented settings. The code is available at https://github.com/gy65896/Neptune-X.
海洋目标检测对于航行安全、监控和自主操作至关重要,然而,它受到两个关键挑战的限制:海洋数据的标注稀缺以及不同海洋属性(如目标类别、观点、位置和成像环境)的泛化能力较差。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Neptune-X,这是一个以数据为中心的生成选择框架,它通过利用带有任务感知样本选择(task-aware sample selection)的合成数据生成来提高训练效率。从生成的角度来看,我们开发了多模式条件生成模型X-to-Maritime,该模型可以合成多样且逼真的海洋场景。其关键组件是双向对象-水注意力模块(Bidirectional Object-Water Attention module),该模块可以捕获对象与其水生环境之间的边界交互,以提高视觉逼真度。为了进一步提高下游任务性能,我们提出了属性相关主动采样(Attribute-correlated Active Sampling),该采样方式会根据任务相关性动态选择合成样本。为了支持稳健的基准测试,我们构建了海洋生成数据集(Maritime Generation Dataset),这是专门为生成式海洋学习定制的第一个数据集,涵盖了广泛的语义条件。大量实验表明,我们的方法在海洋场景合成方面树立了新的基准,特别是在具有挑战性和先前代表性不足的条件下,检测精度得到了显著提高。代码可在https://github.com/gy65896/Neptune-X获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
海事目标检测对于航行安全、监控和自主操作至关重要,面临缺乏标注海事数据和泛化性能差两大挑战。为此,我们提出Neptune-X,一个以数据为中心的生成选择框架,通过利用合成数据生成和任务感知样本选择来提高训练效果。我们开发X-to-Maritime多模式条件生成模型,合成多样且逼真的海事场景。其中的关键组件是双向目标水域注意力模块,可捕获目标与水域边界之间的交互作用,以提高视觉逼真度。为进一步提高下游任务性能,我们提出了与属性相关的主动采样策略,可动态选择与任务相关的合成样本。为支持稳健的基准测试,我们构建了海事生成数据集,这是专门为生成海事学习定制的第一个数据集,涵盖广泛的语义条件。实验表明,我们的方法在海事场景合成方面树立了新的基准,特别是在具有挑战性和先前代表性不足的条件下,检测精度显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 海事目标检测对于航行安全等多个领域具有重大意义。
- 缺乏标注海事数据和泛化性能是当前面临的主要挑战。
- Neptune-X是一个以数据为中心的生成选择框架,旨在解决这些挑战。
- 利用合成数据生成和任务感知样本选择来提升训练效果。
- X-to-Maritime模型用于合成海事场景,包含双向目标水域注意力模块以提高视觉逼真度。
- 提出与属性相关的主动采样策略,动态选择与任务相关的合成样本。
点此查看论文截图

OS-W2S: An Automatic Labeling Engine for Language-Guided Open-Set Aerial Object Detection
Authors:Guoting Wei, Yu Liu, Xia Yuan, Xizhe Xue, Linlin Guo, Yifan Yang, Chunxia Zhao, Zongwen Bai, Haokui Zhang, Rong Xiao
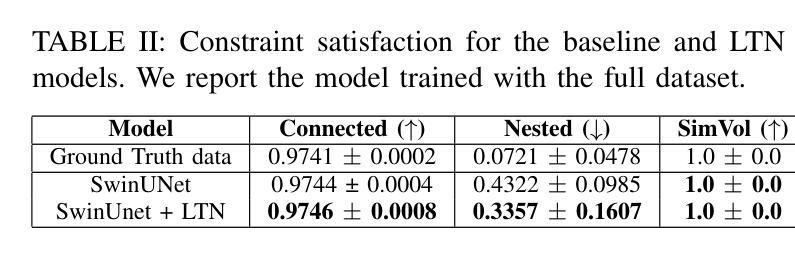
In recent years, language-guided open-set aerial object detection has gained significant attention due to its better alignment with real-world application needs. However, due to limited datasets, most existing language-guided methods primarily focus on vocabulary-level descriptions, which fail to meet the demands of fine-grained open-world detection. To address this limitation, we propose constructing a large-scale language-guided open-set aerial detection dataset, encompassing three levels of language guidance: from words to phrases, and ultimately to sentences. Centered around an open-source large vision-language model and integrating image-operation-based preprocessing with BERT-based postprocessing, we present the OS-W2S Label Engine, an automatic annotation pipeline capable of handling diverse scene annotations for aerial images. Using this label engine, we expand existing aerial detection datasets with rich textual annotations and construct a novel benchmark dataset, called MI-OAD, addressing the limitations of current remote sensing grounding data and enabling effective language-guided open-set aerial detection. Specifically, MI-OAD contains 163,023 images and 2 million image-caption pairs, approximately 40 times larger than comparable datasets. To demonstrate the effectiveness and quality of MI-OAD, we evaluate three representative tasks. On language-guided open-set aerial detection, training on MI-OAD lifts Grounding DINO by +31.1 AP$_{50}$ and +34.7 Recall@10 with sentence-level inputs under zero-shot transfer. Moreover, using MI-OAD for pre-training yields state-of-the-art performance on multiple existing open-vocabulary aerial detection and remote sensing visual grounding benchmarks, validating both the effectiveness of the dataset and the high quality of its OS-W2S annotations. More details are available at https://github.com/GT-Wei/MI-OAD.
近年来,语言引导的开集航空目标检测因更符合现实应用需求而受到广泛关注。然而,由于数据集有限,大多数现有的语言引导方法主要关注词汇层面的描述,这难以满足精细开集世界检测的需求。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了构建大规模语言引导开集航空检测数据集的方法,涵盖三个层次的语言引导:从单词到短语,最终到句子。我们围绕开源的大型视觉语言模型,将基于图像操作的预处理与基于BERT的后处理相结合,推出了OS-W2S标签引擎,这是一条自动注释管道,能够为航空图像提供多样化的场景注释。使用该标签引擎,我们丰富了现有的航空检测数据集,加入了丰富的文本注释,并构建了一个新的基准数据集,称为MI-OAD,解决了当前遥感接地数据的局限性,并实现了有效的语言引导开集航空检测。具体来说,MI-OAD包含163,023张图像和200万张图像-标题对,大约是相似数据集的40倍。为了证明MI-OAD的有效性和质量,我们对三项代表性任务进行了评估。在语言引导的开集航空检测方面,在MI-OAD上进行训练使接地DINO在零样本迁移的句子级输入下提高了+31.1 AP_{50}和+34.7 Recall@10。此外,使用MI-OAD进行预训练可在多个现有的开放词汇航空检测和遥感视觉接地基准测试上达到最新性能水平,验证了数据集的有效性和OS-W2S注释的高质量。更多详情可访问https://github.com/GT-Wei/MI-OAD了解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了语言引导下的开放式设定空中目标检测的重要性及现有数据集的限制。为应对这些限制,提出了一种构建大规模语言引导下的开放式设定空中检测数据集的方法,并开发了OS-W2S标签引擎,实现了自动标注空中图像的功能。基于该标签引擎,构建了名为MI-OAD的新型基准数据集,该数据集包含大量文本标注,解决了遥感接地数据的局限性,并实现了有效的语言引导下的开放式设定空中检测。评估结果显示,MI-OAD在多个任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 语言引导下的空中目标检测符合实际应用需求。
- 现有数据集主要关注词汇级别的描述,无法满足精细开放世界检测的需求。
- 提出构建大规模语言引导下的开放集空中检测数据集,包含三个层次的语言指导。
- 开发OS-W2S标签引擎,实现自动标注空中图像的功能。
- 构建新型基准数据集MI-OAD,包含丰富文本标注,解决遥感接地数据局限性。
- MI-OAD数据集在多个任务上表现优异,能有效提升语言引导下的开放集空中检测性能。
点此查看论文截图